
Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
117 California History Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
California, often referred to as the Golden State, is a land rich in history and diversity. From its indigenous peoples to the Spanish colonization, the Gold Rush, and the rise of Hollywood, California has played a significant role in shaping American history. If you are tasked with writing an essay on California history, here are 117 topic ideas and examples to inspire your research and writing:
Pre-Colonial California:
- The indigenous peoples of California: tribes, cultures, and lifestyles.
- The impact of European diseases on Native American populations.
- The role of art and symbolism in Native American cultures in California.
- The impact of Spanish colonization on indigenous populations in California.
- The Mission System: its goals, successes, and controversies.
- Native American resistance to Spanish colonization in California.
Spanish and Mexican California: 7. The founding of Spanish missions and presidios in California. 8. The impact of Spanish architecture and culture on California. 9. The Mexican period in California: politics, economy, and society. 10. The role of Californios in early California society. 11. The Bear Flag Revolt: causes, events, and consequences. 12. Mexican land grants and the transformation of landownership in California.
The Gold Rush Era: 13. The discovery of gold at Sutter's Mill: causes and immediate effects. 14. The impact of the Gold Rush on California's population and demographics. 15. The transformation of San Francisco during the Gold Rush. 16. The experiences of women during the Gold Rush. 17. The impact of Chinese immigrants on the Gold Rush and California's development. 18. The environmental consequences of the Gold Rush in California.
California's Role in the Civil War: 19. California's political and economic alignment during the Civil War. 20. The role of California volunteers in the Union Army. 21. The impact of the Civil War on California's economy and society. 22. California's efforts to support the Union cause.
The Transcontinental Railroad: 23. The construction of the Transcontinental Railroad in California. 24. Chinese laborers and their contributions to the Transcontinental Railroad. 25. The impact of the railroad on California's economy and population growth. 26. The changing landscape of California due to the railroad.
California's Ethnic Communities: 27. The impact of Chinese immigrants on California's economy and society. 28. Japanese internment during World War II and its lasting effects. 29. Mexican immigration and its influence on California's culture and labor force. 30. The role of African Americans in California during the Civil Rights Movement. 31. The Chicano Movement in California: goals, achievements, and challenges.
California's Natural Disasters: 32. The San Francisco earthquake of 1906: causes, effects, and aftermath. 33. The impact of droughts on California's agriculture and water supply. 34. The role of wildfires in shaping California's landscape and ecology. 35. The consequences of the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake.
California's Environmental Movements: 36. The birth of the Sierra Club and its impact on environmental conservation. 37. The fight to protect California's redwood forests. 38. The impact of the Clean Air Act on air quality in California. 39. The creation of national parks in California: Yosemite, Sequoia, Joshua Tree, etc.
California's Role in World War II: 40. The internment of Japanese Americans in California during World War II. 41. The role of California's military bases in supporting the war effort. 42. The impact of wartime industries on California's economy. 43. The changing demographics of California due to wartime migration.
The Rise of Hollywood: 44. The birth of the American film industry in Hollywood. 45. The impact of Hollywood on American culture and global cinema. 46. The role of women in early Hollywood. 47. The influence of censorship on Hollywood films. 48. The rise and fall of the studio system in Hollywood.
California's Counterculture: 49. The Beat Generation in California: writers, poets, and their impact. 50. The cultural revolution of the 1960s in California. 51. The rise of Hippie communes in California. 52. The impact of the Free Speech Movement at UC Berkeley.
The Tech Boom and Silicon Valley: 53. The birth of Silicon Valley and its impact on California's economy. 54. The rise of tech giants: Apple, Google, Facebook, etc. 55. The impact of venture capitalism on California's startup culture. 56. The challenges of income inequality and gentrification in Silicon Valley.
California's Agricultural Industry: 57. The development of California's agriculture industry: from oranges to almonds. 58. The impact of irrigation systems on California's agricultural success. 59. The challenges of water scarcity and sustainable farming in California. 60. The role of migrant labor in California's agricultural industry.
California's LGBTQ+ Rights Movement: 61. The early LGBTQ+ rights movement in California. 62. The impact of the AIDS crisis on LGBTQ+ communities in California. 63. The fight for marriage equality in California. 64. The influence of LGBTQ+ individuals in California politics.
California's Political Landscape: 65. The role of California in national politics. 66. The impact of Proposition 13 on California's tax system. 67. The rise of the Democratic Party in California. 68. The challenges of governing a diverse state like California.
California's Education System: 69. The rise and challenges of the University of California system. 70. The impact of bilingual education policies in California. 71. The role of community colleges in California's education system. 72. The challenges of funding and inequality in California's schools.
California's Water Wars: 73. The history of water rights and conflicts in California. 74. The impact of the California State Water Project on the state's water supply. 75. The challenges of drought and water scarcity in California. 76. The future of water management in California.
California's Immigration Policies: 77. The history of immigration policies in California. 78. The impact of Proposition 187 on California's immigrant communities. 79. The challenges of undocumented immigrants in California. 80. The role of sanctuary cities in California.
California's Wine Industry: 81. The history of winemaking in California. 82. The impact of the Judgment of Paris on California's wine industry. 83. The challenges of climate change on California's vineyards. 84. The rise of organic and sustainable winemaking in California.
California's Native American Gaming: 85. The establishment of Native American casinos in California. 86. The impact of gaming on Native American communities and economies. 87. The challenges and controversies surrounding Native American gaming.
California's Prison System: 88. The history of California's prison system. 89. The impact of the Three Strikes law on California's prison population. 90. The challenges of prison overcrowding and reform in California.
California's Transportation Systems: 91. The development of California's highway system. 92. The impact of the electric car movement on California's transportation. 93. The challenges of public transportation in California's urban areas.
California's Surfing Culture: 94. The birth of surf culture in California. 95. The impact of surfing on California's lifestyle and tourism. 96. The challenges of coastal erosion and pollution on California's surf spots.
California's LGBTQ+ History: 97. The history of LGBTQ+ activism in California. 98. The impact of the AIDS crisis on LGBTQ+ communities in California. 99. The fight for LGBTQ+ rights and equality in California.
California's Literary Heritage: 100. The impact of California on the works of John Steinbeck. 101. The influence of California on the Beat Generation writers. 102. The rise of Chicano literature in California. 103. The role of California in contemporary literature.
California's Sports Legacy: 104. The history of professional sports teams in California. 105. The impact of the Los Angeles Olympics on California. 106. The challenges of stadium construction and relocation in California.
California's Architectural Heritage: 107. The influence of Spanish and Mexican architecture on California. 108. The birth of the Craftsman style architecture in California. 109. The impact of modernist architecture on California's cities.
California's Native Flora and Fauna: 110. The diversity of California's ecosystems and biomes. 111. The challenges of protecting endangered species in California. 112. The impact of climate change on California's flora and fauna.
California's Celebrity Culture: 113. The rise of Hollywood and its impact on celebrity culture. 114. The challenges of paparazzi and invasion of privacy in California. 115. The influence of celebrity activism on California's politics.
California's Space Industry: 116. The role of California in the aerospace industry. 117. The impact of SpaceX and other private companies on California's space industry.
These topics and examples cover a wide range of aspects of California's rich history and provide ample opportunities for research and analysis. Whether you are interested in politics, culture, environment, or technology, there is a California history essay topic that will suit your interests. Happy writing!
Want to research companies faster?
Instantly access industry insights
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Leverage powerful AI research capabilities
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2024 Pitchgrade
- Share this page to Facebook!
- Tweet this page!
- Email this page!
- Join Our Mailing Lists
- Contact Us
- Get a Library Card
- Log In to Your Account
- Settings

Home | California History Section | California History: Research Guides


California History: Research Guides
Are you stumped? We can help! Along with our how-to guides and our general guide to the collection, the California History Room librarians have spent hundreds of hours plumbing our collections to develop research guides for specific California topics. You can see our current guides below. If you cannot find a guide to the topic you are researching or if you still have questions, please consider using our library databases or contacting us .
General Topics
- African Americans in California (PDF)
- Art and Artists of California (PDF)
- Chinese Americans in California (PDF)
- Fiction in California (PDF)
- Fires and Firefighters in California (PDF)
- German Americans in California (PDF)
- Highways and Byways in California (PDF)
- Horses and Horse Racing in California (PDF)
- Images of California (PDF)
- Japanese Americans in California (PDF)
- Jewish Americans in California (PDF)
- Land grants in California (PDF)
- Latin Americans in California (PDF)
- Medicine in California (PDF)
- Mining in California (PDF)
- Native Americans in California (PDF)
- Oddities in California (PDF)
- Oil in California (PDF)
- Poetry in California (PDF)
- Portuguese Americans in California (PDF)
- Railroads in California (PDF)
- Remote Access: Vital Statistics and Indexes (PDF)
- Ships and Shipping in California (PDF)
- Sutter’s Fort Character Guide (PDF)
- Water in California (PDF)
- Wildflowers in California (PDF)
- Wine in California (PDF)
- Women in California (PDF)
- 1960’s in California (PDF)
How-To and Collection Guides
- Guide to the collection (PDF)
- Basic Search Guide (PDF)
- Advanced Search Tips and Tricks (PDF)
- Online Remote Research Options (PDF)
- Research in Person (PDF)
California Genealogy
- Federal Census Resources (PDF)
- Genealogy resources by date (PDF)
- Immigration and Naturalization Resources (PDF)
- 1852 California State Census Resources (PDF)
Local History
- Alameda County (PDF)
- Alpine County (PDF)
- Amador County (PDF)
- Butte County (PDF)
- Calaveras County (PDF)
- Colusa County (PDF)
- Contra Costa County (PDF)
- Del Norte County (PDF)
- El Dorado County (PDF)
- Fresno County (PDF)
- Humboldt County (PDF)
- Imperial County (PDF)
- Inyo County (PDF)
- Kern County (PDF)
- Kings County (PDF)
- Lassen County (PDF)
- Madera County (PDF)
- Marin County (PDF)
- Mendocino County (PDF)
- Merced County (PDF)
- Modoc County (PDF)
- Monterey County (PDF)
- Orange County (PDF)
- Placer County (PDF)
- Sacramento County (PDF)
- San Francisco County (PDF)
- San Mateo County (PDF)
- Santa Barbara (PDF)
- Santa Cruz County (PDF)
- Shasta County (PDF)
- Sierra County (PDF)
- Siskiyou County (PDF)
- Stanislaus County (PDF)
- Trinity County (PDF)
- Tulare County (PDF)
- Tuolumne County (PDF)
- Ventura County (PDF)
- Yolo County (PDF)
- Yuba County (PDF)
- Auburn (PDF)
- Bakersfield (PDF)
- Calexico (PDF)
- Carmel-by-the-Sea (PDF)
- Crescent City (PDF)
- Fair Oaks (PDF)
- Folsom (PDF)
- Fort Bragg (PDF)
- Modesto (PDF)
- Newport Beach (PDF)
- Placerville (PDF)
- Redwood City (PDF)
- Richmond (PDF)
- Sacramento building research (PDF)
- Sacramento City (PDF)
- San Francisco (PDF)
- San Francisco earthquake (1906) (PDF)
- Watsonville (PDF)
- Weaverville (PDF)
- Visalia (PDF)
Online Librarian
Many of our materials may not be online but our staff are. Reach out to us about arranging a 30-minute video research appointment with one of our librarians to:
- Look at undigitized primary sources
- Check in-house card files
- Discuss remote access options, such as low-resolution scanning
Sessions must be arranged in advance and are not meant to replace other access options such as visiting us or placing inter-library loans. Our video session limit is 30 minutes per patron per week. Up to 5 items may be requested per video call. The State Library reserves the right to refuse to show or scan materials that may be damaged by the process or are otherwise restricted.
Essay: 1848-1865: Gold Rush, Statehood, and the Western Movement
The discovery of gold in California in 1848 vastly accelerated changes that had been occurring since 1769. Already a meeting place for Mexicans, Russians, Americans, Europeans, and natives, the gold rush turned California into a truly global frontier where immigrants from every continent on earth now jostled. More than 300,000 gold seekers flooded California by 1850, bringing to the new American state an astonishing variety of languages, religions, and social customs. Many of these visitors had no interest in settling down in California, intending only to make their "pile" and return home with pockets full of gold. The arrival and departure of thousands of immigrants, the intensely multicultural nature of society, and the newness of American institutions made Gold Rush California a chaotic, confusing landscape for natives and newcomers alike.
Native Population Plummets
The disruptions of the Gold Rush proved devastating for California's native groups, already in demographic decline due to Spanish and Mexican intrusion. The state's native population plummeted from about 150,000 in 1848 to 30,000 just 12 years later. As foreigners methodically mined, hunted, and logged native groups' most remote hiding places, natives began raiding mining camps for subsistence. This led to cycles of violence as American miners — supported by the state government — organized war parties and sometimes slaughtered entire native groups.
The Act for the Government and Protection of Indians, passed by the state legislature in 1850, denied native Californians the right to testify in court and allowed white Americans and Californios to keep natives as indentured servants. "I do not like the white man because he is a liar and a thief," Isidora Filomena de Solano, a Patwin-speaking woman from the Bay Area, told an interviewer in 1874. She echoed the sentiments of many native Californians struggling to preserve traditional ways in the midst of holocaust.
Californios Lose Power, Land, and Privilege
The imposition of American government in California reversed the fortunes of elite Californios, who slowly lost their power, authority, and land. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which ended the US-Mexican War, had granted Californios full US citizenship and promised that their property would be "inviolably respected." But the informality of Mexican land grants made legal claims difficult when miners, squatters, and homesteaders overran Californios' lands.
Even when Californio families won legal title to their lands, many found themselves bankrupt from attorney's fees or taxes. The Peralta family lost all but 700 of their 49,000 acres in the East Bay to lawyers, taxes, squatters, and speculators. Eight Californios participated in the California constitutional convention of 1849, but over time their political power declined along with their land base.
White Americans vs. "Foreign Miners"
Californios feared losing their privileged status and being lumped in with the thousands of Spanish-speaking immigrants from Mexico and other parts of Latin America who arrived in California during the Gold Rush. Mexicans and Chilenos were among the first foreigners to make it to California in 1848, and their proximity and mining expertise gave them an edge in the cutthroat competition of the mines.
Their early success led the California legislature to adopt a foreign miners’ license tax in 1850 aimed at "greasers," as all Latin Americans were called. When Latin American miners refused to pay the impossibly high tax ($20 per month), white Americans had an excuse to drive them out of rich mining areas. In the mining town of Sonora, Mexicans, Chileans, and Peruvians joined with French and German miners to protest the tax, only to be subdued by a hastily formed militia of white Americans.
Rumors began to spread throughout gold country about a swashbuckling Mexican bandit named Joaquín Murieta who was striking back against American injustices. The California legislature offered a huge reward and in 1853 a Texan named Harry Love produced the head of someone he insisted was Murieta. Whether Joaquín Murieta ever actually existed is unknown, but he was celebrated as a hero by many Latin Americans enraged by oppressive American policies.
Chinese Gold Seekers
Chinese gold seekers arrived in great numbers after 1851, and soon comprised about a fifth of the entire population in mining areas. Coming to the mines later than other groups, many Chinese immigrants earned a living by working claims abandoned by other miners. They also took jobs as cooks, launderers, merchants, and herbalists, hoping to return to China with a small fortune. However, low pay, discriminatory hiring practices, and the monthly foreign miners' license tax made this goal all but impossible.
In the face of intense prejudice, some Chinese Californians challenged American racism through the legal system and in the court of public opinion. Chinese community leaders petitioned Sacramento to overturn unfair laws and worked to gain the right to testify in court (finally granted in 1872). Norman Asing, a restaurant owner in San Francisco's booming Chinatown, wrote to California governor John Bigler in 1852, insisting, "We are not the degraded race you would make us."
African Americans Look for Equality and Gold
More than 2,000 African Americans traveled to California by 1852, lured by reports that the California frontier offered a rough-and-tumble egalitarianism along with its gold deposits. Like most gold seekers, they were bitterly disappointed by what they found.
California entered the United States as a free state in 1850, but the lack of government oversight allowed slavery to flourish in certain regions. The state legislature passed a fugitive slave law in 1852, making it illegal for enslaved African Americans to flee their masters within the state's supposedly free borders. All African Americans in California, born free or formerly enslaved, thereafter lived under a constant threat of arrest. They were also barred from testifying in court or sending their children to public schools.
Mifflin Wistar Gibbs, an African American abolitionist who had spent years lecturing with Frederick Douglass, helped organize the First State Convention of Colored Citizens of California in 1855 to fight for suffrage and equal rights. African Americans won the right to testify in California in 1863 but the right to vote came only with the passage of the Fifteenth Amendment in 1870.
Cross-Cultural Cooperation
Although discrimination and violence were rampant, Gold Rush California was also a place of cross-cultural communication and cooperation. Canadian merchant William Perkins described the mining town of Sonora in 1849: "Here were to be seen people of every nation in all varieties of costume, and speaking 50 different languages, and yet all mixing together amicably and socially." In mining camps and in the crowded streets of San Francisco, previously isolated groups came into contact for the first time. Race, language, religion, and class separated Californians but proximity forced groups to accommodate as well as compete. Multiracial even before it was a state, California would be continuously shaped by its diversity.
Bancroft Library. The California Gold Rush
Oakland Museum of California. Gold Rush!: California’s Untold Stories
PBS. The Gold Rush
The Sacramento Bee . Gold Rush Sesquicentennial
In the Library
Johnson, Susan Lee. Roaring Camp: The Social World of the California Gold Rush. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2000.
Kowalewski, Michael, ed. Gold Rush: A Literary Exploration. Berkeley: Heyday Books, 1997.
Starr, Kevin, and Richard J. Orsi, eds. Rooted in Barbarous Soil: People, Culture, and Community in Gold Rush California. Berkeley: University of California Press, 2000.
Related exhibitions
Related themes, about this essay:.
"1848-1865: Gold Rush, Statehood, and the Western Movement" was written by Joshua Paddison and the University of California in 2005 as part of the California Cultures project.
Using this essay:
The text of this essay is available under a Creative Commons CC-BY license . You are free to share and adapt it however you like, provided you provide attribution as follows:
1848-1865: Gold Rush, Statehood, and the Western Movement curated by University of California, available under a ">CC BY 4.0 license . © 2011, Regents of the University of California.
Please note that this license applies only to the descriptive copy and does not apply to any and all digital items that may appear.

About the Journal
California History is the premier journal of historical writing on California. Showcasing exceptional scholarship, engaging writing, and innovative research, California History is essential reading for students and scholars of the history of California and the West, as well as California residents curious to understand the imprint of the state’s rich past.
ISSN: 0162-2897 eISSN : 2327-1485
Published Quarterly – February, May, August, November
Impact Factor: 0.1
Editor: Mary Ann Irwin

Call for Papers
In 2026, the United States celebrates the 250 th anniversary of the Declaration of Independence. In light of this significant occasion, California History is preparing a special issue focusing on “American Revolutions in California.” See the issue's Call for Papers .

- Richard J. Orsi Prize
University of California Press is pleased to announce the establishment of the Richard J. Orsi Prize to honor the best articles published in the journal, California History .
Affiliations
- Recent Content
- Browse Issues
- All Content
- Info for Authors
- Info for Librarians
- Editorial Team
- Online ISSN 2327-1485
- Print ISSN 0162-2897
- Copyright © 2024
Stay Informed
Disciplines.
- Ancient World
- Anthropology
- Communication
- Criminology & Criminal Justice
- Film & Media Studies
- Food & Wine
- Browse All Disciplines
- Browse All Courses
- Book Authors
- Booksellers
- Instructions
- Journal Authors
- Journal Editors
- Media & Journalists
- Planned Giving
About UC Press
- Press Releases
- Seasonal Catalog
- Acquisitions Editors
- Customer Service
- Exam/Desk Requests
- Media Inquiries
- Print-Disability
- Rights & Permissions
- UC Press Foundation
- © Copyright 2024 by the Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved. Privacy policy Accessibility
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
By: History.com Editors
Updated: December 13, 2022 | Original: November 9, 2009

The first Spanish missionaries arrived in California in the 1700s, but California didn’t become part of the United States until 1847, as part of the treaty ending the Mexican-American War . Shortly thereafter, the discovery of gold at Sutter’s Mill in 1848 inspired a wave of settlers to head to the West Coast in search of fortune. In 1850 California became the 31st state.
With millions of acres of farmland, California leads the United States in agricultural production. The state is also home to famous cultural institutions and national parks including Hollywood , Disneyland, Yosemite National Park, Alcatraz , Angel Island and the Golden Gate Bridge .
WATCH: How the States Got Their Shape on HISTORY Vault
California’s Native American History
The first people migrated to California nearly 20,000 years ago from Asia across the Bering Straits. California’s mountain ranges and deserts isolated Native American tribes from each other, and they lived in peaceful family clans with little political structure. More than 500 tribes, each with their unique culture, developed across the state, such as the Pomo, Tolowa, Miwok, Maidu, Cahto, Wintun, Cahuilla, Chemehuevi, Chumash, Karok, Mojave, Yokuts, Paiute and Modoc.
When Spanish missionaries first came to California in the mid-1700s, the native population was estimated to be about 30,000—or 13 percent of the total Indigenous population in North America at the time. The population was gradually decimated, first in the 18th century by disease and forced labor in Spanish missions, and then in the late 19th century by American settlers .
California Missions
Concerned about Russian and English encroachment on western New Spain territory, Spain ordered an expedition north from Baja Mexico in 1769. The first Spanish soldiers and priests traveled and established a presidio (military fort) and mission church in San Diego. This marked the first of at least 21 California missions , which were often accompanied by presidios and pueblos (small towns).
Greatly outnumbered by native inhabitants, Franciscan missionaries came with the blessing of the Spanish state to convert Indigenous people to Christianity and train them into loyal Spanish citizens. Missionaries introduced agriculture and ranching to indigenous peoples. They taught them Spanish culture and language as well as skills like weaving, construction and blacksmithing. They also forced natives to build and stay within their walled communities and flogged those who disobeyed. Forced labor along with foreign disease, which spread rapidly in crowded living conditions, halved the indigenous population by the time the Mexican government secularized the mission system in 1834.
European Exploration
Spanish explorers began sailing the West Coast of North America looking for the mythical “Island of California,” entirely populated by beautiful women, described in Garcí Rodríguez Ordóñez de Montalvo’s book Las Sergas de Esplandián (The Exploits of Esplandián). They named the Baja California peninsula of Mexico after the book.
Spanish conquistador Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo was the first European to explore the West Coast of the United States, naming the area “Alta California.” Sent by New Spain to find a water route to Asia, Cabrillo and his crew left from Mexico and set foot on modern-day San Diego on September 28, 1542, then traveled north to Monterey Bay.
Sailing for the English in 1579, Sir Francis Drake looted Spanish settlements in the Americas and escaped to Point Reyes Peninsula, near San Francisco. Portuguese merchant-adventurer Sebastián Rodríguez Cermeño landed in Drake’s Bay in 1595 and explored parts of northern California including Monterey, an area revisited several years later by Spanish explorer Sebastián Vizcaíno.
The Spanish only settled in California with the Franciscan establishment of presidios and missions beginning in 1769. Spanish commander Juan Bautista de Anza created an overland route from California to New Spain and brought the first families to California in 1776. Fewer than 4,000 settlers lived in California until the mid-1800s.
From Mexico to the United States
Mexico won independence from Spain in 1821 following the Mexican War of Independence , and Alta California became a Mexican province in 1822. The Mexicans established a ranching culture, and Mexico’s liberal trading policies encouraged Californians to trade with the Americans and the English.
In 1826 trapper Jedediah Smith led the first group of U.S. citizens overland into the area. In 1841, John Bidwell and John Bartleson led the first group of organized American settlers into California. Immigration continued until American immigrants outnumbered Mexican citizens by the mid-1840s. American settlers revolted against the Mexican government in 1846 and declared California an independent nation in what became known as the Bear Flag Revolt .
Meanwhile, the U.S. government had gained interest in expanding its territory and was fighting the Mexican-American War . One month after the Bear Flag Revolt, the U.S. military occupied California. In January 1847, California surrendered to the United States. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo at the war’s end gave California to the United States on February 2, 1848. Without ever becoming a territory, California was admitted to the Union as the 31st state on September 9, 1850.
California Gold Rush & Immigration
WATCH: The California Gold Rush
On January 24, 1848, James Marshall discovered gold at a sawmill he was constructing at Sutter’s Mill in Coloma, California, ushering the California Gold Rush . Most of the first treasure-hunting immigrants came from outside the United States, including from Mexico, Chile and China. After President James Polk recognized the discovery that December, prospectors known as “ forty-niners ” began pouring into the state the following year.
In 1849 alone, more than 100,000 people moved to California from the United States and worldwide, including Europe, Australia, New Zealand and China. Some came looking for gold, while others set up saloons and other businesses. Between 1847 and 1860, the state’s population tripled to 308,000 residents. The Gold Rush changed the lives of California’s Native Americans , who within years, were almost wiped out due to the massive immigration the Gold Rush inspired. Most prospectors never struck it rich, but miners did extract an astonishing 28,280,711 ounces of fine gold between 1850 and 1859.
By the 1870s, almost all of the 63,000 Chinese immigrants in America lived in California, and anti-Chinese sentiment arose. Chinese filled jobs building the Transcontinental Railroad in the 1860s and then in agriculture in the early 1870s. This combined with an economic downturn in the 1870s spurred the passage of the Chinese Exclusion Act in 1882, which barred Chinese immigration until China sided with the United States in World War II .
The next big wave of California immigrants came to escape the Great Depression and a series of droughts in the 1930s. More than 300,000 people migrated to California from midwestern “ Dust Bowl ” states, including Oklahoma, Arkansas, Kansas and Texas. These poverty-stricken “Okies” faced discrimination and were the subject of John Steinbeck's Pulitzer-winning novel, The Grapes of Wrath .
When the passage of the 1965 Immigration and Naturalization Act opened up U.S. immigration, people from all over the world arrived in California, especially from Mexico, China, the Philippines, Central America and India.
California's Economy
California’s balmy climate and strong economy continue to attract new residents. As of 2021, the state boasted the largest population in the United States with more than 39 million residents. Many come to work in agriculture. Despite urbanization, drought and the loss of land to industry, California leads the country in agricultural production: More than a third of U.S. vegetables and two-thirds of fruit and nuts are grown in California. As of 2021, California also grew more than 3.9 million tons of wine grapes on 620,000 acres each year, producing more than 80 percent of all U.S. wine.
A thriving tech industry emerged in northern California in the 1960s, earning the area the name Silicon Valley after the main element in integrated circuits. In the 1970s and 80s, California businesses including Intel and entrepreneurs such as Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak of Apple helped create personal computing. As of 2022, California boasted the most tech jobs of any state in the United States, accounting for 1.88 million jobs and a quarter of national tech productivity.
California is also known for its film industry. Los Angeles was home to the first motion picture theater in the United States , which opened in 1902. Industrial jobs and a real estate boom encouraged many people to move to Hollywood from the early to mid-1900s. The 1930s welcomed the “Golden Age” of Hollywood, cemented by the creation of Technicolor and Walt Disney ’s studios. Almost half of today’s film sector jobs in the United States are based in Los Angeles.
As of 2022, California had the largest economy of any state in the U.S. In 1997, it was the first state to reach the trillion-dollar benchmark in gross state product (GDP). As of 2021, California was ranked the fifth-largest economy in the world, with a GDP of $3.1 trillion.

Date of Statehood: September 9, 1850
Capital: Sacramento
Population: 39,538,223 (2020)
Size: 163,694 square miles
Nickname(s): The Golden State; The Land of Milk and Honey; The El Dorado State; The Grape State
Motto: Eureka (“I have found it”)
Tree: California Redwood
Flower : Poppy
Bird: California Valley Quail
Interesting Facts
- The highest and lowest points in the continental United States are located within 100 miles of one another in California: Mount Whitney measures 14,505 feet, and Badwater Basin in Death Valley is 282 feet below sea level.
- Considered to be the hottest, driest place in the United States, Death Valley often reaches temperatures greater than 120 degrees Fahrenheit during the summer and averages only around two inches of rain each year.
- With a trunk slightly greater than 36 feet in diameter at its base and 275 feet tall, the General Sherman in Sequoia National Park is the largest living tree (by volume) in the world. It is estimated to be about 2,200 years old.
- About one-half of California's land is federally owned. National parks located throughout the state are devoted to the preservation of nature and natural resources.
- Southern California has about 10,000 earthquakes each year, although only 15 to 20 of them have a magnitude greater than 4.0.
- Dr. Maya Angelou was San Francisco’s first Black female streetcar conductor. The civil rights activist, poet and author of I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings went on to recite one of her poems at Bill Clinton ’s presidential inauguration.
Agriculture Facts, aeps.calpoly.edu
Native People of California, kids.nationalgeographic.com
"The First Peoples of California," loc.gov
"Religion and Capitalism as Motivators for Colonial Exploitation," gallatin.nyu.edu
"Revealing the history of genocide against California’s Native Americans," newsroom.ucla.edu
"Early California: pre-1769–1840s: Early Explorers," picturethis.museumca.org
Spanish California, loc.gov
"California Indians, Before, During, and After the Mission Era," californiamissionsfoundation.org
"Fourth Grade in California Public Schools," district.mpcsd.org
The Missions, loc.gov
"Early History of the California Coast," nps.gov
"European Exploration: Voyages of Discovery," csun.edu
"Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo - A Voyage of Exploration," nps.gov
"Juan Bautista de Anza National Historic Trail Arizona and California," nps.gov
"Mexican California," loc.gov
Americans Arrive – 1840s to 1890s, ci.emeryville.ca.us
"Gold!," loc.gov
"The Discovery of Gold," loc.gov
"The Forty Niners," loc.gov
"From Gold Rush to Golden State," loc.gov
"U.S. Census Bureau History: The California Gold Rush," census.gov
State Symbols, library.ca.gov
"The Dust Bowl, California, and the Politics of Hard Times," capitolmuseum.ca.gov
"The Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture," okhistory.org
California Migration History 1850-2018, depts.washington.edu
U.S. and World Population Clock, census.gov
Immigrants in California, americanimmigrationcouncil.org
California Agricultural Production Statistics, cdfa.ca.gov
Media & Trade, discovercaliforniawines.com
"California Grape Acreage Report, 2020 Summary," nass.usda.gov
California and U.S. Wine Production, wineinstitute.org
Silicon Valley, California, americanhistory.si.edu
High Tech, business.ca.gov
"California State Facts: The First Time The Golden State...," California.gov
Hollywood, California, americanhistory.si.edu
"Film and Digital Media Industry Los Angeles County Perspective," file.lacounty.gov
"How Might California Really Rank As A Country?" cafwd.org
California, forbes.com
The General Sherman Tree, nps.gov
Maya Angelou, biography.com

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Try AI-powered search
What to read about the history of California
Five books that help explain the power and problems of the golden state.

I T IS DIFFICULT to wrap your mind around California. The Golden State is larger and more populous than many countries, with an economy to match. It is home to towering mountains, unforgiving desert and seemingly endless coastline. No American state has had a greater impact on modern culture and technology—thanks to Hollywood and Silicon Valley . And, like America, California is not just a place but an idea: a golden land of opportunity at the edge of the continent where generations of miners, migrants , farmers, actors and computer geeks have sought success. It is perhaps because of this idealistic vision that California’s troubles , and those of its superstar cities, Los Angeles and San Francisco , can seem especially acute. It is also America’s most liberal state , earning it the admiration of progressives and the ire of conservatives, for whom California has become shorthand for everything wrong in America. No one book can really unpack what California means. But these five, taken together, make for a good start.
California: A History. By Kevin Starr. Modern Library; 416 pages; $20
For a broad overview of California’s story start with Kevin Starr’s one-volume history of the state. The historian and former state librarian somehow manages to cover everything from the Spaniards’ exploratory voyages up the Pacific coast in the 16th century to Arnold Schwarzenegger’s gubernatorial victory in 2003. Naturally, the book won’t answer every question readers may have about the state, but it is an extremely useful jumping-off point, and an introduction to California’s many eras: Indigenous, Spanish, Mexican and, finally, American.
Holy Land: A Suburban Memoir. By D.J. Waldie. W.W. Norton; 208 pages; $14.95
It is hard to understand Los Angeles, and California more broadly, without considering its suburbs. A post-war construction boom transformed the farmland and fruit groves that once covered Los Angeles County. Lakewood was the west coast’s answer to New York’s Levittown: row after row of tract houses that became suburbs that became sprawl. D.J. Waldie grew up in one such house. His book is a reflection on suburban life and the appearance of order and conformity. “I live where a majority of Americans live,” the book begins. It is “one of the places where suburban stories were first mass-produced.”
Slouching Towards Bethlehem. By Joan Didion. Farrar, Straus and Giroux; 256 pages; $18
Several other books by Joan Didion could easily have made this list. She was a daughter of Sacramento, and wrote often about her home state. But it was her unflinching portrait of San Francisco’s Haight-Ashbury neighbourhood in 1967, when “the centre was not holding”, that catapulted Didion into the pantheon of California writers. “San Francisco was where the social haemorrhaging was showing up,” she wrote, when runaways, protesters and rock ‘n rollers disenchanted with America, with their lives, colonised Golden Gate Park. Other essays in this collection explore the rising rivers of the Sacramento Valley, the middle-class striving of the Inland Empire (where LA ’s exurbs meet the desert) and the vagaries of Los Angeles. Didion tried to puzzle out in prose what California meant, and probably came closer than anyone. “California is a place”, she wrote, “in which the mind is troubled by some buried but ineradicable suspicion that things had better work here, because here, beneath that immense bleached sky, is where we run out of continent.”
The Grapes of Wrath . By John Steinbeck. Penguin; 464 pages; $21
More than half of John Steinbeck’s classic book takes place either in Oklahoma or on dusty roads headed west. But California is ever present: first as an idea, even before the Joad family crosses the desert and arrives in Bakersfield’s squalid migrant camps. And then as a disappointing reality, when families can’t find work in the fields and the fruit rots on the trees because small-time farmers can’t pay for labour. Steinbeck manages to capture the devastation that the Dust Bowl wrought on the Great Plains and the promise, and eventual disappointment, that California held for the poor farmers streaming west out of America’s parched middle in the 1930s.
My First Summer in the Sierra. By John Muir. Mariner Books; 336 pages; $21.99
John Muir’s account of his “rambles” through the Sierra Nevada during the summer of 1869 is equal parts diary, poem and field guide. The famed naturalist is ostensibly watching over a flock of sheep, and yet he leaves them at any chance he gets to explore the lakes, peaks and valleys of one of North America’s great mountain ranges. Muir can be tedious when he is rhapsodising about the magnificence of the Yosemite Valley in abstract, almost religious, terms. But he is engaging and funny when he is recounting his adventures, and teaching readers about California’s rich natural environment in the meantime. A grasshopper inspires as much reverence as grizzly bears or giant sequoias. Readers will also see something of California’s long tradition of environmentalism in Muir’s writings. He has only scorn for tourists—but has the presence of mind to realise he is not so different from them.
We wrote about California’s economic troubles in early 2024, as well as about its strength in innovation : San Francisco still rules the tech world despite its toxic politics . Cities in California have struggled, in particular, with housing the homeless . During the pandemic the state lost population for the first time, but some cities are still thriving . For more on California, listen to two recent podcast episodes about Los Angeles and San Francisco .
Explore more
More from the economist reads, what to read about modern feminism.
An introduction to a large, evolving and controversial subject

How Christianity shapes politics in America
Four books and a podcast explain a complicated relationship

What to read about the British economy
Britain used to be the world’s richest country. These six books explain how it came to be, and why it is no longer
Six novels about India, perhaps the world’s most interesting place
Works of fiction about a country whose global clout, already large, is growing
Six novels you can read in a day
Reluctant to start on a big masterpiece? Try these small gems instead
The romance and reality of Paris, the Olympics’ host
Five non-fiction books about a city that is both gilded and gritty
California Beautiful

13 Most Significant Events in California History

California wears its history proudly on its sleeve.
The state’s many prominent structures, ranging from the Cabrillo National Monument to the magnificent Golden Gate Bridge, serve as vivid reminders of the different eras and rulers who have left their mark.
Here are 13 of the most significant events that have shaped the city’s history and contributed to the development of California into what it is today.
The Native American Tribes of California
The first european contact in california – (1542), california exploration and settlement – (1579), spanish colonial period in california – (1769–1821), mexican rule in california – (1821–1846), annexation of california – (1846–1847), california gold rush – (1849) , the slavery compromise of 1850 , becoming the 31st state in america – (1850), california in the american civil war – (1861), opening of transcontinental railroad – (1869), the great san francisco earthquake – (1906), women’s right to vote – (1911).
Various Native American tribes inhabited the present-day state of California for 13,000 to 15,000 years.
Early explorers depicted California as an earthly paradise where native tribes simply lived off what nature provided.
Contrary to popular belief, California Indians established rich cultures and rituals decades before the arrival of Spanish missionaries.
California was home to around 100 native tribes. The pre-European population of Native Americans in California is estimated at approximately 300,000 natives.
Tribes included the Mojave, Yokuts, Karok, Maidu, Cahuilleno, Modoc, Paiute, and Pomo.

A Spanish sailing expedition led by Portuguese captain Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo entered San Diego Bay for the first time in September 1542.
Cabrillo and his crew could not easily exploit California, which was located at the extreme limits of exploration and trade from Spain.
California would remain essentially unexplored for the next 234 years.

Captain Francis Drake explored the California coast in 1579, which led to England claiming the country.
Drake made friends with the Coast Miwok and claimed the territory as Nova Albion, or New Albion, for the English Crown.
However, Spain had been exploring and settling in California long before this, resulting in a tremendous tug of war between England and Spain.
The Jesuit priest Juan Maria Salvatierra established the first permanent mission in Baja California , escorted by a small boat crew and six soldiers.
Spain separated California into two provinces Baja California and Alta California. Baja consisted of the Baja Peninsula and ended roughly near San Diego, California.
The settlement of Alta California was the final colonial initiative to expand Spain’s territory in North America, and it sought to do so at the lowest possible expense and with the least amount of assistance.

Mexico gained independence from Spain in 1821 through The Treaty of Córdoba and ruled California for a quarter of a century.
Ranchos, or massive cattle ranches, developed as the primary establishments of Mexican California.
Soon after, American explorers began to explore the state, eventually establishing American outposts throughout the region.
This resulted in the American rebels establishing the California Republic in 1846, paving the stage for the Mexican war.
Mexico lost its entire northern frontier to the United States only twenty-five years after winning independence in 1821.

In 1846, a gang of around 30 armed Americans led by William Ide stormed into Sonoma, a small city in the Mexican province of Alta California.
There was initially no opposition in California as they replaced the dysfunctional and ineffective Mexican administration, which the Californios had already overthrown.
They made a makeshift flag out of a cotton sheet and red paint, with a rough drawing of a grizzly bear and the words “California Republic” at the bottom. This event became known as the Bear Flag Revolt .

John Sutter and James Marshal first struck gold in 1848 while constructing a water-powered sawmill along the American River in Coloma, California .
The discovery of gold at Sutter’s Mill triggered the most significant migration in US history, drawing migrants from a dozen countries to build a multi-ethnic community on America’s outskirts.
By the end of 1849, the non-native California population of 1000 increased to a staggering 100,000 during the Gold Rush.
Miners flocked from all over the world, extracting more than 800,000 pounds of gold during the gold rush.

The California Constitution of 1849 made all forms of slavery illegal.
Then, in 1850 a Compromise was made of five bills that aimed to settle disagreements over slavery in new territory, allowing California to be admitted to the Union as a free, non-slavery state.
California was officially recognized as the 31st state of the United States on September 9th, 1850.
The following year on July 4th, the 31-star flag entered circulation as the new national flag.
Since then, people of all ethnic backgrounds have come to the Golden State searching for a life of quality and magnificent beauty.

The business elite of California would ensure the war’s success by keeping it well funded with the help of the state’s rich gold mines.
California maintained and built many forts along its borders, restricting Confederate activity and securing the New Mexico Territory against Confederate troops.
Although California did not send organized battalions east, so many Californians joined the Union Army that the 71st Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry was nicknamed the California Regiment.
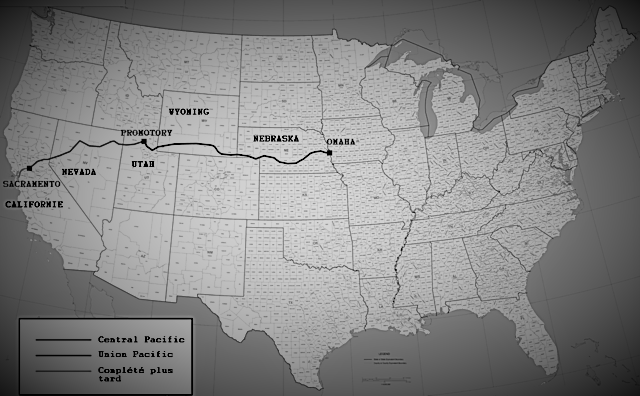
On May 10th, 1869, the Central Pacific Railroad’s lines from the west were linked to the Union Pacific Railroad’s tracks from the east.
President Leland Stanford, in a ceremony, drove the gold “Last Spike” (later dubbed the “ Golden Spike “) at Promontory Summit in Utah.
For the first time in American history, transcontinental railroad travel was made possible.

A foreshock with enough force to be felt throughout the San Francisco Bay area happened on Wednesday, April 18th, 1906, at precisely 5:12 a.m., local time.
Destructive fires raged throughout the city for several days, destroying approximately 28,000 buildings.
Over 3,000 people died due to the 7.8 Richter magnitude earthquake and fires, and more than 80% of San Francisco was destroyed.

In a historic election on October 10th, 1911, California voters narrowly awarded women the right to vote.
The movement was called Women’s suffrage in California and was successful with the passage of proposition 4
Most of those women and men participating in this campaign became politically active in the national suffrage movement.

Privacy Policy | Sitemap
Recent Posts
The ultimate guide to the best surfing beaches in california, 30 beautiful lakes in california: nature’s tranquil escapes, exploring sequoia and kings canyon national parks: your ultimate guide to the finest experiences, 25 ocean & beachfront hotels in san diego for your coastal getaway, 22 best places to see wildflowers in california (south + north), 23 fun & exciting things to do in yosemite national park: unleash your inner explorer.
Search on OralHistory.ws Blog
Navigating Historical Debates: History Argumentative Essay Topics

Dipping your toes into the vast ocean of history is an adventure. Each dive deep into its depths brings a new perspective, a fresh understanding, or a challenging contradiction. As a student of history, you don’t just learn about the past; you argue, debate, and discuss it. That’s where “history argumentative essay topics” come in, giving you the perfect platform to exhibit your persuasive skills while furthering your historical understanding.
Table of content
The Importance of Studying History
History isn’t just a record of ancient days; it’s a vibrant tapestry woven with countless threads, each representing a story, an era, a civilization, or an individual. Understanding history empowers us to make sense of our present, forecast future patterns, and appreciate humanity’s collective journey. Delving into argumentative essays adds depth to this exploration, honing your critical thinking, research understanding, and writing prowess.
The Art of Writing an Argumentative History Essay
In a history argumentative essay, your task goes beyond presenting facts. It would help to form an opinion, defend it with strong evidence, and persuade your reader to view history through your lens. Such essays often explore controversial issues, diverse interpretations, or underrepresented perspectives, making them thrilling.
Remember, an effective argumentative essay balances rigor with creativity. Your arguments should be based on solid research, but your writing style should maintain the reader’s interest. Short sentences, active voice, and transitional words will help ensure your essay is clear, concise, and captivating.
History Argumentative Essay Topics: Your Guide to an Engaging Argument
Picking the right history argumentative essay topics is crucial. Your topic should spark your curiosity, offer ample sources for research, and pose a challenge that motivates you to explore, argue, and persuade. The past is brimming with potential argumentative essay topics, from historical events and famous figures to social movements and cultural trends.
Here are a collection of history argumentative essay topics spanning different eras, regions, and themes to get you started. Use them as they are, or let them inspire you to develop your own.
- The Crusades: Religious Devotion or Political Expediency?
- Was the Bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki Justifiable?
- The Impact of Colonialism: Development or Exploitation?
- The Role of Women in World War II: Homefront or Battlefield?
- The American Civil War: Slavery or States’ Rights?
- The French Revolution: Fight for Liberty or Reign of Terror?
- The Renaissance: A Cultural Rebirth or a Period of Conflict?
- Martin Luther King Jr. vs. Malcolm X: Who Had a Greater Impact on the Civil Rights Movement?
- The Age of Exploration: Discovery or Destruction?
- The Industrial Revolution: Progress or Plight?
- The Fall of the Roman Empire: Invaders or Internal Decay?
- Was the Cold War Inevitable Post-World War II?
- Christopher Columbus: Hero or Villain?
- The Impact of the Protestant Reformation: Unity or Division?
- The Age of Imperialism: Prosperity or Oppression?
- The Vietnam War: A Necessary Stand or a Futile Endeavor?
- The American Revolution: Liberty or Economic Motives?
- The Russian Revolution: People’s Uprising or Bolshevik Coup?
- The Enlightenment: Philosophical Breakthrough or Social Disruption?
- The Emancipation Proclamation: Sincere or Strategic?
- The Role of Propaganda in Nazi Germany
- Was Alexander the Great Really Great?
- The Partition of India: Religious Freedom or Colonial Divide-and-Rule?
- Did the Suffragette Movement Achieve Its Goals?
- The Cuban Missile Crisis: Near-Apocalypse or Diplomatic Triumph?
- The Influence of the Printing Press: Information Revolution or Religious Turmoil?
- The Crusades: A Pathway to Enlightenment or a Dark Age Misstep?
- The Atomic Age: A New Era or a Dangerous Precedent?
- The Impact of the Ming Dynasty on China’s Global Presence
- The American Westward Expansion: Manifest Destiny or Brutal Displacement?
- The British Raj in India: Beneficial or Destructive?
- The War of 1812: Forgotten War or Critical Conflict?
- The Cultural Revolution in China: Necessary Purge or Disastrous Policy?
- Slavery: The True Cause of the American Civil War?
- The Role of Espionage in the Cold War
- The Contributions of Nikola Tesla: Overlooked or Overrated?
- The Great Depression: Natural Economic Cycle or Result of Poor Policy?
- Was the League of Nations Doomed to Fail?
- The Impact of Napoleon’s Reign on Europe
- The Salem Witch Trials: Mass Hysteria or Religious Extremism?
- The Influence of the Ottoman Empire on Modern Middle East
- Did the Treaty of Versailles Cause World War II?
- The Role of the Catholic Church in Medieval Europe
- Manifest Destiny: Expansionism or Cultural Imperialism?
- The Impact of Genghis Khan and the Mongol Empire
- The Spanish Inquisition: Religious Persecution or Political Power Play?
- The Influence of the Harlem Renaissance on African American Culture
- The Ethics of Using Atomic Bombs in WWII
- The Role of Britain in the Creation of Israel
- The Egyptian Revolution of 2011: A Springboard for Democracy?
- The Effect of the Gold Rush on California’s Development
- The Role of Social Media in the Arab Spring
- The Implications of the Scramble for Africa
- The Battle of Stalingrad: Turning Point in World War II?
- The Meiji Restoration: Western Influence or Japanese Initiative?
- The Role of Women in the French Revolution
- The Impact of the Black Death on European Society
- The Effect of the Viking Raids on European History
- The Fall of the Berlin Wall: Inevitable or Surprising?
- The Contributions of the Ancient Greeks to Modern Society
- The Influence of the Catholic Church on the European Age of Discovery
- The Impact of Gunpowder on Medieval Warfare
- The Influence of the Spanish Civil War on WWII
- The Causes and Consequences of the Thirty Years’ War
- The Role of the Railroad in the Expansion of the United States
- The Significance of the Magna Carta in the Modern Legal System
- The Impact of the Silk Road on the Exchange of Cultures
- The Role of the Mafia in Prohibition
- The Effect of Charlemagne’s Reign on Europe
- The Implications of the Columbian Exchange
- The Influence of the Persian Empire on the Modern Middle East
- The Impact of Marco Polo’s Travels on Europe
- The Effect of the French Revolution on European Politics
- The Influence of the Great Schism on Christianity
- The Impact of the Space Race on the Cold War
- The Legacy of the Aztec Empire
- The Effect of the Transatlantic Slave Trade on Africa
- The Role of the Knights Templar in the Crusades
- The Influence of Gutenberg’s Printing Press on the Reformation
- The Impact of the Han Dynasty on China
- The Causes and Effects of the Boxer Rebellion
- The Significance of the Pax Romana
- The Influence of Confucianism on East Asian Cultures
- The Impact of the Opium Wars on China
- The Role of the French Foreign Legion in Colonial France
- The Effect of the Suez Crisis on the Middle East
- The Influence of the Renaissance on Modern Art
- The Impact of the Zulu Nation on South Africa
- The Causes and Consequences of the Irish Potato Famine
- The Role of the Samurai in Feudal Japan
- The Effect of the Hundred Years’ War on England and France
- The Influence of the Roman Republic on Modern Democracies
- The Impact of the US Constitution on the French Revolution
- The Role of the Huns in the Fall of the Roman Empire
- The Causes and Effects of the Haitian Revolution
- The Influence of the Enlightenment on the US Constitution
- The Impact of the Homestead Act on the American West
- The Effect of the Plague of Justinian on the Byzantine Empire
- The Role of the Medici Family in the Italian Renaissance
Remember, the goal is not just to recount history but to form an argument and defend it persuasively. Use reliable sources like scholarly articles, credible news outlets, and respected history websites for your research ( History.com , JSTOR , Fordham University’s Internet History Sourcebooks Project , etc.).
Conclusion: Your Historical Argument Awaits
Choosing from these argumentative history essay topics is just the beginning. You can turn your chosen topic into a compelling essay with thorough research, careful planning, and passionate writing. As you debate the past, you’re not just learning history but contributing to its discussion. Let these argumentative essay topics be your first step toward a thrilling historical discourse.
📎 Related Articles
1. Hot Topic History: A Journey Through Pivotal Moments 2. Engaging 8th Grade Research Paper Topics for Budding Historians 3. Dive Deep into Western Civilization Research Paper Topics 4. Navigating Through the Labyrinth of Ancient History Topics 5. Stirring the Pot: Controversial Topics in History for Research Paper
Worried About Plagiarism?
Get 20% Off
on Plagiarism & AI Check Services!
Top of page
Collection California as I Saw It: First-Person Narratives of California's Early Years, 1849 to 1900
The missions.
After 1769, the life of the California natives who came in contact with the Spanish was reshaped by the mission fathers, not the townspeople of the pueblos or the soldiers of the presidios. The Franciscans came to California not merely to convert the tribes to Christianity but to train them for life in a European colonial society. Conversion was seldom an entirely voluntary process, and converts (neophytes) were not left to return to their old ways but were required to live in the walled mission enclosure or on rancherías, separate settlements sponsored by missions located some distance from the mission proper. There they were taught Spanish as well as the tenets of their new religion and trained in skills that would equip them for their new lives: brickmaking and construction, raising cattle and horses, blacksmithing, weaving, tanning hides, etc.

In theory, the neophytes were to live at the missions only until this process of education was complete, and then they would establish homes in the nearby pueblos. As the native people of one region were Christianized and educated, the missionaries were to move on, leaving the old missions behind to become parish churches as they built new missions in more distant locations peopled by non-converted tribes or "gentiles." In fact, neither the Spanish government nor the Franciscans ever judged any of the neophytes ready for "secularization" or life outside the mission system, and Christian natives or "Mission Indians" and their descendants remained at the missions until the system was abolished in 1834.
By that time, sixty-five years of exposure to Europeans had reduced the number of California's native peoples by half to about 150,000. Although outright warfare cost few lives, Spaniards had introduced not only Christianity but also new diseases to which the neophytes had no resistance, and thousands died in epidemics. Crowded, harsh living conditions at the missions contributed to the Indians' health problems, and infant mortality and death rates among young children soared. It was the tribes of the coast, the "Mission Indians," who were most drastically affected. Tribes like the Modocs in the northern mountains had little or no contact with the Spanish and suffered little.

The California Gold Rush’ History Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
The gold rush changed the history of California. The primary purpose of the paper is to discuss the peculiarities of the gold rush and the impact it had on people’s life.
On January 24, 1848, James Marshall, built a sawmill for John Sutter on the American River in California (Friedman 34). He found the gold nugget. He told about his discovery Sutter, who tested samples and confirmed that it is almost pure gold.
John Sutter wanted to keep everything in secret; he realized that the discovery of gold would cause a stir and prevent him on his way towards developing of the agricultural settlement New Helvetia. He allowed his employees to take gold, but he asked not to inform the world regarding the discovery of precious metal. Very soon the news spread, due to a businessman and journalist Samuel Brennan.
On August 19, 1848, the newspaper The New York Herald published the first report on the discovered gold in California and the gold rush transformed to the global stage (Friedman 61). Thousands of immigrants from around the world traveled to California in search of gold. The period from 1848 till 1855 is considered to be the most famous gold rush (Maxwell-Long 81).
The majority of the residents of San Francisco gave up their jobs and moved to the American River. Thousands of people aimed to get to California; however, it was not so easy those times. There were two ways to get to California, namely by sea or be land. Those treasure seekers, who decided to come to California by sea, were called the Argonauts. They had to either go around South America (journey lasted from five to eight months) or get to the Isthmus of Panama, cross it and wait for the ship to go to the North. By land people travelled through the California trail, from Oregon or Mexico, however, it is worth noting that these roads were difficult and dangerous.
Among those who arrived in California at the end of 1848 or at the beginning of 1849, there were a couple of thousand of Americans, who came from the Northwest of the United States, many Latin Americans (including people from Mexico, Peru, and Chile), residents of Hawaii and China (Maxwell-Long 73). People from all over the world traveled to California. It is believed that by the end of 1849 in California came about ninety thousand of people, and by 1855 more than three hundred thousand.
Not so many people became rich due to the gold rush. Simple and relatively easy production of gold was possible only in the beginning of the gold rush when the precious metal could be collected with ease. Because of this fact, the revenues dropped significantly despite the discovery of additional gold fields.
Gradually, technologies of production became more sophisticated; the expensive equipment was an essential factor. By about mid-fifties of the XIX century, the prospectors who used primitive equipment realized that it is impossible to obtain the goal using old techniques. It stimulated the development of technologies that improved and advanced the production of gold. Later such technologies were used in gold rushes in Colorado, Montana, and Alaska (Maxwell-Long 101).
It is believed that many more people in California made impressive amounts of money during the gold rush, engaged in trade rather than just gold mining. Clothes, equipment, and houses were very expensive. Merchants who sold clothes were popular.
It is commonly believed that the gold rush stimulated the invention of jeans. Jeans are the part of clothes that is the most popular nowadays. It is difficult to imagine life without jeans now, and not so many people know that jeans were invented due to the gold rush. In March 1853, Levi Strauss came to California (Lusted 82). He successfully sold clothes in New York, however, was sure that California would offer new opportunities for his business.
In 1848, son of John Sutter founded Sacramento on the territory where the first Californian gold was found. Within a few years the new city became one of the economic and transportation centers in California, and in 1854, the city became the capital of the state.
Free from immigrants who aimed to become rich and were obsessed with the gold rush, the city developed rapidly. New roads, houses, churches, hotels, and shops were built with impressive speed. In the rapidly growing California legislature was convened and adopted a constitution, and on September 9, 1850, California became the thirty-first state of the USA (Lusted 25). There are still people in California who aim to find gold. However, nowadays it is related to the entertainment and hobbies.
During the period of the gold rush, more than one hundred and twenty-five million ounces of gold (nearly four thousand tons) valued at more than 50 billion of dollars was produced in California. The biggest gold nugget found in California had a weight 195 pounds (Lusted 43).
In conclusion, it should be pointed out that it was a gold rush that has transformed California from a distant and little-known region in one of the richest states in the United States, laying the foundation for its future prosperity.
Works Cited
Friedman, Mel. The California Gold Rush . New York: Children’s, 2010. Print.
Lusted, Marcia. The California Gold Rush: A History Perspectives Book . Ann Arbor: Perspectives Library, 2015. Print.
Maxwell-Long, Thomas. Daily Life during the California Gold Rush . Santa Barbara: ABC CLIO, 2014. Print.
- St. Louis City's Pre-War History and Community
- Korean and Filipino Migrants in the US and Hawaii
- The Wars Between 1815 and WWI in Europe
- Parallels Between the Revolutions of 1848 and Arab Revolutions
- "The Piano Lesson" by August Wilson
- Harada House in Japanese American History
- Irish Immigrants in America and Their Life in 1800
- The American Declaration of Independence
- Slavery in the USA and Its Impact on Americans
- Policemen of the World: U.S. Military Force
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, September 25). The California Gold Rush' History. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-california-gold-rush-history/
"The California Gold Rush' History." IvyPanda , 25 Sept. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/the-california-gold-rush-history/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'The California Gold Rush' History'. 25 September.
IvyPanda . 2020. "The California Gold Rush' History." September 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-california-gold-rush-history/.
1. IvyPanda . "The California Gold Rush' History." September 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-california-gold-rush-history/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The California Gold Rush' History." September 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-california-gold-rush-history/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
- North America
- 12 Defining Moments In History...
12 Defining Moments in History That Shaped California

An American state with a fascinating history, California has experienced a multitude of hardships and victories that has helped define it as it’s known today. Some of these times played a larger role than others in California’s development. These top moments in history are what shaped California into the state it is today.
1579 – california’s settling.
The California coast was explored by Captain Francis Drake in 1579, resulting in the territory’s claim under England. However, even before this, Spain had been exploring and already settled in California, creating a massive tug of war between England and Spain. By the 1600s, Spain had developed missions throughout the lower region of the state, which left behind much of the state’s Latin influence that can be seen today.
1821 – Mexican Rule
California fell under Mexico’s (then called New Spain) rule a year after Mexico gained its independence from Spain in 1821. Shortly after, American travelers began to explore the state and eventually developed American settlements throughout the land. This led to the American rebels founding the California Republic in 1846, breaking way for the Mexican War where the American forces won the long battle for the state.

1849 – The Gold Rush Era
According to History.com , the Gold Rush was “arguably one of the most significant events to shape American history during the first half of the 19th century.” The striking of gold in California soil brought thousands upon thousands of prospectors and settlers to the state, all looking for that same fortuitous metal. It’s estimated that a huge $2 billion worth of gold was mined in California. The huge overflow of settlers caused much distress to the land’s Native American tribes as the arrivals violently forced the tribes uproot themselves.

1906 – Disaster and Rebuilding
The infamous San Francisco earthquake and ensuing fires struck and devastated the area on April 18, 1906. This disaster brought on the largest maritime rescue in the United States’ history. The 1906 earthquake influenced the idea of rebuilding San Francisco with stronger and more earthquake-resistant materials. This way of building is seen throughout San Francisco and earthquake-prone California today.
1911 – Women’s Rights
A special election was held in California on October 10, 1911 to grant women’s suffrage. Proposition 4 was placed on the ballot by power of Senate Constitutional Amendment Number 8 as a legislatively referred constitutional amendment . The amendment passed, granting women’s right to vote. California was the sixth state to pass this civil right, although just by 3,507 votes. Nine years later, women’s right to vote was made legal nationwide, referred to as the 19th Amendment.

1900’s – The Film Capital
California became the filmmaking capital of the country in the early 1900’s when actors and producers were trying to escape the boundaries of Thomas Edison’s Motion Picture Patents, founded in the 1890’s. Edison had a hold on what motion picture productions could and couldn’t do but his patent didn’t legally reach California. Hollywood was already a small settlement but when more and more people in the film industry flocked to California, most came to Hollywood. In 1919, the first motion picture studio was built in Edendale, just outside of Hollywood. This paved the star-studded way for film productions to develop in the Hollywood, Los Angeles, and the entire state.

Become a Culture Tripper!
Sign up to our newsletter to save up to $1,058 on our unique trips..
See privacy policy .

1965 – The Beginning of the Gay Rights Movement
On New Year’s Day 1965, California Hall in San Francisco was the venue of a huge costume party fundraiser for the Council on Religion and the Homosexual organization. The event and its attendees were heavily and unjustly harassed by law enforcement and the organization sued San Francisco Police for its prejudice actions. The ACLU organization took on the case but it was ultimately dismissed. Despite the lack of justice, this was the turning point of San Francisco’s, and eventually California’s, gay rights movement.

Late 1800s – Opening of Transcontinental Railroad
The building and opening of the Transcontinental Railroad meant it was possible to transport commodities such as coal from California to other states. Eventually, the invention of refrigerator cars led to California being the number one agricultural producer, according to the California State Railroad Foundation . California became an incredibly important state, with much needed goods being delivered to the rest of the country.
1905 – Ocean Shore Railroad
After California’s major economic rebound from the 1890’s depression, the Ocean Shore Railway Company developed the idea of building a high-speed electric railway. The plans described a railway that would run between San Francisco and Santa Cruz. In 1905 the construction began to connect this large portion of California’s coast but the project ran into issues right from the start when the 1906 earthquake struck. Development was delayed for over a year but when some of the railways finally opened, passengers enjoyed weekend trips from San Francisco to the coastal town of Pacifica. Despite the popularity, due to economic politics, the entire railway was never completed. However, this paved the way for future railway developments that currently run up and down California’s Bay Area.

1945 – The Signing of the United Nations Charter
What was considered to be the one of the largest and most important international gatherings to ever take place was at the San Francisco Conference in 1945. This meeting was held for the signing of the United Nations Charter which was created to maintain peace and security internationally. With 3,500 important guests from all over the world, the San Francisco Conference is said to be the most important conference in history.
1929 – The Completion of One of the World’s Greatest Highways
Thanks to the Great Highway and Ocean Beach Esplanade’s completion, California is considered to have one of the greatest stretch of highways ever constructed. The construction’s completion was celebrated on June 9, 1929 with one of the state’s biggest celebrations to date with over 50,000 people gathering along Lincoln Way in San Francisco . Travelers from around the globe still come to drive these scenic stretches.
1850 – Becoming the 31st State in America
Of course, one of California’s most defining moments in history was when it officially became a state. California was named the 31st state of the union on September 9, 1850.

The Grand Canyon: 5 Essential Things to Do

The 10 Most Beautiful Coastal Towns In The USA

The 9 Most Stunning Places for Fall Foliage in the USA

The 7 Most Beautiful Beaches In Maine

The 10 Best Beaches In America

The 6 Best Places to See Jean-Michel Basquiat's Art

The Midwest's 15 Most Interesting Landmarks

The 18 Most Beautiful Small Towns in the United States

10 Best Museums in Unexpected Locations in the USA

The 8 Best Beaches Near San Francisco, CA

The 9 Most Beautiful Beaches on St Thomas, US Virgin Islands

Underground Cities: 14 Fascinating Worlds Below the Surface
Culture Trip Fall Sale
Save up to $1,058 on our unique small-group trips! Limited spots.

- Post ID: 1689050
- Sponsored? No
- View Payload
The Edvocate
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- Write For Us
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Assistive Technology
- Best PreK-12 Schools in America
- Child Development
- Classroom Management
- Early Childhood
- EdTech & Innovation
- Education Leadership
- First Year Teachers
- Gifted and Talented Education
- Special Education
- Parental Involvement
- Policy & Reform
- Best Colleges and Universities
- Best College and University Programs
- HBCU’s
- Higher Education EdTech
- Higher Education
- International Education
- The Awards Process
- Finalists and Winners of The 2023 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Award Seals
- GPA Calculator for College
- GPA Calculator for High School
- Cumulative GPA Calculator
- Grade Calculator
- Weighted Grade Calculator
- Final Grade Calculator
- The Tech Edvocate
- AI Powered Personal Tutor
Teaching Students About Latin American Countries
St. norbert college president shares the challenges college students & universities face, uniform audiovisual technology levels the playing field in 4,000 classrooms, forging strategic partnerships, edmund w. gordon honored with 2024 harold w. mcgraw, jr. prize in education, navigating emotional labour in grad school, ui renames road ‘hawkeye wave way’ amid ‘for the kids’ trademark scuffle, university of minnesota libraries publishes ‘dear higher education: letters from the social justice mountain’, ri leaders urge ‘yes’ vote on $160m higher education bond bill, tiny love stories: ‘this quiet, handsome cowboy would never notice’, fascinating california history essay topics to write about.

Fascinating California History Topics to Write about
- The Medical Emancipation of Minors: A California History
- California History Textbooks and the Coming of the Civil War
- Making and Measuring the California History Standards
- Fascinating Women in California History Review
- Pacific Eldorado: A Greater California History
- The Indian and the Politics of Church and State in Provincial California History
- The Citrus Industry and the Revolution of Corporate Capitalism in Southern California History, 1887-1944
- The Need for a Broader Perspective of California History
- The Native American Experience in California History
- A World of Balance and Plenty: Land, Plants, Animals, and Humans in a Pre-European California History
- Between Crucifix and Lance: Indian-White Relations in California History, 1769-1848
- Black Telephones and Blue Denim: Business Archives in California History
- The Representation of Junípero Serra in California History
- Railroads in California History and the Far West
- Making Friends and Converts: Cloth and Clothing in Early California History
- Making Her Fame: Charlotte Perkins Gilman in California History
- Los Angeles and Southern California History Overview
- Milestones in California History: The 1846 Bear Flag Revolt: Early Cultural Conflict in California
California History Essay Titles
- Rush in California History
- More Than Missions: Native Californians and Allies Changing the Story of California History
- Digitizing California History: Issues of Selection and Description
- Empowerment, Expansion, and Engagement: Las Juntas Patrioticas in California History
- California History Knowledge Possessed by High School Seniors Compared With Adults
- History, 1846-1880
- Junipero Serra’s Impact in California History
- Women’s Place in California History
- Land, Labor, and Production: The Colonial Economy of Spanish and Mexican California History
- Splendide Californie !: Selections by French Artists in California History
- Unveiling California History Through Serious Games: Fort Ross Virtual Warehouse
- Early California Exploration and Settlement
- If the Truth Be Told: Revising California History as a Moral Objective
- From Indifference to Imperative Duty: Educating Children in Early California History
- Women, Law, and Government in California History, 1850-1890
Research Questions About Budgeting
Marxism: everything you need to know.
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

Good Essay Topics on Shia Islam

Interesting Economic Inequality Essay Topics

Research Topics About “Antigone”

Research Topics About eBay

Research Topics About Edgar Allan Poe

Fascinating Essay Topics To Write About Construction Management
(Stanford users can avoid this Captcha by logging in.)
- Send to text email RefWorks EndNote printer
Major problems in California history : documents and essays
Available online, at the library.

Green Library
| Call number | Note | Status |
|---|---|---|
| F861.5 .M26 1997B | Unknown |
More options
- Find it at other libraries via WorldCat
- Contributors
Description
Creators/contributors, contents/summary.
- Note: Each chapter concludes with Further Readings.
- 1. The Significance of California History ESSAYS James D. Houston, The Place Called California Carey McWilliams, California as "The Great Exception" James N. Gregory, The Shaping of California History
- 2. The First Californians DOCUMENTS Map of Tribal Territories Indian Material Culture The Three Worlds of the Chumash Pablo Tac Approves of His Tribe"s Conversion, 1835 Father Geronimo Boscana Describes the San Juan Capistrano Indians, 1832 A Sacramento Union Editorial Ponders the Indians" Fate, 1855 ESSAYS Arthur F. McEvoy, California Indians as Capable Resource Managers Albert L. Hurtado, Indian and Hispanic Family Patterns Compared
- 3. The Spanish Impact on the Indians, 1769-1821 DOCUMENTS Father Luis Jayme Criticizes the Behavior of Spanish Soldiers, 1772 Father Junipero Serra Reports the Destruction of the San Diego Mission, 1775 Captain Alejandro Malaspina Praises the Beneficial Impact of Spanish Missions, 1792 Lorenzo Asisara Narrates the Assassination of a Priest by Santa Cruz Indians, 1812 ESSAYS Francis F. Guest, O.F.M., Cultural Perspectives on Death and Whipping in the Missions Antonia I. Castaeda, Spanish Violence Against Amerindian Women
- 4. Mexican California: A Study in Contrasts DOCUMENTS A Mexican Commission Urges the Secularization of the California Missions, 1833 Angustias de la Guerra Ord Defends the Virtue of Mission Priests, 1878 Richard Henry Dana, Jr., Criticizes the Mexicans in California, 1834 Guadalupe Vallejo Reminisces About the Ranchero Period William Robert Garner Promotes the American Annexation of California, 1847 Selected Articles from the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, 1848 ESSAYS Hubert Howe Bancroft, Mexican California as "Lotus-Land" Douglas Monroy, The Making of Mexican Culture in Frontier California
- 5. Conflicts over Land in a New State, 1850s-1870s DOCUMENTS E. Gould Buffum Exults in Gold"s Discovery, 1850 Louisa Clapp Pokes Fun at Her Experience as a Gold "Mineress, " 1851 J. D. Borthwick Observes Chinese Gold Miners, 1851 John F. Morse Supports Traditional Agrarian Values, 1865 Henry George Censures Land Monopoly, 1871 ESSAYS JoAnn Levy, Women in the Gold Rush Paul Wallace Gates, Early California Land Policy Defended Douglas Monroy, Land and the Conflict of Legal Cultures
- 6. Disputes over Water, 1880s-1910s DOCUMENTS Lux v. Haggin Establishes the "California Doctrine, " 1886 The Wright Act Asserts Community Water Rights, 1887, 1889 Congress Acts: Selections from the Reclamation Act of 1902 John Muir Admires the Hetch Hetchy Valley, 1908 Robert Underwood Johnson Decries Paying Too High a Price for Water, 1909 ESSAYS Donald Worster, The Capitalist Control of Water Use Norris Hundley, Jr., American Political Culture and Water Use
- 7. Big Business and Urban Labor, 1860s to 1930s DOCUMENTS Henry George Expresses Skepticism about Railroads, 1868 Leland Stanford Extols the Public Benefits of Railroad Construction, 1887 Collis P. Huntington Shows Contempt for Congress, 1887 Frank Norris Excoriates the Railroad as the "Octopus, " 1901 Denis Kearney Organizes the Workingmen"s Party of California, 1877 Henryk Sienkiewicz Appraises Chinese Labor in California, 1880 The American Federation of Labor Opposes Chinese Immigration, 1902 ESSAYS Michael Kazin, The Rise of the Labor Movement in California William Deverell, The Southern Pacific Railroad Survives the Pullman Strike of 1894
- 8. California Progressives: The Ambiguities of Political and Moral Reform DOCUMENTS Franklin Hichborn Praises Reform Governor Hiram W. Johnson, 1911 John Randolph Haynes Advocates Direct Legislation, 1911 Chester H. Rowell Analyzes the Problem of Japanese Immigration, 1914 Carrie Chapman Catt Argues That Home and Government Are Related, 1907 Katherine Phillips Edson Boasts of Women"s Influence on State Legislation, 1913 Mary S. Gibson Explains Why Progressive Women Should Uplift Immigrant Women, 1914 ESSAYS Gerald Woods, Progressive Efforts to Banish Vice Gayle Gullett, Women Progressives and Immigrant Women
- 9. Hollywood and the California Dream, 1910s-1930s DOCUMENTS Cecil B. DeMille Reveals How He Creates Special Effects, 1927 A. H. Giannini Explains Why He Decided to Finance the Film Industry, 1926 Harmon B. Stephens Exposes How Films Lower Moral Standards, 1926 Ruth Suckow Analyzes the Appeal of Hollywood Movie Sets, 1939 ESSAYS Lary May, Hollywood and the California Dream Mike Davis, California"s Dark Underside
- 10. Farmworker Struggles in the 1930s DOCUMENTS The California Department of Industrial Relations Evaluates Agricultural Labor Contracts, 1930 Carlos Bulosan Describes the Harsh Existence of Filipino Migrant Farmworkers John Steinbeck Portrays Social Pressures in Agricultural California, 1939 James Rorty Reports on Conditions in the Imperial Valley, 1935 Grower Frank Stokes Defends Mexican Farmworkers" Efforts to Organize, 1936 Ralph H. Taylor Rallies California"s Growers to Protect Their Interests, 1938 ESSAYS Cletus E. Daniel, Communist Organizers in the Imperial Valley Labor Struggles Devra Anne Weber, Mexicano Farmworkers on Strike
- 11. The Impact of World War II on California"s Economy DOCUMENTS The U. S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Reports on California"s Airframe Industry, 1945 Kaiser Shipyard Workers Fight on the Home Front, 1943 Marye Stumph Recalls Her Work Experiences in an Aircraft Factory Industrial Leaders Assess the West"s Postwar Economic Prospects, 1946 ESSAYS Gerald D. Nash, World War II Transforms California"s Economy Paul Rhode, An Economic Historian Challenges the Nash Thesis
- 12. The Changing Lives of Women and Minorities, 1940s-1950s DOCUMENTS Charles Kikuchi Observes Life in an American "Concentration Camp, " 1942 Two Poems about the Camps, "Barracho Home" and "Mud" Fanny Christina Hill Fights Discrimination against Black Workers in the Aircraft Industry Willard Waller Announces the Postwar Battle of the Sexes, 1945 ESSAYS Sucheng Chan, The Incarceration of Japanese Americans during World War II Albert S. Broussard, Changes in the Status of African Americans in the 1940s and 1950s Joan M. Jensen and Gloria Ricci Lothrop, Women"s Wartime and Postwar Experiences
- 13. Politics and Protest, 1960s-1970s DOCUMENTS Mario Savio Defends the Free Speech Movement at Berkeley, 1965 Ronald Reagan Denounces "The Morality Gap at Berkeley, " 1966 Bobby Seale Explains What the Black Panther Party Stands For, 1968 Manifesto of the Chicano Student Conference, 1969 Declaration of the Asian American Political Alliance, 1969 Indians of All Tribes Occupy Alcatraz Island, 1970 Why Secretaries in Academia Are Fed Up, 1971 ESSAYS W. J. Rorabaugh, Berkeley in the 1960s Lou Cannon, Ronald Reagan as Governor
- 14. The Rise of Information Capitalism DOCUMENTS California Computer Companies, 1989 Art Garcia Describes California"s New Economic Frontier, 1984 Donald Woutat Comments on the Resignation of Steven Jobs from Apple Computer, 1985 Faith Alchorn Details the Use of Computers in Political Campaigns, 1988 Duane Spilsbury Reports on Telecommuting, 1989 ESSAYS AnnaLee Saxenian, The Origins and Business Culture of Silicon Valley Judith Stacey, Women, Families, and Work in the Information Industry Spencer C. Olin, Globalization and the Politics of Locality in Orange County
- 15. The Environment and the Quality of Life Since 1960 DOCUMENTS Samuel E. Wood and Alfred Heller Oppose Urban Sprawl, 1961 Frank M. Stead Assesses California Water Pollution, 1968 Richard Reinhardt Looks at Air Pollution Problems, 1982 A Government Commission Discusses the Dangers of Pesticides, 1988 Carl Anthony Outlines Why African Americans Should Be Environmentalists, 1990 Ronald Bailey Denounces the "Eco-Scam, " 1993 ESSAYS Tim Palmer, California"s Threatened Environment Dixy Lee Ray, Natural Ways to Reduce Urban Air Pollution Robert D. Bullard, Environmental Racism and Justice
- 16. Racial and Class Tensions, 1960s-1990s DOCUMENTS The McCone Commission Analyzes the Watts Riot, 1965 David Rieff Sees Los Angeles as the Capital of the Third World, 1991 Mwatabu S. Okantah Protests the Beating of Rodney King, 1993 Armando Navarro Provides a Latino Perspective on the 1992 Disorders, 1993 Eui-Young Yu Offers a Korean American Perspective on the Los Angeles Riots, 1992 Patrick J. Buchanan Condemns the "Barbarism" of the Rioters, 1992 John Bryant Encourages Corporate America to Invest in Minority Communities, 1995 Lynell George and David Ferrell Analyze the Staggering Racial Complexity of Los Angeles, 1995 George Regas Advocates a Shared Moral Vision, 1995 ESSAYS Melvin L. Oliver, James H. Johnson, Jr., and Walter C. Farrell, Jr., The Causes of the 1992 Los Angeles Civil Disorders Sumi K. Cho, Perceptions Across the Racial Divide Document Sources Essay Sources.
- (source: Nielsen Book Data)
Bibliographic information
Browse related items.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
california - List of Essay Samples And Topic Ideas
An essay on California can explore the history, geography, culture, and significance of this diverse state in the United States. It can discuss California’s role in industries like technology, entertainment, and agriculture, as well as its natural beauty, environmental challenges, and its place in American pop culture and history. A vast selection of complimentary essay illustrations pertaining to California you can find at PapersOwl Website. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.
The People of the State of California V. Orenthal James Simpson
Trial Orenthal James “O.J.” Simpson was born on July 9, 1947 in San Francisco, California and is a former NFL player, actor, and broadcaster. He is well known for his defence in the murder of Nicole Brown Simpson and Ronald Lyle Goldman. This trial is one of most popular trials in American History and is also one of the most controversial because of the verdict, or outcome. On the night of June 12, 1994, Nicole Brown and Ron Goldman were […]
California Housing Crisis Research Paper
California, the land that once embodied the pioneer spirit and the American dream, now embodies the American nightmare; the rich get richer while the hardworking sink deeper into the mud of fiscal disparity. Those who cannot afford life in large cities often paradoxically cannot afford a higher paying job. Celebrities and lawyers reside in hilltop mansions while the economically lower classes flounder to make a living and stay in their homes. College graduates continue to move back into their parents’, […]
SWOT Analysis: University Comparison
Introduction Student’s high school grades and test scores remain to be the major component to determine their admittance to a higher-ed institution, researchers have indicated that focusing only on the grades and/or test scores is not enough when evaluating the capability of the students’ who apply for admission to a four year degree granting institutions. According to Loftus (2018), most higher-ed institutions in the United States use various admission strategies to ensure that the students admitted into these institutions not […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Homelessness in California is a Real Problem
California is homeless. What I mean when I say homeless is, “without homes.” California, for a long time now, has had an issue with providing homes for citizens to purchase, but in the event they do have a home for sale, it's often too expensive. It was only recently, however, that the issue got so out of hand to the point where the state declared it, a state of emergency. At this level it is now the nations job to […]
History of Criminal Law in California
In searching criminal history, and how it all began I found some interesting websites and my textbook. So what is criminal law according to "Criminal Law Today by Schmalleger, PH. D pg. 3) criminal law means the body of rules and regulations that defines and specifies punishment for offenses of a public nature or for wrongs committed against the state of society. Also called the penal code. I will be talking abut the 5 areas of the history of criminal […]
Unveiling the Varied Terrain of California: a Geographic Mosaic
Unveiling the Varied Terrain of California: A Geographic Mosaic Introduction The state of California, affectionately known as the Golden State, is a realm of geographic diversity and natural splendor. From the sun-kissed Pacific shores to the towering peaks of the Sierra Nevada, and from the arid stretches of its deserts to the verdant expanses of the Central Valley, California's landscape is as multifaceted as its cultural fabric. A Landscape of Contrasts The physical geography of California is a study in […]
California State University of Long Beach
The need for sex education in schools, no matter public or private school, should be provided for all students. Schools are institutions for providing information and informing students all that they need to know to live a knowledgeable life. Withholding comprehensive sex education from students is without a doubt a biased infraction on schools. Although the true criticism falls on the states that only want to provide abstinence-only sex education and not comprehensive. With growing and developing students going through, […]
California Health Insurance Fairness Act
Overview of health problem In the modern society, health insurance is an imperative issue that helps with the firm address of major activities to be carried out. The identification of ardent activities that would drive the health service providers to have a package of insurance has led to a great level of difference in the society. While there are employers who have the capacity to provide their employees with the health insurance and certain benefits, there are others who do […]
Capital Punishment in the State of California
Along with costly trials and imprisonments comes the possibility of wrongfully executing an innocent human being – something of which has unfortunately occurred after past death sentence trials. A wrongful execution can stem anywhere from: inadequate legal representation, police and prosecutorial misconduct to mistaken eyewitness testimonies and racial prejudice or community/political pressures to solve a case. “According to a sweeping new statistical analysis, … the rate of wrongful death sentences in the U.S. is much higher than experts have estimated” […]
California’s Economic Pulse: a Close Look at GDP Per Capita
California, often perceived as a land of dreams and opportunities, holds a distinctive place in the American economic landscape. Its GDP per capita—a measure of the economic output per person—paints a picture of prosperity, dynamism, and complexity. But what does this figure truly reveal about the Golden State? To begin, California's GDP per capita is a staggering testament to its economic prowess. With a GDP per capita that rivals entire countries, California stands as one of the wealthiest regions in […]
The Impact and Legacy of the 1989 Northridge Earthquake
In the early hours of January 17, 1994, Southern California was violently awakened by one of the most significant earthquakes in its modern history – the Northridge Earthquake. Registering a magnitude of 6.7, this seismic event tore through the region, causing widespread destruction and permanently altering the landscape, infrastructure, and the collective consciousness of the affected communities. As the dust settled and the aftershocks subsided, the profound impact and enduring legacy of the 1994 Northridge Earthquake became undeniably clear, leaving […]
California: a Multifaceted Examination
This essay offers a comprehensive analysis of California, encompassing its diverse geographical features, socio-cultural dynamics, economic significance, and environmental challenges. Through a multidimensional lens, it elucidates the state's unique characteristics, historical evolution, and contemporary complexities, shedding light on its enduring allure and enduring challenges. Introduction: California stands as an emblem of diversity and dynamism, encapsulating a myriad of landscapes, cultures, and opportunities. From the sun-kissed beaches of the Pacific Coast to the towering peaks of the Sierra Nevada, the state's […]
Joaquin Murrieta: the Legend of California’s Robin Hood
In the annals of California's rich and tumultuous history, few figures emerge with the mystique and intrigue as Joaquin Murrieta. Born in Mexico during the tumultuous mid-19th century, Murrieta would go on to become a symbol of resistance and rebellion against the injustices faced by the Hispanic community in the American West. The tale of Joaquin Murrieta reads like a thrilling novel, blurring the lines between fact and folklore. Historical records are scarce, and much of what we know about […]
Hotel California: Unraveling the Sonic Enigma of Excess and Existence
In the kaleidoscope of musical mystique, the Eagles' "Hotel California" stands not just as a song but as a beguiling tapestry woven with elusive threads of meaning. Released in the heady days of 1977, this rock anthem has since become a sonic enigma, inviting listeners into a shadowy realm where the California dream transforms into an ethereal nightmare. Beyond its haunting melody lies a narrative that transcends the superficial glamor of a hotel, unraveling a tale of existential complexities, the […]
Additional Example Essays
- Research Paper #1 – The Trail of Tears
- Rosa Parks Vs. Harriet Tubman
- Abraham Lincoln and the Gettysburg Address
- Greek and Roman affects on Western Civilization
- The Philosophies of W.E.B Du Bois and Booker T. Washington
- Martin Luther King as Activist and Outsider
- How Coming To America Changed My Life
- Enlightenment and The French Revolution
- Leadership and the Army Profession
- Letter From Birmingham Jail Rhetorical Analysis
- Compare And Contrast In WW1 And WW2
- Why College Should Not Be Free
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
117 California History Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. California, often referred to as the Golden State, is a land rich in history and diversity. From its indigenous peoples to the Spanish colonization, the Gold Rush, and the rise of Hollywood, California has played a significant role in shaping American history. If you are tasked with writing ...
The California Gold Rush' History. The primary purpose of the paper is to discuss the peculiarities of the gold rush and the impact it had on people's life. California Restaurants' History and Cuisine Style. The primary goal of this essay is to provide an analysis of the aspects of Californian cuisine and food, in general.
153 US History Topics [2024 US History Essay Ideas] American history is not as long as the European one. However, it's one of the richest histories in the world. It's full of controversies, different opinions, and interesting facts. Those who study American history will find how many voices, perspectives, and points of view can coexist.
Along with our how-to guides and our general guide to the collection, the California History Room librarians have spent hundreds of hours plumbing our collections to develop research guides for specific California topics. You can see our current guides below. If you cannot find a guide to the topic you are researching or if you still have ...
History of California Essay. The aftermath of the Second World War had several significant impacts on the United States, especially in California (Schoenherr, 2017). The US entered the war following an attack on Pearl Harbor by the Japanese forces, thereby acting as a turning point in the immense conflict of the 21 st century (Schoenherr, 2017).
The disruptions of the Gold Rush proved devastating for California's native groups, already in demographic decline due to Spanish and Mexican intrusion. The state's native population plummeted from about 150,000 in 1848 to 30,000 just 12 years later. As foreigners methodically mined, hunted, and logged native groups' most remote hiding places ...
The Name and the Geography California's history is so romantic and filled with legend that it is fitting that the region was named for a fictional island paradise described in the 16th century Spanish romance Las Serges de Esplandian, which was popular when Spain's explorers first came to this part of North America's Pacific Coast.
About the Journal. California History is the premier journal of historical writing on California. Showcasing exceptional scholarship, engaging writing, and innovative research, California History is essential reading for students and scholars of the history of California and the West, as well as California residents curious to understand the imprint of the state's rich past.
California became the 31st state in 1850. It leads the U.S. in agricultural production, it is known for its tech industry, and it is home to famous cultural institutions and national parks ...
This volume of original essays by leading scholars is an innovative, thorough introduction to the history and culture of California. Includes 30 essays by leading scholars in the field Essays range widely across perspectives, including political, social, economic, and environmental history Essays with similar approaches are paired and grouped to work as individual pieces and as companions to ...
California: A History. By Kevin Starr. Modern Library; 416 pages; $20. For a broad overview of California's story start with Kevin Starr's one-volume history of the state. The historian and ...
By 1851 California had applied for statehood and became the thirty first state. News traveled fast and far, prospectors came from around the world to try their hand in panning gold. Gold mining had reached its peak by 1852. More than $80 million in gold had been pulled from mines (Encyclopedia.com, 2015). Even though.
Annexation of California - (1846-1847) California Gold Rush - (1849) The Slavery Compromise of 1850. Becoming the 31st State in America - (1850) California in the American Civil War - (1861) Opening of Transcontinental Railroad - (1869) The Great San Francisco Earthquake - (1906)
ISSN. 01622897. EISSN. 23271485. SUBJECTS. History, History, American Studies, Area Studies. COLLECTIONS. Arts & Sciences V Collection, JSTOR Archival Journal & Primary Source Collection. Published since 1922, California History contains scholarly, illustrated essays focusing on California and the West from pre-Columbian to recent times.
2. Engaging 8th Grade Research Paper Topics for Budding Historians. 3. Dive Deep into Western Civilization Research Paper Topics. 4. Navigating Through the Labyrinth of Ancient History Topics. 5. Stirring the Pot: Controversial Topics in History for Research Paper. Ignite historical debates with our 99 compelling history argumentative essay ...
After 1769, the life of the California natives who came in contact with the Spanish was reshaped by the mission fathers, not the townspeople of the pueblos or the soldiers of the presidios. The Franciscans came to California not merely to convert the tribes to Christianity but to train them for life in a European colonial society. Conversion was seldom an entirely voluntary process, and ...
1. The story line I am going to talk about is power and oppression, throughout California 's history there has been many events of power and oppression that has shaped California's history in many ways. I selected this storyline because I am able to relate many of these events that have happened throughout history.
The California Gold Rush' History Essay. The gold rush changed the history of California. The primary purpose of the paper is to discuss the peculiarities of the gold rush and the impact it had on people's life. On January 24, 1848, James Marshall, built a sawmill for John Sutter on the American River in California (Friedman 34).
1906 - Disaster and Rebuilding. The infamous San Francisco earthquake and ensuing fires struck and devastated the area on April 18, 1906. This disaster brought on the largest maritime rescue in the United States' history. The 1906 earthquake influenced the idea of rebuilding San Francisco with stronger and more earthquake-resistant materials.
Spread the love. Fascinating California History Topics to Write about. The Medical Emancipation of Minors: A California History. California History Textbooks and the Coming of the Civil War. Making and Measuring the California History Standards. Fascinating Women in California History Review.
The Significance of California History ESSAYS James D. Houston, The Place Called California Carey McWilliams, California as "The Great Exception" James N. Gregory, The Shaping of California History; 2. The First Californians DOCUMENTS Map of Tribal Territories Indian Material Culture The Three Worlds of the Chumash Pablo Tac Approves of His ...
14 essay samples found. An essay on California can explore the history, geography, culture, and significance of this diverse state in the United States. It can discuss California's role in industries like technology, entertainment, and agriculture, as well as its natural beauty, environmental challenges, and its place in American pop culture ...
California DAR Awards American History Essay Contest. ... Each year, a selected topic for use during the academic year is announced, and contest instructions are published online and sent to schools by participating DAR chapters. Essays are judged for historical accuracy, adherence to the topic, organization of materials, interest, originality ...
From September 15 to October 15, California courts and the Judicial Council of California join the nation in recognizing Hispanic Heritage Month. Learn about historic jurists and landmark state and federal court cases impacting Hispanic/Latino history in California. If you are not able to view the timeline below, click here.