Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Women's Rights — Equal Rights for Women: The Ongoing Struggle for Gender Equality

Equal Rights for Women: The Ongoing Struggle for Gender Equality
- Categories: Women's Rights
About this sample

Words: 613 |
Published: Mar 6, 2024
Words: 613 | Page: 1 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1151 words
2 pages / 926 words
2 pages / 702 words
2 pages / 711 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Women's Rights
Abina and the Important Men, written by Trevor R. Getz and Liz Clarke, is a graphic history that tells the story of Abina Mansah, a young West African woman who was enslaved in the 19th century. The book provides a unique [...]
Abortion is a highly debated and controversial topic that has sparked passionate discussions worldwide. In today's society, where individual rights and freedoms are highly valued, the issue of abortion remains a divisive and [...]
Medically ending a pregnancy before it has the chance to result in the birth of a baby is abortion (Izugbara, Otsola, & Ezeh, 2009). Abortion is yet to be legalized in Kenya due to pro-life and pro-choice squabbles. Pro-life [...]
Feminism, the belief in social, economic, and political equality of the sexes, has been a prominent force in shaping society for many decades. Throughout its history, feminism has made significant advancements in women's rights [...]
Feminism is defined as “the theory of the political, economic, and social equality of the sexes and the organized activities on behalf of women’s rights and interests” (Merriam-Webster). This includes liberation from sexual, [...]
Feminism can mean a lot of things but what it mostly comes down to is gender equality, being able to control your own life and live the choices you make. It is not about hating men or thinking that women are superior. In this [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
A global story
This piece is part of 19A: The Brookings Gender Equality Series . In this essay series, Brookings scholars, public officials, and other subject-area experts examine the current state of gender equality 100 years after the 19th Amendment was adopted to the U.S. Constitution and propose recommendations to cull the prevalence of gender-based discrimination in the United States and around the world.
The year 2020 will stand out in the history books. It will always be remembered as the year the COVID-19 pandemic gripped the globe and brought death, illness, isolation, and economic hardship. It will also be noted as the year when the death of George Floyd and the words “I can’t breathe” ignited in the United States and many other parts of the world a period of reckoning with racism, inequality, and the unresolved burdens of history.
The history books will also record that 2020 marked 100 years since the ratification of the 19th Amendment in America, intended to guarantee a vote for all women, not denied or abridged on the basis of sex.
This is an important milestone and the continuing movement for gender equality owes much to the history of suffrage and the brave women (and men) who fought for a fairer world. Yet just celebrating what was achieved is not enough when we have so much more to do. Instead, this anniversary should be a galvanizing moment when we better inform ourselves about the past and emerge more determined to achieve a future of gender equality.
Australia’s role in the suffrage movement
In looking back, one thing that should strike us is how international the movement for suffrage was though the era was so much less globalized than our own.
For example, how many Americans know that 25 years before the passing of the 19th Amendment in America, my home of South Australia was one of the first polities in the world to give men and women the same rights to participate in their democracies? South Australia led Australia and became a global leader in legislating universal suffrage and candidate eligibility over 125 years ago.
This extraordinary achievement was not an easy one. There were three unsuccessful attempts to gain equal voting rights for women in South Australia, in the face of relentless opposition. But South Australia’s suffragists—including the Women’s Suffrage League and the Woman’s Christian Temperance Union, as well as remarkable women like Catherine Helen Spence, Mary Lee, and Elizabeth Webb Nicholls—did not get dispirited but instead continued to campaign, persuade, and cajole. They gathered a petition of 11,600 signatures, stuck it together page by page so that it measured around 400 feet in length, and presented it to Parliament.
The Constitutional Amendment (Adult Suffrage) Bill was finally introduced on July 4, 1894, leading to heated debate both within the houses of Parliament, and outside in society and the media. Demonstrating that some things in Parliament never change, campaigner Mary Lee observed as the bill proceeded to committee stage “that those who had the least to say took the longest time to say it.” 1
The Bill finally passed on December 18, 1894, by 31 votes to 14 in front of a large crowd of women.
In 1897, Catherine Helen Spence became the first woman to stand as a political candidate in South Australia.
South Australia’s victory led the way for the rest of the colonies, in the process of coming together to create a federated Australia, to fight for voting rights for women across the entire nation. Women’s suffrage was in effect made a precondition to federation in 1901, with South Australia insisting on retaining the progress that had already been made. 2 South Australian Muriel Matters, and Vida Goldstein—a woman from the Australian state of Victoria—are just two of the many who fought to ensure that when Australia became a nation, the right of women to vote and stand for Parliament was included.
Australia’s remarkable progressiveness was either envied, or feared, by the rest of the world. Sociologists and journalists traveled to Australia to see if the worst fears of the critics of suffrage would be realised.
In 1902, Vida Goldstein was invited to meet President Theodore Roosevelt—the first Australian to ever meet a U.S. president in the White House. With more political rights than any American woman, Goldstein was a fascinating visitor. In fact, President Roosevelt told Goldstein: “I’ve got my eye on you down in Australia.” 3
Goldstein embarked on many other journeys around the world in the name of suffrage, and ran five times for Parliament, emphasising “the necessity of women putting women into Parliament to secure the reforms they required.” 4
Muriel Matters went on to join the suffrage movement in the United Kingdom. In 1908 she became the first woman to speak in the British House of Commons in London—not by invitation, but by chaining herself to the grille that obscured women’s views of proceedings in the Houses of Parliament. After effectively cutting her off the grille, she was dragged out of the gallery by force, still shouting and advocating for votes for women. The U.K. finally adopted women’s suffrage in 1928.
These Australian women, and the many more who tirelessly fought for women’s rights, are still extraordinary by today’s standards, but were all the more remarkable for leading the rest of the world.
A shared history of exclusion
Of course, no history of women’s suffrage is complete without acknowledging those who were excluded. These early movements for gender equality were overwhelmingly the remit of privileged white women. Racially discriminatory exclusivity during the early days of suffrage is a legacy Australia shares with the United States.
South Australian Aboriginal women were given the right to vote under the colonial laws of 1894, but they were often not informed of this right or supported to enroll—and sometimes were actively discouraged from participating.
They were later further discriminated against by direct legal bar by the 1902 Commonwealth Franchise Act, whereby Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people were excluded from voting in federal elections—a right not given until 1962.
Any celebration of women’s suffrage must acknowledge such past injustices front and center. Australia is not alone in the world in grappling with a history of discrimination and exclusion.
The best historical celebrations do not present a triumphalist version of the past or convey a sense that the fight for equality is finished. By reflecting on our full history, these celebrations allow us to come together, find new energy, and be inspired to take the cause forward in a more inclusive way.
The way forward
In the century or more since winning women’s franchise around the world, we have made great strides toward gender equality for women in parliamentary politics. Targets and quotas are working. In Australia, we already have evidence that affirmative action targets change the diversity of governments. Since the Australian Labor Party (ALP) passed its first affirmative action resolution in 1994, the party has seen the number of women in its national parliamentary team skyrocket from around 14% to 50% in recent years.
Instead of trying to “fix” women—whether by training or otherwise—the ALP worked on fixing the structures that prevent women getting preselected, elected, and having fair opportunities to be leaders.
There is also clear evidence of the benefits of having more women in leadership roles. A recent report from Westminster Foundation for Democracy and the Global Institute for Women’s Leadership (GIWL) at King’s College London, shows that where women are able to exercise political leadership, it benefits not just women and girls, but the whole of society.
But even though we know how to get more women into parliament and the positive difference they make, progress toward equality is far too slow. The World Economic Forum tells us that if we keep progressing as we are, the global political empowerment gender gap—measuring the presence of women across Parliament, ministries, and heads of states across the world— will only close in another 95 years . This is simply too long to wait and, unfortunately, not all barriers are diminishing. The level of abuse and threatening language leveled at high-profile women in the public domain and on social media is a more recent but now ubiquitous problem, which is both alarming and unacceptable.
Across the world, we must dismantle the continuing legal and social barriers that prevent women fully participating in economic, political, and community life.
Education continues to be one such barrier in many nations. Nearly two-thirds of the world’s illiterate adults are women. With COVID-19-related school closures happening in developing countries, there is a real risk that progress on girls’ education is lost. When Ebola hit, the evidence shows that the most marginalized girls never made it back to school and rates of child marriage, teen pregnancy. and child labor soared. The Global Partnership for Education, which I chair, is currently hard at work trying to ensure that this history does not repeat.
Ensuring educational equality is a necessary but not sufficient condition for gender equality. In order to change the landscape to remove the barriers that prevent women coming through for leadership—and having their leadership fairly evaluated rather than through the prism of gender—we need a radical shift in structures and away from stereotypes. Good intentions will not be enough to achieve the profound wave of change required. We need hard-headed empirical research about what works. In my life and writings post-politics and through my work at the GIWL, sharing and generating this evidence is front and center of the work I do now.
GIWL work, undertaken in partnership with IPSOS Mori, demonstrates that the public knows more needs to be done. For example, this global polling shows the community thinks it is harder for women to get ahead. Specifically, they say men are less likely than women to need intelligence and hard work to get ahead in their careers.
Other research demonstrates that the myth of the “ideal worker,” one who works excessive hours, is damaging for women’s careers. We also know from research that even in families where each adult works full time, domestic and caring labor is disproportionately done by women. 5
In order to change the landscape to remove the barriers that prevent women coming through for leadership—and having their leadership fairly evaluated rather than through the prism of gender—we need a radical shift in structures and away from stereotypes.
Other more subtle barriers, like unconscious bias and cultural stereotypes, continue to hold women back. We need to start implementing policies that prevent people from being marginalized and stop interpreting overconfidence or charisma as indicative of leadership potential. The evidence shows that it is possible for organizations to adjust their definitions and methods of identifying merit so they can spot, measure, understand, and support different leadership styles.
Taking the lessons learned from our shared history and the lives of the extraordinary women across the world, we know evidence needs to be combined with activism to truly move forward toward a fairer world. We are in a battle for both hearts and minds.
Why this year matters
We are also at an inflection point. Will 2020 will be remembered as the year that a global recession disproportionately destroyed women’s jobs, while women who form the majority of the workforce in health care and social services were at risk of contracting the coronavirus? Will it be remembered as a time of escalating domestic violence and corporations cutting back on their investments in diversity programs?
Or is there a more positive vision of the future that we can seize through concerted advocacy and action? A future where societies re-evaluate which work truly matters and determine to better reward carers. A time when men and women forced into lockdowns re-negotiated how they approach the division of domestic labor. Will the pandemic be viewed as the crisis that, through forcing new ways of virtual working, ultimately led to more balance between employment and family life, and career advancement based on merit and outcomes, not presentism and the old boys’ network?
This history is not yet written. We still have an opportunity to make it happen. Surely the women who led the way 100 years ago can inspire us to seize this moment and create that better, more gender equal future.
- December 7,1894: Welcome home meeting for Catherine Helen Spence at the Café de Paris. [ Register , Dec, 19, 1894 ]
- Clare Wright, You Daughters of Freedom: The Australians Who Won the Vote and Inspired the World , (Text Publishing, 2018).
- Janette M. Bomford, That Dangerous and Persuasive Woman, (Melbourne University Press, 1993)
- Cordelia Fine, Delusions of Gender: The Real Science Behind Sex Differences, (Icon Books, 2010)
This piece is part of 19A: The Brookings Gender Equality Series. Learn more about the series and read published work »
About the Author
Julia gillard, distinguished fellow – global economy and development, center for universal education.
Gillard is a distinguished fellow with the Center for Universal Education at the Brookings Institution. She is the Inaugural Chair of the Global Institute for Women’s Leadership at King’s College London. Gillard also serves as Chair of the Global Partnership for Education, which is dedicated to expanding access to quality education worldwide and is patron of CAMFED, the Campaign for Female Education.
Read full bio
MORE FROM JULIA GILLARD

Advancing women’s leadership around the world
More from the 19a series.

The gender revolution is stalling—What would reinvigorate it?
What’s necessary to reinvigorate the gender revolution and create progress in the areas where the movement toward equality has slowed or stalled—employment, desegregation of fields of study and jobs, and the gender pay gap?

The fate of women’s rights in Afghanistan
John R. Allen and Vanda Felbab-Brown write that as peace negotiations between the Afghan government and the Taliban commence, uncertainty hangs over the fate of Afghan women and their rights.
- Media Relations
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Teaching Resources
- Upcoming Events
- On-demand Events
Women's Power in the Struggle for Freedom and Equal Rights
- facebook sharing
- email sharing
“Democracy is a universally recognized ideal based on common values shared by people across the world, irrespective of cultural, political, social and economic differences. As recognized in the Vienna Declaration and Programme of Action , democracy is based on the freely expressed will of the people to determine their own political, economic, social and cultural systems and their full participation in all aspects of their lives . Democracy, development, rule of law and respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms are interdependent and mutually reinforcing.” - United Nations, Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights
The principles of democracy insist on, especially from a twenty-first century perspective, the inclusion of all people, regardless of gender, race, sexual orientation, or ability. And yet governments around the world have a history of barring certain classes of people from being heard, seen, and fairly represented. Throughout history this has been especially true for women. And yet, despite repeated and ongoing attempts to sideline women in society, there has always been a consistent female force, fighting for freedom, equality, and democratic ideals.
For example, Chilean women who lived during Pinochet’s dictatorship were under the threat of constant danger, but they resisted by creating dissident art and forming the Moviemento Pro Emancipación de la Mujer. The Turkish coup of 1980 inspired a feminist movement that existed in open rebellion. They decried their loss of freedom and organized mass protests, including a 1987 march against gender-based violence. And here, in the United States of America, one of the oldest modern democracies in the world, it took a staggering 144 years for women in the US to be granted suffrage with the passage of the 19th amendment in 1920. It would take 45 more years for the Voting Rights Act of 1965 to be passed before Black women gained full access to the vote. But the right to vote was not just granted to women—they had to fight for it.
There are endless examples of “the fairer sex” doing anything in their power to be seen as the equal sex—these examples are a testament to women's impact on society, government, and history. As we celebrate Women’s History Month in March, Facing History has curated a list of resources to showcase female upstanders who have fought for freedom, human rights, and promoted the principles of democracy, even under oppressive regimes and laws restricting them from representation.
The American Revolution and Challenging the Ideals of a Fledgling Democracy
Elizabeth freeman.
Entering the world as Mum Bett in the mid-sixteenth century, Elizabeth Freeman was born into slavery. As the white men around her—and notably her enslaver, Colonel Ashley—spoke of rights and freedoms amidst the creation of the Declaration of Independence and war with England, the idea of her own freedom took root. Freeman acquired legal representation in Massachusetts and sued for her right to be free. She became the first African American to win her freedom from the courts in Massachusetts, leading to abolition of slavery in that state. Learn more about Freeman’s life from the National Women’s History Museum and from the New-York Historical Society .
Judith Sargent Murray
Born into a wealthy family in 1751, Judith Sargent Murray was curious and intelligent, but was not permitted to attend school because of her gender. Undeterred, she turned to her family’s extensive library and became a self-taught intellectual and writer. Murray was a radical (at the time) advocate for white women’s rights, declaring that men and women held equal ability if given equal access to education. Murray penned her first essay, “On the Equality of the Sexes,” in 1770—it was finally published 20 years later.
This Facing History Reading , included in our US History Curriculum Collection , excerpts “On the Equality of the Sexes” and offers questions and exercises for deeper reflection and connection to the text. The entire essay can be found here .
Learn more about Murray’s life from the National Women’s History Museum .
Suffragettes and the Right to Vote
Frances ellen watkins harper.
In 1825 Frances Ellen Watkins Harper was born to free African American parents. Following the death of her parents, she was raised by her aunt and uncle, the latter of whom was an impassioned abolitionist. As a young adult she was mentored by her uncle’s friend William Still known as the “father of the Underground Railroad.” Harper then became a strong voice in the anti-slavery movement and a fierce supporter of women’s rights, publishing works based on these ideals and delivering speeches across the country.
This Facing History Reading excerpts one of her most famous speeches and offers connection questions for deeper learning.
Learn more about Harper’s life from the National Women’s History Museum .
Emmeline Pankhurst
It is perhaps no surprise that Emmeline Pankhurst became among the most influential suffragists in Great Britain. Born in 1858, she was raised by parents committed to the full expansion of rights to women. She went on to found the Women’s Franchise League and later the Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU) whose famous slogan was “Deeds not Words.” Pankhurst threw her body and mind into the suffrage cause including participating in a hunger strike and being jailed on multiple occasions for her provocative protests.
This Facing History Handout on Women in Edwardian Society includes excerpts from Pankhurt’s “Freedom or Death” speech and offers a wide range of connection questions.
Learn more about Pankhurst’s life from the National Park Service .
The Pursuit for Civil Rights and Racial Equality
Anti-apartheid movement.
Apartheid is an Afrikaans word meaning “apartness.” South Africans abolished slavery in 1834, but the colonial influence on the country made segregation the de facto state. It wasn’t until the National Party, which ran on a platform of Afrikaner nationalism, won the 1948 South African election that segregation was codified by law. One way that Black women in South Africa pushed back on segregationist policies was to protest the limitations placed on the free movement of Black Africans in the country. The 1950s saw the formation of the Federation of South African Women. In 1956 this grassroots movement enjoined a crowd 20,000 strong to march to Pretoria. Facing History’s Confronting Apartheid Collection provides a comprehensive set of lessons to explore critical moments in South Africa's history. This collection includes the Reading: Women Rise Up Against Apartheid and Change the Movement .
Mamie Till-Mobley
Mamie Carthan was born in Mississippi in 1921, but as a toddler she moved just outside of Chicago, Illinois with her parents. On July 25, 1941 she gave birth to her only child, Emmett Till. In the summer of 1955, when Emmett was 14, Mamie dropped her son off at the train station in Chicago to go visit her Uncle Moses’s farm in Mississippi and spend some time with family. He never came home. On August 28 Emmett was brutally murdered by a group of white men, led by the husband of a shopkeeper who was incensed that the young boy had allegedly whistled at his wife. The horrific death of her son, and the subsequent acquittal of Emmett’s murderers, resulted in Mamie Till-Mobley’s emergence as a leading activist for the civil rights movement.
Facing History’s “I Wanted the Whole World to See”: The Murder of Emmett Till Unit includes the following moving accounts of Mamie Till-Mobley as a mother and a civil rights pioneer. Reading: “ I Knew I Had to Give Him the Talk ” Lesson: " A Rallying Cry and a Cause "
Today’s Global Advocates for Human Rights
Anti-war sudanese organizers.
During the 30 year rule of President Omar Hassan al-Bashir, Sudanese women came out multiple times to protest the abhorrent treatment of women under his regime, often in open defiance of their family or the law. In 2019 it was estimated that two-thirds of Sudanese protesters were women. The military coup d'état in 2019 prompted the current devastating civil war between rival factions in Sudan, and again women face the biggest obstacles among the violence. Almost 90% of Sudanese people seeking refugee status in neighboring Chad are women. Learn more about the plight of Sudanese women today in these articles from Al Jazeera and the Norwegian Refugee Council . A look at the freedom and peace efforts of Sudanese women can be seen in these reports from the Christian Michelsen Institute and ReliefWeb .
Protest against the Islamic Republic of Iran's Regime
The 2022 arrest and death of Kurdish Iranian woman Mahsa Jhina Amini at the hands of Iran’s morality police has led to what some are calling a new Iranian Revolution. Since Amini’s death the people of Iran—including a flood of girls and women who have risked the same fate—have crowded the streets to demand an end to the brutal tactics and oppressive laws of the theocratic, dictatorial government. Even as the street protests have decreased, Iranian women continue to fight back through acts of civil disobedience including not following the strict veiling regulations or opting to go out publicly without a hijab altogether. The protest call of “Zan, Zendegi, Azadi” (Woman, Life, Freedom - shown above in Kurdish) continues to galvanize the movement, garnering support and participation from Iranians of all backgrounds in Iran and abroad. Learn more about the Iranian women mobilizing government resistance in these articles from Ms. and the Wilson Center . These quotes collected by Women’s Voices Now provide an inspirational glimpse at some of the individuals pushing for change.
You might also be interested in…
Remembering sidney poitier, 5 new ya books on black history and life, black athletes and civil rights: 6 upstanders to introduce to your students, why and how to teach brown girl dreaming, african americans and the history of "human rights", 5 new books on black history, deep dive into black history: 12 events + resources for educators, 9 leaders from black history you should know, 15 classroom resources on black history and life, 13 teaching ideas on human rights, cop26, environmental justice, and human rights, facing history on martin luther king day: a message to our educators, donate now and together we'll build a better world, inspiration, insights, & ways to get involved.

Goal 5: Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls
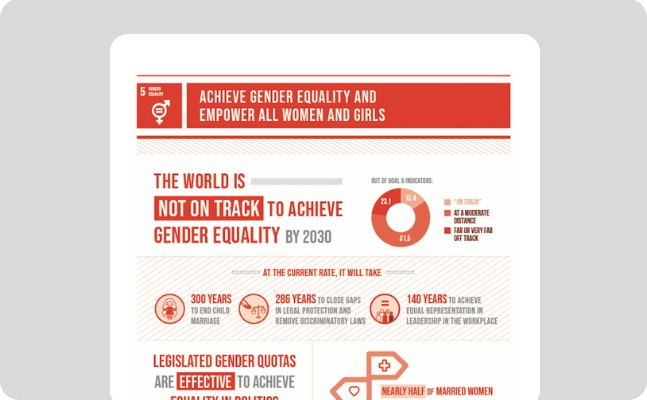
Gender equality is not only a fundamental human right, but a necessary foundation for a peaceful, prosperous and sustainable world. There has been progress over the last decades, but the world is not on track to achieve gender equality by 2030.
Women and girls represent half of the world’s population and therefore also half of its potential. But gender inequality persists everywhere and stagnates social progress. On average, women in the labor market still earn 23 percent less than men globally and women spend about three times as many hours in unpaid domestic and care work as men.
Sexual violence and exploitation, the unequal division of unpaid care and domestic work, and discrimination in public office, all remain huge barriers. All these areas of inequality have been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic: there has been a surge in reports of sexual violence, women have taken on more care work due to school closures, and 70% of health and social workers globally are women.
At the current rate, it will take an estimated 300 years to end child marriage, 286 years to close gaps in legal protection and remove discriminatory laws, 140 years for women to be represented equally in positions of power and leadership in the workplace, and 47 years to achieve equal representation in national parliaments.
Political leadership, investments and comprehensive policy reforms are needed to dismantle systemic barriers to achieving Goal 5 Gender equality is a cross-cutting objective and must be a key focus of national policies, budgets and institutions.
How much progress have we made?
International commitments to advance gender equality have brought about improvements in some areas: child marriage and female genital mutilation (FGM) have declined in recent years, and women’s representation in the political arena is higher than ever before. But the promise of a world in which every woman and girl enjoys full gender equality, and where all legal, social and economic barriers to their empowerment have been removed, remains unfulfilled. In fact, that goal is probably even more distant than before, since women and girls are being hit hard by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Are they any other gender-related challenges?
Yes. Worldwide, nearly half of married women lack decision-making power over their sexual and reproductive health and rights. 35 per cent of women between 15-49 years of age have experienced physical and/ or sexual intimate partner violence or non-partner sexual violence.1 in 3 girls aged 15-19 have experienced some form of female genital mutilation/cutting in the 30 countries in Africa and the Middle East, where the harmful practice is most common with a high risk of prolonged bleeding, infection (including HIV), childbirth complications, infertility and death.
This type of violence doesn’t just harm individual women and girls; it also undermines their overall quality of life and hinders their active involvement in society.
Why should gender equality matter to me?
Regardless of where you live in, gender equality is a fundamental human right. Advancing gender equality is critical to all areas of a healthy society, from reducing poverty to promoting the health, education, protection and the well-being of girls and boys.
What can we do?
If you are a girl, you can stay in school, help empower your female classmates to do the same and fight for your right to access sexual and reproductive health services. If you are a woman, you can address unconscious biases and implicit associations that form an unintended and often an invisible barrier to equal opportunity.
If you are a man or a boy, you can work alongside women and girls to achieve gender equality and embrace healthy, respectful relationships.
You can fund education campaigns to curb cultural practices like female genital mutilation and change harmful laws that limit the rights of women and girls and prevent them from achieving their full potential.
The Spotlight Initiative is an EU/UN partnership, and a global, multi-year initiative focused on eliminating all forms of violence against women and girls – the world’s largest targeted effort to end all forms of violence against women and girls.

Facts and figures
Goal 5 targets.
- With only seven years remaining, a mere 15.4 per cent of Goal 5 indicators with data are “on track”, 61.5 per cent are at a moderate distance and 23.1 per cent are far or very far off track from 2030 targets.
- In many areas, progress has been too slow. At the current rate, it will take an estimated 300 years to end child marriage, 286 years to close gaps in legal protection and remove discriminatory laws, 140 years for women to be represented equally in positions of power and leadership in the workplace, and 47 years to achieve equal representation in national parliaments.
- Political leadership, investments and comprehensive policy reforms are needed to dismantle systemic barriers to achieving Goal 5. Gender equality is a cross-cutting objective and must be a key focus of national policies, budgets and institutions.
- Around 2.4 billion women of working age are not afforded equal economic opportunity. Nearly 2.4 Billion Women Globally Don’t Have Same Economic Rights as Men
- 178 countries maintain legal barriers that prevent women’s full economic participation. Nearly 2.4 Billion Women Globally Don’t Have Same Economic Rights as Men
- In 2019, one in five women, aged 20-24 years, were married before the age of 18. Girls | UN Special Representative of the Secretary-General on Violence Against Children
Source: The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2023
5.1 End all forms of discrimination against all women and girls everywhere
5.2 Eliminate all forms of violence against all women and girls in the public and private spheres, including trafficking and sexual and other types of exploitation
5.3 Eliminate all harmful practices, such as child, early and forced marriage and female genital mutilation
5.4 Recognize and value unpaid care and domestic work through the provision of public services, infrastructure and social protection policies and the promotion of shared responsibility within the household and the family as nationally appropriate
5.5 Ensure women’s full and effective participation and equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decisionmaking in political, economic and public life
5.6 Ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health and reproductive rights as agreed in accordance with the Programme of Action of the International Conference on Population and Development and the Beijing Platform for Action and the outcome documents of their review conferences
5.A Undertake reforms to give women equal rights to economic resources, as well as access to ownership and control over land and other forms of property, financial services, inheritance and natural resources, in accordance with national laws
5.B Enhance the use of enabling technology, in particular information and communications technology, to promote the empowerment of women
5.C Adopt and strengthen sound policies and enforceable legislation for the promotion of gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls at all levels
He for She campaign
United Secretary-General Campaign UNiTE to End Violence Against Women
Every Woman Every Child Initiative
Spotlight Initiative
United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
UN Population Fund: Gender equality
UN Population Fund: Female genital mutilation
UN Population Fund: Child marriage
UN Population Fund: Engaging men & boys
UN Population Fund: Gender-based violence
World Health Organization (WHO)
UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights
UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR)
UN Education, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO)
UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Gender Statistics
Fast Facts: Gender Equality

Infographic: Gender Equality
The Initiative is so named as it brings focused attention to this issue, moving it into the spotlight and placing it at the centre of efforts to achieve gender equality and women’s empowerment, in line with the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
An initial investment in the order of EUR 500 million will be made, with the EU as the main contributor. Other donors and partners will be invited to join the Initiative to broaden its reach and scope. The modality for the delivery will be a UN multi- stakeholder trust fund, administered by the Multi-Partner Trust Fund Office, with the support of core agencies UNDP, UNFPA and UN Women, and overseen by the Executive Office of the UN Secretary-General.
Related news
Press release| the world is failing girls and women, according to new un report.
Yinuo 2023-09-06T19:30:02-04:00 07 Sep 2023 |
The world is failing girls and women, according to new UN report New figure points to the need of an additional $360 billion in investment per year to achieve genderequality and women’s empowerment by 2030. [...]
Liberia, Mexico, Niger, Senegal and Sierra Leone to tackle barriers to the deployment of women in peace operations with the support of the UN Elsie Initiative Fund
Vesna Blazhevska 2021-04-28T13:20:09-04:00 28 Apr 2021 |
PRESS RELEASE 28 APRIL 2021 MEDIA ENQUIRIES [email protected] Liberia, Mexico, Niger, Senegal and Sierra Leone to tackle barriers to the deployment of women in peace operations with the support of the UN Elsie Initiative [...]
Women’s job market participation stagnating at less than 50% for the past 25 years, finds UN report
Vesna Blazhevska 2020-10-20T15:06:56-04:00 20 Oct 2020 |
New York, 20 October – Less than 50% of working-age women are in the labour market, a figure that has barely changed over the last quarter of a century, according to a new UN report launched today. Unpaid domestic and care work falls disproportionately on women, restraining their economic potential as the COVID-19 pandemic additionally affects women’s jobs and livelihoods, the report warns.
Related videos
The world must ‘wake up and help sudan out of the nightmare of conflict’ says who’s tedros.
Sudan’s health system is “near collapse” after 16 months of war have left the country and its people facing what the UN’s top health official described on Sunday as the “perfect storm of crises”, which [...]
Investing in clean air can saves lives and combat climate change
The UN Secretary-General is marking ‘Clean Air Day’ with a call for global investment in solutions that tackle climate change and the increasing public health, environmental, and economic harm caused by air pollution. Read Full [...]
Millions impacted by ‘catastrophic and massive floods’ in Bangladesh
Recent “catastrophic and massive floods” in Bangladesh have affected millions of people across the country, including those in Cox’s Bazar where nearly one million Rohingya refugees from Myanmar live alongside host communities, spokesperson William Spindler [...]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 06 September 2023
Gender equality: the route to a better world
You have full access to this article via your institution.
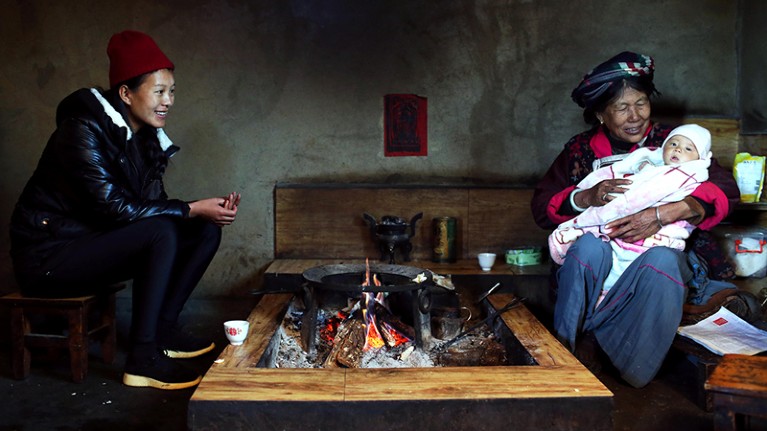

The Mosuo people of China include sub-communities in which inheritance passes down either the male or the female line. Credit: TPG/Getty
The fight for global gender equality is nowhere close to being won. Take education: in 87 countries, less than half of women and girls complete secondary schooling, according to 2023 data. Afghanistan’s Taliban continues to ban women and girls from secondary schools and universities . Or take reproductive health: abortion rights have been curtailed in 22 US states since the Supreme Court struck down federal protections, depriving women and girls of autonomy and restricting access to sexual and reproductive health care .
SDG 5, whose stated aim is to “achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls”, is the fifth of the 17 United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, all of which Nature is examining in a series of editorials. SDG 5 includes targets for ending discrimination and violence against women and girls in both public and private spheres, eradicating child marriage and female genital mutilation, ensuring sexual and reproductive rights, achieving equal representation of women in leadership positions and granting equal rights to economic resources. Globally, the goal is not on track to being achieved, and just a handful of countries have hit all the targets.

How the world should oppose the Taliban’s war on women and girls
In July, the UN introduced two new indices (see go.nature.com/3eus9ue ), the Women’s Empowerment Index (WEI) and the Global Gender Parity Index (GGPI). The WEI measures women’s ability and freedoms to make their own choices; the GGPI describes the gap between women and men in areas such as health, education, inclusion and decision making. The indices reveal, depressingly, that even achieving a small gender gap does not automatically translate to high levels of women’s empowerment: 114 countries feature in both indices, but countries that do well on both scores cover fewer than 1% of all girls and women.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made things worse, with women bearing the highest burden of extra unpaid childcare when schools needed to close, and subjected to intensified domestic violence. Although child marriages declined from 21% of all marriages in 2016 to 19% in 2022, the pandemic threatened even this incremental progress, pushing up to 10 million more girls into risk of child marriage over the next decade, in addition to the 100 million girls who were at risk before the pandemic.
Of the 14 indicators for SDG 5, only one or two are close to being met by the 2030 deadline. As of 1 January 2023, women occupied 35.4% of seats in local-government assemblies, an increase from 33.9% in 2020 (the target is gender parity by 2030). In 115 countries for which data were available, around three-quarters, on average, of the necessary laws guaranteeing full and equal access to sexual and reproductive health and rights had been enacted. But the UN estimates that worldwide, only 57% of women who are married or in a union make their own decisions regarding sexual and reproductive health and rights.
Systemic discrimination against girls and women by men, in many contexts, remains a colossal barrier to achieving gender equality. But patriarchy is not some “natural order of things” , argues Ruth Mace, an anthropologist at University College London. Hundreds of women-centred societies exist around the world. As the science writer Angela Saini describes in her latest book, The Patriarchs , these are often not the polar opposite of male-dominated systems, but societies in which men and women share decision making .

After Roe v. Wade: dwindling US abortion access is harming health a year later
One example comes from the Mosuo people in China, who have both ‘matrilineal’ and ‘patrilineal’ communities, with rights such as inheritance passing down either the male or female line. Researchers compared outcomes for inflammation and hypertension in men and women in these communities, and found that women in matrilineal societies, in which they have greater autonomy and control over resources, experienced better health outcomes. The researchers found no significant negative effect of matriliny on health outcomes for men ( A. Z. Reynolds et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117 , 30324–30327; 2020 ).
When it comes to the SDGs, evidence is emerging that a more gender-equal approach to politics and power benefits many goals. In a study published in May, Nobue Amanuma, deputy director of the Integrated Sustainability Centre at the Institute for Global Environmental Strategies in Hayama, Japan, and two of her colleagues tested whether countries with more women legislators, and more younger legislators, are performing better in the SDGs ( N. Amanuma et al. Environ. Res. Lett. 18 , 054018; 2023 ). They found it was so, with the effect more marked for socio-economic goals such as ending poverty and hunger, than for environmental ones such as climate action or preserving life on land. The researchers recommend further qualitative and quantitative studies to better understand the reasons.
The reality that gender equality leads to better outcomes across other SDGs is not factored, however, into most of the goals themselves. Of the 230 unique indicators of the SDGs, 51 explicitly reference women, girls, gender or sex, including the 14 indicators in SDG 5. But there is not enough collaboration between organizations responsible for the different SDGs to ensure that sex and gender are taken into account. The indicator for the sanitation target (SDG 6) does not include data disaggregated by sex or gender ( Nature 620 , 7; 2023 ). Unless we have this knowledge, it will be hard to track improvements in this and other SDGs.
The road to a gender-equal world is long, and women’s power and freedom to make choices is still very constrained. But the evidence from science is getting stronger: distributing power between genders creates the kind of world we all need and want to be living in.
Nature 621 , 8 (2023)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-023-02745-9
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

- Sustainability
- Public health

Waste management won’t solve the plastics problem — we need to cut consumption
News & Views 04 SEP 24

Light bulbs have energy ratings — so why can’t AI chatbots?
Comment 21 AUG 24
Monitor soil health using advanced technologies
Correspondence 23 JUL 24

Mpox is spreading rapidly. Here are the questions researchers are racing to answer
News Explainer 28 AUG 24
What accelerates brain ageing? This AI ‘brain clock’ points to answers
News 27 AUG 24

Mysterious Oropouche virus is spreading: what you should know
News Q&A 26 AUG 24

Brazil’s ban on X: how scientists are coping with the cut-off
News 06 SEP 24

The Taliban said women could study — three years on they still can’t
News 14 AUG 24

Who is legally responsible for climate harms? The world’s top court will now decide
Editorial 13 AUG 24
Scripps Research Institute, Fellow Position, Fall 2025
Scripps Research Institute is seeking an outstanding candidate for the 2025 Fellow position in La Jolla, CA.
La Jolla, California
Scripps Research Institute
Faculty Positions in Biology and Biological Engineering: Caltech, Pasadena, CA, United States
The Division of Biology and Biological Engineering (BBE) at Caltech is seeking new faculty in the area of Neuroscience.
Pasadena, California
California Institute of Technology (Caltech)
Assistant Professor
Rutgers Biomedical and Health Sciences (RBHS), Center for Cell Signaling, and Rutgers New Jersey Medical School (NJMS) are jointly recruiting multi...
Newark, New Jersey (US)
Rutgers Biomedical and Health Sciences NJMS-Center for Cell Signaling
Postdoctoral fellow in computational biology
We are searching for a highly motivated postdoc interested in developing and applying computational approaches to understand how blood cell clones ...
Gothenburg (Kommun), Västra Götaland (SE)
University of Gothenburg
Faculty Positions in School of Engineering, Westlake University
The School of Engineering (SOE) at Westlake University is seeking to fill multiple tenured or tenure-track faculty positions in all ranks.
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Westlake University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Gender equality and women’s empowerment
Related sdgs, achieve gender equality and empower all women ....
Description
Publications.
- More information
Since its creation 70 years ago, the UN has achieved important results in advancing gender equality, from the establishment of the Commission on the Status of Women - the main global intergovernmental body exclusively dedicated to the promotion of gender equality and the empowerment of women - through the adoption of various landmark agreements such as the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW) and the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action.
On the occasion of the General Debate of the 66th Session of the General Assembly held in September 2011, United Nations Secretary-General BAN KI-MOON highlighted in his Report “We the Peoples”, the crucial role of gender equality as driver of development progress, recognizing that the potential of women had not been fully realized, owing to, inter alia, persistent social, economic and political inequalities.
Gender inequalities are still deep-rooted in every society. Women suffer from lack of access to decent work and face occupational segregation and gender wage gaps. In many situations, they are denied access to basic education and health care and are victims of violence and discrimination. They are under-represented in political and economic decision-making processes.
With the aim of better addressing these challenges and to identify a single recognized driver to lead and coordinate UN activities on gender equality issues, UN Women was established in 2010.
UN Women works for the elimination of discrimination against women and girls, empowerment of women, and achievement of equality between women and men as partners and beneficiaries of development, human rights, humanitarian action and peace and security.
The vital role of women and the need for their full and equal participation and leadership in all areas of sustainable development was reaffirmed in the Future We Want (paragraph 236-244), as well as in the Open Working Group Proposal for Sustainable Development Goals. Open Working Group Proposal for Sustainable Development Goals . The proposed Sustainable Development Goal 5 addresses this and reads "Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls".
Spotlight on SDG11: Harsh realities: Marginalized women in cities of the developing world
For women and girls, urbanization is often associated with greater access to education and employment opportunities, lower fertility rates, and increased independence. Yet women are often denied the same benefits and opportunities that cities offer to men. Moreover, women are frequently excluded fro...
Spotlight on SDG 8: The impact of marriage and children on labour market participation
This paper is being released in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition to being a health crisis unlike any other in recent history, the pandemic is an economic and social crisis. Families—and women within them—are juggling an increase in unpaid care work as well as losses in income and paid...
Women and Sustainable Development Goals
On 25 September, the United Nations General Assembly adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development as the agreed framework for international development. It is the successor to the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). However, unlike the MDGs, the 2030 Agenda presents a much wider scope by del...
Accelerating the Progress Towards the Localization of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Knowledge Management Strategy for Localizing SDGs at the Multi/Country Level Focus on SDG 5 on Gender Equality and Empowerment of Women and Girls This UN Women ESAR Knowledge Management Strategy serves to collect, disseminate and preserve the region’s intellectual output through diverse mechanis...
Against Wind and Tides: A Review of the Status of Women and Gender Equality in the Arab Region (Beijing +20)
As the international community marks the twentieth anniversary of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action, an analytical review of both progress and ongoing challenges in the implementation of this agenda for women’s empowerment is important and timely. Taking stock of efforts that have been...
Emerging Issues for Small Island Developing States
The 2012 UNEP Foresight Process on Emerging Global Environmental Issues primarily identified emerging environmental issues and possible solutions on a global scale and perspective. In 2013, UNEP carried out a similar exercise to identify priority emerging environmental issues that are of concern to ...
Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
This Agenda is a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. It also seeks to strengthen universal peace in larger freedom, We recognize that eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for su...
Demographic Perspectives on Female Genital Mutilation
FGM has been internationally recognized as an extreme form of violation of the rights, health and integrity of women and girls. In 2012, the United Nations General Assembly adopted the first-ever resolution against FGM (67/146), calling for intensified global efforts to eliminate it. The resolution...
SRH and HIV Linkages Compendium
Ensuring universal access to sexual and reproductive health and rights and HIV prevention, treatment, care and support are essential for development, including in the post 2015 agenda. However, while there are many separate sexual and reproductive health (SRH) related and HIV-related indicators, a ...
The World Survey on the role of women in development 2014: Gender equality and sustainable development
The immense social, economic and environmental consequences of climate change and loss of essential ecosystems are becoming clear. Their effects are already being felt in floods, droughts, and devastated landscapes and livelihoods. Among those most affected are women and girls, given the precariousn...
HIV and Sexual and Reproductive Health Programming: Innovative Approaches to Integrated Service Delivery
In light of recent progress towards eliminating paediatric HIV, strong momentum for integrating HIV and sexual and reproductive health (SRH) (including maternal, newborn and child health (MNCH), family planning (FP), and sexually transmitted infection (STI)) programmes, and the recent WHO guidelines...
Adding It Up 2014
Women need sexual and reproductive health services from adolescence through the end of their reproductive years, whether or not they have a birth, and those who give birth need essential care to protect their health and ensure their newborns survive. The declines in maternal and infant deaths in dev...
Session 10: Gender-Responsiveness in Partnerships for the SDGs: consultations, tools, strategies and approaches to overcome barriers towards gender equality
Gender-Responsiveness in Partnerships for the SDGs: consultations, tools, strategies and approaches to overcome barriers towards gender equality Partners: Women's Major Group Center for Migration, Gender, and Justice Mediators Beyond Borders International Centre for Feminist Foreign Policy (C
2022 SDGs Learning, Training and Practice
Please, watch the recordings of all sessions here. Introduction The United Nations high-level political forum on sustainable development (HLPF) in 2022 will be held from Tuesday 5 July to Thursday 7 July, and from Monday 11 July to Friday 15 July 2022, under the auspices of the Econ
Expert Group Meeting on SDG 5 (Gender equality) and its interlinkages with other SDGs
In preparation for the review of SDG 5 – and its role in advancing sustainable development across the 2030 Agenda, the Division for Sustainable Development Goals of the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN-DESA/DSDG), the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), and the United Nations Ent
Expert Group Meetings on 2022 HLPF Thematic Review
The theme of the 2022 high-level political forum on sustainable development (HLPF) is “Building back better from the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) while advancing the full implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development”. The 2022 HLPF will have an
High-level meeting on the twenty-fifth anniversary of the Fourth World Conference on Women
Beijing+25 (csw 64), symposium on women and water security for peacebuilding in the arab region.
The symposium is organized by the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA), in collaboration with the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia (UN- ESCWA) and the Pacific Water Research Centre of Simon Frazier University, Vancouver Canada. The symposiu
UN Women for Peace Association - ISIS and its Impact on Women
Khidher Domle, a Yazidi activist, has coordinated rescues of many of these hostages. A professor, journalist, and the head of the Communications Department at the University of Dohuk in Kurdistan, Iraq, Mr. Domle will testify this week before the U.S. Congress. The event will also include an exclus
Roundtable discussion on Women in the Economy in France and in the United Arab Emirates
The event was held as a joint initiative by the French Business Council of Dubai and Northern Emirates and the Dubai Business Women Council. It was organized at UNESCO Headquarters with support from the Delegation of Palau and the Delegation of France. In her intervention, the Director-General hig
Women and Health: Beijing Declaration +20 - 68th World Health Assembly
The World Health Assembly (WHA) featured a 20-year assessment of the state of women’s health and women’s role in health, as well as the need for gender mainstreaming in this sector. UN Women Deputy Executive Director Lakshmi Puri took a lead on a gender-focused panel on “Women and Health: Beijing D
| Title | Type | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Concept Notes | 18-May-2020 | |
| Other documents | 18-May-2020 | |
| Other documents | 26-Apr-2019 | |
| Other documents | 24-Apr-2018 | |
| Programme | 24-Apr-2018 | |
| Other documents | 22-Mar-2018 | |
| Other documents | 8-Jun-2017 | |
| Background Notes | 26-Apr-2017 | |
| Reports | 16-Mar-2017 | |
| Reports | 16-Mar-2017 | |
| Reports | 16-Mar-2017 | |
| Reports | 16-Mar-2017 | |
| Reports | 16-Mar-2017 | |
| Reports | 16-Mar-2017 | |
| Reports | 16-Mar-2017 |
| Title | Category | |
|---|---|---|
| Session 7 | 10-May-2018 | |
| Session 6 | 10-May-2018 | |
| Session 3 | 9-May-2018 | |
| Session 3 | 9-May-2018 | |
| Session 2 | 9-May-2018 | |
| Session 2 | 9-May-2018 | |
| Opening Session | 9-May-2018 | |
| Session 5 | 9-May-2018 | |
| Session 5 | 9-May-2018 | |
| Session 4 | 9-May-2018 | |
| Session 4 | 9-May-2018 | |
| Session 3 | 9-May-2018 | |
| Session 2 | 9-May-2018 | |
| Session 2 | 9-May-2018 | |
| Session 1 | 9-May-2018 |
- January 2015 Beijing+20 Beijing +20 is committed to renew political will and commitment, revitalize public debate through social mobilization and awareness-raising, strengthen evidence-based knowledge as well as enhance resources to achieve gender equality and women empowerment.
- January 2015 SDG 5 Goal 5 aims at achieving gender equality and empower all women and girls. Its targets include end of all forms of discrimination and violence against women and girls, as well as elimination of harmful practices and the recognition and value of unpaid care and domestic work. Other targets stress the importance of ensuring women's full and effective participation and equal opportunities for leadership as well as universal access to sexual and reproductive health and reproductive rights.
- January 2010 UN Women In the framework of the UN Reform Agenda, the UN General Assembly established UN Women to accelerate the Organization’s goals on gender equality and empowerment of women. UN Women was conceived in order to support inter-governmental bodies in the elaboration of policies, norms and global standards, as well as Member States in the implementation of those standards, the leading and the coordination of the UN System in their work on gender equality.
- January 2000 MDG 3 MDG3 aims at promoting gender equality and empowering women. Its target 3.A focuses on the need to eliminate gender disparity in primary and secondary education, preferably by 2005, and in all levels of education no later than 2015.
- January 1995 Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action The Fourth World Conference on Women produced the Beijing Declaration and its Platform of Action, unanimously adopted by 189 countries and considered as the most progressive scheme and road map for advancing women’s rights. As a defining framework for change, the Platform for Action made comprehensive commitments under 12 critical areas of concern, namely, women and poverty, education and training of women, women and health, violence against women, women and armed conflict, women and the economy, women in power and decision-making, institutional mechanism for the advancement of women, human rights of women, women and the media, women and the environment and the girl- child. The conference represented a crucial milestone in the progress of gender equality and empowerment of women.
- January 1994 PoA The 20-year Programme of Action was adopted by 179 countries, on the occasion of the International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD), held in Cairo in 1994 and aimed to provide a new vision of the links between population, development and individual well-being. The Programme recognized the importance of empowerment of women, gender equality as well as reproductive health and rights as issues at the core of any population and development programmes.
- January 1979 CEDAW Often considered as an international bill of rights for women, the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW), was adopted in 1979 by the UN General Assembly. It defines what constitutes discrimination against women and sets up an agenda for national action to end such discrimination. According to the Convention, discrimination against women can be defined as "any distinction, exclusion or restriction made on the basis of sex which has the effect or purpose of impairing or nullifying the recognition, enjoyment or exercise by women, irrespective of their marital status, on a basis of equality of men and women, of human rights and fundamental freedoms in the political, economic, social, cultural, civil or any other field".
- January 1975 World Conf. Int. Women's Year The First World Conference on Women was held in Mexico City in 1975, reuniting 133 governments and designing a World Plan of Action for the Implementation of the Objectives of the International Women’s Year, providing measures and indications for the advancement of women for the upcoming decade. Furthermore, 6000 NGOs Representatives took part to a parallel forum, the Women’s Year Tribute.
- January 1946 CSW Established by the Economic and Social Council with Resolution 11(II), adopted on 21st June 1946, the Commission was first mandated to prepare recommendations and reports to ECOSOC to promote women’s rights in political, economic, social and educational fields, as well as make recommendations on urgent matters requiring immediate attention as well as submit proposals to the Council regarding its terms of references. In 1996, thanks to ECOSOC Resolution 1996/6, its mandate was extended, recognizing to the Commission a leading role in the monitoring and review process of the implementation of the 1995 Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action.
Progress on the Sustainable Development Goals: The gender snapshot 2019


Thematic spotlight
Where women and girls stand against select SDG targets. Click here for more infographics.

Issue brief
Making the SDGs count for women and girls with disabilities

Essay: Women’s Rights in the Late 20th Century
After World War II, women’s struggle for equality achieved a mixed record of success. The women’s rights movement won equal opportunities in higher education and employment relatively quickly in the 1940s and 1950s. The modern concept of women’s equality as “feminism” appeared in the 1960s, led by activists such as Betty Friedan. Some of its victories in the legislative arena were completely inadvertent, while one of its grandest objects and subject of its greatest efforts resulted in defeat. Moreover, the movement was dominated by an intellectual and professional leadership at some distance from ordinary women. Despite the vagaries of the movement, it was remarkably successful in fundamentally changing society and women’s roles as well as attitudes towards women.
World War II was instrumental in the origins of the Women’s Movement. The classic image of “Rosie the Riveter” reflected the fact that millions of women went into factories when men were mobilized into the military. However, many unmarried and poor women had already participated in the industrial economy for a century. With demobilization after the war, more than three million women quit their jobs to return to their roles as homemakers or were let go to make room for returning men.
There was a lingering split from the 1920s between future First Lady, Eleanor Roosevelt, and feminist leader of the National Women’s Party, Alice Paul. Roosevelt fought to keep protective legislation for women in terms of working hours or physical tasks, and Paul wanted an Equal Rights Amendment (ERA) that made women completely equal under the law. Paul was so frustrated by the lack of progress on the ERA that she resorted to “red-baiting” by labeling its opponents Communists and reporting them to the House Un-American Activities Committee.
Post-war American culture was rather conservative and supported traditional roles for women. The images of women as mothers and homemakers on the new media of television were quite reflective of the reality for many suburban women. The marriage rate was increasing, a Baby Boom resulted in more than 76 million births between 1946 and 1964, and the divorce rate dropped. The American people supported traditional roles for women, and as one post-war poll noted, 63 percent were opposed to married women working outside the home.
In 1963, feminist author Betty Friedan wrote a path-breaking book, The Feminine Mystique that challenged traditional roles for women.
She described the sense of dissatisfaction that many women felt as “the problem with no name” and wrote, “The problem lay buried, unspoken, for many years in the minds of American women. It was a strange stirring, a sense of dissatisfaction…Each suburban wife struggled with it alone. As she made the beds, shopped for groceries, matched slipcover material, ate peanut butter sandwiches with her children, chauffeured Cub Scouts and Brownies, lay besides her husband at night – she was afraid to ask even of herself the silent question – ‘Is this all?’” (Friedan, The Feminine Mystique , 1963).
Friedan’s book was a best-seller and struck a chord with many women, particularly of her social class. But, some women were poorer and did not have the luxury of choosing whether to work or not because necessity forced them into the workplace. Other women did not share Friedan’s dislike of women’s traditional roles as mother and housewife.
In the early 1960s, many changes were developing for women’s equality in employment and education. By 1960, the number of working women had risen to 35 percent of the workforce with increasing numbers of married women. This probably reflected the fact that many families wanted the extra disposable income to participate in the growing consumer economy more than an increasing desire of women to find personal satisfaction from working. Women were attending higher education in higher numbers, earning nearly 40 percent of the degrees by 1960 and the numbers would continue to grow. In May, 1960, the Food and Drug Administration approved the oral contraceptive, “the Pill,” for women, and millions of women were soon using it for birth control despite the fact that many states outlawed contraceptives. The Pill changed the sexual lives of women throughout the nation. Women’s careers would not be shortened by unanticipated pregnancies, and women would have fewer children.
The Pill became involved in constitutional issues when the Supreme Court took up the question. In 1965, the Supreme Court would overturn anti-contraception laws in Griswold v. Connecticut , arguing that the “penumbras” in the Bill of Rights—in the First, Third, Fourth, and Fifth Amendments—create “zones of privacy.” Moreover, the majority also used the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment to argue that there are “certain fundamental rights” not listed in the Bill of Rights as the Ninth Amendment specifically recognizes. But, should the courts lay down new rights in decisions or should the people be the ones who would define those rights through the amendment process? Moreover, the Fourteenth Amendment explicitly states that, “The Congress shall have power to enforce, by appropriate legislation, the provisions of this article,” not the courts (The United States Constitution, Fourteenth Amendment, 1866). By overturning the anti-contraceptive laws of a vast majority of states, the Supreme Court undermined the rights of states to determine laws for their own citizens.

The Pill became involved in constitutional issues when the Supreme Court took up the question. In 1965, the Supreme Court would overturn anti-contraception laws in Griswold v. Connecticut , arguing that the “penumbras” in the Bill of Rights – in the First, Third, Fourth, and Fifth Amendments – create “zones of privacy.”
Women won legal equality in the Civil Rights Act of 1964. The House Rules Committee Chairman, Howard Smith (D-VA), was a segregationist who may have attempted to halt civil rights for African Americans by including additional rights for women by banning discrimination in employment based on sex—although he claimed he supported women’s equality. To further muddy the waters, many northern liberals and labor unions supported protective legislation for women and opposed the amendments to the Civil Rights act that gave legal protection against discrimination to women. Nevertheless, the Civil Rights Act passed both houses of Congress and was signed by President Johnson to become law. The Act established the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), an executive agency that would be charged with enforcing the law.
In 1966, several feminists formed the National Organization of Women (NOW) and issued a “Statement of Purpose.” The NOW statement was primarily a call for an end to discrimination in education, employment, civil society, and culture. The Statement of Purpose sought to ban discrimination against women with legal and constitutional protections by the government.
It called upon “the power of American law, and the protection guaranteed by the U.S. Constitution to the civil rights of all individuals, must be effectively applied and enforced to isolate and remove patterns of sex discrimination, to ensure equality of opportunity in employment and education, and equality of civil and political rights and responsibilities on behalf of women” (National Organization of Women, “Statement of Purpose,” 1966).
Only a year later, at the second annual NOW conference, the organization called for a “Bill of Rights for Women” that included all the items in the Statement of Purpose and added a call for an Equal Rights Amendment (ERA), publicly-funded daycare centers across the nation, and a repeal of all laws banning abortion. Over the next few years, NOW devoted a great deal of its efforts to lobbying several different federal agencies for enforcing Title VII (part of the Civil Rights Act of 1965 that banned employment discrimination on the basis of race, sex, or national origin), to pressuring Congress to pass the ERA, and expanded its agenda to include other feminist issues such as recognizing that lesbian rights were “a legitimate concern of feminism.” The struggle for the ERA was the most public and significant battle in the quest for women’s equality. In 1972, both houses of Congress passed the ERA by overwhelming majorities to fulfill the two-thirds requirement for constitutional amendments. The ERA needed three-fourths of the state legislatures to ratify the amendment before 1979 (later extended to 1982) for it to become the law of the land. The proposed amendment was quickly ratified by dozens of states and then stalled, eventually winning ratification in 35 states just short of the necessary 38, and failed.

The struggle for the ERA was the most public and significant battle in the quest for women’s equality. In 1972, both houses of Congress passed the ERA by overwhelming majorities to fulfill the two-thirds requirement for constitutional amendments. The ERA needed three-fourths of the state legislatures to ratify the amendment before 1979 (later extended to 1982) for it to become the law of the land.
The ERA failed in large part due to the strong grassroots campaign called “STOP ERA” at the state and local level, spearheaded by a conservative lawyer and activist, Phyllis Schlafly. Schlafly advanced the view, embraced by many religious conservatives and other Americans, that the ERA would have baleful consequences for women. She said that the constitutional amendment would subject women equally to the military draft, end protections in child custody and divorce proceedings, lead to the decline of the traditional family, support abortion rights, back homosexual rights, and lead to unisex bathrooms. Whether or not it would have contributed these things, Schlafly organized a grass-roots campaign at the local and state level called “Stop ERA” which successfully defeated the ERA.
Feminists supported legalized abortion to protect women’s reproductive rights and the “right to control her own body.” They campaigned to overturn state abortion laws and then pushed cases to the Supreme Court in order to overturn all state laws. In the landmark case of Roe v. Wade (1973), the Supreme Court legalized abortion throughout the country based upon the precedent established in the Griswold decision. The movement to legalize abortion had adopted a lengthy and costly campaign to change abortion laws in the states, but then it shifted its strategy to the courts. Justice Harry Blackmun wrote the majority opinion for the Supreme Court, and much like Justice Roger B. Taney in the Dred Scott decision, sought to use the Court to settle a highly contentious social and political question. To that end, Justice Blackmun spent time at the Mayo Clinic in Minnesota conducting medical and historical research on the topic. In a 7-2 decision, the Court decided that state laws banning abortion were unconstitutional. It created the trimester framework for pregnancy and stated that during the first trimester there was an unlimited right to abortion. After that, the state had a “compelling interest” in “protecting the potentiality of human life” and could regulate abortions though a physician’s approval. In the last trimester, the state could proscribe abortion except for the protection of the life or health of the mother.
In a dissenting opinion, Justice Byron White called the opinion “an exercise of raw judicial power” because, he argued, the Court “fashions and announces a new constitutional right” which overrides laws in a majority of states. “The upshot is that the people and the legislatures of the 50 states are constitutionally disentitled to weigh the [issue],” White wrote (Justice Byron White, Roe v. Wade Dissenting Opinion, 1973).
The Roe decision hardly settled the question in the minds of the American people and set off a decades-long battle in the public square on the highly contentious subject. In Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992), the Court sowed perhaps more confusion.

The Roe decision hardly settled the question in the minds of the American people and set off a decades-long battle in the public square on the highly contentious subject.
Yet, the Court declared that it must uphold a women’s right to have an abortion because it must always uphold precedent (previous decisions) or the court’s legitimacy would be questioned. However, only a few decades before, it purposefully and famously rejected precedent in the Brown decision that had the effect of overturning Plessy .
The struggle for women’s equality may have lost the battle of the ERA, but it won the war. Affirmative action, or giving preference to certain groups in hiring, for women was highly successful in employment, and women entered the professions in such numbers that it was commonplace. Disparities in pay for the same jobs began to disappear. Affirmative action in college and graduate school admissions was so successful that institutions of higher education had to begin looking for ways to attract more male students. Women entered politics and won higher and higher offices. Most of NOW’s original agenda was achieved, though feminists would still say that the “glass ceiling” for women prevented them from rising to complete parity with men at the highest levels of business or politics.
The women’s movement was on the whole successful in achieving equality for women, and women could now choose whether to have a traditional role or work outside the home professionally. Fifty years after Betty Friedan’s The Feminine Mystique was published, American women continued to debate the meaning of feminism and its relevance to their lives once greater equality and liberty were achieved. While men have shouldered some additional burdens in the home and family, women still have not been released from their traditional roles cooking, cleaning, and caring for children even as they’ve assumed new roles in society. Women have found that although they won greater employment opportunities and equality, they are struggling to “have it all” by bearing the double-burden of traditional roles and work.
Related Content

Women’s Rights in the Late 20th Century
After World War II, women’s struggle for equality achieved a mixed record of success. The women’s rights movement won equal opportunities in higher education and employment relatively quickly in the 1940s and 1950s. The modern concept of women’s equality as “feminism” appeared in the 1960s, led by activists such as Betty Friedan. Some of its victories in the legislative arena were completely inadvertent, while one of its grandest objects and subject of its greatest efforts resulted in defeat. Moreover, the movement was dominated by an intellectual and professional leadership at some distance from ordinary women. Despite the vagaries of the movement, it was remarkably successful in fundamentally changing society and women’s roles as well as attitudes towards women. In this lesson, students will explore the record of successes, and better understand constitutional principles of privacy and due process.
Gender Equality Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on gender equality essay.
Equality or non-discrimination is that state where every individual gets equal opportunities and rights. Every individual of the society yearns for equal status, opportunity, and rights. However, it is a general observation that there exists lots of discrimination between humans. Discrimination exists because of cultural differences, geographical differences, and gender. Inequality based on gender is a concern that is prevalent in the entire world. Even in the 21 st century, across globe men and women do not enjoy equal privileges. Gender equality means providing equal opportunities to both men and women in political, economic, education and health aspects.

Importance of Gender Equality
A nation can progress and attain higher development growth only when both men and women are entitled to equal opportunities. Women in the society are often cornered and are refrained from getting equal rights as men to health, education, decision-making and economic independence in terms of wages.
The social structure that prevails since long in such a way that girls do not get equal opportunities as men. Women generally are the caregivers in the family. Because of this, women are mostly involved in household activities. There is lesser participation of women in higher education, decision-making roles, and leadership roles. This gender disparity is a hindrance in the growth rate of a country. When women participate in the workforce increases the economic growth rate of the country increases. Gender equality increases the overall wellbeing of the nation along with economic prosperity .
How is Gender Equality Measured?
Gender equality is an important factor in determining a country’s overall growth. There are several indexes to measure gender equality.
Gender-Related Development Index (GDI) – GDI is a gender centric measure of Human Development Index. GDI considers parameters like life expectancy, education, and incomes in assessing the gender equality of a country.
Gender Empowerment Measure (GEM) – This measure includes much detail aspects like the proportion of seats than women candidates hold in national parliament, percentage of women at economic decision-making role, the income share of female employees.
Gender Equity Index (GEI) – GEI ranks countries on three parameters of gender inequality, those are education, economic participation, and empowerment. However, GEI ignores the health parameter.
Global Gender Gap Index – The World Economic Forum introduced the Global Gender Gap Index in 2006. This index focuses more on identifying the level of female disadvantage. The four important areas that the index considers are economic participation and opportunity, educational attainment, political empowerment, health, and survival rate.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Gender Inequality in India
As per the World Economic Forum’s gender gap ranking, India stands at rank 108 out of 149 countries. This rank is a major concern as it highlights the immense gap in opportunities in women with comparison to men. In Indian society from a long time back, the social structure has been such that the women are neglected in many areas like education, health, decision-making areas, financial independence, etc.
Another major reason, which contributes to the discriminatory behavior towards women in India, is the dowry system in marriage. Because of this dowry system, most Indian families consider girls as a burden. Preference for son still prevails. Girls have refrained from higher education. Women are not entitled to equal job opportunities and wages. In the 21 st century, women are still preferred gender in home managing activities. Many women quit their job and opt-out from leadership roles because of family commitments. However, such actions are very uncommon among men.
For overall wellbeing and growth of a nation, scoring high on gender equality is the most crucial aspect. Countries with less disparity in gender equality have progressed a lot. The government of India has also started taking steps to ensure gender equality. Several laws and policies are prepared to encourage girls. “Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao Yojana ” (Save girl, and make girls educated) campaign is created to spread awareness of the importance of girl child. Several laws to protect girls are also there. However, we need more awareness of spreading knowledge of women rights . In addition, the government should take initiatives to check the correct and proper implementation of policies.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Essay on Gender Equality And Women’s Empowerment
Students are often asked to write an essay on Gender Equality And Women’s Empowerment in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Gender Equality And Women’s Empowerment
Understanding gender equality.
Gender equality means that men and women have the same rights and opportunities. It’s like having two different types of fruits, say an apple and an orange, and giving them the same amount of care, sunlight, and water to grow. No one is better than the other; they are just different but equally important.
What is Women’s Empowerment?
Women’s empowerment is about making sure women can make their own choices in life. It’s like teaching someone to ride a bike. Once they learn, they can go anywhere they want, do things on their own, and feel strong.
Education and Jobs
For true gender equality, both boys and girls should go to school and learn. When they grow up, women should have the same chances to get good jobs as men. Think of it as a game where everyone gets a fair turn to play and show their skills.
Leadership Roles
Women should also be leaders, like being the captain of a team or the president of a club. This shows everyone that girls can lead and make important decisions just as well as boys can.
Equality at Home
250 words essay on gender equality and women’s empowerment.
Gender equality means that men and women have the same rights, responsibilities, and opportunities. It’s like a game where everyone gets a fair chance to play, no matter if they are a boy or a girl. Everyone should be able to go to school, work, and take part in making decisions.
Women’s Empowerment
Women’s empowerment is about giving girls and women the power to make their own choices. It’s like letting them be the captain of their own ship. They can decide what they want to study, where they want to work, and stand up for what they believe is right.
Why It’s Important
When women and men are equal, it’s good for everyone. Women can bring new ideas and skills to the table, which can help solve problems better and make the world a nicer place to live. It’s also fair that everyone gets to chase their dreams and be happy.
Challenges to Overcome
Sadly, not all places have gender equality. Some girls are kept from going to school, and some women are not allowed to work or have to work harder for less money. It’s important to change this so that everyone has the same chances in life.
How to Support Equality
To help, we can make sure that both boys and girls know that they are equal. We can also stand up for our friends if they are being treated unfairly. By working together, we can build a world where everyone is respected and can live the life they choose.
500 Words Essay on Gender Equality And Women’s Empowerment
Women’s empowerment is about giving girls and women the power to make choices for themselves. It’s like letting them decide what clothes to wear or what games to play, instead of someone else telling them what to do. Empowerment helps women to speak up, get a good education, and find jobs that they want to do.
Why Gender Equality is Important
When girls and boys, or women and men, are treated equally, it’s good for everyone. It’s like a team game where every player gets a fair chance to play, making the team stronger. Countries with gender equality are usually happier and wealthier because everyone can work, create new things, and help make decisions.
Challenges in Achieving Gender Equality
Education and gender equality.
Education is a powerful tool for gender equality. When girls go to school and learn just like boys, they can get better jobs and make better choices for their lives. It’s like giving them a key to a big door that leads to a world of opportunities.
Women in Leadership
Having more women in leadership roles is also important for gender equality. Leaders make big decisions that affect everyone. When women are leaders, they can make sure that the needs and ideas of both women and men are included. It’s like making sure that both sides of a story are heard before deciding what to do.
How to Support Gender Equality
In the end, gender equality and women’s empowerment are about making sure that everyone, no matter if they are a boy or a girl, has the same chances in life. It’s like a game where the rules are fair for all players, and everyone can win. When we work together to treat everyone equally, we make the world a better place for everyone.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Women’s Inequality, Oppression and Well-Being Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Women’s equality and oppression.
In a society that is dedicated to creating equality for girls and women, there is no space for gender oppression. This means that women would have the opportunity to attain high leadership positions and not have a wage gap with their male counterparts, violence would be reduced, while in general, females would be valued and respected. These improvements have the potential to contribute to women’s overall well-being. From the perspective of natural and applied sciences, women’s equality and oppression are relevant to the issue of establishing gender equality in the sciences, which is a research-based challenge that has not been addressed yet.
Gender diversity in science can help bring professionals with unique backgrounds, ideas, and perspectives to facilitate discoveries. In natural and applied sciences, the issue of gender equality and oppression can provide social commentary on the barriers that women researchers face in their respective fields (Tobin, 2017). The lack of equality can decrease the opportunities for self-development and financial prosperity, which are essential contributors to overall well-being (Baciu et al., 2017). Science can help resolve the issue by shedding light on significant gaps that women researchers experience in their fields using real-world data gathered from participants.
The problem can be resolved when more women are allowed to participate in scientific research, when institutions and their policies support diverse research fields, and when the knowledge is fixed by integrating gender and sex analysis into research. In various science fields, more attention must be focused on boosting the opportunities for women when they want to pursue professions in areas such as STEM. Moreover, different programs, policies, and investments in applied sciences are needed to facilitate the integration of women into research fields.
Dismantling the oppressive and unequal social structures is detrimental to improved overall wellness, which is synonymous with good physical and mental health, equal educational and professional opportunities, as well as the potential for personal development. Women’s oppression and inequality have been major social problems, which is why they can be explored through the lens of social sciences. Historically, societies have developed in such a way that it has been accepting of gender violence, the limitations of sociopolitical rights of women, and the understatement of women’s role in society.
Through social sciences, which range from physiology to social anthropology, it is possible to look at the problem from various angles. Notably, the perspective of the social sciences will be instrumental in studying the relationships between female and male genders within societies (McKenzie et al., 2018). A deeper understanding of the social issue can be achieved by looking at the details of relationships, such as career choices and outcomes, roles in raising children, domestic roles, and others (Friebel et al., 2021). Social sciences can also derive methods from natural sciences, which also allows using data from real-life participants who have diverse perspectives and experiences.
To conclude, the issue of women’s oppression and inequality is a natural problem to be explored in the social sciences because it is diverse and can include a range of aspects that pertains to their social lives. It is expected to achieve wellness among women when they are highly valued in society and have opportunities to establish themselves as valuable members who can give value through their experiences.
Friebel, G., Lalanne, M., Richter, B., Schwardmann, P., & Seabright, P. (2021). Gender differences in social interactions. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 186 , 33-45. Web.
McKenzie, S. K., Collings, S., Jenkin, G., & River, J. (2018). Masculinity, social connectedness, and mental health: Men’s diverse patterns of practice. American Journal of Men’s Health, 2018 , 1247-1261. Web.
- The Cyborg Term in the Context of Feminist Studies
- Women in Power and Their Decision-Making
- Social Wellness in Social Media
- Importance of Workplace Wellness for Business
- Wellness in Theoretic Modeling and Counseling Practice
- Negative Influence of Gendered Division of Labor on Women’s Position in Society
- Women’s Challenges and Gender Expectations
- Women in Church, Politics, and Society
- Gender Inequality in the Construction Field
- The Barriers That Gender Minorities Experience in the US
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, March 18). Women’s Inequality, Oppression and Well-Being. https://ivypanda.com/essays/womens-inequality-oppression-and-well-being/
"Women’s Inequality, Oppression and Well-Being." IvyPanda , 18 Mar. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/womens-inequality-oppression-and-well-being/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Women’s Inequality, Oppression and Well-Being'. 18 March.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Women’s Inequality, Oppression and Well-Being." March 18, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/womens-inequality-oppression-and-well-being/.
1. IvyPanda . "Women’s Inequality, Oppression and Well-Being." March 18, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/womens-inequality-oppression-and-well-being/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Women’s Inequality, Oppression and Well-Being." March 18, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/womens-inequality-oppression-and-well-being/.
- Skip to global NPS navigation
- Skip to this park navigation
- Skip to the main content
- Skip to this park information section
- Skip to the footer section

Exiting nps.gov
Alerts in effect, leading the march for women's equality.
Home to the National Woman's Party for more than 90 years, this was the epicenter of the struggle for women's rights. From this house in the shadow of the U.S. Capitol and Supreme Court, Alice Paul and the NWP developed innovative strategies and tactics to advocate for the Equal Rights Amendment and equality for women. President Barack Obama designated the national monument on April 12, 2016.
Located on Capitol Hill in Washington, D.C., the home is a short walk from Union Station.
Once home to the Secretary of the Treasury, then burned by the British in the War of 1812, this house became a hub for women's rights.
Learn about Alice Paul's lifetime of work for women's equality, including her confrontational campaign for the 19th Amendment.
The Historic Resource Study and the legacy of the National Woman's Party in the Woman Suffrage and Equal Rights movements.
The National Woman's Party pushed for the 19th Amendment, which ensured that the right to vote could not be denied based on sex.
Find out more about the National Woman's Party and its legacy. The struggle for women's social, political, and economic equality continues.
Other Sites Nearby
Park footer, contact info, mailing address:.
1100 Ohio Drive SW Washington, DC 20242
(202) 543-2240 This phone is only answered during operating hours when staff is available. Please contact us via email at [email protected]
Stay Connected
Explore subjects and stories related to this park.
- Olympic Studies Centre
- Olympic Refuge Foundation
Paris 2024: The first Games to achieve full gender parity
On International Women’s Day (8 March), Olympics.com looks at the progress made towards gender equality at the Olympic Games and assesses some of the upcoming challenges.

© Getty Images
The Olympic Movement has made great strides with regards to gender equality over recent years. Paris 2024 will be the first Olympics in history to achieve numerical gender parity on the field of play, with the same number of female and male athletes participating in the largest sporting event in the world. This key achievement was made possible due to a large number of initiatives led by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) and delivered in partnership with Olympic Movement stakeholders, such as Paris 2024, International Federations, National Olympic Committees and broadcasters.
“The progress is nice,” said fencing World Champion Ysaora Thibus , who is deeply involved in addressing gender equality issues in sport, before looking forward to the next challenges. “There’s also much to improve with everyone involved in sport, including other employees and leaders.”
To mark International Women’s Day 2023, Olympics.com takes a look at some of the achievements the Olympic Movement has made regarding gender equality.
Olympic Movement: Achievements in gender equality
- Paris 1900: Female athletes first took part in the Olympic Games, four years after the first modern Olympics took place in Athens
- 1996 : Promotion of women becomes a mission of the IOC and is enshrined in the Olympic Charter
- Tokyo 2020 : The last edition of the Games were the most gender-balanced to date with 48.7 per cent of athletes women. At Tokyo 1964, only 13 per cent of the athletes were women.
- Tokyo 2020 : Following a rule change allowing one male and one female athlete to jointly carry their flag during the Opening Ceremony, 91 per cent of NOCs had a female flag bearer
- Tokyo 2020 : Three disciplines achieved gender balance (BMX racing, mountain biking and freestyle wrestling)
- Beijing 2022 : The last Olympic Winter Games were the most gender balanced to date with 45 per cent female athletes
- Paris 2024 : Out of the 10,500 athletes participating in the Games, 5,250 will be men and 5,250 women. These Games will be the first to reach full gender parity in terms of number of athletes.
- Female IOC membership currently stands at 40 per cent, up from 21 per cent at the start of the Olympic Agenda 2020
- Youth Olympic Games : The Youth Games Buenos Aires 2018 and Winter Youth Games Lausanne 2020 reached full gender parity in overall athlete participation (2,000 athletes per gender in 2018 and 936 in 2020)
- Female representation on the IOC Executive Board stands at 33.3 per cent, versus 26.6 per cent before the Olympic Agenda 2020
- 50 per cent of the members of IOC Commissions positions have been held by women since 2022, compared with 20.3 per cent prior to the Olympic Agenda 2020. In addition, a record high of 13 of the 31 commissions were chaired by women in 2022.
Paris 2024’s commitment to gender equality
Today, only one per cent of sports facilities in France are named after women. In order to contribute towards change, 70 local authorities certified “Terre de Jeux 2024”, with the assistance of Paris 2024, have committed to renaming their sports facilities with the names of prominent women.
On International Women’s Day (8 March), the city of Livry-Gargan in the suburb of Paris will name its football pitch “Marianne Mako” to pay tribute to the iconic sports journalist who passed away in 2018.
As the organiser of the world’s biggest sporting event, Paris 2024 is working to improve the position of women in sport. While female athletes first competed at the Games at Paris 1900, France is preparing to host the first Games with full numerical gender parity on the playing field. After choosing a woman’s face for its emblem, Paris 2024 has developed a schedule for the Games that ensures balance between genders for “prime time” sessions in order to promote women’s sport to the public, particularly young girls.
“Because equality also involves visibility, the renaming of these sports facilities with women’s names is a key challenge,” said Tony Estanguet, President of Paris 2024. “We thank the local authorities working with us who, through these symbolic actions - which are not only strong but also concrete - contribute to making sport more inclusive and equal.”
Further challenges for the Olympic Movement
While the same number of female and male athletes will compete at Paris 2024, there is still a real gender gap across all leadership roles at the Olympic Games, such as that of Chef de Mission, Technical Official and coach. At Tokyo 2020, only 13 per cent of coaches were women and 10 per cent at Beijing 2022.
The IOC has launched many initiatives to address this issue, including working in partnership with International Federations, NOCs and Organising Committees to open up more coaching roles and pathways to women, such as the WISH programme (Women in Sport High Performance Pathway) which is funded by Olympic Solidarity . The programme aims to provide training to 100 female coaches in the lead-up to Paris.
The IOC is also committed to going a further step by implementing an ambitious 2021-2024 plan.
In May 2021, the IOC approved 21 Gender Equality and Inclusion Objectives for 2021-2024 . These objectives build on the progress achieved as part of the Olympic Agenda 2020 and the IOC Gender Equality Review Project and set out actions to help achieve Recommendation 13 of the Olympic Agenda 2020+5.
Based on consultations with internal and external stakeholders, and taking into account the global context, the objectives centre around five focus areas: Participation, Leadership, Safe Sport, Portrayal and Resource Allocation, and are categorised into the IOCs three areas of responsibility: the IOC as an organisation, the IOC as owner of the Olympic Games and the IOC as the leader of the Olympic Movement.

5 Women’s Rights Essays You Can Read For Free
Women and girls are the most disenfranchised group in the world. Even in places where huge strides have been made, gaps in equality remain. Women’s rights are important within the realm of human rights. Here are five essays exploring the scope of women’s rights, which you can download or read for free online:
“A Vindication on the Rights of Woman” – Mary Wollstonecraft
Mother of Mary Shelley, who wrote the novel Frankenstein, Mary Wollstonecraft is a juggernaut of history in her own right, though for a different reason. Self-educated, Wollstonecraft dedicated her life to women’s education and feminism. Her 1792 essay A Vindication on the Rights of Woman represents one of the earliest writings on women’s equality. In the Western world, many consider its arguments the foundation of the modern women’s rights movement. In the essay, Wollstonecraft writes that men are not more reasonable or rational than women, and that women must be educated with the same care, so they can contribute to society. If women were left out of the intellectual arena, the progress of society would stop. While most of us believe the idea that women are inherently inferior to men is very outdated, it’s still an accepted viewpoint in many places and in many minds. Wollstonecraft’s Vindication is still relevant.
“The Master’s Tools Will Never Dismantle the Master’s House” – Audre Lorde
Poet and activist Audre Lorde defied the boundaries of traditional feminism and cried out against its racist tendencies. While today debates about intersectional feminism (feminism that takes into account race, sexuality, etc) are common, Audre Lorde wrote her essay on women’s rights and racism back in 1984. In “The Master’s Tools Will Never Dismantle the Master’s House,” Lorde explains how ignoring differences between women – whether its race, class, or sexuality – halts any real change. By pretending the suffering of women is “all the same,” and not defined by differences, white women actually contribute to oppression. Lorde’s essay drew anger from the white feminist community. It’s a debate that feels very current and familiar.
“How to convince sceptics of the value of feminism” – Laura Bates
Laura Bates founded the Everyday Sexism Project website back in 2012. It documents examples of everyday sexism of every degree and has become very influential. In her essay from 2018, Bates takes reader comments into consideration over the essay’s three parts. This unique format allows the essay to encompass multiple views, just not Bates’, and takes into consideration a variety of experiences people have with skeptics of feminism. Why even debate skeptics? Doesn’t that fuel the trolls? In some cases, yes, but skeptics of feminism aren’t trolls, they are numerous, and make up every part of society, including leadership. Learning how to talk to people who don’t agree with you is incredibly important.
“Why Can’t A Smart Woman Love Fashion?” – Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie
Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie is one of the most influential voices in women’s rights writing. Her book, We Should All Be Feminists , is a great exploration of 21st-century feminism. In this essay from Elle, Adichie takes a seemingly “small” topic about fashion and makes a big statement about independence and a woman’s right to wear whatever she wants. There is still a lot of debate about what a feminist should look like, if wearing makeup contributes to oppression, and so on. “Why Can’t A Smart Woman Love Fashion?” is a moving, personal look at these sorts of questions.
“The male cultural elite is staggeringly blind to #MeToo. Now it’s paying for it.” – Moira Donegan
There are countless essays on the Me Too Movement, and most of them are great reads. In this one from The Guardian, Moira Donegan highlights two specific men and the publications that chose to give them a platform after accusations of sexual misconduct. It reveals just how pervasive the problem is in every arena, including among the cultural, intellectual elite, and what detractors of Me Too are saying.
You may also like

13 Facts about Child Labor

Environmental Racism 101: Definition, Examples, Ways to Take Action

11 Examples of Systemic Injustices in the US

Women’s Rights 101: History, Examples, Activists

What is Social Activism?

15 Inspiring Movies about Activism

15 Examples of Civil Disobedience

Academia in Times of Genocide: Why are Students Across the World Protesting?

Pinkwashing 101: Definition, History, Examples

15 Inspiring Quotes for Black History Month

10 Inspiring Ways Women Are Fighting for Equality

15 Trusted Charities Fighting for Clean Water
About the author, emmaline soken-huberty.
Emmaline Soken-Huberty is a freelance writer based in Portland, Oregon. She started to become interested in human rights while attending college, eventually getting a concentration in human rights and humanitarianism. LGBTQ+ rights, women’s rights, and climate change are of special concern to her. In her spare time, she can be found reading or enjoying Oregon’s natural beauty with her husband and dog.
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
Tuesday Sep 10, 2024
Group News Sites
Dailymirror
Sunday Times
Tamil Mirror
Middleast Lankadeepa
Life Online
Home delivery
Advertise with us

UN Women marks decade of empowerment; highlights need to advance gender equality in Sri Lanka
Monday, 9 September 2024 00:17 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
UN Women Sri Lanka Head of Office Ramaaya Salgado
The United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women (UN Women) has been operating in Sri Lanka since 1 September 2014, marking a decade of service dedicated to advancing gender equality and women’s empowerment. In an interview, UN Women Sri Lanka Head of Office Ramaaya Salgado highlights the continued need to advance gender equality in the country. Following are excerpts:
Q: How did the launch of UN Women come about? UN Women was established globally in 2011, following a historic move when the United Nations General Assembly unanimously voted in July 2010 to create a new entity to advance gender equality and women’s empowerment. This was the result of years of advocacy by women’s movements and civil society. The Sri Lanka chapter started in 2014 as a one-woman team, where I was providing policy advisory on gender equality to the UN in Sri Lanka. Since then, UN Women has expanded its areas of work, and over time, has grown to a decent-sized team (12-13 staff members on average).
Q: What are UN Women’s key areas of work? UN Women works on four strategic priority areas. One is to ensure that women lead, participate in, and benefit equally from governance systems. Second is to ensure that women have income security, decent work, and economic autonomy. Third is to ensure that Sri Lankan women and girls can live a life free from all forms of violence. And lastly, to ensure that women and girls contribute to and have greater influence in peacebuilding efforts. The very essence of UN Women’s work is centred on gender equality and ensuring that women are in spaces where they are making decisions about issues that impact their lives.
Q: Why is the gender equality mandate important to fulfil? The gender equality mandate is important to fulfil because it is about upholding human rights. It is about ensuring that everyone, whether it is a woman, a man, or a non-binary person, has the same rights, opportunities, and equal life chances. A critical aspect of achieving gender equality involves empowering women. This is because where inequalities exist, women and girls are the ones who are often excluded and disadvantaged. This forms the premise of our work at UN Women. Our goal is to help everyone, particularly women and girls achieve their full potential.
Q: What has been the most rewarding part of your job and what are three key moments you are proud of? The most rewarding part of my job is being able to serve communities that have been made vulnerable due to unequal access to opportunities and basic rights. To me, if you have changed one life – if one person left a violent home, if one person built a business up to the next level, if one person decided she was going to enter politics because of the training we exposed her to – that is a win because every woman counts. In terms of key moments, the first one would be our multi-party dialogues which saw us bring together first-time elected officials at the local government level from all 25 districts and across political parties to discuss issues that impact social cohesion within their communities. That was a humbling experience because we had people from diverse backgrounds, ethnicities, speaking different languages, come together for a common cause. This initiative was highly effective in its contribution to change dominant traditional attitudes about the role of women and their capacity to lead. Second would be our work on women’s economic empowerment and the work that we do with women entrepreneurs. This has had significant results and transformed their lives, incrementally, over the years. Third is our work on Sri Lanka’s first National Action Plan on Women, Peace and Security. This was a four-year long process which saw us consult all 25 districts and receive invaluable data on the peace and security concerns of women and girls in the country. This policy framework marks significant progress in ensuring that response and recovery efforts are equitable and effective for everyone – during times of crisis and conflict.
Q: While the core concept of gender equality remains the same, its definition is evolving. What crucial steps can be taken to ensure that everyone benefits from gender equality advancements? It is important to understand that people exist outside of the traditional binary of men and women. They are no less human and no less Sri Lankan than the rest of us. It is also important to understand how a person’s identity, such as race, ethnicity, religion, gender, class, and sexual orientation can create challenges that are unique to them. Understanding intersectionality and the complexity of gender helps us create fairer outcomes for everyone. This requires a whole of society approach. Education and awareness raising is crucial. Inclusive policies that recognise people of all genders, and normalising inclusivity at the community level could ensure that everyone, regardless of their gender has the same rights and opportunities.
Q: 2025 marks the 30th anniversary of the adoption of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action (1995) – a global policy framework and blueprint for realising gender equality and the empowerment of women and girls. What emerging challenges and opportunities might Sri Lanka face in advancing gender equality over the next decade? Given that Sri Lanka is still recovering from an economic crisis, the biggest challenge will be resourcing of the gender equality agenda. We know that when there is a funding deficit, the first thing to fall off the agenda are women’s rights and gender equality issues. Globally, there has also been a pushback on women’s rights. At the current rate of progress, reports show that it could take another 286 years to remove discriminatory laws and close the global gender gaps in legal protections for women and girls. Gender disparities are worsening, and recent reports have highlighted an alarming increase in crimes against women and girls in Sri Lanka. The road ahead is therefore quite challenging unless we take urgent action. To ensure that gender equality remains a priority at the national level, it’s crucial to continuously invest in bridging inequalities experienced by different groups within our society. One key way to achieve this is through gender-responsive planning and budgeting, which looks at how public policies and programs takes into consideration the unique and diverse needs of every person and then ensures that government resources are allocated more equitably. This requires a whole of government approach, robust institutional frameworks, and the political will consistently across decades, so that the generations to come will benefit from more inclusive governance systems that respond to the needs of all Sri Lankans. Additionally, it is important to consistently work with communities to change attitudes and social norms that harm women and girls. When women are not perceived as equals, they become more vulnerable to sexual and gender-based violence, fuelling an environment that normalises violence in all forms. While empowering women is a crucial step forward, it is equally important to engage the people around them and challenge harmful social norms that govern us as a society. In terms of opportunities, the policy frameworks that are in place currently in Sri Lanka are adequate to address some of the most salient challenges which prevent people of all genders from fully enjoying their rights. However, it is important to ensure that these policies do not contradict each other but rather complement one another in our efforts to advance gender equality. While some progress has been made, there is still much more work to be done to protect the rights of all individuals.
Q: What’s next for UN Women? What’s next for UN Women is a step back initially – to reflect on these last 10 years because we have treated this first decade as a teething process, by piloting a lot of our programs. So we want to reflect and take stock of what has worked for us, what has not worked for the people we work with and for, and to try and understand how we can improve or build on the programs that we have implemented thus far, and to always improve on how we serve the communities we serve so that their lives are more enriched and more equal.

- Skip to content
- Skip to navigation
- Your Premier
- Your government
- South Australian Economic Statement
- Hydrogen Jobs Plan
- Early Childhood Royal Commission
Premier of South Australia
- Message from the Premier
Blueprint laying out path to gender equality
The state government has outlined its key initiatives to improve gender equality in south australia, with today’s publication of the women’s equality blueprint 2023-2026..
The Blueprint highlights the current Government’s significant gender equality initiatives to help to achieve equality for women and girls, and address issues which inhibit women and girls from equally participating in the community.
It outlines four priority focus areas which will be addressed to support women’s wellbeing and enable all women in South Australia to prosper. These focus areas are:
*Women’s safety and security – including criminalising coercive control and making electronic monitoring a condition of bail for people charged with certain family and domestic violence offences.
*Leadership and participation – including ensuring all State Government Boards comprise 50 per cent women and holding a Women’s Leadership Symposium in conjunction with the FIFA Women’s World Cup in Adelaide in August.
*Economic wellbeing – such as the already established Women in Business Program and Housing Security for Older Women Taskforce, as well as exploring the possibility of extending portable long service leave to the arts and creative sectors.
*Women’s health – including extending support for free sanitary products in public schools.
The Blueprint also describes how the State Government will seek to realise its vision of making South Australia a fair and inclusive state, in which everyone can equally and actively participate in the economy and all aspects of community life.
Current statistics highlighted in the Blueprint show:
*279,300 women in South Australia (39 per cent) have experienced violence (physical and/or sexual) since the age of 15. *40 per cent of homicides in South Australia are family and domestic violence related. *Men are 1.5 times more likely to hold managerial positions than women. *For every dollar a man makes, a woman earns only 93 cents in South Australia.
A copy of the Women’s Equality Blueprint is available here .
Attributable to Katrine Hildyard
I am delighted to release the Women’s Equality Blueprint which will act as a roadmap to guide us towards achieving a fairer society in South Australia over the next three years.
Work is being undertaken right across government and we are making good progress, but there is still more to be done.
Achieving gender equality requires a collective effort, and it is crucial that we work alongside the private and community sectors and different tiers of government to identify gaps and design best practice approaches.

Photo essay: Equality is our goal, access is our right
Date: 01 March 2019

A bus to get to work. A clinic for health care. A monthly pension for old age. Some people can take these for granted. But many others suffer from the lack of infrastructure, public services and social protection that affect their rights and well-being. Women and girls are often foremost among those who miss out.
Progress and real development will only be possible if all people have equal rights and opportunities to thrive. Meeting that goal requires recognizing that women and girls face particular barriers and have different needs. And then taking deliberate steps so that no woman or girl is left behind, regardless of where she lives or how much she earns, or where she comes from.

Infrastructure can provide a way out of poverty and increase the chance of a better future. When there is a lack of infrastructure, communities around the world depend on women to close the gaps with their time-consuming, back-breaking labour.

“I leave home by 7 a.m. to come here by bike. I work until 1 p.m. If there’s no bike to take me back, I walk back home. It can take 2 – 3 hours and I am usually very tired by then. Because of the distance, I cannot carry anything if I am walking back,” says Mohn Malambi, a member of SOCCOMAD, a newly formed women’s cooperative in Yoko, central Cameroon.
Women in this community have grown food for generations but didn’t have land right or access to markets to sell the food they grew. Three years ago, the Government of Cameroon started to build a 250 Km (155 mile) road that would connect rural communities like Yoko with the capital. The women farmers of Yoko seized their moment to start a cooperative, knowing that the road project would bring more people to the area and create access to larger markets for their produce.
“The cassava crop cannot be left in the ground too long, because it rots,” says 52-year-old Tukuri Marie Chantal. It’s a simple equation—with land ownership and better roads, it takes less time and costs less to transport produce, and that means more income for women farmers.

The city of Jakarta, Indonesia, gleams with new buildings and other amenities. Yet safety in public spaces is a concern for women there. Fears about harassment and assault may keep women from using urban transport and other infrastructure even if they have ready access to it. Measures such as bright lighting and visible passageways help alleviate their concerns. With UN Women’s support, the Safe Jakarta project is aimed at pinpointing and closing safety gaps.

In disaster-prone Fiji, recovery efforts after Tropical Cyclone Winston had to involve women, especially the women vendors of Rakiraki Market. “For most of us women market vendors, we focus only on coming to the market to make money. But what if there is a cyclone or flooding that makes it impossible for us to be in the market?” says Varanisese Maisamoa, President of the Rakiraki Market Vendors Association.
The women vendors’ insights informed the market reconstruction to include Category-5 cyclone resilient infrastructure, a rain water harvesting system, flood resistant drainage, and a gender-responsive design.
“I’m looking forward to a market that is safer, better ventilated, with facilities such as changing areas for babies, improved toilets and a female market attendant. Our vendors also know what to do before, during and after a disaster,” Maisamoa added . Read more ►

Communities without electrical grids are increasingly turning to solar devices to jumpstart access to modern energy. Martha Benavente learned to make simple, low-cost solar lamps through a programme supported by UN Women and the governments of Norway and Sweden in a small community in Guatemala. Selling the lamps provides a source of income. Using them in her own home has ended the days when she would race to finish chores before dark because it was too costly to burn candles. Read Martha’s full story ►

Education is a human right and an essential public service with lifelong consequences. Yet many girls still struggle to get an education. In Khayelitsha, the largest informal township in Cape Town, South Africa, girls at the Yomelela Primary School contend with severe poverty and acute risks of violence. With the backing of the UN Trust Fund to End Violence against Women, sports and peer counselling are among the methods that help them cope, feel safe and stay in school.

As the fourth industrial revolution unfolds, the future of jobs will be defined by innovation. While more girls are attending school than before, girls are significantly under-represented in STEM subjects in many settings. The first Coding Camp in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, brought together girls from 34 countries in the African continent to nurture their potential as innovators and technology creators.
What happens when girls get equal access to technology? They build.
“We are trying to build a drone that is controlled by SMS messaging that will be able to dispense medicine in rural areas,” shared 15-year-old participant Eno Ekanem. Read more ►

In the Republic of North Macedonia, many girls and boys with disabilities are still segregated in separate schools; a very low percentage reach university. Activist Elena Kochovska is fighting for their greater inclusion in education and employment. Read her full story ►

Health-care services should reach all women and provide all the services they need. Yet, too many women still die giving birth, especially in poorer countries where services may be limited and poor in quality. With 1,072 maternal deaths for every 100,000 births, Liberia has one of the highest maternal mortality rates in the world. In the remote areas, infrastructure and facilities in clinics are often lacking; midwives and health-care workers have to deliver babies without any electricity at night.
“It’s really challenging to assist with a delivery using my phone’s light, because I can’t see clearly. I have to hold the phone in my mouth while working. Doing [medical] procedures at night is almost impossible,” explains midwife Lorina Karway.
A UN joint programme installed solar lighting systems in 26 health centres and in five maternal waiting rooms in rural Liberia, including the Bodowhea Clinic, where Karway works, to improve maternal and child health-care services. Read more ►

Low-cost, readily accessible legal aid upholds the rights of poorer women, in particular, to obtain justice as well as essential public services. In Kazakhstan, UN Women has trained legal advocates like Natalia Minayeva. They help women living with HIV solve legal issues and find social assistance, including to end drug dependency. Read more ►

Green, open spaces where everyone can convene, relax and take a break may be taken for granted in some parts of the world. For women and girls in Al-Shoka, a conflict affected neighbourhood in Gaza, Palestine, this was a distant dream, until now. In 2018, the only public garden in Al-Shoka, which was destroyed by the conflict, opened to the public. What’s more, it was re-designed by three female architects and a group of young people from the community to be a truly inclusive space. Read about the female architects who redesigned the garden ►

Limited access to childcare remains a major barrier for women seeking paid jobs, underscoring the importance of providing quality public childcare. Time-use surveys in Uruguay revealed that women spent two-third of their week doing unpaid work, and only one-third on paid work. For men, the reverse applied. The data made Uruguay rethink “care” as an issue that impacts the society and ultimately, led to the adoption of a new law in 2015. Under the Care Act (No. 19,353), all children, persons with disabilities and elderly persons, have the right to get care. The State not only provides care services now, but also guarantees their quality by providing training and regulations.
Soledad Rotella is one of the many mothers benefiting from the new law. Since quality and free day care is available for her 2-year-old daughter, Kiara Rotella can get a full-time job without risking the wellbeing of her daughter. Read the full story ►

Longer, healthier lives are now the norm in many countries, an indisputable sign of progress. By 2030, over 16 per cent of people will be over age 60, compared to just over 8 percent in 1970. Pension systems are expanding to support people in old age. Yet women are less likely to be covered and generally receive less than men, even as they live longer on average. In Viet Nam, Phung Thi Vinh spent a lifetime as a primary school teacher but only began contributing to social insurance late in her career. A government programme helped her catch up. “My pensions payments are small,” she says. “But they help keep body and soul together.”
This photo essay has been adapted from a UN Women photo exhibition at the UN Headquarters in New York, running from 7 March - 27 March
- ‘One Woman’ – The UN Women song
- UN Under-Secretary-General and UN Women Executive Director Sima Bahous
- Kirsi Madi, Deputy Executive Director for Resource Management, Sustainability and Partnerships
- Nyaradzayi Gumbonzvanda, Deputy Executive Director for Normative Support, UN System Coordination and Programme Results
- Guiding documents
- Report wrongdoing
- Programme implementation
- Career opportunities
- Application and recruitment process
- Meet our people
- Internship programme
- Procurement principles
- Gender-responsive procurement
- Doing business with UN Women
- How to become a UN Women vendor
- Contract templates and general conditions of contract
- Vendor protest procedure
- Facts and Figures
- Global norms and standards
- Women’s movements
- Parliaments and local governance
- Constitutions and legal reform
- Preguntas frecuentes
- Global Norms and Standards
- Macroeconomic policies and social protection
- Sustainable Development and Climate Change
- Rural women
- Employment and migration
- Facts and figures
- Creating safe public spaces
- Spotlight Initiative
- Essential services
- Focusing on prevention
- Research and data
- Other areas of work
- UNiTE campaign
- Conflict prevention and resolution
- Building and sustaining peace
- Young women in peace and security
- Rule of law: Justice and security
- Women, peace, and security in the work of the UN Security Council
- Preventing violent extremism and countering terrorism
- Planning and monitoring
- Humanitarian coordination
- Crisis response and recovery
- Disaster risk reduction
- Inclusive National Planning
- Public Sector Reform
- Tracking Investments
- Strengthening young women's leadership
- Economic empowerment and skills development for young women
- Action on ending violence against young women and girls
- Engaging boys and young men in gender equality
- Leadership and Participation
- National Planning
- Violence against Women
- Access to Justice
- Regional and country offices
- Regional and Country Offices
- Liaison offices
- 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
- UN Women Global Innovation Coalition for Change
- Commission on the Status of Women
- Economic and Social Council
- General Assembly
- Security Council
- High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development
- Human Rights Council
- Climate change and the environment
- Other Intergovernmental Processes
- World Conferences on Women
- Global Coordination
- Regional and country coordination
- Promoting UN accountability
- Gender Mainstreaming
- Coordination resources
- System-wide strategy
- Focal Point for Women and Gender Focal Points
- Entity-specific implementation plans on gender parity
- Laws and policies
- Strategies and tools
- Reports and monitoring
- Training Centre services
- Publications
- Government partners
- National mechanisms
- Civil Society Advisory Groups
- Benefits of partnering with UN Women
- Business and philanthropic partners
- Goodwill Ambassadors
- National Committees
- UN Women Media Compact
- UN Women Alumni Association
- Editorial series
- Media contacts
- Annual report
- Progress of the world’s women
- SDG monitoring report
- World survey on the role of women in development
- Reprint permissions
- Secretariat
- 2023 sessions and other meetings
- 2022 sessions and other meetings
- 2021 sessions and other meetings
- 2020 sessions and other meetings
- 2019 sessions and other meetings
- 2018 sessions and other meetings
- 2017 sessions and other meetings
- 2016 sessions and other meetings
- 2015 sessions and other meetings
- Compendiums of decisions
- Reports of sessions
- Key Documents
- Brief history
- CSW snapshot
- Preparations
- Official Documents
- Official Meetings
- Side Events
- Session Outcomes
- CSW65 (2021)
- CSW64 / Beijing+25 (2020)
- CSW63 (2019)
- CSW62 (2018)
- CSW61 (2017)
- Member States
- Eligibility
- Registration
- Opportunities for NGOs to address the Commission
- Communications procedure
- Grant making
- Accompaniment and growth
- Results and impact
- Knowledge and learning
- Social innovation
- UN Trust Fund to End Violence against Women
- About Generation Equality
- Generation Equality Forum
- Action packs
Cart expired, please start over.
Your cart will expire in mins
Take The Lead Presents Women’s Equality Day Power Up Concert featuring Marina Arsenijevic, BETTY, and SWEET HONEY IN THE ROCK®
Terrace Theater
Join us for the TAKE THE LEAD® Power Up Concert TOGETHER WE LEAD. A joyful celebration of music in pursuit of advancing women’s leadership which includes performances by world-renowned pianist and composer MARINA ARSENIJEVIC, Indie Pop Band BETTY, and three-time Grammy Award nominated female a'cappella group SWEET HONEY IN THE ROCK® who express their history as black women through song and sign language. Special Appearance by Lynda Carter.
This is a Deaf Friendly event.
Sun. Aug. 25, 2024
Upcoming Dates
Sun. Aug. 25, 2024 6:30p.m.
Production Information
Popular Music
Price Range
$50.00 – $150.00
90 minutes, no intermission

Join us for the TAKE THE LEAD® Power Up Concert TOGETHER WE LEAD. A joyful celebration of music in pursuit of advancing women’s leadership which includes performances by world-renowned pianist and composer MARINA ARSENIJEVIC, Indie Pop Band BETTY, and three-time Grammy Award nominated female a cappella group SWEET HONEY IN THE ROCK® who express their history as black women through song and sign language. During the concert, LYNDA CARTER, the original Wonder Woman, will be receiving the Leading Woman Award presented by the founder of TAKE THE LEAD®, best-selling author, and lifelong activist on behalf of women’s rights, GLORIA FELDT. This is a Deaf Friendly event.
Carousel Controls
- Previous slide.
- Next slide.
Terms and Conditions
All events and artists subject to change without prior notice.
All ticket prices are subject to change based on demand. Purchase early to lock in prices and the best seats!
This event is an external rental presented in coordination with the Kennedy Center Campus Rentals Office and is not produced by the Kennedy Center.
You May Also Like
The kennedy center and 0xcollection present dvořák dreams : an installation by refik anadol.
Sep. 4 - 24, 2024
Refik Anadol’s acclaimed fusion of art, music, history, and artificial intelligence makes its U.S. premiere with an immersive data sculpture transforming the legacy of Czech composer Antonín Dvořák into a multi-sensory experience.

National Symphony Orchestra DC ORIGINALITY: Showcasing the Cultural Beat of Capital City
Sep. 10 - 11, 2024
Hosted by actor Anthony Anderson and Dr. Tonya M. Matthews, this electrifying concert event curated by Carlos Simon features performances by Ginuwine, Kenny Lattimore, Imani-Grace Cooper, The String Queens, Afro Blue, D.C. Go-Go All Stars, and more homegrown heroes! Join the NSO for an evening featuring the music of D.C. natives Marvin Gaye, Chuck Brown, Duke Ellington, and more— come early and stay late for pre- and post-shows, local pop-up vendors, drink tastings, photobooths, and more!
- Student Rush

Millennium Stage (In-Person and Livestream) California State University: Dominguez Hills
Fri. Sep. 13, 2024
Founded in 2009, the Inner City Youth Orchestra of Los Angeles (ICYOLA) is a California 501(c)(3) nonprofit corporation that transforms the lives and minds of young people in inner-city Los Angeles through high quality music education.

National Symphony Orchestra Echoes of America: Music of Carlos Simon, Aaron Copland & Jessie Montgomery
Sat. Sep. 14, 2024
For one night only, the National Symphony Orchestra performs a rousing collection of songs and stories that celebrate and challenge the American narrative—from Jessie Montgomery’s revolutionary anthem Banner to iconic music from Copland’s Billy the Kid and more. The NSO proudly presents Carlos Simon’s Here I Stand: Paul Robeson , a new commission honoring the African American singer, actor, athlete, scholar, and fearless supporter of racial equality. Bass-baritone Morris Robinson and The Washington Chorus join us for this symphonic exploration of the ideals we strive for as a country and community, united by hope.

By using this site, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions which describe our use of cookies.
Reserve Tickets
Review cart.
You have 0 items in your cart.
Your cart is empty.
Keep Exploring Proceed to Cart & Checkout
Donate Today
Support the performing arts with your donation.
To join or renew as a Member, please visit our Membership page .
To make a donation in memory of someone, please visit our Memorial Donation page .
- Custom Other


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What does gender equality look like today?
Conclusion. Gender equality is not a distant ideal; it is a fundamental human right that must be upheld and protected. Achieving equal rights for women requires a collective effort from all sectors of society to challenge discrimination, promote empowerment, and create a more inclusive and equitable world for all.
5 Powerful Essays Advocating for Gender Equality
In this essay series, Brookings scholars, public officials, and other subject-area experts examine the current state of gender equality 100 years after the 19th Amendment was adopted to the U.S ...
Women's Power in the Struggle for Freedom and Equal ...
The 11 biggest hurdles for women's equality by 2030
United Nations: Gender equality and women's empowerment
This essay states that empowerment is the key. When giving authority and control over their own lives, women thrive and contribute more to the world. It's important that programs seeking to end gender inequality focus on empowerment, and not "rescue.". Treating women like victims is not the answer. Axa is a leading global insurer ...
GENDER EQUALITY AND INCLUSIVE GROWTH:
Gender equality: the route to a better world
Gender equality and women's rights
At first glance, it appears that SDG5 (Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls) shares one of MDG3's main limitations, namely, the lack of explicit affirmation of women's human rights in the goal itself. Differently from MDG3, however, human rights did find their way into SDG5's targets, both explicitly as in target 5.6 and 5.a ...
Gender equality and women's empowerment
10 Reasons Why Gender Equality is Important
The women's rights movement won equal opportunities in higher education and employment relatively quickly in the 1940s and 1950s. The modern concept of women's equality as "feminism" appeared in the 1960s, led by activists such as Betty Friedan. Some of its victories in the legislative arena were completely inadvertent, while one of its ...
500 Words Essay On Women Rights
500+ Words Essay on Gender Equality Essay. Equality or non-discrimination is that state where every individual gets equal opportunities and rights. Every individual of the society yearns for equal status, opportunity, and rights. However, it is a general observation that there exists lots of discrimination between humans.
100 Words Essay on Gender Equality And Women's Empowerment Understanding Gender Equality. Gender equality means that men and women have the same rights and opportunities. It's like having two different types of fruits, say an apple and an orange, and giving them the same amount of care, sunlight, and water to grow. No one is better than the ...
Home | Projects at Harvard
CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES IN ACHIEVING ...
In natural and applied sciences, the issue of gender equality and oppression can provide social commentary on the barriers that women researchers face in their respective fields (Tobin, 2017). The lack of equality can decrease the opportunities for self-development and financial prosperity, which are essential contributors to overall well-being ...
Home to the National Woman's Party for more than 90 years, this was the epicenter of the struggle for women's rights. From this house in the shadow of the U.S. Capitol and Supreme Court, Alice Paul and the NWP developed innovative strategies and tactics to advocate for the Equal Rights Amendment and equality for women. President Barack Obama designated the national monument on April 12, 2016.
Paris 2024's commitment to gender equality. Today, only one per cent of sports facilities in France are named after women. In order to contribute towards change, 70 local authorities certified "Terre de Jeux 2024", with the assistance of Paris 2024, have committed to renaming their sports facilities with the names of prominent women.
Her 1792 essay A Vindication on the Rights of Woman represents one of the earliest writings on women's equality. In the Western world, many consider its arguments the foundation of the modern women's rights movement. In the essay, Wollstonecraft writes that men are not more reasonable or rational than women, and that women must be educated ...
British supermarket chain Asda Group Ltd. is set to face a crucial stage in its equal pay fight with workers in what could form the tip of an £8 billion ($10.6 billion) iceberg of claims against ...
Q: How did the launch of UN Women come about? UN Women was established globally in 2011, following a historic move when the United Nations General Assembly unanimously voted in July 2010 to create a new entity to advance gender equality and women's empowerment. This was the result of years of advocacy by women's movements and civil society.
The State Government has outlined its key initiatives to improve gender equality in South Australia, with today's publication of the Women's Equality Blueprint 2023-2026. The Blueprint highlights the current Government's significant gender equality initiatives to help to achieve equality for women and girls, and address issues which ...
A government programme helped her catch up. "My pensions payments are small," she says. "But they help keep body and soul together.". This photo essay has been adapted from a UN Women photo exhibition at the UN Headquarters in New York, running from 7 March - 27 March. A bus to get to work. A clinic for health care.
Terrace Theater. Join us for the TAKE THE LEAD® Power Up Concert TOGETHER WE LEAD. A joyful celebration of music in pursuit of advancing women's leadership which includes performances by world-renowned pianist and composer MARINA ARSENIJEVIC, Indie Pop Band BETTY, and three-time Grammy Award nominated female a'cappella group SWEET HONEY IN THE ROCK® who express their history as black women ...
Workers from Asda have held demonstrations to mark the start of an equal pay claim involving more than 60,000 staff. The GMB union said the supermarket chain's predominantly female retail ...