

Case Study in Hindi Explained – केस स्टडी क्या है और कैसे करें
आपने अक्सर अपने स्कूल या कॉलेज में केस स्टडी के बारे में सुना होगा । खासकर कि Business Studies और Law की पढ़ाई पढ़ रहे छात्रों को कैसे स्टडी करने के लिए कहा जाता है । पर case study kya hai ? इसे कैसे करते हैं , इसके फायदे क्या हैं ? इस आर्टिकल में आप इन सभी प्रश्नों के बारे में विस्तार से जानेंगे ।
Case study in Hindi explained के इस पोस्ट में आप न सिर्फ केस स्टडी के बारे में विस्तार से जानेंगे बल्कि इसके उदाहरणों और प्रकार को भी आप विस्तार से समझेंगे । यह जरूरी है कि आप इसके बारे में सही और विस्तृत जानकारी प्राप्त करें ताकि आपको कभी कोई समस्या न हो । तो चलिए विस्तार से इसके बारे में जानते हैं :
Case Study in Hindi
Case Study एक व्यक्ति , समूह या घटना का गहन अध्ययन है । एक केस स्टडी में , किसी भी घटना या व्यक्ति का सूक्ष्म अध्ययन करके उसके व्यवहार के बारे में पता लगाया जाता है । एजुकेशन , बिजनेस , कानून , मेडिकल इत्यादि क्षेत्रों में केस स्टडी की जाती है ।
case study सिर्फ और सिर्फ एक व्यक्ति , घटना या समूह को केंद्र में रखकर किया जाता है और यह उचित भी है । इसकी मदद से आप सभी के लिए एक ही निष्कर्ष नहीं निकाल सकते । उदहारण के तौर पर , एक बिजनेस जो लगातार घाटा झेल रहा है उसकी केस स्टडी की जा सकती है । इसमें सभी तथ्यों को मिलाकर , परखकर यह जानने की कोशिश होती है कि क्यों बिजनेस लगातार loss में जा रही है ।
परंतु , जरूरी नहीं कि जिस वजह से यह पार्टिकुलर कम्पनी घाटा झेल रही हो , अन्य कंपनियों के घाटे में जाने की यही वजह हो । इसलिए कहा जाता है कि किसी एक मामले के अध्ययन से निकले निष्कर्ष को किसी अन्य मामले पर थोपा नहीं जा सकता । इस तरह आप case study meaning in Hindi समझ गए होंगे ।
Case Study examples in Hindi
अब जबकि आपने case study kya hai के बारे में जान लिया है तो चलिए इसके कुछ उदाहरणों को भी देख लेते हैं । इससे आपको केस स्टडी के बारे में जानने में अधिक मदद मिलेगी ।
ऊपर के उदाहरण को देख कर आप समझ सकते हैं कि case study क्या होती है । अब आप ऊपर दिए case पर अच्छे से study करेंगे तो यह केस स्टडी कहलाएगी यानि किसी मामले का अध्ययन । पर केस स्टडी कैसे करें ? अगर हमारे पास ऊपर दिए उदाहरण का केस स्टडी करने को दिया जाए तो यह कैसे करना होगा ? चलिए जानते हैं :
Case Study कैसे करें ?
अब यह जानना जरूरी है कि एक case study आखिर करते कैसे हैं और किन tools का उपयोग किया जाता है । तो एक केस स्टडी करने के लिए आपको ये steps फॉलो करना चाहिए :

1. सबसे पहले केस को अच्छे से समझें
अगर आप किसी भी केस पर स्टडी करना चाहते हैं तो आपको सबसे पहले उसकी बारीकियों और हर एक डिटेल पर ध्यान देना चाहिए । तभी आप आगे बढ़ पाएंगे और सही निर्णय भी ले पाएंगे । Case को अच्छे से समझने का सबसे बड़ा फायदा यह है कि इसपर स्टडी करते समय आपको ज्यादा मेहनत नहीं करनी पड़ती । केस को अच्छे से समझने के लिए आप यह कर सकते हैं :
- Important points को हाईलाइट करें
- जरूरी समस्याओं को अंडरलाइन करें
- जरूरी और बारीकियों का नोट्स तैयार करें
2. अपने विश्लेषण पर ध्यान दें
Case Study करने के लिए जरूरी है कि आप अपने analysis पर ध्यान दें ताकि बढ़िया रिजल्ट मिल सके । इसके लिए आप विषय के 2 से 5 मुख्य बिंदुओं / समस्याओं को उठाएं और बारीकी से उनके बारे में जानकारी इकट्ठा करें । इसके बारे में पता करें कि ये क्यों exist करती है और संस्था पर इनका क्या प्रभाव है ।
आप उन समस्याओं के लिए जिम्मेदार कारकों पर भी नजर डालें और सभी चीजों को ढंग से समझने की कोशिश करें तभी जाकर आप सही मायने में case study कर पाएंगे ।
3. संभव समाधानों के बारे में सोचें
किसी भी केस स्टडी का तीसरा महत्वपूर्ण पड़ाव है कि आप समस्या के संभावित समाधानों के बारे में सोचें ।इसके लिए आप discussions , research और अपने अनुभव की मदद ले सकते हैं । ध्यान रहें कि सभी समाधान संभव हों ताकि उन्हें लागू किया जा सके ।
4. बेहतरीन समाधान का चुनाव करें
केस स्टडी का अंतिम पड़ाव मौजूदा समाधानों में से एक सबसे बेहतरीन समाधान का चुनाव करना है । आप सभी समाधानों को एक साथ तो बिल्कुल भी implement नहीं कर सकते इसलिए जरूरी है कि बेहतरीन को चुनें ।
Case Study format

अगर आप YouTube video की मदद से देखकर सीखना चाहते हैं कि Case Study कैसे बनाएं तो नीचे दिए गए Ujjwal Patni की वीडियो देख सकते हैं ।
इस पोस्ट में आपने विस्तार से case study meaning in Hindi के बारे में जाना । अगर कोई प्वाइंट छूट गया हो तो कॉमेंट में जरूर बताएं और साथ ही पोस्ट से जुड़ी राय या सुझाव भी आप कॉमेंट में दे सकते हैं । पोस्ट पसंद आया हो और हेल्पफुल साबित हुई हो तो शेयर जरूर करें ।
- लड़कियों / महिलाओं केआई घर बैठे job ideas
- Petrochemical के बारे में पूरी जानकारी
- Print और electronic media के विभिन्न साधन
- Blog meaning in Hindi क्या है
I have always had a passion for writing and hence I ventured into blogging. In addition to writing, I enjoy reading and watching movies. I am inactive on social media so if you like the content then share it as much as possible .
Related Posts
Escrow account meaning in hindi – एस्क्रो अकाउंट क्या है, personality development course free in hindi – पर्सनैलिटी डेवलपमेंट, iso certificate क्या होता है आईएसओ सर्टिफिकेट के फायदे और उपयोग.
nice info sir thanks
Thanks. It is really very helpful.
I’m glad to know that you found this post about case study helpful! Keep visiting.
Leave A Reply Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
- Write with us
- Advertise with us
- Liability Disclaimer
Primary Ka Master ● Com - प्राइमरी का मास्टर ● कॉम
एक छतरी के नीचे 'प्राइमरी का मास्टर' की समस्त ऑनलाइन सेवाएँ
केस स्टडी विधि के उद्देश्य, विशेषताएं और इस विधि की उपयोगितायेँ
- विद्यार्थी स्वतंत्र होकर, स्वयं ही सृजनात्मक ढंग से समस्या पर विचार कर सकेंगें।
- वे समस्या समाधान ( Problem based learning )तक पहुंचने में सक्रिय हो सकेंगें।
- वे अपने पूर्व ज्ञान का प्रयोग करते हुए प्रमाणों को संग्रह कर सकेंगें।
- घटनाक्रम में नवीन तथ्यों को जान सकेंगे।
- स्वयं अपने अनुभव से सीखते हुए ज्ञान प्राप्त कर सकेंगें।
- व्यक्तिगत, सामाजिक संबंधों को उत्तम ढंग से स्थापित कर सकेंगे।
- छात्रों में अभिप्रेरण एवं अभिव्यक्ति की क्षमता में वृद्धि हो सकेगी।
- छात्रों की उपलब्धियों का मूल्यांकन हो सकेगा।

व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन छात्रों को एक सार्थक ज्ञान प्रदान करता है जिसका प्रयोग विभिन्न प्रकार के समाधान या अध्ययन के लिए किया जाता है। यह एक जटिल अधिगम का स्वरूप होता है। इसमें सृजनात्मक चिन्तन निहित होता है और चिन्तन स्तर पर शिक्षण की व्यवस्था होती है।

Post a Comment

Case of study child ka farmet kaise taiyar krein

Prateek Shivalik
#Free Educational Notes

What Is Case Study Method In Hindi? PDF
What is case study method in hindi.
What Is Case Study Method In Hindi? PDF Download, व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन , मामले का अध्ययन, केस स्टडी आदि के बारे में जानेंगे। इन नोट्स के माध्यम से आपके ज्ञान में वृद्धि होगी और आप अपनी आगामी परीक्षा को पास कर सकते है | Notes के अंत में PDF Download का बटन है | तो चलिए जानते है इसके बारे में विस्तार से |
- सामाजिक अनुसंधान पद्धतियों के विशाल परिदृश्य में, केस स्टडी पद्धति मानव व्यवहार और अनुभवों की जटिल जटिलताओं को समझने के लिए एक शक्तिशाली उपकरण के रूप में सामने आती है।
- व्यक्तिगत जीवन या उनके वास्तविक जीवन के संदर्भ में विशिष्ट घटनाओं में गहराई से उतरकर, यह विधि अद्वितीय अंतर्दृष्टि प्रदान करती है जो अक्सर मात्रात्मक विश्लेषण से बच जाती है। यह लेख केस स्टडी पद्धति के सार की पड़ताल करता है, इसकी ताकत, अनुप्रयोगों और सामाजिक विज्ञान के क्षेत्र में इसके प्रभाव पर प्रकाश डालता है।
केस स्टडीज को समझना: परिभाषा और उदाहरण
(understanding case studies: definition and examples).
शब्द “CASE” बहुआयामी है और इसका उपयोग कानून, चिकित्सा और मनोविज्ञान सहित हमारे दैनिक जीवन के विभिन्न पहलुओं में होता है। प्रत्येक संदर्भ में, यह शब्द किसी व्यक्ति के बारे में जानकारी एकत्र करने से जुड़ा है ताकि उनके सामने आने वाले मुद्दों या समस्याओं को हल करने में उनकी सहायता की जा सके। यह सिद्धांत मनोविज्ञान और शिक्षा के क्षेत्र में भी लागू होता है, जहां मनोवैज्ञानिक या शैक्षिक चुनौतियों का सामना करने वाले व्यक्तियों की विस्तार से जांच की जाती है। उनके अतीत, वर्तमान और संभावित भविष्य को शामिल करते हुए इस व्यापक विश्लेषण को केस स्टडी कहा जाता है।
- व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन , जिसे आमतौर पर केस स्टडी कहा जाता है, सामाजिक अनुसंधान में डेटा संग्रह की एक मौलिक विधि है, जिसका व्यापक रूप से विभिन्न सामाजिक विज्ञानों में उपयोग किया जाता है।
- इसमें एक विशिष्ट सामाजिक इकाई का गहन विश्लेषण शामिल है, जिसमें व्यक्तियों, परिवारों, समूहों, संस्थानों, समुदायों, नस्लों, राष्ट्रों, सांस्कृतिक क्षेत्रों या ऐतिहासिक युगों को शामिल किया जा सकता है।
- इस पद्धति की तुलना अक्सर ‘सामाजिक माइक्रोस्कोप’ से की जाती है क्योंकि यह शोधकर्ताओं को उल्लेखनीय गहराई के साथ सामाजिक घटनाओं का पता लगाने में सक्षम बनाता है, जिससे जटिल विवरण सामने आते हैं जो अन्य शोध विधियों के माध्यम से अस्पष्ट रह सकते हैं।
- आम ग़लतफ़हमी के विपरीत कि, यह केवल व्यक्तिगत गतिविधियों और जीवन इतिहास पर केंद्रित है, केस अध्ययन पद्धति अपना दायरा विभिन्न सामाजिक इकाइयों तक बढ़ाती है। शोधकर्ता इस दृष्टिकोण का उपयोग चुनी हुई इकाई के सभी पहलुओं की सावधानीपूर्वक जांच करने के लिए करते हैं, जिससे यह एक व्यापक और विस्तृत अध्ययन बन जाता है।
- केस अध्ययनों के माध्यम से, सामाजिक वैज्ञानिक छिपी हुई बारीकियों को उजागर करते हैं, जो मानव व्यवहार, सामाजिक संरचनाओं और सांस्कृतिक गतिशीलता की जटिलताओं में अमूल्य अंतर्दृष्टि प्रदान करते हैं।
केस स्टडी के मुख्य तत्व
(key elements of a case study).
1. केस स्टडी की परिभाषा (Definition of a Case Study):
- एक केस स्टडी में किसी व्यक्ति की शैक्षिक या मनोवैज्ञानिक समस्या का गहन अन्वेषण शामिल होता है, जिसमें उनका इतिहास, वर्तमान स्थिति और भविष्य की संभावनाएं शामिल होती हैं।
- उदाहरण: सीखने में कठिनाइयों का सामना कर रहे एक छात्र की जांच करना ताकि उसके कारणों, वर्तमान सीखने के माहौल और अकादमिक रूप से सफल होने में मदद करने के लिए संभावित हस्तक्षेपों को समझा जा सके।
2. कानूनी और चिकित्सीय मामलों में समानताएँ (Similarities to Legal and Medical Cases):
- उसी तरह, जैसे एक वकील एक कानूनी मामले का अध्ययन करता है और एक डॉक्टर एक मरीज के मामले का मूल्यांकन करता है, मनोवैज्ञानिक और शिक्षक मनोवैज्ञानिक या शैक्षिक चुनौतियों का सामना करने वाले व्यक्ति के मामले की जांच करते हैं।
- उदाहरण: एक मनोवैज्ञानिक व्यवहार संबंधी मुद्दों वाले बच्चे के मामले में पारिवारिक पृष्ठभूमि, स्कूल के माहौल और बच्चे की भावनात्मक स्थिति जैसे कारकों पर विचार करता है।
3. डेटा संग्रह और विश्लेषण (Data Collection and Analysis):
- केस अध्ययन में विभिन्न प्रकार के डेटा एकत्र करना शामिल है, जिसमें साक्षात्कार, अवलोकन, मनोवैज्ञानिक मूल्यांकन और अकादमिक रिकॉर्ड शामिल हो सकते हैं।
- उदाहरण: शिक्षकों, अभिभावकों और छात्रों के साथ साक्षात्कार के माध्यम से जानकारी एकत्र करना, साथ ही कक्षा में छात्र के शैक्षणिक प्रदर्शन और व्यवहार का विश्लेषण करना।
4. विस्तृत समझ (Comprehensive Understanding):
- केस अध्ययन का उद्देश्य व्यक्ति की अद्वितीय परिस्थितियों और अनुभवों को ध्यान में रखते हुए उसकी समस्या की समग्र समझ प्रदान करना है।
- उदाहरण: एक किशोर के स्कूल से इनकार करने के मामले का अध्ययन करना, न केवल शैक्षणिक दबाव बल्कि सामाजिक संपर्क, मानसिक स्वास्थ्य और पारिवारिक गतिशीलता पर भी विचार करना।
5. समस्या-समाधान दृष्टिकोण (Problem-Solving Approach):
- सकारात्मक परिणामों को बढ़ावा देने के लिए व्यक्ति की विशिष्ट आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप प्रभावी समाधानों और हस्तक्षेपों की पहचान करने के लिए केस अध्ययनों का उपयोग किया जाता है।
- उदाहरण: एक व्यापक केस अध्ययन के निष्कर्षों के आधार पर ध्यान घाटे की सक्रियता विकार (ADHD: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) वाले छात्र के लिए एक व्यक्तिगत शिक्षा योजना विकसित करना।
निष्कर्ष: शिक्षा और मनोविज्ञान में केस अध्ययन व्यक्तियों के सामने आने वाली चुनौतियों को समझने और उनका समाधान करने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं। समग्र दृष्टिकोण अपनाकर और किसी व्यक्ति के इतिहास, वर्तमान स्थिति और संभावित भविष्य में गहराई से जाकर, मनोवैज्ञानिक और शिक्षक लक्षित हस्तक्षेप विकसित कर सकते हैं, जो अंततः व्यक्ति की वृद्धि, विकास और कल्याण को सुविधाजनक बना सकता है।
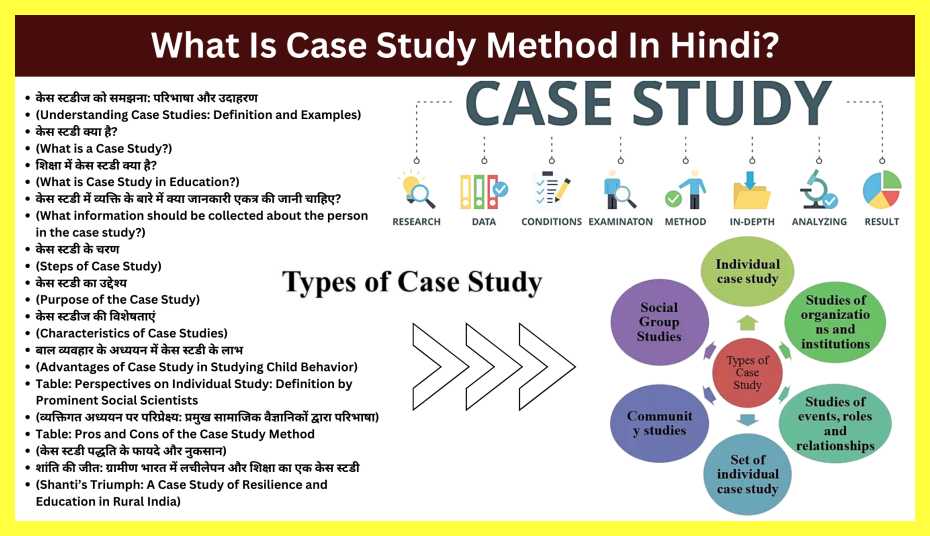
केस स्टडी क्या है?
(what is a case study).
केस स्टडी एक शोध पद्धति है जो किसी विशिष्ट व्यक्ति का उसके प्राकृतिक वातावरण में अध्ययन करने पर केंद्रित होती है। यह दृष्टिकोण शोधकर्ताओं को व्यक्ति के व्यवहार और व्यक्तित्व के विभिन्न पहलुओं में व्यापक अंतर्दृष्टि प्राप्त करने की अनुमति देता है। व्यक्ति की संपूर्णता में जांच करके, केस अध्ययन वास्तविक जीवन के संदर्भ में मानव व्यवहार की गहरी समझ प्रदान करते हैं।
1. व्यवहार अध्ययन की विधि (Method of Behavior Study):
- केस स्टडीज़ मानव व्यवहार का अध्ययन करने के लिए नियोजित अनुसंधान विधियां हैं। शोधकर्ता अपने वातावरण में व्यक्ति के कार्यों, प्रतिक्रियाओं और अंतःक्रियाओं का बारीकी से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करते हैं।
- उदाहरण: एक मनोवैज्ञानिक एक किशोर में सामाजिक चिंता विकार को समझने के लिए एक केस स्टडी कर रहा है, और विभिन्न सामाजिक स्थितियों में उनके व्यवहार का अवलोकन कर रहा है।
2. किसी विशेष व्यक्ति पर ध्यान दें (Focus on a Particular Person):
- केस अध्ययन किसी समूह या जनसंख्या के बजाय किसी विशिष्ट व्यक्ति पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हैं। यह केंद्रित दृष्टिकोण शोधकर्ताओं को किसी व्यक्ति के व्यवहार की जटिलताओं को गहराई से समझने की अनुमति देता है।
- उदाहरण : ऑटिज़्म स्पेक्ट्रम विकार वाले बच्चे के मामले का अध्ययन करके उनकी अनूठी चुनौतियों, संचार पैटर्न और सामाजिक संपर्कों का पता लगाना।
3. प्राकृतिक पर्यावरण के भीतर अध्ययन (Study within the Natural Environment):
- केस अध्ययन व्यक्ति के प्राकृतिक वातावरण में आयोजित किए जाते हैं, यह सुनिश्चित करते हुए कि एकत्र किए गए अवलोकन और डेटा उनके विशिष्ट व्यवहार के प्रतिनिधि हैं।
- उदाहरण: कक्षा सेटिंग में एक शिक्षक का अवलोकन करके उनकी शिक्षण विधियों, छात्रों की बातचीत और कक्षा प्रबंधन तकनीकों को समझना।
4. व्यवहार और व्यक्तित्व की व्यापक समझ (Comprehensive Understanding of Behavior and Personality):
- केस अध्ययन का उद्देश्य व्यक्ति के व्यवहार और व्यक्तित्व के सभी पहलुओं के बारे में जानकारी इकट्ठा करना है। इसमें उनके विचार, भावनाएँ, कार्य और विभिन्न उत्तेजनाओं के प्रति प्रतिक्रियाएँ शामिल हैं।
- उदाहरण: पोस्ट-ट्रॉमैटिक स्ट्रेस डिसऑर्डर (PTHD) वाले एक वयस्क के मामले का विश्लेषण करके उनके ट्रिगर्स, मुकाबला करने के तंत्र और समग्र मनोवैज्ञानिक कल्याण का पता लगाना।
5. व्यवहार विज्ञान में अनुप्रयोग (Applications in Behavioral Sciences):
- अद्वितीय या दुर्लभ घटनाओं का पता लगाने के लिए मनोविज्ञान, समाजशास्त्र, शिक्षा और संबंधित क्षेत्रों में केस स्टडीज का व्यापक रूप से उपयोग किया जाता है, जो सिद्धांत विकास और व्यावहारिक अनुप्रयोगों के लिए मूल्यवान अंतर्दृष्टि प्रदान करता है।
- उदाहरण: एक प्रतिभाशाली बच्चे की सीखने की ज़रूरतों को समझने और उनकी प्रतिभा को निखारने के लिए उचित शैक्षिक रणनीतियाँ विकसित करने के लिए उन पर एक केस अध्ययन आयोजित करना।
निष्कर्ष: केस अध्ययन उनके प्राकृतिक वातावरण में विशिष्ट व्यक्तियों पर ध्यान केंद्रित करके मानव व्यवहार और व्यक्तित्व को समझने में एक शक्तिशाली उपकरण के रूप में कार्य करता है। यह विधि शोधकर्ताओं को व्यवहार की जटिलताओं का पता लगाने की अनुमति देती है, व्यवहार विज्ञान के विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में अकादमिक अनुसंधान और व्यावहारिक हस्तक्षेप दोनों के लिए मूल्यवान ज्ञान प्रदान करती है।
Also Read: CTET COMPLETE NOTES IN HINDI FREE DOWNLOAD
शिक्षा में केस स्टडी क्या है?
(what is case study in education).
शिक्षा में केस स्टडी एक विशिष्ट शैक्षिक स्थिति, परिदृश्य या समस्या की विस्तृत और गहन जांच है। इसमें किसी शैक्षिक सेटिंग, जैसे स्कूल, कक्षा या शैक्षिक कार्यक्रम के भीतर वास्तविक जीवन की घटनाओं का व्यापक अनुसंधान और विश्लेषण शामिल है। शिक्षा में केस अध्ययन शिक्षण, सीखने और शैक्षिक प्रशासन में शामिल जटिलताओं की सूक्ष्म समझ प्रदान करते हैं।
शिक्षा में केस स्टडीज की मुख्य विशेषताएं
(key characteristics of case studies in education).
1. वास्तविक जीवन शैक्षिक संदर्भ (Real-Life Educational Context):
- शिक्षा में केस अध्ययन शैक्षिक वातावरण के भीतर वास्तविक जीवन की स्थितियों पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हैं। ये परिस्थितियाँ कक्षा की चुनौतियों से लेकर स्कूल-व्यापी नीतियों और हस्तक्षेपों तक हो सकती हैं।
- उदाहरण: एक विशिष्ट ग्रेड-स्तरीय कक्षा में एक नई शिक्षण पद्धति के कार्यान्वयन का विश्लेषण करना।
2. गहन जांच (In-Depth Investigation):
- केस अध्ययन में चुने गए शैक्षणिक मामले की गहन जांच शामिल होती है। शोधकर्ता गहरी अंतर्दृष्टि प्राप्त करने के लिए साक्षात्कार, अवलोकन, सर्वेक्षण और दस्तावेज़ विश्लेषण जैसे विभिन्न तरीकों के माध्यम से डेटा एकत्र करते हैं।
- उदाहरण: शिक्षकों, छात्रों और अभिभावकों के साथ साक्षात्कार आयोजित करना, कक्षा की गतिविधियों का अवलोकन करना और छात्र प्रदर्शन डेटा का विश्लेषण करना।
3. बहुआयामी परिप्रेक्ष्य (Multifaceted Perspective):
- केस अध्ययन कई दृष्टिकोणों पर विचार करता है, जिनमें शिक्षक, छात्र, प्रशासक और कभी-कभी माता-पिता या समुदाय के सदस्य शामिल होते हैं। यह समग्र दृष्टिकोण शैक्षिक मुद्दे का एक सर्वांगीण दृष्टिकोण प्रदान करता है।
- उदाहरण: समावेशी शिक्षा के लिए स्कूल के दृष्टिकोण का अध्ययन करते समय शिक्षकों, छात्रों और अभिभावकों के दृष्टिकोण की जांच करना।
4. समस्या-समाधान पर ध्यान (Problem-Solving Focus):
- शिक्षा में केस अध्ययन अक्सर समस्याओं, चुनौतियों या सुधार के क्षेत्रों की पहचान करने के लिए आयोजित किए जाते हैं। शोधकर्ता इन मुद्दों के समाधान के लिए संभावित समाधान और रणनीतियों का पता लगाते हैं।
- उदाहरण: कम छात्र सहभागिता स्तर की जांच करना और कक्षा में भागीदारी और सीखने में रुचि बढ़ाने के लिए रणनीतियों का प्रस्ताव करना।
5. समृद्ध गुणात्मक डेटा (Rich Qualitative Data):
- शैक्षिक मामले का विस्तृत विवरण प्रदान करने के लिए शोधकर्ता आख्यानों, उद्धरणों और टिप्पणियों सहित समृद्ध गुणात्मक डेटा इकट्ठा करते हैं। गुणात्मक निष्कर्षों का समर्थन करने के लिए मात्रात्मक डेटा को भी शामिल किया जा सकता है।
- उदाहरण: व्यापक केस स्टडी रिपोर्ट बनाने के लिए कक्षा अवलोकन नोट्स के साथ छात्र और शिक्षक प्रशंसापत्र का उपयोग करना।
6. शैक्षिक प्रथाओं को सूचित करना (Informing Educational Practices):
- केस स्टडीज के निष्कर्ष शैक्षिक प्रथाओं, नीतिगत निर्णयों और निर्देशात्मक तरीकों की जानकारी देते हैं। शिक्षक, प्रशासक और नीति निर्माता साक्ष्य-आधारित निर्णय लेने के लिए इन अंतर्दृष्टि का उपयोग कर सकते हैं।
- उदाहरण: शिक्षकों के लिए व्यावसायिक विकास कार्यशालाओं का मार्गदर्शन करने के लिए प्रभावी शिक्षण विधियों पर एक केस अध्ययन के परिणामों का उपयोग करना।
निष्कर्ष: शिक्षा में केस अध्ययन शैक्षिक प्रणाली के भीतर चुनौतियों और अवसरों की गहन समझ प्रदान करते हैं। विशिष्ट मामलों में गहराई से जाकर, शिक्षक और शोधकर्ता मूल्यवान अंतर्दृष्टि प्राप्त कर सकते हैं, शिक्षण और सीखने की प्रथाओं में निरंतर सुधार और नवाचार को बढ़ावा दे सकते हैं। ये अध्ययन जटिल शैक्षिक समस्याओं के साक्ष्य-आधारित समाधान प्रदान करके शिक्षा के भविष्य को आकार देने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं।
केस स्टडी में व्यक्ति के बारे में क्या जानकारी एकत्र की जानी चाहिए?
(what information should be collected about the person in the case study).
किसी मामले का अध्ययन करते समय, जांच के अधीन व्यक्ति के बारे में विशिष्ट जानकारी एकत्र करना गहन और व्यावहारिक विश्लेषण के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है। यह जानकारी व्यक्ति की पृष्ठभूमि, क्षमताओं, व्यवहार और व्यक्तिगत लक्षणों का समग्र दृष्टिकोण प्रदान करती है। इस संदर्भ में, एक व्यापक केस अध्ययन बनाने के लिए कई श्रेणियों के डेटा को एकत्र करने और उनका विश्लेषण करने की आवश्यकता है।
यहां उदाहरणों के साथ प्रत्येक श्रेणी का स्पष्टीकरण दिया गया है:
1. Identifying Data (परिचयात्मक विवरण): इस श्रेणी में व्यक्ति के बारे में बुनियादी जानकारी शामिल है, जैसे उनका नाम, उम्र, लिंग, पता, संपर्क विवरण और कोई अन्य प्रासंगिक व्यक्तिगत पहचान विवरण। ये विवरण यह समझने के लिए आधार प्रदान करते हैं कि व्यक्ति कौन है।
- नाम: जॉन स्मिथ
- लिंग: पुरुष
- पता: 123 मेन स्ट्रीट, एनीटाउन, यूएसए
- फ़ोन नंबर: (555) 123-4567
2. Birth Information (जन्म सम्बन्धी जानकारी): इस श्रेणी में व्यक्ति के जन्म से संबंधित विवरण शामिल हैं, जिसमें उनकी जन्मतिथि, जन्म स्थान और उनके जन्म के आसपास की कोई भी महत्वपूर्ण घटना या परिस्थितियाँ शामिल हैं।
- जन्मतिथि: 10 जून 1998
- जन्म स्थान: सिटी जनरल हॉस्पिटल, एनीटाउन, यूएसए
3. Health Record (स्वास्थ्य सम्बन्धी जानकारी): इस अनुभाग में व्यक्ति के शारीरिक और मानसिक स्वास्थ्य के बारे में जानकारी एकत्र करना शामिल है। इसमें चिकित्सा इतिहास, वर्तमान स्वास्थ्य स्थितियां, दवाएं, एलर्जी और कोई भी प्रासंगिक स्वास्थ्य मूल्यांकन या निदान शामिल हो सकता है।
- चिकित्सा इतिहास : बचपन से अस्थमा
- वर्तमान स्वास्थ्य स्थिति: अवसाद और चिंता का प्रबंधन
- एलर्जी: कोई नहीं
4. Family Data (परिवार सम्बन्धी जानकारी): यह श्रेणी व्यक्ति की पारिवारिक पृष्ठभूमि पर केंद्रित है, जिसमें माता-पिता, भाई-बहन और परिवार के अन्य करीबी सदस्यों के बारे में विवरण शामिल हैं। पारिवारिक गतिशीलता और रिश्तों पर जानकारी महत्वपूर्ण हो सकती है।
- माता-पिता: जेन स्मिथ (मां) और मार्क स्मिथ (पिता)
- भाई-बहन: सारा (बड़ी बहन) और डेविड (छोटा भाई)
5. Socio- Economic Status (सामाजिक-आर्थिक स्थिति): यहां, आप व्यक्ति की आर्थिक और सामाजिक स्थिति, उनके व्यवसाय, आय, शैक्षिक पृष्ठभूमि और किसी भी प्रासंगिक सामाजिक-आर्थिक कारकों सहित डेटा एकत्र करते हैं।
- व्यवसाय: पूर्णकालिक छात्र और अंशकालिक कैशियर
- आय: $20,000 प्रति वर्ष
- शैक्षिक पृष्ठभूमि: हाई स्कूल स्नातक
6. Level of Intelligence (बुद्धि का स्तर ): यह अनुभाग व्यक्ति की बौद्धिक क्षमताओं और संज्ञानात्मक कार्यप्रणाली का आकलन करता है। इसमें आईक्यू स्कोर, मानकीकृत परीक्षण परिणाम या बुद्धि के अन्य आकलन शामिल हो सकते हैं।
- आईक्यू स्कोर: 120 (औसत से ऊपर)
7. Educational Records (शिक्षात्मक जानकारी): व्यक्ति के शैक्षणिक इतिहास से संबंधित जानकारी इकट्ठा करें, जिसमें स्कूल में पढ़ाई, ग्रेड, शैक्षणिक उपलब्धियां और किसी भी प्रासंगिक शैक्षणिक मूल्यांकन शामिल हैं।
- हाई स्कूल: एनीटाउन हाई स्कूल
- पुरस्कार: वेलेडिक्टोरियन
8. Co- Curricular Activities (पाठ्य सहगामी क्रियाएँ): इस श्रेणी में क्लब, खेल, शौक या स्वयंसेवी कार्य जैसे पाठ्येतर या सह-पाठयक्रम गतिविधियों में व्यक्ति की भागीदारी के बारे में विवरण शामिल हैं।
- पाठ्येतर गतिविधियाँ: शतरंज क्लब, स्थानीय पशु आश्रय में स्वयंसेवक
9. Adjustment (समायोजन): इस बारे में जानकारी एकत्र करें कि व्यक्ति विभिन्न परिस्थितियों या वातावरणों में कैसे अनुकूलन और समायोजन करता है। इसमें उनके मुकाबला करने के तंत्र, तनाव कारक और परिवर्तन को संभालने के तरीके शामिल हो सकते हैं।
- समायोजन: परिवर्तन और नए वातावरण के साथ संघर्ष करता है, दिनचर्या को प्राथमिकता देता है
10. Behaviour in the classroom (कक्षा- कक्ष में व्यवहार): यह अनुभाग शैक्षणिक सेटिंग में व्यक्ति के व्यवहार और प्रदर्शन की जांच करता है, जिसमें उनकी भागीदारी, शिक्षकों और साथियों के साथ बातचीत और सीखने की शैली शामिल है।
- कक्षा व्यवहार: सक्रिय रूप से भाग लेता है, साथियों के साथ सहयोग करता है
11. Behaviour in the playground (खेल के मैदान में व्यवहार): गैर-शैक्षणिक सेटिंग्स में व्यक्ति के व्यवहार और बातचीत का पता लगाएं, जैसे कि अवकाश या खाली समय के दौरान। इससे उनके सामाजिक कौशल और रिश्तों के बारे में जानकारी मिल सकती है।
- खेल का मैदान व्यवहार : टीम खेल खेलना पसंद करता है, और उसके करीबी दोस्तों का एक छोटा समूह है
12. Personality Traits (व्यक्तित्व के गुण): व्यक्ति के व्यक्तित्व लक्षणों के बारे में जानकारी एकत्र करें, जिसमें उनका स्वभाव, ताकत, कमजोरियां और किसी भी व्यक्तित्व का आकलन शामिल है।
- व्यक्तित्व लक्षण: बहिर्मुखी, सहानुभूतिपूर्ण, विस्तार-उन्मुख
13. Educational and Vocational Plan (शैक्षिक तथा व्यावसायिक योजना): यह श्रेणी व्यक्ति के भविष्य के शैक्षिक और व्यावसायिक लक्ष्यों, आकांक्षाओं और कैरियर विकास या आगे की शिक्षा की योजनाओं की रूपरेखा तैयार करती है।
- शैक्षिक योजना (Educational Plan): मनोविज्ञान में स्नातक की डिग्री हासिल करें
- व्यावसायिक योजना (Vocational Plan): परामर्शदाता या चिकित्सक के रूप में कार्य करें
- उदाहरण: पर्यावरण विज्ञान में डिग्री हासिल करने और एक पर्यावरण संरक्षण संगठन के लिए काम करने की इच्छा रखता है।
14. Analysis (विश्लेषण):
- यह वह जगह है जहां आप सभी एकत्रित जानकारी का गहन विश्लेषण करते हैं, निष्कर्ष निकालते हैं और व्यक्ति के जीवन, व्यवहार और विशेषताओं में पैटर्न या रुझान की पहचान करते हैं।
- उदाहरण: विश्लेषण इंगित करता है कि व्यक्ति के मजबूत नेतृत्व कौशल और पर्यावरण संरक्षण के जुनून को परामर्श कार्यक्रमों और पारिस्थितिकी और स्थिरता से संबंधित पाठ्येतर गतिविधियों के माध्यम से पोषित किया जा सकता है।
कुल मिलाकर, जानकारी के इस व्यापक सेट को इकट्ठा करने से मामले के अध्ययन में व्यक्ति की पूरी समझ मिलती है, यदि आवश्यक हो तो सूचित निर्णय लेने और हस्तक्षेप की सुविधा मिलती है।
Also Read: DSSSB COMPLETE NOTES IN HINDI (FREE)
केस स्टडी के चरण
(steps of case study).
एक केस स्टडी में किसी विशेष समस्या या परिदृश्य को समझने, विश्लेषण करने और हल करने की एक व्यवस्थित प्रक्रिया शामिल होती है। ये चरण किसी केस अध्ययन को प्रभावी ढंग से संचालित करने के लिए एक संरचित ढांचे के रूप में काम करते हैं। प्रत्येक चरण मामले की जटिलताओं को सुलझाने और सूचित निष्कर्ष पर पहुंचने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है।
1. मामले को समझना (Understanding the Case):
- परिभाषा: मामले की पृष्ठभूमि, संदर्भ और मुख्य विवरण को अच्छी तरह से समझें। इसमें शामिल बारीकियों की गहरी समझ हासिल करने के लिए स्थिति में खुद को डुबो देना शामिल है।
- उदाहरण: छात्रों के प्रदर्शन में गिरावट की प्रवृत्ति से जुड़े मामले के अध्ययन के लिए, स्कूल की जनसांख्यिकी, शिक्षण विधियों और पाठ्यक्रम में हाल के बदलावों को समझना महत्वपूर्ण है।
2. समस्या का चयन (Selecting the Problem):
- परिभाषा: मामले के भीतर उस विशिष्ट समस्या या मुद्दे को पहचानें और परिभाषित करें जिसे संबोधित करने की आवश्यकता है। इस कदम में गहन विश्लेषण के लिए मामले के एक विशेष पहलू पर ध्यान केंद्रित करना शामिल है।
- उदाहरण: समस्या की पहचान पिछले दो वर्षों में हाई स्कूल में छात्रों के गणित दक्षता अंकों में गिरावट के रूप में की जा सकती है।
3. समस्या के कारणों का पता लगाना (Finding Out the Causes of the Problem):
- परिभाषा: पहचानी गई समस्या के मूल कारणों की जांच और विश्लेषण करें। इस चरण में समस्या में योगदान देने वाले विभिन्न कारकों की जांच करना शामिल है।
- उदाहरण: कारणों में अप्रभावी शिक्षण विधियां, संसाधनों की कमी, अपर्याप्त शिक्षक प्रशिक्षण, या छात्रों की सीखने की क्षमताओं को प्रभावित करने वाले सामाजिक-आर्थिक कारक शामिल हो सकते हैं।
4. संभावित समाधानों के बारे में सोचना (Thinking of Possible Solutions):
- परिभाषा: पहचाने गए कारणों के समाधान के लिए संभावित समाधानों या हस्तक्षेपों पर विचार-मंथन करें। रचनात्मक सोच को प्रोत्साहित करें और विभिन्न दृष्टिकोणों पर विचार करें।
- उदाहरण: संभावित समाधानों में इंटरैक्टिव शिक्षण तकनीकों को लागू करना, पाठ्यपुस्तकें और शैक्षिक सॉफ्टवेयर जैसे अतिरिक्त संसाधन प्रदान करना, शिक्षक प्रशिक्षण कार्यशालाओं का आयोजन करना या सामुदायिक सहभागिता कार्यक्रम शुरू करना शामिल हो सकता है।
5. सर्वोत्तम समाधान का चयन (Selecting the Best Solution):
- परिभाषा: मामले के संदर्भ के साथ व्यवहार्यता, प्रभावशीलता और संरेखण के आधार पर प्रस्तावित समाधानों का मूल्यांकन करें। वह समाधान चुनें जिससे समस्या का प्रभावी ढंग से समाधान होने की सबसे अधिक संभावना हो।
- उदाहरण: प्रस्तावित समाधानों का मूल्यांकन करने के बाद, नियमित शिक्षक प्रशिक्षण सत्रों के साथ इंटरैक्टिव शिक्षण तकनीकों को लागू करना छात्रों को संलग्न करने और शिक्षक प्रभावशीलता को बढ़ाने की क्षमता के कारण सर्वोत्तम समाधान के रूप में चुना गया है।
6. मूल्यांकन करना (To Evaluate):
- परिभाषा: चयनित समाधान को लागू करें और उसके प्रभाव की बारीकी से निगरानी करें। परिणामों का मूल्यांकन करें और मूल्यांकन करें कि क्या कार्यान्वित समाधान ने समस्या का प्रभावी ढंग से समाधान किया है।
- उदाहरण: इंटरैक्टिव शिक्षण विधियों और शिक्षक प्रशिक्षण कार्यशालाओं को लागू करने के बाद, नियमित रूप से मानकीकृत परीक्षणों और कक्षा अवलोकनों के माध्यम से छात्रों की प्रगति का आकलन करें। यदि गणित दक्षता स्कोर में महत्वपूर्ण सुधार होता है, तो समाधान को सफल माना जा सकता है।
निष्कर्ष: इन चरणों का व्यवस्थित रूप से पालन करने से केस अध्ययन के लिए एक व्यापक और रणनीतिक दृष्टिकोण सुनिश्चित होता है। मामले को समझकर, एक केंद्रित समस्या का चयन करके, उसके कारणों की पहचान करके, समाधानों पर विचार-मंथन करके, सर्वश्रेष्ठ का चयन करके और परिणामों का मूल्यांकन करके, शोधकर्ता और चिकित्सक वास्तविक दुनिया की समस्याओं को प्रभावी ढंग से संबोधित करने के लिए सूचित रणनीति विकसित कर सकते हैं। यह संरचित प्रक्रिया निर्णय लेने को बढ़ाती है, आलोचनात्मक सोच को प्रोत्साहित करती है और अध्ययन और अभ्यास के विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में साक्ष्य-आधारित समाधानों को बढ़ावा देती है।
केस स्टडी का उद्देश्य
(purpose of the case study).
व्यवहार विश्लेषण और परामर्श के संदर्भ में एक केस अध्ययन का उद्देश्य विशिष्ट व्यक्तियों या स्थितियों की विस्तृत जांच प्रदान करना है, जिसका उद्देश्य व्यवहार संबंधी समस्याओं का सटीक निदान करना और प्रभावी मार्गदर्शन और परामर्श प्रदान करना है। प्रत्येक मामले की अनूठी परिस्थितियों में गहराई से जाकर, पेशेवर लक्षित हस्तक्षेप विकसित कर सकते हैं, व्यक्तिगत मार्गदर्शन प्रदान कर सकते हैं और इसमें शामिल व्यक्तियों की समग्र भलाई को बढ़ा सकते हैं।
1. व्यवहार संबंधी समस्याओं का निदान और उपचार (Diagnosing and Treating Behavioral Problems):
- उद्देश्य: व्यवहार संबंधी मामले के अध्ययन का एक प्राथमिक उद्देश्य व्यक्तियों में अंतर्निहित व्यवहार संबंधी समस्याओं का निदान करना है। विस्तृत विश्लेषण के माध्यम से, पेशेवर समस्याग्रस्त व्यवहार के पैटर्न, ट्रिगर और संभावित कारणों की पहचान कर सकते हैं।
- उदाहरण: एक ऐसे बच्चे के मामले के अध्ययन पर विचार करें जो स्कूल में आक्रामक व्यवहार प्रदर्शित करता है। बच्चे की बातचीत, पारिवारिक गतिशीलता और स्कूल के माहौल का विश्लेषण करके, एक मनोवैज्ञानिक अंतर्निहित कारणों का निदान कर सकता है, जैसे कि बदमाशी के अनुभव या अनसुलझे भावनात्मक मुद्दे, और एक अनुरूप हस्तक्षेप योजना विकसित कर सकता है।
2. बेहतर मार्गदर्शन और परामर्श प्रदान करना (Providing Better Guidance and Counseling):
- उद्देश्य: केस अध्ययन व्यक्तिगत मार्गदर्शन और परामर्श प्रदान करने के लिए एक आधार के रूप में कार्य करता है। किसी व्यक्ति के सामने आने वाली अनोखी चुनौतियों को समझकर, परामर्शदाता व्यक्ति की आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप विशिष्ट सलाह, मुकाबला करने की रणनीतियाँ और समर्थन तंत्र प्रदान कर सकते हैं।
- उदाहरण: एक केस स्टडी की कल्पना करें जिसमें एक किशोर शैक्षणिक तनाव और आत्मसम्मान के मुद्दों से जूझ रहा हो। निष्कर्षों के आधार पर, एक परामर्शदाता किशोरों की चिंताओं को प्रभावी ढंग से संबोधित करने के लिए तनाव प्रबंधन तकनीकों, आत्मविश्वास निर्माण अभ्यास और शैक्षणिक सहायता सहित लक्षित मार्गदर्शन प्रदान कर सकता है।
निष्कर्ष: व्यवहार विश्लेषण और परामर्श में केस अध्ययन का उद्देश्य अंतर्निहित मुद्दों का निदान करना और अनुकूलित मार्गदर्शन और समर्थन प्रदान करना है। व्यक्तिगत मामलों पर ध्यान केंद्रित करके, पेशेवर व्यवहार संबंधी समस्याओं की सूक्ष्म समझ हासिल कर सकते हैं, जिससे वे सटीक हस्तक्षेप लागू करने में सक्षम हो सकते हैं जो शामिल व्यक्तियों के जीवन की समग्र गुणवत्ता को बढ़ाते हैं। ये अध्ययन प्रत्येक व्यक्ति की विशिष्ट आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप साक्ष्य-आधारित समाधान पेश करके मानसिक और भावनात्मक कल्याण को बढ़ावा देने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं।
Also Read: B.Ed COMPLETE Project File IN HINDI FREE DOWNLOAD
केस स्टडीज की विशेषताएं
(characteristics of case studies).
केस स्टडीज़ एक शोध पद्धति है जो उनकी गहराई और किसी विशेष व्यक्ति, इकाई या संस्थान के अध्ययन पर ध्यान केंद्रित करने की विशेषता है। जांच के तहत विषय की व्यापक समझ हासिल करने के प्राथमिक उद्देश्य के साथ शिक्षा, व्यवसाय, कानून और चिकित्सा जैसे विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में इनका व्यापक रूप से उपयोग किया जाता है। निम्नलिखित विशेषताएँ केस अध्ययन की प्रकृति को परिभाषित करने में मदद करती हैं:
1. किसी व्यक्ति या संस्था का गहन अध्ययन (In-Depth Study of a Person or Institution):
- विशेषताएँ: केस अध्ययन में किसी विशिष्ट व्यक्ति, संगठन या संस्था की विस्तृत और गहन जाँच शामिल होती है। यह व्यापक दृष्टिकोण शोधकर्ताओं को विषय के विभिन्न पहलुओं का पता लगाने की अनुमति देता है।
- उदाहरण: चिकित्सा के क्षेत्र में, एक केस स्टडी में एक दुर्लभ चिकित्सा स्थिति को समझने के लिए रोगी के चिकित्सा इतिहास, लक्षण, उपचार और परिणामों की गहन जांच शामिल हो सकती है।
2. अध्ययन के माध्यम से सूचना संग्रहण (Information Collection through Study):
- विशेषताएँ: विषय का गहनता से अध्ययन करके डेटा एकत्र किया जाता है। शोधकर्ता प्रासंगिक जानकारी इकट्ठा करने के लिए साक्षात्कार, अवलोकन, सर्वेक्षण और दस्तावेज़ विश्लेषण जैसे विभिन्न तरीकों का इस्तेमाल करते हैं।
- उदाहरण: व्यावसायिक संदर्भ में, एक केस अध्ययन में प्रमुख हितधारकों का साक्षात्कार लेना, वित्तीय रिकॉर्ड का विश्लेषण करना और कंपनी की सफलता या विफलता में योगदान देने वाले कारकों का आकलन करने के लिए व्यावसायिक संचालन का अवलोकन करना शामिल हो सकता है।
3. अनेक क्षेत्रों में प्रयोज्यता (Applicability Across Multiple Fields):
- विशेषताएँ: केस अध्ययन बहुमुखी हैं और शिक्षा, व्यवसाय, कानून, चिकित्सा और अन्य सहित विभिन्न विषयों में आयोजित किए जा सकते हैं। यह विधि विभिन्न शोध प्रश्नों और उद्देश्यों के अनुकूल है।
- उदाहरण: शिक्षा के क्षेत्र में, एक केस स्टडी का उपयोग एक नई शिक्षण पद्धति की प्रभावशीलता का पता लगाने के लिए किया जा सकता है, जबकि कानून में, इसे एक हाई-प्रोफाइल अदालती मामले में उपयोग की जाने वाली कानूनी रणनीतियों का विश्लेषण करने के लिए नियोजित किया जा सकता है।
4. व्यक्ति या इकाई पर ध्यान दें (Focus on the Individual or Entity):
- विशेषताएँ: केस अध्ययन एक केंद्रीय विषय के इर्द-गिर्द घूमते हैं, चाहे वह कोई व्यक्ति, संस्था या विशिष्ट मुद्दा हो। संपूर्ण शोध प्रक्रिया के दौरान यह विषय अध्ययन के केंद्र में रहता है।
- उदाहरण: शैक्षिक अनुसंधान के संदर्भ में, यदि कोई छात्र एक ही कक्षा में लगातार असफल होता है, तो व्यक्तिगत छात्र केस स्टडी का केंद्र बिंदु बन जाता है।
5. विस्तृत जांच और डेटा विश्लेषण (Detailed Investigation and Data Analysis):
- विशेषताएँ: केस अध्ययन में सावधानीपूर्वक जांच और डेटा संग्रह शामिल होता है। शोधकर्ता विषय वस्तु में गहराई से उतरते हैं, डेटा का सावधानीपूर्वक विश्लेषण करते हैं, और अंतर्निहित कारणों और कारकों को उजागर करने का प्रयास करते हैं।
- उदाहरण: संघर्षरत छात्र के मामले में, शोधकर्ता छात्र, शिक्षकों और अभिभावकों के साथ साक्षात्कार आयोजित कर सकते हैं, पिछले शैक्षणिक रिकॉर्ड का विश्लेषण कर सकते हैं और आवर्ती विफलताओं के कारणों का पता लगाने के लिए कक्षा की बातचीत का निरीक्षण कर सकते हैं।
निष्कर्ष: केस अध्ययन की विशेषताएं, जिसमें उनकी गहन प्रकृति, सूचना एकत्र करने का दृष्टिकोण, अंतर-विषयक प्रयोज्यता, विषय-केंद्रित पद्धति और कठोर जांच शामिल है, उन्हें विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में एक मूल्यवान अनुसंधान उपकरण बनाती है। केस अध्ययन जटिल वास्तविक दुनिया के परिदृश्यों में अंतर्दृष्टि प्रदान करते हैं और विशिष्ट मुद्दों की गहरी समझ प्रदान करते हैं, अंततः साक्ष्य-आधारित निर्णय लेने और समस्या-समाधान में योगदान करते हैं।
बाल व्यवहार के अध्ययन में केस स्टडी के लाभ
(advantages of case study in studying child behavior).
केस अध्ययन एक मूल्यवान शोध पद्धति है, खासकर जब बच्चों जैसे जटिल व्यवहारों का अध्ययन किया जाता है। यह दृष्टिकोण बच्चे के प्राकृतिक वातावरण के भीतर उसके व्यवहार की गहराई से खोज करने की अनुमति देता है, जिससे उनके कार्यों, प्रतिक्रियाओं और बातचीत की व्यापक समझ बनती है।
1. बाल व्यवहार का विस्तृत अध्ययन (Detailed Study of Child Behavior):
- लाभ: केस अध्ययन शोधकर्ताओं को उनके विशिष्ट वातावरण में बच्चे के व्यवहार के हर पहलू का अध्ययन करने में सक्षम बनाता है, और उन बारीकियों को पकड़ता है जो व्यापक अनुसंधान विधियों में छूट सकती हैं।
- उदाहरण: स्कूल और घर पर साथियों, शिक्षकों और परिवार के सदस्यों के साथ एक बच्चे की बातचीत का अवलोकन और दस्तावेजीकरण करना, उनके सामाजिक व्यवहार का एक व्यापक दृष्टिकोण प्रदान करना।
2. बाल व्यवहार और उसके कारणों को समझना (Understanding Child Behavior and Its Reasons):
- लाभ: केस अध्ययन से शोधकर्ताओं को बच्चे के व्यवहार के पीछे के कारणों का पता लगाने में मदद मिलती है। यह गहरी समझ ट्रिगर्स, प्रेरणाओं और अंतर्निहित कारणों की पहचान करने में मदद करती है, जिससे अधिक सूचित हस्तक्षेप होता है।
- उदाहरण: ऐसे मामले का पता लगाना जहां एक बच्चा आक्रामक व्यवहार प्रदर्शित करता है; विस्तृत विश्लेषण से पता चल सकता है कि यह व्यवहार पिछले आघात या अनसुलझे भावनात्मक मुद्दों से उत्पन्न होता है।
3. समस्याग्रस्त और कुसमायोजित बच्चों का अध्ययन (Studying Problematic and Maladjusted Children):
- लाभ: समस्याग्रस्त या कुसमायोजित बच्चों से निपटने के दौरान केस अध्ययन विशेष रूप से उपयोगी होते हैं। व्यक्तिगत मामलों पर ध्यान केंद्रित करके, पेशेवर बच्चे की विशिष्ट आवश्यकताओं को संबोधित करते हुए, अनुरूप सहायता और समर्थन प्रदान कर सकते हैं।
- उदाहरण: स्कूल से इनकार करने वाले व्यवहार वाले बच्चे का अध्ययन करना; एक केस अध्ययन के माध्यम से, शिक्षक और मनोवैज्ञानिक सामाजिक चिंता या बदमाशी जैसे मूल कारणों की पहचान कर सकते हैं, और बच्चे को स्कूल के माहौल में समायोजित करने में मदद करने के लिए रणनीतियों को लागू कर सकते हैं।
4. सावधानीपूर्वक तैयारी के कारण विश्वसनीयता (Reliability Due to Careful Preparation):
- लाभ: केस अध्ययन में सावधानीपूर्वक तैयारी शामिल होती है, जिससे यह सुनिश्चित होता है कि डेटा संग्रह और विश्लेषण सटीक और विश्वसनीय हैं। यह सावधानीपूर्वक दृष्टिकोण अध्ययन के परिणामों की विश्वसनीयता को बढ़ाता है।
- उदाहरण: शिक्षकों, अभिभावकों और बच्चे के साथ साक्षात्कार आयोजित करने के साथ-साथ कक्षा के व्यवहार का अवलोकन करना और शैक्षणिक रिकॉर्ड का विश्लेषण करना, एक व्यापक और विश्वसनीय केस अध्ययन परिणाम सुनिश्चित करता है।
निष्कर्ष: बच्चे के व्यवहार का अध्ययन करने में केस स्टडी के फायदे महत्वपूर्ण हैं, जो बच्चे के कार्यों और प्रेरणाओं की गहरी समझ प्रदान करते हैं। व्यक्तिगत मामलों पर ध्यान केंद्रित करके, शोधकर्ता और चिकित्सक लक्षित सहायता प्रदान कर सकते हैं, जिससे व्यवहार संबंधी चुनौतियों का सामना करने वाले बच्चों के लिए अधिक प्रभावी हस्तक्षेप और बेहतर परिणाम प्राप्त हो सकते हैं। मामले के अध्ययन में शामिल सावधानीपूर्वक तैयारी और विस्तृत विश्लेषण उनकी विश्वसनीयता में योगदान देता है और उन्हें बाल व्यवहार को समझने और संबोधित करने में अमूल्य उपकरण बनाता है।
Also Read: Complete UPSC PPT Study Material
Table: Perspectives on Individual Study: Definition by Prominent Social Scientists
(व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन पर परिप्रेक्ष्य: प्रमुख सामाजिक वैज्ञानिकों द्वारा परिभाषा).
| Definition | Author | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| “A detailed study of a social unit – whether that unit is an individual, a group, a social institution, a district or a community, a detailed study is called individual study.” | P.V. Young | पी.वी. यंग व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन को किसी भी सामाजिक इकाई की विस्तृत परीक्षा के रूप में परिभाषित करता है, चाहे वह व्यक्ति, समूह, संस्था या समुदाय हो। यह परिभाषा अध्ययन की व्यापक प्रकृति पर प्रकाश डालती है, विभिन्न सामाजिक इकाइयों को समझने में शामिल विश्लेषण की गहराई पर जोर देती है। |
| “The personal study method is a form of qualitative analysis under which a very careful and complete observation of a person, situation or organization is made.” | B. Seng and B. Seng | बी. सेंग और बी. सेंग व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन को एक गुणात्मक विश्लेषणात्मक दृष्टिकोण के रूप में वर्णित करते हैं, जो व्यक्तियों, स्थितियों या संगठनों के सावधानीपूर्वक और गहन अवलोकन पर ध्यान केंद्रित करता है। यह परिभाषा सामाजिक घटनाओं को समझने में इसके गुणात्मक पहलुओं पर प्रकाश डालते हुए, अवलोकन प्रक्रिया की सावधानीपूर्वक और व्यापक प्रकृति पर जोर देती है। |
| “Individual study is a method by which every individual factor, whether it is an organization or a total event in the life of an individual or group, is analyzed in the context of some other unit of that group.” | Howard Odom and Katherine Zocher | हॉवर्ड ओडोम और कैथरीन ज़ोचर व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन को एक विश्लेषणात्मक पद्धति के रूप में परिभाषित करते हैं जहां किसी संगठन के भीतर या किसी व्यक्ति या समूह के जीवन के व्यक्तिगत कारकों की उस समूह के भीतर अन्य इकाइयों से संबंधित जांच की जाती है। यह परिभाषा व्यापक सामाजिक संदर्भ में व्यक्तिगत तत्वों के प्रासंगिक विश्लेषण को रेखांकित करती है, जो समग्र परिप्रेक्ष्य प्रदान करती है। |
| “Personal study method can be defined as a small, complete and in-depth study, under which the researcher uses all his abilities and methods to systematically collect sufficient information about a person so that it can ‘To know how a man and a woman function as a unit of society.’” | Sin Pao Yeung | सिन पाओ युंग व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन को एक केंद्रित, विस्तृत और व्यापक शोध दृष्टिकोण के रूप में चित्रित करते हैं। इसमें किसी व्यक्ति के बारे में व्यवस्थित रूप से पर्याप्त जानकारी इकट्ठा करने के लिए विभिन्न शोध कौशल का उपयोग करना शामिल है, जिससे समाज के भीतर उनकी भूमिका को समझने में मदद मिलती है। यह परिभाषा अध्ययन की गहन प्रकृति पर प्रकाश डालती है, जिसका उद्देश्य व्यक्तियों की सामाजिक कार्यप्रणाली को समझना है। |
स्पष्टीकरण:
- तालिका विभिन्न सामाजिक वैज्ञानिकों द्वारा प्रदान की गई व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन की विविध परिभाषाएँ प्रस्तुत करती है। प्रत्येक परिभाषा सामाजिक अनुसंधान में व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन की गहराई, दायरे और उद्देश्य पर एक अद्वितीय परिप्रेक्ष्य प्रदान करती है।
- पी.वी. यंग व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन की व्यापक प्रकृति पर जोर देते हैं, विभिन्न सामाजिक इकाइयों पर इसकी प्रयोज्यता को रेखांकित करते हैं।
- बी. सेंग और बी. सेंग गुणात्मक पहलुओं पर ध्यान केंद्रित करते हैं, इस पद्धति के अभिन्न अंग सावधानीपूर्वक अवलोकन पर प्रकाश डालते हैं।
- हॉवर्ड ओडोम और कैथरीन ज़ोचर प्रासंगिक विश्लेषण पर जोर देते हैं, एक व्यापक सामाजिक ढांचे के भीतर व्यक्तिगत तत्वों की जांच पर जोर देते हैं।
- सिन पाओ युंग व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन की गहन, व्यवस्थित प्रकृति पर जोर देते हैं, जिसका लक्ष्य समाज के भीतर व्यक्तियों की भूमिकाओं को समझना है।
- ये विविध परिभाषाएँ सामूहिक रूप से सामाजिक अनुसंधान में व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन पद्धति की समग्र समझ में योगदान करती हैं।
Table: Pros and Cons of the Case Study Method
(केस स्टडी पद्धति के फायदे और नुकसान).
यहां केस स्टडी पद्धति के गुण और दोषों का सारांश देने वाली एक तालिका है:
| Merits of Case Study Method | Demerits of Case Study Method |
|---|---|
| किसी सामाजिक इकाई की विस्तृत जांच की अनुमति देता है। | सिद्धांत विकास के लिए अपर्याप्त एवं अवैज्ञानिक माना जाता है। |
| चयनित इकाई के अतीत, वर्तमान और भविष्य को समझने में सक्षम बनाता है। | शोधकर्ता की व्यक्तिपरकता के कारण निष्कर्ष पक्षपातपूर्ण हो सकते हैं। |
| भविष्य के अनुसंधान के लिए व्यवस्थित परिकल्पनाओं के निर्माण की सुविधा प्रदान करता है। | प्राप्त तथ्यों की विश्वसनीयता को हमेशा सत्यापित नहीं किया जा सकता है। |
| प्रश्नावली या साक्षात्कार जैसे अनुसंधान उपकरणों को बढ़ाने के अवसर प्रदान करता है। | अन्य तरीकों की तुलना में अधिक समय और संसाधनों की आवश्यकता होती है। |
| विभिन्न इकाइयों के लिए सर्वोत्तम नमूनाकरण विधियों को निर्धारित करने में सहायता करता है। | निष्कर्ष कम संख्या में मामलों पर आधारित होते हैं, जो सामान्यीकरण को सीमित करते हैं। |
| विरोधाभासी या अप्रासंगिक प्रतीत होने वाली इकाइयों से महत्वपूर्ण तथ्य प्रकट करता है। | इकाइयों को अक्सर व्यवस्थित तरीकों के बजाय जानबूझकर चुना जाता है। |
| विषय में शोधकर्ता की रुचि और ज्ञान को बढ़ाता है, विश्लेषण को बढ़ाता है। | संभावित रूप से त्रुटिपूर्ण सरकारी और गैर-सरकारी जानकारी पर निर्भर करता है। |
| दृष्टिकोण और सामाजिक मूल्यों जैसे गुणात्मक पहलुओं का अध्ययन करने के लिए आदर्श। |
विशिष्ट मामलों में विस्तृत अंतर्दृष्टि प्रदान करने में केस अध्ययन पद्धति की अपनी ताकत है, लेकिन इसमें सीमाएं भी हैं, विशेष रूप से सामान्यीकरण, पूर्वाग्रह और बाहरी डेटा पर निर्भरता के संदर्भ में। शोधकर्ता अक्सर इसकी सीमाओं को संतुलित करने के लिए अन्य शोध विधियों के साथ इसका उपयोग करते हैं।
- सामाजिक शोध में केस स्टडी पद्धति विद्वानों के बीच व्यापक बहस का विषय रही है। कुछ आलोचकों का तर्क है कि व्यक्तिगत डेटा, विशेष रूप से जीवन इतिहास, का मात्रात्मक विश्लेषण नहीं किया जा सकता है, जिससे सांख्यिकीय प्रक्रियाओं के बिना यह विधि अव्यावहारिक और अवैज्ञानिक लगती है। हालाँकि, विधि के समर्थकों का तर्क है कि यदि किसी विशिष्ट समूह के प्रतिनिधियों के रूप में चुने गए व्यक्ति ठोस जीवन अनुभव प्रदान कर सकते हैं, तो उनका डेटा उसी समूह के अन्य लोगों पर लागू किया जा सकता है। सांख्यिकीय परीक्षणों की अनुपस्थिति में, केस स्टडी पद्धति को गहन गुणात्मक विश्लेषण के लिए एक मूल्यवान उपकरण बनाने के लिए शोधकर्ताओं को अपने अच्छी तरह से प्रशिक्षित अनुभव, अंतर्दृष्टि और निर्णय पर भरोसा करना चाहिए। अपनी चुनौतियों के बावजूद, यह विधि सामाजिक अनुसंधान में जटिल मानवीय अनुभवों और व्यवहारों को समझने के लिए एक मूल्यवान दृष्टिकोण बनी हुई है।
Also Read: Psychology in English FREE PDF DOWNLOAD
शांति की जीत: ग्रामीण भारत में लचीलेपन और शिक्षा का एक केस स्टडी
(shanti’s triumph: a case study of resilience and education in rural india).
ग्रामीण भारत की हरी-भरी हरियाली के बीच बसे एक सुदूर गाँव में, शैक्षिक परिवर्तन की एक उल्लेखनीय कहानी मौजूद है। सुंदरपुर नाम के इस गांव को गरीबी, गुणवत्तापूर्ण शिक्षा तक सीमित पहुंच और लैंगिक असमानता सहित कई चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ा। हालाँकि, युवा लड़कियों को सशक्त बनाने, सामाजिक मानदंडों को तोड़ने और सीखने की संस्कृति को बढ़ावा देने के उद्देश्य से एक अभिनव शैक्षिक पहल के कारण समुदाय बदलाव के कगार पर था।
केस स्टडी उद्देश्य:
- सुंदरपुर में शैक्षिक सशक्तिकरण कार्यक्रम के परिवर्तनकारी प्रभाव का पता लगाने के लिए, एक वंचित पृष्ठभूमि की युवा लड़की शांति के जीवन और शैक्षणिक सफलता और सशक्तिकरण की दिशा में उसकी यात्रा पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया जाएगा।
- केस स्टडी सुंदरपुर की एक दृढ़निश्चयी और उज्ज्वल युवा लड़की शांति के इर्द-गिर्द घूमती है, जिसने अपने समुदाय को बांधने वाली निरक्षरता की जंजीरों से मुक्त होने का सपना देखा था। स्थानीय गैर सरकारी संगठनों और उत्साही शिक्षकों द्वारा समर्थित एक शैक्षिक सशक्तिकरण कार्यक्रम के कार्यान्वयन के साथ, सुंदरपुर की युवा लड़कियों को गुणवत्तापूर्ण शिक्षा, परामर्श और व्यावसायिक प्रशिक्षण के अवसर प्रदान किए गए।
अनुसंधान प्रश्न:
- शैक्षिक सशक्तिकरण कार्यक्रम ने शांति के शैक्षणिक प्रदर्शन, आत्मविश्वास और आकांक्षाओं को कैसे प्रभावित किया?
- शांति की शैक्षिक यात्रा में मार्गदर्शन और सामुदायिक समर्थन ने क्या भूमिका निभाई?
- कार्यक्रम ने गांव के भीतर सामाजिक मानदंडों और लैंगिक असमानताओं को कैसे संबोधित किया?
- शांति को किन चुनौतियों का सामना करना पड़ा और सहायता कार्यक्रमों ने इन बाधाओं पर काबू पाने में उसकी कैसे सहायता की?
- गहन साक्षात्कार: शांति, उसके माता-पिता, शिक्षकों और कार्यक्रम समन्वयकों के साथ उसके अनुभवों और कार्यक्रम के प्रभाव के बारे में जानकारी प्राप्त करने के लिए साक्षात्कार आयोजित करें।
- फ़ील्ड अवलोकन: कार्यक्रम के कार्यान्वयन और उसके प्रभावों को समझने के लिए कक्षाओं, परामर्श सत्रों और सामुदायिक बातचीत का निरीक्षण करने के लिए सुंदरपुर का दौरा करें।
- दस्तावेज़ विश्लेषण: शांति की प्रगति और परिवर्तन को मापने के लिए उसके अकादमिक रिकॉर्ड, उपस्थिति रिपोर्ट और प्रशंसापत्र की समीक्षा करें।
- फोकस समूह चर्चाएँ: गाँव पर कार्यक्रम के व्यापक प्रभाव का आकलन करने के लिए अन्य लड़कियों और समुदाय के सदस्यों के साथ चर्चाएँ आयोजित करें।
- एक उत्साही युवा लड़की शांति को सुंदरपुर में ग्रामीण जीवन की कठोर वास्तविकताओं का सामना करना पड़ा। शैक्षिक सशक्तिकरण कार्यक्रम की शुरुआत के साथ, उन्हें चुनौतियों के बीच आशा की एक किरण दिखी। समर्पित शिक्षकों और गुरुओं के समर्थन से, शांति अकादमिक रूप से आगे बढ़ी। इंटरैक्टिव शिक्षण विधियों और पाठ्येतर गतिविधियों के माध्यम से, उन्होंने विज्ञान के प्रति अपने जुनून को खोजा और डॉक्टर बनने का सपना देखा, एक ऐसा पेशा जो कभी उनके गांव में लड़कियों के लिए अप्राप्य माना जाता था।
- अपने परिवार द्वारा गले लगाए जाने और अपने गुरुओं द्वारा प्रोत्साहित किए जाने पर, शांति सामाजिक दबावों के बावजूद डटी रही। केस स्टडी पद्धति ने शोधकर्ताओं को उसकी यात्रा की परतों को खोलने की अनुमति दी, जिससे न केवल उसकी शैक्षणिक उपलब्धियों बल्कि उसके बढ़ते आत्मविश्वास और दृढ़ संकल्प पर भी प्रकाश पड़ा।
निष्कर्ष: शांति की कहानी शिक्षा और सामुदायिक समर्थन की परिवर्तनकारी शक्ति का एक प्रमाण है। केस स्टडी पद्धति के माध्यम से, शोधकर्ताओं ने प्रतिकूलता से सशक्तिकरण तक का मार्ग उजागर किया, यह दिखाते हुए कि कैसे समर्पित प्रयास और अनुरूप शैक्षिक पहल लैंगिक बाधाओं को तोड़ सकते हैं, समुदायों का उत्थान कर सकते हैं और ग्रामीण भारत के दिल में आने वाली पीढ़ियों को प्रेरित कर सकते हैं।
- केस स्टडी पद्धति सामाजिक अनुसंधान के क्षेत्र में एक प्रकाशस्तंभ के रूप में खड़ी है, जो मानवीय अनुभवों की गहराई और विविधता को उजागर करती है। सिद्धांत और वास्तविक जीवन के अनुप्रयोग के बीच अंतर को पाटने की इसकी क्षमता इसे गहन अंतर्दृष्टि चाहने वाले शोधकर्ताओं के लिए एक अनिवार्य उपकरण बनाती है। जैसे-जैसे हम मानव व्यवहार की जटिलताओं से निपटते हैं, केस स्टडी पद्धति एक मार्गदर्शक बनी रहती है, जो एक समय में एक कहानी के साथ हमारी सामाजिक दुनिया की जटिल टेपेस्ट्री को उजागर करती है।
- ICT Techniques For Evaluation In Social Science in Hindi
- What Is Continuous And Comprehensive Evaluation In Hindi?
- What Is Achievement Test In Hindi? PDF
- Diagnostic Testing And Remedial Measures In Hindi (PDF)
Download or Copy link
- Print or Download (PDF)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved September 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions

- Social Science
- Lesson Plan
केस स्टडी का प्रारूप
| Sr. No. | Headings | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | पाठ योजना प्रकार (Lesson Plan Type) | Case Study |
| 2 | विषय (Subject) | केस स्टडी (Case Study) |
| 3 | उपविषय (Sub-Subject) | - |
| 4 | प्रकरण (Topic) | Case Study ka Prarup |
| 5 | कक्षा (Class) | - |
| 6 | समयावधि (Time Duration) | - |
| 7 | उपयोगी (Useful for) | B.ed, Deled, BSTC, BTC, Nios Deled |
- आदर्श दैनिक पाठ योजना प्रारूप
- व्याकरण की पाठ योजना का प्रारूप
- Structure of Lesson Plan in Hindi
- Teaching Learning Material Chart Model
- How to Make a Good Final Lesson Plan
- क्रियात्मक अनुसंधान का प्रारूप
Case Study Ka Prarup
Case study format in hindi, case study prarup pdf file, case study prarup page_1.

Case Study Prarup Page_2

Download PDF
You may like these posts
Search lesson plans, random posts, follow us on.
- Application
- D. El. Ed. Old Paper
- English Lesson Plan
- Hindi Lesson Plan
- Kala Shiksha Lesson Plan
- Maths Lesson Plan
- Sanskrit Lesson Plan
- Science Lesson plan
- Swasthya Avam Sharirik Shiksha
Popular Posts

बीएड डी एल एड प्रथम एवं द्वितीय वर्ष मूल्यांकन प्रपत्र

राष्ट्रपति - नागरिक शास्त्र पाठ योजना बी एड

Social Science Class 8 Lesson Plan

ग्राम पंचायत | नागरिक शास्त्र लेसन प्लान

Lesson Plan of Civics in Hindi | नागरिक शास्त्र लेसन प्लान
Menu footer widget.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction
The case study creation process
Types of case studies, benefits and limitations.

- Where was science invented?
- When did science begin?

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Academia - Case Study
- Verywell Mind - What is a Case Study?
- Simply Psychology - Case Study Research Method in Psychology
- CORE - Case study as a research method
- National Center for Biotechnology Information - PubMed Central - The case study approach
- BMC Journals - Evidence-Based Nursing - What is a case study?
- Table Of Contents
case study , detailed description and assessment of a specific situation in the real world created for the purpose of deriving generalizations and other insights from it. A case study can be about an individual, a group of people, an organization, or an event, among other subjects.
By focusing on a specific subject in its natural setting, a case study can help improve understanding of the broader features and processes at work. Case studies are a research method used in multiple fields, including business, criminology , education , medicine and other forms of health care, anthropology , political science , psychology , and social work . Data in case studies can be both qualitative and quantitative. Unlike experiments, where researchers control and manipulate situations, case studies are considered to be “naturalistic” because subjects are studied in their natural context . ( See also natural experiment .)
The creation of a case study typically involves the following steps:
- The research question to be studied is defined, informed by existing literature and previous research. Researchers should clearly define the scope of the case, and they should compile a list of evidence to be collected as well as identify the nature of insights that they expect to gain from the case study.
- Once the case is identified, the research team is given access to the individual, organization, or situation being studied. Individuals are informed of risks associated with participation and must provide their consent , which may involve signing confidentiality or anonymity agreements.
- Researchers then collect evidence using multiple methods, which may include qualitative techniques, such as interviews, focus groups , and direct observations, as well as quantitative methods, such as surveys, questionnaires, and data audits. The collection procedures need to be well defined to ensure the relevance and accuracy of the evidence.
- The collected evidence is analyzed to come up with insights. Each data source must be reviewed carefully by itself and in the larger context of the case study so as to ensure continued relevance. At the same time, care must be taken not to force the analysis to fit (potentially preconceived) conclusions. While the eventual case study may serve as the basis for generalizations, these generalizations must be made cautiously to ensure that specific nuances are not lost in the averages.
- Finally, the case study is packaged for larger groups and publication. At this stage some information may be withheld, as in business case studies, to allow readers to draw their own conclusions. In scientific fields, the completed case study needs to be a coherent whole, with all findings and statistical relationships clearly documented.

Case studies have been used as a research method across multiple fields. They are particularly popular in the fields of law, business, and employee training; they typically focus on a problem that an individual or organization is facing. The situation is presented in considerable detail, often with supporting data, to discussion participants, who are asked to make recommendations that will solve the stated problem. The business case study as a method of instruction was made popular in the 1920s by instructors at Harvard Business School who adapted an approach used at Harvard Law School in which real-world cases were used in classroom discussions. Other business and law schools started compiling case studies as teaching aids for students. In a business school case study, students are not provided with the complete list of facts pertaining to the topic and are thus forced to discuss and compare their perspectives with those of their peers to recommend solutions.
In criminology , case studies typically focus on the lives of an individual or a group of individuals. These studies can provide particularly valuable insight into the personalities and motives of individual criminals, but they may suffer from a lack of objectivity on the part of the researchers (typically because of the researchers’ biases when working with people with a criminal history), and their findings may be difficult to generalize.
In sociology , the case-study method was developed by Frédéric Le Play in France during the 19th century. This approach involves a field worker staying with a family for a period of time, gathering data on the family members’ attitudes and interactions and on their income, expenditures, and physical possessions. Similar approaches have been used in anthropology . Such studies can sometimes continue for many years.

Case studies provide insight into situations that involve a specific entity or set of circumstances. They can be beneficial in helping to explain the causal relationships between quantitative indicators in a field of study, such as what drives a company’s market share. By introducing real-world examples, they also plunge the reader into an actual, concrete situation and make the concepts real rather than theoretical. They also help people study rare situations that they might not otherwise experience.
Because case studies are in a “naturalistic” environment , they are limited in terms of research design: researchers lack control over what they are studying, which means that the results often cannot be reproduced. Also, care must be taken to stay within the bounds of the research question on which the case study is focusing. Other limitations to case studies revolve around the data collected. It may be difficult, for instance, for researchers to organize the large volume of data that can emerge from the study, and their analysis of the data must be carefully thought through to produce scientifically valid insights. The research methodology used to generate these insights is as important as the insights themselves, for the latter need to be seen in the proper context. Taken out of context, they may lead to erroneous conclusions. Like all scientific studies, case studies need to be approached objectively; personal bias or opinion may skew the research methods as well as the results. ( See also confirmation bias .)
Business case studies in particular have been criticized for approaching a problem or situation from a narrow perspective. Students are expected to come up with solutions for a problem based on the data provided. However, in real life, the situation is typically reversed: business managers face a problem and must then look for data to help them solve it.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer

You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Applied Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Correlational Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types...
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
5 Benefits of Learning Through the Case Study Method

- 28 Nov 2023
While several factors make HBS Online unique —including a global Community and real-world outcomes —active learning through the case study method rises to the top.
In a 2023 City Square Associates survey, 74 percent of HBS Online learners who also took a course from another provider said HBS Online’s case method and real-world examples were better by comparison.
Here’s a primer on the case method, five benefits you could gain, and how to experience it for yourself.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is the Harvard Business School Case Study Method?
The case study method , or case method , is a learning technique in which you’re presented with a real-world business challenge and asked how you’d solve it. After working through it yourself and with peers, you’re told how the scenario played out.
HBS pioneered the case method in 1922. Shortly before, in 1921, the first case was written.
“How do you go into an ambiguous situation and get to the bottom of it?” says HBS Professor Jan Rivkin, former senior associate dean and chair of HBS's master of business administration (MBA) program, in a video about the case method . “That skill—the skill of figuring out a course of inquiry to choose a course of action—that skill is as relevant today as it was in 1921.”
Originally developed for the in-person MBA classroom, HBS Online adapted the case method into an engaging, interactive online learning experience in 2014.
In HBS Online courses , you learn about each case from the business professional who experienced it. After reviewing their videos, you’re prompted to take their perspective and explain how you’d handle their situation.
You then get to read peers’ responses, “star” them, and comment to further the discussion. Afterward, you learn how the professional handled it and their key takeaways.
Learn more about HBS Online's approach to the case method in the video below, and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more.
HBS Online’s adaptation of the case method incorporates the famed HBS “cold call,” in which you’re called on at random to make a decision without time to prepare.
“Learning came to life!” said Sheneka Balogun , chief administration officer and chief of staff at LeMoyne-Owen College, of her experience taking the Credential of Readiness (CORe) program . “The videos from the professors, the interactive cold calls where you were randomly selected to participate, and the case studies that enhanced and often captured the essence of objectives and learning goals were all embedded in each module. This made learning fun, engaging, and student-friendly.”
If you’re considering taking a course that leverages the case study method, here are five benefits you could experience.
5 Benefits of Learning Through Case Studies
1. take new perspectives.
The case method prompts you to consider a scenario from another person’s perspective. To work through the situation and come up with a solution, you must consider their circumstances, limitations, risk tolerance, stakeholders, resources, and potential consequences to assess how to respond.
Taking on new perspectives not only can help you navigate your own challenges but also others’. Putting yourself in someone else’s situation to understand their motivations and needs can go a long way when collaborating with stakeholders.
2. Hone Your Decision-Making Skills
Another skill you can build is the ability to make decisions effectively . The case study method forces you to use limited information to decide how to handle a problem—just like in the real world.
Throughout your career, you’ll need to make difficult decisions with incomplete or imperfect information—and sometimes, you won’t feel qualified to do so. Learning through the case method allows you to practice this skill in a low-stakes environment. When facing a real challenge, you’ll be better prepared to think quickly, collaborate with others, and present and defend your solution.
3. Become More Open-Minded
As you collaborate with peers on responses, it becomes clear that not everyone solves problems the same way. Exposing yourself to various approaches and perspectives can help you become a more open-minded professional.
When you’re part of a diverse group of learners from around the world, your experiences, cultures, and backgrounds contribute to a range of opinions on each case.
On the HBS Online course platform, you’re prompted to view and comment on others’ responses, and discussion is encouraged. This practice of considering others’ perspectives can make you more receptive in your career.
“You’d be surprised at how much you can learn from your peers,” said Ratnaditya Jonnalagadda , a software engineer who took CORe.
In addition to interacting with peers in the course platform, Jonnalagadda was part of the HBS Online Community , where he networked with other professionals and continued discussions sparked by course content.
“You get to understand your peers better, and students share examples of businesses implementing a concept from a module you just learned,” Jonnalagadda said. “It’s a very good way to cement the concepts in one's mind.”
4. Enhance Your Curiosity
One byproduct of taking on different perspectives is that it enables you to picture yourself in various roles, industries, and business functions.
“Each case offers an opportunity for students to see what resonates with them, what excites them, what bores them, which role they could imagine inhabiting in their careers,” says former HBS Dean Nitin Nohria in the Harvard Business Review . “Cases stimulate curiosity about the range of opportunities in the world and the many ways that students can make a difference as leaders.”
Through the case method, you can “try on” roles you may not have considered and feel more prepared to change or advance your career .
5. Build Your Self-Confidence
Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader’s perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and defend your opinions and decisions to peers, you prepare to do the same in your career.
According to a 2022 City Square Associates survey , 84 percent of HBS Online learners report feeling more confident making business decisions after taking a course.
“Self-confidence is difficult to teach or coach, but the case study method seems to instill it in people,” Nohria says in the Harvard Business Review . “There may well be other ways of learning these meta-skills, such as the repeated experience gained through practice or guidance from a gifted coach. However, under the direction of a masterful teacher, the case method can engage students and help them develop powerful meta-skills like no other form of teaching.”

How to Experience the Case Study Method
If the case method seems like a good fit for your learning style, experience it for yourself by taking an HBS Online course. Offerings span eight subject areas, including:
- Business essentials
- Leadership and management
- Entrepreneurship and innovation
- Digital transformation
- Finance and accounting
- Business in society
No matter which course or credential program you choose, you’ll examine case studies from real business professionals, work through their challenges alongside peers, and gain valuable insights to apply to your career.
Are you interested in discovering how HBS Online can help advance your career? Explore our course catalog and download our free guide —complete with interactive workbook sections—to determine if online learning is right for you and which course to take.

About the Author

ऑनलाइन अध्ययन के लाभ और नुकसान पर निबंध (Advantages and Disadvantages of Online Study Essay in Hindi)
इन दिनों ऑनलाइन अध्ययन एकप्रचलन सा बन गया है, कोविड-19 के चलते इस लॉकडाउन में कई स्कूलों ने पिछले कुछ महिनों से ऑनलाइन अध्ययन की प्रक्रिया को अपनाकर इसे अधिक उपयोग में लाया है। ऑनलाइन अध्ययन की प्रक्रिया को देखते हुए, मैं इससे होने वाले लाभ और नुकसान के तीन अलग-अलग शब्द सीमा के निबंध का विस्तार कर रहा हुँ। आप सभी इस विस्तार के माध्यम से ऑनलाइन अध्ययन से होने वालें लाभ और नुकसान के बारें में अधिक जानकारी प्राप्त कर सकतें है।
ऑनलाइन शिक्षा से होने वाले लाभ और नुकसान पर निबंध (Essay on Advantages and Disadvantages of Online Study in Hindi, Online Shiksha se hone wale Labh aur Nuksan par Nibandh)
ऑनलाइन अध्ययन के लाभ और नुकसान पर निबंध – 1 (250 – 300 शब्द).
ऑनलाइन स्टडी अपनी सुविधा और आसान संचालन की प्रक्रिया से अधिक लोकप्रिय हो रहा है। इन दिनों कई स्कूल छात्रों की सुरक्षा को देखते हुए ऑनलाइन अध्ययन की प्रक्रिया को अपना रहें है। वास्तव में ऑनलाइन अध्ययन की प्रक्रिया स्कूली शिक्षा के लिए एक सुरक्षित विकल्प है।
ऑनलाइन तरीके से अध्ययन के कई फायदे है। यह बहुत सुविधाजनक है, इस सुविधा के उपयोग से आप अपने घर पर ही रहकर बातचीत कर सकते है। आप क्लासरूम की तरह यहाँ पर भी एक दुसरे से सवाल जबाब कर सकते है। प्राकृतिक आपदा या आपातकाल की स्थिति में ऑनलाइन अध्ययन की प्रक्रिया का महत्व और भी अधिक बढ़ जाता है। इस प्रक्रिया का सही उदाहरण हाल ही में फैली कोविड-19 महामारी है, जिसका प्रभाव सारी दुनियाँ में है और इसके प्रभाव से बचने के लिए सभी प्रयत्नशील है।
ऑनलाइन अध्ययन की प्रक्रिया में कई लाभों के अलावा कुछ नुकसान भी हमारें सामनें प्रस्तुत होते है। जिस तरह वास्तविक कक्षा में जो उत्साह का वातावरण होता है यहाँ उस वातावरण का अभाव होता है। एक जीवंत कक्षा या लाइव क्लास में जो आनंद का माहौल होता है, ऑनलाइन अध्ययन में उस माहौल की कमी होती है। यहाँ पर एक शिक्षक और छात्र एक दुसरे से केवल एक ही विषय को लेकर बातचीत और चर्चा कर सकते है। इसके अलावा इसके कारण गैजेट का ओवर एक्सपोजर से स्वास्थ के कई खतरे जैसे कि सिरदर्द, आंखों का कमजोर होना और एकाग्रता में कमी आना इत्यादि का खतरा भी बढ़ जाता है।
स्वास्थ्य सम्बन्धित इतने नुकसान के बाद भी इस अध्ययन प्रक्रिया का उपयोग विशिष्ट परिस्थितियों में बहुत ही फायदेमंद साबित हुआ है। जब कि आपका घर छोड़ना आपकी सुविधा और स्वास्थ्य के लिए हानिकारक है तो उस स्थिति में ऑनलाइन अध्ययन की प्रक्रिया आपके लिए एक वरदान साबित हो जाता है।
इसे यूट्यूब पर देखें : ऑनलाइन अध्ययन के लाभ और नुकसान
निबंध 2 (400 शब्द) – ऑनलाइन स्टडी छात्रों को कैसे प्रभावित करता है?
ऑनलाइन शिक्षा की प्रक्रिया में फायदें और नुकसान दोनों ही शामिल है। इस निबंध में हम इससे होने वाले नुकसान के बारें में चर्चा करेंगें और अगले निबंध में आपको इससे होने वाले लाभ के बारे में भी आपको बताएंगें। यहां पर मैने ऑनलाइन अध्ययन से होने वाले कुछ नुकसान के बारे में बताया है।
कैसे ऑनलाइन स्टडी छात्रों के लिए अच्छा नहीं है
ऑनलाइन अध्ययन के कई फाँयदों के बावजूद इसके ढ़ेरों नुकसान भी है। यहां नीचे इससे होने वाले कुछ नुकसान के बारें में आपको बताया गया है।
- खुद पर नियंत्रण
एक ऑनलाइन अध्ययन की सफलता आपके खुद के आचरण पर निर्भर करता है, चाहे वह किसी भी क्षेत्र में हो। किसी भी ऑनलाइन अध्ययन की प्रक्रिया सफल हुई या नहीं यह बात केवल आपके सीखने की उत्सुकता पर ही निर्भर करती है, हो सकता है कि आपका अध्यापक आपको न देंख सकें, यह आपकी स्वतंत्रता पर निर्भर करता है कि आप सीखने के कितने इच्छुक है। आप खुद के मन को कैसे नियंत्रित कर उस कक्षा से कितना सीखते है यह आप पर निर्भर करता है।
- ईमानदारी पर निर्भर
यह ऑनलाइन अध्ययन की एक महत्वपूर्ण कमीयों में से एक है। ऑनलाइन कक्षा में रहते हुए आपका ध्यान हमेशा के लिए उपर होनी चाहिए, उसके लिए आप कक्षा में स्वतंत्र नहीं है। आप ऑनलाइन कक्षा के प्रति कितने इमानदार है यह आपकी उपस्थिति पर निर्भर करता है। ऐसी कक्षा में सभी छात्र पर ध्यान देना शिक्षक के लिए संभव नहीं है।
- केवल कोर्स सम्बन्धित बातें
अक्सर एक ऑनलाइन कक्षा में विषय के उस बिन्दु पर चर्चा की जाती है जिस विषय में चर्चा की जानी होती है। आमतौर की कक्षाओं में शिक्षक जहां अपनी निजी तथ्य और जोक्स भी शामिल करता है, ऑनलाइन कक्षा में इसकी कमी रहती है। कक्षा में जहां शिक्षक कई अन्य बातों के बारे में भी बात कर सकता है वही वह ऑनलाइन कक्षा में केवल विषय से सम्बन्धित बाते ही बताता है।
- ओवर एक्सपोजर टू स्क्रीन
ऑनलाइन अध्ययन में कक्षाओं के संचालन के लिए इलेक्ट्रानिक स्क्रीन गैजेट्स की आवश्यकता होती है। छात्रों को लम्बे समय तक, कभी-कभी 2 से 3 घंटे तक लगातार स्क्रीन पर देखना पड़ता है। इस तरह लम्बे समय तक स्क्रीन के ऊपर देखने के कारण हमारे स्वास्थ के प्रतिरोधक क्षमता पर गहरा प्रभाव पड़ता है। इसके कारण कुछ छात्रों में सिरदर्द और आंखों की समस्या देखने को मिलती है।
- सीमित बातचीत
हाँलाकि शिक्षक और छात्रों के बीच ऑनलाइन कक्षा में बातचीत की कोई सीमा तय नहीं की गई है, फिर भी यहाँ एक सीमीत मात्रा में बात की जाती है। एक शिक्षक को सभी छात्रों के प्रश्नों के उत्तर देने पड़ते है इस कारण शिक्षक छात्रों को बस कुछ मिनट ही दें पाता है, इसके लिए वह बाध्य होता है।
ऑनलाइन अध्ययन का तरीका कुछ मामलों में पूर्ण नहीं है। यह तो निश्चित है कि इसके अपने कई नुकसान है, पर कुछ महत्वपूर्ण परिस्थितियों में यह हमारे बहुत फायदेमंद साबित हुआ है। जैसे कि कोविड-19 महामारी में लॉकडाउन होने के उपरान्त यह कई स्कूल और बहुत सारें छात्रों के लिए एक आशिर्वाद के रूप उन्हे मिला है।
निबंध 3 (500 शब्द) – ऑनलाइन स्टडी छात्रों के लिए कैसे अच्छा है?
ऑनलाइन अध्ययन शिक्षा का एक आधुनिक डिजिटल तरीका है, जहाँ पर शिक्षक और छात्र उपकरणों जैसे कि लैपटॉप, स्मार्टफोन, टैब या अन्य उपकरणों का उपयोग कर एक दूसरे से बातचीत करतें है। अध्ययन की यह पद्धति या प्रणाली इन दिनों काफी प्रचलित है, जबकि इस महामारी के फैलने के बाद हमें घर से बाहर न निकलने को कहा गया है। कोविड़-19 महामारी को देखते हुए कई स्कूलों ने ऑनलाइन अध्ययन के तरीके को अपनाया है और इस प्रक्रिया को काफी हद तक सफल भी बनाया है।
ऑनलाइन स्टडी छात्रों के लिए कितनी अच्छी है
अध्ययन की यह प्रक्रिया के अपने ही फायदें है। यह काफी सुविधाजनक और अध्ययन की बहुत सस्ती प्रक्रिया है। ऑनलाइन स्टडी के लाभों में कुछ महत्वपूर्ण लाभ का विवरण नीचे किया गया है।
ऑनलाइन अध्ययन की इस विधी द्वारा छात्रों के साथ-साथ शिक्षको के लिए भी काफी उपयोगी और सुविधाजनक है। दोनों ही अपने घर के बाहर बिना कदम रखें ही शिक्षा के सत्र में इस प्रक्रिया द्वारा भाग ले सकते है। उन्हें एक दूसरे से जुड़ने के लिए केवल एक अच्छे डिवाइस और इंटरनेट कनेक्शन की आवश्यकता होती है। बस आप अपनी आवश्यकता की किताबों के साथ अपने कमरे में एक उचित स्थान पर आराम से बैठकर अपने क्लासमेट्स के साथ ऑनलाइन कक्षा में भाग ले सकते है।
ऑनलाइन अध्ययन स्कूली शिक्षा प्रणाली के कई मामलों में काफी सस्ती विधी है। सबसे पहला यह कि आपको स्कूल जाने और वापस आने में ट्रान्सपोर्ट व अन्य खर्चों की आवश्यकता नहीं पड़ती है, दूसरा यह कि स्कूल के अन्य सभी खर्चे कम हो जाते है। कभी-कभी पुस्तकें भी हमें ऑनलाइन ही उपलब्ध हो जाती है जिसकी कीमत हार्ड कापी की तुलना में काफी कम होती है। आप अपनी आवश्यकता के अनुसार इसे डाउनलोड कर सकते है, जिसमें की वास्तविक किताबों की तरह ही सामग्री उपलब्ध होती है। यहां तक आपको बस इंटरनेट कनेक्सन के पैसे ही खर्च करने होते है और कुछ नहीं।
इसमें कोई संदेह नहीं कि ऑनलाइन अध्ययन सुरक्षित विकल्प है, जिसमे खतरे की संभावना बहुत कम होती है। यह आपके लिए एक वरदान के रूप में है, जबकि आपका घर से बाहर निकलना आपको खतरनाक साबित हो सकता है। हम सभी कोविड-19 महामारी के बारे में अच्छी तरह से जान चुकें है, जिसने पूरे पृथ्वी को लॉकडाउन में डाल दिया है। जिसके कारण छात्र एक दूसरे के शारिरीक सम्पर्क में नहीं आते है और इसके कारण उनमे इस महामारी के फैलने की संभावना काफी कम हो जाती है। शुक्र है कि छात्र नियमीत रूप से ऑनलाइन कक्षा में भाग लें रहें है जिसके कारण पाठ्यक्रम भी नहीं पिछड़ा है।
ऑनलाइन स्टडी पाठ्यक्रमों के दौड़ में आगे जाकर एक जबरजस्त लचीलापन ला सकता है। हमारे यहां कुछ विश्वविद्यालय आपके द्वारा चुने गये विषयों की ऑनलाइन सर्टिफिकेट प्रदान करता है। जिसका पंजिकरण से लेकर परीक्षा तक की प्रक्रिया सब कुछ ऑनलाइन के माध्यम से किया जाता है। इसके अलावा इसके समय में भी लचीलापन है। यदि आप थोड़ी देर से भी इसमें शामिल होते है तो चिन्ता की कोई बात नहीं है, इनके सत्र की कक्षाएं रिकार्ड हो जाती है जिसे आप बाद में भी इसका उपयोग कर सकते है।
- कम पेपर का स्तेमाल
ऑनलाइन शिक्षा की प्रक्रिया का एक और लाभ यह भी है कि इसमे कागजों का उपयोग बहुत कम हो जाता है। क्लासरूम प्रणाली की अपेक्षा डिजिटल प्रणाली से अध्ययन करने में पेपर के उपयोग की मात्रा लगभग न के बराबर हो जाती है। आपको बस अपने में ये सब नोट करना होता है, जबकि आपका शिक्षक आपको बिना किसी पेपर के भी आपको पढ़ा सकता है। इसके अलावा ऑनलाइन स्टडी टेस्ट भी आयोजित किये जाते है जिसके कारण पेपर का स्तेमाल बहुत कम हो जाता है।
क्लासरूम एनवायरमेंट की तुलना में ऑनलाइन अध्ययन में छात्र शिक्षक के बीच अधिक तालमेल देखा जा सकता है। आमतौर पर कक्षा में व्याकुलता ज्यादा मौजूद होते है जबकि ऑनलाइन कक्षा में इसकी संभावना काफी कम हो जाती है जिसके कारण छात्र शिक्षक द्वारा बतायी गयी बातों पर ज्य़ादा ध्यान केन्द्रित करने में मदद मिलती है। इसके अलावा छात्र अधिक संवेदनशील हो जाते है जिससे कि वो अपने संकोच को अपने शिक्षक के साथ बात करके उसका हल निकाल सकते है।
ऑनलाइन अध्ययन का माध्यम शिक्षा और तकनिक का एक संलयन है। यह हमें सीखाती है कि नयी तकनीक के माध्यम से हम कैसे शिक्षा प्रणाली का लाभ उठा सकते है और हम इसमें विकास और सुधार के लिए और अधिक प्रयास कर सकते है। शिक्षा के क्षेत्र में यह प्रणाली एक क्रांति लाने की दिशा में हर दिन नये कदम की ओर अग्रसर है जो कि पहले कभी नहीं हुआ।

संबंधित पोस्ट

मेरी रुचि पर निबंध (My Hobby Essay in Hindi)

धन पर निबंध (Money Essay in Hindi)

समाचार पत्र पर निबंध (Newspaper Essay in Hindi)

मेरा स्कूल पर निबंध (My School Essay in Hindi)

शिक्षा का महत्व पर निबंध (Importance of Education Essay in Hindi)

बाघ पर निबंध (Tiger Essay in Hindi)
Leave a comment.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Voice speed
Text translation, source text, translation results, document translation, drag and drop.

Website translation
Enter a URL
Image translation
- Media Center
- Not yet translated
Psychological Theories
What are psychological theories.
Psychological theories are systematic explanations of human mental processes and behaviors, developed through both empirical research and field observation. These theories provide frameworks for understanding how and why people think, feel, and act the way they do, and guide both academic research and practical applications in areas like therapy, education, marketing, and public policy.
The Basic Idea
Theory, meet practice.
TDL is an applied research consultancy. In our work, we leverage the insights of diverse fields—from psychology and economics to machine learning and behavioral data science—to sculpt targeted solutions to nuanced problems.
If you’ve ever snoozed your alarm and then been late to work or school, you may look back and ask yourself: why did I do that? Maybe your bus driver saw you running for the bus and chose to keep on driving, and you ask yourself: what was going through his mind? Or maybe the day turned out okay, because you came home to your loving partner, and you thought to yourself: why am I so compatible with this person but not others? To begin unpacking these questions and more, we can turn to psychological theories to help us understand ourselves and the people around us.
Psychological theories are systematic frameworks for understanding, predicting, and explaining human behavior and mental processes. These theories include everything from cognitive theories , which focus on mental processes such as perception and memory, to behavioral theories , which examine the relationship between stimuli and responses. Although there are many ways to explain how and why we are the way we are, it is the constant testing and refining of different psychological theories that guides research and helps us to consistently improve our understanding of humans—both within academia and beyond.
Most Influential Psychological Theories:
- Psychoanalytic Theory (Sigmund Freud): Focuses on the influence of the unconscious mind on behavior and uses concepts like the id, ego, superego, and psychosexual stages of development.
- Behaviorism (John B. Watson, B.F. Skinner): Emphasizes the study of observable behaviors and the role of environmental stimuli in shaping behavior, including classical conditioning and operant conditioning.
- Cognitive Development Theory (Jean Piaget): Explains how children's thinking evolves as they grow, identifying four stages of cognitive development (sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational).
- Humanistic Psychology (Carl Rogers, Abraham Maslow): Emphasizes individual potential, self-actualization, and the importance of personal growth and free will. This also includes Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Rogers' client-centered therapy.
- Social Learning Theory (Albert Bandura): Proposes that people learn behaviors through observation, imitation, and modeling, rather than solely through direct reinforcement and uses reciprocal determinism, where behavior, personal factors, and the environment interact and influence each other.
The world makes much less sense than you think. The coherence comes mostly from the way your mind works. – Daniel Kahneman
Cognition: Mental processes involved in gaining knowledge and comprehension, including thinking, knowing, remembering, judging, and problem-solving.
Psychoanalysis: A therapy developed aimed at exploring the unconscious mind to understand and treat psychological disorders.
Positive Reinforcement : In behaviorism, the process of encouraging or establishing a pattern of behavior by offering a reward when the desired behavior is exhibited.
Montessori Method: An educational approach developed by Dr. Maria Montessori that emphasizes self-directed learning, hands-on activities, creativity, and a love for learning and collaborative play in a child-centered environment.
Herzberg's Motivation Theory: Also known as the two-factor theory, this theory proposes that job satisfaction is influenced by two distinct sets of factors: hygiene factors and motivator factors. Hygiene factors pertain to external conditions such as the workplace environment and salary, while motivator factors are typically intangible elements like receiving recognition or opportunities for personal growth.
As long as there have been humans, there have been questions about why we think and act the way we do. There have likely been countless theories developed throughout time that we have no written record of, such as those developed by native peoples. For many, the known history of psychological theories goes back to ancient philosophical inquiries about the human mind and behavior. Early thinkers like Plato and Aristotle laid the groundwork for understanding the mind's complexities, focusing on issues of perception, memory, and motivation. Hundreds of years later, the 17th century marked a significant shift with the rise of empiricism, championed by philosophers like John Locke who proposed that knowledge is derived from sensory experience. This idea laid the foundation for later psychological theories that emphasize the role of the environment in shaping behavior. 1
The formal birth of psychology as a scientific discipline is often credited to Wilhelm Wundt, who established the first psychology laboratory in Leipzig, Germany, in 1879. Wundt's work marked the beginning of experimental psychology, where he used introspection to explore the structure of the conscious mind. His approach, known as structuralism, aimed to break down mental processes into their most basic components. Around the same time, William James in the United States was developing his own approach called functionalism, which focused on the purpose of consciousness and behavior in helping individuals adapt to their environment. These early schools of thought laid the groundwork for more complex psychological theories. 1
The early 20th century saw the emergence of several influential psychological theories that have shaped the field as we know it today. Sigmund Freud's psychoanalytic theory introduced the idea of the unconscious mind and the role of early childhood experiences in shaping personality (he’s the guy who you usually picture talking to a patient while they lay on a couch, discovering a repressed memory). While Freud's ideas were revolutionary, they were (and still are) controversial, spurring the development of alternative theories. Behaviorism, led by John Watson and later B.F. Skinner, rejected the introspective methods of the past and focused instead on observable behavior, emphasizing the role of environmental stimuli in shaping actions. Behaviorism dominated psychology from the 1920s to the 1950s, particularly in the United States, influencing everything from education to advertising. 1
Toward the mid-20th century emerged a cognitive revolution, as cognitive psychologists began challenging the behaviorist movement by reintroducing the importance of mental processes. Pioneers like Jean Piaget and Noam Chomsky argued that studying internal cognitive processes (like thinking, memory, and language) was crucial for a complete understanding of behavior. This shift led to the development of cognitive psychology, which remains one of the most prominent areas of the field today. Additionally, humanistic psychology, which was considered more of a ‘counter-movement’ to behaviorism, emerged during this time, with figures like Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow emphasizing personal growth, self-actualization, and the inherent goodness of people. All of these diverse perspectives have contributed to a more comprehensive and multifaceted understanding of human behavior, continuing to influence psychological research and practice today. 2
Plato (c. 427-347 BCE) : Greek philosopher from Athens known for his works on philosophy and the mind, including the theory of forms and the allegory of the cave.
Aristotle (384-322 BCE) : Greek philosopher from Stagira who studied under Plato and is renowned for his contributions to logic, metaphysics, and psychology, particularly his theory of the soul.
John Locke (1632-1704) : English philosopher, often called the "father of liberalism," known for his theory of empiricism, which posits that knowledge is derived from sensory experience.
Wilhelm Wundt (1832-1920) : German psychologist, often regarded as the "father of modern psychology," who established the first psychology laboratory and developed the theory of structuralism.
William James (1842-1910) : American philosopher and psychologist, known as the "father of American psychology," who founded the school of functionalism and authored the first psychology textbook, The Principles of Psychology.
Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) : Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, known for his theories on the unconscious mind, psychosexual development, and defense mechanisms.
John B. Watson (1878-1958) : American psychologist, best known for founding behaviorism, which focuses on the study of observable behavior rather than internal mental processes.
B.F. Skinner (1904-1990) : American psychologist and behaviorist, known for developing the theory of operant conditioning and his work on reinforcement and punishment.
Jean Piaget (1896-1980) : Swiss psychologist, famous for his theory of cognitive development, which outlines how children's thinking evolves through distinct stages.
Noam Chomsky (b. 1928) : American linguist, philosopher, and cognitive scientist, known for his theory of universal grammar and his critique of behaviorism in language acquisition.
Carl Rogers (1902-1987) : American psychologist, one of the founders of humanistic psychology, known for his client-centered therapy and emphasis on self-actualization.
Abraham Maslow (1908-1970) : American psychologist, best known for creating Maslow's hierarchy of needs, a theory that outlines the stages of human motivation from basic needs to self-actualization.
Consequences
The impact of psychological theories extends far beyond academic research; scientifically understanding our own thoughts and behavior has influenced almost all aspects of modern life, shaping practices in education, marketing, public policy, and business.
In the realm of education, psychological theories have revolutionized teaching and learning methodologies. For example, certain developmental theories have provided educators with insights into how children think and learn at different stages. Jean Piaget’s theory of cognitive development suggests that children progress through specific stages of cognitive growth, with each stage characterized by distinct thinking patterns. 3 Understanding these stages allows teachers to adjust their teaching strategies to better match the cognitive capacity of their students.
Meanwhile, Lev Vygotsky’s concept of the zone of proximal development explains the gap between what a student can learn on their own versus with help. This theory posits that the role of education is to provide children with experiences that are in their proximal development stage, encouraging and advancing individual learning through social interaction. Students can solve problems independently, applying knowledge from conversations with peers and teachers to gradually develop the skills to perform tasks without direct help. 4 Understanding this theory has helped shape the role of teachers in the classroom; sometimes, it’s more about putting students in a situation where they can teach themselves to succeed rather than being explicitly taught.
For better or worse, psychological theories have also left a huge mark on the field of marketing and consumer behavior. Behaviorism, with its focus on conditioning and reinforcement, has been particularly influential in understanding and shaping consumer habits. Marketers have applied principles of operant conditioning to design reward systems—like loyalty programs or memberships—that encourage repeat purchases by reinforcing desired behaviors. The understanding of cognitive biases, such as the availability heuristic and the framing effect , has also allowed many marketers to craft persuasive messages that influence buyer decision-making. All of these psychological insights have helped businesses increase sales and foster brand loyalty—potentially misleading or even taking advantage of customers.
Public policy
Public policy is another major area where psychological theories have had significant consequences. Understanding human behavior has helped policymakers create more effective campaigns to improve public health, environmental protection, education systems, and programs that better address social issues such as poverty and crime. The application of small interventions that capitalize on our biases in a nonrestrictive way (often referred to as “ nudging ”), has gained prominence in recent years. This approach, popularized by Richard Thaler and Cass Sunstein, is based on the idea that small changes in the way choices are presented can have a substantial impact on behavior, like automatically enrolling employees in retirement savings plans, with the option to opt-out. A change as simple as this has been shown to dramatically increase participation rates in retirement plans.
Organizations
If you’re in a traditional workplace, you may have experienced the influence of psychological theories in your office without realizing it. Organizational behavior and human resource management have been hugely shaped by Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and Herzberg’s two-factor theory. Both of these theories have changed how companies understand and manage employee motivation and satisfaction. Maslow’s theory suggests that employees (and all humans) are motivated by a hierarchy of needs, starting with basic physiological needs like food and water and progressing to self-actualization. Thus, companies that recognize and address these needs by providing a safe working environment, opportunities for social interaction, and chances for personal growth, are more likely to foster a motivated and productive workforce (perhaps this is why having free coffee and snacks in the office is so motivating?). Herzberg’s two-factor theory, which distinguishes between hygiene factors (e.g., salary, work conditions) and motivators (e.g., recognition, achievement), has also guided organizations in designing jobs and work environments to maximize employee satisfaction.
Controversies
Psychological theories, while important to our understanding of human behavior, are theories, not facts. We can still only speculate and make educated guesses as to how and why our brains function the way they do. Many of the theories we’ve previously developed haven’t withstood the test of time, or at least not without serious criticism.
Psychoanalytic Theory
One of the most contentious figures in psychology is Freud, whose psychoanalytic theory has faced huge criticism. Although Freud's focus on the unconscious mind and his theories of psychosexual development were groundbreaking at the time, they were also largely unscientific and overly deterministic. Critics argue that many of Freud’s ideas, such as the Oedipus complex (briefly, that boys are repressing attraction to their moms and jealousy of their fathers’ genitals) and the emphasis on sexual drives, lack empirical support and are difficult if not impossible to test systematically. His theories have also been accused of being culturally biased, reflecting the patriarchal and sexually repressive values of his time, which are largely not applicable (or at least hopefully less so) today.
Behaviorism
Behaviorism, another major psychological theory, has also faced significant criticism, particularly for its reductionist approach. Watson and Skinner’s theory focuses exclusively on observable external behaviors and their environmental conditioning, largely ignoring the importance of internal mental processes like emotion. To no surprise, humans have a lot going on under the surface, and not taking this into account can be problematic. That’s because we are much more than machines reacting directly to the environment around us, and internal or unobservable processes (like our preferences, hunger, hormones, and social upbringing) can have dramatic influences on the way we react to stimuli. This critique helped propel the cognitive revolution to take into account the other missing piece of the puzzle: the mind.
Cognitive Theory
Enter cognitive psychology, which has also been criticized for its heavy reliance on computational models of the mind, which can oversimplify the complexities of human cognition—after all, the brain is not a computer. Since these models usually compare the mind to a computer processing information, they’ve also been accused of neglecting the emotional, social, and cultural factors that influence thought and behavior. Thus, cognitive psychology, just like behaviorism before it, tends to focus on “universal” principles—when, of course, there are huge individual differences among people, places, and cultures.
Humanistic Psychology
Humanistic psychology emerged as a response to both behaviorism and psychoanalysis to introduce a more optimistic view of human nature—but hasn’t escaped its share of criticisms. While prominent figures like Rogers and Maslow emphasized the potential for personal growth and self-actualization, proposing that people are inherently good and capable of achieving their full potential, many critics argue that this perspective is overly idealistic. Much like Freud’s psychoanalysis, it can be incredibly hard to test humanistic psychology empirically which can make it even harder to find acceptance from the scientific community. Also, due to the focus on the individual’s growth and self-fulfillment, it can be easy to overlook the social and structural factors that limit personal development; essentially, the individual is responsible for their own shortcomings or inadequacies, ignoring systemic issues like poverty, discrimination, and lack of access to education.
Cultural Context
Much of the existing psychology research is on a WEIRD (Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, and Democratic) population, which has raised concerns about the generalizability of its findings to non-WEIRD populations. All theories involve some sort of bias, and no population will ever be truly representative. The role of psychological theories in perpetuating or challenging societal norms is a controversial subject because, while the field has contributed to understanding and reducing prejudice, critics argue that some research in social psychology specifically can inadvertently reinforce stereotypes or fail to account for cultural and contextual differences.
For example, the application of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs discussed earlier posits that individuals prioritize their needs in a specific order, starting with basic physiological needs and moving up through safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. This model aligns well with WEIRD cultures, which tend to emphasize individualism and personal achievement since cultural values prioritize personal growth and self-fulfillment. However, in more collectivist cultures, where community, family, and social harmony are often prioritized over individual needs, Maslow’s hierarchy doesn’t fit quite as well. In addition, studies that categorize people into rigid social groups based on race, gender, or socioeconomic status may unintentionally perpetuate the very biases they aim to study. These critiques have led to a growing recognition of the need for more culturally sensitive research and a broader, more inclusive approach to studying behavior.
Behavioral Psychology in Education
Behavioral psychology—particularly the principles of operant conditioning—has been instrumental in shaping modern educational practices. Operant conditioning, a theory developed by Skinner, posits that behavior is influenced by the consequences that follow it. Specifically, reinforcement increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated, while punishment decreases it. This approach can be applied to classroom management when teachers try to promote positive behavior that leads to academic achievement.
For instance, many schools implement reward systems like tokens or points that use positive reinforcement to encourage good behavior like completing homework on time, participating in class discussions, or staying silent during reading times. Usually, these tokens are traded in for rewards like extra recess time, which can help keep kids motivated. We can also see how punishment systems like detention or extra homework can be used to discourage unwanted or disruptive behavior. All of these systems are designed based on our understanding of different psychological theories, from how we best learn to which tools are appropriate for which ages, and have informed interventions for students with special needs, behavioral disorders, or learning disabilities.
The Montessori Method is an educational approach that is based on principles from Piaget’s developmental psychology and Vygotsky’s zone of proximal learning principles. Montessori classrooms emphasize self-directed learning, hands-on activities, and collaborative play, giving kids the chance to explore their environment at their own pace and in their own way. Educational materials are designed to support the children’s developmental stages and foster independence, curiosity, and a love of learning: key components of the developmental theory.
Psychological Theories in Therapy
One of the most direct applications of psychological theories is in the field of clinical psychology, where theories of human behavior and mental processes have informed the development of many therapeutic techniques. For example, many people are familiar with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) , as it’s one of the most widely used therapeutic approaches today. This type of therapy is grounded in cognitive theory by helping individuals identify and change distorted thinking patterns that lead to negative emotions and behaviors. This theory-based approach has proven effective in treating a variety of psychological disorders, including depression, anxiety, and PTSD. 5
Understanding psychological theories is crucial for developing effective therapeutic approaches to provide the foundational knowledge needed to comprehend complex mechanisms underlying mental health issues. These theories can offer structured frameworks that guide therapists in assessing, diagnosing, and treating various psychological conditions and help them address the specific needs of individuals. Since so much of the work is built on tested theory, treatment can be both scientifically grounded and practically effective.
Related TDL Content
How might behavioral science transform education.
With so much discussion about the impact of psychological theories on education, it’s important to understand some of the biggest challenges in education reform and how they can be improved.
Financial Planning Education That Puts Humans First
Another important application is looking at how we use psychological theory to shape our financial decisions, and how banks use these same understandings for themselves.
- Cherry, K. (2023, May 17). A Brief History of Psychology Through the Years . Verywell Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/a-brief-history-of-psychology-through-the-years-2795245
- Wikipedia contributors. (2023, August 7). Cognitive revolution . Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cognitive_revolution
- Cherry, K. (2023, July 20). Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development . Verywell Mind. https://www.verywellmind.com/piagets-stages-of-cognitive-development-2795457
- McLeod, S. (2023). Zone of Proximal Development . Simply Psychology. https://www.simplypsychology.org/zone-of-proximal-development.html
- Gaudiano, B. A. (2008). Cognitive-behavioural therapies: achievements and challenges. Evidence-based mental health, 11(1), 5-7.
Case studies
From insight to impact: our success stories, is there a problem we can help with, about the author.

Annika Steele
Annika completed her Masters at the London School of Economics in an interdisciplinary program combining behavioral science, behavioral economics, social psychology, and sustainability. Professionally, she’s applied data-driven insights in project management, consulting, data analytics, and policy proposal. Passionate about the power of psychology to influence an array of social systems, her research has looked at reproductive health, animal welfare, and perfectionism in female distance runners.
We are the leading applied research & innovation consultancy
Our insights are leveraged by the most ambitious organizations.

I was blown away with their application and translation of behavioral science into practice. They took a very complex ecosystem and created a series of interventions using an innovative mix of the latest research and creative client co-creation. I was so impressed at the final product they created, which was hugely comprehensive despite the large scope of the client being of the world's most far-reaching and best known consumer brands. I'm excited to see what we can create together in the future.
Heather McKee
BEHAVIORAL SCIENTIST
GLOBAL COFFEEHOUSE CHAIN PROJECT
OUR CLIENT SUCCESS
Annual revenue increase.
By launching a behavioral science practice at the core of the organization, we helped one of the largest insurers in North America realize $30M increase in annual revenue .
Increase in Monthly Users
By redesigning North America's first national digital platform for mental health, we achieved a 52% lift in monthly users and an 83% improvement on clinical assessment.
Reduction In Design Time
By designing a new process and getting buy-in from the C-Suite team, we helped one of the largest smartphone manufacturers in the world reduce software design time by 75% .
Reduction in Client Drop-Off
By implementing targeted nudges based on proactive interventions, we reduced drop-off rates for 450,000 clients belonging to USA's oldest debt consolidation organizations by 46%

The COM-B Model for Behavior Change

The Transtheoretical Model (TTM)

Randomized Controlled Trial

Qualitative Research

Eager to learn about how behavioral science can help your organization?
Get new behavioral science insights in your inbox every month..
The Quality of Digital Technology in Higher Education: A Case Study from Gulf Universities
- First Online: 31 August 2024
Cite this chapter

- Abdulsadek Hassan 9 , 10 ,
- Abdulla Mahdi Hassan 9 , 10 &
- Tariq Mana Ali Al Numis 9 , 10
Part of the book series: Studies in Systems, Decision and Control ((SSDC,volume 538))
This article explores the usage of digital technology in higher education within Gulf universities. The educational landscape in this region has witnessed significant transformations driven by advancements in technology. Gulf universities are embracing various digital tools and platforms to enhance the teaching and learning experience, improve access to education, and foster engagement among students and faculty members. This article examines the implementation of digital technology in Gulf universities, highlights its advantages and challenges, and explores the potential impact on the overall quality of education. Additionally, it discusses the key initiatives and strategies adopted by Gulf universities to leverage digital technology effectively. The findings of this study provide valuable insights for policymakers, educators, and institutions seeking to leverage digital technology in higher education within Gulf countries.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Abdellatif, S., Shomotova, A., Trabelsi, S., Husain, S., Alsalhi, N., Eltahir, M.: Transition to distance learning: student experience and communication during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Arab Emirates. Sustainability 15 (8), 6456 (2023)
Article Google Scholar
Aboud, Y.Z.: Evaluating the status of gifted education in the Gulf cooperation council countries. Cogent Educ. 10 (1), 2206080 (2023)
Abu Talib, M., Bettayeb, A.M., Omer, R.I.: Analytical study on the impact of technology in higher education during the age of COVID-19: systematic literature review. Educ. Inf. Technol., 1–28 (2021)
Google Scholar
Aburayya, A., Salloum, S., Alderbashi, K., Shwedeh, F., Shaalan, Y., Alfaisal, R., Malaka, S. and Shaalan, K.: SEM-machine learning-based model for perusing the adoption of metaverse in higher education in UAE. Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 7 (2), 667–676 (2023)
Ahmed, E., Shaukat, A., AlDhaen, E.: A review of the recent developments in the higher education sector globally and in the GCC region. In: Artificial Intelligence and Transforming Digital Marketing, 635–651 (2023)
Akhmedov, B.: A new approach to teaching information technologies in education. Central Asian J. Educ. Comput. Sci. (CAJECS) 1 (2), 73–78 (2022)
Akhmedov, B.A.: Improvement of the digital economy and its significance in higher education in tashkent region. Uzbek Scholar J. 12 , 18–21 (2023)
Akour, M., Alenezi, M.: Higher education future in the era of digital transformation. Educ. Sci. 12 (11), 784 (2022)
Al Rawashdeh, A.Z., Mohammed, E.Y., Al Arab, A.R., Alara, M., Al-Rawashdeh, B.: Advantages and disadvantages of using e-learning in university education: analyzing students’ perspectives. Electron. J. E-learn. 19 (3), 107–117 (2021)
Alarefi, M.: Adoption of IoT by telecommunication companies in GCC: the role of blockchain. Decis. Sci. Lett. 12 (1), 55–68 (2023)
Alastal, A.Y.M., Salman, M.A.H., Allaymoun, M.H.: Accounting students’ perceptions on e-learning during Covid-19 pandemic: case study of accounting and financial students in Gulf university—Bahrain. In: Artificial Intelligence and Transforming Digital Marketing, pp. 879–890. Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham (2023)
Alenezi, M.: Deep dive into digital transformation in higher education institutions. Educ. Sci. 11 (12), 770 (2021)
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Alenezi, M.: Digital learning and digital institution in higher education. Educ. Sci. 13 (1), 88 (2023)
Al-Harthi, A.S.A., Ani, W.T.A.: Learner readiness for MOOCs in Omani higher education institutions: disparities between projections and reality. Educ. Inf. Technol. 28 (1), 303–319 (2023)
Alkaabi, K., Ramadani, V., Zeqiri, J.: Universities, entrepreneurial ecosystem, and family business performance: evidence from the United Arab Emirates. J. Knowl. Econ., 1–28 (2023)
Almahamid, S.M., Ayoub, A.E.A., Al Salah, L.F.: New ways of working scale development and psychometric properties: validation in higher education institutions in the GCC countries. J. Facil. Manag. 21 (3), 453–471 (2023)
Almaiah, M.A., Alfaisal, R., Salloum, S.A., Al-Otaibi, S., Al Sawafi, O.S., Al-Maroof, R.S., Lutfi, A., Alrawad, M., Mulhem, A.A., Awad, A.B.: Determinants influencing the continuous intention to use digital technologies in higher education. Electronics 11 (18), 2827 (2022)
Almaiah, M.A., Alhumaid, K., Aldhuhoori, A., Alnazzawi, N., Aburayya, A., Alfaisal, R., Salloum, S.A., Lutfi, A., Al Mulhem, A., Alkhdour, T., Awad, A.B., Shehab, R.: Factors affecting the adoption of digital information technologies in higher education: an empirical study. Electronics 11 (21), 3572 (2022)
Anthony, B., Kamaludin, A., Romli, A., Raffei, A.F.M., Phon, D.N.A.E., Abdullah, A., Ming, G.L.: Blended learning adoption and implementation in higher education: a theoretical and systematic review. In: Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 1–48 (2022)
Aseeri, M., Kang, K.: Organisational culture and big data socio-technical systems on strategic decision making: case of Saudi Arabian higher education. In: Education and Information Technologies, 1–26 (2023)
Ayoub, A.E.A.H., Almahamid, S.M., Al Salah, L.F.: Innovative work behavior scale: development and validation of psychometric properties in higher education in the GCC countries. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 26 (1), 119–133 (2023)
Ayu, M.: Online learning: leading e-learning at higher education. J. English Literacy Educ. Teach. Learn. English Foreign Lang. 7 (1), 47–54 (2020)
Bhat, S., Antony, J., Maalouf, M., EV, G., Salah, S.: Applications of six sigma for service quality enhancement in the UAE: a multiple case study analysis and lessons learned. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma (2023)
Fakrudeen, M., Rajan, A., Alameri, A.H.M., Almheiri, A.M.L.O.: Assessing higher education websites in the middle east: a comparative analysis of UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar. In: 2023 9th International Conference on Information Technology Trends (ITT), pp. 226–231. IEEE (2023)
Fenech, R., Abdulla, A., Zairi, A., Kinsella, K., Misra, A.: Culture of excellence in academia in the UAE: a model of transformational leadership and leadership development. J. Res. Leadersh. Educ., 19427751231188388 (2023)
Ghamrawi, N., Tamim, M.R.: A typology for digital leadership in higher education: the case of a large-scale mobile technology initiative (using tablets). Educ. Inf. Technol. 28 (6), 7089–7110 (2023)
Islam, M., Mazlan, N.H., Al Murshidi, G., Hoque, M.S., Karthiga, S.V., Reza, M.: UAE university students’ experiences of virtual classroom learning during Covid 19. Smart Learn. Environ. 10 (1), 5 (2023)
Karkouti, I.M.: Integrating technology in Qatar’s higher education settings: what helps faculty accomplish the job. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 28 (1), 279–305 (2023)
Niankara, I.: The impact of financial inclusion on digital payment solution uptake within the Gulf cooperation council economies. Int. J. Innov. Stud. 7 (1), 1–17 (2023)
Shaya, N., Madani, R., Mohebi, L.: An application and extension of the UTAUT model: factors influencing behavioral intention to utilize mobile learning in UAE higher education. J. Interact. Learn. Res. 34 (1), 153–180 (2023)
Shomotova, A., Karabchuk, T.: Transition to online teaching under COVID-19: the case study of UAE University. In: Social Change in the Gulf Region: Multidisciplinary Perspectives, pp. 141–160. Springer Nature Singapore, Singapore (2023)
Siddique, N., Ur Rehman, S., Ahmad, S., Abbas, A., Khan, M.A.: Library and information science research in the Arab world: a bibliometric analysis 1951–2021. Global Knowl. Memory Commun. 72 (1/2), 138–159 (2023)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Ahlia University, Manama, Kingdom of Bahrain
Abdulsadek Hassan, Abdulla Mahdi Hassan & Tariq Mana Ali Al Numis
University of Business and Technology, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Abdulsadek Hassan .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
College of Business of Finance, Ahlia University, Manama, Bahrain
Allam Hamdan
Department of Business Studies, Box Hill College Kuwait, Kuwait, Kuwait
Arezou Harraf
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Hassan, A., Hassan, A.M., Al Numis, T.M.A. (2024). The Quality of Digital Technology in Higher Education: A Case Study from Gulf Universities. In: Hamdan, A., Harraf, A. (eds) Business Development via AI and Digitalization. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control, vol 538. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-62102-4_50
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-62102-4_50
Published : 31 August 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-62101-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-62102-4
eBook Packages : Intelligent Technologies and Robotics Intelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- ₹ 10 Lakh,1" data-value="Loan ₹ 10 Lakh">Loan ₹ 10 Lakh
- Games & Puzzles

- Entertainment
- Latest News
- Telangana Rain Live Updates
- Web Stories
- Mumbai News
- Bengaluru News
- Daily Digest

Amitabh Bachchan’s granddaughter Navya Nanda gets admission in IIM Ahmedabad: ‘Dreams come true’
Amitabh bachchan's granddaughter, navya naveli nanda, took to instagram to share the update that she'll be studying bpgp mba for the next two years..
Navya Naveli Nanda has joined the Indian Institute of Management (IIM) in Ahmedabad and will study BPGP MBA there for the next two years. For the unversed, Navya is Amitabh Bachchan and Jaya Bachchan’s granddaughter and Shweta Bachchan and Nikhil Nanda’s daughter. (Also Read: Shweta Bachchan shuts down rumours of daughter Navya Naveli Nanda’s acting debut )

Navya Nanda at IIM
Navya took to Instagram to share numerous pictures from IIM and write about just how happy she is to be there. She wrote, “Dreams do come true !!!!!! Home for the next 2 years... with the best people & faculty! BPGP MBA Class of 2026.” The first picture she shared shows her dressed in a black suit and standing beside the IIM sign.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Navya Naveli Nanda (@navyananda)
She also shared photos of the lush green campus and the friends she seems to have made there. Navya also shared a picture of her cutting a cake on her Instagram stories, thanking her teacher Prasad for coaching her in cracking the CAT/IAT entrance exams.

Navya not interested in acting
Navya used to host her own podcast - What The Hell Navya - with her grandmother Jaya, and mother, Shweta. They discussed various topics revolving around feminism and the role of women in society. At an event, Shweta clarified that Navya is not interested in following in her grandparents, uncle Abhishek Bachchan, aunt Aishwarya Rai Bachchan or brother Agastya Nanda’s footsteps.
At the event in June, when Shweta was asked if Navya will also act, she replied, “I think you are very well acquainted with the work Navya does and she has her hands full. I don't think Bollywood is the way to go for her.” She was there on behalf of her daughter to accept an award for the podcast.
Navya had also told Hindustan Times in the past, “Well, I also come from a business family too. So, I was very clear that (I don’t want to join acting and do this). At the end of college, I realised that this is what I wanted to do.”
- Navya Nanda
- Navya Naveli
- Navya Naveli Nanda
- Terms of use
- Privacy policy
- Weather Today
- HT Newsletters
- Subscription
- Print Ad Rates
- Code of Ethics
- India vs Sri Lanka
- Live Cricket Score
- Cricket Teams
- Cricket Players
- ICC Rankings
- Cricket Schedule
- Shreyas Iyer
- Harshit Rana
- Kusal Mendis
- Ravi Bishnoi
- Rinku Singh
- Riyan Parag
- Washington Sundar
- Avishka Fernando
- Charith Asalanka
- Dasun Shanaka
- Khaleel Ahmed
- Pathum Nissanka
- Other Cities
- Income Tax Calculator
- Petrol Prices
- Reliance AGM 2024 Live
- Diesel Prices
- Silver Rate
- Relationships
- Art and Culture
- Taylor Swift: A Primer
- Telugu Cinema
- Tamil Cinema
- Board Exams
- Exam Results
- Admission News
- Employment News
- Competitive Exams
- BBA Colleges
- Engineering Colleges
- Medical Colleges
- BCA Colleges
- Medical Exams
- Engineering Exams
- Love Horoscope
- Annual Horoscope
- Festival Calendar
- Compatibility Calculator
- Career Horoscope
- Manifestation
- The Economist Articles
- Lok Sabha States
- Lok Sabha Parties
- Lok Sabha Candidates
- Explainer Video
- On The Record
- Vikram Chandra Daily Wrap
- Entertainment Photos
- Lifestyle Photos
- News Photos
- Olympics 2024
- Olympics Medal Tally
- Other Sports
- EPL 2023-24
- ISL 2023-24
- Asian Games 2023
- Public Health
- Economic Policy
- International Affairs
- Climate Change
- Gender Equality
- future tech
- HT Friday Finance
- Explore Hindustan Times
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Subscription - Terms of Use

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
केस स्टडी विधि (Case-Study Method) शिक्षा तकनीकि के आर्विभाव तथा विकास के साथ शिक्षा की प्रक्रिया में अनेक परिवर्तन हुए तथा नये आयामों ...
Case study in Hindi explained के इस पोस्ट में आप न सिर्फ केस स्टडी के बारे में विस्तार से जानेंगे बल्कि इसके उदाहरणों और प्रकार को भी आप विस्तार से ...
केस स्टडी विधि (Case-Study Method) शिक्षा तकनीकि के आर्विभाव तथा विकास के साथ शिक्षा की प्रक्रिया में अनेक परिवर्तन हुए तथा नये आयामों ...
Download PDF of this Case Study From Here - https://imojo.in/Beingabestteacher32CONTACT SALES EXECUTIVE FOR BOOKS AND NOTES AT - https://wa.me/message/AI3GER...
What Is Case Study Method In Hindi? PDF Download, व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन , मामले का अध्ययन, केस स्टडी आदि के बारे में जानेंगे। इन नोट्स के माध्यम से आपके ज्ञान में
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Exam TrickyCase Study Method In Hindi |l,वैयक्तिक अध्ययन विधि , D.Ed SE (I.D) || 🔴 Join Our Telegram Channel - https://t.me ...
Case Study Format in Hindi. दोस्तों अगर आप Case Study ka Prarup hindi में खोज रहे है तो आप बिलकुल सही जगह पर आये है, क्योंकि आज हमने इस पेज के माध्यम से केस स्टडी का ...
Read this article in Hindi to learn about:- 1. Meaning of Case Study 2. Characteristics of Case Study 3. Sources of Information 4. Merits 5. Limitations. Contents: व्यक्तिगत अध्ययन पद्धति का अर्थ (Meaning of Case Study) वैयक्तिक अध्ययन पद्धति की विशेषताएँ (Characteristics of Case ...
A case study is an in-depth, detailed examination of a particular case within a real-world context. For example, case studies in medicine may focus on an individual patient or ailment; case studies in business might cover a particular firm's strategy or a broader market; similarly, case studies in politics can range from a narrow happening over time like the operations of a specific political ...
शिक्षा. शिक्षा का मतलब ज्ञान,सदाचार,उचित आचरण,तकनीकी शिक्षा तकनीकी दक्षता, विद्या आदि को प्राप्त करने की प्रक्रिया को कहते हैं। डा0 ...
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
case-sensitive. cash. cashier. 'C' से शुरू होने वाले सभी अंग्रेजी शब्द. CASE STUDY का हिन्दी अनुवाद |। आधिकारिक कोलिन्स अंग्रेज़ी-हिन्दी शब्दकोश ऑनलाइन। 100,000 से ...
This report constitutes a qualitative case study aimed at understanding the major challenges faced by students of Hindi-medium in institutions of higher learning in general, and in three Central ...
#casestudymethodinhindi #TerminologiesJunction #terminologiesjunction #casestudymethod, Es Video mein aap dekhenge Case Study Method ke bare mein simplify ta...
A case study is a detailed description and assessment of a specific situation in the real world, often for the purpose of deriving generalizations and other insights about the subject of the case study. Case studies can be about an individual, a group of people, an organization, or an event, and they are used in multiple fields, including business, health care, anthropology, political science ...
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
Case study in urdu/Hindi| methods of psychology |By dear knowledgeExperimental Method & Case Study History Method || Urdu / HindiCASE STUDY Reading, Understa...
5. Build Your Self-Confidence. Finally, learning through the case study method can build your confidence. Each time you assume a business leader's perspective, aim to solve a new challenge, and express and defend your opinions and decisions to peers, you prepare to do the same in your career. According to a 2022 City Square Associates survey ...
A case study is an in-depth, detailed examination of a particular case (or cases) within a real-world context. [1] [2] For example, case studies in medicine may focus on an individual patient or ailment; case studies in business might cover a particular firm's strategy or a broader market; similarly, case studies in politics can range from a narrow happening over time like the operations of a ...
ऑनलाइन शिक्षा की प्रक्रिया का एक और लाभ यह भी है कि इसमे कागजों का उपयोग बहुत कम हो जाता है। क्लासरूम प्रणाली की अपेक्षा डिजिटल ...
Google's service, offered free of charge, instantly translates words, phrases, and web pages between English and over 100 other languages.
Cognition: Mental processes involved in gaining knowledge and comprehension, including thinking, knowing, remembering, judging, and problem-solving. Psychoanalysis: A therapy developed aimed at exploring the unconscious mind to understand and treat psychological disorders. Positive Reinforcement: In behaviorism, the process of encouraging or establishing a pattern of behavior by offering a ...
Sharada Vidyanikethana Public School is one of the schools providing value -based education with. modern facilities in reaching the demands of young student's genera tion in India. This school ...
Distance education: It is defined in the UNESCO Guide for Policymakers in Academic, Vocational and Technical Education (2020) as the process of transferring knowledge to the educational institution, and it is built on the basis of delivering knowledge [].The learner is transferred to his place of residence or work instead of the learner moving away or separately from the teacher through ...
What is case study (in Hindi) Lesson 6 of 10 • 52 upvotes • 12:20mins. Sunil Singh. Ethics Integrity and Aptitude - - Case study introduction /what is case study. Continue on app (Hindi) Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude With Case Study Strategy: UPSC. 10 lessons • 2h 10m . 1.
case study hindi.pdf - Free download as PDF File (.pdf) or read online for free.
Navya Naveli Nanda has joined the Indian Institute of Management (IIM) in Ahmedabad and will study BPGP MBA there for the next two years. For the unversed, Navya is Amitabh Bachchan and Jaya ...