- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Questions
Definition:
Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
Types of Research Questions
Types of Research Questions are as follows:
Descriptive Research Questions
These aim to describe a particular phenomenon, group, or situation. For example:
- What are the characteristics of the target population?
- What is the prevalence of a particular disease in a specific region?
Exploratory Research Questions
These aim to explore a new area of research or generate new ideas or hypotheses. For example:
- What are the potential causes of a particular phenomenon?
- What are the possible outcomes of a specific intervention?
Explanatory Research Questions
These aim to understand the relationship between two or more variables or to explain why a particular phenomenon occurs. For example:
- What is the effect of a specific drug on the symptoms of a particular disease?
- What are the factors that contribute to employee turnover in a particular industry?
Predictive Research Questions
These aim to predict a future outcome or trend based on existing data or trends. For example :
- What will be the future demand for a particular product or service?
- What will be the future prevalence of a particular disease?
Evaluative Research Questions
These aim to evaluate the effectiveness of a particular intervention or program. For example:
- What is the impact of a specific educational program on student learning outcomes?
- What is the effectiveness of a particular policy or program in achieving its intended goals?
How to Choose Research Questions
Choosing research questions is an essential part of the research process and involves careful consideration of the research problem, objectives, and design. Here are some steps to consider when choosing research questions:
- Identify the research problem: Start by identifying the problem or issue that you want to study. This could be a gap in the literature, a social or economic issue, or a practical problem that needs to be addressed.
- Conduct a literature review: Conducting a literature review can help you identify existing research in your area of interest and can help you formulate research questions that address gaps or limitations in the existing literature.
- Define the research objectives : Clearly define the objectives of your research. What do you want to achieve with your study? What specific questions do you want to answer?
- Consider the research design : Consider the research design that you plan to use. This will help you determine the appropriate types of research questions to ask. For example, if you plan to use a qualitative approach, you may want to focus on exploratory or descriptive research questions.
- Ensure that the research questions are clear and answerable: Your research questions should be clear and specific, and should be answerable with the data that you plan to collect. Avoid asking questions that are too broad or vague.
- Get feedback : Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, feasible, and meaningful.
How to Write Research Questions
Guide for Writing Research Questions:
- Start with a clear statement of the research problem: Begin by stating the problem or issue that your research aims to address. This will help you to formulate focused research questions.
- Use clear language : Write your research questions in clear and concise language that is easy to understand. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that may be unfamiliar to your readers.
- Be specific: Your research questions should be specific and focused. Avoid broad questions that are difficult to answer. For example, instead of asking “What is the impact of climate change on the environment?” ask “What are the effects of rising sea levels on coastal ecosystems?”
- Use appropriate question types: Choose the appropriate question types based on the research design and objectives. For example, if you are conducting a qualitative study, you may want to use open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed responses.
- Consider the feasibility of your questions : Ensure that your research questions are feasible and can be answered with the resources available. Consider the data sources and methods of data collection when writing your questions.
- Seek feedback: Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, appropriate, and meaningful.
Examples of Research Questions
Some Examples of Research Questions with Research Titles:
Research Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- Research Question : What is the relationship between social media use and mental health, and how does this impact individuals’ well-being?
Research Title: Factors Influencing Academic Success in High School
- Research Question: What are the primary factors that influence academic success in high school, and how do they contribute to student achievement?
Research Title: The Effects of Exercise on Physical and Mental Health
- Research Question: What is the relationship between exercise and physical and mental health, and how can exercise be used as a tool to improve overall well-being?
Research Title: Understanding the Factors that Influence Consumer Purchasing Decisions
- Research Question : What are the key factors that influence consumer purchasing decisions, and how do these factors vary across different demographics and products?
Research Title: The Impact of Technology on Communication
- Research Question : How has technology impacted communication patterns, and what are the effects of these changes on interpersonal relationships and society as a whole?
Research Title: Investigating the Relationship between Parenting Styles and Child Development
- Research Question: What is the relationship between different parenting styles and child development outcomes, and how do these outcomes vary across different ages and developmental stages?
Research Title: The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy in Treating Anxiety Disorders
- Research Question: How effective is cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders, and what factors contribute to its success or failure in different patients?
Research Title: The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity
- Research Question : How is climate change affecting global biodiversity, and what can be done to mitigate the negative effects on natural ecosystems?
Research Title: Exploring the Relationship between Cultural Diversity and Workplace Productivity
- Research Question : How does cultural diversity impact workplace productivity, and what strategies can be employed to maximize the benefits of a diverse workforce?
Research Title: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Research Question: How can artificial intelligence be leveraged to improve healthcare outcomes, and what are the potential risks and ethical concerns associated with its use?
Applications of Research Questions
Here are some of the key applications of research questions:
- Defining the scope of the study : Research questions help researchers to narrow down the scope of their study and identify the specific issues they want to investigate.
- Developing hypotheses: Research questions often lead to the development of hypotheses, which are testable predictions about the relationship between variables. Hypotheses provide a clear and focused direction for the study.
- Designing the study : Research questions guide the design of the study, including the selection of participants, the collection of data, and the analysis of results.
- Collecting data : Research questions inform the selection of appropriate methods for collecting data, such as surveys, interviews, or experiments.
- Analyzing data : Research questions guide the analysis of data, including the selection of appropriate statistical tests and the interpretation of results.
- Communicating results : Research questions help researchers to communicate the results of their study in a clear and concise manner. The research questions provide a framework for discussing the findings and drawing conclusions.
Characteristics of Research Questions
Characteristics of Research Questions are as follows:
- Clear and Specific : A good research question should be clear and specific. It should clearly state what the research is trying to investigate and what kind of data is required.
- Relevant : The research question should be relevant to the study and should address a current issue or problem in the field of research.
- Testable : The research question should be testable through empirical evidence. It should be possible to collect data to answer the research question.
- Concise : The research question should be concise and focused. It should not be too broad or too narrow.
- Feasible : The research question should be feasible to answer within the constraints of the research design, time frame, and available resources.
- Original : The research question should be original and should contribute to the existing knowledge in the field of research.
- Significant : The research question should have significance and importance to the field of research. It should have the potential to provide new insights and knowledge to the field.
- Ethical : The research question should be ethical and should not cause harm to any individuals or groups involved in the study.
Purpose of Research Questions
Research questions are the foundation of any research study as they guide the research process and provide a clear direction to the researcher. The purpose of research questions is to identify the scope and boundaries of the study, and to establish the goals and objectives of the research.
The main purpose of research questions is to help the researcher to focus on the specific area or problem that needs to be investigated. They enable the researcher to develop a research design, select the appropriate methods and tools for data collection and analysis, and to organize the results in a meaningful way.
Research questions also help to establish the relevance and significance of the study. They define the research problem, and determine the research methodology that will be used to address the problem. Research questions also help to determine the type of data that will be collected, and how it will be analyzed and interpreted.
Finally, research questions provide a framework for evaluating the results of the research. They help to establish the validity and reliability of the data, and provide a basis for drawing conclusions and making recommendations based on the findings of the study.
Advantages of Research Questions
There are several advantages of research questions in the research process, including:
- Focus : Research questions help to focus the research by providing a clear direction for the study. They define the specific area of investigation and provide a framework for the research design.
- Clarity : Research questions help to clarify the purpose and objectives of the study, which can make it easier for the researcher to communicate the research aims to others.
- Relevance : Research questions help to ensure that the study is relevant and meaningful. By asking relevant and important questions, the researcher can ensure that the study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge and address important issues.
- Consistency : Research questions help to ensure consistency in the research process by providing a framework for the development of the research design, data collection, and analysis.
- Measurability : Research questions help to ensure that the study is measurable by defining the specific variables and outcomes that will be measured.
- Replication : Research questions help to ensure that the study can be replicated by providing a clear and detailed description of the research aims, methods, and outcomes. This makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study and verify the results.
Limitations of Research Questions
Limitations of Research Questions are as follows:
- Subjectivity : Research questions are often subjective and can be influenced by personal biases and perspectives of the researcher. This can lead to a limited understanding of the research problem and may affect the validity and reliability of the study.
- Inadequate scope : Research questions that are too narrow in scope may limit the breadth of the study, while questions that are too broad may make it difficult to focus on specific research objectives.
- Unanswerable questions : Some research questions may not be answerable due to the lack of available data or limitations in research methods. In such cases, the research question may need to be rephrased or modified to make it more answerable.
- Lack of clarity : Research questions that are poorly worded or ambiguous can lead to confusion and misinterpretation. This can result in incomplete or inaccurate data, which may compromise the validity of the study.
- Difficulty in measuring variables : Some research questions may involve variables that are difficult to measure or quantify, making it challenging to draw meaningful conclusions from the data.
- Lack of generalizability: Research questions that are too specific or limited in scope may not be generalizable to other contexts or populations. This can limit the applicability of the study’s findings and restrict its broader implications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Research Summary – Structure, Examples and...

Background of The Study – Examples and Writing...

Significance of the Study – Examples and Writing...

Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write a Research Question

Academic writing and research require a distinct focus and direction. A well-designed research question gives purpose and clarity to your research. In addition, it helps your readers understand the issue you are trying to address and explore.
Every time you want to know more about a subject, you will pose a question. The same idea is used in research as well. You must pose a question in order to effectively address a research problem. That's why the research question is an integral part of the research process. Additionally, it offers the author writing and reading guidelines, be it qualitative research or quantitative research.
In your research paper , you must single out just one issue or problem. The specific issue or claim you wish to address should be included in your thesis statement in order to clarify your main argument.
A good research question must have the following characteristics.

- Should include only one problem in the research question
- Should be able to find the answer using primary data and secondary data sources
- Should be possible to resolve within the given time and other constraints
- Detailed and in-depth results should be achievable
- Should be relevant and realistic.
- It should relate to your chosen area of research
While a larger project, like a thesis, might have several research questions to address, each one should be directed at your main area of study. Of course, you can use different research designs and research methods (qualitative research or quantitative research) to address various research questions. However, they must all be pertinent to the study's objectives.
What is a Research Question?

A research question is an inquiry that the research attempts to answer. It is the heart of the systematic investigation. Research questions are the most important step in any research project. In essence, it initiates the research project and establishes the pace for the specific research A research question is:
- Clear : It provides enough detail that the audience understands its purpose without any additional explanation.
- Focused : It is so specific that it can be addressed within the time constraints of the writing task.
- Succinct: It is written in the shortest possible words.
- Complex : It is not possible to answer it with a "yes" or "no", but requires analysis and synthesis of ideas before somebody can create a solution.
- Argumental : Its potential answers are open for debate rather than accepted facts.
A good research question usually focuses on the research and determines the research design, methodology, and hypothesis. It guides all phases of inquiry, data collection, analysis, and reporting. You should gather valuable information by asking the right questions.
Why are Research Questions so important?
Regardless of whether it is a qualitative research or quantitative research project, research questions provide writers and their audience with a way to navigate the writing and research process. Writers can avoid "all-about" papers by asking straightforward and specific research questions that help them focus on their research and support a specific thesis.
Types of Research Questions

There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research . There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection.
The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused research question.
Below is a list of common research questions that can be used in a dissertation. Keep in mind that these are merely illustrations of typical research questions used in dissertation projects. The real research questions themselves might be more difficult.
Research Question Type | Question |
Descriptive | What are the properties of A? |
Comparative | What are the similarities and distinctions between A and B? |
Correlational | What can you do to correlate variables A and B? |
Exploratory | What factors affect the rate of C's growth? Are A and B also influencing C? |
Explanatory | What are the causes for C? What does A do to B? What's causing D? |
Evaluation | What is the impact of C? What role does B have? What are the benefits and drawbacks of A? |
Action-Based | What can you do to improve X? |
Example Research Questions

The following are a few examples of research questions and research problems to help you understand how research questions can be created for a particular research problem.
Problem | Question |
Due to poor revenue collection, a small-sized company ('A') in the UK cannot allocate a marketing budget next year. | What practical steps can the company take to increase its revenue? |
Many graduates are now working as freelancers even though they have degrees from well-respected academic institutions. But what's the reason these young people choose to work in this field? | Why do fresh graduates choose to work for themselves rather than full-time? What are the benefits and drawbacks of the gig economy? What do age, gender, and academic qualifications do with people's perceptions of freelancing? |
Steps to Write Research Questions

You can focus on the issue or research gaps you're attempting to solve by using the research questions as a direction.
If you're unsure how to go about writing a good research question, these are the steps to follow in the process:
- Select an interesting topic Always choose a topic that interests you. Because if your curiosity isn’t aroused by a subject, you’ll have a hard time conducting research around it. Alos, it’s better that you pick something that’s neither too narrow or too broad.
- Do preliminary research on the topic Search for relevant literature to gauge what problems have already been tackled by scholars. You can do that conveniently through repositories like Scispace , where you’ll find millions of papers in one place. Once you do find the papers you’re looking for, try our reading assistant, SciSpace Copilot to get simple explanations for the paper . You’ll be able to quickly understand the abstract, find the key takeaways, and the main arguments presented in the paper. This will give you a more contextual understanding of your subject and you’ll have an easier time identifying knowledge gaps in your discipline.
Also: ChatPDF vs. SciSpace Copilot: Unveiling the best tool for your research
- Consider your audience It is essential to understand your audience to develop focused research questions for essays or dissertations. When narrowing down your topic, you can identify aspects that might interest your audience.
- Ask questions Asking questions will give you a deeper understanding of the topic. Evaluate your question through the What, Why, When, How, and other open-ended questions assessment.
- Assess your question Once you have created a research question, assess its effectiveness to determine if it is useful for the purpose. Refine and revise the dissertation research question multiple times.
Additionally, use this list of questions as a guide when formulating your research question.
Are you able to answer a specific research question? After identifying a gap in research, it would be helpful to formulate the research question. And this will allow the research to solve a part of the problem. Is your research question clear and centered on the main topic? It is important that your research question should be specific and related to your central goal. Are you tackling a difficult research question? It is not possible to answer the research question with a simple yes or no. The problem requires in-depth analysis. It is often started with "How" and "Why."
Start your research Once you have completed your dissertation research questions, it is time to review the literature on similar topics to discover different perspectives.
Strong Research Question Samples
Uncertain: How should social networking sites work on the hatred that flows through their platform?
Certain: What should social media sites like Twitter or Facebook do to address the harm they are causing?
This unclear question does not specify the social networking sites that are being used or what harm they might be causing. In addition, this question assumes that the "harm" has been proven and/or accepted. This version is more specific and identifies the sites (Twitter, Facebook), the type and extent of harm (privacy concerns), and who might be suffering from that harm (users). Effective research questions should not be ambiguous or interpreted.
Unfocused: What are the effects of global warming on the environment?
Focused: What are the most important effects of glacial melting in Antarctica on penguins' lives?
This broad research question cannot be addressed in a book, let alone a college-level paper. Focused research targets a specific effect of global heating (glacial melting), an area (Antarctica), or a specific animal (penguins). The writer must also decide which effect will have the greatest impact on the animals affected. If in doubt, narrow down your research question to the most specific possible.
Too Simple: What are the U.S. doctors doing to treat diabetes?
Appropriately complex: Which factors, if any, are most likely to predict a person's risk of developing diabetes?
This simple version can be found online. It is easy to answer with a few facts. The second, more complicated version of this question is divided into two parts. It is thought-provoking and requires extensive investigation as well as evaluation by the author. So, ensure that a quick Google search should not answer your research question.
How to write a strong Research Question?

The foundation of all research is the research question. You should therefore spend as much time as necessary to refine your research question based on various data.
You can conduct your research more efficiently and analyze your results better if you have great research questions for your dissertation, research paper , or essay .
The following criteria can help you evaluate the strength and importance of your research question and can be used to determine the strength of your research question:
- Researchable
- It should only cover one issue.
- A subjective judgment should not be included in the question.
- It can be answered with data analysis and research.
- Specific and Practical
- It should not contain a plan of action, policy, or solution.
- It should be clearly defined
- Within research limits
- Complex and Arguable
- It shouldn't be difficult to answer.
- To find the truth, you need in-depth knowledge
- Allows for discussion and deliberation
- Original and Relevant
- It should be in your area of study
- Its results should be measurable
- It should be original
Conclusion - How to write Research Questions?
Research questions provide a clear guideline for research. One research question may be part of a larger project, such as a dissertation. However, each question should only focus on one topic.
Research questions must be answerable, practical, specific, and applicable to your field. The research type that you use to base your research questions on will determine the research topic. You can start by selecting an interesting topic and doing preliminary research. Then, you can begin asking questions, evaluating your questions, and start your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace ResearchGPT . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, read, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)

Research Question Examples 🧑🏻🏫
25+ Practical Examples & Ideas To Help You Get Started
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | October 2023
A well-crafted research question (or set of questions) sets the stage for a robust study and meaningful insights. But, if you’re new to research, it’s not always clear what exactly constitutes a good research question. In this post, we’ll provide you with clear examples of quality research questions across various disciplines, so that you can approach your research project with confidence!
Research Question Examples
- Psychology research questions
- Business research questions
- Education research questions
- Healthcare research questions
- Computer science research questions
Examples: Psychology
Let’s start by looking at some examples of research questions that you might encounter within the discipline of psychology.
How does sleep quality affect academic performance in university students?
This question is specific to a population (university students) and looks at a direct relationship between sleep and academic performance, both of which are quantifiable and measurable variables.
What factors contribute to the onset of anxiety disorders in adolescents?
The question narrows down the age group and focuses on identifying multiple contributing factors. There are various ways in which it could be approached from a methodological standpoint, including both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Do mindfulness techniques improve emotional well-being?
This is a focused research question aiming to evaluate the effectiveness of a specific intervention.
How does early childhood trauma impact adult relationships?
This research question targets a clear cause-and-effect relationship over a long timescale, making it focused but comprehensive.
Is there a correlation between screen time and depression in teenagers?
This research question focuses on an in-demand current issue and a specific demographic, allowing for a focused investigation. The key variables are clearly stated within the question and can be measured and analysed (i.e., high feasibility).

Examples: Business/Management
Next, let’s look at some examples of well-articulated research questions within the business and management realm.
How do leadership styles impact employee retention?
This is an example of a strong research question because it directly looks at the effect of one variable (leadership styles) on another (employee retention), allowing from a strongly aligned methodological approach.
What role does corporate social responsibility play in consumer choice?
Current and precise, this research question can reveal how social concerns are influencing buying behaviour by way of a qualitative exploration.
Does remote work increase or decrease productivity in tech companies?
Focused on a particular industry and a hot topic, this research question could yield timely, actionable insights that would have high practical value in the real world.
How do economic downturns affect small businesses in the homebuilding industry?
Vital for policy-making, this highly specific research question aims to uncover the challenges faced by small businesses within a certain industry.
Which employee benefits have the greatest impact on job satisfaction?
By being straightforward and specific, answering this research question could provide tangible insights to employers.
Examples: Education
Next, let’s look at some potential research questions within the education, training and development domain.
How does class size affect students’ academic performance in primary schools?
This example research question targets two clearly defined variables, which can be measured and analysed relatively easily.
Do online courses result in better retention of material than traditional courses?
Timely, specific and focused, answering this research question can help inform educational policy and personal choices about learning formats.
What impact do US public school lunches have on student health?
Targeting a specific, well-defined context, the research could lead to direct changes in public health policies.
To what degree does parental involvement improve academic outcomes in secondary education in the Midwest?
This research question focuses on a specific context (secondary education in the Midwest) and has clearly defined constructs.
What are the negative effects of standardised tests on student learning within Oklahoma primary schools?
This research question has a clear focus (negative outcomes) and is narrowed into a very specific context.
Need a helping hand?
Examples: Healthcare
Shifting to a different field, let’s look at some examples of research questions within the healthcare space.
What are the most effective treatments for chronic back pain amongst UK senior males?
Specific and solution-oriented, this research question focuses on clear variables and a well-defined context (senior males within the UK).
How do different healthcare policies affect patient satisfaction in public hospitals in South Africa?
This question is has clearly defined variables and is narrowly focused in terms of context.
Which factors contribute to obesity rates in urban areas within California?
This question is focused yet broad, aiming to reveal several contributing factors for targeted interventions.
Does telemedicine provide the same perceived quality of care as in-person visits for diabetes patients?
Ideal for a qualitative study, this research question explores a single construct (perceived quality of care) within a well-defined sample (diabetes patients).
Which lifestyle factors have the greatest affect on the risk of heart disease?
This research question aims to uncover modifiable factors, offering preventive health recommendations.

Examples: Computer Science
Last but certainly not least, let’s look at a few examples of research questions within the computer science world.
What are the perceived risks of cloud-based storage systems?
Highly relevant in our digital age, this research question would align well with a qualitative interview approach to better understand what users feel the key risks of cloud storage are.
Which factors affect the energy efficiency of data centres in Ohio?
With a clear focus, this research question lays a firm foundation for a quantitative study.
How do TikTok algorithms impact user behaviour amongst new graduates?
While this research question is more open-ended, it could form the basis for a qualitative investigation.
What are the perceived risk and benefits of open-source software software within the web design industry?
Practical and straightforward, the results could guide both developers and end-users in their choices.
Remember, these are just examples…
In this post, we’ve tried to provide a wide range of research question examples to help you get a feel for what research questions look like in practice. That said, it’s important to remember that these are just examples and don’t necessarily equate to good research topics . If you’re still trying to find a topic, check out our topic megalist for inspiration.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Research ideas on Political Science
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Craft a Strong Research Question (With Research Question Examples)
A sound and effective research question is a key element that must be identified and pinned down before researchers can even begin their research study or work. A strong research question lays the foundation for your entire study, guiding your investigation and shaping your findings. Hence, it is critical that researchers spend considerable time assessing and refining the research question based on in-depth reading and comprehensive literature review. In this article, we will discuss how to write a strong research question and provide you with some good examples of research questions across various disciplines.
Table of Contents
The importance of a research question
A research question plays a crucial role in driving scientific inquiry, setting the direction and purpose of your study, and guiding your entire research process. By formulating a clear and focused research question, you lay the foundation for your investigation, ensuring that your research remains on track and aligned with your objectives so you can make meaningful contribution to the existing body of knowledge. A well-crafted research question also helps you define the scope of your study and identify the appropriate methodologies and data collection techniques to employ.
Key components of a strong research question
A good research question possesses several key components that contribute to the quality and impact of your study. Apart from providing a clear framework to generate meaningful results, a well-defined research question allows other researchers to understand the purpose and significance of your work. So, when working on your research question, incorporate the following elements:
- Specificity : A strong research question should be specific about the main focus of your study, enabling you to gather precise data and draw accurate conclusions. It clearly defines the variables, participants, and context involved, leaving no room for ambiguity.
- Clarity : A good research question is clear and easily understood, so articulate the purpose and intent of your study concisely without being generic or vague. Ensuring clarity in your research question helps both you and your readers grasp the research objective.
- Feasibility : While crafting a research question, consider the practicality of conducting the research and availability of necessary data or access to participants. Think whether your study is realistic and achievable within the constraints of time, resources, and ethical considerations.
How to craft a well-defined research question
A first step that will help save time and effort is knowing what your aims are and thinking about a few problem statements on the area or aspect one wants to study or do research on. Contemplating these statements as one undertakes more progressive reading can help the researcher in reassessing and fine-tuning the research question. This can be done over time as they read and learn more about the research topic, along with a broad literature review and parallel discussions with peer researchers and supervisors. In some cases, a researcher can have more than one research question if the research being undertaken is a PhD thesis or dissertation, but try not to cover multiple concerns on a topic.
A strong research question must be researchable, original, complex, and relevant. Here are five simple steps that can make the entire process easier.
- Identify a broad topic from your areas of interest, something that is relevant, and you are passionate about since you’ll be spending a lot of time conducting your research.
- Do a thorough literature review to weed out potential gaps in research and stay updated on what’s currently being done in your chosen topic and subject area.
- Shortlist possible research questions based on the research gaps or see how you can build on or refute previously published ideas and concepts.
- Assess your chosen research question using the FINER criteria that helps you evaluate whether the research is Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant. 1
- Formulate the final research question, while ensuring it is clear, well-written, and addresses all the key elements of a strong research question.
Examples of research questions
Remember to adapt your research question to suit your purpose, whether it’s exploratory, descriptive, comparative, experimental, qualitative, or quantitative. Embrace the iterative nature of the research process, continually evaluating and refining your question as you progress. Here are some good examples of research questions across various disciplines.
Exploratory research question examples
- How does social media impact interpersonal relationships among teenagers?
- What are the potential benefits of incorporating mindfulness practices in the workplace?
Descriptive research question examples
- What factors influence customer loyalty in the e-commerce industry?
- Is there a relationship between socioeconomic status and academic performance among elementary school students?
Comparative research question examples
- How does the effectiveness of traditional teaching methods compare to online learning platforms in mathematics education?
- What is the impact of different healthcare policies on patient outcomes in various countries?
Experimental research question examples
- What are the effects of a new drug on reducing symptoms of a specific medical condition?
- Does a dietary intervention have an impact on weight loss among individuals with obesity?
Qualitative research question examples
- What are the lived experiences of immigrants adapting to a new culture?
- What factors influence job satisfaction among healthcare professionals?
Quantitative research question examples
- Is there a relationship between sleep duration and academic performance among college students?
- How effective is a specific intervention in reducing anxiety levels among individuals with phobias?
With these simple guidelines and inspiring examples of research questions, you are equipped to embark on your research journey with confidence and purpose. Here’s wishing you all the best for your future endeavors!
References:
- How to write a research question: Steps and examples. Indeed Career Guide. Available online at https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-research-questions
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

What are Experimental Groups in Research

What is a Review Article? How to Write it?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 December 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
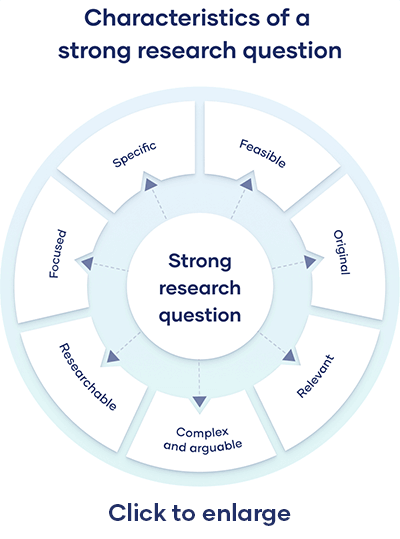
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, research questions quiz, frequently asked questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
| Research question formulations | |
|---|---|
| Describing and exploring | |
| Explaining and testing | |
| Evaluating and acting |
Using your research problem to develop your research question
| Example research problem | Example research question(s) |
|---|---|
| Teachers at the school do not have the skills to recognize or properly guide gifted children in the classroom. | What practical techniques can teachers use to better identify and guide gifted children? |
| Young people increasingly engage in the ‘gig economy’, rather than traditional full-time employment. However, it is unclear why they choose to do so. | What are the main factors influencing young people’s decisions to engage in the gig economy? |
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Focused on a single topic | Your central research question should work together with your research problem to keep your work focused. If you have multiple questions, they should all clearly tie back to your central aim. |
| Answerable using | Your question must be answerable using and/or , or by reading scholarly sources on the topic to develop your argument. If such data is impossible to access, you likely need to rethink your question. |
| Not based on value judgements | Avoid subjective words like , , and . These do not give clear criteria for answering the question. |
Feasible and specific
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Answerable within practical constraints | Make sure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific. |
| Uses specific, well-defined concepts | All the terms you use in the research question should have clear meanings. Avoid vague language, jargon, and too-broad ideas. |
| Does not demand a conclusive solution, policy, or course of action | Research is about informing, not instructing. Even if your project is focused on a practical problem, it should aim to improve understanding rather than demand a ready-made solution. |
Complex and arguable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cannot be answered with or | Closed-ended, / questions are too simple to work as good research questions—they don’t provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. |
| Cannot be answered with easily-found facts | If you can answer the question through a single Google search, book, or article, it is probably not complex enough. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation prior to providing an answer. |
Relevant and original
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Addresses a relevant problem | Your research question should be developed based on initial reading around your . It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline. |
| Contributes to a timely social or academic debate | The question should aim to contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on. |
| Has not already been answered | You don’t have to ask something that nobody has ever thought of before, but your question should have some aspect of originality. For example, you can focus on a specific location, or explore a new angle. |
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarised in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, December 12). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 12 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-question/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, how to write a results section | tips & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
How to write a research question
Last updated
7 February 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
In this article, we take an in-depth look at what a research question is, the different types of research questions, and how to write one (with examples). Read on to get started with your thesis, dissertation, or research paper .
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is a research question?
A research question articulates exactly what you want to learn from your research. It stems directly from your research objectives, and you will arrive at an answer through data analysis and interpretation.
However, it is not that simple to write a research question—even when you know the question you intend to answer with your study. The main characteristics of a good research question are:
Feasible. You need to have the resources and abilities to examine the question, collect the data, and give answers.
Interesting. Create research questions that offer fascinating insights into your industry.
Novel. Research questions have to offer something new within your field of study.
Ethical. The research question topic should be approved by the relevant authorities and review boards.
Relevant. Your research question should lead to visible changes in society or your industry.
Usually, you write one single research question to guide your entire research paper. The answer becomes the thesis statement—the central position of your argument. A dissertation or thesis, on the other hand, may require multiple problem statements and research questions. However, they should be connected and focused on a specific problem.
- Importance of the research question
A research question acts as a guide for your entire study. It serves two vital purposes:
to determine the specific issue your research paper addresses
to identify clear objectives
Therefore, it helps split your research into small steps that you need to complete to provide answers.
Your research question will also provide boundaries for your study, which help set limits and ensure cohesion.
Finally, it acts as a frame of reference for assessing your work. Bear in mind that research questions can evolve, shift, and change during the early stages of your study or project.
- Types of research questions
The type of research you are conducting will dictate the type of research question to use. Primarily, research questions are grouped into three distinct categories of study:
qualitative
quantitative
mixed-method
Let’s look at each of these in turn:
Quantitative research questions
The number-one rule of quantitative research questions is that they are precise. They mainly include:
independent and dependent variables
the exact population being studied
the research design to be used
Therefore, you must frame and finalize quantitative research questions before starting the study.
Equally, a quantitative research question creates a link between itself and the research design. These questions cannot be answered with simple 'yes' or' no' responses, so they begin with words like 'does', 'do', 'are', and 'is'.
Quantitative research questions can be divided into three categories:
Relationship research questions usually leverage words such as 'trends' and 'association' because they include independent and dependent variables. They seek to define or explore trends and interactions between multiple variables.
Comparative research questions tend to analyze the differences between different groups to find an outcome variable. For instance, you may decide to compare two distinct groups where a specific variable is present in one and absent in the other.
Descriptive research questions usually start with the word 'what' and aim to measure how a population will respond to one or more variables.
Qualitative research questions
Like quantitative research questions, these questions are linked to the research design. However, qualitative research questions may deal with a specific or broad study area. This makes them more flexible, very adaptable, and usually non-directional.
Use qualitative research questions when your primary aim is to explain, discover, or explore.
There are seven types of qualitative research questions:
Explanatory research questions investigate particular topic areas that aren't well known.
Contextual research questions describe the workings of what is already in existence.
Evaluative research questions examine the effectiveness of specific paradigms or methods.
Ideological research questions aim to advance existing ideologies.
Descriptive research questions describe an event.
Generative research questions help develop actions and theories by providing new ideas.
Emancipatory research questions increase social action engagement, usually to benefit disadvantaged people.
Mixed-methods studies
With mixed-methods studies, you combine qualitative and quantitative research elements to get answers to your research question. This approach is ideal when you need a more complete picture. through a blend of the two approaches.
Mixed-methods research is excellent in multidisciplinary settings, societal analysis, and complex situations. Consider the following research question examples, which would be ideal candidates for a mixed-methods approach
How can non-voter and voter beliefs about democracy (qualitative) help explain Town X election turnout patterns (quantitative)?
How does students’ perception of their study environment (quantitative) relate to their test score differences (qualitative)?
- Developing a strong research question—a step-by-step guide
Research questions help break up your study into simple steps so you can quickly achieve your objectives and find answers. However, how do you develop a good research question? Here is our step-by-step guide:
1. Choose a topic
The first step is to select a broad research topic for your study. Pick something within your expertise and field that interests you. After all, the research itself will stem from the initial research question.
2. Conduct preliminary research
Once you have a broad topic, dig deeper into the problem by researching past studies in the field and gathering requirements from stakeholders if you work in a business setting.
Through this process, you will discover articles that mention areas not explored in that field or products that didn’t resonate with people’s expectations in a particular industry. For instance, you could explore specific topics that earlier research failed to study or products that failed to meet user needs.
3. Keep your audience in mind
Is your audience interested in the particular field you want to study? Are the research questions in your mind appealing and interesting to the audience? Defining your audience will help you refine your research question and ensure you pick a question that is relatable to your audience.
4. Generate a list of potential questions
Ask yourself numerous open-ended questions on the topic to create a potential list of research questions. You could start with broader questions and narrow them down to more specific ones. Don’t forget that you can challenge existing assumptions or use personal experiences to redefine research issues.
5. Review the questions
Evaluate your list of potential questions to determine which seems most effective. Ensure you consider the finer details of every question and possible outcomes. Doing this helps you determine if the questions meet the requirements of a research question.
6. Construct and evaluate your research question
Consider these two frameworks when constructing a good research question: PICOT and PEO.
PICOT stands for:
P: Problem or population
I: Indicator or intervention to be studied
C: Comparison groups
O: Outcome of interest
T: Time frame
PEO stands for:
P: Population being studied
E: Exposure to any preexisting conditions
To evaluate your research question once you’ve constructed it, ask yourself the following questions:
Is it clear?
Your study should produce precise data and observations. For qualitative studies, the observations need to be delineable across categories. Quantitative studies must have measurable and empirical data.
Is it specific and focused?
An excellent research question must be specific enough to ensure your testing yields objective results. General or open-ended research questions are often ambiguous and subject to different kinds of interpretation.
Is it sufficiently complex?
Your research needs to yield substantial and consequential results to warrant the study. Merely supporting or reinforcing an existing paper is not good enough.
- Examples of good research questions
A robust research question actively contributes to a specific body of knowledge; it is a question that hasn’t been answered before within your research field.
Here are some examples of good and bad research questions :
Good: How effective are A and B policies at reducing the rates of Z?
Bad: Is A or B a better policy?
The first is more focused and researchable because it isn't based on value judgment. The second fails to give clear criteria for answering the question.
Good: What is the effect of daily Twitter use on the attention span of college students?
Bad: What is the effect of social media use on people's minds?
The first includes specific and well-defined concepts, which the second lacks.
Ensure all terms within your research question have precise meanings. Avoid vague or general language that makes the topic too broad.
- The bottom line
The success of any research starts with formulating the right questions that ensure you collect the most insightful data. A good research question will showcase the objectives of your systematic investigation and emphasize specific contexts.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- How it works

How to Write the Research Questions – Tips & Examples
Published by Owen Ingram at August 13th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Conducting research and writing an academic paper requires a clear direction and focus.
A good research question provides purpose to your research and clarifies the direction. It further helps your readers to understand what issue your research aims to explore and address.
If you are unsure about how to write research questions, here is a list of the attributes of a good research question;
- The research question should contain only a single problem
- You should be able to find the answer to it using primary and secondary data sources
- You should be able to address it within the time limit and other constraints
- Can attain in-depth and detailed results
- Relevant and applicable
- Should relate to your chosen field of research
Whenever you want to discover something new about a topic , you will ask a question about it. Therefore, the research question is important in the overall research process and provides the author with the reading and writing guidelines.
In a research paper or an essay, you will need to create a single research question that highlights just one problem or issue. The thesis statement should include the specific problem you aim to investigate to establish your argument’s central position or claim.
A larger project such as a dissertation or thesis , on the other hand, can have multiple research questions, but every question should focus on your main research problem . Different types of research will help you answer different research questions, but they should all be relevant to the research scope.
How to Write a Research Question
Steps to develop your research question.
- Choose a topic with a wide range of published literature
- Read and skim relevant articles to find out different problems and issues
- Specify a theoretical or practical research problem that your research question will address
- Narrow down the focus of your selected core niche

Example Research Question (s)
Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem.
| Example Research Problem | Example Research Question (s) |
|---|---|
| A small-scale company, ‘A’ in the UK, cannot allocate a marketing budget for next year due to their poor revenue collection in the running year. | What practical steps can the company take to improve its revenue? |
| Many fresh graduates in the UK are working as freelancers despite having attained degrees well known academic institutes, but what is causing these youngsters to engage in this type of work? | What is the cause of fresh graduates engaging in freelance activities rather than going for full-time employment? What are the advantages and disadvantages of the gig economy for young people? How do age, gender, and academic qualification relate to people’s perception of freelancing? |
Types of Research Questions
There are two main types of research; quantitative and qualitative research . Both types of research require research questions. What research question you will answer is dependent on the type of research you wish to employ.
The first part of designing research is to find a gap and create a fully focused research question.
The following table shows common research questions for a dissertation project. However, it is important to note that these examples of dissertation research questions are straightforward, and the actual research questions may be more complicated than these examples.
| Research question type | Formulation |
|---|---|
| Descriptive approach | What will be the properties of A? |
| Comparative approach | What are the similarities and differences between A and B? |
| Correlational approach | How can you correlate variables A and B? |
| Exploratory approach | Factors affecting the rate of C? Does A and B also influence C? |
| Explanatory approach | What are the causes of C? How does B impact A? What is causing D? |
| Evaluation approach | How useful and influential is C? What role does B play? What are the advantages and disadvantages of A? |
| Action research | How can you improve X with different interventions? |
What data collection method best suits your research?
- Find out by hiring an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Despite how challenging the subject may be, we are here to help you.
Steps to Write Research Questions
The research question provides you with a path and focuses on the real problem and the research gap you aim to fill. These are steps you need to take if you are unsure about how to write a research question:
Choose an Interesting Topic
Choose a topic of research according to your interest. The selected topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow.
Do Preliminary Research on the Topic
Find articles, books, journals, and theses relevant to your chosen topic. Understand what research problem each scholar addressed as part of their research project.
Consider your Audience
It is necessary to know your audience to develop focused research questions for your essay or dissertation. You can find aspects of your topic that could be interesting to your audience when narrowing your topic.
Start Asking Questions
What, why, when, how, and other open-ended questions will provide in-depth knowledge about the topic.
Evaluate your Question
After formulating a research question, evaluate to check its effectiveness and how it can serve the purpose. Revise and refine the dissertation research question.
- Do you have a clear research question?
It would help if you formed the research question after finding a research gap. This approach will enable the research to solve part of the problem.
- Do you have a focused research question?
It is necessary that the research question is specific and relating to the central aim of your research.
- Do you have a complex research question?
The research question cannot be answered by yes or no but requires in-depth analysis. It often begins with “How” or “Why.”
Begin your Research
After you have prepared dissertation research questions, you should research the existing literature on similar topics to find various perspectives.
Also See: Formulation of Research Question
If you have been struggling to devise research questions for your dissertation or are unsure about which topic would be suitable for your needs, then you might be interested in taking advantage of our dissertation topic and outline service, which includes several topic ideas in your preferred area of study and a 500/1000 words plan on your chosen topic. Our topic and outline service will help you jump-start your dissertation project.
Find out How Our Topics & Outline Service Can Help You!
Tips on How to Write a Strong Research Question
A research question is the foundation of the entire research. Therefore, you should spend as much time as required to refine the research question.
If you have good research questions for the dissertation, research paper , or essay, you can perform the research and analyse your results more effectively. You can evaluate the strength of the research question with the help of the following criteria. Your research question should be;
Intensive and Researchable
- It should cover a single issue
- The question shouldn’t include a subjective judgment
- It can be answerable with the data analysis or research=
Practical and Specific
- It should not include a course of action, policy, or solution
- It should be well-defined
- Answerable within research limits
Complicated and Arguable
- It should not be simple to answer
- Need in-depth knowledge to find facts
- Provides scope for debate and deliberation
Unique and Relevant
- It should lie in your field of study
- Its results should be contributable
- It should be unique
Conclusion – How to Write Research Questions
A research question provides a clear direction for research work. A bigger project, such as a dissertation, may have more than one research question, but every question should focus on one issue only.
Your research questions should be researchable, feasible to answer, specific to find results, complex (for Masters and PhD projects), and relevant to your field of study. Dissertation research questions depend upon the research type you are basing your paper on.
Start creating a research question by choosing an interesting topic, do some preliminary research, consider your audience, start asking questions, evaluating your question, and begin your research.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over. You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over.
You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
Place Order
Frequently Asked Questions
How are research questions written.
Research questions are written by:
- Identifying your topic.
- Considering what you want to explore.
- Making questions clear and concise.
- Ensuring they’re researchable.
- Avoiding bias or leading language.
- Focusing on one main idea per question.
What are examples of research questions?
- Does regular exercise improve mental well-being in adults over 50?
- How do online courses impact student engagement compared to traditional classes?
- What are the economic effects of prolonged pandemic lockdowns?
- How does early childhood nutrition influence academic performance in later life?
- Does urban green space reduce stress levels?
How to write a research question?
- Identify a specific topic or issue of interest.
- Conduct preliminary research to understand existing knowledge.
- Narrow the focus to address gaps or unresolved issues.
- Phrase the question to be clear, concise, and researchable.
- Ensure it is specific enough for systematic investigation.
How to formulate my research questions for my geography dissertation?
- Identify a geographical topic or phenomenon of interest.
- Review existing literature to find gaps.
- Consider spatial, temporal, environmental, or societal aspects.
- Ensure questions are specific, feasible, and significant.
- Frame questions to guide methodology: quantitative, qualitative, or mixed.
- Seek feedback from peers/advisors.
You May Also Like
Make sure that your selected topic is intriguing, manageable, and relevant. Here are some guidelines to help understand how to find a good dissertation topic.
Struggling to find relevant and up-to-date topics for your dissertation? Here is all you need to know if unsure about how to choose dissertation topic.
Here we explore what is research problem in dissertation with research problem examples to help you understand how and when to write a research problem.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
The research process, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Ask a Research Question
When we perform research, we enter the community of scholars who, before us, sought to answer questions for themselves and others. We set out on a journey of discovery that draws us into the ongoing conversation about that subject matter. This is also your opportunity to add your voice to the scholarly work that has already been written about your topic.
BEGIN WITH A QUESTION
As you dive into the scholarly conversation about your topic, you need to begin with a question that you are going to answer in your paper. To begin this process, you need to brainstorm some ideas that interest you. You can brainstorm with a classmate or coworker or even ask your professor for suggestions, but the question you generate is the one you will be invested in answering.
KEEP THE SCOPE MANAGEABLE
As you explore the research question you want to answer, keep in mind that your question and research should be sized to fit the assignment you have been given. Keep the scope of your research manageable. Ask a question that will lead you into your research—a specific, concrete question that will help you devise a working thesis and give you direction for your information search. Generally, the answer to your question should take a stance.
TEST YOUR RESEARCH QUERY
When you have tentatively decided on your research question and have a working thesis, answer these questions to test your research inquiry:
Is the scope of the question appropriate for the assignment?
Is my question specific enough so that I know what I'm looking for? Or is my question too broad or too narrow?
Can I find enough information on the subject?
- Will the answer to my question take a specific stance on the topic?
- Do I really care about finding the answers to my question?
- Does my answer result in more than a "yes" or "no" answer?
When the answers to these questions are yes, you are ready to research in more depth and manage your research resources.
Key Takeaways
- The answer to your research question will eventually be your thesis statement, which will take a stance.
- Frame your research question so that it does not result in a "yes" or "no" answer, but an in-depth answer.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.

Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Introduction
Why are research questions so important?
Research question examples, types of qualitative research questions, writing a good research question, guiding your research through research questions.
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
- Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Research questions
The research question plays a critical role in the research process, as it guides the study design, data collection , analysis , and interpretation of the findings.
A research paper relies on a research question to inform readers of the research topic and the research problem being addressed. Without such a question, your audience may have trouble understanding the rationale for your research project.

People can take for granted the research question as an essential part of a research project. However, explicitly detailing why researchers need a research question can help lend clarity to the research project. Here are some of the key roles that the research question plays in the research process:
Defines the scope and focus of the study
The research question helps to define the scope and focus of the study. It identifies the specific topic or issue that the researcher wants to investigate, and it sets the boundaries for the study. A research question can also help you determine if your study primarily contributes to theory or is more applied in nature. Clinical research and public health research, for example, may be more concerned with research questions that contribute to practice, while a research question focused on cognitive linguistics are aimed at developing theory.
Provides a rationale for the study
The research question provides a rationale for the study by identifying a gap or problem in existing literature or practice that the researcher wants to address. It articulates the purpose and significance of the study, and it explains why the study is important and worth conducting.
Guides the study design
The research question guides the study design by helping the researcher select appropriate research methods , sampling strategies, and data collection tools. It also helps to determine the types of data that need to be collected and the best ways to analyze and interpret the data because the principal aim of the study is to provide an answer to that research question.

Shapes the data analysis and interpretation
The research question shapes the data analysis and interpretation by guiding the selection of appropriate analytical methods and by focusing the interpretation of the findings. It helps to identify which patterns and themes in the data are more relevant and worth digging into, and it guides the development of conclusions and recommendations based on the findings.
Generates new knowledge
The research question is the starting point for generating new knowledge. By answering the research question, the researcher contributes to the body of knowledge in the field and helps to advance the understanding of the topic or issue under investigation.
Overall, the research question is a critical component of the research process, as it guides the study from start to finish and provides a foundation for generating new knowledge.
Supports the thesis statement
The thesis statement or main assertion in any research paper stems from the answers to the research question. As a result, you can think of a focused research question as a preview of what the study aims to present as a new contribution to existing knowledge.
Here area few examples of focused research questions that can help set the stage for explaining different types of research questions in qualitative research . These questions touch upon various fields and subjects, showcasing the versatility and depth of research.
- What factors contribute to the job satisfaction of remote workers in the technology industry?
- How do teachers perceive the implementation of technology in the classroom, and what challenges do they face?
- What coping strategies do refugees use to deal with the challenges of resettlement in a new country?
- How does gentrification impact the sense of community and identity among long-term residents in urban neighborhoods?
- In what ways do social media platforms influence body image and self-esteem among adolescents?
- How do family dynamics and communication patterns affect the management of type 2 diabetes in adult patients?
- What is the role of mentorship in the professional development and career success of early-career academics?
- How do patients with chronic illnesses experience and navigate the healthcare system, and what barriers do they encounter?
- What are the motivations and experiences of volunteers in disaster relief efforts, and how do these experiences impact their future involvement in humanitarian work?
- How do cultural beliefs and values shape the consumer preferences and purchasing behavior of young adults in a globalized market?
- How do individuals whose genetic factors predict a high risk for developing a specific medical condition perceive, cope with, and make lifestyle choices based on this information?
These example research questions highlight the different kinds of inquiries common to qualitative research. They also demonstrate how qualitative research can address a wide range of topics, from understanding the experiences of specific populations to examining the impact of broader social and cultural phenomena.
Also, notice that these types of research questions tend to be geared towards inductive analyses that describe a concept in depth or develop new theory. As such, qualitative research questions tend to ask "what," "why," or "how" types of questions. This contrasts with quantitative research questions that typically aim to verify an existing theory. and tend to ask "when," "how much," and "why" types of questions to nail down causal mechanisms and generalizable findings.
Whatever your research inquiry, turn to ATLAS.ti
Powerful tools to help turn your research question into meaningful analysis, starting with a free trial.
As you can see above, the research questions you ask play a critical role in shaping the direction and depth of your study. These questions are designed to explore, understand, and interpret social phenomena, rather than testing a hypothesis or quantifying data like in quantitative research. In this section, we will discuss the various types of research questions typically found in qualitative research, making it easier for you to craft appropriate questions for your study.
Descriptive questions
Descriptive research questions aim to provide a detailed account of the phenomenon being studied. These questions usually begin with "what" or "how" and seek to understand the nature, characteristics, or functions of a subject. For example, "What are the experiences of first-generation college students?" or "How do small business owners adapt to economic downturns?"
Comparative questions
Comparative questions seek to examine the similarities and differences between two or more groups, cases, or phenomena. These questions often include the words "compare," "contrast," or "differences." For example, "How do parenting practices differ between single-parent and two-parent families?" or "What are the similarities and differences in leadership styles among successful female entrepreneurs?"
Exploratory questions
Exploratory research questions are open-ended and intended to investigate new or understudied areas. These questions aim to identify patterns, relationships, or themes that may warrant further investigation. For example, "How do teenagers use social media to construct their identities?" or "What factors influence the adoption of renewable energy technologies in rural communities?"
Explanatory questions
Explanatory research questions delve deeper into the reasons or explanations behind a particular phenomenon or behavior. They often start with "why" or "how" and aim to uncover underlying motivations, beliefs, or processes. For example, "Why do some employees resist organizational change?" or "How do cultural factors influence decision-making in international business negotiations?"
Evaluative questions
Evaluative questions assess the effectiveness, impact, or outcomes of a particular intervention, program, or policy. They seek to understand the value or significance of an initiative by examining its successes, challenges, or unintended consequences. For example, "How effective is the school's anti-bullying program in reducing incidents of bullying?" or "What are the long-term impacts of a community-based health promotion campaign on residents' well-being?"
Interpretive questions
Interpretive questions focus on understanding how individuals or groups make sense of their experiences, actions, or social contexts. These questions often involve the analysis of language, symbols, or narratives to uncover the meanings and perspectives that shape human behavior. For example, "How do cancer survivors make sense of their illness journey?" or "What meanings do members of a religious community attach to their rituals and practices?"
There are mainly two overarching ways to think about how to devise a research question. Many studies are built on existing research, but others can be founded on personal experiences or pilot research.
Using the literature review
Within scholarly research, the research question is often built from your literature review . An analysis of the relevant literature reporting previous studies should allow you to identify contextual, theoretical, or methodological gaps that can be addressed in future research.

A compelling research question built on a robust literature review ultimately illustrates to your audience what is novel about your study's objectives.
Conducting pilot research
Researchers may conduct preliminary research or pilot research when they are interested in a particular topic but don't yet have a basis for forming a research question on that topic. A pilot study is a small-scale, preliminary study that is conducted in order to test the feasibility of a research design, methods, and procedures. It can help identify unresolved puzzles that merit further investigation, and pilot studies can draw attention to potential issues or problems that may arise in the full study.
One potential benefit of conducting a pilot study in qualitative research is that it can help the researcher to refine their research question. By collecting and analyzing a small amount of data, the researcher can get a better sense of the phenomenon under investigation and can develop a more focused and refined research question for the full study. The pilot study can also help the researcher to identify key themes, concepts, or variables that should be included in the research question.
In addition to helping to refine the research question, a pilot study can also help the researcher to develop a more effective data collection and analysis plan. The researcher can test different methods for collecting and analyzing data, and can make adjustments based on the results of the pilot study. This can help to ensure that the full study is conducted in the most effective and efficient manner possible.
Overall, conducting a pilot study in qualitative research can be a valuable tool for refining the research question and developing a more effective research design, methods, and procedures. It can help to ensure that the full study is conducted in a rigorous and effective manner, and can increase the likelihood of generating meaningful and useful findings.
When you write a research question for your qualitative study, consider which type of question best aligns with your research objectives and the nature of the phenomenon you are investigating. Remember, qualitative research questions should be open-ended, allowing for a range of perspectives and insights to emerge. As you progress in your research, these questions may evolve or be refined based on the data you collect, helping to guide your analysis and deepen your understanding of the topic.

Use ATLAS.ti for every step of your research project
From the research question to the key insights, ATLAS.ti is there for you. See how with a free trial.

The Best PhD and Masters Consulting Company

How to ask a good Research Questions?
Developing the right research questions is a critical first step in the research process. A research question is a question that a study or research project aims to answer. This question often addresses an issue or a problem, which, through analysis and interpretation of data, is answered in the study’s conclusion.
Types of Research Questions
Steps to developing a good research question, 1. start with a broad topic: , 2. narrow down your topic and determine potential research questions: , 3. another way of identifying and constructing research questions:.
- The development of a research question is an iterative process that involves continuously updating one’s knowledge on the topic and refining ideas at all stages.
- Remain updated on current trends, state-of-the-art research studies, and technological advances in the field of study you are pursuing.
- Make the research question as specific and concise as possible to ensure clarity. Avoid using words or terms that don’t add to the meaning of the research question.
- Aside from doing a literature review, seek the input of experts in the field, mentors, and colleagues. Such inputs can prove beneficial not only for the research question but also for creating the rest of the study.
- Finally, refrain from committing the two most common mistakes in framing research questions: posing a question as an anticipated contribution and framing a question as a method.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How to appropriately email a researcher to ask for details about their paper?
Often when I am reading a newly published article, I will encounter some points that are difficult to understand. For example, some details of the methodology that I think the authors did not explain in enough detail.
I'm not sure how to write an appropriate email to ask for clarification, especially on how to phrase, so as to be polite. For example, should I write "Ask for details on methodology" or "Inquiry on details on methodology" or ...?
- 1 You can also ask if there is an appendix (published or not) containing more methodological details than appeared in the published article. – Alexis Commented Jul 6, 2020 at 23:24
- 2 Does this answer your question? How should I phrase an important question that I need to ask a professor? – Anonymous Physicist Commented Jul 6, 2020 at 23:42
- 3 Be warned that authors of papers can be of varying degrees of helpfulness when you ask them about details of their papers or more explicit details of their methodology/computations. – Tom Commented Jul 7, 2020 at 0:45
- 2 There is a website called pubpeer, which is useful for public comments of papers, if you have a question it's possible other people may too, maybe someone has asked it before – Rainb Commented Jul 7, 2020 at 5:10
- 1 By the way, it should go without saying but also make sure you have thoroughly read the paper before asking :) – a3nm Commented Jul 7, 2020 at 8:26
9 Answers 9
Showing interest is nice, accusing people is not. So, show interest, something like "I saw your article XXX in YYY and I am working on something similar. I was wondering how exactly you dealt with ZZZ."
This probably is a bit culturally determined, but almost anything polite will do. I personally prefer your second formulation, but others might not. Don't overthink it.
But in a first mail to the author(s) I suggest asking questions that can be answered fairly simply/quickly and don't ask for too much. If it seems like it will be a lot of work to reply, then you might not get any answer. You can always follow up with additional questions if the authors seem open to communication.
In the best case it can open the possibility of future collaboration if the topic is of mutual interest.
Contacting researchers for clarification is good practice. Before you do, ask yourself why you think the authors did not provide enough details . In formulating an answer, you may find they did provide enough details. Otherwise, you'll have established a better understanding for what you need to know, and you can put that to the researchers. Always be humble in asking.
Let's get more templated . What about this?
To: %Corresponding author% Subject: %Paper title% Dear Prof. %NAME% , With a great interest I read your paper on %TOPIC% . Since I work in a similar area, I would like to %short presentation of what you want% [e.g., to compare my approach [1, 2, 3] to yours]. Do you have %your actual inquiry, detailed% ? Thank you very much in advance. [1] Paper [2] Paper [3] Paper Best regards, %Your name% -- %Your signature, including your institution, email, phone, and further ways to contact you%
If you are asking for code, try searching GitHub and further usual places first. Googling the corresponding author would also help. Take a look at their most recent papers, may be your question is already answered.
- What if I'm not sure if they are a professor or not. – hotohoto Commented Jan 31, 2023 at 6:12
- 1 Just google them? – Oleg Lobachev Commented Feb 1, 2023 at 10:33
So long as what you write is not rude or arrogant, nobody will care much.
The important thing is to ask some specific questions. If you just asked me for "details of methodology" I would hit the delete button, because I'm not going to write a comprehensive reply that is probably longer than the published paper telling you every little detail about what I did - especially if the paper was published years ago and I have forgotten most of the details anyway.
- That depends imho. If you write an article about Nuclear Power and completely leave out the part about uranium atoms splitting, well, do you assume your readers will know ? – clockw0rk Commented Jul 8, 2020 at 8:09
- @clockw0rk yes? For a journal article, I think you can safely assume a decent general science background, especially in the topic of the journal (e.g., fission for a Modern Physics Letters paper). – Matt Commented Jul 9, 2020 at 0:11
- @Matt u maybe right about that, but I encountered papers about advanced hacking techniques where the author completely leaves out facts about what he is refferring to when he says "... because it is simply a fact" or "...as is common knowledge". Not the topic of this question, but definately provide at least sources to your readers where they can find the basics of your research. Well, I guess it's part of the topic that these papers always come a little "mysterious" or "arcane", so to speak. – clockw0rk Commented Jul 9, 2020 at 12:31
I was for 5 or so years a university researcher and co-wrote a few papers. I would have been thrilled if someone had written to me asking a sensible question (they never did) but horrified if they had found an error. Professors, on the other hand, can be time poor, so it will be best to write to the most junior author if this is an option. In my experience many academics build upon their previous work and answers to any questions will often be found in previous papers. To be specific I would suggest: "Do you use the [your best guess at the techniques/methodology used] system in your research?" after a preamble much as Oleg has given above.
If the paper is published it is because the editor (and presumably the referees) believe there are enough details either in the manuscript per se , in the references or that the procedure is sufficiently well-known not to waste time on it.
Thus I would encourage you to be very careful in suggesting there is not enough information: it might not be enough information for you but presumably it’s enough information for that typical reader of the journal.
You might ask for clarifications on a few specific points but do so selectively, making sure you include significant context and references so that your query is legitimate.
A while ago I also read a paper and had a question which was not answered in the paper (or maybe it was and I just wasn't capable of interpreting it).
I searched for the address of the main author and wrote a polite, kind email without much fluff (because I had often heard that scientists don't like fluff).
I also mentioned that I had asked another scientist I knew first, but that no one knew the answer (just to add some justification for why I was writing him instead of asking others or consulting books).
For me, he was something like a famous Professor and I thought he would never answer my mail. But not even a day later I received a kind and helpful answer from him.
I would also like to add here to encourage everyone to answer emails like this if possible. For him it was maybe just an email but his answer meant so very much to me, I nearly even cried because I was so happy and I felt taken seriously and acknowledged.
This is what I used to do when I was a math grad student:
- Be extra polite (I would start with "Dear Prof. NNN")
- Introduce yourself. Say what level you're at, what institution you're at, and who you're working with. (Briefly.) It will help them understand what level you're at and indicate a connection.
- Be somewhat detailed about what you do understand. Don't just say "I didn't understand this step in the methods." Say "When you say that you did XXX, did you mean YYY, or ZZZ? Or perhaps I misunderstand completely?" Just like with Stack Exchange you want to make it clear you put some effort in, and you also want to make it clear just what needs to be explained.
- Include a phone number in case they want to talk further.
I want to re-emphasize the importance of being clear about where you are uncertain. You want to make it as easy as possible for them to answer your question. And as you try to put your confusion into words, it may actually become more clear to you.
But don't be afraid to make the contact. It could even lead to a future collaboration. Connecting with other researchers is a good thing to do.
One other note: Even though I suggested "Dear Prof. NNN", that's just for the first contact. After that, look at how they talk to you. If they close with just their first name, that's generally an invitation to address them that way.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged etiquette email ..
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- Using the higrī date instead of the Gregorian date
- Does H3PO exist?
- Power line crossing data lines via the ground plane
- Polar coordinate plot incorrectly plotting with PGF Plots
- Has technology regressed in the Alien universe?
- Unknown tool. Not sure what this tool is, found it in a tin of odds and ends
- Are there jurisdictions where an uninvolved party can appeal a court decision?
- Making wobbly 6x4’ table stable
- Does each unique instance of Nietzsche's superman have the same virtues and values?
- How to allow just one user to use SSH?
- Is a *magnetized* ferrite less ideal as a core?
- Why does characteristic equation and DC model equation for drain current in JFETs do not agree?
- Why was I was allowed to bring 1.5 liters of liquid through security at Frankfurt Airport?
- Who became an oligarch after the collapse of the USSR
- DIN Rail Logic Gate
- Advice needed: Team needs developers, but company isn't posting jobs
- Can I use "Member, IEEE" as my affiliation for publishing papers?
- Is It Possible to Assign Meaningful Amplitudes to Properties in Quantum Mechanics?
- Using illustrations and comics in dissertations
- Age is just a number!
- What majority age is taken into consideration when travelling from country to country?
- What was the reason for not personifying God's spirit in NABRE's translation of John 14:17?
- Sci-fi book about humanity warring against aliens that eliminate all species in the galaxy
- Discrete cops and robbers

Oxford University Press's Academic Insights for the Thinking World

Effective ways to communicate research in a journal article

Oxford Academic: Journals
We publish over 500 high-quality journals, with two-thirds in partnership with learned societies and prestigious institutions. Our diverse journal offerings ensure that your research finds a home alongside award-winning content, reaching a global audience and maximizing impact.
- By Megan Taphouse , Anne Foster , Eduardo Franco , Howard Browman , and Michael Schnoor
- August 12 th 2024
In this blog post, editors of OUP journals delve into the vital aspect of clear communication in a journal article. Anne Foster (Editor of Diplomatic History ), Eduardo Franco (Editor-in-Chief of JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute and JNCI Monographs ), Howard Browman (Editor-in-Chief of ICES Journal of Marine Science ), and Michael Schnoor (Editor-in-Chief of Journal of Leukocyte Biology ) provide editorial recommendations on achieving clarity, avoiding common mistakes, and creating an effective structure.
Ensuring clear communication of research findings
AF : To ensure research findings are clearly communicated, you should be able to state the significance of those findings in one sentence—if you don’t have that simple, clear claim in your mind, you will not be able to communicate it.
MS : The most important thing is clear and concise language. It is also critical to have a logical flow of your story with clear transitions from one research question to the next.
EF : It is crucial to write with both experts and interested non-specialists in mind, valuing their diverse perspectives and insights.
Common mistakes that obscure authors’ arguments and data
AF : Many authors do a lovely job of contextualizing their work, acknowledging what other scholars have written about the topic, but then do not sufficiently distinguish what their work is adding to the conversation.
HB : Be succinct—eliminate repetition and superfluous material. Do not attempt to write a mini review. Do not overinterpret your results or extrapolate far beyond the limits of the study. Do not report the same data in the text, tables, and figures.
The importance of the introduction
AF : The introduction is absolutely critical. It needs to bring them straight into your argument and contribution, as quickly as possible.
EF : The introduction is where you make a promise to the reader. It is like you saying, “I identified this problem and will solve it.” What comes next in the paper is how you kept that promise.
Structural pitfalls
EF : Remember, editors are your first audience; make sure your writing is clear and compelling because if the editor cannot understand your writing, chances are that s/he will reject your paper without sending it out for external peer review.
HB : Authors often misplace content across sections, placing material in the introduction that belongs in methods, results, or discussion, and interpretive phrases in results instead of discussion. Additionally, they redundantly present information in multiple sections.
Creating an effective structure
AF : I have one tip which is more of a thinking and planning strategy. I write myself letters about what I think the argument is, what kinds of support it needs, how I will use the specific material I have to provide that support, how it fits together, etc.
EF : Effective writing comes from effective reading—try to appreciate good writing in the work of others as you read their papers. Do you like their writing? Do you like their strategy of advancing arguments? Are you suspicious of their methods, findings, or how they interpret them? Do you see yourself resisting? Examine your reactions. You should also write frequently. Effective writing is like a physical sport; you develop ‘muscle memory’ by hitting a golf ball or scoring a 3-pointer in basketball.
The importance of visualizing data and findings
MS : It is extremely important to present your data in clean and well-organized figures—they act as your business card. Also, understand and consider the page layout and page or column dimensions of your target journal and format your tables and figures accordingly.
EF : Be careful when cropping gels to assemble them in a figure. Make sure that image contrasts are preserved from the original blots. Image cleaning for the sake of readability can alter the meaning of results and eventually be flagged by readers as suspicious.
The power of editing
AF : Most of the time, our first draft is for ourselves. We write what we have been thinking about most, which means the article reflects our questions, our knowledge, and our interests. A round or two of editing and refining before submission to the journal is valuable.
HB : Editing does yourself a favour by minimizing distractions-annoyances-cosmetic points that a reviewer can criticize. Why give reviewers things to criticize when you can eliminate them by submitting a carefully prepared manuscript?
Editing mistakes to avoid
AF : Do not submit an article which is already at or above the word limit for articles in the journal. The review process rarely asks for cuts; usually, you will be asked to clarify or add material. If you are at the maximum word count in the initial submission, you then must cut something during the revision process.
EF : Wait 2-3 days and then reread your draft. You will be surprised to see how many passages in your great paper are too complicated and inscrutable even for you. And you wrote it!
Featured image by Charlotte May via Pexels .
Megan Taphouse , Marketing Executive
Anne Foster , (Editor of Diplomatic History)
Eduardo Franco , (Editor-in-Chief of JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer institute and JNCI Monographs)
Howard Browman , (Editor-in-Chief of ICES Journal of Marine Science)
Michael Schnoor , (Editor-in-Chief of Journal of Leukocyte Biology)
- Publishing 101
- Series & Columns
Our Privacy Policy sets out how Oxford University Press handles your personal information, and your rights to object to your personal information being used for marketing to you or being processed as part of our business activities.
We will only use your personal information to register you for OUPblog articles.
Or subscribe to articles in the subject area by email or RSS
Related posts:

Recent Comments
There are currently no comments.
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Burning Questions: “What’s the Best Way to Approach a Research Paper When You Don’t Know Where to Start?”
We, librarians, are fortunate that we get to meet a lot of incoming Hopkins students. We often request that they give us their “burning questions” — about Baltimore, Hopkins, the library, life and love, etc. We’ve curated some of their questions and their answers into a series of blog posts that we hope will address some “burning questions” of your own.
Q: “What’s the best way to approach a research paper when you don’t know where to start?”
A: You find yourself staring at the blank page. The cursor is blinking with expectation, adding to the pressure of getting started on your research paper but your mind is as blank as the page. Where do you begin?
We’ve all been there! Starting your research can be daunting! Luckily, you’ve got the library (and the librarians) waiting in the wings, ready to help! There are a few basic steps that can get you started.
1 – A Topic: Even if you’ve got a topic in mind, it’s worth interrogating it and making sure that you’re able to write something interesting about it.
- Do I know this topic/field well enough to contribute to the academic conversation?
- Is your topic specific enough? If it’s not you’ll have an impossible time describing the phenomenon you are hoping to address. If it is too specific, you may struggle to find resources that address your subject.
- Do you have access to what you’ll need to conduct your research? This is where you can depend on the library! If you are looking for a resource, let us know and we can help you find it. If we don’t have it, we can get it!
2 – Preliminary Research: Do a quick survey of what resources are out there that address your subject. Reviewing the literature on your topic will give you an idea of where you can look for more information and what angle you can take in your paper. Ask yourself who, what, where, and when you need to know to address your subject. You can use the information you find in this stage to construct a research strategy to make life easier for yourself. Pull keywords, key figures, dates, places, events, etc., from your preliminary research and let it inform your search going forward. This is the perfect stage to check out the library’s Research Guides . These guides act as signposts that can direct you toward where you can look for books , articles , datasets , and other resources about your topic.
3 – Create a Rough Outline: Ask yourself what you are trying to say with your research. Once you know that, create an outline of the arguments you intend to make that will bring the reader from Point A to Point Z. Start fleshing out your outline with your ideas, thoughts, and preliminary research. Make sure that your points flow together, following a logical order so that the reader can understand your thinking.
4 – Conduct further research: Now that you have your outline you can ask yourself “What am I trying to say in this portion of my research?” Then hit the library to find the resources you need to support the point you are making. Can’t find what you’re after? Getting frustrated? Reach out to your librarian. We can talk through your ideas, help you organize, and help you to find resources that may be eluding you.
5 – Write! Remember that writing and research is an iterative process. As you write, don’t be surprised to find yourself coming back to the library to find additional resources. Keep track of your research using a citation manager. Edit, rewrite, and get feedback!
Don’t let the blank page intimidate you. You’ve got things to say and ideas to contribute! We can’t wait to see what you do!
Related posts:
- Burning Questions: Getting Out on the Town
- Burning Questions: “Is There a Graphic Novel Section?
- Paper Due Tomorrow? Here’s Where to Start
- Burning Questions: “Is the Library Strictly Academic or Are There Recreational Books as Well?”
- Burning Questions: Writers’ Associations
- Call 410-516-8335
- Text 410-692-8874
- [email protected]
Search all Blog Posts
- Special Collections on Flickr
- Special Collections on Instagram
- Hopkins Retrospective on Instagram
- Evergreen Museum & Library on Instagram
- Evergreem Museum & Library on Facebook
- Homewood Museum on Facebook
- Homewood Museum on Instagram
Other Links
- For Contributors
- Innovative Instructor
- JHU Press Blog
- Libraries Exhibition Schedule
- Sheridan Libraries Homepage

How to Write a Research Proposal: (with Examples & Templates)

Table of Contents
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers’ plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed research that you intend to undertake. It provides readers with a snapshot of your project by describing what you will investigate, why it is needed, and how you will conduct the research.
Your research proposal should aim to explain to the readers why your research is relevant and original, that you understand the context and current scenario in the field, have the appropriate resources to conduct the research, and that the research is feasible given the usual constraints.
This article will describe in detail the purpose and typical structure of a research proposal , along with examples and templates to help you ace this step in your research journey.
What is a Research Proposal ?
A research proposal¹ ,² can be defined as a formal report that describes your proposed research, its objectives, methodology, implications, and other important details. Research proposals are the framework of your research and are used to obtain approvals or grants to conduct the study from various committees or organizations. Consequently, research proposals should convince readers of your study’s credibility, accuracy, achievability, practicality, and reproducibility.
With research proposals , researchers usually aim to persuade the readers, funding agencies, educational institutions, and supervisors to approve the proposal. To achieve this, the report should be well structured with the objectives written in clear, understandable language devoid of jargon. A well-organized research proposal conveys to the readers or evaluators that the writer has thought out the research plan meticulously and has the resources to ensure timely completion.
Purpose of Research Proposals
A research proposal is a sales pitch and therefore should be detailed enough to convince your readers, who could be supervisors, ethics committees, universities, etc., that what you’re proposing has merit and is feasible . Research proposals can help students discuss their dissertation with their faculty or fulfill course requirements and also help researchers obtain funding. A well-structured proposal instills confidence among readers about your ability to conduct and complete the study as proposed.
Research proposals can be written for several reasons:³
- To describe the importance of research in the specific topic
- Address any potential challenges you may encounter
- Showcase knowledge in the field and your ability to conduct a study
- Apply for a role at a research institute
- Convince a research supervisor or university that your research can satisfy the requirements of a degree program
- Highlight the importance of your research to organizations that may sponsor your project
- Identify implications of your project and how it can benefit the audience
What Goes in a Research Proposal?
Research proposals should aim to answer the three basic questions—what, why, and how.
The What question should be answered by describing the specific subject being researched. It should typically include the objectives, the cohort details, and the location or setting.
The Why question should be answered by describing the existing scenario of the subject, listing unanswered questions, identifying gaps in the existing research, and describing how your study can address these gaps, along with the implications and significance.
The How question should be answered by describing the proposed research methodology, data analysis tools expected to be used, and other details to describe your proposed methodology.
Research Proposal Example
Here is a research proposal sample template (with examples) from the University of Rochester Medical Center. 4 The sections in all research proposals are essentially the same although different terminology and other specific sections may be used depending on the subject.

Structure of a Research Proposal
If you want to know how to make a research proposal impactful, include the following components:¹
1. Introduction
This section provides a background of the study, including the research topic, what is already known about it and the gaps, and the significance of the proposed research.
2. Literature review
This section contains descriptions of all the previous relevant studies pertaining to the research topic. Every study cited should be described in a few sentences, starting with the general studies to the more specific ones. This section builds on the understanding gained by readers in the Introduction section and supports it by citing relevant prior literature, indicating to readers that you have thoroughly researched your subject.
3. Objectives
Once the background and gaps in the research topic have been established, authors must now state the aims of the research clearly. Hypotheses should be mentioned here. This section further helps readers understand what your study’s specific goals are.
4. Research design and methodology
Here, authors should clearly describe the methods they intend to use to achieve their proposed objectives. Important components of this section include the population and sample size, data collection and analysis methods and duration, statistical analysis software, measures to avoid bias (randomization, blinding), etc.
5. Ethical considerations
This refers to the protection of participants’ rights, such as the right to privacy, right to confidentiality, etc. Researchers need to obtain informed consent and institutional review approval by the required authorities and mention this clearly for transparency.
6. Budget/funding
Researchers should prepare their budget and include all expected expenditures. An additional allowance for contingencies such as delays should also be factored in.
7. Appendices
This section typically includes information that supports the research proposal and may include informed consent forms, questionnaires, participant information, measurement tools, etc.
8. Citations

Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal begins much before the actual task of writing. Planning the research proposal structure and content is an important stage, which if done efficiently, can help you seamlessly transition into the writing stage. 3,5
The Planning Stage
- Manage your time efficiently. Plan to have the draft version ready at least two weeks before your deadline and the final version at least two to three days before the deadline.
- What is the primary objective of your research?
- Will your research address any existing gap?
- What is the impact of your proposed research?
- Do people outside your field find your research applicable in other areas?
- If your research is unsuccessful, would there still be other useful research outcomes?
The Writing Stage
- Create an outline with main section headings that are typically used.
- Focus only on writing and getting your points across without worrying about the format of the research proposal , grammar, punctuation, etc. These can be fixed during the subsequent passes. Add details to each section heading you created in the beginning.
- Ensure your sentences are concise and use plain language. A research proposal usually contains about 2,000 to 4,000 words or four to seven pages.
- Don’t use too many technical terms and abbreviations assuming that the readers would know them. Define the abbreviations and technical terms.
- Ensure that the entire content is readable. Avoid using long paragraphs because they affect the continuity in reading. Break them into shorter paragraphs and introduce some white space for readability.
- Focus on only the major research issues and cite sources accordingly. Don’t include generic information or their sources in the literature review.
- Proofread your final document to ensure there are no grammatical errors so readers can enjoy a seamless, uninterrupted read.
- Use academic, scholarly language because it brings formality into a document.
- Ensure that your title is created using the keywords in the document and is neither too long and specific nor too short and general.
- Cite all sources appropriately to avoid plagiarism.
- Make sure that you follow guidelines, if provided. This includes rules as simple as using a specific font or a hyphen or en dash between numerical ranges.
- Ensure that you’ve answered all questions requested by the evaluating authority.
Key Takeaways
Here’s a summary of the main points about research proposals discussed in the previous sections:
- A research proposal is a document that outlines the details of a proposed study and is created by researchers to submit to evaluators who could be research institutions, universities, faculty, etc.
- Research proposals are usually about 2,000-4,000 words long, but this depends on the evaluating authority’s guidelines.
- A good research proposal ensures that you’ve done your background research and assessed the feasibility of the research.
- Research proposals have the following main sections—introduction, literature review, objectives, methodology, ethical considerations, and budget.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How is a research proposal evaluated?
A1. In general, most evaluators, including universities, broadly use the following criteria to evaluate research proposals . 6
- Significance —Does the research address any important subject or issue, which may or may not be specific to the evaluator or university?
- Content and design —Is the proposed methodology appropriate to answer the research question? Are the objectives clear and well aligned with the proposed methodology?
- Sample size and selection —Is the target population or cohort size clearly mentioned? Is the sampling process used to select participants randomized, appropriate, and free of bias?
- Timing —Are the proposed data collection dates mentioned clearly? Is the project feasible given the specified resources and timeline?
- Data management and dissemination —Who will have access to the data? What is the plan for data analysis?
Q2. What is the difference between the Introduction and Literature Review sections in a research proposal ?
A2. The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand, provides references to all prior relevant literature to help corroborate the gaps identified and the research need.
Q3. How long should a research proposal be?
A3. Research proposal lengths vary with the evaluating authority like universities or committees and also the subject. Here’s a table that lists the typical research proposal lengths for a few universities.
| Arts programs | 1,000-1,500 | |
| University of Birmingham | Law School programs | 2,500 |
| PhD | 2,500 | |
| 2,000 | ||
| Research degrees | 2,000-3,500 |
Q4. What are the common mistakes to avoid in a research proposal ?
A4. Here are a few common mistakes that you must avoid while writing a research proposal . 7
- No clear objectives: Objectives should be clear, specific, and measurable for the easy understanding among readers.
- Incomplete or unconvincing background research: Background research usually includes a review of the current scenario of the particular industry and also a review of the previous literature on the subject. This helps readers understand your reasons for undertaking this research because you identified gaps in the existing research.
- Overlooking project feasibility: The project scope and estimates should be realistic considering the resources and time available.
- Neglecting the impact and significance of the study: In a research proposal , readers and evaluators look for the implications or significance of your research and how it contributes to the existing research. This information should always be included.
- Unstructured format of a research proposal : A well-structured document gives confidence to evaluators that you have read the guidelines carefully and are well organized in your approach, consequently affirming that you will be able to undertake the research as mentioned in your proposal.
- Ineffective writing style: The language used should be formal and grammatically correct. If required, editors could be consulted, including AI-based tools such as Paperpal , to refine the research proposal structure and language.
Thus, a research proposal is an essential document that can help you promote your research and secure funds and grants for conducting your research. Consequently, it should be well written in clear language and include all essential details to convince the evaluators of your ability to conduct the research as proposed.
This article has described all the important components of a research proposal and has also provided tips to improve your writing style. We hope all these tips will help you write a well-structured research proposal to ensure receipt of grants or any other purpose.
References
- Sudheesh K, Duggappa DR, Nethra SS. How to write a research proposal? Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(9):631-634. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037942/
- Writing research proposals. Harvard College Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships. Harvard University. Accessed July 14, 2024. https://uraf.harvard.edu/apply-opportunities/app-components/essays/research-proposals
- What is a research proposal? Plus how to write one. Indeed website. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-proposal
- Research proposal template. University of Rochester Medical Center. Accessed July 16, 2024. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/pediatrics/research/documents/Research-proposal-Template.pdf
- Tips for successful proposal writing. Johns Hopkins University. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://research.jhu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Tips-for-Successful-Proposal-Writing.pdf
- Formal review of research proposals. Cornell University. Accessed July 18, 2024. https://irp.dpb.cornell.edu/surveys/survey-assessment-review-group/research-proposals
- 7 Mistakes you must avoid in your research proposal. Aveksana (via LinkedIn). Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-mistakes-you-must-avoid-your-research-proposal-aveksana-cmtwf/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
How to write a phd research proposal.
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- How to Avoid Plagiarism When Using Generative AI Tools
- What is Hedging in Academic Writing?
How to Write Your Research Paper in APA Format
The future of academia: how ai tools are changing the way we do research, you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.
Ask a Question, Get Answers Directly from Research Article
Today, we're excited to introduce the capability for scite users to ask research questions in plain language and get answers directly from the full text of research articles..
Today, we’re excited to introduce the capability for scite users to ask research questions in plain language and get answers directly from the full text of research articles ( Try it out now ).
Think of all the questions you’ve had and how difficult it was to find a reliable answer. Maybe you wondered whether Tanning beds increase the risk of cancer, or Does drinking hard water have any negative health effects?
On google, you get ads. Elsewhere, you’re not sure if you can trust the source. Or you have to construct your question in a way that a scientific expert can.
Our new “Ask a Question” search lets you ask frequent questions like this in simple, human terms. And we show you results straight from the full-text of over 32 million research articles that have the answer you’re looking for, or at least a clue to point you in the right direction.
Asking, “Do tanning beds increase the risk of cancer?” surfaces answers like this, which indicate that there is an associated cancer risk, with the confidence that these results are backed by peer-reviewed research.

And asking “Does drinking hard water have any negative health effects?” yields a number of results indicating some of the adverse effects of drinking hard water.
By the way, these results are not summarized or AI-generated, but snippets from full-text articles that real researchers wrote and published.
How is this possible?
At scite, we’ve built the world’s largest database of Citation Statements – the sentences from full-text articles where references are used in-text.
When we started years ago, we leveraged these to disambiguate traditional citation counts through our badge, and helped users read exactly how a particular paper and its findings were cited in newer research through our article report pages.
Then, we built a unique search experience across those Citation Statements, allowing users across domains to find facts straight from the full-text of articles. But even this required some advanced knowledge of querying.
Now, with “Ask a Question”, that wealth of information is even more accessible to anyone who engages with research.
Try it out now , and let us know what you think . For a deep dive into how it works on a technical level, check out our blog post
scite is a Brooklyn-based organization that helps researchers better discover and understand research articles through Smart Citations–citations that display the context of the citation and describe whether the article provides supporting or contrasting evidence. scite is used by students and researchers from around the world and is funded in part by the National Science Foundation and the National Institute on Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health.
Contact Info
10624 S. Eastern Ave., Ste. A-614
Henderson, NV 89052, USA
Blog Terms and Conditions API Terms Privacy Policy Contact Cookie Preferences Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
Copyright © 2024 scite LLC. All rights reserved.
Made with 💙 for researchers
Part of the Research Solutions Family.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
How to Write a Research Paper | A Beginner's Guide
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research.
Research papers are similar to academic essays , but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research. Writing a research paper requires you to demonstrate a strong knowledge of your topic, engage with a variety of sources, and make an original contribution to the debate.
This step-by-step guide takes you through the entire writing process, from understanding your assignment to proofreading your final draft.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Understand the assignment, choose a research paper topic, conduct preliminary research, develop a thesis statement, create a research paper outline, write a first draft of the research paper, write the introduction, write a compelling body of text, write the conclusion, the second draft, the revision process, research paper checklist, free lecture slides.
Completing a research paper successfully means accomplishing the specific tasks set out for you. Before you start, make sure you thoroughly understanding the assignment task sheet:
- Read it carefully, looking for anything confusing you might need to clarify with your professor.
- Identify the assignment goal, deadline, length specifications, formatting, and submission method.
- Make a bulleted list of the key points, then go back and cross completed items off as you’re writing.
Carefully consider your timeframe and word limit: be realistic, and plan enough time to research, write, and edit.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

There are many ways to generate an idea for a research paper, from brainstorming with pen and paper to talking it through with a fellow student or professor.
You can try free writing, which involves taking a broad topic and writing continuously for two or three minutes to identify absolutely anything relevant that could be interesting.
You can also gain inspiration from other research. The discussion or recommendations sections of research papers often include ideas for other specific topics that require further examination.
Once you have a broad subject area, narrow it down to choose a topic that interests you, m eets the criteria of your assignment, and i s possible to research. Aim for ideas that are both original and specific:
- A paper following the chronology of World War II would not be original or specific enough.
- A paper on the experience of Danish citizens living close to the German border during World War II would be specific and could be original enough.
Note any discussions that seem important to the topic, and try to find an issue that you can focus your paper around. Use a variety of sources , including journals, books, and reliable websites, to ensure you do not miss anything glaring.
Do not only verify the ideas you have in mind, but look for sources that contradict your point of view.
- Is there anything people seem to overlook in the sources you research?
- Are there any heated debates you can address?
- Do you have a unique take on your topic?
- Have there been some recent developments that build on the extant research?
In this stage, you might find it helpful to formulate some research questions to help guide you. To write research questions, try to finish the following sentence: “I want to know how/what/why…”
A thesis statement is a statement of your central argument — it establishes the purpose and position of your paper. If you started with a research question, the thesis statement should answer it. It should also show what evidence and reasoning you’ll use to support that answer.
The thesis statement should be concise, contentious, and coherent. That means it should briefly summarize your argument in a sentence or two, make a claim that requires further evidence or analysis, and make a coherent point that relates to every part of the paper.
You will probably revise and refine the thesis statement as you do more research, but it can serve as a guide throughout the writing process. Every paragraph should aim to support and develop this central claim.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
A research paper outline is essentially a list of the key topics, arguments, and evidence you want to include, divided into sections with headings so that you know roughly what the paper will look like before you start writing.
A structure outline can help make the writing process much more efficient, so it’s worth dedicating some time to create one.
Your first draft won’t be perfect — you can polish later on. Your priorities at this stage are as follows:
- Maintaining forward momentum — write now, perfect later.
- Paying attention to clear organization and logical ordering of paragraphs and sentences, which will help when you come to the second draft.
- Expressing your ideas as clearly as possible, so you know what you were trying to say when you come back to the text.
You do not need to start by writing the introduction. Begin where it feels most natural for you — some prefer to finish the most difficult sections first, while others choose to start with the easiest part. If you created an outline, use it as a map while you work.
Do not delete large sections of text. If you begin to dislike something you have written or find it doesn’t quite fit, move it to a different document, but don’t lose it completely — you never know if it might come in useful later.
Paragraph structure
Paragraphs are the basic building blocks of research papers. Each one should focus on a single claim or idea that helps to establish the overall argument or purpose of the paper.
Example paragraph
George Orwell’s 1946 essay “Politics and the English Language” has had an enduring impact on thought about the relationship between politics and language. This impact is particularly obvious in light of the various critical review articles that have recently referenced the essay. For example, consider Mark Falcoff’s 2009 article in The National Review Online, “The Perversion of Language; or, Orwell Revisited,” in which he analyzes several common words (“activist,” “civil-rights leader,” “diversity,” and more). Falcoff’s close analysis of the ambiguity built into political language intentionally mirrors Orwell’s own point-by-point analysis of the political language of his day. Even 63 years after its publication, Orwell’s essay is emulated by contemporary thinkers.
Citing sources
It’s also important to keep track of citations at this stage to avoid accidental plagiarism . Each time you use a source, make sure to take note of where the information came from.
You can use our free citation generators to automatically create citations and save your reference list as you go.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
The research paper introduction should address three questions: What, why, and how? After finishing the introduction, the reader should know what the paper is about, why it is worth reading, and how you’ll build your arguments.
What? Be specific about the topic of the paper, introduce the background, and define key terms or concepts.
Why? This is the most important, but also the most difficult, part of the introduction. Try to provide brief answers to the following questions: What new material or insight are you offering? What important issues does your essay help define or answer?
How? To let the reader know what to expect from the rest of the paper, the introduction should include a “map” of what will be discussed, briefly presenting the key elements of the paper in chronological order.
The major struggle faced by most writers is how to organize the information presented in the paper, which is one reason an outline is so useful. However, remember that the outline is only a guide and, when writing, you can be flexible with the order in which the information and arguments are presented.
One way to stay on track is to use your thesis statement and topic sentences . Check:
- topic sentences against the thesis statement;
- topic sentences against each other, for similarities and logical ordering;
- and each sentence against the topic sentence of that paragraph.
Be aware of paragraphs that seem to cover the same things. If two paragraphs discuss something similar, they must approach that topic in different ways. Aim to create smooth transitions between sentences, paragraphs, and sections.
The research paper conclusion is designed to help your reader out of the paper’s argument, giving them a sense of finality.
Trace the course of the paper, emphasizing how it all comes together to prove your thesis statement. Give the paper a sense of finality by making sure the reader understands how you’ve settled the issues raised in the introduction.
You might also discuss the more general consequences of the argument, outline what the paper offers to future students of the topic, and suggest any questions the paper’s argument raises but cannot or does not try to answer.
You should not :
- Offer new arguments or essential information
- Take up any more space than necessary
- Begin with stock phrases that signal you are ending the paper (e.g. “In conclusion”)
There are four main considerations when it comes to the second draft.
- Check how your vision of the paper lines up with the first draft and, more importantly, that your paper still answers the assignment.
- Identify any assumptions that might require (more substantial) justification, keeping your reader’s perspective foremost in mind. Remove these points if you cannot substantiate them further.
- Be open to rearranging your ideas. Check whether any sections feel out of place and whether your ideas could be better organized.
- If you find that old ideas do not fit as well as you anticipated, you should cut them out or condense them. You might also find that new and well-suited ideas occurred to you during the writing of the first draft — now is the time to make them part of the paper.
The goal during the revision and proofreading process is to ensure you have completed all the necessary tasks and that the paper is as well-articulated as possible. You can speed up the proofreading process by using the AI proofreader .
Global concerns
- Confirm that your paper completes every task specified in your assignment sheet.
- Check for logical organization and flow of paragraphs.
- Check paragraphs against the introduction and thesis statement.
Fine-grained details
Check the content of each paragraph, making sure that:
- each sentence helps support the topic sentence.
- no unnecessary or irrelevant information is present.
- all technical terms your audience might not know are identified.
Next, think about sentence structure , grammatical errors, and formatting . Check that you have correctly used transition words and phrases to show the connections between your ideas. Look for typos, cut unnecessary words, and check for consistency in aspects such as heading formatting and spellings .
Finally, you need to make sure your paper is correctly formatted according to the rules of the citation style you are using. For example, you might need to include an MLA heading or create an APA title page .
Scribbr’s professional editors can help with the revision process with our award-winning proofreading services.
Discover our paper editing service
Checklist: Research paper
I have followed all instructions in the assignment sheet.
My introduction presents my topic in an engaging way and provides necessary background information.
My introduction presents a clear, focused research problem and/or thesis statement .
My paper is logically organized using paragraphs and (if relevant) section headings .
Each paragraph is clearly focused on one central idea, expressed in a clear topic sentence .
Each paragraph is relevant to my research problem or thesis statement.
I have used appropriate transitions to clarify the connections between sections, paragraphs, and sentences.
My conclusion provides a concise answer to the research question or emphasizes how the thesis has been supported.
My conclusion shows how my research has contributed to knowledge or understanding of my topic.
My conclusion does not present any new points or information essential to my argument.
I have provided an in-text citation every time I refer to ideas or information from a source.
I have included a reference list at the end of my paper, consistently formatted according to a specific citation style .
I have thoroughly revised my paper and addressed any feedback from my professor or supervisor.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (page numbers, headers, spacing, etc.).
You've written a great paper. Make sure it's perfect with the help of a Scribbr editor!
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
- Writing a Research Paper Conclusion | Step-by-Step Guide
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
More interesting articles
- Academic Paragraph Structure | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Checklist: Writing a Great Research Paper
- How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- How to Write Topic Sentences | 4 Steps, Examples & Purpose
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Research Paper Damage Control | Managing a Broken Argument
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Skip navigation

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
Handling sensitive questions in surveys and screeners.

August 9, 2024 2024-08-09
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
Frequently, surveys and screeners contain questions that some respondents may find sensitive or be reluctant to answer. Even questions that might seem innocuous to a researcher, like age, gender, or income level, could cause an emotional response from your respondents.
This article guides you through handling sensitive questions in surveys and screeners and provides some example wording for you to use in the future.
In This Article:
Which questions are sensitive, guidelines for handling sensitive questions, specific question wordings.
Researchers should always attempt to avoid any possible discomfort experienced by their research participants. In addition to the obvious ethical implications, sensitive questions could cause participants to either abandon the survey or, worse, provide unreliable answers.
A sensitive question is one that respondents might find embarrassing or invasive.
There are multiple categories of sensitive questions to be aware of, but two are particularly worthy of consideration for user researchers: demographic questions and questions about socially undesirable behaviors.
Demographic Questions
Survey researchers often add demographic questions to a questionnaire without considering how they might be construed. While many survey takers might breeze through demographic questions, they can be potentially triggering or offensive for some respondents.
Demographic questions that have the potential to be perceived as sensitive include those asking about:
- Income level
Income level can be especially problematic and lead to high rates of nonresponse. One study by Jeffrey Moore and colleagues found that questions about income are 10 times more likely to be left blank than other demographic questions.
Sex and gender are other categories of questions that can be sensitive depending on one’s gender identity. Take this question from a recent Nielsen Radio Ratings survey.

Many people would easily complete this question without a second thought. However, consider this account from genderqueer essayist s.e. smith:
“For some trans* folk, it is a place of endless heartbreak. Every. Single. Time. I fill out a form, I stop here. There is a long pause. A hesitation. A sigh. I am not male. I am not female. On paper forms, I often leave it blank [...] Imagine dreading the filling out of forms not because it’s a hassle and it’s repetitive and it’s not very fun. Imagine dreading it because you know that you are going to have to lie and erase yourself every time you fill out a form.”
User researchers like to refer to themselves as user advocates. This lofty designation extends not only to designing delightful user experiences and interfaces but also to protecting the human experiences of our research participants. This includes all participants, not just those that fall into a perceived norm.
Questions About Socially Undesirable Behaviors
Social-desirability bias is a cognitive bias that dictates that people are less likely to disclose behaviors or preferences that are deemed to be undesirable by society. Behaviors that are considered socially undesirable can vary from person to person and, therefore, are likely to slip undetected through a survey creation process.
Common behaviors known to lead to underreporting in surveys include:
- Alcohol consumption
- Cigarette smoking (especially during pregnancy)
However, there are less obvious behaviors as well. For example, voting is also considered a socially desirable behavior, and in many surveys, the reported voting rate is higher than the real one.
Beyond these categories, additional topics that might include sensitive questions include the following:
- Questions about illegal activity
- Identifying information (e.g., home address)
- Emotionally upsetting topics (e.g., health concerns or victimization)
- Information that might be threatening in the wrong hands (e.g., disclosing a preexisting health condition)
While the strategy for addressing sensitive survey questions will vary based on multiple factors, some general guidelines are always helpful.
Determine if You Really Need to Ask
Researchers frequently include demographic questions in a survey just out of habit, without considering whether asking is truly necessary. To optimize response rate, surveys should be kept as short as possible, and therefore any question should be included only if necessary for the research at hand.
Here are 2 questions you should ask yourself before including any question in a questionnaire, regardless of sensitivity.
1. Do You Truly Care About the Answer?
Don’t ask questions because you’re merely curious, or assume all questionnaires should include basic demographic questions. If you have no plans to make decisions based on the outcome, you probably shouldn’t include the question.
2. Can You Find the Answer Another Way?
Are you using a recruiting panel like UserTesting.com or User Interviews? If so, a lot of demographic data about respondents is already included in their profiles and, therefore, doesn’t need to be asked.
Are you asking about browsing behavior on your site, data that could be gathered more accurately from analytics? Don’t ask users to provide you with information that you can access in another, less intrusive way.
Emphasize Confidentiality and Anonymity
Whether to keep participant data confidential, anonymous, or both is an important consideration in survey methodology. While often conflated, these two terms describe two different concepts.
Anonymity means a participant's data cannot be traced back to their identity. Ensuring anonymity may mean using a pseudonym or code number instead of the participant’s name in reporting.
Confidentiality limits the people who are permitted to view the response. Ensuring confidentiality might mean that no one beyond the immediate research team will ever view the survey data.
Anonymity is typically required in most cases of user research, and confidentiality is typically overkill. That said, adding the promise of confidentiality can sometimes increase the likelihood of complete and honest responses to sensitive questions.
Respondents should never have to guess whether a survey is anonymous, confidential, both, or neither. This information should be readily available to respondents when they are deciding whether to take the survey. For example:
Your privacy is important to us. All responses to this survey will be kept strictly confidential. Individual answers will be anonymized and aggregated for analysis. Your personal information will not be shared with any third parties, and will only be used for the purpose of this research. Thank you for your participation.
Lead Up to Sensitive Questions
Sensitive questions placed too early in a questionnaire or screener are more likely to lead to dropoffs. Build respondent trust with nonsensitive questions first, allowing them to invest effort in the process.
This guideline also applies to demographic questions, which should be optional and placed at the end of a questionnaire, not at the beginning, as is often the case. Demographic questions at the beginning are much more likely to lead to dropoffs than demographic questions at the end, even when they are not deemed to be sensitive.
Also, avoid placing particularly sensitive questions at the very end of a survey. If you inadvertently offend a respondent, you don’t want that to be their lasting impression of the survey.
Provide Context and Use “Question Loading”
UXers love to remove unnecessary text from interfaces and forms. Sometimes, however, adding more information is necessary.
First, you may use question loading (not to be confused with a leading question ). Question loading is the inclusion of additional context that may assuage respondent guilt or shame around questionable behavior.
Original question: Do you save a portion of your income each month?
With question loading: Given the rising cost of living and various financial commitments, many people find it challenging to save regularly. How often are you able to save a portion of your income each month?
Additionally, if a question or topic may raise eyebrows, consider explaining the purpose of asking it and the benefit that could come from answering it honestly. For example, if a survey asks a question about abortion, the drafter may include language such as the following:
We are conducting a survey to understand people's experiences with abortion. Please know that your responses are completely anonymous and will be used solely to improve access to abortion care for those who need it. We approach this topic with sensitivity and without judgment.
Use Ranges Rather than Specific Values
Imagine you want to ask about someone’s income — something they may reasonably feel sensitive about sharing. Imagine someone’s reaction to reading the following question:
What is your annual household income: __________
A respondent would likely feel very apprehensive about sharing their specific income for several reasons. They may:
- Worry about how their income will compare to the rest of the sample and whether they would be an outlier on either end of the scale
- Be confused about input formats (Do I include a dollar sign? Do I include “.00 ”? Do I include “ per year ”?)
- Worry about whether giving an exact number may be somehow identifying or overly revealing
- Be reluctant to do math if their income is variable or complex
Now consider the following format instead:
What is your total annual household income?
- $24,999 or less
- $25,000 to $49,999
- $50,000 to $74,999
- $75,000 to $99,999
- $100,000 to $149,999
- $150,000 to $199,999
- $200,000 or more
This tweak addresses all the previous concerns. With this question format, a respondent would:
- Have a sense of how their income compares to the range, and hopefully get some reassurance that they are not alone in whatever range they fall into
- Not need to worry about an input format
- Not need to provide an exact number
- Be less likely to need to do math
Ranges feel less sensitive than asking for specific values. The larger the ranges provided, the less sensitive the request feels.
Ask About Frequency Rather than Yes/No Questions
Consider the following question from the 2019 Youth Risk Behaviors Survey.
During your life, how many times have you used marijuana?
- 1 or 2 times
- 3 to 9 times
- 10 to 19 times
- 20 to 39 times
- 40 to 99 times
- 100 or more times
Rather than simply asking Have you ever used marijuana? (which, admittedly, would probably have been easier for respondents to answer correctly if they had been willing to share that information) , the researchers asked about the frequency of use. While the Yes/No formulation may imply a moral judgment and encourage lying, the frequency question makes a slight assumption that the respondent has indeed used marijuana in the past, which encourages honesty.
Additionally, you may wish to provide additional response options at the end of the range that may be perceived as undesirable, to skew the responses away from bias. For example, consider the following question about exercise frequency.
How often do you engage in physical exercise each month?
- 0 to 3 times a month
- 4 to 7 times a month
- 8 to 12 times a month
- 13 to 20 times a month
- More than 20 times a month
Someone who only works out once or twice per month may feel shame around selecting the bottommost option, and dishonestly select a response towards the middle of the range (see central-tendency bias ).
The following formulation would likely encourage more honest responses from infrequent exercisers.
- 0 times a month
- 1 to 2 times a month
- 3 to 4 times a month
- 5 to 7 times a month
Ask Indirectly
For particularly sensitive topics, researchers may wish to employ an indirect surveying technique, such as the item-count method.
In this approach, the respondent population is divided into two groups. Each group is asked an identical question about how many behaviors from a list they have engaged in, with the addition of the behavior in question for only one of the groups.
For example, consider this question from a 2014 study by Jouni Kuha and Jonathan Jackson at the London School of Economics:
I am now going to read you a list of five [six] things that people may do or that may happen to them. Please listen to them and tell me how many of them you have done or have happened to you in the last 12 months. Do not tell me which ones are and are not true for you. Just tell me how many you have done at least once. Attended a religious service, except for a special occasion like a wedding or funeral Went to a sporting event Attended an opera Visited a country outside [your country] Had personal belongings such as money or a mobile phone stolen from you or from your house? Treatment group only: Bought something you thought might have been stolen
During the analysis, the research will then compare the differences between the two groups in order to estimate the frequency of the behavior in question.
Embed the Sensitive Question
A single sensitive question in an otherwise mundane questionnaire can stand out and be jarring. Researchers may attempt to disarm the respondent with other slightly sensitive questions to mask the question of interest.
Some questions (e.g., demographic questions) are very common and potentially sensitive. The following section includes recommendations for specific wording for these questions. You are welcome to utilize these wordings in your own surveys and screeners.
Sex and Gender
Sex and gender, while frequently conflated and confused, are different (sex is biological characteristics, whereas gender is one’s social identity). The first question you need to ask yourself when asking about sex or gender (after asking, “Do I really need to be asking at all?”) is, “Which one do I care about?” Most of the time, UX researchers care about gender, not sex.
The most important thing to remember when asking about gender is to use inclusive and gender-expansive language that captures the full breadth of gender identity that society now recognizes.
First, consider the question wording. Please select your gender implies that one of the options provided will be a perfect match for the respondent’s gender identity and, therefore, requires the inclusion of an Other:_______ option.
On the other hand, Which of the following best represents your gender? implies only a best fit, so the use of a fill-in-the-blank Other option, while still advisable, is not required.
Next, consider the options provided. It is no longer acceptable to limit gender identity options to simply man and woman . Society’s understanding of gender identity has expanded, and research methods must reflect that.
In most instances, it is sufficient to limit options to the following categories:
- Prefer to self-describe:_______
- Prefer not to disclose
If you additionally have a need to know whether someone is transgender (e.g., in order to differentiate between cisgender men and transgender men, both of whom would select Man from the above options), ask a followup question:
Do you identify as transgender?
If you are conducting research for which a granular and inclusive capturing of one’s gender identity is necessary, consider using the following options to the first question and omitting the followup transgender question.
- Cisgender man
- Cisgender woman
- Transgender man
- Transgender woman
- Nonbinary person
- Genderqueer/genderfluid person
- Agender person
- Two-spirit person
- Intersex person
- Prefer to self-describe:______
Age is a common question in in user-research surveys, as age may correlate to distinct persona traits. Adhere to the following best practices when asking about age:
| Rule | ❌ | ✅ |
| Provide options with ranges, rather than an open text field. | ? [text field] |
|
| Ensure ranges are all-inclusive (i.e., include all possible ages within the options provided). | ||
| Ensure ranges are nonoverlapping. | ||
| Frontload the number. |
|
|
| Avoid language that may cause shame or judgement. |
|
|
| Use to rather than dashes for better readability ( |
|
|
| Use conversational questions rather than more “accurate” but confusing ones (e.g., How old are you? rather than Which age range best describes you?). |
|
|
One recommended wording is:
How old are you? (single select)
- 17 or under
Race and Ethnicity
Like sex and gender, race and ethnicity are often confused but are different (race refers to physical traits; ethnicity refers to cultural identity and heritage).
Determine first which you care about. It is possible to formulate questions that ask about race only, about ethnicity only, or about both.
Additionally, be aware that many people identify with more than one racial and ethnic group and will be excluded if you force them to pick one. For this reason, use multiselect question formats for these questions.
How do you describe yourself? (multiselect)
- American Indian or Alaska Native
- Black or African American
- Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander
- White or Caucasian
- Other:______
Just Ethnicity
Are you of Hispanic, Latinx, or of Spanish origin? (single select)
You can ask about both race and ethnicity separately, using the two questions above, or you can combine them into a single question:
How do you describe yourself? (multi-select)
- Hispanic or Latinx
Accessibility Needs and Disabilities
When asking about accessibility needs or disability, do so directly, using language used by the communities in question.
Do you have any of the following accessibility needs? (Select all that apply)
- Cognitive: such as dyslexia or ADHD
- Emotional: such as anxiety or depression
- Hearing: such as deafness or hearing loss
- Motor: such as cerebral Palsy or arthritis
- Visual: such as blindness or vision loss
- Other:________
- No, I don’t have any accessibility needs
Make sure to avoid language that implies negativity (e.g., Do you have diabetes? instead of Do you suffer from diabetes?; Do you use a wheelchair ? instead of Are you confined to a wheelchair? ).
Language Proficiency
Suppose you need to know about someone’s qualitative assessment of their own language proficiency. In that case, it is helpful to provide a brief description of each answer option to ensure understanding, particularly if the reader is less proficient with the language.
How would you describe your English language level (or proficiency)?
- Native / Mother-tongue: English is my first language
- Fluent: I can speak, read, and write in English fluently
- Proficient: I am skilled in English but not fluent
- Conversational: I can communicate effectively in English in most situations
- Basic knowledge: I have a basic knowledge of the language
Groves, R.M., Fowler Jr, F.J., Couper, M.P., Lepkowski, J.M., Singer, E., and Tourangeau, R. 2009. Survey Methodology . 2nd ed. Wiley.
Jarrett, C. 2021. Surveys That Work . Rosenfeld Media.
Kuha, J. and Jackson, J. 2014. The item count method for sensitive survey questions: modelling criminal behaviour. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series C (Applied Statistics) 63, 2 (Feb. 2014), 321-341. Published by Oxford University Press.
Moore, J., Stinson, L., and Welniak, E. 1997. Income Measurement Error in Surveys: A Review. In Cognition and Survey Research, Sirken, M., Herrmann, D., Schechter, S., Schwarz, N., Tanur, J., and Tourangeau, R. (Eds.). Wiley, New York, 155-174.
smith, s.e. 2009. Beyond the Binary: Forms. Retrieved March 31, 2021, from meloukhia.net/2009/12/beyond_the_binary_forms/.
Related Courses
Survey design and execution.
Use surveys to drive and evaluate UX design
Assessing UX Designs Using Proven Principles
Analyze user experiences using heuristics and assessments
Analytics and User Experience
Study your users’ real-life behaviors and make data-informed design decisions
Related Topics
- Research Methods Research Methods
Learn More:

What Is a SWOT Analysis?
Therese Fessenden · 5 min

What Is User Research?
Caleb Sponheim · 3 min

Competitive Reviews vs. Competitive Research
Therese Fessenden · 4 min
Related Articles:
Should You Run a Survey?
Maddie Brown · 6 min
How to Run Surveys at Every Stage of the Design Cycle
Writing Good Survey Questions: 10 Best Practices
Maddie Brown · 9 min
10 Survey Challenges and How to Avoid Them
Tanner Kohler · 15 min
User-Feedback Requests: 5 Guidelines
Anna Kaley · 10 min
28 Tips for Creating Great Qualitative Surveys
Susan Farrell · 9 min
Free Al Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
- Articles of Word
How to Write a Research Paper [Steps & Examples]
As a student, you are often required to complete numerous academic tasks, which can demand a lot of extra effort. Writing a research paper is one of these tasks. If researching for the topic isn't challenging enough, writing it down in a specific format adds another layer of difficulty. Having gone through this myself, I want to help you have a smoother journey in writing your research paper. I'll guide you through everything you need to know about writing a research paper, including how to write a research paper and all the necessary factors you need to consider while writing one.
Order for Preparation of your research paper
Before beginning your research paper, start planning how you will organize your paper. Follow the specific order I have laid out to ensure you assemble everything correctly, cover all necessary components, and write more effectively. This method will help you avoid missing important elements and improve the overall quality of your paper.
Figures and Tables
Assemble all necessary visual aids to support your data and findings. Ensure they are labeled correctly and referenced appropriately in your text.
Detail the procedures and techniques used in your research. This section should be thorough enough to allow others to replicate your study.
Summarize the findings of your research without interpretation. Use figures and tables to illustrate your data clearly.
Interpret the results, discussing their implications and how they relate to your research question. Address any limitations and suggest areas for future research.
Summarize the key points of your research, restating the significance of your findings and their broader impact.
Introduction
Introduce the topic, provide background information, and state the research problem or hypothesis. Explain the purpose and scope of your study.
Write a concise summary of your research, including the objective, methods, results, and conclusion. Keep it brief and to the point.
Create a clear and informative title that accurately reflects the content and focus of your research paper.
Identify key terms related to your research that will help others find your paper in searches.
Acknowledgements
Thank those who contributed to your research, including funding sources, advisors, and any other significant supporters.
Compile a complete list of all sources cited in your paper, formatted according to the required citation style. Ensure every reference is accurate and complete.
Types of Research Papers
There are multiple types of research papers, each with distinct characteristics, purposes, and structures. Knowing which type of research paper is required for your assignment is crucial, as each demands different preparation and writing strategies. Here, we will delve into three prominent types: argumentative, analytical, and compare and contrast papers. We will discuss their characteristics, suitability, and provide detailed examples to illustrate their application.
A.Argumentative Papers
Characteristics:
An argumentative or persuasive paper is designed to present a balanced view of a controversial issue, but ultimately aims to persuade the reader to adopt the writer's perspective. The key characteristics of this type of paper include:
Purpose: The primary goal is to convince the reader to support a particular stance on an issue. This is achieved by presenting arguments, evidence, and refuting opposing viewpoints.
Structure: Typically structured into an introduction, a presentation of both sides of the issue, a refutation of the opposing arguments, and a conclusion that reinforces the writer’s position.
Tone: While the tone should be logical and factual, it should not be overly emotional. Arguments must be supported with solid evidence, such as statistics, expert opinions, and factual data.
Suitability:
Argumentative papers are suitable for topics that have clear, opposing viewpoints. They are often used in debates, policy discussions, and essays aimed at influencing public opinion or academic discourse.
Topic: "Should governments implement universal basic income?"
Pro Side: Universal basic income provides financial security, reduces poverty, and can lead to a more equitable society.
Con Side: It could discourage work, lead to higher government expenditure, and might not be a sustainable long-term solution.
Argument: After presenting both sides, the paper would argue that the benefits of reducing poverty and financial insecurity outweigh the potential drawbacks, using evidence from various studies and real-world examples.
Writing Tips:
Clearly articulate your position on the issue from the beginning.
Present balanced arguments by including credible sources that support both sides.
Refute counterarguments effectively with logical reasoning and evidence.
Maintain a factual and logical tone, avoiding excessive emotional appeals.
B.Analytical Papers
An analytical research paper is focused on breaking down a topic into its core components, examining various perspectives, and drawing conclusions based on this analysis. The main characteristics include:
Purpose: To pose a research question, collect data from various sources, analyze different viewpoints, and synthesize the information to arrive at a personal conclusion.
Structure: Includes an introduction with a clear research question, a literature review that summarizes existing research, a detailed analysis, and a conclusion that summarizes findings.
Tone: Objective and neutral, avoiding personal bias or opinion. The focus is on data and logical analysis.
Analytical research papers are ideal for topics that require detailed examination and evaluation of various aspects. They are common in disciplines such as social sciences, humanities, and natural sciences, where deep analysis of existing research is crucial.
Topic: "The impact of social media on mental health."
Research Question: How does social media usage affect mental well-being among teenagers?
Analysis: Examine studies that show both positive (e.g., social support) and negative (e.g., anxiety and depression) impacts of social media. Analyze the methodologies and findings of these studies.
Conclusion: Based on the analysis, conclude whether the overall impact is more beneficial or harmful, remaining neutral and presenting evidence without personal bias.
Maintain an objective and neutral tone throughout the paper.
Synthesize information from multiple sources, ensuring a comprehensive analysis.
Develop a clear thesis based on the findings from your analysis.
Avoid inserting personal opinions or biases.
C.Compare and Contrast Papers
Compare and contrast papers are used to analyze the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. The key characteristics include:
Purpose: To identify and examine the similarities and differences between two or more subjects, providing a comprehensive understanding of their relationship.
Structure: Can be organized in two ways:
Point-by-Point: Each paragraph covers a specific point of comparison or contrast.
Subject-by-Subject: Each subject is discussed separately, followed by a comparison or contrast.
Tone: Informative and balanced, aiming to provide a thorough and unbiased comparison.
Compare and contrast papers are suitable for topics where it is important to understand the distinctions and similarities between elements. They are commonly used in literature, history, and various comparative studies.
Topic: "Compare and contrast the leadership styles of Martin Luther King Jr. and Malcolm X."
Comparison Points: Philosophies (non-violence vs. militant activism), methods (peaceful protests vs. more radical approaches), and impacts on the Civil Rights Movement.
Analysis: Describe each leader's philosophy and method, then analyze how these influenced their effectiveness and legacy.
Conclusion: Summarize the key similarities and differences, and discuss how both leaders contributed uniquely to the movement.
Provide equal and balanced coverage to each subject.
Use clear criteria for comparison, ensuring logical and coherent analysis.
Highlight both similarities and differences, ensuring a nuanced understanding of the subjects.
Maintain an informative tone, focusing on objective analysis rather than personal preference.
How to Write A Research Paper [Higher Efficiency & Better Results]
Conduct Preliminary Research
Before we get started with the research, it's important to gather relevant information related to it. This process, also known as the primary research method, helps researchers gain preliminary knowledge about the topic and identify research gaps. Whenever I begin researching a topic, I usually utilize Google and Google Scholar. Another excellent resource for conducting primary research is campus libraries, as they provide a wealth of great articles that can assist with your research.
Now, let's see how WPS Office and AIPal can be great research partners:
Let's say that I have some PDFs which I have gathered from different sources. With WPS Office, these PDFs can be directly uploaded not just to extract key points but also to interact with the PDF with special help from WPS AI.
Step 1: Let's open the PDF article or research paper that we have downloaded on WPS Office.
Step 2: Now, click on the WPS AI widget at the top right corner of the screen.
Step 3: This will open the WPS PDF AI pane on the right side of the screen. Click on "Upload".
Step 4: Once the upload is complete, WPS PDF AI will return with the key points from the PDF article, which can then be copied to a fresh new document on WPS Writer.
Step 5: To interact further with the document, click on the "Inquiry" tab to talk with WPS AI and get more information on the contents of the PDF.
Research is incomplete without a Google search, but what exactly should you search for? AIPal can help you with these answers. AIPal is a Chrome extension that can help researchers make their Google searches and interactions with Chrome more effective and efficient. If you haven't installed AIPal on Chrome yet, go ahead and download the extension; it's completely free to use:
Step 1: Let's search for a term on Google related to our research.
Step 2: An AIPal widget will appear right next to the Google search bar, click on it.
Step 3: Upon clicking it, an AIPal window will pop up. In this window, you will find a more refined answer for your searched term, along with links most relevant to your search, providing a more refined search experience.
WPS AI can also be used to extract more information with the help of WPS Writer.
Step 1: We might have some information saved in a Word document, either from lectures or during preliminary research. We can use WPS AI within Writer to gain more insights.
Step 2: Select the entire text you want to summarize or understand better.
Step 3: Once the text is selected, a hover menu will appear. Click on the "WPS AI" icon in this menu.
Step 4: From the list of options, click on "Explain" to understand the content more deeply, or click on "Summarize" to shorten the paragraph.
Step 5: The results will be displayed in a small WPS AI window.
Develop the Thesis statement
To develop a strong thesis statement, start by formulating a central question your paper will address. For example, if your topic is about the impact of social media on mental health, your thesis statement might be:
"Social media use has a detrimental effect on mental health by increasing anxiety, depression, and loneliness among teenagers."
This statement is concise, contentious, and sets the stage for your research. With WPS AI, you can use the "Improve" feature to refine your thesis statement, ensuring it is clear, coherent, and impactful.
Write the First draft
Begin your first draft by focusing on maintaining forward momentum and clearly organizing your thoughts. Follow your outline as a guide, but be flexible if new ideas emerge. Here's a brief outline to get you started:
Using WPS AI’s "Make Longer" feature, you can quickly elaborate key ideas and points of your studies and articles into a descriptive format to include in your draft, saving time and ensuring clarity.
Compose Introduction, Body and Conclusion paragraphs
When writing a research paper, it’s essential to transform your key points into detailed, descriptive paragraphs. WPS AI can help you streamline this process by enhancing your key points, ensuring each section of your paper is well-developed and coherent. Here’s how you can use WPS AI to compose your introduction, body, and conclusion paragraphs:
Let's return to the draft and start composing our introduction. The introduction should provide the background of the research paper and introduce readers to what the research paper will explore.
If your introduction feels too brief or lacks depth, use WPS AI’s "Make Longer" feature to expand on key points, adding necessary details and enhancing the overall narrative.
Once the introduction is completed, the next step is to start writing the body paragraphs and the conclusion of our research paper. Remember, the body paragraphs will incorporate everything about your research: methodologies, challenges, results, and takeaways.
If this paragraph is too lengthy or repetitive, WPS AI’s "Make Shorter" feature can help you condense it without losing essential information.
Write the Second Draft
In the second draft, refine your arguments, ensure logical flow, and check for clarity. Focus on eliminating any unnecessary information, ensuring each paragraph supports your thesis statement, and improving transitions between ideas. Incorporate feedback from peers or advisors, and ensure all citations are accurate and properly formatted. The second draft should be more polished and coherent, presenting your research in a clear and compelling manner.
WPS AI’s "Improve Writing" feature can be particularly useful here to enhance the overall quality and readability of your paper.
WPS Spellcheck can assist you in correcting spelling and grammatical errors, ensuring your paper is polished and professional. This tool helps you avoid common mistakes and enhances the readability of your paper, making a significant difference in the overall quality.
Bonus Tips: How to Get Inspiration for your Research Paper- WPS AI
WPS Office is a phenomenal office suite that students find to be a major blessing. Not only is it a free office suite equipped with advanced features that make it competitive in the market, but it also includes a powerful AI that automates and enhances many tasks, including writing a research paper. In addition to improving readability with its AI Proofreader tool, WPS AI offers two features, "Insight" and "Inquiry", that can help you gather information and inspiration for your research paper:
Insight Feature:
The Insight feature provides deep insights and information on various topics and fields. It analyzes literature to extract key viewpoints, trends, and research directions. For instance, if you're writing a research paper on the impact of social media on mental health, you can use the Insight feature to gather a comprehensive overview of the latest studies, key arguments, and emerging trends in this field. This helps you build a solid foundation for your paper and ensure you are covering all relevant aspects.
Inquiry Feature:
The Inquiry feature allows you to ask specific questions related to your research topic. This helps you gather necessary background information and refine your research focus effectively. For example, if you need detailed information on how social media usage affects teenagers' self-esteem, you can use the Inquiry feature to ask targeted questions and receive relevant answers based on the latest research.
FAQs about writing a research paper
1. can any source be used for academic research.
No, it's essential to use credible and relevant sources. Here is why:
Developing a Strong Argument: Your research paper relies on evidence to substantiate its claims. Using unreliable sources can undermine your argument and harm the credibility of your paper.
Avoiding Inaccurate Information: The internet is abundant with data, but not all sources can be considered reliable. Credible sources guarantee accuracy.
2. How can I avoid plagiarism?
To avoid plagiarism, follow these steps:
Keep Records of Your Sources: Maintain a record of all the sources you use while researching. This helps you remember where you found specific ideas or phrases and ensures proper attribution.
Quote and Paraphrase Correctly: When writing a paper, use quotation marks for exact words from a source and cite them properly. When paraphrasing, restate the idea in your own words and include a citation to acknowledge the original source.
Utilize a Plagiarism Checker: Use a plagiarism detection tool before submitting your paper. This will help identify unintentional plagiarism, ensuring your paper is original and properly referenced.
3. How can I cite sources properly?
Adhere to the citation style guide (e.g., APA, MLA) specified by your instructor or journal. Properly citing all sources both within the text and in the bibliography or references section is essential for maintaining academic integrity and providing clear credit to the original authors. This practice also helps readers locate and verify the sources you've used in your research.
4. How long should a research paper be?
The length of a research paper depends on its topic and specific requirements. Generally, research papers vary between 4,000 to 6,000 words, with shorter papers around 2,000 words and longer ones exceeding 10,000 words. Adhering to the length requirements provided for academic assignments is essential. More intricate subjects or extensive research often require more thorough explanations, which can impact the overall length of the paper.
Write Your Research Paper with the Comfort of Using WPS Office
Writing a research paper involves managing numerous complicated tasks, such as ensuring the correct formatting, not missing any crucial information, and having all your data ready. The process of how to write a research paper is inherently challenging. However, if you are a student using WPS Office, the task becomes significantly simpler. WPS Office, especially with the introduction of WPS AI, provides all the resources you need to write the perfect research paper. Download WPS Office today and discover how it can transform your research paper writing experience for the better.
- 1. Free Graph Paper: Easy Steps to Make Printable Graph Paper PDF
- 2. How to Write a Hook- Steps With Examples
- 3. How to Use WPS AI/Chatgpt to Write Research Papers: Guide for Beginners
- 4. How to Write a Proposal [ Steps & Examples]
- 5. How to Write an Abstract - Steps with Examples
- 6. How to Write a Conclusion - Steps with Examples

15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Learn how to turn a weak research question into a strong one with examples suitable for a research paper, thesis or dissertation.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
Framing the research question is the first step in any research project, and you can learn how to write a research question that is focused, achievable, and answerable! Check this detailed article to know what a research question is, the different types, and a step-by-step process to formulate effective research questions, with examples.
Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
You will ask a question whenever you are interested in learning more about a topic. That's why the research question is an integral part of the research process. Also, it provides the author with reading and writing guidelines.
Learn what a research question is, how it's different from a research aim or objective, and how to write a high-quality research question.
A well-crafted research question (or set of questions) sets the stage for a robust study and meaningful insights. But, if you're new to research, it's not always clear what exactly constitutes a good research question. In this post, we'll provide you with clear examples of quality research questions across various disciplines, so that you can approach your research project with confidence!
Why is a research question essential to the research process? Research questions help writers focus their research by providing a path through the research and writing process. The specificity of a well-developed research question helps writers avoid the "all-about" paper and work toward supporting a specific, arguable thesis.
A well-written research question is a key element that must be identified and pinned down before researchers can even begin their research study or work. Read this article to learn how to write a strong research question with some good examples of research questions across disciplines.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
In this article, we take an in-depth look at what a research question is, the different types of research questions, and how to write one (with examples). Read on to get started with your thesis, dissertation, or research paper.
Learn to write research questions with the mentioned steps required for a perfect research question. Choose a topic and begin your research.
Given this challenge, I have created this guide on how to create a good research question based on actual practices in the academe. Through this guide, I hope to impart knowledge that can help you in identifying a research question and also in creating a study that can significantly impact your field.
Keep the scope of your research manageable. Ask a question that will lead you into your research—a specific, concrete question that will help you devise a working thesis and give you direction for your information search. Generally, the answer to your question should take a stance. Is the scope of the question appropriate for the assignment?
A research paper relies on a research question to inform readers of the research topic and the research problem being addressed. Without such a question, your audience may have trouble understanding the rationale for your research project. A research question highlights knowledge gaps that research can address.
How do I write questions to ask for research? All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly. Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis.
Asking a Research Question A good research topic isn't about the answers you find: it's about the questions you ask. Asking the right research question can help you narrow your topic to a manageable scope for your project, find keywords to look for sources, and eventually find a more nuanced angle on your topic.
Developing the right research questions is a critical first step in the research process. A research question is a question that a study or research project aims to answer. This question often addresses an issue or a problem, which, through analysis and interpretation of data, is answered in the study's conclusion.
Find out how to email a researcher to ask for details about their paper. Get tips on etiquette, tone and content from experienced academics and peers.
Go to the Q&A overview page. Click Ask a technical question or Start discussion. Enter your question or title in the box provided at the top of the page. Enter an explanation in the second field and provide as much contextual detail as possible to help other researchers answer your question. Attach resources that support your question, such as ...
Ensuring clear communication of research findings. AF: To ensure research findings are clearly communicated, you should be able to state the significance of those findings in one sentence—if you don't have that simple, clear claim in your mind, you will not be able to communicate it. MS: The most important thing is clear and concise ...
2 - Preliminary Research: Do a quick survey of what resources are out there that address your subject. Reviewing the literature on your topic will give you an idea of where you can look for more information and what angle you can take in your paper. Ask yourself who, what, where, and when you need to know to address your subject.
A research paper explores and evaluates previously and newly gathered information on a topic, then offers evidence for an argument. It follows academic writing standards, and virtually every college student will write at least one. Research papers are also integral to scientific fields, among others, as the most reliable way to share knowledge.
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers' plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed ...
Today, we're excited to introduce the capability for scite users to ask research questions in plain language and get answers directly from the full text of research articles.
Research papers are similar to academic essays, but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research. Writing a research paper requires you to demonstrate a strong knowledge of your topic, engage with a variety of sources, and make an original contribution to the debate.
Get help with your research. Join ResearchGate to ask questions, get input, and advance your work. ... This research paper aims to investigate the extent to which SHA-3 is a better cryptographic ...
To optimize response rate, surveys should be kept as short as possible, and therefore any question should be included only if necessary for the research at hand. Here are 2 questions you should ask yourself before including any question in a questionnaire, regardless of sensitivity. 1. Do You Truly Care About the Answer?
The Inquiry feature allows you to ask specific questions related to your research topic. This helps you gather necessary background information and refine your research focus effectively. For example, if you need detailed information on how social media usage affects teenagers' self-esteem, you can use the Inquiry feature to ask targeted ...
The document proposes slashing federal money for research and investment in renewable energy, and calls for the next president to "stop the war on oil and natural gas".