- Log in / Register

- Getting started
- Criteria for a problem formulation
- Find who and what you are looking for
- Too broad, too narrow, or o.k.?
- Test your knowledge
- Lesson 5: Meeting your supervisor
- Getting started: summary
- Literature search
- Searching for articles
- Searching for Data
- Databases provided by your library
- Other useful search tools
- Free text, truncating and exact phrase
- Combining search terms – Boolean operators
- Keep track of your search strategies
- Problems finding your search terms?
- Different sources, different evaluations
- Extract by relevance
- Lesson 4: Obtaining literature
- Literature search: summary
- Research methods
- Combining qualitative and quantitative methods
- Collecting data
- Analysing data

Strengths and limitations
- Explanatory, analytical and experimental studies
- The Nature of Secondary Data
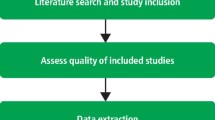
- How to Conduct a Systematic Review
- Directional Policy Research
- Strategic Policy Research
- Operational Policy Research
- Conducting Research Evaluation
- Research Methods: Summary
- Project management
- Project budgeting
- Data management plan
- Quality Control
- Project control
- Project management: Summary
- Writing process
- Title page, abstract, foreword, abbreviations, table of contents
- Introduction, methods, results
- Discussion, conclusions, recomendations, references, appendices, layout
- Use citations correctly
- Use references correctly
- Bibliographic software
- Writing process – summary
- Research methods /
- Lesson 1: Qualitative and quan… /
Quantitative method Quantitive data are pieces of information that can be counted and which are usually gathered by surveys from large numbers of respondents randomly selected for inclusion. Secondary data such as census data, government statistics, health system metrics, etc. are often included in quantitative research. Quantitative data is analysed using statistical methods. Quantitative approaches are best used to answer what, when and who questions and are not well suited to how and why questions.
| Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Findings can be generalised if selection process is well-designed and sample is representative of study population | Related secondary data is sometimes not available or accessing available data is difficult/impossible |
| Relatively easy to analyse | Difficult to understand context of a phenomenon |
| Data can be very consistent, precise and reliable | Data may not be robust enough to explain complex issues |
Qualitative method Qualitative data are usually gathered by observation, interviews or focus groups, but may also be gathered from written documents and through case studies. In qualitative research there is less emphasis on counting numbers of people who think or behave in certain ways and more emphasis on explaining why people think and behave in certain ways. Participants in qualitative studies often involve smaller numbers of tools include and utilizes open-ended questionnaires interview guides. This type of research is best used to answer how and why questions and is not well suited to generalisable what, when and who questions.
| Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Complement and refine quantitative data | Findings usually cannot be generalised to the study population or community |
| Provide more detailed information to explain complex issues | More difficult to analyse; don’t fit neatly in standard categories |
| Multiple methods for gathering data on sensitive subjects | Data collection is usually time consuming |
| Data collection is usually cost efficient |
Learn more about using quantitative and qualitative approaches in various study types in the next lesson.
Your friend's e-mail
Message (Note: The link to the page is attached automtisk in the message to your friend)

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
A simplified approach to critically appraising research evidence
Affiliation.
- 1 School of Health and Life Sciences, Teesside University, Middlesbrough, England.
- PMID: 33660465
- DOI: 10.7748/nr.2021.e1760
Background Evidence-based practice is embedded in all aspects of nursing and care. Understanding research evidence and being able to identify the strengths, weaknesses and limitations of published primary research is an essential skill of the evidence-based practitioner. However, it can be daunting and seem overly complex.
Aim: To provide a single framework that researchers can use when reading, understanding and critically assessing published research.
Discussion: To make sense of published research papers, it is helpful to understand some key concepts and how they relate to either quantitative or qualitative designs. Internal and external validity, reliability and trustworthiness are discussed. An illustration of how to apply these concepts in a practical way using a standardised framework to systematically assess a paper is provided.
Conclusion: The ability to understand and evaluate research builds strong evidence-based practitioners, who are essential to nursing practice.
Implications for practice: This framework should help readers to identify the strengths, potential weaknesses and limitations of a paper to judge its quality and potential usefulness.
Keywords: literature review; qualitative research; quantitative research; research; systematic review.
©2021 RCN Publishing Company Ltd. All rights reserved. Not to be copied, transmitted or recorded in any way, in whole or part, without prior permission of the publishers.
PubMed Disclaimer
Conflict of interest statement
None declared
Similar articles
- The Effectiveness of Integrated Care Pathways for Adults and Children in Health Care Settings: A Systematic Review. Allen D, Gillen E, Rixson L. Allen D, et al. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(3):80-129. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907030-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27820426
- The future of Cochrane Neonatal. Soll RF, Ovelman C, McGuire W. Soll RF, et al. Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
- Promoting and supporting self-management for adults living in the community with physical chronic illness: A systematic review of the effectiveness and meaningfulness of the patient-practitioner encounter. Rees S, Williams A. Rees S, et al. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(13):492-582. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907130-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27819974
- Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature. Eddy K, Jordan Z, Stephenson M. Eddy K, et al. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314 Review.
- The nursing contribution to qualitative research in palliative care 1990-1999: a critical evaluation. Bailey C, Froggatt K, Field D, Krishnasamy M. Bailey C, et al. J Adv Nurs. 2002 Oct;40(1):48-60. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2648.2002.02339.x. J Adv Nurs. 2002. PMID: 12230529 Review.
- Special Collection Editorial: The digital movement in nursing. Cronin C. Cronin C. J Res Nurs. 2022 Aug;27(5):411-420. doi: 10.1177/17449871221117437. Epub 2022 Sep 17. J Res Nurs. 2022. PMID: 36131703 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
- Search in MeSH
LinkOut - more resources
Other literature sources.
- scite Smart Citations
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Published: 20 January 2009
How to critically appraise an article
- Jane M Young 1 &
- Michael J Solomon 2
Nature Clinical Practice Gastroenterology & Hepatology volume 6 , pages 82–91 ( 2009 ) Cite this article
52k Accesses
99 Citations
433 Altmetric
Metrics details
Critical appraisal is a systematic process used to identify the strengths and weaknesses of a research article in order to assess the usefulness and validity of research findings. The most important components of a critical appraisal are an evaluation of the appropriateness of the study design for the research question and a careful assessment of the key methodological features of this design. Other factors that also should be considered include the suitability of the statistical methods used and their subsequent interpretation, potential conflicts of interest and the relevance of the research to one's own practice. This Review presents a 10-step guide to critical appraisal that aims to assist clinicians to identify the most relevant high-quality studies available to guide their clinical practice.
Critical appraisal is a systematic process used to identify the strengths and weaknesses of a research article
Critical appraisal provides a basis for decisions on whether to use the results of a study in clinical practice
Different study designs are prone to various sources of systematic bias
Design-specific, critical-appraisal checklists are useful tools to help assess study quality
Assessments of other factors, including the importance of the research question, the appropriateness of statistical analysis, the legitimacy of conclusions and potential conflicts of interest are an important part of the critical appraisal process
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
195,33 € per year
only 16,28 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Making sense of the literature: an introduction to critical appraisal for the primary care practitioner
How to appraise the literature: basic principles for the busy clinician - part 2: systematic reviews and meta-analyses

How to appraise the literature: basic principles for the busy clinician - part 1: randomised controlled trials
Druss BG and Marcus SC (2005) Growth and decentralisation of the medical literature: implications for evidence-based medicine. J Med Libr Assoc 93 : 499–501
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Glasziou PP (2008) Information overload: what's behind it, what's beyond it? Med J Aust 189 : 84–85
PubMed Google Scholar
Last JE (Ed.; 2001) A Dictionary of Epidemiology (4th Edn). New York: Oxford University Press
Google Scholar
Sackett DL et al . (2000). Evidence-based Medicine. How to Practice and Teach EBM . London: Churchill Livingstone
Guyatt G and Rennie D (Eds; 2002). Users' Guides to the Medical Literature: a Manual for Evidence-based Clinical Practice . Chicago: American Medical Association
Greenhalgh T (2000) How to Read a Paper: the Basics of Evidence-based Medicine . London: Blackwell Medicine Books
MacAuley D (1994) READER: an acronym to aid critical reading by general practitioners. Br J Gen Pract 44 : 83–85
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hill A and Spittlehouse C (2001) What is critical appraisal. Evidence-based Medicine 3 : 1–8 [ http://www.evidence-based-medicine.co.uk ] (accessed 25 November 2008)
Public Health Resource Unit (2008) Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) . [ http://www.phru.nhs.uk/Pages/PHD/CASP.htm ] (accessed 8 August 2008)
National Health and Medical Research Council (2000) How to Review the Evidence: Systematic Identification and Review of the Scientific Literature . Canberra: NHMRC
Elwood JM (1998) Critical Appraisal of Epidemiological Studies and Clinical Trials (2nd Edn). Oxford: Oxford University Press
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (2002) Systems to rate the strength of scientific evidence? Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No 47, Publication No 02-E019 Rockville: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
Crombie IK (1996) The Pocket Guide to Critical Appraisal: a Handbook for Health Care Professionals . London: Blackwell Medicine Publishing Group
Heller RF et al . (2008) Critical appraisal for public health: a new checklist. Public Health 122 : 92–98
Article Google Scholar
MacAuley D et al . (1998) Randomised controlled trial of the READER method of critical appraisal in general practice. BMJ 316 : 1134–37
Article CAS Google Scholar
Parkes J et al . Teaching critical appraisal skills in health care settings (Review). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 3. Art. No.: cd001270. 10.1002/14651858.cd001270
Mays N and Pope C (2000) Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ 320 : 50–52
Hawking SW (2003) On the Shoulders of Giants: the Great Works of Physics and Astronomy . Philadelphia, PN: Penguin
National Health and Medical Research Council (1999) A Guide to the Development, Implementation and Evaluation of Clinical Practice Guidelines . Canberra: National Health and Medical Research Council
US Preventive Services Taskforce (1996) Guide to clinical preventive services (2nd Edn). Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins
Solomon MJ and McLeod RS (1995) Should we be performing more randomized controlled trials evaluating surgical operations? Surgery 118 : 456–467
Rothman KJ (2002) Epidemiology: an Introduction . Oxford: Oxford University Press
Young JM and Solomon MJ (2003) Improving the evidence-base in surgery: sources of bias in surgical studies. ANZ J Surg 73 : 504–506
Margitic SE et al . (1995) Lessons learned from a prospective meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc 43 : 435–439
Shea B et al . (2001) Assessing the quality of reports of systematic reviews: the QUORUM statement compared to other tools. In Systematic Reviews in Health Care: Meta-analysis in Context 2nd Edition, 122–139 (Eds Egger M. et al .) London: BMJ Books
Chapter Google Scholar
Easterbrook PH et al . (1991) Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet 337 : 867–872
Begg CB and Berlin JA (1989) Publication bias and dissemination of clinical research. J Natl Cancer Inst 81 : 107–115
Moher D et al . (2000) Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUORUM statement. Br J Surg 87 : 1448–1454
Shea BJ et al . (2007) Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Medical Research Methodology 7 : 10 [10.1186/1471-2288-7-10]
Stroup DF et al . (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283 : 2008–2012
Young JM and Solomon MJ (2003) Improving the evidence-base in surgery: evaluating surgical effectiveness. ANZ J Surg 73 : 507–510
Schulz KF (1995) Subverting randomization in controlled trials. JAMA 274 : 1456–1458
Schulz KF et al . (1995) Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 273 : 408–412
Moher D et al . (2001) The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel group randomized trials. BMC Medical Research Methodology 1 : 2 [ http://www.biomedcentral.com/ 1471-2288/1/2 ] (accessed 25 November 2008)
Rochon PA et al . (2005) Reader's guide to critical appraisal of cohort studies: 1. Role and design. BMJ 330 : 895–897
Mamdani M et al . (2005) Reader's guide to critical appraisal of cohort studies: 2. Assessing potential for confounding. BMJ 330 : 960–962
Normand S et al . (2005) Reader's guide to critical appraisal of cohort studies: 3. Analytical strategies to reduce confounding. BMJ 330 : 1021–1023
von Elm E et al . (2007) Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. BMJ 335 : 806–808
Sutton-Tyrrell K (1991) Assessing bias in case-control studies: proper selection of cases and controls. Stroke 22 : 938–942
Knottnerus J (2003) Assessment of the accuracy of diagnostic tests: the cross-sectional study. J Clin Epidemiol 56 : 1118–1128
Furukawa TA and Guyatt GH (2006) Sources of bias in diagnostic accuracy studies and the diagnostic process. CMAJ 174 : 481–482
Bossyut PM et al . (2003)The STARD statement for reporting studies of diagnostic accuracy: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med 138 : W1–W12
STARD statement (Standards for the Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies). [ http://www.stard-statement.org/ ] (accessed 10 September 2008)
Raftery J (1998) Economic evaluation: an introduction. BMJ 316 : 1013–1014
Palmer S et al . (1999) Economics notes: types of economic evaluation. BMJ 318 : 1349
Russ S et al . (1999) Barriers to participation in randomized controlled trials: a systematic review. J Clin Epidemiol 52 : 1143–1156
Tinmouth JM et al . (2004) Are claims of equivalency in digestive diseases trials supported by the evidence? Gastroentrology 126 : 1700–1710
Kaul S and Diamond GA (2006) Good enough: a primer on the analysis and interpretation of noninferiority trials. Ann Intern Med 145 : 62–69
Piaggio G et al . (2006) Reporting of noninferiority and equivalence randomized trials: an extension of the CONSORT statement. JAMA 295 : 1152–1160
Heritier SR et al . (2007) Inclusion of patients in clinical trial analysis: the intention to treat principle. In Interpreting and Reporting Clinical Trials: a Guide to the CONSORT Statement and the Principles of Randomized Controlled Trials , 92–98 (Eds Keech A. et al .) Strawberry Hills, NSW: Australian Medical Publishing Company
National Health and Medical Research Council (2007) National Statement on Ethical Conduct in Human Research 89–90 Canberra: NHMRC
Lo B et al . (2000) Conflict-of-interest policies for investigators in clinical trials. N Engl J Med 343 : 1616–1620
Kim SYH et al . (2004) Potential research participants' views regarding researcher and institutional financial conflicts of interests. J Med Ethics 30 : 73–79
Komesaroff PA and Kerridge IH (2002) Ethical issues concerning the relationships between medical practitioners and the pharmaceutical industry. Med J Aust 176 : 118–121
Little M (1999) Research, ethics and conflicts of interest. J Med Ethics 25 : 259–262
Lemmens T and Singer PA (1998) Bioethics for clinicians: 17. Conflict of interest in research, education and patient care. CMAJ 159 : 960–965
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
JM Young is an Associate Professor of Public Health and the Executive Director of the Surgical Outcomes Research Centre at the University of Sydney and Sydney South-West Area Health Service, Sydney,
Jane M Young
MJ Solomon is Head of the Surgical Outcomes Research Centre and Director of Colorectal Research at the University of Sydney and Sydney South-West Area Health Service, Sydney, Australia.,
Michael J Solomon
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jane M Young .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Young, J., Solomon, M. How to critically appraise an article. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 6 , 82–91 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpgasthep1331
Download citation
Received : 10 August 2008
Accepted : 03 November 2008
Published : 20 January 2009
Issue Date : February 2009
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpgasthep1331
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Emergency physicians’ perceptions of critical appraisal skills: a qualitative study.
- Sumintra Wood
- Jacqueline Paulis
- Angela Chen
BMC Medical Education (2022)
An integrative review on individual determinants of enrolment in National Health Insurance Scheme among older adults in Ghana
- Anthony Kwame Morgan
- Anthony Acquah Mensah
BMC Primary Care (2022)
Autopsy findings of COVID-19 in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Anju Khairwa
- Kana Ram Jat
Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology (2022)
The use of a modified Delphi technique to develop a critical appraisal tool for clinical pharmacokinetic studies
- Alaa Bahaa Eldeen Soliman
- Shane Ashley Pawluk
- Ousama Rachid
International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy (2022)
Critical Appraisal: Analysis of a Prospective Comparative Study Published in IJS
- Ramakrishna Ramakrishna HK
- Swarnalatha MC
Indian Journal of Surgery (2021)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Download Free PDF
Evaluating research methods: Assumptions, strengths, and weaknesses of three research paradigms

Related papers
British Journal of Sociology, 1984
Introduction Educational researchers in every discipline need to be cognisant of alternative research traditions to make decisions about which method to use when embarking on a research study. There are two major approaches to research that can be used in the study of the social and the individual world. These are quantitative and qualitative research. Although there are books on research methods that discuss the differences between alternative approaches, it is rare to find an article that examines the design issues at the intersection of the quantitative and qualitative divide based on eminent research literature. The purpose of this article is to explain the major differences between the two research paradigms by comparing them in terms of their epistemological, theoretical, and methodological underpinnings. Since quantitative research has well-established strategies and methods but qualitative research is still growing and becoming more differentiated in methodological approaches, greater consideration will be given to the latter.
Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung Forum Qualitative Social Research, 2001
Issues in Educational Research, 2006
How doctoral programs train future researchers in quantitative methods has important implications for the quality of scientifically based research in education. The purpose of this article, therefore, is to examine how quantitative methods are used in the literature and taught in doctoral programs. Evidence points to deficiencies in quantitative training and application in several areas: (a) methodological reporting problems, (b) researcher misconceptions and inaccuracies, (c) overreliance on traditional methods, and (d) a lack of coverage of modern advances. An argument is made that a culture supportive of quantitative methods is not consistently available to many applied education researchers. Collective quantitative proficiency is defined as a vision for a culture representative of broader support for quantitative methodology (statistics, measurement, and research design).
Research on Humanities and Social Sciences, 2021
How do we decide whether to use a quantitative or qualitative methodology for our study? Quantitative and qualitative research (are they a dichotomy or different ends on a continuum?). How do we analyse and write the results of a study for the research article or our thesis? Further questions can be asked such as; is the paradigm same as research design? How can we spot a paradigm in our research article? Although the questions are answered quietly explicitly, the discussion on the paradigm and research design remains technical. This can be evidenced by the confusion that people still face in differentiating between a paradigm, methodology, approach and design when doing research. The confusion is further worsened by the quantitative versus qualitative research dichotomies. This article addresses quantitative and qualitative research while discussing scientific research paradigms from educational measurement and evaluation perspective.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
Educational Researcher, 2006
Educational Researcher, 2004
Journal of Research in Nursing, 2006
Educational Researcher, 1987
Proceedings of the 4th European …, 2005
New Directions for Program Evaluation, 1994
Qualitative & Multi-Method Research, 2007
Quality & Quantity, 2009
International Journal of Value-based Management, 2000
Related topics
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- YJBM Updates
- Editorial Board
- Colloquium Series
- Podcast Series
- Open Access
- Call for Papers
- PubMed Publications
- News & Views
- Article Request Form
- Why Publish in YJBM?
- Types of Articles Published
- Manuscript Submission Guidelines
- YJBM Ethical Guidelines
Points to Consider When Reviewing Articles
- Writing and Submitting a Review
- Join Our Peer Reviewer Database
INFORMATION FOR
- Residents & Fellows
- Researchers
General questions that Reviewers should keep in mind when reviewing articles are the following:
- Is the article of interest to the readers of YJBM ?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the manuscript?
- How can the Editors work with the Authors to improve the submitted manuscripts, if the topic and scope of the manuscript is of interest to YJBM readers?
The following contains detailed descriptions as to what should be included in each particular type of article as well as points that Reviewers should keep in mind when specifically reviewing each type of article.
YJBM will ask Reviewers to Peer Review the following types of submissions:
Download PDF
Frequently asked questions.
These manuscripts should present well-rounded studies reporting innovative advances that further knowledge about a topic of importance to the fields of biology or medicine. The conclusions of the Original Research Article should clearly be supported by the results. These can be submitted as either a full-length article (no more than 6,000 words, 8 figures, and 4 tables) or a brief communication (no more than 2,500 words, 3 figures, and 2 tables). Original Research Articles contain five sections: abstract, introduction, materials and methods, results and discussion.
Reviewers should consider the following questions:
- What is the overall aim of the research being presented? Is this clearly stated?
- Have the Authors clearly stated what they have identified in their research?
- Are the aims of the manuscript and the results of the data clearly and concisely stated in the abstract?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background information to enable readers to better understand the problem being identified by the Authors?
- Have the Authors provided sufficient evidence for the claims they are making? If not, what further experiments or data needs to be included?
- Are similar claims published elsewhere? Have the Authors acknowledged these other publications? Have the Authors made it clear how the data presented in the Author’s manuscript is different or builds upon previously published data?
- Is the data presented of high quality and has it been analyzed correctly? If the analysis is incorrect, what should the Authors do to correct this?
- Do all the figures and tables help the reader better understand the manuscript? If not, which figures or tables should be removed and should anything be presented in their place?
- Is the methodology used presented in a clear and concise manner so that someone else can repeat the same experiments? If not, what further information needs to be provided?
- Do the conclusions match the data being presented?
- Have the Authors discussed the implications of their research in the discussion? Have they presented a balanced survey of the literature and information so their data is put into context?
- Is the manuscript accessible to readers who are not familiar with the topic? If not, what further information should the Authors include to improve the accessibility of their manuscript?
- Are all abbreviations used explained? Does the author use standard scientific abbreviations?
Case reports describe an unusual disease presentation, a new treatment, an unexpected drug interaction, a new diagnostic method, or a difficult diagnosis. Case reports should include relevant positive and negative findings from history, examination and investigation, and can include clinical photographs. Additionally, the Author must make it clear what the case adds to the field of medicine and include an up-to-date review of all previous cases. These articles should be no more than 5,000 words, with no more than 6 figures and 3 tables. Case Reports contain five sections: abstract; introduction; case presentation that includes clinical presentation, observations, test results, and accompanying figures; discussion; and conclusions.
- Does the abstract clearly and concisely state the aim of the case report, the findings of the report, and its implications?
- Does the introduction provide enough details for readers who are not familiar with a particular disease/treatment/drug/diagnostic method to make the report accessible to them?
- Does the manuscript clearly state what the case presentation is and what was observed so that someone can use this description to identify similar symptoms or presentations in another patient?
- Are the figures and tables presented clearly explained and annotated? Do they provide useful information to the reader or can specific figures/tables be omitted and/or replaced by another figure/table?
- Are the data presented accurately analyzed and reported in the text? If not, how can the Author improve on this?
- Do the conclusions match the data presented?
- Does the discussion include information of similar case reports and how this current report will help with treatment of a disease/presentation/use of a particular drug?
Reviews provide a reasoned survey and examination of a particular subject of research in biology or medicine. These can be submitted as a mini-review (less than 2,500 words, 3 figures, and 1 table) or a long review (no more than 6,000 words, 6 figures, and 3 tables). They should include critical assessment of the works cited, explanations of conflicts in the literature, and analysis of the field. The conclusion must discuss in detail the limitations of current knowledge, future directions to be pursued in research, and the overall importance of the topic in medicine or biology. Reviews contain four sections: abstract, introduction, topics (with headings and subheadings), and conclusions and outlook.
- Is the review accessible to readers of YJBM who are not familiar with the topic presented?
- Does the abstract accurately summarize the contents of the review?
- Does the introduction clearly state what the focus of the review will be?
- Are the facts reported in the review accurate?
- Does the Author use the most recent literature available to put together this review?
- Is the review split up under relevant subheadings to make it easier for the readers to access the article?
- Does the Author provide balanced viewpoints on a specific topic if there is debate over the topic in the literature?
- Are the figures or tables included relevant to the review and enable the readers to better understand the manuscript? Are there further figures/tables that could be included?
- Do the conclusions and outlooks outline where further research can be done on the topic?
Perspectives provide a personal view on medical or biomedical topics in a clear narrative voice. Articles can relate personal experiences, historical perspective, or profile people or topics important to medicine and biology. Long perspectives should be no more than 6,000 words and contain no more than 2 tables. Brief opinion pieces should be no more than 2,500 words and contain no more than 2 tables. Perspectives contain four sections: abstract, introduction, topics (with headings and subheadings), and conclusions and outlook.
- Does the abstract accurately and concisely summarize the main points provided in the manuscript?
- Does the introduction provide enough information so that the reader can understand the article if he or she were not familiar with the topic?
- Are there specific areas in which the Author can provide more detail to help the reader better understand the manuscript? Or are there places where the author has provided too much detail that detracts from the main point?
- If necessary, does the Author divide the article into specific topics to help the reader better access the article? If not, how should the Author break up the article under specific topics?
- Do the conclusions follow from the information provided by the Author?
- Does the Author reflect and provide lessons learned from a specific personal experience/historical event/work of a specific person?
Analyses provide an in-depth prospective and informed analysis of a policy, major advance, or historical description of a topic related to biology or medicine. These articles should be no more than 6,000 words with no more than 3 figures and 1 table. Analyses contain four sections: abstract, introduction, topics (with headings and subheadings), and conclusions and outlook.
- Does the abstract accurately summarize the contents of the manuscript?
- Does the introduction provide enough information if the readers are not familiar with the topic being addressed?
- Are there specific areas in which the Author can provide more detail to help the reader better understand the manuscript? Or are there places where the Author has provided too much detail that detracts from the main point?
Profiles describe a notable person in the fields of science or medicine. These articles should contextualize the individual’s contributions to the field at large as well as provide some personal and historical background on the person being described. More specifically, this should be done by describing what was known at the time of the individual’s discovery/contribution and how that finding contributes to the field as it stands today. These pieces should be no more than 5,000 words, with up to 6 figures, and 3 tables. The article should include the following: abstract, introduction, topics (with headings and subheadings), and conclusions.
- Does the Author provide information about the person of interest’s background, i.e., where they are from, where they were educated, etc.?
- Does the Author indicate how the person focused on became interested or involved in the subject that he or she became famous for?
- Does the Author provide information on other people who may have helped the person in his or her achievements?
- Does the Author provide information on the history of the topic before the person became involved?
- Does the Author provide information on how the person’s findings affected the field being discussed?
- Does the introduction provide enough information to the readers, should they not be familiar with the topic being addressed?
Interviews may be presented as either a transcript of an interview with questions and answers or as a personal reflection. If the latter, the Author must indicate that the article is based on an interview given. These pieces should be no more than 5,000 words and contain no more than 3 figures and 2 tables. The articles should include: abstract, introduction, questions and answers clearly indicated by subheadings or topics (with heading and subheadings), and conclusions.
- Does the Author provide relevant information to describe who the person is whom they have chosen to interview?
- Does the Author explain why he or she has chosen the person being interviewed?
- Does the Author explain why he or she has decided to focus on a specific topic in the interview?
- Are the questions relevant? Are there more questions that the Author should have asked? Are there questions that the Author has asked that are not necessary?
- If necessary, does the Author divide the article into specific topics to help the reader better access the article? If not, how should the author break up the article under specific topics?
- Does the Author accurately summarize the contents of the interview as well as specific lesson learned, if relevant, in the conclusions?
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- BMJ Journals
You are here
- Volume 25, Issue 1
- Critical appraisal of qualitative research: necessity, partialities and the issue of bias
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5660-8224 Veronika Williams ,
- Anne-Marie Boylan ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4597-1276 David Nunan
- Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences , University of Oxford, Radcliffe Observatory Quarter , Oxford , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Veronika Williams, Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford, Oxford OX2 6GG, UK; veronika.williams{at}phc.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjebm-2018-111132
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
- qualitative research
Introduction
Qualitative evidence allows researchers to analyse human experience and provides useful exploratory insights into experiential matters and meaning, often explaining the ‘how’ and ‘why’. As we have argued previously 1 , qualitative research has an important place within evidence-based healthcare, contributing to among other things policy on patient safety, 2 prescribing, 3 4 and understanding chronic illness. 5 Equally, it offers additional insight into quantitative studies, explaining contextual factors surrounding a successful intervention or why an intervention might have ‘failed’ or ‘succeeded’ where effect sizes cannot. It is for these reasons that the MRC strongly recommends including qualitative evaluations when developing and evaluating complex interventions. 6
Critical appraisal of qualitative research
Is it necessary.
Although the importance of qualitative research to improve health services and care is now increasingly widely supported (discussed in paper 1), the role of appraising the quality of qualitative health research is still debated. 8 10 Despite a large body of literature focusing on appraisal and rigour, 9 11–15 often referred to as ‘trustworthiness’ 16 in qualitative research, there remains debate about how to —and even whether to—critically appraise qualitative research. 8–10 17–19 However, if we are to make a case for qualitative research as integral to evidence-based healthcare, then any argument to omit a crucial element of evidence-based practice is difficult to justify. That being said, simply applying the standards of rigour used to appraise studies based on the positivist paradigm (Positivism depends on quantifiable observations to test hypotheses and assumes that the researcher is independent of the study. Research situated within a positivist paradigm isbased purely on facts and consider the world to be external and objective and is concerned with validity, reliability and generalisability as measures of rigour.) would be misplaced given the different epistemological underpinnings of the two types of data.
Given its scope and its place within health research, the robust and systematic appraisal of qualitative research to assess its trustworthiness is as paramount to its implementation in clinical practice as any other type of research. It is important to appraise different qualitative studies in relation to the specific methodology used because the methodological approach is linked to the ‘outcome’ of the research (eg, theory development, phenomenological understandings and credibility of findings). Moreover, appraisal needs to go beyond merely describing the specific details of the methods used (eg, how data were collected and analysed), with additional focus needed on the overarching research design and its appropriateness in accordance with the study remit and objectives.
Poorly conducted qualitative research has been described as ‘worthless, becomes fiction and loses its utility’. 20 However, without a deep understanding of concepts of quality in qualitative research or at least an appropriate means to assess its quality, good qualitative research also risks being dismissed, particularly in the context of evidence-based healthcare where end users may not be well versed in this paradigm.
How is appraisal currently performed?
Appraising the quality of qualitative research is not a new concept—there are a number of published appraisal tools, frameworks and checklists in existence. 21–23 An important and often overlooked point is the confusion between tools designed for appraising methodological quality and reporting guidelines designed to assess the quality of methods reporting. An example is the Consolidate Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) 24 checklist, which was designed to provide standards for authors when reporting qualitative research but is often mistaken for a methods appraisal tool. 10
Broadly speaking there are two types of critical appraisal approaches for qualitative research: checklists and frameworks. Checklists have often been criticised for confusing quality in qualitative research with ‘technical fixes’ 21 25 , resulting in the erroneous prioritisation of particular aspects of methodological processes over others (eg, multiple coding and triangulation). It could be argued that a checklist approach adopts the positivist paradigm, where the focus is on objectively assessing ‘quality’ where the assumptions is that the researcher is independent of the research conducted. This may result in the application of quantitative understandings of bias in order to judge aspects of recruitment, sampling, data collection and analysis in qualitative research papers. One of the most widely used appraisal tools is the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) 26 and along with the JBI QARI (Joanna Briggs Institute Qualitative Assessment and Assessment Instrument) 27 presents examples which tend to mimic the quantitative approach to appraisal. The CASP qualitative tool follows that of other CASP appraisal tools for quantitative research designs developed in the 1990s. The similarities are therefore unsurprising given the status of qualitative research at that time.
Frameworks focus on the overarching concepts of quality in qualitative research, including transparency, reflexivity, dependability and transferability (see box 1 ). 11–13 15 16 20 28 However, unless the reader is familiar with these concepts—their meaning and impact, and how to interpret them—they will have difficulty applying them when critically appraising a paper.
The main issue concerning currently available checklist and framework appraisal methods is that they take a broad brush approach to ‘qualitative’ research as whole, with few, if any, sufficiently differentiating between the different methodological approaches (eg, Grounded Theory, Interpretative Phenomenology, Discourse Analysis) nor different methods of data collection (interviewing, focus groups and observations). In this sense, it is akin to taking the entire field of ‘quantitative’ study designs and applying a single method or tool for their quality appraisal. In the case of qualitative research, checklists, therefore, offer only a blunt and arguably ineffective tool and potentially promote an incomplete understanding of good ‘quality’ in qualitative research. Likewise, current framework methods do not take into account how concepts differ in their application across the variety of qualitative approaches and, like checklists, they also do not differentiate between different qualitative methodologies.
On the need for specific appraisal tools
Current approaches to the appraisal of the methodological rigour of the differing types of qualitative research converge towards checklists or frameworks. More importantly, the current tools do not explicitly acknowledge the prejudices that may be present in the different types of qualitative research.

Concepts of rigour or trustworthiness within qualitative research 31
Transferability: the extent to which the presented study allows readers to make connections between the study’s data and wider community settings, ie, transfer conceptual findings to other contexts.
Credibility: extent to which a research account is believable and appropriate, particularly in relation to the stories told by participants and the interpretations made by the researcher.
Reflexivity: refers to the researchers’ engagement of continuous examination and explanation of how they have influenced a research project from choosing a research question to sampling, data collection, analysis and interpretation of data.
Transparency: making explicit the whole research process from sampling strategies, data collection to analysis. The rationale for decisions made is as important as the decisions themselves.
However, we often talk about these concepts in general terms, and it might be helpful to give some explicit examples of how the ‘technical processes’ affect these, for example, partialities related to:
Selection: recruiting participants via gatekeepers, such as healthcare professionals or clinicians, who may select them based on whether they believe them to be ‘good’ participants for interviews/focus groups.
Data collection: poor interview guide with closed questions which encourage yes/no answers and/leading questions.
Reflexivity and transparency: where researchers may focus their analysis on preconceived ideas rather than ground their analysis in the data and do not reflect on the impact of this in a transparent way.
The lack of tailored, method-specific appraisal tools has potentially contributed to the poor uptake and use of qualitative research for informing evidence-based decision making. To improve this situation, we propose the need for more robust quality appraisal tools that explicitly encompass both the core design aspects of all qualitative research (sampling/data collection/analysis) but also considered the specific partialities that can be presented with different methodological approaches. Such tools might draw on the strengths of current frameworks and checklists while providing users with sufficient understanding of concepts of rigour in relation to the different types of qualitative methods. We provide an outline of such tools in the third and final paper in this series.
As qualitative research becomes ever more embedded in health science research, and in order for that research to have better impact on healthcare decisions, we need to rethink critical appraisal and develop tools that allow differentiated evaluations of the myriad of qualitative methodological approaches rather than continuing to treat qualitative research as a single unified approach.
- Williams V ,
- Boylan AM ,
- Lingard L ,
- Orser B , et al
- Brawn R , et al
- Van Royen P ,
- Vermeire E , et al
- Barker M , et al
- McGannon KR
- Dixon-Woods M ,
- Agarwal S , et al
- Greenhalgh T ,
- Dennison L ,
- Morrison L ,
- Conway G , et al
- Barrett M ,
- Mayan M , et al
- Lockwood C ,
- Santiago-Delefosse M ,
- Bruchez C , et al
- Sainsbury P ,
- ↵ CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme). date unknown . http://www.phru.nhs.uk/Pages/PHD/CASP.htm .
- ↵ The Joanna Briggs Institute . JBI QARI Critical appraisal checklist for interpretive & critical research . Adelaide : The Joanna Briggs Institute , 2014 .
- Stephens J ,
Contributors VW and DN: conceived the idea for this article. VW: wrote the first draft. AMB and DN: contributed to the final draft. All authors approve the submitted article.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Correction notice This article has been updated since its original publication to include a new reference (reference 1.)
Read the full text or download the PDF:
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Perspect Med Educ
- v.8(4); 2019 Aug

Limited by our limitations
Paula t. ross.
Medical School, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI USA
Nikki L. Bibler Zaidi
Study limitations represent weaknesses within a research design that may influence outcomes and conclusions of the research. Researchers have an obligation to the academic community to present complete and honest limitations of a presented study. Too often, authors use generic descriptions to describe study limitations. Including redundant or irrelevant limitations is an ineffective use of the already limited word count. A meaningful presentation of study limitations should describe the potential limitation, explain the implication of the limitation, provide possible alternative approaches, and describe steps taken to mitigate the limitation. This includes placing research findings within their proper context to ensure readers do not overemphasize or minimize findings. A more complete presentation will enrich the readers’ understanding of the study’s limitations and support future investigation.
Introduction
Regardless of the format scholarship assumes, from qualitative research to clinical trials, all studies have limitations. Limitations represent weaknesses within the study that may influence outcomes and conclusions of the research. The goal of presenting limitations is to provide meaningful information to the reader; however, too often, limitations in medical education articles are overlooked or reduced to simplistic and minimally relevant themes (e.g., single institution study, use of self-reported data, or small sample size) [ 1 ]. This issue is prominent in other fields of inquiry in medicine as well. For example, despite the clinical implications, medical studies often fail to discuss how limitations could have affected the study findings and interpretations [ 2 ]. Further, observational research often fails to remind readers of the fundamental limitation inherent in the study design, which is the inability to attribute causation [ 3 ]. By reporting generic limitations or omitting them altogether, researchers miss opportunities to fully communicate the relevance of their work, illustrate how their work advances a larger field under study, and suggest potential areas for further investigation.
Goals of presenting limitations
Medical education scholarship should provide empirical evidence that deepens our knowledge and understanding of education [ 4 , 5 ], informs educational practice and process, [ 6 , 7 ] and serves as a forum for educating other researchers [ 8 ]. Providing study limitations is indeed an important part of this scholarly process. Without them, research consumers are pressed to fully grasp the potential exclusion areas or other biases that may affect the results and conclusions provided [ 9 ]. Study limitations should leave the reader thinking about opportunities to engage in prospective improvements [ 9 – 11 ] by presenting gaps in the current research and extant literature, thereby cultivating other researchers’ curiosity and interest in expanding the line of scholarly inquiry [ 9 ].
Presenting study limitations is also an ethical element of scientific inquiry [ 12 ]. It ensures transparency of both the research and the researchers [ 10 , 13 , 14 ], as well as provides transferability [ 15 ] and reproducibility of methods. Presenting limitations also supports proper interpretation and validity of the findings [ 16 ]. A study’s limitations should place research findings within their proper context to ensure readers are fully able to discern the credibility of a study’s conclusion, and can generalize findings appropriately [ 16 ].
Why some authors may fail to present limitations
As Price and Murnan [ 8 ] note, there may be overriding reasons why researchers do not sufficiently report the limitations of their study. For example, authors may not fully understand the importance and implications of their study’s limitations or assume that not discussing them may increase the likelihood of publication. Word limits imposed by journals may also prevent authors from providing thorough descriptions of their study’s limitations [ 17 ]. Still another possible reason for excluding limitations is a diffusion of responsibility in which some authors may incorrectly assume that the journal editor is responsible for identifying limitations. Regardless of reason or intent, researchers have an obligation to the academic community to present complete and honest study limitations.
A guide to presenting limitations
The presentation of limitations should describe the potential limitations, explain the implication of the limitations, provide possible alternative approaches, and describe steps taken to mitigate the limitations. Too often, authors only list the potential limitations, without including these other important elements.
Describe the limitations
When describing limitations authors should identify the limitation type to clearly introduce the limitation and specify the origin of the limitation. This helps to ensure readers are able to interpret and generalize findings appropriately. Here we outline various limitation types that can occur at different stages of the research process.
Study design
Some study limitations originate from conscious choices made by the researcher (also known as delimitations) to narrow the scope of the study [ 1 , 8 , 18 ]. For example, the researcher may have designed the study for a particular age group, sex, race, ethnicity, geographically defined region, or some other attribute that would limit to whom the findings can be generalized. Such delimitations involve conscious exclusionary and inclusionary decisions made during the development of the study plan, which may represent a systematic bias intentionally introduced into the study design or instrument by the researcher [ 8 ]. The clear description and delineation of delimitations and limitations will assist editors and reviewers in understanding any methodological issues.
Data collection
Study limitations can also be introduced during data collection. An unintentional consequence of human subjects research is the potential of the researcher to influence how participants respond to their questions. Even when appropriate methods for sampling have been employed, some studies remain limited by the use of data collected only from participants who decided to enrol in the study (self-selection bias) [ 11 , 19 ]. In some cases, participants may provide biased input by responding to questions they believe are favourable to the researcher rather than their authentic response (social desirability bias) [ 20 – 22 ]. Participants may influence the data collected by changing their behaviour when they are knowingly being observed (Hawthorne effect) [ 23 ]. Researchers—in their role as an observer—may also bias the data they collect by allowing a first impression of the participant to be influenced by a single characteristic or impression of another characteristic either unfavourably (horns effect) or favourably (halo effort) [ 24 ].
Data analysis
Study limitations may arise as a consequence of the type of statistical analysis performed. Some studies may not follow the basic tenets of inferential statistical analyses when they use convenience sampling (i.e. non-probability sampling) rather than employing probability sampling from a target population [ 19 ]. Another limitation that can arise during statistical analyses occurs when studies employ unplanned post-hoc data analyses that were not specified before the initial analysis [ 25 ]. Unplanned post-hoc analysis may lead to statistical relationships that suggest associations but are no more than coincidental findings [ 23 ]. Therefore, when unplanned post-hoc analyses are conducted, this should be clearly stated to allow the reader to make proper interpretation and conclusions—especially when only a subset of the original sample is investigated [ 23 ].
Study results
The limitations of any research study will be rooted in the validity of its results—specifically threats to internal or external validity [ 8 ]. Internal validity refers to reliability or accuracy of the study results [ 26 ], while external validity pertains to the generalizability of results from the study’s sample to the larger, target population [ 8 ].
Examples of threats to internal validity include: effects of events external to the study (history), changes in participants due to time instead of the studied effect (maturation), systematic reduction in participants related to a feature of the study (attrition), changes in participant responses due to repeatedly measuring participants (testing effect), modifications to the instrument (instrumentality) and selecting participants based on extreme scores that will regress towards the mean in repeat tests (regression to the mean) [ 27 ].
Threats to external validity include factors that might inhibit generalizability of results from the study’s sample to the larger, target population [ 8 , 27 ]. External validity is challenged when results from a study cannot be generalized to its larger population or to similar populations in terms of the context, setting, participants and time [ 18 ]. Therefore, limitations should be made transparent in the results to inform research consumers of any known or potentially hidden biases that may have affected the study and prevent generalization beyond the study parameters.
Explain the implication(s) of each limitation
Authors should include the potential impact of the limitations (e.g., likelihood, magnitude) [ 13 ] as well as address specific validity implications of the results and subsequent conclusions [ 16 , 28 ]. For example, self-reported data may lead to inaccuracies (e.g. due to social desirability bias) which threatens internal validity [ 19 ]. Even a researcher’s inappropriate attribution to a characteristic or outcome (e.g., stereotyping) can overemphasize (either positively or negatively) unrelated characteristics or outcomes (halo or horns effect) and impact the internal validity [ 24 ]. Participants’ awareness that they are part of a research study can also influence outcomes (Hawthorne effect) and limit external validity of findings [ 23 ]. External validity may also be threatened should the respondents’ propensity for participation be correlated with the substantive topic of study, as data will be biased and not represent the population of interest (self-selection bias) [ 29 ]. Having this explanation helps readers interpret the results and generalize the applicability of the results for their own setting.
Provide potential alternative approaches and explanations
Often, researchers use other studies’ limitations as the first step in formulating new research questions and shaping the next phase of research. Therefore, it is important for readers to understand why potential alternative approaches (e.g. approaches taken by others exploring similar topics) were not taken. In addition to alternative approaches, authors can also present alternative explanations for their own study’s findings [ 13 ]. This information is valuable coming from the researcher because of the direct, relevant experience and insight gained as they conducted the study. The presentation of alternative approaches represents a major contribution to the scholarly community.
Describe steps taken to minimize each limitation
No research design is perfect and free from explicit and implicit biases; however various methods can be employed to minimize the impact of study limitations. Some suggested steps to mitigate or minimize the limitations mentioned above include using neutral questions, randomized response technique, force choice items, or self-administered questionnaires to reduce respondents’ discomfort when answering sensitive questions (social desirability bias) [ 21 ]; using unobtrusive data collection measures (e.g., use of secondary data) that do not require the researcher to be present (Hawthorne effect) [ 11 , 30 ]; using standardized rubrics and objective assessment forms with clearly defined scoring instructions to minimize researcher bias, or making rater adjustments to assessment scores to account for rater tendencies (halo or horns effect) [ 24 ]; or using existing data or control groups (self-selection bias) [ 11 , 30 ]. When appropriate, researchers should provide sufficient evidence that demonstrates the steps taken to mitigate limitations as part of their study design [ 13 ].
In conclusion, authors may be limiting the impact of their research by neglecting or providing abbreviated and generic limitations. We present several examples of limitations to consider; however, this should not be considered an exhaustive list nor should these examples be added to the growing list of generic and overused limitations. Instead, careful thought should go into presenting limitations after research has concluded and the major findings have been described. Limitations help focus the reader on key findings, therefore it is important to only address the most salient limitations of the study [ 17 , 28 ] related to the specific research problem, not general limitations of most studies [ 1 ]. It is important not to minimize the limitations of study design or results. Rather, results, including their limitations, must help readers draw connections between current research and the extant literature.
The quality and rigor of our research is largely defined by our limitations [ 31 ]. In fact, one of the top reasons reviewers report recommending acceptance of medical education research manuscripts involves limitations—specifically how the study’s interpretation accounts for its limitations [ 32 ]. Therefore, it is not only best for authors to acknowledge their study’s limitations rather than to have them identified by an editor or reviewer, but proper framing and presentation of limitations can actually increase the likelihood of acceptance. Perhaps, these issues could be ameliorated if academic and research organizations adopted policies and/or expectations to guide authors in proper description of limitations.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Mixed Methods Research | Definition, Guide & Examples
Mixed Methods Research | Definition, Guide & Examples
Published on August 13, 2021 by Tegan George . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Mixed methods research combines elements of quantitative research and qualitative research in order to answer your research question . Mixed methods can help you gain a more complete picture than a standalone quantitative or qualitative study, as it integrates benefits of both methods.
Mixed methods research is often used in the behavioral, health, and social sciences, especially in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research.
- To what extent does the frequency of traffic accidents ( quantitative ) reflect cyclist perceptions of road safety ( qualitative ) in Amsterdam?
- How do student perceptions of their school environment ( qualitative ) relate to differences in test scores ( quantitative ) ?
- How do interviews about job satisfaction at Company X ( qualitative ) help explain year-over-year sales performance and other KPIs ( quantitative ) ?
- How can voter and non-voter beliefs about democracy ( qualitative ) help explain election turnout patterns ( quantitative ) in Town X?
- How do average hospital salary measurements over time (quantitative) help to explain nurse testimonials about job satisfaction (qualitative) ?
Table of contents
When to use mixed methods research, mixed methods research designs, advantages of mixed methods research, disadvantages of mixed methods research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
Mixed methods research may be the right choice if your research process suggests that quantitative or qualitative data alone will not sufficiently answer your research question. There are several common reasons for using mixed methods research:
- Generalizability : Qualitative research usually has a smaller sample size , and thus is not generalizable. In mixed methods research, this comparative weakness is mitigated by the comparative strength of “large N,” externally valid quantitative research.
- Contextualization: Mixing methods allows you to put findings in context and add richer detail to your conclusions. Using qualitative data to illustrate quantitative findings can help “put meat on the bones” of your analysis.
- Credibility: Using different methods to collect data on the same subject can make your results more credible. If the qualitative and quantitative data converge, this strengthens the validity of your conclusions. This process is called triangulation .
As you formulate your research question , try to directly address how qualitative and quantitative methods will be combined in your study. If your research question can be sufficiently answered via standalone quantitative or qualitative analysis, a mixed methods approach may not be the right fit.
But mixed methods might be a good choice if you want to meaningfully integrate both of these questions in one research study.
Keep in mind that mixed methods research doesn’t just mean collecting both types of data; you need to carefully consider the relationship between the two and how you’ll integrate them into coherent conclusions.
Mixed methods can be very challenging to put into practice, and comes with the same risk of research biases as standalone studies, so it’s a less common choice than standalone qualitative or qualitative research.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
There are different types of mixed methods research designs . The differences between them relate to the aim of the research, the timing of the data collection , and the importance given to each data type.
As you design your mixed methods study, also keep in mind:
- Your research approach ( inductive vs deductive )
- Your research questions
- What kind of data is already available for you to use
- What kind of data you’re able to collect yourself.
Here are a few of the most common mixed methods designs.
Convergent parallel
In a convergent parallel design, you collect quantitative and qualitative data at the same time and analyze them separately. After both analyses are complete, compare your results to draw overall conclusions.
- On the qualitative side, you analyze cyclist complaints via the city’s database and on social media to find out which areas are perceived as dangerous and why.
- On the quantitative side, you analyze accident reports in the city’s database to find out how frequently accidents occur in different areas of the city.
In an embedded design, you collect and analyze both types of data at the same time, but within a larger quantitative or qualitative design. One type of data is secondary to the other.
This is a good approach to take if you have limited time or resources. You can use an embedded design to strengthen or supplement your conclusions from the primary type of research design.
Explanatory sequential
In an explanatory sequential design, your quantitative data collection and analysis occurs first, followed by qualitative data collection and analysis.
You should use this design if you think your qualitative data will explain and contextualize your quantitative findings.
Exploratory sequential
In an exploratory sequential design, qualitative data collection and analysis occurs first, followed by quantitative data collection and analysis.
You can use this design to first explore initial questions and develop hypotheses . Then you can use the quantitative data to test or confirm your qualitative findings.
“Best of both worlds” analysis
Combining the two types of data means you benefit from both the detailed, contextualized insights of qualitative data and the generalizable , externally valid insights of quantitative data. The strengths of one type of data often mitigate the weaknesses of the other.
For example, solely quantitative studies often struggle to incorporate the lived experiences of your participants, so adding qualitative data deepens and enriches your quantitative results.
Solely qualitative studies are often not very generalizable, only reflecting the experiences of your participants, so adding quantitative data can validate your qualitative findings.
Method flexibility
Mixed methods are less tied to disciplines and established research paradigms. They offer more flexibility in designing your research, allowing you to combine aspects of different types of studies to distill the most informative results.
Mixed methods research can also combine theory generation and hypothesis testing within a single study, which is unusual for standalone qualitative or quantitative studies.
Mixed methods research is very labor-intensive. Collecting, analyzing, and synthesizing two types of data into one research product takes a lot of time and effort, and often involves interdisciplinary teams of researchers rather than individuals. For this reason, mixed methods research has the potential to cost much more than standalone studies.
Differing or conflicting results
If your analysis yields conflicting results, it can be very challenging to know how to interpret them in a mixed methods study. If the quantitative and qualitative results do not agree or you are concerned you may have confounding variables , it can be unclear how to proceed.
Due to the fact that quantitative and qualitative data take two vastly different forms, it can also be difficult to find ways to systematically compare the results, putting your data at risk for bias in the interpretation stage.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
Triangulation in research means using multiple datasets, methods, theories and/or investigators to address a research question. It’s a research strategy that can help you enhance the validity and credibility of your findings.
Triangulation is mainly used in qualitative research , but it’s also commonly applied in quantitative research . Mixed methods research always uses triangulation.
These are four of the most common mixed methods designs :
- Convergent parallel: Quantitative and qualitative data are collected at the same time and analyzed separately. After both analyses are complete, compare your results to draw overall conclusions.
- Embedded: Quantitative and qualitative data are collected at the same time, but within a larger quantitative or qualitative design. One type of data is secondary to the other.
- Explanatory sequential: Quantitative data is collected and analyzed first, followed by qualitative data. You can use this design if you think your qualitative data will explain and contextualize your quantitative findings.
- Exploratory sequential: Qualitative data is collected and analyzed first, followed by quantitative data. You can use this design if you think the quantitative data will confirm or validate your qualitative findings.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, June 22). Mixed Methods Research | Definition, Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 23, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/mixed-methods-research/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, what is quantitative research | definition, uses & methods, what is qualitative research | methods & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Strengths and weaknesses of qualitative research in social science studies
8 Pages Posted: 2 Jul 2024
Kelvin Mwita
Mzumbe University - School of Public Administration & Management (SOPAM)
Date Written: January 06, 2022
This study aimed at examining the strengths and weaknesses of qualitative research in social science studies. The study conducted a systematic literature review of 22 published journal articles to achieve the objective. The review revealed that the qualitative approach was flexible, offered in-depth and detailed information, allowed the use of multiple data collection methods and minimised the chance of having missing data. Moreover, the approach was found to integrate human touch, was cost-effective and was indeed the only option in some cases of research problems. On the other hand, the approach is prone to researchers' subjectivity, involves complex data analysis, makes anonymity difficult and has limited scope in its generalizability. Similarly, the approach makes replication of findings challenging, and the findings may be influenced by the researcher's bias. It is concluded, therefore, that researchers should take necessary precautions when using the approach to ensure that weaknesses of qualitative research do not bar them from achieving research objectives.
Keywords: Qualitative Research, Quantitative Research, Constructivists, Positivist Paradigm, Critical Paradigm, Interpretative Paradigm
JEL Classification: I23
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Kelvin Mwita (Contact Author)
Mzumbe university - school of public administration & management (sopam) ( email ).
P.O Box 2 Mzumbe Morogoro Tanzania +255659081838 (Phone)
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics, related ejournals, sociological research methods ejournal.
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
- DOI: 10.1177/136140960501000505
- Corpus ID: 54014105
The strengths and weaknesses of research designs involving quantitative measures
- Published 1 September 2005
- Journal of Research in Nursing
117 Citations
The value of developing a mixed-methods program of research, the challenges of conducting a nurse-led intervention in a randomized controlled trial with vulnerable participants, clinical trials for evidence-based nursing: a possible challenge, an overview of research designs relevant to nursing: part 1: quantitative research designs..
- Highly Influenced
Internal validity: A must in research designs
[analysis of research papers published in the journal of the korean academy of nursing-focused on research trends, intervention studies, and level of evidence in the research]., quantitative research: a successful investigation in natural and social sciences, a preliminary analysis of master's theses in pediatric nursing, the research evidence published in high impact nursing journals between 2000 and 2006: a quantitative content analysis., witnessed resuscitation: a conceptual exploration, 82 references, the strengths and weaknesses of quantitative and qualitative research: what method for nursing, designing nursing research: the qualitative-quantitative debate..
- Highly Influential
In search of more complete answers to research questions. Quantitative versus qualitative research methods: is there a way forward?
If you could just provide me with a sample: examining sampling in qualitative and quantitative research papers, mixed messages in nursing research: their contribution to the persisting hiatus between evidence and practice., study guide to accompany essentials of nursing research: methods, appraisal, and utilization, developing a protocol for a randomised controlled trial: factors to consider., the dilemma of incorporating research into clinical practice., longitudinal quantitative research designs., why we need observational studies to evaluate the effectiveness of health care, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical appraisal is a systematic process used to identify the strengths and weaknesses of a research article in order to assess the usefulness and validity of research findings.
Learn how to identify the strengths and limitations of quantitative and qualitative research approaches in different study types. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of using quantitative data (such as surveys and statistics) and qualitative data (such as interviews and observations) to answer different types of research questions.
This web page explains various research methods and their applications to student learning, such as descriptive, correlational, experimental, and mixed methods. It does not address the query about continuous assessment, which is a specific type of assessment that involves ongoing feedback and evaluation.
This paper compares and contrasts the strengths and weaknesses of qualitative and quantitative approaches in social science research. It also discusses the complementary and alternative uses of both methods for different research topics and objectives.
Critical appraisal is a systematic process used to identify the strengths and weaknesses of a research article in order to assess the usefulness and validity of research findings. The most important components of a critical appraisal are an evaluation of the appropriateness of the study design for the research question and a careful assessment ...
Conclusion: The ability to understand and evaluate research builds strong evidence-based practitioners, who are essential to nursing practice. Implications for practice: This framework should help readers to identify the strengths, potential weaknesses and limitations of a paper to judge its quality and potential usefulness.
Learn how to write an article critique that evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of a research article. Find out the difference between a critique and a summary, and follow the steps and structure of a critique.
Scientific research adopts qualitative and quantitative methodologies in the modeling and analysis of numerous phenomena. The qualitative methodology intends to understand a complex reality and ...
Critical appraisal is a systematic process used to identify the strengths and weaknesses of a research article in order to assess the usefulness and validity of research findings.
Assumptions, Strengths, and Weaknesses of Paradigms Assumptions: Quantitative Research Quantitative research, like other research paradigms, has its own set of assumptions. For example, it seeks to understand the facts or causes of phenomena and does not regard the subjective states of a situation or of individuals (Reichardt & Cook, 1979); it ...
This paper presents a critical review of the strengths and weaknesses of research designs involving quantitative measures and, in particular, experimental research. The review evolved during the planning stage of a PhD project that sought to determine the effects of witnessed resuscitation on bereaved relatives.
are able to constructively critique the research process. Roughly, I'm after around half a page (at most one page) with the following: • One or two sentence summary. This is your takeaways in your own words. • Key strengths of the paper. Again, where you think the value of the paper lies. • Key weaknesses of the paper.
The absence of a critical appraisal hinders the reader's ability to interpret research findings in light of the strengths and weaknesses of the methods investigators used to obtain their data. Reviewers in sport and exercise psychology who are aware of what critical appraisal is, its role in systematic reviewing, how to undertake one, and how ...
Learn how to review articles for YJBM, a peer-reviewed journal that publishes original research, case reports, reviews, perspectives, and analyses in biology and medicine. Find out what to consider when reviewing each type of article, such as the aims, methods, results, discussion, and references.
The human factor is the greatest strength and the fundamental weakness of phenomenological qualitative inquiry and analysis—a scientific two-edged sword (Patton, 2002, p. 433).
Is it necessary? Although the importance of qualitative research to improve health services and care is now increasingly widely supported (discussed in paper 1), the role of appraising the quality of qualitative health research is still debated.8 10 Despite a large body of literature focusing on appraisal and rigour,9 11-15 often referred to as 'trustworthiness'16 in qualitative research ...
Limitations represent weaknesses within the study that may influence outcomes and conclusions of the research. The goal of presenting limitations is to provide meaningful information to the reader; however, too often, limitations in medical education articles are overlooked or reduced to simplistic and minimally relevant themes (e.g., single ...
There are several common reasons for using mixed methods research: Generalizability: Qualitative research usually has a smaller sample size, and thus is not generalizable. In mixed methods research, this comparative weakness is mitigated by the comparative strength of "large N," externally valid quantitative research.
Similarly, the approach makes replication of findings challenging, and the findings may be influenced by the researcher's bias. It is concluded, therefore, that researchers should take necessary precautions when using the approach to ensure that weaknesses of qualitative research do not bar them from achieving research objectives.
This paper conducts a sy stematic literature review in the quest to identify the weaknesses and strengths of qualitat ive resear ch with reference to 22 pub lished journa l articles.
synthesis research evidence, often adhering to guidelines on the conduct of a review. Seeks to include all knowledge on a topic Is restrictive to focusing a certain method used in studies. Systematic research and review Combines strength of critical review with a comprehensive search process. Typically addresses broad questions to produce 'best
This paper presents a critical review of the strengths and weaknesses of research designs involving quantitative measures and, in particular, experimental research. The review evolved during the planning stage of a PhD project that sought to determine the effects of witnessed resuscitation on bereaved relatives. The discussion is therefore supported throughout by reference to bereavement research.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright ...