PowerPoint Charts, Graphs, & Tables Made Easy | Tips & Tricks

In today's digital world, effective communication is key, especially in presentations. After all, in a world saturated with information, the power to express your message clearly and impactfully can make all the difference.
We know that conveying complex information can be challenging, but guess what? It doesn't have to be! After discussing this with our 200+ expert presentation designers , I've gathered their best practices and strategies to create this comprehensive guide.
Below, you will find expert tips and tricks for making, customizing, and presenting PowerPoint charts, graphs, and tables. Stay with us!

Today, we'll explore the following topics:
- PowerPoint Charts and Graphs

Tables in PowerPoint
Free powerpoint charts, graphs, and tables templates, ready to enhance your presentations our team at 24slides is here to help, powerpoint charts and graphs.
If you are thinking of adding tables to your PowerPoint presentation, let me first show you two other great options: charts and graphs.
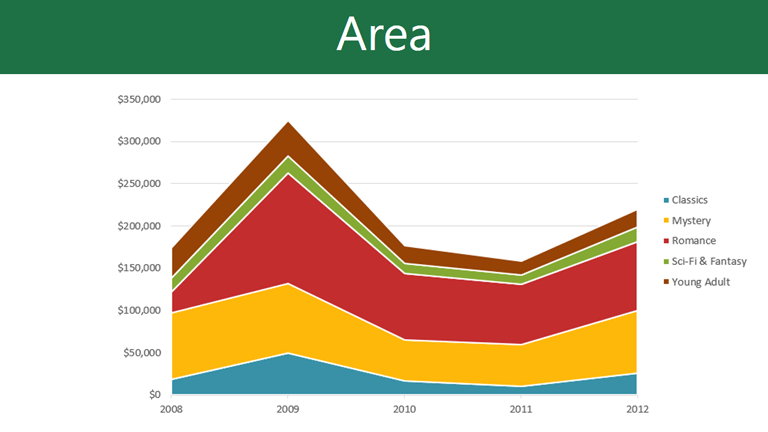
Charts and graphs stand out for making complex information easy to read at a glance. They’re ideal for identifying trends, representing patterns, and making decisions easier. In addition, charts and graphs capture the audience's attention.
You have many types to choose from, and we'll go over the most important ones later. In the meantime, here are some examples:
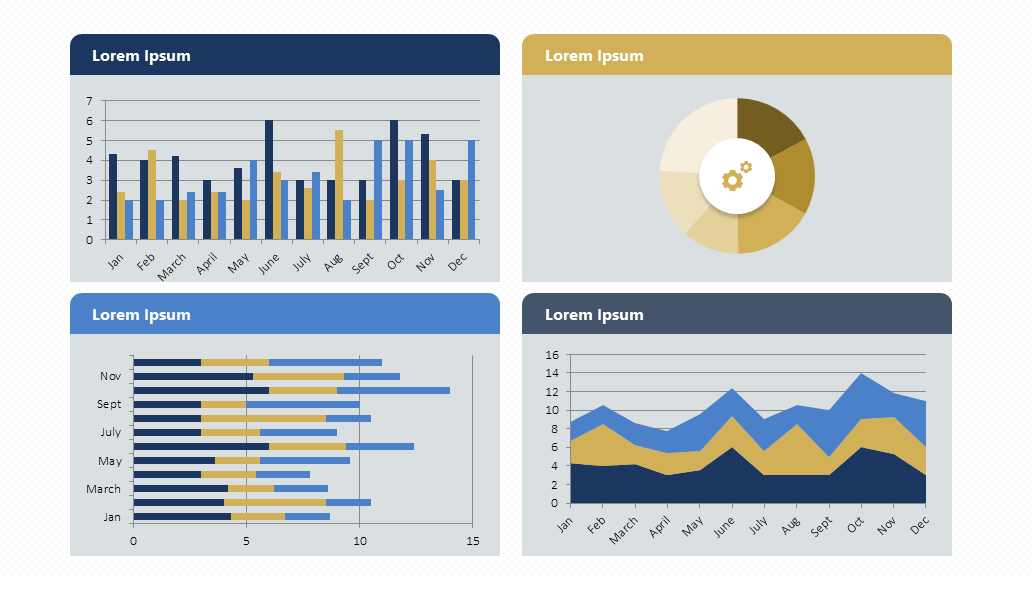
Undoubtedly, one of the best ways to take your presentations to the next level.
But you may have a question in mind: What is the difference between a chart and a graph in PowerPoint? Charts refer to any visual representation of data, whether graphical or non-graphical (such as tables). Graphs, on the other hand, refer specifically to the graphical representation of data (such as bar charts).
In other words, all graphs are charts, but not all charts are graphs.
People often confuse these terms in PowerPoint, but they actually refer to different visual elements.
How to Make a Chart in PowerPoint?
First, go to the Insert tab. Then, click on Chart and select your favorite chart type. Finally, enter your data or copy it from somewhere else. Simple!
Here you have the detailed step-by-step instructions:
- Select the slide where you want to add the chart. Choose the Insert tab, then select the Illustrations group's Chart option.
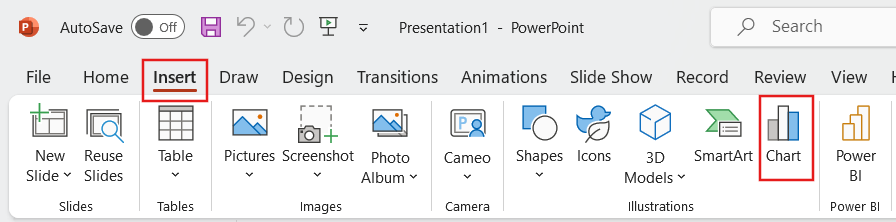
- A dialog box for inserting charts will appear. Choose a category on the left, then double-click the chart you want on the right.
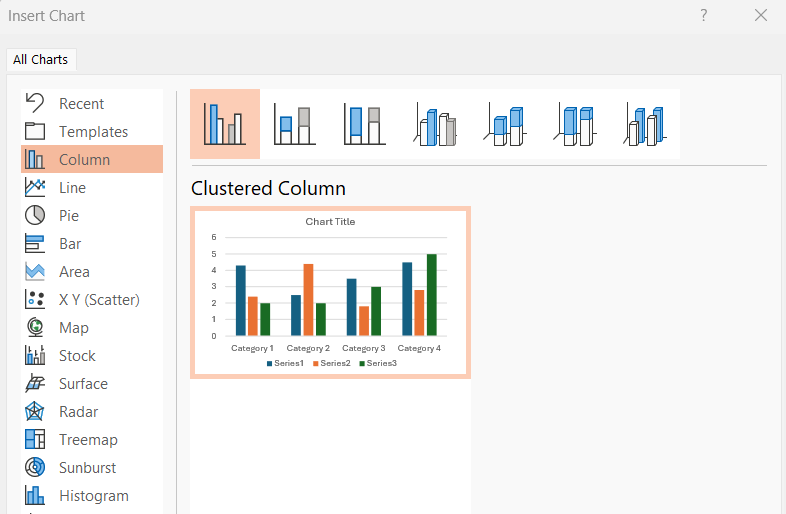
- When inserted, the chart appears alongside a spreadsheet. Here, you have to replace the placeholder data with your own details.
To edit your chart's content, use the selection handles in the spreadsheet to add or remove data.
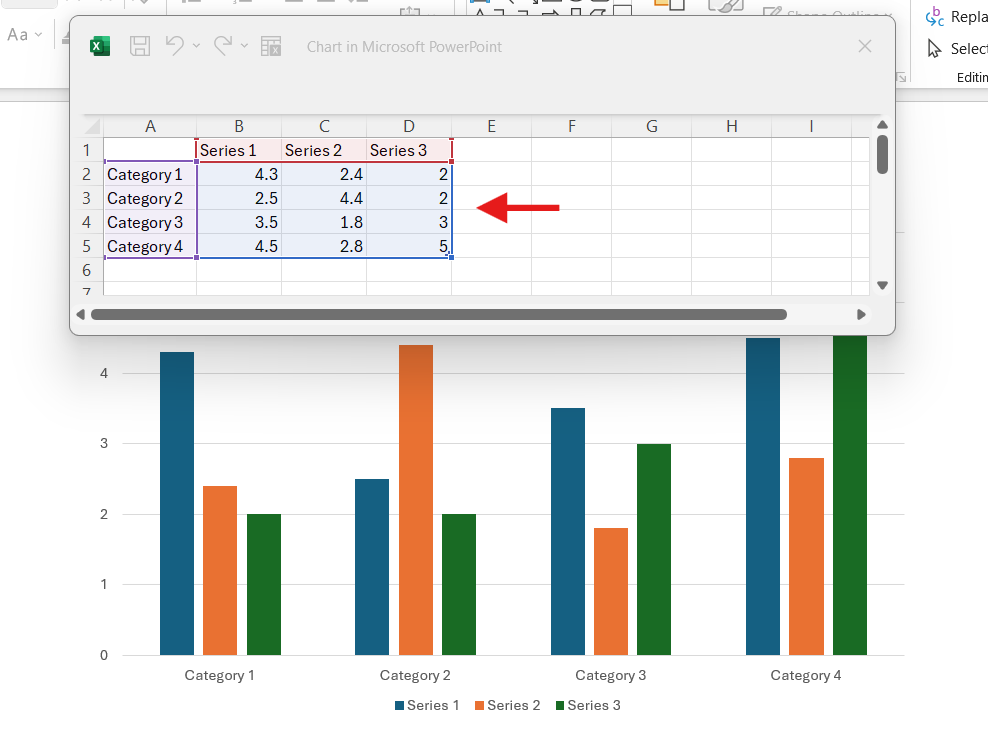
- When inserting a chart, you will see small buttons on the upper right side of the chart.
Format using the Chart Elements button. Click on “+” to tweak the chart title, data labels, and more. Use the Chart Styles button (brush) to change the chart's color or style. Finally, the Chart Filters button (funnel) will show or hide data from your chart.
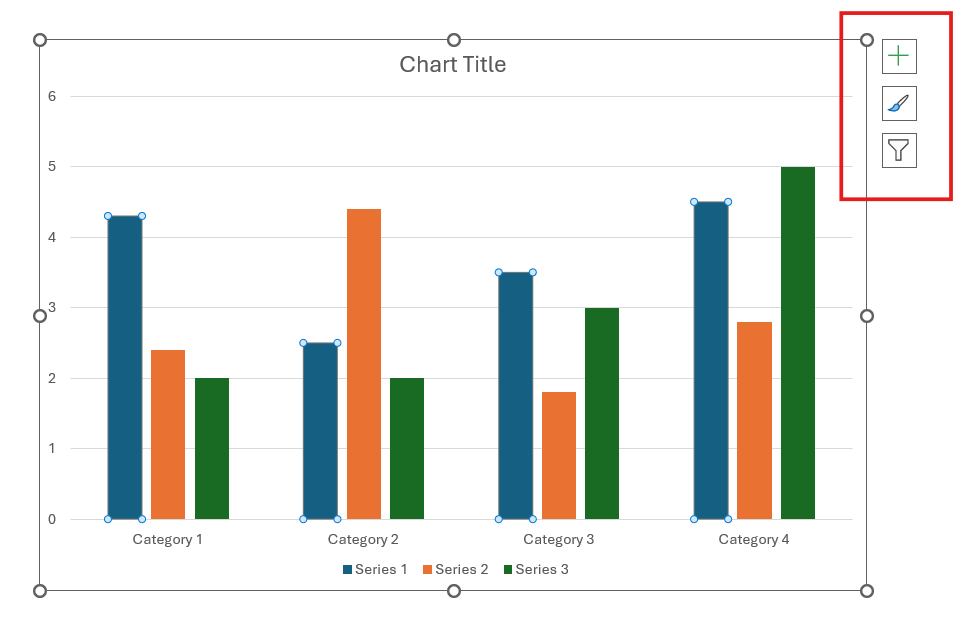
Customizing Charts in PowerPoint
We already know about the power of PowerPoint charts, but we still have one more step to take: customizing them.
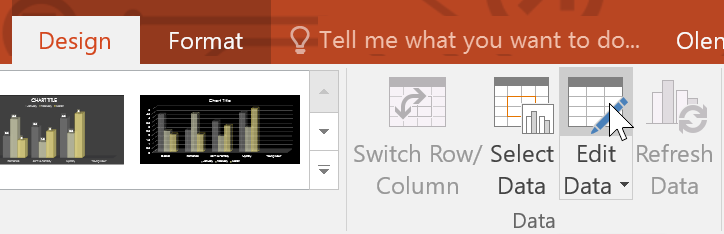
- Edit data: You can modify data directly in PowerPoint. Just double-click on the chart to open the associated Excel spreadsheet. Here, you can add, delete, or edit data. If you want to do it like a pro, check out how to Link or Embed an Excel File in PowerPoint.
- Change the design: Go to the design tab. Here, you can add or remove elements such as titles, captions, labels, etc.
- Change color and style: Select the format tab. In this section, you will find options to change the chart's color and style. You can even make individual changes.
- Add shape effects: Go to the format tab and unleash your creativity. You can add shadows, reflections, and 3D effects.
And there you have it; now you know how to customize your PowerPoint Chart. If you are looking for more inspiration, take a look at our detailed Flowchart and Gantt Chart articles.
Chart vs table
Is a chart better than a table?
We already know the importance of using tables in PowerPoint presentations. However, you may have a question in mind: are charts better than tables? The short answer is: it depends.
First off, think about what type of data you are dealing with and, most importantly, what message you are trying to get across.
Charts are great for showing trends, making comparisons, and connecting data points. They’re also visually appealing. Conversely, tables could be your perfect selection for numerical data and comprehensive details.
The most important types of charts in PPT and which one is best for you
We have checked out why adding visuals is a game-changer for your presentations. However, which one is best for your needs?
Based on our more than 10 years of expertise and creating around 17,500 slides per month, these are the charts most requested by our customers. Let's explore each one!
“Columns, bars, lines, and pie charts are top picks for clients because they're more descriptive and easier to get for the audience.” Briana/ Design Manager
Column Chart
Ideal for making comparisons. You can represent data in an attractive and clear way. It’s also a great option for showing changes over time. Here, you can emphasize the difference in quantities.
Imagine you're tracking sales for a store. If you have many categories of sales data and need to compare them, a column chart could be just what you need.
Download our Free Column Chart Template here.
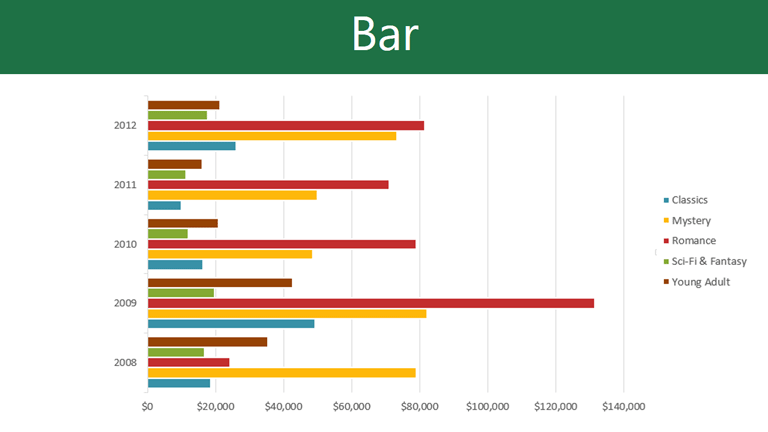
Like the column chart, the bar chart can simplify complex information quickly , especially when comparing data. But, the horizontal layout might influence how people see things, potentially altering how they understand your data. Keep this in mind!
When you have long category labels or many categories, choose a bar chart instead of a column chart. Horizontal bars are easier to read and take up less space in the presentation.
Download our Free Bar Chart Template here.
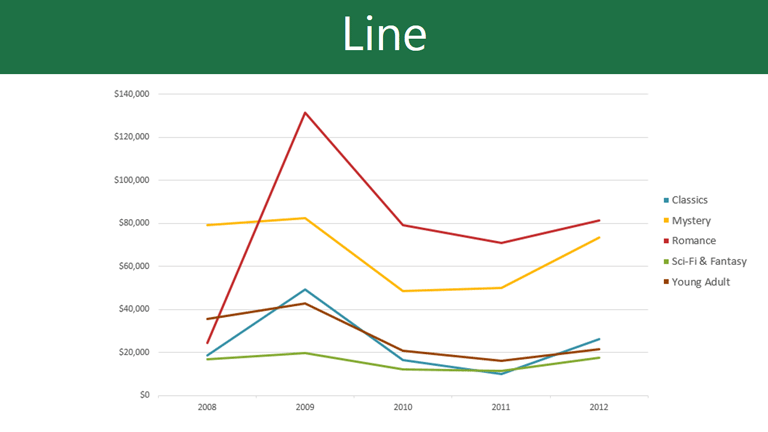
The top choice for showing trends over time. You can even combine it with other charts. For example, you can add them to a column chart to display different data at a glance. This makes it easier for viewers to understand complex information.
But how to make a line graph in PowerPoint? First, click on the Insert tab. Then, click on Graph and select Line Graph. That's it—it's as simple as that.
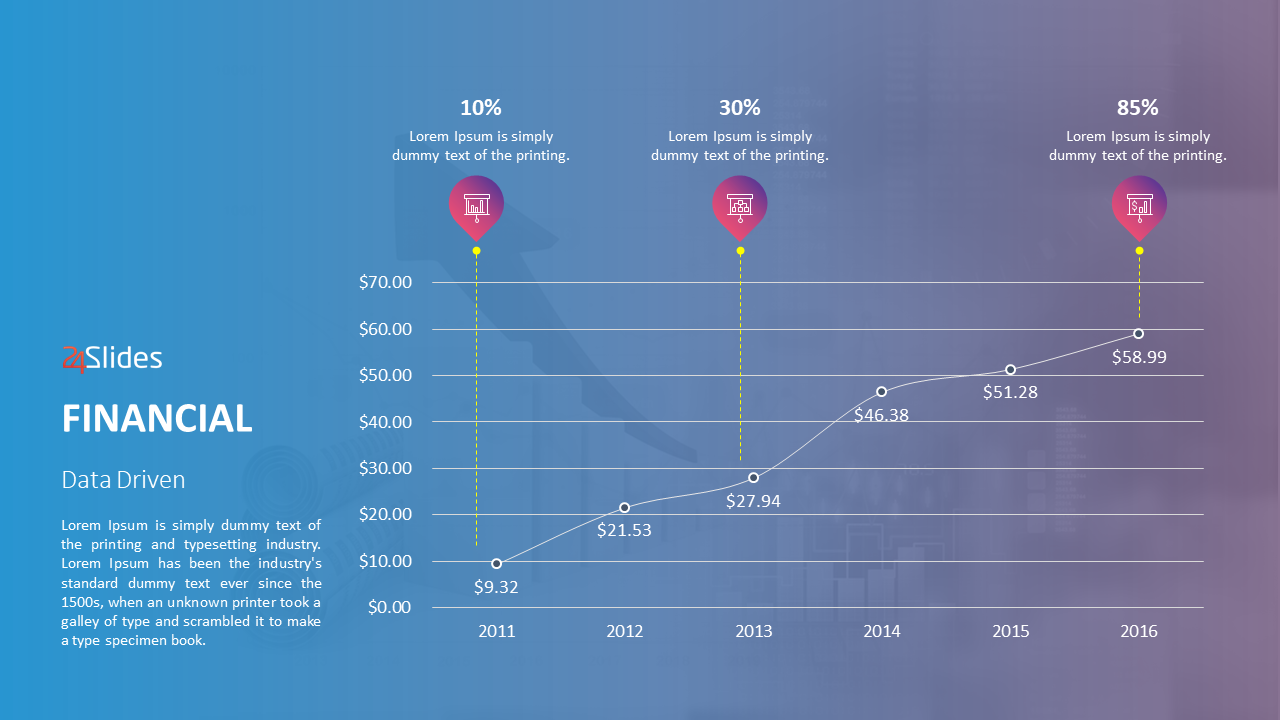
Download our Free Line Chart Template here .
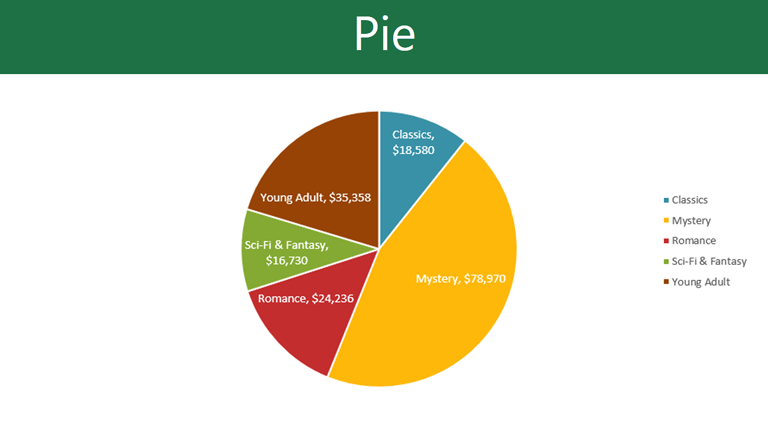
The best for showing proportions. Not only is it easy to understand, but you will also be able to illustrate percentages or parts of a whole.
Pie charts are easy to create, you need to figure out the percentages or proportions of each data category. But remember, keep the chart to six or fewer sections. This maintains data impact, avoiding confusion.
Download our Free Pie Chart Template here .
How to Use Charts and Graphs Effectively?
We already know how to use PowerPoint charts, graphs, and tables, but we want to go one step further. Here are the best tips for making effective PowerPoint presentations.
- Choose the right type of chart. Choose graphics that best suit your data. For example, use column or bar charts to compare categories, line charts to show trends over time, and pie charts to display parts of a whole.
- Be selective. Avoid using too much information, eliminate irrelevant details, and keep it simple. By focusing on the most important data points, you enhance the clarity of the information for your audience.
- Pay attention to color. When presenting data , keep in mind the consistency of the colors and make sure essential information stands out. Avoid using too many colors here, as this can be distracting.
- Add context. Make your titles clear and descriptive. Labels should also serve as a guide for viewers to understand everything easily. This could mean explaining trends, defining terms, or just describing where the data comes from.
- Consistency. Use the same style and format for your graphics and data. Ensure brand consistency in a presentation is key. This creates a professional and polished visual presentation.
- Be creative. Try unique ways to showcase your data, like infographics or custom graphics. For example, you can use a bar chart to compare categories and a line chart to show the trend over time.
Pro Tip: Creating a PowerPoint infographic is one of the most creative ways to present data. They provide a visually engaging and easy-to-follow format for presenting complex information. Briana/ Design Manager
PowerPoint tables help organize and display data in a structured way for presentations. They’re made up of rows and columns containing text, numerical data, or other information.
Tables are awesome for showing comparisons, summarizing information, sharing research findings, and planning. Because of all that, they are a top choice for visualizing financial or statistical data. They’re incredibly versatile and practical!
All you need to do is put the right labels on, and reading should be a breeze. Believe us, your audience will appreciate it. Do you want to present data in detail and make comparisons? Then, this is your best option.
People have been using PowerPoint tables for a long time. Why? That's simple: they’re easy to read.
Here's an example:

Download our Free Table Template here .
How to Make a Table in PowerPoint?
Inserting tables in PowerPoint is quite simple. Just click on Insert and then on Table . Next, just drag the mouse down to choose the number of rows and columns you need.
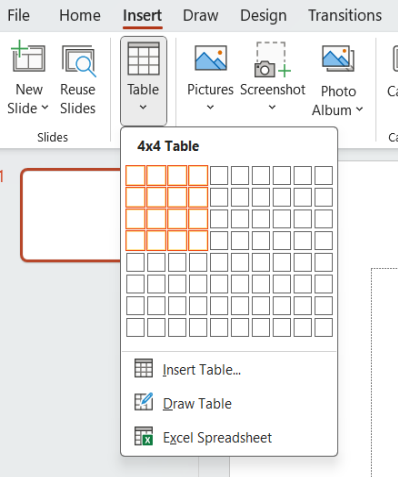
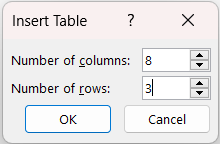
Should you require a bigger table? You can manually select the values for the columns and rows.
Customizing tables in PowerPoint
Now that we know how to create a table in PowerPoint, let's customize it. But first, let's learn how to add rows and columns in PowerPoint.
- How to add a row to a table in PowerPoint?
Click on a cell in the existing table. Go to the Layout tab in the ribbon and select Insert . Select Insert Rows Above or Insert Rows Below , depending on where you want to add the new row.
- How to add a column to a table in PowerPoint?
Click on an adjacent cell in the table. Go to the Layout tab in the ribbon and then select Insert . Choose either Insert Columns Left or Insert Columns Right , depending on where you want to add the new column.
Now that you have the structure of your table ready, let's give it some styling:
- Applying style in your table presentation
To edit your tables, first select a cell. Then, click on the Design tab to pick the style you like best. Finally, click on the drop-down arrow to see the complete Table Styles gallery .
That's it. Now you know how to use tables in PowerPoint.
How to Use Tables Effectively?
Tables are powerful tools for presenting data in a structured format. They can enhance clarity, facilitate comparisons, and convey complex information.
However, when you don't use them correctly, they can have the opposite effect, making the information flat and boring. So here are golden rules to help you:
Keep it simple
Don't overload your table with too much information. Focus on the most important information to keep it clear and easy to read. Remember, the powerful presentation of data is in simplicity.
Consider whether gridlines are necessary for your table. Removing them can make your board look cleaner and more professional.
Although many don't mention it, choosing the right words is vital. The more you can say of the same idea in fewer words, the better. Avoid using words or connectors that add nothing to the message.
Highlight key data points
Make your table pop using bold, italics, or fun colors to highlight important data or headings. This will make the table easier to read.
Consider adding shades for alternate rows to make your table easier to read. Make the shadow subtle, to avoid distraction from the data itself.
You can use color to emphasize backgrounds or text. No matter which method you opt for to add contrast, remember that “less is more” when creating an effective table.
Consistency
Consistency is crucial in tables, as it is in graphics. Ensure that the font style, size, and color are the same across the entire table. This helps maintain visual harmony.
Align your text and numbers properly so they're easier to read and give your table a polished look. If you will use decimals, think about aligning them to facilitate comparisons.
In this article, we have explored the benefits of incorporating visuals like charts, graphs, and presentation tables in PowerPoint . We also know how to add them and ensure they look good.
Just remember to pick the right chart and keep your presentations consistent.
And as I said at the beginning, conveying complex information doesn't have to be challenging! Our Templates by 24Slides platform has hundreds of free PowerPoint charts, graphs, and table templates.
You can download and combine different templates to create a shiny PowerPoint Presentation. All the examples in this article are fully customizable, allowing you to insert your data without worrying about design. Enjoy them!
Knowing how to use PowerPoint charts, graphs, and tables can make the difference between a successful presentation and a failed one. However, mastering the art of presenting data takes more time and effort.
The good news? You can always trust professionals to do the heavy work, allowing you to focus on improving your product or service — what really matters to your business.
With an average satisfaction score of 4.8 out of 5 from over 1.3 million redesigned slides, it's safe to say we're incredibly proud of the product we deliver.
We're the world's largest presentation design company.
Not only will you receive an attractive presentation, but we will create one that fits your brand's visual guidelines. Most importantly, it will help emphasize your message and engage your audience.

Ready to elevate your PowerPoint presentations? Explore this content:
- Mastering the Art of Presenting Data in PowerPoint
- 20+ Free PowerPoint and Google Slides Templates for Data Presentations
- The Ultimate Brand Identity Presentation Guide [FREE PPT Template]
- The Cost of PowerPoint Presentations: Discover the hidden expenses you might overlook!
Create professional presentations online
Other people also read
How To Write Effective Emails That Will Improve Your Communi...

How to Make a Marketing Plan Presentation in PowerPoint

Alternative presentation styles: Takahashi


Are looking for custom service?
- Presentation Design
- Report Design
- Brochure Design
- Infographic Design
- Illustration Design
- Package Design
- Exhibition Design
- Print Design
- Logo Design
- Video Animation
- Motion Graphics
Presentation ideas • Tips and Tricks
15 Creative Ways to Use Charts and Graphs in Presentations
Emily Bryce
12 December 2022

In today’s data-driven world, presentations are no longer just about presenting ideas and concepts, but also about presenting data in an engaging and easy-to-understand manner. This is where charts and graphs come in. They help to visualize data, making it easier for the audience to grasp and retain information. In this blog post, we will explore creative ways to use charts and graphs in presentations.
1. Use charts and graphs to compare data
One of the most common uses of charts and graphs is to compare data. Whether you are comparing sales figures, market trends or customer feedback, charts and graphs can help you present the information in a visually compelling way. Use bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, and scatter plots to showcase the data in a way that makes it easy to understand and compare.
2. Use charts and graphs to show trends
Another way to use charts and graphs in presentations is to show trends over time. For example, if you are presenting the growth of your business over the last five years, use a line graph to show the upward trend. If you want to show the fluctuations in your business over a period of time, use a scatter plot to highlight the highs and lows.
3. Use charts and graphs to show relationships
Charts and graphs can also be used to show the relationship between different sets of data. For example, if you are presenting the correlation between customer satisfaction and sales, use a scatter plot to show the relationship between the two variables. You can also use bubble charts to show the relationship between three different variables.
4. Use charts and graphs to show distribution
If you are presenting data that is distributed across a range, such as the ages of your customers, use a histogram to show the distribution. Histograms are great for showing the frequency distribution of data, and they can help you identify patterns and trends in the data.
5. Use charts and graphs to show proportions
Pie charts are a great way to show proportions. Use pie charts to show the proportion of sales for different products or the proportion of the budget allocated to different departments. Make sure to keep the number of categories to a minimum to ensure that the chart is easy to read.
6. Use creative chart and graph designs
Charts and graphs don’t have to be boring. Use creative designs and colors to make your charts and graphs stand out. For example, you can use a bar chart with a gradient background to make it more visually appealing. You can also use icons and images to make your charts and graphs more engaging.
7. Use charts and graphs to tell a story
Finally, use charts and graphs to tell a story. Don’t just present the data, but use it to support your message. Use a combination of charts and graphs to create a narrative that engages your audience and leaves them with a clear understanding of your message.
In conclusion, charts and graphs are a powerful tool for presenting data in an engaging and easy-to-understand manner. Use them creatively to showcase data, tell a story, and leave a lasting impression on your audience. With the right use of charts and graphs, you can take your presentations to the next level.
Stay Updated
Join our exclusive subscribers list to receive the latest design trends, industry updates and digital world insights in your inbox.
You can read our privacy policy here .
Related Posts

The Psychology of Color in Presentation Design

10 Tips for Creating Effective Presentations

How to Choose the Right Font for Your Presentation

Top 5 Mistakes to Avoid in Your Next Presentation

My Presentation Designer is a brand of Out of Box Ltd. which is a registered company in England and Wales under company no. 06937876 and VAT ID GB381889149 .
Copyright © 2015-2023 • My Presentation Designer • All rights reserved.

- Announcements
- Brainstorming
- Development
- HR Planning
- Infographics
- IT & Operations
- Marketing & Sales
- Meeting & Visual Collaboration
- Product Management
- Production & Manufacturing
- Project Management
- Remote Working
- Research & Analysis
- Software Teams
- Strategy & Planning
- Template Roundup
- Uncategorized
Jazz Up Your Presentation: 6 Ways to Put an End to Ugly Charts and Graphs
Updated on: 22 December 2020

People often add charts and graphs to their presentation trying to make it more interesting. Unfortunately, most efforts to make it unique usually end up having the exact opposite effect.
Often, the enormous collection of slides with colorful presentation charts and graphs blows up your brain by the end of the presentation rather than arousing your interest in the data. You don’t want to be the person who puts his audience through this agonizing experience every time you fire up your laptop.
So, is there a way to jazz up your presentation with beautiful charts and graphs?
The short answer to this question is ‘Yes.’ Here are 6 ways to improve your presentation charts and graphs to effortlessly strengthen your message.
Refrain from Using Backgrounds
When it comes to decorating the graph background, you should avoid using gradients of color or varying the background color in any other way.
It not only undermines your ability to present the data unambiguously but also adds distraction. The context surrounding an object often influences our perception of it.

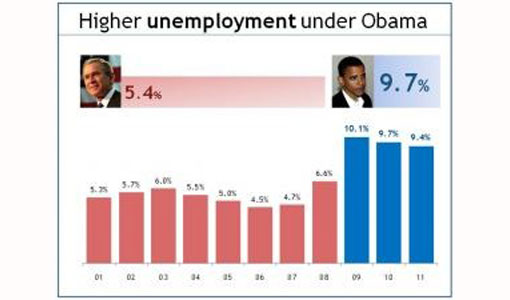
See the two graphs above, the grey background in the left graph doesn’t provide any information. On the contrary, it doesn’t contrast sufficiently with the object. As a result, it undermines the visibility of the objects in the graph. So, make sure the background is consistent with the slide background.
If you always use the default slide background, you should use ‘No Fill’ ‘or White’ background color as it matches the slide background.
Eliminate Redundant Labels
Why do you want to waste the space on redundant labels? Most graphs charts are quite self-explanatory. Repeated axis labels and legend are the two things that occupy the space for no reason.
In fact, they are taking up space that would be better spent on the graph. So, make sure to remove duplicate labels. The graph on the right looks better than the original graph to the left, as it is much easier to understand.

Alternatively, you can also label the bars directly. However, if you do, remove the Y-axis completely. As the exact value of each element is displayed, you don’t need to use the grid lines either.

Mind the Border Formatting
When it comes to graphs and charts, less is more. You should format the graph background to reduce the lines as far as possible while retaining the meaning of the data presented in it.
Though the default gridlines and borders are a sensible choice, they are a distraction as your audience is most likely not interested in knowing the exact figures for each data point.
If you want to display exact values, label the bars directly as discussed in the previous point. Removing the lines highlights the data and the pattern dramatically. So, remove all of the outer borders as well as grid lines as shown below.

Use Colors Meaningfully
Contrary to the popular belief, you should avoid using bright colors for presentation charts and graphs as far as possible. In fact, you should use natural colors to display general information and use the bright color only to highlight information that demands attention.
Using same colored bars on a graph makes it easier to compare the data. Use different colors only if they correspond to different elements in the data.
Sometimes, however, you can use different colors to highlight particular data or assemble different parts. In other words, you need to use colors meaningfully and with caution. The following examples will help explain the points mentioned above.
A) Using Natural Colors for Easier Comparison

B) Using Bright Colors to Pop Important Data

C) Using Different Colors to Point out Differences in Data Elements

Avoid Using Special Effects (Shadowing and Shading)
Avoid using special effects such as shadowing, shading, and 3D effects when creating presentation charts and graphs, especially for professional purposes. They just make it hard to compare the elements and confuse the reader.
You should, however, stick to presenting only essential information. So, keep it simple and avoid flashy special effects.

Text and Font
Using bold font isn’t going to make much difference in your graph. As far as possible, avoid using bold, underline or italic fonts. Keep the font size and type consistent throughout the presentation.
Avoid effects such as shading, outline, and 3D letters. Always lighten secondary data labels. The less you format the better.

Have More Tips for Creating Better Presentation Charts and Graphs?
When it comes to creating an attention-grabbing presentation , the rule of thumb is to display the data in a simple and clear way.
With the help of these 6 tried and tested tips, your presentation charts and graphs will look phenomenal without compromising your data. What about you? What tricks have you used to make your graphs look unique? Feel free to share your ideas and suggestions in the comments box below.
About the Author
Swati Kapoor is a qualified dietitian at Practo . She has a Masters degree in Dietetics and Food Service Management. She is a strong believer in spreading the goodness of ‘nutrition through healthy eating’. As a responsible dietitian, Swati examines her patients’ health history carefully before recommending any diet or workout regimen, because everybody has different requirements.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.

More Related Articles

Leave a comment Cancel reply
Please enter an answer in digits: six − 2 =
Download our all-new eBook for tips on 50 powerful Business Diagrams for Strategic Planning.

- Chart Guide
- Data Makeover
0 comments
Choosing the Right Chart or Graph for Your Data: A Comprehensive Guide
By STC
August 12, 2023

Data is everywhere. We use it to make decisions, communicate, to persuade, and to learn. But data alone is not enough. We need to present it in a way that makes sense, that tells a story, that reveals insights. That’s where charts and graphs come in.
Charts and graphs are visual representations of data that help us to understand, analyze, and communicate complex information. They can show patterns, trends, relationships, comparisons, and more. But not all charts and graphs are created equal. Some are better suited for certain types of data than others. Some are more effective at conveying a message than others. Some are more appealing to the eye than others.
How do you choose the right chart or graph for your data? How do you make sure that your visualizations are clear, accurate, and engaging? How do you avoid common pitfalls and mistakes that can confuse or mislead your audience? These are the questions that this comprehensive guide will answer.
In this guide, you will learn:
- The basic principles of data visualization and why they matter.
- The different types of charts and graphs and how to use them for different purposes.
- The best practices and tips for creating effective and attractive charts and graphs.
- The tools and resources that can help you create stunning visualizations.
By the end of this guide, you will be able to choose the right chart or graph for your data and create visualizations that will wow your audience. Whether you are a student, a teacher, a researcher, a marketer, a journalist, or anyone who works with data, this guide is for you.
So buckle up and get ready for a journey into the world of data visualization. It’s going to be fun, informative, and eye-opening. Let’s get started!
Choosing the Right Chart
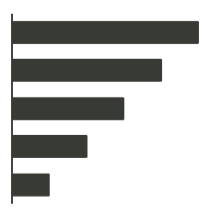
Are you comparing sales across different regions? A bar chart might be your answer.
Bar charts are one of the most common and simple types of charts that you can use to visualize your data. They consist of rectangular bars with lengths proportional to the values that they represent. Bar charts are ideal for comparing individual groups or categories. For example, if you want to compare sales across different regions, a bar chart might be your answer. You can easily see which region has the highest or lowest sales, and how the regions differ from each other. A bar chart can also show the distribution of data across categories, such as the frequency or percentage of each category. Bar charts are versatile and easy to understand, making them a great choice for many situations.
Line Charts

Line charts are best for showing trends over time. Want to see the growth of your website’s traffic over a year? Line charts can present this data cleanly.
Line charts are another popular and simple type of chart that you can use to visualize your data. They consist of a series of points connected by straight lines, forming a line that shows the change in values over time. Line charts are best for showing trends over time. For example, if you want to see the growth of your website’s traffic over a year, line charts can present this data cleanly. You can easily see the ups and downs, the peaks and valleys, and the overall direction of your traffic. A line chart can also show the relationship between two or more variables over time, such as the correlation between temperature and ice cream sales. Line charts are useful and intuitive, making them a great choice for many situations.
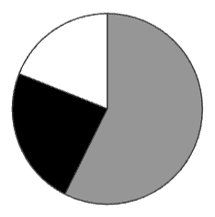
Pie charts are great for displaying a part-to-whole relationship. Need to illustrate a budget? Pie charts give a clear picture.
Pie charts are another common and simple type of chart that you can use to visualize your data. They consist of a circular shape divided into slices, each representing a proportion of the whole. The size of each slice is proportional to the percentage of the total value that it represents. Pie charts are great for displaying a part-to-whole relationship. For example, if you need to illustrate a budget, pie charts give a clear picture of how much money is allocated to each category, and how each category compares to the others. A pie chart can also show the composition of a population, such as the age groups, genders, or ethnicities. Pie charts are colorful and easy to read, making them a great choice for many situations.
Scatter Plots
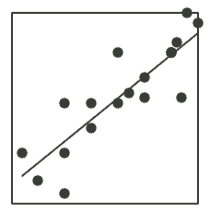
Scatter plots are perfect for showing relationships between two variables. Looking to find correlation between age and income? This is the graph for you.
Scatter plots consist of a collection of points on a two-dimensional plane, each representing the values of two variables for a single observation. Scatter plots are perfect for showing relationships between two variables. For example, if you are looking to find correlation between age and income, this is the graph for you. You can easily see how the two variables vary together, and whether there is a positive, negative, or no correlation. A scatter plot can also show outliers, clusters, and gaps in your data. Scatter plots are powerful and insightful, making them a great choice for many situations.
Area Charts
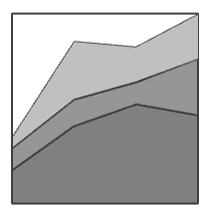
Area charts can illustrate trends and are particularly useful for showing cumulative totals. Interested in how savings accumulate over time? Consider an area chart.
Area charts are similar to line charts, but they have a shaded area below the line that shows the magnitude of the values. Area charts can illustrate trends and are particularly useful for showing cumulative totals. For example, if you are interested in how savings accumulate over time, consider an area chart. You can easily see how much money you have saved at any point in time, and how the savings rate changes over time. An area chart can also show the contribution of different components to a total, such as the sources of revenue or the types of expenses. Area charts are expressive and informative, making them a great choice for many situations
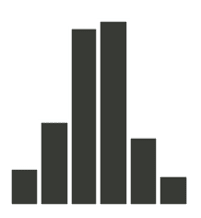
Histograms are used for displaying frequency distributions. Studying the distribution of customer satisfaction scores? A histogram will serve you well.
Histograms are similar to bar charts, but they have no gaps between the bars and they show the frequency of values in a continuous variable. Histograms are used for displaying frequency distributions. For example, if you are studying the distribution of customer satisfaction scores, a histogram will serve you well. You can easily see how many customers gave a certain score, and how the scores are spread across the range. A histogram can also show the shape of the distribution, such as whether it is symmetric, skewed, or bimodal. Histograms are descriptive and revealing, making them a great choice for many situations.
Graph Types
Time series.
Time series graphs are vital for tracking changes over periods. Monitoring stock prices? Time series graphs are the way to go.
Time series graphs are similar to line charts, but they show the change in values over a specific period of time, such as days, months, or years. Time series graphs are vital for tracking changes over periods. For example, if you are monitoring stock prices, time series graphs are the way to go. You can easily see how the prices fluctuate over time, and how they respond to external events, such as news, earnings, or market trends. A time series graph can also show the seasonality, cycles, and trends of your data. Time series graphs are dynamic and insightful, making them a great choice for many situations.
Correlation
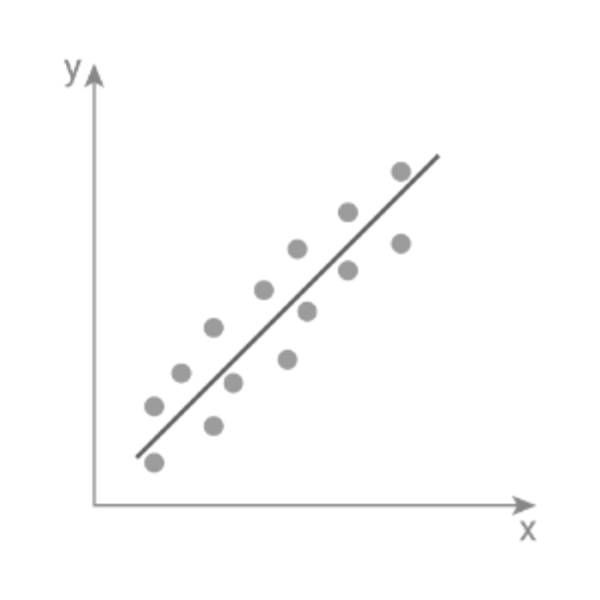
Correlation graphs help in identifying patterns between two variables. Investigating how temperature affects sales? Use this graph.
Correlation graphs are another type of chart that you can use to visualize your data. They are similar to scatter plots, but they show the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables. Correlation graphs help in identifying patterns between two variables. For example, if you are investigating how temperature affects sales, use this graph. You can easily see if there is a positive correlation (higher temperature leads to higher sales), a negative correlation (higher temperature leads to lower sales), or no correlation (temperature has no effect on sales). A correlation graph can also show the correlation coefficient, which is a numerical measure of how closely the variables are related. Correlation graphs are helpful and informative, making them a great choice for many situations.
Distribution
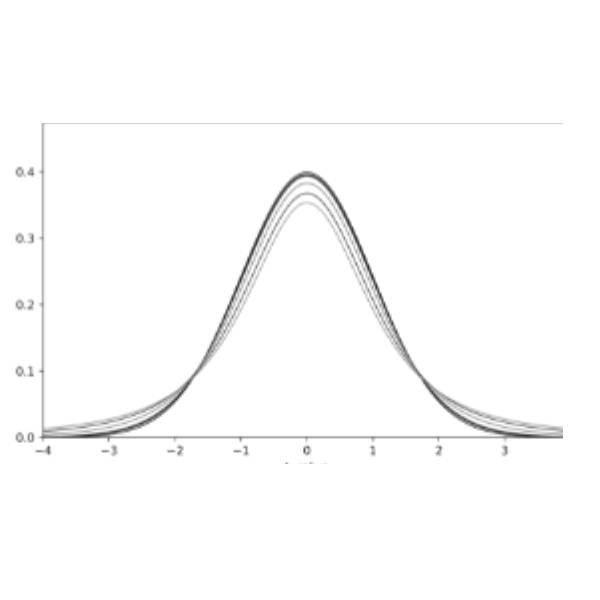
Distribution graphs depict how variables are spread out. Analyzing product quality? This is your choice.
Distribution graphs are similar to histograms, but they show the probability density of a continuous variable, rather than the frequency. Distribution graphs depict how variables are spread out. For example, if you are analyzing product quality, this is your choice. You can easily see the mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range of your data. You can also see the shape of the distribution, such as whether it is normal, skewed, or uniform. A distribution graph can also show the confidence intervals, which indicate how certain you are about the true value of the mean. Distribution graphs are descriptive and analytical, making them a great choice for many situations.
Comparison graphs are used to contrast different data sets. Comparing marketing channels? Select this type.
Comparison graphs are similar to bar charts, but they show two or more data sets side by side, or stacked on top of each other, to highlight the differences and similarities between them. Comparison graphs are used to contrast different data sets. For example, if you are comparing marketing channels, select this type of graph. You can easily see how each channel performs in terms of reach, engagement, conversion, and revenue. You can also see how the channels compare to each other, and to the overall average. A comparison graph can also show the variance, which indicates how much the data varies from the mean. Comparison graphs are useful and informative, making them a great choice for many situations.
Common Mistakes in Data Visualization
Data visualization is a powerful tool that can help you communicate your data in a clear and compelling way. But it can also backfire if you make some common mistakes that can distort, confuse, or mislead your audience. Here are some of the pitfalls that you should avoid when creating charts and graphs:
- Misleading Scales: Scales are the numbers that show the range of values on the axes of your chart. They can easily misrepresent data if not chosen wisely. For example, if you use a scale that is too large or too small, you can make the differences between data points look bigger or smaller than they really are. Or if you use a scale that is not consistent across charts, you can make unfair comparisons between data sets. To avoid misleading scales, you should always choose a scale that is appropriate for your data, and that is consistent and transparent for your audience.
- Too Many Colors: Colors are a great way to add visual interest and contrast to your chart. But too many colors can lead to confusion rather than clarity. For example, if you use too many colors to represent different categories, you can make it hard for your audience to distinguish between them. Or if you use colors that are too similar or too different, you can make it hard for your audience to see the patterns or trends in your data. To avoid too many colors, you should always use a color scheme that is suitable for your data, and that is simple and intuitive for your audience.
- Overcomplicating: Simplicity often wins. Ever felt overwhelmed by a complex chart? You’re not alone. Sometimes, we try to cram too much information or detail into our chart, thinking that more is better. But this can make our chart look cluttered and confusing, and distract our audience from the main message. To avoid overcomplicating, you should always focus on the key point that you want to convey with your chart and eliminate any unnecessary or redundant elements that might obscure it.
You have reached the end of this comprehensive guide on choosing the right chart or graph for your data. We hope that you have learned a lot from this guide and that you are now ready to create your own stunning and effective visualizations.
Choosing the right chart or graph for your data is crucial for accurate and effective data presentation. By understanding the differences and uses of various charts and avoiding common mistakes, you can create compelling and insightful visualizations that will capture the attention and interest of your audience. You can also communicate your data in a clear and concise way, and reveal the hidden stories and insights that lie within your data.
We hope that this guide has been helpful and informative for you and that you have enjoyed reading it as much as we have enjoyed writing it. Data visualization is a fascinating and rewarding field, and we encourage you to explore it further and apply it to your own projects. Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words, but a good chart or graph is worth even more. Happy visualizing!

About the author
We are passionate about the power of visual storytelling and believe that charts can convey complex information in a captivating and easily understandable way. Whether you're a data enthusiast, a business professional, or simply curious about the world around you, this page is your gateway to the world of data visualization.
Never miss a good story!
Subscribe to our newsletter to keep up with the latest trends!

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
PowerPoint - Charts
Powerpoint -, powerpoint charts.

PowerPoint: Charts
Lesson 23: charts.
/en/powerpoint/tables/content/
Introduction
A chart is a tool you can use to communicate data graphically . Including a chart in a presentation allows your audience to see the meaning behind the numbers , which makes it easy to visualize comparisons and trends .
Optional: Download our practice presentation for this lesson.
Watch the video below to learn more about using charts in PowerPoint.
Types of charts
PowerPoint has several types of charts, allowing you to choose the one that best fits your data. To use charts effectively, you'll need to understand how different charts are used.
Click the arrows in the slideshow below to learn more about the types of charts in PowerPoint.
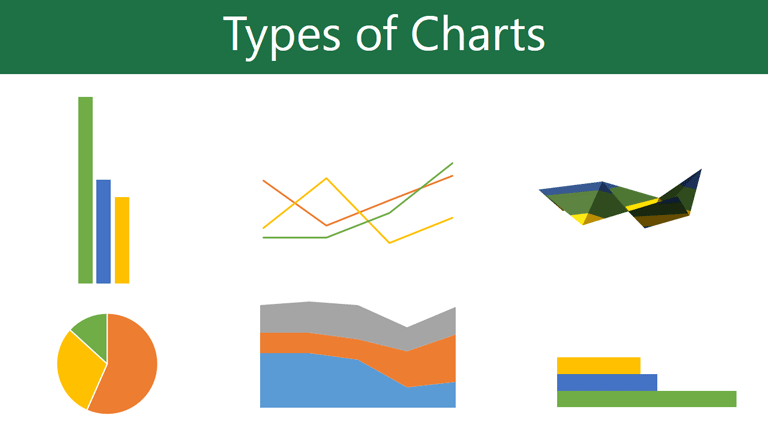
PowerPoint has a variety of chart types, each with its own advantages. Click the arrows to see some of the different types of charts available in PowerPoint.
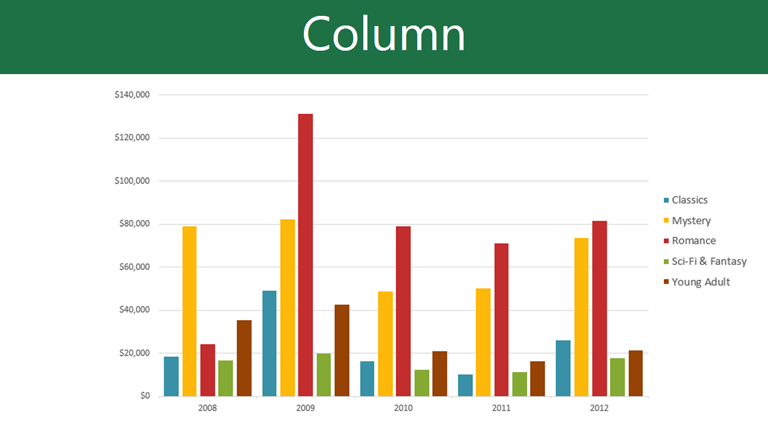
Column charts use vertical bars to represent data. They can work with many different types of data, but they're most frequently used for comparing information.
Line charts are ideal for showing trends. The data points are connected with lines, making it easy to see whether values are increasing or decreasing over time.
Pie charts make it easy to compare proportions. Each value is shown as a slice of the pie, so it's easy to see which values make up the percentage of a whole.
Bar charts work just like column charts, but they use horizontal bars instead of vertical bars.
Area charts are similar to line charts, except the areas under the lines are filled in.
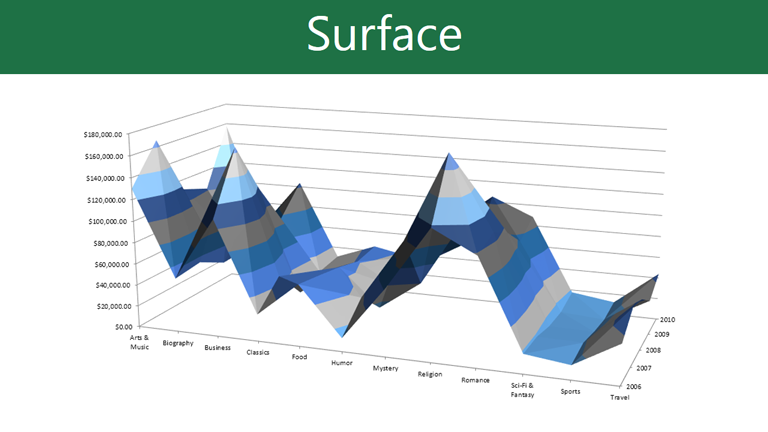
Surface charts allow you to display data across a 3D landscape. They work best with large data sets, allowing you to see a variety of information at the same time.

Identifying the parts of a chart
In addition to chart types, you'll need to understand how to read a chart . Charts contain several different elements—or parts—that can help you interpret data.
Click the buttons in the interactive below to learn about the different parts of a chart.
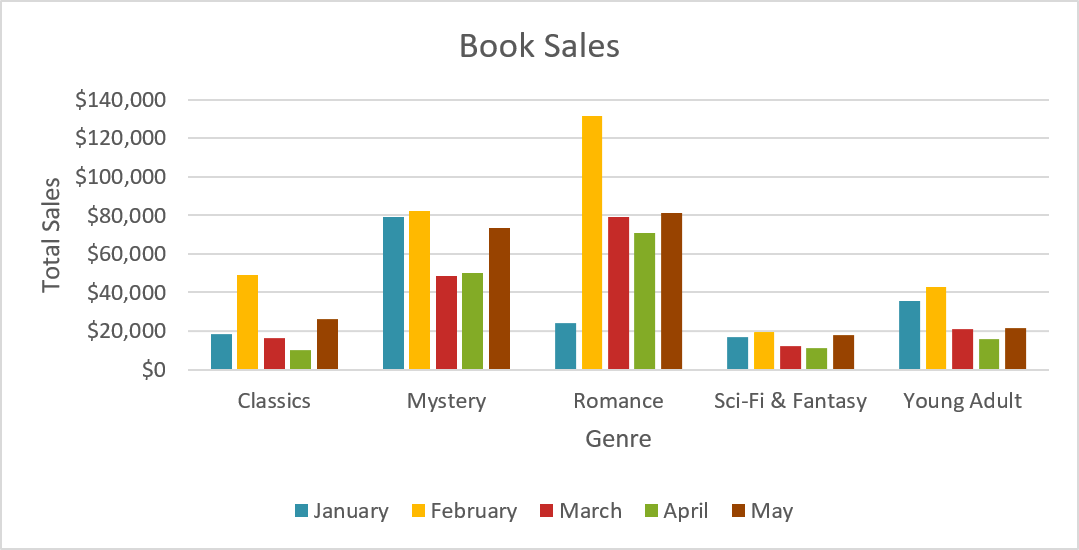
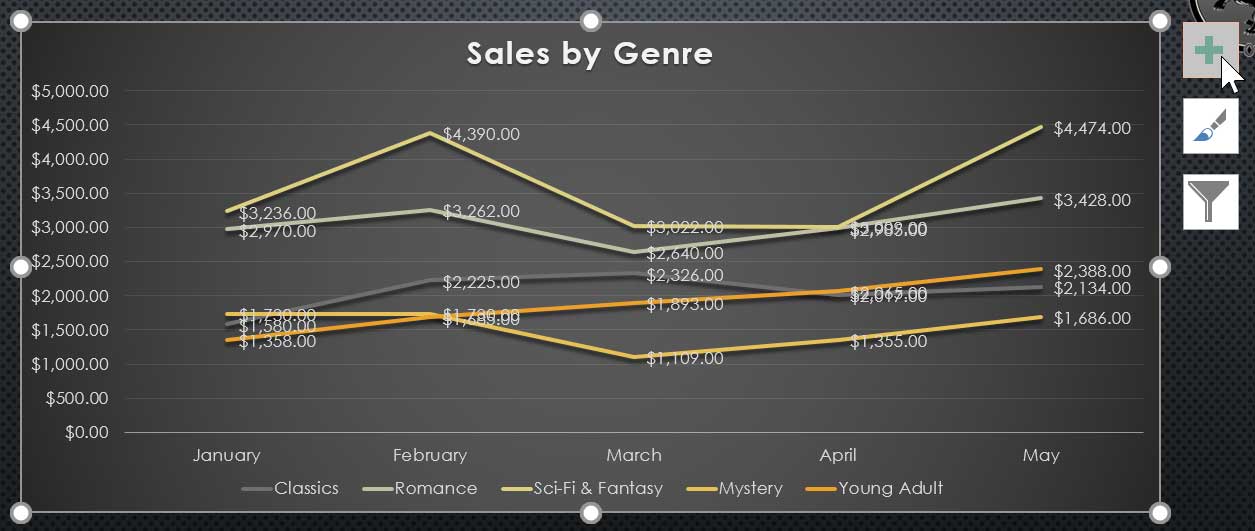
Data Series
The data series consists of the related data points in a chart. In this example, as we can see in the legend, the yellow columns represent net sales in February.
Horizontal Axis
The horizontal axis (also known as the x axis ) is the horizontal part of the chart. Here, the horizontal axis identifies the categories in the chart. In this example, each genre is placed in its own group .
The legend identifies which data series each color on the chart represents. In this example, the legend identifies the different months in the chart.
Chart Title
The title should clearly describe what the chart is illustrating.
Vertical Axis
The vertical axis (also known as the y axis ) is the vertical part of the chart. Here, the vertical axis measures the value of the columns. In this example, the measured value is each genre's total sales.
Inserting charts
PowerPoint uses a spreadsheet as a placeholder for entering chart data, much like Excel . The process of entering data is fairly simple, but if you are unfamiliar with Excel you might want to review our Excel Cell Basics lesson.
To insert a chart:
- A dialog box will appear. Select a category from the left pane, and review the charts that appear in the right pane.
You can edit the chart data at any time by selecting your chart and clicking the Edit Data command on the Design tab.
You can also click the Insert Chart command in a placeholder to insert a new chart.

Creating charts with existing Excel data
If you already have data in an existing Excel file you want to use for a chart, you can transfer the data by copying and pasting it. Just open the spreadsheet in Excel, select and copy the desired data, and paste it into the source data area for your chart.
You can also embed an existing Excel chart into your PowerPoint presentation. This may be useful when you know you'll need to update the data in your Excel file and want the chart to automatically update whenever the Excel data is changed.
Read our guide on Embedding an Excel Chart for more information.
Modifying charts with chart tools
There are many other ways to customize and organize your charts. For example, PowerPoint allows you to change the chart type , rearrange a chart's data, and even change the layout and style of a chart.
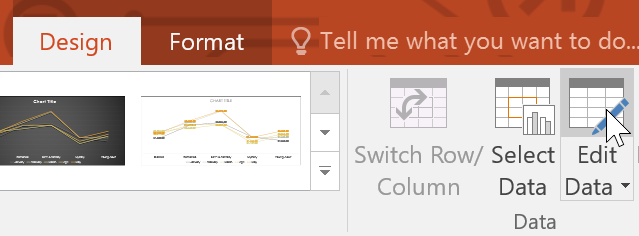
To change the chart type:
If you find that your data isn't working with a certain chart, it's easy to switch to a new chart type . In our example, we'll change our chart from a column chart to a line chart.
To switch row and column data:
Sometimes you may want to change the way charts group your data. For example, in the chart below the book sales data is grouped by genre , with lines for each month . However, we could switch the rows and columns so the chart will group the data by month , with lines for each genre . In both cases, the chart contains the same data; it's just organized differently.
- Select the chart you want to modify. The Design tab will appear.
We've noticed that when numerical data has been entered in the first column of the spreadsheet, switching rows and columns may cause unexpected results. One solution is to type an apostrophe before each number, which tells the spreadsheet to format it as text instead of a numerical value. For example, the year 2016 would be entered as '2016 .
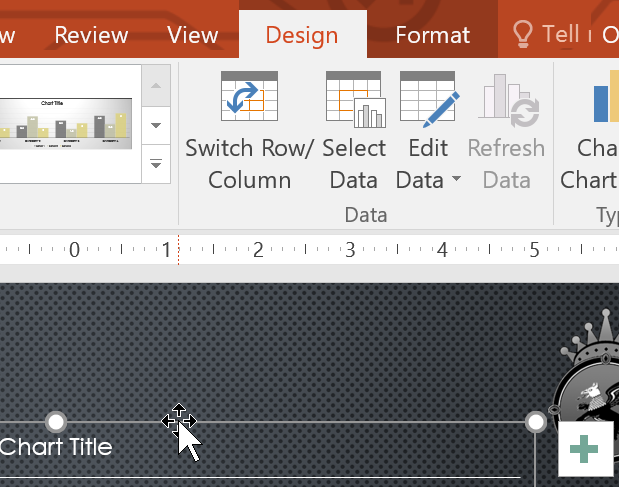
To change the chart layout:
Predefined chart layouts allow you to modify chart elements—including chart titles , legends , and data labels —to make your chart easier to read.
To change a chart element (like the chart title), click the element and begin typing.

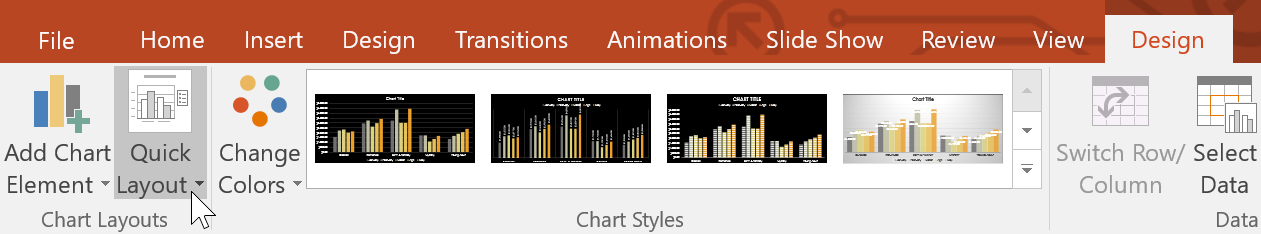
To change the chart style:
Chart styles allow you to quickly modify the look and feel of your chart.
You can also use the chart formatting shortcut buttons to quickly add chart elements , change the chart style , and filter the chart data.
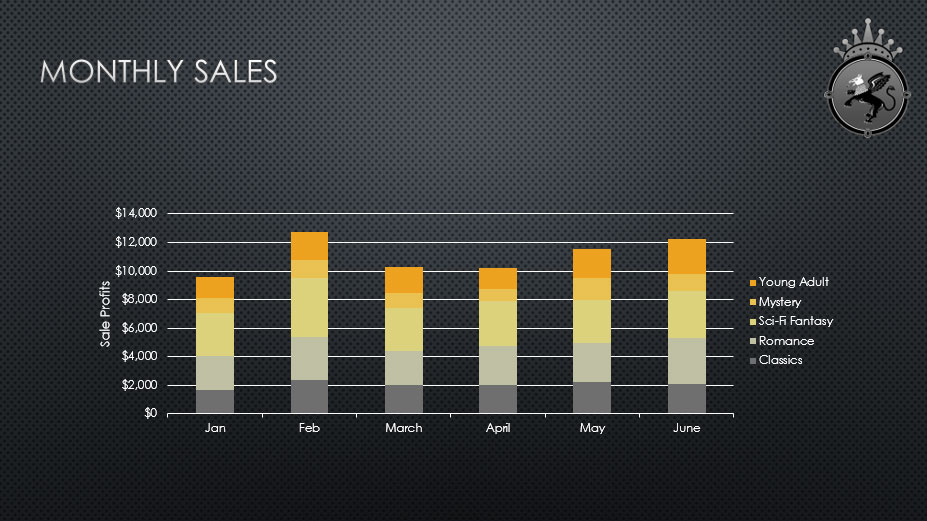
- Open our practice presentation . You will also need to download our practice workbook .
- On the last slide, insert a line chart.
- Open our practice workbook in Excel. Copy the data and paste it into the chart's spreadsheet.
- Delete the chart title .
- Change the chart type to Stacked Column .
- Use the Quick Layout drop-down menu to change to Layout 10 .
- Click the Chart Elements shortcut button, click the arrow next to Axis Titles , and select the Primary Vertical axis title.
- Double-click the axis title, then rename it Sale Profits .
- Switch the Row/Column data.
/en/powerpoint/smartart-graphics/content/
Home Blog Design Chart vs. Graph: Understanding the Graphical Representation of Data
Chart vs. Graph: Understanding the Graphical Representation of Data

Presenters face a common question when representing data whether to pick graphs vs. charts. Which one do you need to visualize your information? Well, the short answer is: it depends.
The trick to confidently knowing if you need a chart or a graph when visualizing information is knowing how the two are related to each other hierarchically.
Did you know that all graphs are charts, but not all charts are graphs? The two terms are often used interchangeably but do have unique distinctions. Knowing these characteristics will help you create and present better data presentations .
Let’s go deeper into the semantics of it all.
Difference Between a Chart and a Graph
As a person that creates presentations, it’s important that you know the relationship between charts and graphs and how they support the visual and graphical representation of data. The differences between a chart and a graph lie in semantics and hierarchy.
In biology, we have systems of classification to understand the hierarchical relationship between animal genera, kingdoms, and species. In the same way, charts are graphs are two parts of a larger hierarchical classification system of data visualizations.
Think of a tree diagram (or organizational chart) with a Data Visualization label at the top. The next tier underneath includes labels like charts , infographics , and dashboards. The next tier branches from these terms into their subcategories. Underneath charts, you find; graphs, flowcharts, organizational charts , Gantt charts, maps, and diagrams .
Charts and graphs are related hierarchically. When you define the term “chart,” graphs are inherently included in that definition.
A chart is a visual representation of information or data. The purpose of a chart is to help viewers understand and analyze information easily with the help of visuals. Charts can be stand-alone visuals or grouped to create infographics, dashboards, and other more complex data visualizations.
A graph is a chart that uses mathematical equations to visualize data and analyze relationships and trends. For a chart to be a graph—and not another type of chart—it must involve a mathematical analysis, generally using the x and y axis to plot data points. Common graphs use lines and bars to visualize data quantities, relationships, and trends.

Edward Tufte, a pioneer in the field of data visualization, has profoundly influenced how we understand and present data. His principles of clarity, efficiency, and truthful communication in data presentation serve as foundational guidelines for creating more effective and insightful visual representations. Tufte advocates for the use of high-resolution data displays, the integration of words, numbers, and images into a single narrative, and the elimination of non-data ink to focus attention on the data itself.
Good design is clear thinking made visible, bad design is stupidity made visible. Edward Tufte
By applying Tufte’s principles to the design of charts and graphs, presenters can significantly enhance their ability to convey complex information in an accessible and engaging manner. Whether you’re working with PowerPoint, Google Slides, Microsoft Excel, Tableau, R or any other tool, incorporating Tufte’s insights can elevate the clarity of your data visualizations in presentations and book reports.
Types of Graphs & Types of Charts
The tree diagram above shows the big picture: graphs are a subset of charts. Now let’s look at the details.
Charts can be separated into two main categories; numerical and non-numerical. Graphs are the numerical type. Here’s an outline to help you visualize the hierarchy of these terms.
- Line graphs
- Gantt Charts
- Network Diagrams
- Venn Diagrams
When to use a Chart or Graph
This is not a question of choosing between a chart or a graph. Because inherently, If you choose a graph, you are also choosing to use a chart. So let’s rephrase it.
Question: When is a good time to use a chart or—more specifically—a graph while creating a presentation ?
Answer: If you want to steer away from blocks of text and visualize information across slides engagingly, then you should use a chart.
Now the question is, which one? The chart you use depends on the nature of your data, so you’ll have to choose according to that.
Here are some questions to help make a decision:
- What type of data do you need to visualize?
- Is the data numerical (quantitative) or categorical (qualitative)?
- compare values or represent relationships between variables?
- show patterns or trends over time?
- show proportions or parts of a whole ?
- show distribution or frequency of data?
- highlight specific values or data points?
- What is the message you want to convey with the chart?
- What is the target audience , and what charts are they familiar with?
- What is the context, and how is it relevant to your audience?
How to create Charts and Graphs in PowerPoint and Google Slides?
Creating charts and graphs in PowerPoint and Google Slides is easy. Here are instructions to guide you.
How to add charts inside PowerPoint
1. Open your PowerPoint presentation and navigate to the slide where you want to add the chart.
2. In the top menu bar, click on Insert > Charts. The popup window will show you chart options, most of which are graphs. Select the type you want to use by selecting it and clicking ok.
3. Input the data in the worksheet that pops up for your graph.
4. Customize the design with colors and fonts for the chart’s legend.
How to add charts inside Google Slides
1. Open your Google Slides presentation and navigate to the slide where you want to add the chart.
2. In the top menu bar, click on Insert > Charts. The dropdown offers four simple graphs; choose one by clicking on it. You can also insert a graph from a Google Sheet that you own or have access to.
3. A default graph is placed into your slide, offering a prompt to edit the data in Sheets. For every new graph, Google creates a separate sheet for the data. The Sheet remains linked to the graph in the presentation unless you unlink it.
4. Customize the design with colors and fonts for the visualization and the legend.
You can browse more detailed information on how to make charts & graphs in Google Slides in this article on “ How to Make a Graph in Google Slides .”
A better way to add charts and graphs to PowerPoint and Google Slides
Yes, it’s easy to add charts and graphs to presentations in PowerPoint and Google Slides, but there’s a way to make them look better easily.
Download chart and graph templates from SlideModel and give your presentations a more refined look. In the SlideModel template repository, you’ll find plenty of professionally designed charts. Most of which are compatible with both PowerPoint and Google Slides.
Start with a comprehensive slide deck template with various ppt charts and graphs to choose from. Or download individual ppt graph templates to mix and match freely.
You’ll also find charts—that aren’t graphs—like flowcharts, tree diagrams, bubble charts , and concept maps .
After downloading from SlideModel, you can select either PowerPoint or Google Slides as your presentation design software, and customize the data, colors, and fonts to match the rest of your presentation.

How to Present Charts & Graphs
What is the purpose of graphs, charts, and diagrams? To help people understand and analyze information visually and effectively. We use them in presentations, reports, proposals, and other business communication.
The most efficient way to present charts and graphs is to follow this formula:
- Introduce the graph.
- Identify the variables.
- Highlight key info.
- Share conclusions.
This formula works for presentation slides and your speech during a keynote or talk.
Let’s break it down.
Introduce the Graph
Add a descriptive title at the top of the slide. The title must say exactly what the chart is about, and an optional subtitle to reinforce the message. While presenting, seamlessly say the chart’s name as you speak and tell a two-sentence story about it, like an elevator pitch.
Identify the variables
Identify the variables by using color, size, and location concerning the chart. While presenting, speak about each variable succinctly and mention its visual characteristic. For example, “As you can see, telephone calls—here in the blue line—have increased yearly.”
Highlight key info
Highlight key info using subtle and not-so-subtle design techniques to bring attention to specific areas of the chart. Use icons to visualize the most critical variables in the chart legend. Add noticeable colors and bigger fonts. During your talk, speak about these data points and then about the others as support.
Share conclusions
Share conclusions in small text boxes below the chart legend. These don’t necessarily need to be in your slides, but they do need to appear in your speech. The conclusions are what bring everything full circle with the introduction.

Charts and Graphs in Action
All charts—including graphs—help you share information and data across presentations, reports , proposals , scientific posters , etc.
Including charts and graphs in slides is a necessary step in creating analytic presentations, so why not maximize their efficiency by taking the time to customize them visually according to your brand or project?
Discover all the chart and graph options in the SlideModel template library. Browse flowcharts, Gantt charts, and all types of graphs for your slides.
And remember, charts and graphs are different and related, all rolled into one.
Like this article? Please share
Business Presentations, Data Visualization, Presentation Approaches Filed under Design , Presentation Ideas
Related Articles

Filed under Design • August 14th, 2024
Creating Custom Themes for PowerPoint and Google Slides
Do you want your slides to go beyond the average result from a template? If so, learn how to create custom themes for presentations with this guide.

Filed under Business • August 8th, 2024
How to Create Engaging and Persuasive Proposal Presentations
Secure your business deals and build your brand’s reputation by mastering the art of proposal presentations. Tips and recommended PPT templates included.

Filed under Business • July 24th, 2024
How to Create a Demo Presentation
Discover the secrets behind successful demo presentations and what they should contain with this article. Recommended PPT templates included.
Leave a Reply
Top Tips for Using Graphs and Charts in your Presentations

Graphs and charts are a great way to convey complex information. But it is also easy to deliver information overload. We asked a range of expert presenters for their hints and tips on using graphs and charts in presentations.
Types of Graphs
Although texts carry ideas among individuals, there is no replacement for the pictorial representations that exist right from the days men lived in caves. In order to standardise the communication, many types of graphs evolved in the man’s quest for quick, easy and precise representation of data. Graphs range from simple lines to complex cosmograms that even animate.
The below infographic will share some interesting information about different graph types:
1. Less is more
I think one of the big things is to make sure you are using the right kind of chart to display the story you want your data to tell. Also, less is more. Charts are busy enough and any extra axis numbers, tick marks and such should be removed and the gridlines should be subtle colours that don’t overwhelm the image.
2. Highlight key data points
I am asked to do a lot of creative tinkering with charts, and one of the most requested items is to highlight particular data points on a line chart. An easy and effective way to do this is by assigning a unique graphic to selected data points.
To do this you simply have to insert the graphic (could also be a text box with a relevant symbol character or wingding) somewhere on the slide. Then cut the graphic item to the clipboard. Go into your chart and select the single data point you want to affect (make sure you have the single data point and not the data series selected) and paste the graphic.

Valary Oleinik
Now that data point will carry the unique appearance even as the chart figures change.
I use this in instances such as a stock price timeline where you want to highlight the price at a certain date or you want to highlight where a change occurred in a business and you want a visual marker to make a comparison of the effects prior to and after the change. I could work up a chart sample if you would like.
3. Simplify your slides
Many graphs can be simplified to make them easier to read.
Take this example.
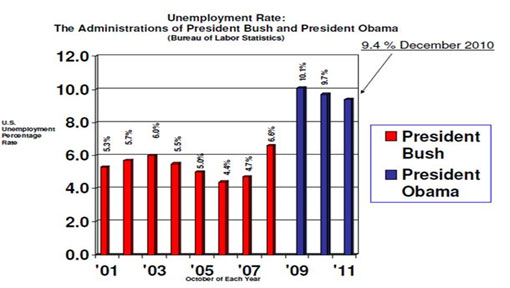
- Too much clutter, what I call mumblers and what Edward Tufte calls chartjunk. These mumblers are like the dense foliage in a jungle; you need to hack away at them with effort to work your way further into the jungle. Mumblers in this chart include horizontal lines, unnecessarily large numbers on the x- and y-axes, unnecessary detailed text.
- Large gaps between the columns. The rule of thumb is the bars should be TWICE as large as the gap.
- Sideways numbers above the bars, which are unnecessarily hard to read. In fact, you don’t need the y-axis at all if the bar values are included.
- No pictures. Whenever possible, try to convert your graphs into concrete pictures. Adding a pictures of Bush and Obama can replace the legend.
Here is an example of how this slide can be improved.
Bruce Gabrielle
4. Pie charts are not always easy to understand
Use the correct graph to display data. Pie charts are generally poor because viewers cannot quickly understand relative sizes of pie slices. Horizontal bar charts, sorted from high to low, communicate more clearly and are easier for the reader to scan quickly.
Both have their place, depending on what the audience needs.
Bruce Gabrielle – author, Speaking PowerPoint – www.speakingppt.com
5. Create better-looking graphs in PowerPoint 2010
PowerPoint 2010 creates much better graphs than the standard graphs that you get with PowerPoint 2003. Something we often do here if we are creating a PowerPoint 2003 presentation and the client does NOT need to edit the graphs themselves: we would create much better-looking graphs in PowerPoint 2010 and then copy them into the 2003 presentation as images. We know we are in the very fortunate position of having easy access to all versions of PowerPoint and this might not be possible for everyone.
6. Be careful of embedding sensitive data

But there are more reasons for doing this than just more visually aesthetic graphs. Whatever version of PowerPoint you are using, it’s still a good idea to keep the editable graph separate from your main presentation.
We know of a horror story where a presentation was left behind after an event and the Excel files that linked to the graphs contained some very commercially sensitive information.
7. Convey data in other ways than PowerPoint
Very few people remember the numbers. Convey them in some other meaningful way.
I had a participant on a course recently who was talking about a number of people that had been taken out of poverty in recent years. The number is meaningless, because I wouldn’t remember and cannot comprehend the number of people.
When he paused for a moment and said “That’s the same as the population of America”, it was easily understandable and extremely memorable.
8. Use props to convey data
Use props – check out Hans Rosling at TED on population statistics. He uses boxes and models of cars, planes and flip flops.

Paul Hayden
I once used steel buckets and coins – for the effect of the noise. If you show your market share by tipping in a (proportional number of ) few coins and then show the size of the available market left by tipping in another proportional number, people will not remember the number, but they will remember how long that noise lasted and how much share is up for grabs.
9. Only present key information
Think of what it means to the audience, perhaps just some of the data is enough (e.g. top 3 or 5 instead of the whole chart)
10. Concentrate on trends and changes
Concentrate on trends and changes rather than numbers and data.
11. 3D graphs are hard to read
Avoid 3-d graphs as much as possible, they are hard to read.
12. Animate your graphs
Try to animate the data instead of showing everything at once (overwhelming). By animating I don’t mean the custom animation on the software, but show the data gradually, one bar at a time for comparisons, one year at a time on a line chart, one piece of the pie on pie charts.
It will be like storytelling your data and the audience will be able to keep up.
Dr.Ahmad Al-Ani
13. Take a look at data visualisation

Yolanthe Smit
I find graphs and charts usually rather boring unless they are on paper or a webpage so I can study them at my leisure.
We recently devoted an entire TEDxTheHague Salon to data visualisation and watched these great presentations:
Recommended Pages

- All Templates
- Persuasive Speech Topics
- Informative
- Architecture
- Celebration
- Educational
- Engineering
- Food and Drink
- Subtle Waves Template
- Business world map
- Filmstrip with Countdown
- Blue Bubbles
- Corporate 2
- Vector flowers template
- Editable PowerPoint newspapers
- Hands Template
- Red blood cells slide
- Circles Template on white
- Maps of America
- Light Streaks Business Template
- Zen stones template
- Heartbeat Template
- Web icons template

Presentation Guru
The 2 most effective strategies for presenting data and graphs.

Far too many presenters pack their slides with far too much information: text, bullet points, graphs, data markers, data labels, and collections of images. This information-dump encourages the audience to read the slides and spend less time listening to you speak.
Graphs present a particular challenge for many presenters, especially those used to working with detailed data and numbers. In my experience, researchers and analysts tend to put all of their data on the screen, filling up graphs with lines and bars and packing tables full of numbers.
Even what seem to be the simplest graphs can give your audience difficulties discerning patterns or trends. Take this slide, for example. With only four lines, this graph doesn’t have so much information, but the different (ugh, Excel default!) colors and the crisscrossing patterns make it difficult to identify a single trend.

There are (at least) two strategies you can take to make this graph easier for your reader.
Strategy #1: “Layer” the Graph
One strategy I often use is something I call “Layering.” Here, you present each data element sequentially, building up your story one data element at a time and walking your audience through your argument. The Layering technique can be applied to almost any slide object including images, graphs, and text.
In this example, instead of throwing the entire slide on the screen for the audience to decipher at one time, you can build up the graph one series at a time. (In some cases where the graph type may be non-standard or more complex, you may find it valuable to first show just the axes, describe what the graph is going to do, and then sequentially add the data.) Notice how in this case, the final graph has all four series, but you have brought the audience along with you to that final graph.

Strategy #2: Small Multiples
Another strategy is to take the “Small Multiples” approach. With small multiples, you create multiple, small versions of the graph. For presentations, you can also use small multiples with a layering approach, by sequentially adding each additional graph.

In either case, when using these approaches, be sure to make your last graph first and get everything arranged exactly the way you like. Then, when you start deleting the different data series, only the data values will change and not the axes or gridlines.
It’s especially important to lock the minimum and maximum values of the y-axis, because the software may change the axis values once you start deleting different data series.
When it comes to coloring the particular series of interest, the presenter needs to consider what is most important. Perhaps presenting every single line is not as important as focusing on a single data series. In that case, the Layering and Small Multiples approaches may not be entirely necessary and instead a single graph is best. I find that I begin building your graphs in the same color—gray works great—and then purposefully add color to help support the written or spoken word.

In the end, presentations are a fundamentally different form of communication than what you might write down and publish in a journal, report, or blog post. Simply copying and pasting portions of text, tables, and graphs disrupts how the speaker communicates information.
Instead, consider how you can visualize your content, unify what you say and what you show, and focus your audience’s attention where you want it when you want it.
These, and other important lessons about designing, creating, and delivering presentations can be found in my forthcoming book, Better Presentations: A Guide for Scholars, Researchers, and Wonks.
- Latest Posts

Jon Schwabish
Latest posts by jon schwabish ( see all ).
- The Guru’s Big Five Questions – Jon Schwabish - 25th August 2016
- The 2 Most Effective Strategies for Presenting Data and Graphs - 19th May 2016

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Follow The Guru

Join our Mailing List
Join our mailing list to get monthly updates and your FREE copy of A Guide for Everyday Business Presentations

The Only PowerPoint Templates You’ll Ever Need
Anyone who has a story to tell follows the same three-act story structure to...
18 Types of Diagrams in PowerPoint: Which is the Right Chart Type for Your Presentation?
Presenting data is one of the most common content types in presentations. Speakers are often faced with the task of presenting their data in a way that directs the audience’s attention to the key messages.
Today, we will show you 18 chart types with examples of their usage. This way, you can find the right diagram for your presentation purposes.
Storytelling & Data Visualization
Speakers should focus on telling a story with data. Storytelling is one of the most effective means of connecting with the audience and capturing their attention. Why? Because stories generate emotions and allow you to better reach your audience.
Presenting raw data without proper preparation will inevitably lead to losing the audience’s interest . The audience will unconsciously begin to orient themselves in the presented data series and interpret it, which consumes a significant portion of their concentration.
The challenge is to integrate complex and dry numbers into the narrative in a way that the audience can follow the argumentation. The key to success lies in communicating through targeted data visualizations.
The most well-known and popular form of data visualization is the diagram . The use of diagrams in PowerPoint presentations is practical due to the convenient integration of PowerPoint with Excel functions .
However, it is important to always consider the message that the presented data is intended to convey and the type of data involved. Not every diagram is suitable for every dataset.
- Is it relative or absolute numbers?
- How many dimensions do I want to represent?
- Am I presenting compositions or developments?
These are just a few examples of the questions you should ask yourself before choosing a diagram for your presentation.
The 18 most important types of diagrams in PowerPoint
We have summarized the most well-known chart types, along with their advantages, applications, and limitations .
Now, let’s explore these diagram types and find the one that best suits your data and goals, allowing you to create a clear and compelling presentation.
1. Column Chart
The bar chart is the most commonly used and simplest type of diagram. By representing data through the varying heights of the bars, you can visually illustrate data and its differences.
The strengths of the bar chart type lie in depicting fluctuations over a period of time or comparing different subjects of investigation.
For example : Revenues of different departments per year.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for bar charts from PresentationLoad!
2. Bar Chart
The bar chart is nothing more than a rotated version of the column chart . Like the column chart, the bar chart represents data and their differences through the distribution of bar sizes.
The major advantage of this chart type is that the horizontal orientation of the bars allows for the use of longer labels, such as survey questions.
Example: This chart type is excellent for representing rankings.
For tips on designing an appealing bar chart , you can refer to the article “ Bar Charts .”

3. Stacked Column Chart
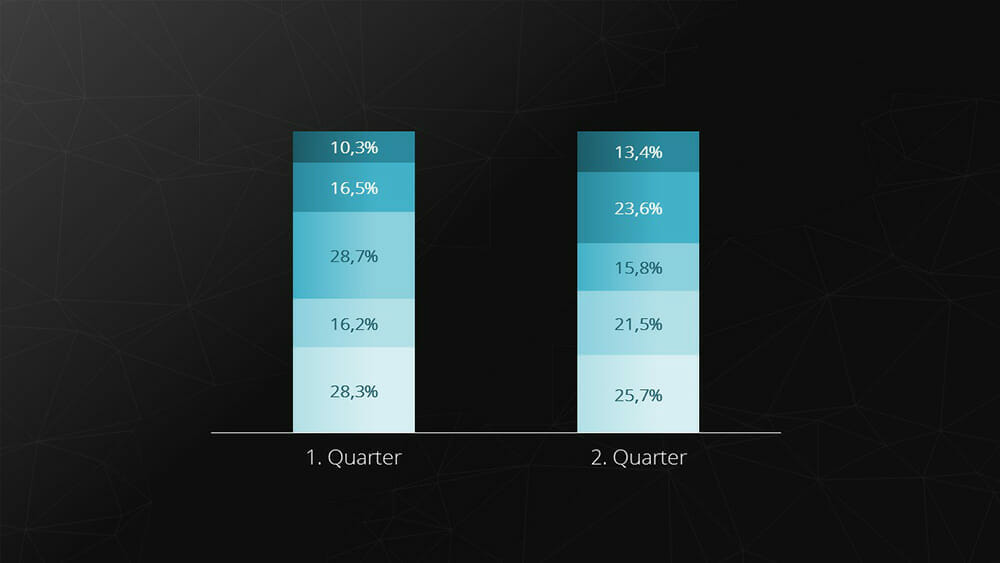
The stacked chart (also known as a cumulative or stacked chart) is a chart type that can represent the individual components of a composite whole. This chart type is suitable when comparing the composition of something over different time periods or with a different composition.
Example: Composition of cost components over a period of time.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for stacked charts from PresentationLoad!

4. Line Chart
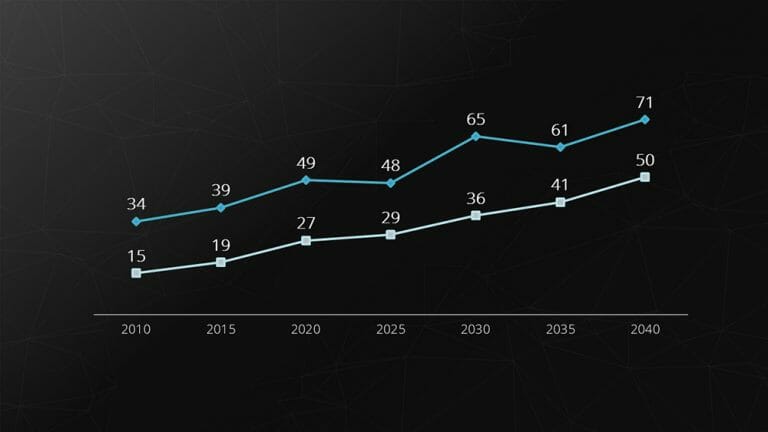
The line chart is used for comparing and representing temporal trends . The overlapping lines can be directly compared, making it easy to visualize developments and trends .
Example: Stock prices.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for line charts from PresentationLoad!
5. Area Chart
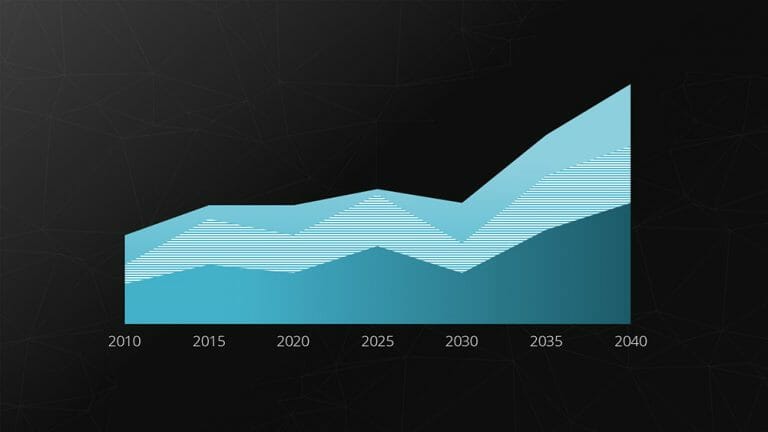
The area chart is a modified form of the line chart . In this chart, the area between two lines or between the line and the X-axis is filled with color.
This allows for highlighting the relative relationship between two quantities graphically. This type of representation is particularly useful for visualizing operational and strategic gaps.
Example: Gap analysis.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for area charts from PresentationLoad!
6. Pie Chart
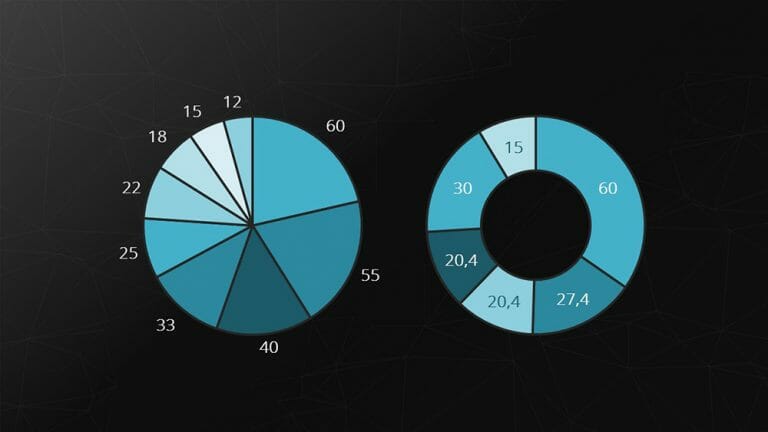
Pie and donut charts represent compositions of a whole as slices of a pie. The major strength of these charts is visualizing relative proportions.
Example: However, pie charts are not suitable for representing temporal sequences.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for pie charts from PresentationLoad!
7. Combination Chart
Combination charts are a combination of two different chart types. They are excellent for presenting the relationship between two data series with different scales. The most common variant is the combination of bar and line charts.
Example: Revenue (in millions) and number of employees (up to 100).
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for combination charts from PresentationLoad!
8. Radar Chart
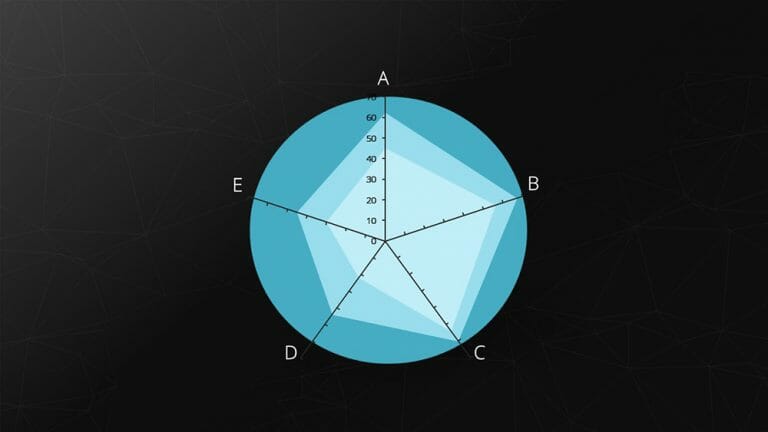
The spider chart, also known as a star or radar chart, is particularly useful for displaying the development or characteristics of predefined criteria . Each category has its own axis, with the zero point located at the center.
Example: Comparing two companies based on predefined criteria (including benchmarking).
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for spider charts from PresentationLoad!
9. Portfolio Diagram
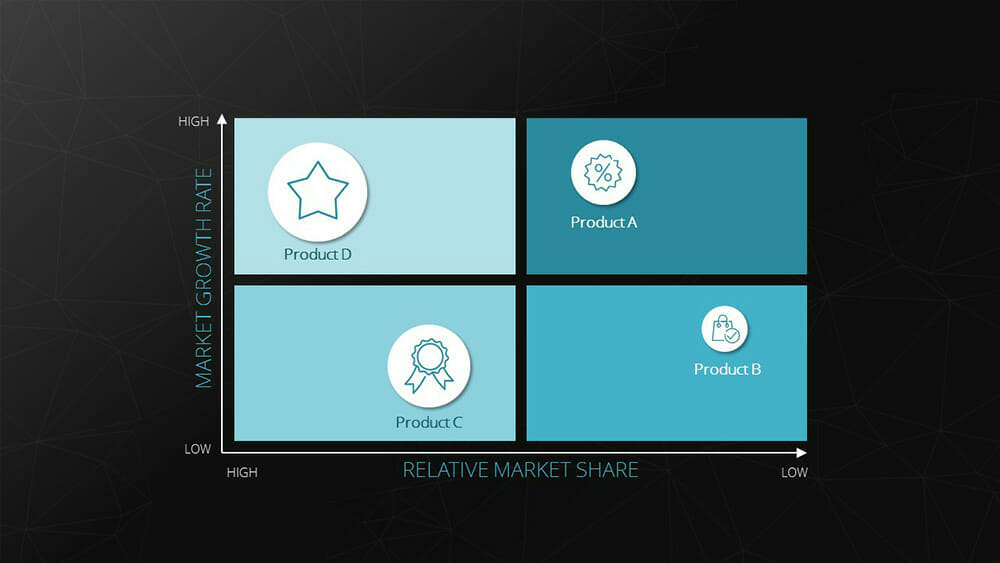
The bubble chart, also known as a portfolio chart, stands out with its three dimensions. The X and Y axes represent the measurement of a variable defined for each axis. This creates an accurate position of the bubble within the coordinate system. Additionally, the size of the bubble represents a third dimension.
Example : BCG matrix (depicting market growth, relative market share, and revenue).
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for bubble charts from PresentationLoad!
10. Waterfall Chart
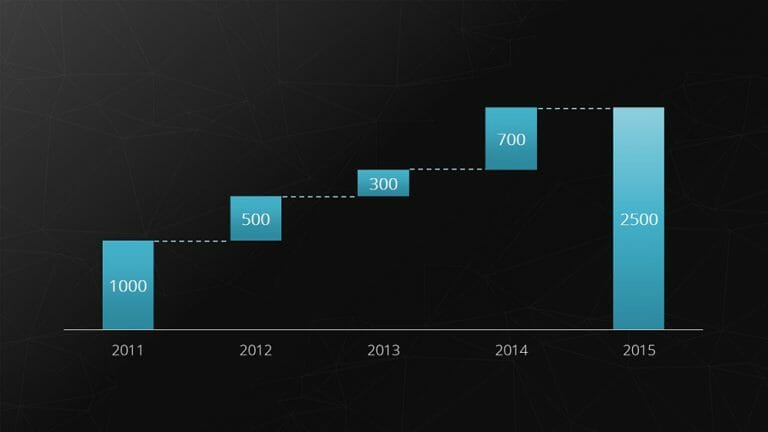
The waterfall chart is a special form of the bar chart. It shows an initial value that is increased or decreased by additional values . Finally, the end value is depicted.
Example: Breaking down total costs into individual costs.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for waterfall charts from PresentationLoad!
11. Bubble Chart
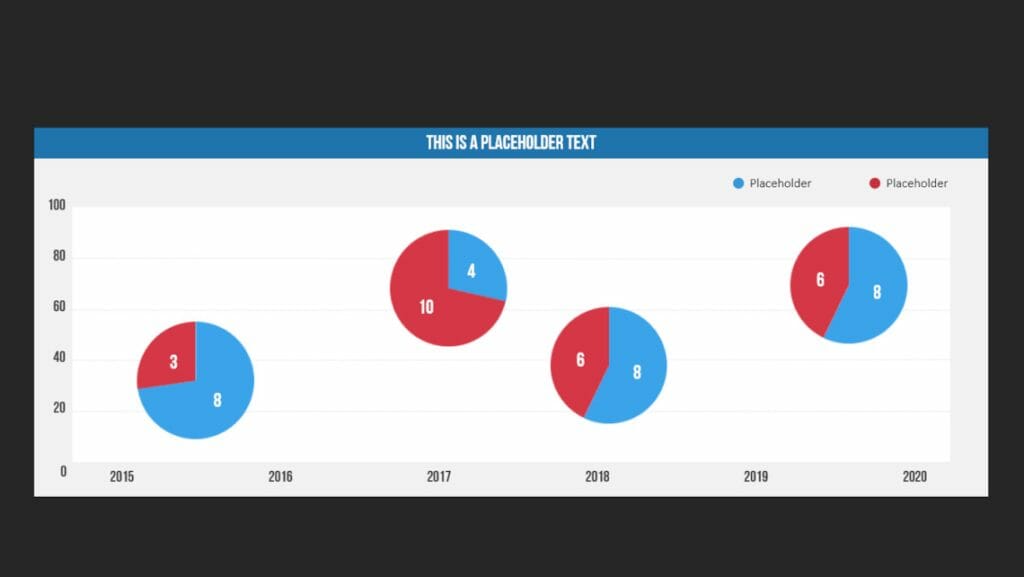
A bubble chart is used in data visualization to represent relationships between three or more variables . The purpose of a bubble chart is to visualize complex datasets in a simple and easily understandable way.
In a bubble chart, data points are represented as circles (bubbles), where the position of the bubbles on the X and Y axes represents the two main variables. The size of the bubbles represents a third variable, and in some cases, the color of the bubbles can be used to represent a fourth variable.
Companies use bubble charts to illustrate relationships between various financial data, such as in strategic management when visualizing BCG matrices.
Example: Creating a market share overview where revenue and product quantity are represented on the X and Y axes, and the respective market share is indicated by the different sizes of the bubbles.
12. Scatter Diagram
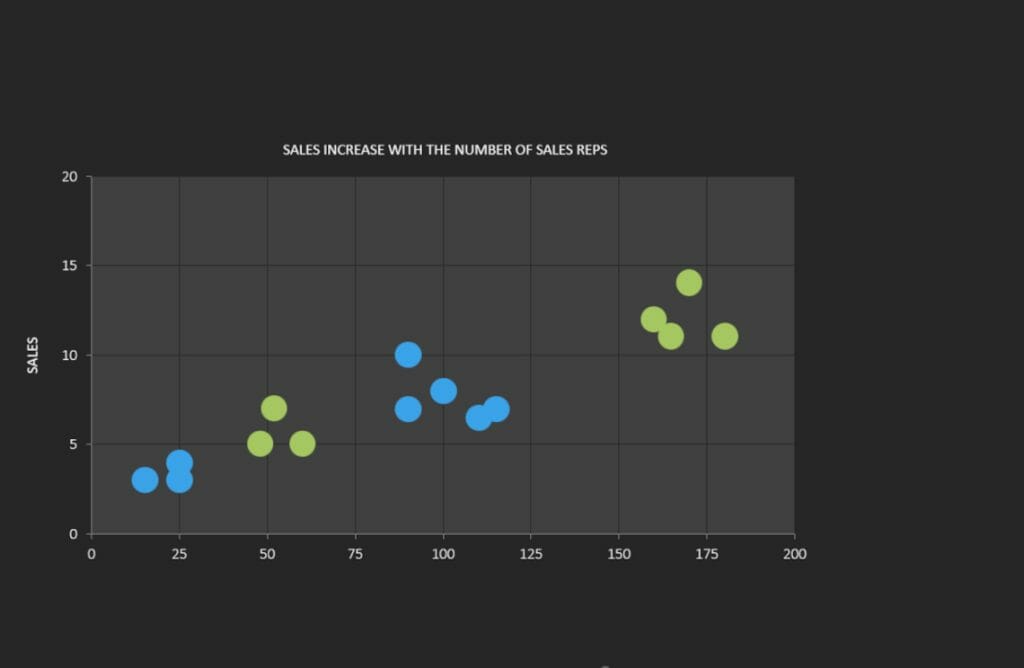
A scatter plot is used to represent the relationship between two continuous variables. The purpose of a scatter plot is to visualize the c orrelation or pattern between these variables in a simple and easily understandable way . If there are dependencies between the two variables, patterns or structures such as linear or quadratic relationships can be observed, revealing average values, trends/developments, or concentrations.
In a scatter plot, data points are represented as dots or symbols, where the position of the points on the X and Y axes represents the two variables. The points are plotted independently, and their distribution in the chart shows the relationship between the variables.
Example: Examining the relationship between age and income.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for scatter plots from PresentationLoad!

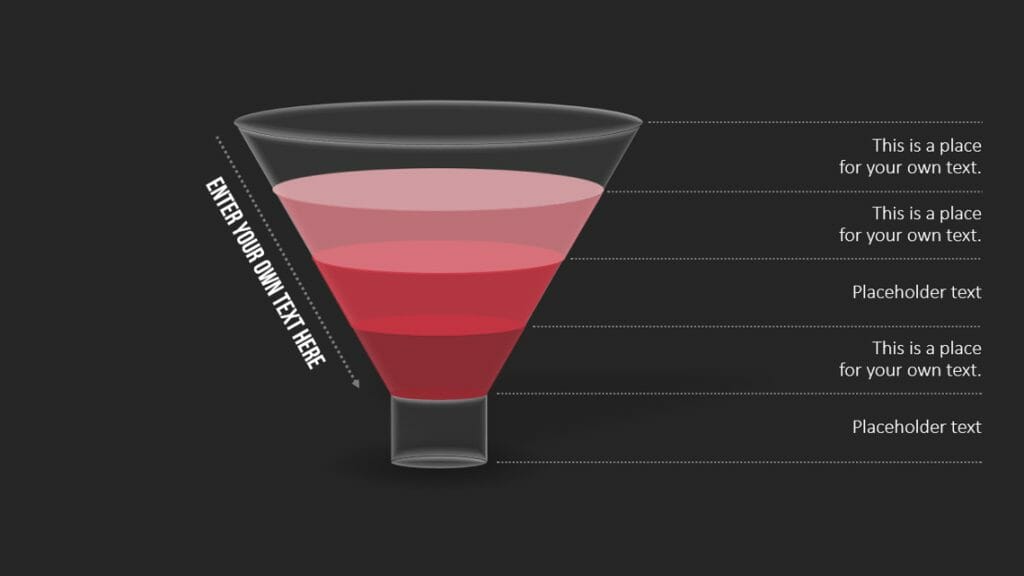
13. Sales Funnel
A funnel chart is used to represent the different stages of a process or sales pipeline . The shape of the funnel is crucial in the visualization. The first stage of the process is represented by the wider end, and the narrower end represents the final stage. The size of the sections within the funnel represents the number of items or data points in each stage of the process. The decreasing width of the funnel represents the decreasing magnitude of items transitioning from one stage to the next.
The purpose of a funnel chart is to visualize the number of items or data points going through the different stages of a process in a simple and easily understandable way. Funnel charts are often used to identify and analyze bottlenecks or weaknesses in a process.
Example: Analyzing a sales pipeline.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for funnel charts from PresentationLoad!
14. Pyramid Chart
Pyramid charts are primarily used to represent demographic information in an easily understandable way. The chart depicts a vertically oriented, two-dimensional histogram.
Example: Visualizing the age structure and gender distribution of a population.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for pyramid charts from PresentationLoad!
15. Gantt Chart
A Gantt chart is used to visually represent the activities of a project in a time-oriented table format. The structure of the chart allows for listing all project-related activities and their duration. This is displayed in the form of a bar that indicates both the start and end points of a time-based activity.
The chart provides an overview of how much time is required for each activity and when it will be completed, allowing project managers to have better control over the project timeline. It enables them to identify areas where the project is successful or not, thereby optimizing process flows through appropriate interventions.
Example: Presentation and management of a construction project.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for Gantt charts from PresentationLoad!
16. Venn Diagram
Venn diagrams, using two, three, or more circles, are a practical method for illustrating overlapping or interconnected relationships. They provide a visual representation of the relationships and dependencies within a complex set of elements.
Venn diagrams can be a valuable tool for capturing the entirety of complex situations and understanding the relationships between elements. For more information, feel free to check out our blog post on “ Venn Diagrams “.
Example: Analyzing the similarities and differences between different customer segments in a company.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for Venn diagrams from PresentationLoad!
17. Process Diagram (for example Flowchart)
Process diagrams, such as flowcharts, are excellent for presenting processes and workflows in a clear and organized manner. They can represent both general concepts and specific relationships, making them a valuable tool for any company looking to showcase their business processes and workflows to stakeholders. Algorithms, workflows, and processes can be translated into flowcharts, facilitating analysis, documentation, and management of programs and workspaces.
Flowcharts are widely used and established in sectors such as business, finance, IT, and data processing, thanks to their effective visual representation.
Example: Illustrating and analyzing a customer service process in a company.
For more information, feel free to check out our blog post on “ Flowcharts “.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for flowcharts from PresentationLoad!
18. Organizational Chart
An organizational chart is a chart typed used to structure and organize a company or project , allowing for the clear representation of hierarchies. There are various types of organizational charts to choose from, including the single-line system, multiple-line system, matrix organization, and staff line representation.
The typica l single-line system emphasizes clear responsibilities and a streamlined structure, while the multiple-line system shortens information pathways and contributes to specialization within individual instances.
Example: Presenting a product range or service offering in a clear and organized manner.
For more information, feel free to check out our blog post on “ Organizational Charts “.
Feel free to use professionally designed slide templates for organizational charts from PresentationLoad!
Conclusion: Finding the right chart types for your purposes
In conclusion, you can find the right type of diagram for your purposes by referring to our 18 chart types and determining which one best suits your needs. With the appropriate diagram, you can visualize content much more easily and quickly, making it understandable for your audience.
If you have any questions regarding the article, feel free to contact us via email at [email protected] . We are here to assist you!
If you’re looking for visually supportive and professionally designed slide templates , be sure to check out our shop. We have a wide range of slides available for download on various (business) topics. Visit our shop today! ► Go to Shop
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- Create a Flowchart in PowerPoint
- Create a Venn Diagram
- Create an Organizational Chart
- 8 Tips for better Bar Chart in PowerPoint
- Present Numbers and Tables in an Engaging Way
Share this post
- share
- save

Design Thinking: Problem Solving with a Difference

Why Corporate Mission Statements Are So Important

7 Tips & Learnings from the Apple Keynote
18 Best Types of Charts and Graphs for Data Visualization [+ Guide]
Published: May 22, 2024
As a writer for the marketing blog, I frequently use various types of charts and graphs to help readers visualize the data I collect and better understand their significance. And trust me, there's a lot of data to present.

In fact, the volume of data in 2025 will be almost double the data we create, capture, copy, and consume today.

This makes data visualization essential for businesses. Different types of graphs and charts can help you:
- Motivate your team to take action.
- Impress stakeholders with goal progress.
- Show your audience what you value as a business.
Data visualization builds trust and can organize diverse teams around new initiatives. So, I'm going to talk about the types of graphs and charts that you can use to grow your business.
And, if you still need a little more guidance by the end of this post, check out our data visualization guide for more information on how to design visually stunning and engaging charts and graphs.
.png)
Free Excel Graph Templates
Tired of struggling with spreadsheets? These free Microsoft Excel Graph Generator Templates can help.
- Simple, customizable graph designs.
- Data visualization tips & instructions.
- Templates for two, three, four, and five-variable graph templates.
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Charts vs Graphs: What's the Difference?
A lot of people think charts and graphs are synonymous (I know I did), but they're actually two different things.
Charts visually represent current data in the form of tables and diagrams, but graphs are more numerical in data and show how one variable affects another.
For example, in one of my favorite sitcoms, How I Met Your Mother, Marshall creates a bunch of charts and graphs representing his life. One of these charts is a Venn diagram referencing the song "Cecilia" by Simon and Garfunkle.
Marshall says, "This circle represents people who are breaking my heart, and this circle represents people who are shaking my confidence daily. Where they overlap? Cecilia."
The diagram is a chart and not a graph because it doesn't track how these people make him feel over time or how these variables are influenced by each other.
It may show where the two types of people intersect but not how they influence one another.

Later, Marshall makes a line graph showing how his friends' feelings about his charts have changed in the time since presenting his "Cecilia diagram.
Note: He calls the line graph a chart on the show, but it's acceptable because the nature of line graphs and charts makes the terms interchangeable. I'll explain later, I promise.
The line graph shows how the time since showing his Cecilia chart has influenced his friends' tolerance for his various graphs and charts.

Image source
I can't even begin to tell you all how happy I am to reference my favorite HIMYM joke in this post.
Now, let's dive into the various types of graphs and charts.
Different Types of Graphs for Data Visualization
1. bar graph.
I strongly suggest using a bar graph to avoid clutter when one data label is long or if you have more than 10 items to compare. Also, fun fact: If the example below was vertical it would be a column graph.
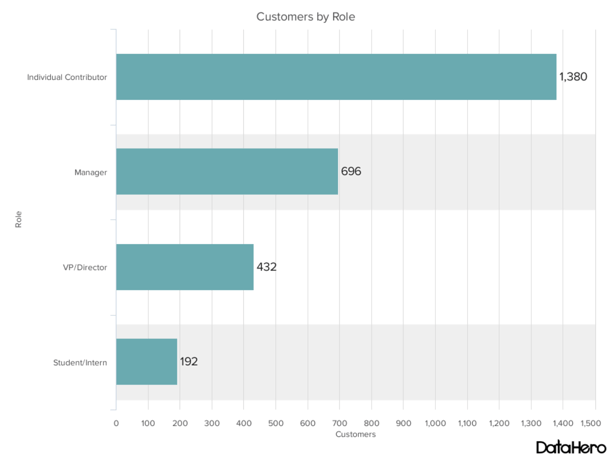
Best Use Cases for These Types of Graphs
Bar graphs can help track changes over time. I've found that bar graphs are most useful when there are big changes or to show how one group compares against other groups.
The example above compares the number of customers by business role. It makes it easy to see that there is more than twice the number of customers per role for individual contributors than any other group.
A bar graph also makes it easy to see which group of data is highest or most common.
For example, at the start of the pandemic, online businesses saw a big jump in traffic. So, if you want to look at monthly traffic for an online business, a bar graph would make it easy to see that jump.
Other use cases for bar graphs include:
- Product comparisons.
- Product usage.
- Category comparisons.
- Marketing traffic by month or year.
- Marketing conversions.
Design Best Practices for Bar Graphs
- Use consistent colors throughout the chart, selecting accent colors to highlight meaningful data points or changes over time.
You should also use horizontal labels to improve its readability, and start the y-axis at 0 to appropriately reflect the values in your graph.
2. Line Graph
A line graph reveals trends or progress over time, and you can use it to show many different categories of data. You should use it when you track a continuous data set.
This makes the terms line graphs and line charts interchangeable because the very nature of both is to track how variables impact each other, particularly how something changes over time. Yeah, it confused me, too.
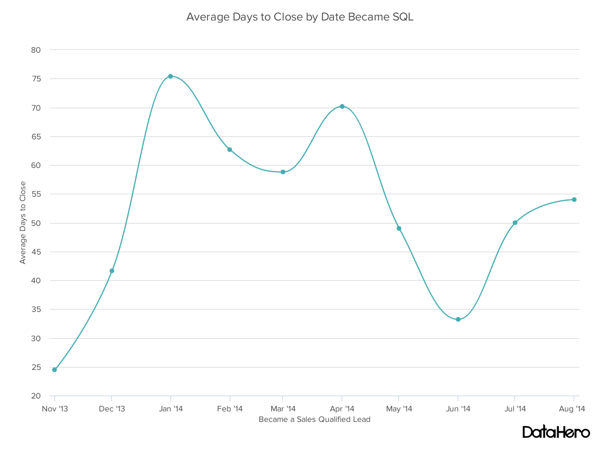
Line graphs help users track changes over short and long periods. Because of this, I find these types of graphs are best for seeing small changes.
Line graphs help me compare changes for more than one group over the same period. They're also helpful for measuring how different groups relate to each other.
A business might use this graph to compare sales rates for different products or services over time.
These charts are also helpful for measuring service channel performance. For example, a line graph that tracks how many chats or emails your team responds to per month.
Design Best Practices for Line Graphs
- Use solid lines only.
- Don't plot more than four lines to avoid visual distractions.
- Use the right height so the lines take up roughly 2/3 of the y-axis' height.
3. Bullet Graph
A bullet graph reveals progress towards a goal, compares this to another measure, and provides context in the form of a rating or performance.
In the example above, the bullet graph shows the number of new customers against a set customer goal. Bullet graphs are great for comparing performance against goals like this.
These types of graphs can also help teams assess possible roadblocks because you can analyze data in a tight visual display.
For example, I could create a series of bullet graphs measuring performance against benchmarks or use a single bullet graph to visualize these KPIs against their goals:
- Customer satisfaction.
- Average order size.
- New customers.
Seeing this data at a glance and alongside each other can help teams make quick decisions.
Bullet graphs are one of the best ways to display year-over-year data analysis. YBullet graphs can also visualize:
- Customer satisfaction scores.
- Customer shopping habits.
- Social media usage by platform.
Design Best Practices for Bullet Graphs
- Use contrasting colors to highlight how the data is progressing.
- Use one color in different shades to gauge progress.
4. Column + Line Graph
Column + line graphs are also called dual-axis charts. They consist of a column and line graph together, with both graphics on the X axis but occupying their own Y axis.
Download our FREE Excel Graph Templates for this graph and more!
Best Use Cases
These graphs are best for comparing two data sets with different measurement units, such as rate and time.
As a marketer, you may want to track two trends at once.
Design Best Practices
Use individual colors for the lines and colors to make the graph more visually appealing and to further differentiate the data.
The Four Basic Types of Charts
Before we get into charts, I want to touch on the four basic chart types that I use the most.
1. Bar Chart
Bar charts are pretty self-explanatory. I use them to indicate values by the length of bars, which can be displayed horizontally or vertically. Vertical bar charts, like the one below, are sometimes called column charts.

2. Line Chart
I use line charts to show changes in values across continuous measurements, such as across time, generations, or categories. For example, the chart below shows the changes in ice cream sales throughout the week.

3. Scatter Plot
A scatter plot uses dotted points to compare values against two different variables on separate axes. It's commonly used to show correlations between values and variables.
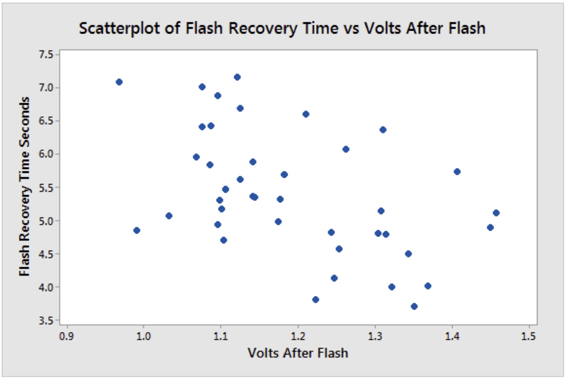
4. Pie Chart
Pie charts are charts that represent data in a circular (pie-shaped) graphic, and each slice represents a percentage or portion of the whole.
Notice the example below of a household budget. (Which reminds me that I need to set up my own.)
Notice that the percentage of income going to each expense is represented by a slice.

Different Types of Charts for Data Visualization
To better understand chart types and how you can use them, here's an overview of each:
1. Column Chart
Use a column chart to show a comparison among different items or to show a comparison of items over time. You could use this format to see the revenue per landing page or customers by close date.
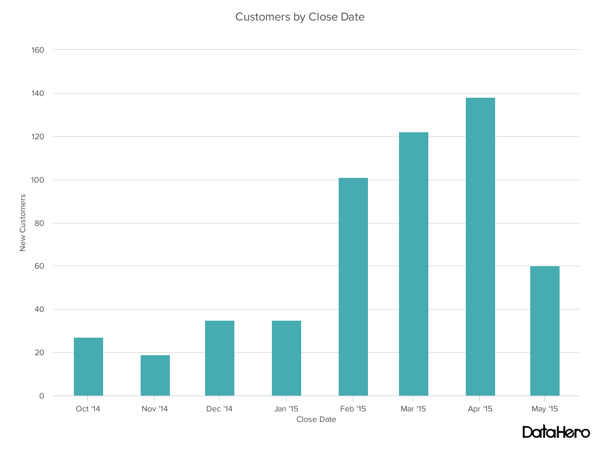
Best Use Cases for This Type of Chart
I use both column charts to display changes in data, but I've noticed column charts are best for negative data. The main difference, of course, is that column charts show information vertically while bar charts show data horizontally.
For example, warehouses often track the number of accidents on the shop floor. When the number of incidents falls below the monthly average, a column chart can make that change easier to see in a presentation.
In the example above, this column chart measures the number of customers by close date. Column charts make it easy to see data changes over a period of time. This means that they have many use cases, including:
- Customer survey data, like showing how many customers prefer a specific product or how much a customer uses a product each day.
- Sales volume, like showing which services are the top sellers each month or the number of sales per week.
- Profit and loss, showing where business investments are growing or falling.
Design Best Practices for Column Charts
- Use horizontal labels to improve readability.
- Start the y-axis at 0 to appropriately reflect the values in your chart .
2. Area Chart
Okay, an area chart is basically a line chart, but I swear there's a meaningful difference.
The space between the x-axis and the line is filled with a color or pattern. It is useful for showing part-to-whole relations, like showing individual sales reps’ contributions to total sales for a year.
It helps me analyze both overall and individual trend information.
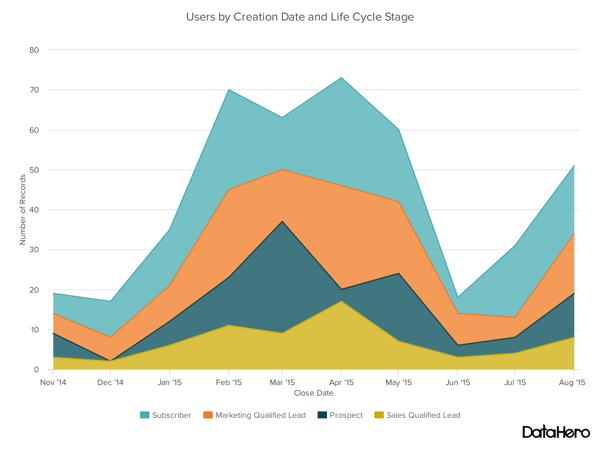
Best Use Cases for These Types of Charts
Area charts help show changes over time. They work best for big differences between data sets and help visualize big trends.
For example, the chart above shows users by creation date and life cycle stage.
A line chart could show more subscribers than marketing qualified leads. But this area chart emphasizes how much bigger the number of subscribers is than any other group.
These charts make the size of a group and how groups relate to each other more visually important than data changes over time.
Area charts can help your business to:
- Visualize which product categories or products within a category are most popular.
- Show key performance indicator (KPI) goals vs. outcomes.
- Spot and analyze industry trends.

Design Best Practices for Area Charts
- Use transparent colors so information isn't obscured in the background.
- Don't display more than four categories to avoid clutter.
- Organize highly variable data at the top of the chart to make it easy to read.
3. Stacked Bar Chart
I suggest using this chart to compare many different items and show the composition of each item you’re comparing.
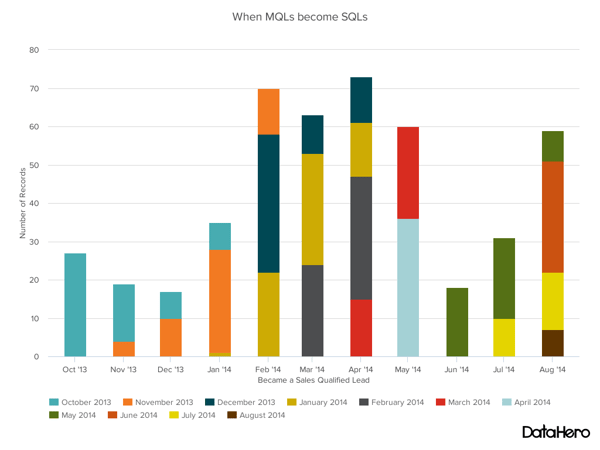
These charts are helpful when a group starts in one column and moves to another over time.
For example, the difference between a marketing qualified lead (MQL) and a sales qualified lead (SQL) is sometimes hard to see. The chart above helps stakeholders see these two lead types from a single point of view — when a lead changes from MQL to SQL.
Stacked bar charts are excellent for marketing. They make it simple to add a lot of data on a single chart or to make a point with limited space.
These charts can show multiple takeaways, so they're also super for quarterly meetings when you have a lot to say but not a lot of time to say it.
Stacked bar charts are also a smart option for planning or strategy meetings. This is because these charts can show a lot of information at once, but they also make it easy to focus on one stack at a time or move data as needed.
You can also use these charts to:
- Show the frequency of survey responses.
- Identify outliers in historical data.
- Compare a part of a strategy to its performance as a whole.
Design Best Practices for Stacked Bar Charts
- Best used to illustrate part-to-whole relationships.
- Use contrasting colors for greater clarity.
- Make the chart scale large enough to view group sizes in relation to one another.
4. Mekko Chart
Also known as a Marimekko chart, this type of chart can compare values, measure each one's composition, and show data distribution across each one.
It's similar to a stacked bar, except the Mekko's x-axis can capture another dimension of your values — instead of time progression, like column charts often do. In the graphic below, the x-axis compares the cities to one another.
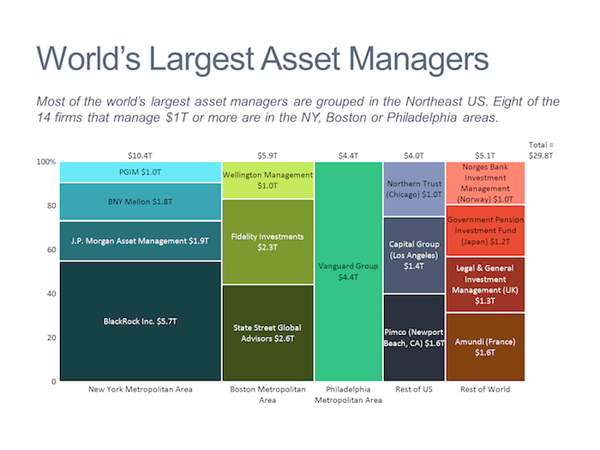
Image Source
I typically use a Mekko chart to show growth, market share, or competitor analysis.
For example, the Mekko chart above shows the market share of asset managers grouped by location and the value of their assets. This chart clarifies which firms manage the most assets in different areas.
It's also easy to see which asset managers are the largest and how they relate to each other.
Mekko charts can seem more complex than other types of charts, so it's best to use these in situations where you want to emphasize scale or differences between groups of data.
Other use cases for Mekko charts include:
- Detailed profit and loss statements.
- Revenue by brand and region.
- Product profitability.
- Share of voice by industry or niche.
Design Best Practices for Mekko Charts
- Vary your bar heights if the portion size is an important point of comparison.
- Don't include too many composite values within each bar. Consider reevaluating your presentation if you have a lot of data.
- Order your bars from left to right in such a way that exposes a relevant trend or message.
5. Pie Chart
Remember, a pie chart represents numbers in percentages, and the total sum of all segments needs to equal 100%.
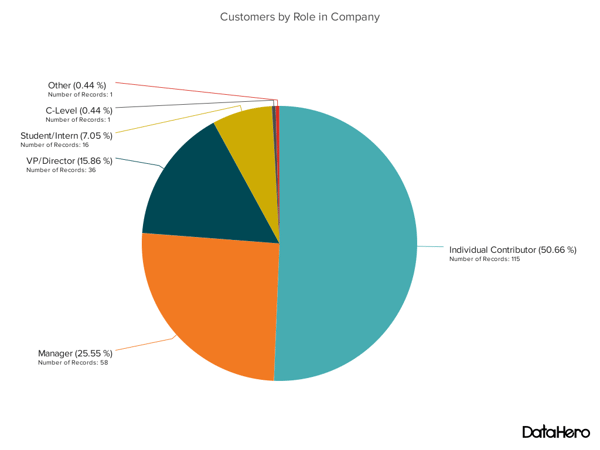
The image above shows another example of customers by role in the company.
The bar chart example shows you that there are more individual contributors than any other role. But this pie chart makes it clear that they make up over 50% of customer roles.
Pie charts make it easy to see a section in relation to the whole, so they are good for showing:
- Customer personas in relation to all customers.
- Revenue from your most popular products or product types in relation to all product sales.
- Percent of total profit from different store locations.
Design Best Practices for Pie Charts
- Don't illustrate too many categories to ensure differentiation between slices.
- Ensure that the slice values add up to 100%.
- Order slices according to their size.
6. Scatter Plot Chart
As I said earlier, a scatter plot or scattergram chart will show the relationship between two different variables or reveal distribution trends.
Use this chart when there are many different data points, and you want to highlight similarities in the data set. This is useful when looking for outliers or understanding your data's distribution.
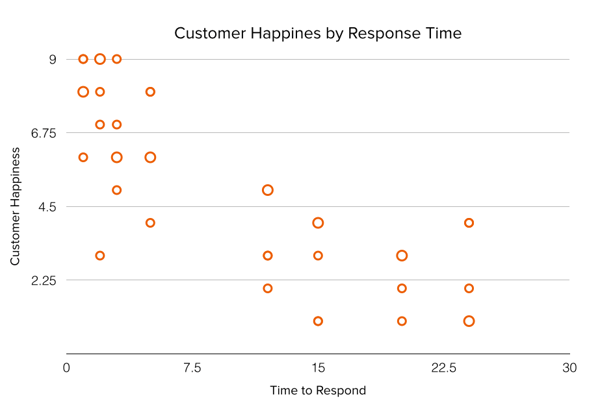
Scatter plots are helpful in situations where you have too much data to see a pattern quickly. They are best when you use them to show relationships between two large data sets.
In the example above, this chart shows how customer happiness relates to the time it takes for them to get a response.
This type of chart makes it easy to compare two data sets. Use cases might include:
- Employment and manufacturing output.
- Retail sales and inflation.
- Visitor numbers and outdoor temperature.
- Sales growth and tax laws.
Try to choose two data sets that already have a positive or negative relationship. That said, this type of chart can also make it easier to see data that falls outside of normal patterns.
Design Best Practices for Scatter Plots
- Include more variables, like different sizes, to incorporate more data.
- Start the y-axis at 0 to represent data accurately.
- If you use trend lines, only use a maximum of two to make your plot easy to understand.
7. Bubble Chart
A bubble chart is similar to a scatter plot in that it can show distribution or relationship. There is a third data set shown by the size of the bubble or circle.
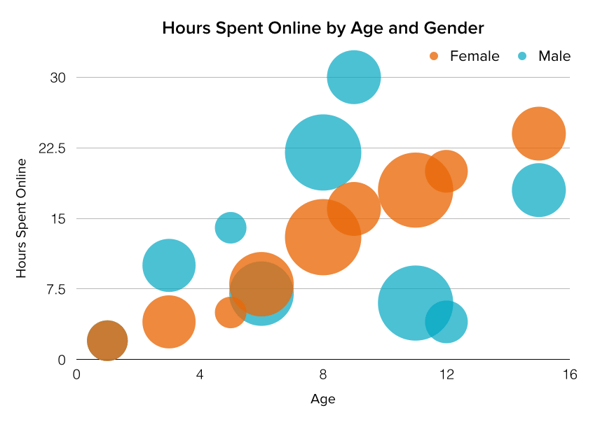
In the example above, the number of hours spent online isn't just compared to the user's age, as it would be on a scatter plot chart.
Instead, you can also see how the gender of the user impacts time spent online.
This makes bubble charts useful for seeing the rise or fall of trends over time. It also lets you add another option when you're trying to understand relationships between different segments or categories.
For example, if you want to launch a new product, this chart could help you quickly see your new product's cost, risk, and value. This can help you focus your energies on a low-risk new product with a high potential return.
You can also use bubble charts for:
- Top sales by month and location.
- Customer satisfaction surveys.
- Store performance tracking.
- Marketing campaign reviews.
Design Best Practices for Bubble Charts
- Scale bubbles according to area, not diameter.
- Make sure labels are clear and visible.
- Use circular shapes only.
8. Waterfall Chart
I sometimes use a waterfall chart to show how an initial value changes with intermediate values — either positive or negative — and results in a final value.
Use this chart to reveal the composition of a number. An example of this would be to showcase how different departments influence overall company revenue and lead to a specific profit number.
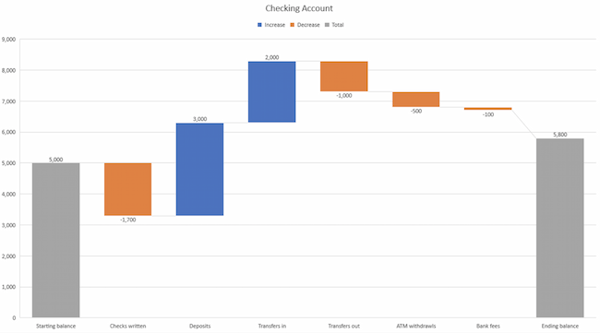
The most common use case for a funnel chart is the marketing or sales funnel. But there are many other ways to use this versatile chart.
If you have at least four stages of sequential data, this chart can help you easily see what inputs or outputs impact the final results.
For example, a funnel chart can help you see how to improve your buyer journey or shopping cart workflow. This is because it can help pinpoint major drop-off points.
Other stellar options for these types of charts include:
- Deal pipelines.
- Conversion and retention analysis.
- Bottlenecks in manufacturing and other multi-step processes.
- Marketing campaign performance.
- Website conversion tracking.
Design Best Practices for Funnel Charts
- Scale the size of each section to accurately reflect the size of the data set.
- Use contrasting colors or one color in graduated hues, from darkest to lightest, as the size of the funnel decreases.
10. Heat Map
A heat map shows the relationship between two items and provides rating information, such as high to low or poor to excellent. This chart displays the rating information using varying colors or saturation.
Best Use Cases for Heat Maps
In the example above, the darker the shade of green shows where the majority of people agree.
With enough data, heat maps can make a viewpoint that might seem subjective more concrete. This makes it easier for a business to act on customer sentiment.
There are many uses for these types of charts. In fact, many tech companies use heat map tools to gauge user experience for apps, online tools, and website design .
Another common use for heat map charts is location assessment. If you're trying to find the right location for your new store, these maps can give you an idea of what the area is like in ways that a visit can't communicate.
Heat maps can also help with spotting patterns, so they're good for analyzing trends that change quickly, like ad conversions. They can also help with:
- Competitor research.
- Customer sentiment.
- Sales outreach.
- Campaign impact.
- Customer demographics.
Design Best Practices for Heat Map
- Use a basic and clear map outline to avoid distracting from the data.
- Use a single color in varying shades to show changes in data.
- Avoid using multiple patterns.
11. Gantt Chart
The Gantt chart is a horizontal chart that dates back to 1917. This chart maps the different tasks completed over a period of time.
Gantt charting is one of the most essential tools for project managers. It brings all the completed and uncompleted tasks into one place and tracks the progress of each.
While the left side of the chart displays all the tasks, the right side shows the progress and schedule for each of these tasks.
This chart type allows you to:
- Break projects into tasks.
- Track the start and end of the tasks.
- Set important events, meetings, and announcements.
- Assign tasks to the team and individuals.
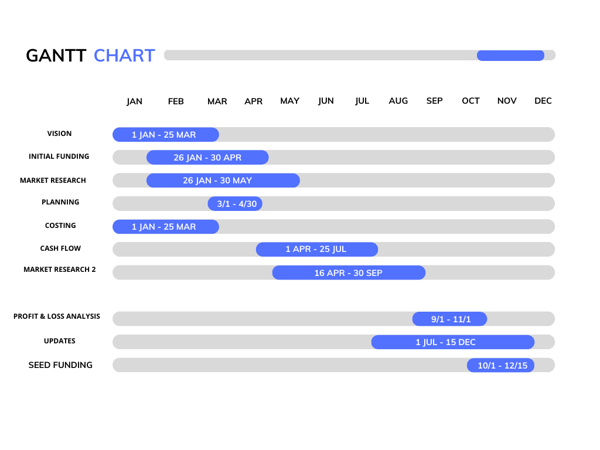
I use donut charts for the same use cases as pie charts, but I tend to prefer the former because of the added benefit that the data is easier to read.
Another benefit to donut charts is that the empty center leaves room for extra layers of data, like in the examples above.
Design Best Practices for Donut Charts
Use varying colors to better differentiate the data being displayed, just make sure the colors are in the same palette so viewers aren't put off by clashing hues.
14. Sankey Diagram
A Sankey Diagram visually represents the flow of data between categories, with the link width reflecting the amount of flow. It’s a powerful tool for uncovering the stories hidden in your data.
As data grows more complex, charts must evolve to handle these intricate relationships. Sankey Diagrams excel at this task.
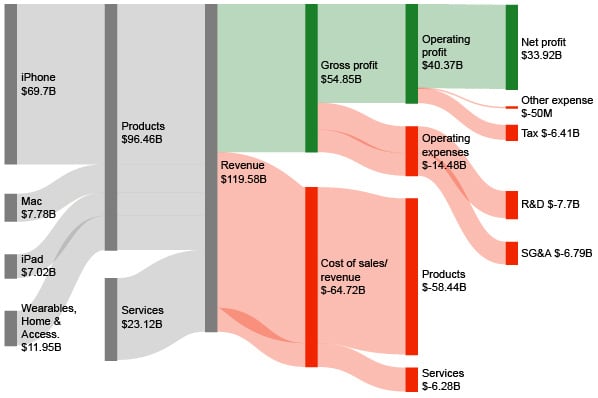
With ChartExpo , you can create a Sankey Chart with up to eight levels, offering multiple perspectives for analyzing your data. Even the most complicated data sets become manageable and easy to interpret.
You can customize your Sankey charts and every component including nodes, links, stats, text, colors, and more. ChartExpo is an add-in in Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, and Power BI, you can create beautiful Sankey diagrams while keeping your data safe in your favorite tools.
Sankey diagrams can be used to visualize all types of data which contain a flow of information. It beautifully connects the flows and presents the data in an optimum way.
Here are a few use cases:
- Sankey diagrams are widely used to visualize energy production, consumption, and distribution. They help in tracking how energy flows from one source (like oil or gas) to various uses (heating, electricity, transportation).
- Businesses use Sankey diagrams to trace customer interactions across different channels and touchpoints. It highlights the flow of users through a funnel or process, revealing drop-off points and success paths.
- I n supply chain management, these diagrams show how resources, products, or information flow between suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers, identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
Design Best Practices for Sankey Diagrams
When utilizing a Sankey diagram, it is essential to maintain simplicity while ensuring accuracy in proportions. Clear labeling and effective color usage are key factors to consider. Emphasizing the logical flow direction and highlighting significant flows will enhance the visualization.
How to Choose the Right Chart or Graph for Your Data
Channels like social media or blogs have multiple data sources, and managing these complex content assets can get overwhelming. What should you be tracking? What matters most?
How do you visualize and analyze the data so you can extract insights and actionable information?
1. Identify your goals for presenting the data.
Before creating any data-based graphics, I ask myself if I want to convince or clarify a point. Am I trying to visualize data that helped me solve a problem? Or am I trying to communicate a change that's happening?
A chart or graph can help compare different values, understand how different parts impact the whole, or analyze trends. Charts and graphs can also be useful for recognizing data that veers away from what you’re used to or help you see relationships between groups.
So, clarify your goals then use them to guide your chart selection.
2. Figure out what data you need to achieve your goal.
Different types of charts and graphs use different kinds of data. Graphs usually represent numerical data, while charts are visual representations of data that may or may not use numbers.
So, while all graphs are a type of chart, not all charts are graphs. If you don't already have the kind of data you need, you might need to spend some time putting your data together before building your chart.
3. Gather your data.
Most businesses collect numerical data regularly, but you may need to put in some extra time to collect the right data for your chart.
Besides quantitative data tools that measure traffic, revenue, and other user data, you might need some qualitative data.
These are some other ways you can gather data for your data visualization:
- Interviews
- Quizzes and surveys
- Customer reviews
- Reviewing customer documents and records
- Community boards
Fill out the form to get your templates.
4. select the right type of graph or chart..
Choosing the wrong visual aid or defaulting to the most common type of data visualization could confuse your viewer or lead to mistaken data interpretation.
But a chart is only useful to you and your business if it communicates your point clearly and effectively.
Ask yourself the questions below to help find the right chart or graph type.
Download the Excel templates mentioned in the video here.
5 Questions to Ask When Deciding Which Type of Chart to Use
1. do you want to compare values.
Charts and graphs are perfect for comparing one or many value sets, and they can easily show the low and high values in the data sets. To create a comparison chart, use these types of graphs:
- Scatter plot
2. Do you want to show the composition of something?
Use this type of chart to show how individual parts make up the whole of something, like the device type used for mobile visitors to your website or total sales broken down by sales rep.
To show composition, use these charts:
- Stacked bar
3. Do you want to understand the distribution of your data?
Distribution charts help you to understand outliers, the normal tendency, and the range of information in your values.
Use these charts to show distribution:
4. Are you interested in analyzing trends in your data set?
If you want more information about how a data set performed during a specific time, there are specific chart types that do extremely well.
You should choose one of the following:
- Dual-axis line
5. Do you want to better understand the relationship between value sets?
Relationship charts can show how one variable relates to one or many different variables. You could use this to show how something positively affects, has no effect, or negatively affects another variable.
When trying to establish the relationship between things, use these charts:
Featured Resource: The Marketer's Guide to Data Visualization

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

9 Great Ways to Use Data in Content Creation

Data Visualization: Tips and Examples to Inspire You

17 Data Visualization Resources You Should Bookmark
![what is a graphs presentation An Introduction to Data Visualization: How to Create Compelling Charts & Graphs [Ebook]](https://53.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/53/data-visualization-guide.jpg)
An Introduction to Data Visualization: How to Create Compelling Charts & Graphs [Ebook]

Why Data Is The Real MVP: 7 Examples of Data-Driven Storytelling by Leading Brands
![what is a graphs presentation How to Create an Infographic Using Poll & Survey Data [Infographic]](https://53.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/53/00-Blog_Thinkstock_Images/Survey_Data_Infographic.jpg)
How to Create an Infographic Using Poll & Survey Data [Infographic]

Data Storytelling 101: Helpful Tools for Gathering Ideas, Designing Content & More
Tired of struggling with spreadsheets? These free Microsoft Excel Graph Generator Templates can help
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Types of Graphs and Charts And Their Uses
If you are wondering what are the different types of graphs and charts , their uses and names, this page summarizes them with examples and pictures.
Although it is hard to tell what are all the types of graphs, this page consists all of the common types of statistical graphs and charts (and their meanings) widely used in any science.
1. Line Graphs
A line chart graphically displays data that changes continuously over time. Each line graph consists of points that connect data to show a trend (continuous change). Line graphs have an x-axis and a y-axis. In the most cases, time is distributed on the horizontal axis.
Uses of line graphs:
- When you want to show trends . For example, how house prices have increased over time.
- When you want to make predictions based on a data history over time.
- When comparing two or more different variables, situations, and information over a given period of time.
The following line graph shows annual sales of a particular business company for the period of six consecutive years:
Note: the above example is with 1 line. However, one line chart can compare multiple trends by several distributing lines.
2. Bar Charts
Bar charts represent categorical data with rectangular bars (to understand what is categorical data see categorical data examples ). Bar graphs are among the most popular types of graphs and charts in economics, statistics, marketing, and visualization in digital customer experience . They are commonly used to compare several categories of data.
Each rectangular bar has length and height proportional to the values that they represent.
One axis of the bar chart presents the categories being compared. The other axis shows a measured value.
Bar Charts Uses:
- When you want to display data that are grouped into nominal or ordinal categories (see nominal vs ordinal data ).
- To compare data among different categories.
- Bar charts can also show large data changes over time.
- Bar charts are ideal for visualizing the distribution of data when we have more than three categories.
The bar chart below represents the total sum of sales for Product A and Product B over three years.
The bars are 2 types: vertical or horizontal. It doesn’t matter which kind you will use. The above one is a vertical type.
3. Pie Charts
When it comes to statistical types of graphs and charts, the pie chart (or the circle chart) has a crucial place and meaning. It displays data and statistics in an easy-to-understand ‘pie-slice’ format and illustrates numerical proportion.
Each pie slice is relative to the size of a particular category in a given group as a whole. To say it in another way, the pie chart brakes down a group into smaller pieces. It shows part-whole relationships.
To make a pie chart, you need a list of categorical variables and numerical variables.
Pie Chart Uses:
- When you want to create and represent the composition of something.
- It is very useful for displaying nominal or ordinal categories of data.
- To show percentage or proportional data.
- When comparing areas of growth within a business such as profit.
- Pie charts work best for displaying data for 3 to 7 categories.
The pie chart below represents the proportion of types of transportation used by 1000 students to go to their school.
Pie charts are widely used by data-driven marketers for displaying marketing data.
4. Histogram
A histogram shows continuous data in ordered rectangular columns (to understand what is continuous data see our post discrete vs continuous data ). Usually, there are no gaps between the columns.
The histogram displays a frequency distribution (shape) of a data set. At first glance, histograms look alike to bar graphs. However, there is a key difference between them. Bar Chart represents categorical data and histogram represent continuous data.
Histogram Uses:
- When the data is continuous .
- When you want to represent the shape of the data’s distribution .
- When you want to see whether the outputs of two or more processes are different.
- To summarize large data sets graphically.
- To communicate the data distribution quickly to others.
The histogram below represents per capita income for five age groups.
Histograms are very widely used in statistics, business, and economics.
5. Scatter plot
The scatter plot is an X-Y diagram that shows a relationship between two variables. It is used to plot data points on a vertical and a horizontal axis. The purpose is to show how much one variable affects another.
Usually, when there is a relationship between 2 variables, the first one is called independent. The second variable is called dependent because its values depend on the first variable.
Scatter plots also help you predict the behavior of one variable (dependent) based on the measure of the other variable (independent).
Scatter plot uses:
- When trying to find out whether there is a relationship between 2 variables .
- To predict the behavior of dependent variable based on the measure of the independent variable.
- When having paired numerical data.
- When working with root cause analysis tools to identify the potential for problems.
- When you just want to visualize the correlation between 2 large datasets without regard to time .
The below Scatter plot presents data for 7 online stores, their monthly e-commerce sales, and online advertising costs for the last year.
The orange line you see in the plot is called “line of best fit” or a “trend line”. This line is used to help us make predictions that are based on past data.
The Scatter plots are used widely in data science and statistics. They are a great tool for visualizing linear regression models .
More examples and explanation for scatter plots you can see in our post what does a scatter plot show and simple linear regression examples .
6. Venn Chart
Venn Diagram (also called primary diagram, set diagram or logic diagrams) uses overlapping circles to visualize the logical relationships between two or more group of items.
Venn Diagram is one of the types of graphs and charts used in scientific and engineering presentations, in computer applications, in maths, and in statistics.
The basic structure of the Venn diagram is usually overlapping circles. The items in the overlapping section have specific common characteristics. Items in the outer portions of the circles do not have common traits.
Venn Chart Uses:
- When you want to compare and contrast groups of things.
- To categorize or group items.
- To illustrate logical relationships from various datasets.
- To identify all the possible relationships between collections of datasets.
The following science example of Venn diagram compares the features of birds and bats.
7. Area Charts
Area Chart Uses:
- When you want to show trends , rather than express specific values.
- To show a simple comparison of the trend of data sets over the period of time.
- To display the magnitude of a change.
- To compare a small number of categories.
The area chart has 2 variants: a variant with data plots overlapping each other and a variant with data plots stacked on top of each other (known as stacked area chart – as the shown in the following example).
The area chart below shows quarterly sales for product categories A and B for the last year.
This area chart shows you a quick comparison of the trend in the quarterly sales of Product A and Product B over the period of the last year.
8. Spline Chart
The Spline Chart is one of the most widespread types of graphs and charts used in statistics. It is a form of the line chart that represent smooth curves through the different data points.
Spline charts possess all the characteristics of a line chart except that spline charts have a fitted curved line to join the data points. In comparison, line charts connect data points with straight lines.
Spline Chart Uses:
- When you want to plot data that requires the usage of curve-fitting such as a product lifecycle chart or an impulse-response chart.
- Spline charts are often used in designing Pareto charts .
- Spline chart also is often used for data modeling by when you have limited number of data points and estimating the intervening values.
The following spline chart example shows sales of a company through several months of a year:
9. Box and Whisker Chart
A box and whisker chart is a statistical graph for displaying sets of numerical data through their quartiles. It displays a frequency distribution of the data.
The box and whisker chart helps you to display the spread and skewness for a given set of data using the five number summary principle: minimum, maximum, median, lower and upper quartiles. The ‘five-number summary’ principle allows providing a statistical summary for a particular set of numbers. It shows you the range (minimum and maximum numbers), the spread (upper and lower quartiles), and the center (median) for the set of data numbers.
A very simple figure of a box and whisker plot you can see below:
Box and Whisker Chart Uses:
- When you want to observe the upper, lower quartiles, mean, median, deviations, etc. for a large set of data.
- When you want to see a quick view of the dataset distribution .
- When you have multiple data sets that come from independent sources and relate to each other in some way.
- When you need to compare data from different categories.
The table and box-and-whisker plots below shows test scores for Maths and Literature for the same class.
| 35 | 77 | 92 | 43 | 55 | 66 | 73 | 70 | |
| 35 | 43 | 40 | 43 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 92 |
Box and Whisker charts have applications in many scientific areas and types of analysis such as statistical analysis, test results analysis, marketing analysis, data analysis, and etc.
10. Bubble Chart
Bubble charts are super useful types of graphs for making a comparison of the relationships between data in 3 numeric-data dimensions: the Y-axis data, the X-axis data, and data depicting the bubble size.
Bubble charts are very similar to XY Scatter plots but the bubble chart adds more functionality – a third dimension of data that can be extremely valuable.
Both axes (X and Y) of a bubble chart are numeric.
Bubble Chart Uses:
- When you have to display three or four dimensions of data.
- When you want to compare and display the relationships between categorized circles, by the use of proportions.
The bubble chart below shows the relationship between Cost (X-Axis), Profit (Y-Axis), and Probability of Success (%) (Bubble Size).
11. Pictographs
The pictograph or a pictogram is one of the more visually appealing types of graphs and charts that display numerical information with the use of icons or picture symbols to represent data sets.
They are very easy to read statistical way of data visualization. A pictogram shows the frequency of data as images or symbols. Each image/symbol may represent one or more units of a given dataset.
Pictograph Uses:
- When your audience prefers and understands better displays that include icons and illustrations. Fun can promote learning.
- It’s habitual for infographics to use of a pictogram.
- When you want to compare two points in an emotionally powerful way.
The following pictographic represents the number of computers sold by a business company for the period from January to March.
The pictographic example above shows that in January are sold 20 computers (4×5 = 20), in February are sold 30 computers (6×5 = 30) and in March are sold 15 computers.
12. Dot Plot
Dot plot or dot graph is just one of the many types of graphs and charts to organize statistical data. It uses dots to represent data. A Dot Plot is used for relatively small sets of data and the values fall into a number of discrete categories.
If a value appears more than one time, the dots are ordered one above the other. That way the column height of dots shows the frequency for that value.
Dot Plot Uses:
- To plot frequency counts when you have a small number of categories .
- Dot plots are very useful when the variable is quantitative or categorical .
- Dot graphs are also used for univariate data (data with only one variable that you can measure).
Suppose you have a class of 26 students. They are asked to tell their favorite color. The dot plot below represents their choices:
It is obvious that blue is the most preferred color by the students in this class.
13. Radar Chart
A radar chart is one of the most modern types of graphs and charts – ideal for multiple comparisons. Radar charts use a circular display with several different quantitative axes looking like spokes on a wheel. Each axis shows a quantity for a different categorical value.
Radar charts are also known as spider charts, web charts, star plots, irregular polygons, polar charts, cobweb charts or Kiviat diagram.
Radar Chart has many applications nowadays in statistics, maths, business, sports analysis, data intelligence, and etc.
Radar Chart Uses:
- When you want to observe which variables have similar values or whether there are any outliers amongst each variable.
- To represent multiple comparisons .
- When you want to see which variables are scoring low or high within a dataset. This makes radar chart ideal for displaying performance .
For example, we can compare employee’s performance with the scale of 1-8 on subjects such as Punctuality, Problem-solving, Meeting Deadlines, Marketing Knowledge, Communications. A point that is closer to the center on an axis shows a lower value and a worse performance.
| Punctuality | Problem-solving | Meeting Deadlines | Marketing Knowledge | Communications | |
| 6 | 5 | 8 | 7 | 8 | |
| 7 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 8 |
It is obvious that Jane has a better performance than Samanta.
14. Pyramid Graph
When it comes to easy to understand and good looking types of graphs and charts, pyramid graph has a top place.
A pyramid graph is a chart in a pyramid shape or triangle shape. These types of charts are best for data that is organized in some kind of hierarchy. The levels show a progressive order.
Pyramid Graph Uses:
- When you want to indicate a hierarchy level among the topics or other types of data.
- Pyramid graph is often used to represent progressive orders such as: “older to newer”, “more important to least important”, “specific to least specific”‘ and etc.
- When you have a proportional or interconnected relationship between data sets.
A classic pyramid graph example is the healthy food pyramid that shows fats, oils, and sugar (at the top) should be eaten less than many other foods such as vegetables and fruits (at the bottom of the pyramid).
Conclusion:
You might know that choosing the right type of chart is some kind of tricky business.
Anyway, you have a wide choice of types of graphs and charts. Used in the right way, they are a powerful weapon to help you make your reports and presentations both professional and clear.
What are your favorite types of graphs and charts? Share your thoughts on the field below.
About The Author
Silvia Valcheva
Silvia Valcheva is a digital marketer with over a decade of experience creating content for the tech industry. She has a strong passion for writing about emerging software and technologies such as big data, AI (Artificial Intelligence), IoT (Internet of Things), process automation, etc.
10 Comments
I have learned a lot from your presentation. Very informative
Nicely described different graphs, I learned a lot.
very useful. exiting
I love this. I learned a lot.
Very good representation of date. I would suggest an addition of “stem and leaf” diagrams.
I have only one thing to say and that is this is the best representation of every graphs and charts I have ever seen 😀
Very well described. Great learning article for beginners on Charts.
Really helpful thanks
Very Helpful text; Thanks Silvia Valcheva for your hard work
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Unsupported browser
This site was designed for modern browsers and tested with Internet Explorer version 10 and later.
It may not look or work correctly on your browser.
- Presentations
25 Best PowerPoint PPT Chart & Graph Templates for Data Presentations for 2024
PowerPoint Charts and graphs for presentations help visual learners understand data quickly. They're perfect for presentations. Let's look at the very best PowerPoint chart templates from Envato Elements.
Discover top PowerPoint graph templates . Let's learn more!
Top 25 PowerPoint PPT Chart & Graph Templates From Envato Elements For 2024
Envato Elements is the best place to find premium PowerPoint chart templates . Take a look at some of the best PPT chart templates. These are all included with a subscription to Elements:
1. Annual Startup Infographic - PowerPoint Template

Let's start with this cool PowerPoint chart design template. Are you running a startup? Looking for chart ideas for presentation.
Check the graphs for business presentations in this template. A good graph presentation design is key for that. It's very easy to use and this could help you attract loads of customers.
This download features:
- 60 total slides
- 30 slides light + 30 slides dark
- widescreen ratio 16:9
- easy to customize
- free font used
2. Maxim - PowerPoint Template

A strong PowerPoint chart design can land you your next business opportunity. Find a bunch of PowerPoint chart examples in this download. It's a multipurpose template that can be used for different kinds of businesses.
Present creative ideas, startup projects, educational learning and more. Free PowerPoint charts and graphs templates won't offer this much design quality. This PowerPoint chart template features:
- 30+ total slides
- free web fonts used
- picture placeholders
- easy color change
- vector based icons
- free support
3. Proposal PowerPoint Presentation Template

This PowerPoint chart template offers graphs for presentations. Data helps to support the thesis of the business concept. Show growth, revenue, or other data that'll attract investors or employers.
Use this PPT chart template! Make a winning proposal backed by data. Free PowerPoint charts and graphs templates won't offer this much design quality.
4. Charts Modern & Clean Presentation

Modern and clean chart designs eschew flashy design and cluttered elements. That's precisely the style you'll see in this winning PowerPoint data chart template. Fill in any of the colorful slides with your data and present with success.
5. Data Charts PowerPoint Presentation

PowerPoint graph templates like the 198 options in this are flexible. Re-use them for any number of presentations without repeating yourself. Use the flow charts, bar charts, and stacked bar charts to present your data visually.
It's a great PowerPoint chart template!
6. Business Plan PowerPoint Template

Looking for professional and cool graphs in PowerPoint? Find some of the best PowerPoint charts ideas with this template. It comes with plenty of functional graphs for business presentations.
This graph presentation comes with infographic elements and icons. Use PPT chart templates like this one for real estate. It could also work for business funding request or marketing research.
7. Infographic Solutions PowerPoint Template

Looking for graphs for presentations? Free PowerPoint charts and graphs templates won't offer this much design quality. Instead work with this set of infographic solutions and charts for PPT.
It's a multipurpose collection of 42 graph and chart templates in PowerPoint. You'll find great PowerPoint chart examples. Start creating a stunning chart presentation with this download!
8. Environment Infographic PowerPoint

This is great if you're looking for original graphs for business presentations. This environmental graph presentation template has illustrated PowerPoint chart examples. This might be one of the best PowerPoint charts.
This PowerPoint chart template features:
- customize elements, colors, shapes and charts
- HD 16: 9 widescreen slide format (1920×1080 pixels).
9. Organizational Data Chart Presentation

Modern organizations rely on data-driven charts and graphs for presentations. This way they can explain business conditions. Find PowerPoint charts and graphs that present critical data in an appealing way.
You've got a choice of colors, styles, and visuals. Start with a great chart template for PPT like this.
10. PowerPoint Chart Templates for PPT

Remember: data shines when you put it into a chart or graph. And it's even better when you use a template like this one. Work with area, line, bar, or stacked bar charts, the styles.
This PowerPoint chart PowerPoint is perfect for converting flat data. This pack is much better than any free PowerPoint chart templates you find online.
11. Creative Real Estate PowerPoint Chart Template

This is a great PowerPoint chart template for anyone in real estate. It can also give you plenty of PowerPoint chart ideas. Start working the cool graphs in PowerPoint included with this download.
This template comes with great graphs for business presentations. This PPT chart presentation includes:
- PPTX, PPT file
- 16:9 widescreen ratio
- 30 unique layout slides
- 400+ icon designs
- resizable and editable graphics and charts for PPT
- cool graphs in PowerPoint
- editable infographics
12. Business Plan PowerPoint Chart Template

Get started with a modern graph presentation. This a beautiful design with functional and business focused chart ideas for presentation. It comes with infographic elements to use as graphs for business presentations.
This professional PowerPoint chart template includes:
- Master slide layout
- 180 animated and unique slides
- full HD 16:9 ratio
- resizable vector elements
- professional, minimal and creative design
- free fonts used
- Excel linked smart art
13. Marketing - PowerPoint Chart Template

This multipurpose PowerPoint chart template is perfect for anyone in marketing. Use it also for business, creative, startup and educational PPT chart presentations. Grab your audience’s attention with professional and modern chart ideas for presentation.
PowerPoint chart and graph templates like this one feature:
- cool PowerPoint chart ideas
- vector based icons
14. CLING - Simple Presentation PowerPoint Graph Templates

Looking for original PowerPoint chart ideas? CLING is a simple presentation chart PowerPoint template full of those. It has a professional, ultra-modern and unique design.
Cool PPT chart templates like this one can be used for any type of presentation. Work with graphs for presentations used in the 40+ unique slide designs. You won't get this much quality with free PowerPoint charts and graphs templates.
15. Chart Infographic Presentation Template

Check out this versatile presentation chart template. It's suitable for many different business and personal purposes. Use PowerPoint chart examples for pitch decks, marketing strategies or company reports.
Get plenty of PowerPoint chart ideas with this download. Create a unique PPT chart presentation with the editable 100 pages. This template has some of best PowerPoint charts and graphs!
16. Piekisu Charts - PowerPoint Graph Templates

Looking for PowerPoint chart ideas? Do you need versatile graphs for business presentations? This PowerPoint chart template is all you need.
Get lots of charts for PPT and chart ideas for presentations. You'll get 60 total slides full of cool graphs in PowerPoint. Work with the best PowerPoint chart templates!
17. Creative Dark Simple Yellow Modern Business Plan

Laylo is the best way to share your message and ideas. This PowerPoint chart template comes with an original design. It's a versatile presentation template.
You can add all your PowerPoint chart ideas. It features 30 unique slide designs with cool graphs for business presentations. It's one of the best PowerPoint graph templates.
18. MUTI - Minimal Presentation Template

Are you into minimalism? Work with a PowerPoint chart template like Muti. Create the best PowerPoint chart design with this unique template.
Engage with your audience with a design that comes with the right style. Let your minimalist PowerPoint chart ideas speak up for your work. This PowerPoint chart template features:
- full screen and responsive features
- vector elements
- easy to edit, insert images and change color
- full user guide
19. Project Proposal PowerPoint Graph Templates

Create an engaging project proposal with graphs for business presentations. This is a clean, creative and modern PowerPoint chart template. Professional PPT chart templates come with everything you need.
Find the best chart ideas for presentations. This PowerPoint chart design comes with:
- 30+ unique slides
- 20+ color themes
- 4000+ icons pack
- 16:9 full HD ratio
- resizable and editable graphics
- free and fast support
20. Competitor Analysis PowerPoint Graph Templates

A professional competitor analysis must include graphs for business presentations. This PowerPoint chart template has everything you need. Find lots of amazing graphs for presentations and PowerPoint chart ideas.
Work with the infographic pack to create the best PowerPoint charts. You'll get 35 unique slides to work with. This PowerPoint chart template is a great place to start!
21. Creative Light Green Blue Design Business

Looking for creative chart ideas for presentation? Check out the cool graphs in PowerPoint included in this template. Versatile PowerPoint graph templates like this one can be used for different purposes.
It could work for a cool pitch deck, marketing strategy or product portfolio. Find great PowerPoint chart examples. Add all your chart ideas for presentation to this cool template!
22. Medika Infographic - PowerPoint Graph Templates

This professional chart template for PowerPoint is very easy to use. It comes with a set of medical illustrations. These will support your chart ideas for presentation.
You'll be working with 62 total slides. Choose between dark or light mode. You'll also find some of the best PowerPoint chart examples.
23. Data Visualization Report Presentation

Are you into data visualization? Then this PowerPoint chart template is for you. This will give you plenty of chart ideas for presentation.
Present your analytical findings and results with the best PowerPoint charts ideas. Free PowerPoint graphic templates aren't as customizable as this one. You'll get 38 unique slides, plus a selection of icons and illustrations.
Create the best PowerPoint charts with this download.
24. Creative Gray Navy Education Business

Check out this versatile PowerPoint chart template. Professional chart templates in PowerPoint like this one are suitable for different purposes. Forget about ineffective free PowerPoint charts and graphs templates.
Create instead quality graphs for business presentations. This download features:
- PPTX, PPT files
- 30 unique slides
- cool PowerPoint chart design
25. XHOTS - Digital Business Presentation

Last but definitely not least, here's XHOTS. This PowerPoint chart template is a new way to share your ideas and data. You'll get cool graphs in PowerPoint that are easy to edit.
Share your creative PowerPoint chart ideas and impress your audience. Forget about free PowerPoint charts and graphs templates! Upgrade to premium PowerPoint graph templates like this one.
Free Premium Templates to Create a Chart Presentation
We have great news for you! Envato Elements has some top assets that you can try for free.
Get these premium PowerPoint chart templates now:
1. Bole - Free PowerPoint Chart Template

Here's an ideal multipurpose PowerPoint chart template with lots of graph designs. You'll find:
- full HD layout
- 213 unique slides
- 10 color variations
- fully editable vector icons
- creative image placeholders
As there are so many graphs to choose from, you can try a variety of slides with a chart.
2. Exhaustive - Chart Template for PowerPoint

This is a multipurpose data PowerPoint template. With this free graphic PPT , you'll get:
- 40+ unique slides
- help guide included
- light and dark themes
- handmade infographics
- fully customizable chart presentation
3. NOVUS - Multipurpose PowerPoint Graphic PPT

Looking for the best PowerPoint graph templates? Take a look at NOVUS and its myriad of diagrams. Decorate all the slides with a chart!
The different features include:
- easy to use file
- 280 vector icons
- 100 unique slides
- 12 color variations
- master slides for quick editing
4. Zapnu - Multipurpose Data PowerPoint Template

You can't go wrong with PPT graph templates like Zapnu. By downloading it for free, you can create a chart presentation with:
- dark and light versions
- premade setup sections
- 3 premade color themes
- widescreen and standard formats
5. SpotON - Chart Template for PowerPoint

SpotON is one of the top PowerPoint graphic templates. As it's multipurpose, you can use it many times to present different ideas.
- full HD resolution
- 117 unique slides
- all elements are editable
- drag-and-drop image placeholders
How to Quickly Customize a Premium Graph and Chart PPT Template
Found your favorite PPT template? It’s time to customize it to match your style and to reflect your data. It'll only take 5 easy steps:

This template has a clean and professional design. It can be adapted for all industries. Let's start customizing it:
1. Choose Your Slides
To do this, open your template in PowerPoint, click on the View tab and select Slide Sorter . Hold the SHIFT key. Click on all the slides that you don’t want to use.
Then, right-click on them and select Delete Slide . Then switch back to the Normal view.

2. Customize Your Chart Data
Customize the chart data. Right click on a chart or graph and then select the Edit Data in Excel option. Once Excel opens, customize the information. Click Save when you’re done.

3. Change Colors
Choose the Format Shape option. Then choose a different color under Solid Fill options.

4. Use Your Own Fonts
Customize the fonts used in the PowerPoint template. Click on any text. Then choose a different font from the drop-down menu.

5. Save and Present Your Data
Do this by going to File > Save . If you need to export it to other formats, such as a PDF. Do this by going to File > Save as .

5 Tips for Using Charts and Graphs in Your PowerPoint Presentation
There are so many possibilities when it comes to using PPT graph templates. If you find it overwhelming, we're here to help! Take a look at the following tips to design the perfect graphic PPT:
1. Use Different Types of Charts
There are so many different kinds of charts. Why settle with only one design? When using PowerPoint graphic templates, play with variety to keep your chart presentation dynamic.

2. Be Colorful
The best PPT graph templates are colorful. This doesn't necessarily mean that you have to use many different colors. Maybe just two or three, with a vibrant color that stands out from the rest.
3. Don't Limit the Graphs
If you're working with a data PowerPoint template, you probably have lots of information to explain. Don't be afraid to add many slides with a chart each.
Of course, you don't want to leave any key facts out. And at the end of the day, it's better to use visual aid than typing big chunks of text.

4. Animate Your Graphic PPT
Most premium PowerPoint graph templates come animated! But if you choose one that isn't, try adding some cool animations. When used right, these will help you keep the audience engaged.
5. Distribute the Charts Wisely
Again, you don't need to limit the amount of graphs you use. However, make sure to distribute them in a way that maintains the harmonious look and feel of your PowerPoint chart template.

Discover More Top Premium Microsoft PowerPoint Template Designs
We just went through some of the very best PowerPoint graph templates. If you'd like to explore more premium options, check out these top selections for 2024:

Learn More About Using Charts & Graphs in PowerPoint
Working with PowerPoint for data-driven presentations might be a bit intimidating at first. You need all the help you can get to present confidently.
On Envato Tuts+, we've got a library with the best PowerPoint resources. Start by checking out our PowerPoint tutorial guide . Go over some of the tutorials below. Become a complete master of the art of PowerPoint charts!
Learn skills that help you show data visually:

Top Premium PowerPoint Graph Templates on Envato Elements for 2024 (Unlimited Use)
You don't have to settle for simple PowerPoint chart templates. Data-driven presenters often turn to PPT chart templates like the ones featured here. It helps your audience understand it in a quick and effective way.
Get an Envato Elements subscription for a low monthly fee. You'll get access to premium creative assets such as web templates, stock images and videos, PPT graph templates , and so much more!
Enjoy unlimited access to these digital premium assets on Envato Elements. Download as many premium templates as you want.
Graph PPT Templates

Plus, now Envato Elements has introduced an AI-powered search feature ! This new tool allows you to input a description of your project to effortlessly locate the finest human-crafted resources.

Start creating your next presentation with an Envato Elements template!
Design a Presentation With PowerPoint Chart Templates Now
A data-driven presentation is a winner choice. And it's always easier to do when you use pre-built PowerPoint graph templates.
Don't be taken in by offers of free PowerPoint chart templates. A professionally designed chart presentation template will help you make a good impression.
Experiment with unlimited PowerPoint chart templates with a low-cost subscription to Envato Elements. Why not download your favorite PowerPoint chart templates today?
Editorial Note: This post has been updated with contributions from Brenda Barron , Daniel Strongin , Janila Castañeda , and Renata Martín Intriago . Brenda and Daniel are freelance instructors for Envato Tuts+. Janila is the Associate Business Editor for Tuts+. Renata is a staff writer with Envato Tuts+.

- Insert a picture in PowerPoint Article
- Edit pictures Article
- Add SmartArt to a slide Article
- Put a background picture on your slides Article
- Add a background picture to slides Article
- Use charts and graphs in your presentation Article
- Insert icons in PowerPoint Article

Use charts and graphs in your presentation
You can make a chart in PowerPoint or Excel. If you have lots of data to chart, create your chart in Excel , and then copy it into your presentation . This is also the best way if your data changes regularly and you want your chart to always reflect the latest numbers. In that case, when you copy and paste the chart, keep it linked to the original Excel file .
To create a simple chart from scratch in PowerPoint, click Insert > Chart and pick the chart you want.

Click Insert > Chart .
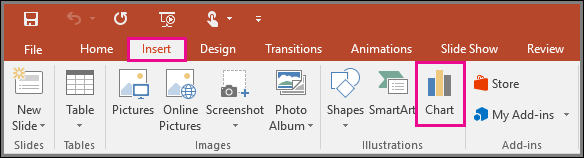
Click the chart type and then double-click the chart you want.
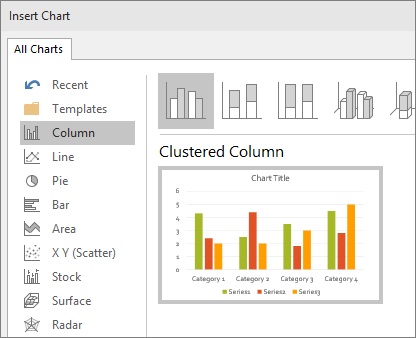
Tip: For help deciding which chart is best for your data, see Available chart types .
In the worksheet that appears, replace the placeholder data with your own information.

When you’ve finished, close the worksheet.
Create an org chart in PowerPoint
Create charts in Excel

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
Graphical Representation of Data
Graphical representation of data is an attractive method of showcasing numerical data that help in analyzing and representing quantitative data visually. A graph is a kind of a chart where data are plotted as variables across the coordinate. It became easy to analyze the extent of change of one variable based on the change of other variables. Graphical representation of data is done through different mediums such as lines, plots, diagrams, etc. Let us learn more about this interesting concept of graphical representation of data, the different types, and solve a few examples.
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. | |
| 4. | |
| 5. | |
| 6. | |
| 7. |
Definition of Graphical Representation of Data
A graphical representation is a visual representation of data statistics-based results using graphs, plots, and charts. This kind of representation is more effective in understanding and comparing data than seen in a tabular form. Graphical representation helps to qualify, sort, and present data in a method that is simple to understand for a larger audience. Graphs enable in studying the cause and effect relationship between two variables through both time series and frequency distribution. The data that is obtained from different surveying is infused into a graphical representation by the use of some symbols, such as lines on a line graph, bars on a bar chart, or slices of a pie chart. This visual representation helps in clarity, comparison, and understanding of numerical data.
Representation of Data
The word data is from the Latin word Datum, which means something given. The numerical figures collected through a survey are called data and can be represented in two forms - tabular form and visual form through graphs. Once the data is collected through constant observations, it is arranged, summarized, and classified to finally represented in the form of a graph. There are two kinds of data - quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative data is more structured, continuous, and discrete with statistical data whereas qualitative is unstructured where the data cannot be analyzed.
Principles of Graphical Representation of Data
The principles of graphical representation are algebraic. In a graph, there are two lines known as Axis or Coordinate axis. These are the X-axis and Y-axis. The horizontal axis is the X-axis and the vertical axis is the Y-axis. They are perpendicular to each other and intersect at O or point of Origin. On the right side of the Origin, the Xaxis has a positive value and on the left side, it has a negative value. In the same way, the upper side of the Origin Y-axis has a positive value where the down one is with a negative value. When -axis and y-axis intersect each other at the origin it divides the plane into four parts which are called Quadrant I, Quadrant II, Quadrant III, Quadrant IV. This form of representation is seen in a frequency distribution that is represented in four methods, namely Histogram, Smoothed frequency graph, Pie diagram or Pie chart, Cumulative or ogive frequency graph, and Frequency Polygon.
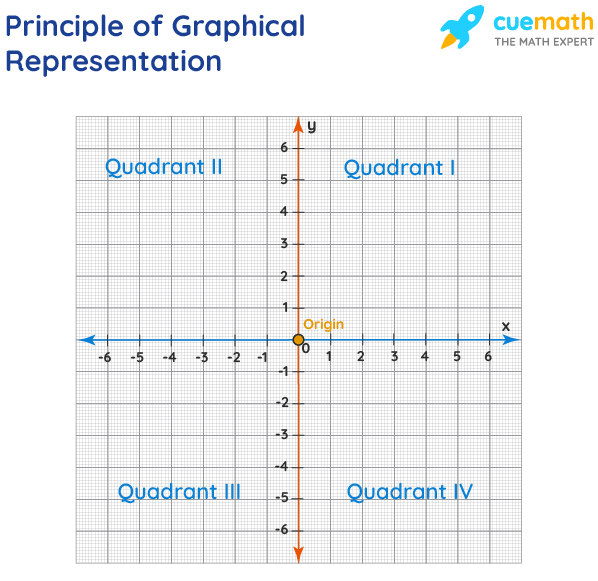
Advantages and Disadvantages of Graphical Representation of Data
Listed below are some advantages and disadvantages of using a graphical representation of data:
- It improves the way of analyzing and learning as the graphical representation makes the data easy to understand.
- It can be used in almost all fields from mathematics to physics to psychology and so on.
- It is easy to understand for its visual impacts.
- It shows the whole and huge data in an instance.
- It is mainly used in statistics to determine the mean, median, and mode for different data
The main disadvantage of graphical representation of data is that it takes a lot of effort as well as resources to find the most appropriate data and then represent it graphically.
Rules of Graphical Representation of Data
While presenting data graphically, there are certain rules that need to be followed. They are listed below:
- Suitable Title: The title of the graph should be appropriate that indicate the subject of the presentation.
- Measurement Unit: The measurement unit in the graph should be mentioned.
- Proper Scale: A proper scale needs to be chosen to represent the data accurately.
- Index: For better understanding, index the appropriate colors, shades, lines, designs in the graphs.
- Data Sources: Data should be included wherever it is necessary at the bottom of the graph.
- Simple: The construction of a graph should be easily understood.
- Neat: The graph should be visually neat in terms of size and font to read the data accurately.
Uses of Graphical Representation of Data
The main use of a graphical representation of data is understanding and identifying the trends and patterns of the data. It helps in analyzing large quantities, comparing two or more data, making predictions, and building a firm decision. The visual display of data also helps in avoiding confusion and overlapping of any information. Graphs like line graphs and bar graphs, display two or more data clearly for easy comparison. This is important in communicating our findings to others and our understanding and analysis of the data.
Types of Graphical Representation of Data
Data is represented in different types of graphs such as plots, pies, diagrams, etc. They are as follows,
| Data Representation | Description |
|---|---|
|
A group of data represented with rectangular bars with lengths proportional to the values is a . The bars can either be vertically or horizontally plotted. | |
|
The is a type of graph in which a circle is divided into Sectors where each sector represents a proportion of the whole. Two main formulas used in pie charts are: | |
|
The represents the data in a form of series that is connected with a straight line. These series are called markers. | |
|
Data shown in the form of pictures is a . Pictorial symbols for words, objects, or phrases can be represented with different numbers. | |
|
The is a type of graph where the diagram consists of rectangles, the area is proportional to the frequency of a variable and the width is equal to the class interval. Here is an example of a histogram. | |
|
The table in statistics showcases the data in ascending order along with their corresponding frequencies. The frequency of the data is often represented by f. | |
|
The is a way to represent quantitative data according to frequency ranges or frequency distribution. It is a graph that shows numerical data arranged in order. Each data value is broken into a stem and a leaf. | |
|
Scatter diagram or is a way of graphical representation by using Cartesian coordinates of two variables. The plot shows the relationship between two variables. |
Related Topics
Listed below are a few interesting topics that are related to the graphical representation of data, take a look.
- x and y graph
- Frequency Polygon
- Cumulative Frequency
Examples on Graphical Representation of Data
Example 1 : A pie chart is divided into 3 parts with the angles measuring as 2x, 8x, and 10x respectively. Find the value of x in degrees.
We know, the sum of all angles in a pie chart would give 360º as result. ⇒ 2x + 8x + 10x = 360º ⇒ 20 x = 360º ⇒ x = 360º/20 ⇒ x = 18º Therefore, the value of x is 18º.
Example 2: Ben is trying to read the plot given below. His teacher has given him stem and leaf plot worksheets. Can you help him answer the questions? i) What is the mode of the plot? ii) What is the mean of the plot? iii) Find the range.
| Stem | Leaf |
| 1 | 2 4 |
| 2 | 1 5 8 |
| 3 | 2 4 6 |
| 5 | 0 3 4 4 |
| 6 | 2 5 7 |
| 8 | 3 8 9 |
| 9 | 1 |
Solution: i) Mode is the number that appears often in the data. Leaf 4 occurs twice on the plot against stem 5.
Hence, mode = 54
ii) The sum of all data values is 12 + 14 + 21 + 25 + 28 + 32 + 34 + 36 + 50 + 53 + 54 + 54 + 62 + 65 + 67 + 83 + 88 + 89 + 91 = 958
To find the mean, we have to divide the sum by the total number of values.
Mean = Sum of all data values ÷ 19 = 958 ÷ 19 = 50.42
iii) Range = the highest value - the lowest value = 91 - 12 = 79
go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Graphical Representation of Data
Faqs on graphical representation of data, what is graphical representation.
Graphical representation is a form of visually displaying data through various methods like graphs, diagrams, charts, and plots. It helps in sorting, visualizing, and presenting data in a clear manner through different types of graphs. Statistics mainly use graphical representation to show data.
What are the Different Types of Graphical Representation?
The different types of graphical representation of data are:
- Stem and leaf plot
- Scatter diagrams
- Frequency Distribution
Is the Graphical Representation of Numerical Data?
Yes, these graphical representations are numerical data that has been accumulated through various surveys and observations. The method of presenting these numerical data is called a chart. There are different kinds of charts such as a pie chart, bar graph, line graph, etc, that help in clearly showcasing the data.
What is the Use of Graphical Representation of Data?
Graphical representation of data is useful in clarifying, interpreting, and analyzing data plotting points and drawing line segments , surfaces, and other geometric forms or symbols.
What are the Ways to Represent Data?
Tables, charts, and graphs are all ways of representing data, and they can be used for two broad purposes. The first is to support the collection, organization, and analysis of data as part of the process of a scientific study.
What is the Objective of Graphical Representation of Data?
The main objective of representing data graphically is to display information visually that helps in understanding the information efficiently, clearly, and accurately. This is important to communicate the findings as well as analyze the data.
- Math Article
Graphical Representation

Graphical Representation is a way of analysing numerical data. It exhibits the relation between data, ideas, information and concepts in a diagram. It is easy to understand and it is one of the most important learning strategies. It always depends on the type of information in a particular domain. There are different types of graphical representation. Some of them are as follows:
- Line Graphs – Line graph or the linear graph is used to display the continuous data and it is useful for predicting future events over time.
- Bar Graphs – Bar Graph is used to display the category of data and it compares the data using solid bars to represent the quantities.
- Histograms – The graph that uses bars to represent the frequency of numerical data that are organised into intervals. Since all the intervals are equal and continuous, all the bars have the same width.
- Line Plot – It shows the frequency of data on a given number line. ‘ x ‘ is placed above a number line each time when that data occurs again.
- Frequency Table – The table shows the number of pieces of data that falls within the given interval.
- Circle Graph – Also known as the pie chart that shows the relationships of the parts of the whole. The circle is considered with 100% and the categories occupied is represented with that specific percentage like 15%, 56%, etc.
- Stem and Leaf Plot – In the stem and leaf plot, the data are organised from least value to the greatest value. The digits of the least place values from the leaves and the next place value digit forms the stems.
- Box and Whisker Plot – The plot diagram summarises the data by dividing into four parts. Box and whisker show the range (spread) and the middle ( median) of the data.
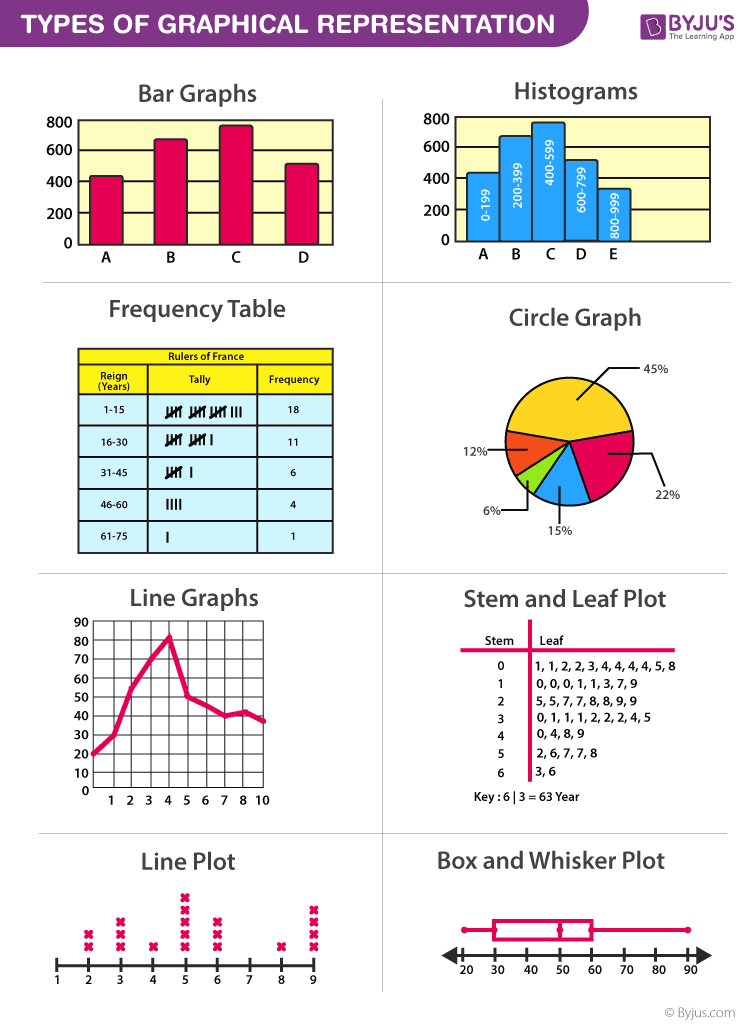
General Rules for Graphical Representation of Data
There are certain rules to effectively present the information in the graphical representation. They are:
- Suitable Title: Make sure that the appropriate title is given to the graph which indicates the subject of the presentation.
- Measurement Unit: Mention the measurement unit in the graph.
- Proper Scale: To represent the data in an accurate manner, choose a proper scale.
- Index: Index the appropriate colours, shades, lines, design in the graphs for better understanding.
- Data Sources: Include the source of information wherever it is necessary at the bottom of the graph.
- Keep it Simple: Construct a graph in an easy way that everyone can understand.
- Neat: Choose the correct size, fonts, colours etc in such a way that the graph should be a visual aid for the presentation of information.
Graphical Representation in Maths
In Mathematics, a graph is defined as a chart with statistical data, which are represented in the form of curves or lines drawn across the coordinate point plotted on its surface. It helps to study the relationship between two variables where it helps to measure the change in the variable amount with respect to another variable within a given interval of time. It helps to study the series distribution and frequency distribution for a given problem. There are two types of graphs to visually depict the information. They are:
- Time Series Graphs – Example: Line Graph
- Frequency Distribution Graphs – Example: Frequency Polygon Graph
Principles of Graphical Representation
Algebraic principles are applied to all types of graphical representation of data. In graphs, it is represented using two lines called coordinate axes. The horizontal axis is denoted as the x-axis and the vertical axis is denoted as the y-axis. The point at which two lines intersect is called an origin ‘O’. Consider x-axis, the distance from the origin to the right side will take a positive value and the distance from the origin to the left side will take a negative value. Similarly, for the y-axis, the points above the origin will take a positive value, and the points below the origin will a negative value.
Generally, the frequency distribution is represented in four methods, namely
- Smoothed frequency graph
- Pie diagram
- Cumulative or ogive frequency graph
- Frequency Polygon
Merits of Using Graphs
Some of the merits of using graphs are as follows:
- The graph is easily understood by everyone without any prior knowledge.
- It saves time
- It allows us to relate and compare the data for different time periods
- It is used in statistics to determine the mean, median and mode for different data, as well as in the interpolation and the extrapolation of data.
Example for Frequency polygonGraph
Here are the steps to follow to find the frequency distribution of a frequency polygon and it is represented in a graphical way.
- Obtain the frequency distribution and find the midpoints of each class interval.
- Represent the midpoints along x-axis and frequencies along the y-axis.
- Plot the points corresponding to the frequency at each midpoint.
- Join these points, using lines in order.
- To complete the polygon, join the point at each end immediately to the lower or higher class marks on the x-axis.
Draw the frequency polygon for the following data
| 10-20 | 20-30 | 30-40 | 40-50 | 50-60 | 60-70 | 70-80 | 80-90 | |
| 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 7 | 5 |
Mark the class interval along x-axis and frequencies along the y-axis.
Let assume that class interval 0-10 with frequency zero and 90-100 with frequency zero.
Now calculate the midpoint of the class interval.
| 0-10 | 5 | 0 |
| 10-20 | 15 | 4 |
| 20-30 | 25 | 6 |
| 30-40 | 35 | 8 |
| 40-50 | 45 | 10 |
| 50-60 | 55 | 12 |
| 60-70 | 65 | 14 |
| 70-80 | 75 | 7 |
| 80-90 | 85 | 5 |
| 90-100 | 95 | 0 |
Using the midpoint and the frequency value from the above table, plot the points A (5, 0), B (15, 4), C (25, 6), D (35, 8), E (45, 10), F (55, 12), G (65, 14), H (75, 7), I (85, 5) and J (95, 0).
To obtain the frequency polygon ABCDEFGHIJ, draw the line segments AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG, GH, HI, IJ, and connect all the points.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of graphical representation.
Some of the various types of graphical representation include:
- Line Graphs
- Frequency Table
- Circle Graph, etc.
Read More: Types of Graphs
What are the Advantages of Graphical Method?
Some of the advantages of graphical representation are:
- It makes data more easily understandable.
- It saves time.
- It makes the comparison of data more efficient.
| MATHS Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Very useful for understand the basic concepts in simple and easy way. Its very useful to all students whether they are school students or college sudents
Thanks very much for the information
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Graphic Presentation of Data
Apart from diagrams, Graphic presentation is another way of the presentation of data and information. Usually, graphs are used to present time series and frequency distributions. In this article, we will look at the graphic presentation of data and information along with its merits, limitations , and types.
Suggested Videos
Construction of a graph.
The graphic presentation of data and information offers a quick and simple way of understanding the features and drawing comparisons. Further, it is an effective analytical tool and a graph can help us in finding the mode, median, etc.
We can locate a point in a plane using two mutually perpendicular lines – the X-axis (the horizontal line) and the Y-axis (the vertical line). Their point of intersection is the Origin .
We can locate the position of a point in terms of its distance from both these axes. For example, if a point P is 3 units away from the Y-axis and 5 units away from the X-axis, then its location is as follows:

Browse more Topics under Descriptive Statistics
- Definition and Characteristics of Statistics
- Stages of Statistical Enquiry
- Importance and Functions of Statistics
- Nature of Statistics – Science or Art?
- Application of Statistics
- Law of Statistics and Distrust of Statistics
- Meaning and Types of Data
- Methods of Collecting Data
- Sample Investigation
- Classification of Data
- Tabulation of Data
- Frequency Distribution of Data
- Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
- Measures of Central Tendency
- Mean Median Mode
- Measures of Dispersion
- Standard Deviation
- Variance Analysis
Some points to remember:
- We measure the distance of the point from the Y-axis along the X-axis. Similarly, we measure the distance of the point from the X-axis along the Y-axis. Therefore, to measure 3 units from the Y-axis, we move 3 units along the X-axis and likewise for the other coordinate .
- We then draw perpendicular lines from these two points.
- The point where the perpendiculars intersect is the position of the point P.
- We denote it as follows (3,5) or (abscissa, ordinate). Together, they are the coordinates of the point P.
- The four parts of the plane are Quadrants.
- Also, we can plot different points for a different pair of values.
General Rules for Graphic Presentation of Data and Information
There are certain guidelines for an attractive and effective graphic presentation of data and information. These are as follows:
- Suitable Title – Ensure that you give a suitable title to the graph which clearly indicates the subject for which you are presenting it.
- Unit of Measurement – Clearly state the unit of measurement below the title.
- Suitable Scale – Choose a suitable scale so that you can represent the entire data in an accurate manner.
- Index – Include a brief index which explains the different colors and shades, lines and designs that you have used in the graph. Also, include a scale of interpretation for better understanding.
- Data Sources – Wherever possible, include the sources of information at the bottom of the graph.
- Keep it Simple – You should construct a graph which even a layman (without any exposure in the areas of statistics or mathematics) can understand.
- Neat – A graph is a visual aid for the presentation of data and information. Therefore, you must keep it neat and attractive. Choose the right size, right lettering, and appropriate lines, colors, dashes, etc.
Merits of a Graph
- The graph presents data in a manner which is easier to understand.
- It allows us to present statistical data in an attractive manner as compared to tables. Users can understand the main features, trends, and fluctuations of the data at a glance.
- A graph saves time.
- It allows the viewer to compare data relating to two different time-periods or regions.
- The viewer does not require prior knowledge of mathematics or statistics to understand a graph.
- We can use a graph to locate the mode, median, and mean values of the data.
- It is useful in forecasting, interpolation, and extrapolation of data.
Limitations of a Graph
- A graph lacks complete accuracy of facts.
- It depicts only a few selected characteristics of the data.
- We cannot use a graph in support of a statement.
- A graph is not a substitute for tables.
- Usually, laymen find it difficult to understand and interpret a graph.
- Typically, a graph shows the unreasonable tendency of the data and the actual values are not clear.
Types of Graphs
Graphs are of two types:
- Time Series graphs
- Frequency Distribution graphs
Time Series Graphs
A time series graph or a “ histogram ” is a graph which depicts the value of a variable over a different point of time. In a time series graph, time is the most important factor and the variable is related to time. It helps in the understanding and analysis of the changes in the variable at a different point of time. Many statisticians and businessmen use these graphs because they are easy to understand and also because they offer complex information in a simple manner.
Further, constructing a time series graph does not require a user with technical skills. Here are some major steps in the construction of a time series graph:
- Represent time on the X-axis and the value of the variable on the Y-axis.
- Start the Y-value with zero and devise a suitable scale which helps you present the whole data in the given space.
- Plot the values of the variable and join different point with a straight line.
- You can plot multiple variables through different lines.
You can use a line graph to summarize how two pieces of information are related and how they vary with each other.
- You can compare multiple continuous data-sets easily
- You can infer the interim data from the graph line
Disadvantages
- It is only used with continuous data.
Use of a false Base Line
Usually, in a graph, the vertical line starts from the Origin. However, in some cases, a false Base Line is used for a better representation of the data. There are two scenarios where you should use a false Base Line:
- To magnify the minor fluctuation in the time series data
- To economize the space
Net Balance Graph
If you have to show the net balance of income and expenditure or revenue and costs or imports and exports, etc., then you must use a net balance graph. You can use different colors or shades for positive and negative differences.
Frequency Distribution Graphs
Let’s look at the different types of frequency distribution graphs.
A histogram is a graph of a grouped frequency distribution. In a histogram, we plot the class intervals on the X-axis and their respective frequencies on the Y-axis. Further, we create a rectangle on each class interval with its height proportional to the frequency density of the class.

Frequency Polygon or Histograph
A frequency polygon or a Histograph is another way of representing a frequency distribution on a graph. You draw a frequency polygon by joining the midpoints of the upper widths of the adjacent rectangles of the histogram with straight lines.

Frequency Curve
When you join the verticals of a polygon using a smooth curve, then the resulting figure is a Frequency Curve. As the number of observations increase, we need to accommodate more classes. Therefore, the width of each class reduces. In such a scenario, the variable tends to become continuous and the frequency polygon starts taking the shape of a frequency curve.
Cumulative Frequency Curve or Ogive
A cumulative frequency curve or Ogive is the graphical representation of a cumulative frequency distribution. Since a cumulative frequency is either of a ‘less than’ or a ‘more than’ type, Ogives are of two types too – ‘less than ogive’ and ‘more than ogive’.

Scatter Diagram
A scatter diagram or a dot chart enables us to find the nature of the relationship between the variables. If the plotted points are scattered a lot, then the relationship between the two variables is lesser.

Solved Question
Q1. What are the general rules for the graphic presentation of data and information?
Answer: The general rules for the graphic presentation of data are:
- Use a suitable title
- Clearly specify the unit of measurement
- Ensure that you choose a suitable scale
- Provide an index specifying the colors, lines, and designs used in the graph
- If possible, provide the sources of information at the bottom of the graph
- Keep the graph simple and neat.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Descriptive Statistics
- Nature of Statistics – Science or Art?
2 responses to “Stages of Statistical Enquiry”
Im trying to find out if my mother ALICE Desjarlais is registered with the Red Pheasant Reserve, I applied with Metie Urban Housing and I need my Metie card. Is there anyway you can help me.
Quite useful details about statistics. I’d also like to add one point. If you need professional help with a statistics project? Find a professional in minutes!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


COMMENTS
How to Describe Graphs, Charts, and Diagrams in ... - Preply
Use charts and graphs in your presentation
PowerPoint Charts, Graphs, & Tables Made Easy
A presentation graph is a visual representation of data, crafted in either 2D or 3D format, designed to illustrate relationships among two or more variables. Its primary purpose is to facilitate understanding of complex information, trends, and patterns, making it easier for an audience to grasp insights during a presentation. ...
In this screencast, you'll learn how to quickly make a chart in MS PowerPoint. Download unlimited PPT templates: https://elements.envato.com/presentation-t...
1. Use charts and graphs to compare data. One of the most common uses of charts and graphs is to compare data. Whether you are comparing sales figures, market trends or customer feedback, charts and graphs can help you present the information in a visually compelling way. Use bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, and scatter plots to showcase ...
How to Make Great PPT Charts & Graphs in Microsoft ...
How to Use Charts and Graphs Effectively
Text and Font. Using bold font isn't going to make much difference in your graph. As far as possible, avoid using bold, underline or italic fonts. Keep the font size and type consistent throughout the presentation. Avoid effects such as shading, outline, and 3D letters. Always lighten secondary data labels.
Choosing the right chart or graph for your data is crucial for accurate and effective data presentation. By understanding the differences and uses of various charts and avoiding common mistakes, you can create compelling and insightful visualizations that will capture the attention and interest of your audience.
PowerPoint: Charts
Chart vs. Graph: Understanding the Graphical ...
Concentrate on trends and changes. Concentrate on trends and changes rather than numbers and data. 11. 3D graphs are hard to read. Avoid 3-d graphs as much as possible, they are hard to read. 12. Animate your graphs. Try to animate the data instead of showing everything at once (overwhelming).
Strategy #1: "Layer" the Graph. One strategy I often use is something I call "Layering.". Here, you present each data element sequentially, building up your story one data element at a time and walking your audience through your argument. The Layering technique can be applied to almost any slide object including images, graphs, and text.
3. Stacked Column Chart. The stacked chart (also known as a cumulative or stacked chart) is a chart type that can represent the individual components of a composite whole. This chart type is suitable when comparing the composition of something over different time periods or with a different composition.
Presenting and Arranging Data: How To Explain a Graph
17 Best Types of Charts and Graphs for Data Visualization ...
Types of Graphs and Charts and Their Uses
25 Best PowerPoint PPT Chart & Graph Templates for Data ...
To create a simple chart from scratch in PowerPoint, click Insert > Chart and pick the chart you want. Click Insert > Chart. Click the chart type and then double-click the chart you want. Tip: For help deciding which chart is best for your data, see Available chart types. In the worksheet that appears, replace the placeholder data with your own ...
Definition of Graphical Representation of Data
Graphical Representation - Types, Rules ... - BYJU'S
Data Sources - Wherever possible, include the sources of information at the bottom of the graph. Keep it Simple - You should construct a graph which even a layman (without any exposure in the areas of statistics or mathematics) can understand. Neat - A graph is a visual aid for the presentation of data and information.