

Inter-Agency Toolkit | Child Labour Case Studies

Find ALL 34 Case Studies in the Inter-Agency Toolkit on Preventing and Responding to Child Protection in Humanitarian Action!
This website uses cookies
The only cookies we store on your device by default let us know anonymously whether you have seen this message. With your permission, we also set Google Analytics cookies. You can click “Accept all” below if you are happy for us to store cookies (you can always change your mind later). For more information please see our Cookie Policy .
Google Analytics will anonymize and store information about your use of this website, to give us data with which we can improve our users’ experience.
Created in partnership with the Helpdesk on Business & Human Rights
Child Labour
What is child labour.
Child labour is work that harms children’s well-being and hinders their education, development and future livelihood, according to the International Labour Organization ( ILO ). Not all child labour is harmful; for example, if it is light work and does not interfere with a child’s education or right to leisure, such as, children helping their parents on a farm with non-harmful activities or in a shop outside of school hours. Moreover, youth employment and student work are considered legal and may contribute positively to the development of children and young people.
What is the Dilemma?
The dilemma for responsible business is how to address child labour responsibly given the complex social and economic context in which it occurs. While a business may seek to respect the principles contained in international labour standards and national laws on minimum age, removing children (or having children removed) from their operations or supply chains without considering the implications for them could potentially worsen their situation. For example, removing children from the workplace without providing safer and suitable alternatives may leave them vulnerable to more exploitative work elsewhere (e.g. in subcontractor companies), as well as potentially lead to negative health and well-being implications due to increased poverty within their family.

Prevalence of Child Labour
The ILO and UNICEF estimate that 160 million children — 63 million girls and 97 million boys — were in child labour globally at the beginning of 2020, accounting for almost 1 in 10 of all children worldwide. [2] 79 million children (nearly 50% of all children in child labour) were involved in hazardous work such as agriculture or mining, operating dangerous machinery or working at height. However, this number is an approximation — child labour is difficult to quantify as it is often hidden due to its illegal nature. The identification of children in the workplace can be further impeded by a lack of reliable documents such as birth certificates and the fact that it often occurs in rural settings or in areas of cities where authorities have little visibility.
Key trends include:
- Global progress against child labour has stagnated since 2016 despite global efforts to eradicate child labour by 2025, as per target 8.7 [1] of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The COVID-19 crisis threatened to further erode global progress against child labour. ILO estimates suggested that a further 8.9 million children would be in child labour by the end of 2022 due to rising poverty and parental deaths driven by the pandemic.
- Since the start of the pandemic, child labour risks increased in more than 83 countries. Africa remains the highest risk region, with 6 of the 10 highest risk countries ( Verisk Maplecroft ). According to an ILO report published in June 2021, there are more children in child labour in sub-Saharan Africa than in the rest of the world combined.
- The year 2021 was designated as the International Year for the Elimination of Child Labour by UN Member States to further increase global efforts in eliminating child labour.
Impacts on Businesses
Businesses can be impacted by child labour risks in their operations and supply chains in multiple ways:
- Reputational and brand risk : Campaigns by NGOs, trade unions, consumers, media and other stakeholders can result in reduced sales and/or brand erosion.
- Financial risk : Divestment and/or avoidance by investors and finance providers (many of which are increasingly applying environmental, social and governance (ESG) criteria to their decision-making) can result in reduced or more expensive access to capital and reduced shareholder value.
- Legal risk : Legal charges can be brought against the company, up to and including criminal charges, which can result in imprisonment in some countries and usually involve significant fines and/or surrendering of goods produced by child labour (see section ‘ Definition and Legal Instruments ’). Former child workers may also be able to sue their exploitative employers, potentially including companies further up in the supply chain.
- Operational risk : Changes to a company’s supply chains made in response to the discovery of child labour may result in disruption. For example, companies may feel the need to terminate supplier contracts (resulting in potentially higher costs and/or disruption) and direct sourcing activities to lower-risk locations.
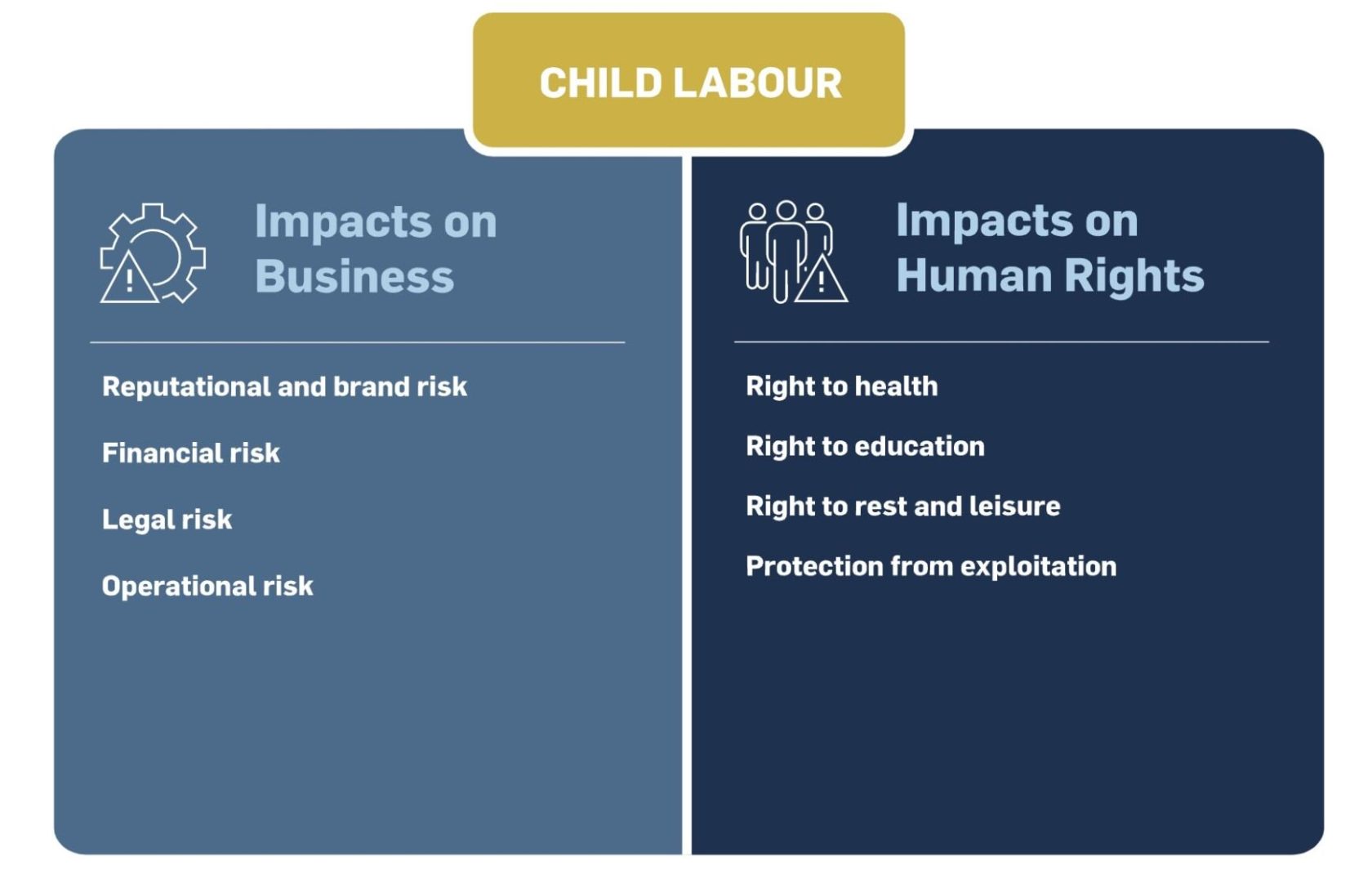
Impacts on Children’s Rights
Child labour has the potential to impact a range of children’s rights, [3] including but not limited to:
- Right to health and to an adequate standard of living ( CRC , Articles 6.2 and 27.1): Children’s health and personal development may be negatively impacted through engagement in work activities, which are not age-appropriate.
- Right to education ( CRC , Article 28): Working hours may preclude children from attending school. Likewise, working children may be too tired to benefit fully from their studies. Children’s ability to learn and join the formal labour market at a later date may also be compromised by child labour.
- Right to rest and leisure and to cultural life ( CRC , Article 31.1): Children involved in child labour often do not have sufficient time to develop socially and culturally through play and interaction with other children.
- Right to protection from economic exploitation ( CRC , Article 32): Children have the right to be protected from economic exploitation. This includes the right to be protected from work that is hazardous or likely to interfere with the child’s health or physical, mental, spiritual, moral or social development.
For further information on children’s rights, please refer to UNICEF’s helpful summary of children’s rights listed in the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
The following SDG targets relate to child labour :
- Goal 8 ( “Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all” ), Target 8.7 : Take immediate and effective measures to eradicate forced labour, end modern slavery and human trafficking and secure the prohibition and elimination of the worst forms of child labour, including recruitment and use of child soldiers, and by 2025 end child labour in all its forms
- Goal 16 ( “Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels” ), Target 16.2 : End abuse, exploitation, trafficking and all forms of violence and torture against children
Progress on these targets and Global Goals will also help advance other goals, for example Goal 3 ( “Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages” ) and Goal 4 ( “Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all” ).
Key Resources
The following resources provide further information on how businesses can address child labour responsibly in their operations and supply chains:
- ILO and UNICEF, Child Labour: Global Estimates 2020, Trends and the Road Forward : The most up-to-date global estimates of child labour from the ILO and UNICEF, including an overview of the impact on child labour from COVID-19.
- ILO and International Organisation of Employers (IOE), Child Labour Guidance Tool for Business : This tool helps companies meet the due diligence requirements laid out in the UN Guiding Principles , as they pertain to child labour.
- Ethical Trading Initiative, Base Code Guidance: Child Labour : A step-by-step guide for businesses on eliminating child labour in global supply chains.
- [email protected]

- High contrast
- Press Centre
Search UNICEF
Action against child labour, selected case studies from unicef programmes.
The International Labour Organization (ILO) and UNICEF latest estimates indicate that 160 million children worldwide are engaged in child labour – that is, work that they are too young to perform or that, by its nature or circumstances, is likely to harm children’s health, safety or morals. This underscores the urgent need for immediate action to eliminate child labour by 2025, a commitment enshrined within Sustainable Development Goal 8.7.1. The persistence of child labour is a human rights violation that not only undermines the health and well-being of children but also poses a challenging threat to national economies and the realization of global development objectives.
Five case studies from different corners of the globe – Costa Rica, Jordan, Timor, Leste, Türkiye and Viet Nam – offer a glimpse into UNICEF continuous efforts to address child labour and tackle its underlying causes. They demonstrate UNICEF collaborative initiatives with national governments, the private sector, international donors and civil society.

Files available for download
Related topics, more to explore, kingdom of saudi arabia pledges us $500 million to protect children around the world from polio and end the disease for good, who and france convene high-level meeting to defeat meningitis.
Acute hunger remains persistently high in 59 countries with 1 in 5 people assessed in need of critical urgent action - Global Report on Food Crises
Global immunization efforts have saved at least 154 million lives over the past 50 years

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Palestinian child labourer at the Israeli settlement of Kalya on the Dead Sea A child labourer in Dhaka, Bangladesh Child coal miners in Prussia, late 19th century A succession of laws on child labour, the Factory Acts, were passed in the UK in the 19th century.Children younger than 9 were not allowed to work, those aged 9-16 could work 12 hours per day per the Cotton Mills Act.
According to the 2016 National Child Labour Survey,6. over 75,000 children are engaged in economic activities, including nearly 45,000 children who are engaged in hazardous forms of labour. Poverty and lack of livelihood opportunities for the family are the main reasons why children work.
Economic hardship exacts a toll on millions of families worldwide - and in some places, it comes at the price of a child's safety. Roughly 160 million children were subjected to child labour at the beginning of 2020, with 9 million additional children at risk due to the impact of COVID-19. This accounts for nearly 1 in 10 children worldwide.
NEW YORK/GENEVA, 10 June 2021 - The number of children in child labour has risen to 160 million worldwide - an increase of 8.4 million children in the last four years - with millions more at risk due to the impacts of COVID-19, according to a new report by the International Labour Organization (ILO) and UNICEF.. Child Labour: Global estimates 2020, trends and the road forward ...
Child Labour Case Studies: 69.9 MB: Find ALL 34 Case Studies in the Inter-Agency Toolkit on Preventing and Responding to Child Protection in Humanitarian Action! Publication type. Learning tools and packages. Topics. Case study. Child Labour. Tags. Child labour. Child Labour Task Force.
than offset the impact of COVID-19 on child labour, returning us to progress on the issue. Other key results from the 2020 global estimates include: • Involvement in child labour is higher for boys than girls at all ages. Among all boys, 11.2 per cent are in child labour compared to 7.8 per cent of all girls. In absolute numbers, boys in child
The purpose of this paper is to review some of the more recent theoretical and empirical research into the topic of child labour, and to illustrate the fact that no one factor on its own can account for the phenomenon of child labour. Therefore, policies aimed at eradicating child labour will need to address the broad range of underlying ...
The ILO and UNICEF estimate that 160 million children — 63 million girls and 97 million boys — were in child labour globally at the beginning of 2020, accounting for almost 1 in 10 of all children worldwide. [2] 79 million children (nearly 50% of all children in child labour) were involved in hazardous work such as agriculture or mining ...
Drawing on a qualitative case study of child labour in Ghana's ASM sector, it is argued that, at the community level, views on maturity and readiness to enter the labour market contrast sharply ...
This study, approved by the Arizona State University Institutional Review Board, focused on criminal cases of persons arrested for child labor trafficking defined as individuals found to be recruiters, contractors, employers, and others who use violence, threats, lies, debt bondage, or other forms of coercion to force people to work against their will in many different industries.
The International Labour Organization (ILO) and UNICEF latest estimates indicate that 160 million children worldwide are engaged in child labour - that is, work that they are too young to perform or that, by its nature or circumstances, is likely to harm children's health, safety or morals. This underscores the urgent need for immediate ...
A Case Study of Child Labour Krishna Raj Fellowship 2012 Ananya Smriti, Devkanya Chakravarty, Garima Wahi, Jasmine Kaur, Shiny Kundu . Abstract ... Child labour is a grave developmental problem and a potential impediment to the overall socio-economic progress of a country. It is a violation of child as well as human rights.
The studies identify new feature osf child labour with important policy implica-tions. First b, y comparing the participation rate ans d age at first participatio onf 2 Edward Higgs, ... Case Studies from Europe, Japan and Colombia. Ed. by Hugh Cunningham and Pier Paolo Viazzo. UNICEF International Child Development Centre, Florence; Istituto ...
The List of countries by child labour rate provides rankings of countries based on their rates of child labour.Child labor is defined by the International Labour Organization (ILO) as participation in economic activity by underage persons aged 5 to 17. Child work harms children, interferes with their education, and prevents their development. The prevalence of child labor is notable in regions ...
The ban on Oct. 10 was incorporated into the Child Labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Act of 1986 which had already banned children under 14 from working in high-risk industries such as matchstick-making. Those convicted of employing a child under 14 can be jailed for up to two years and/or fined a maximum amount of 20,000 rupees ($450).
The International Labour Organization (ILO) and UNICEF latest estimates indicate that 160 million children worldwide are engaged in child labour - that is, work that they are too young to perform or that, by its nature or circumstances, is likely to harm children's health, safety or morals. This underscores the urgent need for immediate action to eliminate child labour by 2025, a ...
Labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Act 1986, the term child labour refers to a person who has not completed the age of 14. Like age, what constitutes work (i.e. child labour) is also not uniquely defined. According to the International Labour Organisation (ILO), the term ―child labour‖ is often defined as work
Case 1: Case Study of Puii. Puii is a thirteen and half year old girl living in Aizawl District. She is the eldest child in her family and has three sisters and two brothers. Family does not own a house and is living in rented house. Her parents are uneducated and their occupation is stone crushing on daily basis.
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. [7] In 2019, there were about 140.11 million human births globally. [9] In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, [10 ...