

Speech On Social Media- Advantages, Disadvantages and Importance

Table of Contents
Speech On Social Media: In a world where clicks, likes, and shares have become the currency of our social interactions, there’s no denying the pervasive influence of social media. It’s a digital realm that has seamlessly woven itself into the fabric of our lives, altering how we connect, communicate, and consume information. From connecting with long-lost friends to voicing our opinions on global issues, social media has transformed the way we navigate our interconnected world. But what lies beneath the surface of those enticing timelines and trending hashtags?
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---

Students often encounter the task of giving speeches on various topics, and social media is a fascinating subject for exploration. In this article, we will embark on a journey to explore the captivating and complex realm of social media. We have provided a few sample speech topics on social media, highlighting its advantages, disadvantages, and the profound impact it has on our lives.
Long and Short Speeches on Social Media in English
Speech on advantages and disadvantages of social media for students – sample 1.
Ladies and gentlemen,
Today, I stand before you to discuss a topic that has become an integral part of our lives – social media. It’s hard to imagine a world without platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok. Social media has transformed the way we connect, communicate, and share information. But, like every coin has two sides, social media has its advantages and disadvantages.
Let’s start with the positive aspects. Here are the pros of social media. Social media bridges geographical gaps, allowing us to connect with friends and family worldwide. It’s a powerful tool for sharing our thoughts, experiences, and achievements. Students benefit from it as a valuable resource for learning and research. Moreover, it’s a platform for raising social awareness, promoting businesses, and even finding job opportunities.
However, we must also acknowledge the downsides. Excessive use of social media can lead to addiction and affect mental health. It’s a breeding ground for cyberbullying, misinformation, and privacy invasion. Moreover, the constant exposure to idealized images and lives can negatively impact self-esteem.
In conclusion, social media is a double-edged sword. It has revolutionized the way we communicate and share, offering numerous advantages. Yet, we must navigate it cautiously, being mindful of its pitfalls. Let’s use it responsibly and harness its potential for good.
Speech on Technology Speech on Internet Essay on Uses of Internet

Speech on Impact of Social Media – Sample 2
Good day, everyone,
The topic I’d like to address today is the impact of social media on our lives. There’s no denying that social media has become an inseparable part of our daily routine. From connecting with friends to keeping up with the latest trends, it’s all at our fingertips.
Let’s dive into the advantages of social media. Social media allows us to stay connected with friends and family, regardless of distance. It’s a treasure trove of information, news, and educational content. For students, it offers a platform to collaborate on projects and access a wealth of knowledge. Businesses utilize it for marketing and customer engagement.
However, there’s another side to the story. Social media can be addictive, leading to time wastage and reduced productivity. Privacy concerns are a pressing issue, with personal information often at risk. Cyberbullying and the spread of fake news are unfortunate consequences of its widespread use.
So, where do we stand? Social media is a tool, and its impact depends on how we use it. It can bring us closer or push us apart. It can educate or misinform. The choice is ours.
In conclusion, social media has its merits and demerits. It’s up to us to harness its advantages while being vigilant about its pitfalls. Let’s use it wisely, striking a balance between the virtual and real worlds.
Thank you for your attention.
Speech on Social Media Topic in English – Sample 3
I’m delighted to address you on a topic that has reshaped our world – social media. In today’s digital age, it’s nearly impossible to escape its influence. So, let’s explore the impact and significance of social media.
To begin with, social media has revolutionized communication. It connects people worldwide, making the world a smaller place. It’s a powerful tool for staying informed about current events and trends. For students, it’s a treasure trove of educational resources. Entrepreneurs and businesses leverage it for promotion and brand building.
Yet, there’s a flip side. The addictive nature of social media can lead to time wastage. Privacy concerns loom large, as our personal information is often shared and exploited. The spread of misinformation and cyberbullying are unfortunate consequences.
So, where do we go from here? It’s crucial to strike a balance. Use social media as a tool for enrichment, connection, and empowerment. But also, be mindful of its addictive nature and potential pitfalls. Let’s make informed choices in our digital journeys.
In conclusion, social media is a force that’s here to stay. It’s up to us to harness its advantages while being vigilant about its drawbacks. Let’s make our online presence a positive and enriching one.
Social media has become an integral part of our daily lives, revolutionizing the way we connect, communicate, and share information. From its myriad benefits to the nuanced drawbacks, understanding the multifaceted role of social platforms is crucial in today’s digital landscape.
Lets see the Advantages, Disadvantages and Importance of Online Networking

1. Global Connectivity and Networking Social media bridges geographical barriers, enabling individuals to connect globally. It facilitates networking opportunities, fostering professional relationships and personal connections.
2. Information Dissemination and Awareness Instantaneous sharing allows for rapid dissemination of information. Be it news, trends, or educational content, social media serves as a powerful tool for spreading awareness and initiating discussions on various topics.
3. Business Growth and Marketing Businesses leverage social platforms to expand their reach, engage with audiences, and market their products/services. Targeted ads and analytics help businesses create effective strategies.
4. Community Building and Support Social media brings people together around common interests, creating spaces for support, self-expression, advice, and finding similar-minded individuals.
Disadvantages
1. Privacy and Security Concerns Privacy breaches and data misuse remain significant concerns. Users often share sensitive information unknowingly, leading to potential security risks and exploitation by third parties.
2. Addiction and Mental Health Impact Excessive usage can lead to addiction and have adverse effects on mental health. Constant exposure to curated, often idealized content can fuel feelings of inadequacy and anxiety.
3. Spread of Misinformation False information can spread rapidly, impacting opinions and beliefs. Misleading content, rumors, and fake news pose a challenge in maintaining an informed society.
4. Online Harassment and Cyberbullying Social media platforms can be breeding grounds for cyberbullying and harassment. Anonymity and easy accessibility empower individuals to engage in harmful behaviors.
1. Communication Evolution Social media has transformed communication by providing instant connectivity across the globe. It has redefined how people interact, share ideas, and collaborate.
2. Information Accessibility It democratizes information, making knowledge accessible to diverse populations regardless of geographic or socioeconomic barriers.
3. Catalyst for Change It serves as a catalyst for societal change by amplifying voices, raising awareness about social issues, and mobilizing movements for positive causes.
4. Business Adaptation For businesses, social media is an indispensable tool, enabling them to adapt to changing consumer behaviors, innovate marketing strategies, and engage with their target audience effectively.
Also Read: Disadvantages of Using Social Media During Online classes

FAQ’s
Why is social media important speech.
A speech on the importance of social media can highlight its role in connecting people, facilitating communication, sharing information, and its impact on various aspects of our lives.
What is social media in easy words?
Social media is websites and applications that enable users to create and share content, connect with others, and participate in online communities by sharing thoughts, pictures, videos, and messages.
What is the importance of social media in students?
Social media offers students platforms for collaboration, learning, networking, and accessing information. It can aid in educational research, career opportunities, and building connections.
Why is social media important?
Social media is important as it helps in staying connected with friends and family, accessing news and information, promoting businesses, fostering communities, and providing a platform for self-expression.
Write a 1-minute speech on social media?
Social media has revolutionized the way we connect and communicate. It bridges distances, opens doors to new opportunities, and allows us to share our stories with the world. From keeping in touch with loved ones to exploring new interests, social media has become an integral part of our lives, shaping how we learn, work, and interact in today's digital age.
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
The power of social media
Social media is an undeniable force in today's world. These talks highlight its impact -- from big history-defining moments to the silliness we’ve come to expect.

How social media can make history

What does it mean to be a citizen of the world?

How social networks predict epidemics

Social media and the end of gender

The power and the danger of online crowds

How to make a splash in social media

Inside the Egyptian revolution

Online social change: easy to organize, hard to win
- Speech Topics For Kids
Speech on Social Media
Still thinking about what to include in your speech on social media? How to make your speech stand apart from others? This article will help you to give a good speech on social media. Social media is considered to be both a blessing and a curse. Let’s see how social media plays a role in inspiring and motivating people as well as demotivating and distracting people.
Table of Contents
What do you mean by social media, advantages of social media, disadvantages of social media.
- FAQs on Speech on Social Media
We all have heard about the term ‘social media’ and are quite familiar with it, but what does the term mean? Social media is one of the mediums for communication and content development. Social media allows one to share information, opinions, ideas and many other things and also to create one. Now, there are two different views about social media. One group of people think that social media has a bad influence on people, whereas the other thinks that social media has a lot of positive outcomes. A good speech on social media will cover both aspects.
There are those who vouch for social media, these are the reasons why they do so:
- It is through social media that one develops a large audience. If someone is all set to promote their art, business or work, social media turns out to be a tool to reach a large number of people easily.
- Social media has a major role in connecting people. People who live far away from their families and friends who have grown apart with time can get connected to one another. With social media, the distance decreases between people.
- It is through social media that people learn about events/happenings from around the world. Any news travels faster and reaches peoples’ ears within no time.
Apart from acting as a boon, social media has some disadvantages too. Some of them are mentioned below.
- Frequent use of social media has increased the screen time, which in turn, has caused a rise in physical ailments.
- Continuous use of social media can also make people lazy and lethargic.
Frequently Asked Questions on Speech on Social Media
Does social media have both pros and cons.
Yes, just like two faces of a coin, social media too, has both pros and cons.
What are the advantages of social media?
- It is through social media that people learn about events/happenings from around the world. Any news travels faster and reaches peoples’ ears within no time.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Table of Contents
Benefits of social media for businesses, social media trends and future outlook, importance of social media in 2024 and beyond.

Key Takeaways: Social media fosters global connectivity by bridging communication gaps across demographics and professions. Strategic social media usage yields success through direct audience engagement and targeted content creation. Businesses benefit from social media's diverse advantages, including direct audience contact, increased exposure, and lasting brand impressions.
Everyone today is on some social media platform . Teenagers on TikTok, influencers and small businesses on Instagram and Facebook , or professionals on LinkedIn - social media is the first option that comes to mind when looking for expanding connections in any field.
Social media - if used intelligently - can bring in loads of success. Since it is the best form of direct contact with the target audience, these platforms have what it takes to make anyone's life better. To understand this better, here are a few aspects that reflect the importance of social media in today's world.
1. Staying Connected With the People
It is next to impossible to meet your friends and relatives every day in today's world of increasing stress and workload. However, dropping a short text asking about their day or sharing your achievements are a few ways you can still maintain healthy contact with your close ones or corporate colleagues. Social media platforms have effectively bridged this communication gap.
2. Staying Opinionated
In our daily lives, we may not necessarily be surrounded by people who think in the same direction as we do. A difference in opinion is bound to occur. However, we can share our opinions safely and even find people online who think the same way as us on social media platforms. It even paves the way to gaining a strong voice for the situations you feel are essential to discuss and have a fruitful discussion.
Become a Digital Marketing Professional
Post graduate program in digital marketing.
- Joint Purdue-Simplilearn Digital Marketer Certificate
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Allan Joaquin
Senior copywriter , ami group.
Completing the PGP in Digital Marketing course and gaining knowledge in the field allowed me to service new clients who needed consultancy on digital marketing strategies. I was also able to increase my revenue by 50%.
Michael Anastasiadis
I have recently completed Simplilearn’s Digital Marketing Program. This unique experience was full of live classes, e-learning content, real-world projects and tests. And I gained extensive knowledge regarding all basic disciplines of digital marketing: SEO, Social Media, Content Marketing, Email Marketing, PPC, and more.
3. Entertainment
There is so much more to social media than just work, communication and branding. Sometimes, all we want is a little entertainment at the end of the day. Social media platforms provide tired individuals with customized feeds consisting of memes, news, and short clips of videos as per the user's activity. It provides people with a much-needed break from their busy schedules.
1. Direct Contact With Target Audience
Thanks to social media platforms, you don't have to call or email people randomly to check if they are interested in your brand or not. With almost the whole world on social media, it is now possible that your target audience is simply a click away from you. Using hashtags, you can directly land your brand on your target audiences' page - giving yourself an enormous reach.
2. Increasing Popularity With Ease
For people in the content and digital marketing arena, the ability to attract popularity is what matters most. The social media platforms provide such a section of people with precisely what they're looking for - increased exposure. Carrying out simple, engaging tasks such as answering queries, posting times, and so on would ensure that you blow up on these sites after some time. Even though it requires some time investment, the hefty returns are worth it at the end of the day.
3. Better Traffic
Since there is a wide diversity of active people on social media, the scope for diverse traffic is also broadened. Optimizing social media per your needs can ensure that you receive visits and traffic from various people. Since today people are on their phones most of the time, it is highly likely that people would come across your brand or work. Proper usage of keywords and other SEO guidelines would also ensure heavier and better traffic.
4. Create a Lasting Image
If you are looking to work so that your piece of content leaves an imprint on the viewer's brain, using social media is the best way to go about it. Granted, people do look at their emails too. But how often can we find people spending hours surfing through their emails? In contrast, people love spending countless hours surfing through social media on their phones. Hence, if you can optimize your work efficiently there, you will likely leave your mark.
5. Collaborations
Another effective way social media platforms benefit businesses is by providing the means to collaborate with appropriate accounts. Today, there are many influencers on every social media platform - each open to promoting the product they deem fit for their followers. Businesses looking to grow usually contact such influencers who do pay ads on their page, bringing heavy traffic to the business account.
6. Availability of Tools for Analysis
Another aspect of social media that fuels its importance amongst businesses and content creators is the option to look into the insights. Hence, business and content accounts can analyze their posts and understand which post gained the most popularity and why - and how they can improve their feed. On Instagram, there is an option for post insights for professional accounts - where one can see which posts got the most saves, likes, or reaches.
7. Get Inspired
Since most content and business pages are public, one can quickly go through their feeds and gain inspiration. If your account is not doing exceptionally well compared to the other accounts in the field, you can analyze their feeds and see what you're missing out on. Fixing these problems may help boost your popularity immensely.
In the fast-paced world of digital connectivity, social media platforms continue to shape how we communicate, consume information, and interact with brands. As we venture further into the digital age, understanding the latest social media trends and anticipating future developments becomes paramount for individuals and businesses alike. Let's delve into the evolving landscape of social media and explore what the future may hold.
Rise of New Platforms and Features
Social media is a dynamic ecosystem, constantly evolving with the introduction of new platforms and features. From the explosive growth of TikTok to the emergence of audio-based platforms like Clubhouse, users are seeking novel ways to engage and express themselves. Additionally, platforms like Instagram and LinkedIn are rolling out innovative features such as Reels and Stories, catering to the growing demand for short-form, visually compelling content.
Changing User Behavior
As technology advances and consumer preferences shift, so too does user behavior on social media. The era of passive scrolling is giving way to more interactive and immersive experiences. Live streaming, interactive polls, and AR filters are becoming increasingly popular, providing users with opportunities for real-time engagement and co-creation of content. Moreover, the preference for authentic, relatable content is driving users to seek out genuine connections with creators and brands.
Privacy and Trust
With concerns about data privacy and online security on the rise, social media platforms are under increasing scrutiny to prioritize user privacy and transparency. Stricter regulations, such as the GDPR and CCPA, are reshaping the way platforms collect, store, and utilize user data. As consumers become more discerning about sharing personal information, brands must navigate this landscape carefully, earning trust through transparent data practices and ethical use of customer data.
Social Commerce and the Future of E-Commerce
The convergence of social media and e-commerce, known as social commerce, is transforming the way we shop and discover products online. Platforms like Facebook and Instagram are blurring the lines between content and commerce, enabling users to shop directly from posts and ads. As social commerce continues to evolve, we can expect to see more personalized shopping experiences, influencer-driven purchasing decisions, and integration of AR technology for virtual try-on experiences.
Influencer Marketing and Authenticity
Influencer marketing has become a cornerstone of many brands' digital strategies, leveraging the reach and influence of content creators to connect with target audiences. However, as consumers grow weary of inauthentic endorsements and sponsored content, the demand for genuine, relatable influencers is on the rise. Micro-influencers, with their niche audiences and high engagement rates, are gaining traction as brands seek to forge deeper connections with consumers.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
The regulatory landscape surrounding social media is evolving rapidly, with governments around the world enacting legislation to protect user privacy and combat misinformation. Platforms are facing increasing pressure to implement robust content moderation policies, combat hate speech and disinformation, and ensure transparency in political advertising. Navigating these regulations requires a nuanced understanding of legal requirements and a commitment to ethical practices.
Even though the extreme usage of social media is a debatable topic, we can never overlook the importance of social media and the immense opportunities that it provides its users with. With various benefits and validations of the importance of social media listed above, hopefully, you will be able to use these platforms for your benefit as much as possible. If you wish to master social media marketing you should enroll in Simplilearn's Post Graduate Program in Digital Marketing and become a successful AI-driven marketer!
1. What makes Social Media so impactful in today’s world?
Ans. One of the most important impacts of social media in today's world lies within its ability to distribute information to the whole world. With most people on some other social media platforms today, no news of importance cools down without proper discussion. By doing so, social media platforms act as a unifying unit of various kinds of people.
2. What will happen if Social Media goes down in the near future?
Ans. As we head closer to a developed society every single day, the scope of digitalization broadens. With this key fact in mind, there are no chances of social media and its importance going down anytime soon. If anything, the importance and dependence on social media are only predicted to increase as time passes.
Our Digital Marketing Courses Duration And Fees
Digital Marketing Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Digital Marketing
Introduction to Digital Marketing Fundamentals Course
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
Get the First Mover Advantage with AI in Digital Marketing
How to Pivot Your Digital Marketing to the New Normal: Expert Tips and Strategies
Deep Dive into AI's Impact on Content in Digital Age
Recommended Reads
Free eBook: Essentials of Social Media Marketing
Top Social Media Apps for 2024
What is Social Media Marketing?
Introductory Digital Marketing Guide
Are You Making These Social Media Mistakes
The Top Social Media Marketing Tips and Tricks for 2020
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

Social Media's Impact on Society

This article was updated on: 11/19/2021
Social media is an undeniable force in modern society. With over half the global population using social platforms, and the average person spending at least two hours scrolling through them every day , it can’t be overstated that our digital spaces have altered our lives as we knew them. From giving us new ways to come together and stay connected with the world around us, to providing outlets for self-expression, social media has fundamentally changed the way we initiate, build and maintain our relationships.
But while these digital communities have become commonplace in our daily lives, researchers are only beginning to understand the consequences of social media use on future generations. Social media models are changing every day, with major platforms like Meta and Instagram evolving into primary digital advertising spaces as much as social ones. A critical responsibility falls on marketers to spread messages that inform, rather than contribute to the sea of misinformation that thrives on social media.
Read on to see what’s on marketers’ minds when it comes to the impact of social media on society:
MENTAL HEALTH
You’ve likely heard about the negative impacts that social media can have on mental health. Experts are weighing in on the role that the algorithms and design of social platforms play in exasperating these concerns.
At SXSW 2019 , Aza Raskin, co-founder of the Center for Human Technology, talked about the “digital loneliness epidemic,” which focused on the rise of depression and loneliness as it relates to social media use. During the panel, Raskin spoke about the “infinite scroll,” the design principle that enables users to continuously scroll through their feeds, without ever having to decide whether to keep going—it’s hard to imagine what the bottom of a TikTok feed would look like, and that’s intentional. But with the knowledge that mental health concerns are undeniably linked to social media use, the dilemma we’re now facing is when does good design become inhumane design?
Arguably, Rankin’s term for social media use could now be renamed the “digital loneliness pandemic ” as the world faces unprecedented isolation during the COVID-19 outbreak. In 2020 the Ad Council released a study exploring factors that cause loneliness, and what can be done to alleviate it. Interestingly, our research found that while social isolation is one factor that can cause loneliness, 73% of respondents typically maintain interpersonal relationships via technology, including engaging with others on social media. Simply put, social media use can both contribute to and help mitigate feelings of isolation. So how do we address this Catch-22? We should ask ourselves how we can use social media as a platform to foster positive digital communities as young adults rely on it more and more to cope with isolation.
Findings like these have been useful as we reexamine the focuses of Ad Council campaigns. In May 2020, our iconic Seize the Awkward campaign launched new creative highlighting ways young people could use digital communications tools to stay connected and check in on one another’s mental health while practicing physical distancing. A year later, we launched another mental health initiative, Sound It Out , which harnesses the power of music to speak to 10-14-year-olds’ emotional wellbeing. Ad Council has seen the importance of spreading awareness around mental health concerns as they relate to social media consumption in young adults—who will become the next generation of marketers.
EXTREMISM & HATE
Another trend on experts’ minds is how the algorithms behind these massively influential social media platforms may contribute to the rise of extremism and online radicalization.
Major social networking sites have faced criticism over how their advanced algorithms can lead users to increasingly fringe content. These platforms are central to discussions around online extremism, as social forums have become spaces for extreme communities to form and build influence digitally. However, these platforms are responding to concerns and troubleshooting functionalities that have the potential to result in dangerous outcomes. Meta, for example, announced test prompts to provide anti-extremism resources and support for users it believes have been exposed to extremist content on their feeds.
But as extremist groups continue to turn to fringe chatrooms and the “dark web” that begin on social media, combing through the underbelly of the internet and stopping the spread of hateful narratives is a daunting task. Promoting public service messages around Racial Justice and Diversity & Inclusion are just some of the ways that Ad Council and other marketers are using these platforms to move the needle away from hateful messaging and use these platforms to change mindsets in a positive way.
PUBLIC HEALTH CRISES
Social media can be both a space to enlighten and spread messages of doubt. The information age we’re all living in has enabled marketers to intervene as educators and providers of informative messaging to all facets of the American public. And no time has this been more urgent than during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Public health efforts around mask mandates and vaccine rollouts have now become increasingly polarized issues. Social media platforms have turned into breeding grounds for spreading disinformation around vaccinations, and as a result, has contributed to vaccine hesitancy among the American public. Meta, Instagram, and other platforms have begun to flag certain messages as false, but the work of regulating misinformation, especially during a pandemic, will be an enduring problem. To combat this, Ad Council and the COVID Collaborative have put a particular emphasis on our historic COVID-19 Vaccine Education initiative, which has connected trusted messengers with the “uncommitted” American public who feel the most uncertainty around getting the vaccine.
Living during a global pandemic has only solidified a societal need for social media as a way to stay connected to the world at large. During the pandemic, these platforms have been used to promote hopeful and educational messages, like #AloneTogether , and ensures that social media marketing can act as a public service.
DIGITAL ACTIVISM
Beyond serving as an educational resource, social media has been the space for digital activism across a myriad of social justice issues. Movements like #MeToo and #BlackLivesMatter have gone viral thanks to the power of social media. What starts as a simple hashtag has resulted in real change, from passing sexual harassment legislation in response to #MeToo, to pushing for criminal justice reform because of BLM activists. In these cases, social media empowered likeminded people to organize around a specific cause in a way not possible before.
It’s impossible to separate the role of social media from the scalable impact that these movements have had on society. #MeToo and BLM are just two examples of movements that have sparked national attention due in large part to conversations that began on social media.
SO, WHAT DOES THIS MEAN FOR MARKETERS?
Social media is a great equalizer that allows for large-scale discourse and an endless, unfiltered stream of content. Looking beyond the repercussions for a generation born on social media, these platforms remain an essential way for marketers to reach their audiences.
Whether you argue there are more benefits or disadvantages to a world run on social media, we can all agree that social media has fundamentally shifted how society communicates. With every scroll, view, like, comment and share, we’re taught something new about the impact of social media on the way we think and see the world.
But until we find a way to hold platforms more accountable for the global consequences of social media use, it’s up to marketers to use these digital resources as engines of progressive messaging. We can’t control the adverse effects of the Internet, but as marketers, we can do our part in ensuring that the right messages are being spread and that social media remains a force for social good.

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTERS
Want to stay up to date on industry news, insights, and all our latest work? Subscribe to our email newsletters!
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
How to Use Social Media Wisely and Mindfully
It was no one other than Facebook’s former vice president for user growth, Chamath Palihapitiya, who advised people to take a “hard break” from social media. “We have created tools that are ripping apart the social fabric of how society works,” he said recently .
His comments echoed those of Facebook founding president Sean Parker . Social media provides a “social validation feedback loop (‘a little dopamine hit…because someone liked or commented on a photo or a post’),” he said. “That’s exactly the thing a hacker like myself would come up with because you’re exploiting a vulnerability in human psychology.”
Are their fears overblown? What is social media doing to us as individuals and as a society?

Since over 70 percent of American teens and adults are on Facebook and over 1.2 billion users visit the site daily—with the average person spending over 90 minutes a day on all social media platforms combined—it’s vital that we gain wisdom about the social media genie, because it’s not going back into the bottle. Our wish to connect with others and express ourselves may indeed come with unwanted side effects.
The problems with social media
Social media is, of course, far from being all bad. There are often tangible benefits that follow from social media use. Many of us log on to social media for a sense of belonging, self-expression, curiosity, or a desire to connect. Apps like Facebook and Twitter allow us to stay in touch with geographically dispersed family and friends, communicate with like-minded others around our interests, and join with an online community to advocate for causes dear to our hearts.
Honestly sharing about ourselves online can enhance our feelings of well-being and online social support, at least in the short term. Facebook communities can help break down the stigma and negative stereotypes of illness, while social media, in general, can “serve as a spring board” for the “more reclusive…into greater social integration,” one study suggested.
But Parker and Palihapitiya are on to something when they talk about the addictive and socially corrosive qualities of social media. Facebook “addiction” (yes, there’s a test for this) looks similar on an MRI scan in some ways to substance abuse and gambling addictions. Some users even go to extremes to chase the highs of likes and followers. Twenty-six-year-old Wu Yongning recently fell to his death in pursuit of selfies precariously taken atop skyscrapers.
Facebook can also exacerbate envy . Envy is nothing if not corrosive of the social fabric, turning friendship into rivalry, hostility, and grudges. Social media tugs at us to view each other’s “highlight reels,” and all too often, we feel ourselves lacking by comparison. This can fuel personal growth, if we can turn envy into admiration, inspiration, and self-compassion ; but, instead, it often causes us to feel dissatisfied with ourselves and others.
For example, a 2013 study by Ethan Kross and colleagues showed quite definitively that the more time young adults spent on Facebook, the worse off they felt. Participants were texted five times daily for two weeks to answer questions about their well-being, direct social contact, and Facebook use. The people who spent more time on Facebook felt significantly worse later on, even after controlling for other factors such as depression and loneliness.
Interestingly, those spending significant time on Facebook, but also engaging in moderate or high levels of direct social contact, still reported worsening well-being. The authors hypothesized that the comparisons and negative emotions triggered by Facebook were carried into real-world contact, perhaps damaging the healing power of in-person relationships.
More recently, Holly Shakya and Nicholas Christakis studied 5,208 adult Facebook users over two years, measuring life satisfaction and mental and physical health over time. All these outcomes were worse with greater Facebook use, and the way people used Facebook (e.g., passive or active use, liking, clicking, or posting) didn’t seem to matter.
“Exposure to the carefully curated images from others’ lives leads to negative self-comparison, and the sheer quantity of social media interaction may detract from more meaningful real-life experiences,” the researchers concluded.
How to rein in social media overuse
So, what can we do to manage the downsides of social media? One idea is to log out of Facebook completely and take that “hard break.” Researcher Morten Tromholt of Denmark found that after taking a one-week break from Facebook, people had higher life satisfaction and positive emotions compared to people who stayed connected. The effect was especially pronounced for “heavy Facebook users, passive Facebook users, and users who tend to envy others on Facebook.”
We can also become more mindful and curious about social media’s effects on our minds and hearts, weighing the good and bad. We should ask ourselves how social media makes us feel and behave, and decide whether we need to limit our exposure to social media altogether (by logging out or deactivating our accounts) or simply modify our social media environment. Some people I’ve spoken with find ways of cleaning up their newsfeeds—from hiding everyone but their closest friends to “liking” only reputable news, information, and entertainment sources.
Knowing how social media affects our relationships, we might limit social media interactions to those that support real-world relationships. Instead of lurking or passively scrolling through a never-ending bevy of posts, we can stop to ask ourselves important questions, like What are my intentions? and What is this online realm doing to me and my relationships?
We each have to come to our own individual decisions about social media use, based on our own personal experience. Grounding ourselves in the research helps us weigh the good and bad and make those decisions. Though the genie is out of the bottle, we may find, as Shakya and Christakis put it, that “online social interactions are no substitute for the real thing,” and that in-person, healthy relationships are vital to society and our own individual well-being. We would do well to remember that truth and not put all our eggs in the social media basket.
About the Author

Ravi Chandra
Ravi Chandra is a psychiatrist, writer, and compassion educator in San Francisco, and a distinguished fellow of the American Psychiatric Association. Here’s his linktree .
You May Also Enjoy

What Is Your Phone Doing to Your Relationships?

Can Mindfulness Stop Internet Addiction in Teens?

How Smartphones Are Killing Conversation

How—and Why—to Take Your Life Back from Email

Five Tips for Helping Teens Manage Technology

Happiness Tip: Stop Checking Your Freaking Phone

1 Minute Speech on the Importance of Social Media In English
A very good morning to one and all present here. Today, I’ll be giving a short speech on the topic of the importance of social media.
Google defines the term ‘social media’ to be “websites and applications that enable users to create and share content or to participate in social networking.” Simply put, social media is an amalgamation of the predominant rulers of our lives- namely, Whatsapp, Instagram, and Twitter to say a few!
Now yes, social media, arguably, can cause harm. At the same time, it is important to understand that we also cannot simply do away with social media or live without it, given its importance.
Social media today is a very important source of communication, news, and the happenings of the world not just regionally but on the global level. With social media, one is enabled to gain a lot of knowledge and a better understanding of the world. Social media thus offers a wide platform to explore various things.
Use it wisely!
Related Posts:
- The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock Poem By Thomas Stearns Eliot Summary, Notes And Line By Line Analysis In English
- Michael Poem by William Wordsworth Summary, Notes and Line by Line Explanation in English
- How to Summarize a Presentation: 5 Easy Steps
- Howl Poem By Allen Ginsberg Summary, Notes and Line by Line Explanation in English
- Random University Name Generator
- How Does Homework Help You Be Smarter?

Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Why social media has changed the world — and how to fix it
Press contact :, media download.

*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."

Previous image Next image
Are you on social media a lot? When is the last time you checked Twitter, Facebook, or Instagram? Last night? Before breakfast? Five minutes ago?
If so, you are not alone — which is the point, of course. Humans are highly social creatures. Our brains have become wired to process social information, and we usually feel better when we are connected. Social media taps into this tendency.
“Human brains have essentially evolved because of sociality more than any other thing,” says Sinan Aral, an MIT professor and expert in information technology and marketing. “When you develop a population-scale technology that delivers social signals to the tune of trillions per day in real-time, the rise of social media isn’t unexpected. It’s like tossing a lit match into a pool of gasoline.”
The numbers make this clear. In 2005, about 7 percent of American adults used social media. But by 2017, 80 percent of American adults used Facebook alone. About 3.5 billion people on the planet, out of 7.7 billion, are active social media participants. Globally, during a typical day, people post 500 million tweets, share over 10 billion pieces of Facebook content, and watch over a billion hours of YouTube video.
As social media platforms have grown, though, the once-prevalent, gauzy utopian vision of online community has disappeared. Along with the benefits of easy connectivity and increased information, social media has also become a vehicle for disinformation and political attacks from beyond sovereign borders.
“Social media disrupts our elections, our economy, and our health,” says Aral, who is the David Austin Professor of Management at the MIT Sloan School of Management.
Now Aral has written a book about it. In “The Hype Machine,” published this month by Currency, a Random House imprint, Aral details why social media platforms have become so successful yet so problematic, and suggests ways to improve them.
As Aral notes, the book covers some of the same territory as “The Social Dilemma,” a documentary that is one of the most popular films on Netflix at the moment. But Aral’s book, as he puts it, "starts where ‘The Social Dilemma’ leaves off and goes one step further to ask: What can we do about it?”
“This machine exists in every facet of our lives,” Aral says. “And the question in the book is, what do we do? How do we achieve the promise of this machine and avoid the peril? We’re at a crossroads. What we do next is essential, so I want to equip people, policymakers, and platforms to help us achieve the good outcomes and avoid the bad outcomes.”
When “engagement” equals anger
“The Hype Machine” draws on Aral’s own research about social networks, as well as other findings, from the cognitive sciences, computer science, business, politics, and more. Researchers at the University of California at Los Angeles, for instance, have found that people obtain bigger hits of dopamine — the chemical in our brains highly bound up with motivation and reward — when their social media posts receive more likes.
At the same time, consider a 2018 MIT study by Soroush Vosoughi, an MIT PhD student and now an assistant professor of computer science at Dartmouth College; Deb Roy, MIT professor of media arts and sciences and executive director of the MIT Media Lab; and Aral, who has been studying social networking for 20 years. The three researchers found that on Twitter, from 2006 to 2017, false news stories were 70 percent more likely to be retweeted than true ones. Why? Most likely because false news has greater novelty value compared to the truth, and provokes stronger reactions — especially disgust and surprise.
In this light, the essential tension surrounding social media companies is that their platforms gain audiences and revenue when posts provoke strong emotional responses, often based on dubious content.
“This is a well-designed, well-thought-out machine that has objectives it maximizes,” Aral says. “The business models that run the social-media industrial complex have a lot to do with the outcomes we’re seeing — it’s an attention economy, and businesses want you engaged. How do they get engagement? Well, they give you little dopamine hits, and … get you riled up. That’s why I call it the hype machine. We know strong emotions get us engaged, so [that favors] anger and salacious content.”
From Russia to marketing
“The Hype Machine” explores both the political implications and business dimensions of social media in depth. Certainly social media is fertile terrain for misinformation campaigns. During the 2016 U.S. presidential election, Russia spread false information to at least 126 million people on Facebook and another 20 million people on Instagram (which Facebook owns), and was responsible for 10 million tweets. About 44 percent of adult Americans visited a false news source in the final weeks of the campaign.
“I think we need to be a lot more vigilant than we are,” says Aral.
We do not know if Russia’s efforts altered the outcome of the 2016 election, Aral says, though they may have been fairly effective. Curiously, it is not clear if the same is true of most U.S. corporate engagement efforts.
As Aral examines, digital advertising on most big U.S. online platforms is often wildly ineffective, with academic studies showing that the “lift” generated by ad campaigns — the extent to which they affect consumer action — has been overstated by a factor of hundreds, in some cases. Simply counting clicks on ads is not enough. Instead, online engagement tends to be more effective among new consumers, and when it is targeted well; in that sense, there is a parallel between good marketing and guerilla social media campaigns.
“The two questions I get asked the most these days,” Aral says, “are, one, did Russia succeed in intervening in our democracy? And two, how do I measure the ROI [return on investment] from marketing investments? As I was writing this book, I realized the answer to those two questions is the same.”
Ideas for improvement
“The Hype Machine” has received praise from many commentators. Foster Provost, a professor at New York University’s Stern School of Business, says it is a “masterful integration of science, business, law, and policy.” Duncan Watts, a university professor at the University of Pennsylvania, says the book is “essential reading for anyone who wants to understand how we got here and how we can get somewhere better.”
In that vein, “The Hype Machine” has several detailed suggestions for improving social media. Aral favors automated and user-generated labeling of false news, and limiting revenue-collection that is based on false content. He also calls for firms to help scholars better research the issue of election interference.
Aral believes federal privacy measures could be useful, if we learn from the benefits and missteps of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and a new California law that lets consumers stop some data-sharing and allows people to find out what information companies have stored about them. He does not endorse breaking up Facebook, and suggests instead that the social media economy needs structural reform. He calls for data portability and interoperability, so “consumers would own their identities and could freely switch from one network to another.” Aral believes that without such fundamental changes, new platforms will simply replace the old ones, propelled by the network effects that drive the social-media economy.
“I do not advocate any one silver bullet,” says Aral, who emphasizes that changes in four areas together — money, code, norms, and laws — can alter the trajectory of the social media industry.
But if things continue without change, Aral adds, Facebook and the other social media giants risk substantial civic backlash and user burnout.
“If you get me angry and riled up, I might click more in the short term, but I might also grow really tired and annoyed by how this is making my life miserable, and I might turn you off entirely,” Aral observes. “I mean, that’s why we have a Delete Facebook movement, that’s why we have a Stop Hate for Profit movement. People are pushing back against the short-term vision, and I think we need to embrace this longer-term vision of a healthier communications ecosystem.”
Changing the social media giants can seem like a tall order. Still, Aral says, these firms are not necessarily destined for domination.
“I don’t think this technology or any other technology has some deterministic endpoint,” Aral says. “I want to bring us back to a more practical reality, which is that technology is what we make it, and we are abdicating our responsibility to steer technology toward good and away from bad. That is the path I try to illuminate in this book.”
Share this news article on:
Press mentions.
Prof. Sinan Aral’s new book, “The Hype Machine,” has been selected as one of the best books of the year about AI by Wired . Gilad Edelman notes that Aral’s book is “an engagingly written shortcut to expertise on what the likes of Facebook and Twitter are doing to our brains and our society.”
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with Danny Crichton of TechCrunch about his new book, “The Hype Machine,” which explores the future of social media. Aral notes that he believes a starting point “for solving the social media crisis is creating competition in the social media economy.”
New York Times
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with New York Times editorial board member Greg Bensinger about how social media platforms can reduce the spread of misinformation. “Human-in-the-loop moderation is the right solution,” says Aral. “It’s not a simple silver bullet, but it would give accountability where these companies have in the past blamed software.”
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with Kara Miller of GBH’s Innovation Hub about his research examining the impact of social media on everything from business re-openings during the Covid-19 pandemic to politics.
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with NPR’s Michael Martin about his new book, “The Hype Machine,” which explores the benefits and downfalls posed by social media. “I've been researching social media for 20 years. I've seen its evolution and also the techno utopianism and dystopianism,” says Aral. “I thought it was appropriate to have a book that asks, 'what can we do to really fix the social media morass we find ourselves in?'”
Previous item Next item
Related Links
- MIT Sloan School of Management
Related Topics
- Business and management
- Social media
- Books and authors
- Behavioral economics
Related Articles

The catch to putting warning labels on fake news

Our itch to share helps spread Covid-19 misinformation

Better fact-checking for fake news

Study: On Twitter, false news travels faster than true stories

Social networking
More mit news.

Understanding why autism symptoms sometimes improve amid fever
Read full story →

School of Engineering welcomes new faculty

Study explains why the brain can robustly recognize images, even without color
Turning up the heat on next-generation semiconductors

Sarah Millholland receives 2024 Vera Rubin Early Career Award

A community collaboration for progress
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
How to Use Social Media While Public Speaking
- Career Advice
- Public Speaking
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Deciding the Best Mediums to Use to Communicate a Message to Others in the Workplace
Texting vs. e-mail in business, meeting presentation tips.
- Types of Business Etiquette
- Tools for Disseminating Workplace Information
Seasoned public speakers understand the importance of choosing relevant topics, careful preparation and keeping their audiences engaged throughout. Using social media during your speech can help it to reach a large audience and be available both in real-time and after the fact. In addition, speaking about social media itself is also relevant to many listeners.
Public Speech on Social Media
If you will be giving a speech, you can choose to use the power of social media during your talk. Use tools like YouTube to offer a live stream of your talk. You can also tweet on Twitter or post to other social media sites during your speech to engage listeners who are both present and absent.
A speech shared on social media can also be done from the comfort of your home or office; thanks to modern technology, there’s no need to be located in the same place as your audience. Whether or not your speech is presented to a live audience, you can also use visual aids and maintain a connection with off-site users through Zoom or another platform. Audience feedback should be encouraged to make the speech an interesting, interactive event.
Your speech could also include the latest developments in social media to really make an impact. The team at Social Media Today discusses augmented reality (AR), which overlays virtual objects in real-world environments. This has been hailed as an effective marketing tool, as it blends virtual reality and real-world experiences. Another hot topic is omnichannel personalization tools, which offers integrated, targeted messaging to consumers. Sharing examples of these and other innovations can be the finishing touch on a successful social media speech.
Considerations for Social Speeches
Be sure to keep social media best practices in mind when public speaking. The writers from Kami , an educator website, make some helpful points that can be integrated into this kind of speech for all ages. The first tip is the most important one, too: use social media properly and responsibly.
Safety and discretion should always be the priority when using social media. Remember, once something is posted it could be accessed by practically anyone, especially if a system is hacked. Sharing personal information makes one vulnerable, and this pertains to photos, details about activities and passwords. It is also unwise to say unfavorable things about other people and events unless they are worded very carefully. Many reputations have been damaged or destroyed by thoughtless postings, and speeches shared on social media last forever on the internet.
Safety settings are another important subject to discuss when using social media for sharing a speech. The speaker should understand how privacy settings work, whether they are for a personal or business account. Be sure to not screen share during a Zoom speech or other streamed talk if you have personal information or other sensitive details open on screen.
A speech on social media does not have to be very long to be effective, since it can be shared over and over again after the fact. In fact, there are countless online examples of some very popular one-minute speeches on social media. Speakers need to understand their audiences – a presentation to a group of corporate executives needs to be different from a speech to a class of middle school students.
Speaking about social media itself while using the latest in social media tools may be a good way to get your point across. The team at WebFX explains that social media allows people to connect directly with large groups of other people, and joining social networks is usually free. Companies can build their brands, drive traffic to their websites, get customer feedback and evaluate their performance metrics. Social media also allows us to link up with people from across the globe, share important news, information and education and help needy populations.
On the downside, writers from Roots of Action post that social media decreases the amount of in-person communication, paving the way for less emotional connection and more inauthentic expressions of feelings. The anonymity makes it easier for people to be hurtful, can lead to skewed self-images, can make people lazy and can be highly distracting. Then, of course, there are the questions of rumors, fake news, theft and privacy.
- Social Media Today: 3 Evolving Social Media Trends to Embrace in 2020
- WebFX: Top 13 Advantages and Disadvantages of Social Media
- Kami: How to Use Social Media Properly
Danielle Smyth is a writer and content marketer from upstate New York. She has been writing on business-related topics for nearly 10 years. She owns her own content marketing agency, Wordsmyth Creative Content Marketing, and she works with a number of small businesses to develop B2B content for their websites, social media accounts, and marketing materials. In addition to this content, she has written business-related articles for sites like Sweet Frivolity, Alliance Worldwide Investigative Group, Bloom Co and Spent.
Related Articles
Office etiquette on speakerphones, how can technology enhance teamwork & groups in the workplace, how to give an informative speech, how to become a good public speaker, psychological barriers in communication, the importance of communication skills in oral presentations, key elements of a good meeting, how to use good communication skills for cross-cultural diversity, disadvantages of a teleconference, most popular.
- 1 Office Etiquette on Speakerphones
- 2 How Can Technology Enhance Teamwork & Groups in the Workplace?
- 3 How to Give an Informative Speech
- 4 How to Become a Good Public Speaker
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Social Media Seen as Mostly Good for Democracy Across Many Nations, But U.S. is a Major Outlier
2. Views of social media and its impacts on society
Table of contents.
- Most do not think they can influence politics in their country
- The perceived impacts of the internet and social media on society
- Majorities view social media as a way to raise awareness among the public and elected officials
- Widespread smartphone ownership while very few do not own a mobile phone at all
- Most say they use social media sites
- Frequent posting about social or political issues on social media is uncommon
- Acknowledgments
- Appendix A: Classifying democracies
- Appendix B: Negative Impact of the Internet and Social Media Index
- Appendix C: Political categorization
- Classifying parties as populist
- Classifying parties as left, right or center
- Appendix E: Country-specific examples of smartphones
- Appendix F: Country-specific examples of social media sites
- Pew Research Center’s Spring 2022 Global Attitudes Survey
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
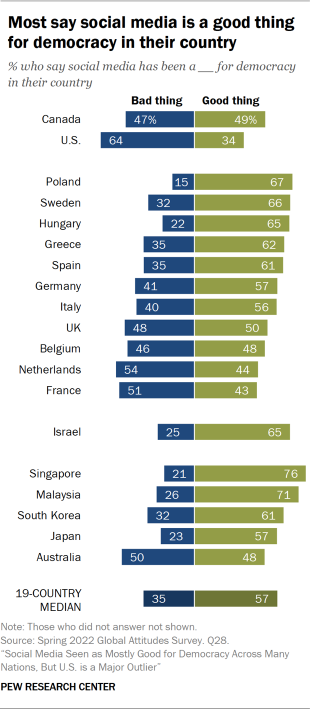
When asked whether social media is a good or bad thing for democracy in their country, a median of 57% across 19 countries say that it is a good thing. In almost every country, close to half or more say this, with the sentiment most common in Singapore, where roughly three-quarters believe social media is a good thing for democracy in their country. However, in the Netherlands and France, about four-in-ten agree. And in the U.S., only around a third think social media is positive for democracy – the smallest share among all 19 countries surveyed.
In eight countries, those who believe that the political system in their country allows them to have an influence on politics are also more likely to say that social media is a good thing for democracy. This gap is most evident in Belgium, where 62% of those who feel their political system allows them to have a say in politics also say that social media is a good thing for democracy in their country, compared with 44% among those who say that their political system does not allow them much influence on politics.
Those who view the spread of false information online as a major threat to their country are less likely to say that social media is a good thing for democracy, compared with those who view the spread of misinformation online as either a minor threat or not a threat at all. This is most clearly observed in the Netherlands, where only four-in-ten (39%) among those who see the spread of false information online as a major threat say that social media has been a good thing for democracy in their country, as opposed to the nearly six-in-ten (57%) among those who do not consider the spread of misinformation online to be a threat who say the same. This pattern is evident in eight other countries as well.
Views also vary by age. Older adults in 12 countries are less likely to say that social media is a good thing for democracy in their country when compared to their younger counterparts. In Japan, France, Israel, Hungary, the UK and Australia, the gap between the youngest and oldest age groups is at least 20 percentage points and ranges as high as 41 points in Poland, where nearly nine-in-ten (87%) younger adults say that social media has been a good thing for democracy in the country and only 46% of adults over 50 say the same.
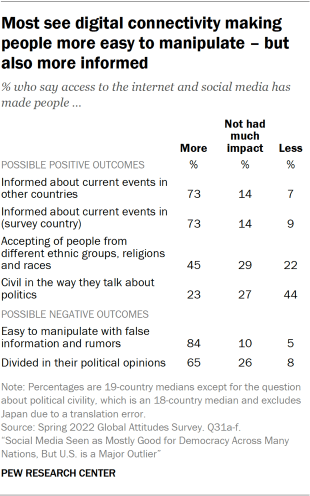
The publics surveyed believe the internet and social media are affecting societies. Across the six issues tested, few tend to say they see no changes due to increased connectivity – instead seeing things changing both positively and negatively – and often both at the same time.
A median of 84% say technological connectivity has made people easier to manipulate with false information and rumors – the most among the six issues tested. Despite this, medians of 73% describe people being more informed about both current events in other countries and about events in their own country. Indeed, in most countries, those who think social media has made it easier to manipulate people with misinformation and rumors are also more likely to think that social media has made people more informed.
When it comes to politics, the internet and social media are generally seen as disruptive, with a median of 65% saying that people are now more divided in their political opinions. Some of this may be due to the sense – shared by a median of 44% across the 19 countries – that access to the internet and social media has led people to be less civil in the way they talk about politics. Despite this, slightly more people (a median of 45%) still say connectivity has made people more accepting of people from different ethnic groups, religions and races than say it has made people less accepting (22%) or had no effect (29%).
There is widespread concern over misinformation – and a sense that people are more susceptible to manipulation
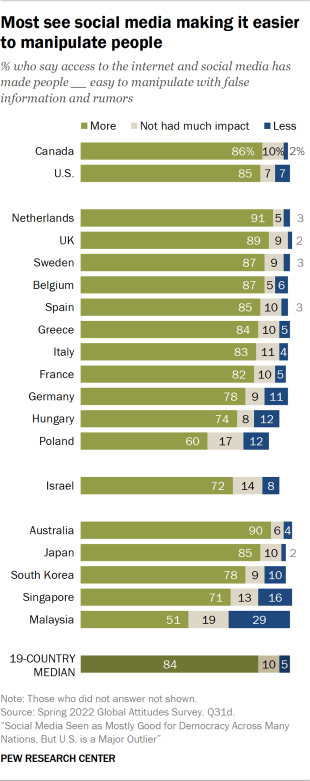
Previously reported results indicate that a median of 70% across the 19 countries surveyed believe that the spread of false information online is a major threat to their country. In places like Canada, Germany and Malaysia, more people name this as a threat than say the same of any of the other issues asked about.
This sense of threat is related to the widespread belief that people today are now easier to manipulate with false information and rumors thanks to the internet and social media. Around half or more in every country surveyed shares this view. And in places like the Netherlands, Australia and the UK, around nine-in-ten see people as more manipulable.
In many places, younger people – who tend to be more likely to use social media (for more on usage, see Chapter 3 ) – are also more likely to say it makes people easier to manipulate with false information and rumors. For example, in South Korea, 90% of those under age 30 say social media makes people easier to manipulate, compared with 65% of those 50 and older. (Interestingly, U.S.-focused research has found older adults are more likely to share misinformation than younger ones.) People with more education are also often more likely than those with less education to say that social media has led to people being easier to manipulate.
In 2018, when Pew Research Center asked a similar question about whether access to mobile phones, the internet and social media has made people easier to manipulate with false information and rumors, the results were largely similar. Across the 11 emerging economies surveyed as part of that project , at least half in every country thought this was the case and in many places, around three-quarters or more saw this as an issue. Large shares in many places were also specifically concerned that people in their country might be manipulated by domestic politicians. For more on how the two surveys compare, see “ In advanced and emerging economies, similar views on how social media affects democracy and society .”
Spotlight on the U.S.: Attitudes and experiences with misinformation
Misinformation has long been seen as a source of concern for Americans. In 2016 , for example, in the wake of the U.S. presidential election, 64% of U.S. adults thought completely made-up news had caused a great deal of confusion about the basic facts of current events. At the time, around a third felt that they often encountered political news online that was completely made up and another half said they often encountered news that was not fully accurate. Moreover, about a quarter (23%) said they had shared such stories – whether knowingly or not.
When asked in 2019 who was the cause of made-up news, Americans largely singled out two groups of people: political leaders (57%) and activists (53%). Fewer placed blame on journalists (36%), foreign actors (35%) or the public (26%). A large majority of Americans that year (82%) also described themselves as either “very” or “somewhat” concerned about the potential impact of made-up news on the 2020 presidential election. People who followed political and election news more closely and those with higher levels of political knowledge also tended to be more concerned.
Among adult American Twitter users in 2021, in particular, there was widespread concern about misinformation: 53% said inaccurate or misleading information is a major problem on the platform and 33% reported seeing a lot of that type of content when using the site.
As of 2021 , around half (48%) of Americans thought the government should take steps to restrict false information, even if it meant losing freedom to access and publish content – a share that had increased somewhat substantially since 2018, when 39% felt the same.
Most say people are more informed about current events – foreign and domestic – thanks to social media and the internet
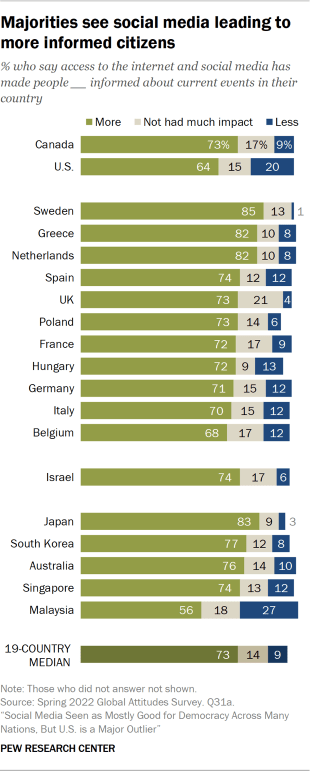
A majority in every country surveyed thinks that access to the internet and social media has made people in their country more informed about domestic current events. In Sweden, Japan, Greece and the Netherlands, around eight-in-ten or more share this view, while in Malaysia, a smaller majority (56%) says the same.
Younger adults tend to see social media making people more informed than older adults do. Older adults, for their part, don’t necessarily see the internet and social media making people less informed about what’s happening in their country; rather, they’re somewhat more likely to describe these platforms as having little effect on people’s information levels. In the case of the U.S., for example, 71% of adults under 30 say social media has made people more informed about current events in the U.S., compared with 60% of those ages 50 and older. But those ages 50 and older are about twice as likely to say social media has not had much impact on how informed people are compared with those under 30: 19% vs. 11%, respectively.
In seven of the surveyed countries, people with higher levels of education are more likely than those with lower levels to see social media informing the public on current events in their own country.
Majorities in every country also agree that the internet and social media are making people more informed about current events happening in other countries. The two questions are extremely highly correlated ( r = 0.94), meaning that in most places where people say social media is making people more informed about domestic events, they also say the same of international events. (See the topline for detailed results for both questions, by country.)
In the 2018 survey of emerging economies , results of a slightly different question also found that a majority in every country – and around seven-in-ten or more in most places – said people were more informed thanks to social media, the internet and smartphones, rather than less.
In some countries, those who think social media has made it easier to manipulate people with misinformation and rumors are also more likely to think that social media has made people more informed. This finding, too, was similar in the 2018 11-country study of emerging economies: Generally speaking, individuals who are most attuned to the potential benefits technology can bring to the political domain are also the ones most anxious about the possible harms.
Spotlight on the U.S.: Social media use and news consumption
In the U.S. , around half of adults say they either get news often (17%) or sometimes (33%) from social media. When it comes to where Americans regularly get news on social media, Facebook outpaces all other social media sites. Roughly a third of U.S. adults (31%) say they regularly get news from Facebook. While Twitter is only used by about three-in-ten U.S. adults (27%), about half of its users (53%) turn to the site to regularly get news there. And a quarter of U.S. adults regularly get news from YouTube, while smaller shares get news from Instagram (13%), TikTok (10%) or Reddit (8%). Notably, TikTok has seen rapid growth as a source of news among younger Americans in recent years.
On several social media sites asked about, adults under 30 make up the largest share of those who regularly get news on the site. For example, half or more of regular news consumers on Snapchat (67%), TikTok (52%) or Reddit (50%) are ages 18 to 29.
While this survey finds that 64% of Americans think the public has become more informed thanks to social media, results of Center analyses do show that Americans who mainly got election and political information on social media during the 2020 election were less knowledgeable and less engaged than those who primarily got their news through other methods (like cable TV, print, etc.).
Majorities or pluralities tend to see social media leading to more political divisions
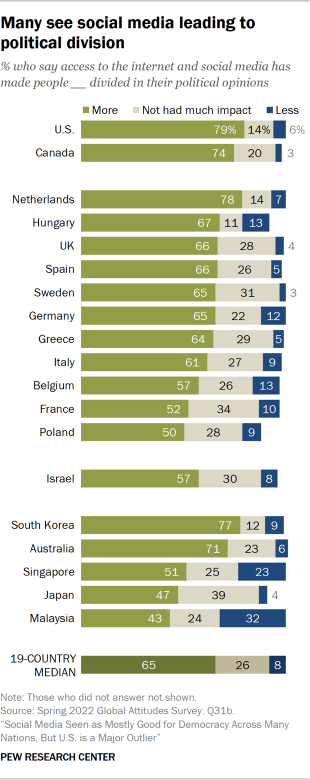
Around half or more in almost every country surveyed think social media has made people more divided in their political opinions. The U.S., South Korea and the Netherlands are particularly likely to hold this view. As a separate analysis shows, the former two also stand out for being the countries where people are most likely to report conflicts between people who support different political parties . While perceived political division in the Netherlands is somewhat lower, it, too, stands apart: Between 2021 and 2022, the share who said there were conflicts increased by 23 percentage points – among the highest year-on-year shifts evident in the survey.
More broadly, across each of the countries surveyed, people who see social division between people who support different political parties, are, in general, more likely to see social media leading people to be more divided in their political opinions.
In a number of countries, younger people are somewhat more likely to see social media enlarging political differences than older people. More educated people, too, often see social media exacerbating political divisions more than those with less education.
Similarly, in the survey of 11 emerging economies conducted in 2018, results of a slightly different question indicated that around four-in-ten or more in every country – and a majority in most places – thought social media had made people more divided.
Publics diverge over whether social media has made people more accepting of differences
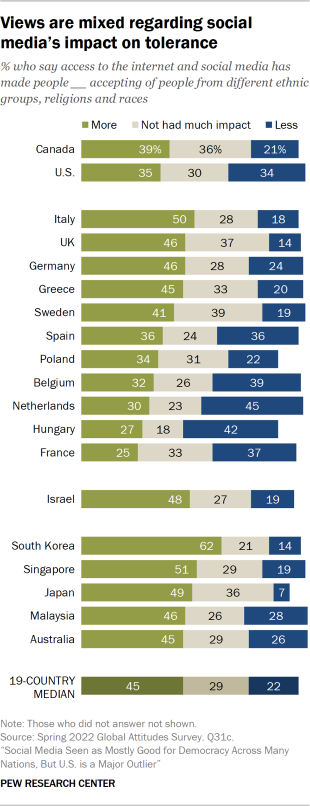
There is less consensus over what role social media has played when it comes to tolerance: A 19-country median of 45% say it has made people more accepting of people from different ethnic backgrounds, religions and races, while a median of 22% say it has made them less so, and 29% say that it has not had much impact either way.
South Korea, Singapore, Italy and Japan are the most likely to see social media making people more tolerant. On the flip side, the Netherlands and Hungary stand out as the two countries where a plurality says the internet and social media have made people less accepting of people with racial or religious differences. Most other societies are somewhat divided, as in the case of the U.S., where around a third of the public falls into each of the three groups.
Younger people are more likely than older ones in most countries to say that social media has increased tolerance. This is the case, for example, in Canada, where 54% of adults under 30 say social media has contributed to people being more accepting of people from different ethnic groups, religions and races, compared with a third of those ages 50 and older. In some places – and in Canada – older people are more likely to see social media leading to less tolerance, though in other places, older people are simply less likely to see much impact from the technology.
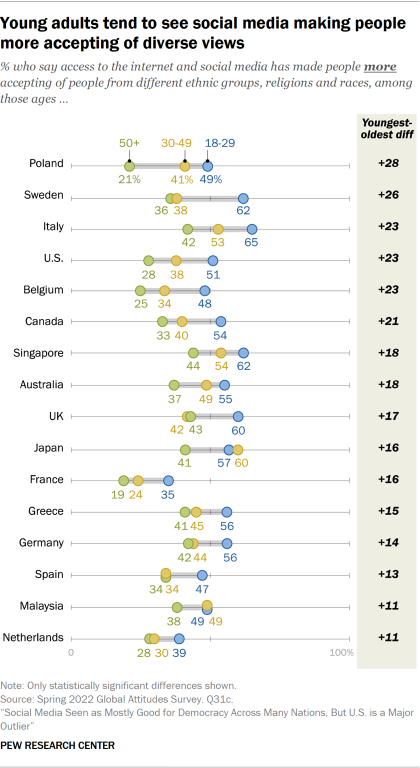
In most countries, people who see social media leading to more divisions between people with different political opinions are more likely to say social media has made people less accepting of those racially and religiously different from them than those who say social media is having no effect on political division. People who see more conflicts between partisans in their society are also more likely than those who see fewer divisions to place some of the blame on social media, describing it as making people less accepting of differences.
Results of an analysis of the 11-country poll did find that people who used smartphones and social media were more likely to regularly interact with people from diverse backgrounds – though the question did not ask about acceptance , just about interactions. The publics in these emerging economies were also somewhat divided when it came to their opinions on how social media has led to people being more or less accepting of those with different viewpoints.
Mixed views on whether social media has made people discuss politics civilly
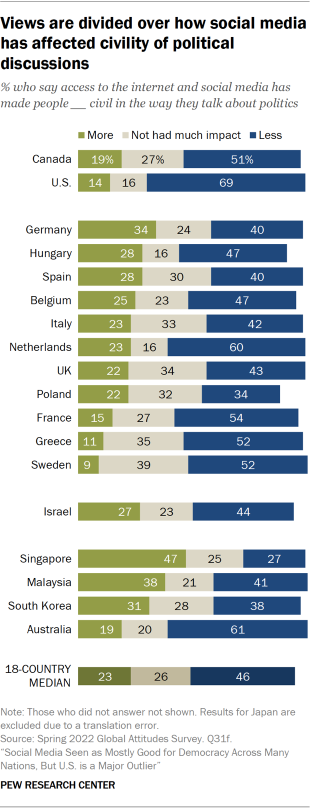
Across the countries surveyed, a median of 46% say access to the internet and social media has made people less civil when they talk about politics. This is more than the 23% who say it has made them more civil – though a median of 26% see little impact either way.
In the U.S., the Netherlands and Australia, a majority sees the internet and social media making people less civil. Roughly seven-in-ten Americans say this. Singapore stands out as the only country where around half see these technologies increasing civility. All other countries surveyed are somewhat divided.
People with higher levels of education tend to see less civility thanks to social media relative to those with lower levels of education.
In most places surveyed, those who think social media has made people more divided politically, compared with those who say it has had no impact on divisions, are also more likely to say social media has made people less civil in how they talk about politics.
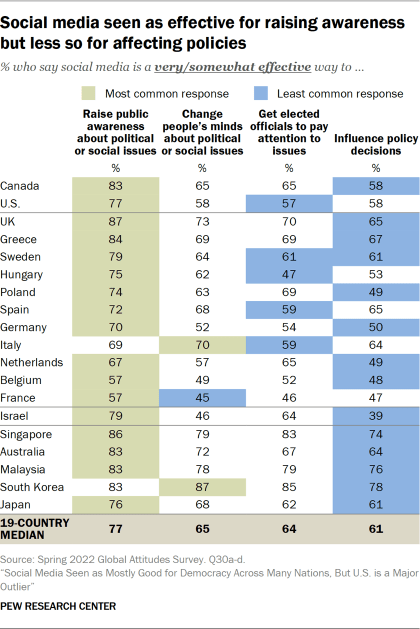
Across advanced economies, people generally recognize social media as useful for bringing the public’s and elected officials’ attention to certain issues, for changing people’s minds and for influencing policy choices. A median of 77% across the 19 countries surveyed say social media is an effective way to raise public awareness about sociopolitical issues. Those in the UK are particularly optimistic about social media as a way of bringing public attention to a topic, with about nine-in-ten holding this belief. People in France and Belgium are the least convinced about social media’s role in raising public awareness, but majorities in both countries still say it’s effective for highlighting certain issues among the public.
Many also consider social media effective for changing people’s minds on social or political issues (65% median). Confidence in social media’s effect on changing people’s minds is strongest in South Korea, Singapore and Malaysia. Germans, Belgians, Israelis and French adults are more skeptical, with no more than about half seeing social media as effective for changing people’s minds on sociopolitical issues.
Views on social media as a way to bring the attention of elected officials to certain issues are similar. A median of 64% consider social media effective for directing elected officials’ attention to issues, and this view is especially prevalent in South Korea, Singapore and Malaysia. People in Belgium, Hungary and France are less convinced.
Somewhat fewer consider social media effective for influencing policy decisions (61% median). Israelis are particularly doubtful of social media as a way for affecting policy change: A majority of Israelis say social media is an ineffective way of influencing policy decisions, and about half in France, Belgium, the Netherlands and Germany agree. About a fifth in Poland also did not provide an answer.
An additional question was asked in the U.S. about social media’s role in creating sustained social movements; roughly seven-in-ten Americans say social media is effective for this. Younger Americans, as well as those with more education or higher incomes, are more likely than others to hold this view. Social media users and those who say social media has been generally good for U.S. democracy are also more likely to believe social media is effective at creating sustained social movements.
Age plays a role in how people in many of the 19 nations surveyed view social media’s role in public discourse. Those ages 18 to 29 are especially likely to see social media as effective for raising public awareness. For example, in France, 70% of those ages 18 to 29 see social media as an effective way of raising public awareness. Only 48% of those 50 and older share this view, a difference of 22 percentage points.
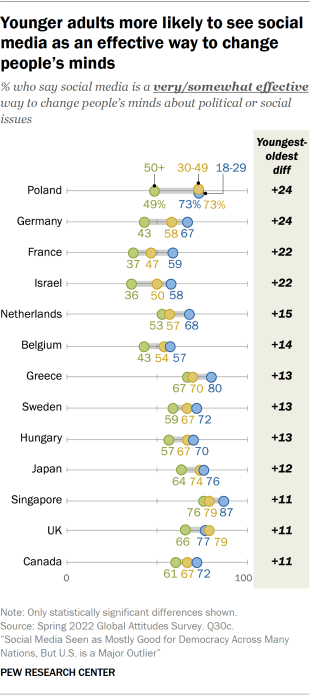
Similarly, younger adults are also more likely to consider social media an effective way for changing people’s minds on issues. The difference is greatest in Poland and Germany, where younger adults are 24 points more likely than their older counterparts to see social media this way. There are fewer differences between younger and older adults when it comes to social media’s effectiveness for directing elected officials’ attention and influencing policy decisions. Younger adults are also generally more likely to be social media users and provide answers to these questions.
Education and income are other demographic characteristics related to people’s view of social media as a way to influence public discourse. In 11 countries, those with incomes higher than the median income are more likely than those with lower incomes to consider social media effective for raising public awareness about sociopolitical issues. Those with more education are similarly more likely to consider social media effective for elevating sociopolitical issues in the public consciousness in eight countries. People with lower levels of education and income are somewhat less likely than others to provide answers to questions about social media’s effectiveness for influencing policies, changing minds and bringing attention to issues.
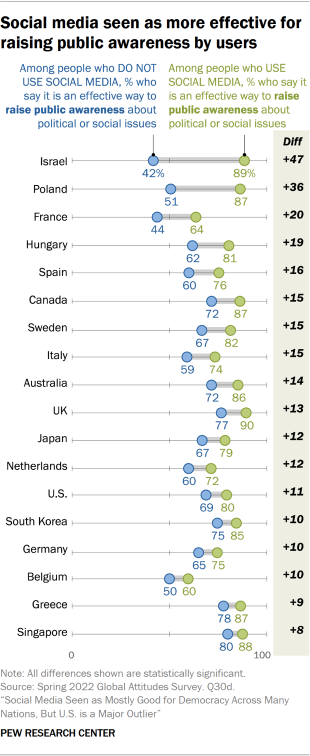
Social media usage is also connected to how people evaluate these platforms as a way to affect public discourse and policy choices. In nearly all countries, social media users are more likely than those who are not on social media to say social media is effective for raising public awareness, and social media users are also more likely to consider social media useful for changing people’s minds in 11 of 19 countries. The differences are greatest in Israel in both cases. Israeli social media users are 47 points more likely than non-users to say social media is effective for raising awareness and 38 points more likely to consider it effective for changing people’s minds on sociopolitical issues. Different views between social media users and non-users are less common when it comes to social media as an effective way for bringing elected officials’ attention to issues or influencing policy decisions. Social media users are also more likely than non-users to answer these questions.
Among social media users, those who are more active are more likely to consider social media an effective avenue for shaping people’s views and attention. Those who post about political or social issues at least sometimes on social media have a greater chance of seeing social media as effective for raising awareness for sociopolitical issues than those who post rarely or never in 16 countries. For example, in Spain, 84% of social media users who post sometimes or often see social media as an effective way to bring awareness to issues, compared to 71% of users who never or rarely post. Similarly, social media users who post more frequently are more likely to see social media as effective for changing minds in 13 countries, for influencing policy decisions in 15 countries, and bringing elected officials’ attention to issues in 12 nations.
People’s views of social media as a way to spread awareness or affect change are additionally related to how they see democracy. The beliefs that social media is effective for influencing policy decisions and for bringing issues to the attention of elected officials or the public are especially common among people who also believe they have a say in politics. For example, in Germany, 60% of people who say people like them have at least a fair amount of influence on politics also say social media is effective for affecting policy choices. In comparison, 43% of Germans who do not think they have a say in politics also think social media can influence policy decisions.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Global Tech & Cybersecurity
- International Political Values
- Internet Connectivity
- Misinformation
- Political Discourse
- Politics & Media
- Politics Online
- Smartphones
- Social Media
- Social Media & the News
- Trust, Facts & Democracy
- U.S. Democracy
More than 80% of Americans believe elected officials don’t care what people like them think
Support for democracy is strong in hong kong and taiwan, how people in 24 countries think democracy can improve, what can improve democracy, representative democracy remains a popular ideal, but people around the world are critical of how it’s working, most popular, report materials.
- Detailed tables: Internet, smartphone and social media use in advanced economies (2022)
- American Trends Panel Wave 105
- Spring 2022 Survey Data
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Donate to liberties
Tech & rights, free speech on social media: filtering methods, rights, future prospects, yes, our right to free speech absolutely exists online. but there is serious debate about how to regulate our freedom of speech in the online sphere, particularly on social media..

by LibertiesEU

Knowledge is power. Your contribution counts.
The rise of social media has implications for our fundamental rights, perhaps none more so than our freedom of speech. There is no doubt that our right to free speech extends online. But there is considerable and complex debate on how to regulate the online sphere, particularly social media. How the regulations are constructed, where the lines are drawn, will have huge implications for our freedom of speech on social media.
What does free speech mean?
Free speech means you have the freedom to express yourself in any way that does not take away the rights of other people. You can (and should) feel free to criticize the work your elected officials are doing. You should not feel free to hold band practice late into the night, because that could take away your neighbors’ right to privacy. And when they complain about the noise, you can’t encourage people to destroy their property or worse. But up to that point, you’re free to express yourself.
This is why free speech is so central to democracy. Democracy means that everyone in society makes collective decisions about the laws they live under and who administers them. The free exchange of ideas, opinions and information provide us with the knowledge we need to make those decisions. That’s also why free speech and the organs that support it, such as free media and civil society, are often the first things that disappear in autocracies.
We all deserve to have our say
But it is becoming harder to speak up about the issues we care about. Support Liberties standing up for our right to free speech.
Free speech gives us our voice
How free is speech on social media and on the internet in general.
The extent to which someone can freely express themselves online varies from country to country. In the EU, the bloc has laws that protect our freedom to express ourselves online. In some cases, the ease of online speech has allowed it to step far beyond the bounds of free speech – consider online bullying or threats, or the sharing of extremist content or child pornography. These forms of “expression” are not protected speech.
But in other areas, drawing the line is more complicated. The EU has been dealing with how to protect the rights of copyright owners against the right of people to share legal content. Should such an enormous and difficult task be farmed out to AI? Surely some of it must be, but how this is done could have profound implications for free speech.
Liberties has been adamant that compromising free speech, even putting it at potential risk, is a no-go. And that’s how it should be – if we are to err, let it be that not enough of our fundamental right to free speech was limited, and not that we gave too much of it away. That’s why we’ve advocated for users’ free speech during the EU’s work on new copyright law. And why we warned European decision-makers that their plan to regulate online terrorist content might unduly restrict free speech .
We are also mindful of the role online platforms have in determining free speech. Although we may use their services to share our thoughts, there is an obvious danger in making them arbiters of what is and is not free speech. Such decisions need to be made by independent judges, and certainly not by companies with a vested interest in making sure the content they allow and promote is good business for them.
What is important to know about free speech rights on social media?
The rise of social media has given new importance to protecting free speech. People are often able to stay anonymous when they say things – not necessarily a bad thing, especially in places where criticizing the government can put you or your family in danger. Or when you want to seek help for a private medical issue. But social media allows people to use anonymity to bully, harass, intimidate or stalk people.
Social media also gives everyone a platform. Again, this is not an inherently bad thing. It not only allows anyone to share their ideas, but connects us faster and cheaper, allowing us to exchange ideas and create things. But it also gives people the ability to easily spread disinformation that can cause harm both to individuals and society as a whole.

How do social media companies filter speech?
Social media companies can filter speech, and thus limit free speech, by using both humans and artificial intelligence to review content that might not be free to share. They can remove what you share or block you from sharing content lawfully if your content is not protected speech, for instance if you use social media to incite violence against someone. And, of course, social media companies have terms of service that have myriad more causes for sanction. (Although it can be the case that their terms of services can breach the law by limiting lawful content.)
Speaking up starts with getting informed.
Perhaps the most drastic form of social media filtering speech is by blocking some people from using their service at all. This has the effect of limiting the voices that can be heard on a platform. Some would argue that’s a good thing, and this is certainly the case when people have spread hate speech or incited violence. These issues were front and center when a certain former president of the United States was blocked from Twitter and Facebook following the attack on the U.S. Capitol.
What does the future hold for free speech on social media?
It may be a short and disappointing answer, but the truth is that we don’t know what the future holds. There seems to be a consensus that we shouldn’t allow illegal content to be shared on the internet. But it’s easier said than done. Companies, politicians and rights groups all have disagreements about how exactly to do this, and which considerations should be given more weight than others.
Regulating online speech is complicated. But if we leave it up to social media companies and their algorithms, our free speech, and thus our democracy, will suffer. They should use a fraction of their profits to create a complaints system where you can always request human review of a decision to filter content. And, if necessary, anyone should be able to go to a judge to have their case heard.
Help us fight for free speech Donate Social media platforms should not just be held accountable for leaving illegal content online. They should also bear responsibility for taking down legal content. This incentivizes them to create a review system that appropriately considers the free speech of the user. And to ensure that this remains the case, the tech industry must be properly regulated. This ensures that they can continue to grow and prosper without our rights being restricted.
But the truth is, at the moment we don’t really know how their algorithms work. We don’t really know how much material they remove or block, or for what reasons, or how they curate our news feed. To make sure they’re doing their best to protect free speech, all this information has to be available to researchers, authorities and independent watchdogs, like Liberties, who can check on them.
Value knowledge by supporting Liberties All great movements begin with sharing information. Our explainer articles help you understand the most pressing human rights issues, so together we can stand up for what matters. Support us by buying one of our activist authors a cup of coffee. Add your voice to ours. Donate today.
More Stories


Liberties' April Recap | Media freedom, 'megabus' of EU legislation and election influences

What’s missing from the Commission’s guidelines on the mitigation of online systemic risks for elections?

Bumper Round Of Approvals For New EU Legislation
Your contribution matters.
As a watchdog organisation, Liberties reminds politicians that respect for human rights is non-negotiable. We're determined to keep championing your civil liberties, will you stand with us? Every donation, big or small, counts.
We’re grateful to all our supporters
Your contributions help us in the following ways
► Liberties remains independent ► It provides a stable income, enabling us to plan long-term ► We decide our mission, so we can focus on the causes that matter ► It makes us stronger and more impactful
Subscribe to stay in
You will get the latest reports before anyone else!
You can follow what we are doing for your rights!
You will know about our achivements!
Show me a sample!
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- JEE Advanced Admit Card 2024
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Answer Key
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Result 2024
- NEET Asnwer Key 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET DU Cut off 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET Result 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET 2024 Exam Live
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Speech on Social Media
- Social Media Speech
A website or program that facilitates social interaction is known as social media. Information, ideas, opinions, images, and videos can all be shared. It is a "virtual space" where people may conduct business, follow their icons, and share information. Individuals like YouTubers, Instagram influencers, and others have made it their job to influence users on social media. A fresh avenue for self-expression is now available because of social media.
10 Lines Speech on Social Media
Short speech on social media, long speech on social media.

Social Media refers to group interactions in which users build, share, or trade knowledge and concepts in online communities.
The ability to interact with others has evolved into a fundamental human need.
The remarkable advancements in communications and inventive, astounding entertainment have made knowledge more accessible and provided voices to those who otherwise would not have been heard.
The current generation has had the good fortune to experience some of the most astonishing technological advancements in human history.
Additionally, it is becoming increasingly obvious how significant social media has become in everyday life as the number of individuals using them keeps rising.
People can now purchase and talk to their friends about what they are buying easily due to B2B social, reviews, and travel sites on social media. To provide customers with an enjoyable shopping experience, certain websites provide group buying deals.
Because of the vast network of social media, distance is no longer a barrier. Through social media websites, you are consistently kept updated on the most recent events and news in the world.
The ability to teach from a distance is a benefit for academics and teachers.
It gives hackers the opportunity to conduct viral assaults and commit fraud.
Due to excessive usage and addiction to various social media platforms, people's productivity is being hindered.
Social media sites like WhatsApp, Instagram, Snapchat, Facebook, and Twitter are becoming more and more essential as a result of their ability to link individuals all over the world.
Benefits of Social Media
Social media has several benefits, one of which is that it is a wealth of knowledge and contributes to education. For instance, kids use social media to find out what they want to know. It is an excellent tool for schooling. Online teaching is now available because of it. By simply sitting in front of a device in our country, we can attend a session taking place somewhere else in the world.
Social media is an excellent tool for keeping up with local news and events. Information can be found without us having to wait for the newspaper. There are numerous applications relating to news that can immediately inform us of any significant events taking place elsewhere in the world.
Drawbacks of Social Media
However, despite its several advantages, it has drawn criticism. Additionally, there are drawbacks. It is also regarded as one of society's darker sides. It is risky to share too much information online. Our privacy may be attacked. Additionally, excessive use results in hours spent on social media, which can divert kids from their education.
We can exchange our ideas and facts on social media, which is an interactive platform. In our everyday lives, we all use it. Our lives now revolve around it constantly. Both locally and internationally, they are used by every one of us for socializing and communication. Social networking offers both benefits and drawbacks.
Advantages of Social Media
We have countless options because of the social media platform's digital world, which is an entirely different world. The freedom of expression and action provided by social media is undoubtedly beneficial. The Internet has made everything possible, from communicating with our loved ones to posting happy moments and memories, learning from others and imparting information to our peers. We may collect money for charitable causes and public awareness of social issues via social media platforms.
Social media allows us to communicate with people all around the world, which is its main advantage. Today, anyone can voice their views on a national or international subject. People can promote their talents on social media, which is an additional advantage. Showing off their skills on social media has helped many people become famous. People can also make money from social media. The public can be made aware of issues by using social media. On this forum, those knowledgeable about issues like diet and health raise public awareness.
Disadvantages of Social Media
However, there are also restrictions and guidelines that each person must go by in order to use their rights on these platforms. Criminals conduct a vast list of crimes and wrongdoings that we innocent people become victims of, and such cases are growing daily. The issue is not the social media platform but rather our need for familiarity with how to interact with strangers.
The main disadvantage of social media is addiction. Checking one's social media profiles has become a frequent habit. Some information may be accurate, while other information may be false. Fake news may circulate over this medium like wildfire. On the Internet, many people have easy access to our personal information. Therefore, we must be careful against hackers. Another major downside of social media is cyberbullying. Some users annoy other accounts by leaving harmful and abusive comments.
The benefits of social interaction have made life easier and more convenient. A few drawbacks also exist. To maximize the potential of these new platforms, we must use them strategically and efficiently.
Real-Life Example
After the pandemic, I have lost my concentration and focus on my studies due to social media. I procrastinate, and because of this, I cannot manage my time correctly. Social media has impacted my academic life, and I had lost academic validation, which I used to have when I did not have an account on any social media applications, basically when I did not own a smartphone. Social media has created a trap that makes me spend hours just scrolling the whole day on Youtube or Instagram. I feel I have lost all my productivity; even when I want to learn or open some notes from my smartphone or laptop, I end up scrolling and watching unnecessary stuff which is of no benefit to me.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in

The Often Overlooked Positive Side of Social Media
What healthy tech use actually looks like..
Updated May 16, 2024 | Reviewed by Jessica Schrader
- Young Americans flourish digitally, feeling connected and benefiting from positive social comparison.
- Social comparison online can inspire well-being, especially with similar peers and inspiring content.
- Social media can strengthen teen friendships and support, enhanced by parental involvement and digital skills.

Yes, social media poses many challenges. They are designed to keep us hooked and release the neurotransmitter dopamine that makes us spend way more time on it then we intended to. And yes, specifically for young female adolescents, image-based platforms can significantly impact body image and self-esteem . But , social media can also lead to digital flourishing, inspiration, feelings of loving connection and social support.
Do these positive effects make up for all the negative ones? Probably not. But, thinking about the problems from a solution-oriented, positive framework can broaden the ways in which we can think about solving such issues. That is, in addition to pushing for phone-free schools and norms to push the age limit for social media use to 16 years, as proposed in Jonathan Haidt’s new book The Anxious Generation, we can think about what healthy and nourishing technology looks like that fosters well-being, resilience , and character strengths in young adults. We need to know what “healthy” tech use actually looks like to foster it.
My research is based on the framework of positive psychology, which explores ways in which we can live our best lives, rather than lives in the absence of illness. Over the past 10 years, I have explored ways in which media in general, as well as new media such as social media and computer-mediated communication, can lead to happiness and fulfillment for ourselves as well as prosociality and greater connectedness to others.
Here are three key insights from positive media psychology:
1. Young Americans do digitally flourish. With a sample representative of the American population, my recent research revealed that younger individuals (18-34) perceive themselves to flourish digitally more than older individuals, even when controlling for the amount of time spent communicating online in general. Young adults specifically indicated feeling more connected when communicating digitally and engaged in positive social comparison more so than older adults. The latter finding specifically speaks against a lot of earlier research, and press releases for that matter, that showcase the detriments of online social comparison for well-being. But, if we look closely, more recent evidence accumulates that indicates positive well-being effects from social comparison processes online.
2. Social comparison online can lead to inspiration and positive well-being effects. A recent review on the role of social comparison on social media from one of my colleagues from the University of Nuremberg shows that social comparison can lead to well-being for specific people under specific conditions. For example, one of my own studies showed that when college students share inspiring content on Facebook with others, over time, they feel more love and compassion toward others. In another study , we found that inspiring social media and online video use, but not overall time spent on social media, was positively related to everyday experiences of gratitude , awe , vitality and prosocial motivations and behaviors. Similarly, research from Sheffield Institute in the U.K. further shows that social comparison on Instagram is more likely to lead to inspiration when adolescents compare themselves to similar others instead of unachievable influencers. Thus, one of the conditions for whether social comparison may lead to positive or negative effects also stems from the content we consume and the people we follow. So, let’s keep in mind: social comparison is not always bad and young adults do experience inspiration online that is oftentimes overlooked.

3. Social media strengthens teens' friendships more so than it harms them. We are living in a digitized world. And while us old millennials picked up the home phone to talk to our friends for hours in our room, today teens do this on their mobile device. In a Pew Research study from 2022 that surveyed U.S. teens 13-17 years of age, 80% of teens say that social media makes them more connected to what’s going on in their friend’s life, 71% say they have a place where they can show their creative side, and 67% say they like that they have people on social media who can support them through tough times. Moreover, a teenager's mindset matters . The Pew study also revealed that those who believe social media has a general positive effect on their peers also experience more positive personal experiences than those that believe social media has an overall negative effect on their peers. Such a positive outlook on technology can be influenced by a multitude of factors, but specifically for young teenagers , parents play an active role in their kids' digital lives. In fact, parental involvement can be the deciding factor whether a teen digitally flourishes or not. In a study I co-authored that was just published last month, in April 2024, in the Journal of Child Development , we tracked adolescents’ (11-21 years of age, average age 15) digital flourishing for a year and found that for half of the sample their digital flourishing score was high to begin with and remained mostly stable over time (with slight increases in positive social comparison). For the other half of the sample, digital flourishing was lower to begin with and specifically self-control decreased over time. What differentiated the two groups was that the first, highly flourishing group, had parents with high digital skills and a keen investment into their teenager’s tech live.
Don’t get me wrong. I am no denier of the problems that social media brings and I'm all for new COPPA2.0 regulations and other initiatives put forth by admirable institutions such as The Center for Humane Technology and the Digital Wellness Institute. But when we approach these problems from a positive psychology perspective, we might discover resources and strength in the consumer and tech platforms themselves that we can leverage to avoid or lessen the harm and promote thriving.

Sophie H. Janicke-Bowles, Ph.D., is a positive media psychologist working as an Associate Professor at Chapman University in California.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

The Importance of Free Speech on Social Media
Micah Sifry discussed the importance of free speech on social media platforms, such as twitter, in an open society.
Javascript must be enabled in order to access C-SPAN videos.
- Text type Text
- Filter by Speaker All Speakers Micah L. Sifry
- Search this text
*This text was compiled from uncorrected Closed Captioning.
People in this video
- Micah L. Sifry Co-Founder and Executive Editor Personal Democracy Media->Personal Democracy Forum
Hosting Organization
- PEN America Center PEN America Center
- Fordham University School of Law Fordham University School of Law
Related Video
Online Activity in the Workplace
Panelists talked about issues arising from online activity in the workplace, including employee privacy, legitimate busi…
Social Media and Employment
Panelists spoke about the privacy, social and policy implications that arise when employers use social media and other p…
What Stays in Vegas
Adam Tanner talked about his book, What Stays in Vegas: The World of Personal Data-Lifeblood of Big Business-and the End …
Communicators with Tim Wu
Timothy Wu, who coined the phrase “net neutrality,” talked about technology issues and the debate over how to manage the…
User Created Clips from This Video
Find anything you save across the site in your account
The Evolving Free-Speech Battle Between Social Media and the Government
By Isaac Chotiner

Earlier this month, a federal judge in Louisiana issued a ruling that restricted various government agencies from communicating with social-media companies. The plaintiffs, which include the attorneys general of Missouri and Louisiana, argued that the federal government was coercing social-media companies into limiting speech on topics such as vaccine skepticism. The judge wrote, in a preliminary injunction, “If the allegations made by plaintiffs are true, the present case arguably involves the most massive attack against free speech in United States’ history. The plaintiffs are likely to succeed on the merits in establishing that the government has used its power to silence the opposition.” The injunction prevented agencies such as the Department of Health and Human Services and the F.B.I. from communicating with Facebook , Twitter, or other platforms about removing or censoring content. (The Biden Administration appealed the injunction and, on Friday, the Fifth Circuit paused it. A three-judge panel will soon decide whether it will be reinstated as the case proceeds.) Critics have expressed concern that such orders will limit the ability of the government to fight disinformation.
To better understand the issues at stake, I recently spoke by phone with Genevieve Lakier, a professor of law at the University of Chicago Law School who focusses on issues of social media and free speech. (We spoke before Friday’s pause.) During our conversation, which has been edited for length and clarity, we discussed why the ruling was such a radical departure from the way that courts generally handle these issues, how to apply concepts like free speech to government actors, and why some of the communication between the government and social-media companies was problematic.
In a very basic sense, what does this decision actually do?
Well, in practical terms, it prevents a huge swath of the executive branch of the federal government from essentially talking to social-media platforms about what they consider to be bad or harmful speech on the platforms.
There’s an injunction and then there’s an order, and both are important. The order is the justification for the injunction, but the injunction itself is what actually has effects on the world. And the injunction is incredibly broad. It says all of these defendants—and we’re talking about the President, the Surgeon General, the White House press secretary, the State Department, the F.B.I.—may not urge, encourage, pressure, or induce in any manner the companies to do something different than what they might otherwise do about harmful speech. This is incredibly broad language. It suggests, and I think is likely to be interpreted to mean, that, basically, if you’re a member of one of the agencies or if you’re named in this injunction, you just cannot speak to the platforms about harmful speech on the platform until, or unless, the injunction ends.
But one of the puzzling things about the injunction is that there are these very significant carve-outs. For example, my favorite is that the injunction says, basically, “On the other hand, you may communicate with the platforms about threats to public safety or security of the United States.” Now, of course, the defendants in the lawsuit would say, “That’s all we’ve been doing. When we talk to you, when we talk to the platforms about election misinformation or health misinformation, we are alerting them to threats to the safety and security of the United States.”
So, read one way, the injunction chills an enormous amount of speech. Read another way, it doesn’t really change anything at all. But, of course, when you get an injunction like this from a federal court, it’s better to be safe than sorry. I imagine that all of the agencies and government officials listed in the injunction are going to think, We’d better shut up.
And the reason that specific people, jobs, and agencies are listed in the injunction is because the plaintiffs say that these entities were communicating with social-media companies, correct?
Correct. And communicating in these coercive or harmful, unconstitutional ways. The presumption of the injunction is that if they’ve been doing it in the past, they’re probably going to keep doing it in the future. And let’s stop continuing violations of the First Amendment.
As someone who’s not an expert on this issue, I find the idea that you could tell the White House press secretary that he or she cannot get up at the White House podium and say that Twitter should take down COVID misinformation—
Does this injunction raise issues on two fronts: freedom of speech and separation of powers?
Technically, when the press secretary is operating as the press secretary, she’s not a First Amendment-rights holder. The First Amendment limits the government, constrains the government, but protects private people. And so when she’s a private citizen, she has all her ordinary-citizen rights. Government officials technically don’t have First Amendment rights.
That said, it’s absolutely true that, when thinking about the scope of the First Amendment, courts take very seriously the important democratic and expressive interests in government speech. And so government speakers don’t have First Amendment rights, but they have a lot of interests that courts consider. A First Amendment advocate would say that this injunction constrains and has negative effects on really important government speech interests.
More colloquially, I would just say the irony of this injunction is that in the name of freedom of speech it is chilling a hell of a lot of speech. That is how complicated these issues are. Government officials using their bully pulpit can have really powerful speech-oppressive effects. They can chill a lot of important speech. But one of the problems with the way the district court approaches the analysis is that it doesn’t seem to be taking into account the interest on the other side. Just as we think that the government can go too far, we also think it’s really important for the government to be able to speak.
And what about separation-of-powers issues? Or is that not relevant here?
I think the way that the First Amendment is interpreted in this area is an attempt to protect some separation of powers. Government actors may not have First Amendment rights, but they’re doing important business, and it’s important to give them a lot of freedom to do that business, including to do things like express opinions about what private citizens are doing or not doing. Courts generally recognize that government actors, legislators, and executive-branch officials are doing important business. The courts do not want to second-guess everything that they’re doing.
So what exactly does this order say was illegal?
The lawsuit was very ambitious. It claimed that government officials in a variety of positions violated the First Amendment by inducing or encouraging or incentivizing the platforms to take down protected speech. And by coercing or threatening them into taking down protected speech. And by collaborating with them to take down protected speech. These are the three prongs that you can use in a First Amendment case to show that the decision to take down speech that looks like it’s directly from a private actor is actually the responsibility of the government. The plaintiffs claimed all three. What’s interesting about that district-court order is that it agreed with all three. It says, Yeah, there was encouragement, there was coercion, and there was joint action or collaboration.
And what sort of examples are they providing? What would be an example of the meat of what the plaintiffs argued, and what the judge found to violate the First Amendment?
A huge range of activities—some that I find troubling and some that don’t seem to be troubling. Public statements by members of the White House or the executive branch expressing dissatisfaction with what the platforms are doing. For instance, President Biden’s famous statement that the platforms are killing people. Or the Surgeon General’s warning that there is a health crisis caused by misinformation, and his urging the platforms to do something about it. That’s one bucket.
There is another bucket in which the platforms were going to agencies like the C.D.C. to ask them for information about the COVID pandemic and the vaccine—what’s true and what’s false, or what’s good and what’s bad information—and then using that to inform their content-moderation rules.
Very different and much more troubling, I think, are these e-mails that they found in discovery between White House officials and the platforms in which the officials more or less demand that the platforms take down speech. There is one e-mail from someone in the White House who asked Twitter to remove a parody account that was linked to President Biden’s granddaughter, and said that he “cannot stress the degree to which this needs to be resolved immediately”—and within forty-five minutes, Twitter takes it down. That’s a very different thing than President Biden saying, “Hey, platforms, you’re doing a bad job with COVID misinformation.”
The second bucket seems full of the normal give-and-take you’d expect between the government and private actors in a democratic society, right?
Yeah. Threats and government coercion on private platforms seem the most troubling from a First Amendment perspective. And traditionally that is the kind of behavior that these cases have been most worried about.
This is not the first case to make claims of this kind. This is actually one of dozens of cases that have been filed in federal court over the last years alleging that the Biden Administration or members of the government had put pressure on or encouraged platforms to take down vaccine-skeptical speech and speech about election misinformation. What is unusual about this case is the way that the district court responded to these claims. Before this case, courts had, for the most part, thrown these cases out. I think this was largely because they thought that there was insufficient evidence of coercion, and coercion is what we’re mostly worried about. They have found that this kind of behavior only violates the First Amendment if there is some kind of explicit threat, such as “If you don’t do X, we will do Y,” or if the government actors have been directly involved in the decision to take down the speech.
In this case, the court rejects that and has a much broader test, where it says, basically, that government officials violate the First Amendment if they significantly encourage the platforms to act. And that may mean just putting pressure on them through rhetoric or through e-mails on multiple occasions—there’s a campaign of pressure, and that’s enough to violate the First Amendment. I cannot stress enough how significant a departure that is from the way courts have looked at the issue before.
So, in this case, you’re saying that the underlying behavior may constitute something bad that the Biden Administration did, that voters should know about it and judge them on it, but that it doesn’t rise to the level of being a First Amendment issue?
Yes. I think that this opinion goes too far. It’s insufficiently attentive to the interests on the other side. But I think the prior cases have been too stingy. They’ve been too unwilling to find a problem—they don’t want to get involved because of this concern with separation of powers.
The platforms are incredibly powerful speech regulators. We have largely handed over control of the digital public sphere to these private companies. I think there is this recognition that when the government criticizes the platforms or puts pressure on the platforms to change their policies, that’s some form of political or democratic oversight, a way to promote public welfare. And those kinds of democratic and public-welfare concerns are pretty significant. The courts have wanted to give the government a lot of room to move.
But you think that, in the past, the courts have been too willing to give the government space? How could they develop a better approach?
Yeah. So, for example, the e-mails that are identified in this complaint—I think that’s the kind of pressure that is inappropriate for government actors in a democracy to be employing against private-speech platforms. I’m not at all convinced that, if this had come up in a different court, those would have been found to be a violation of the First Amendment. But there need to be some rules of the road.
On the one hand, I was suggesting that there are important democratic interests in not having too broad a rule. But, on the other hand, I think part of what’s going on here—part of what the facts that we see in this complaint are revealing—is that, in the past, we’ve thought about this kind of government pressure on private platforms, which is sometimes called jawboning, as episodic. There’s a local sheriff or there’s an agency head who doesn’t like a particular policy, and they put pressure on the television station, or the local bookseller, to do something about it. Today, what we’re seeing is that there’s just this pervasive, increasingly bureaucratized communication between the government and the platforms. The digital public theatre has fewer gatekeepers; journalists are not playing the role of leading and determining the news that is fit to print or not fit to print. And so there’s a lot of stuff, for good or for ill, that is circulating in public. You can understand why government officials and expert agencies want to be playing a more significant role in informing, influencing, and persuading the platforms to operate one way or the other. But it does raise the possibility of abuse, and I’m worried about that.
That was a fascinating response, but you didn’t totally answer the question. How should a court step in here without going too far?
The traditional approach that courts have taken, until now, has been to say that there’s only going to be a First Amendment violation if the coercion, encouragement, or collaboration is so strong that, essentially, the platform had no choice but to act. It had no alternatives; there was no private discretion. Because then we can say, Oh, yes, it was the government actor, not the platform, that ultimately was responsible for the decision.
I think that that is too restrictive a standard. Platforms are vulnerable to pressure from the government that’s a lot less severe. They’re in the business of making money by disseminating a lot of speech. They don’t particularly care about any particular tweet or post or speech act. And their economic incentives will often mean that they want to curry favor with the government and with advertisers by being able to continue to circulate a lot of speech. If that means that they have to break some eggs, that they have to suppress particular kinds of posts or tweets, they will do that. It’s economically rational for them to do so.
The challenge for courts is to develop rules of the road for how government officials can interact with platforms. It has to be the case that some forms of communication are protected, constitutionally O.K., and even democratically good. I want expert agencies such as the C.D.C. to be able to communicate to the platforms. And I want that kind of expert information to be constitutionally unproblematic to deliver. On the other hand, I don’t think that White House officials should be writing to platforms and saying, “Hey, take this down immediately.”
I never thought about threatening companies as a free-speech issue that courts would get involved with. Let me give you an example. If you had told me four years ago that the White House press secretary had got up and said, “I have a message from President Trump. If CNN airs one more criticism of me, I am going to try and block its next merger,” I would’ve imagined that there would be a lot of outrage about that. What I could not have imagined was a judge releasing an injunction saying that people who worked for President Trump were not allowed to pass on the President’s message from the White House podium. It would be an issue for voters to decide. Or, I suppose, CNN, during the merger decision, could raise the issue and say, “See, we didn’t get fair treatment because of what President Trump said,” and courts could take that into account. But the idea of blocking the White House press secretary from saying anything seems inconceivable to me.
I’ll say two things in response. One is that there is a history of this kind of First Amendment litigation, but it’s usually about private speech. We might think that public speech has a different status because there is more political accountability. I don’t know. I find this question really tricky, because I think that the easiest cases from a First Amendment perspective, and the easiest reason for courts to get involved, is when the communication is secret, because there isn’t political accountability.
You mentioned the White House press secretary saying something in public. O.K., that’s one thing. But what about if she says it in private? We might think, Well, then the platforms are going to complain. But often regulated parties do not want to say that they have been coerced by the government into doing something against their interests, or that they were threatened. There’s often a conspiracy of silence.
In those cases, it doesn’t seem to me as if there’s democratic accountability. But, even when it is public, we’ve seen over the past year that government officials are writing letters to the platforms: public letters criticizing them, asking for information, badgering them, pestering them about their content-moderation policies. And we might think, Sure, people know that that’s happening. Maybe the government officials will face political accountability if it’s no good. But we might worry that, even then, if the behavior is sufficiently serious, if it’s repeated, it might give the officials too much power to shape the content-moderation policies of the platforms. From a First Amendment perspective, I don’t know why that’s off the table.
Now, from a practical perspective, you’re absolutely right. Courts have not wanted to get involved. But that’s really worrying. I think this desire to just let the political branches work it out has meant that, certainly with the social-media platforms, it’s been like the Wild West. There are no rules of the road. We have no idea what’s O.K. or not for someone in the White House to e-mail to a platform. One of the benefits of the order and the injunction is that it’s opening up this debate about what’s O.K. and what’s not. It might be the case that the way to establish rules of the road will not be through First Amendment-case litigation. Maybe we need Congress to step in and write the rules, or there needs to be some kind of agency self-regulation. But I think it’s all going to have to ultimately be viewed through a First Amendment lens. This order and injunction go way too far, but I think the case is at least useful in starting a debate. Because up until now we’ve been stuck in this arena where there are important free-speech values that are at stake and no one is really doing much to protect them. ♦
More New Yorker Conversations
Naomi Klein sees uncanny doubles in our politics .
Olivia Rodrigo considers the meanings of “Guts.”
Isabel Allende’s vision of history .
Julia Fox didn’t want to be famous, but she knew she would be .
John Waters is ready for his Hollywood closeup .
Patrick Stewart boldly goes there .
Sign up for our daily newsletter to receive the best stories from The New Yorker .
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Kyle Chayka

By Susan B. Glasser

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

Social Media and Mental Health: Benefits, Risks, and Opportunities for Research and Practice
John a. naslund.
a Department of Global Health and Social Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Ameya Bondre
b CareNX Innovations, Mumbai, India
John Torous
c Department of Psychiatry, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA
Kelly A. Aschbrenner
d Department of Psychiatry, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, NH
Social media platforms are popular venues for sharing personal experiences, seeking information, and offering peer-to-peer support among individuals living with mental illness. With significant shortfalls in the availability, quality, and reach of evidence-based mental health services across the United States and globally, social media platforms may afford new opportunities to bridge this gap. However, caution is warranted, as numerous studies highlight risks of social media use for mental health. In this commentary, we consider the role of social media as a potentially viable intervention platform for offering support to persons with mental disorders, promoting engagement and retention in care, and enhancing existing mental health services. Specifically, we summarize current research on the use of social media among mental health service users, and early efforts using social media for the delivery of evidence-based programs. We also review the risks, potential harms, and necessary safety precautions with using social media for mental health. To conclude, we explore opportunities using data science and machine learning, for example by leveraging social media for detecting mental disorders and developing predictive models aimed at characterizing the aetiology and progression of mental disorders. These various efforts using social media, as summarized in this commentary, hold promise for improving the lives of individuals living with mental disorders.
Introduction
Social media has become a prominent fixture in the lives of many individuals facing the challenges of mental illness. Social media refers broadly to web and mobile platforms that allow individuals to connect with others within a virtual network (such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Snapchat, or LinkedIn), where they can share, co-create, or exchange various forms of digital content, including information, messages, photos, or videos ( Ahmed, Ahmad, Ahmad, & Zakaria, 2019 ). Studies have reported that individuals living with a range of mental disorders, including depression, psychotic disorders, or other severe mental illnesses, use social media platforms at comparable rates as the general population, with use ranging from about 70% among middle-age and older individuals, to upwards of 97% among younger individuals ( Aschbrenner, Naslund, Grinley, et al., 2018 ; M. L. Birnbaum, Rizvi, Correll, Kane, & Confino, 2017 ; Brunette et al., 2019 ; Naslund, Aschbrenner, & Bartels, 2016 ). Other exploratory studies have found that many of these individuals with mental illness appear to turn to social media to share their personal experiences, seek information about their mental health and treatment options, and give and receive support from others facing similar mental health challenges ( Bucci, Schwannauer, & Berry, 2019 ; Naslund, Aschbrenner, Marsch, & Bartels, 2016b ).
Across the United States and globally, very few people living with mental illness have access to adequate mental health services ( Patel et al., 2018 ). The wide reach and near ubiquitous use of social media platforms may afford novel opportunities to address these shortfalls in existing mental health care, by enhancing the quality, availability, and reach of services. Recent studies have explored patterns of social media use, impact of social media use on mental health and wellbeing, and the potential to leverage the popularity and interactive features of social media to enhance the delivery of interventions. However, there remains uncertainty regarding the risks and potential harms of social media for mental health ( Orben & Przybylski, 2019 ), and how best to weigh these concerns against potential benefits.
In this commentary, we summarized current research on the use of social media among individuals with mental illness, with consideration of the impact of social media on mental wellbeing, as well as early efforts using social media for delivery of evidence-based programs for addressing mental health problems. We searched for recent peer reviewed publications in Medline and Google Scholar using the search terms “mental health” or “mental illness” and “social media”, and searched the reference lists of recent reviews and other relevant studies. We reviewed the risks, potential harms, and necessary safety precautions with using social media for mental health. Overall, our goal was to consider the role of social media as a potentially viable intervention platform for offering support to persons with mental disorders, promoting engagement and retention in care, and enhancing existing mental health services, while balancing the need for safety. Given this broad objective, we did not perform a systematic search of the literature and we did not apply specific inclusion criteria based on study design or type of mental disorder.
Social Media Use and Mental Health
In 2020, there are an estimated 3.8 billion social media users worldwide, representing half the global population ( We Are Social, 2020 ). Recent studies have shown that individuals with mental disorders are increasingly gaining access to and using mobile devices, such as smartphones ( Firth et al., 2015 ; Glick, Druss, Pina, Lally, & Conde, 2016 ; Torous, Chan, et al., 2014 ; Torous, Friedman, & Keshavan, 2014 ). Similarly, there is mounting evidence showing high rates of social media use among individuals with mental disorders, including studies looking at engagement with these popular platforms across diverse settings and disorder types. Initial studies from 2015 found that nearly half of a sample of psychiatric patients were social media users, with greater use among younger individuals ( Trefflich, Kalckreuth, Mergl, & Rummel-Kluge, 2015 ), while 47% of inpatients and outpatients with schizophrenia reported using social media, of which 79% reported at least once-a-week usage of social media websites ( Miller, Stewart, Schrimsher, Peeples, & Buckley, 2015 ). Rates of social media use among psychiatric populations have increased in recent years, as reflected in a study with data from 2017 showing comparable rates of social media use (approximately 70%) among individuals with serious mental illness in treatment as compared to low-income groups from the general population ( Brunette et al., 2019 ).
Similarly, among individuals with serious mental illness receiving community-based mental health services, a recent study found equivalent rates of social media use as the general population, even exceeding 70% of participants ( Naslund, Aschbrenner, & Bartels, 2016 ). Comparable findings were demonstrated among middle-age and older individuals with mental illness accessing services at peer support agencies, where 72% of respondents reported using social media ( Aschbrenner, Naslund, Grinley, et al., 2018 ). Similar results, with 68% of those with first episode psychosis using social media daily were reported in another study ( Abdel-Baki, Lal, D.-Charron, Stip, & Kara, 2017 ).
Individuals who self-identified as having a schizophrenia spectrum disorder responded to a survey shared through the National Alliance of Mental Illness (NAMI), and reported that visiting social media sites was one of their most common activities when using digital devices, taking up roughly 2 hours each day ( Gay, Torous, Joseph, Pandya, & Duckworth, 2016 ). For adolescents and young adults ages 12 to 21 with psychotic disorders and mood disorders, over 97% reported using social media, with average use exceeding 2.5 hours per day ( M. L. Birnbaum et al., 2017 ). Similarly, in a sample of adolescents ages 13-18 recruited from community mental health centers, 98% reported using social media, with YouTube as the most popular platform, followed by Instagram and Snapchat ( Aschbrenner et al., 2019 ).
Research has also explored the motivations for using social media as well as the perceived benefits of interacting on these platforms among individuals with mental illness. In the sections that follow (see Table 1 for a summary), we consider three potentially unique features of interacting and connecting with others on social media that may offer benefits for individuals living with mental illness. These include: 1) Facilitate social interaction; 2) Access to a peer support network; and 3) Promote engagement and retention in services.
Summary of potential benefits and challenges with social media for mental health
Facilitate Social Interaction
Social media platforms offer near continuous opportunities to connect and interact with others, regardless of time of day or geographic location. This on demand ease of communication may be especially important for facilitating social interaction among individuals with mental disorders experiencing difficulties interacting in face-to-face settings. For example, impaired social functioning is a common deficit in schizophrenia spectrum disorders, and social media may facilitate communication and interacting with others for these individuals ( Torous & Keshavan, 2016 ). This was suggested in one study where participants with schizophrenia indicated that social media helped them to interact and socialize more easily ( Miller et al., 2015 ). Like other online communication, the ability to connect with others anonymously may be an important feature of social media, especially for individuals living with highly stigmatizing health conditions ( Berger, Wagner, & Baker, 2005 ), such as serious mental disorders ( Highton-Williamson, Priebe, & Giacco, 2015 ).
Studies have found that individuals with serious mental disorders ( Spinzy, Nitzan, Becker, Bloch, & Fennig, 2012 ) as well as young adults with mental illness ( Gowen, Deschaine, Gruttadara, & Markey, 2012 ) appear to form online relationships and connect with others on social media as often as social media users from the general population. This is an important observation because individuals living with serious mental disorders typically have few social contacts in the offline world, and also experience high rates of loneliness ( Badcock et al., 2015 ; Giacco, Palumbo, Strappelli, Catapano, & Priebe, 2016 ). Among individuals receiving publicly funded mental health services who use social media, nearly half (47%) reported using these platforms at least weekly to feel less alone ( Brusilovskiy, Townley, Snethen, & Salzer, 2016 ). In another study of young adults with serious mental illness, most indicated that they used social media to help feel less isolated ( Gowen et al., 2012 ). Interestingly, more frequent use of social media among a sample of individuals with serious mental illness was associated with greater community participation, measured as participation in shopping, work, religious activities or visiting friends and family, as well as greater civic engagement, reflected as voting in local elections ( Brusilovskiy et al., 2016 ).
Emerging research also shows that young people with moderate to severe depressive symptoms appear to prefer communicating on social media rather than in-person ( Rideout & Fox, 2018 ), while other studies have found that some individuals may prefer to seek help for mental health concerns online rather than through in-person encounters ( Batterham & Calear, 2017 ). In a qualitative study, participants with schizophrenia described greater anonymity, the ability to discover that other people have experienced similar health challenges, and reducing fears through greater access to information as important motivations for using the Internet to seek mental health information ( Schrank, Sibitz, Unger, & Amering, 2010 ). Because social media does not require the immediate responses necessary in face-to-face communication, it may overcome deficits with social interaction due to psychotic symptoms that typically adversely affect face-to-face conversations ( Docherty et al., 1996 ). Online social interactions may not require the use of non-verbal cues, particularly in the initial stages of interaction ( Kiesler, Siegel, & McGuire, 1984 ), with interactions being more fluid, and within the control of users, thereby overcoming possible social anxieties linked to in-person interaction ( Indian & Grieve, 2014 ). Furthermore, many individuals with serious mental disorders can experience symptoms including passive social withdrawal, blunted affect and attentional impairment, as well as active social avoidance due to hallucinations or other concerns ( Hansen, Torgalsbøen, Melle, & Bell, 2009 ); thus, potentially reinforcing the relative advantage, as perceived by users, of using social media over in person conversations.
Access to a Peer Support Network
There is growing recognition about the role that social media channels could play in enabling peer support ( Bucci et al., 2019 ; Naslund, Aschbrenner, et al., 2016b ), referred to as a system of mutual giving and receiving where individuals who have endured the difficulties of mental illness can offer hope, friendship, and support to others facing similar challenges ( Davidson, Chinman, Sells, & Rowe, 2006 ; Mead, Hilton, & Curtis, 2001 ). Initial studies exploring use of online self-help forums among individuals with serious mental illnesses have found that individuals with schizophrenia appeared to use these forums for self-disclosure, and sharing personal experiences, in addition to providing or requesting information, describing symptoms, or discussing medication ( Haker, Lauber, & Rössler, 2005 ), while users with bipolar disorder reported using these forums to ask for help from others about their illness ( Vayreda & Antaki, 2009 ). More recently, in a review of online social networking in people with psychosis, Highton-Williamson et al (2015) highlight that an important purpose of such online connections was to establish new friendships, pursue romantic relationships, maintain existing relationships or reconnect with people, and seek online peer support from others with lived experience ( Highton-Williamson et al., 2015 ).
Online peer support among individuals with mental illness has been further elaborated in various studies. In a content analysis of comments posted to YouTube by individuals who self-identified as having a serious mental illness, there appeared to be opportunities to feel less alone, provide hope, find support and learn through mutual reciprocity, and share coping strategies for day-to-day challenges of living with a mental illness ( Naslund, Grande, Aschbrenner, & Elwyn, 2014 ). In another study, Chang (2009) delineated various communication patterns in an online psychosis peer-support group ( Chang, 2009 ). Specifically, different forms of support emerged, including ‘informational support’ about medication use or contacting mental health providers, ‘esteem support’ involving positive comments for encouragement, ‘network support’ for sharing similar experiences, and ‘emotional support’ to express understanding of a peer’s situation and offer hope or confidence ( Chang, 2009 ). Bauer et al. (2013) reported that the main interest in online self-help forums for patients with bipolar disorder was to share emotions with others, allow exchange of information, and benefit by being part of an online social group ( Bauer, Bauer, Spiessl, & Kagerbauer, 2013 ).
For individuals who openly discuss mental health problems on Twitter, a study by Berry et al. (2017) found that this served as an important opportunity to seek support and to hear about the experiences of others ( Berry et al., 2017 ). In a survey of social media users with mental illness, respondents reported that sharing personal experiences about living with mental illness and opportunities to learn about strategies for coping with mental illness from others were important reasons for using social media ( Naslund et al., 2017 ). A computational study of mental health awareness campaigns on Twitter provides further support with inspirational posts and tips being the most shared ( Saha et al., 2019 ). Taken together, these studies offer insights about the potential for social media to facilitate access to an informal peer support network, though more research is necessary to examine how these online interactions may impact intentions to seek care, illness self-management, and clinically meaningful outcomes in offline contexts.
Promote Engagement and Retention in Services
Many individuals living with mental disorders have expressed interest in using social media platforms for seeking mental health information ( Lal, Nguyen, & Theriault, 2018 ), connecting with mental health providers ( M. L. Birnbaum et al., 2017 ), and accessing evidence-based mental health services delivered over social media specifically for coping with mental health symptoms or for promoting overall health and wellbeing ( Naslund et al., 2017 ). With the widespread use of social media among individuals living with mental illness combined with the potential to facilitate social interaction and connect with supportive peers, as summarized above, it may be possible to leverage the popular features of social media to enhance existing mental health programs and services. A recent review by Biagianti et al (2018) found that peer-to-peer support appeared to offer feasible and acceptable ways to augment digital mental health interventions for individuals with psychotic disorders by specifically improving engagement, compliance, and adherence to the interventions, and may also improve perceived social support ( Biagianti, Quraishi, & Schlosser, 2018 ).
Among digital programs that have incorporated peer-to-peer social networking consistent with popular features on social media platforms, a pilot study of the HORYZONS online psychosocial intervention demonstrated significant reductions in depression among patients with first episode psychosis ( Alvarez-Jimenez et al., 2013 ). Importantly, the majority of participants (95%) in this study engaged with the peer-to-peer networking feature of the program, with many reporting increases in perceived social connectedness and empowerment in their recovery process ( Alvarez-Jimenez et al., 2013 ). This moderated online social therapy program is now being evaluated as part of a large randomized controlled trial for maintaining treatment effects from first episode psychosis services ( Alvarez-Jimenez et al., 2019 ).
Other early efforts have demonstrated that use of digital environments with the interactive peer-to-peer features of social media can enhance social functioning and wellbeing in young people at high risk of psychosis ( Alvarez-Jimenez et al., 2018 ). There has also been a recent emergence of several mobile apps to support symptom monitoring and relapse prevention in psychotic disorders. Among these apps, the development of PRIME (Personalized Real-time Intervention for Motivational Enhancement) has involved working closely with young people with schizophrenia to ensure that the design of the app has the look and feel of mainstream social media platforms, as opposed to existing clinical tools ( Schlosser et al., 2016 ). This unique approach to the design of the app is aimed at promoting engagement, and ensuring that the app can effectively improve motivation and functioning through goal setting and promoting better quality of life of users with schizophrenia ( Schlosser et al., 2018 ).
Social media platforms could also be used to promote engagement and participation in in-person services delivered through community mental health settings. For example, the peer-based lifestyle intervention called PeerFIT targets weight loss and improved fitness among individuals living with serious mental illness through a combination of in-person lifestyle classes, exercise groups, and use of digital technologies ( Aschbrenner, Naslund, Shevenell, Kinney, & Bartels, 2016 ; Aschbrenner, Naslund, Shevenell, Mueser, & Bartels, 2016 ). The intervention holds tremendous promise as lack of support is one of the largest barriers toward exercise in patients with serious mental illness ( Firth et al., 2016 ) and it is now possible to use social media to counter such. Specifically, in PeerFIT, a private Facebook group is closely integrated into the program to offer a closed platform where participants can connect with the lifestyle coaches, access intervention content, and support or encourage each other as they work towards their lifestyle goals ( Aschbrenner, Naslund, & Bartels, 2016 ; Naslund, Aschbrenner, Marsch, & Bartels, 2016a ). To date, this program has demonstrate preliminary effectiveness for meaningfully reducing cardiovascular risk factors that contribute to early mortality in this patient group ( Aschbrenner, Naslund, Shevenell, Kinney, et al., 2016 ), while the Facebook component appears to have increased engagement in the program, while allowing participants who were unable to attend in-person sessions due to other health concerns or competing demands to remain connected with the program ( Naslund, Aschbrenner, Marsch, McHugo, & Bartels, 2018 ). This lifestyle intervention is currently being evaluated in a randomized controlled trial enrolling young adults with serious mental illness from a variety of real world community mental health services settings ( Aschbrenner, Naslund, Gorin, et al., 2018 ).
These examples highlight the promise of incorporating the features of popular social media into existing programs, which may offer opportunities to safely promote engagement and program retention, while achieving improved clinical outcomes. This is an emerging area of research, as evidenced by several important effectiveness trials underway ( Alvarez-Jimenez et al., 2019 ; Aschbrenner, Naslund, Gorin, et al., 2018 ), including efforts to leverage online social networking to support family caregivers of individuals receiving first episode psychosis services ( Gleeson et al., 2017 ).
Challenges with Social Media for Mental Health
The science on the role of social media for engaging persons with mental disorders needs a cautionary note on the effects of social media usage on mental health and well being, particularly in adolescents and young adults. While the risks and harms of social media are frequently covered in the popular press and mainstream news reports, careful consideration of the research in this area is necessary. In a review of 43 studies in young people, many benefits of social media were cited, including increased self-esteem, and opportunities for self-disclosure ( Best, Manktelow, & Taylor, 2014 ). Yet, reported negative effects were an increased exposure to harm, social isolation, depressive symptoms and bullying ( Best et al., 2014 ). In the sections that follow (see Table 1 for a summary), we consider three major categories of risk related to use of social media and mental health. These include: 1) Impact on symptoms; 2) Facing hostile interactions; and 3) Consequences for daily life.
Impact on Symptoms
Studies consistently highlight that use of social media, especially heavy use and prolonged time spent on social media platforms, appears to contribute to increased risk for a variety of mental health symptoms and poor wellbeing, especially among young people ( Andreassen et al., 2016 ; Kross et al., 2013 ; Woods & Scott, 2016 ). This may partly be driven by the detrimental effects of screen time on mental health, including increased severity of anxiety and depressive symptoms, which have been well documented ( Stiglic & Viner, 2019 ). Recent studies have reported negative effects of social media use on mental health of young people, including social comparison pressure with others and greater feeling of social isolation after being rejected by others on social media ( Rideout & Fox, 2018 ). In a study of young adults, it was found that negative comparisons with others on Facebook contributed to risk of rumination and subsequent increases in depression symptoms ( Feinstein et al., 2013 ). Still, the cross sectional nature of many screen time and mental health studies makes it challenging to reach causal inferences ( Orben & Przybylski, 2019 ).
Quantity of social media use is also an important factor, as highlighted in a survey of young adults ages 19 to 32, where more frequent visits to social media platforms each week were correlated with greater depressive symptoms ( Lin et al., 2016 ). More time spent using social media is also associated with greater symptoms of anxiety ( Vannucci, Flannery, & Ohannessian, 2017 ). The actual number of platforms accessed also appears to contribute to risk as reflected in another national survey of young adults where use of a large number of social media platforms was associated with negative impact on mental health ( Primack et al., 2017 ). Among survey respondents using between 7 and 11 different social media platforms compared to respondents using only 2 or fewer platforms, there was a 3 times greater odds of having high levels of depressive symptoms and a 3.2 times greater odds of having high levels of anxiety symptoms ( Primack et al., 2017 ).
Many researchers have postulated that worsening mental health attributed to social media use may be because social media replaces face-to-face interactions for young people ( Twenge & Campbell, 2018 ), and may contribute to greater loneliness ( Bucci et al., 2019 ), and negative effects on other aspects of health and wellbeing ( Woods & Scott, 2016 ). One nationally representative survey of US adolescents found that among respondents who reported more time accessing media such as social media platforms or smartphone devices, there was significantly greater depressive symptoms and increased risk of suicide when compared to adolescents who reported spending more time on non-screen activities, such as in-person social interaction or sports and recreation activities ( Twenge, Joiner, Rogers, & Martin, 2018 ). For individuals living with more severe mental illnesses, the effects of social media on psychiatric symptoms have received less attention. One study found that participation in chat rooms may contribute to worsening symptoms in young people with psychotic disorders ( Mittal, Tessner, & Walker, 2007 ), while another study of patients with psychosis found that social media use appeared to predict low mood ( Berry, Emsley, Lobban, & Bucci, 2018 ). These studies highlight a clear relationship between social media use and mental health that may not be present in general population studies ( Orben & Przybylski, 2019 ), and emphasize the need to explore how social media may contribute to symptom severity and whether protective factors may be identified to mitigate these risks.
Facing Hostile Interactions
Popular social media platforms can create potential situations where individuals may be victimized by negative comments or posts. Cyberbullying represents a form of online aggression directed towards specific individuals, such as peers or acquaintances, which is perceived to be most harmful when compared to random hostile comments posted online ( Hamm et al., 2015 ). Importantly, cyberbullying on social media consistently shows harmful impact on mental health in the form of increased depressive symptoms as well as worsening of anxiety symptoms, as evidenced in a review of 36 studies among children and young people ( Hamm et al., 2015 ). Furthermore, cyberbullying disproportionately impacts females as reflected in a national survey of adolescents in the United States, where females were twice as likely to be victims of cyberbullying compared to males ( Alhajji, Bass, & Dai, 2019 ). Most studies report cross-sectional associations between cyberbullying and symptoms of depression or anxiety ( Hamm et al., 2015 ), though one longitudinal study in Switzerland found that cyberbullying contributed to significantly greater depression over time ( Machmutow, Perren, Sticca, & Alsaker, 2012 ).
For youth ages 10 to 17 who reported major depressive symptomatology, there was over 3 times greater odds of facing online harassment in the last year compared to youth who reported mild or no depressive symptoms ( Ybarra, 2004 ). Similarly, in a 2018 national survey of young people, respondents ages 14 to 22 with moderate to severe depressive symptoms were more likely to have had negative experiences when using social media, and in particular, were more likely to report having faced hostile comments, or being “trolled”, from others when compared to respondents without depressive symptoms (31% vs. 14%) ( Rideout & Fox, 2018 ). As these studies depict risks for victimization on social media and the correlation with poor mental health, it is possible that individuals living with mental illness may also experience greater hostility online compared to individuals without mental illness. This would be consistent with research showing greater risk of hostility, including increased violence and discrimination, directed towards individuals living with mental illness in in-person contexts, especially targeted at those with severe mental illnesses ( Goodman et al., 1999 ).
A computational study of mental health awareness campaigns on Twitter reported that while stigmatizing content was rare, it was actually the most spread (re-tweeted) demonstrating that harmful content can travel quickly on social media ( Saha et al., 2019 ). Another study was able to map the spread of social media posts about the Blue Whale Challenge, an alleged game promoting suicide, over Twitter, YouTube, Reddit, Tumblr and other forums across 127 countries ( Sumner et al., 2019 ). These findings show that it is critical to monitor the actual content of social media posts, such as determining whether content is hostile or promotes harm to self or others. This is pertinent because existing research looking at duration of exposure cannot account for the impact of specific types of content on mental health and is insufficient to fully understand the effects of using these platforms on mental health.
Consequences for Daily Life
The ways in which individuals use social media can also impact their offline relationships and everyday activities. To date, reports have described risks of social media use pertaining to privacy, confidentiality, and unintended consequences of disclosing personal health information online ( Torous & Keshavan, 2016 ). Additionally, concerns have been raised about poor quality or misleading health information shared on social media, and that social media users may not be aware of misleading information or conflicts of interest especially when the platforms promote popular content regardless of whether it is from a trustworthy source ( Moorhead et al., 2013 ; Ventola, 2014 ). For persons living with mental illness there may be additional risks from using social media. A recent study that specifically explored the perspectives of social media users with serious mental illnesses, including participants with schizophrenia spectrum disorders, bipolar disorder, or major depression, found that over one third of participants expressed concerns about privacy when using social media ( Naslund & Aschbrenner, 2019 ). The reported risks of social media use were directly related to many aspects of everyday life, including concerns about threats to employment, fear of stigma and being judged, impact on personal relationships, and facing hostility or being hurt ( Naslund & Aschbrenner, 2019 ). While few studies have specifically explored the dangers of social media use from the perspectives of individuals living with mental illness, it is important to recognize that use of these platforms may contribute to risks that extend beyond worsening symptoms and that can affect different aspects of daily life.
In this commentary we considered ways in which social media may yield benefits for individuals living with mental illness, while contrasting these with the possible harms. Studies reporting on the threats of social media for individuals with mental illness are mostly cross-sectional, making it difficult to draw conclusions about direction of causation. However, the risks are potentially serious. These risks should be carefully considered in discussions pertaining to use of social media and the broader use of digital mental health technologies, as avenues for mental health promotion, or for supporting access to evidence-based programs or mental health services. At this point, it would be premature to view the benefits of social media as outweighing the possible harms, when it is clear from the studies summarized here that social media use can have negative effects on mental health symptoms, can potentially expose individuals to hurtful content and hostile interactions, and can result in serious consequences for daily life, including threats to employment and personal relationships. Despite these risks, it is also necessary to recognize that individuals with mental illness will continue to use social media given the ease of accessing these platforms and the immense popularity of online social networking. With this in mind, it may be ideal to raise awareness about these possible risks so that individuals can implement necessary safeguards, while also highlighting that there could also be benefits. For individuals with mental illness who use social media, being aware of the risks is an essential first step, and then highlighting ways that use of these popular platforms could also contribute to some benefits, ranging from finding meaningful interactions with others, engaging with peer support networks, and accessing information and services.
To capitalize on the widespread use of social media, and to achieve the promise that these platforms may hold for supporting the delivery of targeted mental health interventions, there is need for continued research to better understand how individuals living with mental illness use social media. Such efforts could inform safety measures and also encourage use of social media in ways that maximize potential benefits while minimizing risk of harm. It will be important to recognize how gender and race contribute to differences in use of social media for seeking mental health information or accessing interventions, as well as differences in how social media might impact mental wellbeing. For example, a national survey of 14- to 22-year olds in the United States found that female respondents were more likely to search online for information about depression or anxiety, and to try to connect with other people online who share similar mental health concerns, when compared to male respondents ( Rideout & Fox, 2018 ). In the same survey, there did not appear to be any differences between racial or ethnic groups in social media use for seeking mental health information ( Rideout & Fox, 2018 ). Social media use also appears to have a differential impact on mental health and emotional wellbeing between females and males ( Booker, Kelly, & Sacker, 2018 ), highlighting the need to explore unique experiences between gender groups to inform tailored programs and services. Research shows that lesbian, gay, bisexual or transgender individuals frequently use social media for searching for health information and may be more likely compared to heterosexual individuals to share their own personal health experiences with others online ( Rideout & Fox, 2018 ). Less is known about use of social media for seeking support for mental health concerns among gender minorities, though this is an important area for further investigation as these individuals are more likely to experience mental health problems and more likely to experience online victimization when compared to heterosexual individuals ( Mereish, Sheskier, Hawthorne, & Goldbach, 2019 ).
Similarly, efforts are needed to explore the relationship between social media use and mental health among ethnic and racial minorities. A recent study found that exposure to traumatic online content on social media showing violence or hateful posts directed at racial minorities contributed to increases in psychological distress, PTSD symptoms, and depression among African American and Latinx adolescents in the United States ( Tynes, Willis, Stewart, & Hamilton, 2019 ). These concerns are contrasted by growing interest in the potential for new technologies including social media to expand the reach of services to underrepresented minority groups ( Schueller, Hunter, Figueroa, & Aguilera, 2019 ). Therefore, greater attention is needed to understanding the perspectives of ethnic and racial minorities to inform effective and safe use of social media for mental health promotion efforts.
Research has found that individuals living with mental illness have expressed interest in accessing mental health services through social media platforms. A survey of social media users with mental illness found that most respondents were interested in accessing programs for mental health on social media targeting symptom management, health promotion, and support for communicating with health care providers and interacting with the health system ( Naslund et al., 2017 ). Importantly, individuals with serious mental illness have also emphasized that any mental health intervention on social media would need to be moderated by someone with adequate training and credentials, would need to have ground rules and ways to promote safety and minimize risks, and importantly, would need to be free and easy to access.
An important strength with this commentary is that it combines a range of studies broadly covering the topic of social media and mental health. We have provided a summary of recent evidence in a rapidly advancing field with the goal of presenting unique ways that social media could offer benefits for individuals with mental illness, while also acknowledging the potentially serious risks and the need for further investigation. There are also several limitations with this commentary that warrant consideration. Importantly, as we aimed to address this broad objective, we did not conduct a systematic review of the literature. Therefore, the studies reported here are not exhaustive, and there may be additional relevant studies that were not included. Additionally, we only summarized published studies, and as a result, any reports from the private sector or websites from different organizations using social media or other apps containing social media-like features would have been omitted. Though it is difficult to rigorously summarize work from the private sector, sometimes referred to as “gray literature”, because many of these projects are unpublished and are likely selective in their reporting of findings given the target audience may be shareholders or consumers.
Another notable limitation is that we did not assess risk of bias in the studies summarized in this commentary. We found many studies that highlighted risks associated with social media use for individuals living with mental illness; however, few studies of programs or interventions reported negative findings, suggesting the possibility that negative findings may go unpublished. This concern highlights the need for a future more rigorous review of the literature with careful consideration of bias and an accompanying quality assessment. Most of the studies that we described were from the United States, as well as from other higher income settings such as Australia or the United Kingdom. Despite the global reach of social media platforms, there is a dearth of research on the impact of these platforms on the mental health of individuals in diverse settings, as well as the ways in which social media could support mental health services in lower income countries where there is virtually no access to mental health providers. Future research is necessary to explore the opportunities and risks for social media to support mental health promotion in low-income and middle-income countries, especially as these countries face a disproportionate share of the global burden of mental disorders, yet account for the majority of social media users worldwide ( Naslund et al., 2019 ).
Future Directions for Social Media and Mental Health
As we consider future research directions, the near ubiquitous social media use also yields new opportunities to study the onset and manifestation of mental health symptoms and illness severity earlier than traditional clinical assessments. There is an emerging field of research referred to as ‘digital phenotyping’ aimed at capturing how individuals interact with their digital devices, including social media platforms, in order to study patterns of illness and identify optimal time points for intervention ( Jain, Powers, Hawkins, & Brownstein, 2015 ; Onnela & Rauch, 2016 ). Given that most people access social media via mobile devices, digital phenotyping and social media are closely related ( Torous et al., 2019 ). To date, the emergence of machine learning, a powerful computational method involving statistical and mathematical algorithms ( Shatte, Hutchinson, & Teague, 2019 ), has made it possible to study large quantities of data captured from popular social media platforms such as Twitter or Instagram to illuminate various features of mental health ( Manikonda & De Choudhury, 2017 ; Reece et al., 2017 ). Specifically, conversations on Twitter have been analyzed to characterize the onset of depression ( De Choudhury, Gamon, Counts, & Horvitz, 2013 ) as well as detecting users’ mood and affective states ( De Choudhury, Gamon, & Counts, 2012 ), while photos posted to Instagram can yield insights for predicting depression ( Reece & Danforth, 2017 ). The intersection of social media and digital phenotyping will likely add new levels of context to social media use in the near future.
Several studies have also demonstrated that when compared to a control group, Twitter users with a self-disclosed diagnosis of schizophrenia show unique online communication patterns ( Michael L Birnbaum, Ernala, Rizvi, De Choudhury, & Kane, 2017 ), including more frequent discussion of tobacco use ( Hswen et al., 2017 ), symptoms of depression and anxiety ( Hswen, Naslund, Brownstein, & Hawkins, 2018b ), and suicide ( Hswen, Naslund, Brownstein, & Hawkins, 2018a ). Another study found that online disclosures about mental illness appeared beneficial as reflected by fewer posts about symptoms following self-disclosure (Ernala, Rizvi, Birnbaum, Kane, & De Choudhury, 2017). Each of these examples offers early insights into the potential to leverage widely available online data for better understanding the onset and course of mental illness. It is possible that social media data could be used to supplement additional digital data, such as continuous monitoring using smartphone apps or smart watches, to generate a more comprehensive ‘digital phenotype’ to predict relapse and identify high-risk health behaviors among individuals living with mental illness ( Torous et al., 2019 ).
With research increasingly showing the valuable insights that social media data can yield about mental health states, greater attention to the ethical concerns with using individual data in this way is necessary ( Chancellor, Birnbaum, Caine, Silenzio, & De Choudhury, 2019 ). For instance, data is typically captured from social media platforms without the consent or awareness of users ( Bidargaddi et al., 2017 ), which is especially crucial when the data relates to a socially stigmatizing health condition such as mental illness ( Guntuku, Yaden, Kern, Ungar, & Eichstaedt, 2017 ). Precautions are needed to ensure that data is not made identifiable in ways that were not originally intended by the user who posted the content, as this could place an individual at risk of harm or divulge sensitive health information ( Webb et al., 2017 ; Williams, Burnap, & Sloan, 2017 ). Promising approaches for minimizing these risks include supporting the participation of individuals with expertise in privacy, clinicians, as well as the target individuals with mental illness throughout the collection of data, development of predictive algorithms, and interpretation of findings ( Chancellor et al., 2019 ).
In recognizing that many individuals living with mental illness use social media to search for information about their mental health, it is possible that they may also want to ask their clinicians about what they find online to check if the information is reliable and trustworthy. Alternatively, many individuals may feel embarrassed or reluctant to talk to their clinicians about using social media to find mental health information out of concerns of being judged or dismissed. Therefore, mental health clinicians may be ideally positioned to talk with their patients about using social media, and offer recommendations to promote safe use of these sites, while also respecting their patients’ autonomy and personal motivations for using these popular platforms. Given the gap in clinical knowledge about the impact of social media on mental health, clinicians should be aware of the many potential risks so that they can inform their patients, while remaining open to the possibility that their patients may also experience benefits through use of these platforms. As awareness of these risks grows, it may be possible that new protections will be put in place by industry or through new policies that will make the social media environment safer. It is hard to estimate a number needed to treat or harm today given the nascent state of research, which means the patient and clinician need to weigh the choice on a personal level. Thus offering education and information is an important first step in that process. As patients increasingly show interest in accessing mental health information or services through social media, it will be necessary for health systems to recognize social media as a potential avenue for reaching or offering support to patients. This aligns with growing emphasis on the need for greater integration of digital psychiatry, including apps, smartphones, or wearable devices, into patient care and clinical services through institution-wide initiatives and training clinical providers ( Hilty, Chan, Torous, Luo, & Boland, 2019 ). Within a learning healthcare environment where research and care are tightly intertwined and feedback between both is rapid, the integration of digital technologies into services may create new opportunities for advancing use of social media for mental health.
As highlighted in this commentary, social media has become an important part of the lives of many individuals living with mental disorders. Many of these individuals use social media to share their lived experiences with mental illness, to seek support from others, and to search for information about treatment recommendations, accessing mental health services, and coping with symptoms ( Bucci et al., 2019 ; Highton-Williamson et al., 2015 ; Naslund, Aschbrenner, et al., 2016b ). As the field of digital mental health advances, the wide reach, ease of access, and popularity of social media platforms could be used to allow individuals in need of mental health services or facing challenges of mental illness to access evidence-based treatment and support. To achieve this end and to explore whether social media platforms can advance efforts to close the gap in available mental health services in the United States and globally, it will be essential for researchers to work closely with clinicians and with those affected by mental illness to ensure that possible benefits of using social media are carefully weighed against anticipated risks.
Acknowledgements
Dr. Naslund is supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health (U19MH113211). Dr. Aschbrenner is supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health (1R01MH110965-01).
Publisher's Disclaimer: This Author Accepted Manuscript is a PDF file of a an unedited peer-reviewed manuscript that has been accepted for publication but has not been copyedited or corrected. The official version of record that is published in the journal is kept up to date and so may therefore differ from this version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
- Abdel-Baki A, Lai S, D.-Charron O, Stip E, & Kara N, (2017). Understanding access and use of technology among youth with first - episode psychosis to inform the development of technology - enabled therapeutic interventions . Early intervention in psychiatry , 77 ( 1 ), 72–76. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ahmed YA, Ahmad MN, Ahmad N, & Zakaria NH (2019). Social media for knowledge-sharing: A systematic literature review . Telematics and informatics , 37 , 72–112 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Alhajji M, Bass S, & Dai T (2019). Cyberbullying, mental health, and violence in adolescents and associations with sex and race: data from the 2015 Youth Risk Behavior Survey . Global pediatric health , 6 , 2333794X19868887. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alvarez-Jimenez M, Bendall S, Koval P, Rice S, Cagliarini D, Valentine L, … Penn DL (2019). HORYZONS trial: protocol for a randomised controlled trial of a moderated online social therapy to maintain treatment effects from first-episode psychosis services . BMJ open , 9 ( 2 ), e024104. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alvarez-Jimenez M, Bendall S, Lederman R, Wadley G, Chinnery G, Vargas S, … Gleeson JF (2013). On the HORYZON: moderated online social therapy for long-term recovery in first episode psychosis . Schizophrenia research , 143 ( 1 ), 143–149. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alvarez-Jimenez M, Gleeson J, Bendall S, Penn D, Yung A, Ryan R, … Miles C (2018). Enhancing social functioning in young people at Ultra High Risk (UHR) for psychosis: A pilot study of a novel strengths and mindfulness-based online social therapy . Schizophrenia research , 202 , 369–377. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Andreassen CS, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, & Pallesen S (2016). The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: A large-scale cross-sectional study . Psychology of Addictive Behaviors , 30 ( 2 ), 252. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aschbrenner KA, Naslund JA, & Bartels SJ (2016). A mixed methods study of peer-to-peer support in a group-based lifestyle intervention for adults with serious mental illness . Psychiatric rehabilitation journal , 39 ( 4 ), 328. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aschbrenner KA, Naslund JA, Gorin AA, Mueser KT, Scherer EA, Viron M, … Bartels SJ, (2018). Peer support and mobile health technology targeting obesity-related cardiovascular risk in young adults with serious mental illness: Protocol for a randomized controlled trial . Contemporary clinical trials , 74 , 97–106. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aschbrenner KA, Naslund JA, Grinley T, Bienvenida JCM, Bartels SJ, & Brunette M (2018). A Survey of Online and Mobile Technology Use at Peer Support Agencies . Psychiatric Quarterly , 1–10. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aschbrenner KA, Naslund JA, Shevenell M, Kinney E, & Bartels SJ (2016). A pilot study of a peer-group lifestyle intervention enhanced with mHealth technology and social media for adults with serious mental illness . The Journal of nervous and mental disease , 204 ( 6 ), 483–486. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aschbrenner KA, Naslund JA, Shevenell M, Mueser KT, & Bartels SJ (2016). Feasibility of behavioral weight loss treatment enhanced with peer support and mobile health technology for individuals with serious mental illness . Psychiatric Quarterly , 57 ( 3 ), 401–415. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aschbrenner KA, Naslund JA, Tomlinson EF, Kinney A, Pratt SI, & Brunette MF (2019). Adolescents’ Use of Digital Technologies and Preferences for Mobile Health Coaching in Mental Health Settings . Frontiers in Public Health . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Badcock JC, Shah S, Mackinnon A, Stain HJ, Galletly C, Jablensky A, & Morgan VA (2015). Loneliness in psychotic disorders and its association with cognitive function and symptom profile . Schizophrenia research , 169 ( 1-3 ), 268–273. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Batterham PJ, & Calear AJ (2017). Preferences for internet-based mental health interventions in an adult online sample: Findings from ann online community survey . JMIR mental health , 4 ( 2 ), e26. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bauer R, Bauer M, Spiessl H, & Kagerbauer T (2013). Cyber-support: an analysis of online self-help forums (online self-help forums in bipolar disorder) . Nordic journal of psychiatry , 67 ( 3 ), 185–190. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berger M, Wagner TH, & Baker LC (2005). Internet use and stigmatized illness . Social science & medicine , 67 ( 8 ), 1821–1827. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berry N, Emsley R, Lobban F, & Bucci S (2018). Social media and its relationship with mood, self - esteem and paranoia in psychosis . Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica , 138 , 558–570. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berry N, Lobban F, Belousov M, Emsley R, Nenadic G, & Bucci S (2017). # Why We Tweet MH: understanding why people use Twitter to discuss mental health problems . Journal of medical Internet research , 19 ( 4 ), e107. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Best P, Manktelow R, & Taylor B (2014). Online communication, social media and adolescent wellbeing: A systematic narrative review . Children and Youth Services Review , 41 , 27–36. [ Google Scholar ]
- Biagianti B, Quraishi SH, & Schlosser DA (2018). Potential benefits of incorporating peer-to-peer interactions into digital interventions for psychotic disorders: a systematic review . Psychiatric Services , 69 ( 4 ), 377–388. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bidargaddi N, Musiat P, Makinen V-P, Ermes M, Schrader G, & Licinio J (2017). Digital footprints: facilitating large-scale environmental psychiatric research in naturalistic settings through data from everyday technologies . Molecular psychiatry , 22 ( 2 ), 164. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Birnbaum ML, Emala SK, Rizvi AF, De Choudhury M, & Kane JM (2017). A Collaborative Approach to Identifying Social Media Markers of Schizophrenia by Employing Machine Learning and Clinical Appraisals . Journal of medical Internet research , 79 ( 8 ), e289. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Birnbaum ML, Rizvi AF, Correll CU, Kane JM, & Confino J (2017). Role of social media and the Internet in pathways to care for adolescents and young adults with psychotic disorders and non - psychotic mood disorders . Early intervention in psychiatry , 77 ( 4 ), 290–295. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Booker CL, Kelly YJ, & Sacker A (2018). Gender differences in the associations between age trends of social media interaction and well-being among 10-15 year olds in the UK . BMC public health , 18 ( 1 ), 321. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brunette M, Achtyes E, Pratt S, Stilwell K, Opperman M, Guarino S, & Kay-Lambkin F (2019). Use of smartphones, computers and social media among people with SMI: opportunity for intervention . Community mental health journal , 1–6. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brusilovskiy E, Townley G, Snethen G, & Salzer MS (2016). Social media use, community participation and psychological well-being among individuals with serious mental illnesses . Computers in Human Behavior , 65 , 232–240. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bucci S, Schwannauer M, & Berry N (2019). The digital revolution and its impact on mental health care . Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice , 1–21. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chancellor S, Birnbaum ML, Caine ED, Silenzio V, & De Choudhury M (2019). A taxonomy of ethical tensions in inferring mental health states from social media . Paper presented at the Proceedings of the Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang HJ (2009). Online supportive interactions: Using a network approach to examine communication patterns within a psychosis social support group in Taiwan . Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology , 60 ( 7 ), 1504–1517. [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidson L, Chinman M, Sells D, & Rowe M (2006). Peer support among adults with serious mental illness: a report from the field . Schizophrenia bulletin , 32 ( 3 ), 443–450. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- De Choudhury M, Gamon M, & Counts S (2012). Happy, nervous or surprised? classification of human affective states in social media . Paper presented at the Sixth International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media. [ Google Scholar ]
- De Choudhury M, Gamon M, Counts S, & Horvitz E (2013). Predicting Depression via Social Media . Paper presented at the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence. [ Google Scholar ]
- Docherty NM, Hawkins KA, Hoffman RE, Quinlan DM, Rakfeldt J, & Sledge WH (1996). Working memory, attention, and communication disturbances in schizophrenia . Journal of Abnormal Psychology , 105 ( 2 ), 212. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Emala SK, Rizvi AF, Birnbaum ML, Kane JM, & De Choudhury M (2017). Linguistic Markers Indicating Therapeutic Outcomes of Social Media Disclosures of Schizophrenia . Proc. ACMHum.-Comput. Interact , 1 ( 1 ), 43. [ Google Scholar ]
- Feinstein BA, Hershenberg R, Bhatia V, Latack JA, Meuwly N, & Davila J (2013). Negative social comparison on Facebook and depressive symptoms: Rumination as a mechanism . Psychology of Popular Media Culture , 2 ( 3 ), 161. [ Google Scholar ]
- Firth J, Cotter J, Torous J, Bucci S, Firth JA, & Yung AR (2015). Mobile phone ownership and endorsement of “mHealth” among people with psychosis: a meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies . Schizophrenia bulletin , 42 ( 2 ), 448–455. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Firth J, Rosenbaum S, Stubbs B, Gorczynski P, Yung AR, & Vancampfort D (2016). Motivating factors and barriers towards exercise in severe mental illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Psychological medicine , 46 ( 14 ), 2869–2881. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gay K, Torous J, Joseph A, Pandya A, & Duckworth K (2016). Digital technology use among individuals with schizophrenia: results of an online survey . JMIR mental health , 3 ( 2 ), el5. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giacco D, Palumbo C, Strappelli N, Catapano F, & Priebe S (2016). Social contacts and loneliness in people with psychotic and mood disorders . Comprehensive Psychiatry , 66 , 59–66. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gleeson J, Lederman R, Herrman H, Koval P, Eleftheriadis D, Bendall S, … Alvarez-Jimenez M (2017). Moderated online social therapy for carers of young people recovering from first-episode psychosis: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial . Trials , 75 ( 1 ), 27. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Glick G, Druss B, Pina J, Lally C, & Conde M (2016). Use of mobile technology in a community mental health setting . Journal of telemedicine and telecare , 22 ( 7 ), 430–435. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Goodman LA, Thompson KM, Weinfurt K, Corl S, Acker P, Mueser KT, & Rosenberg SD (1999). Reliability of reports of violent victimization and posttraumatic stress disorder among men and women with serious mental illness . Journal of Traumatic Stress: Official Publication of the International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies , 12 ( 4 ), 587–599. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gowen K, Deschaine M, Gruttadara D, & Markey D (2012). Young adults with mental health conditions and social networking websites: seeking tools to build community . Psychiatric rehabilitation journal , 35 ( 3 ), 245–250. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Guntuku SC, Yaden DB, Kern ML, Ungar LH, & Eichstaedt JC (2017). Detecting depression and mental illness on social media: an integrative review . Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences , 18 , 43–49. [ Google Scholar ]
- Haker EL, Lauber C, & Rossler W (2005). Internet forums: a self - help approach for individuals with schizophrenia? Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica , 112 ( 6 ), 474–477. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hamm MP, Newton AS, Chisholm A, Shulhan J, Milne A, Sundar P, … Hartling L (2015). Prevalence and effect of cyberbullying on children and young people: A scoping review of social media studies . JAMA pediatrics , 769 ( 8 ), 770–777. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hansen CF, Torgalsboen A-K, Melle I, & Bell MD (2009). Passive/apathetic social withdrawal and active social avoidance in schizophrenia: difference in underlying psychological processes . The Journal of nervous and mental disease , 197 ( 4 ), 274–277. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Highton-Williamson E, Priebe S, & Giacco D (2015). Online social networking in people with psychosis: a systematic review . International Journal of Social Psychiatry , 61 ( 1 ), 92–101. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hilty DM, Chan S, Torous J, Luo J, & Boland RJ (2019). Mobile health, smartphone/device, and apps for psychiatry and medicine: competencies, training, and faculty development issues . Psychiatric Clinics , 42 ( 2 ), 513–534. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hswen Y, Naslund JA, Brownstein JS, & Hawkins JB (2018a). Monitoring online discussions about suicide among Twitter users with schizophrenia: exploratory study . JMIR mental health , 5 ( 4 ), e11483. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hswen Y, Naslund JA, Brownstein JS, & Hawkins JB (2018b). Online communication about depression and anxiety among twitter users with schizophrenia: preliminary findings to inform a digital phenotype using social media . Psychiatric Quarterly , 89 ( 3 ), 569–580. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hswen Y, Naslund JA, Chandrashekar P, Siegel R, Brownstein JS, & Hawkins JB (2017). Exploring online communication about cigarette smoking among Twitter users who self-identify as having schizophrenia . Psychiatry research , 257 , 479–484. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Indian M, & Grieve R (2014). When Facebook is easier than face-to-face: social support dervied from Facebook in socially anxious individuals . Personality and Individual Differences , 59 , 102–106. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jain SH, Powers BW, Hawkins JB, & Brownstein JS (2015). The digital phenotype . Nature Biotechnology , 33 ( 5 ), 462. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kiesler S, Siegel J, & McGuire TW (1984). Social psychological aspects of computer-mediated communication . American Psychologist , 39 , 1123–1134. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kross E, Verduyn P, Demiralp E, Park J, Lee DS, Lin N, … Ybarra O (2013). Facebook use predicts declines in subjective well-being in young adults . PloS one , 5 ( 8 ), e69841. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lai S, Nguyen V, & Theriault J (2018). Seeking mental health information and support online: experiences and perspectives of young people receiving treatment for first - episode psychosis . Early intervention in psychiatry , 72 ( 3 ), 324–330. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lin LY, Sidani JE, Shensa A, Radovic A, Miller E, Colditz JB, … Primack BA (2016). Association between social media use and depression among US young adults . Depression and anxiety , 22 ( 4 ), 323–331. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Machmutow K, Perren S, Sticca F, & Alsaker FD (2012). Peer victimisation and depressive symptoms: can specific coping strategies buffer the negative impact of cybervictimisation? Emotional and Behavioural Difficulties , 17 ( 3-4 ), 403–420. [ Google Scholar ]
- Manikonda L, & De Choudhury M (2017). Modeling and understanding visual attributes of mental health disclosures in social media . Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mead S, Hilton D, & Curtis L (2001). Peer support: A theoretical perspective . Psychiatric rehabilitation journal , 25 ( 2 ), 134. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mereish EH, Sheskier M, Hawthorne DJ, & Goldbach JT (2019). Sexual orientation disparities in mental health and substance use among Black American young people in the USA: effects of cyber and bias-based victimisation . Culture, health & sexuality , 21 ( 9 ), 985–998. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miller BJ, Stewart A, Schrimsher J, Peeples D, & Buckley PF (2015). How connected are people with schizophrenia? Cell phone, computer, email, and social media use . Psychiatry research , 225 ( 3 ), 458–463. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mittal VA, Tessner KD, & Walker EF (2007). Elevated social Internet use and schizotypal personality disorder in adolescents . Schizophrenia research , 94 ( 1-3 ), 50–57. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Moorhead SA, Hazlett DE, Harrison L, Carroll JK, Irwin A, & Hoving C (2013). A new dimension of health care: systematic review of the uses, benefits, and limitations of social media for health communication . Journal of medical Internet research , 15 ( 4 ), e85. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naslund JA, & Aschbrenner KA (2019). Risks to privacy with use of social media: understanding the views of social media users with serious mental illness . Psychiatric Services , appi. ps. 201800520. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naslund JA, Aschbrenner KA, & Bartels SJ (2016). How people living with serious mental illness use smartphones, mobile apps, and social media . Psychiatric rehabilitation journal , 39 ( 4 ), 364–367. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naslund JA, Aschbrenner KA, Marsch LA, & Bartels SJ (2016a). Feasibility and acceptability of Facebook for health promotion among people with serious mental illness . Digital health , 2 , 2055207616654822. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naslund JA, Aschbrenner KA, Marsch LA, & Bartels SJ (2016b). The future of mental health care: peer-to-peer support and social media . Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences , 25 ( 2 ), 113–122. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naslund JA, Aschbrenner KA, Marsch LA, McHugo GJ, & Bartels SJ (2018). Facebook for supporting a lifestyle intervention for people with major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia: an exploratory study . Psychiatric Quarterly , 59 ( 1 ), 81–94. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naslund JA, Aschbrenner KA, McHugo GJ, Unutzer J, Marsch LA, & Bartels SJ (2017). Exploring opportunities to support mental health care using social media: A survey of social media users with mental illness . Early intervention in psychiatry . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naslund JA, Gonsalves PP, Gruebner O, Pendse SR, Smith SL, Sharma A, & Raviola G (2019). Digital innovations for global mental health: opportunities for data science, task sharing, and early intervention . Current Treatment Options in Psychiatry , 1–15. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naslund JA, Grande SW, Aschbrenner KA, & Elwyn G (2014). Naturally occurring peer support through social media: the experiences of individuals with severe mental illness using YouTube . PloS one , 9 ( 10 ), e110171. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Onnela J-P, & Rauch SL (2016). Harnessing smartphone-based digital phenotyping to enhance behavioral and mental health . Neuropsychopharmacology , 41 ( 7 ), 1691. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Orben A, & Przybylski AK (2019). The association between adolescent well-being and digital technology use . Nature Human Behaviour , 3 ( 2 ), 173. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Patel V, Saxena S, Lund C, Thornicroft G, Baingana F, Bolton P, … Eaton J (2018). The Lancet Commission on global mental health and sustainable development . The Lancet . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Primack BA, Shensa A, Escobar-Viera CG, Barrett EL, Sidani JE, Colditz JB, & James AE (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults . Computers in Human Behavior , 69 , 1–9. [ Google Scholar ]
- Reece AG, & Danforth CM (2017). Instagram photos reveal predictive markers of depression . EPJ Data Science , 6 ( 1 ), 15. [ Google Scholar ]
- Reece AG, Reagan AJ, Lix KL, Dodds PS, Danforth CM, & Langer EJ (2017). Forecasting the onset and course of mental illness with Twitter data . Scientific reports , 7 ( 1 ), 13006. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rideout V, & Fox S (2018). Digital health practices, social media use, and mental well-being among teens and young adults in the U.S Retrieved from San Francisco, CA: https://www.hopelab.org/reports/pdf/a-national-survey-by-hopelab-and-well-being-trust-2018.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Saha K, Torous J, Ernala SK, Rizuto C, Stafford A, & De Choudhury M (2019). A computational study of mental health awareness campaigns on social media . Translational behavioral medicine . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schlosser DA, Campellone T, Kim D, Truong B, Vergani S, Ward C, & Vinogradov S (2016). Feasibility of PRIME: a cognitive neuroscience-informed mobile app intervention to enhance motivated behavior and improve quality of life in recent onset schizophrenia . JMIR research protocols , 5 ( 2 ). [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schlosser DA, Campellone TR, Truong B, Etter K, Vergani S, Komaiko K, & Vinogradov S (2018). Efficacy of PRIME, a mobile app intervention designed to improve motivation in young people with schizophrenia . Schizophrenia bulletin , 44 ( 5 ), 1010–1020. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schrank B, Sibitz I, Unger A, & Amering M (2010). How patients with schizophrenia use the internet: qualitative study . Journal of medical Internet research , 12 ( 5 ), e70. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schueller SM, Hunter JF, Figueroa C, & Aguilera A (2019). Use of digital mental health for marginalized and underserved populations . Current Treatment Options in Psychiatry , 6 ( 3 ), 243–255. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shatte AB, Hutchinson DM, & Teague SJ (2019). Machine learning in mental health: a scoping review of methods and applications . Psychological medicine , 49 ( 9 ), 1426–1448. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Spinzy Y, Nitzan U, Becker G, Bloch Y, & Fennig S (2012). Does the Internet offer social opportunities for individuals with schizophrenia? a cross-sectional pilot study . Psychiatry research , 198 ( 2 ), 319–320. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stiglic N, & Viner RM (2019). Effects of screentime on the health and well-being of children and adolescents: a systematic review of reviews . BMJopen , 9 ( 1 ), e023191. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sumner SA, Galik S, Mathieu J, Ward M, Kiley T, Bartholow B, … Mork P (2019). Temporal and geographic patterns of social media posts about an emerging suicide game . Journal of Adolescent Health . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Torous J, Chan SR, Tan SY-M, Behrens J, Mathew I, Conrad EJ, … Keshavan M (2014). Patient smartphone ownership and interest in mobile apps to monitor symptoms of mental health conditions: a survey in four geographically distinct psychiatric clinics . JMIR mental health , 1 ( 1 ), e5. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Torous J, Friedman R, & Keshavan M (2014). Smartphone ownership and interest in mobile applications to monitor symptoms of mental health conditions . JMIR mHealth and uHealth , 2 ( 1 ), e2. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Torous J, & Keshavan M (2016). The role of social media in schizophrenia: evaluating risks, benefits, and potential . Current opinion in psychiatry , 29 ( 3 ), 190–195. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Torous J, Wisniewski H, Bird B, Carpenter E, David G, Elejalde E, … Henson P (2019). Creating a digital health smartphone app and digital phenotyping platform for mental health and diverse healthcare needs: an interdisciplinary and collaborative approach . Journal of Technology in Behavioral Science , 1–13. [ Google Scholar ]
- Trefflich F, Kalckreuth S, Mergl R, & Rummel-Kluge C (2015). Psychiatric patients’ internet use corresponds to the internet use of the general public . Psychiatry research , 226 , 136–141. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Twenge JM, & Campbell WK (2018). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study . Preventive medicine reports , 12 , 271–283. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Twenge JM, Joiner TE, Rogers ML, & Martin GN (2018). Increases in depressive symptoms, suicide-related outcomes, and suicide rates among US adolescents after 2010 and links to increased new media screen time . Clinical Psychological Science , 6 ( 1 ), 3–17. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tynes BM, Willis HA, Stewart AM, & Hamilton MW (2019). Race-related traumatic events online and mental health among adolescents of color . Journal of Adolescent Health , 65 ( 3 ), 371–377. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vannucci A, Flannery KM, & Ohannessian CM (2017). Social media use and anxiety in emerging adults . Journal of affective disorders , 207 , 163–166. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vayreda A, & Antaki C (2009). Social support and unsolicited advice in a bipolar disorder online forum . Qualitative health research , 19 ( 7 ), 931–942. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ventola CL (2014). Social media and health care professionals: benefits, risks, and best practices . Pharmacy and Therapeutics , 39 ( 7 ), 491. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- We Are Social. (2020). Digital in 2020 . Retrieved from https://wearesocial.com/global-digital-report-2019
- Webb H, Jirotka M, Stahl BC, Housley W, Edwards A, Williams M, … Burnap P (2017). The ethical challenges of publishing Twitter data for research dissemination . Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Web Science Conference. [ Google Scholar ]
- Williams ML, Burnap P, & Sloan L (2017). Towards an ethical framework for publishing Twitter data in social research: Taking into account users’ views, online context and algorithmic estimation . Sociology , 57 ( 6 ), 1149–1168. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Woods HC, & Scott H (2016). # Sleepyteens: Social media use in adolescence is associated with poor sleep quality, anxiety, depression and low self-esteem . Journal of adolescence , 57 , 41–49. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ybarra ML (2004). Linkages between depressive symptomatology and Internet harassment among young regular Internet users . Cyber Psychology & Behavior , 7 ( 2 ), 247–257. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Money Report

For protest-minded workers, employment law and free speech are not clearly on your side
By cheryl winokur munk,cnbc • published may 24, 2024 • updated on may 24, 2024 at 11:03 am.
- Recent Google worker protests over the tech giant's contracts in Israel led to employees being fired.
- The National Labor Relations Board is reviewing a complaint from the dismissed employees.
- In an era of intense political protests, and an election season, knowing your speech rights as an employee are important to job security, especially for younger millennial and Gen Z workers more inclined to speak out.
Attention workers: what you say or do — even outside of normal working hours — could get you fired.
24/7 Philadelphia news stream: Watch NBC10 free wherever you are
This is especially pertinent for workers now, given the wave of protests and charged social media posts related to Middle East tensions, the presidential election and other hot-button social issues. Workers may think they have more protections than they do, which can lead them to say or do things that get them fired.
"It's not considered illegal for an employer to say, 'You're representing us; we think that behavior reflects badly on us and so you're fired,'" said Nicole Page, partner at Reavis Page Jump, whose firm represents employees and employers in employment matters.
Get Philly local news, weather forecasts, sports and entertainment stories to your inbox. Sign up for NBC Philadelphia newsletters.
That's not to say there won't be legal wrangling over the firing, such as the case with Google, which recently terminated 28 employees in April after a series of protests against labor conditions and the company's contract to provide the Israeli government and military with cloud computing and artificial intelligence services. This occurred a day after nine Google workers were arrested on trespassing charges after staging a sit-in at the company's offices in New York and Sunnyvale, California, including a protest in Google Cloud CEO Thomas Kurian's office. The fired employees have since filed a complaint with the National Labor Relations Board.
Employment attorneys say the outcomes of these types of cases turn heavily on the specific facts and circumstances. And there isn't always a quick resolution, which makes it even more important for workers who want to protest political or social issues to know what they could be getting themselves into — before they act in a way that could have long-term repercussions.
Here's where to start in understanding employee rights versus the rights of a company to discipline workers up to and including dismissal:

FDIC did not report allegations of senior officials' misconduct ‘in a timely manner,' watchdog says

UAW challenges Mercedes-Benz union vote, asks NLRB for new election
Remember: the first amendment does not apply to private-sector workers.
Many people participating in protests, sit-ins, or making charged statements on social media may think the First Amendment offers them a blanket of protection, but the U.S. Constitution places restrictions on the government, not private-sector employers.
Workers who think they have impunity when it comes to free speech and employment law are wrong. In fact, bosses may legitimately have grounds to terminate their employment.
Broadly speaking, the federal government is not allowed to limit your ability to speak, but the same is not true for private employers, Page said. However, there are certain state laws that protect an employee's right to speak, and there are certain protections for union members, who have some built-in protections under the National Labor Relations Act. That includes the ability to talk to coworkers about joining a union, pass out literature about joining a union (in non-work areas during non-work times), sign up co-workers on petitions in non-work areas and during non-work times, join with co-workers for the purpose of improving on-the-job working conditions.
Workers also have the right to speak out about an employer's unlawful conduct that harms them or other workers, such as discrimination, harassment, wage violations, and opposition to union efforts to improve conditions, said Jahan Sagafi, partner-in-charge of Outten & Golden's San Francisco office, where he represents workers in employment class actions.
Know how 'pro-worker' your state is
Many states have agencies equivalent to the federal Equal Employment Opportunity Commission and Department of Labor to protect workers from discrimination and other workplace harm. You may be able to find them by searching your state's name plus "fair employment practices agency" or "department of labor."
Some states known to be more pro-worker, including on speech issues, include California, New York and Illinois, Sagafi said.
In California, for example, there are protections for workers' expression of political ideas, which has been interpreted broadly, especially when an employee can show, for instance, that an employer has a pattern of discrimination when it comes to that employee. In many cases, courts have allowed lawsuits to proceed past summary judgment because there are significant enough questions of fact to allow it to move forward.
Make 'common sense' protest choices to protect yourself
Discipline and termination are always risks. But there are things you can do to protect yourself.
First: Use common sense and don't be disruptive at work, Sagafi said. Don't plan a protest for societal change on company grounds or on company time, or using company resources. "In general, the company has the right to maintain an orderly, inclusive, productive environment for everyone," Sagafi said.
Second, limit the degree to which your actions can be attributed to the company. "You don't want to make it look like you're speaking on behalf of the company, because the company may be concerned that its image or brand is being tarnished," Sagafi said.
"If you work for a company whose biggest clients include oil industry titans and you chain yourself to a tree because you're protesting oil drilling, you can get fired for that," Page said.
Simply going to a protest might not rise to the level of firing, but if you're posting publicly, or there's a photo of you holding up a sign or throwing something or even just putting something on social media like "I hate oil," it could be reasonable grounds for a company to fire you, she added.
It can be difficult for an employee to know every client of their firm, let alone rank them in order of importance, but again, common sense applies. If you know your company is heavily involved or invested in a particular industry, and you thumb your nose at that in a very public way, legal experts say you could be fired.
In the end, employers have a much better case for a reasonable business justification for termination if a worker breaks the law, acts violently, incites violence, or states blatantly hateful, violent or discriminatory things, said Devin McRae, partner at Early Sullivan Wright Gizer & McRae. Also, don't skip work without permission and don't lie to your employer by taking a sick day, for example, and then attend a public protest. If you show up on the evening news, "conceivably your employer could fire you for lying to them," McRae said.
Social media will get you in trouble
Especially with social media, people have a false sense of security sitting behind a computer and posting what they want. But companies can fire you for what you post, as long as they are not doing it in a discriminatory way. "There can be consequences in the real world," Page said.
She offered the example of NYU Langone, which recently fired two doctors — one for expressing pro-Palestinian views and the other for posting pro-Israel views. One of the doctors has sued, claiming discrimination and the case is ongoing.
It's good to start by thinking twice before you post anything political — especially if you are feeling emotional — and become familiar with your employers' policies on social media posts. Some companies prohibit employees from posting political views on social media, for instance. Going against the policy may be grounds for immediate termination.
Taking an employer to court after being fired is a wildcard
Of course, a worker fired for protesting or expressing views on social media may decide to sue the company for wrongful termination, but that requires time and money. These cases are highly fact-specific, and there's no telling how a jury would decide, if a case even goes that far.
An employee might have a good case, for example, if they can point to multiple examples where another employee wasn't fired for violating the same policy. There is often legal wrangling over what the company's motivations were in firing the employee, McRae said.
Also on CNBC
- Did ChatGPT write your resume?: How to answer No. 1 job interview AI question
- Paid time off for pregnant women could become national movement, led by New York
- Warren Buffett says one AI question has stumped economists for a century

This article tagged under:

- The Star ePaper
- Subscriptions
- Manage Profile
- Change Password
- Manage Logins
- Manage Subscription
- Transaction History
- Manage Billing Info
- Manage For You
- Manage Bookmarks
- Package & Pricing
US prison social media crackdown plan raises free speech concerns
- Social media
Friday, 24 May 2024
Related News

Early education on digital literacy important to produce responsible social media users
Study: children who spend more time on social media ‘more likely to vape’, trump's social media company discloses inquiry from finra.
The Federal Correctional Institution is shown in Dublin, California on March 11, 2024. Part of a broader overhaul of disciplinary procedures, the US Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP) wants to increase penalties for inmates' use of social media for the purpose of committing crimes, which has some legal precedent, according to the proposal. — AP
RICHMOND, Virginia: A US federal proposal to step up penalties barring incarcerated people from using social media is likely to infringe on the right to free speech of both those inside and outside jail, rights advocates said.
A ban on people like family members from posting on behalf of prisoners could create a "chilling effect" on anyone considering helping inmates, or even attempting to contact them about conditions inside, the campaigners said.
"Let's be clear: prisons and jails do not, under any circumstances, want people who are incarcerated to be able to speak freely to the public," said Bianca Tylek, executive director of the advocacy group Worth Rises.
Christopher Blackwell, an incarcerated writer, said at first sight such a proposal sounded "extremely far-reaching".
"The First Amendment right (doesn't) come with strings, and it's one of the only rights prisoners still retain when they become incarcerated," Blackwell told the Thomson Reuters Foundation.
"So any attack on stripping down or boxing off how those rights are used and protected – we can't allow that as Americans."
Safety and security?
Part of a broader overhaul of disciplinary procedures, the US Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP) wants to increase penalties for inmates' use of social media for the purpose of committing crimes, which has some legal precedent, according to the proposal.
But included in the proposals is a more open-ended ban that would greatly deter people providing assistance to prisoners, or even attempting to contact them, according to groups that have formally weighed in against it.
A BOP spokesperson said the proposed rule did not change anything immediately and that they appreciated the public's input.
Federal inmates are already banned from using cell phones, are restricted from accessing the internet, and generally do not have access to social media – leading critics of the proposal to wonder what the new penalties were trying to accomplish.
The new rules could be read so broadly as to restrict groups like the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU), or the spouse of an incarcerated person from posting online about conditions inside a facility, said Corene Kendrick, deputy director of the ACLU National Prison Project.
"There's really no rationale given for what the problem is other than just saying oh, it helps safety and security," Kendrick said.
"And the courts have made clear for decades that just ... invoking safety and security is not enough to justify these sorts of restrictions on the constitutional rights of incarcerated people."
Blackwell, who is currently incarcerated at a Washington state facility and serving a 45-year sentence for murder and robbery, pointed the finger at prison authorities.
"If they weren't doing bad stuff, they wouldn't have to worry about what people were posting," he said.
Alternative communications
The new rules are part of a sweeping set of changes to disciplinary regulations the BOP proposed this year, including expanded penalties for misusing email and using obscene language, among others.
There are multiple sections regarding the use of social media. One adds a new "greatest severity level" prohibited act code for the use of a social media account, or directing others, "for the purpose of committing or aiding in the commission of a criminal act."
"Greatest severity" prohibited acts are the most serious and can include killing and assault, and are punishable by sanctions including delayed parole or segregation.
The second and more expansive section establishes a new "high" severity prohibition on using, accessing, or maintaining a social media account, or directing others to do so, while not involving the commission or aid in the commission of a criminal act.
That would put it on par with acts like fighting and extortion.
In the proposal, the government notes there are alternative forms of communication available for prisoners, including in-person visits, physical mail, phone calls and electronic messaging.
But social media can be the most immediate way for people to get the word out about poor conditions and "alternative" forms of communication can be out of reach for some people, said Jennifer Jones, staff attorney with the Knight First Amendment Institute at Columbia University.
"Visiting hours, for example, have been tightened since the Covid-19 pandemic, and then a lot of times phone calls or virtual visits tend to be expensive and people face technical difficulties in using them," Jones said.
Blackwell said his wife runs his social media accounts and that communication with the outside was vital for his work.
"That's how everybody has their work now is through social media, right?" he said. "So having access to that has also offered me the availability of connecting with a lot of publishers and editors and journalists that I wouldn't necessarily have had access to."
"And I think even passing this in the federal system just kind of shows states that this can be done and maybe it emboldens some states to do it, right?"
Jones' group cited Martin Luther King Jr.'s "Letter from Birmingham Jail" about the Black American experience and the importance of nonviolent protest in its comment opposing the new proposal.
"Martin Luther King wrote his letter from a Birmingham jail that went out on scraps of paper and was published in newspapers," the ACLU's Kendrick said. "Nowadays, it probably would have gone out and (his wife) Coretta would have put it on her Twitter account." – Thomson Reuters Foundation
Found a mistake in this article?
Report it to us.
Thank you for your report!

PTPTN HOSTS APPRECIATION CEREMONY FOR CUSTOMERS
Next in tech news.

Trending in Tech
Air pollutant index, highest api readings, select state and location to view the latest api reading.
- Select Location
Source: Department of Environment, Malaysia
Others Also Read
Best viewed on Chrome browsers.

We would love to keep you posted on the latest promotion. Kindly fill the form below
Thank you for downloading.
We hope you enjoy this feature!
Eight Supreme Court Cases To Watch

The Supreme Court’s docket this term includes many of the complex issues American society is currently facing, including gun control, free speech online, race-based discrimination in voting, reproductive rights, presidential immunity from criminal accountability, and more.
The ACLU has served as counsel or filed friend-of-the-court briefs in all of the cases addressing these hot-button issues. The court will decide all its cases by the beginning of July. Here are eight undecided cases to watch, and what they mean for the future of our civil liberties.
Reproductive freedom: Protections for medication abortion and access to abortion during medical emergencies
Fda v. alliance for hippocratic medicine.
The Facts: Anti-abortion doctors, who do not prescribe medication abortion, are asking the Supreme Court to force the Food & Drug Administration (FDA) to impose severe restrictions on mifepristone – a safe and effective medication used in this country in most abortions and for miscarriage management – in every state, even where abortion is protected by state law.
Our Argument: The FDA approved mifepristone more than 20 years ago, finding that it is safe, effective, and medically necessary. Since its approval, more than 5 million people in the U.S. have used this medication. Our brief argued that the two lower courts – a district court in Texas and the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit – relied on junk science and discredited witnesses to override the FDA’s expert decision to eliminate medically-unnecessary restrictions on an essential medication with a stronger safety record than Tylenol. We urged the Supreme Court to protect access to medication abortion and reverse the lower courts’ rulings.
Danco Laboratories, LLC, v. Alliance for Hippocratic Medicine; U.S. FDA v. Alliance for Hippocratic Medicine
The American Civil Liberties Union joined over 200 reproductive health, rights, and justice organizations in an amicus brief to the Supreme Court...
Source: American Civil Liberties Union
Why it Matters: Today, with abortion access already severely restricted, the ability to get medication-abortion care using mifepristone is more important than ever. If the Fifth Circuit’s ruling is allowed to stand, individuals would be blocked from filling mifepristone prescriptions through mail-order pharmacies, forcing many to travel, sometimes hundreds of miles, just to pick up a pill they can safely receive through the mail. Healthcare professionals with specialized training, like advanced practice clinicians, would also be prohibited from prescribing mifepristone, further limiting where patients can access this critical medication. The American Cancer Society and other leading patient advocacy groups are also sounding the alarm that overturning the FDA’s decision would upend drug innovation and research, with consequences well beyond reproductive health care.
The Last Word: “As this case shows, overturning Roe v. Wade wasn’t the end goal for extremists. In addition to targeting nationwide-access to mifepristone, politicians in some states have already moved on to attack birth control and IVF. We need to take these extremists seriously when they show us they’re coming for every aspect of our reproductive lives.” – Jennifer Dalven, director of the ACLU Reproductive Freedom Project.
Idaho & Moyle et. al v. US
The Facts: Idaho politicians want the power to disregard the Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act (EMTALA) that requires emergency rooms to provide stabilizing treatment to patients in emergency situations, including abortion where that is the appropriate stabilizing treatment. If the state prevails, it would jail doctors for providing pregnant patients with the necessary emergency care required under this federal law.
Our Argument: The ACLU and its legal partners filed a friend-of-the-court brief explaining that the law requires hospitals to provide whatever emergency care is required; there is no carve-out for patients who need an abortion to stabilize an emergency condition. All three branches of government have long recognized that hospitals are required under EMTALA to provide emergency abortion care to any patient who needs it.
Idaho and Moyle, et al. v. United States
Idaho and Moyle, et al. v. United States was appealed to the U.S. Supreme Court by Idaho politicians seeking to disregard a federal statute — the...
Why it Matters: Because Idaho’s current abortion ban prohibits providing the emergency care required under EMTALA, medical providers have found themselves having to decide between providing necessary emergency care to a pregnant patient or facing criminal prosecution from the state. Depending on how the court rules, medical providers and patients in several other states with extreme abortion bans could find themselves in a similar position.
The Last Word: “If these politicians succeed, doctors will be forced to withhold critical care from their patients. We’re already seeing the devastating impact of this case play out in Idaho, and we fear a ripple effect across the country.” – Alexa Kolbi-Molinas, deputy director of the ACLU Reproductive Freedom Project
Free speech: Government authority over online and political speech
National rifle association v. vullo.
The Facts: In 2018, Maria Vullo, New York’s former chief financial regulator, in coordination with then-Mayor Andrew Cuomo, threatened to use her regulatory power over banks and insurance companies to coerce them into denying basic financial services to the National Rifle Association (NRA) because she and Cuomo disagreed with its pro-gun rights advocacy. The NRA argued that Vullo’s alleged efforts to blacklist the NRA penalized it for its political advocacy, in violation of the First Amendment.
Our Argument: The ACLU, representing the NRA at the Supreme Court, argued that any government attempt to blacklist an advocacy group and deny it financial services because of its viewpoint violates the right to free speech. Our brief urges the court to apply the precedent it set in 1963 in Bantam Books v. Sullivan , which established that even informal, indirect efforts to censor speech violate the First Amendment.

On January 9th, 2024, the American Civil Liberties Union filed its opening brief on behalf of the National Rifle Association (NRA) in National...
Why it Matters: While the ACLU stands in stark opposition to the NRA on many issues, this case is about securing basic First Amendment rights for all advocacy organizations. If New York State is allowed to blacklist the NRA, then Oklahoma could similarly penalize criminal justice reformers advocating for bail reform, and Texas could target climate change organizations advancing the view that all fossil fuel extraction must end. The ACLU itself could be targeted for its advocacy.

Why is the ACLU Representing the NRA Before the US Supreme Court?
The ACLU has always stood up for free speech – no matter the speaker.
The Last Word: “The right to advocate views the government opposes safeguards our ability to organize for the country we want to see. It’s a principle the ACLU has defended for more than 100 years, and one we will continue to protect from government censorship of all kinds, whether we agree or disagree with the views of those being targeted.” – David Cole, ACLU legal director
NetChoice v. Paxton and Moody v. NetChoice
The Facts: Motivated by a perception that social media platforms disproportionately silence conservative voices, Florida and Texas passed laws that give the government authority to regulate how large social media companies like Facebook and YouTube curate content posted on their sites.
Our Argument: In a friend-of-the-court brief, the ACLU, the ACLU of Florida and the ACLU of Texas argued that the First Amendment right to speak includes the right to choose what to publish and how to prioritize what is published. The government’s desire to have private speakers, like social media companies, distribute more conservative viewpoints–or any specific viewpoints–is not a permissible basis for state control of what content appears on privately-owned platforms.
Why it Matters: If these laws are allowed to stand, platforms may fear liability and decide to publish nothing at all, effectively eliminating the internet’s function as a modern public square. Or, in an attempt to comply with government regulations, social media companies may be forced to publish a lot more distracting and unwanted content. For example, under the Texas law, which requires “viewpoint neutrality,” a platform that publishes posts about suicide prevention would also have to publish posts directing readers to websites that encourage suicide. .
The Last Word: “Social media companies have a First Amendment right to choose what to host, display, and publish. The Supreme Court has recognized that right for everyone from booksellers to newspapers to cable companies, and this case should make clear that the same is true for social media platforms.” — Vera Eidelman, staff attorney with the ACLU’s Speech, Privacy, & Technology Project
Voting rights: Racial gerrymandering and the fight for fair maps
Alexander v. south carolina naacp.
The Facts: In 2022, South Carolina adopted a racially-gerrymandered congressional map. The state legislature singled out Black communities, “cracking” predominantly Black communities and neighborhoods across two districts to reduce their electoral influence in the state’s first congressional district.
Our Argument: The ACLU and its legal partners sued on behalf of the South Carolina NAACP and an affected voter to challenge the constitutionality of the new congressional map. We argued that the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment forbids the sorting of voters on the basis of their race, absent a compelling interest, which the state failed to provide.
Alexander v. South Carolina State Conference of the NAACP (Congressional Map Challenge)
South Carolina unlawfully assigned voters to congressional districts based on their race and intentionally discriminated against Black voters in...
Why it Matters: This racially-gerrymandered congressional map deprives Black South Carolinians the political representation they deserve in all but one of seven districts, limiting the power and influence of more than a quarter of the state’s population just before the 2024 election.
The Last Word: “South Carolina’s failure to rectify its racially-gerrymandered congressional map blatantly disregards the voices and the rights of Black voters. The ACLU is determined to fight back until Black South Carolina voters have a lawful map that fairly represents them.” – Adriel I. Cepeda Derieux, deputy director of the ACLU Voting Rights Project
Gender justice: Denying guns to persons subject to domestic violence restraining orders
United states v. rahimi.
The Facts: Zackey Rahimi was convicted under a federal law that forbids individuals subject to domestic violence protective orders from possessing a firearm. Mr. Rahimi challenged the law as a violation of his Second Amendment right to bear arms.
Our Argument: The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit ruled that individuals subject to domestic violence protective orders have a constitutional right to possess guns. It invalidated the federal gun law because it found no historical analogues in the 1700s or 1800s that prohibited those subject to domestic violence protective orders from possessing a firearm. The ACLU argued that the Fifth Circuit’s analysis is a misapplication of the Supreme Court’s decision in New York State Rifle & Pistol Association, Inc. v. Bruen because it effectively required a “historical twin” law in order to uphold a law today. There were no identical laws at the time of the Framing because there were no domestic violence protective orders then, but that should not be a basis for invalidating the laws today. We also argued that imposing time-limited firearms restrictions based on civil restraining orders is a critical tool for protecting those who have experienced domestic violence and face a threat of further violence.

Whether 18 U.S.C. § 922(g)(8), which prohibits the possession of firearms by persons subject to domestic-violence restraining orders, violates the...
Why it Matters: If the Fifth Circuit’s rationale is affirmed, then governments would lose the ability to prohibit gun possession by persons subject to restraining orders — and presumably even to run pre-acquisition background checks, which have stopped more than 77,000 purchases of weapons by individuals subject to domestic violence orders in the 25 years that the federal law has been in place. This “originalist” interpretation of the Second Amendment not only hinders our ability to protect individuals against newly recognized threats, but also tethers the authority to regulate gun possession to periods when governments disregarded many forms of violence directed against women, Black people, Indigenous people, and others.
The Last Word: “It would be a radical mistake to allow historical wrongs to defeat efforts today to protect women and other survivors of domestic abuse. The Supreme Court should affirm that the government can enact laws aimed at preventing intimate partner violence, consistent with the Second Amendment.” – Ria Tabacco Mar, director of the ACLU Women’s Rights Project
Criminal justice: Eighth-Amendment protections for unhoused persons accused of sleeping in public when they have nowhere else to go
City of grants pass v. johnson.
The Facts: Grants Pass, Oregon, enacted ordinances that make it illegal for people, including unhoused persons with no access to shelter, to sleep outside in public using a blanket, pillow, or even a cardboard sheet to lie on. Last year, the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals ruled that punishing unhoused people for sleeping in public when they have no other choice violates the Eighth Amendment’s ban on cruel and unusual punishment.
Our Argument: In Oregon, and elsewhere in the United States, the population of unhoused persons often exceeds the number of shelter beds available, forcing many to sleep on the streets or in parks. The ACLU and 19 state affiliates submitted a friend-of-the-court brief arguing that it is cruel and unusual to punish unhoused people for the essential life-sustaining activity of sleeping outside when they lack access to any alternative shelter.

Why it Matters: When applied to people with nowhere else to go, fines and arrests for sleeping outside serve no purpose and are plainly disproportionately punitive. Arresting and fining unhoused people for sleeping in public only exacerbates cycles of homelessness and mass incarceration.
The Last Word: “There is no punishment that fits the ‘crime’ of being forced to sleep outside. Instead of saddling people with fines, jail time, and criminal records, cities should focus on proven solutions, like affordable housing, accessible and voluntary services, and eviction protections.” – Scout Katovich, staff attorney with the ACLU Trone Center for Justice and Equality
Democracy: Presidential immunity from prosecution for criminal acts after leaving office
Trump v. united states.
The Facts: Former President Donald Trump is asking the Supreme Court to rule that he cannot be held criminally liable for any official acts as president, even after leaving office, and even where the crimes concern efforts to resist the peaceful transition of power after an election. This claim runs contrary to fundamental principles of constitutional accountability, and decades of precedent.
Our Argument: Our friend-of-the-court brief argues that former President Trump is not immune from criminal prosecution, and that the Constitution and long-established Supreme Court precedent support the principle that in our democracy, nobody is above the law — even the president. Our brief warns that there are “few propositions more dangerous” in a democracy than the notion that an elected head of state has blanket immunity from criminal prosecution.
Why it Matters: No other president has asserted that presidents can never be prosecuted for official acts that violate criminal law. The president’s accountability to the law is an integral part of the separation of powers and the rule of law. If the President is free, as Trump’s legal counsel argued, to order the assassination of his political opponents and escape all criminal accountability even after he leaves office, both of these fundamental principles of our system would have a fatal Achilles’ heel.
The Last Word: “The United States does not have a king, and former presidents have no claim to being above the law. A functioning democracy depends on our ability to critically reckon with the troubling actions of government officials and hold them accountable.” – David Cole, ACLU legal director
Learn More About the Issues on This Page
- Civil Liberties
- Reproductive Freedom
- Free Speech
- Voting Rights
- Women's Rights
- Criminal Law Reform
Related Content

Penncrest School District v. Cagle

Quiz: State Legislation and the Part You Play

State Legislative Sessions: How They Impact Your Rights

Despair and Resignation Are Not A Strategy: How to Fight Back In A Second Trump Term.
Frontiers | Science News
- Science News
Social science
Screen time not the main factor making parent-child interactions worse, study finds.

Which is worse for parent-child interaction, if parents use their phones, or if they are distracted otherwise? A team of researchers investigated if the common perception that screens are bad for parent-child interactions holds. They found it does, but also that screens are no worse than other forms of distraction. Instead, it might be distraction in itself that has detrimental effects on parents’ communication with their toddlers.
Technology use is at an all-time high and understanding how this impacts daily life is crucial. When it comes to parent-child interactions, scientists have coined the term ‘technoference,’ meaning technology interference. It occurs when parent-child interaction and communication are disrupted by the use of digital devices.
But is distraction caused by digital devices more detrimental to parent-child interaction than when parental distraction comes from different sources? Researchers in Switzerland have investigated.
“In this study, we show that when parents are distracted, the quality and quantity of parent-child interaction is impaired compared to when parents are not being distracted,” said Prof Nevena Dimitrova, a researcher at the University of Applied Sciences and Arts Western Switzerland and principal investigator of the study published in Frontiers in Child and Adolescent Psychiatry . “This was regardless of if that distraction came from a digital or a non-digital activity.”
Screening distraction
Although the negative impact of parents being distracted by their phones while around their children has been established, less is known about whether these negative effects come from the fact that the parent uses a screen or from the fact that the parent is distracted in general.
To fill this gap, the team around Dimitrova tasked 50 parent-child pairs, in which children were 22 months old on average, to play together for 10 minutes. Participant pairs were divided in three groups. In the first group, there was no disruption. In the second group, after five minutes of play, the parent was given a questionnaire to fill out on paper, whereas in the third group, also after five minutes, the parent was instructed to fill out the same questionnaire using a tablet. Parents that filled out the questionnaire were instructed to continue interacting with their children.
The researchers found that parents who filled out the questionnaire were less sensitive to children’s communication signals, and that children showed lower levels of social involvement towards their parents.
Technoference, however, did not affect parent-child interactions more negatively than non-digital distractions. Instead, all distraction, regardless of whether it was caused by screens or pen and paper, had negative effects on parents, children, and pairs. “We interpret this finding—that was equally surprising for us—as the possibility that screens are so ubiquitous nowadays that young children might be becoming used to the reality of seeing their parents use screens,” said Dimitrova.
Regardless of their findings, the researchers stressed that parent-child interaction is at its best when parents are not distracted at all. This might be especially important for parents who find it difficult to bond with their children.
Read and download the article
Curbing a ‘moral panic’
In the media, mostly alarmistic messages about the risks of screen use are discussed, said the researchers. However, research does not support the thesis that screen use by or in the presence of children is exclusively bad. For example, positive effects of screens on child psychological development have been shown in previous research.
“This study shows how important it is to rely on scientific evidence rather that public opinion about screen use. We see that it’s not screens per se that are detrimental to the quality of parent-child interaction,” concluded Dimitrova. “Instead, it seems to be the fact that the parent is not fully engaged in the interaction that negatively impacts parent-child communication.”
The researchers, however, also pointed out that it is difficult to make definitive statements about parental screen use based on one study alone. This is partly because everyday parent-child interaction differs from the experimental set-up. For example, the ways in which parents use screen while around their children cannot always be replicated fully. Studies in naturalistic context are needed and might lead to different results, the scientists noted.
REPUBLISHING GUIDELINES: Open access and sharing research is part of Frontiers’ mission . Unless otherwise noted, you can republish articles posted in the Frontiers news site — as long as you include a link back to the original research. Selling the articles is not allowed.
Post related info
May 21, 2024
Deborah Pirchner
Post categories, featured news, related subjects, social sciences, frontiers in child and adolescent psychiatry, related content.

Parents underestimate the importance of guided play in education, finds US study

Watching others visibly dislike vegetables might make onlookers dislike them, too

Do mild depressive and anxiety symptoms in fathers predict behavioral and cognitive problems in their children?
Latest posts.
Big data, AI, and personalized medicine: scientists reveal playbook aiming to revolutionize healthcare

Registration open: Dr Eric Topol to explore how AI will shape the future of healthcare at Frontiers Forum virtual event

Babies in the womb exposed to two languages hear speech differently when born

Biodiversity loss: three Research Topics revealing threats and solutions


Kansas City Chiefs' Harrison Butker attacked LGBTQ rights and said women grads were excited about marriage and kids. Here’s what social media said.
People online are reacting after Kansas City Chiefs kicker Harrison Butker gave a speech last weekend at a college commencement ceremony in which he spoke about his duty to be “unapologetically Catholic,” and cited abortion, surrogacy, IVF and “a growing support for degenerate cultural values in media.”
While the recent Super Bowl champion, a teammate of Taylor Swift’s boyfriend Travis Kelce, claimed to be telling “hard truths,” his statements have come off to many as homophobic and misogynistic.
🧑🎓 What happened
On May 11, Butker, the 28-year-old three-time Super Bowl champion, addressed graduates at the commencement of Benedictine College, a Catholic college in Atchison, Kan.
During his 20-minute speech, he railed against President Biden, LGBTQ rights, the “tyranny of diversity, equity, and inclusion,” and assumed the majority of women graduates were “excited” about the prospect of marriage and having children.
In his speech, Butker called Biden, who is also Catholic, “delusional” for his support of women’s reproductive rights.
“He has been so vocal in his support for the murder of innocent babies that I’m sure to many people that it appears that you can be both Catholic and pro-choice,” said Butker.
Butker then wove in “glaring” commonalities between Biden and “people pushing dangerous gender ideologies onto the youth of America.”
“They are all Catholic. This is an important reminder that being Catholic alone doesn’t cut it.”
One of the moments that has drawn considerable pushback happened when Butker singled out women in his speech, addressing what he called “the most diabolic lies” told to them.
“Some of you may go on to lead successful careers in the world, but I would venture to guess that the majority of you are most excited about your marriage and the children you will bring into this world,” he said.
Butker then mentioned his wife, Isabelle, saying that her “life truly started when she began living her vocation as a wife and a mother.”
“I’m beyond blessed with the many talents God has given me, but it cannot be overstated that all of my success is made possible because a girl I met in band class back in middle school would convert to the faith, become my wife, and embrace one of the most important titles of all: homemaker,” Butker said, his voice breaking.
Butker even went on to directly quote Swift, who he called his “teammate’s girlfriend,” and also referenced Catholic saint Josemaría Escrivá’s teaching about the divine order and how priests shouldn’t seek praise from their parishioners.
📲 Social media fallout
One recent graduate of Benedictine’s 2024 class slammed Butker’s speech as “horrible.” This graduate posted a video on X describing the mixed reactions during his speech. She said while Butker received a standing ovation from the audience, she and a few other women stayed seated.
“Did he just come here to speak about politics and his views on women? That’s all you got for a graduation commencement speech? … It definitely made graduation feel a little less special knowing I had to sit through that and get told I’m nothing but a homemaker,” @Ms_LilShadow .
One Swiftie took to social media to call Butker an “anti-hero.”
“Taylor, please leave the NFL and these football players behind. You and your brand are too good for this. Please live your truth and remember that it’s not all about the money. The real ones will stay,” wrote @thatsthefunofme .
“If anyone could hold the @NFL , @Chiefs , and Butker accountable for misogynistic speeches, it’s the #Swifties . We generated millions of new income for their organization. It is not a fan base to mess with. Do better Harrison,” @mtrlguy .
On TikTok, the Human Rights Campaign, an LGTBQ advocacy group, posted a clip of Butker singling out women during his speech, followed by a clip of Swift’s music video for “You Need to Calm Down” a song where she voices her support for the LGBTQ community and slams homophobia.
While there was plenty of backlash, many endorsed his speech.
“Harrison Butker didn't say anything wrong, and a commencement ceremony was the perfect place to deliver that message,” posted X user @harmonizedgrace . “If you listen to his entire speech, he also addressed men in a similar fashion & the speech was honestly lovely. Stop getting triggered over clips. It just makes you seem irrational.”
“Not a word Harrison Butker says here should be remotely controversial. He’s 100% correct,” former football player turned media personality, T.J. Moe posted on X. “Those trying to convince women that being assistant VP of lending & intentionally childless at age 40 is more fulfilling than making a family and home are evil.”
On Thursday, the NFL released a statement distancing Butker’s speech from the organization.
"His views are not those of the NFL as an organization. The NFL is steadfast in our commitment to inclusion, which only makes our league stronger," the statement read.
The Los Angeles Chargers also took a swipe at Butker in their NFL schedule release video on Wednesday, placing a Sims version of him in a kitchen, poking fun at his “homemaker” comment.
Additionally, there’s a petition on Change.org , calling for Butker to be removed from the Chiefs for what they called his “dehumanizing remarks.”

Chiefs' Harrison Butker blasted for commencement speech encouraging women to be homemakers
Kansas City Chiefs kicker Harrison Butker has aggravated one of the internet's biggest culture wars by telling a class of college graduates that one of the “most important” titles a woman can hold is homemaker.
During a commencement speech last weekend at Benedictine College, a Catholic liberal arts school in Atchison, Kansas, the NFL player railed against abortion, Pride month and Covid-19 lockdown measures.
Drawing the most viral backlash this week, however, was a section of his speech in which he addressed the female graduates specifically — telling them that it’s women who have had “the most diabolical lies” told to them.
“How many of you are sitting here now, about to cross this stage, and are thinking about all the promotions and titles you are going to get in your career? Some of you may go on to lead successful careers in the world,” Butker said. “But I would venture to guess that the majority of you are most excited about your marriage and the children you will bring into this world.”
The criticisms that followed took aim at Butker as well as the NFL.

"Hey @NFL — If you want to continue to grow your female fan base and any other marginalized group (straight white men are already watching your product), come get your boy," wrote Lisa Guerrero, a former NFL sideline reporter and now an investigative journalist for "Inside Edition."
He went on to tell the graduates that his wife would agree that her life “truly started when she began living her vocation as a wife and as a mother.” It is her embrace of this role, he said, that made his own professional success possible.
Butker’s comments share similarities with some of the more extreme ideas around gender roles that have gained traction in communities that promote “ tradwife ” lifestyles or other relationship dynamics that center on traditional gender roles .
“Listen, there’s nothing wrong with his wife being a homemaker. Homemakers are wonderful, that’s not the point,” filmmaker Michael McWhorter, known by his more than 6 million TikTok followers as TizzyEnt, said in a video response. “The point is he seemed to be acting as if you should be ashamed if you don’t want to be a homemaker, or, ‘I know what you really want to do is just stay home and have babies.’"
The speech was the latest incident to add fuel to the flames of this increasingly vocal cultural battle, much of which is playing out online. While many prominent right-wing men have voiced such beliefs before, they’re usually confined to internet forums, podcasts and other online communities where these ideologies thrive.
A spokesperson for Butker did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Benedictine College and the Kansas City Chiefs did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
A spokesperson for the NFL told People Magazine that Butker "gave a speech in his personal capacity" and his "views are not those of the NFL as an organization."
"The NFL is steadfast in our commitment to inclusion, which only makes our league stronger," a spokesperson told the publication.
Butker, who is teammates with Chiefs tight end Travis Kelce, further drew surprise and criticism when he quoted Kelce’s girlfriend, Taylor Swift, whose monumental career success as a global pop star has inspired college courses .
“As my teammate’s girlfriend says, ‘familiarity breeds contempt,’” he said, drawing murmurs from the crowd as he used the “Bejeweled” lyric as an analogy for why Catholic priests should not become “overly familiar” with their parishioners.
In the days since his speech, a Change.org petition for the Chiefs to dismiss Butker for “discriminatory remarks” has garnered nearly 19,000 signatures.
“These comments reinforce harmful stereotypes that threaten social progress,” the petition stated. “They create a toxic environment that hinders our collective efforts towards equality, diversity and inclusion in society. It is unacceptable for such a public figure to use their platform to foster harm rather than unity.”
Those who criticized Butker’s speech online include actor Bradley Whitford as well as DJ and rapper (and self-proclaimed Swiftie ) Flavor Flav .
But his speech was also lauded by some on the religious right, including conservative sports media personalities such as Clay Travis and Jason Whitlock , who defended Butker’s statements toward women.
“Not a word Harrison Butker says here should be remotely controversial. He’s 100% correct,” former NFL wide receiver T.J. Moe posted on X . “Those trying to convince women that being assistant VP of lending & intentionally childless at age 40 is more fulfilling than making a family and home are evil.”
Sports and culture commentator Jon Root also posted that Butker “exposed the lies that the world has been telling women.” Women, he wrote, are wrongly encouraged to climb the corporate ladder, view children as a “burden” and see marriage as “not worth pursuing.”
Still, a deluge of viewers online took issue with his attitude toward women and the LGBTQ community. Many women also rejected the premise that they would be happier staying at home in lieu of paid work, even if they do have a husband and children.
“I am moved. I actually had no idea that my life began when I met my husband,” neurosurgeon Betsy Grunch, known as Ladyspinedoc on TikTok, said sarcastically in a TikTok video . “It did not begin when I graduated magna cum laude from the University of Georgia with honors. It certainly did not begin when I graduated with a 4.0 GPA, Alpha Omega Alpha, from medical school. And I had no idea that it did not begin when I completed my residency in neurosurgery.”
Angela Yang is a culture and trends reporter for NBC News.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Excessive use of social media can lead to addiction and affect mental health. It's a breeding ground for cyberbullying, misinformation, and privacy invasion. Moreover, the constant exposure to idealized images and lives can negatively impact self-esteem. In conclusion, social media is a double-edged sword.
The media is an integral part of our lives and has a major impact on our culture. Because of the high level of accessibility that occurs around the world, the relevance of media is increasing by the day. As a result, it is critical that each of us become mindful of the media's influence. With this, I come to the end of my speech on importance ...
The power and the danger of online crowds. James Surowiecki pinpoints the moment when social media became an equal player in the world of news-gathering: the 2005 tsunami, when YouTube video, blogs, IMs and txts carried the news -- and preserved moving personal stories from the tragedy. 04:09. Alexis Ohanian.
Good morning everyone present here, today I am going to give a speech on the importance of social media. One of the social media's most important consequences in the current world is its capacity to spread knowledge globally. Since the majority of people these days use other social media sites, no important story can be allowed to die out ...
With social media, the distance decreases between people. It is through social media that people learn about events/happenings from around the world. Any news travels faster and reaches peoples' ears within no time. Social media speech is one of the most important topics that anyone can be asked to talk about.
Importance of Social Media in 2024 and Beyond. Social media fosters global connectivity by bridging communication gaps across demographics and professions. Strategic social media usage yields success through direct audience engagement and targeted content creation. Businesses benefit from social media's diverse advantages, including direct ...
Ad Council has seen the importance of spreading awareness around mental health concerns as they relate to social media consumption in young adults—who will become the next generation of marketers. EXTREMISM & HATE. Another trend on experts' minds is how the algorithms behind these massively influential social media platforms may contribute ...
Apps like Facebook and Twitter allow us to stay in touch with geographically dispersed family and friends, communicate with like-minded others around our interests, and join with an online community to advocate for causes dear to our hearts. Honestly sharing about ourselves online can enhance our feelings of well-being and online social support ...
Social media has also created opportunities for people such as to show their talent. It is also great for advertisements. But despite being so many benefits, it has been criticized. It has disadvantages too. It is also considered as one of the harmful elements of society. The oversharing on social media can be dangerous. It can attack our privacy.
However, like all things, social media also has its downsides. Here are a few: Excessive use of social media has led to an increase in screen time, which can contribute to various health issues like eye strain and sedentary lifestyle diseases. The convenience of social media can also foster laziness and procrastination, hampering productivity ...
1-Short Speech on Social Media Bane or Boon. 'I greet you all present here. I'm here to present a short speech on Social Media Bane or Boon. We are all connected to social media, directly or indirectly. Social media has transformed the traditional way we communicate, share information, and connect with the world around us.
Today, I'll be giving a short speech on the topic of the importance of social media. Google defines the term 'social media' to be "websites and applications that enable users to create and share content or to participate in social networking.". Simply put, social media is an amalgamation of the predominant rulers of our lives- namely ...
As social media platforms have grown, though, the once-prevalent, gauzy utopian vision of online community has disappeared. Along with the benefits of easy connectivity and increased information, social media has also become a vehicle for disinformation and political attacks from beyond sovereign borders.
Public Speech on Social Media. If you will be giving a speech, you can choose to use the power of social media during your talk. Use tools like YouTube to offer a live stream of your talk. You can also tweet on Twitter or post to other social media sites during your speech to engage listeners who are both present and absent. A speech shared on ...
Views of social media and its impacts on society. When asked whether social media is a good or bad thing for democracy in their country, a median of 57% across 19 countries say that it is a good thing. In almost every country, close to half or more say this, with the sentiment most common in Singapore, where roughly three-quarters believe ...
Yes, our right to free speech absolutely exists online. But there is serious debate about how to regulate our freedom of speech in the online sphere, particularly on social media. Knowledge is power. Your contribution counts. The rise of social media has implications for our fundamental rights, perhaps none more so than our freedom of speech.
10 Lines Speech on Social Media. Social Media refers to group interactions in which users build, share, or trade knowledge and concepts in online communities. The ability to interact with others has evolved into a fundamental human need. The remarkable advancements in communications and inventive, astounding entertainment have made knowledge ...
The Future of Free Speech in the Social Media Era. One of the most fiercely debated issues of the current era is what to do about "bad" speech on the internet, particularly on social media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter. Problematic language, including hate speech, disinformation, and propaganda have been around throughout human history.
So, let's keep in mind: social comparison is not always bad and young adults do experience inspiration online that is oftentimes overlooked. article continues after advertisement. Phone with ...
The right to free speech is a human right. Constitutionally, it is our absolute right to freely express our views. And, in social media, it must also come in lock step with the mechanisms to ...
The Importance of Free Speech on Social Media. MP3 audio - Standard. Price: $0.99. Request Download. See all on Online Technology Regulation.
The plaintiffs, which include the attorneys general of Missouri and Louisiana, argued that the federal government was coercing social-media companies into limiting speech on topics such as vaccine ...
Introduction. Social media has become a prominent fixture in the lives of many individuals facing the challenges of mental illness. Social media refers broadly to web and mobile platforms that allow individuals to connect with others within a virtual network (such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Snapchat, or LinkedIn), where they can share, co-create, or exchange various forms of digital ...
Knowing speech law in an era of protest is important job training. ... Especially with social media, people have a false sense of security sitting behind a computer and posting what they want. But ...
Here is how US federal prison restrictions on social media could infringe free speech rights. ... Jail" about the Black American experience and the importance of nonviolent protest in its comment ...
ACLU. May 16, 2024. The Supreme Court's docket this term includes many of the complex issues American society is currently facing, including gun control, free speech online, race-based discrimination in voting, reproductive rights, presidential immunity from criminal accountability, and more. The ACLU has served as counsel or filed friend-of ...
Technoference, however, did not affect parent-child interactions more negatively than non-digital distractions. Instead, all distraction, regardless of whether it was caused by screens or pen and paper, had negative effects on parents, children, and pairs. "We interpret this finding—that was equally surprising for us—as the possibility ...
📲 Social media fallout One recent graduate of Benedictine's 2024 class slammed Butker's speech as "horrible." This graduate posted a video on X describing the mixed reactions during his ...
By Angela Yang. Kansas City Chiefs kicker Harrison Butker has aggravated one of the internet's biggest culture wars by telling a class of college graduates that one of the "most important ...