- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides

Citation Machine® — Write Smarter
Start a new citation or manage your existing bibliographies.
Scan your paper for plagiarism and grammar errors.
Check your paper for grammar and plagiarism
Catch plagiarism and grammar mistakes with our paper checker
Use Citation Machine® Plus to get smart recommendations!
Scan your paper for unintentional plagiarism and get advanced recommendations for sentence structure, writing style, grammar and more!
- expert check

Know you're citing correctly
No matter what citation style you're using (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) we'll help you create the right bibliography
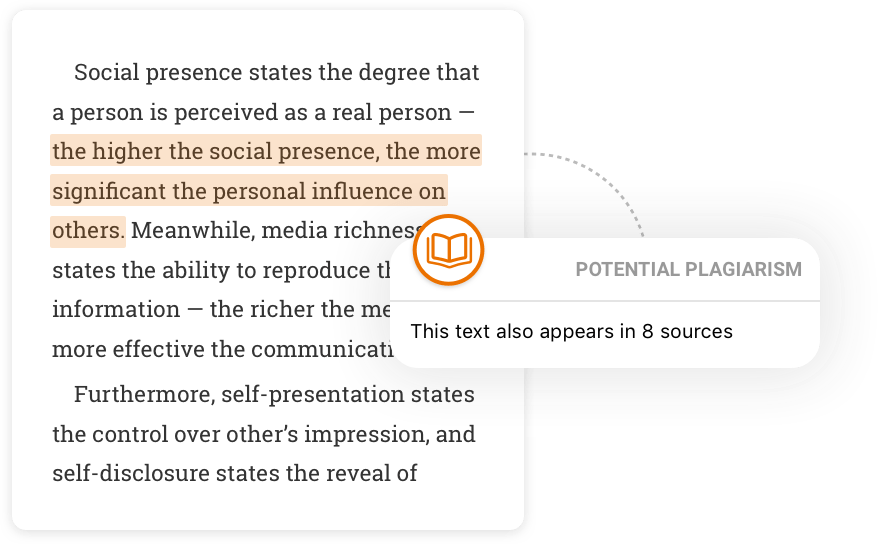
Check for unintentional plagiarism
Scan your paper the way your teacher would to catch unintentional plagiarism. Then, easily add the right citation
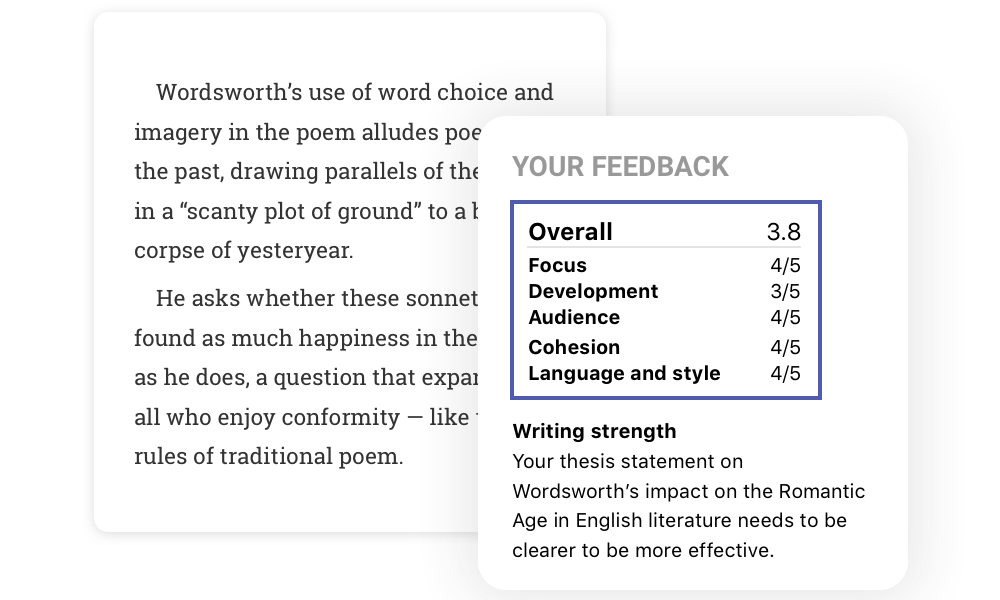
Strengthen your writing
Give your paper an in-depth check. Receive feedback within 24 hours from writing experts on your paper's main idea, structure, conclusion, and more.

Find and fix grammar errors
Don't give up sweet paper points for small mistakes. Our algorithms flag grammar and writing issues and provide smart suggestions
Citation Machine® Guides & Resources
Mla format: everything you need to know and more.
Filled with a wide variety of examples and visuals, our Citation Machine® MLA guide will help you master the citation process. Learn how to cite websites, books, journal articles, magazines, newspapers, films, social media, and more!
MLA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDFs
Comprehensive Guide to APA Format
Our Citation Machine® APA guide is a one-stop shop for learning how to cite in APA format. Read up on what APA is, or use our citing tools and APA examples to create citations for websites, books, journals, and more!
APA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDFs
Everything You Need to Know About Chicago Style
Creating citations in Chicago style has never been easier thanks to our extensive Citation Machine® Chicago style guide and tools. Learn about footnotes, endnotes, and everything in between, or easily create citations for websites, books, journal articles, and more!
Chicago Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDFs
Citation Machine®’s Ultimate Writing Guides
Whether you’re a student, writer, foreign language learner, or simply looking to brush up on your grammar skills, our comprehensive grammar guides provide an extensive overview on over 50 grammar-related topics. Confused about reflexive verbs, demonstrative adjectives, or conjunctive adverbs? Look no further! Learn about these grammar topics and many, many more in our thorough and easy to understand reference guides!
Citing Sources Guide | Grammar Guide | Plagiarism Guide | Writing Tips
Student Blog
Stay up to date! Get research tips and citation information or just enjoy some fun posts from our student blog.
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / How to Cite Sources
How to Cite Sources
Here is a complete list for how to cite sources. Most of these guides present citation guidance and examples in MLA, APA, and Chicago.
If you’re looking for general information on MLA or APA citations , the EasyBib Writing Center was designed for you! It has articles on what’s needed in an MLA in-text citation , how to format an APA paper, what an MLA annotated bibliography is, making an MLA works cited page, and much more!
MLA Format Citation Examples
The Modern Language Association created the MLA Style, currently in its 9th edition, to provide researchers with guidelines for writing and documenting scholarly borrowings. Most often used in the humanities, MLA style (or MLA format ) has been adopted and used by numerous other disciplines, in multiple parts of the world.
MLA provides standard rules to follow so that most research papers are formatted in a similar manner. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the information. The MLA in-text citation guidelines, MLA works cited standards, and MLA annotated bibliography instructions provide scholars with the information they need to properly cite sources in their research papers, articles, and assignments.
- Book Chapter
- Conference Paper
- Documentary
- Encyclopedia
- Google Images
- Kindle Book
- Memorial Inscription
- Museum Exhibit
- Painting or Artwork
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Sheet Music
- Thesis or Dissertation
- YouTube Video
APA Format Citation Examples
The American Psychological Association created the APA citation style in 1929 as a way to help psychologists, anthropologists, and even business managers establish one common way to cite sources and present content.
APA is used when citing sources for academic articles such as journals, and is intended to help readers better comprehend content, and to avoid language bias wherever possible. The APA style (or APA format ) is now in its 7th edition, and provides citation style guides for virtually any type of resource.
Chicago Style Citation Examples
The Chicago/Turabian style of citing sources is generally used when citing sources for humanities papers, and is best known for its requirement that writers place bibliographic citations at the bottom of a page (in Chicago-format footnotes ) or at the end of a paper (endnotes).
The Turabian and Chicago citation styles are almost identical, but the Turabian style is geared towards student published papers such as theses and dissertations, while the Chicago style provides guidelines for all types of publications. This is why you’ll commonly see Chicago style and Turabian style presented together. The Chicago Manual of Style is currently in its 17th edition, and Turabian’s A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations is in its 8th edition.
Citing Specific Sources or Events
- Declaration of Independence
- Gettysburg Address
- Martin Luther King Jr. Speech
- President Obama’s Farewell Address
- President Trump’s Inauguration Speech
- White House Press Briefing
Additional FAQs
- Citing Archived Contributors
- Citing a Blog
- Citing a Book Chapter
- Citing a Source in a Foreign Language
- Citing an Image
- Citing a Song
- Citing Special Contributors
- Citing a Translated Article
- Citing a Tweet
6 Interesting Citation Facts
The world of citations may seem cut and dry, but there’s more to them than just specific capitalization rules, MLA in-text citations , and other formatting specifications. Citations have been helping researches document their sources for hundreds of years, and are a great way to learn more about a particular subject area.
Ever wonder what sets all the different styles apart, or how they came to be in the first place? Read on for some interesting facts about citations!
1. There are Over 7,000 Different Citation Styles
You may be familiar with MLA and APA citation styles, but there are actually thousands of citation styles used for all different academic disciplines all across the world. Deciding which one to use can be difficult, so be sure to ask you instructor which one you should be using for your next paper.
2. Some Citation Styles are Named After People
While a majority of citation styles are named for the specific organizations that publish them (i.e. APA is published by the American Psychological Association, and MLA format is named for the Modern Language Association), some are actually named after individuals. The most well-known example of this is perhaps Turabian style, named for Kate L. Turabian, an American educator and writer. She developed this style as a condensed version of the Chicago Manual of Style in order to present a more concise set of rules to students.
3. There are Some Really Specific and Uniquely Named Citation Styles
How specific can citation styles get? The answer is very. For example, the “Flavour and Fragrance Journal” style is based on a bimonthly, peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1985 by John Wiley & Sons. It publishes original research articles, reviews and special reports on all aspects of flavor and fragrance. Another example is “Nordic Pulp and Paper Research,” a style used by an international scientific magazine covering science and technology for the areas of wood or bio-mass constituents.
4. More citations were created on EasyBib.com in the first quarter of 2018 than there are people in California.
The US Census Bureau estimates that approximately 39.5 million people live in the state of California. Meanwhile, about 43 million citations were made on EasyBib from January to March of 2018. That’s a lot of citations.
5. “Citations” is a Word With a Long History
The word “citations” can be traced back literally thousands of years to the Latin word “citare” meaning “to summon, urge, call; put in sudden motion, call forward; rouse, excite.” The word then took on its more modern meaning and relevance to writing papers in the 1600s, where it became known as the “act of citing or quoting a passage from a book, etc.”
6. Citation Styles are Always Changing
The concept of citations always stays the same. It is a means of preventing plagiarism and demonstrating where you relied on outside sources. The specific style rules, however, can and do change regularly. For example, in 2018 alone, 46 new citation styles were introduced , and 106 updates were made to exiting styles. At EasyBib, we are always on the lookout for ways to improve our styles and opportunities to add new ones to our list.
Why Citations Matter
Here are the ways accurate citations can help your students achieve academic success, and how you can answer the dreaded question, “why should I cite my sources?”
They Give Credit to the Right People
Citing their sources makes sure that the reader can differentiate the student’s original thoughts from those of other researchers. Not only does this make sure that the sources they use receive proper credit for their work, it ensures that the student receives deserved recognition for their unique contributions to the topic. Whether the student is citing in MLA format , APA format , or any other style, citations serve as a natural way to place a student’s work in the broader context of the subject area, and serve as an easy way to gauge their commitment to the project.
They Provide Hard Evidence of Ideas
Having many citations from a wide variety of sources related to their idea means that the student is working on a well-researched and respected subject. Citing sources that back up their claim creates room for fact-checking and further research . And, if they can cite a few sources that have the converse opinion or idea, and then demonstrate to the reader why they believe that that viewpoint is wrong by again citing credible sources, the student is well on their way to winning over the reader and cementing their point of view.
They Promote Originality and Prevent Plagiarism
The point of research projects is not to regurgitate information that can already be found elsewhere. We have Google for that! What the student’s project should aim to do is promote an original idea or a spin on an existing idea, and use reliable sources to promote that idea. Copying or directly referencing a source without proper citation can lead to not only a poor grade, but accusations of academic dishonesty. By citing their sources regularly and accurately, students can easily avoid the trap of plagiarism , and promote further research on their topic.
They Create Better Researchers
By researching sources to back up and promote their ideas, students are becoming better researchers without even knowing it! Each time a new source is read or researched, the student is becoming more engaged with the project and is developing a deeper understanding of the subject area. Proper citations demonstrate a breadth of the student’s reading and dedication to the project itself. By creating citations, students are compelled to make connections between their sources and discern research patterns. Each time they complete this process, they are helping themselves become better researchers and writers overall.
When is the Right Time to Start Making Citations?
Make in-text/parenthetical citations as you need them.
As you are writing your paper, be sure to include references within the text that correspond with references in a works cited or bibliography. These are usually called in-text citations or parenthetical citations in MLA and APA formats. The most effective time to complete these is directly after you have made your reference to another source. For instance, after writing the line from Charles Dickens’ A Tale of Two Cities : “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times…,” you would include a citation like this (depending on your chosen citation style):
(Dickens 11).
This signals to the reader that you have referenced an outside source. What’s great about this system is that the in-text citations serve as a natural list for all of the citations you have made in your paper, which will make completing the works cited page a whole lot easier. After you are done writing, all that will be left for you to do is scan your paper for these references, and then build a works cited page that includes a citation for each one.
Need help creating an MLA works cited page ? Try the MLA format generator on EasyBib.com! We also have a guide on how to format an APA reference page .
2. Understand the General Formatting Rules of Your Citation Style Before You Start Writing
While reading up on paper formatting may not sound exciting, being aware of how your paper should look early on in the paper writing process is super important. Citation styles can dictate more than just the appearance of the citations themselves, but rather can impact the layout of your paper as a whole, with specific guidelines concerning margin width, title treatment, and even font size and spacing. Knowing how to organize your paper before you start writing will ensure that you do not receive a low grade for something as trivial as forgetting a hanging indent.
Don’t know where to start? Here’s a formatting guide on APA format .
3. Double-check All of Your Outside Sources for Relevance and Trustworthiness First
Collecting outside sources that support your research and specific topic is a critical step in writing an effective paper. But before you run to the library and grab the first 20 books you can lay your hands on, keep in mind that selecting a source to include in your paper should not be taken lightly. Before you proceed with using it to backup your ideas, run a quick Internet search for it and see if other scholars in your field have written about it as well. Check to see if there are book reviews about it or peer accolades. If you spot something that seems off to you, you may want to consider leaving it out of your work. Doing this before your start making citations can save you a ton of time in the long run.
Finished with your paper? It may be time to run it through a grammar and plagiarism checker , like the one offered by EasyBib Plus. If you’re just looking to brush up on the basics, our grammar guides are ready anytime you are.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Scribbr Referencing Generator
Accurate Harvard, APA, MLA, and Chicago references, verified by experts, trusted by millions.
Reference sources in seconds with Autocite
Look up your source by its title, URL, ISBN, or DOI, and let Scribbr do the rest! The reference generator will automatically find all the necessary information to generate a perfect reference, including the author(s), publication date, and publisher.
| ⚙️ Styles | , , MLA, Chicago |
|---|---|
| 📚 Source types | Websites, books, articles, reports, and more |
| 🔎 Autocite | Search by title, URL, DOI, or ISBN |
Perfectly formatted references every time
Inaccurate references can cost you points on your assignments, so our seasoned referencing experts have invested countless hours in perfecting Scribbr’s reference generator algorithms. We’re proud to be recommended by teachers and universities across the UK.
Enjoy a referencing generator without flashy ads
Staying focused is already difficult enough, so unlike other reference generators, Scribbr won’t slow you down with flashing banner ads and video pop-ups. That’s a promise!
Citation Generator features you'll love
Look up your source by its title, URL, ISBN, or DOI, and let Scribbr find and fill in all the relevant information automatically.
Harvard, APA, MLA, Chicago
Generate flawless references according to the official Harvard , APA , MLA, or Chicago style rules. More referencing styles will be available soon!
Export to Word
When your reference list is complete, export it to Word. We’ll apply the official formatting guidelines automatically.
Lists and folders
Create separate reference lists for each of your assignments to stay organized. You can also group related lists into folders.
Export to Bib(La)TeX
Are you using a LaTex editor like Overleaf? If so, you can easily export your references in Bib(La)TeX format with a single click.
Custom fonts
Change the typeface used for your reference list to match the rest of your document. Options include Times New Roman, Arial, and Calibri.
Industry-standard technology
Scribbr’s Referencing Generator is built using the same citation software (CSL) as Mendeley and Zotero, but with an added layer for improved accuracy.
Annotations
Describe or evaluate your sources in annotations, and Scribbr will generate a perfectly formatted annotated bibliography.
Referencing guides
Scribbr’s popular guides and videos will help you understand everything related to finding, evaluating, and referencing sources.
Secure backup
Your work is saved automatically after every change and stored securely in your Scribbr account.
- Introduction
- Finding sources
Evaluating sources
- Integrating sources
Referencing sources
Tools and resources, a quick guide to working with sources.
Working with sources is an important skill that you’ll need throughout your academic career.
It includes knowing how to find relevant sources, assessing their authority and credibility, and understanding how to integrate sources into your work with proper referencing.
This quick guide will help you get started!
Finding relevant sources
Sources commonly used in academic writing include academic journals, scholarly books, websites, newspapers, and encyclopedias. There are three main places to look for such sources:
- Research databases: Databases can be general or subject-specific. To get started, check out this list of databases by academic discipline . Another good starting point is Google Scholar .
- Your institution’s library: Use your library’s database to narrow down your search using keywords to find relevant articles, books, and newspapers matching your topic.
- Other online resources: Consult popular online sources like websites, blogs, or Wikipedia to find background information. Be sure to carefully evaluate the credibility of those online sources.
When using academic databases or search engines, you can use Boolean operators to refine your results.
Generate Harvard, APA, MLA, and Chicago style references in seconds
Get started
In academic writing, your sources should be credible, up to date, and relevant to your research topic. Useful approaches to evaluating sources include the CRAAP test and lateral reading.
CRAAP is an abbreviation that reminds you of a set of questions to ask yourself when evaluating information.
- Currency: Does the source reflect recent research?
- Relevance: Is the source related to your research topic?
- Authority: Is it a respected publication? Is the author an expert in their field?
- Accuracy: Does the source support its arguments and conclusions with evidence?
- Purpose: What is the author’s intention?
Lateral reading
Lateral reading means comparing your source to other sources. This allows you to:
- Verify evidence
- Contextualize information
- Find potential weaknesses
If a source is using methods or drawing conclusions that are incompatible with other research in its field, it may not be reliable.
Integrating sources into your work
Once you have found information that you want to include in your paper, signal phrases can help you to introduce it. Here are a few examples:
| Function | Example sentence | Signal words and phrases |
|---|---|---|
| You present the author’s position neutrally, without any special emphasis. | recent research, food services are responsible for one-third of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. | According to, analyzes, asks, describes, discusses, explains, in the words of, notes, observes, points out, reports, writes |
| A position is taken in agreement with what came before. | Recent research Einstein’s theory of general relativity by observing light from behind a black hole. | Agrees, confirms, endorses, reinforces, promotes, supports |
| A position is taken for or against something, with the implication that the debate is ongoing. | Allen Ginsberg artistic revision … | Argues, contends, denies, insists, maintains |
Following the signal phrase, you can choose to quote, paraphrase or summarize the source.
- Quoting : This means including the exact words of another source in your paper. The quoted text must be enclosed in quotation marks or (for longer quotes) presented as a block quote . Quote a source when the meaning is difficult to convey in different words or when you want to analyze the language itself.
- Paraphrasing: This means putting another person’s ideas into your own words. It allows you to integrate sources more smoothly into your text, maintaining a consistent voice. It also shows that you have understood the meaning of the source.
- Summarizing : This means giving an overview of the essential points of a source. Summaries should be much shorter than the original text. You should describe the key points in your own words and not quote from the original text.
Whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize a source, you must include a citation crediting the original author.
Referencing your sources is important because it:
- Allows you to avoid plagiarism
- Establishes the credentials of your sources
- Backs up your arguments with evidence
- Allows your reader to verify the legitimacy of your conclusions
The most common citation styles in the UK are APA, MLA, Harvard, Vancouver, MHRA, and Oscola. Each citation style has specific rules for formatting citations.
Scribbr’s free Reference Generator can generate perfect references and in-text citations in both APA and MLA styles. More citation styles will be available soon!
Scribbr and partners offer tons of tools and resources to make working with sources easier and faster. Take a look at our top picks:
- Reference Generator: Automatically generate Harvard and APA references .
- Plagiarism Checker : Detect plagiarism in your paper using the most accurate Turnitin-powered plagiarism software available to students.
- Proofreading services : Have a human editor improve your writing.
- Knowledge Base : Explore hundreds of articles, bite-sized videos, time-saving templates, and handy checklists that guide you through the process of research, writing, and citation.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Reference citations in text are covered on pages 261-268 of the Publication Manual. What follows are some general guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay.
Note: On pages 117-118, the Publication Manual suggests that authors of research papers should use the past tense or present perfect tense for signal phrases that occur in the literature review and procedure descriptions (for example, Jones (1998) found or Jones (1998) has found ...). Contexts other than traditionally-structured research writing may permit the simple present tense (for example, Jones (1998) finds ).
APA Citation Basics
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
If you are referring to an idea from another work but NOT directly quoting the material, or making reference to an entire book, article or other work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication and not the page number in your in-text reference.
On the other hand, if you are directly quoting or borrowing from another work, you should include the page number at the end of the parenthetical citation. Use the abbreviation “p.” (for one page) or “pp.” (for multiple pages) before listing the page number(s). Use an en dash for page ranges. For example, you might write (Jones, 1998, p. 199) or (Jones, 1998, pp. 199–201). This information is reiterated below.
Regardless of how they are referenced, all sources that are cited in the text must appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
In-text citation capitalization, quotes, and italics/underlining
- Always capitalize proper nouns, including author names and initials: D. Jones.
- If you refer to the title of a source within your paper, capitalize all words that are four letters long or greater within the title of a source: Permanence and Change . Exceptions apply to short words that are verbs, nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and adverbs: Writing New Media , There Is Nothing Left to Lose .
( Note: in your References list, only the first word of a title will be capitalized: Writing new media .)
- When capitalizing titles, capitalize both words in a hyphenated compound word: Natural-Born Cyborgs .
- Capitalize the first word after a dash or colon: "Defining Film Rhetoric: The Case of Hitchcock's Vertigo ."
- If the title of the work is italicized in your reference list, italicize it and use title case capitalization in the text: The Closing of the American Mind ; The Wizard of Oz ; Friends .
- If the title of the work is not italicized in your reference list, use double quotation marks and title case capitalization (even though the reference list uses sentence case): "Multimedia Narration: Constructing Possible Worlds;" "The One Where Chandler Can't Cry."
Short quotations
If you are directly quoting from a work, you will need to include the author, year of publication, and page number for the reference (preceded by "p." for a single page and “pp.” for a span of multiple pages, with the page numbers separated by an en dash).
You can introduce the quotation with a signal phrase that includes the author's last name followed by the date of publication in parentheses.
If you do not include the author’s name in the text of the sentence, place the author's last name, the year of publication, and the page number in parentheses after the quotation.
Long quotations
Place direct quotations that are 40 words or longer in a free-standing block of typewritten lines and omit quotation marks. Start the quotation on a new line, indented 1/2 inch from the left margin, i.e., in the same place you would begin a new paragraph. Type the entire quotation on the new margin, and indent the first line of any subsequent paragraph within the quotation 1/2 inch from the new margin. Maintain double-spacing throughout, but do not add an extra blank line before or after it. The parenthetical citation should come after the closing punctuation mark.
Because block quotation formatting is difficult for us to replicate in the OWL's content management system, we have simply provided a screenshot of a generic example below.

Formatting example for block quotations in APA 7 style.
Quotations from sources without pages
Direct quotations from sources that do not contain pages should not reference a page number. Instead, you may reference another logical identifying element: a paragraph, a chapter number, a section number, a table number, or something else. Older works (like religious texts) can also incorporate special location identifiers like verse numbers. In short: pick a substitute for page numbers that makes sense for your source.
Summary or paraphrase
If you are paraphrasing an idea from another work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication in your in-text reference and may omit the page numbers. APA guidelines, however, do encourage including a page range for a summary or paraphrase when it will help the reader find the information in a longer work.
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!


😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:
| ⚙️ Styles | MLA 8 & MLA 9 |
|---|---|
| 📚 Sources | Websites, books, journals, newspapers |
| 🔎 Autocite | Yes |
| 📥 Download to | Microsoft Word, Google Docs |

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Cite an Essay
Last Updated: February 4, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Diya Chaudhuri, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Diya Chaudhuri holds a PhD in Creative Writing (specializing in Poetry) from Georgia State University. She has over 5 years of experience as a writing tutor and instructor for both the University of Florida and Georgia State University. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 559,102 times.
If you're writing a research paper, whether as a student or a professional researcher, you might want to use an essay as a source. You'll typically find essays published in another source, such as an edited book or collection. When you discuss or quote from the essay in your paper, use an in-text citation to relate back to the full entry listed in your list of references at the end of your paper. While the information in the full reference entry is basically the same, the format differs depending on whether you're using the Modern Language Association (MLA), American Psychological Association (APA), or Chicago citation method.
Template and Examples

- Example: Potter, Harry.

- Example: Potter, Harry. "My Life with Voldemort."

- Example: Potter, Harry. "My Life with Voldemort." Great Thoughts from Hogwarts Alumni , by Bathilda Backshot,

- Example: Potter, Harry. "My Life with Voldemort." Great Thoughts from Hogwarts Alumni , by Bathilda Backshot, Hogwarts Press, 2019,

- Example: Potter, Harry. "My Life with Voldemort." Great Thoughts from Hogwarts Alumni , by Bathilda Backshot, Hogwarts Press, 2019, pp. 22-42.
MLA Works Cited Entry Format:
LastName, FirstName. "Title of Essay." Title of Collection , by FirstName Last Name, Publisher, Year, pp. ##-##.

- For example, you might write: While the stories may seem like great adventures, the students themselves were terribly frightened to confront Voldemort (Potter 28).
- If you include the author's name in the text of your paper, you only need the page number where the referenced material can be found in the parenthetical at the end of your sentence.
- If you have several authors with the same last name, include each author's first initial in your in-text citation to differentiate them.
- For several titles by the same author, include a shortened version of the title after the author's name (if the title isn't mentioned in your text).

- Example: Granger, H.

- Example: Granger, H. (2018).

- Example: Granger, H. (2018). Adventures in time turning.

- Example: Granger, H. (2018). Adventures in time turning. In M. McGonagall (Ed.), Reflections on my time at Hogwarts

- Example: Granger, H. (2018). Adventures in time turning. In M. McGonagall (Ed.), Reflections on my time at Hogwarts (pp. 92-130). Hogwarts Press.
APA Reference List Entry Format:
LastName, I. (Year). Title of essay. In I. LastName (Ed.), Title of larger work (pp. ##-##). Publisher.

- For example, you might write: By using a time turner, a witch or wizard can appear to others as though they are actually in two places at once (Granger, 2018).
- If you use the author's name in the text of your paper, include the parenthetical with the year immediately after the author's name. For example, you might write: Although technically against the rules, Granger (2018) maintains that her use of a time turner was sanctioned by the head of her house.
- Add page numbers if you quote directly from the source. Simply add a comma after the year, then type the page number or page range where the quoted material can be found, using the abbreviation "p." for a single page or "pp." for a range of pages.

- Example: Weasley, Ron.

- Example: Weasley, Ron. "Best Friend to a Hero."

- Example: Weasley, Ron. "Best Friend to a Hero." In Harry Potter: Wizard, Myth, Legend , edited by Xenophilius Lovegood, 80-92.

- Example: Weasley, Ron. "Best Friend to a Hero." In Harry Potter: Wizard, Myth, Legend , edited by Xenophilius Lovegood, 80-92. Ottery St. Catchpole: Quibbler Books, 2018.
' Chicago Bibliography Format:
LastName, FirstName. "Title of Essay." In Title of Book or Essay Collection , edited by FirstName LastName, ##-##. Location: Publisher, Year.

- Example: Ron Weasley, "Best Friend to a Hero," in Harry Potter: Wizard, Myth, Legend , edited by Xenophilius Lovegood, 80-92 (Ottery St. Catchpole: Quibbler Books, 2018).
- After the first footnote, use a shortened footnote format that includes only the author's last name, the title of the essay, and the page number or page range where the referenced material appears.
Tip: If you use the Chicago author-date system for in-text citation, use the same in-text citation method as APA style.
Community Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://style.mla.org/essay-in-authored-textbook/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_page_books.html
- ↑ https://utica.libguides.com/c.php?g=703243&p=4991646
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide/intext
- ↑ https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/c.php?g=27779&p=170363
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ http://libguides.heidelberg.edu/chicago/book/chapter
- ↑ https://librarybestbets.fairfield.edu/citationguides/chicagonotes-bibliography#CollectionofEssays
- ↑ https://libguides.heidelberg.edu/chicago/book/chapter
About This Article

To cite an essay using MLA format, include the name of the author and the page number of the source you’re citing in the in-text citation. For example, if you’re referencing page 123 from a book by John Smith, you would include “(Smith 123)” at the end of the sentence. Alternatively, include the information as part of the sentence, such as “Rathore and Chauhan determined that Himalayan brown bears eat both plants and animals (6652).” Then, make sure that all your in-text citations match the sources in your Works Cited list. For more advice from our Creative Writing reviewer, including how to cite an essay in APA or Chicago Style, keep reading. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Mbarek Oukhouya
Mar 7, 2017
Did this article help you?

Sarah Sandy
May 25, 2017
Skyy DeRouge
Nov 14, 2021
Diana Ordaz
Sep 25, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
APA In-Text Citations and Sample Essay 7th Edition
This handout focuses on how to format in-text citations in APA.
Proper citation of sources is a two-part process . You must first cite each source in the body of your essay; these citations within the essay are called in-text citations . You MUST cite all quoted, paraphrased, or summarized words, ideas, and facts from sources. Without in-text citations, you are technically in danger of plagiarism, even if you have listed your sources at the end of the essay.
In-text citations point the reader to the sources’ information on the references page. The in-text citation typically includes the author's last name and the year of publication. If you use a direct quote, the page number is also provided.
More information can be found on p. 253 of the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association.
Citation Rules
Direct quotation with the author named in the text.
Heinze and Lu (2017) stated, “The NFL shifted its responses to institutional change around concussions significantly as the field itself evolved” (p. 509).
Note: The year of publication is listed in parenthesis after the names of the authors, and the page number is listed in parenthesis at the end of the quote.
Direct Quotation without the Author Named in the Text
As the NFL developed as an organization, it “shifted its responses to institutional change around concussions significantly” (Heinze & Lu, 2017, p. 509).
Note: At the end of the quote, the names of the authors, year of publication, and page number are listed in parenthesis.
Paraphrase with 1-2 Authors
As the NFL developed as an organization, its reactions toward concussions also transformed (Heinze & Lu, 2017).
Note: For paraphrases, page numbers are encouraged but not required.
Paraphrase with 3 or More Authors
To work toward solving the issue of violence in prisons begins with determining aspects that might connect with prisoners' violent conduct (Thomson et al., 2019).
Direct Quotation without an Author
The findings were astonishing "in a recent study of parent and adult child relationships" ("Parents and Their Children," 2007, p. 2).
Note: Since the author of the text is not stated, a shortened version of the title is used instead.
Secondary Sources
When using secondary sources, use the phrase "as cited in" and cite the secondary source on the References page.
In 1936, Keynes said, “governments should run deficits when the economy is slow to avoid unemployment” (as cited in Richardson, 2008, p. 257).
Long (Block) Quotations
When using direct quotations of 40 or more words, indent five spaces from the left margin without using quotation marks. The final period should come before the parenthetical citation.
At Meramec, an English department policy states:
To honor and protect their own work and that of others, all students must give credit to proprietary sources that are used for course work. It is assumed that any information that is not documented is either common knowledge in that field or the original work of that student. (St. Louis Community College, 2001, p. 1)
Website Citations
If citing a specific web document without a page number, include the name of the author, date, title of the section, and paragraph number in parentheses:
In America, “Two out of five deaths among U.S. teens are the result of a motor vehicle crash” (National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, 2004, Overview section, para. 1).
Here is a print-friendly version of this content.
Learn more about the APA References page by reviewing this handout .
For information on STLCC's academic integrity policy, check out this webpage .
For additional information on APA, check out STLCC's LibGuide on APA .
Sample Essay
A sample APA essay is available at this link .
Essay Writing: In-Text Citations
- Essay Writing Basics
- Purdue OWL Page on Writing Your Thesis This link opens in a new window
- Paragraphs and Transitions
- How to Tell if a Website is Legitimate This link opens in a new window
- Formatting Your References Page
- Cite a Website
- Common Grammatical and Mechanical Errors
- Additional Resources
- Proofread Before You Submit Your Paper
- Structuring the 5-Paragraph Essay
In-text Citations
What are In-Text Citations?
You must cite (give credit) all information sources used in your essay or research paper whenever and wherever you use them.
When citing sources in the text of your paper, you must list:
● The author’s last name
● The year the information was published.
Types of In-Text Citations: Narrative vs Parenthetical
A narrative citation gives the author's name as part of the sentence .
- Example of a Narrative Citation: According to Edwards (2017) , a lthough Smith and Carlos's protest at the 1968 Olympics initially drew widespread criticism, it also led to fundamental reforms in the organizational structure of American amateur athletics.
A parenthetical citation puts the source information in parentheses—first or last—but does not include it in the narrative flow.
- Example of a Parenthetical Citation: Although Tommie Smith and John Carlos paid a heavy price in the immediate aftermath of the protests, they were later vindicated by society at large (Edwards, 2017) .
Full citation for this source (this belongs on the Reference Page of your research paper or essay):
Edwards, H. (2017). The Revolt of the Black Athlete: 50th Anniversary Edition. University of Illinois Press.
Sample In-text Citations
| Studies have shown music and art therapies to be effective in aiding those dealing with mental disorders as well as managing, exploring, and gaining insight into traumatic experiences their patients may have faced. (Stuckey & Nobel, 2010). |
| - FIRST INITIAL, ARTICLE TITLE -- |
| Hint: (Use an when they appear in parenthetical citations.) e.g.: (Jones & Smith, 2022) |
| Stuckey and Nobel (2010) noted, "it has been shown that music can calm neural activity in the brain, which may lead to reductions in anxiety, and that it may help to restore effective functioning in the immune system." |
|
|
Note: This example is a direct quote. It is an exact quotation directly from the text of the article. All direct quotes should appear in quotation marks: "...."
Try keeping direct quotes to a minimum in your writing. You need to show your understanding of the source material by being able to paraphrase or summarize it.
List the author’s last name only (no initials) and the year the information was published, like this:
(Dodge, 2008 ). ( Author , Date).
IF you use a direct quote, add the page number to your citation, like this:
( Dodge , 2008 , p. 125 ).
( Author , Date , page number )
What information should I cite in my paper/essay?
Credit these sources when you mention their information in any way: direct quotation, paraphrase, or summarize.
What should you credit?
Any information that you learned from another source, including:
● statistics
EXCEPTION: Information that is common knowledge: e.g., The Bronx is a borough of New York City.
Quick Sheet: APA 7 Citations
Quick help with apa 7 citations.
- Quick Sheet - Citing Journal Articles, Websites & Videos, and Creating In-Text Citations A quick guide to the most frequently-used types of APA 7 citations.
In-text Citation Tutorial
- Formatting In-text Citations, Full Citations, and Block Quotes In APA 7 Style This presentation will help you understand when, why, and how to use in-text citations in your APA style paper.
Download the In-text Citations presentation (above) for an in-depth look at how to correctly cite your sources in the text of your paper.
SIgnal Phrase Activity
Paraphrasing activity from the excelsior owl, in-text citation quiz.
- << Previous: Formatting Your References Page
- Next: Cite a Website >>
- Last Updated: Jun 25, 2024 3:33 PM
- URL: https://monroecollege.libguides.com/essaywriting
- Research Guides |
- Databases |
APA Citation Generator
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
What Is Cite This For Me’s APA Citation Generator?
If you are working on a paper in the APA style, you know that formatting APA citations can be a complicated task that requires a lot of patience. Fortunately, referencing has never been so easy. Introducing your new best friend: the Cite This For Me APA citation generator. Using this automated citation machine to create accurate citations allows students to work smarter, leaving them more time to focus on their studies.
The Cite This For Me powerful citation generator fully-formats all of your APA citations in just a click. So if you’re unsure how to accurately create your citations in the APA format, or you need to cite all of your sources in record time, using the Cite This For Me accurate generator will help ensure you don’t lose valuable points on your work unnecessarily.
This guide provides you with everything you need to know to help ensure that your paper reflects all your hard work. Read ahead for tips on how to structure and present your work according to the APA formatting guidelines, how to avoid charges of plagiarism, and how to cite sources both in-text and in your reference list and bibliography.
Popular APA Citation Examples
- Dictionary entry
- Edited book
- Image or video online
- PDF or E-book
- Presentation or lecture
- Video, film, or DVD
Why Do I Need to Cite?
Essentially, citing is the crediting of sources used in academic work. When another source contributes to your work you must acknowledge the original author with an accurate reference, unless it is common knowledge (e.g., the Magna Carta was signed in 1215). Failing to cite all of your sources or citing them incorrectly constitutes plagiarism , which is considered a serious academic offense. It is important to remember that information doesn’t just belong to anyone who happens to stumble upon it. If you are caught plagiarizing it is more than likely that you will lose points on your assignment, or even face expulsion from your university.
APA citation format also stipulates that students and researchers should be wary of a type of plagiarism called “self-plagiarism.” This is when you reuse material that you previously wrote for a new writing assignment without signaling to the reader that you have done so by creating an APA format citation for your work. Presenting your own past work as new scholarship is still plagiarism, and could still have serious consequences.
Aside from avoiding plagiarism, attributing your research to its proper source is crucial in ensuring that your work is firmly anchored in academic tradition. Correctly citing your sources validates the statements and conclusions you make in your work by providing supporting evidence. For many students, citing can be a frustrating process, but it’s an excellent way to enhance the quality of your work and inject it with authority.
Imagine if all the stress of referencing simply vanished. Well, Cite This For Me’s APA citation generator is here to help you make that stress disappear – now you can create in-text citations and reference lists in the APA format without all of the usual frustrations of referencing.
What is the APA Citation Style?
The APA citation style is a parenthetical author-date style, meaning that you need to put the author’s last name and the publishing date into parentheses wherever another source is used in the narrative.
The APA format consists of in-text citations and a reference list, along with guidelines for formatting the paper itself. Both the in-text citations and the reference list can be created in the blink of an eye using the Cite This For Me APA reference generator.
Although primarily used by students and researchers studying the social and behavioral sciences, the APA format is used amongst other scientific publications for its editorial efficiency. The Cite This For Me APA citation generator uses an up to date version of the APA format, helping to ensure accuracy whether you are using the APA format generator for university assignments or are preparing research projects for publishing.
Aside from the APA format, there is a plethora of different citation styles out there – the use of which depends on your discipline, university requirements, your professor’s preference, or the publication you are submitting the work to. It is important to make sure that you are using the correct style – so if you’re unsure, consult your department and follow their guidelines exactly.
It is important to note that APA style citation rules are fundamentally an editorial style, not a writing style per se. An editorial style refers to rules and guidelines a publisher uses to ensure that materials in their publications are presented consistently.
The citation generator above will generate your references in APA format as standard, and can show you how to cite APA sources in a few clicks. You can also sign up to Cite This For Me to select from thousands of widely used global college styles, including individual university variations. So, whether your professor prefers that you use the MLA format , or your discipline requires you to adopt the Chicago style citation , your referencing will be supported. Cite This For Me includes citation generators and handy guides for styles such as ASA , AMA or IEEE .
How Do I Create and Format My Citations?
Ever find yourself searching the web for things like “How to cite a website APA?” Then you’re in the right place. When you reference a source within an APA style paper; whether it is using a direct quote, repurposing an image, or simply referring to an idea or theory, you should:
- Insert an in-text citation (the author’s surname and the date of publication within parentheses) straight after a direct quote
- Insert an in-text citation at the end of the sentence where a source has contributed, but was not a direct quote
- If you have already mentioned the author’s name in the sentence, you only need to insert the date immediately after their surname
- Include page numbers within the parentheses (after the date), if referring to a particular page or section of the source
- When citing a source with three to five authors, include all surnames for the first in-text citation, then use the first author’s surname followed by et al. for subsequent citations
- When citing six or more authors – use the first author’s surname followed by et al. for all citations
- If you are mentioning both the year and author in the text, don’t include an additional citation in parentheses – unless you are referring to a particular section of the source, in which case you should cite the page number
- Provide an alphabetical list (ordered by author’s surname) of all sources used, titled ‘References’, on a separate page at the end of the narrative
- Inclusive page numbers for the electronic version of a print source (i.e., a PDF)
- Provide your appendices on a separate page after the reference list
- Use ‘&’ in place of ‘and’ in both in-text citations and full references
Use the Cite This For Me APA citation maker to create citations with ease; this will allow you to add citations to your project, edit on the spot, and export separate in-text citations as well as fully-formatted reference lists.
APA Citation Examples (7th Edition)
Each APA reference must adhere to the rules set forth in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 7th edition . The following examples follow guidelines from Chapter 10 of the manual. Here are a few examples for you to get started:
In-text citation APA examples:
- Page specified, author mentioned in text:
Lutz & Huitt (2010, p. 4) argue that “the statistical significance of …”
- Page specified, author not mentioned in text:
The results were consistent throughout the study (Fernández-Manzanal, Rodríguez-Barreiro, & Carrasquer, 2007).
- Six authors:
The study found that … (Sania et al., 2011)
The data presented …. (“How sleep enhances memory retention”, 2015).
Reference list examples:
- Book citation, one author, multiple editions:
Hawking, S. W. (1998). A brief history of time: From the big bang to black holes (10th ed.). New York: Bantam Doubleday Dell Publishing Group.
- Ebook, online only:
Tyler, G. (n.d.). Evolution in the systems age . Retrieved from http://www.onlineoriginals.com/showitem.asp?itemID=142&action=setvar&vartype=history&varname=bookmark&v1=1&v2=46&v3=2
- Journal article, three authors, with a DOI:
Fernández-Manzanal, R., Rodríguez-Barreiro, L., & Carrasquer, J. (2007). Evaluation of environmental attitudes: Analysis and results of a scale applied to university students. Science Education , 91(6), 988–1009. doi:10.1002/sce.20218
* Note: For more information on the different types of journal article citations that can be made under APA 7, see section 10.1 of the Publication Manual, pp. 316-321.
- How to cite a website in APA:
Veterans Affairs Canada. (2019, February 14). Indigenous people in the Second World War . https://www.veterans.gc.ca/eng/remembrance/history/historical-sheets/aborigin
- Online newspaper article:
Smith, D. (2019, October 22). The banner, the rings, the season opener: Champion Raptors return on a night like no other. The Toronto Star . https://www.thestar.com/sports/raptors/2019/10/22/the-banner-the-rings-the-season-opener-champion-raptors-return-on-a-night-like-no-other.html
- Article from an online news website (HuffPost, MSNBC, Vox, etc.):
Wade, L. (2013, March 6). ‘Sunstone’ crystal from British shipwreck may be vikings’ legendary navigation aid . HuffPost. https://www.huffpost.com/entry/sunstone-british-shipwreck-viking-navigation_n_2818858
- Video, online:
CrashCourse. (2015, April 30). Mars: Crash course astronomy #15 [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I-88YWx71gE
How Do I Format My Reference List?
Drawing on a range of relevant sources in your work proves that you have read widely around your chosen topic, so it’s a surefire way to impress your reader.
To ensure your reader’s ease of comprehension you must adhere to the style’s formatting guidelines. In APA format, a list of all the sources that have directly contributed to your work should be placed on a new page at the end of the narrative and titled ‘References’ (center align the title), otherwise known as an APA works cited list. The references should all have a hanging indentation – the second and subsequent lines of each reference should start ½ inch from the margin.
You may also be required to provide a full APA bibliography. This is a comprehensive list of all the source material you used to complete the assignment, even if it was not cited in the text. It should include any book, journal, article etc. that you may have consulted throughout your research and writing process in order to get a deeper understanding of the subject at hand.
APA Format Example:
Sound like a lot of work? Although the style guidelines are strict in regard to how references should be formatted, the Cite This For Me APA citation machine can help take the weight off your shoulders by quickly compiling your reference list and bibliography.
APA Style Paper Formatting Guidelines (7th Edition)
When following the APA format guidelines, you must pay attention to presentation details such as font type, line spacing, margins and page headers to ensure your work is easily legible. The information below, as well as further formatting details, can be found in Chapter 2 of the APA 7 Publication Manual .
- 1-inch margins on all sides
- Easily readable font – Times New Roman recommended, 12pt. size
- Double-space the entirety of the paper
- Page numbers in the header, aligned to the right
- Title of the paper in all capitals, 50 characters or less, in the header on each page of the body (the ‘running head’), aligned to the left. Only include a running head if you’re writing a professional paper
- The paper should typically include four major sections – Title Page, Abstract, Main Body and References.
- If infographics (tables, charts) were used in the narrative you should also add Appendices as a separate section at the end of the paper.
APA Title Page
Not all instructors will require a title page, also sometimes called an APA cover page. If they do, include these four parts:
- Title of your paper
- Running head (see above section)
- Author’s/Your name
- Institutional affiliation
The title of your paper should:
- Be centered on the page and use title case (a combination of lower and uppercase letters).
- Not be italicized, bolded, or underlined
- Use a 12-point font
- Be a maximum of 2 lines and not more than 12 words long
- Not include abbreviations
Underneath the title, place the author’s name. If you wrote the paper, put your full name here. There’s no need to include titles or degrees (e.g., Ms., PhD, etc.).
Under the author’s name, place the institutional affiliation. For most students, this would be the name of the school, college or university you are attending. The title, author’s name, and institutional affiliation should all be double spaced. Here’s an example of an APA format title page:

Writing Guidelines
The American Psychological Association also provides some helpful guidelines regarding overall best practices when writing academic and scientific papers. One important thing to be on the lookout for is bias in your writing. For instance, using the word “man” to represent humans as a species is neither scientific nor without potential bias.
Here are some good rules of thumb to help you avoid bias in your paper:
- Always be specific in your writing and avoid generalizations.
- Do not label people or test subjects unnecessarily.
- When writing about participants in your experiment or study, be sure to acknowledge them as such appropriately. Use the term “participants” instead of “subjects.”
- Use active voice instead of passive voice in your writing. For example, “the participants completed the task” vs. “the task was completed by the participants.”
- Always be cautious when discussing topics such as sexual orientation, racial and ethnic identity, disabilities, etc.
- Never change quotations to better serve your own ends or to better fit with your conclusions.
Important Terms for an APA Paper
Have you come across terms such as “abstract” or “appendices” in the manual and been unsure of their meanings? Here are some important terms to know when writing your next APA paper.
- Abstract – A brief and concise summary of your paper’s contents.
- Keywords – A list of significant keywords that the reader should be on the lookout for in your paper.
- Introduction – Generally kicks of the rest of your paper by describing what you’re writing about. In scientific papers, this would outline the problem you are solving and your research strategy.
- References – An APA reference page is the place where you list each source that you have cited via an APA in-text citation within the body of your paper.
- Running Head – Running head is the name of APA headings that are used in research papers. They contain the title of the paper, the page number, and the term “Running head.”
A Brief History of the APA Format
APA stands for American Psychological Association , the scientific organization that assembles the publishing manual of the APA format. The style was developed in 1929 by a group of scientists to standardize scientific writing. It was created in the hopes that it would provide a coherent and professional manner of citing sources for students and researchers in the fields of social and behavioral sciences.
The first publication manual of the APA format was published in pursuit of a neat and efficient research formatting style, mainly for editorial purposes. Although some contemporary scientists argued that having such strict regulations restricted personal writing styles, the format has since become one of the most popular referencing styles. Today it is adopted in term papers, research reports, literature reviews, theoretical articles, case studies etc.
What’s New in the 7th Edition of APA Format?
It is important to note that citation styles and referencing formats change over time as they adapt to new source types and trends in academic publishing. APA format is no different, and in the fall of 2019 released the 7th edition of its Publication Manual.
Are you curious to know what the differences are between the 7th and 6th edition of APA style? Here are some of the important updates listed in the 7th edition of APA citing:
- The location of the source’s publisher no longer needs to be included in the citation.
- DOIs are formatted as URLs (i.e. https://doi.org/xxx), and no longer require the label “DOI” preceding them in the reference.
- When making an APA website citation, URLs no longer need to be preceded by “Retrieved from.” The exception to this is when you include a date of retrieval, which is optional.
- When making an APA book citation for an ebook, you no longer need to include the device or platform that you read the book on (i.e. “Kindle) is no longer required in the citation.
- There is more flexibility in the 7th edition regarding APA paper format specifications on font.
- The running head in an APA format title page no longer requires the words “Running head,” and instead now only requires a page number and a shortened version of your paper’s title.
- You now need to only use one space after each period in your paper.
Before you switch to the newest version, it is a good idea to confirm with your teacher or instructor that this is the version of the style that they prefer you use.
How do I Create Accurate Citations with the Cite This For Me APA Generator?
Referencing giving you a headache? Let the Cite This For Me APA format generator remove the stress caused by citations by helping to turn in any of your sources into a fully-formatted citation. The generator will create your reference in two parts; an in-text citation and a full reference that is ready to be copied straight into your work.
To unlock the full potential of the APA citation maker, simply login to Cite This For Me multi-platform tool. Use the web platform to add and edit citations, export full projects and individual entries, utilize the add-ons, and save all of your citations in the cloud. Or, you can make use of Cite This For Me for Chrome – the browser extension for Google Chrome that allows you to cite APA sources and instantly create and edit a citation for any online web page, without leaving the one you’re viewing.
Cite This For Me gives students the confidence to achieve their full academic potential by encouraging them to research and cite diverse sources. The APA citation generator can help you cite many different kinds of sources; whether it be a PDF report, podcast, a musical score or many more .
Manage All Your Citations in One Place
Create projects, add notes, cite directly from the browser.
Sign up to Cite This For Me – the ultimate citation management tool.
Section 8.17 of the APA Manual, 7 th edition, provides details on the number of authors to be included in in-text citations. As per this section, any work having 3 or more authors will not be written fully. Instead, the Latin words “et al” meaning “and others” have to be used after writing the first author’s name.
Example In-Text Citation Entry for more than 3 authors:
Almost all suppressed persons end up becoming an oppressed person when the same set of situations is presented in their lives (Camus et al., 1975).
In a rare instance, multiple sets of three or more authors might have the same initial pair or initial author. Under such rare situations, Section 8.18 of the APA manual requires you to write out the names of authors in order to distinguish between such confusing references.
Example In-Text Citation Entries:
Bandopadhyay, Schmidt, Wagner et al. (2000)
Bandopadhyay, Schmidt, Meyer et al. (1975)
Section 2.8 of the APA Manual, 7 th edition, provides details on the running head. A shortened version of the paper’s title (50 characters or fewer, including spaces and punctuation), the running head appears on top of each page so that the readers can connect the paper’s content with the title. While running heads are not required for student papers unless explicitly stated by the organization or instructor, manuscripts for publication absolutely require them.
Running heads should be in all-capital letters, flush left (directly across from the page number, which is flush right), and presented in the page header including the title page. You do not need to use the words, “Running head” because it is implied from its presence in the header.
Comparison of Loan Repayment Between Traditional Lending and Online Lending Models (Heading)
COMPARISON OF LOAN REPAYMENT MODELS (Running Head)
Section 2.3 of the APA Manual, 7 th edition provides details on what should appear in a title page for both professionals and students. While students are advised to follow the guidelines from their respective institutions or instructors, the following elements (from top to bottom) are necessary in the absence of any such information.
- Page number at the right hand side top in the header portion (also to be included in all pages)
- Title of the paper in bold, centered and appearing in the middle
- Author’s name
- Affiliation of the author (this will be the university’s name along with the department’s or division’s name)
- Name of the course (format used in the course materials. For example, PSY101)
- Name of the instructor (check with the instructor for their preference of salutation like Dr., Professor, etc.)
- Due date of the assignment with the month spelled out (June 1, 2021, or 1 June, 2021)
Section 2.3 of the APA Manual, 7 th edition provides details on what should appear on a title page for both professional and student papers. The following elements (from top to bottom) are necessary for the professional version of the title page.
- Running head in capitals at the left-hand side of the header portion (included on every page)
- Page number at the right-hand side of the header portion (included on every page)
- Title of the paper in bold, centered, and on the upper portion of the page (usually three or four lines down from the top)
- Authors’ name(s) in full, including first name, middle initial, and last name
- Affiliation of the authors (the university’s or institution’s name where the work referenced in the paper was conducted and the department’s or division’s name)
- Author Note (below the information listed above, this section provides additional pertinent information about authors along with contact information for those interested)
According to section 9.16 of the APA manual, 7th edition, you only need to add “retrieved from” and a retrieval date in a reference entry for web sources designed to be continuously updated. For example, an online reference entry from a dictionary or encyclopedia, or a social media page. Including a retrieval date signals to readers that the source may differ in content if retrieved on a different date. When including the retrieval date, insert it before the URL or DOI at the end of the entry:
Retrieved January 1, 2022, from https://chegg.com
For web sources with stable URLs or DOIs that do not change, do not include a retrieval date. Only include the URL or DOI. Section 9.5 of the APA manual, 7 th edition provides information on how to format DOIs (Digital Object Identifiers) and URLs (Uniform Resource Locators). Both DOIs and URLs are to be presented as hyperlinks (use http:// or https:// as the case may be). Since these are presented as hyperlinks that the readers can use to access the content, it is NOT necessary to have the words, “Retrieved from” or “Accessed from” before a DOI or an URL. However, test the resource to ensure the hyperlink works.
Section 8.11 of the APA Publication Manual , 7 th edition, provides details on parenthetical citations. A parenthetical citation provides the authors’ names and publication date of the source within parentheses along with the cited text. If two authors are present in the source, both authors’ last names should be mentioned in the in-text citation. Their names should be separated by an ampersand (&). The publication date should follow the second surname, separated by a comma.
A parenthetical citation can appear either at the end of the sentence or within the sentence depending on how the sentence is framed. The period or end punctuation appears after the closing parenthesis.
Example parenthetical citation at the end of a sentence:
The reach of fake news is greatly underrated (Rameses & Hudgson, 2021).
If more text appears along with the parenthetical citation, include commas to separate the year and help the reader distinguish the citation from the surrounding text.
Example parenthetical citation with additional text:
The reach of fake news is greatly underrated (see Rameses & Hudgson, 2021, for more detail).
Section 8.11 of the APA Publication Manual , 7 th edition, provides details on narrative citations. A narrative citation provides the authors’ names in running text, and the publication date appears within parentheses immediately after the names. If two authors are present in the source, both authors’ last names should be mentioned in the in-text citation. In narrative citations, the word “and” should be spelled out between the two names.
Example narrative citation with two authors:
Crompton and Williams (2020) noted that gut health is of paramount importance in maintaining mental health.
In some circumstances, the year may also appear within the text along with the authors’ names. In such a scenario, the date should not appear within parentheses.
Example narrative citation with two authors and date:
In 2020, Crompton and Williams broke new ground with their hypothesis that mental health is strongly linked with gut health.
As per Section 2.4 of the APA Publication Manual , 7 th edition, the title of a research paper should summarize the main idea in a succinct manner. While there is no prescribed title length in APA style, authors are advised to keep their titles brief and focused. The manual also provides examples between effective and ineffective titles, including “fluff” words that can be cut from titles and substantive information that should be included in a title to make it relevant to the reader(s).
When the whole book or article is being referenced, there is no need to include a page number. However, when you are referring to a specific page or pages (either in a paraphrase or a direct quote), include the page number(s) in your in-text citation.
If you are referring to information or a quote contained on a single page, add the page number after the author and date, preceded by “p.” If you are citing multiple pages, the page numbers should be preceded by “pp.” and separated by an en-dash.
Example in-text citation with single page number:
(Rayden, 2014, p. 308)
Example in-text citation with page range:
(Rayden, 2014, pp. 308-311)
If there are no page numbers in a work, you can use some other type of locator in in-text citations to help your reader find the information you are citing, like chapter names, headings, or paragraph numbers.
As per Section 8.14 of the APA Publication Manual , 7 th edition, for sources with an unknown author, include the title of the source and year of publication in your in-text citations instead.
If the title of the source is italicized in your reference list, it should also be italicized in your in-text citation. If the title is not in italics in the reference list, it should be in quotation marks in your in-text citation. Titles should be listed in title case (with all important words capitalized) when included in in-text citations.
In-text citation templates:
( Full Name of the Source , year)
(“Full Name of the Source,” year)
In-text citation examples:
( How to Be Awesomely You , 2021)
(“Social Dynamics in US Colleges,” 2018)
If a work’s author is designated as “Anonymous,” use “Anonymous” as the author in in-text citations, as shown below.
(Anonymous, 2020)
As per Section 2.14 of the APA Publication Manual , 7 th edition, an appendix or appendices are included after the references, footnotes, tables, and figures of the paper. In other words, appendices are the last item in your paper. Each appendix should be separately mentioned within the main text (e.g., “see Appendix A”). Appendices are to be self-contained; they should describe the contents and clearly have a label and title.
For a parenthetical in-text citation in APA style, the basic elements needed are the author’s last name (or the group author’s name) and the publication year. For parenthetical citations, format this information by inputting it in parentheses.
For a narrative in-text citation, include the information in the running text. Usually, this means you include the author’s last name followed by the year in parentheses. However, if needed, you may include both the author’s last name and the year in the running text.
For audio, visual, or audiovisual works, replace the author’s last name with a director’s last name (for a film), an uploader’s last name (for YouTube), the artist’s name (for an artwork), and so on.
As per section 2 of the APA 7 manual, papers require the following elements presented in the order below. Since the required elements differ depending on whether your paper is a professional or student paper, there are two lists to distinguish the differences. Sections like Figures, Tables, and Appendices may not be relevant to your paper, so you may exclude those.
Professional Papers*
- Title Page (with title, author(s), affiliations, and an author note)
- Page Headers including a running head and page numbers
- Reference List
- Keywords (optional)
- Footnotes (optional)
- Tables (optional)
- Figures (optional)
- Appendices (optional)
- Supplemental Materials (optional)
*Always refer to the professional journal’s instructions or submission guidelines.
Student Papers
- Page Numbers
An APA reference list comprises the publication details of the studies that specifically quote or support the ideas and concepts presented in a paper. Cite sources in the text, with a narrative or parenthetical citation, and include corresponding reference entries in the reference list.
An APA bibliography is similar to a reference list because it also includes full reference entries for sources cited in the text. However, they also include other sources that support or give background for further research related to the listed source.
An APA annotated bibliography includes short annotations below the reference entry in a separate paragraph(s). Annotations summarize and/or describe a source in detail.
Both the 6 th and 7 th editions of APA style are available on the Cite This For Me citation generator .
For a webpage/website, journal article, or book, you’ll need 1-2 pieces of basic publication information. For example:
- Website : URL, page title, etc.
- Journal article : Article title, DOI number, author(s), etc.
- Book : Book title, author, date published, etc.
Using those pieces of information, you can search for the source in the Cite This For Me APA citation generator and it will help you to create a citation.
Other source types (newspaper article, video, government document, etc.) will provide a form on which you provide all source information. Using that information, the citation generator will create a properly formatted APA citation for you.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
- How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples
How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples
Published on March 5, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 17, 2024.
To cite a page from a website, you need a short in-text citation and a corresponding reference stating the author’s name, the date of publication, the title of the page, the website name, and the URL.
This information is presented differently in different citation styles. APA , MLA , and Chicago are the most commonly used styles.
Use the interactive example generator below to explore APA and MLA website citations.
Note that the format is slightly different for citing YouTube and other online video platforms, or for citing an image .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Citing a website in mla style, citing a website in apa style, citing a website in chicago style, frequently asked questions about citations.
An MLA Works Cited entry for a webpage lists the author’s name , the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the site (in italics), the date of publication, and the URL.
The in-text citation usually just lists the author’s name. For a long page, you may specify a (shortened) section heading to locate the specific passage. Don’t use paragraph numbers unless they’re specifically numbered on the page.
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. “Page Title.” , Day Month Year, URL. |
|---|---|
| Brice, Makini. “U.S. Senate Expected to Begin Debating Coronavirus Package on Thursday.” , 4 March 2021, www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-usa-congress/u-s-senate-expected-to-begin-debating-coronavirus-package-on-thursday-idUSKBN2AW18U. | |
| (Brice) |
The same format is used for blog posts and online articles from newspapers and magazines.
You can also use our free MLA Citation Generator to generate your website citations.
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Citing a whole website.
When you cite an entire website rather than a specific page, include the author if one can be identified for the whole site (e.g. for a single-authored blog). Otherwise, just start with the site name.
List the copyright date displayed on the site; if there isn’t one, provide an access date after the URL.
| MLA format | Author last name, First name. . Year or Year range, URL. Accessed Day Month Year. |
|---|---|
| . www.scribbr.com. Accessed 4 March 2021. | |
| ( ) |
Webpages with no author or date
When no author is listed, cite the organization as author only if it differs from the website name.
If the organization name is also the website name, start the Works Cited entry with the title instead, and use a shortened version of the title in the in-text citation.
When no publication date is listed, leave it out and include an access date at the end instead.
| MLA format | Organization Name. “Page Title.” , URL. Accessed Day Month Year. |
|---|---|
| “Citing Sources in Academic Writing.” . www.scribbr.com/category/citing-sources/. Accessed 4 March 2021. | |
| (“Citing Sources”) |
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
An APA reference for a webpage lists the author’s last name and initials, the full date of publication, the title of the page (in italics), the website name (in plain text), and the URL.
The in-text citation lists the author’s last name and the year. If it’s a long page, you may include a locator to identify the quote or paraphrase (e.g. a paragraph number and/or section title).
| APA format | Author last name, Initials. (Year, Month Day). . Website Name. URL |
|---|---|
| Brice, M. (2021, March 4). . Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-usa-congress/u-s-senate-expected-to-begin-debating-coronavirus-package-on-thursday-idUSKBN2AW18U | |
| (Brice, 2021, para. 6) |
Note that a general reference to an entire website doesn’t require a citation in APA Style; just include the URL in parentheses after you mention the site.
You can also use our free APA Citation Generator to create your webpage citations. Search for a URL to retrieve the details.
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
Blog posts and online articles.
Blog posts follow a slightly different format: the title of the post is not italicized, and the name of the blog is.
The same format is used for online newspaper and magazine articles—but not for articles from news sites like Reuters and BBC News (see the previous example).
| APA format | Author last name, Initials. (Year, Month Day). Article title. . URL |
|---|---|
| McKenna, J. (2021, March 3). Assisted reproduction science could be a lifeline for koalas. . https://jmckenna.scienceblog.com/2021/03/03/assisted-reproduction-science-could-be-a-lifeline-for-koalas/ | |
| (McKenna, 2021) |
When a page has no author specified, list the name of the organization that created it instead (and omit it later if it’s the same as the website name).
When it doesn’t list a date of publication, use “n.d.” in place of the date. You can also include an access date if the page seems likely to change over time.
| APA format | Organization Name. (n.d.). . Website Name. Retrieved Month Day, Year, from URL |
|---|---|
| Scribbr. (n.d.). . Retrieved March 4, 2021, from https://www.scribbr.com/category/citing-sources/ | |
| (Scribbr, n.d.) |
In Chicago notes and bibliography style, footnotes are used to cite sources. They refer to a bibliography at the end that lists all your sources in full.
A Chicago bibliography entry for a website lists the author’s name, the page title (in quotation marks), the website name, the publication date, and the URL.
| Chicago format | Author last name, First name. “Page Title.” Website Name. Month Day, Year. URL. |
|---|---|
| Brice, Makini. “U.S. Senate Expected to Begin Debating Coronavirus Package on Thursday.” Reuters. March 4, 2021. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-usa-congress/u-s-senate-expected-to-begin-debating-coronavirus-package-on-thursday-idUSKBN2AW18U. | |
| 1. Makini Brice, “U.S. Senate Expected to Begin Debating Coronavirus Package on Thursday,” Reuters, March 4, 2021, https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-usa-congress/u-s-senate-expected-to-begin-debating-coronavirus-package-on-thursday-idUSKBN2AW18U. 2. Brice, “Coronavirus Package.” |
Chicago also has an alternative author-date citation style . Examples of website citations in this style can be found here .
For blog posts and online articles from newspapers, the name of the publication is italicized. For a blog post, you should also add the word “blog” in parentheses, unless it’s already part of the blog’s name.
| Chicago format | Author last name, First name. “Page Title.” (blog). Month Day, Year. URL. |
|---|---|
| McKenna, Jarrod. “Assisted Reproduction Science Could Be a Lifeline for Koalas.” . March 3, 2021. https://jmckenna.scienceblog.com/2021/03/03/assisted-reproduction-science-could-be-a-lifeline-for-koalas/. | |
| 1. Jarrod McKenna, “Assisted Reproduction Science Could Be a Lifeline for Koalas,” , March 3, 2021, https://jmckenna.scienceblog.com/2021/03/03/assisted-reproduction-science-could-be-a-lifeline-for-koalas/. 2. McKenna, “Assisted Reproduction.” |
When a web source doesn’t list an author , you can usually begin your bibliography entry and short note with the name of the organization responsible. Don’t repeat it later if it’s also the name of the website. A full note should begin with the title instead.
When no publication or revision date is shown, include an access date instead in your bibliography entry.
| Chicago format | Organization Name. “Page Title.” Website Name. Accessed Month Day, Year. URL. |
|---|---|
| Scribbr. “Citing Sources in Academic Writing.” Accessed March 4, 2021. https://www.scribbr.com/category/citing-sources/. | |
| 1. “Citing Sources in Academic Writing,” Scribbr, accessed March 4, 2021, https://www.scribbr.com/category/citing-sources/. 2. Scribbr, “Citing Sources.” |
The main elements included in website citations across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the author, the date of publication, the page title, the website name, and the URL. The information is presented differently in each style.
In APA , MLA , and Chicago style citations for sources that don’t list a specific author (e.g. many websites ), you can usually list the organization responsible for the source as the author.
If the organization is the same as the website or publisher, you shouldn’t repeat it twice in your reference:
- In APA and Chicago, omit the website or publisher name later in the reference.
- In MLA, omit the author element at the start of the reference, and cite the source title instead.
If there’s no appropriate organization to list as author, you will usually have to begin the citation and reference entry with the title of the source instead.
When you want to cite a specific passage in a source without page numbers (e.g. an e-book or website ), all the main citation styles recommend using an alternate locator in your in-text citation . You might use a heading or chapter number, e.g. (Smith, 2016, ch. 1)
In APA Style , you can count the paragraph numbers in a text to identify a location by paragraph number. MLA and Chicago recommend that you only use paragraph numbers if they’re explicitly marked in the text.
For audiovisual sources (e.g. videos ), all styles recommend using a timestamp to show a specific point in the video when relevant.
Check if your university or course guidelines specify which citation style to use. If the choice is left up to you, consider which style is most commonly used in your field.
- APA Style is the most popular citation style, widely used in the social and behavioral sciences.
- MLA style is the second most popular, used mainly in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography style is also popular in the humanities, especially history.
- Chicago author-date style tends to be used in the sciences.
Other more specialized styles exist for certain fields, such as Bluebook and OSCOLA for law.
The most important thing is to choose one style and use it consistently throughout your text.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, January 17). How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/cite-a-website/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to cite an image | photographs, figures, diagrams, how to cite a lecture | apa, mla & chicago examples, how to cite a youtube video | mla, apa & chicago, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
What it means for the Supreme Court to throw out Chevron decision, undercutting federal regulators
FILE- Gulls follow a commercial fishing boat as crewmen haul in their catch in the Gulf of Maine, in this Jan. 17, 2012 file photo. TExecutive branch agencies will likely have more difficulty regulating the environment, public health, workplace safety and other issues under a far-reaching decision by the Supreme Court. The court’s 6-3 ruling on Friday overturned a 1984 decision colloquially known as Chevron that has instructed lower courts to defer to federal agencies when laws passed by Congress are not crystal clear. (AP Photo/Robert F. Bukaty, File)
The Supreme Court building is seen on Friday, June 28, 2024, in Washington. (AP Photo/Mark Schiefelbein)
- Copy Link copied

WASHINGTON (AP) — Executive branch agencies will likely have more difficulty regulating the environment, public health, workplace safety and other issues under a far-reaching decision by the Supreme Court .
The court’s 6-3 ruling on Friday overturned a 1984 decision colloquially known as Chevron that has instructed lower courts to defer to federal agencies when laws passed by Congress are not crystal clear.
The 40-year-old decision has been the basis for upholding thousands of regulations by dozens of federal agencies, but has long been a target of conservatives and business groups who argue that it grants too much power to the executive branch, or what some critics call the administrative state.
The Biden administration has defended the law, warning that overturning so-called Chevron deference would be destabilizing and could bring a “convulsive shock” to the nation’s legal system.
Chief Justice John Roberts, writing for the court, said federal judges “must exercise their independent judgment in deciding whether an agency has acted within its statutory authority.”
The ruling does not call into question prior cases that relied on the Chevron doctrine, Roberts wrote.
Here is a look at the court’s decision and the implications for government regulations going forward.
What is the Chevron decision?
Atlantic herring fishermen sued over federal rules requiring them to pay for independent observers to monitor their catch. The fishermen argued that the 1976 Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act did not authorize officials to create industry-funded monitoring requirements and that the National Marine Fisheries Service failed to follow proper rulemaking procedure.
In two related cases, the fishermen asked the court to overturn the 40-year-old Chevron doctrine, which stems from a unanimous Supreme Court case involving the energy giant in a dispute over the Clean Air Act. That ruling said judges should defer to the executive branch when laws passed by Congress are ambiguous.
In that case, the court upheld an action by the Environmental Protection Agency under then-President Ronald Reagan.
In the decades following the ruling, Chevron has been a bedrock of modern administrative law, requiring judges to defer to agencies’ reasonable interpretations of congressional statutes.
But the current high court, with a 6-3 conservative majority has been increasingly skeptical of the powers of federal agencies. Justices Brett Kavanaugh, Clarence Thomas, Samuel Alito and Neil Gorsuch have questioned the Chevron decision. Ironically, it was Gorsuch’s mother, former EPA Administrator Anne Gorsuch, who made the decision that the Supreme Court upheld in 1984.
What’s at stake?
With a closely divided Congress, presidential administrations have increasingly turned to federal regulation to implement policy changes. Federal rules impact virtually every aspect of everyday life, from the food we eat and the cars we drive to the air we breathe and homes we live in.
President Joe Biden’s administration, for example, has issued a host of new regulations on the environment and other priorities, including restrictions on emissions from power plants and vehicle tailpipes , and rules on student loan forgiveness , overtime pay and affordable housing.
Those actions and others could be opened up to legal challenges if judges are allowed to discount or disregard the expertise of the executive-branch agencies that put them into place.
With billions of dollars potentially at stake, groups representing the gun industry and other businesses such as tobacco, agriculture, timber and homebuilding, were among those pressing the justices to overturn the Chevron doctrine and weaken government regulation.
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce filed an amicus brief last year on behalf of business groups arguing that modern application of Chevron has “fostered aggrandizement’’ of the executive branch at the expense of Congress and the courts.
David Doniger, a lawyer and longtime Natural Resources Defense Council official who argued the original Chevron case in 1984, said he feared that a ruling to overturn the doctrine could “free judges to be radical activists” who could “effectively rewrite our laws and block the protections they are supposed to provide.”
“The net effect will be to weaken our government’s ability to meet the real problems the world is throwing at us — big things like COVID and climate change,″ Doniger said.
More than just fish
“This case was never just about fish,’' said Meredith Moore of the environmental group Ocean Conservancy. Instead, businesses and other interest groups used the herring fishery “to attack the foundations of the public agencies that serve the American public and conserve our natural resources,’' she said.
The court ruling will likely open the floodgates to litigation that could erode critical protections for people and the environment, Moore and other advocates said.
“For more than 30 years, fishery observers have successfully helped ensure that our oceans are responsibly managed so that fishing can continue in the future,’' said Dustin Cranor of Oceana, another conservation group.
He called the case “just the latest example of the far right trying to undermine the federal government’s ability to protect our oceans, waters, public lands, clean air and health.’'
West Virginia Attorney General Patrick Morrisey called the decision a fitting follow-up to a 2022 decision — in a case he brought — that limits the EPA’s ability to control greenhouse gas emissions from power plants. The court held that Congress must speak with specificity when it wants to give an agency authority to regulate on an issue of major national significance.
Morrisey, now the GOP nominee for governor, called Chevron “a misguided doctrine under which courts defer to legally dubious interpretations of statutes put out by federal administrative agencies.”
A shift toward judicial power
The Supreme Court ruling will almost certainly shift power away from the executive branch and Congress and toward courts, said Craig Green, a professor at Temple University’s Beasley School of Law.
“Federal judges will now have the first and final word about what statutes mean,″ he said. “That’s a big shift in power.″
In what some observers see as a historic irony, many conservatives who now attack Chevron once celebrated it. The late Supreme Court Justice Antonin Scalia was among those who hailed the original ruling as a way to rein in liberal laws.
“Conservatives believed in this rule until they didn’t,’' Green said in an interview.
In recent years, conservatives have focused on “deconstruction of the administrative state,’' even if the result lessens the ability of a conservative president to impose his beliefs on government agencies.
“If you weaken the federal government, you get less government,’' Green said — an outcome that many conservatives, including those who back former President Donald Trump, welcome.
The ruling will likely “gum up the works for federal agencies and make it even harder for them to address big problems. Which is precisely what the critics of Chevron want,” said Jody Freeman, director of the environmental and energy law program at Harvard Law School.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Citation Generator: Automatically generate accurate references and in-text citations using Scribbr's APA Citation Generator, MLA Citation Generator, Harvard Referencing Generator, and Chicago Citation Generator. Plagiarism Checker: Detect plagiarism in your paper using the most accurate Turnitin-powered plagiarism software available to students.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays, research papers, and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises). Add a citation whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays, research papers, and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises). Add a citation whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
Create manual citation. The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number (s).
Stay up to date! Get research tips and citation information or just enjoy some fun posts from our student blog. Citation Machine® helps students and professionals properly credit the information that they use. Cite sources in APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, and Harvard for free.
Know you're citing correctly. No matter what citation style you're using (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) we'll help you create the right bibliography. ... Avoid common grammar mistakes and unintentional plagiarism with our essay checker. Receive personalized feedback to help identify citations that may be missing, and help improve your sentence ...
The Chicago/Turabian style of citing sources is generally used when citing sources for humanities papers, and is best known for its requirement that writers place bibliographic citations at the bottom of a page (in Chicago-format footnotes) or at the end of a paper (endnotes). The Turabian and Chicago citation styles are almost identical, but ...
MyBib is a free bibliography and citation generator that makes accurate citations for you to copy straight into your academic assignments and papers. If you're a student, academic, or teacher, and you're tired of the other bibliography and citation tools out there, then you're going to love MyBib. MyBib creates accurate citations automatically ...
Referencing your sources is important because it: The most common citation styles in the UK are APA, MLA, Harvard, Vancouver, MHRA, and Oscola. Each citation style has specific rules for formatting citations. Scribbr's free Reference Generator can generate perfect references and in-text citations in both APA and MLA styles.
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write ...
APA Citation Basics. When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
Cite This For Me™ citation guides cover a lot of this additional information, so your paper is more properly prepped and less likely to get points taken off for these details. The guides cover several citation styles, but the most popular are Harvard referencing , APA format , MLA format , and Chicago style .
Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form. The generator will produce a formatted MLA ...
On the first line of the page, write the section label "References" (in bold and centered). On the second line, start listing your references in alphabetical order. Apply these formatting guidelines to the APA reference page: Double spacing (within and between references) Hanging indent of ½ inch.
2. List the title of the essay in quotation marks. After the author's name, type the title of the essay in title case, capitalizing the first word and all nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, and verbs in the title. Place a period at the end of the title, inside the closing quotation marks. [2] Example: Potter, Harry.
To use the works cited generator, simply: Select from APA, MLA, Chicago, ASA, IEEE and AMA * styles. Choose the type of source you would like to cite (e.g. website, book, journal, video). Enter the URL, DOI, ISBN, title, or other unique source information into the citation generator to find your source. Click the 'Cite' button on the ...
Get 100% accurate citations for free. QuillBot's Citation Generator can quickly and easily create references for books, articles, and web pages in APA, MLA, Chicago, and many more styles. Follow the simple steps below to create, edit, and export both in-text and full citations for your source material.
You must first cite each source in the body of your essay; these citations within the essay are called in-text citations. You MUST cite all quoted, paraphrased, or summarized words, ideas, and facts from sources. Without in-text citations, you are technically in danger of plagiarism, even if you have listed your sources at the end of the essay ...
To use the generator: Choose the type of source you would like to cite (e.g., website, book, journal & video) Enter the URL, DOI, ISBN, title, or other unique source information to locate your source. Click the 'Search' button to begin looking for your source. Look through the search results and click the 'Cite' button next to the ...
When citing sources in the text of your paper, you must list: The author's last name. The year the information was published. Types of In-Text Citations: Narrative vs Parenthetical. A narrative citation gives the author's name as part of the sentence. Example of a Narrative Citation: According to Edwards (2017), although Smith and Carlos's ...
Let the Cite This For Me APA format generator remove the stress caused by citations by helping to turn in any of your sources into a fully-formatted citation. The generator will create your reference in two parts; an in-text citation and a full reference that is ready to be copied straight into your work.
Citing a website in MLA Style. An MLA Works Cited entry for a webpage lists the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the site (in italics), the date of publication, and the URL. The in-text citation usually just lists the author's name. For a long page, you may specify a (shortened) section heading to ...
FILE- Gulls follow a commercial fishing boat as crewmen haul in their catch in the Gulf of Maine, in this Jan. 17, 2012 file photo. TExecutive branch agencies will likely have more difficulty regulating the environment, public health, workplace safety and other issues under a far-reaching decision by the Supreme Court.