

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
10 Everyday uses for Problem Solving Skills

- Problem Solving & Decision Making Real world training delivers real world results. Learn More
Many employers are recognizing the value and placing significant investments in developing the problem solving skills of their employees. While we often think about these skills in the work context, problem solving isn’t just helpful in the workplace. Here are 10 everyday uses for problem solving skills that can you may not have thought about
1. Stuck in traffic and late for work, again
With busy schedules and competing demands for your time, getting where you need to be on time can be a real challenge. When traffic backs up, problem solving skills can help you figure out alternatives to avoid congestion, resolve the immediate situation and develop a solution to avoid encountering the situation in the future.
2. What is that stain on the living room carpet?
Parents, pet owners and spouses face this situation all the time. The living room carpet was clean yesterday but somehow a mysterious stain has appeared and nobody is claiming it. In order to clean it effectively, first you need to figure out what it is. Problem solving can help you track down the culprit, diagnose the cause of the stain and develop an action plan to get your home clean and fresh again.
3. What is that smell coming from my garden shed?
Drawing from past experiences, the seasoned problem solver in you suspects that the source of the peculiar odor likely lurks somewhere within the depths of the shed. Your challenge now lies in uncovering the origin of this scent, managing its effects, and formulating a practical plan to prevent such occurrences in the future.
4. I don’t think the car is supposed to make that thumping noise
As with many problems in the workplace, this may be a situation to bring in problem solving experts in the form of your trusted mechanic. If that isn’t an option, problem solving skills can be helpful to diagnose and assess the impact of the situation to ensure you can get where you need to be.
5. Creating a budget
Tap into your problem-solving prowess as you embark on the journey of budgeting. Begin by determining what expenses to include in your budget, and strategize how to account for unexpected financial surprises. The challenge lies in crafting a comprehensive budget that not only covers your known expenses but also prepares you for the uncertainties that may arise.
6. My daughter has a science project – due tomorrow
Sometimes the challenge isn’t impact, its urgency. Problem solving skills can help you quickly assess the situation and develop an action plan to get that science project done and turned in on time.
7. What should I get my spouse for his/her birthday?
As with many problems, this one may not have a “right answer” or apparent solution. Its time to apply those problem solving skills to evaluate the effects of past decisions combined with current environmental signals and available resources to select the perfect gift to put a smile on your significant other’s face.
8. The office printer suddenly stopped working, and there are important documents that need to be printed urgently.
Uh oh, time to think quickly. There is an urgent situation that must be addressed to get things back to normal, a cause to be identified (what’s causing the printer issue), and an action plan to resolve it. Problem solving skills can help you avoid stress and ensure that your documents are printed on time.
9. I’m torn between two cars! Which one should I choose?
In a world brimming with countless choices, employ decision analysis as your trusty tool to navigate the sea of options. Whether you’re selecting a car (or any other product), the challenge is to methodically identify and evaluate the best choices that align with your unique needs and preferences.
10. What’s for dinner?
Whether you are planning to eat alone, with family or entertaining friends and colleagues, meal planning can be a cause of daily stress. Applying problem solving skills can put the dinner dilemma into perspective and help get the food on the table and keep everyone happy.
Problem Solving skills aren’t just for the workplace – they can be applied in your everyday life. Kepner-Tregoe can help you and your team develop your problem solving skills through a combination of training and consulting with our problem solving experts.

We are experts in:
For inquiries, details, or a proposal!
Subscribe to the KT Newsletter
5 Examples of Problem Solving Scenarios + ROLE PLAY SCRIPTS
Problem-solving is an essential skill in our daily lives. It enables us to analyze situations, identify challenges, and find suitable solutions. In this article, we’ll explore five real-life problem-solving scenarios from various areas, including business, education, and personal growth. By understanding these examples, you can develop your problem-solving abilities and effectively tackle challenges in your life.
Examples of Problem Solving Scenarios
Improving customer service scenario:.
A retail store is experiencing a decline in customer satisfaction, with clients complaining about slow service and unhelpful staff.
Solution : The store manager assembles a team to analyze customer feedback, identify key issues, and propose solutions. They implement a new training program focused on customer service skills, streamline the checkout process, and introduce an incentive system to motivate employees. As a result, customer satisfaction improves, and the store’s reputation is restored.
Enhancing Learning Outcomes Scenario:
A high school teacher notices that her students struggle with understanding complex concepts in her science class, leading to poor performance on tests.
Overcoming Procrastination Scenario:
An individual consistently procrastinates, leading to increased stress and reduced productivity.
Solution : The person identifies the root cause of their procrastination, such as fear of failure or lack of motivation. They establish clear goals and deadlines, break tasks into manageable steps, and use time management tools, like the Pomodoro Technique , to stay focused. By consistently applying these strategies, they successfully overcome procrastination and enhance their productivity.
Reducing Patient Wait Times Scenario:
Solution : The clinic’s management team conducts a thorough analysis of the appointment scheduling process and identifies bottlenecks. They implement a new appointment system, hire additional staff, and optimize the workflow to reduce wait times. As a result, patient satisfaction increases, and staff stress levels decrease.
Reducing Plastic Waste Scenario:
A local community is struggling with an excessive amount of plastic waste, causing environmental pollution and health concerns.
Solution : Community leaders organize a task force to address the issue. They implement a recycling program, educate residents about the environmental impact of plastic waste, and collaborate with local businesses to promote the use of eco-friendly packaging alternatives. These actions lead to a significant reduction in plastic waste and a cleaner, healthier community.
Conclusion : These five examples of problem-solving scenarios demonstrate how effective problem-solving strategies can lead to successful outcomes in various aspects of life. By learning from these scenarios, you can develop your problem-solving skills and become better equipped to face challenges in your personal and professional life. Remember to analyze situations carefully, identify the root causes, and implement solutions that address these issues for optimal results.
Role Play: Improving Customer Service in a Retail Store
Scenario : A retail store is experiencing a decline in customer satisfaction, with clients complaining about slow service and unhelpful staff.
Role Play Script:
Assistant Manager : I agree. We could also implement a new training program for our staff, focusing on customer service skills and techniques.
Sales Associate : (Smiling) Of course! I’d be happy to help. What product are you looking for?
Customer : That would be great! Thank you for your help.
More Examples of Problem Solving Scenarios on the next page…
Problem solving skills and how to improve them (with examples)
What’s life without its challenges? All of us will at some point encounter professional and personal hurdles. That might mean resolving a conflict with coworkers or making a big life decision. With effective problem solving skills, you’ll find tricky situations easier to navigate, and welcome challenges as opportunities to learn, grow and thrive.
In this guide, we dive into the importance of problem solving skills and look at examples that show how relevant they are to different areas of your life. We cover how to find creative solutions and implement them, as well as ways to refine your skills in communication and critical thinking. Ready to start solving problems? Read on.
What is problem solving?
Before we cover strategies for improving problem solving skills, it's important to first have a clear understanding of the problem solving process. Here are the steps in solving a problem:
- Recognise the issue you are facing
- Take a look at all the information to gain insights
- Come up with solutions
- Look at the pros and cons of each solution and how it might play out
- Plan, organise and implement your solution
- Continuously assess the effectiveness of the solution and make adjustments as needed
Problem solving skills
There’s more to problem solving than coming up with a quick fix. Effective problem solving requires wide range of skills and abilities, such as:
- Critical thinking: the ability to think logically, analyse information and look at situations from different perspectives.
- Creativity: being able to come up with innovative, out-of-the-box solutions.
- Decision-making: making informed choices by considering all the available information.
- Communication: being able to express ideas clearly and effectively.
- Analytical skills: breaking down complex problems into smaller parts and examining each one.
- Time management: allocating time and resources effectively to address problems.
- Adaptability: being open to change and willing to adjust strategies.
- Conflict resolution: skillfully managing conflicts and finding solutions that work for all.
Examples of problem solving skills
Problem solving skills in the workplace are invaluable, whether you need them for managing a team, dealing with clients or juggling deadlines. To get a better understanding of how you might use these skills in real-life scenarios, here are some problem solving examples that are common in the workplace.
- Analytical thinking
Analytical thinking is something that comes naturally to some, while others have to work a little harder. It involves being able to look at problem solving from a logical perspective, breaking down the issues into manageable parts.
Example scenarios of analytical thinking
Quality control: in a manufacturing facility, analytical thinking helps identify the causes of product defects in order to pinpoint solutions.
Market research: marketing teams rely on analytical thinking to examine consumer data, identify market trends and make informed decisions on ad campaigns.
- Critical thinking
Critical thinkers are able to approach problems objectively, looking at different viewpoints without rushing to a decision. Critical thinking is an important aspect of problem solving, helping to uncover biases and assumptions and weigh up the quality of the information before making any decisions.
Example scenarios of critical thinking
- Strategic planning: in the boardroom, critical thinking is important for assessing economic trends, competitor threats and more. It guides leaders in making informed decisions about long-term company goals and growth strategies.
- Conflict resolution: HR professionals often use critical thinking when dealing with workplace conflicts. They objectively analyse the issues at hand and find an appropriate solution.
Decision-making
Making decisions is often the hardest part of problem solving. How do you know which solution is the right one? It involves evaluating information, considering potential outcomes and choosing the most suitable option. Effective problem solving relies on making well-informed decisions.
Example scenarios of decision-making
- Budget allocation: financial managers must decide how to allocate resources to various projects or departments.
- Negotiation: salespeople and procurement professionals negotiate terms, pricing and agreements with clients, suppliers and partners.
Research skills
Research skills are pivotal when it comes to problem solving, to ensure you have all the information you need to make an informed decision. These skills involve searching for relevant data, critically evaluating information sources, and drawing meaningful conclusions.
Example scenarios of research skills
- Product development: a tech startup uses research skills to conduct market research to identify gaps and opportunities in the market.
- Employee engagement: an HR manager uses research skills to conduct employee surveys and focus groups.
A little creative flair goes a long way. By thinking outside the box, you can approach problems from different angles. Creative thinking involves combining existing knowledge, experiences and perspectives in new and innovative ways to come up with inventive solutions.
Example scenarios of creativity
- Cost reduction: creative problem solvers within a manufacturing company might look at new ways to reduce production costs by using waste materials.
- Customer experience: a retail chain might look at implementing interactive displays and engaging store layouts to increase customer satisfaction and sales.
Collaboration
It’s not always easy to work with other people, but collaboration is a key element in problem solving, allowing you to make use of different perspectives and areas of expertise to find solutions.
Example scenarios
- Healthcare diagnosis: in a hospital setting, medical professionals collaborate to diagnose complex medical cases.
- Project management: project managers coordinate efforts, allocate resources and address issues that may arise during a project's lifecycle.
Conflict Resolution
Being able to mediate conflicts is a great skill to have. It involves facilitating open communication, understanding different perspectives and finding solutions that work for everyone. Conflict resolution is essential for managing any differences in opinion that arise.
Example scenarios of conflict resolution
- Client dispute: a customer might be dissatisfied with a product or service and demand a refund. The customer service representative addresses the issue through active listening and negotiation to reach a solution.
- Project delay: a project manager might face resistance from team members about a change in project scope and will need to find a middle ground before the project can continue.
Risk management
Risk management is essential across many workplaces. It involves analysing potential threats and opportunities, evaluating their impact and implementing strategies to minimise negative consequences. Risk management is closely tied to problem solving, as it addresses potential obstacles and challenges that may arise during the problem solving process.
Example scenarios of risk management
- Project risk management: in a construction project, risk management involves identifying potential delays, cost overruns and safety hazards. Risk mitigation strategies are developed, such as scheduling buffers and establishing safety protocols.
- Financial risk management: in financial institutions, risk management assesses and manages risks associated with investments and lending.
Communication
Effective communication is a skill that will get you far in all areas of life. When it comes to problem solving, communication plays an important role in facilitating collaboration, sharing insights and ensuring that all stakeholders have the same expectations.
Example scenarios of communication
- Customer service improvement: in a retail environment, open communication channels result in higher customer satisfaction scores.
- Safety enhancement: in a manufacturing facility, a robust communication strategy that includes safety briefings, incident reporting and employee training helps minimise accidents and injuries.
How to improve problem solving skills
Ready to improve your problem solving skills? In this section we explore strategies and techniques that will give you a head start in developing better problem solving skills.
Adopt the problem solving mindset
Developing a problem solving mindset will help you tackle challenges effectively . Start by accepting problems as opportunities for growth and learning, rather than as obstacles or setbacks. This will allow you to approach every challenge with a can-do attitude.
Patience is also essential, because it will allow you to work through the problem and its various solutions mindfully. Persistence is also important, so you can keep adapting your approach until you find the right solution.
Finally, don’t forget to ask questions. What do you need to know? What assumptions are you making? What can you learn from previous attempts? Approach problem solving as an opportunity to acquire new skills . Stay curious, seek out solutions, explore new possibilities and remain open to different problem solving approaches.
Understand the problem
There’s no point trying to solve a problem you don’t understand. To analyse a problem effectively, you need to be able to define it. This allows you to break it down into smaller parts, making it easier to find causes and potential solutions. Start with a well-defined problem statement that is precise and specific. This will help you focus your efforts on the core issue, so you don’t waste time and resources on the wrong concerns.
Strategies for problem analysis
- Start with the problem statement and ask ‘Why?’ multiple times to dig deeper.
- Gather relevant data and information related to the problem.
- Include those affected by the problem in the analysis process.
- Compare the current problem with similar situations or cases to gain valuable insights.
- Use simulations to explore potential outcomes of different solutions.
- Continuously gather feedback during the problem solving process.
Develop critical thinking and creativity skills
Critical thinking and creativity are both important when it comes to looking at the problem objectively and thinking outside the box. Critical thinking encourages you to question assumptions, recognise biases and seek evidence to support your conclusions. Creative thinking allows you to look at the problem from different angles to reveal new insights and opportunities.
Enhance research and decision-making skills
Research and decision-making skills are pivotal in problem solving as they enable you to gather relevant information, analyse options and choose the best course of action. Research provides the information and data needed, and ensures that you have a comprehensive understanding of the problem and its context. Effective decision-making is about selecting the solution that best addresses the problem.
Strategies to improve research and decision-making skills
- Clearly define what you want to achieve through research.
- Use a variety of sources, including books, articles, research papers, interviews, surveys and online databases.
- Evaluate the credibility and reliability of your information sources.
- Incorporate risk assessment into your decision-making process.
- Seek input from experts, colleagues and mentors when making important decisions.
- After making decisions, reflect on the outcomes and lessons learned. Use this to improve your decision-making skills over time.
Strengthen collaboration skills
Being able to work with others is one of the most important skills to have at work. Collaboration skills enable everyone to work effectively as a team, share their perspectives and collectively find solutions.
Tips for improving teamwork and collaboration
- Define people’s roles and responsibilities within the team.
- Encourage an environment of open communication where team members feel comfortable sharing ideas.
- Practise active listening by giving full attention to others when they speak.
- Hold regular check-in sessions to monitor progress, discuss challenges and make adjustments as needed.
- Use collaboration tools and platforms to facilitate communication and document progress.
- Acknowledge and celebrate team achievements and milestones.
Learn from past experiences
Once you’ve overcome a challenge, take the time to look back with a critical eye. How effective was the outcome? Could you have tweaked anything in your process? Learning from past experiences is important when it comes to problem solving. It involves reflecting on both successes and failures to gain insights, refine strategies and make more informed decisions in the future.
Strategies for learning from past mistakes
- After completing a problem solving effort, gather your team for a debriefing session. Discuss what went well and what could have been better.
- Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) of resolved problems.
- Evaluate the outcomes of past solutions. Did they achieve the desired results?
- Commit to continuous learning and improvement.
Leverage problem solving tools and resources
Problem-solving tools and resources are a great help when it comes to navigating complex challenges. These tools offer structured approaches, methodologies and resources that can streamline the process.
Tools and resources for problem solving
- Mind mapping: mind maps visually organise ideas, concepts and their relationships.
- SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) Analysis: helps in strategic planning and decision-making.
- Fishbone diagram (Ishikawa Diagram): this tool visually represents the potential root causes of a problem, helping you identify underlying factors contributing to an issue.
- Decision matrices: these assist in evaluating options by assigning weights and scores to criteria and alternatives.
- Process flowcharts: these allow you to see the steps of a process in sequence, helping identify where the problem is occuring.
- Decision support software: software applications and tools, such as data analytics platforms, can help in data-driven decision-making and problem solving.
- Online courses and training: allow you to acquire new skills and knowledge.
Regular practice
Practice makes perfect! Using your skills in real life allows you to refine them, adapt to new challenges and build confidence in your problem solving capabilities. Make sure to try out these skills whenever you can.
Practical problem solving exercises
- Do puzzles, riddles and brainteasers regularly.
- Identify real-life challenges or dilemmas you encounter and practice applying problem solving techniques to these situations.
- Analyse case studies or scenarios relevant to your field or industry.
- Regularly review past problem solving experiences and consider what you learned from them.
- Attend workshops, webinars or training sessions focused on problem solving.
How to highlight problem solving skills on a resumé
Effectively showcasing your problem solving skills on your resumé is a great way to demonstrate your ability to address challenges and add value to a workplace. We'll explore how to demonstrate problem solving skills on your resumé, so you stand out from the crowd.
Incorporating problem solving skills in the resumé summary
A resumé summary is your introduction to potential employers and provides an opportunity to succinctly showcase your skills. The resumé summary is often the first section employers read. It offers a snapshot of your qualifications and sets the tone for the rest of your resumé.
Your resumé summary should be customised for different job applications, ensuring that you highlight the specific problem solving skills relevant to the position you’re applying for.
Example 1: Project manager with a proven track record of solving complex operational challenges. Skilled in identifying root causes, developing innovative solutions and leading teams to successful project completion.
Example 2: Detail-oriented data analyst with strong problem solving skills. Proficient in data-driven decision-making, quantitative analysis and using statistical tools to solve business problems.
Highlighting problem solving skills in the experience section
The experience section of your resumé presents the perfect opportunity to demonstrate your problem solving skills in action.
- Start with action verbs: begin each bullet point in your job descriptions with strong action verbs such as, analysed, implemented, resolved and optimised.
- Quantify achievements: use numbers and percentages to illustrate the impact of your solutions. For example: Increased efficiency by 25% by implementing a new workflow process.
- Emphasise challenges: describe the specific challenges or problems you faced in your roles.
- Solution-oriented language: mention the steps you took to find solutions and the outcomes achieved.
Including problem solving skills in the skills section
The skills section of your resumé should showcase your top abilities, including problem solving skills. Here are some tips for including these skills.
- Use a subsection: within your skills section, you could create a subsection specifically dedicated to problem solving skills – especially if the role calls for these skills.
- Be specific: when listing problem solving skills, be specific about the types of role-related problems you can address.
- Prioritise relevant skills: tailor the list of problem solving skills to match the requirements of the job you're applying for.
Examples of problem solving skills to include:
- Creative problem solving
- Decision making
- Root cause analysis
- Strategic problem solving
- Data-driven problem solving
- Interpersonal conflict resolution
- Adaptability
- Communication skills
- Problem solving tools
- Negotiation skills
Demonstrating problem solving skills in project sections or case studies
Including a dedicated section for projects or case studies in your resumé allows you to provide specific examples of your problem solving skills in action. It goes beyond simply listing skills, to demonstrate how you are able to apply those skills to real-world challenges.
Example – Data Analysis
Case Study: Market Expansion Strategy
- Challenge: the company was looking to expand into new markets but lacked data on consumer preferences and market dynamics.
- Solution: conducted comprehensive market research, including surveys and competitor analysis. Applied this research to identify target customer segments and developed a data-driven market-entry strategy.
- Result: successfully launched in two new markets, reaching our target of 30% market share within the first year.
Using problem solving skills in cover letters
A well-crafted cover letter is your first impression on any potential employer. Integrating problem solving skills can support your job application by showcasing your ability to address challenges and contribute effectively to their team. Here’s a quick run-down on what to include:
- Begin your cover letter by briefly mentioning the position you're applying for and your enthusiasm for it.
- Identify a specific challenge or issue that the company may be facing, to demonstrate your research and understanding of their needs.
- Include a brief story or scenario from your past experiences where you successfully applied problem solving skills to address a similar challenge.
- Highlight the positive outcomes or results achieved through your problem solving efforts.
- Explain how your skills make you the ideal person to address their specific challenges.
Problem solving skills are essential in all areas of life, enabling you to overcome challenges, make informed decisions, settle conflicts and drive innovation. We've explored the significance of problem solving skills and how to improve, demonstrate and leverage them effectively. It’s an ever-evolving skill set that can be refined over time.
By actively incorporating problem solving skills into your day-to-day, you can become a more effective problem solver at work and in your personal life as well.
What are some common problem solving techniques?
Common problem solving techniques include brainstorming, root cause analysis, SWOT analysis, decision matrices, the scientific method and the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle. These techniques offer structured approaches to identify, analyse and address problems effectively.
How can I improve my critical thinking skills?
Improving critical thinking involves practising skills such as analysis, evaluation and problem solving. It helps to engage in activities like reading, solving puzzles, debating and self-reflection.
What are some common obstacles to problem solving?
Common obstacles to problem solving include biases, lack of information or resources, and resistance to change. Recognising and addressing these obstacles is essential for effective problem solving.
How can I overcome resistance to change when implementing a solution?
To overcome resistance to change, it's essential to communicate the benefits of the proposed solution clearly, involve stakeholders in the decision-making process, address concerns and monitor the implementation's progress to demonstrate its effectiveness.
How can problem solving skills benefit my career?
Problem solving skills are highly valuable in a career as they enable you to navigate challenges, make informed decisions, adapt to change and contribute to innovation and efficiency. These skills enhance your professional effectiveness and can lead to career advancement and increased job satisfaction.
Top search terms
Popular on seek, explore related topics, subscribe to career advice.
39 Best Problem-Solving Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Problem-solving is a process where you’re tasked with identifying an issue and coming up with the most practical and effective solution.
This indispensable skill is necessary in several aspects of life, from personal relationships to education to business decisions.
Problem-solving aptitude boosts rational thinking, creativity, and the ability to cooperate with others. It’s also considered essential in 21st Century workplaces.
If explaining your problem-solving skills in an interview, remember that the employer is trying to determine your ability to handle difficulties. Focus on explaining exactly how you solve problems, including by introducing your thoughts on some of the following frameworks and how you’ve applied them in the past.
Problem-Solving Examples
1. divergent thinking.
Divergent thinking refers to the process of coming up with multiple different answers to a single problem. It’s the opposite of convergent thinking, which would involve coming up with a singular answer .
The benefit of a divergent thinking approach is that it can help us achieve blue skies thinking – it lets us generate several possible solutions that we can then critique and analyze .
In the realm of problem-solving, divergent thinking acts as the initial spark. You’re working to create an array of potential solutions, even those that seem outwardly unrelated or unconventional, to get your brain turning and unlock out-of-the-box ideas.
This process paves the way for the decision-making stage, where the most promising ideas are selected and refined.
Go Deeper: Divervent Thinking Examples
2. Convergent Thinking
Next comes convergent thinking, the process of narrowing down multiple possibilities to arrive at a single solution.
This involves using your analytical skills to identify the best, most practical, or most economical solution from the pool of ideas that you generated in the divergent thinking stage.
In a way, convergent thinking shapes the “roadmap” to solve a problem after divergent thinking has supplied the “destinations.”
Have a think about which of these problem-solving skills you’re more adept at: divergent or convergent thinking?
Go Deeper: Convergent Thinking Examples
3. Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a group activity designed to generate a multitude of ideas regarding a specific problem. It’s divergent thinking as a group , which helps unlock even more possibilities.
A typical brainstorming session involves uninhibited and spontaneous ideation, encouraging participants to voice any possible solutions, no matter how unconventional they might appear.
It’s important in a brainstorming session to suspend judgment and be as inclusive as possible, allowing all participants to get involved.
By widening the scope of potential solutions, brainstorming allows better problem definition, more creative solutions, and helps to avoid thinking “traps” that might limit your perspective.
Go Deeper: Brainstorming Examples
4. Thinking Outside the Box
The concept of “thinking outside the box” encourages a shift in perspective, urging you to approach problems from an entirely new angle.
Rather than sticking to traditional methods and processes, it involves breaking away from conventional norms to cultivate unique solutions.
In problem-solving, this mindset can bypass established hurdles and bring you to fresh ideas that might otherwise remain undiscovered.
Think of it as going off the beaten track when regular routes present roadblocks to effective resolution.
5. Case Study Analysis
Analyzing case studies involves a detailed examination of real-life situations that bear relevance to the current problem at hand.
For example, if you’re facing a problem, you could go to another environment that has faced a similar problem and examine how they solved it. You’d then bring the insights from that case study back to your own problem.
This approach provides a practical backdrop against which theories and assumptions can be tested, offering valuable insights into how similar problems have been approached and resolved in the past.
See a Broader Range of Analysis Examples Here
6. Action Research
Action research involves a repetitive process of identifying a problem, formulating a plan to address it, implementing the plan, and then analyzing the results. It’s common in educational research contexts.
The objective is to promote continuous learning and improvement through reflection and action. You conduct research into your problem, attempt to apply a solution, then assess how well the solution worked. This becomes an iterative process of continual improvement over time.
For problem-solving, this method offers a way to test solutions in real-time and allows for changes and refinements along the way, based on feedback or observed outcomes. It’s a form of active problem-solving that integrates lessons learned into the next cycle of action.
Go Deeper: Action Research Examples
7. Information Gathering
Fundamental to solving any problem is the process of information gathering.
This involves collecting relevant data , facts, and details about the issue at hand, significantly aiding in the understanding and conceptualization of the problem.
In problem-solving, information gathering underpins every decision you make.
This process ensures your actions are based on concrete information and evidence, allowing for an informed approach to tackle the problem effectively.
8. Seeking Advice
Seeking advice implies turning to knowledgeable and experienced individuals or entities to gain insights on problem-solving.
It could include mentors, industry experts, peers, or even specialized literature.
The value in this process lies in leveraging different perspectives and proven strategies when dealing with a problem. Moreover, it aids you in avoiding pitfalls, saving time, and learning from others’ experiences.
9. Creative Thinking
Creative thinking refers to the ability to perceive a problem in a new way, identify unconventional patterns, or produce original solutions.
It encourages innovation and uniqueness, often leading to the most effective results.
When applied to problem-solving, creative thinking can help you break free from traditional constraints, ideal for potentially complex or unusual problems.
Go Deeper: Creative Thinking Examples
10. Conflict Resolution
Conflict resolution is a strategy developed to resolve disagreements and arguments, often involving communication, negotiation, and compromise.
When employed as a problem-solving technique, it can diffuse tension, clear bottlenecks, and create a collaborative environment.
Effective conflict resolution ensures that differing views or disagreements do not become roadblocks in the process of problem-solving.
Go Deeper: Conflict Resolution Examples
11. Addressing Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks refer to obstacles or hindrances that slow down or even halt a process.
In problem-solving, addressing bottlenecks involves identifying these impediments and finding ways to eliminate them.
This effort not only smooths the path to resolution but also enhances the overall efficiency of the problem-solving process.
For example, if your workflow is not working well, you’d go to the bottleneck – that one point that is most time consuming – and focus on that. Once you ‘break’ this bottleneck, the entire process will run more smoothly.
12. Market Research
Market research involves gathering and analyzing information about target markets, consumers, and competitors.
In sales and marketing, this is one of the most effective problem-solving methods. The research collected from your market (e.g. from consumer surveys) generates data that can help identify market trends, customer preferences, and competitor strategies.
In this sense, it allows a company to make informed decisions, solve existing problems, and even predict and prevent future ones.
13. Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is a method used to identify the origin or the fundamental reason for a problem.
Once the root cause is determined, you can implement corrective actions to prevent the problem from recurring.
As a problem-solving procedure, root cause analysis helps you to tackle the problem at its source, rather than dealing with its surface symptoms.
Go Deeper: Root Cause Analysis Examples
14. Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a visual tool used to structure information, helping you better analyze, comprehend and generate new ideas.
By laying out your thoughts visually, it can lead you to solutions that might not have been apparent with linear thinking.
In problem-solving, mind mapping helps in organizing ideas and identifying connections between them, providing a holistic view of the situation and potential solutions.
15. Trial and Error
The trial and error method involves attempting various solutions until you find one that resolves the problem.
It’s an empirical technique that relies on practical actions instead of theories or rules.
In the context of problem-solving, trial and error allows you the flexibility to test different strategies in real situations, gaining insights about what works and what doesn’t.
16. SWOT Analysis
SWOT is an acronym standing for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
It’s an analytic framework used to evaluate these aspects in relation to a particular objective or problem.
In problem-solving, SWOT Analysis helps you to identify favorable and unfavorable internal and external factors. It helps to craft strategies that make best use of your strengths and opportunities, whilst addressing weaknesses and threats.
Go Deeper: SWOT Analysis Examples
17. Scenario Planning
Scenario planning is a strategic planning method used to make flexible long-term plans.
It involves imagining, and then planning for, multiple likely future scenarios.
By forecasting various directions a problem could take, scenario planning helps manage uncertainty and is an effective tool for problem-solving in volatile conditions.
18. Six Thinking Hats
The Six Thinking Hats is a concept devised by Edward de Bono that proposes six different directions or modes of thinking, symbolized by six different hat colors.
Each hat signifies a different perspective, encouraging you to switch ‘thinking modes’ as you switch hats. This method can help remove bias and broaden perspectives when dealing with a problem.
19. Decision Matrix Analysis
Decision Matrix Analysis is a technique that allows you to weigh different factors when faced with several possible solutions.
After listing down the options and determining the factors of importance, each option is scored based on each factor.
Revealing a clear winner that both serves your objectives and reflects your values, Decision Matrix Analysis grounds your problem-solving process in objectivity and comprehensiveness.
20. Pareto Analysis
Also known as the 80/20 rule, Pareto Analysis is a decision-making technique.
It’s based on the principle that 80% of problems are typically caused by 20% of the causes, making it a handy tool for identifying the most significant issues in a situation.
Using this analysis, you’re likely to direct your problem-solving efforts more effectively, tackling the root causes producing most of the problem’s impact.
21. Critical Thinking
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze facts to form a judgment objectively.
It involves logical, disciplined thinking that is clear, rational, open-minded, and informed by evidence.
For problem-solving, critical thinking helps evaluate options and decide the most effective solution. It ensures your decisions are grounded in reason and facts, and not biased or irrational assumptions.
Go Deeper: Critical Thinking Examples
22. Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing usually involves formulating a claim, testing it against actual data, and deciding whether to accept or reject the claim based on the results.
In problem-solving, hypotheses often represent potential solutions. Hypothesis testing provides verification, giving a statistical basis for decision-making and problem resolution.
Usually, this will require research methods and a scientific approach to see whether the hypothesis stands up or not.
Go Deeper: Types of Hypothesis Testing
23. Cost-Benefit Analysis
A cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is a systematic process of weighing the pros and cons of different solutions in terms of their potential costs and benefits.
It allows you to measure the positive effects against the negatives and informs your problem-solving strategy.
By using CBA, you can identify which solution offers the greatest benefit for the least cost, significantly improving efficacy and efficiency in your problem-solving process.
Go Deeper: Cost-Benefit Analysis Examples
24. Simulation and Modeling
Simulations and models allow you to create a simplified replica of real-world systems to test outcomes under controlled conditions.
In problem-solving, you can broadly understand potential repercussions of different solutions before implementation.
It offers a cost-effective way to predict the impacts of your decisions, minimizing potential risks associated with various solutions.
25. Delphi Method
The Delphi Method is a structured communication technique used to gather expert opinions.
The method involves a group of experts who respond to questionnaires about a problem. The responses are aggregated and shared with the group, and the process repeats until a consensus is reached.
This method of problem solving can provide a diverse range of insights and solutions, shaped by the wisdom of a collective expert group.
26. Cross-functional Team Collaboration
Cross-functional team collaboration involves individuals from different departments or areas of expertise coming together to solve a common problem or achieve a shared goal.
When you bring diverse skills, knowledge, and perspectives to a problem, it can lead to a more comprehensive and innovative solution.
In problem-solving, this promotes communal thinking and ensures that solutions are inclusive and holistic, with various aspects of the problem being addressed.
27. Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves comparing one’s business processes and performance metrics to the best practices from other companies or industries.
In problem-solving, it allows you to identify gaps in your own processes, determine how others have solved similar problems, and apply those solutions that have proven to be successful.
It also allows you to compare yourself to the best (the benchmark) and assess where you’re not as good.
28. Pros-Cons Lists
A pro-con analysis aids in problem-solving by weighing the advantages (pros) and disadvantages (cons) of various possible solutions.
This simple but powerful tool helps in making a balanced, informed decision.
When confronted with a problem, a pro-con analysis can guide you through the decision-making process, ensuring all possible outcomes and implications are scrutinized before arriving at the optimal solution. Thus, it helps to make the problem-solving process both methodical and comprehensive.
29. 5 Whys Analysis
The 5 Whys Analysis involves repeatedly asking the question ‘why’ (around five times) to peel away the layers of an issue and discover the root cause of a problem.
As a problem-solving technique, it enables you to delve into details that you might otherwise overlook and offers a simple, yet powerful, approach to uncover the origin of a problem.
For example, if your task is to find out why a product isn’t selling your first answer might be: “because customers don’t want it”, then you ask why again – “they don’t want it because it doesn’t solve their problem”, then why again – “because the product is missing a certain feature” … and so on, until you get to the root “why”.
30. Gap Analysis
Gap analysis entails comparing current performance with potential or desired performance.
You’re identifying the ‘gaps’, or the differences, between where you are and where you want to be.
In terms of problem-solving, a Gap Analysis can help identify key areas for improvement and design a roadmap of how to get from the current state to the desired one.
31. Design Thinking
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that involves empathy, experimentation, and iteration.
The process focuses on understanding user needs, challenging assumptions , and redefining problems from a user-centric perspective.
In problem-solving, design thinking uncovers innovative solutions that may not have been initially apparent and ensures the solution is tailored to the needs of those affected by the issue.
32. Analogical Thinking
Analogical thinking involves the transfer of information from a particular subject (the analogue or source) to another particular subject (the target).
In problem-solving, you’re drawing parallels between similar situations and applying the problem-solving techniques used in one situation to the other.
Thus, it allows you to apply proven strategies to new, but related problems.

33. Lateral Thinking
Lateral thinking requires looking at a situation or problem from a unique, sometimes abstract, often non-sequential viewpoint.
Unlike traditional logical thinking methods, lateral thinking encourages you to employ creative and out-of-the-box techniques.
In solving problems, this type of thinking boosts ingenuity and drives innovation, often leading to novel and effective solutions.
Go Deeper: Lateral Thinking Examples
34. Flowcharting
Flowcharting is the process of visually mapping a process or procedure.
This form of diagram can show every step of a system, process, or workflow, enabling an easy tracking of the progress.
As a problem-solving tool, flowcharts help identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies in a process, guiding improved strategies and providing clarity on task ownership and process outcomes.
35. Multivoting
Multivoting, or N/3 voting, is a method where participants reduce a large list of ideas to a prioritized shortlist by casting multiple votes.
This voting system elevates the most preferred options for further consideration and decision-making.
As a problem-solving technique, multivoting allows a group to narrow options and focus on the most promising solutions, ensuring more effective and democratic decision-making.
36. Force Field Analysis
Force Field Analysis is a decision-making technique that identifies the forces for and against change when contemplating a decision.
The ‘forces’ represent the differing factors that can drive or hinder change.
In problem-solving, Force Field Analysis allows you to understand the entirety of the context, favoring a balanced view over a one-sided perspective. A comprehensive view of all the forces at play can lead to better-informed problem-solving decisions.
TRIZ, which stands for “The Theory of Inventive Problem Solving,” is a problem-solving, analysis, and forecasting methodology.
It focuses on finding contradictions inherent in a scenario. Then, you work toward eliminating the contraditions through finding innovative solutions.
So, when you’re tackling a problem, TRIZ provides a disciplined, systematic approach that aims for ideal solutions and not just acceptable ones. Using TRIZ, you can leverage patterns of problem-solving that have proven effective in different cases, pivoting them to solve the problem at hand.
38. A3 Problem Solving
A3 Problem Solving, derived from Lean Management, is a structured method that uses a single sheet of A3-sized paper to document knowledge from a problem-solving process.
Named after the international paper size standard of A3 (or 11-inch by 17-inch paper), it succinctly records all key details of the problem-solving process from problem description to the root cause and corrective actions.
Used in problem-solving, this provides a straightforward and logical structure for addressing the problem, facilitating communication between team members, ensuring all critical details are included, and providing a record of decisions made.
39. Scenario Analysis
Scenario Analysis is all about predicting different possible future events depending upon your decision.
To do this, you look at each course of action and try to identify the most likely outcomes or scenarios down the track if you take that course of action.
This technique helps forecast the impacts of various strategies, playing each out to their (logical or potential) end. It’s a good strategy for project managers who need to keep a firm eye on the horizon at all times.
When solving problems, Scenario Analysis assists in preparing for uncertainties, making sure your solution remains viable, regardless of changes in circumstances.
How to Answer “Demonstrate Problem-Solving Skills” in an Interview
When asked to demonstrate your problem-solving skills in an interview, the STAR method often proves useful. STAR stands for Situation, Task, Action, and Result.
Situation: Begin by describing a specific circumstance or challenge you encountered. Make sure to provide enough detail to allow the interviewer a clear understanding. You should select an event that adequately showcases your problem-solving abilities.
For instance, “In my previous role as a project manager, we faced a significant issue when our key supplier abruptly went out of business.”
Task: Explain what your responsibilities were in that situation. This serves to provide context, allowing the interviewer to understand your role and the expectations placed upon you.
For instance, “It was my task to ensure the project remained on track despite this setback. Alternative suppliers needed to be found without sacrificing quality or significantly increasing costs.”
Action: Describe the steps you took to manage the problem. Highlight your problem-solving process. Mention any creative approaches or techniques that you used.
For instance, “I conducted thorough research to identify potential new suppliers. After creating a shortlist, I initiated contact, negotiated terms, assessed samples for quality and made a selection. I also worked closely with the team to re-adjust the project timeline.”
Result: Share the outcomes of your actions. How did the situation end? Did your actions lead to success? It’s particularly effective if you can quantify these results.
For instance, “As a result of my active problem solving, we were able to secure a new supplier whose costs were actually 10% cheaper and whose quality was comparable. We adjusted the project plan and managed to complete the project just two weeks later than originally planned, despite the major vendor setback.”
Remember, when you’re explaining your problem-solving skills to an interviewer, what they’re really interested in is your approach to handling difficulties, your creativity and persistence in seeking a resolution, and your ability to carry your solution through to fruition. Tailoring your story to highlight these aspects will help exemplify your problem-solving prowess.
Go Deeper: STAR Interview Method Examples
Benefits of Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is beneficial for the following reasons (among others):
- It can help you to overcome challenges, roadblocks, and bottlenecks in your life.
- It can save a company money.
- It can help you to achieve clarity in your thinking.
- It can make procedures more efficient and save time.
- It can strengthen your decision-making capacities.
- It can lead to better risk management.
Whether for a job interview or school, problem-solving helps you to become a better thinking, solve your problems more effectively, and achieve your goals. Build up your problem-solving frameworks (I presented over 40 in this piece for you!) and work on applying them in real-life situations.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 101 Class Group Name Ideas (for School Students)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 19 Top Cognitive Psychology Theories (Explained)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 119 Bloom’s Taxonomy Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ All 6 Levels of Understanding (on Bloom’s Taxonomy)
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

How to Solve Problems Like an Expert
It's not so much what you know as how easily you can retrieve what you know..
Posted September 7, 2013
You have a problem when your current situation differs from your desired goal. You want to be rich, but your checking account balance is circling the drain. You want to date that gorgeous person, but you get tongue-tied whenever you even think about it. You are running late for work, and your car won’t start. In each case, what you want and what you have are decidedly different.
Problem solving is nothing more and nothing less searching for means to reduce the differences between your goal state and your current state. Yes, that’s right: All problem solving, at bottom, is search. When there is a clear procedure that will take you from the one to the other, we call that a well-defined problem. Making scrambled eggs is a well-defined problem. For the first, you simply follow a recipe, and voila, you’ve got breakfast.
If there is no clear procedure, we call that an ill-defined problem. Unfortunately, most of life’s important problems are ill defined. How do you make enough money to save for retirement , how do you avoid war, or how do you get that girl or guy to go out with you? These are all ill-defined problems because they don’t have clear goal states (how much is “enough” for retirement?) or they don’t have clear solution paths (how do you attract the interest of someone you find attractive?).
In 1945, the brilliant mathematician, George Pólya (1887–1985) wrote the quintessential text for solving problems, aptly titled How to Solve It. Here is how he summarized the problem-solving process.
1. First, make sure you understand the problem. You do this by developing a representation of the essential aspects of the problem. You do that by searching your knowledge base for information that seems to you to be solution-relevant.
2. After understanding, then make a plan for solving the problem. This will also usually involve searching one’s knowledge base for solutions that are appropriate for the problem as represented.
3. Carry out the plan by executing your solutions.
4. Look back on your work and ask “how could it be better?”
That is how it should be done. But most people make one huge mistake that derails the entire process, making it far less likely that they will succeed. What is that mistake?
They skip the first step.
Regardless of the domain, inexperienced problem-solvers tend to jump right to the solution stage of problem solving, with typically disastrous consequences. They often use a trial-and-error strategy in which the first solution that comes to mind is put into play. Because they didn’t take the time to fully understand the problem, their solution attempts fail when foreseeable glitches arise.
In contrast, experts tend to spend more time developing a full understanding of the problem, comparing what they currently know about the problem with what they need to know in order to get a complete picture of the situation. Because they spend more time in the problem representation stage, they are more likely to derive successful solutions, and to spend less time overall in generating a successful solution.
Here are three tips for executing step one like an expert.
1. Organize knowledge correctly. Often, novices have all the knowledge they need to solve the problem at hand. They just can’t get to it because their knowledge is organized in ways that make it difficult to see the connection between the current problem and what they already know.
Experts organize their knowledge in problem schemas that include relevant information about a type of problem and the procedures for solving problems of that type. This means that when experts think about problems, relevant information is automatically activated in memory , along with relevant solution procedures. In contrast, when novices think about a problem, their knowledge is too general and too scattered throughout memory, making problem-solving a tedious trial-and-error search. For example, a novice salesperson will focus on the general goal of “make the sale”, and will apply sales techniques in willy-nilly or fixed fashion to reach that goal. An experienced salesperson will focus on the specific goal of understanding what the customer needs and wants, and in developing a trust relationship with the customer. As a result, the experienced salesperson spends less time “working” the customer or showing them things in which they have no interest.

2. Ask the right questions. If you’ve ever done a Google search, you know that the quality of the search results depends entirely on the quality of the keywords you use. Garbage in, garbage out. This in a nutshell, is the key to developing a strong understanding of a problem—asking the right questions.
Experts are more likely to ask the right questions because their domain-specific knowledge is organized more efficiently. Continuing with the previous example, an expert salesperson’s schema is organized around understanding customer wants and needs. As a result, he or she will spend more time asking specific questions about those needs and wants, and then tailoring subsequent choices to match the answers given. Sometimes the customer isn’t aware that there are product features that may be attractive to them. For example, they may focus on price yet be unaware that a higher priced item carries a better warranty. Because the salesperson has taken the time to impress upon the customer that their needs and wants matter, a relationship of trust is established that makes it easier for the salesperson to introduce these relevant features without putting the customer off. In contrast, novice salespeople will often deluge the customer with more product features than they can possibly remember and process, or will try hard-sell techniques that create an atmosphere of distrust .
3. Work forward from known to unknown. Because of the way expert knowledge is organized, experts solve problems by working forward from the information given (or information obtained) to arrive at a viable solution. Novices, on the other hand, tend to work backwards because they are focused more at arriving at a quick solution that at ensuring that they fully understand the problem. As a result, the typically have incomplete problem-solving schemas that are full of irrelevant information. This slows down the problem-solving process, and makes it less likely that a viable solution will be reached—or remembered!
For three more tips on how to be a better problem solver, see this article Dr. Art Markman.
References: Pólya, George (1957). How to Solve It. Garden City, NY: Doubleday.
Dr. Denise Cummins is a Fellow of the Association for Psychological Science, and the author of Good Thinking: Seven Powerful Ideas That Influence the Way We Think (2012, Cambridge University Press).

Denise Dellarosa Cummins, Ph.D. , is the author of Good Thinking, The Historical Foundations of Cognitive Science , and Evolution of Mind.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
More From Forbes
Stumped five ways to hone your problem-solving skills.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Respect the worth of other people's insights
Problems continuously arise in organizational life, making problem-solving an essential skill for leaders. Leaders who are good at tackling conundrums are likely to be more effective at overcoming obstacles and guiding their teams to achieve their goals. So, what’s the secret to better problem-solving skills?
1. Understand the root cause of the problem
“Too often, people fail because they haven’t correctly defined what the problem is,” says David Ross, an international strategist, founder of consultancy Phoenix Strategic Management and author of Confronting the Storm: Regenerating Leadership and Hope in the Age of Uncertainty .
Ross explains that as teams grapple with “wicked” problems – those where there can be several root causes for why a problem exists – there can often be disagreement on the initial assumptions made. As a result, their chances of successfully solving the problem are low.
“Before commencing the process of solving the problem, it is worthwhile identifying who your key stakeholders are and talking to them about the issue,” Ross recommends. “Who could be affected by the issue? What is the problem – and why? How are people affected?”
He argues that if leaders treat people with dignity, respecting the worth of their insights, they are more likely to successfully solve problems.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024, 2. unfocus the mind.
“To solve problems, we need to commit to making time to face a problem in its full complexity, which also requires that we take back control of our thinking,” says Chris Griffiths, an expert on creativity and innovative thinking skills, founder and CEO of software provider OpenGenius, and co-author of The Focus Fix: Finding Clarity, Creativity and Resilience in an Overwhelming World .
To do this, it’s necessary to harness the power of the unfocused mind, according to Griffiths. “It might sound oxymoronic, but just like our devices, our brain needs time to recharge,” he says. “ A plethora of research has shown that daydreaming allows us to make creative connections and see abstract solutions that are not obvious when we’re engaged in direct work.”
To make use of the unfocused mind in problem solving, you must begin by getting to know the problem from all angles. “At this stage, don’t worry about actually solving the problem,” says Griffiths. “You’re simply giving your subconscious mind the information it needs to get creative with when you zone out. From here, pick a monotonous or rhythmic activity that will help you to activate the daydreaming state – that might be a walk, some doodling, or even some chores.”
Do this regularly, argues Griffiths, and you’ll soon find that flashes of inspiration and novel solutions naturally present themselves while you’re ostensibly thinking of other things. He says: “By allowing you to access the fullest creative potential of your own brain, daydreaming acts as a skeleton key for a wide range of problems.”
3. Be comfortable making judgment calls
“Admitting to not knowing the future takes courage,” says Professor Stephen Wyatt, founder and lead consultant at consultancy Corporate Rebirth and author of Antidote to the Crisis of Leadership: Opportunity in Complexity . “Leaders are worried our teams won’t respect us and our boards will lose faith in us, but what doesn’t work is drawing up plans and forecasts and holding yourself or others rigidly to them.”
Wyatt advises leaders to heighten their situational awareness – to look broadly, integrate more perspectives and be able to connect the dots. “We need to be comfortable in making judgment calls as the future is unknown,” he says. “There is no data on it. But equally, very few initiatives cannot be adjusted, refined or reviewed while in motion.”
Leaders need to stay vigilant, according to Wyatt, create the capacity of the enterprise to adapt and maintain the support of stakeholders. “The concept of the infallible leader needs to be updated,” he concludes.
4. Be prepared to fail and learn
“Organisations, and arguably society more widely, are obsessed with problems and the notion of problems,” says Steve Hearsum, founder of organizational change consultancy Edge + Stretch and author of No Silver Bullet: Bursting the Bubble of the Organisational Quick Fix .
Hearsum argues that this tendency is complicated by the myth of fixability, namely the idea that all problems, however complex, have a solution. “Our need for certainty, to minimize and dampen the anxiety of ‘not knowing,’ leads us to oversimplify and ignore or filter out anything that challenges the idea that there is a solution,” he says.
Leaders need to shift their mindset to cultivate their comfort with not knowing and couple that with being OK with being wrong, sometimes, notes Hearsum. He adds: “That means developing reflexivity to understand your own beliefs and judgments, and what influences these, asking questions and experimenting.”
5. Unleash the power of empathy
Leaders must be able to communicate problems in order to find solutions to them. But they should avoid bombarding their teams with complex, technical details since these can overwhelm their people’s cognitive load, says Dr Jessica Barker MBE , author of Hacked: The Secrets Behind Cyber Attacks .
Instead, she recommends that leaders frame their messages in ways that cut through jargon and ensure that their advice is relevant, accessible and actionable. “An essential leadership skill for this is empathy,” Barker explains. “When you’re trying to build a positive culture, it is crucial to understand why people are not practicing the behaviors you want rather than trying to force that behavioral change with fear, uncertainty and doubt.”
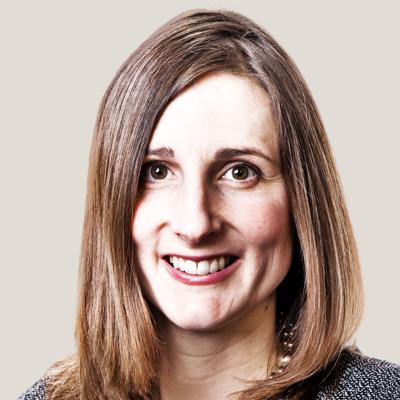

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
50 Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking Examples
Critical thinking and problem solving are essential skills for success in the 21st century. Critical thinking is the ability to analyze information, evaluate evidence, and draw logical conclusions. Problem solving is the ability to apply critical thinking to find effective solutions to various challenges. Both skills require creativity, curiosity, and persistence. Developing critical thinking and problem solving skills can help students improve their academic performance, enhance their career prospects, and become more informed and engaged citizens.
Sanju Pradeepa

In today’s complex and fast-paced world, the ability to think critically and solve problems effectively has become a vital skill for success in all areas of life. Whether it’s navigating professional challenges, making sound decisions, or finding innovative solutions, critical thinking and problem-solving are key to overcoming obstacles and achieving desired outcomes. In this blog post, we will explore problem-solving and critical thinking examples.
Table of Contents
Developing the skills needed for critical thinking and problem solving.

It is not enough to simply recognize an issue; we must use the right tools and techniques to address it. To do this, we must learn how to define and identify the problem or task at hand, gather relevant information from reliable sources, analyze and compare data to draw conclusions, make logical connections between different ideas, generate a solution or action plan, and make a recommendation.
The first step in developing these skills is understanding what the problem or task is that needs to be addressed. This requires careful consideration of all available information in order to form an accurate picture of what needs to be done. Once the issue has been identified, gathering reliable sources of data can help further your understanding of it. Sources could include interviews with customers or stakeholders, surveys, industry reports, and analysis of customer feedback.
After collecting relevant information from reliable sources, it’s important to analyze and compare the data in order to draw meaningful conclusions about the situation at hand. This helps us better understand our options for addressing an issue by providing context for decision-making. Once you have analyzed the data you collected, making logical connections between different ideas can help you form a more complete picture of the situation and inform your potential solutions.
Once you have analyzed your options for addressing an issue based on all available data points, it’s time to generate a solution or action plan that takes into account considerations such as cost-effectiveness and feasibility. It’s also important to consider the risk factors associated with any proposed solutions in order to ensure that they are responsible before moving forward with implementation. Finally, once all the analysis has been completed, it is time to make a recommendation based on your findings, which should take into account any objectives set out by stakeholders at the beginning of this process as well as any other pertinent factors discovered throughout the analysis stage.
By following these steps carefully when faced with complex issues, one can effectively use critical thinking and problem-solving skills in order to achieve desired outcomes more efficiently than would otherwise be possible without them, while also taking responsibility for decisions made along the way.

What Does Critical Thinking Involve: 5 Essential Skill
Problem-solving and critical thinking examples.

Problem-solving and critical thinking are key skills that are highly valued in any professional setting. These skills enable individuals to analyze complex situations, make informed decisions, and find innovative solutions. Here, we present 25 examples of problem-solving and critical thinking. problem-solving scenarios to help you cultivate and enhance these skills.
Ethical dilemma: A company faces a situation where a client asks for a product that does not meet quality standards. The team must decide how to address the client’s request without compromising the company’s credibility or values.
Brainstorming session: A team needs to come up with new ideas for a marketing campaign targeting a specific demographic. Through an organized brainstorming session, they explore various approaches and analyze their potential impact.
Troubleshooting technical issues : An IT professional receives a ticket indicating a network outage. They analyze the issue, assess potential causes (hardware, software, or connectivity), and solve the problem efficiently.
Negotiation : During contract negotiations, representatives from two companies must find common ground to strike a mutually beneficial agreement, considering the needs and limitations of both parties.
Project management: A project manager identifies potential risks and develops contingency plans to address unforeseen obstacles, ensuring the project stays on track.
Decision-making under pressure: In a high-stakes situation, a medical professional must make a critical decision regarding a patient’s treatment, weighing all available information and considering potential risks.
Conflict resolution: A team encounters conflicts due to differing opinions or approaches. The team leader facilitates a discussion to reach a consensus while considering everyone’s perspectives.
Data analysis: A data scientist is presented with a large dataset and is tasked with extracting valuable insights. They apply analytical techniques to identify trends, correlations, and patterns that can inform decision-making.
Customer service: A customer service representative encounters a challenging customer complaint and must employ active listening and problem-solving skills to address the issue and provide a satisfactory resolution.
Market research : A business seeks to expand into a new market. They conduct thorough market research, analyzing consumer behavior, competitor strategies, and economic factors to make informed market-entry decisions.
Creative problem-solvin g: An engineer faces a design challenge and must think outside the box to come up with a unique and innovative solution that meets project requirements.
Change management: During a company-wide transition, managers must effectively communicate the change, address employees’ concerns, and facilitate a smooth transition process.
Crisis management: When a company faces a public relations crisis, effective critical thinking is necessary to analyze the situation, develop a response strategy, and minimize potential damage to the company’s reputation.
Cost optimization : A financial analyst identifies areas where expenses can be reduced while maintaining operational efficiency, presenting recommendations for cost savings.
Time management : An employee has multiple deadlines to meet. They assess the priority of each task, develop a plan, and allocate time accordingly to achieve optimal productivity.
Quality control: A production manager detects an increase in product defects and investigates the root causes, implementing corrective actions to enhance product quality.
Strategic planning: An executive team engages in strategic planning to define long-term goals, assess market trends, and identify growth opportunities.
Cross-functional collaboration: Multiple teams with different areas of expertise must collaborate to develop a comprehensive solution, combining their knowledge and skills.
Training and development : A manager identifies skill gaps in their team and designs training programs to enhance critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities.
Risk assessment : A risk management professional evaluates potential risks associated with a new business venture, weighing their potential impact and developing strategies to mitigate them.
Continuous improvement: An operations manager analyzes existing processes, identifies inefficiencies, and introduces improvements to enhance productivity and customer satisfaction.
Customer needs analysis: A product development team conducts extensive research to understand customer needs and preferences, ensuring that the resulting product meets those requirements.
Crisis decision-making: A team dealing with a crisis must think quickly, assess the situation, and make timely decisions with limited information.
Marketing campaign analysis : A marketing team evaluates the success of a recent campaign, analyzing key performance indicators to understand its impact on sales and customer engagement.
Constructive feedback: A supervisor provides feedback to an employee, highlighting areas for improvement and offering constructive suggestions for growth.
Conflict resolution in a team project: Team members engaged in a project have conflicting ideas on the approach. They must engage in open dialogue, actively listen to each other’s perspectives, and reach a compromise that aligns with the project’s goals.
Crisis response in a natural disaster: Emergency responders must think critically and swiftly in responding to a natural disaster, coordinating rescue efforts, allocating resources effectively, and prioritizing the needs of affected individuals.
Product innovation : A product development team conducts market research, studies consumer trends, and uses critical thinking to create innovative products that address unmet customer needs.
Supply chain optimization: A logistics manager analyzes the supply chain to identify areas for efficiency improvement, such as reducing transportation costs, improving inventory management, or streamlining order fulfillment processes.
Business strategy formulation: A business executive assesses market dynamics, the competitive landscape, and internal capabilities to develop a robust business strategy that ensures sustainable growth and competitiveness.
Crisis communication: In the face of a public relations crisis, an organization’s spokesperson must think critically to develop and deliver a transparent, authentic, and effective communication strategy to rebuild trust and manage reputation.
Social problem-solving: A group of volunteers addresses a specific social issue, such as poverty or homelessness, by critically examining its root causes, collaborating with stakeholders, and implementing sustainable solutions for the affected population.

Problem-Solving Mindset: How to Achieve It (15 Ways)
Risk assessment in investment decision-making: An investment analyst evaluates various investment opportunities, conducting risk assessments based on market trends, financial indicators, and potential regulatory changes to make informed investment recommendations.
Environmental sustainability: An environmental scientist analyzes the impact of industrial processes on the environment, develops strategies to mitigate risks, and promotes sustainable practices within organizations and communities.
Adaptation to technological advancements : In a rapidly evolving technological landscape, professionals need critical thinking skills to adapt to new tools, software, and systems, ensuring they can effectively leverage these advancements to enhance productivity and efficiency.
Productivity improvement: An operations manager leverages critical thinking to identify productivity bottlenecks within a workflow and implement process improvements to optimize resource utilization, minimize waste, and increase overall efficiency.
Cost-benefit analysis: An organization considering a major investment or expansion opportunity conducts a thorough cost-benefit analysis, weighing potential costs against expected benefits to make an informed decision.
Human resources management : HR professionals utilize critical thinking to assess job applicants, identify skill gaps within the organization, and design training and development programs to enhance the workforce’s capabilities.
Root cause analysis: In response to a recurring problem or inefficiency, professionals apply critical thinking to identify the root cause of the issue, develop remedial actions, and prevent future occurrences.
Leadership development: Aspiring leaders undergo critical thinking exercises to enhance their decision-making abilities, develop strategic thinking skills, and foster a culture of innovation within their teams.
Brand positioning : Marketers conduct comprehensive market research and consumer behavior analysis to strategically position a brand, differentiating it from competitors and appealing to target audiences effectively.
Resource allocation: Non-profit organizations distribute limited resources efficiently, critically evaluating project proposals, considering social impact, and allocating resources to initiatives that align with their mission.
Innovating in a mature market: A company operating in a mature market seeks to innovate to maintain a competitive edge. They cultivate critical thinking skills to identify gaps, anticipate changing customer needs, and develop new strategies, products, or services accordingly.
Analyzing financial statements : Financial analysts critically assess financial statements, analyze key performance indicators, and derive insights to support financial decision-making, such as investment evaluations or budget planning.
Crisis intervention : Mental health professionals employ critical thinking and problem-solving to assess crises faced by individuals or communities, develop intervention plans, and provide support during challenging times.
Data privacy and cybersecurity : IT professionals critically evaluate existing cybersecurity measures, identify vulnerabilities, and develop strategies to protect sensitive data from threats, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Process improvement : Professionals in manufacturing or service industries critically evaluate existing processes, identify inefficiencies, and implement improvements to optimize efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Multi-channel marketing strategy : Marketers employ critical thinking to design and execute effective marketing campaigns across various channels such as social media, web, print, and television, ensuring a cohesive brand experience for customers.
Peer review: Researchers critically analyze and review the work of their peers, providing constructive feedback and ensuring the accuracy, validity, and reliability of scientific studies.
Project coordination : A project manager must coordinate multiple teams and resources to ensure seamless collaboration, identify potential bottlenecks, and find solutions to keep the project on schedule.
These examples highlight the various contexts in which problem-solving and critical-thinking skills are necessary for success. By understanding and practicing these skills, individuals can enhance their ability to navigate challenges and make sound decisions in both personal and professional endeavors.
Conclusion:
Critical thinking and problem-solving are indispensable skills that empower individuals to overcome challenges, make sound decisions, and find innovative solutions. By honing these skills, one can navigate through the complexities of modern life and achieve success in both personal and professional endeavors. Embrace the power of critical thinking and problem-solving, and unlock the door to endless possibilities and growth.
- Problem solving From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- Critical thinking From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- The Importance of Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Skills for Students (5 Minutes)

Let’s boost your self-growth with Believe in Mind.
Interested in self-reflection tips, learning hacks, and knowing ways to calm down your mind? We offer you the best content which you have been looking for.
Follow Me on
You May Like Also
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Personal Development
- Sales Training
- Business Training
- Time Management
- Leadership Training
- Book Writing
- Public Speaking
- Live Speaker Training With Brian
- See Brian Speak
- Coaching Programs
- Become a Coach
- Personal Success
- Sales Success
- Business Success
- Leadership Success
Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills – Steps, Processes & Technique
When you are faced with a problem, how do you go about solving it? Do you let it overwhelm you, or do you flex your problem-solving muscles and figure out the best possible solution?
People who allow themselves to be overwhelmed or ignore complex problems often become frantic and confused. They usually take a haphazard approach to thinking, and then they are dismayed when they find themselves floundering and making no progress.
Luckily, there is a much better way.
I’d like to introduce you to a problem-solving process that can help you face and tackle any type of challenge. With these 10 problem-solving strategies, you will strengthen your ability to always find a solution while enabling yourself to see real progress.
Once you begin to execute these problem-solving techniques, you will feel confident to face a problem right away.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?
Problem-solving skills involve identifying a problem, coming up with possible solutions, choosing an appropriate solution, and then implementing it.
Often, there is more than one correct solution to a problem. But frequently, you are looking for the best solution that applies to your particular circumstance.
For instance, possible solutions to losing weight include eating less, adding healthier foods to your diet, walking 30 minutes a day, swimming three times a week, training for a 5K race, drinking more water, and many other effective solutions.
Your job is to find the solution that will work best for you and give you the most success.
Good problem-solving skills are essential in all areas of your life because we encounter problems to solve in one form or another nearly every day, from small things like getting stuck in traffic to major events like being diagnosed with a chronic illness.
A problem can be defined in one of two ways:
“Any question or matter involving doubt, uncertainty, or difficulty; a question proposed for solution or discussion.”
The Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning explains that a problem:
“…is generally considered to be a task, a situation, or person which is difficult to deal with or control due to complexity and transparency. In everyday language, a problem is a question proposed for a solution, a matter stated for examination or proof.”
In short, a problem is something that’s hard to deal with and needs to be solved.
Examples of common problems in the workplace might include:
- Lack of motivation or boredom
- Discrimination
- Conflict with a boss or coworkers
- Performance issues
- Burnout or stress
- Bad working conditions
Or maybe you’re dealing with problems in your personal life. For example:
- A strained marriage or divorce
- Financial worries
- Health issues
- Grief over the death of loved ones
- Issues your children are experiencing
- A decision to move, change jobs, or get an education
No matter what you’re facing, it’s important to actively cultivate your creative thinking and learn problem-solving techniques.
When you’re able to solve problems effectively, you will enjoy greater satisfaction in life. Your relational skills will improve, and your problem-solving abilities will make you highly valuable in the workplace.
The Importance of Solving Problems
We solve problems daily in all aspects of life. People who are good problem solvers are more likely to be successful in getting around obstacles and achieving their desired end result.
What’s more, solving complex problems doesn’t only help change your external circumstances. You’ll also feel happier and more confident in yourself, knowing you can solve future problems.
Problem-solving allows you to:
- Fix things that are broken
- Address risk
- Improve performance
- Seize opportunity
- Lower stress and anxiety
- Prevent more serious consequences
Having a problem-solving strategy will make you more attractive to hiring managers. In many cases, you might be asked in a job interview about your problem-solving skills.
It’s smart to think of an example ahead of time–a problem that came up at your last job and how you solved it–so you’ll be prepared. You can also mention the soft skills listed above:
“My communication skills, flexibility, and ability to think outside the box help me deal with problems in a timely manner.”
The more you practice effective problem-solving techniques, the better you will get at solving problems and the more reliable and trustworthy you will become in your field as well as in your personal life.
Understanding the Problem-Solving Process
When you’re setting out to solve a problem, what should you do first?
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to problem-solving, there is a general framework that you can use to help solve problems.
The problem-solving process is often broken down into seven steps:
- Identify the issue and its root cause
- Understand every angle of the problem
- List possible solutions
- Evaluate the options
- Choose an option
- Evaluate the results
I’ll explain this process and each of these steps, plus a few bonus steps. I’ll also share some further problem-solving strategies so you are well-equipped with solution-finding techniques that you can apply to various situations.
The important thing to understand now, though, is that you can use a structured process to improve problem-solving skills. You don’t have to shoot in the dark–simply follow the steps listed in this process.
Problem-Solving Skills
What kind of skills should you cultivate to become a better problem-solver?
You can also work on things like your communication skills, analytical skills, and other key skills in life that will make you a better problem solver. These soft skills go hand in hand with being able to come up with solutions quickly.
Focus on the following:
Brainstorming
This is a method of free-thinking used to generate ideas that involve thinking of a long list of possible solutions without making an initial judgment about how effective they might be. You can brainstorm with a group of people or on your own.
Data gathering
Collecting information related to the issue is a vital problem-solving tool as the more information you have about the root cause and contributing factors to a problem, the easier it will be to find solutions that work. Fact-finding can come from interviewing people involved, researching related problems, reading documents, analyzing data, and more.
Creative thinking
When you’re a creative thinker, you’re able to look at a complex problem or an everyday problem and think of unique, original solutions. Your ability to come up with creative solutions will make you more marketable as well as more successful in meeting complex problems head-on.
Communication
Having communication skills is essential to work with others to solve problems. You need to not only be able to express your thoughts clearly and concisely without causing offense or contention, but you also need to be able to listen to others as they express their views until everyone is on the same page.
Like communication skills, teamwork involves being able to work collectively with others to apply problem-solving strategies. Often, two heads are better than one, and the wisdom you gain from collective intelligence will make identifying underlying causes and finding solutions much easier.
Analyzing involves being able to break up a complex problem into smaller parts so you can examine and evaluate it to understand the problem better.
You may find the root cause of the problem as well as contributing factors. Ill-defined problems are difficult to solve, so it is important to be able to apply problem analysis to any issue you are dealing with.
Time management
Time-management skills help you avoid procrastination and spending time on unnecessary tasks.
You can develop good time management skills by setting goals, making daily to-do lists, prioritizing your tasks, and reducing or eliminating distractions.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is applying a step-by-step process to find the cause of a problem and then working your way to different solutions.
Common, well-defined problems, such as those that occur in the computer science field or automotive industry, may have a preset list of troubleshooting steps to follow.
Other problems will require you to develop a troubleshooting process as you go. Troubleshooting skills make you a valuable asset to any team.
When you take initiative, you do not wait for others to tell you what to do. You see a need and seek to fill that need. Often, by taking initiative, you can address an issue before a problem occurs.
One example in the workplace would be to sign up for training that will keep you up to date on the newest developments in your industry.
Flexibility
Being flexible is an important tool you will use to solve problems. It’s an essential skill in all aspects of your life. When you are too rigid, you often are not able to see creative solutions and different strategies that can help make your life easier.
There is often more than one good way to solve the same problem, and being open-minded will help you move from your existing beliefs to other effective ways of solving problems.
I know this is a long list, but you don’t have to do everything at once.
Even more, chances are you’ve already picked up some of these skills in your daily life without even realizing it. Keeping these skills in mind as you practice solving problems will help you become better at not only solution-finding but at everything you do.
10 Steps to Solving a Problem
In this 10-step problem-solving process, I’ll walk you through how to identify and implement the right solution to the problem at hand. In learning these steps, you will develop your critical thinking and elevate your problem-solving skills.
1. Take a Positive Approach
When a problem arises, it’s easy to enter panic mode or envision worst-case scenarios. Before you let your mind go there, take a step back and address every problem as simply another situation.
It is a challenge that you can handle, with the right approach. Part of that approach is thinking positively and creatively about the situation.
When figuring out ways to use creative thinking for problem-solving, I like to explore how geniuses solve challenges . They think outside the box, keep an open mind, and take a systematic approach.
It all starts with thinking positively about the problem.
One problem-solving strategy I like to use is to think of it as a situation, not a problem.
Problems are a fact of life; you can’t control when or how they occur, but you can control your attitude. The more positive your language and mental process are, the more confident and optimistic you will be when approaching any complication.
How can you develop a more positive outlook on life? This mindset shift can take some time.
You can’t snap your fingers and instantly become a more positive person overnight. However, there are actionable steps you can take to be more positive.
Start by focusing on the good things in your life. Yes, you have problems, but you have good things too. If you’re struggling to come up with anything that makes you smile, consider keeping a gratitude journal where you make an entry every day.
I also recommend positive affirmations and self-talk. Repeat phrases to yourself such as “There are good things in my life,” “I can come up with creative solutions,” or “I have good problem-solving skills.”
And of course, it’s important to surround yourself with people who are equally as positive and upbeat as you’re trying to be. The same applies to all aspects of your life. Read positive books, articles, and social media posts. Listen to uplifting music, and watch videos and movies that leave you feeling positive and optimistic.
Remember that every problem comes with a solution already custom-made for it. You just need to find it, and you can by maintaining a calm, positive attitude and steadily progressing through the different stages of the problem-solving process.
2. Define The Problem
Problem identification is a vital step in problem-solving processes so that you know exactly what you are dealing with. What might seem to be the root cause of your situation may be something entirely different.
Also, defining the problem will help you gather data, analyze the issues surrounding it, and find a potential solution.
What exactly is the challenge you are facing? What about this particular situation is causing you stress and anxiety? You must clearly define the problem to resolve it.
Not only should you clarify what the problem is, but you should also see what caused the problem. If you can’t conclude the cause of the problem, you may need to meet with other parties involved to determine the root before moving forward.
Sometimes a clear root cause cannot be determined, or there may be several factors that are causing the problem. In these cases, you can still move forward in finding solutions by defining what is currently hard to deal with and what needs to be changed or solved.
If you are working with a group, it’s important to write and rewrite the problem until everyone agrees that the problem is clearly and correctly defined. Each person will bring a unique perspective that will help clarify what the situation is.
Identify important details that define that problem, and weed out information that is extraneous or useless so that it doesn’t distract you from your ability to solve it or waste your time.
It can help to ask the following questions:
- Who is involved in the problem?
- What exactly is happening that is preventing forward progress?
- When did the problem occur and how often?
- Why is the problem happening?
- How is it affecting workflow or people?
Write out the problem so that it is easy for you and everyone else to see exactly what it is. It may help to draw a picture, diagram, or graph to fully visualize the problem.
When the issue is clearly defined, the solution may be obvious. But you may never find the solution at all if the problem isn’t defined.
3. Use Creative Thinking
As I mentioned in the first step, geniuses solve issues with out-of-the-box thinking. So you need to see the problem from every angle before you begin moving down solution paths.
You should think: Are there other problems that are affecting this obstacle? If so, you need to address it first.
It can be easy to have tunnel vision when you’re problem-solving, but there are usually multiple things at play with any dilemma. Zoom out from the situation at hand and see all contributing factors to the issue and listen to everyone’s point of view.
Meeting with others who may be involved in the process can offer you more brainpower to shed light on the problem. That’s why teamwork is so important. You can work together to look at what the issue is affecting, what is affecting it, and how to solve it.
It might feel as if you can work faster on your own. But when you collaborate with others, you’ll be able to come up with higher-quality solutions.
In fact, statistics show that 86% of employees and executives say lack of collaboration or ineffective communication causes workplace failures.
Don’t be afraid to sit down with people involved in the problem to work things out. People outside the problem can also offer a valuable third-party opinion. Their advice and ideas may actually be more helpful because they don’t have a personal stake in the issue.
When discussing the problem with others, replace “No, but” with “Yes, and.” For example, if someone says, “I think part of the problem stems from a lack of communication within the team.” Respond with, “Yes, and it can also come from people arriving late to meetings.”
This approach validates what the other person is saying so that all input is accepted as valuable and ideas are not negated. It also gives you an equal opportunity to add your ideas and input.
Think creatively by looking outside of your industry or situation for solutions. While it is helpful to analyze how others within your field or circumstances have solved a similar problem, you might find helpful insight in looking at how companies or individuals in other walks of life that have seemingly non-matching characteristics have approached related problems.
Ask “what if” questions. This can often help you think outside the box when solving problems creatively. As you look at potential solutions, ask,
“Why not?”
“What assumptions can we get rid of?”
“What can we add beyond the expected solutions?” and similar questions to take a broader view of the problem and possible solutions.
State the opposite of the problem to get a different perspective on it. For example, instead of asking, “How can we encourage our existing customers to buy more products?” ask, “How can we discourage our existing customers from buying more products.” This process can lead to surprisingly effective solutions.
4. Brainstorm Possible Solutions
Part of addressing the situation from different directions is to come up with not just one but several solutions. There are likely to be multiple solutions to any single problem.
The first conclusion that comes to mind may not be the best one, but the more you focus, the more solutions you will find. That’s why brainstorming all possible resolutions is an essential step to problem-solving .
If you’re brainstorming together with a group of others, make sure to define a clear goal for the brainstorming session before you begin. Allow people time before the meeting to reflect on the problem. This will allow them to come prepared with ideas.
Throughout the session, record any suggestions that come up. You can write them on a physical whiteboard so that everyone can see them, or simply jot them down in a digital folder. Share these notes with attendees post-meeting and assign any follow-up tasks.
Reserve judgment until after your brainstorming session is complete. Some ideas may seem ridiculous or impractical, but say them and record them anyway. The goal is to move beyond existing ideas and look at the problem and possible solutions from every angle. Sometimes, an idea that seems far-flung can begin a conversation and flow of ideas that lead to the best solution.
Defining your end goal will help inspire unique ways you can get there. It can also help to pose the problem as a question and come up with conclusions to that question. Use the examples offered earlier of who, what, when, where, and how questions to get you started.
5. Find The Best Solution
Now, not all possible solutions you outlined will be a good fit. You should be able to narrow down each method and see which is the most effective for your issue.
After brainstorming all potential solutions, ask yourself, “What solution will likely produce the best outcome?”
Do this by comparing each of the results with the one you believe to be the most ideal. Which one is the best under the current circumstances? What will successfully solve the problem? Which one will lead to a better outcome in the future? What will prevent further problems? Is there more than one solution that we should apply for the best results?
It might take some time to work through each of your potential solutions. Some will quickly weed themselves out. In other cases, though, don’t be afraid to spend some time thinking about how a given solution would work.
Identify the pros and cons or benefits and costs of each solution to help you determine which one or more is best.
After looking in-depth at the various approaches, decide on the best solution for the situation.
6. Expect the Best and Prepare for the Worst
Before you jump at the chance to solve your problem with the best-fit solution, consider the repercussions of the solution.
Now is the time to jump to worst-case scenarios. What will happen if the solution fails? Knowing the answer to this will allow you to prepare if it doesn’t resolve your dilemma.
Even if at first you don’t succeed, you will learn something in the end. Don’t take it as a failure but as a learning opportunity.
Accept that it didn’t work and try something new. Determine what didn’t work and why to come up with additional possible strategies. Thankfully, you already have a list of alternative solutions that can help you find the right one.
Preparing for the worst is not about thinking negatively. Remember, the power of positive thinking will allow you to uncover more solutions. If you can train your mind to think this way, the more solution-oriented you will become.
Instead, thinking through worst-case scenarios is simply being realistic. This allows you to create a Plan B.
If one solution doesn’t work, which solution will you try next? Come up with a backup plan. You might move on to the next solution on your shortlist, or you might tweak things and continue working with your #1 idea.
Preparing for the worst allows you to end up with the best possible solution.
7. Set a Deadline
The next of my 10 problem-solving strategies is to create a timeframe for your solution. Determine:
- When to implement the solution
- How long it will take to complete
- When you expect to see results
What actions are necessary to meet this deadline, and who will be accomplishing it? List out the tasks needed and assign each one to an appropriate person.
It’s important to not only set a deadline, but also place standards on how you will measure its success. How will you know that you’re making progress, or in other words, what will be your key performance indicators (KPIs)? How will you compare the success of this solution against the success of another?
Determine what key performance indicators will allow you to measure the success of your outcomes and set a series of short-term deadlines to report. Clearly communicate these benchmarks with everyone involved.
Make sure people understand how you’re choosing to measure success so they can be successful by your standards.
8. Take Responsibility
Now that you’ve found the solution to the problem that you want to implement, consider how it will impact the situation if it works or if it doesn’t.
If your outcome doesn’t work, that’s okay, but it is your job to accept responsibility. Be ready to admit any mistakes and continue working to make things right.
Some of the most creative ideas never transpire because no one is assigned the authority to carry out the decision.
Taking responsibility for your decision doesn’t necessarily mean you need to be the one to implement it. There may be various people involved in the problem and different jobs required to accomplish the solution.
By taking responsibility for the decision you make, you’ll ensure that everyone involved knows what job they need to do, when they need to do it, and how the successful or unsuccessful completion of that job is defined.
9. Solve the Problem
Now, it’s finally time to take action.
Execute your solution so you can reach your defined goals and learn what works best. Continue communicating with everyone on board as you all work together to solve the problem.
However, not every problem will be solved easily.
You may encounter additional obstacles as you attempt to solve the initial problem. You can overcome any drawback by tapping into your creative mind and taking action consistently and persistently until you reach your goal.
As you work hard, you can develop your capacity to achieve more in the future. Every time you successfully solve a problem, you are developing your analytical skills, communication skills, and problem-solving abilities. You’re also increasing your confidence.
Next time you need to solve a problem, you can look back on the successful jobs you’ve done before.
10. Track Your Results
The final step of my problem-solving process is to track the results. Using the deadlines, KPIs, and scheduled reports you set in step seven will let you know immediately if you’re on track or falling behind.
When you reach your deadline, ask yourself if you met the goals you set out to achieve.
What worked and what didn’t work? Did you solve the problem? Did you solve it with the approach and timeframe you expected?
Answering these questions will allow you to understand if you need to take further action and help you improve your problem-solving methods for the future.
The best way to learn to problem solve is to simply do it. Jump in with both feet and start coming up with potential solutions to issues that need fixing. Over time, you’ll learn about problem-solving without even realizing it.
However, in addition to learning “on the job,” you can also take courses to help boost your skills.
Studying subjects like project management or data analysis is a good way to help you succeed in identifying problems, thinking of better solutions, and leading others with good communication as you work together to put your solutions in place.
Bonus: Further Problem-Solving Strategies
More good news: The process outlined above isn’t the only way to solve complex problems. In fact, there are many strategies you can implement for solving a problem.
Here are summaries of a few more problem-solving methods that you can learn more about:
The IDEAL process of solving a problem can help you look at situations objectively and remove the emotional aspects that can arise when a problem occurs. It works especially well for problems that may not seem to have a clear cause or may need more than one solution. The steps involve:
- Identifying the problem
- Defining what the problem is and the desired outcome
- Exploring possible solutions
- Acting on a solution
- Looking back to evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is actually a set of various problem-solving processes that aim to identify the main cause of a problem so that you can find appropriate solutions. The purpose of root cause analysis is to get to the root of a problem and prevent further difficulties instead of treating the symptoms of a problem.
At the same time, this approach to solving complex problems recognizes that there is value in treating symptoms for short-term relief while the larger problem-finding process is going on.
It also assumes that there can be more than one root cause and focuses on how and why a problem occurs instead of who causes it.
This method provides a structured approach to solving a complex problem, especially those that do not have a clear solution. Simplex problem-solving involves eight steps:
- Problem finding: Identifying what the problem is
- Fact-finding: Collecting information and data about the problem
- Problem definition: Clearly define the complex problem so you know what you are solving
- Idea finding: Generating possible solutions to the problem
- Evaluation and Selection: Choosing the solution that seems to like it will best address the complex problem
- Planning: Deciding how you will implement the solution
- Sell the idea: Get stakeholders on board with implementing the solution
- Action: Carrying out the solution
Appreciative Inquiry
Appreciative inquiry looks at a problem from a different angle, or not at all. It focuses on what is going right instead of what is going wrong. It is often best applied when a change is needed within an organization or individual. This approach leans heavily on cognitive science and positive thinking.
It involves five steps:
- Define the desired outcome
- Discover what our strengths are
- Dream of what would work well in the future
- Design a plan to make it happen
- Deploy the action
Six Thinking Hats
This approach to solving a complex problem focuses on approaching solutions in a balanced way. Using the six thinking hats approach, you will ask yourself a series of questions based on six principles or divide your team into six different groups:
- The white hat will focus on facts and logic (objective)
- The red hat will focus on emotion and instinct (intuitive)
- The black hat will focus on predicting negative outcomes (cautious)
- The yellow hat will look for positive outcomes (optimistic)
- The green hat will focus on reducing criticism and increasing ideas (creative)
- The blue hat will focus on management and organization (control)
The 5 whys is an example of a root cause analysis tool. The purpose of using this problem-solving technique is to find the exact reason a problem is occurring by asking a series of “why” questions. After asking why five times, the cause of the problem and its accompanying solution should be clear.
Start Implementing Solutions to Problems Today
You don’t need to feel overwhelmed and confused when a problem arises anymore. Stress and unhappiness are simply byproducts of how you respond to those situations. Instead, you can look at each problem or difficulty by asking, “What is the opportunity in this?”
When you enhance your problem-solving skills, you will experience determination and a sense of calmness when the next difficult situation arises.
While you may not know how to resolve most issues right away, you will know the problem-solving steps to take to uncover the best response: Define the problem, determine the cause, discover the best problem-solving technique, take action, and analyze the outcome.
Follow this process over and over again and you will creatively solve your problems. After all, an effective way to solve problems is a skill that you can develop with practice.
To help you enhance your success, download my free SMART Goals Template . This resource is a good fit for someone who wants to achieve their goals and optimize their success. I walk you through how to set goals and plan ahead the right way. As you advance your problem-solving skills, you will experience more success in your daily life—for big-picture items and small ones alike.
« Previous Post How To Negotiate A Raise The Effective Way Next Post » How To Trust Yourself And Build Real Self-Confidence
About Brian Tracy — Brian is recognized as the top sales training and personal success authority in the world today. He has authored more than 60 books and has produced more than 500 audio and video learning programs on sales, management, business success and personal development, including worldwide bestseller The Psychology of Achievement. Brian's goal is to help you achieve your personal and business goals faster and easier than you ever imagined. You can follow him on Twitter , Facebook , Pinterest , Linkedin and Youtube .
- Most Recent
- How to End a Speech: What You Need for a Bang
- Goal Setting for Success & Developing SMART Habits
- 15 Simple Ways to Be Successful in Life
- How to Start a Speech: The Best Ways to Capture Your Audience
- How to Develop Self-Discipline to Succeed
- Free Webinar: How To Write a Book and Become a Published Author
- Free Video Series: 3-Part Sales Mastery Training Series
- Free Assessment: The Confidence Factor
- Free Assessment: Discovering Your Talents
Browse Categories
- Financial Success
Follow Brian & Join the Discussion
- Free Resources
- Best Sellers
- Knowledge Base
- Shipping & Returns
- Privacy Policy
- About Brian
- Brian Recommends
Your Privacy is Guaranteed. We will never give, lease or sell your personal information. Period!
© Copyright 2001-2024 Brian Tracy International. All Rights Reserved.

Problem Solving – How To Tackle Life’s Problems

Life is a constant struggle. Each one of us faces problems in his/her life in one way or another. In order to lead a happy and successful life we have to be a good problem solver. Problem solving skills are one of the basic life skills required to survive and succeed in this competitive and hard world.
What is Problem Solving?
Problem solving is the process that involves your abilities to resolve an issue and come out with a feasible solution. Every individual has his/her own way to solve or deal with the problems they encounter:
- Some of us learn from real life examples or observing other people handling similar situations.
- Others learn to deal with problems on their own when they actually face them in practical life.
- Now, the question is, whichever way we learn and choose to solve our problems, is it easy solving problem in day-to-day life or, do we FACE PROBLEMS while SOLVING PROBLEMS.
Whenever we face a problem or a challenge in life, however big or small it is, we do go through certain stages of problem solving mentally:
- To begin with, we identify the problem.
- Then, we look for possible solutions to deal with the problem.
- Next we choose the best possible solution which will work best in that problem situation.
- Finally, we implement the best solution to overcome our problem.
Apart from these stages, we should also be able to look at the following qualities of becoming an effective problem solver:
- Determination to solve a problem
- Remaining calm and patient while dealing with a problem
- Taking problems as a challenge
- Being analytical, thoughtful and creative
- Adequate information of possible solutions
- Ability to implement the best solution appropriately
Robert’s older brother wanted to buy some electronic spare parts for his computer urgently, but he had to go out for a meeting, so he asked Robert to go and get them for him. He wrote the specifications on a piece of paper and left. Robert left for the electronic store after some time had passed. The market was at a distant place and it took him more than an hour to reach there. After reaching the store, he realized that he had left that paper mentioning the details at home. He panicked and without thinking about a solution to this problem, he went back home, got the paper and came back to the electronic store. By the time he reached the electronic store again, it had already closed for the day. He returned home empty-handed. His brother was back and asked him what took him so long. Robert narrated the whole incident to his brother. His brother got upset, but then he told him, instead of coming back home to get the paper, if Robert would have called him and asked him about the details, then he would have told him again and it would have saved him from this trouble. Robert realized that he did not look for an alternate solution for his problem. If he would have done so, it would have been lot easier for him.
We all have different ways of looking at our problems and we solve them according to our own sensibilities.
But we should always remember that when we are stuck in a problem situation, it is always good to think of possible solutions to solve our problem and then apply the best one for that situation.
Using such an approach helps explore different ways of problem solving and we become more thoughtful, analytical and creative. Remember, when we face a problem and successfully solve it, we become more confident in ourselves, grow as a person, and become more independent in handling our lives.
- personal skills

About the Author
Varsha tyagi.
Varsha Tyagi is a Master's in Psychology with 5 years of Experience as a Life Skills Coach and a Counseling Psychologist. She has worked with many schools, colleges and corporates as a Counselor and a Life Skills Trainer and dealt with both children and adults. She is currently working as a Life Skills Facilitator with an organization.
Leave a Reply
Video courses to transform your life, popular blogs.

Popular Tracks
UserID (EmailID)
Remember Me
How To Solve Problems In Life [All Of Them]: The Definitive Guide
This article has everything you need to know about how to solve problems in life. The problem solving process involves the ability to logically think through a situation or issue in search for a solution(s) to solve the problem. A problem is a gap between a current condition of what is and what must be, should be, or could be.
A problem exists when situation in life fails to meet the expectations of what a person wants in his or her life. The principles needed for increasing the wanted outcome in life, are identifying the problem, and fixing the problem with improve or new solutions. Problem solving and decision making can involve any issue or task that needs to be resolve.
How To Solve Problems In Life:
The first rule of problem solving.
The first thing to do is to define the problem and make sure it is a real problem, particularly your problem and not someone else’s problem or someone else’s fault. Approaching the problem for answers using the what, where, when, why, how and who questions of the current situation.
If the problem is too big or overwhelming, step back and stay calm, and analyze small pieces of information pertaining to the problem. Manage the problem using levels of priorities pertaining to which one needs to be addressed or responded to first using common sense and learned procedures or training. Remember there is nothing new under the sun and keep a positive mind and approach that the problem can be solved and may take time.
Analyze the problem from all angles is very important in clearly defining the problem and ensuring that best solutions to be presented. Collect all the information as you can about the problem to continue to analyze the extent of the problem and do not make any early impulsive decisions for final solution. Use self-discipline and write down a list of solutions that may be used while you are brainstorming.
Get the agreement from all the people involved in the problem solving process, establish a task schedule and time frame to continue to monitor the progress for an evaluation of the outcome to see if the solution is working.
Steps for Problem Solving
1. define and identify the problem, 2. analyze the problem.
In this stage of problem solving, questions should be asked and information gathered and sifted. It is essential to spend some time researching the problem.
Questions to Ask When Analyzing the Problem:
3. Identify Possible Solutions
Viewing problems from a different perspective.
As a leader, you can’t be surprised by problems. The best you can do is to be prepared for them. One of the ways a leader prepares is to have the right perspective when problems occur. The questions you ask about the problem has a way of shaping the perspective you have toward the problem. What do I need to do differently to solve this problem? What is keeping me from solving this problem? What will solving this problem make possible? What kind of story do I want to tell a year from now about this problem?
Solving Problems as a Leader
Are you a leader or a follower? When faced with a difficult problem, how do you react? How you face problems is one of the critical factors that help determine how successful you will be in life. It is also one of the key qualities of a leader! Leaders solve problems – followers go to leaders to get their problems solved.
The examination of the facts will help you find a better solution. Decide if this really a problem that needs solving? How bad is the problem? What is the worst thing could happen if the problem is ignored? If the problem does need solving, what actions are needed to solve the problem. Brainstorm all the ideas and write them down to use for solutions to solve the problems in the future.
If the problem is too big, seek assistance from support teams. Know when to let go of problems and used systematic approaches to solve your problems. Break the problems into small steps and components to track the progress of each one at a time. Test and monitor the solutions that are implemented, and do not be frustrated by any setbacks or failures, but continue to solve problems with integrity and honesty.
Solving Problems Effectively In Marriage/Relationships
Conflict happens; it’s a normal part of any relationship. Problems themselves are not necessarily a sign that a marriage or relationship is in trouble. Dealing with problems in unhealthy ways, however, is a signal of a troubled relationship. If a couple cannot develop an effective strategy for addressing problems, the result will be a backlog of unresolved issues, leading to bitterness, resentment and the breakdown of the relationship.
Problem Solving With Teenagers
As children become teenagers, they’ll come across problems they need to sort out themselves. You won’t always be there to give your child advice, but you can help him develop skills and strategies so he can solve problems on his own. Everybody needs to solve problems every day. But we’re not born with the skills we need to do this – we have to develop them.
I want to thank you for taking the time to read my article about how to solve problems in life. I sincerely hope its contents have been a good help to you.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
How to create a more present-focused life: 14 practical ways, how to develop thick skin and become mentally tough: 14 ways, how to take control of your life back: 22 simple strategies, how to have a perfect lazy day: best 12-step guide, how to stop obsessing over something that happened: 11 tips, how to increase your willpower and determination: 14 tips, how to become more diligent person: 15 fulfilling tips, how to stop feeling like a failure: 17 healthy strategies, how to explain things better: 13 effective tips and techniques, how to think clearly and logically: 20 quick strategies, how to practice non attachment in relationship: 17, how to think like a genius: 13 powerful strategies.

Creative Problem-Solving Approach: Skills, Framework, 3 Real-life Examples
What is creative problem-solving, creative problem-solving framework, 3 real-life examples of creative problem solving:, skills to develop for creative problem-solving.
Other Related Blogs
- Finding a new solution for a recurring issue at work
- Generating new marketing ideas for an upcoming product launch
- Coming up with unique ways to engage employees during meetings
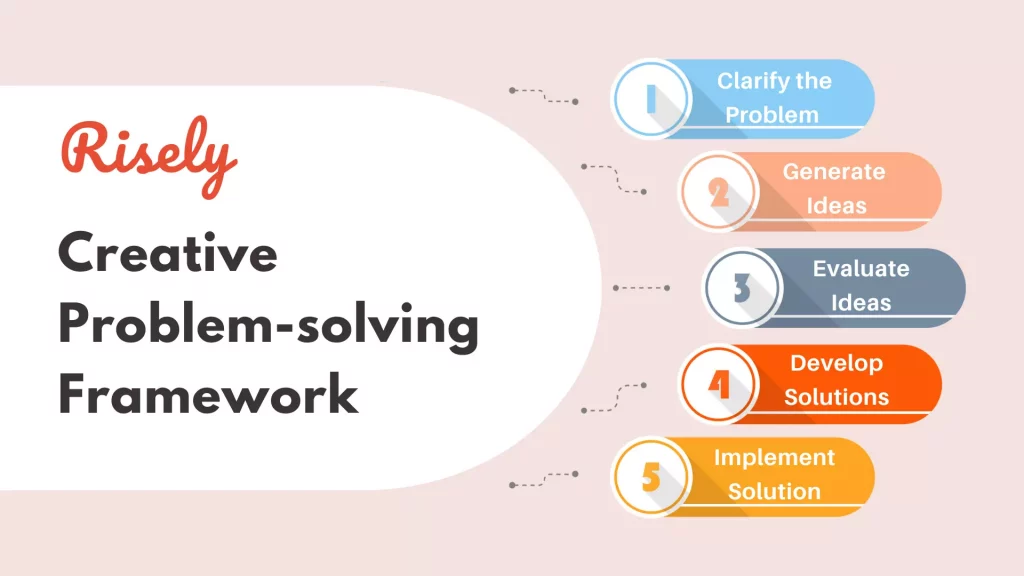
- Identifying the Real Problem : Imagine you wake up to a cold shower. The obvious problem? No hot water! But before you start dismantling the showerhead, take a step back. Is it a faulty heating element, a low thermostat setting, or a bigger issue with the building’s plumbing? This initial step is crucial. Ask yourself questions like “What are the symptoms?” and “When did this problem start?”. In our shower scenario, identifying the root cause (a faulty heating element) saves you time and unnecessary tinkering.
- Generating Wild Ideas : Now, it’s time to unleash your creativity! Remember that brainstorming session in school where every idea, no matter how wacky, was welcome? That’s the spirit! Back to our chilly shower situation, ideas might include: boiling water on the stove for a makeshift bath (not ideal!), calling the landlord for repairs (the most likely solution!), or – if you’re feeling adventurous – installing a solar water heater (hey, it could work!).
- Evaluating Ideas: Okay, so you have a list of ideas, from the practical to the downright peculiar. Here comes the filter. Evaluate each idea based on realistic criteria. For the shower scenario, fixing the heating element is likely the most feasible and impactful solution. While a solar water heater might be innovative, the cost and practicality might not make it the best choice at this moment.
- From Idea to Action Plan: We’ve identified the best course of action (fixing the heating element). Now, it’s time to develop a concrete solution. This might involve calling a plumber, gathering the necessary tools, or researching DIY repair tutorials (if you’re handy!). The key is to create a clear plan that addresses the problem directly.
- Putting Your Solution to the Test : The plan is in place, it’s time to implement! In our case, this means calling the plumber and getting that heating element fixed. Once the repair is done, take a celebratory hot shower! But remember, even the best plans can have hiccups. If the hot water issue persists, you might need to re-evaluate your initial diagnosis or call the plumber back for further troubleshooting.
- 12 Effective Practices For Becoming Learning Leaders To Encourage Learning
- 37 Constructive Feedback Examples to Supercharge Your Leadership
- Identifying & Breaking Your Learning Plateau: The Top 5 Tips
- 5 Benefits Of Becoming A Mentor In The Workplace For Managers
- Coaching Employee with Negative Attitude to turn them around in 5 easy steps
- Social Intelligence: Building Strong Workplace Relationships as a Leader
- 5+ Examples & Tips Of Goal Setting For Managers At Work
- 8 Steps Managers Should Take When A Team Member Leaves
- 5 Reasons to Leave Behind One on One Leadership Coaching Today
- How Persuasive Management Style Helps You Succeed: 5 Examples And Benefits
- Netflix: The company revolutionized how we watch TV shows and movies. However, when the company started, it faced a big challenge – getting people to watch their content when they were not a well-known brand. Instead of relying on traditional advertising, Netflix used creative problem-solving to develop a unique solution. They created an algorithm recommending TV shows and movies based on a user’s viewing history, leading to a highly personalized viewing experience. This recommendation engine became a critical factor in the company’s success, helping them attract and retain customers.
- NASA: NASA had to devise an instant solution to save the Apollo 13 mission and their team. Their spacecraft was damaged, and they needed a solution to bring their astronauts safely back to Earth. The team fitted a square CO2 filter into a round hole using available materials on the spacecraft; the team used creative problem-solving to develop this approach. This innovative solution allowed the astronauts to return safely to Earth and set this incident as a classic creative solving example.
- IKEA: IKEA makes stylish and affordable furniture and is a well-versed company. However, they faced significant challenges entering the Japanese market. Japanese apartments are comparatively smaller than the rest of the world, so the regular product range was irrelevant to Japanese customers. So, IKEA used creative problem-solving to develop a solution appealing to the Japanese market. They launched a variety of products specially created for smaller spaces that are easy to assemble and disassemble—they also introduced a range of futons designed to look like beds, appealing to Japanese customers who prefer sleeping on the floor. This innovative and creative approach helped IKEA successfully enter the Japanese market.
- Flexibility: Being able to adapt to changing circumstances and consider multiple perspectives.
- Open-mindedness: Being open to new ideas and willing to challenge assumptions.
- Curiosity: Seek more information by questioning and better understanding the problem.
- Persistence: If a solution does not work, apply another solution, but continue until the problem is solved.
- Divergent thinking: Generating multiple ideas and exploring different possibilities.
- Convergent thinking: Evaluating and selecting the best ideas based on specific criteria.
- Visualization: Using mental imagery to explore solutions and ideas.
- Collaboration: Working with others to combine different perspectives and knowledge.
- Risk-taking: Being willing to take calculated risks and try new approaches.
- Innovation: Combining ideas and approaches in novel ways to create new solutions.
Evaluate your problem-solving skills for free now
Take the free problem-solving assessment by Risely to get started on your journey.
What are the five steps in creative problem-solving?
What are the 4 ps of creative problem solving, is creative problem solving a skill, how is creative problem solving a logical process.

Top 15 Tips for Effective Conflict Mediation at Work
Top 10 games for negotiation skills to make you a better leader, manager effectiveness: a complete guide for managers in 2024, 5 proven ways managers can build collaboration in a team.
16 Critical Thinking Examples in Real Life
What is critical thinking.
While making your academic assignments or thesis, you are required to do some research and analyze various things, or for making a career decision or any other decision you are required to think of all pros and cons of that decision. Well, the most important thing that helps us to effectively take these decisions is what we call critical thinking. Critical thinking is very important in both personal and professional life. The process of critical thinking involves the analysis of the various facts and figures in a particular situation before straightaway acting on that situation. Critical thinking demands keen observation, creativity, problem-solving skills, which helps the individual to thoroughly evaluate the gathered information and then use this available information as a guide to making accurate decisions. From doing academic works or regular activities to solving various large scale problems, critical thinking is required in everyday life. In this article, we will learn about some real-life examples where critical thinking plays an important role.
Critical Thinking Examples in Real Life
1. critical thinking in problem solving.
Suppose your manager asks you to find an effective solution to a problem that is affecting the business. What would be your first step? Like most people, you may also start looking for potential solutions to deal with that situation. Well, one requires the use of critical thinking here. Before looking for the solution one needs to take a step back and try to understand the cause of the problem first. One should ask for the opinions of the other people that how does this particular problem impact them and the overall business. If you arrive at a solution, you should not only just rely on one solution, instead, you should always have various backup plans in case the first solution does not work as expected. Most people feel that they are great at problem-solving, but if one is not following all these above discussed steps before making a final judgement, he/she is not a critical thinker. Critical thinking allows people to find the best possible solution to any problem. Critical thinking is an important factor of problem-solving skills, one needs to look at any situation from multiple perspectives because in some cases, your decisions not only impact you but also the people in your surrounding.
2. Critical Thinking in Analysing Risks
Risk assessment is another important factor, which requires the use of critical thinking. Risk assessment is required in various sectors, from children analysing the impact of eating junk food on their health to large businesses in analysing the impact of certain policies on the growth of the company. Let us understand the implication of critical thinking in analysing the risks with some examples.
3. Critical Thinking in Data Analysis
Whether analysing the performance of the children in the schools or analysing the business growth of a multi-national company, the skill of data analysis is very crucial. In today’s era, almost every sector demands experts that can accurately evaluate the available data or information and draw out effective conclusions from it. With the rise in technology, the various tasks of the data analysis such as finding profit and loss, creating balance sheets, and issuing invoices are done with the help of various software, but it does not mean that human skill is not required. Various kinds of software can just convert a large amount of data into some simpler and readable format, but it is the critical thinking of the humans that is required to effectively interpret the data and apply the obtained insight for the benefits. The data analysis can even help us to estimate the future trends and potential risks of taking any decisions.
4. Critical Thinking in Hiring Employees
The ability to objectively view any situation without getting influenced by your personal beliefs or thoughts is one of the important characteristics of critical thinking. In business, the hiring managers require critical thinking to evaluate a large number of resume’s to choose the suitable candidates for the required position. Critical thinking here enables the hiring managers not to hire a candidate on the basis of various factors like gender, age, religion or country, these factors may influence the hiring managers unconsciously. The hiring manager may tend to choose the candidate on his/her subjective beliefs if he/she does not use critical thinking. Hence, critical thinking can help HR’s to hire the best employees that may eventually lead to the growth of the company.
5. Promoting the Teamwork
In a team, every individual is unique and has his/her different ideas to tackle the proposed problem. It is the responsibility of the team leader to understand the perspective of each member and encourage them to work collectively to solve the common problem. You may find the opinion of the other members of your team as ineffective, but instead of straightway denying their opinions one should logically analyse their suggestions and try to put your point of view regarding the problem in an effective and calm manner. If the team leader does not use critical thinking, instead, he/she boost his/her opinions on others, the team is sure to collapse.
6. Critical Thinking in Self-Evaluation
Critical thinking plays a major role in self-evaluation. The knowledge of critical thinking skills allows you to accurately analyse your performance by controlling various subjective biases. People should always evaluate their reactions towards any situation and the way they think, this may help them to get a deep insight into their thought processes, hence improving their thinking abilities to take accurate decisions. Self-evaluation is very important in professional life too. Suppose your manager has set a new target for the company. Every employee is thus required to analyse his/her contribution to the company and try to accomplish the set target. If you know your contribution to the company, it will help you to analyse your performance, and you can try to improve your performance in the areas where you lag.
7. Critical Thinking in Choosing the Career
Almost all of us face various dilemmas in our lives such as choosing the stream, the type of job, choosing between the regular college degree or the online programme. Whatever you choose, every option has its pros and cons. However, critical thinking allows us to accurately weigh the positives and negatives of each option and choose the one that offers more benefits than drawbacks. The best way to do this is to make a list of the pros and the cons and then analyse. Well, this is not just limited to choosing the career path, it can be used in other situations also such as professionally, and financially. One can list the pros and cons of selecting to work in a specific company or choosing the right insurance plan. It is often seen that our choices are greatly influenced by the choices of our friends or known, but one should understand that every individual’s beliefs, desires, and ambitions are different so, if the particular carrear or job is best for the others it does not mean that it would be the best option for you also. Hence, to choose the right carrear path, one requires critical thinking.
8. Critical Thinking in Time Management
Time is the most valuable asset that we have, hence utilizing it appropriately is very crucial. Critical thinking in time management helps you to wisely plan your schedule according to the importance of the particular task or the activity. For example, if the task to which you devote most of your time, is not giving you much return then you need to reconsider your schedule and should devote more time to the tasks that give you high returns.
9. Critical Thinking in Analysing the Fake News
Suppose, one of your friends shares a piece of news with you. Do you bother to analyse that whether this piece of news is real or not? Many of us just believe in the news and shares this with others too without thinking that this can be fake news too. A study conducted by Stanford University showed that around 82 per cent of the teenagers failed to distinguish between the real news and the advertisement with the ‘sponsored content’ label. This problem arises because the standard education curriculum does not emphasise much on critical thinking skills much because of the assumption that critical thinking is inbuilt in every person. By introducing certain lessons or activities that may help to increase the knowledge or overall thinking skills, the critical thinking of the children can be improved. Well, it is also seen that not only children, but adults also fall for these fake news and articles that circulate on various social media platforms. Before believing any piece of information, one should think of various questions like the source of the publication, the intention of the article, the author of the article, and the agenda behind the article. Critical thinking helps us to precisely evaluate any information before straightway believing it.
10. Critical Thinking in Distinguishing between Right and Wrong
Most people, especially teenagers are very much conscious about what their friends or relatives think of their behaviour. You may have had been through the situation, wherein if your friends think that certain behaviour is cool then you start acting in that way to fit in your friend’s circle without even considering that what you are doing is good or bad, and is your actions are related to your beliefs or not? One should understand that if a certain behaviour seems cool to some people, it may also seem bad to some others. One should not change his/her actions depending upon the approval of certain people, rather one should look at the broader aspect and should deeply analyse that whether their actions are morally right or wrong.
11. Critical Thinking in Decoding Fashion Trends
Nowadays, some people are so crazy about following the latest fashion trends, they start following every trend that some popular actor, actress, or fashion influencer suggest. If you are a critical thinker you may have had thought of the questions like why the particular trend that was so popular a few years back seems foolish now? why does a particular trend that does not even look good is so popular? Do the particular fashion trend that suits the other person suits yourself or not? Critical thinking helps people from falling victim to the bandwagon fallacy; it is fallacy in which people starts believing a particular thing or idea as good or bad if the majority of the population thinks so. Fashion trends are a common example of bandwagon fallacy.
12. Critical Thinking in Choosing the Suitable Diet and Exercise
You must have heard of various types of diets such as the Keto diet, Whole 30 diet, Gluten-free diet, Vegan diet and so on. It seems complex to choose the diet that is best for you. What people usually do is that they search online, go through several videos and choose the diet that showed the best results to the person in the video. Well, this is not the right approach, choosing the best diet for yourself requires critical thinking. People who use critical thinking evaluate the pros and cons of the particular diet on their own body, they generally ask about the suitable diet from professional dieticians rather than just following the advice of a random person online. Like choosing a suitable diet, choosing a suitable exercise also demands critical thinking. For example, What are your goals? How can you achieve this? At what time you can do exercise? Do you have any injuries that may get affected by the particular exercise? People who use critical thinking tend to ask all these questions, and then by utilizing the knowledge they have and the following routine for a few weeks, and by analyzing the results they are getting from it, they finally plan a proper schedule for them.
13. Critical Thinking in Online Shopping
In today’s digital era, online shopping is preferred by most people. However, there are various tactics and psychological tricks such as the anchoring effect , Stroop effect , and Serial position effect that are used by the various e-commerce websites, which makes the customers buy more things or things that they don’t even need. Critical thinking can help people to smartly buy items without falling victim to all these effects or tactics. While making the purchase you should focus on the price that you are paying for the particular item rather than the discount you are getting on that item because the chances are that the price that you are paying for that item is not worth paying even after the discount.
14. Critical Thinking in Job Search
Critical thinking plays an important role in the Job search. If you are applying for a job, you may consider the following points to get the desired job.
Use of Keywords in Resume: One should always understand the job post and its requirements before straightaway applying for the job. It is important to update your resume according to the job and add some keywords (mentioned in the job requirements) into your resume to get the job. If you possess some critical thinking skills such as problem-solving, analytical, communication, or creativity skills, it is better to put that in your resume. However, one should always restrain from adding any random critical thinking skills that you do not possess.
Cover Letter: Hiring managers receive hundreds of resumes daily, hence the chances that they will read every resume are quite less. Well, you can make your resume different from others by adding a good cover letter. You can add some of the critical skills that you have to your resume, it is better to explain a little about the tasks or activities where you showed these skills in your previous jobs or work experiences rather than just simply writing the skill. This assures the recruiter that you are not randomly writing the skills and you possess these qualities.
Interviews: Nowadays, some interviewers present the interviewees with hypothetical stories to check their critical thinking skills. You may be asked to explain what you think of the given situation or your first reaction after looking at the given image. You are required to solve any random problem, and then you have to explain to the recruiter about your thought processes. The interviewer here is more focused on the way you reach the conclusion rather than the conclusion itself. Your thought process helps the interviewer to analyse and evaluate the way you approach various problems
15. Critical Thinking While Driving
Imagine you are driving on a busy road and your phone starts ringing. It’s an urgent call that you have to pick. What would you do? Would you pick up the call and risk yourself into an accident or stop your car on the roadside to take the call. Critical thinking helps you to make accurate decisions while driving, it includes finding the right place to park your car, analysing whether you can pass the car through that narrow street or not, or how to handle if any animal suddenly comes in front of your car. Hence, critical thinking is must require skill in driving.
16. Critical Thinking in Business
Critical thinking is one of the most important things that the owner of the business needs to possess. One has to make several important decisions, effectively communicate with the clients, hire suitable employees, take certain risks, and deal with several ups and downs in the business, and much more; all these things require critical thinking.
Related Posts
Role Morality
Social Cognitive Theory
Freud’s Psychoanalytic Theories Explained
Vision Statement Examples for Students
15 Acts of Altruism Examples
10 Real Life Examples Of Gestalt Principles
Great post! I’ve been trying to apply critical thinking to my life, and these examples are a great way to start.
critical thinking is what anyone of us should have in spoiled world
Add Comment Cancel Reply

You are here
Pattern recognition and use in real life problem solving.

Pattern recognition forms the basis of learning and action for all living things in nature.
Patterns are all around us - from human fingerprints, zebra crossings, warm current flows in oceans to the beautiful arrangement of a rose bud.
A baby begins to recognize various objects around it, learns how to react on events in its immediate environment and finally recognize, understand and respond to the words spoken to it - all by identifying patterns, associating the patterns with objects or concepts and use the concepts for responses leading to positive results.
Learning to speak in the language used in its immediate environment is one of the most difficult tasks effortlessly performed by every baby - that too without any teacher.
Pattern recognition and use continue throughout our lives. Our learning ability depends on how strong is our ability to identify a new useful pattern and use it suitably.
When a child goes to school first it learns new behavioral patterns to adapt to. When you take up a new position in your workplace, you have to acquire new patterns necessary for functioning effectively in the new position. Sometimes you change track in your career and go into a totally new but promising area. How can you be effective unless you learn all the required concept patterns in your new work domain?
We use the Pattern recognition technique all the time involuntarily and sometimes voluntarily or consciously in our daily life. When we navigate the city streets by car, we try to identify whether the streets are in a two axis grid or a star shaped formation. When we are to find a particular house in a street we see whether the numbers on one side of the street are even or odd, increasing or decreasing.
In emergent decision making situations of fire fighting or in a battle, the fighters don't have time to think, they must continuously act instinctively on the input patterns from the immediate environment and with the help of response patterns learnt through training, drills or earlier experiences embedded in their reflexes.
Pattern discovery in problem solving
Case example 1: can you solve it.
Find the unit’s digit of $2^{23}$.
Before going through the solution, please try to solve the problem for 10 minutes.
At first thought you might want to use your calculator, but on second thoughts and being a problem solver, you will start analyzing the problem systematically instead. A problem solver adopts trial and error method, if at all, only as a last resort.
What actions are available to you? You know from experience that no calculator will take such a large calculation. Can you do anything else?
You examine the problem more closely and realize that full calculation is not to be done at all , only the single unit’s digit is to be found out. Now you have a clear and precise problem definition. This step is very important. You are actually adopting a problem solver’s approach. You are not trying to solve the problem in any random way.
The main problem is now transformed to a simpler problem of finding one digit, and not the whole result of 2 to the power 23.
Searching for suitable further actions, and finding none that are obvious, you resort to the enumeration technique that can always be done by you. You start enumerating the results of $2^{1}$, $2^{2}$, $2^{3}$ and so on. A powerful principle of problem solving says,
If you find no promising action that can be taken at a stage except one, take that step and see what happens.
$2^{1} = 2$ with units digit 2, $2^{2} = 4$ with units digit 4, $2^{3} = 8$ with digit 8, $2^{4} = 16$ with units digit 6, $2^{5} = 32$ with digit 2, $2^{6} = 64$ with digit 4.
Here you stop and form a conjecture that after every 4th power of 2, its units digit is repeating the same four values again. The all important 4-length repeating cycle of units digit values being, 2, 4, 8 and 6.
You test and verify your conjecture by calculating a few more powers of 2 and confirm that your conjecture was indeed right.
This is test and discovery of the repeating pattern of digits that is crucial to solving your problem.
The last step is easy. You divide 23 by 4, the length of the repeating cycle, getting remainder 3 and quotient 5. So, you clarify the situation in your mind, "units digit of $2^{23}$ will be the third value of the repeating 6th cycle of 2, 4, 8 and 6.
The answer is then 8.
In academic problems, specially in maths or reasoning where the problem solving capability of a candidate is tested, useful pattern discovery in the problems is vitally important.
We believe, pattern discovery is important not only in academic problem solving but also in dealing with complex real world problems. After all, patterns are so very integrated in every fabric of nature and human life, it should also be an important component of any real life problem. And if you can discover such a pattern in your problem, your problem understanding not only gets a big boost, problem solving using methods based on the pattern discovered comes within reach.
Pattern recognition in language understanding
Case example 2: can you read it.
I cnduo't bvleiee taht I culod aulaclty uesdtannrd waht I was rdnaieg. Unisg the icndeblire pweor of the hmuan mnid, aocdcrnig to rseecrah at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it dseno't mttaer in waht oderr the lterets in a wrod are, the olny irpoamtnt tihng is taht the frsit and lsat ltteer be in the rhgit pclae. The rset can be a taotl mses and you can sitll raed it whoutit a pboerlm. Tihs is bucseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey ltteer by istlef, but the wrod as a wlohe. Aaznmig, huh? Yaeh and I awlyas tghhuot slelinpg was ipmorantt! See if yuor fdreins can raed tihs too.
This text appeared somewhere during late nineties and soon attained enormous popularity. Can you read it effortlessly? Most probably you can. The jumbling of the letters in the individual words pose no barrier to your recognizing the original words in the jumbled text.
As explained in the text, keeping the first and the last letter of every word untouched, all the other letters in every word have been scrambled randomly. But your mind ignores this scrambling and effortlessly identifies each of the words and continues to read the whole passage without any significant hitch.
Have you followed any special techniques or methods to achieve this seemingly impossible task? Nope. At least you don't know consciously of any such technique. You just read through.
This example shows inherent pattern recognition power of your mind in language understanding and is in the domain of Cognitive Science or Artificial Intelligence.
Case example 3: Can you read it?
This example has also used the same principle of letter scrambling, but with a twist. Please try it for some time. It is not easy. If you still are able to read the whole text correctly, then you must be having significantly higher pattern recognition power compared to common people like us.
The solution is given after the discussion on this text. Here goes the problem text.
Anidroccg to crad–cniyrrag lcitsiugnis planoissefors at an uemannd utisreviny in Bsitirh Cibmuloa, and crartnoy to the duoibus cmials of the ueticnd rcraeseh, a slpmie, macinahcel ioisrevnn of ianretnl cretcarahs araepps sneiciffut to csufnoe the eadyrevy oekoolnr.
The difficulty level of understanding the text has been increased significantly by introducing a pattern in the scrambling operation itself. It is no longer random. Can you discover this hidden pattern in scrambling of letters of each word keeping the first and last letters fixed?
In this case, you can take up the role of problem solver again, and examine suitable words to discover the fixed pattern of scrambling hidden in them. If you are able to find the pattern, you can immediately unscramble the whole text.
We find this example interesting as, using it you can test your
- inherent pattern recognition ability in language understanding, and also
- problem solving ability using pattern discovery.
Give it a serious try and then proceed with the solution.
Pattern: Instead of random scrambling, the letters between the first and the last were just inverted - a simple action resulting in powerful effect.
The original text is,
According to card-carrying linguistics professionals at an unnamed university in British Columbia, and contrary to the dubious claims of the uncited research, a simple, mechanical inversion of internal characters appears sufficient to confuse the everyday onlooker.
Examining this text further we notice that the words in the text are not very commonly encountered ones in everyday use - many of these are quite uncommon. This leads us to the first conjecture ,
For understanding scrambled running text using inherent pattern recognition, familiarity with the words is essential.
At least once you should have seen a word to be able to unscramble it.
Analysing further, we notice that the degree of familiarity is an important factor in our ability to unscramble. Though trivial, we note this as our second conjecture ,
Degree of familiarity increases the ease of unscrambling scrambled words using inherent pattern recognition.
Exploring further we ask, won't you find it easy to decipher a running text instead of a fragmented text? This is the area of meaning of the sentences as a whole, not just a few words carrying no meaning. This leads us to the third conjecture ,
Associative meaning of the words together forming meaningful sentences helps understanding scrambled text using inherent pattern recognition.
Learning a language: Our experience supports this idea. When we read a novel, we encounter some words never seen before. From the meaning of the surrounding text we guess the meaning of the unknown words and form the vague idea as a concept in our mind. Later in another occasion when we encounter the word again, our mind automatically tests the validity of our concept about the word and either strengthens or weakens the belief on the concept earlier formed.
A sure way of learning a new language is to read its literature or long text that is especially interesting to you.
Coming back to the case example again, we now state our fourth conjecture.
The first case example of scrambled text is easier to understand because it used random shuffling of the letters inside two boundary letters in each word, whereas inversion of the lettters inside in the second case example increases the distance between a letter in scrambled word and its original position compared to the random shuffling. This increased distance created an increasing mismatch between the new pattern and the old pattern of a word and made the pattern matching activity more difficult.
At the end we need to reiterate, Pattern recognition and corresponding decision making are at the heart of human decision making. In most situations, this process is involuntary, but in many cases, we may be able to reach a just solution by explicitly searching for a pattern in the given problem world.
Most experts work on pattern recognition basis and most emergent decision making are basically pattern based and thus intuitive and instantaneous.
By working on your pattern recognition skills it should be possible for you to improve its power and so your ability to solve everyday problems.

Using Math in the Real World
There’s a popular math meme that says, “Math: The only place where people buy 60 watermelons and no one wonders why.”
After a chuckle, you might realize there’s some truth to this joke. Sometimes, it may seem like math has nothing to do with the real world. In fact, it’s likely your students have asked you, “Why do I need to know this? When will I ever use this in real life?”

Of course, as a teacher, you know that math matters. Making math relevant to your students can be challenging, however.
You can talk about the importance of learning addition, subtraction, statistics, geometry, algebra, and more , but your students might not see the real-world applications. The truth is, we all need math. Math teaches us how to solve problems , a skill that’s useful in all career fields and just for navigating everyday life.
So, how can you make math relevant to your students? Try these examples of math in the real world.
Cooking and baking are great ways to show your students how math applies to life outside of the classroom . Lead your students in reading recipes, discuss fractions, and talk about how to double a recipe or cut one in half. Then, reward their hard work with a hands-on lesson. Try this classic recipe that will let them get sticky while they learn!
- Checks and Balances
Create a checkbook system in your classroom, where students can learn how to balance a bank account—a real-world skill we all need! Make your own “classroom dollars” and give them opportunities to spend and save throughout the year, from renting their desks monthly to earning cash for good behavior. They’ll practice basic math in the process, and, if you end the unit with the opportunity to purchase items with their hard-earned money, you’ll teach them the value of saving and budgeting.
- Buying Power
After your class has earned classroom dollars throughout the year, hold a yard sale or class auction. Have students donate items and let them spend their money however they’d like. Add to the challenge by announcing discounts—“everything’s 30 percent off for the next 10 minutes”—and let them do the real-world math to see what the new price would be.
- Measure for Measure
Many jobs, from construction workers to architects, require accurate measuring skills. Measuring and math go hand-in-hand, and you can up the fun factor in math by setting your students free throughout the classroom—or even the school. How tall is the principal? How long is the hallway? What’s the square footage of the gym? The possibilities are endless.
- Map a Course
With GPS as a regular part of our daily lives, many students have lost the art of reading a map . Map reading uses math skills, too, requiring an understanding of scale, coordinates, distances, fractions, and more. Chances are, your students have never really had to use a map to get anywhere. Go on a virtual field trip by following a map to your favorite destination, and practice math in the process.
Shop ’til You Drop

Make problem solving meaningful for students. Lessons feature kid-friendly topics such as movie marathons and summer fun to reinforce problem solving skills and understanding of math in daily life.
- Shop 'til You Drop
520 East Bainbridge Street Elizabethtown, PA 17022 Phone: 800.233.0759 Fax: 888.834.1303
- Privacy Policy
©2024 Continental. All Rights Reserved.
Found the perfect materials for your classroom? Email your shopping cart to your school/district contacts to request purchasing approval. Step #1: Save My Cart Step #2: Personalize My Email

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In insight problem-solving, the cognitive processes that help you solve a problem happen outside your conscious awareness. 4. Working backward. Working backward is a problem-solving approach often ...
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
Here are 10 everyday uses for problem solving skills that can you may not have thought about. 1. Stuck in traffic and late for work, again. With busy schedules and competing demands for your time, getting where you need to be on time can be a real challenge. When traffic backs up, problem solving skills can help you figure out alternatives to ...
Problem-solving is an essential skill in our daily lives. It enables us to analyze situations, identify challenges, and find suitable solutions. In this article, we'll explore five real-life problem-solving scenarios from various areas, including business, education, and personal growth.
Problem-solving is a vital skill for coping with various challenges in life. This webpage explains the different strategies and obstacles that can affect how you solve problems, and offers tips on how to improve your problem-solving skills. Learn how to identify, analyze, and overcome problems with Verywell Mind.
Here are the seven steps of the rational approach: Define the problem. Identify possible causes. Brainstorm options to solve the problem. Select an option. Create an implementation plan. Execute the plan and monitor the results. Evaluate the solution. Read more: Effective Problem Solving Steps in the Workplace.
Make sure to try out these skills whenever you can. Practical problem solving exercises Do puzzles, riddles and brainteasers regularly. Identify real-life challenges or dilemmas you encounter and practice applying problem solving techniques to these situations. Analyse case studies or scenarios relevant to your field or industry.
Analyzing case studies involves a detailed examination of real-life situations that bear relevance to the current problem at hand. ... You conduct research into your problem, attempt to apply a solution, then assess how well the solution worked. ... Using TRIZ, you can leverage patterns of problem-solving that have proven effective in different ...
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
1. First, make sure you understand the problem. You do this by developing a representation of the essential aspects of the problem. You do that by searching your knowledge base for information ...
Problems often arise in organizational life. From understanding the root cause of a problem to using the power of empathy, here are five strategies for solving problems. Subscribe To Newsletters
Here are the basic steps involved in problem-solving: 1. Define the problem. The first step is to analyze the situation carefully to learn more about the problem. A single situation may solve multiple problems. Identify each problem and determine its cause. Try to anticipate the behavior and response of those affected by the problem.
These skills enable individuals to analyze complex situations, make informed decisions, and find innovative solutions. Here, we present 25 examples of problem-solving and critical thinking. problem-solving scenarios to help you cultivate and enhance these skills. Ethical dilemma: A company faces a situation where a client asks for a product ...
10 Steps to Solving a Problem. In this 10-step problem-solving process, I'll walk you through how to identify and implement the right solution to the problem at hand. In learning these steps, you will develop your critical thinking and elevate your problem-solving skills. 1. Take a Positive Approach.
Apart from these stages, we should also be able to look at the following qualities of becoming an effective problem solver: Determination to solve a problem. Remaining calm and patient while dealing with a problem. Taking problems as a challenge. Being analytical, thoughtful and creative. Adequate information of possible solutions.
The First Rule of Problem Solving. The first thing to do is to define the problem and make sure it is a real problem, particularly your problem and not someone else's problem or someone else's fault. Approaching the problem for answers using the what, where, when, why, how and who questions of the current situation.
Following are some of the Static problem sub-classes: Choice problems - such as choosing a vendor, recruiting a new employee, choosing life partner, buying a new car, choosing an out-sourcing partner. Analytic Hierarchic Process or AHP is an effective method for solving these problems.
Alex Osborn and Sydney Parnes originated the creative problem-solving approach in the 1940s. The approach involves three main steps: problem identification, ideation, and implementation. Firstly, it is essential to identify the specific problem or issue that needs solving. Then, once you have identified the problem, it's time for ideation ...
You are required to solve any random problem, and then you have to explain to the recruiter about your thought processes. The interviewer here is more focused on the way you reach the conclusion rather than the conclusion itself. Your thought process helps the interviewer to analyse and evaluate the way you approach various problems. 15.
This is test and discovery of the repeating pattern of digits that is crucial to solving your problem. The last step is easy. You divide 23 by 4, the length of the repeating cycle, getting remainder 3 and quotient 5. So, you clarify the situation in your mind, "units digit of 223 2 23 will be the third value of the repeating 6th cycle of 2, 4 ...
Algebraic thinking: Basic algebraic concepts can be applied to real-life situations, such as solving for an unknown variable in a recipe or a budget. 5 ways children use math in everyday life. Money matters: Understanding and managing allowances, budgeting for spending, and calculating change while shopping.
Life situations are difficulties, challenges, issues and problems faced by an individual. These are faced by all people at some point such that the process of dealing with difficult situations is a basic element of the human experience.Techniques for resolving life situations include staying positive, asking for help and planning out ways to solve problems over time.
You can talk about the importance of learning addition, subtraction, statistics, geometry, algebra, and more, but your students might not see the real-world applications. The truth is, we all need math. Math teaches us how to solve problems, a skill that's useful in all career fields and just for navigating everyday life.