

MilitaryHistoryNow.com
The Premier Online Military History Magazine
The Business Plot – Did American Billionaires Really Plan a Fascist Coup?
“a coalition of america’s wealthiest industrial magnates allegedly hatched a scheme to topple the roosevelt administration.”.
DONALD TRUMP ADDED a touch of levity to the U.S. Presidential election last November , albeit unintentionally.
As the major news networks declared an Obama victory the night of Nov. 6, the notorious billionaire and one-time White House wannabe took to Twitter to register his outrage over the result.
“We should have a revolution in this country!” Trump tweeted.
“We can’t let this happen. We should march on Washington and stop this travesty!” he added moments later.
While the outbursts were roundly mocked in the days following the vote, Trump isn’t the only American one-percenter to have advocated the overthrow of a democratically-elected president. In the early 1930s, a coalition of America’s wealthiest industrial magnates allegedly hatched a scheme to topple the Roosevelt Administration and replace it with a fascist dictatorship.
Known as the Business Plot , the plan was supposedly dreamed up by a prominent tycoons and Wall Street big shots who controlled many of the country’s major corporations like Chase Bank , Maxwell House , General Motors , Goodyear , Standard Oil , Dupont and Heinz , as well as other noted Americans, including Prescott Bush , grandfather of former U.S. president George W. Bush. [ 1 ] [ 2 ]
The conspirators were fuming over the 1932 election victory of Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt. Once in office, FDR pledged a raft of measures to alleviate the effects of the Great Depression, which were known collectively as the New Deal . America’s 32nd president was also an advocate for the abandonment of the gold standard , something that horrified many elites. Critics condemned the White House for placing the country on what they saw as a slippery slope to outright Bolshevism .
In 1933, the conspirators planned to recruit half a million military veterans from the First World War through various American Legion branches. They even pledged $3 million to buy weapons for their army so the troops could capture and hold the American capital. Once the seat of power was theirs, the plotters would install an ultra-nationalist, business-friendly regime modelled after Mussolini’s Italy. (Many conspirators were also admirers of Hitler even before the Nazis came to power, largely because of his ardent anti-communism).[ 3 ]
The cabal planned to offer command of their rebel army to a celebrated U.S. Marine general by the name of Smedley Butler . The 52-year-old veteran of the war in France had also fought counter-insurgencies in Latin America and the Philippines and was perhaps the most respected military leader in the country at the time.
Just a year earlier, that very same Smedley Butler had publicly voiced support for a march on Washington by Great War veterans who were demanding the government make good on its promises to provide benefits. On the orders of then-president Herbert Hoover, this so-called Bonus Army was eventually broken up by another well-known military leader of the day, General Douglas MacArthur . The Business Plotters felt that Butler’s patriotism along with his popularity among veterans would make him an ideal leader for their putsch.
Little did the conspirators realize, Butler had long-since become a critic of corporate greed, seeing it as an engine that drove many of America’s foreign wars. In fact, in 1935, he committed his thoughts on the matter to a famous book entitled War is a Racket .
In 1933, American Legion leaders involved in the plot approached Butler, offering him command of the rebel army. The decorated war hero immediately alerted Washington of the conspiracy, which admittedly hadn’t progressed much beyond the discussion phase. Nevertheless, a Congressional committee was struck in 1934 to look into the matter.
The McCormack-Dickstein Committee , which would go onto become the House Committee on Un-American Activities , examined the allegations, declaring that there was some evidence of a scheme by Wall Street elites, anti-communists and fascist sympathizers. Even though the findings were declared by Congress to be “alarmingly true,” no charges were ever laid against anyone involved.
“The [committee] received evidence showing that certain persons had made an attempt to establish a fascist organization in this country. There is no question that these attempts were discussed, were planned, and might have been placed in execution when and if the financial backers deemed it expedient,” Congress declared. [ 4 ]
Many blasted the committee’s findings as pure make-believe. The New York Times declared it a “giant hoax,” while historians since have argued that there is little proof that any plot ever posed a threat.
To listen to a full BBC podcast on the Business Plot, click here .
Help spread the word. Share this article with your friends.
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
9 thoughts on “ The Business Plot – Did American Billionaires Really Plan a Fascist Coup? ”
About a decade ago Micheal Moore asked for help from the UN in one of his books to help free the US from an unelected president. And from a democratic point of view, he had more of a pint there than Trump. 😉
Believe Clinton did away with the House Committee on Un-American Activities and now we do not have any safeguards and the Organized Criminals have indeed overthrown our Constitution in their continued effort to form their NWO 🙁 Boo Hiss
Have you ever read the Constitution? There is not a single word defining our system as a capitalist system, but, it definitely accepts the slavery system. HUAC was an extension of the Slavery
“a democratically-elected president” ! Yeah Right ! One that got 200% of the vote in numerous voting precincts throughout the U.S. Yeah, democratically-elected by imaginary and dead people.
- Pingback: Perhaps America’s Greatest Hero was a U.S. Marine – Apocalypse News Watch
- Pingback: Quick Fact: Wealthy magnates plotted to overthrow Roosevelt but were foiled by... - Quick Facts
Are we ever going to accept the fact that slavery was wrong, and had to end?
- Pingback: War, Oil and Omicron – Then, Now and Trump: Part III – Dynastic Bush – POLITICAL MOONSHINE
- Pingback: Did Smedley Butler Save America In 1933? - Speaking For A Change
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

From the MHN Archives

Top Posts & Pages
© COPYRIGHT MilitaryHistoryNow.com
The Business Plot, or When J.P. Morgan’s Pals Tried To Overthrow FDR
Smedley butler, a marine general, exposed the coup attempt.

The Man Who Exposed the Business Plot
I spent 33 years and four months in active military service and during that period I spent most of my time as a high class muscle man for Big Business, for Wall Street and the bankers. In short, I was a racketeer; a gangster for capitalism. I helped make Mexico and especially Tampico safe for American oil interests in 1914. I helped make Haiti and Cuba a decent place for the National City Bank boys to collect revenues in. I helped in the raping of half a dozen Central American republics for the benefit of Wall Street. I helped purify Nicaragua for the International Banking House of Brown Brothers in 1902–1912. I brought light to the Dominican Republic for the American sugar interests in 1916. I helped make Honduras right for the American fruit companies in 1903. In China in 1927 I helped see to it that Standard Oil went on its way unmolested.
Smedley Butler in China
The business plotters, jerry macguire, uncovering the business plot, a closed hearing.
A Washington correspondent asked: “What can we believe?” Apparently anything, to judge by the number of people who lend a credulous ear to the story of General Butler’s 500,000 Fascists in buckram marching on Washington to seize the government.
Report on the Business Plot
…evidence was obtained showing that certain persons had made an attempt to establish a fascist organization in this country. There is no question that these attempts were discussed, were planned, and might have been placed in execution when and if the financial backers deemed it expedient.
With thanks to The Business Plot: Smedley D. Butler, Anti-Democratic Dissidence, and the Recession of the American Right 1932-1936 By Grant Hamilton Stone, August 2021.
Provincetown Dune Shacks, Remarkable and Never Repeated
When teddy roosevelt barnstormed new england, subscribe to our newsletter, thanks for signing up, you have successfully subscribed.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Author Interviews
When the bankers plotted to overthrow fdr.

The Plots Against the President
Buy featured book.
Your purchase helps support NPR programming. How?
- Independent Bookstores

Sally Denton is also the author of The Pink Lady , American Massacre and The Bluegrass Conspiracy . Ursula Coyote/Bloomsbury hide caption
It was a dangerous time in America: The economy was staggering, unemployment was rampant and a banking crisis threatened the entire monetary system.
The newly elected president pursued an ambitious legislative program aimed at easing some of the troubles. But he faced vitriolic opposition from both sides of the political spectrum. "This is despotism, this is tyranny, this is the annihilation of liberty," one senator wrote to a colleague. "The ordinary American is thus reduced to the status of a robot. The president has not merely signed the death warrant of capitalism, but has ordained the mutilation of the Constitution, unless the friends of liberty, regardless of party, band themselves together to regain their lost freedom."
Those words could be ripped from today's headlines. In fact, author Sally Denton tells weekends on All Things Considered host Guy Raz, they come from a letter written in 1933 by Republican Sen. Henry D. Hatfield of West Virginia, bemoaning the policies of Franklin Delano Roosevelt.
Denton is the author of a new book, The Plots Against the President: FDR, a Nation in Crisis, and the Rise of the American Right .
She says that during the tense months between FDR's election in November and his inauguration in March 1933, democracy hung in the balance.
"There was a lot at play. It could have gone very different directions," Denton says.
Though it's hard for us to imagine today, she says fascism, communism, even Naziism seemed like possible solutions to the country's ills.
"There were suggestions that capitalism was not working, that democracy was not working," she says.
Some people even called for a dictator to pull America out of the Great Depression.
When Roosevelt finally took office, he embarked on the now-legendary First Hundred Days, an ambitious legislative program aimed at reopening and stabilizing the country's banks and getting the economy moving again.
"There was just this sense that he was upsetting the status quo," Denton says.
Critics on the right worried that Roosevelt was a Communist, a socialist or the tool of a Jewish conspiracy. Critics on the left complained his policies didn't go far enough. Some of Roosevelt's opponents didn't stop at talk. Though it's barely remembered today, there was a genuine conspiracy to overthrow the president.
The Wall Street Putsch, as it's known today, was a plot by a group of right-wing financiers.
"They thought that they could convince Roosevelt, because he was of their, the patrician class, they thought that they could convince Roosevelt to relinquish power to basically a fascist, military-type government," Denton says.
"It was a cockamamie concept," she adds, "and the fact that it even got as far as it did is pretty shocking."
The conspirators had several million dollars, a stockpile of weapons and had even reached out to a retired Marine general, Smedley Darlington Butler, to lead their forces.
"Had he been a different kind of person, it might have gone a lot further," Denton says. "But he saw it as treason and he reported it to Congress."
Denton says that as she was writing the book, she was struck by the parallels between the treatment of Roosevelt and that of Barack Obama. For example, a cottage industry much like the birther movement grew up around proving that the Dutch-descended Roosevelt was actually a secret Jew.
"It seems to me that going through history here, there are times that we need to have a demon, somebody that's not of us, in order to solidify our fears and our anxieties," Denton says.
"And I don't know what that is in the impulse of the American body politic, but... this is 75 years later, and some of these same impulses continue."
The Plot Against American Democracy That Isn’t Taught in Schools
By Jonathan M. Katz
Jonathan M. Katz
Award-winning journalist Jonathan M. Katz’s new book, Gangsters of Capitalism: Smedley Butler, the Marines, and the Making and Breaking of America’s Empire , is an explosive deep dive into the forgotten history of American military imperialism in the early twentieth century. At its center is one of the United States’s most fascinating yet little-known characters — Gen. Smedley Butler, a Marine who fought in nearly every U.S. overseas war in the early twentieth century. In this exclusive excerpt, Katz documents how Butler played a pivotal role in an equally little-known episode, in which a cadre of powerful businessmen tried to overthrow the government of the United States, in an episode that anticipated the events of Jan. 6 , 2021. Read the exclusive excerpt below.
Smedley Butler knew a coup when he smelled one. He had been involved in many himself. He had overthrown governments and protected “friendly” client ones around the world on behalf of some of the same U.S. bankers, lawyers, and businessmen apparently now looking for his help.
For 33 years and four months Butler had been a United States Marine, a veteran of nearly every overseas conflict back to the war against Spain in 1898. Respected by his peers, beloved by his men, he was known as “The Fighting Hell-Devil Marine,” “Old Gimlet Eye,” “The Leatherneck’s Friend,” and the famous “Fighting Quaker” of the Devil Dogs. Bestselling books had been written about him. Hollywood adored him. President Roosevelt’s cousin, the late Theodore himself, was said to have called Butler “the ideal American soldier.” Over the course of his career, he had received the Army and Navy Distinguished Service medals, the French Ordre de l’Étoile Noir, and, in the distinction that would ensure his place in the Marine Corps pantheon, the Medal of Honor — twice.
Butler knew what most Americans did not: that in all those years, he and his Marines had destroyed democracies and helped put into power the Hitlers and Mussolinis of Latin America, dictators like the Dominican Republic’s Rafael Trujillo and Nicaragua’s soon-to-be leader Anastasio Somoza — men who would employ violent repression and their U.S.-created militaries to protect American investments and their own power. He had done so on behalf of moneyed interests like City Bank, J. P. Morgan, and the Wall Street financier Grayson M.P. Murphy.
Editor’s picks
Every awful thing trump has promised to do in a second term, the 250 greatest guitarists of all time, the 500 greatest albums of all time, the 50 worst decisions in movie history.
And now a bond salesman, who worked for Murphy, was pitching Butler on a domestic operation that set off the old veteran’s alarm bells. The bond salesman was Gerald C. MacGuire, a 37-year-old Navy veteran with a head Butler thought looked like a cannonball. MacGuire had been pursuing Butler relentlessly throughout 1933 and 1934, starting with visits to the Butler’s converted farmhouse on Philadelphia’s Main Line. In Newark, where Butler was attending the reunion of a National Guard division, MacGuire showed up at his hotel room and tossed a wad of cash on the bed — $18,000, he said. In early 1934, Butler had received a series of postcards from MacGuire, sent from the hotspots of fascist Europe, including Hitler’s Berlin.
In August 1934, MacGuire called Butler from Philadelphia and asked to meet. Butler suggested an abandoned café at the back of the lobby of the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel.
First MacGuire recounted all he had seen in Europe. He’d learned that Mussolini and Hitler were able to stay in power because they kept soldiers on their payrolls in various ways. “But that setup would not suit us at all,” the businessman opined.
But in France, MacGuire had “found just exactly the organization we’re going to have.” Called the Croix de Feu, or Fiery Cross, it was like a more militant version of the American Legion: an association of French World War veterans and paramilitaries. On Feb. 6, 1934 — six weeks before MacGuire arrived — the Croix de Feu had taken part in a riot of mainly far-right and fascist groups that had tried to storm the French legislature. The insurrection was stopped by police; at least 15 people, mostly rioters, were killed. But in the aftermath, France’s center-left prime minister had been forced to resign in favor of a conservative.
MacGuire had attended a meeting of the Croix de Feu in Paris. It was the sort of “super-organization” he believed Americans could get behind — especially with a beloved war hero like Butler at the helm.
Then he made his proposal: The Marine would lead half a million veterans in a march on Washington, blending the Croix de Feu’s assault on the French legislature with the March on Rome that had put Mussolini’s Fascisti in power in Italy a decade earlier. They would be financed and armed by some of the most powerful corporations in America — including DuPont, the nation’s biggest manufacturer of explosives and synthetic materials.
Related Stories
Trump leverages supreme court immunity decision in bid to overturn criminal conviction, joe biden briefly criticizes supreme court immunity ruling.
The purpose of the action was to stop Roosevelt’s New Deal, the president’s program to end the Great Depression, which one of the millionaire du Pont brothers deemed “nothing more or less than the Socialistic doctrine called by another name.” Butler’s veteran army, MacGuire explained, would pressure the president to appoint a new secretary of state, or “secretary of general affairs,” who would take on the executive powers of government. If Roosevelt went along, he would be allowed to remain as a figurehead, like the king of Italy. Otherwise, he would be forced to resign, placing the new super-secretary in the White House.
Butler recognized this immediately as a coup. He knew the people who were allegedly behind it. He had made a life in the overlapping seams of capital and empire, and he knew that the subversion of democracy by force had turned out to be a required part of the job he had chosen. “I spent most of my time being a high-class muscle man for big business, for Wall Street, and for the bankers,” Butler would write a year later. “In short, I was a racketeer for capitalism.”
And Butler knew another thing that most Americans didn’t: how much they would suffer if anyone did to their democracy what he had done to so many others across the globe.
“Now, about this super-organization,” MacGuire asked the general. “Would you be interested in heading it?”
“I am interested in it, but I do not know about heading it,” Butler told the bond salesman, as he resolved to report everything he had learned to Congress. “I am very greatly interested in it, because, you know, Jerry, my interest is, my one hobby is, maintaining a democracy. If you get these 500,000 soldiers advocating anything smelling of fascism, I am going to get 500,000 more and lick the hell out of you, and we will have a real war right at home.”
Eight decades after he publicly revealed his conversations about what became known as the Business Plot, Smedley Butler is no longer a household name. A few history buffs — and a not-inconsiderable number of conspiracy-theory enthusiasts — remember him for his whistleblowing of the alleged fascist coup. Another repository of his memory is kept among modern-day Marines, who learn one detail of his life in boot camp — the two Medals of Honor — and to sing his name along with those of his legendary Marine contemporaries, Dan Daly and Lewis “Chesty” Puller, in a running cadence about devotion to the Corps: “It was good for Smedley Butler/And it’s good enough for me.”
I first encountered the other side of Butler’s legacy in Haiti, after I moved there to be the correspondent for the Associated Press. To Haitians, Butler is no hero. He is remembered by scholars there as the most mechan — corrupt or evil — of the Marines. He helped lead the U.S. invasion of that republic in 1915 and played a singular role in setting up an occupation that lasted nearly two decades. Butler also instigated a system of forced labor, the corvée, in which Haitians were required to build hundreds of miles of roads for no pay, and were killed or jailed if they did not comply. Haitians saw it for what it was: a form of slavery, enraging a people whose ancestors had freed themselves from enslavement and French colonialism over a century before.
Such facts do not make a dent in the mainstream narrative of U.S. history. Most Americans prefer to think of ourselves as plucky heroes: the rebels who topple the empire, not the storm troopers running its battle stations. U.S. textbooks — and more importantly the novels, video games, monuments, tourist sites, and films where most people encounter versions of American history — are more often about the Civil War or World War II, the struggles most easily framed in moral certitudes of right and wrong, and in which those fighting under the U.S. flag had the strongest claims to being on the side of good.
“Imperialism,” on the other hand, is a foreign-sounding word. It brings up images, if it brings any at all, of redcoats terrorizing Boston, or perhaps British officials in linen suits sipping gin and tonics in Bombay. The idea that the United States, a country founded in rebellion against empire, could have colonized and conquered other peoples seems anathema to everything we are taught America stands for.
And it is. It was no coincidence that thousands of young men like Smedley Butler were convinced to sign up for America’s first overseas war of empire on the promise of ending Spanish tyranny and imperialism in Cuba. Brought up as a Quaker on Philadelphia’s Main Line, Butler held on to principles of equality and fairness throughout his life, even as he fought to install and defend despotic regimes all over the world. That tension — between the ideal of the United States as a leading champion of democracy on the one hand and a leading destroyer of democracy on the other — remains the often unacknowledged fault line running through American politics today.
For some past leaders, there was never a tension at all. When the U.S. seized its first inhabited overseas colonies in 1898, some proudly wore the label. “I am, as I expected I would be, a pretty good imperialist,” Theodore Roosevelt mused to a British friend while on safari in East Africa in 1910. But as the costs of full-on annexation became clear, and control through influence and subterfuge became the modus operandi of U.S. empire, American leaders reverted seamlessly back to republican rhetoric.
The denial deepened during the Cold War. In 1955, the historian William Appleman Williams wrote, “One of the central themes of American historiography is that there is no American Empire.” It was essential for the conflict against the Soviet Union — “the Evil Empire,” as Ronald Reagan would call it — to heighten the supposed contrasts: They overthrew governments, we defended legitimate ones; they were expansionist, we went abroad only in defense of freedom.
As long as the United States seemed eternally ascendant, it was easy to tell ourselves, as Americans, that the global dominance of U.S. capital and the unparalleled reach of the U.S. military had been coincidences, or fate; that America’s rise as a cultural and economic superpower was just natural — a galaxy of individual choices, freely made, by a planet hungry for an endless supply of Marvel superheroes and the perfect salty crunch of McDonald’s fries.
But the illusion is fading. The myth of American invulnerability was shattered by the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks. The attempt to recover a sense of dominance resulted in the catastrophic “forever wars” launched in Afghanistan, Iraq, Libya, Syria, Somalia, and elsewhere. The deaths of well over half a million Americans in the coronavirus pandemic, and our seeming inability to halt or contend with the threats of climate change, are further reminders that we can neither accumulate nor consume our way out of a fragile and interconnected world.
As I looked through history to find the origins of the patterns of self-dealing and imperiousness that mark so much of American policy, I kept running into the Quaker Marine with the funny name. Smedley Butler’s military career started in the place where the United States’ overseas empire truly began, and the place that continues to symbolize the most egregious abuses of American power: Guantánamo Bay. His last overseas deployment, in China from 1927 to 1929, gave him a front-row seat to both the start of the civil war between the Communists and the Nationalists and the slowly materializing Japanese invasion that would ultimately open World War II.
In the years between, Butler blazed a path for U.S. empire, helping seize the Philippines and the land for the Panama Canal, and invading and helping plunder Honduras, Nicaragua, Haiti, the Dominican Republic, Mexico, and more. Butler was also a pioneer of the militarization of police: first spearheading the creation of client police forces across Latin America, then introducing those tactics to U.S. cities during a two-year stint running the Philadelphia police during Prohibition.
Yet Butler would spend the last decade of his life trying to keep the forces of tyranny and violence he had unleashed abroad from consuming the country he loved. He watched the rise of fascism in Europe with alarm. In 1935, Butler published a short book about the collusion between business and the armed forces called War Is a Racket . The warnings in that thin volume would be refined and amplified years later by his fellow general, turned president, Dwight Eisenhower, whose speechwriters would dub it the military-industrial complex.
Late in 1935, Butler would go further, declaring in a series of articles for a radical magazine: “Only the United Kingdom has beaten our record for square miles of territory acquired by military conquest. Our exploits against the American Indian, against the Filipinos, the Mexicans, and against Spain are on a par with the campaigns of Genghis Khan, the Japanese in Manchuria, and the African attack of Mussolini.”
Butler was not just throwing stones. In that article, he repeatedly called himself a racketeer — a gangster — and enumerated his crimes:
I helped make Mexico and especially Tampico safe for American oil interests in 1914. I helped make Haiti and Cuba a decent place for the National City Bank boys to collect revenues in. I helped in the raping of half a dozen Central American republics for the benefit of Wall Street.…
I helped purify Nicaragua for the international banking house of Brown Brothers in 1909-12. I brought light to the Dominican Republic for American sugar interests in 1916. I helped make Honduras “right” for American fruit companies in 1903. In China, in 1927, I helped see to it that Standard Oil went its way unmolested.
During those years, I had, as the boys in the back room would say, a swell racket. I was rewarded with honors, medals, promotion. Looking back on it, I feel I might have given Al Capone a few hints. The best he could do was operate in three city districts. We Marines operated on three continents.
Butler was telling a messier story than the ones Americans like to hear about ourselves. But we ignore the past at our peril. Americans may not recognize the events Butler referred to in his confession, but America’s imperial history is well remembered in the places we invaded and conquered — where leaders and elites use it and shape it to their own ends. Nowhere is more poised to use its colonial past to its future advantage than China, once a moribund kingdom in which U.S. forces, twice led by Butler, intervened at will in the early 20th century. As they embark on their own imperial project across Asia, Africa, and Latin America, Chinese officials use their self-story of “national humiliation” to position themselves as an antidote to American control, finding willing audiences in countries grappling with their own histories of subjugation by the United States.
The dangers are greater at home. Donald Trump preyed on American anxieties by combining the worst excesses of those early-20th-century imperial chestnuts — militarism, white supremacy, and the cult of manhood — with a newer fantasy: that Americans could reclaim our sense of safety and supremacy by disengaging from the world we made, by literally building walls along our border and making the countries we conquered pay for them.
To those who did not know or have ignored America’s imperial history, it could seem that Trump was an alien force (“This is not who we are,” as the liberal saying goes), or that the implosion of his presidency has made it safe to slip back into comfortable amnesias. But the movement Trump built — a movement that stormed the Capitol, tried to overturn an election, and, as I write these words, still dreams of reinstalling him by force — is too firmly rooted in America’s past to be dislodged without substantial effort. It is a product of the greed, bigotry, and denialism that were woven into the structure of U.S. global supremacy from the beginning — forces that now threaten to break apart not only the empire but the society that birthed it.
On Nov. 20, 1934, readers of the New York Post were startled by a headline: “Gen. Butler Accuses N.Y. Brokers of Plotting Dictatorship in U.S.; $3,000,000 Bid for Fascist Army Bared; Says He Was Asked to Lead 500,000 for Capital ‘Putsch’; U.S. Probing Charge.”
Smedley Butler revealed the Business Plot before a two-man panel of the Special House Committee on Un-American Activities. The executive session was held in the supper room of the New York City Bar Association on West 44th Street. Present were the committee chairman, John W. McCormack of Massachusetts, and vice chairman, Samuel Dickstein of New York.
For 30 minutes, Butler told the story, starting with the first visit of the bond salesman Gerald C. MacGuire to his house in Newtown Square in 1933.
Finally, Butler told the congressmen about his last meeting with MacGuire at the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel. At that meeting, Butler testified, MacGuire had told him to expect to see a powerful organization forming to back the putsch from behind the scenes. “He says: ‘You watch. In two or three weeks you will see it come out in the paper. There will be big fellows in it. This is to be the background of it. These are to be the villagers in the opera.’” The bond salesman told the Marine this group would advertise itself as a “society to maintain the Constitution.”
“And in about two weeks,” Butler told the congressmen, “the American Liberty League appeared, which was just about what he described it to be.”
The Liberty League was announced on Aug. 23, 1934, on the front page of The New York Times . The article quoted its founders’ claim that it was a “nonpartisan group” whose aim was to “combat radicalism, preserve property rights, uphold and preserve the Constitution.” Its real goal, other observers told the Times , was to oppose the New Deal and the taxes and controls it promised to impose on their fortunes.
Among the Liberty League’s principal founders was the multimillionaire Irénée du Pont, former president of the explosives and chemical manufacturing giant. Other backers included the head of General Motors, Alfred P. Sloan, as well as executives of Phillips Petroleum, Sun Oil, General Foods, and the McCann Erickson ad agency. The former Democratic presidential candidates Al Smith and John W. Davis — both of them foes of FDR, the latter counsel to J.P. Morgan & Co. — were among the League’s members as well. Its treasurer was MacGuire’s boss, Grayson Murphy.
Sitting beside Butler in the hearing room was the journalist who wrote the Post article, Paul Comly French. Knowing the committee might find his story hard to swallow — or easy to suppress — Butler had called on the reporter, whom he knew from his time running the Philadelphia police, to conduct his own investigation. French told the congressmen what MacGuire had told him: “We need a fascist government in this country, he insisted, to save the nation from the communists who want to tear it down and wreck all that we have built in America. The only men who have the patriotism to do it are the soldiers, and Smedley Butler is the ideal leader. He could organize a million men overnight.”
MacGuire, the journalist added, had “continually discussed the need of a man on a white horse, as he called it, a dictator who would come galloping in on his white horse. He said that was the only way to save the capitalistic system.”
Butler added one more enticing detail. MacGuire had told him that his group in the plot — presumably a clique headed by Grayson Murphy — was eager to have Butler lead the coup, but that “the Morgan interests” — that is, bankers or businessmen connected to J. P. Morgan & Co. — were against him. “The Morgan interests say you cannot be trusted, that you are too radical and so forth, that you are too much on the side of the little fellow,” he said the bond salesman had explained. They preferred a more authoritarian general: Douglas MacArthur.
All of these were, in essence, merely leads. The committee would have to investigate to make the case in full. What evidence was there to show that anyone beside MacGuire, and likely Murphy, had known about the plot? How far had the planning gone? Was Butler — or whoever would lead the coup — to be the “man on a white horse,” or were they simply to pave the way for the dictator who would “save the capitalistic system”?
But the committee’s investigation would be brief and conducted in an atmosphere of overweening incredulity. As soon as Butler’s allegations became public, the most powerful men in media did everything they could to cast doubt on them and the Marine. The New York Times fronted its story with the denials of the accused: Grayson M.P. Murphy called it “a fantasy.” “Perfect moonshine! Too unutterably ridiculous to comment upon!” exclaimed Thomas W. Lamont, the senior partner at J.P. Morgan & Co. “He’d better be damn careful,” said the ex-Army general and ex-FDR administration official Hugh S. Johnson, whom Butler said was mooted as a potential “secretary of general affairs.” “Nobody said a word to me about anything of the kind, and if they did, I’d throw them out the window.”
Douglas MacArthur called it “the best laugh story of the year.”
Time magazine lampooned the allegations in a satire headlined “Plot Without Plotters.” The writer imagined Butler on horseback, spurs clinking, as he led a column of half a million men and bankers up Pennsylvania Avenue. In an unsigned editorial, Adolph Ochs’ New York Times likened Butler to an early-20th-century Prussian con man.
There would only be one other witness of note before the committee. MacGuire spent three days testifying before McCormack and Dickstein, contradicting, then likely perjuring himself. He admitted having met the Croix de Feu in Paris, though he claimed it was in passing at a mass at Notre-Dame. The bond salesman also admitted having met many times with Butler — but insisted, implausibly, that it was Butler who told him he was involved with “some vigilante committee somewhere,” and that the bond salesman had tried to talk him out of it.
There was no further inquiry. The committee was disbanded at the end of 1934. McCormack argued, unpersuasively, that it was not necessary to subpoena Grayson Murphy because the committee already had “cold evidence linking him with this movement.”
“We did not want,” the future speaker of the House added, “to give him a chance to pose as an innocent victim.”
The committee’s final report was both complimentary to Butler and exceptionally vague:
In the last few weeks of the committee’s official life it received evidence showing that certain persons had made an attempt to establish a fascist organization in this country There is no question but that these attempts were discussed, were planned, and might have been placed in execution when and if the financial backers deemed it expedient.
The committee said it had “verified all the pertinent statements made by General Butler.” But it named no one directly in connection with the alleged coup.
Was there a Business Plot? In the absence of a full investigation, it is difficult to say. It seems MacGuire was convinced he was a front man for one. (He would not live long enough to reveal more: Four months after the hearings, the bond salesman died at the age of 37.)
It seems possible that at least some of the alleged principals’ denials were honest. MacGuire’s claim that all the members of the Liberty League were planning to back a coup against Roosevelt does not make it so. The incredulity with which men like Thomas Lamont and Douglas MacArthur greeted the story could be explained by the possibility that they had not heard of such a plan before Butler blew the whistle.
But it is equally plausible that, had Butler not come forward, or had MacGuire approached someone else, the coup or something like it might have been attempted. Several alleged in connection with the plot were avid fans of fascism. Lamont described himself as “something like a missionary” for Mussolini, as he made J.P. Morgan one of fascist Italy’s main overseas banking partners. The American Legion, an alleged source of manpower for the putsch, featured yearly convention greetings from “a wounded soldier in the Great War … his excellency, Benito Mussolini.” The capo del governo himself was invited to speak at the 1930 convention, until the invitation was rescinded amid protests from organized labor.
Hugh S. Johnson, Time ’s 1933 Man of the Year, had lavishly praised the “shining name” of Mussolini and the fascist stato corporativo as models of anti-labor collectivism while running the New Deal’s short-lived National Recovery Administration. Johnson’s firing by FDR from the NRA in September 1934 was predicted by MacGuire, who told Butler the former Army general had “talked too damn much.” (Johnson would later help launch the Nazi-sympathizing America First Committee, though he soon took pains to distance himself from the hardcore antisemites in the group.)
Nothing lends more plausibility to the idea that a coup to sideline Roosevelt was at least discussed — and that Butler’s name was floated to lead it — than the likely involvement of MacGuire’s boss, the banker Grayson M.P. Murphy. The financier’s biography reads like a shadow version of Butler’s. Born in Philadelphia, he transferred to West Point during the war against Spain. Murphy then joined the Military Intelligence Division, running spy missions in the Philippines in 1902 and Panama in 1903. Then he entered the private sector, helping J.P. Morgan conduct “dollar diplomacy” in the Dominican Republic and Honduras. In 1920, Murphy toured war-ravaged Europe to make “intelligence estimates and establish a private intelligence network” with William J. “Wild Bill” Donovan — who would later lead the Office of Strategic Services, the forerunner to the CIA. This was the résumé of someone who, at the very least, knew his way around the planning of a coup.
Again, all of that is circumstantial evidence; none of it points definitively to a plan to overthrow the U.S. government. But it was enough to warrant further investigation. So why did no one look deeper at the time? Why was the idea that a president could be overthrown by a conspiracy of well-connected businessmen — and a few armed divisions led by a rabble-rousing general — considered so ridiculous that the mere suggestion was met with peals of laughter across America?

It was because, for decades, Americans had been trained to react in just that way: by excusing, covering up, or simply laughing away all evidence that showed how many of those same people had been behind similar schemes all over the world. Butler had led troops on the bankers’ behalf to overthrow presidents in Nicaragua and Honduras, and gone on a spy run to investigate regime change on behalf of the oil companies in Mexico. He had risked his Marines’ lives for Standard Oil in China and worked with Murphy’s customs agents in an invasion that helped lead to a far-right dictatorship in the Dominican Republic. In Haiti, Butler had done what even the Croix de Feu and its French fascist allies could not: shut down a national assembly at gunpoint.
In his own country, in his own time, Smedley Butler drew a line. “My interest, my one hobby, is maintaining a democracy,” he told the bond salesman. Butler clung to an idea of America as a place where the whole of the people chose their leaders, the “little guy” got a fair shot against the powerful, and everyone could live free from tyranny. It was an idea that had never existed in practice for all, and seldom for most. As long as Americans refused to grasp the reality of what their country actually was — of what their soldiers and emissaries did with their money and in their name all over the world — the idea would remain a self-defeating fairy tale. Still, as long as that idea of America survived, there was a chance its promise might be realized.
The real danger, Butler knew, lay in that idea’s negation. If a faction gained power that exemplified the worst of America’s history and instincts — with a leader willing to use his capital and influence to destroy what semblance of democracy existed for his own ends — that faction could overwhelm the nation’s fragile institutions and send one of the most powerful empires the world had ever seen tumbling irretrievably into darkness.
Twenty-one U.S. presidential elections later , on Jan. 6, 2021, Donald Trump stood before an angry crowd on the White House Ellipse. For weeks, Trump had urged supporters to join him in an action against the joint session of Congress slated to recognize his opponent, Joe Biden, as the next president that day. Among the thousands who heeded his call were white supremacists, neo-Nazis, devotees of the antisemitic QAnon conspiracy theory, far-right militias, and elements of his most loyal neo-fascist street gang, the Proud Boys. “It is time for war,” a speaker at a warm-up rally the night before had declared.
On the rally stage, the defeated president spoke with the everyman style and bluntness of a Smedley Butler. He mirrored the Marine’s rhetoric, too, saying his purpose was to “save our democracy.” But that was not really his goal. Trump, and his faction, wanted to destroy the election — to dismantle democracy rather than cede power to a multiethnic, cross-class majority who had chosen someone else. Trump lied to the thousands in winter coats and “Make America Great Again” hats by claiming he still had a legitimate path to victory. His solution: to intimidate his vice president and Congress into ignoring the Constitution and refusing to certify the election, opening the door for a critical mass of loyal state governments to reverse their constituents’ votes and declare him the winner instead. In this, Trump echoed the French fascists of 1934, who claimed their attack on parliament would defend the popular will against “socialist influence” and “give the nation the leaders it deserves.”
Trump then did what the Business Plotters — however many there were — could not. He sent his mob, his version of Mussolini’s Black Shirts and the Croix de Feu, to storm the Capitol. “We fight like hell,” the 45th president instructed them. “And if you don’t fight like hell, you’re not going to have a country anymore.”
It was not just Trump’s personal embodiment of fascist logic and authoritarian populism that should have prepared Americans for the Jan. 6 attack. Over a century of imperial violence had laid the groundwork for the siege at the heart of U.S. democracy.
Many of the putschists, including a 35-year-old California woman shot to death by police as she tried to break into the lobby leading to the House floor, were veterans of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan. Some wore tactical armor and carried “flex cuffs” — nylon restraints the military and police use for mass arrests of insurgents and dissidents. The QAnon rioters were devotees of a supposed “military intelligence” officer who prophesized, among other things, the imminent detention and execution of liberals at Guantánamo. A Washington Post reporter heard some of the rioters chanting for “military tribunals.”
Even many of those opposed to the insurrection struggled to see what was happening: that the boundaries between the center and the periphery were collapsing. “I expected violent assault on democracy as a U.S. Marine in Iraq. I never imagined it as a United States congressman in America,” Rep. Seth Moulton, a Massachusetts Democrat, wrote as he sheltered in the Capitol complex. George W. Bush, the president who ordered Moulton into Baghdad, observed: “This is how election results are disputed in a banana republic — not our democratic republic.” Watching from home, I wished Smedley Butler was around to remind the former president how those “banana republics” came to be.
A few weeks after the siege, I talked to Butler’s 85-year-old granddaughter, Philippa Wehle. I asked her over Skype what her grandfather would have thought of the events of Jan. 6.
Her hazel eyes narrowed as she pondered: “I think he would have been in there. He would have been in the fray somehow.”
For an unsettling moment, I was unsure what she meant. Butler had much in common with both sides of the siege: Like Trump’s mob, he had often doubted the validity of democracy when practiced by nonwhites. (The most prominent Trumpist conspiracy theories about purported fraud in the 2020 election centered on cities with large immigrant and Black populations.) Like many of the putschists, Butler saw himself as a warrior for the “little guy” against a vast constellation of elite interests — even though he, also like most of the Capitol attackers, was relatively well-off. Moreover, the greatest proportion of veterans arrested in connection with the attempted putsch were Marines. An active-duty Marine major — a field artillery officer at Quantico — was caught on video pushing open the doors to the East Rotunda and accused by federal prosecutors of allowing other rioters to stream in.
But I knew too that Butler had taken his stand for democracy and against the Business Plot. I would like to think he would have seen through Trump as well. Butler had rejected the radio host Father Charles Coughlin’s proto-Trumpian brand of red-baiting, antisemetic conspiratorial populism, going so far as to inform FBI director J. Edgar Hoover of an alleged 1936 effort involving the reactionary priest to overthrow the left-leaning government of Mexico. When a reporter for the Marxist magazine New Masses asked Butler “just where he stood politically” in the wake of the Business Plot, he name-checked several of the most left-leaning members of Congress, and said the only group he would give his “blanket approval to” was the American Federation of Labor. Butler added that he would not only “die to preserve democracy” but also, crucially, “fight to broaden it.”
Perhaps it would have come down to timing: at what point in his life the attack on the government might have taken place.
“Do you think he would have been with the people storming the Capitol?” I asked Philippa, tentatively.
This time she answered immediately. “No! Heavens no. He would have been trying to do something about it.” He might have been killed, she added, given that the police were so unprepared. “Which is so disturbing, because of course they should have known. They would have known. They only had to read the papers.”
From Gangsters of Capitalism by Jonathan Katz. Copyright © 2022 by the author and reprinted by permission of St. Martin’s Publishing Group. Click here to pre-order.
RFK Jr. Doesn't Deny Alleged Sexual Assault of Babysitter: 'I Am Not a Church Boy’
- ‘I am who I am’
- By Charisma Madarang
Democrats Start Calling for Biden to End Campaign
- By Nikki McCann Ramirez
Manhattan DA Agrees to Postpone Trump’s Sentencing Following SCOTUS Immunity Ruling
- Delay Delay Delay
No One Is Buying the Biden Campaign’s Spin
- By Andrew Perez and Nikki McCann Ramirez
The Supreme Court Fails Again
- By Jay Michaelson
Most Popular
The ho-hum box office of kevin costner’s ‘horizon’ carries a message: don’t turn movies into television, eddie murphy says elvis presley, michael jackson and prince all serve as "cautionary tales" for him, nicole kidman & keith urban’s daughter sunday is apparently going by a different name, florida's ron desantis says 'sexual' festival caused him to veto $32 m. in arts grants, you might also like, ‘beverly hills cop: axel f.’ review: eddie murphy works hard to act game in a sequel made to tickle your nostalgia, top street-style trends from paris couture week: statement dressing, conversational bags and more, the best yoga mats for any practice, according to instructors, 2025 oscar predictions: who will win at the academy awards, new york mets introduce $5 food and beverage promotion.
Rolling Stone is a part of Penske Media Corporation. © 2024 Rolling Stone, LLC. All rights reserved.
Verify it's you
Please log in.
This site uses cookies to improve user experience. By continuing to browse, you accept the use of cookies and other technologies.
The Conspiratorial Business Plot of 1933
This would-be coup aimed to overthrow FDR.

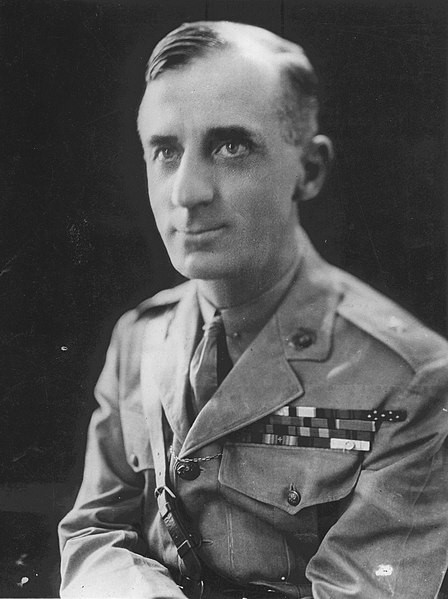
- Maj. Gen. Smedley D. Butler, one-time Commander of the U.S. Marines, and Senator Homer T. Bone. Photo Credit: Wikimedia Commons
The year 1933 saw several consequential worldwide events brewing. Adolf Hitler was appointed chancellor of Germany. Engelbert Dollfuss dissolved the Austrian parliament and assumed dictatorial powers as Chancellor of Austria. Alejandro Lerroux came to power in the Spanish general election, igniting a brief and bloody insurrection attempt committed by the anarchist National Confederation of Trabajo.
Across the Atlantic, a similar insurgency attempted to destabilize the United States earlier that year. The Business Plot of 1933 was a failed attempt to overthrow FDR and install a dictator. And it was not led by a fringe group of working-class radicals, but covertly bankrolled by a Wall Street coalition of affluent businessmen.
Related: The Importance of FDR’s Fireside Chats
Leading up to the Business Plot, Western powers had been scrambling to alleviate the devastating effects of the 1929 stock market crash on tens of millions of workers. At the time, Farm Bureau Federation president Edward O'Neal famously told a Senate committee that "unless something is done for the American farmer, we will have revolution in the countryside in less than twelve months."
Dust off exclusive book deals and tales from the past when you join The Archive 's newsletter.
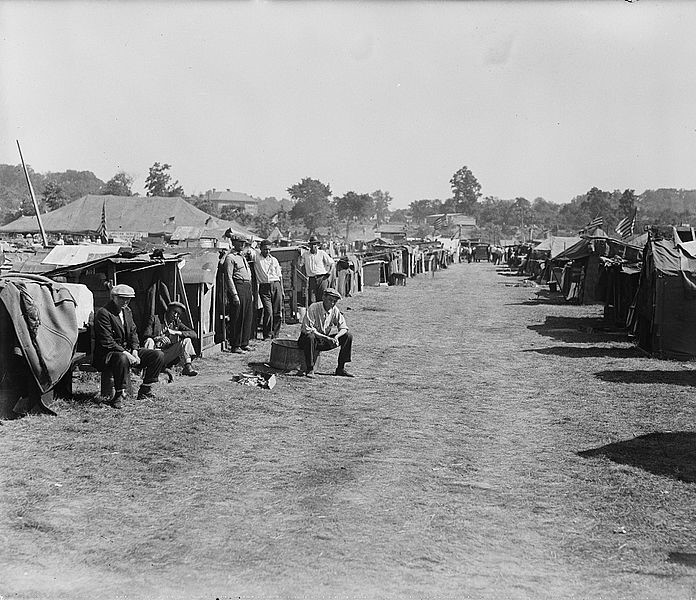
Thousands of unemployed World War I veterans were among those stifled by the Depression and the limited government intervention. In July 17 1932, tens of thousands of veterans and their families descended on Washington, D.C. to set up tent camps and demand immediate payment of the bonuses promised to them by the World War Adjusted Compensation Act of 1924.
The veterans were dubbed th e Bonus Army by t he media, and after 11 days, US Attorney General William D. Mitchell ordered that they be removed from all government property. Resistance ensued.
Major General Smedley Butler, a popular and decorated military figure at the time, appeared at the Bonus Army marches. Butler had emerged as a fervent public advocate against capitalist exploitation of the masses by that point. In the 1932 presidential election, he backed Roosevelt over Hoover.
Related: Black Tuesday: 1929's Stock Market Crash Signaled the Great Depression's Start
Many conservative businessmen were upset by Roosevelt's election because of his campaign promise to have the government provide jobs for the unemployed. Wealthy businessmen were concerned that he would introduce reckless spending and economic socialism. Roosevelt’s New Deal policies, which addressed almost every sector of the economy in the form of regulations, social programs, and financial reforms, made him an ever-growing problem in the eyes of big business and banks.
Furthermore, the United States' adherence to the gold standard deteriorated with the onset of the Great Depression, even after Western European countries abandoned it. Roosevelt officially removed the United States from the gold standard when he signed the Gold Reserve Act of 1934, which made most forms of gold illegal for the general public to possess. The end of the gold standard was said to have shocked Wall Street because they saw a currency that was not solidly backed by gold as inflationary, undermining both private and business fortunes. The 1973 book The Plot to Seize the White House notes that “Roosevelt was damned as a socialist or Communist out to destroy private enterprise by sapping the gold backing of wealth in order to subsidize the poor.”

Smedley Butler in uniform.
This formidable class of disproportionate money and influence began plotting to take action for their grievances, a scheme that finally unraveled before public eyes in November 1934. In a series of allegations, General Smedley Butler revealed the existence of a political conspiracy by business leaders to depose President Roosevelt. A special House committee heard his testimony in private.
Butler testified under oath that Gerald P. MacGuire approached him about leading a private army of 500,000 ex-soldiers funded by $300 million provided by a group of wealthy businessmen. MacGuire, a bond salesman with Grayson M-P Murphy & Co. and a member of the Connecticut American Legion, told Butler that he was to lead this coup d'état to overthrow the United States government and replace it with a system more favorable to big business interests.
According to Butler, Roosevelt was to be deposed and replaced by General Hugh S. Johnson, former head of the National Recovery Administration, with the J.P. Morgan banking firm financing the plot. The number of veterans outnumbered active duty service members at the time, and it was thought that such a large force could swiftly pull off a coup of that magnitude.
Related: 17 Remarkable Books About the Great Depression
Butler and MacGuire's meetings began in July 1933 and lasted until the first half of 1934. MacGuire's initial proposal seemed innocent; he asked Butler to run for National Commander of the American Legion, a well-known veterans' organization. When MacGuire steered the conversation toward getting the American Legion to pass a resolution in favor of restoring the gold standard, Butler’s suspicions grew. According to Butler, MacGuire's reasoning was that the gold standard was a veterans' issue because their bonuses would be "worthless paper'' if the currency was not backed by gold.
Eventually, MacGuire revealed the extent of the true plot to Butler. In return for his participation, Butler's mortgage and his children's college education would be paid for. MacGuire allegedly told Butler's former personal secretary that the plot's conspirators would meet at a Veterans of Foreign Wars convention to plan their next steps, which Butler passed on to Veterans of Foreign Wars commander James E. Van Zandt.
Butler alleged that the entire scheme was backed by a new conservative lobbying group called the American Liberty League. This group included J.P. Morgan Jr., Irénée du Pont, and the CEOs of General Motors, Birds Eye, and General Foods, among others, with nearly $40 billion in assets—equivalent to $778 billion today.
In addition, the list of alleged conspirators included former presidential candidate John W. Davis, J. P. Morgan partner Thomas W. Lamont, Prescott Bush, and numerous military leaders. Butler named Bill Doyle, the commander of the Massachusetts American Legion, as a co-conspirator, as Doyle apparently attended the first few meetings. Butler also gave the name Robert Sterling Clerk, who served as a second lieutenant under Butler during the Boxer Rebellion in China. He came from a wealthy family and was the heir to the Singer Corporation fortune, earning him the nickname "the millionaire lieutenant."
Instead of following through with MacGuire’s instructions and personal favors, Butler turned to the head of the FBI, J. Edgar Hoover, in the fall of 1934.
All parties alleged to be involved, however, publicly denied Butler's story, dismissing it as a joke, fantasy, or slander. But Butler, a distinguished veteran and two-time Medal of Honor recipient, was the most decorated Marine in US history at the time and had no apparent motive to lie.
Related: Enriching FDR Biographies that Explore the President's Impactful Life and Legacy
After hearing Butler out and collecting additional information, the congressional committee informed Congress it “had received evidence that certain persons had made an attempt to establish a fascist organization in this country. There is no question that these attempts were discussed, were planned, and might have been placed in execution when and if the financial backers deemed it expedient.”
There were no further investigations or prosecutions. At the time, the plot was completely dismissed by the news media, with a New York Times editorial calling it a "gigantic hoax" and a "bald and unconvincing narrative." However, the publication swiftly changed its tune after the congressional committee released its last report. Today, most historians agree that the Business Plot was real. The only question is whether it was ever as close to execution as Butler claimed, or if it was merely a harebrained scheme brought up in discussions that never gained traction.
Butler was well-known for his book War Is a Racket , published shortly after the events of the Business Plot, in which he stated that he had named names, and that those names had been removed from his testimony before it was released to the public. “Like most committees, it has slaughtered the little and allowed the big to escape. The big shots weren’t even called to testify,” he stated in a radio interview.
Sources: History.com , Time magazine , BBC , Washington Post
Get historic book deals and news delivered to your inbox
© 2024 OPEN ROAD MEDIA
- We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
January 4, 2023
Considering History , History
Considering History: The 1933 Business Plot to Overthrow America
In 1933, a group on businessmen conspired to unseat President Roosevelt and overthrow the government. One man stopped them.
Ben Railton
- Share on Facebook (opens new window)
- Share on Twitter (opens new window)
- Share on Pinterest (opens new window)

Weekly Newsletter
The best of The Saturday Evening Post in your inbox!
This series by American studies professor Ben Railton explores the connections between America’s past and present.
EDITOR’S NOTE: This column contains spoilers for the new film Amsterdam .
Toward the climax of director and screenwriter David O. Russell’s new historical drama Amsterdam (2022), Dr. Burt Berendsen (Christian Bale) narrates a line that is not only central to the film’s plot and themes, but also one of the most telling quotes in recent American film history. Burt and his friends have begun to uncover the shadowy and sinister plan at the film’s center, a plan by powerful moneyed figures to overthrow the president of the United States and replace him with an unelected dictator. And Burt asks both himself and the audience, in the voiceover narration to which the film returns frequently, “What’s more un-American than a dictatorship built by American business?”
Subscribe and get unlimited access to our online magazine archive.
Amsterdam pulls together, fictionalizes, and at times troublingly misrepresents a number of threads from the 1930s and early 20 th century American history. But that sinister plan is based on very real 1933 histories: the so-called Business Plot. Those histories reveal that Burt’s quote is both profoundly wrong and inspiringly right about the battle for American identity and ideals.
Given the entirely justified recent attention to the history of American coups, past and present , it’s quite striking that the 1933 Business Plot isn’t yet better known ( Gangsters of Capitalism , a 2022 book by Jonathan Katz, who also wrote the Rolling Stone article “ The Plot Against American Democracy That Isn’t Taught in Schools ,” is the place to begin learning a lot more). A group of prominent American businessmen , featuring such noteworthy figures as Robert Sterling Clark and Prescott Bush, had become dissatisfied with newly elected President Franklin Roosevelt’s responses to the Great Depression, including both government programs to counter unemployment (which these figures saw as creeping socialism) and the end of the gold standard for U.S. currency (which threatened their own wealth). These men and their allies began planning for a possible coup , supported by the military and based on the rationalization that Roosevelt’s physical infirmities made him unable to perform presidential duties.
So contrary to Burt’s quote, such a plan was conceived and could indeed have happened here in America. A main reason it did not was because of the man whom the plotters approached to serve as that unelected dictator: General Smedley D. Butler (1881-1940). At the time of his death Butler was the most decorated Marine in U.S. history , having commanded the 13 th Regiment in World War I as well as serving in countless other military actions in the Philippines, China, Honduras, Nicaragua, Mexico, and Haiti. But by the 1930s he had become disillusioned with both war and the U.S. government, delivering a series of impassioned speeches to veterans’ groups and other audiences that became the basis for his subsequent book War Is a Racket (1935). Perhaps those speeches and his increasingly anti-authoritarian views led the Business Plot leaders to assume that Butler would be on their side in opposing and helping overthrow the government.

Butler apparently shared the fictional Burt’s sentiments about the profoundly un-American nature of such plans, however. After leading the conspiracy’s members along for a time in an effort to learn more about their intentions, in November 1934 Butler began testifying about the plot to the House of Representatives Special Committee on Un-American Activities (also known as the McCormack-Dickstein Committee ). At first Butler’s claims were largely dismissed in the media, with the New York Times referring to the idea as nothing more than a “gigantic hoax.” But when the committee released its report in February 1935, after more than two months of testimony and other committee hearings and investigations, Time magazine noted that “a two-month investigation had convinced [the committee] that General Butler’s story of a Fascist march on Washington was alarmingly true” and that the committee “also alleged that definite proof had been found that the much publicized Fascist march on Washington, which was to have been led by Butler, … was actually contemplated.”
Butler refused to lead and instead exposed that proposed march on Washington. Ironically, just a year earlier, he had supported a very different march on the nation’s capital. In the summer of 1932, a group of World War I veterans calling themselves the Bonus Expeditionary Force marched from around the country to Washington, seeking long-delayed (and in the depths of the Depression, desperately needed) compensation for their military service. The participants in this “Bonus Army ” would camp in the city’s Anacostia Flats area for weeks, where they were visited and addressed by none other than Smedley Butler. Indeed, Butler and his son Thomas ate and spent the night with the veterans, and the next morning he gave an impassioned speech to the Bonus Army, calling them fine soldiers, praising their cause, and noting that they had every right to protest and lobby the government on its behalf. Unfortunately the Hoover Administration disagreed , and soon after Butler’s visit, the marchers were violently evicted and their camp was burned down. But in 1933 Franklin and Eleanor Roosevelt (who had also visited the camp) offered them jobs with the newly created CCC. Amsterdam also incorporates the story of the Bonus Army; Burt and his friends are veterans themselves and advocates for veterans who had attended the 1932 Bonus March.

Both the Business Plot’s proposed march and the Bonus Army’s achieved one were tellingly part of 1932-33 America, so I can’t entirely agree with Burt’s perspective that “What’s more un-American than a dictatorship built by American business?” That alliance of business and Fascism ( abroad and at home ) was a frustratingly central element of America in the 1930s . But at the same time, in the battle for America, I entirely agree with Smedley Butler — that the Bonus Army represents the best of America, in direct contrast to such creeping Fascism. As this film helps remind us, those battles are crucial parts of our past and entirely ongoing in our present.
Become a Saturday Evening Post member and enjoy unlimited access. Subscribe now
Recommended

Jun 27, 2024
History , Women's Work
Women’s Work: Give Her Liberty — Mitsuye Endo and the Fight Against Japanese American Internment

Jun 24, 2024
Considering History , History , Sports
Considering History: The Boston Celtics and the City’s History of Race and Sports

Jun 11, 2024
The Gay Deceivers Was an Early Landmark for Queer Cinema
Read Phillip Roth’s Novel, “Plot Against America,” probably based upon these historical facts!
Big Business has gotten its dictatorship in the last forty years, hasn’t it? The Democrat, Clinton, could have reversed much of it, but instead became its ally and advocate.
Smedley Butler’s revelation of the plot has been validated and accurately portrays the intention of the coup – to install a corporate-fascist dictatorship. My disagreement is that in no document I have read did it indicate that the plotters were looking to install Butler a in any political post. His role was to get the military forces (500,000) on board; he was chosen because he had the most loyalty and support of that group than anyone.
The most interesting fact in the “Fascists Plot” was the investigation only took two months with nothing more than testimonies. The most recent attempt to overthrow the government with video of the actual event and criminal prosecutions has gone on for two years. Even more alarming is the Congressional response is to conduct investigations against the minority party and no action on the results of the January investigation.
Business Plot -recruit half a million veterans into private army to overthrow government. I suspect the main source of it was Butler’s imagination following some wild talk!
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Newsletters
- Best Industries
- Business Plans
- Home-Based Business
- The UPS Store
- Customer Service
- Black in Business
- Your Next Move
- Female Founders
- Best Workplaces
- Company Culture
- Public Speaking
- HR/Benefits
- Productivity
- All the Hats
- Digital Transformation
- Artificial Intelligence
- Bringing Innovation to Market
- Cloud Computing
- Social Media
- Data Detectives
- Exit Interview
- Bootstrapping
- Crowdfunding
- Venture Capital
- Business Models
- Personal Finance
- Founder-Friendly Investors
- Upcoming Events
- Inc. 5000 Vision Conference
- Become a Sponsor
- Cox Business
- Verizon Business
- Branded Content
- Apply Inc. 5000 US
Inc. Premium

How to Write a Summary Business Plan
A business plan doesn't have to be all encompassing, especially when you're trying to generate buzz. here are the elements you really need..

When writing a business plan, it's easy to get lost in the details. You want to demonstrate how you've studied the ins and outs of the marketplace and have crunched every conceivable number. But, really, writing a 100+ page business plan is not the best use of your energy.
'I vividly remember years of lengthy business planning cycles that literally produced books - encased in three-ring binders,' says Denise Barnwell, president of Transformation Marketing in West Orange, New Jersey. 'The ritual of producing these big-company business plan ‘bibles' was mostly endured by all. But small business owners don't have time or patience to produce lengthy business plans – they need action plans.'
Fleshing out your business in such detail can be a worthwhile exercise for an entrepreneur, but the truth is that it's not likely anyone else will ever spend the time to read it – whether you're competing in a business plan competition or trying to raise money from investors. That's why you also should be thinking about how to put together a summary or short-form business plan that ranges anywhere from two pages to 15.
The shorter you can make your summary business plan, the better. You want to focus on just a few key elements of your business that will generate the most excitement among those reading it -- without requiring them to invest a weekend in doing so. You can always pass along a more detailed plan to those interested later. 'One of the most common mistakes is for people to get bogged down in details,' says Mark Herschberg, a veteran entrepreneur and instructor at MIT. 'You don't need to describe every feature, or have detailed product designs. If your investors have detailed questions, they'll ask for more information.'
Dig Deeper: How to Write a Great Business Plan
How to Write a Summary Business Plan: A Few Don'ts
With that in mind, here are some suggestions for things to leave OUT of your summary business plan, according to Malla Haridat, founder and CEO of New York City-based New Designs for Life, an organization that teaches children about entrepreneurship:
- Excessive market research: 'You need to do a tight analysis of your product or service and the competitors. But you should be able to summarize it into one page max.'
- An overwritten product description: 'You need to spend no more than a paragraph on this.'
- Detailed finances: 'Bottom line - How much money do you have? How much does it take to run the business? How much will you earn (hopefully)?'
Dig Deeper: 10 Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Business Plan
How to Write a Summary Business Plan: The Essential Pieces
Turning to what you DO want to focus on, consider the following tips offered by Ken Halkin , a business consultant in Amesbury, Massachusetts:
1. Description: Kick off your plan with a one-page description of your business. Give a brief history of the business and its ownership structure by focusing on:
- Who you are
- What you do
- Where you are
2. Vision Statement: Write a concise one- or two-paragraph vision statement, which gives your answer to the question: 'What do we want this company to become over the next five to 10 years?'
3. Mission Statement: Lay the groundwork for your 'brand promise' in a one or two paragraph description of what your company will be to its customers.
4. Values: Provide a list of three to five core principles upon which you will build the business and stick to no matter what.
5. Goals: Make a list of three to five long-term goals that translate your company's vision into specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time-specific objectives.
6. Market research: Take the next two to three pages to briefly answer the following questions:
- What do you know about your industry?
- What do you know about your competition?
- Who is your target customer and what do you know about them (i.e. demographics, buying patterns)?
6(a). Market differentiation: Take the next page to detail what makes your product or service unique in the market by answering questions like:
- What makes you different from your competition that actually matters to your target customer?
- What is your unique value proposition?
- What is your big bold brand promise?
6(b). Marketing message: Based on the answers you outline above, take the next half page to explain the message you plan to communicate to your target market.
6(c). Marketing mix: Use the next page or so to detail the methods you will use to deliver that message.
6(d). Measurement: Follow the previous two sections with another half-page describing how you will measure the effectiveness of each of those delivery methods and, based on the results, adjust your plan accordingly.
7. Sales: Take the next full page to summarize your sales plan by answering these questions:
- What is your overall sales process?
- What are the specific steps in your process?
- How are leads generated? - How are they researched/qualified? - How do you get in front of your customer? - How do you close the sale?
- How will you achieve the optimal sales cycle?
8. Operations plan: Now, take one to two pages to answer the following questions:
- How will you produce the product and/or deliver the service?
- What are the logistics?
- What business process will you employ?
- What facility, equipment, and other resource needs are involved?
- How will you assure and measure quality and customer satisfaction?
- Who are the key players?
- What are their backgrounds and qualifications?
- What are their specific roles?
- How will the business be organized (org. chart)?
9. Personnel Plan: Use one page to describe your 'people' plan by answering questions like:
- What personnel are needed now to accomplish current goals?
- How will the number of people needed change with the growth of the business?
10. Financial Plan: As noted earlier, keep the details about your financials brief, using the same narrative style you have been using throughout the plan. Then, use a footnote to alert readers that more detailed financial schedules and assumptions will exist in a separate document. To keep focused, consider telling your story by providing the following information:
- Start-up costs, if applicable
- Revenue projections with detailed assumptions
- Three- to five-year cash-flow projections
- Three- to five-year balance sheet projections
- Sources and uses of funds if you are raising capital
11. Executive Summary: Save the beginning for the end by taking one to two pages to write a concise synopsis of the entire plan.
If you have followed these guidelines, the narrative portion of your plan should be 10 to 15 pages, with perhaps another eight to 15 pages of attachments and schedules related to the additional details of the marketing and financial sections. Halkin also recommends that you put together a detailed strategic plan that establishes the strategies, steps, accountability and timelines for achieving the one-year goals of the business.
For additional help, look to resources such as the ' The One-Page Business Plan ' or entrepreneurial coach Verne Harnish's book, Mastering The Rockefeller Habits , that espouse summarizing your business with a single page of text.
Dig Deeper: Tools for Creating a Business Plan
The Daily Digest for Entrepreneurs and Business Leaders
Privacy Policy
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Rosalie Murphy is a small-business writer at NerdWallet. Since 2021, she has covered business insurance, banking, credit cards and e-commerce software, and her reporting has been featured by The Associated Press, MarketWatch, Entrepreneur and many other publications. Rosalie holds a graduate certificate in Quantitative Business Management from Kent State University and is now pursuing an MBA. She is based in Chicago.

Ryan Lane is an editor on NerdWallet’s small-business team. He joined NerdWallet in 2019 as a student loans writer, serving as an authority on that topic after spending more than a decade at student loan guarantor American Student Assistance. In that role, Ryan co-authored the Student Loan Ranger blog in partnership with U.S. News & World Report, as well as wrote and edited content about education financing and financial literacy for multiple online properties, e-courses and more. Ryan also previously oversaw the production of life science journals as a managing editor for publisher Cell Press. Ryan is located in Rochester, New York.

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
How to Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps (+ Template and Examples)
Every successful business has one thing in common, a good and well-executed business plan. A business plan is more than a document, it is a complete guide that outlines the goals your business wants to achieve, including its financial goals . It helps you analyze results, make strategic decisions, show your business operations and growth.
If you want to start a business or already have one and need to pitch it to investors for funding, writing a good business plan improves your chances of attracting financiers. As a startup, if you want to secure loans from financial institutions, part of the requirements involve submitting your business plan.
Writing a business plan does not have to be a complicated or time-consuming process. In this article, you will learn the step-by-step process for writing a successful business plan.
You will also learn what you need a business plan for, tips and strategies for writing a convincing business plan, business plan examples and templates that will save you tons of time, and the alternatives to the traditional business plan.
Let’s get started.
What Do You Need A Business Plan For?
Businesses create business plans for different purposes such as to secure funds, monitor business growth, measure your marketing strategies, and measure your business success.
1. Secure Funds
One of the primary reasons for writing a business plan is to secure funds, either from financial institutions/agencies or investors.
For you to effectively acquire funds, your business plan must contain the key elements of your business plan . For example, your business plan should include your growth plans, goals you want to achieve, and milestones you have recorded.
A business plan can also attract new business partners that are willing to contribute financially and intellectually. If you are writing a business plan to a bank, your project must show your traction , that is, the proof that you can pay back any loan borrowed.
Also, if you are writing to an investor, your plan must contain evidence that you can effectively utilize the funds you want them to invest in your business. Here, you are using your business plan to persuade a group or an individual that your business is a source of a good investment.
2. Monitor Business Growth
A business plan can help you track cash flows in your business. It steers your business to greater heights. A business plan capable of tracking business growth should contain:
- The business goals
- Methods to achieve the goals
- Time-frame for attaining those goals
A good business plan should guide you through every step in achieving your goals. It can also track the allocation of assets to every aspect of the business. You can tell when you are spending more than you should on a project.
You can compare a business plan to a written GPS. It helps you manage your business and hints at the right time to expand your business.
3. Measure Business Success
A business plan can help you measure your business success rate. Some small-scale businesses are thriving better than more prominent companies because of their track record of success.
Right from the onset of your business operation, set goals and work towards them. Write a plan to guide you through your procedures. Use your plan to measure how much you have achieved and how much is left to attain.
You can also weigh your success by monitoring the position of your brand relative to competitors. On the other hand, a business plan can also show you why you have not achieved a goal. It can tell if you have elapsed the time frame you set to attain a goal.
4. Document Your Marketing Strategies
You can use a business plan to document your marketing plans. Every business should have an effective marketing plan.
Competition mandates every business owner to go the extraordinary mile to remain relevant in the market. Your business plan should contain your marketing strategies that work. You can measure the success rate of your marketing plans.
In your business plan, your marketing strategy must answer the questions:
- How do you want to reach your target audience?
- How do you plan to retain your customers?
- What is/are your pricing plans?
- What is your budget for marketing?

How to Write a Business Plan Step-by-Step
1. create your executive summary.
The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans . Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.

Generally, there are nine sections in a business plan, the executive summary should condense essential ideas from the other eight sections.
A good executive summary should do the following:
- A Snapshot of Growth Potential. Briefly inform the reader about your company and why it will be successful)
- Contain your Mission Statement which explains what the main objective or focus of your business is.
- Product Description and Differentiation. Brief description of your products or services and why it is different from other solutions in the market.
- The Team. Basic information about your company’s leadership team and employees
- Business Concept. A solid description of what your business does.
- Target Market. The customers you plan to sell to.
- Marketing Strategy. Your plans on reaching and selling to your customers
- Current Financial State. Brief information about what revenue your business currently generates.
- Projected Financial State. Brief information about what you foresee your business revenue to be in the future.
The executive summary is the make-or-break section of your business plan. If your summary cannot in less than two pages cannot clearly describe how your business will solve a particular problem of your target audience and make a profit, your business plan is set on a faulty foundation.
Avoid using the executive summary to hype your business, instead, focus on helping the reader understand the what and how of your plan.
View the executive summary as an opportunity to introduce your vision for your company. You know your executive summary is powerful when it can answer these key questions:
- Who is your target audience?
- What sector or industry are you in?
- What are your products and services?
- What is the future of your industry?
- Is your company scaleable?
- Who are the owners and leaders of your company? What are their backgrounds and experience levels?
- What is the motivation for starting your company?
- What are the next steps?
Writing the executive summary last although it is the most important section of your business plan is an excellent idea. The reason why is because it is a high-level overview of your business plan. It is the section that determines whether potential investors and lenders will read further or not.
The executive summary can be a stand-alone document that covers everything in your business plan. It is not uncommon for investors to request only the executive summary when evaluating your business. If the information in the executive summary impresses them, they will ask for the complete business plan.
If you are writing your business plan for your planning purposes, you do not need to write the executive summary.
2. Add Your Company Overview
The company overview or description is the next section in your business plan after the executive summary. It describes what your business does.
Adding your company overview can be tricky especially when your business is still in the planning stages. Existing businesses can easily summarize their current operations but may encounter difficulties trying to explain what they plan to become.
Your company overview should contain the following:
- What products and services you will provide
- Geographical markets and locations your company have a presence
- What you need to run your business
- Who your target audience or customers are
- Who will service your customers
- Your company’s purpose, mission, and vision
- Information about your company’s founders
- Who the founders are
- Notable achievements of your company so far
When creating a company overview, you have to focus on three basics: identifying your industry, identifying your customer, and explaining the problem you solve.
If you are stuck when creating your company overview, try to answer some of these questions that pertain to you.
- Who are you targeting? (The answer is not everyone)
- What pain point does your product or service solve for your customers that they will be willing to spend money on resolving?
- How does your product or service overcome that pain point?
- Where is the location of your business?
- What products, equipment, and services do you need to run your business?
- How is your company’s product or service different from your competition in the eyes of your customers?
- How many employees do you need and what skills do you require them to have?
After answering some or all of these questions, you will get more than enough information you need to write your company overview or description section. When writing this section, describe what your company does for your customers.

The company description or overview section contains three elements: mission statement, history, and objectives.
- Mission Statement
The mission statement refers to the reason why your business or company is existing. It goes beyond what you do or sell, it is about the ‘why’. A good mission statement should be emotional and inspirational.
Your mission statement should follow the KISS rule (Keep It Simple, Stupid). For example, Shopify’s mission statement is “Make commerce better for everyone.”
When describing your company’s history, make it simple and avoid the temptation of tying it to a defensive narrative. Write it in the manner you would a profile. Your company’s history should include the following information:
- Founding Date
- Major Milestones
- Location(s)
- Flagship Products or Services
- Number of Employees
- Executive Leadership Roles
When you fill in this information, you use it to write one or two paragraphs about your company’s history.
Business Objectives
Your business objective must be SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.) Failure to clearly identify your business objectives does not inspire confidence and makes it hard for your team members to work towards a common purpose.
3. Perform Market and Competitive Analyses to Proof a Big Enough Business Opportunity
The third step in writing a business plan is the market and competitive analysis section. Every business, no matter the size, needs to perform comprehensive market and competitive analyses before it enters into a market.
Performing market and competitive analyses are critical for the success of your business. It helps you avoid entering the right market with the wrong product, or vice versa. Anyone reading your business plans, especially financiers and financial institutions will want to see proof that there is a big enough business opportunity you are targeting.
This section is where you describe the market and industry you want to operate in and show the big opportunities in the market that your business can leverage to make a profit. If you noticed any unique trends when doing your research, show them in this section.
Market analysis alone is not enough, you have to add competitive analysis to strengthen this section. There are already businesses in the industry or market, how do you plan to take a share of the market from them?
You have to clearly illustrate the competitive landscape in your business plan. Are there areas your competitors are doing well? Are there areas where they are not doing so well? Show it.
Make it clear in this section why you are moving into the industry and what weaknesses are present there that you plan to explain. How are your competitors going to react to your market entry? How do you plan to get customers? Do you plan on taking your competitors' competitors, tap into other sources for customers, or both?
Illustrate the competitive landscape as well. What are your competitors doing well and not so well?
Answering these questions and thoughts will aid your market and competitive analysis of the opportunities in your space. Depending on how sophisticated your industry is, or the expectations of your financiers, you may need to carry out a more comprehensive market and competitive analysis to prove that big business opportunity.
Instead of looking at the market and competitive analyses as one entity, separating them will make the research even more comprehensive.
Market Analysis
Market analysis, boarding speaking, refers to research a business carried out on its industry, market, and competitors. It helps businesses gain a good understanding of their target market and the outlook of their industry. Before starting a company, it is vital to carry out market research to find out if the market is viable.

The market analysis section is a key part of the business plan. It is the section where you identify who your best clients or customers are. You cannot omit this section, without it your business plan is incomplete.
A good market analysis will tell your readers how you fit into the existing market and what makes you stand out. This section requires in-depth research, it will probably be the most time-consuming part of the business plan to write.
- Market Research
To create a compelling market analysis that will win over investors and financial institutions, you have to carry out thorough market research . Your market research should be targeted at your primary target market for your products or services. Here is what you want to find out about your target market.
- Your target market’s needs or pain points
- The existing solutions for their pain points
- Geographic Location
- Demographics
The purpose of carrying out a marketing analysis is to get all the information you need to show that you have a solid and thorough understanding of your target audience.
Only after you have fully understood the people you plan to sell your products or services to, can you evaluate correctly if your target market will be interested in your products or services.
You can easily convince interested parties to invest in your business if you can show them you thoroughly understand the market and show them that there is a market for your products or services.
How to Quantify Your Target Market
One of the goals of your marketing research is to understand who your ideal customers are and their purchasing power. To quantify your target market, you have to determine the following:
- Your Potential Customers: They are the people you plan to target. For example, if you sell accounting software for small businesses , then anyone who runs an enterprise or large business is unlikely to be your customers. Also, individuals who do not have a business will most likely not be interested in your product.
- Total Households: If you are selling household products such as heating and air conditioning systems, determining the number of total households is more important than finding out the total population in the area you want to sell to. The logic is simple, people buy the product but it is the household that uses it.
- Median Income: You need to know the median income of your target market. If you target a market that cannot afford to buy your products and services, your business will not last long.
- Income by Demographics: If your potential customers belong to a certain age group or gender, determining income levels by demographics is necessary. For example, if you sell men's clothes, your target audience is men.
What Does a Good Market Analysis Entail?
Your business does not exist on its own, it can only flourish within an industry and alongside competitors. Market analysis takes into consideration your industry, target market, and competitors. Understanding these three entities will drastically improve your company’s chances of success.

You can view your market analysis as an examination of the market you want to break into and an education on the emerging trends and themes in that market. Good market analyses include the following:
- Industry Description. You find out about the history of your industry, the current and future market size, and who the largest players/companies are in your industry.
- Overview of Target Market. You research your target market and its characteristics. Who are you targeting? Note, it cannot be everyone, it has to be a specific group. You also have to find out all information possible about your customers that can help you understand how and why they make buying decisions.
- Size of Target Market: You need to know the size of your target market, how frequently they buy, and the expected quantity they buy so you do not risk overproducing and having lots of bad inventory. Researching the size of your target market will help you determine if it is big enough for sustained business or not.
- Growth Potential: Before picking a target market, you want to be sure there are lots of potential for future growth. You want to avoid going for an industry that is declining slowly or rapidly with almost zero growth potential.
- Market Share Potential: Does your business stand a good chance of taking a good share of the market?
- Market Pricing and Promotional Strategies: Your market analysis should give you an idea of the price point you can expect to charge for your products and services. Researching your target market will also give you ideas of pricing strategies you can implement to break into the market or to enjoy maximum profits.
- Potential Barriers to Entry: One of the biggest benefits of conducting market analysis is that it shows you every potential barrier to entry your business will likely encounter. It is a good idea to discuss potential barriers to entry such as changing technology. It informs readers of your business plan that you understand the market.
- Research on Competitors: You need to know the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and how you can exploit them for the benefit of your business. Find patterns and trends among your competitors that make them successful, discover what works and what doesn’t, and see what you can do better.
The market analysis section is not just for talking about your target market, industry, and competitors. You also have to explain how your company can fill the hole you have identified in the market.
Here are some questions you can answer that can help you position your product or service in a positive light to your readers.
- Is your product or service of superior quality?
- What additional features do you offer that your competitors do not offer?
- Are you targeting a ‘new’ market?
Basically, your market analysis should include an analysis of what already exists in the market and an explanation of how your company fits into the market.
Competitive Analysis
In the competitive analysis section, y ou have to understand who your direct and indirect competitions are, and how successful they are in the marketplace. It is the section where you assess the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, the advantage(s) they possess in the market and show the unique features or qualities that make you different from your competitors.

Many businesses do market analysis and competitive analysis together. However, to fully understand what the competitive analysis entails, it is essential to separate it from the market analysis.
Competitive analysis for your business can also include analysis on how to overcome barriers to entry in your target market.
The primary goal of conducting a competitive analysis is to distinguish your business from your competitors. A strong competitive analysis is essential if you want to convince potential funding sources to invest in your business. You have to show potential investors and lenders that your business has what it takes to compete in the marketplace successfully.
Competitive analysis will s how you what the strengths of your competition are and what they are doing to maintain that advantage.
When doing your competitive research, you first have to identify your competitor and then get all the information you can about them. The idea of spending time to identify your competitor and learn everything about them may seem daunting but it is well worth it.
Find answers to the following questions after you have identified who your competitors are.
- What are your successful competitors doing?
- Why is what they are doing working?
- Can your business do it better?
- What are the weaknesses of your successful competitors?
- What are they not doing well?
- Can your business turn its weaknesses into strengths?
- How good is your competitors’ customer service?
- Where do your competitors invest in advertising?
- What sales and pricing strategies are they using?
- What marketing strategies are they using?
- What kind of press coverage do they get?
- What are their customers saying about your competitors (both the positive and negative)?
If your competitors have a website, it is a good idea to visit their websites for more competitors’ research. Check their “About Us” page for more information.

If you are presenting your business plan to investors, you need to clearly distinguish yourself from your competitors. Investors can easily tell when you have not properly researched your competitors.
Take time to think about what unique qualities or features set you apart from your competitors. If you do not have any direct competition offering your product to the market, it does not mean you leave out the competitor analysis section blank. Instead research on other companies that are providing a similar product, or whose product is solving the problem your product solves.
The next step is to create a table listing the top competitors you want to include in your business plan. Ensure you list your business as the last and on the right. What you just created is known as the competitor analysis table.
Direct vs Indirect Competition
You cannot know if your product or service will be a fit for your target market if you have not understood your business and the competitive landscape.
There is no market you want to target where you will not encounter competition, even if your product is innovative. Including competitive analysis in your business plan is essential.
If you are entering an established market, you need to explain how you plan to differentiate your products from the available options in the market. Also, include a list of few companies that you view as your direct competitors The competition you face in an established market is your direct competition.
In situations where you are entering a market with no direct competition, it does not mean there is no competition there. Consider your indirect competition that offers substitutes for the products or services you offer.
For example, if you sell an innovative SaaS product, let us say a project management software , a company offering time management software is your indirect competition.
There is an easy way to find out who your indirect competitors are in the absence of no direct competitors. You simply have to research how your potential customers are solving the problems that your product or service seeks to solve. That is your direct competition.
Factors that Differentiate Your Business from the Competition
There are three main factors that any business can use to differentiate itself from its competition. They are cost leadership, product differentiation, and market segmentation.
1. Cost Leadership
A strategy you can impose to maximize your profits and gain an edge over your competitors. It involves offering lower prices than what the majority of your competitors are offering.
A common practice among businesses looking to enter into a market where there are dominant players is to use free trials or pricing to attract as many customers as possible to their offer.
2. Product Differentiation
Your product or service should have a unique selling proposition (USP) that your competitors do not have or do not stress in their marketing.
Part of the marketing strategy should involve making your products unique and different from your competitors. It does not have to be different from your competitors, it can be the addition to a feature or benefit that your competitors do not currently have.
3. Market Segmentation
As a new business seeking to break into an industry, you will gain more success from focusing on a specific niche or target market, and not the whole industry.
If your competitors are focused on a general need or target market, you can differentiate yourself from them by having a small and hyper-targeted audience. For example, if your competitors are selling men’s clothes in their online stores , you can sell hoodies for men.
4. Define Your Business and Management Structure
The next step in your business plan is your business and management structure. It is the section where you describe the legal structure of your business and the team running it.
Your business is only as good as the management team that runs it, while the management team can only strive when there is a proper business and management structure in place.
If your company is a sole proprietor or a limited liability company (LLC), a general or limited partnership, or a C or an S corporation, state it clearly in this section.
Use an organizational chart to show the management structure in your business. Clearly show who is in charge of what area in your company. It is where you show how each key manager or team leader’s unique experience can contribute immensely to the success of your company. You can also opt to add the resumes and CVs of the key players in your company.
The business and management structure section should show who the owner is, and other owners of the businesses (if the business has other owners). For businesses or companies with multiple owners, include the percent ownership of the various owners and clearly show the extent of each others’ involvement in the company.
Investors want to know who is behind the company and the team running it to determine if it has the right management to achieve its set goals.
Management Team
The management team section is where you show that you have the right team in place to successfully execute the business operations and ideas. Take time to create the management structure for your business. Think about all the important roles and responsibilities that you need managers for to grow your business.
Include brief bios of each key team member and ensure you highlight only the relevant information that is needed. If your team members have background industry experience or have held top positions for other companies and achieved success while filling that role, highlight it in this section.

A common mistake that many startups make is assigning C-level titles such as (CMO and CEO) to everyone on their team. It is unrealistic for a small business to have those titles. While it may look good on paper for the ego of your team members, it can prevent investors from investing in your business.
Instead of building an unrealistic management structure that does not fit your business reality, it is best to allow business titles to grow as the business grows. Starting everyone at the top leaves no room for future change or growth, which is bad for productivity.
Your management team does not have to be complete before you start writing your business plan. You can have a complete business plan even when there are managerial positions that are empty and need filling.
If you have management gaps in your team, simply show the gaps and indicate you are searching for the right candidates for the role(s). Investors do not expect you to have a full management team when you are just starting your business.
Key Questions to Answer When Structuring Your Management Team
- Who are the key leaders?
- What experiences, skills, and educational backgrounds do you expect your key leaders to have?
- Do your key leaders have industry experience?
- What positions will they fill and what duties will they perform in those positions?
- What level of authority do the key leaders have and what are their responsibilities?
- What is the salary for the various management positions that will attract the ideal candidates?
Additional Tips for Writing the Management Structure Section
1. Avoid Adding ‘Ghost’ Names to Your Management Team
There is always that temptation to include a ‘ghost’ name to your management team to attract and influence investors to invest in your business. Although the presence of these celebrity management team members may attract the attention of investors, it can cause your business to lose any credibility if you get found out.
Seasoned investors will investigate further the members of your management team before committing fully to your business If they find out that the celebrity name used does not play any actual role in your business, they will not invest and may write you off as dishonest.
2. Focus on Credentials But Pay Extra Attention to the Roles
Investors want to know the experience that your key team members have to determine if they can successfully reach the company’s growth and financial goals.
While it is an excellent boost for your key management team to have the right credentials, you also want to pay extra attention to the roles they will play in your company.
Organizational Chart

Adding an organizational chart in this section of your business plan is not necessary, you can do it in your business plan’s appendix.
If you are exploring funding options, it is not uncommon to get asked for your organizational chart. The function of an organizational chart goes beyond raising money, you can also use it as a useful planning tool for your business.
An organizational chart can help you identify how best to structure your management team for maximum productivity and point you towards key roles you need to fill in the future.
You can use the organizational chart to show your company’s internal management structure such as the roles and responsibilities of your management team, and relationships that exist between them.
5. Describe Your Product and Service Offering
In your business plan, you have to describe what you sell or the service you plan to offer. It is the next step after defining your business and management structure. The products and services section is where you sell the benefits of your business.
Here you have to explain how your product or service will benefit your customers and describe your product lifecycle. It is also the section where you write down your plans for intellectual property like patent filings and copyrighting.
The research and development that you are undertaking for your product or service need to be explained in detail in this section. However, do not get too technical, sell the general idea and its benefits.
If you have any diagrams or intricate designs of your product or service, do not include them in the products and services section. Instead, leave them for the addendum page. Also, if you are leaving out diagrams or designs for the addendum, ensure you add this phrase “For more detail, visit the addendum Page #.”
Your product and service section in your business plan should include the following:
- A detailed explanation that clearly shows how your product or service works.
- The pricing model for your product or service.
- Your business’ sales and distribution strategy.
- The ideal customers that want your product or service.
- The benefits of your products and services.
- Reason(s) why your product or service is a better alternative to what your competitors are currently offering in the market.
- Plans for filling the orders you receive
- If you have current or pending patents, copyrights, and trademarks for your product or service, you can also discuss them in this section.
What to Focus On When Describing the Benefits, Lifecycle, and Production Process of Your Products or Services
In the products and services section, you have to distill the benefits, lifecycle, and production process of your products and services.
When describing the benefits of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Unique features
- Translating the unique features into benefits
- The emotional, psychological, and practical payoffs to attract customers
- Intellectual property rights or any patents
When describing the product life cycle of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Upsells, cross-sells, and down-sells
- Time between purchases
- Plans for research and development.
When describing the production process for your products or services, you need to think about the following:
- The creation of new or existing products and services.
- The sources for the raw materials or components you need for production.
- Assembling the products
- Maintaining quality control
- Supply-chain logistics (receiving the raw materials and delivering the finished products)
- The day-to-day management of the production processes, bookkeeping, and inventory.
Tips for Writing the Products or Services Section of Your Business Plan
1. Avoid Technical Descriptions and Industry Buzzwords
The products and services section of your business plan should clearly describe the products and services that your company provides. However, it is not a section to include technical jargons that anyone outside your industry will not understand.
A good practice is to remove highly detailed or technical descriptions in favor of simple terms. Industry buzzwords are not necessary, if there are simpler terms you can use, then use them. If you plan to use your business plan to source funds, making the product or service section so technical will do you no favors.
2. Describe How Your Products or Services Differ from Your Competitors
When potential investors look at your business plan, they want to know how the products and services you are offering differ from that of your competition. Differentiating your products or services from your competition in a way that makes your solution more attractive is critical.
If you are going the innovative path and there is no market currently for your product or service, you need to describe in this section why the market needs your product or service.
For example, overnight delivery was a niche business that only a few companies were participating in. Federal Express (FedEx) had to show in its business plan that there was a large opportunity for that service and they justified why the market needed that service.
3. Long or Short Products or Services Section
Should your products or services section be short? Does the long products or services section attract more investors?
There are no straightforward answers to these questions. Whether your products or services section should be long or relatively short depends on the nature of your business.
If your business is product-focused, then automatically you need to use more space to describe the details of your products. However, if the product your business sells is a commodity item that relies on competitive pricing or other pricing strategies, you do not have to use up so much space to provide significant details about the product.
Likewise, if you are selling a commodity that is available in numerous outlets, then you do not have to spend time on writing a long products or services section.
The key to the success of your business is most likely the effectiveness of your marketing strategies compared to your competitors. Use more space to address that section.
If you are creating a new product or service that the market does not know about, your products or services section can be lengthy. The reason why is because you need to explain everything about the product or service such as the nature of the product, its use case, and values.
A short products or services section for an innovative product or service will not give the readers enough information to properly evaluate your business.
4. Describe Your Relationships with Vendors or Suppliers
Your business will rely on vendors or suppliers to supply raw materials or the components needed to make your products. In your products and services section, describe your relationships with your vendors and suppliers fully.
Avoid the mistake of relying on only one supplier or vendor. If that supplier or vendor fails to supply or goes out of business, you can easily face supply problems and struggle to meet your demands. Plan to set up multiple vendor or supplier relationships for better business stability.
5. Your Primary Goal Is to Convince Your Readers
The primary goal of your business plan is to convince your readers that your business is viable and to create a guide for your business to follow. It applies to the products and services section.
When drafting this section, think like the reader. See your reader as someone who has no idea about your products and services. You are using the products and services section to provide the needed information to help your reader understand your products and services. As a result, you have to be clear and to the point.
While you want to educate your readers about your products or services, you also do not want to bore them with lots of technical details. Show your products and services and not your fancy choice of words.
Your products and services section should provide the answer to the “what” question for your business. You and your management team may run the business, but it is your products and services that are the lifeblood of the business.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing your Products and Services Section
Answering these questions can help you write your products and services section quickly and in a way that will appeal to your readers.
- Are your products existing on the market or are they still in the development stage?
- What is your timeline for adding new products and services to the market?
- What are the positives that make your products and services different from your competitors?
- Do your products and services have any competitive advantage that your competitors’ products and services do not currently have?
- Do your products or services have any competitive disadvantages that you need to overcome to compete with your competitors? If your answer is yes, state how you plan to overcome them,
- How much does it cost to produce your products or services? How much do you plan to sell it for?
- What is the price for your products and services compared to your competitors? Is pricing an issue?
- What are your operating costs and will it be low enough for you to compete with your competitors and still take home a reasonable profit margin?
- What is your plan for acquiring your products? Are you involved in the production of your products or services?
- Are you the manufacturer and produce all the components you need to create your products? Do you assemble your products by using components supplied by other manufacturers? Do you purchase your products directly from suppliers or wholesalers?
- Do you have a steady supply of products that you need to start your business? (If your business is yet to kick-off)
- How do you plan to distribute your products or services to the market?
You can also hint at the marketing or promotion plans you have for your products or services such as how you plan to build awareness or retain customers. The next section is where you can go fully into details about your business’s marketing and sales plan.
6. Show and Explain Your Marketing and Sales Plan
Providing great products and services is wonderful, but it means nothing if you do not have a marketing and sales plan to inform your customers about them. Your marketing and sales plan is critical to the success of your business.
The sales and marketing section is where you show and offer a detailed explanation of your marketing and sales plan and how you plan to execute it. It covers your pricing plan, proposed advertising and promotion activities, activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success, and the benefits of your products and services.
There are several ways you can approach your marketing and sales strategy. Ideally, your marketing and sales strategy has to fit the unique needs of your business.
In this section, you describe how the plans your business has for attracting and retaining customers, and the exact process for making a sale happen. It is essential to thoroughly describe your complete marketing and sales plans because you are still going to reference this section when you are making financial projections for your business.
Outline Your Business’ Unique Selling Proposition (USP)

The sales and marketing section is where you outline your business’s unique selling proposition (USP). When you are developing your unique selling proposition, think about the strongest reasons why people should buy from you over your competition. That reason(s) is most likely a good fit to serve as your unique selling proposition (USP).
Target Market and Target Audience
Plans on how to get your products or services to your target market and how to get your target audience to buy them go into this section. You also highlight the strengths of your business here, particularly what sets them apart from your competition.

Before you start writing your marketing and sales plan, you need to have properly defined your target audience and fleshed out your buyer persona. If you do not first understand the individual you are marketing to, your marketing and sales plan will lack any substance and easily fall.
Creating a Smart Marketing and Sales Plan
Marketing your products and services is an investment that requires you to spend money. Like any other investment, you have to generate a good return on investment (ROI) to justify using that marketing and sales plan. Good marketing and sales plans bring in high sales and profits to your company.
Avoid spending money on unproductive marketing channels. Do your research and find out the best marketing and sales plan that works best for your company.
Your marketing and sales plan can be broken into different parts: your positioning statement, pricing, promotion, packaging, advertising, public relations, content marketing, social media, and strategic alliances.
Your Positioning Statement
Your positioning statement is the first part of your marketing and sales plan. It refers to the way you present your company to your customers.
Are you the premium solution, the low-price solution, or are you the intermediary between the two extremes in the market? What do you offer that your competitors do not that can give you leverage in the market?
Before you start writing your positioning statement, you need to spend some time evaluating the current market conditions. Here are some questions that can help you to evaluate the market
- What are the unique features or benefits that you offer that your competitors lack?
- What are your customers’ primary needs and wants?
- Why should a customer choose you over your competition? How do you plan to differentiate yourself from the competition?
- How does your company’s solution compare with other solutions in the market?
After answering these questions, then you can start writing your positioning statement. Your positioning statement does not have to be in-depth or too long.
All you need to explain with your positioning statement are two focus areas. The first is the position of your company within the competitive landscape. The other focus area is the core value proposition that sets your company apart from other alternatives that your ideal customer might consider.
Here is a simple template you can use to develop a positioning statement.
For [description of target market] who [need of target market], [product or service] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [top competition], it [most essential distinguishing feature].
For example, let’s create the positioning statement for fictional accounting software and QuickBooks alternative , TBooks.
“For small business owners who need accounting services, TBooks is an accounting software that helps small businesses handle their small business bookkeeping basics quickly and easily. Unlike Wave, TBooks gives small businesses access to live sessions with top accountants.”
You can edit this positioning statement sample and fill it with your business details.
After writing your positioning statement, the next step is the pricing of your offerings. The overall positioning strategy you set in your positioning statement will often determine how you price your products or services.
Pricing is a powerful tool that sends a strong message to your customers. Failure to get your pricing strategy right can make or mar your business. If you are targeting a low-income audience, setting a premium price can result in low sales.
You can use pricing to communicate your positioning to your customers. For example, if you are offering a product at a premium price, you are sending a message to your customers that the product belongs to the premium category.
Basic Rules to Follow When Pricing Your Offering
Setting a price for your offering involves more than just putting a price tag on it. Deciding on the right pricing for your offering requires following some basic rules. They include covering your costs, primary and secondary profit center pricing, and matching the market rate.
- Covering Your Costs: The price you set for your products or service should be more than it costs you to produce and deliver them. Every business has the same goal, to make a profit. Depending on the strategy you want to use, there are exceptions to this rule. However, the vast majority of businesses follow this rule.
- Primary and Secondary Profit Center Pricing: When a company sets its price above the cost of production, it is making that product its primary profit center. A company can also decide not to make its initial price its primary profit center by selling below or at even with its production cost. It rather depends on the support product or even maintenance that is associated with the initial purchase to make its profit. The initial price thus became its secondary profit center.
- Matching the Market Rate: A good rule to follow when pricing your products or services is to match your pricing with consumer demand and expectations. If you price your products or services beyond the price your customer perceives as the ideal price range, you may end up with no customers. Pricing your products too low below what your customer perceives as the ideal price range may lead to them undervaluing your offering.
Pricing Strategy
Your pricing strategy influences the price of your offering. There are several pricing strategies available for you to choose from when examining the right pricing strategy for your business. They include cost-plus pricing, market-based pricing, value pricing, and more.

- Cost-plus Pricing: This strategy is one of the simplest and oldest pricing strategies. Here you consider the cost of producing a unit of your product and then add a profit to it to arrive at your market price. It is an effective pricing strategy for manufacturers because it helps them cover their initial costs. Another name for the cost-plus pricing strategy is the markup pricing strategy.
- Market-based Pricing: This pricing strategy analyses the market including competitors’ pricing and then sets a price based on what the market is expecting. With this pricing strategy, you can either set your price at the low-end or high-end of the market.
- Value Pricing: This pricing strategy involves setting a price based on the value you are providing to your customer. When adopting a value-based pricing strategy, you have to set a price that your customers are willing to pay. Service-based businesses such as small business insurance providers , luxury goods sellers, and the fashion industry use this pricing strategy.
After carefully sorting out your positioning statement and pricing, the next item to look at is your promotional strategy. Your promotional strategy explains how you plan on communicating with your customers and prospects.
As a business, you must measure all your costs, including the cost of your promotions. You also want to measure how much sales your promotions bring for your business to determine its usefulness. Promotional strategies or programs that do not lead to profit need to be removed.
There are different types of promotional strategies you can adopt for your business, they include advertising, public relations, and content marketing.
Advertising
Your business plan should include your advertising plan which can be found in the marketing and sales plan section. You need to include an overview of your advertising plans such as the areas you plan to spend money on to advertise your business and offers.
Ensure that you make it clear in this section if your business will be advertising online or using the more traditional offline media, or the combination of both online and offline media. You can also include the advertising medium you want to use to raise awareness about your business and offers.
Some common online advertising mediums you can use include social media ads, landing pages, sales pages, SEO, Pay-Per-Click, emails, Google Ads, and others. Some common traditional and offline advertising mediums include word of mouth, radios, direct mail, televisions, flyers, billboards, posters, and others.
A key component of your advertising strategy is how you plan to measure the effectiveness and success of your advertising campaign. There is no point in sticking with an advertising plan or medium that does not produce results for your business in the long run.
Public Relations
A great way to reach your customers is to get the media to cover your business or product. Publicity, especially good ones, should be a part of your marketing and sales plan. In this section, show your plans for getting prominent reviews of your product from reputable publications and sources.
Your business needs that exposure to grow. If public relations is a crucial part of your promotional strategy, provide details about your public relations plan here.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is a popular promotional strategy used by businesses to inform and attract their customers. It is about teaching and educating your prospects on various topics of interest in your niche, it does not just involve informing them about the benefits and features of the products and services you have,

Businesses publish content usually for free where they provide useful information, tips, and advice so that their target market can be made aware of the importance of their products and services. Content marketing strategies seek to nurture prospects into buyers over time by simply providing value.
Your company can create a blog where it will be publishing content for its target market. You will need to use the best website builder such as Wix and Squarespace and the best web hosting services such as Bluehost, Hostinger, and other Bluehost alternatives to create a functional blog or website.
If content marketing is a crucial part of your promotional strategy (as it should be), detail your plans under promotions.
Including high-quality images of the packaging of your product in your business plan is a lovely idea. You can add the images of the packaging of that product in the marketing and sales plan section. If you are not selling a product, then you do not need to include any worry about the physical packaging of your product.
When organizing the packaging section of your business plan, you can answer the following questions to make maximum use of this section.
- Is your choice of packaging consistent with your positioning strategy?
- What key value proposition does your packaging communicate? (It should reflect the key value proposition of your business)
- How does your packaging compare to that of your competitors?
Social Media
Your 21st-century business needs to have a good social media presence. Not having one is leaving out opportunities for growth and reaching out to your prospect.
You do not have to join the thousands of social media platforms out there. What you need to do is join the ones that your customers are active on and be active there.

Businesses use social media to provide information about their products such as promotions, discounts, the benefits of their products, and content on their blogs.
Social media is also a platform for engaging with your customers and getting feedback about your products or services. Make no mistake, more and more of your prospects are using social media channels to find more information about companies.
You need to consider the social media channels you want to prioritize your business (prioritize the ones your customers are active in) and your branding plans in this section.

Strategic Alliances
If your company plans to work closely with other companies as part of your sales and marketing plan, include it in this section. Prove details about those partnerships in your business plan if you have already established them.
Strategic alliances can be beneficial for all parties involved including your company. Working closely with another company in the form of a partnership can provide access to a different target market segment for your company.
The company you are partnering with may also gain access to your target market or simply offer a new product or service (that of your company) to its customers.
Mutually beneficial partnerships can cover the weaknesses of one company with the strength of another. You should consider strategic alliances with companies that sell complimentary products to yours. For example, if you provide printers, you can partner with a company that produces ink since the customers that buy printers from you will also need inks for printing.
Steps Involved in Creating a Marketing and Sales Plan
1. Focus on Your Target Market
Identify who your customers are, the market you want to target. Then determine the best ways to get your products or services to your potential customers.
2. Evaluate Your Competition
One of the goals of having a marketing plan is to distinguish yourself from your competition. You cannot stand out from them without first knowing them in and out.
You can know your competitors by gathering information about their products, pricing, service, and advertising campaigns.
These questions can help you know your competition.
- What makes your competition successful?
- What are their weaknesses?
- What are customers saying about your competition?
3. Consider Your Brand
Customers' perception of your brand has a strong impact on your sales. Your marketing and sales plan should seek to bolster the image of your brand. Before you start marketing your business, think about the message you want to pass across about your business and your products and services.
4. Focus on Benefits
The majority of your customers do not view your product in terms of features, what they want to know is the benefits and solutions your product offers. Think about the problems your product solves and the benefits it delivers, and use it to create the right sales and marketing message.
Your marketing plan should focus on what you want your customer to get instead of what you provide. Identify those benefits in your marketing and sales plan.
5. Focus on Differentiation
Your marketing and sales plan should look for a unique angle they can take that differentiates your business from the competition, even if the products offered are similar. Some good areas of differentiation you can use are your benefits, pricing, and features.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing Your Marketing and Sales Plan
- What is your company’s budget for sales and marketing campaigns?
- What key metrics will you use to determine if your marketing plans are successful?
- What are your alternatives if your initial marketing efforts do not succeed?
- Who are the sales representatives you need to promote your products or services?
- What are the marketing and sales channels you plan to use? How do you plan to get your products in front of your ideal customers?
- Where will you sell your products?
You may want to include samples of marketing materials you plan to use such as print ads, website descriptions, and social media ads. While it is not compulsory to include these samples, it can help you better communicate your marketing and sales plan and objectives.
The purpose of the marketing and sales section is to answer this question “How will you reach your customers?” If you cannot convincingly provide an answer to this question, you need to rework your marketing and sales section.
7. Clearly Show Your Funding Request
If you are writing your business plan to ask for funding from investors or financial institutions, the funding request section is where you will outline your funding requirements. The funding request section should answer the question ‘How much money will your business need in the near future (3 to 5 years)?’
A good funding request section will clearly outline and explain the amount of funding your business needs over the next five years. You need to know the amount of money your business needs to make an accurate funding request.
Also, when writing your funding request, provide details of how the funds will be used over the period. Specify if you want to use the funds to buy raw materials or machinery, pay salaries, pay for advertisements, and cover specific bills such as rent and electricity.
In addition to explaining what you want to use the funds requested for, you need to clearly state the projected return on investment (ROI) . Investors and creditors want to know if your business can generate profit for them if they put funds into it.
Ensure you do not inflate the figures and stay as realistic as possible. Investors and financial institutions you are seeking funds from will do their research before investing money in your business.
If you are not sure of an exact number to request from, you can use some range of numbers as rough estimates. Add a best-case scenario and a work-case scenario to your funding request. Also, include a description of your strategic future financial plans such as selling your business or paying off debts.
Funding Request: Debt or Equity?
When making your funding request, specify the type of funding you want. Do you want debt or equity? Draw out the terms that will be applicable for the funding, and the length of time the funding request will cover.
Case for Equity
If your new business has not yet started generating profits, you are most likely preparing to sell equity in your business to raise capital at the early stage. Equity here refers to ownership. In this case, you are selling a portion of your company to raise capital.
Although this method of raising capital for your business does not put your business in debt, keep in mind that an equity owner may expect to play a key role in company decisions even if he does not hold a major stake in the company.
Most equity sales for startups are usually private transactions . If you are making a funding request by offering equity in exchange for funding, let the investor know that they will be paid a dividend (a share of the company’s profit). Also, let the investor know the process for selling their equity in your business.
Case for Debt
You may decide not to offer equity in exchange for funds, instead, you make a funding request with the promise to pay back the money borrowed at the agreed time frame.
When making a funding request with an agreement to pay back, note that you will have to repay your creditors both the principal amount borrowed and the interest on it. Financial institutions offer this type of funding for businesses.
Large companies combine both equity and debt in their capital structure. When drafting your business plan, decide if you want to offer both or one over the other.
Before you sell equity in exchange for funding in your business, consider if you are willing to accept not being in total control of your business. Also, before you seek loans in your funding request section, ensure that the terms of repayment are favorable.
You should set a clear timeline in your funding request so that potential investors and creditors can know what you are expecting. Some investors and creditors may agree to your funding request and then delay payment for longer than 30 days, meanwhile, your business needs an immediate cash injection to operate efficiently.
Additional Tips for Writing the Funding Request Section of your Business Plan
The funding request section is not necessary for every business, it is only needed by businesses who plan to use their business plan to secure funding.
If you are adding the funding request section to your business plan, provide an itemized summary of how you plan to use the funds requested. Hiring a lawyer, accountant, or other professionals may be necessary for the proper development of this section.
You should also gather and use financial statements that add credibility and support to your funding requests. Ensure that the financial statements you use should include your projected financial data such as projected cash flows, forecast statements, and expenditure budgets.
If you are an existing business, include all historical financial statements such as cash flow statements, balance sheets and income statements .
Provide monthly and quarterly financial statements for a year. If your business has records that date back beyond the one-year mark, add the yearly statements of those years. These documents are for the appendix section of your business plan.
8. Detail Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projections
If you used the funding request section in your business plan, supplement it with a financial plan, metrics, and projections. This section paints a picture of the past performance of your business and then goes ahead to make an informed projection about its future.
The goal of this section is to convince readers that your business is going to be a financial success. It outlines your business plan to generate enough profit to repay the loan (with interest if applicable) and to generate a decent return on investment for investors.
If you have an existing business already in operation, use this section to demonstrate stability through finance. This section should include your cash flow statements, balance sheets, and income statements covering the last three to five years. If your business has some acceptable collateral that you can use to acquire loans, list it in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
Apart from current financial statements, this section should also contain a prospective financial outlook that spans the next five years. Include forecasted income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and capital expenditure budget.
If your business is new and is not yet generating profit, use clear and realistic projections to show the potentials of your business.
When drafting this section, research industry norms and the performance of comparable businesses. Your financial projections should cover at least five years. State the logic behind your financial projections. Remember you can always make adjustments to this section as the variables change.
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section create a baseline which your business can either exceed or fail to reach. If your business fails to reach your projections in this section, you need to understand why it failed.
Investors and loan managers spend a lot of time going through the financial plan, metrics, and projection section compared to other parts of the business plan. Ensure you spend time creating credible financial analyses for your business in this section.
Many entrepreneurs find this section daunting to write. You do not need a business degree to create a solid financial forecast for your business. Business finances, especially for startups, are not as complicated as they seem. There are several online tools and templates that make writing this section so much easier.
Use Graphs and Charts
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section is a great place to use graphs and charts to tell the financial story of your business. Charts and images make it easier to communicate your finances.
Accuracy in this section is key, ensure you carefully analyze your past financial statements properly before making financial projects.
Address the Risk Factors and Show Realistic Financial Projections
Keep your financial plan, metrics, and projection realistic. It is okay to be optimistic in your financial projection, however, you have to justify it.
You should also address the various risk factors associated with your business in this section. Investors want to know the potential risks involved, show them. You should also show your plans for mitigating those risks.
What You Should In The Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection Section of Your Business Plan
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section of your business plan should have monthly sales and revenue forecasts for the first year. It should also include annual projections that cover 3 to 5 years.
A three-year projection is a basic requirement to have in your business plan. However, some investors may request a five-year forecast.
Your business plan should include the following financial statements: sales forecast, personnel plan, income statement, income statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and an exit strategy.
1. Sales Forecast
Sales forecast refers to your projections about the number of sales your business is going to record over the next few years. It is typically broken into several rows, with each row assigned to a core product or service that your business is offering.
One common mistake people make in their business plan is to break down the sales forecast section into long details. A sales forecast should forecast the high-level details.
For example, if you are forecasting sales for a payroll software provider, you could break down your forecast into target market segments or subscription categories.

Your sales forecast section should also have a corresponding row for each sales row to cover the direct cost or Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). The objective of these rows is to show the expenses that your business incurs in making and delivering your product or service.
Note that your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) should only cover those direct costs incurred when making your products. Other indirect expenses such as insurance, salaries, payroll tax, and rent should not be included.
For example, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for a restaurant is the cost of ingredients while for a consulting company it will be the cost of paper and other presentation materials.

2. Personnel Plan
The personnel plan section is where you provide details about the payment plan for your employees. For a small business, you can easily list every position in your company and how much you plan to pay in the personnel plan.
However, for larger businesses, you have to break the personnel plan into functional groups such as sales and marketing.
The personnel plan will also include the cost of an employee beyond salary, commonly referred to as the employee burden. These costs include insurance, payroll taxes , and other essential costs incurred monthly as a result of having employees on your payroll.

3. Income Statement
The income statement section shows if your business is making a profit or taking a loss. Another name for the income statement is the profit and loss (P&L). It takes data from your sales forecast and personnel plan and adds other ongoing expenses you incur while running your business.

Every business plan should have an income statement. It subtracts your business expenses from its earnings to show if your business is generating profit or incurring losses.
The income statement has the following items: sales, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), gross margin, operating expenses, total operating expenses, operating income , total expenses, and net profit.
- Sales refer to the revenue your business generates from selling its products or services. Other names for sales are income or revenue.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to the total cost of selling your products. Other names for COGS are direct costs or cost of sales. Manufacturing businesses use the Costs of Goods Manufactured (COGM) .
- Gross Margin is the figure you get when you subtract your COGS from your sales. In your income statement, you can express it as a percentage of total sales (Gross margin / Sales = Gross Margin Percent).
- Operating Expenses refer to all the expenses you incur from running your business. It exempts the COGS because it stands alone as a core part of your income statement. You also have to exclude taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Your operating expenses include salaries, marketing expenses, research and development (R&D) expenses, and other expenses.
- Total Operating Expenses refers to the sum of all your operating expenses including those exemptions named above under operating expenses.
- Operating Income refers to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is simply known as the acronym EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). Calculating your operating income is simple, all you need to do is to subtract your COGS and total operating expenses from your sales.
- Total Expenses refer to the sum of your operating expenses and your business’ interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
- Net profit shows whether your business has made a profit or taken a loss during a given timeframe.
4. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the money you have in the bank at any given point. It is often confused with the income statement or the profit and loss statement. They are both different types of financial statements. The income statement calculates your profits and losses while the cash flow statement shows you how much you have in the bank.

5. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides an overview of the financial health of your business. It contains information about the assets and liabilities of your company, and owner’s or shareholders’ equity.
You can get the net worth of your company by subtracting your company’s liabilities from its assets.

6. Exit Strategy
The exit strategy refers to a probable plan for selling your business either to the public in an IPO or to another company. It is the last thing you include in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
You can choose to omit the exit strategy from your business plan if you plan to maintain full ownership of your business and do not plan on seeking angel investment or virtual capitalist (VC) funding.
Investors may want to know what your exit plan is. They invest in your business to get a good return on investment.
Your exit strategy does not have to include long and boring details. Ensure you identify some interested parties who may be interested in buying the company if it becomes a success.

Key Questions to Answer with Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection
Your financial plan, metrics, and projection section helps investors, creditors, or your internal managers to understand what your expenses are, the amount of cash you need, and what it takes to make your company profitable. It also shows what you will be doing with any funding.
You do not need to show actual financial data if you do not have one. Adding forecasts and projections to your financial statements is added proof that your strategy is feasible and shows investors you have planned properly.
Here are some key questions to answer to help you develop this section.
- What is your sales forecast for the next year?
- When will your company achieve a positive cash flow?
- What are the core expenses you need to operate?
- How much money do you need upfront to operate or grow your company?
- How will you use the loans or investments?
9. Add an Appendix to Your Business Plan
Adding an appendix to your business plan is optional. It is a useful place to put any charts, tables, legal notes, definitions, permits, résumés, and other critical information that do not fit into other sections of your business plan.
The appendix section is where you would want to include details of a patent or patent-pending if you have one. You can always add illustrations or images of your products here. It is the last section of your business plan.
When writing your business plan, there are details you cut short or remove to prevent the entire section from becoming too lengthy. There are also details you want to include in the business plan but are not a good fit for any of the previous sections. You can add that additional information to the appendix section.
Businesses also use the appendix section to include supporting documents or other materials specially requested by investors or lenders.
You can include just about any information that supports the assumptions and statements you made in the business plan under the appendix. It is the one place in the business plan where unrelated data and information can coexist amicably.
If your appendix section is lengthy, try organizing it by adding a table of contents at the beginning of the appendix section. It is also advisable to group similar information to make it easier for the reader to access them.
A well-organized appendix section makes it easier to share your information clearly and concisely. Add footnotes throughout the rest of the business plan or make references in the plan to the documents in the appendix.
The appendix section is usually only necessary if you are seeking funding from investors or lenders, or hoping to attract partners.
People reading business plans do not want to spend time going through a heap of backup information, numbers, and charts. Keep these documents or information in the Appendix section in case the reader wants to dig deeper.
Common Items to Include in the Appendix Section of Your Business Plan
The appendix section includes documents that supplement or support the information or claims given in other sections of the business plans. Common items you can include in the appendix section include:
- Additional data about the process of manufacturing or creation
- Additional description of products or services such as product schematics
- Additional financial documents or projections
- Articles of incorporation and status
- Backup for market research or competitive analysis
- Bank statements
- Business registries
- Client testimonials (if your business is already running)
- Copies of insurances
- Credit histories (personal or/and business)
- Deeds and permits
- Equipment leases
- Examples of marketing and advertising collateral
- Industry associations and memberships
- Images of product
- Intellectual property
- Key customer contracts
- Legal documents and other contracts
- Letters of reference
- Links to references
- Market research data
- Organizational charts
- Photographs of potential facilities
- Professional licenses pertaining to your legal structure or type of business
- Purchase orders
- Resumes of the founder(s) and key managers
- State and federal identification numbers or codes
- Trademarks or patents’ registrations
Avoid using the appendix section as a place to dump any document or information you feel like adding. Only add documents or information that you support or increase the credibility of your business plan.
Tips and Strategies for Writing a Convincing Business Plan
To achieve a perfect business plan, you need to consider some key tips and strategies. These tips will raise the efficiency of your business plan above average.
1. Know Your Audience
When writing a business plan, you need to know your audience . Business owners write business plans for different reasons. Your business plan has to be specific. For example, you can write business plans to potential investors, banks, and even fellow board members of the company.
The audience you are writing to determines the structure of the business plan. As a business owner, you have to know your audience. Not everyone will be your audience. Knowing your audience will help you to narrow the scope of your business plan.
Consider what your audience wants to see in your projects, the likely questions they might ask, and what interests them.
- A business plan used to address a company's board members will center on its employment schemes, internal affairs, projects, stakeholders, etc.
- A business plan for financial institutions will talk about the size of your market and the chances for you to pay back any loans you demand.
- A business plan for investors will show proof that you can return the investment capital within a specific time. In addition, it discusses your financial projections, tractions, and market size.
2. Get Inspiration from People
Writing a business plan from scratch as an entrepreneur can be daunting. That is why you need the right inspiration to push you to write one. You can gain inspiration from the successful business plans of other businesses. Look at their business plans, the style they use, the structure of the project, etc.
To make your business plan easier to create, search companies related to your business to get an exact copy of what you need to create an effective business plan. You can also make references while citing examples in your business plans.
When drafting your business plan, get as much help from others as you possibly can. By getting inspiration from people, you can create something better than what they have.
3. Avoid Being Over Optimistic
Many business owners make use of strong adjectives to qualify their content. One of the big mistakes entrepreneurs make when preparing a business plan is promising too much.
The use of superlatives and over-optimistic claims can prepare the audience for more than you can offer. In the end, you disappoint the confidence they have in you.
In most cases, the best option is to be realistic with your claims and statistics. Most of the investors can sense a bit of incompetency from the overuse of superlatives. As a new entrepreneur, do not be tempted to over-promise to get the interests of investors.
The concept of entrepreneurship centers on risks, nothing is certain when you make future analyses. What separates the best is the ability to do careful research and work towards achieving that, not promising more than you can achieve.
To make an excellent first impression as an entrepreneur, replace superlatives with compelling data-driven content. In this way, you are more specific than someone promising a huge ROI from an investment.
4. Keep it Simple and Short
When writing business plans, ensure you keep them simple throughout. Irrespective of the purpose of the business plan, your goal is to convince the audience.
One way to achieve this goal is to make them understand your proposal. Therefore, it would be best if you avoid the use of complex grammar to express yourself. It would be a huge turn-off if the people you want to convince are not familiar with your use of words.
Another thing to note is the length of your business plan. It would be best if you made it as brief as possible.
You hardly see investors or agencies that read through an extremely long document. In that case, if your first few pages can’t convince them, then you have lost it. The more pages you write, the higher the chances of you derailing from the essential contents.
To ensure your business plan has a high conversion rate, you need to dispose of every unnecessary information. For example, if you have a strategy that you are not sure of, it would be best to leave it out of the plan.
5. Make an Outline and Follow Through
A perfect business plan must have touched every part needed to convince the audience. Business owners get easily tempted to concentrate more on their products than on other sections. Doing this can be detrimental to the efficiency of the business plan.
For example, imagine you talking about a product but omitting or providing very little information about the target audience. You will leave your clients confused.
To ensure that your business plan communicates your full business model to readers, you have to input all the necessary information in it. One of the best ways to achieve this is to design a structure and stick to it.
This structure is what guides you throughout the writing. To make your work easier, you can assign an estimated word count or page limit to every section to avoid making it too bulky for easy reading. As a guide, the necessary things your business plan must contain are:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Product or service description
- Target audience
- Market size
- Competition analysis
- Financial projections
Some specific businesses can include some other essential sections, but these are the key sections that must be in every business plan.
6. Ask a Professional to Proofread
When writing a business plan, you must tie all loose ends to get a perfect result. When you are done with writing, call a professional to go through the document for you. You are bound to make mistakes, and the way to correct them is to get external help.
You should get a professional in your field who can relate to every section of your business plan. It would be easier for the professional to notice the inner flaws in the document than an editor with no knowledge of your business.
In addition to getting a professional to proofread, get an editor to proofread and edit your document. The editor will help you identify grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inappropriate writing styles.
Writing a business plan can be daunting, but you can surmount that obstacle and get the best out of it with these tips.
Business Plan Examples and Templates That’ll Save You Tons of Time
1. hubspot's one-page business plan.

The one-page business plan template by HubSpot is the perfect guide for businesses of any size, irrespective of their business strategy. Although the template is condensed into a page, your final business plan should not be a page long! The template is designed to ask helpful questions that can help you develop your business plan.
Hubspot’s one-page business plan template is divided into nine fields:
- Business opportunity
- Company description
- Industry analysis
- Target market
- Implementation timeline
- Marketing plan
- Financial summary
- Funding required
2. Bplan’s Free Business Plan Template

Bplans' free business plan template is investor-approved. It is a rich template used by prestigious educational institutions such as Babson College and Princeton University to teach entrepreneurs how to create a business plan.
The template has six sections: the executive summary, opportunity, execution, company, financial plan, and appendix. There is a step-by-step guide for writing every little detail in the business plan. Follow the instructions each step of the way and you will create a business plan that impresses investors or lenders easily.
3. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

HubSpot’s downloadable business plan template is a more comprehensive option compared to the one-page business template by HubSpot. This free and downloadable business plan template is designed for entrepreneurs.
The template is a comprehensive guide and checklist for business owners just starting their businesses. It tells you everything you need to fill in each section of the business plan and how to do it.
There are nine sections in this business plan template: an executive summary, company and business description, product and services line, market analysis, marketing plan, sales plan, legal notes, financial considerations, and appendix.
4. Business Plan by My Own Business Institute

My Own Business Institute (MOBI) which is a part of Santa Clara University's Center for Innovation and Entrepreneurship offers a free business plan template. You can either copy the free business template from the link provided above or download it as a Word document.
The comprehensive template consists of a whopping 15 sections.
- The Business Profile
- The Vision and the People
- Home-Based Business and Freelance Business Opportunities
- Organization
- Licenses and Permits
- Business Insurance
- Communication Tools
- Acquisitions
- Location and Leasing
- Accounting and Cash Flow
- Opening and Marketing
- Managing Employees
- Expanding and Handling Problems
There are lots of helpful tips on how to fill each section in the free business plan template by MOBI.
5. Score's Business Plan Template for Startups

Score is an American nonprofit organization that helps entrepreneurs build successful companies. This business plan template for startups by Score is available for free download. The business plan template asks a whooping 150 generic questions that help entrepreneurs from different fields to set up the perfect business plan.
The business plan template for startups contains clear instructions and worksheets, all you have to do is answer the questions and fill the worksheets.
There are nine sections in the business plan template: executive summary, company description, products and services, marketing plan, operational plan, management and organization, startup expenses and capitalization, financial plan, and appendices.
The ‘refining the plan’ resource contains instructions that help you modify your business plan to suit your specific needs, industry, and target audience. After you have completed Score’s business plan template, you can work with a SCORE mentor for expert advice in business planning.
6. Minimalist Architecture Business Plan Template by Venngage

The minimalist architecture business plan template is a simple template by Venngage that you can customize to suit your business needs .
There are five sections in the template: an executive summary, statement of problem, approach and methodology, qualifications, and schedule and benchmark. The business plan template has instructions that guide users on what to fill in each section.
7. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two free business plan templates, filled with practical real-life examples that you can model to create your business plan. Both free business plan templates are written by fictional business owners: Rebecca who owns a consulting firm, and Andrew who owns a toy company.
There are five sections in the two SBA’s free business plan templates.
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Service Line
- Marketing and Sales
8. The $100 Startup's One-Page Business Plan

The one-page business plan by the $100 startup is a simple business plan template for entrepreneurs who do not want to create a long and complicated plan . You can include more details in the appendices for funders who want more information beyond what you can put in the one-page business plan.
There are five sections in the one-page business plan such as overview, ka-ching, hustling, success, and obstacles or challenges or open questions. You can answer all the questions using one or two sentences.
9. PandaDoc’s Free Business Plan Template

The free business plan template by PandaDoc is a comprehensive 15-page document that describes the information you should include in every section.
There are 11 sections in PandaDoc’s free business plan template.
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Products and services
- Operations plan
- Management organization
- Financial plan
- Conclusion / Call to action
- Confidentiality statement
You have to sign up for its 14-day free trial to access the template. You will find different business plan templates on PandaDoc once you sign up (including templates for general businesses and specific businesses such as bakeries, startups, restaurants, salons, hotels, and coffee shops)
PandaDoc allows you to customize its business plan templates to fit the needs of your business. After editing the template, you can send it to interested parties and track opens and views through PandaDoc.
10. Invoiceberry Templates for Word, Open Office, Excel, or PPT

InvoiceBerry is a U.K based online invoicing and tracking platform that offers free business plan templates in .docx, .odt, .xlsx, and .pptx formats for freelancers and small businesses.
Before you can download the free business plan template, it will ask you to give it your email address. After you complete the little task, it will send the download link to your inbox for you to download. It also provides a business plan checklist in .xlsx file format that ensures you add the right information to the business plan.
Alternatives to the Traditional Business Plan
A business plan is very important in mapping out how one expects their business to grow over a set number of years, particularly when they need external investment in their business. However, many investors do not have the time to watch you present your business plan. It is a long and boring read.
Luckily, there are three alternatives to the traditional business plan (the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck). These alternatives are less laborious and easier and quicker to present to investors.
Business Model Canvas (BMC)
The business model canvas is a business tool used to present all the important components of setting up a business, such as customers, route to market, value proposition, and finance in a single sheet. It provides a very focused blueprint that defines your business initially which you can later expand on if needed.

The sheet is divided mainly into company, industry, and consumer models that are interconnected in how they find problems and proffer solutions.
Segments of the Business Model Canvas
The business model canvas was developed by founder Alexander Osterwalder to answer important business questions. It contains nine segments.

- Key Partners: Who will be occupying important executive positions in your business? What do they bring to the table? Will there be a third party involved with the company?
- Key Activities: What important activities will production entail? What activities will be carried out to ensure the smooth running of the company?
- The Product’s Value Propositions: What does your product do? How will it be different from other products?
- Customer Segments: What demography of consumers are you targeting? What are the habits of these consumers? Who are the MVPs of your target consumers?
- Customer Relationships: How will the team support and work with its customer base? How do you intend to build and maintain trust with the customer?
- Key Resources: What type of personnel and tools will be needed? What size of the budget will they need access to?
- Channels: How do you plan to create awareness of your products? How do you intend to transport your product to the customer?
- Cost Structure: What is the estimated cost of production? How much will distribution cost?
- Revenue Streams: For what value are customers willing to pay? How do they prefer to pay for the product? Are there any external revenues attached apart from the main source? How do the revenue streams contribute to the overall revenue?
Lean Canvas
The lean canvas is a problem-oriented alternative to the standard business model canvas. It was proposed by Ash Maurya, creator of Lean Stack as a development of the business model generation. It uses a more problem-focused approach and it majorly targets entrepreneurs and startup businesses.

Lean Canvas uses the same 9 blocks concept as the business model canvas, however, they have been modified slightly to suit the needs and purpose of a small startup. The key partners, key activities, customer relationships, and key resources are replaced by new segments which are:
- Problem: Simple and straightforward number of problems you have identified, ideally three.
- Solution: The solutions to each problem.
- Unfair Advantage: Something you possess that can't be easily bought or replicated.
- Key Metrics: Important numbers that will tell how your business is doing.
Startup Pitch Deck
While the business model canvas compresses into a factual sheet, startup pitch decks expand flamboyantly.
Pitch decks, through slides, convey your business plan, often through graphs and images used to emphasize estimations and observations in your presentation. Entrepreneurs often use pitch decks to fully convince their target audience of their plans before discussing funding arrangements.

Considering the likelihood of it being used in a small time frame, a good startup pitch deck should ideally contain 20 slides or less to have enough time to answer questions from the audience.
Unlike the standard and lean business model canvases, a pitch deck doesn't have a set template on how to present your business plan but there are still important components to it. These components often mirror those of the business model canvas except that they are in slide form and contain more details.

Using Airbnb (one of the most successful start-ups in recent history) for reference, the important components of a good slide are listed below.
- Cover/Introduction Slide: Here, you should include your company's name and mission statement. Your mission statement should be a very catchy tagline. Also, include personal information and contact details to provide an easy link for potential investors.
- Problem Slide: This slide requires you to create a connection with the audience or the investor that you are pitching. For example in their pitch, Airbnb summarized the most important problems it would solve in three brief points – pricing of hotels, disconnection from city culture, and connection problems for local bookings.
- Solution Slide: This slide includes your core value proposition. List simple and direct solutions to the problems you have mentioned
- Customer Analysis: Here you will provide information on the customers you will be offering your service to. The identity of your customers plays an important part in fundraising as well as the long-run viability of the business.
- Market Validation: Use competitive analysis to show numbers that prove the presence of a market for your product, industry behavior in the present and the long run, as well as the percentage of the market you aim to attract. It shows that you understand your competitors and customers and convinces investors of the opportunities presented in the market.
- Business Model: Your business model is the hook of your presentation. It may vary in complexity but it should generally include a pricing system informed by your market analysis. The goal of the slide is to confirm your business model is easy to implement.
- Marketing Strategy: This slide should summarize a few customer acquisition methods that you plan to use to grow the business.
- Competitive Advantage: What this slide will do is provide information on what will set you apart and make you a more attractive option to customers. It could be the possession of technology that is not widely known in the market.
- Team Slide: Here you will give a brief description of your team. Include your key management personnel here and their specific roles in the company. Include their educational background, job history, and skillsets. Also, talk about their accomplishments in their careers so far to build investors' confidence in members of your team.
- Traction Slide: This validates the company’s business model by showing growth through early sales and support. The slide aims to reduce any lingering fears in potential investors by showing realistic periodic milestones and profit margins. It can include current sales, growth, valuable customers, pre-orders, or data from surveys outlining current consumer interest.
- Funding Slide: This slide is popularly referred to as ‘the ask'. Here you will include important details like how much is needed to get your business off the ground and how the funding will be spent to help the company reach its goals.
- Appendix Slides: Your pitch deck appendix should always be included alongside a standard pitch presentation. It consists of additional slides you could not show in the pitch deck but you need to complement your presentation.
It is important to support your calculations with pictorial renditions. Infographics, such as pie charts or bar graphs, will be more effective in presenting the information than just listing numbers. For example, a six-month graph that shows rising profit margins will easily look more impressive than merely writing it.
Lastly, since a pitch deck is primarily used to secure meetings and you may be sharing your pitch with several investors, it is advisable to keep a separate public version that doesn't include financials. Only disclose the one with projections once you have secured a link with an investor.
Advantages of the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck over the Traditional Business Plan
- Time-Saving: Writing a detailed traditional business plan could take weeks or months. On the other hand, all three alternatives can be done in a few days or even one night of brainstorming if you have a comprehensive understanding of your business.
- Easier to Understand: Since the information presented is almost entirely factual, it puts focus on what is most important in running the business. They cut away the excess pages of fillers in a traditional business plan and allow investors to see what is driving the business and what is getting in the way.
- Easy to Update: Businesses typically present their business plans to many potential investors before they secure funding. What this means is that you may regularly have to amend your presentation to update statistics or adjust to audience-specific needs. For a traditional business plan, this could mean rewriting a whole section of your plan. For the three alternatives, updating is much easier because they are not voluminous.
- Guide for a More In-depth Business Plan: All three alternatives have the added benefit of being able to double as a sketch of your business plan if the need to create one arises in the future.
Business Plan FAQ
Business plans are important for any entrepreneur who is looking for a framework to run their company over some time or seeking external support. Although they are essential for new businesses, every company should ideally have a business plan to track their growth from time to time. They can be used by startups seeking investments or loans to convey their business ideas or an employee to convince his boss of the feasibility of starting a new project. They can also be used by companies seeking to recruit high-profile employee targets into key positions or trying to secure partnerships with other firms.
Business plans often vary depending on your target audience, the scope, and the goals for the plan. Startup plans are the most common among the different types of business plans. A start-up plan is used by a new business to present all the necessary information to help get the business up and running. They are usually used by entrepreneurs who are seeking funding from investors or bank loans. The established company alternative to a start-up plan is a feasibility plan. A feasibility plan is often used by an established company looking for new business opportunities. They are used to show the upsides of creating a new product for a consumer base. Because the audience is usually company people, it requires less company analysis. The third type of business plan is the lean business plan. A lean business plan is a brief, straight-to-the-point breakdown of your ideas and analysis for your business. It does not contain details of your proposal and can be written on one page. Finally, you have the what-if plan. As it implies, a what-if plan is a preparation for the worst-case scenario. You must always be prepared for the possibility of your original plan being rejected. A good what-if plan will serve as a good plan B to the original.
A good business plan has 10 key components. They include an executive plan, product analysis, desired customer base, company analysis, industry analysis, marketing strategy, sales strategy, financial projection, funding, and appendix. Executive Plan Your business should begin with your executive plan. An executive plan will provide early insight into what you are planning to achieve with your business. It should include your mission statement and highlight some of the important points which you will explain later. Product Analysis The next component of your business plan is your product analysis. A key part of this section is explaining the type of item or service you are going to offer as well as the market problems your product will solve. Desired Consumer Base Your product analysis should be supplemented with a detailed breakdown of your desired consumer base. Investors are always interested in knowing the economic power of your market as well as potential MVP customers. Company Analysis The next component of your business plan is your company analysis. Here, you explain how you want to run your business. It will include your operational strategy, an insight into the workforce needed to keep the company running, and important executive positions. It will also provide a calculation of expected operational costs. Industry Analysis A good business plan should also contain well laid out industry analysis. It is important to convince potential investors you know the companies you will be competing with, as well as your plans to gain an edge on the competition. Marketing Strategy Your business plan should also include your marketing strategy. This is how you intend to spread awareness of your product. It should include a detailed explanation of the company brand as well as your advertising methods. Sales Strategy Your sales strategy comes after the market strategy. Here you give an overview of your company's pricing strategy and how you aim to maximize profits. You can also explain how your prices will adapt to market behaviors. Financial Projection The financial projection is the next component of your business plan. It explains your company's expected running cost and revenue earned during the tenure of the business plan. Financial projection gives a clear idea of how your company will develop in the future. Funding The next component of your business plan is funding. You have to detail how much external investment you need to get your business idea off the ground here. Appendix The last component of your plan is the appendix. This is where you put licenses, graphs, or key information that does not fit in any of the other components.
The business model canvas is a business management tool used to quickly define your business idea and model. It is often used when investors need you to pitch your business idea during a brief window.
A pitch deck is similar to a business model canvas except that it makes use of slides in its presentation. A pitch is not primarily used to secure funding, rather its main purpose is to entice potential investors by selling a very optimistic outlook on the business.
Business plan competitions help you evaluate the strength of your business plan. By participating in business plan competitions, you are improving your experience. The experience provides you with a degree of validation while practicing important skills. The main motivation for entering into the competitions is often to secure funding by finishing in podium positions. There is also the chance that you may catch the eye of a casual observer outside of the competition. These competitions also provide good networking opportunities. You could meet mentors who will take a keen interest in guiding you in your business journey. You also have the opportunity to meet other entrepreneurs whose ideas can complement yours.
Exlore Further
- 12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
- 13 Sources of Business Finance For Companies & Sole Traders
- 5 Common Types of Business Structures (+ Pros & Cons)
- How to Buy a Business in 8 Steps (+ Due Diligence Checklist)
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
How to Write a Great Business Plan
Whether you’re bootstrapping, fundraising, or pivoting plans for your company, every entrepreneur needs one.

Coming up with the million-dollar idea was the fun part. But turning that idea into a successful company requires a business plan. Here’s why: A great business plan helps you plot your course and focus your efforts, which is what it takes to meet short- and long-term goals. It also demonstrates to interested parties—employees, investors, lenders, partners, yourself —that you’re committed to building the company and that you’ve got what it takes.
A considered business plan also shows how you’ll generate revenue and handle expense management, gets honest about how long it will take to turn a profit, maps out how you’ll attract and retain customers, and lays out hiring and operating practices. It can be intimidating to get started, but here are a few key things to know that will make the process much easier.
Get honest about potential problems.
To make sure your business plan is thorough, perform a SWOT analysis. That stands for: strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This exercise brings hidden assumptions or overlooked challenges to the forefront. Pro tip: Go through the weaknesses and threats first. It won’t be easy to stare down all of the potential pitfalls, but it’s important to get comfortable being uncomfortable about your business. And ultimately, being prepared will make you feel more empowered and in control.
Your list should be comprehensive and include weaknesses such as:
- Possible cash flow blocks
- Lack of experience or assets
- Gaps in your capabilities
- A small network
As for threats, you’ll need to look at the macro environment, including:
- The economy
- Seasonality of the business
- Industry changes
- Market demand
- The competitor landscape
Now that you’ve faced the headwinds, turn to the positives that will push your business forward:
- Why are you building the business?
- What are the strengths and experiences that you and/or your product will bring to the market?
- What are your differentiators?
Focus on what you bring to the table as the founder, your experience and background, any financial reserves you might have or are able to access, your network, and overall value proposition. Outline the opportunities your business has in the market, such as new innovations and collaborations, leveraging market conditions or industry changes.
Stay In The Know
Marie Claire email subscribers get intel on fashion and beauty trends, hot-off-the-press celebrity news, and more. Sign up here.
With the good stuff laid out on paper, look at the weaknesses and threats again and see how you can mitigate them with your strengths and capitalize on new opportunities. This will ensure a business plan that shows you’re aware and prepared for what’s (potentially) to come.
Include your research.
A good business plan shows you’re ready. That means clearly explaining who and what your company does and why you’re leading it. You’ll also need to include competitive analysis—industry trends, market sizing, and what role your business will play—and who your target customer is . An understanding of the industry serves as a feasibility study for your success.
Be clear on how you’ll operate.
The bottom line is important. This means you’ll need to show what resources it will require to build, run, and grow your company. To do that, make sure your business plan includes an operating plan, as well as a thorough breakdown of your financials —start-up capital, ongoing expenses, and other key costs.
Having a handle on your numbers, current and forecasted, is critical for success. It will also enable you to answer important questions that will come up from potential lenders or investors. Tell a great story, but have the facts to back it up.
Former finance executive Cate Luzio founded and self-funded Luminary in late 2018 with the mission to up-lift, up-skill, and propel women forward through all phases of their professional journeys. Luminary is a global professional education and networking platform created to address the systemic challenges impacting women across all industries and sectors.

Sponsor Content Created With FP Movement
By Natalie Gray Herder Published 1 July 24

Her personal style doesn't take time off.
By Julia Gray Published 1 July 24

“She loves to see them being kids.”
By Rachel Burchfield Published 1 July 24
- Contact Future's experts
- Advertise Online
- Terms and conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
Marie Claire is part of Future plc, an international media group and leading digital publisher. Visit our corporate site . © Future US, Inc. Full 7th Floor, 130 West 42nd Street, New York, NY 10036.
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 28, 2024
Years ago, I had an idea to launch a line of region-specific board games. I knew there was a market for games that celebrated local culture and heritage. I was so excited about the concept and couldn't wait to get started.

But my idea never took off. Why? Because I didn‘t have a plan. I lacked direction, missed opportunities, and ultimately, the venture never got off the ground.

And that’s exactly why a business plan is important. It cements your vision, gives you clarity, and outlines your next step.
In this post, I‘ll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you’d need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
Table of Contents
What is a business plan?
What is a business plan used for.
- Business Plan Template [Download Now]
Purposes of a Business Plan
What does a business plan need to include, types of business plans.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. It provides a detailed description of the business, including its products or services, target market, competitive landscape, and marketing and sales strategies. The plan also includes a financial section that forecasts revenue, expenses, and cash flow, as well as a funding request if the business is seeking investment.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]


8. Serves as a Marketing Tool
A business plan is not only an internal guide but also serves as a powerful marketing tool. Your business plan can showcase your company‘s strengths, unique value proposition, and growth potential when you’re looking for investors, partnerships, or new clients.
It provides a professional and polished overview of your business, which shows your commitment and strategic thinking to potential stakeholders.
Your business plan helps you attract the right people by clearly articulating your target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. In summary, it acts as a persuasive sales pitch.
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read.
The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement.
You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can.
This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

18 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![the business plan plot 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-1-20240625-3861486-1.webp)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![the business plan plot How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]
20 Free & Paid Small Business Tools for Any Budget

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2024
![the business plan plot The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://newinboundblog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
How To Write A Business Plan (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 17, 2024, 11:59am

Table of Contents
Brainstorm an executive summary, create a company description, brainstorm your business goals, describe your services or products, conduct market research, create financial plans, bottom line, frequently asked questions.
Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and dreams, a strong business plan outlines short-term and long-term goals, budget and whatever else you might need to get started. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to write a business plan that you can stick to and help guide your operations as you get started.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
$0 + State Fee
On Formations' Website
Drafting the Summary
An executive summary is an extremely important first step in your business. You have to be able to put the basic facts of your business in an elevator pitch-style sentence to grab investors’ attention and keep their interest. This should communicate your business’s name, what the products or services you’re selling are and what marketplace you’re entering.
Ask for Help
When drafting the executive summary, you should have a few different options. Enlist a few thought partners to review your executive summary possibilities to determine which one is best.
After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you’ll need to include your business’s registered name , your business address and any key employees involved in the business.
The business description should also include the structure of your business, such as sole proprietorship , limited liability company (LLC) , partnership or corporation. This is the time to specify how much of an ownership stake everyone has in the company. Finally, include a section that outlines the history of the company and how it has evolved over time.
Wherever you are on the business journey, you return to your goals and assess where you are in meeting your in-progress targets and setting new goals to work toward.
Numbers-based Goals
Goals can cover a variety of sections of your business. Financial and profit goals are a given for when you’re establishing your business, but there are other goals to take into account as well with regard to brand awareness and growth. For example, you might want to hit a certain number of followers across social channels or raise your engagement rates.
Another goal could be to attract new investors or find grants if you’re a nonprofit business. If you’re looking to grow, you’ll want to set revenue targets to make that happen as well.
Intangible Goals
Goals unrelated to traceable numbers are important as well. These can include seeing your business’s advertisement reach the general public or receiving a terrific client review. These goals are important for the direction you take your business and the direction you want it to go in the future.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you’re offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are providing something necessary or entirely new. If you have any patents or trademarks, this is where you can include those too.
If you have any visual aids, they should be included here as well. This would also be a good place to include pricing strategy and explain your materials.
This is the part of the business plan where you can explain your expertise and different approach in greater depth. Show how what you’re offering is vital to the market and fills an important gap.
You can also situate your business in your industry and compare it to other ones and how you have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Other than financial goals, you want to have a budget and set your planned weekly, monthly and annual spending. There are several different costs to consider, such as operational costs.
Business Operations Costs
Rent for your business is the first big cost to factor into your budget. If your business is remote, the cost that replaces rent will be the software that maintains your virtual operations.
Marketing and sales costs should be next on your list. Devoting money to making sure people know about your business is as important as making sure it functions.
Other Costs
Although you can’t anticipate disasters, there are likely to be unanticipated costs that come up at some point in your business’s existence. It’s important to factor these possible costs into your financial plans so you’re not caught totally unaware.
Business plans are important for businesses of all sizes so that you can define where your business is and where you want it to go. Growing your business requires a vision, and giving yourself a roadmap in the form of a business plan will set you up for success.
How do I write a simple business plan?
When you’re working on a business plan, make sure you have as much information as possible so that you can simplify it to the most relevant information. A simple business plan still needs all of the parts included in this article, but you can be very clear and direct.
What are some common mistakes in a business plan?
The most common mistakes in a business plan are common writing issues like grammar errors or misspellings. It’s important to be clear in your sentence structure and proofread your business plan before sending it to any investors or partners.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best VPN Services
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Antivirus Software
- Best LLC Services
- Best POS Systems
- Best Business VOIP Services
- Best Credit Card Processing Companies
- Best CRM Software for Small Business
- Best Fleet Management Software
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Software
- Best Business Apps
- Best Free Software For Business
- How to Start a Business
- How To Make A Small Business Website
- How To Trademark A Name
- What Is An LLC?
- How To Set Up An LLC In 7 Steps
- What is Project Management?

Best West Virginia Registered Agent Services Of 2024
Best Vermont Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best Rhode Island Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best Wisconsin Registered Agent Services Of 2024

Best South Dakota Registered Agent Services Of 2024

B2B Marketing In 2024: The Ultimate Guide
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry.
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
How to Write a Business Plan: Beginner’s Guide (& Templates)

Written by: Chloe West

Thinking about starting a business? One of the first steps you’ll need to take is to write a business plan. A business plan can help guide you through your financial planning, marketing strategy, unique selling point and more.
Making sure you start your new business off on the right foot is key, and we’re here to help. We’ve put together this guide to help you write your first business plan. Or, you can skip the guide and dive right into a business plan template .
Ready to get started?
Here’s a short selection of 8 easy-to-edit business plan templates you can edit, share and download with Visme. View more templates below:

8-Step Process for Writing a Business Plan
What is a business plan, why is a business plan important, step #1: write your executive summary, step #2: put together your company description, step #3: conduct your market analysis, step #4: research your competition, step #5: outline your products or services, step #6: summarize your financial plan, step #7: determine your marketing strategy, step #8: showcase your organizational chart, 14 business plan templates to help you get started.
A business plan is a document that helps potential new business owners flesh out their business idea and put together a bird’s eye view of their business. Writing a business plan is an essential step in any startup’s ideation process.
Business plans help determine demographics, market analysis, competitive analysis, financial projections, new products or services, and so much more.
Each of these bits of information are important to have on hand when you’re trying to start a business or pitching investors for funds.
Here’s an example of a business plan that you can customize to incorporate your own business information.

We’re going to walk you through some of the most important parts of your business plan as well as how to write your own business plan in 8 easy steps.
If you’re in the beginning stages of starting a business , you might be wondering if it’s really worth your time to write out your business plan.
We’re here to tell you that it is.
A business plan is important for a number of reasons, but mostly because it helps to set you up for success right from the start.
Here are four reasons to prove to you why you need to start your business off on the right foot with a plan.
Reason #1: Set Realistic Goals and Milestones
Putting together a business plan helps you to set your objectives for growth and make realistic goals while you begin your business.
By laying out each of the steps you need to take in order to build a successful business, you’re able to be more reasonable about what your timeline is for achieving everything as well as what your financial projections are.
The best way to set goals is using the SMART goals guidelines, outlined below.

Reason #2: Grow Your Business Faster
Having a business plan helps you be more organized and strategic, improving the overall performance of your business as you start out. In fact, one study found that businesses with a plan grow 30% faster than businesses that don’t.
Doesn’t that sound reason enough alone to start out your business venture with a solidified plan? We thought so too, but we’ve still got two more reasons.
Reason #3: Minimize Risk
Starting a new business is uncharted territory. However, when you start with a roadmap for your journey, it makes it easier to see success and minimize the risks that come with startups.
Minimize risk and maximize profitability by documenting the most important parts of your business planning.
Reason #4: Secure Funding
And finally, our last reason that business plans are so important is that if you plan to pitch investors for funding for your new venture, they’re almost always going to want to see a detailed business plan before deciding whether or not to invest.
You can easily create your business plan and investor pitch deck right here with Visme. Just sign up for a free account below to get started.
Hey executives! Looking to cut design costs?
- Spend less time on presentations and more time strategizing
- Ensure your brand looks and feels visually consistent across all your organization's documents
- Impress clients and stakeholders with boardroom ready presentations
Sign up. It’s free.

The executive summary is a brief overview of your entire business plan, giving anyone who reads through your document a quick understanding of what they’re going to learn about your business idea.
However, you need to remember that some of the people who are going to read your business plan don’t want to or have time to read the entire thing. So your executive summary needs to incorporate all of the most important aspects of your plan.
Here’s an example of an executive summary from a business plan template you can customize and turn into your own.

Your executive summary should include:
- Key objective(s)
- Market research
- Competitor information
- Products/services
- Value proposition
- Overview of your financial plan
- How you’re going to actually start your business
One thing to note is that you should actually write your executive summary after the rest of your business plan so that you can properly summarize everything you’ve already created.
So at this point, simply leave a page blank for your executive summary so you can come back to it at the end of your business plan.

The next step is to write out a full description of your business and its core offerings. This section of your business plan should include your mission statement and objectives, along with your company history or overview.
In this section, you may also briefly describe your business formation details from a legal perspective.
Mission Statement
Don’t spend too much time trying to craft this. Your mission statement is a simple “why” you started this business. What are you trying to achieve? Or what does your business solve?
This can be anything from one single quote or a paragraph, but it doesn’t need to be much longer than that. In fact, this could be very similar to your value proposition.

What are your goals? What do you plan to achieve in the first 90 days or one year of your business? What kind of impact do you hope to make on the market?
These are all good points to include in your objectives section so anyone reading your business plan knows upfront what you hope to achieve.
History or Overview
If you’re not launching a brand new business or if you’ve previously worked on another iteration of this business, let potential investors know the history of your company.
If not, simply provide an overview of your business, sharing what it does or what it will do.

Your third step is to conduct a market analysis so you know how your business will fit into its target market. This page in your business plan is simply meant to summarize your findings. Most of your time should be spent actually doing the research.
Your market analysis needs to look at things like:
- Market size, and if it’s grown in recent years or shrinking
- The segment of the market you plan to target
- Demographics and behavior of your target audience
- The demand for your product or service
- Your competitive advantage or differentiation strategy
- The average price of your product or service
Put together a summary of your market analysis and industry research in a 1-2 page format, like we see below.

Your next step is to conduct a competitive analysis. While you likely touched on this briefly during your market analysis, now is the time to do a deep dive so that you have a good grasp on what your competitors are doing and how they are generating customers.
Start by creating a profile of all your existing competitors, or at the very least, your closest competitors – the ones who are offering very similar products or services to you, or are in a similar vicinity (if you’re opening a brick and mortar store).
Focus on their strengths and what they’re doing really well so that you can emulate their best qualities in your own way. Then, look at their weaknesses and what your business can do better.
Take note of their current marketing strategy, including the outlets you see a presence, whether it’s on social media, you hear a radio ad, you see a TV ad, etc. You won’t always find all of their marketing channels, but see what you can find online and on their website.

After this, take a minute to identify potential competitors based on markets you might try out in the future, products or services you plan to add to your offerings, and more.
Then put together a page or two in your business plan that highlights your competitive advantage and how you’ll be successful breaking into the market.
Step five is to dedicate a page to the products or services that your business plans to offer.
Put together a quick list and explanation of what each of the initial product or service offerings will be, but steer clear of industry jargon or buzzwords. This should be written in plain language so anyone reading has a full understanding of what your business will do.

You can have a simple list like we see in the sample page above, or you can dive a little deeper. Depending on your type of business, it might be a good idea to provide additional information about what each product or service entails.
The next step is to work on the financial data of your new business. What will your overhead be? How will your business make money? What are your estimated expenses and profits over the first few months to a year? The expenses should cover all the spending whether they are recurring costs or just one-time LLC filing fees .
There is so much that goes into your financial plan for a new business, so this is going to take some time to compile. Especially because this section of your business plan helps potential cofounders or investors understand if the idea is even viable.

Your financial plan should include at least five major sections:
- Sales Forecast: The first thing you want to include is a forecast or financial projection of how much you think your business can sell over the next year or so. Break this down into the different products, services or facets of your business.
- Balance Sheet: This section is essentially a statement of your company’s financial position. It includes existing assets, liabilities and equity to demonstrate the company’s overall financial health.
- Income Statement: Also known as a profit and loss statement (P&L), this covers your projected expenses and revenue, showcasing whether your business will be profitable or not.
- Operating Budget: A detailed outline of your business’s income and expenses. This should showcase that your business is bringing in more than it’s spending.
- Cash Flow Statements: This tracks how much cash your business has at any given point, regardless of whether customers or clients have paid their bills or have 30-60+ days to do so.
While these are the most common financial statements, you may discover that there are other sections that you want to include or that lenders may want to see from you.
You can automate the process of looking through your documents with an OCR API , which will collect the data from all your financial statements and invoices.
The next step is coming up with a successful marketing plan so that you can actually get the word out about your business.
Throughout your business plan, you’ve already researched your competitors and your target market, both of which are major components of a good marketing strategy. You need to know who you’re marketing to, and you want to do it better than your competition.

On this page or throughout this section of your business plan, you need to focus on your chosen marketing channels and the types of marketing content you plan to create.
Start by taking a look at the channels that your competitors are on and make sure you have a good understanding of the demographics of each channel as well. You don’t want to waste time on a marketing channel that your target audience doesn’t use.
Then, create a list of each of your planned marketing avenues. It might look something like:
- Social media ( Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest)
- Email newsletter
- Digital ads
Depending on the type of business you’re starting, this list could change quite a bit — and that’s okay. There is no one-size-fits-all marketing strategy, and you need to find the one that brings in the highest number of potential customers.
Your last section will be all about your leadership and management team members. Showcasing that you have a solid team right from the start can make potential investors feel better about funding your venture.
You can easily put together an organizational chart like the one below, with the founder/CEO at the top and each of your team leaders underneath alongside the department they’re in charge of.

Simply add an organizational chart like this as a page into your overall business plan and make sure it matches the rest of your design to create a cohesive document.
If you want to create a good business plan that sets your new business up for success and attracts new investors, it’s a good idea to start with a template.
We’ve got 14 options below from a variety of different industries for you to choose from. You can customize every aspect of each template to fit your business branding and design preferences.
Template #1: Photography Business Plan Template

This feminine and minimalistic business plan template is perfect for getting started with any kind of creative business. Utilize this template to help outline the step-by-step process of getting your new business idea up and running.
Template #2: Real Estate Business Plan Template

Looking for a more modern business plan design? This template is perfect for plainly laying out each of your business plans in an easy-to-understand format. Adjust the red accents with your business’s colors to personalize this template.
Template #3: Nonprofit Business Plan Template

Creating a business and marketing plan for your nonprofit is still an essential step when you’re just starting out. You need to get the word out to increase donations and awareness for your cause.
Template #4: Restaurant Business Plan Template

If your business plan needs to rely heavily on showcasing photos of your products (like food), this template is perfect for you. Get potential investors salivating at the sight of your business plan, and they’re sure to provide the capital you need.
Template #5: Fashion Business Plan Template

Serifs are in. Utilize this template with stunning serif as all the headers to create a contemporary and trendy business plan design that fits your business. Adjust the colors to match your brand and easily input your own content.
Template #6: Daycare Business Plan Template

Creating a more kid-friendly or playful business? This business plan template has bold colors and design elements that will perfectly represent your business and its mission.
Use the pages you need, and remove any that you don’t. You can also duplicate pages and move the elements around to add even more content to your business plan.
Template #7: Consulting Business Plan Template

This classic business plan template is perfect for a consulting business that wants to use a stunning visual design to talk about its services.
Template #8: Coffee Shop Business Plan Template

Customize this coffee shop business plan template to match your own business idea. Adjust the colors to fit your brand or industry, replace photos with your own photography or stock photos that represent your business, and insert your own logo, fonts and colors throughout.
Template #9: SaaS Business Plan Template

A SaaS or service-based company also needs a solid business plan that lays out its financials, list of services, target market and more. This template is the perfect starting point.
Template #10: Small Business Plan Template

Every startup or small business needs to start out with a strong business plan in order to start off on the right foot and set yourself up for success. This template is an excellent starting point for any small business.
Template #11: Ecommerce Business Plan Template

An ecommerce business plan is ideal for planning out your pricing strategy of all of your online products, as well as the site you plan to use for setting up your store, whether WordPress, Shopify, Wix or something else.
Template #12: Startup Business Plan Template

Customize this template and make it your own! Edit and Download
This is another generic business plan template for any type of startup to customize. Switch out the content, fonts and colors to match your startup branding and increase brand equity.
Template #13: One-Page Business Plan Template

Want just a quick business plan to get your idea going before you bite the bullet and map out your entire plan? This one-page template is perfect for those just starting to flesh out a new business idea.
Template #14: Salon Business Plan Template

This salon business plan template is easy on the design and utilizes a light color scheme to put more focus on the actual content. You can use the design as is or keep it as a basis for your own design elements.
Create Your Own Business Plan Today
Ready to write your business plan? Once you’ve created all of the most important sections, get started with a business plan template to really wow your investors and organize your startup plan.
Design beautiful visual content you can be proud of.

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Chloe West is the content marketing manager at Visme. Her experience in digital marketing includes everything from social media, blogging, email marketing to graphic design, strategy creation and implementation, and more. During her spare time, she enjoys exploring her home city of Charleston with her son.
How to Write a Business Plan: Your Step-by-Step Guide

So, you’ve got an idea and you want to start a business —great! Before you do anything else, like seek funding or build out a team, you'll need to know how to write a business plan. This plan will serve as the foundation of your company while also giving investors and future employees a clear idea of your purpose.
Below, Lauren Cobello, Founder and CEO of Leverage with Media PR , gives her best advice on how to make a business plan for your company.
Build your dream business with the help of a high-paying job—browse open jobs on The Muse »
What is a business plan, and when do you need one?
According to Cobello, a business plan is a document that contains the mission of the business and a brief overview of it, as well as the objectives, strategies, and financial plans of the founder. A business plan comes into play very early on in the process of starting a company—more or less before you do anything else.
“You should start a company with a business plan in mind—especially if you plan to get funding for the company,” Cobello says. “You’re going to need it.”
Whether that funding comes from a loan, an investor, or crowdsourcing, a business plan is imperative to secure the capital, says the U.S. Small Business Administration . Anyone who’s considering giving you money is going to want to review your business plan before doing so. That means before you head into any meeting, make sure you have physical copies of your business plan to share.
Different types of business plans
The four main types of business plans are:
Startup Business Plans
Internal business plans, strategic business plans, one-page business plans.
Let's break down each one:
If you're wondering how to write a business plan for a startup, Cobello has advice for you. Startup business plans are the most common type, she says, and they are a critical tool for new business ventures that want funding. A startup is defined as a company that’s in its first stages of operations, founded by an entrepreneur who has a product or service idea.
Most startups begin with very little money, so they need a strong business plan to convince family, friends, banks, and/or venture capitalists to invest in the new company.
Internal business plans “are for internal use only,” says Cobello. This kind of document is not public-facing, only company-facing, and it contains an outline of the company’s business strategy, financial goals and budgets, and performance data.
Internal business plans aren’t used to secure funding, but rather to set goals and get everyone working there tracking towards them.
As the name implies, strategic business plans are geared more towards strategy and they include an assessment of the current business landscape, notes Jérôme Côté, a Business Advisor at BDC Advisory Services .
Unlike a traditional business plan, Cobello adds, strategic plans include a SWOT analysis (which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) and an in-depth action plan for the next six to 12 months. Strategic plans are action-based and take into account the state of the company and the industry in which it exists.
Although a typical business plan falls between 15 to 30 pages, some companies opt for the much shorter One-Page Business Plan. A one-page business plan is a simplified version of the larger business plan, and it focuses on the problem your product or service is solving, the solution (your product), and your business model (how you’ll make money).
A one-page plan is hyper-direct and easy to read, making it an effective tool for businesses of all sizes, at any stage.
How to create a business plan in 7 steps
Every business plan is different, and the steps you take to complete yours will depend on what type and format you choose. That said, if you need a place to start and appreciate a roadmap, here’s what Cobello recommends:
1. Conduct your research
Before writing your business plan, you’ll want to do a thorough investigation of what’s out there. Who will be the competitors for your product or service? Who is included in the target market? What industry trends are you capitalizing on, or rebuking? You want to figure out where you sit in the market and what your company’s value propositions are. What makes you different—and better?
2. Define your purpose for the business plan
The purpose of your business plan will determine which kind of plan you choose to create. Are you trying to drum up funding, or get the company employees focused on specific goals? (For the former, you’d want a startup business plan, while an internal plan would satisfy the latter.) Also, consider your audience. An investment firm that sees hundreds of potential business plans a day may prefer to see a one-pager upfront and, if they’re interested, a longer plan later.
3. Write your company description
Every business plan needs a company description—aka a summary of the company’s purpose, what they do/offer, and what makes it unique. Company descriptions should be clear and concise, avoiding the use of jargon, Cobello says. Ideally, descriptions should be a few paragraphs at most.
4. Explain and show how the company will make money
A business plan should be centered around the company’s goals, and it should clearly explain how the company will generate revenue. To do this, Cobello recommends using actual numbers and details, as opposed to just projections.
For instance, if the company is already making money, show how much and at what cost (e.g. what was the net profit). If it hasn’t generated revenue yet, outline the plan for how it will—including what the product/service will cost to produce and how much it will cost the consumer.
5. Outline your marketing strategy
How will you promote the business? Through what channels will you be promoting it? How are you going to reach and appeal to your target market? The more specific and thorough you can be with your plans here, the better, Cobello says.
6. Explain how you’ll spend your funding
What will you do with the money you raise? What are the first steps you plan to take? As a founder, you want to instill confidence in your investors and show them that the instant you receive their money, you’ll be taking smart actions that grow the company.
7. Include supporting documents
Creating a business plan is in some ways akin to building a legal case, but for your business. “You want to tell a story, and to be as thorough as possible, while keeping your plan succinct, clear, interesting, and visually appealing,” Cobello says. “Supporting documents could include financial projects, a competitive analysis of the market you’re entering into, and even any licenses, patents, or permits you’ve secured.”
A business plan is an individualized document—it’s ultimately up to you what information to include and what story you tell. But above all, Cobello says, your business plan should have a clear focus and goal in mind, because everything else will build off this cornerstone.
“Many people don’t realize how important business plans are for the health of their company,” she says. “Set aside time to make this a priority for your business, and make sure to keep it updated as you grow.”
Holly Willoughby kidnap plot suspect swore plan was real, court told
A security guard accused of a plot to kidnap, rape and murder Holly Willoughby gained sexual arousal from his "real" plans, a court has heard. The prosecution argued "boring" details in his messages were damning.
Wednesday 3 July 2024 09:29, UK

A security guard accused of a plot to kidnap, rape and murder Holly Willoughby went to "great lengths" to suggest to others his plans were not mere fantasy, a court has heard.
Jurors at Chelmsford Crown Court heard on Monday that Gavin Plumb's sexual motive was clear in his "appalling messages" to people online.
Prosecuting, Alison Morgan KC said Plumb, 37, who went by the username Big Bear online, swore "it's really happening" when an undercover police officer sent an image of a flight booking.
"These, members of the jury, were the defendant's words when he realised that another person, who he believed to be called David Nelson, was genuinely prepared to join him in his plan to attack Holly Willoughby," she said in closing remarks.
'It's really happening'
"When he believed that David Nelson had just booked a flight to travel from the US... to join in that attack - 'it's really happening'.
"He didn't say: 'Don't do that, I was just kidding.' He didn't say: 'This is just fantasy, you haven't bought a flight, have you?'
"He didn't say: 'I don't really trust you because the name on your flight booking doesn't match with your username'."
Ms Morgan also referred to Plumb's previous convictions, which she argued showed he had a "tendency" to commit acts to control and terrify women.
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player

He is a man who has "done this for real", she told jurors.
"He has terrified, subdued, threatened and detained real women against their will," she said.
"He has carried weapons for that purpose. He has carried ropes for that purpose.
"Real people exist in the world now who were threatened and touched by this man and he was looking... to learn how to avoid those mistakes again.
"Looking to make sure that he didn't fall into the errors that led to women being able to get away from him."
Boring detail is the giveaway
The "boring detail" in Plumb's messages is "what tells you it's real", she added.
Read more: Moment Gavin Plumb is arrested shown in court Willoughby kidnap accused was on 'Abduct Lovers' group
Keep up with all the latest news from the UK and around the world by following Sky News
Ms Morgan gave an example of Plumb writing, "He can't get time off until early February so when he gets them off we can get them off as well".
The prosecutor said: "What's sexually gratifying about booking dates and times off work?"
Plumb, of Harlow in Essex, denies soliciting murder, incitement to rape and incitement to kidnap.
The trial continues.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

Related Topics
- Holly Willoughby
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
What Happens to Biden’s Student Loan Repayment Plan Now?
More than eight million borrowers are enrolled in the income-driven plan known as SAVE. The Education Department is assessing the rulings.

By Tara Siegel Bernard
President Biden’s new student loan repayment plan was hobbled on Monday after two federal judges in Kansas and Missouri issued separate rulings that temporarily blocked some of the plan’s benefits, leaving questions about its fate.
The preliminary injunctions, which suspend parts of the program known as SAVE, leave millions of borrowers in limbo until lawsuits filed by two groups of Republican-led states challenging the legality of the plan are decided.
That means the Biden administration cannot reduce borrowers’ monthly bills by as much as half starting July 1, as had been scheduled, and it must pause debt forgiveness to SAVE enrollees. The administration has canceled $5.5 billion in debt for more than 414,000 borrowers through the plan, which opened in August.
If you’re among the eight million borrowers making payments through SAVE — the Saving on a Valuable Education plan — you probably have many questions. Here’s what we know so far, though the Education Department has yet to release its official guidance.
Let’s back up for a minute. What does SAVE do?
Like the income-driven repayment plans that came before it, the SAVE program ties borrowers’ monthly payments to their income and household size. After payments are made for a certain period of years, generally 20 or 25, any remaining debt is canceled.
But the SAVE plan — which replaced the Revised Pay as You Earn program, or REPAYE — is more generous than its predecessor plans in several ways.
Ask us your questions about the SAVE student loan repayment plan.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
Quickbooks (Coming soon...) Sync and compare with your quickbooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
How to Write a Business Plan Conclusion?
- Vinay Kevadia
- June 20, 2024

Completed writing your business plan?
Let’s wrap it up with a conclusion that ends your business plan on an exciting and positive note. Not to forget—a conclusion that convinces the readers about your business’s potential to succeed.
In this blog post, you will learn exactly how to write a conclusion of a business plan and get an example to guide you.
Let’s get started.
What is a business plan conclusion?
A business plan conclusion is the final section concluding very concisely the points discussed in your business plan.
It reinforces the business’s strengths and feasibility and reassures the readers of potential business success. It clarifies the reader’s benefit of associating with your business and convinces them of a profitable investment opportunity.
A conclusion is about 3-4 paragraphs long and is designed to drive action and leave a lasting impression on reader’s minds.
Business plan conclusion vs. executive summary
Many people confuse a conclusion and an executive summary to be the same. However, they are not. Let’s see how.
- An executive summary is a broad overview of your entire business plan. The conclusion, on the other hand, is a concise summary reinforcing the key takeaways of your plan.
- While an executive summary introduces the readers to your business idea, a conclusion convinces them to take the desired action.
- An executive summary is a preview of what the plan will be about. The conclusion, on the contrary, is a review of what the plan has discussed.
- An executive summary is concise. However, conclusions are more concise covering only the aspects that can drive decisions and actions.
Clear enough, right? Let’s move ahead.
Why is a business plan conclusion important?
Although a conclusion is not mandatory, it is an important aspect of a business plan. It communicates your passion and commitment to a business idea and convinces the readers of your ability to succeed.
A conclusion synthesizes the key insights of your business plan focusing on aspects such as market analysis, business strategy, competitive advantage, and milestones. It reinforces your plan’s vision and establishes your strategic position amongst readers.
A well-crafted conclusion will drive desired actions from the readers. It can seal the deal and fulfill your objective of writing a business plan .
How to write a conclusion for your business plan?
From what information to include to where to place the conclusion—this section will guide you to write an impactful conclusion for your business plan.
1. Choose the right placement
There are two places for you to place your conclusion. It can either be after your executive summary or at the end of the document.
The location changes depending on who you plan to present your business plan with.
If you prepare a business plan for investors , placing your conclusion after the executive summary will increase the likelihood of it getting read.
However, the conclusion should be placed at the end for business plans that are prepared for internal use and business partners. Conclusion in this case reviews and emphasizes the company’s strengths.
2. Place the right information
The information in your conclusion changes depending on your audience and the intent of the business plan.
For instance, if you’re a new business trying to secure funds, your conclusion can synthesize the key details about the following:
- Funding demands
- Benefit to the investors
- Target market and target customers
- Solution for the problem
- Marketing strategy
- Team members and their expertise
- Financial projections
- Competitive advantage
- Launch plan
However, if you’re a small business trying to grow or use this plan for internal use, consider covering key insights from the following aspects:
- Mission statement
- History and the milestones
- Data supporting growth
- Industry trends
- Financial summary
- Long-term goals and objectives
These are the details you can cover while writing your conclusion. However, including every bit of these in your conclusion is unnecessary.
Think from your reader’s perspective. Determine the information that would excite them about your business and form your conclusion accordingly.
3. Include stats and visuals
Now that you’ve decided on the placement and information to be included in your conclusion, it’s time to make your conclusion zesty.
How? Get the facts and stats that would support the claims you make in your conclusion.
For instance, if you’re promising growth, show market research that supports your claim. Again, if you’re promising a certain return on investment, include the statistics that can make investors believe you.
Sway away from vague statements and assumptions. And, if you feel that the statistic would be best absorbed through visual charts or graphics, don’t be afraid to add one.
4. Add a CTA
If you want the readers to take action, guide them. Add a crisp clear call to action(CTA) and explain how the readers would benefit from taking that action.
For instance,
- Join us as a silent partner by investing in Beanco.
- Invest $2 M and secure a 20% stake in equity.
- Support our growth by sharing references.
Don’t beat around the bush. If you are making a funding request, be unapologetic. And even if not, your CTA should suggest how a reader can support your growth.
5. Review and proofread
Once your conclusion is ready, re-read and proofread it for any grammatical or spelling errors. Fix the flow and remove fluff to make your conclusion crisp and persuasive.
Get your friends and business partners to read the conclusion and check if the message you are trying to send is crisp and clear. If not, make the necessary adjustments.
Business plan conclusion example
Use this business plan conclusion as a reference and tailor yours keeping in mind the needs, objectives, and audience for your business plan.
Launching EcoRide Electric Scooters will revolutionize urban transportation by providing an eco-friendly, efficient, and affordable solution for city commuters. Our innovative design and advanced technology will set us apart in the rapidly growing market for sustainable transport options.
We are poised to make a significant impact on urban mobility, and we want [Investor’s Name] to be a foundational part of our journey. By investing in EcoRide Electric Scooters, [Investor’s Name] will benefit in the following ways:
- Joining a groundbreaking startup with a vision to reduce urban pollution and traffic congestion, led by a passionate team with over 20 years of combined experience in the automotive and tech industries.
- Supporting the development and deployment of cutting-edge electric scooters, contributing to a cleaner, greener urban environment.
- Gaining equity in a high-potential startup with a scalable business model and the potential for significant returns as we expand to new markets.
Together, we can transform urban transportation, reduce carbon footprints, and create a sustainable future for city dwellers. If you share our vision for a cleaner, more efficient urban commute, partner with us.
Let’s conclude your business plan
Now that you have understood the process and referred to an example, let’s conclude your business plan.
Identify the information you must highlight, encapsulate it into a powerful conclusion, and pair it with an even more powerful CTA.
However, remember that the conclusion just seals the deal. It’s the business plan that will hook your readers till the end. With Upmetrics’s AI business plan generator , you can create truly engaging business plans in just about 10 minutes.
So, improvise your business plan, sum it up with a convincing conclusion, and send over your business plan to your potential investors to secure funding.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should a business plan conclusion be.
A conclusion of your business plan can be anywhere between 2-3 paragraphs long. In this ideal length, you must outline the key takeaways of your plan, clarify the next step to the readers, and explain to them the benefit of supporting your business.
What is the most important part of a business plan conclusion?
A CTA is the most important part of the conclusion, especially if you are trying to raise funds. However, if you are writing a plan for internal purposes, focus more on synthesizing the key essentials of a plan.
Can I include new information in the conclusion?
A conclusion does not introduce any new information. It simply reinforces the business’s position and convinces the readers to take the desired action for one last time. For instance, offer funding for your business.
Is it necessary to include a call to action in the conclusion?
It is very important to add a crisp clear CTA while concluding your plan. You can’t expect the readers to invest in your business or help you grow if you don’t clarify the steps to take action.
About the Author

Vinay Kevadiya
Vinay Kevadiya is the founder and CEO of Upmetrics, the #1 business planning software. His ultimate goal with Upmetrics is to revolutionize how entrepreneurs create, manage, and execute their business plans. He enjoys sharing his insights on business planning and other relevant topics through his articles and blog posts. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
22 Best Business Plan PowerPoint Templates
Use these business plan PowerPoint templates to launch your next enterprise.

In this post, we’ll look at some of the best business plan PowerPoint templates you can download and use. And, as a bonus, we’re offering two templates completely free! Just click below to download them.
2 Free PowerPoint Business Plan Templates
Yefora multi-purpose powerpoint template.

- 60 sample business plans PPT slides
- fully editable text
- RGB color mode
- simple slides to make your key points clearer
Evolved: Business Plan PowerPoint Template for Free

- 40+ slides for creative, education, or business presentations
- one of the best fundraising presentations PPT
- easily editable
- vector-based icons
More Business Plan PPT Templates to Download
Explore all of these business plan presentation PPT examples. See how a polished, engaging presentation can captivate your audience. You can even find an amazing fundraising presentation template for your next project.
1. Influencers Business Plan Presentation

- ultra-modern design
- great for business, portfolio, corporate, branding, advertising
- 35 sample business plans PPT layouts
- business plan examples PPT guidelines
2. Corporary Business PowerPoint Template

- clean, modern, and easy to edit
- perfect for PowerPoint business plan or portfolio
- easy to customize and fully editable
3. Opus Business PowerPoint Template

- colorful and innovative design
- 12 .PPTX files and 12 .PPT files
- 3 premade color themes
- includes business plan examples PPT layouts
4. Modern Blue Green Digital Marketing Presentation

- versatile business plan template PPT
- perfect for presenting a marketing strategy
- fully editable
- 25 unique slides
5. Modern Minimalist Business Plan Presentation

- suitable for many businesses
- all elements are fully editable
- 30 unique slides with data charts and infographics
- 16:9 widescreen ratio
6. Business Plan PowerPoint Template Presentation

- trendy and colorful presentation
- ideal for pitching your business plans
- 30 PowerPoint business plan slides
- free web fonts used and recommended
7. Business Plan PowerPoint

- PowerPoint business plan presentation
- drag and drop images
- strong focus on typography and usability
- predefined text styles
8. Radeon Presentation Template

- 30 modern, creative, unique slides
- 5 color schemes
- perfect business plan template PPT and startup PPT
- works for a non-profit organization PowerPoint presentation
9. SWOT Business Presentation

- perfect for corporate presentations
- 20+ color themes
- 111 simple unique slides
- multiple aspect ratio (16:9, 4:3, US Letter)
10. Proxima Business PowerPoint Template

- clean business plan template PPT
- big typefaces to focus on data
- 72+ unique slides and 6 color schemes
- transitions (not over-animated)
11. Business Planning PowerPoint Template

- 150+ slides
- handcrafted infographic
- Pixel-perfect illustrations
- all graphics are resizable and editable
12. Business Plan for Presentation Template

- easy-to-use presentation template
- unique and creative slides
- PowerPoint, Keynote, and Google Slides template
- easy drag and drop to change images
13. Fritz Business Plan

- 30 editable slides for Google Slides and PowerPoint
- perfect for your startup or business
- 16:9 aspect ratio
- Google Fonts
14. Planning Modern Business PowerPoint Template

- infographic pack for building recognition
- 80 unique slides
- light and dark versions
- fully customizable
15. Business Plan PowerPoint Template

- professional presentation template
- 16:9 aspect ratio (HD)
- perfect for your business, startup, or tech and finance presentation
16. Business Plan Presentation PowerPoint Template

- modern presentation with 32 PowerPoint slides
- includes creative layouts and infographics
- easily edit and adjust to suit your business needs
- Google Fonts used
17. Sunne Creative Agency Business Plan Presentation

- creative agency business plan presentation
- 15 unique slides (PPT and PPTX)
- uses free fonts from Google Fonts
18. Keria Business Plan PowerPoint Template

- engaging business plan examples for PPT
- 50 unique and editable presentation slides
- 2 color variations
- vector shape illustrations are included
19. Reka Business Plan

- theme suitable for PowerPoint and Google Slides
- 30 editable slides
- aspect ratio 16:9
- dynamic business plan PowerPoint example
- works as a non-profit pitch deck example
20. Conderi Marketing PowerPoint Template

- 15 PowerPoint slides
- 16:9 widescreen ratio (1920×1080px)
- picture placeholder
Which Template Will You Use for Your PowerPoint Business Plan?
Are you ready to take your business to new heights? Elevate your strategy with premium and free business plan PowerPoint templates from Envato Elements . Also find plenty of sample fundraising PowerPoint presentations for you to customize in no time.
We’ve seen a bunch of business plan PowerPoint presentation examples in this article. Looking for a non-profit fundraising PowerPoint presentation? We’ve also featured some of the best fundraising presentations PPT for your startup.
Choose from the business plan PowerPoint examples featured to make your brand shine. Boost your business towards success for 2024 and the future!
Related Articles


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The plot planned to install retired Major General Smedley Butler as dictator of the United States.. The Business Plot, also called the Wall Street Putsch and The White House Putsch, was a political conspiracy in 1933, in the United States, to overthrow the government of President Franklin D. Roosevelt and install Smedley Butler as dictator. Butler, a retired Marine Corps major general ...
In the early 1930s, a coalition of America's wealthiest industrial magnates allegedly hatched a scheme to topple the Roosevelt Administration and replace it with a fascist dictatorship. Known as the Business Plot, the plan was supposedly dreamed up by a prominent tycoons and Wall Street big shots who controlled many of the country's major ...
"The Business Plot reminds us that threats to democracy have defined our past as much as they threaten democracy's future," concluded Stone. The Man Who Exposed the Business Plot. Smedley Butler joined the Marines at 16 after the USS Maine blew up in Havana Harbor. In his 33 years with the Marines, he received five medals for bravery and ...
Some of the country's wealthiest men - furious with President Franklin D. Roosevelt - decided to install a dictator who was more business friendly, according to the congressional testimony of ...
Though it's barely remembered today, there was a genuine conspiracy to overthrow the president. The Wall Street Putsch, as it's known today, was a plot by a group of right-wing financiers. "They ...
In an excerpt from Gangsters of Capitalism, Jonathan M. Katz details how the authors of the Depression-era "Business Plot" aimed to take power away from FDR and stop his "socialist" New Deal. By ...
Across the Atlantic, a similar insurgency attempted to destabilize the United States earlier that year. The Business Plot of 1933 was a failed attempt to overthrow FDR and install a dictator. And it was not led by a fringe group of working-class radicals, but covertly bankrolled by a Wall Street coalition of affluent businessmen. Related:
Amsterdam pulls together, fictionalizes, and at times troublingly misrepresents a number of threads from the 1930s and early 20 th century American history. But that sinister plan is based on very real 1933 histories: the so-called Business Plot. Those histories reveal that Burt's quote is both profoundly wrong and inspiringly right about the battle for American identity and ideals.
This series will chronicle the federal investigation of the Business Plot, a conspiracy that sought to overthrow the recently-elected President, Franklin Delano Roosevelt, and replace him with ...
4. Values: Provide a list of three to five core principles upon which you will build the business and stick to no matter what. 5. Goals: Make a list of three to five long-term goals that translate ...
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
2. Draft an executive summary. An executive summary is the first page of your business plan. Like an elevator pitch, this section should provide a high-level summary of your company, and entice reviewers to keep reading. Include a mission statement, the products or services offered, and a broad overview of your financial plans.
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
Get honest about potential problems. To make sure your business plan is thorough, perform a SWOT analysis. That stands for: strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This exercise brings ...
A business plan provides a detailed roadmap for your company's future. It outlines your objectives, strategies, and the specific actions you need to achieve your goals. When you define your path forward, a business plan helps you stay focused and on track, even when you face challenges or distractions.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
1. Investors Are Short On Time. If your chief goal is using your business plan to secure funding, then it means you intend on getting it in front of an investor. And if there's one thing investors are, it's busy. So keep this in mind throughout writing a business plan.
The Business Plan. Get a hint. serves as a reality check for the entrepreneur who will be forced to think about every aspect of operating the business, an operating guide for the business, statement of intent for interested third parties. Click the card to flip 👆. purpose of business plan.
Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections. Executive summary. Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company's leadership team, employees, and location.
An Effective Business Plan Can Plot the Course for Small Business Success. By U.S. Small Business Administration Published on November 30, 2023. December is National Write a Business Plan Month. The SBA encourages you to mark the occasion by learning how to put together an efficient, high-quality plan that will increase your chances of small ...
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
And How to Create One. 1. Executive summary. This is a short section that introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, your goals for developing it, and why it will be successful.
A one-page business plan is a simplified version of the larger business plan, and it focuses on the problem your product or service is solving, the solution (your product), and your business model (how you'll make money). A one-page plan is hyper-direct and easy to read, making it an effective tool for businesses of all sizes, at any stage ...
A security guard accused of a plot to kidnap, rape and murder Holly Willoughby gained sexual arousal from his "real" plans, a court has heard. The prosecution argued "boring" details in his ...
The plot outlined by Ukraine's domestic intelligence agency and prosecutors on Monday fit squarely in that pattern. It was meant to start with a riot, according to Ukrainian officials.
HEADLINES with Courage Is The Cure 3rd July 2024 Episode 5. Looking at MSM headlines where logic doesn't matter, feelings do and 2+2=banana. Courage Is...
More than eight million borrowers are enrolled in the income-driven plan known as SAVE. The Education Department is assessing the rulings. By Tara Siegel Bernard President Biden's new student ...
It's the business plan that will hook your readers till the end. With Upmetrics's AI business plan generator, you can create truly engaging business plans in just about 10 minutes. So, improvise your business plan, sum it up with a convincing conclusion, and send over your business plan to your potential investors to secure funding.
Explore all of these business plan presentation PPT examples. See how a polished, engaging presentation can captivate your audience. You can even find an amazing fundraising presentation template for your next project. 1. Influencers Business Plan Presentation. ultra-modern design;