An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul


Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

- What Is a PhD Literature Review?
- Doing a PhD
A literature review is a critical analysis of published academic literature, mainly peer-reviewed papers and books, on a specific topic. This isn’t just a list of published studies but is a document summarising and critically appraising the main work by researchers in the field, the key findings, limitations and gaps identified in the knowledge.
- The aim of a literature review is to critically assess the literature in your chosen field of research and be able to present an overview of the current knowledge gained from previous work.
- By the conclusion of your literature review, you as a researcher should have identified the gaps in knowledge in your field; i.e. the unanswered research questions which your PhD project will help to answer.
- Quality not quantity is the approach to use when writing a literature review for a PhD but as a general rule of thumb, most are between 6,000 and 12,000 words.
What Is the Purpose of a Literature Review?
First, to be clear on what a PhD literature review is NOT: it is not a ‘paper by paper’ summary of what others have done in your field. All you’re doing here is listing out all the papers and book chapters you’ve found with some text joining things together. This is a common mistake made by PhD students early on in their research project. This is a sign of poor academic writing and if it’s not picked up by your supervisor, it’ll definitely be by your examiners.
The biggest issue your examiners will have here is that you won’t have demonstrated an application of critical thinking when examining existing knowledge from previous research. This is an important part of the research process as a PhD student. It’s needed to show where the gaps in knowledge were, and how then you were able to identify the novelty of each research question and subsequent work.
The five main outcomes from carrying out a good literature review should be:
- An understanding of what has been published in your subject area of research,
- An appreciation of the leading research groups and authors in your field and their key contributions to the research topic,
- Knowledge of the key theories in your field,
- Knowledge of the main research areas within your field of interest,
- A clear understanding of the research gap in knowledge that will help to motivate your PhD research questions .
When assessing the academic papers or books that you’ve come across, you must think about the strengths and weaknesses of them; what was novel about their work and what were the limitations? Are different sources of relevant literature coming to similar conclusions and complementing each other, or are you seeing different outcomes on the same topic by different researchers?
When Should I Write My Literature Review?
In the structure of your PhD thesis , your literature review is effectively your first main chapter. It’s at the start of your thesis and should, therefore, be a task you perform at the start of your research. After all, you need to have reviewed the literature to work out how your research can contribute novel findings to your area of research. Sometimes, however, in particular when you apply for a PhD project with a pre-defined research title and research questions, your supervisor may already know where the gaps in knowledge are.
You may be tempted to skip the literature review and dive straight into tackling the set questions (then completing the review at the end before thesis submission) but we strongly advise against this. Whilst your supervisor will be very familiar with the area, you as a doctoral student will not be and so it is essential that you gain this understanding before getting into the research.
How Long Should the Literature Review Be?
As your literature review will be one of your main thesis chapters, it needs to be a substantial body of work. It’s not a good strategy to have a thesis writing process here based on a specific word count, but know that most reviews are typically between 6,000 and 12,000 words. The length will depend on how much relevant material has previously been published in your field.
A point to remember though is that the review needs to be easy to read and avoid being filled with unnecessary information; in your search of selected literature, consider filtering out publications that don’t appear to add anything novel to the discussion – this might be useful in fields with hundreds of papers.
How Do I Write the Literature Review?
Before you start writing your literature review, you need to be clear on the topic you are researching.
1. Evaluating and Selecting the Publications
After completing your literature search and downloading all the papers you find, you may find that you have a lot of papers to read through ! You may find that you have so many papers that it’s unreasonable to read through all of them in their entirety, so you need to find a way to understand what they’re about and decide if they’re important quickly.
A good starting point is to read the abstract of the paper to gauge if it is useful and, as you do so, consider the following questions in your mind:
- What was the overarching aim of the paper?
- What was the methodology used by the authors?
- Was this an experimental study or was this more theoretical in its approach?
- What were the results and what did the authors conclude in their paper?
- How does the data presented in this paper relate to other publications within this field?
- Does it add new knowledge, does it raise more questions or does it confirm what is already known in your field? What is the key concept that the study described?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of this study, and in particular, what are the limitations?
2. Identifying Themes
To put together the structure of your literature review you need to identify the common themes that emerge from the collective papers and books that you have read. Key things to think about are:
- Are there common methodologies different authors have used or have these changed over time?
- Do the research questions change over time or are the key question’s still unanswered?
- Is there general agreement between different research groups in the main results and outcomes, or do different authors provide differing points of view and different conclusions?
- What are the key papers in your field that have had the biggest impact on the research?
- Have different publications identified similar weaknesses or limitations or gaps in the knowledge that still need to be addressed?
Structuring and Writing Your Literature Review
There are several ways in which you can structure a literature review and this may depend on if, for example, your project is a science or non-science based PhD.
One approach may be to tell a story about how your research area has developed over time. You need to be careful here that you don’t just describe the different papers published in chronological order but that you discuss how different studies have motivated subsequent studies, how the knowledge has developed over time in your field, concluding with what is currently known, and what is currently not understood.
Alternatively, you may find from reading your papers that common themes emerge and it may be easier to develop your review around these, i.e. a thematic review. For example, if you are writing up about bridge design, you may structure the review around the themes of regulation, analysis, and sustainability.
As another approach, you might want to talk about the different research methodologies that have been used. You could then compare and contrast the results and ultimate conclusions that have been drawn from each.
As with all your chapters in your thesis, your literature review will be broken up into three key headings, with the basic structure being the introduction, the main body and conclusion. Within the main body, you will use several subheadings to separate out the topics depending on if you’re structuring it by the time period, the methods used or the common themes that have emerged.
The important thing to think about as you write your main body of text is to summarise the key takeaway messages from each research paper and how they come together to give one or more conclusions. Don’t just stop at summarising the papers though, instead continue on to give your analysis and your opinion on how these previous publications fit into the wider research field and where they have an impact. Emphasise the strengths of the studies you have evaluated also be clear on the limitations of previous work how these may have influenced the results and conclusions of the studies.
In your concluding paragraphs focus your discussion on how your critical evaluation of literature has helped you identify unanswered research questions and how you plan to address these in your PhD project. State the research problem you’re going to address and end with the overarching aim and key objectives of your work .
When writing at a graduate level, you have to take a critical approach when reading existing literature in your field to determine if and how it added value to existing knowledge. You may find that a large number of the papers on your reference list have the right academic context but are essentially saying the same thing. As a graduate student, you’ll need to take a methodological approach to work through this existing research to identify what is relevant literature and what is not.
You then need to go one step further to interpret and articulate the current state of what is known, based on existing theories, and where the research gaps are. It is these gaps in the literature that you will address in your own research project.
- Decide on a research area and an associated research question.
- Decide on the extent of your scope and start looking for literature.
- Review and evaluate the literature.
- Plan an outline for your literature review and start writing it.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Undergraduate courses
- Postgraduate courses
- Foundation courses
- Apprenticeships
- Part-time and short courses
- Apply undergraduate
- Apply postgraduate
Search for a course
Search by course name, subject, and more
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- (suspended) - Available in Clearing Not available in Clearing location-sign UCAS
Fees and funding
- Tuition fees
- Scholarships
- Funding your studies
- Student finance
- Cost of living support
Why study at Kent
Student life.
- Careers and employability
- Student support and wellbeing
- Our locations
- Placements and internships
- Year abroad
- Student stories
- Schools and colleges
- International
- International students
- Your country
- Applicant FAQs
- International scholarships
- University of Kent International College
- Campus Tours
- Applicant Events
- Postgraduate events
- Maps and directions
- Research strengths
- Research centres
- Research impact
Research institutes
- Durrell Institute of Conservation and Ecology
- Institute of Cyber Security for Society
- Institute of Cultural and Creative Industries
- Institute of Health, Social Care and Wellbeing
Research students
- Graduate and Researcher College
- Research degrees
- Find a supervisor
- How to apply
Popular searches
- Visits and Open Days
- Jobs and vacancies
- Accommodation
- Student guide
- Library and IT
- Partner with us
- Student Guide
- Student Help
- Health & wellbeing
- Student voice
- Living at Kent
- Careers & volunteering
- Diversity at Kent
- Finance & funding
- Life after graduation
Literature reviews
Writing a literature review.
The following guide has been created for you by the Student Learning Advisory Service . For more detailed guidance and to speak to one of our advisers, please book an appointment or join one of our workshops . Alternatively, have a look at our SkillBuilder skills videos.
Preparing a literature review involves:
- Searching for reliable, accurate and up-to-date material on a topic or subject
- Reading and summarising the key points from this literature
- Synthesising these key ideas, theories and concepts into a summary of what is known
- Discussing and evaluating these ideas, theories and concepts
- Identifying particular areas of debate or controversy
- Preparing the ground for the application of these ideas to new research
Finding and choosing material
Ensure you are clear on what you are looking for. ask yourself:.
- What is the specific question, topic or focus of my assignment?
- What kind of material do I need (e.g. theory, policy, empirical data)?
- What type of literature is available (e.g. journals, books, government documents)?
What kind of literature is particularly authoritative in this academic discipline (e.g. psychology, sociology, pharmacy)?
How much do you need?
This will depend on the length of the dissertation, the nature of the subject, and the level of study (undergraduate, Masters, PhD). As a very rough rule of thumb – you may choose 8-10 significant pieces (books and/or articles) for an 8,000 word dissertation, up to 20 major pieces of work for 12-15,000 words, and so on. Bear in mind that if your dissertation is based mainly around an interaction with existing scholarship you will need a longer literature review than if it is there as a prelude to new empirical research. Use your judgement or ask your supervisor for guidance.
Where to find suitable material
Your literature review should include a balance between substantial academic books, journal articles and other scholarly publications. All these sources should be as up-to-date as possible, with the exception of ‘classic texts’ such as major works written by leading scholars setting out formative ideas and theories central to your subject. There are several ways to locate suitable material:
Module bibliography: for undergraduate dissertations, look first at the bibliography provided with the module documentation. Choose one or two likely looking books or articles and then scan through the bibliographies provided by these authors. Skim read some of this material looking for clues: can you use these leads to identify key theories and authors or track down other appropriate material?
Library catalogue search engine: enter a few key words to capture a range of items, but avoid over-generalisations; if you type in something as broad as ‘social theory’ you are likely to get several thousand results. Be more specific: for example, ‘Heidegger, existentialism’. Ideally, you should narrow the field to obtain just a few dozen results. Skim through these quickly to identity texts which are most likely to contribute to your study.
Library bookshelves: browse the library shelves in the relevant subject area and examine the books that catch your eye. Check the contents and index pages, or skim through the introductions (or abstracts, in the case of journal articles) to see if they contain relevant material, and replace them if not. Don’t be afraid to ask one of the subject librarians for further help. Your supervisor may also be able to point you in the direction of some of the important literature , but remember this is your literature search, not theirs.
Online: for recent journal articles you will almost certainly need to use one of the online search engines. These can be found on the ‘Indexing Services’ button on the Templeman Library website. Kent students based at Medway still need to use the Templeman pages to access online journals, although you can get to these pages through the Drill Hall Library catalogue. Take a look as well at the Subject Guides on both the Templeman and DHL websites.
Check that you have made the right selection by asking:
- Has my search been wide enough to ensure that I have identified all the relevant material, but narrow enough to exclude irrelevant material?
- Is there a good enough sample of literature for the level (PhD, Masters, undergraduate) of my dissertation or thesis?
- Have I considered as many alternative points of view as possible?
- Will the reader find my literature review relevant and useful?
Assessing the literature
Read the material you have chosen carefully, considering the following:
- The key point discussed by the author: is this clearly defined
- What evidence has the author produced to support this central idea?
- How convincing are the reasons given for the author’s point of view?
- Could the evidence be interpreted in other ways?
- What is the author's research method (e.g. qualitative, quantitative, experimental, etc.)?
- What is the author's theoretical framework (e.g. psychological, developmental, feminist)?
- What is the relationship assumed by the author between theory and practice?
- Has the author critically evaluated the other literature in the field?
- Does the author include literature opposing their point of view?
- Is the research data based on a reliable method and accurate information?
- Can you ‘deconstruct’ the argument – identify the gaps or jumps in the logic?
- What are the strengths and limitations of this study?
- What does this book or article contribute to the field or topic?
- What does this book or article contribute to my own topic or thesis?
As you note down the key content of each book or journal article (together with the reference details of each source) record your responses to these questions. You will then be able to summarise each piece of material from two perspectives:
Content: a brief description of the content of the book or article. Remember, an author will often make just one key point; so, what is the point they are making, and how does it relate to your own research project or assignment?
Critical analysis: an assessment of the relative strengths and weaknesses of the evidence used, and the arguments presented. Has anything conveniently been left out or skated over? Is there a counter-argument, and has the author dealt with this adequately? Can the evidence presented be interpreted another way? Does the author demonstrate any obvious bias which could affect their reliability? Overall, based on the above analysis of the author’s work, how do you evaluate its contribution to the scholarly understanding and knowledge surrounding the topic?
Structuring the literature review
In a PhD thesis, the literature review typically comprises one chapter (perhaps 8-10,000 words), for a Masters dissertation it may be around 2-3,000 words, and for an undergraduate dissertation it may be no more than 2,000 words. In each case the word count can vary depending on a range of factors and it is always best, if in doubt, to ask your supervisor.
The overall structure of the section or chapter should be like any other: it should have a beginning, middle and end. You will need to guide the reader through the literature review, outlining the strategy you have adopted for selecting the books or articles, presenting the topic theme for the review, then using most of the word limit to analyse the chosen books or articles thoroughly before pulling everything together briefly in the conclusion.
Some people prefer a less linear approach. Instead of simply working through a list of 8-20 items on your book review list, you might want to try a thematic approach, grouping key ideas, facts, concepts or approaches together and then bouncing the ideas off each other. This is a slightly more creative (and interesting) way of producing the review, but a little more risky as it is harder to establish coherence and logical sequencing.
Whichever approach you adopt, make sure everything flows smoothly – that one idea or book leads neatly to the next. Take your reader effortlessly through a sequence of thought that is clear, accurate, precise and interesting.
Writing up your literature review
As with essays generally, only attempt to write up the literature review when you have completed all the reading and note-taking, and carefully planned its content and structure. Find an appropriate way of introducing the review, then guide the reader through the material clearly and directly, bearing in mind the following:
- Be selective in the number of points you draw out from each piece of literature; remember that one of your objectives is to demonstrate that you can use your judgement to identify what is central and what is secondary.
- Summarise and synthesise – use your own words to sum up what you think is important or controversial about the book or article.
- Never claim more than the evidence will support. Too many dissertations and theses are let down by sweeping generalisations. Be tentative and careful in the way you interpret the evidence.
- Keep your own voice – you are entitled to your own point of view provided it is based on evidence and clear argument.
- At the same time, aim to project an objective and tentative tone by using the 3rd person, (for example, ‘this tends to suggest’, ‘it could be argued’ and so on).
- Even with a literature review you should avoid using too many, or overlong, quotes. Summarise material in your own words as much as possible. Save the quotes for ‘punch-lines’ to drive a particular point home.
- Revise, revise, revise: refine and edit the draft as much as you can. Check for fluency, structure, evidence, criticality and referencing, and don’t forget the basics of good grammar, punctuation and spelling.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How Long Should a Literature Review Be?

4-minute read
- 7th October 2023
If you’re writing a research paper or dissertation , then you know how important it is to include a thorough, comprehensive literature review. But exactly how long should your literature review be in relation to the rest of your work? While there’s no one-size-fits-all answer to that question, there are some factors that will help determine the length of your review. In this post, we’ll discuss what information to include in your literature review and how long it should be.
Keep reading to learn more.
What Is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the current resources (e.g., books and journal articles) on a specific topic or research question. It is a crucial part of academic writing, such as dissertations, in all categories and fields. Essentially, literature reviews help contextualize your investigations and show how your work is building on existing research.
No matter how long your literature review is, it should generally:
● Establish context for your research (i.e., provide relevant background information so your reader understands the historical significance of your study ).
● Identify gaps in the existing literature (such as unaddressed questions or aspects of your topic).
● Highlight significant concepts related to your topic.
● Cite relevant studies.
● Support your argument.
It’s also essential that a literature review critically analyze the sources cited in your study, considering factors such as sample size, research design, and potential biases. Be sure to structure your literature review using the same referencing style as the rest of your research paper (e.g., APA , Chicago , MLA ).
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
The length of your literature review depends on several factors, including the scope and purpose of your research. In general, the length of the review should be proportionate to your overall paper. For example, if you’re writing a fifty-thousand-word dissertation, then your literature review will likely be an entire chapter comprising about 20 pages. If it’s for a 15-page research paper, your literature review may only be a few pages.
Here are several factors that could affect the length of your literature review:
● Institutional guidelines : Always check the guidelines provided by your institution or journal (such as an APA journal ). There may be a specific length or word count required for publication.
● Scope : If your research topic is narrow and focused, your literature review may be shorter. Conversely, if your topic is broad and encompasses a large body of literature, your review may need to be longer.
● Field of study : Different academic fields may have different expectations regarding the length of literature reviews. For example, literature reviews in the humanities might be longer than those in the natural sciences.
Also, consider your audience. If your literature review is for a general audience or a class assignment, it can probably be shorter and less specialized. However, if it’s for an academic audience in your field of study, you may need to be more thorough and provide an extensive review of the existing literature.
Most literature reviews follow the same basic structure of an introduction, body, and conclusion. Most of the time, they are part of a larger work, so the introduction and conclusion paragraphs will be relatively brief.
However, if the review is a standalone piece, then your introduction and conclusion will be longer since you will need to discuss your research objectives, methods, and findings as well as analyze the literature used in your study.
To ensure your literature review makes an impression, have it professionally proofread by our expert literature review editing services . Submit your free sample of 500 words or less to get started today!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
2-minute read
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...
8 Press Release Distribution Services for Your Business
In a world where you need to stand out, press releases are key to being...
How to Get a Patent
In the United States, the US Patent and Trademarks Office issues patents. In the United...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
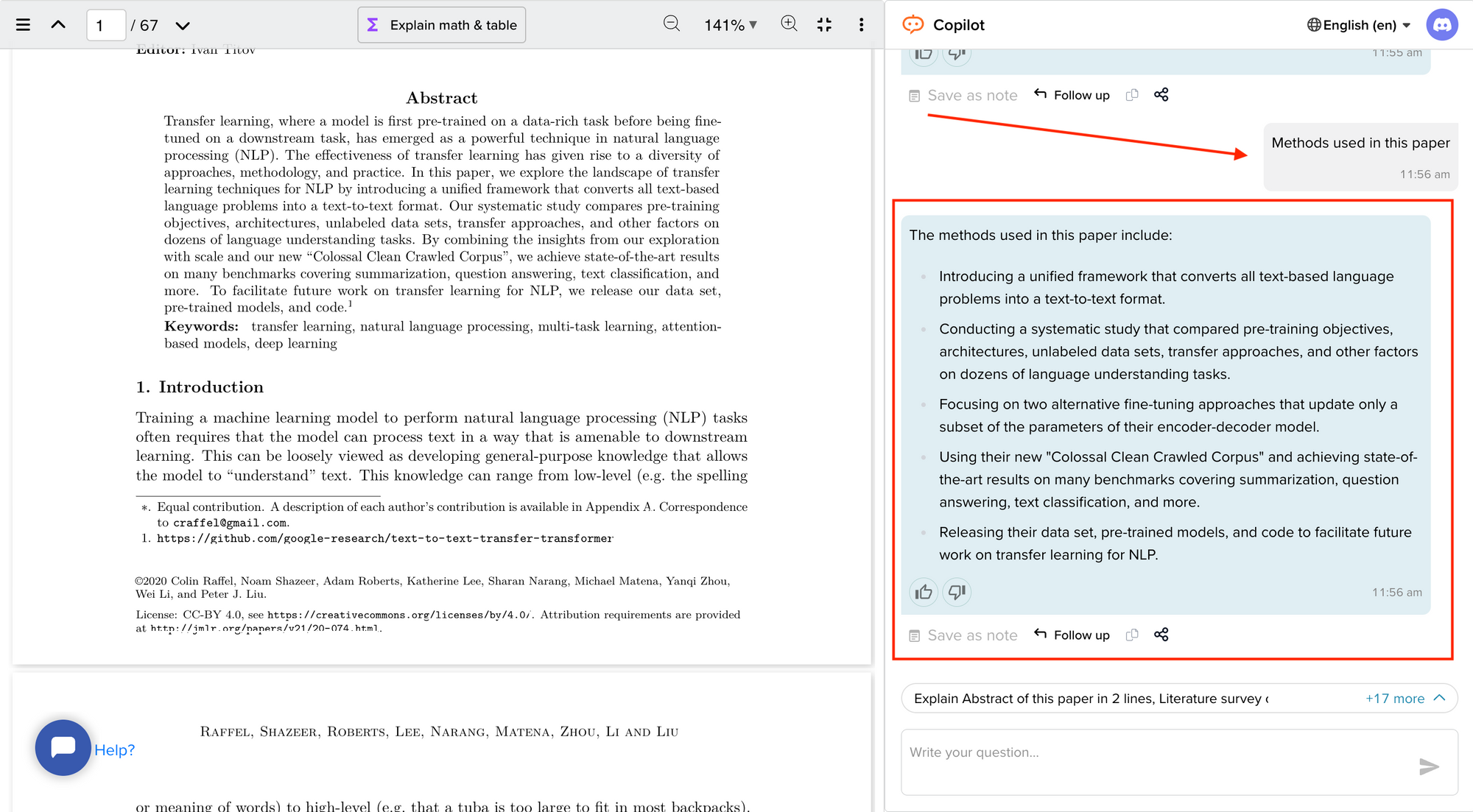
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references

Related Articles

- Research management

How I harnessed media engagement to supercharge my research career
Career Column 09 APR 24

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Career Column 08 APR 24

Three ways ChatGPT helps me in my academic writing

How two PhD students overcame the odds to snag tenure-track jobs
Adopt universal standards for study adaptation to boost health, education and social-science research
Correspondence 02 APR 24

Is ChatGPT corrupting peer review? Telltale words hint at AI use
News 10 APR 24

Rwanda 30 years on: understanding the horror of genocide
Editorial 09 APR 24
Junior Group Leader Position at IMBA - Institute of Molecular Biotechnology
The Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) is one of Europe’s leading institutes for basic research in the life sciences. IMBA is located on t...
Austria (AT)
IMBA - Institute of Molecular Biotechnology
Open Rank Faculty, Center for Public Health Genomics
Center for Public Health Genomics & UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center seek 2 tenure-track faculty members in Cancer Precision Medicine/Precision Health.
Charlottesville, Virginia
Center for Public Health Genomics at the University of Virginia
Husbandry Technician I
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Lead Researcher – Department of Bone Marrow Transplantation & Cellular Therapy
Researcher in the center for in vivo imaging and therapy.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
How To Structure Your Literature Review
3 options to help structure your chapter.
By: Amy Rommelspacher (PhD) | Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | November 2020 (Updated May 2023)
Writing the literature review chapter can seem pretty daunting when you’re piecing together your dissertation or thesis. As we’ve discussed before , a good literature review needs to achieve a few very important objectives – it should:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure . Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you’ll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don’t worry though – in this post, we’ll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

27 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
Literature Review
What is a literature review.
Students are often unsure of how to write a literature review. This is usually because, unlike other stages of a thesis such as Methods and Results, they have never written a literature review before.
FAQs about literature reviews
In the table below, you will find some of the questions that students ask, and some suggested answers.
Examples of literature reviews: organisation
Here you will find some examples from past Honours theses. The first set of examples shows part of the Table of Contents, so that you can see the kind of information included in a literature review. What can you notice about how the students have organised their reviews?
From the School of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences
1. INTRODUCTION ............................................... 1
1.1 HEPATITIS C VIRUS................................. 1
1.1.1 Genome ................................................ 1 1.1.2 Pathogenesis.......................................... 2 1.1.3 Transmission.......................................... 3 1.1.4 Epidemiology.......................................... 5 1.1.5 Treatment.............................................. 5
1.2 QUASISPECIES............................................ 7
1.2.1 Quasispecies and Treatment Outcome....... 7
1.3 METHODS TO ANLAYSE QUASISPECIES........... 8
1.3.1 Cloning and Sequencing........................... 9 1.3.2 Heteroduplex Mobility Analysis (HMA)........ 9 1.3.3 Capillary Electrophoresis......................... 11
1.4 HYPOTHESIS AND AIMS ............................... 11
(Oon 2005, p.ii)
What organisational approach has the student taken in example A?
From the School of Photovoltaic and Renewable Energy Engineering
2. LITERATURE REVIEW .......................................... 2-1
2.1 CLASSIC DIFFUSION CONCEPT....................... 2-1
2.1.1diffusion mechanisms................................ 2-1 2.1.2 Fick’s law .................................................. 2-4
2.2 BORON DIFFUSION ........................................ 2-9
2.2.1 diffusivity ................................................ 2-9 2.2.2 segregation coefficient ............................. 2-10 2.2.3 silicon self-interstitial and diffusion rate....... 2-12 2.2.4 formation of boron rich layer (brl).............. 2-12 2.2.5 boron diffusion systems............................. 2-14
2.3 BORON NITRIDE SOLID SOURCE DIFFUSION..... 2-15
2.3.1 benefits and challenges.............................. 2-15 2.3.2 diffusion process........................................ 2-16
2.4 SOLAR CELL CHARACTERISATION..................... 2-18
What organisational approach has the student taken in example B?
Examples of literature reviews: language
Here you will find some more examples of literature reviews, showing how the students refer to and comment on previous research. Look at the following examples and see how the students summarise a number of studies and contrast differing findings. Also notice the use of evaluative language to show the student's evaluation of the previous research.
- Summarising language
- Contrast language
- Evaluative language
"Several studies [5, 6, 7] have reported the benefits of using boron solid sources over other types of boron diffusion source. … On the contrary, Warabisako et al [9] demonstrated that obtaining high efficiencies with boron solid source was no easy task. They reported severe degradation of bulk minority carrier lifetime after boron solid source diffusion" (Chen, 2003, pp.2-14-2-15).
"On evaluation of the studies performed thus far, genotype 1b RdRp proteins have been studied extensively while RdRp proteins from other genotypes have been somewhat ignored. Kim et al. was the only group to have published a 3a RdRp paper, although their focus was on the template requirement for the NS5B gene as opposed to polymerase activity" (Tan, 2004, pp.15-16)
See next: Exercise for getting started on your literature review
Engineering & science.
- Report writing
- Technical writing
- Writing lab reports
- Introductions
- Literature Review Exercise
- Writing up results
- Discussions
- Conclusions
- Writing tools
- Case study report in (engineering)
- ^ More support
Study Hacks Workshops | All the hacks you need! 7 Feb – 10 Apr 2024
Discover your Library: Main Library 21 May 2024

Tips for writing a PhD dissertation: FAQs answered
From how to choose a topic to writing the abstract and managing work-life balance through the years it takes to complete a doctorate, here we collect expert advice to get you through the PhD writing process
Campus team
Additional links.

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
A diy guide to starting your own journal, universities, ai and the common good, artificial intelligence and academic integrity: striking a balance, create an onboarding programme for neurodivergent students.
Embarking on a PhD is “probably the most challenging task that a young scholar attempts to do”, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith in their practical guide to dissertation and thesis writing. After years of reading and research to answer a specific question or proposition, the candidate will submit about 80,000 words that explain their methods and results and demonstrate their unique contribution to knowledge. Here are the answers to frequently asked questions about writing a doctoral thesis or dissertation.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
Whatever the genre of the doctorate, a PhD must offer an original contribution to knowledge. The terms “dissertation” and “thesis” both refer to the long-form piece of work produced at the end of a research project and are often used interchangeably. Which one is used might depend on the country, discipline or university. In the UK, “thesis” is generally used for the work done for a PhD, while a “dissertation” is written for a master’s degree. The US did the same until the 1960s, says Oxbridge Essays, when the convention switched, and references appeared to a “master’s thesis” and “doctoral dissertation”. To complicate matters further, undergraduate long essays are also sometimes referred to as a thesis or dissertation.
The Oxford English Dictionary defines “thesis” as “a dissertation, especially by a candidate for a degree” and “dissertation” as “a detailed discourse on a subject, especially one submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of a degree or diploma”.
- Ten platinum rules for PhD supervisors
- Fostering freedom in PhD students: how supervisors can shape accessible paths for doctoral research
- Lessons from students on effective research supervision
The title “doctor of philosophy”, incidentally, comes from the degree’s origins, write Dr Felix, an associate professor at Mahidol University in Thailand, and Dr Smith, retired associate professor of education at the University of Sydney , whose co-authored guide focuses on the social sciences. The PhD was first awarded in the 19th century by the philosophy departments of German universities, which at that time taught science, social science and liberal arts.
How long should a PhD thesis be?
A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words ( 100 to 300 pages in length ) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) – from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion.
The structure of a dissertation will vary depending on discipline (humanities, social sciences and STEM all have their own conventions), location and institution. Examples and guides to structure proliferate online. The University of Salford , for example, lists: title page, declaration, acknowledgements, abstract, table of contents, lists of figures, tables and abbreviations (where needed), chapters, appendices and references.
A scientific-style thesis will likely need: introduction, literature review, materials and methods, results, discussion, bibliography and references.
As well as checking the overall criteria and expectations of your institution for your research, consult your school handbook for the required length and format (font, layout conventions and so on) for your dissertation.
A PhD takes three to four years to complete; this might extend to six to eight years for a part-time doctorate.
What are the steps for completing a PhD?
Before you get started in earnest , you’ll likely have found a potential supervisor, who will guide your PhD journey, and done a research proposal (which outlines what you plan to research and how) as part of your application, as well as a literature review of existing scholarship in the field, which may form part of your final submission.
In the UK, PhD candidates undertake original research and write the results in a thesis or dissertation, says author and vlogger Simon Clark , who posted videos to YouTube throughout his own PhD journey . Then they submit the thesis in hard copy and attend the viva voce (which is Latin for “living voice” and is also called an oral defence or doctoral defence) to convince the examiners that their work is original, understood and all their own. Afterwards, if necessary, they make changes and resubmit. If the changes are approved, the degree is awarded.
The steps are similar in Australia , although candidates are mostly assessed on their thesis only; some universities may include taught courses, and some use a viva voce. A PhD in Australia usually takes three years full time.
In the US, the PhD process begins with taught classes (similar to a taught master’s) and a comprehensive exam (called a “field exam” or “dissertation qualifying exam”) before the candidate embarks on their original research. The whole journey takes four to six years.
A PhD candidate will need three skills and attitudes to get through their doctoral studies, says Tara Brabazon , professor of cultural studies at Flinders University in Australia who has written extensively about the PhD journey :
- master the academic foundational skills (research, writing, ability to navigate different modalities)
- time-management skills and the ability to focus on reading and writing
- determined motivation to do a PhD.

How do I choose the topic for my PhD dissertation or thesis?
It’s important to find a topic that will sustain your interest for the years it will take to complete a PhD. “Finding a sustainable topic is the most important thing you [as a PhD student] would do,” says Dr Brabazon in a video for Times Higher Education . “Write down on a big piece of paper all the topics, all the ideas, all the questions that really interest you, and start to cross out all the ones that might just be a passing interest.” Also, she says, impose the “Who cares? Who gives a damn?” question to decide if the topic will be useful in a future academic career.
The availability of funding and scholarships is also often an important factor in this decision, says veteran PhD supervisor Richard Godwin, from Harper Adams University .
Define a gap in knowledge – and one that can be questioned, explored, researched and written about in the time available to you, says Gina Wisker, head of the Centre for Learning and Teaching at the University of Brighton. “Set some boundaries,” she advises. “Don’t try to ask everything related to your topic in every way.”
James Hartley, research professor in psychology at Keele University, says it can also be useful to think about topics that spark general interest. If you do pick something that taps into the zeitgeist, your findings are more likely to be noticed.
You also need to find someone else who is interested in it, too. For STEM candidates , this will probably be a case of joining a team of people working in a similar area where, ideally, scholarship funding is available. A centre for doctoral training (CDT) or doctoral training partnership (DTP) will advertise research projects. For those in the liberal arts and social sciences, it will be a matter of identifying a suitable supervisor .
Avoid topics that are too broad (hunger across a whole country, for example) or too narrow (hunger in a single street) to yield useful solutions of academic significance, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith. And ensure that you’re not repeating previous research or trying to solve a problem that has already been answered. A PhD thesis must be original.
What is a thesis proposal?
After you have read widely to refine your topic and ensure that it and your research methods are original, and discussed your project with a (potential) supervisor, you’re ready to write a thesis proposal , a document of 1,500 to 3,000 words that sets out the proposed direction of your research. In the UK, a research proposal is usually part of the application process for admission to a research degree. As with the final dissertation itself, format varies among disciplines, institutions and countries but will usually contain title page, aims, literature review, methodology, timetable and bibliography. Examples of research proposals are available online.
How to write an abstract for a dissertation or thesis
The abstract presents your thesis to the wider world – and as such may be its most important element , says the NUI Galway writing guide. It outlines the why, how, what and so what of the thesis . Unlike the introduction, which provides background but not research findings, the abstract summarises all sections of the dissertation in a concise, thorough, focused way and demonstrates how well the writer understands their material. Check word-length limits with your university – and stick to them. About 300 to 500 words is a rough guide – but it can be up to 1,000 words.
The abstract is also important for selection and indexing of your thesis, according to the University of Melbourne guide , so be sure to include searchable keywords.
It is the first thing to be read but the last element you should write. However, Pat Thomson , professor of education at the University of Nottingham , advises that it is not something to be tackled at the last minute.
How to write a stellar conclusion
As well as chapter conclusions, a thesis often has an overall conclusion to draw together the key points covered and to reflect on the unique contribution to knowledge. It can comment on future implications of the research and open up new ideas emanating from the work. It is shorter and more general than the discussion chapter , says online editing site Scribbr, and reiterates how the work answers the main question posed at the beginning of the thesis. The conclusion chapter also often discusses the limitations of the research (time, scope, word limit, access) in a constructive manner.
It can be useful to keep a collection of ideas as you go – in the online forum DoctoralWriting SIG , academic developer Claire Aitchison, of the University of South Australia , suggests using a “conclusions bank” for themes and inspirations, and using free-writing to keep this final section fresh. (Just when you feel you’ve run out of steam.) Avoid aggrandising or exaggerating the impact of your work. It should remind the reader what has been done, and why it matters.
How to format a bibliography (or where to find a reliable model)
Most universities use a preferred style of references , writes THE associate editor Ingrid Curl. Make sure you know what this is and follow it. “One of the most common errors in academic writing is to cite papers in the text that do not then appear in the bibliography. All references in your thesis need to be cross-checked with the bibliography before submission. Using a database during your research can save a great deal of time in the writing-up process.”
A bibliography contains not only works cited explicitly but also those that have informed or contributed to the research – and as such illustrates its scope; works are not limited to written publications but include sources such as film or visual art.
Examiners can start marking from the back of the script, writes Dr Brabazon. “Just as cooks are judged by their ingredients and implements, we judge doctoral students by the calibre of their sources,” she advises. She also says that candidates should be prepared to speak in an oral examination of the PhD about any texts included in their bibliography, especially if there is a disconnect between the thesis and the texts listed.
Can I use informal language in my PhD?
Don’t write like a stereotypical academic , say Kevin Haggerty, professor of sociology at the University of Alberta , and Aaron Doyle, associate professor in sociology at Carleton University , in their tongue-in-cheek guide to the PhD journey. “If you cannot write clearly and persuasively, everything about PhD study becomes harder.” Avoid jargon, exotic words, passive voice and long, convoluted sentences – and work on it consistently. “Writing is like playing guitar; it can improve only through consistent, concerted effort.”
Be deliberate and take care with your writing . “Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense,” advises THE ’s Ms Curl. “Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency. If you are too involved with the text to be able to take a step back and do this, then ask a friend or colleague to read it with a critical eye. Remember Hemingway’s advice: ‘Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.’ Clarity is key.”
How often should a PhD candidate meet with their supervisor?
Since the PhD supervisor provides a range of support and advice – including on research techniques, planning and submission – regular formal supervisions are essential, as is establishing a line of contact such as email if the candidate needs help or advice outside arranged times. The frequency varies according to university, discipline and individual scholars.
Once a week is ideal, says Dr Brabazon. She also advocates a two-hour initial meeting to establish the foundations of the candidate-supervisor relationship .
The University of Edinburgh guide to writing a thesis suggests that creating a timetable of supervisor meetings right at the beginning of the research process will allow candidates to ensure that their work stays on track throughout. The meetings are also the place to get regular feedback on draft chapters.
“A clear structure and a solid framework are vital for research,” writes Dr Godwin on THE Campus . Use your supervisor to establish this and provide a realistic view of what can be achieved. “It is vital to help students identify the true scientific merit, the practical significance of their work and its value to society.”
How to proofread your dissertation (what to look for)
Proofreading is the final step before printing and submission. Give yourself time to ensure that your work is the best it can be . Don’t leave proofreading to the last minute; ideally, break it up into a few close-reading sessions. Find a quiet place without distractions. A checklist can help ensure that all aspects are covered.
Proofing is often helped by a change of format – so it can be easier to read a printout rather than working off the screen – or by reading sections out of order. Fresh eyes are better at spotting typographical errors and inconsistencies, so leave time between writing and proofreading. Check with your university’s policies before asking another person to proofread your thesis for you.
As well as close details such as spelling and grammar, check that all sections are complete, all required elements are included , and nothing is repeated or redundant. Don’t forget to check headings and subheadings. Does the text flow from one section to another? Is the structure clear? Is the work a coherent whole with a clear line throughout?
Ensure consistency in, for example, UK v US spellings, capitalisation, format, numbers (digits or words, commas, units of measurement), contractions, italics and hyphenation. Spellchecks and online plagiarism checkers are also your friend.

How do you manage your time to complete a PhD dissertation?
Treat your PhD like a full-time job, that is, with an eight-hour working day. Within that, you’ll need to plan your time in a way that gives a sense of progress . Setbacks and periods where it feels as if you are treading water are all but inevitable, so keeping track of small wins is important, writes A Happy PhD blogger Luis P. Prieto.
Be specific with your goals – use the SMART acronym (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and timely).
And it’s never too soon to start writing – even if early drafts are overwritten and discarded.
“ Write little and write often . Many of us make the mistake of taking to writing as one would take to a sprint, in other words, with relatively short bursts of intense activity. Whilst this can prove productive, generally speaking it is not sustainable…In addition to sustaining your activity, writing little bits on a frequent basis ensures that you progress with your thinking. The comfort of remaining in abstract thought is common; writing forces us to concretise our thinking,” says Christian Gilliam, AHSS researcher developer at the University of Cambridge ’s Centre for Teaching and Learning.
Make time to write. “If you are more alert early in the day, find times that suit you in the morning; if you are a ‘night person’, block out some writing sessions in the evenings,” advises NUI Galway’s Dermot Burns, a lecturer in English and creative arts. Set targets, keep daily notes of experiment details that you will need in your thesis, don’t confuse writing with editing or revising – and always back up your work.
What work-life balance tips should I follow to complete my dissertation?
During your PhD programme, you may have opportunities to take part in professional development activities, such as teaching, attending academic conferences and publishing your work. Your research may include residencies, field trips or archive visits. This will require time-management skills as well as prioritising where you devote your energy and factoring in rest and relaxation. Organise your routine to suit your needs , and plan for steady and regular progress.
How to deal with setbacks while writing a thesis or dissertation
Have a contingency plan for delays or roadblocks such as unexpected results.
Accept that writing is messy, first drafts are imperfect, and writer’s block is inevitable, says Dr Burns. His tips for breaking it include relaxation to free your mind from clutter, writing a plan and drawing a mind map of key points for clarity. He also advises feedback, reflection and revision: “Progressing from a rough version of your thoughts to a superior and workable text takes time, effort, different perspectives and some expertise.”
“Academia can be a relentlessly brutal merry-go-round of rejection, rebuttal and failure,” writes Lorraine Hope , professor of applied cognitive psychology at the University of Portsmouth, on THE Campus. Resilience is important. Ensure that you and your supervisor have a relationship that supports open, frank, judgement-free communication.
If you found this interesting and want advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the THE Campus newsletter .
Authoring a PhD Thesis: How to Plan, Draft, Write and Finish a Doctoral Dissertation (2003), by Patrick Dunleavy
Writing Your Dissertation in Fifteen Minutes a Day: A Guide to Starting, Revising, and Finishing Your Doctoral Thesis (1998), by Joan Balker
Challenges in Writing Your Dissertation: Coping with the Emotional, Interpersonal, and Spiritual Struggles (2015), by Noelle Sterne
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
Global perspectives: navigating challenges in higher education across borders, how to help young women see themselves as coders, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, authentic assessment in higher education and the role of digital creative technologies, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
How to write a literature review for a dissertation, published by steve tippins on july 5, 2019 july 5, 2019.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 04:45 am
Chapter 2 of your dissertation, your literature review, may be the longest chapter. It is not uncommon to see lit reviews in the 40- to 60-page range. That may seem daunting, but I contend that the literature review could be the easiest part of your dissertation.
It is also foundational. To be able to select an appropriate research topic and craft expert research questions, you’ll need to know what has already been discovered and what mysteries remain.
Remember, your degree is meant to indicate your achieving the highest level of expertise in your area of study. The lit review for your dissertation could very well form the foundation for your entire career.
In this article, I’ll give you detailed instructions for how to write the literature review of your dissertation without stress. I’ll also provide a sample outline.
When to Write the Literature Review for your Dissertation
Though technically Chapter 2 of your dissertation, many students write their literature review first. Why? Because having a solid foundation in the research informs the way you write Chapter 1.
Also, when writing Chapter 1, you’ll need to become familiar with the literature anyway. It only makes sense to write down what you learn to form the start of your lit review.
Some institutions even encourage students to write Chapter 2 first. But it’s important to talk with your Chair to see what he or she recommends.
How Long Should a Literature Review Be?
There is no set length for a literature review. The length largely depends on your area of study. However, I have found that most literature reviews are between 40-60 pages.
If your literature review is significantly shorter than that, ask yourself (a) if there is other relevant research that you have not explored, or (b) if you have provided enough of a discussion about the information you did explore.
Preparing to Write the Literature Review for your Dissertation

1. Search Using Key Terms
Most people start their lit review searching appropriate databases using key terms. For example, if you’re researching the impact of social media on adult learning, some key terms you would use at the start of your search would be adult learning, androgogy, social media, and “learning and social media” together.
If your topic was the impact of natural disasters on stock prices, then you would need to explore all types of natural disasters, other market factors that impact stock prices, and the methodologies used.
You can save time by skimming the abstracts first; if the article is not what you thought it might be you can move on quickly.
Once you start finding articles using key terms, two different things will usually happen: you will find new key terms to search, and the articles will lead you directly to other articles related to what you are studying. It becomes like a snowball rolling downhill.
Note that the vast majority of your sources should be articles from peer-reviewed journals.
2. Immerse Yourself in the Literature

When people ask what they should do first for their dissertation the most common answer is “immerse yourself in the literature.” What exactly does this mean?
Think of this stage as a trip into the quiet heart of the forest. Your questions are at the center of this journey, and you’ll need to help your reader understand which trees — which particular theories, studies, and lines of reasoning — got you there.
There are lots of trees in this particular forest, but there are particular trees that mark your path. What makes them unique? What about J’s methodology made you choose that study over Y’s? How did B’s argument triumph over A’s, thus leading you to C’s theory?
You are showing your reader that you’ve fully explored the forest of your topic and chosen this particular path, leading to these particular questions (your research questions), for these particular reasons.
3. Consider Gaps in the Research
The gaps in the research are where current knowledge ends and your study begins. In order to build a case for doing your study, you must demonstrate that it:
- Is worthy of doctoral-level research, and
- Has not already been studied
Defining the gaps in the literature should help accomplish both aims. Identifying studies on related topics helps make the case that your study is relevant, since other researchers have conducted related studies.
And showing where they fall short will help make the case that your study is the appropriate next step. Pay special attention to the recommendations for further research that the authors of studies make.
4. Organize What You Find
As you find articles, you will have to come up with methods to organize what you find.
Whether you find a computer-based system (three popular systems are Zotero, endNote, and Mendeley) or some sort of manual system such as index cards, you need to devise a method where you can easily group your references by subject and methodology and find what you are looking for when you need it. It is very frustrating to know you have found an article that supports a point that you are trying to make, but you can’t find the article!

One way to save time and keep things organized is to cut and paste relevant quotations (and their references) under topic headings. You’ll be able to rearrange and do some paraphrasing later, but if you’ve got the quotations and the citations that are important to you already embedded in your text, you’ll have an easier time of it.
If you choose this method, be sure to list the whole reference on the reference/bibliography page so you don’t have to do this page separately later. Some students use Scrivener for this purpose, as it offers a clear way to view and easily navigate to all sections of a written document.
Need help with your literature review? Take a look at my dissertation coaching and dissertation editing services.
How to Write the Literature Review for your Dissertation
Once you have gathered a sufficient number of pertinent references, you’ll need to string them together in a way that tells your story. Explain what previous researchers have done by telling the story of how knowledge on this topic has evolved. Here, you are laying the support for your topic and showing that your research questions need to be answered. Let’s dive into how to actually write your dissertation’s literature review.
1. Create an Outline
If you’ve created a system for keeping track of the sources you’ve found, you likely already have the bones of an outline. Even if not, it may be relatively easy to see how to organize it all. The main thing to remember is, keep it simple and don’t overthink it. There are several ways to organize your dissertation’s literature review, and I’ll discuss some of the most common below:
- By topic. This is by far the most common approach, and it’s the one I recommend unless there’s a clear reason to do otherwise. Topics are things like servant leadership, transformational leadership, employee retention, organizational knowledge, etc. Organizing by topic is fairly simple and it makes sense to the reader.
- Chronologically. In some cases, it makes sense to tell the story of how knowledge and thought on a given subject have evolved. In this case, sub-sections may indicate important advances or contributions.
- By methodology. Some students organize their literature review by the methodology of the studies. This makes sense when conducting a mixed-methods study, and in cases where methodology is at the forefront.
2. Write the Paragraphs
I said earlier that I thought the lit review was the easiest part to write, and here is why. When you write about the findings of others, you can do it in small, discrete time periods. You go down the path awhile, then you rest.
Once you have many small pieces written, you can then piece them together. You can write each piece without worrying about the flow of the chapter; that can all be done at the end when you put the jigsaw puzzle of references together.

The literature review is a demonstration of your ability to think critically about existing research and build meaningfully on it in your study. Avoid simply stating what other researchers said. Find the relationships between studies, note where researchers agree and disagree, and– especiallyy–relate it to your own study.
Pay special attention to controversial issues, and don’t be afraid to give space to researchers who you disagree with. Including differing opinions will only strengthen the credibility of your study, as it demonstrates that you’re willing to consider all sides.
4. Justify the Methodology
In addition to discussing studies related to your topic, include some background on the methodology you will be using. This is especially important if you are using a new or little-used methodology, as it may help get committee members onboard.
I have seen several students get slowed down in the process trying to get committees to buy into the planned methodology. Providing references and samples of where the planned methodology has been used makes the job of the committee easier, and it will also help your reader trust the outcomes.
Advice for Writing Your Dissertation’s Literature Review
- Remember to relate each section back to your study (your Problem and Purpose statements).
- Discuss conflicting findings or theoretical positions. Avoid the temptation to only include research that you agree with.
- Sections should flow together, the way sections of a chapter in a nonfiction book do. They should relate to each other and relate back to the purpose of your study. Avoid making each section an island.
- Discuss how each study or theory relates to the others in that section.
- Avoid relying on direct quotes–you should demonstrate that you understand the study and can describe it accurately.
Sample Outline of a Literature Review (Dissertation Chapter 2)

Here is a sample outline, with some brief instructions. Note that your institution probably has specific requirements for the structure of your dissertation’s literature review. But to give you a general idea, I’ve provided a sample outline of a dissertation ’s literature review here.
- Introduction
- State the problem and the purpose of the study
- Give a brief synopsis of literature that establishes the relevance of the problem
- Very briefly summarize the major sections of your chapter
Documentation of Literature Search Strategy
- Include the library databases and search engines you used
- List the key terms you used
- Describe the scope (qualitative) or iterative process (quantitative). Explain why and based on what criteria you selected the articles you did.
Literature Review (this is the meat of the chapter)

- Sub-topic a
- Sub-topic b
- Sub-topic c
See below for an example of what this outline might look like.
How to Write a Literature Review for a Dissertation: An Example
Let’s take an example that will make the organization, and the outline, a little bit more clear. Below, I’ll fill out the example outline based on the topics discussed.
If your questions have to do with the impact of the servant leadership style of management on employee retention, you may want to saunter down the path of servant leadership first, learning of its origins , its principles , its values , and its methods .
You’ll note the different ways the style is employed based on different practitioners’ perspectives or circumstances and how studies have evaluated these differences. Researchers will draw conclusions that you’ll want to note, and these conclusions will lead you to your next questions.

Next, you’ll want to wander into the territory of management styles to discover their impact on employee retention in general. Does management style really make a difference in employee retention, and if so, what factors, exactly, make this impact?
Employee retention is its own path, and you’ll discover factors, internal and external, that encourage people to stick with their jobs.
You’ll likely find paradoxes and contradictions in here that just bring up more questions. How do internal and external factors mix and match? How can employers influence both psychology and context ? Is it of benefit to try and do so?
At first, these three paths seem somewhat remote from one another, but your interest is where the three converge. Taking the lit review section by section like this before tying it all together will not only make it more manageable to write but will help you lead your reader down the same path you traveled, thereby increasing clarity.
Example Outline
So the main sections of your literature review might look something like this:
- Literature Search Strategy
- Conceptual Framework or Theoretical Foundation
- Literature that supports your methodology
- Origins, principles, values
- Seminal research
- Current research
- Management Styles’ Impact on employee retention
- Internal Factors
- External Factors
- Influencing psychology and context
- Summary and Conclusion
Final Thoughts on Writing Your Dissertation’s Chapter 2
The lit review provides the foundation for your study and perhaps for your career. Spend time reading and getting lost in the literature. The “aha” moments will come where you see how everything fits together.
At that point, it will just be a matter of clearly recording and tracing your path, keeping your references organized, and conveying clearly how your research questions are a natural evolution of previous work that has been done.
PS. If you’re struggling with your literature review, I can help. I offer dissertation coaching and editing services.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
What makes a good research question.
Creating a good research question is vital to successfully completing your dissertation. Here are some tips that will help you formulate a good research question. What Makes a Good Research Question? These are the three Read more…

Dissertation Structure
When it comes to writing a dissertation, one of the most fraught questions asked by graduate students is about dissertation structure. A dissertation is the lengthiest writing project that many graduate students ever undertake, and Read more…

Choosing a Dissertation Chair
Choosing your dissertation chair is one of the most important decisions that you’ll make in graduate school. Your dissertation chair will in many ways shape your experience as you undergo the most rigorous intellectual challenge Read more…
Make This Your Last Round of Dissertation Revision.
Learn How to Get Your Dissertation Accepted .
Discover the 5-Step Process in this Free Webinar .
Almost there!
Please verify your email address by clicking the link in the email message we just sent to your address.
If you don't see the message within the next five minutes, be sure to check your spam folder :).
Hack Your Dissertation
5-Day Mini Course: How to Finish Faster With Less Stress
Interested in more helpful tips about improving your dissertation experience? Join our 5-day mini course by email!
Understanding the Length of a Literature Review

A literature review is an academic piece of writing acknowledging the authenticity and comprehension of academic literature in light of the topic. It summarizes the key elements of the research and previous research and demonstration in a specific field of study. In a literature review, you use historical data and available information to generate a new understanding. It will guide you throughout your research to understand your limits and your position. From writing an introduction to concluding your paper, the literature review can be your best friend. However, the question is, how long should a literature review be for a research paper?
Table of Contents
Understanding the ideal length of a research paper’s literature review

There is no one answer to how long a literature review should be. Every field of study has its requirements and conventions, which dictate the appropriate length for a given type of literature review. In general, however, a good rule of thumb is that the deeper the research topic , the more detailed and extensive the literature review should be.
For example, a literature review for a business research topic might be relatively short and to the point, focusing mostly on key figures and data points. On the other hand, a literature review for a history research topic could be much longer and more detailed, delving into the various interpretations and implications of the research.
Ultimately, the decision of how long a literature review should be is up to the individual researcher and the specific requirements of the research project. However, no matter the length, a literature review should be comprehensive, clear, and concise, providing a thorough overview of the current state of knowledge on the chosen research topic.
Let’s talk about literature lengths for the various types of writings.
Literature Review Ideal Length for A Research Paper

What is your purpose, and who are your readers? That is the first question you must ask yourself when writing a research paper. Interestingly, this question will be valid for every aspect of your research. You are choosing a topic; you must consider your purpose and target audience. When writing an introduction for a research paper, you must think about the same question.
A literature review is an important part of any research paper. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge on a topic and helps to identify areas where further research is needed.
The length of a literature review varies depending on the depth and purpose of the research. For example, a literature review for a PhD thesis will be much longer than one for a high school research paper. The length also depends on the scope of the research, with broader topics requiring more extensive reviews.
Generally speaking, a literature review should be at least 20 pages long. However, this will vary depending on the specific requirements of your assignment. A few paragraphs may suffice for high school paper topics, while a more comprehensive review is necessary for longer papers.
No matter the length, a literature review must be well-written and provide a critical overview of the current state of knowledge on a topic. It should identify gaps in the literature and offer suggestions for further research.
Ideal Length Of A Stand-alone literature review

A literature review can be a very impeccable treat to read as a stand-alone article. As a stand-alone write-up, a literature review can cover as many aspects as to provide much thorough background. It includes providing full background and contemporary backgrounds to provide authentic value to your topic. Still, the inspiration is like a river; sooner or later, you must have built a dam around it somewhere. A too-short stand-alone literature review will fail to provide enough insights.
On the other hand, the too-long literature review will wear the reader out and undermine your stance. The ideal length for a literature review as a stand-alone article is at least 20 pages. You can add more pages if you need to, but remember that there is a limit.
How long a literature review should be for a research paper could be answered in various ways. However, it all comes down to the type and the scope of your research paper and how you decide the length. By now, we are confident that you can answer this question and ace your literature review. You can consult us at Paper Perk if you still need paper writing help .
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score

How long should a literature review be? Writing a literature review properly.
Embarking on a journey through academic research, one is often faced with the question: How long should a thesis literature review be?
Typically, a literature review comprises 20-40% of the thesis, equating to around 20-40 pages, yet this can fluctuate based on the topic, field, and institutional guidelines. However, if the literature review is for an assignment/project report it only needs to be a few pages long.
A literature review represents a critical exploration of existing scholarship on a specific topic, serving as the backbone for dissertations, research articles, book chapters, conference papers, and more.
This comprehensive, concise, and well-structured survey of the current knowledge landscape provides insight into established findings, research methodologies, and highlights the gaps that your research aims to fill.

The endeavor of writing a literature review not only deepens your understanding of your chosen area but also lays a strong foundation for your unique inquiry and contribution to the field.
How Long Should a Thesis Literature Review Be? Dissertation, research paper, journal article, and more
The length of a thesis literature review can vary based on the topic, research field, and guidelines provided by your institution.
However, as a general rule, it often comprises 20-40% of the thesis. This equates to around 20-40 pages.
However, if the literature review is for an assignment it only needs to be a few pages long.
It’s crucial to ensure your review is comprehensive, concise, and well-structured, adequately summarizing existing research, identifying gaps, discussing limitations, and suggesting future research directions.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a critical examination of existing research on a particular topic. It is often the beginning of any area of study and is often used as the introduction to a dissertation.
I have done one at the beginning of any research project, the beginning of my PhD and postdocs and in industry research positions.
It involves analyzing relevant resources such as books, journal articles, and other scholarly works to gain a comprehensive understanding of the current knowledge in your area of interest.
For example, if your topic is the impact of social media on the mental health of younger generations, you’ll explore previous studies to understand established findings, methodologies, and gaps in the field.
The purpose is threefold:
- to comprehend what is already known,
- to give your readers an overview of existing knowledge (showing where your research fits in), and
- to identify any unexplored areas or gaps, thus allowing you to contribute something original to the field.
The process aids in refining your research question and defining your unique angle of inquiry.
How do I create a literature review?
Creating a literature review involves several key steps:
- Conceptualize : Start by forming a conceptual framework. It’s an overview of the topic, helping you structure your review.
- Synthesis : Synthesize the literature. Read, categorize, and summarize the material to create a narrative.
- Analysis : This is your main body of work. Develop arguments and critique the literature.
- Conclusion : Recap your findings, discussing the implications of your work and highlighting any limitations.
- Future Research : If applicable, suggest areas for future research or policy actions based on your findings.
- Introduction : Write the introduction last. It includes the importance of the topic, gaps in knowledge, and your motivation for the review.
- Transparency : Always be transparent about limitations in your work and the body of evidence reviewed.
How many sources do you need in a literature review?
The number of sources required in a literature review can vary significantly depending on several factors such as:
- the nature of your research topic,
- the length of the literature review, and
- the specific instructions from your professor or institution.
In general, it’s crucial to include a wide range of sources to fully capture the breadth of scholarship on your research topic.
For a dissertation or thesis, a literature review might involve dozens of sources. For a stand-alone literature review or an overview for a journal article, fewer sources might be appropriate. For instance, a PhD thesis literature review might require anywhere from 50 to 300+ sources.
My PhD thesis had 256 papers cited
Rather than focusing on a specific number, the key is to ensure that your literature review provides a comprehensive, balanced overview of existing scholarship on your research topic.
This should ideally include both seminal works and recent publications, highlighting any gaps your research aims to fill.
Remember, the quality of your sources is as important as the quantity.
Your literature review should demonstrate that you have critically engaged with a variety of scholarly sources to gain a deep understanding of your research topic.
What Makes a Good Literature Review?
A good literature review for a dissertation or thesis is a comprehensive survey of existing scholarship on a particular topic, demonstrating your understanding of current research in your field of study.
The length of a literature review can vary depending on the research topic and level of study, but the University of Kent suggests that for a PhD thesis, it could range up to 20 pages or more.
Start by organizing your literature review either thematically, chronologically, or by methodology.
An annotated bibliography can assist in this process.
You must summarize the main points of each source, focusing on its relevance to your research project. Scholarly sources are preferable; consult your instructor for the minimum number of sources required.
It is essential to identify a gap in knowledge within the existing scholarship, which your research aims to fill.
This should be highlighted in your review, underlining the significance and worthiness of your proposed research. It’s crucial that your review provides a complete overview of the current state of research and shows why your research is important.
Bear in mind the word count, as a concise, focused review is typically preferred.
Structure is key and the title page, introduction, and conclusion should be included.
Despite the absence of a hard and fast rule on length, your review must provide a robust base of knowledge for your research, allowing readers to understand your research’s purpose and audience.
Wrapping up – How long should a literature review be?
The question “how long should a literature review be?” hinges on various factors, including the nature of the research project, area of study, and instructions from your instructor.
Whether it’s for a thesis, dissertation, or a research paper, writing a literature review requires a comprehensive survey of existing scholarship on your particular topic.
Remember, the length of a literature review is not a hard and fast rule; it could comprise anywhere from 20 pages to much more in a PhD thesis, or be a stand-alone brief overview in a journal article.
The structure of your review, whether thematically, chronologically, or by methodology, helps to summarize and highlight specific findings in the field of study.
Bear in mind the importance of identifying a gap in knowledge, which your research aims to fill.
Above all, your literature review should be a concise, scholarly synthesis of your research topic, providing a robust base of knowledge for your audience and demonstrating the significance and worthiness of your proposed research.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider
- Learning Tips
- Exam Guides
- School Life
Best Length for Literature Review: Thesis, Essays or Papers
- by Joseph Kenas
- November 30, 2023
- Writing Tips

Literature reviews are surveys on different topics using scholarly sources. Literature reviews help understand the current knowledge on different topics and hence identify gaps, methods, and relevant theories existing in an area of study.
To write a literature review, one needs to search for relevant literature, evaluate sources, identify themes and gaps, and outline structures. A good literature review will analyze, synthesize, and evaluate a study critically to give a clear picture of knowledge on that subject.
How Long Should a Literature Review Be?
The length of a literature review depends on the audience and its purpose. The level of study also determines the length of a literature review.

Literature reviews of topics done by undergraduate students are expected to be shorter than literature reviews of postgraduate students.
Literature reviews of essays are also expected to be shorter than literature reviews done for a thesis or dissertation. But how long should it be?
Overall, The length of a literature review should be between 20% and 40% of the total project. This is because the length of your paper also determines the length of the literature review.
Papers with a lot of content have longer literature reviews than papers with lesser amounts of content.
There is a general rule that the length of the literature review should be proportional to the length of your paper.
Optimal Length of a Literature Review for Different Projects
1. optimal literature for thesis.
A thesis can be defined as a long essay that includes personal research done by undergraduate and post-graduate students. The length of a thesis depends on the level of study.
A thesis written by bachelor’s degree students should be between 40-60 pages, while a thesis written for master’s and doctorate studies should be between 60-100 pages.
The length of the literature review for a thesis should be at least 8 pages to the minimum. The optimal length of the literature review for this should be 20% of the total length of the thesis project.
The length varies with the length of the thesis a student is writing. For example, in a 40-page thesis, the literature review should be not less than 8 pages.
Not less than 12 pages for a 60-page thesis and not less than 16 pages for an 80-page thesis. The literature review for a thesis should at least be a whole chapter.
2. Literature Review Length for Dissertation
A dissertation is a research project that is completed as part of a postgraduate or undergraduate degree. Dissertations allow students to present their findings on areas of research that they choose themselves. The length of a dissertation varies depending on the field of study.

The discipline, type of analysis, and area of research all determine the length of a dissertation.
The general length of a dissertation is usually between 150-300 pages.
A literature review for a dissertation should at least be between 40-60 pages. There is no specific set length for dissertation literature reviews. The length depends largely on your area of study.
If you have a short literature review, ask yourself whether there is other relevant research that you have not explored or if the information you have provided for what you explored is enough.
For proper preparation when writing a dissertation literature review, do the following:
- Search using key terms
Using key terms will help you do proper research and find many key terms to search. You will also find articles that are directly related to your area of study.
- Immerse yourself in literature
Immersing yourself in literature helps you massively explore your area of study and choose the right approach for your dissertation.
- Consider the research gaps
Focus on an area that has not been studied for your research. Recommendations made by authors can help you identify gaps in different areas of study.
- Organize what you find
Note down what you find in sections to avoid mixing of ideas. Copy and paste your findings to avoid losing them. Note the references of each researched work to avoid inconveniences later.
To write a literature review of your dissertations, create an outline, write the paragraphs, analyze the study, and justify the methodology.
3. Literature review length for Published Journal Articles
These are articles that are shorter than books and are written about very specific topics.

Journal articles are written regularly throughout the year and are written by experts for experts.
Journal articles can be original research, short reports or letters, review articles, case studies, or methodologies.
A published journal article should have an average of 5000 words.
The best length of the literature review section of published journal articles should be at least 2 pages or a few pages. This depends on t he length of the journal. Different topics vary in content which determines the length of the journal article.
The literature review of a 5000-word journal article should be between 1200 and 2000 words.
4. Literature review length for Research Paper
A research paper argues a point and analyses perspectives. It is centered on the writer’s thinking which is backed by other ideas and information. To write a research paper , pick a topic if you are not provided with one, do research, and present it.
Conduct the research, organize the research, form a thesis, create an outline, and then write your research. After writing, edit the content and re-read it to make sure that your research is ready for submission.
The length of a research paper should be at least 25% of the research paper or term paper. However, this usually depends on the area of study. There are also short research papers and long research papers. Short research papers are between 5 and 8 pages long and are usually direct to the point.
The literature review of research papers depends on the length of the research papers. Short research papers can have 2-3-page research reviews. The longer the research paper gets, the longer the literature review should be.
Research papers are common and instructors can give a maximum length of the literature review. In such cases, the instructions of the instructor have to be followed.
5. Best length for Capstone Paper Literature
This is a form of academic paper that students write to summarize their experiences. They are usually written in the last year of high school or middle school as part of a university or college course.
To write a capstone research paper, think of the topic you want to write, create a capstone project proposal, gather information, and come up with a structure.
After writing your paper, proofread the text and prepare the defense. The average length of a capstone paper is between 20-25 pages. A capstone paper should not exceed the length of 45 pages.
A literature review of a capstone paper depends on its length and the instructions given by your faculty. For instance, a 20-25-page capstone paper should have a 5 to 6-page long literature review. The longer the paper gets, the longer the literature review should be.
After writing the literature review, submit a draft to your capstone adviser for corrections before proceeding.
Optimal Length for Essays
An essay is a piece of writing that can be used to support an argument, present an idea, express emotion, or initiate debate. Ideas are presented in essays in a non-fictional way. There are many different types of essays. Essays can be as short as 500 words and as long as 10,00 words.
The length of the literature review section for an essay depends on the length of your essay. A 15-page essay can have a 3-page long literature review. The lesser the pages the lesser the literature review. Therefore, there is no universal length for the literature review of an essay.
The more the pages, the longer the literature review. Literature reviews of essays should have an introduction, main body, and conclusion.
The introduction part should introduce your topic, introduce your point of view, review the literature and state the scope of the literature.
The main body should organize the literature into themes, show the relation between the chosen topic and the wider subject, and move from a general view to a specific view.
The conclusion should summarize the important aspects of the main body, identify areas for future study, and link your research to existing knowledge.
Factors Determining the Length of a Literature Review
1. type of the project.
The type of project you have determines the length of your literature review.

Dissertations have longer literature reviews than published journal articles.
A thesis has a longer literature review compared to essays.
One, therefore, will need to know the type of project at hand before starting and writing the literature review to avoid making mistakes.
Each type of project has its specified length of the literature review.
2. The Number of Sources
The number of sources one has regarding a certain topic will determine the length of the work they right. Longer writings have longer literature reviews and shorter writing has shorter literature reviews.
Sources of information determine the content one will gather before writing an essay. It is the sources of information that will help you gain knowledge of the topic you are handling.
The less content and knowledge about a topic one has, the lesser the content and knowledge one will write. Without content and knowledge about a topic, even formulating a literature review becomes hard.
When one has many sources of information, ideas will flow and understanding of the area of study will increase. This helps one formulate accurate literature reviews and include the majority of information obtained from the sources in them.
3. Your Experience in Writing
You can have everything needed to write a literature review of the required length, but without experience writing, it may prove to be hard. If one has never written a literature review before, he or she will experience difficulties in writing it.
In most cases, one may write literature reviews that are too short or too long. Transforming the information gathered into a literature review is hard.
This is why one may use too much or less information in the literature review. Such writers are advised to go through beginner tutorials to explain the writing of literature reviews to avoid too many mistakes.
Experienced writers, on the other hand, know how to utilize every piece of information gathered and transform it into a literature review of the required size. Amateur literature review writers are also advised to seek help from experienced writers.
4. The Length of the Entire Project
In most academic assignments, instructors give students the length required in different projects. This length should guide students in determining the length of the literature review.
A literature review should not take the majority of your project. Longer assignments have longer literature reviews, while shorter assignments have shorter literature reviews.
Students should consider the number of words or pages provided by the instructor for certain assignments and gauge the length that the literature review.
The literature review reflects the whole content of your project. You can’t have a short literature review and a very long essay. You will probably include things that do not relate to your literature review in the essay.
Short projects like essays and term papers mostly have mini-reviews. Read this guide on how long a mini literature review is so that you can get the point.
5. The Topic Involved
Different topics usually have different sources of information. Some topics are majorly researched on the internet, and some topics are rarely researched.
The topics that many people have looked into have a lot of information that one can use in writing literature reviews. This is contrary to the topics that have been looked into by few people and have little content.
A writer will usually find it hard to write long literature reviews on such topics. When you are asked for a specific length of an essay and given the mandate to choose a topic yourself, never choose a topic that has not been majorly researched which is likely to cause you problems writing the length required by the instructor.
6. The Technicality of the Research
Some topics are usually hard for students to understand, while others are easy for students to understand. This usually varies among students.
Some students will find history projects harder than science projects, while to other students, it is different.
It is hard for students to write long literature reviews or essays on subjects or topics that they find hard to understand. This is different in the subjects and topics that students enjoy.
7. Level of Study
This is the most obvious reason that influences the length of literature reviews. Postgraduate students will always be required to write longer essays than undergraduate students. Their level of knowledge and understanding is different.
Though the post-graduate level is more complex, the students are expected to be able to handle the problems that the project poses. Postgraduate students are also required to conduct research that provides them with more information about their projects, unlike undergraduate students.
8. Professor Factors
Professor factors that determine the length of the of literature review include:
- The number of words expected.
Most professors usually give the length that they expect the assignment they give to be. This length determines the length of the literature review. Some professors can be specific and give the length they expect the literature review of projects to be.
- Availability.
If the professor feels like he will not have enough time to deal with the projects of all students, he can give shorter projects that he will be able to handle. If the professor is available, he can give longer assignments to the students.
- Gauging students’ understanding.
Professors can give long assignments to students to establish their level of understanding of an already tackled area. They use this to find out how well can students apply the knowledge gained in different areas.
Types of Literature Reviews
The most common types of literature reviews include argumentative reviews, integrative reviews, historical reviews, systematic reviews, systematic reviews, methodological reviews, and theoretical reviews. Argumentative and historical reviews are usually longer than the other types of reviews.
Projects Deadlines
Shorter deadlines usually limit students from conducting enough research. The lesser the research one conducts the lesser the amount of information one has to write about.
This leads to short literature reviews. When one is given enough time to conduct research, they gather all the information needed to write full-length projects hence longer literature reviews as well.
FAQs on Optimal Literature Review
How long should a literature review be in a research proposal .
Research proposals vary in length depending on the level of study and the topics involved. Longer literature proposals should have longer literature reviews, whereas shorter research proposals should have shorter literature reviews.
Literature reviews are usually the longest part of research proposals. The introduction and the methodology parts are always shorter. If your introduction part is 2 pages long and the methodology part is 4 pages long, the research proposal should be longer than the two.
How long does it take to write a literature review?
Most students do not know how long it should take to write a literature review because the deadlines are determined by the professors.
Most believe that the time the professor sets the deadline is the time required to write a literature review. The time one uses to write a literature review usually depends on the hours allocated per day to do the work.
The more hours, the fewer days it will take. The fewer the hours, the longer it will take. A literature review can take between 2-6 months to be completed.
How long should a literature review be for a PhD
A Ph.D. literature review is the main chapter of your Ph.D. thesis. Your Ph.D. literature review should assess your field of research critically and present the current knowledge that you have gained from previous work.
The literature review should help you identify the gaps in your knowledge of your field. Most Ph.D. literature reviews are always between 6000-12000 words. The main focus of Ph.D. literature reviews is the quality of the work and not the quantity.

Joseph is a freelance journalist and a part-time writer with a particular interest in the gig economy. He writes about schooling, college life, and changing trends in education. When not writing, Joseph is hiking or playing chess.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How long should a literature review be? The length of a PhD literature review varies greatly by subject. In Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences the review will typically be around 5,000 words long, while STEM literature reviews will usually be closer to 10,000 words long.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say "literature review" or refer to "the literature," we are talking about the research (scholarship) in a given field. You will often see the terms "the research," "the ...
Make sure you develop a good system that works for you and use it. 3. Don't write a laundry list of papers A literature review should be a synthesis of the papers you have read to tell a meaningful story about the literature, not a simple list of paraphrases of what each paper said. 4.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
In general, the length of a literature review should make up 10-20% of your research paper, thesis or dissertation and have its own chapter. For a thesis, this means a literature review should be approximately 6,000 to 12,000 words long, with the actual length varying based on your subject.
In a PhD thesis, the literature review typically comprises one chapter (perhaps 8-10,000 words), for a Masters dissertation it may be around 2-3,000 words, and for an undergraduate dissertation it may be no more than 2,000 words. ... Even with a literature review you should avoid using too many, or overlong, quotes. Summarise material in your ...
In general, the length of the review should be proportionate to your overall paper. For example, if you're writing a fifty-thousand-word dissertation, then your literature review will likely be an entire chapter comprising about 20 pages. If it's for a 15-page research paper, your literature review may only be a few pages.
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
2. MOTIVATE YOUR RESEARCH in addition to providing useful information about your topic, your literature review must tell a story about how your project relates to existing literature. popular literature review narratives include: ¡ plugging a gap / filling a hole within an incomplete literature ¡ building a bridge between two "siloed" literatures, putting literatures "in conversation"
Option 1: Chronological (according to date) Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
How long is a piece of string? Unless your School specifies the length, you can use the following as a rough guide: Around 15-30% of the whole thesis ( see FAQs) OR. Your thesis is expected to be 60% your own work. If your literature review is more than 40% of your thesis, it's probably too long.
How long should a PhD thesis be? A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words (100 to 300 pages in length) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions ... literature review, materials and methods, results, discussion, bibliography and references.
23. The purpose and expectations of a PhD literature review is likely to vary from field to field. My PhD was in Physics, but my views might be taken to apply generally. There is likely to be some repetition or paraphrasing between students in the same research group, when it comes to the literature review.
Preparing to Write the Literature Review for your Dissertation. 1. Search Using Key Terms. Most people start their lit review searching appropriate databases using key terms. For example, if you're researching the impact of social media on adult learning, some key terms you would use at the start of your search would be adult learning ...
The job of a literature review is to show five things (if you're using our PhD Writing Template, you may recognise these): 1. What has been written on your topic 2. Who the key authors are and what the key works are 3. The main theories and hypotheses 4. The main themes that exist in the literature 5.
How To Conduct A PhD Literature Review A PhD literature review is a critical assessment of the literature in your field and related to your specific research topic. By the end, the reader should understand the case for your research. The job of a PhD thesis literature review is to explain: It involves nine steps: Tips to elevate your review:
For example, a literature review for a PhD thesis will be much longer than one for a high school research paper. The length also depends on the scope of the research, with broader topics requiring more extensive reviews. Generally speaking, a literature review should be at least 20 pages long.
The length of a thesis literature review can vary based on the topic, research field, and guidelines provided by your institution. However, as a general rule, it often comprises 20-40% of the thesis. This equates to around 20-40 pages. However, if the literature review is for an assignment it only needs to be a few pages long.
The length of a thesis depends on the level of study. A thesis written by bachelor's degree students should be between 40-60 pages, while a thesis written for master's and doctorate studies should be between 60-100 pages. The length of the literature review for a thesis should be at least 8 pages to the minimum.
For a paper, what you want is about 2-5 double spaced pages.For a thesis, what you want is about 30-50 double spaced pages. Ideally, what you are looking for...
Background/Objectives: Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause variable symptoms, which may be irreversible if not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner. We aimed to develop a widely accepted expert consensus to guide the practice of diagnosing and treating B12 deficiency. Methods: We conducted a scoping review of the literature published in PubMed since January 2003. Data were used to design a ...