- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications

How to Do Research
Last Updated: March 13, 2023 References
This article was co-authored by Matthew Snipp, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . C. Matthew Snipp is the Burnet C. and Mildred Finley Wohlford Professor of Humanities and Sciences in the Department of Sociology at Stanford University. He is also the Director for the Institute for Research in the Social Science’s Secure Data Center. He has been a Research Fellow at the U.S. Bureau of the Census and a Fellow at the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences. He has published 3 books and over 70 articles and book chapters on demography, economic development, poverty and unemployment. He is also currently serving on the National Institute of Child Health and Development’s Population Science Subcommittee. He holds a Ph.D. in Sociology from the University of Wisconsin—Madison. This article has been viewed 227,401 times.
The idea of doing research may seem daunting, but as long as you keep yourself organized and focus on the question you want to answer, you'll be fine. If you're curious and interested in the topic, you might even find it fun! We here at wikiHow have gathered answers to all your most common questions about how to do research, from finding a good topic to identifying the best sources and writing your final paper.
How do I find a topic to research?

- For example, if you're researching in the political science field, you might be interested in determining what leads people to believe that the 2020 US presidential election was illegitimate.
How do I get started on my research?

- For example, if you're researching the 2020 election, you might find that "absentee ballots" and "voting by mail" come up frequently. Those are issues you could look into further to figure out how they impacted the final election results.
- You don't necessarily have to use the overview articles you look at as resources in your actual paper. Even Wikipedia articles can be a good way to learn more about a topic and you can check the references for more reputable sources that might work for your paper.
What's the best way to keep track of my sources?

- Research papers typically discuss 2 or 3 separate things that work together to answer the research question. You might also want to make a note on the front of which thing that source relates to. That'll make it easier for you to organize your sources later.
- For example, if you're researching the 2020 election, you might have a section of your paper discussing voting by mail. For the sources that directly address that issue, write "voting by mail" in the corner.
What kind of notes should I be taking as I research?

- If you find something that you think would make a good quote, copy it out exactly with quote marks around it, then add the page number where it appears so you can correctly cite it in your paper without having to go back and hunt for it again.
How do I evaluate the quality of a source?

- Does the article discuss or reference another article? (If so, use that article instead.)
- What expertise or authority does the author have?
- When was the material written? (Is it the most up-to-date reference you could use?)
- Why was the article published? (Is it trying to sell you something or persuade you to adopt a certain viewpoint?)
- Are the research methods used consistent and reliable? (Appropriate research methods depend on what was studied.)
What if I'm having a hard time finding good sources?

- For example, if you're writing about the 2020 election, you might find tons of stories online, but very little that is reputable enough for you to use in your paper. Because the election happened so recently, it might be too soon for there to be a lot of solid academic research on it. Instead, you might focus on the 2016 election.
- You can also ask for help. Your instructor might be able to point you toward good sources. Research librarians are also happy to help you.
How do I organize my research for my paper?

- For example, if you're researching the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the 2020 election, you might have sections on social distancing and cleaning at in-person voting locations, the accessibility of mail-in ballots, and early voting.
What's the best way to start writing my paper?

- Include an in-text citation for everything that needs one, even in your initial rough draft. That'll help you make sure that you don't inadvertently misattribute or fail to cite something as you work your way through substantive drafts.
- Write your introduction and conclusion only after you're satisfied that the body of your paper is essentially what you want to turn in. Then, you can polish everything up for the final draft.
How can I make sure I'm not plagiarizing?

- If you have any doubt over whether you should cite something, go ahead and do it. You're better off to err on the side of over-citing than to look like you're taking credit for an idea that isn't yours.
- ↑ https://www.nhcc.edu/student-resources/library/doinglibraryresearch/basic-steps-in-the-research-process
- ↑ Matthew Snipp, PhD. Sociology Professor, Stanford University. Expert Interview. 26 March 2020.
- ↑ https://library.taylor.edu/eng-212/research-paper
- ↑ http://www.butte.edu/departments/cas/tipsheets/research/research_paper.html
- ↑ https://www.potsdam.edu/sites/default/files/documents/support/tutoring/cwc/6-Simple-Steps-for-Writing-a-Research-Paper.pdf
- ↑ https://www.umgc.edu/current-students/learning-resources/writing-center/online-guide-to-writing/tutorial/chapter4/ch4-05.html
Expert Q&A
You might also like.

About This Article

If you need to do research on a particular topic, start by searching the internet for any information you can find on the subject. In particular, look for sites that are sourced by universities, scientists, academic journals, and government agencies. Next, visit your local library and use the electric card catalog to research which books, magazines, and journals will have information on your topic. Take notes as you read, and write down all of the information you’ll need to cite your sources in your final project. To learn how interviewing a first-hand source can help you during your research, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Shenuka Ranawaka
Sep 16, 2016
Did this article help you?

Ismail El Omari
Mar 3, 2022

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Research: Where to Begin

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Research isn't something that only scientists and professors do. Any time you use sources to investigate claims or reach new conclusions, you are performing research. Research happens in virtually all fields, so it’s vitally important to know how to conduct research and navigate through source material regardless of your professional or academic role.
Choosing and Narrowing Your Research Topic
Before beginning the process of looking for sources, it’s important to choose a research topic that is specific enough to explore in-depth. If your focus is too broad, it will be difficult to find sources that back up what you’re trying to say.
If your instructor gives you the flexibility to choose your own research topic, you might begin by brainstorming a list of topics that interest you ( click here to visit an OWL page that can help you get started brainstorming or prewriting ). Once you find something that grabs your attention, the next step is to narrow your topic to a manageable scope. Some ways to narrow your focus are by sub-topic, demographic, or time period.
For example, suppose that you want to research cancer treatments. Cancer treatment is a fairly broad topic, so you would be wise to at least consider narrowing your scope. For example, you could focus on a sub-topic of cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. However, these are still broad topics, so you might also narrow your topic to a narrower sub-topic or even examine how these topics relate to a specific demographic or time period. In the end, you might decide to research how radiation therapy for women over fifty has changed in the past twenty years. In sum, having a specific idea of what you want to research helps you find a topic that feels more manageable.
Writing Your Research Question
Writing your research topic as a question helps you focus your topic in a clear and concise way. It ensure that your topic is arguable. While not all research papers have to offer an explicit argument, many do.
For the above example, you might phrase your research question like this: "How has radiation therapy changed in the past twenty years for women over fifty?" Of course, phrasing this topic as a question assumes that the research has, in fact, changed. Reading your sources (or, to begin with, at least summaries and abstracts of those sources) will help you formulate a research question that makes sense.
Knowing What Types of Sources You Need
Depending on the type of research you’re doing, you may need to use different types of sources. Research is usually divided into scholarly and popular, and primary and secondary. For more information on specific details about these types of sources, visit our "Where to Begin" page in our "Evaluating Sources" subsection. This subsection contains additional pages that explore various kinds of sources (like, e.g., internet sources) in more detail.
Asking Productive Questions
Before you begin your research, you should ask yourself questions that help narrow your search parameters.
What kind of information are you looking for?
Different types of research will require different sources. It’s important to know what kinds of sources your research demands. Ask whether you need facts or opinions, news reports, research studies, statistics and data, personal reflections, archival research, etc. Restricting yourself to only the most relevant kinds of sources will make the research process seem less daunting.
Where do you need to look for your research?
Your research topic will also dictate where you find your sources. This extends beyond simply whether you use the internet or a print source. For example, if you are searching for information on a current event, a well-regarded newspaper like the New York Times or Wall Street Journal could be a useful source. If you are searching for statistics on some aspect of the U.S. population, then you might want to start with government documents, such as census reports. While much high-level academic research relies mainly on the sorts of academic journal articles and scholarly books that can be found in university libraries, depending the nature of your research project, you may need to look elsewhere.
How much information do you need?
Different research projects require different numbers of sources. For example, if you need to address both sides of a controversial issue, you may need to find more sources than if you were pursuing a non-controversial topic. Be sure to speak with your instructor if you are unclear on how many sources you will be expected to use.
How timely does your research need to be?
Depending on your research topic, the timeliness of your source may or may not matter. For example, if you are looking into recent changes in a specific scientific field, you would want the most up-to-date research. However, if you were researching the War of 1812, you might benefit from finding primary sources written during that time period.
Basic Steps in the Research Process
The following steps outline a simple and effective strategy for writing a research paper. Depending on your familiarity with the topic and the challenges you encounter along the way, you may need to rearrange these steps.
Step 1: Identify and develop your topic
Selecting a topic can be the most challenging part of a research assignment. Since this is the very first step in writing a paper, it is vital that it be done correctly. Here are some tips for selecting a topic:
- Select a topic within the parameters set by the assignment. Many times your instructor will give you clear guidelines as to what you can and cannot write about. Failure to work within these guidelines may result in your proposed paper being deemed unacceptable by your instructor.
- Select a topic of personal interest to you and learn more about it. The research for and writing of a paper will be more enjoyable if you are writing about something that you find interesting.
- Select a topic for which you can find a manageable amount of information. Do a preliminary search of information sources to determine whether existing sources will meet your needs. If you find too much information, you may need to narrow your topic; if you find too little, you may need to broaden your topic.
- Be original. Your instructor reads hundreds of research papers every year, and many of them are on the same topics (topics in the news at the time, controversial issues, subjects for which there is ample and easily accessed information). Stand out from your classmates by selecting an interesting and off-the-beaten-path topic.
- Still can't come up with a topic to write about? See your instructor for advice.
Once you have identified your topic, it may help to state it as a question. For example, if you are interested in finding out about the epidemic of obesity in the American population, you might pose the question "What are the causes of obesity in America ?" By posing your subject as a question you can more easily identify the main concepts or keywords to be used in your research.
Step 2 : Do a preliminary search for information
Before beginning your research in earnest, do a preliminary search to determine whether there is enough information out there for your needs and to set the context of your research. Look up your keywords in the appropriate titles in the library's Reference collection (such as encyclopedias and dictionaries) and in other sources such as our catalog of books, periodical databases, and Internet search engines. Additional background information may be found in your lecture notes, textbooks, and reserve readings. You may find it necessary to adjust the focus of your topic in light of the resources available to you.
Step 3: Locate materials
With the direction of your research now clear to you, you can begin locating material on your topic. There are a number of places you can look for information:
If you are looking for books, do a subject search in One Search . A Keyword search can be performed if the subject search doesn't yield enough information. Print or write down the citation information (author, title,etc.) and the location (call number and collection) of the item(s). Note the circulation status. When you locate the book on the shelf, look at the books located nearby; similar items are always shelved in the same area. The Aleph catalog also indexes the library's audio-visual holdings.
Use the library's electronic periodical databases to find magazine and newspaper articles. Choose the databases and formats best suited to your particular topic; ask at the librarian at the Reference Desk if you need help figuring out which database best meets your needs. Many of the articles in the databases are available in full-text format.
Use search engines ( Google , Yahoo , etc.) and subject directories to locate materials on the Internet. Check the Internet Resources section of the NHCC Library web site for helpful subject links.
Step 4: Evaluate your sources
See the CARS Checklist for Information Quality for tips on evaluating the authority and quality of the information you have located. Your instructor expects that you will provide credible, truthful, and reliable information and you have every right to expect that the sources you use are providing the same. This step is especially important when using Internet resources, many of which are regarded as less than reliable.
Step 5: Make notes
Consult the resources you have chosen and note the information that will be useful in your paper. Be sure to document all the sources you consult, even if you there is a chance you may not use that particular source. The author, title, publisher, URL, and other information will be needed later when creating a bibliography.
Step 6: Write your paper
Begin by organizing the information you have collected. The next step is the rough draft, wherein you get your ideas on paper in an unfinished fashion. This step will help you organize your ideas and determine the form your final paper will take. After this, you will revise the draft as many times as you think necessary to create a final product to turn in to your instructor.
Step 7: Cite your sources properly
Give credit where credit is due; cite your sources.
Citing or documenting the sources used in your research serves two purposes: it gives proper credit to the authors of the materials used, and it allows those who are reading your work to duplicate your research and locate the sources that you have listed as references. The MLA and the APA Styles are two popular citation formats.
Failure to cite your sources properly is plagiarism. Plagiarism is avoidable!
Step 8: Proofread
The final step in the process is to proofread the paper you have created. Read through the text and check for any errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Make sure the sources you used are cited properly. Make sure the message that you want to get across to the reader has been thoroughly stated.
Additional research tips:
- Work from the general to the specific -- find background information first, then use more specific sources.
- Don't forget print sources -- many times print materials are more easily accessed and every bit as helpful as online resources.
- The library has books on the topic of writing research papers at call number area LB 2369.
- If you have questions about the assignment, ask your instructor.
- If you have any questions about finding information in the library, ask the librarian.
Contact Information
Craig larson.
Librarian 763-424-0733 [email protected] Zoom: myzoom Available by appointment
Get Started
How to Research: Ultimate Guide [+Online Tools]

The ability to effectively research is a skill that every student needs to succeed in their educational career. However, most people don’t really understand what research entails. Does it mean spending hours at your university library exploring archives? Or is searching for information online from the comfort of your home enough? And why can’t you just rely on Wikipedia, after all?
Our specialists have created this guide for students who feel lost when putting together an essay, paper, or presentation. Here, we will describe how to research in a detailed, step-by-step manner. We have also provided links to useful tools and resources that will help you along the way. First of all, let’s cover the definitions.
❓ What Is Research?
- Develop a Topic
- Look Through Sources
- Evaluate the Sources
- Write Your Paper
- Cite Your Sources
💡 9 Online Tools for Research
Research refers to the systematic process of discovering information and developing knowledge. We use it to understand new topics and to gain more insight into known issues. This happens through the collection and analysis of relevant data. The ability to research efficiently is one of the most fundamental skills in academia.
Any type of research will include the following features:
- A sound hypothesis on which the rest of the study is based. It will be either proven or disproven by the evidence gathered.
- Systematic investigative methods . These are controlled and follow a pre-established set of rules.
- Logical analysis . It follows a set procedure that involves deductive and inductive reasoning.
- Empirical data based on actual observation and evidence.
- Analytical study of the findings . This ensures in-depth exploration and minimizes mistakes.
- Creation of new questions and new lines of inquiry about the subject via the research.
With that being said, a research paper is more than just the sum of its sources. Its primary purpose is to analyze or argue a particular perspective. In the end, your thoughts and ideas should be the ones you investigate. The evidence you discover during the research process will be the basis for your hypothesis.
There are three universal purposes of research that you should know about:
📚 How to Research: Step-by-Step Guide
As all the definitions you need are covered, we can proceed to learn about the process itself. We have developed this guide so that you won’t have any trouble conducting your research. In the image below, you can see all the required steps.

In the following sections, you will examine each step in detail. Also, you’ll see the reasons why our tips are practical and how to find sources for your research. Good luck!
1. Develop a Topic
1.1. pick or create a topic.
The first step to research is landing on the right idea. This process isn’t always easy, especially when you aren’t familiar with the chosen area of study. However, don’t fret. You can always change your topic later.
Let’s explore how to select your first research idea.
Research is always conducted for a particular reason. It will always relate to writing a paper, creating a project, validating existing results, etc. Your research depends on the goal of your assignment.
The answers will help you define the direction of your work:
- Do you have a list of pre-assigned topics? Can you come up with one yourself?
- What is the due date for your work? How much time does that leave for research?
- What is the scope of your assignment? (Presentation length, number of words/pages, etc.)
- Are there any specific requirements regarding the sources that you are allowed to use?
- Is it essential to use recent information and current sources?
When you have the answers to all the key questions, you can think of your topic. The following tips will help you:
- Choose an idea that is relevant to your assignment. Usually, your instructor will give you detailed instructions before you start working. If you are unsure about your guidelines, don’t be afraid to ask for clarification.
- Ensure that there are enough resources for you to use. When you think of an idea, do a quick preliminary search. It will allow you to determine whether there is enough available information on your topic. Take time to validate those resources and make sure they’re reliable.
- Search for a topic that is not too broad or too narrow. This step directly correlates with the one above. If you are finding too much general information, narrowing down your search might be a good idea. However, if you struggle to find credible sources, it could be a sign to broaden your topic.
- Try to be original. Restating the same ideas that have been explored thousands of times could damage your grade. Chances are, your instructor has heard it all before and isn’t all that interested in hearing it again. Yet, choosing an unconventional approach with a fresh perspective might earn you extra credit for creativity.
- Aim to find an area that will be interesting to explore. If you find a topic that you, personally, are curious about, researching it will be much more pleasant. This way, when you start writing or searching for information, you might actually enjoy the process.
1.2. Formulate Research Questions
As soon as you have chosen a topic, take the time to format it correctly. Wording it as a question will ensure that your focus is precise and nuanced.

And here is how you create research questions:
Step 1 : Do some research.
Take a look at the most recent discussions and debates on your selected topic. You can check out academic journals and scholarly conferences. Keep your focus on the main arguments to acquaint yourself with the concepts.
Step 2 : Try narrowing down your topic.
It is a lot more effective to target a single dimension of a broader topic than to tackle everything. To do this, try focusing on a particular aspect, such as a specific location or time period. You can also aim to discuss certain debates or issues that exist within the topic.
Step 3 : Keep your audience in mind.
There is a difference between crafting a presentation for your classmates and writing a research paper. Your audience will determine the level of detail that goes into your question.
Step 4 : Ask questions.
Once you have considered the above steps, it is time to begin asking yourself questions. Make sure they’re open-ended and start with ‘why,’ ‘how,’ or ‘what.’
Step 5 : Evaluate your questions.
After you come up with a couple of ideas, jot them down on paper. Look back at all the requirements for a successful research question. Which one of them will be the most effective for your assignment?
1.3. Choose a Research Strategy
To develop constructive research questions, you will need to conduct an initial survey of your resources. Take everything you’ve learned so far as your foundation. Now, you will need to create an efficient strategy for your further actions.
Your research strategy will depend on the following:
1.4. Figure out Keywords
With your research questions, strategy, and some background info covered, it will be easier to determine the keywords . They will help you look for resources and locate your work in the future. Over here, see how to work with keywords.

Once you have a selection of keywords, you can improve them by doing the following:
- Break them into related concepts. By the end, you should have four or five columns with associated keywords.
- Choose one keyword from each column. Use your library’s search engine to look them up. Don’t forget to type ‘AND’ in-between the words. It will narrow down the search so that only articles containing all the selected keywords will appear.
- Explore the results! Don’t be afraid to try several different combinations. You should also make sure to list all those keywords that bring you the most valuable results.
- If you don’t have enough results, try using fewer keywords. Alternatively, you can try to make your keywords broader.
- If you have too many results, try using more keywords. Alternatively, you can try to make your keywords narrower.
- Pay attention to which articles are the most relevant to your needs. Make sure to save them and skim them for a list of keywords. Write them down, and create a new list!
- Once you have exhausted your first list, you can create another one. Run another search following these steps. Don’t forget to note down the relevant materials – you’ll need them for your citations!
1.5. Improve Your Topic
As we mentioned above, you can change and refine your topic as many times as you need before you begin writing. That is why in this section, we will talk about how to polish and improve your idea. At the very least, we’ll give you tips on how to format it correctly.
First of all, we need to make sure that your topic is researchable. To accomplish this, answer the 5 ‘w’ questions :
- Why are you choosing this particular topic? How is it interesting or different from the rest? What is your stance on the matter?
- What are the main issues your topic is trying to explore? Is it controversial? What other opinions and questions exist on the subject?
- Who is talking about the topic? What points of view exist, and who is giving them? What is their agenda?
- When was this topic discussed? Is the issue recent or historical? Does the time frame matter?
- Where lays the importance of your topic? Is it debated on an international, national, or local level? Is there a particular place that is more affected than the rest of the world?
After answering these questions, you need to evaluate your idea from these two perspectives:
- Is your topic too broad?
It may happen if you find far too much information on the subject that doesn’t seem relevant. You will want to narrow it down and include some specifics, such as:
- Place (country, city, street, part of the world, etc.);
- Time (year, era, century, etc.);
- Populace (ethnicity, gender, age, occupation, etc.);
- Event or characteristic (historical occurrence, institutional perspective, etc.);
- Individual or group (a particular point of view, specific person or persons, etc.).
- Is your topic too narrow?
If you are discovering too few sources to build a proper case, your topic is too narrow. Try to broaden it using the following methods:
- Remove some of the specifics (place, time, populace, etc.).
- Expand some of the specifics (place, time, populace, etc.).
- Use synonyms to reword your topic.
- Look in other databases to broaden your horizons.
- Consider looking into a less current issue (the newer an idea is, the harder it is to find sources).
2. Look Through Sources
2.1. determine possible sources.
By this time, you most probably looked for background information on your topic a couple of times. Now it’s time to look for more specific info.
For starters, get the keywords you’ve chosen and see if there is enough information available. You can start by checking appropriate titles in the online libraries. Look for sources in encyclopedias and dictionaries to overview what books or articles you can use.
You can use the following websites for this purpose:
- Oxford English Dictionary
- Wordreference.com
- Encyclopedia Britannica Online
- Oxford Reference Online
Apart from encyclopedias and dictionaries, there are, of course, other places you can check. For instance, you can search for books in your local or university library . When you look through the text on the shelf, pay attention to the books nearby – they can become useful too in the subject area.
Additionally, you can find information in your textbooks and assigned readings. Use your library’s electronic databases that keep magazines and newspapers on the topic. In case you are not sure how to do that, ask your librarian. Also, use search engines to locate materials on the Internet. These types of sources will be helpful when looking for generic information.
2.2. Skim Some Books
When it comes to using books for your research, both hard and electronic copies work as well. In this section, we will tell you how to use them for your research.

If you are a student, you probably do not have time to read every single book. When working on a short paper, essay, or presentation with limited time, you are simply looking for citations. Luckily, there is no need to waste your time examining each book thoroughly. Skimming is enough to understand if the source works for you or not.
To get the needed information in the book, look at the following elements:
- Title Page. There, you can find all the essential details about the book, the author’s name, title, the publisher’s name, the date of publication, etc.
- Table of Contents. This part provides you with a list of all the chapters in the book. You can get a general idea of what topics the author covered.
- List of Illustrations. In some books, authors use illustrations, tables, drawings to support the arguments and the facts. Looking through them can help you see the stats or some other facts quickly.
- Preface or Introduction. Usually, this part of the book provides the author’s intentions and the purpose of the book. Read it to see whether the book’s topic is necessary for your research.
- Bibliography. This part of the book provides a list of materials that the author used. You can check the bibliography for additional resources or references.
- Index. Skimming an index is excellent for identifying where the relevant information is located in the book. It can also give you some additional keywords that might be helpful for your research.
How to Find Books: Free Resources
You can find paperback books in your school’s library or ask your professor if he can lend you some helpful resources. To look for ebooks, we recommend using one of the following services:
For more free books and textbooks, check out the list of online learning resources for different subjects.
2.3. Find Relevant Articles
Scholarly articles are essential parts of every research. Even small argumentative essays usually contain citations from these resources. Here, we will explain how to work with them.
But first, you have to understand how to differentiate based on where these articles are being published. There are two types:
- Peer-reviewed journals
These journals include articles written by an expert in the field. Another expert (experts) read the article and provided feedback. Thus, the author implemented the needed changes based on the review.
- Scholarly journals
Experts write articles for these journals. They address the papers to other academics in the same field. Usually, scholarly journals are written by professional associations or academic press.
Usually, students can use academic and scholarly journals interchangeably. However, you should ask your instructor to explain if sources called “academic” are acceptable.

Not to read every single piece of writing, you need to learn how to identify if the article is credible or not. For that, pay attention to the following elements:
- Author. Look out for the author’s degrees and credentials. Additionally, see if they are a member of any association or work at a university or official organization.
- Intended audience. Understanding the article’s aim is essential. If the author intends to entertain and inform the general public, it may not be the best source for a student. You can still read and learn from without citing.
- Publication type. Some of the ways to recognize the type are:
- Go online and read the sections’ “aims and scope.”
- Check the visual appearance. If the article has colorful images and graphics, it is most probably written for the general public.
- Structure. You can also look at the length and formatting of the article. If it has a clear organization with headings, then most probably, the piece is scholarly. Same with the size. Short papers (with less than five pages) in general are likely to be not academic articles.
- Style. Examine the language, the point of view, and the tone of the article. If the document has many technical terms and professional jargon, then it is usually scholarly or peer-reviewed. Ask yourself what level of education one needs to comprehend the text entirely.
If all of the following parameters fit your expectations, you can only start by reading and analyzing the article.
How to Find Articles: Free Resources
Not sure where to look for articles? Check the following resources that our team recommends:
2.4. Examine Useful Databases
If you still don’t know what sources to use, you can study databases. These collections contain many high-quality books and articles and conference presentations, video lectures, illustrations, etc. In this section, see how to use them and how to benefit from doing this.
A database is a collection of stored and structured information, usually controlled by a dates management system (DBMS). Information is generally modeled in rows and columns in different tables. Thus, even your university’s online library can be considered a database.

Here are some crucial tips on using databases:
- AND ➡️ when you want to use both terms.
- OR ➡️ when you can choose either time.
- NOT ➡️ when you want to exclude words.
- Type asterisks, exclamation points, and questions marks. If you don’t use asterisks and wildcards, some databases will not provide the search you need. They are also beneficial in making your search more specific.
- Look out for the “subject search” option. This way, you will search for information located on the heading field. It is possible due to a system called controlled vocabulary .
- Improve your keywords. Try to be creative with your key phrases and words. Look for all the possible ways to express your topic by using synonyms and associated concepts.
- Try using parentheses . When you look for complex queries, use parentheses. They will allow you to group terms together.
- Search for clues. Carefully look for tips and hints in the results. Analysis of the trends, indications, and numbers can help you understand the information better.
- Check the stacks . Stacks are linear data structures that follow a specific pattern. As collections of elements, they can help you with one particular search.
- Look through different databases. You can look across other databases and combine what you’ve found. The more data you will consider, the more precise your results are.
Free Databases to Use for Research
There are many open-access databases that you can use when conducting your research. Our experts previously mentioned a lot of those in the sections about ebooks and scholarly articles.
Here are some more databases that you can find to be helpful:
We also recommend looking at the available open databases prepared by the University of California at Santa Barbara and Elmira College .
2.5. See Other Websites
Besides search engines and databases, there are other online resources that you can use as a starting point for your research. The only issue is that you might not know if the information is legit.
These websites are suitable for academic research:
- Educational sites (*.edu)
- Government sites (*.gov)
- News sites (CNN, NBC News, FOX News, etc.)
- Professional, nonprofit organizations (Unicef, WWF, etc.)
- General informative websites (Wikipedia)
Of course, you can use online resources for research. They are especially great when you’re looking for background information or defining the topic. Yet, one thing to keep in mind is to choose the websites and data from them carefully.

Here are some cons of using these online sources:
- Unreliable. Anyone can write websites, and they are rarely checked for accuracy, bias, and credibility. They are also regularly filled with old content.
- Chargeable. A lot of websites are free of charge. Yet, very often, to read the full article or cite the page you need, you have to pay.
- Tricky to cite. Most websites do not have any citation tools, so it can be hard to add them as references.
- Unstable. Websites are usually not permanent. Both the content and the address change – the link might not be available later on.
Free Websites to Use for Research
Using different websites for background information search and a general understanding of a given topic makes total sense. But when needed, you can use them for actual research.
For this purpose, we recommend the following websites:
3. Evaluate the Sources
3.1. select what sources to use.
By this step, you have collected many sources for your work. Now is the time to sort through them and get rid of the ones you don’t need. Here, we will explain how to choose appropriate sources for your research.
When checking the quality and credibility of a source, use this checklist:
3.2. Take Notes
When you have sorted through your sources, you can start reading through them at length. You will still have the opportunity to filter out unneeded information. To accomplish this, we recommend marking down the relevant fragments that you will use in your work.

We advise you to study your sources in the following order:
Step 1 : Skim through the text.
Don’t immediately spend an excessive amount of time reading paragraphs and paragraphs of text. First, run through the source to identify the most relevant passages and headings. Note any words or terminology that catch your eye. It will allow you to form a rough idea of the author’s main arguments.
Step 2 : Ask questions.
After you finish skimming through the text, write down any questions that formed in your mind. Make sure that you keep them relevant to your topic. These questions will help you figure out what information you are hoping to obtain from the source.
Step 3 : Underline or highlight.
It’s time to read the source actively. Grab a highlighter or a pen and note down anything that seems relevant or interesting. Pay special attention to the passages that caught your eye earlier. Once you find answers to your questions (or think of even more questions), make sure to jot them in the margins.
Step 4 : Summarize .
As you have finished reading, write down a quick summary of your findings. Do this immediately after you finish while the information is still fresh in your mind. Organize your notes and look up any terminology that isn’t familiar. Also, take a quick look at the bibliography provided by the source – you could find something useful!
Step 5 : Write down key information.
Before moving on to the next source, don’t forget to note everything you need for the bibliography. Write down the title, the author’s name, the publisher, and the date of publishing. If you are using a website, save the URL. Double-check which citation format you’re required to use.
4. Write Your Paper
4.1. formulate your thesis.
A thesis statement is often referred to as the heart of your work since it contains the main idea and stance of the author. The writing process starts with figuring out what you want to say. State it in one sentence, referring back to all the research that you have conducted thus far.
Here are a few tips you could use in writing a compelling thesis statement based on your research:
- State your point clearly. Your argument needs to be explicit and direct. Remember that you will have to address it within the limited confines of your work. There isn’t the space to consider too many points of view. That is why your audience must be clear on the direction your debate is going to follow.
- Be specific. You have to ensure that your wording is as clear-cut as possible. The thesis needs to state the exact idea you will be exploring. If you formulate it too vaguely, the content of your work will be all over the place. Polish your thesis until it becomes specific to your argument.
- Question what you think. To accomplish this, you will need to keep your target audience in mind. Consider what views your readers must have to understand the point you are trying to make. Your statement must be grounded to those who don’t necessarily have the same ideas as you.
- Showcase a strong position. Don’t forget that your thesis statement is a reflection of your comprehension of the topic. While it must be clear and coherent, it should also advance your unique position on the matter. Instead of simply making an observation about something, don’t hesitate to take a stance.
Formulating a successful thesis statement takes time and practice. It is likely that you will not get it completely right on your first try. If you feel like you need some training or require examples, try using our thesis statement generator .
4.2. Outline Your Paper
If you have reached this stage in your work process, it means that you have everything you need. You have composed a strong thesis statement and have your notes and arguments beside you. Now, you have to put them together in a logical order. This way, your reader will see your thought process clearly.

To organize your paper , try this approach:
- Determine the research problem. This isn’t just your thesis statement but is also the key to creating your title. It is the central point of your work. Try formulating it in a single sentence or phrase for efficiency.
- Identify the key arguments. Think of what points you are trying to make with your research. Very briefly note them in your introduction. You will proceed to explore and build on them throughout the rest of your paper.
- Formulate the first category. Consider which point you should cover first. Typically, it is a good idea to start with definitions and clarifications of any critical terminology. You may also want to introduce the background of a particular theory or concept you are exploring.
- Include subcategories if needed. For now, try listing them in the form of a bullet list. The subcategories should provide the basis and support the main points you’re making.
- Sum up and conclude. Once you have created the rough draft, tie everything together. Conclude your project and refer back to your thesis. Make sure that you haven’t strayed away from your research question in creating your outline.
If you have followed these steps, you should end up with a defined beginning, middle, and end. Naturally, different research papers will have carrying outlines. For example, a term paper will have a smaller number of subcategories than a dissertation. Moreover, some projects will require you to mention your research methods, results, etc. You can find more information on how to write an essay or another type of paper in specialized online guides.
4.3. Add Quotes and Examples
To prove that you aren’t making up arguments on the fly, you should provide supporting evidence. You have to refer back to your sources and cite articles and books found during your research.
You can cite a source as supporting evidence like this:
You will be rephrasing and analyzing others’ opinions on your chosen topic for most of your work. However, from time to time, a direct quotation is necessary to support your arguments. This is suitable in the following cases:
- You don’t want to lose the author’s original meaning by summarizing or paraphrasing their words.
- The language in the source material is very effective and would be weakened if you tried to reword it.
- The language that the author is using is important historically.
- The authority found in the source will lend more credibility to the point you are trying to make.
5. Cite Your Sources
Congratulations – your work is nearly finished! You have only a couple of steps left. To round up your research, compile a list of sources you have used. You should also indicate which parts you have cited in your text. That is what we are going to discuss in this section.
Simply put, a citation is used to refer back to the source material. You can cite anything, from an academic article or book to a video or even a viral tweet. This is how you give credit to the original author for their work.

There are a couple of ways to utilize citations in your work correctly:
- When employing quotations, summarizing, or paraphrasing in your text, use in-text citations . These must be placed directly in the body of the work in parenthesis, following the cited fragment. The in-text citations are always shortened, referring only to the author and the year of publishing. Sometimes, for larger works, the page number is also included.
- The full citations go into the references/works cited page at the end of your work. This is also sometimes referred to as a bibliography. These include various features, such as the title of the work, the author’s name, date of publishing, etc. Different citation styles require different elements to be mentioned. Make sure to double-check which one your institution expects you to use.
As we mentioned, while creating any academic work, you are expected to use references. You will have to choose a particular citation style or be directed to one by your instructor. This style will be used consistently throughout your work. Each one has its specific features and guidelines.
Here is what you can expect from them:
You can read more about each citation style if you follow the links for the related referencing guides .
In the previous sections, we have examined search engines, databases, and websites that you can use in your research. However, there are plenty of other online tools that can be very useful for your work process. We are going to talk about them here.
The following online tools can help you immensely while you research:
- ProCon.org is a website that allows you to consider several viewpoints on debatable issues. It features multiple controversial topics and lets the readers experience different sides of the arguments in a non-biased manner.
- Journal TOCs is a service that allows you to discover the newest academic papers as soon as they are available online. When writing about current events, it is essential to stay up-to-date, especially concerning research.
- EndNote is a multifunctional tool with many valuable features. It provides you with fast database search, automatic bibliography, and more. Research takes an incredible amount of time and effort, and this program is determined to save you time and resources.
- Paperpile is an extension for your browser and can be installed on your mobile devices as well. Tracking down and compiling your references can become a hassle – this is why Paperpile manages them for you.
- Zotero is another useful extension for your browser. It collects and organizes your research for you. It can also help you with the creation of your citations and allows you to collaborate with others.
- RefWorks is a tool that allows you to save your references from any webpage. It also helps you import them from online databases. You will be able to annotate and highlight your texts, as well as quickly search through them.
- Science Daily allows its readers to browse through all the latest news in several different spheres. Keeping up with updates in the scientific sphere is essential for any researcher, but especially those in the STEM fields. ScienceDaily is a must-have if you need to save time.
- DeepDyve gives you access to different current research articles for a limited time. A large number of valuable sources online are locked behind a paywall. It tends to be troublesome and expensive. DeepDyve allows you to check articles for free to see whether you need them for your research or not.
Thank you for your attention! We hope that you are now feeling more prepared to approach research in any sphere. Share this page with other students who you think could use our guide.
🔗 References
- Basic Steps in the Research Process – North Hennepin Community College
- How to Do Research A Step-By-Step Guide: Get Started – LibGuides at Elmira College
- Conducting Research: the Process – Research Guides at Washington University in St. Louis
- Research Process: Select your Topic – Nash Library & Student Learning Commons at Gannon University
- Developing Research Questions – Research & Learning Online, Monash University
- How to Write a Research Question – Guides at The Writing Center, George Mason University
- Research Process Step by Step: Identify Keywords – Subject and Course Guides at University of Texas at Arlington
- Start Your Research: Evaluate Your Info – Library Guides at University of California, Santa Cruz
- 19 Notetaking Tips for College Students – Post University
- Writing a Paper: Outlining – Academic Guides at Walden University
- How to Outline – Purdue Online Writing Lab, College of Liberal Arts, Purdue University
- What Is Research: Definition, Types, Methods & Examples – QuestionPro
- Thesis Statements – The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- 5 Steps to Create the Perfect Outline – Brandon Ramey, Herzing University
- How to Cite – University of Arizona Libraries
- The Research Process: How to Cite – LibGuides at Franklin & Marshall College
- Share via Facebook
- Share via Twitter
- Share via LinkedIn
- Share via email
Productive tips of information in advancing research skills. I recommend this content to all potential professionals. Thanks for your anticipatory contribution to all the budding academic and research communities.
This is strictly a rich content that goes along way in advancing the research prowess more importantly to the budding researchers. Thank you so much for this.
We are glad to hear your opinion! Thank you, Benard!
How to Do Research: A Step-By-Step Guide: Get Started
- Get Started
- 1a. Select a Topic
- 1b. Develop Research Questions
- 1c. Identify Keywords
- 1d. Find Background Information
- 1e. Refine a Topic
- 2a. Search Strategies
- 2d. Articles
- 2e. Videos & Images
- 2f. Databases
- 2g. Websites
- 2h. Grey Literature
- 2i. Open Access Materials
- 3a. Evaluate Sources
- 3b. Primary vs. Secondary
- 3c. Types of Periodicals
- 4a. Take Notes
- 4b. Outline the Paper
- 4c. Incorporate Source Material
- 5a. Avoid Plagiarism
- 5b. Zotero & MyBib
- 5c. MLA Formatting
- 5d. MLA Citation Examples
- 5e. APA Formatting
- 5f. APA Citation Examples
- 5g. Annotated Bibliographies
Research Essentials Video Tutorials
Related guides.
- Elmira College Writing Center Get one-on-one assistance for all types of writing.
Recommended Websites
- Purdue University's Online Writing Lab (OWL)
Research Process Overview
Step 1. Develop a topic Select a Topic | Develop Research Questions | Identify Keywords | Find Background Information | Refine a Topic
Step 2. Locate information Search Strategies | Books | eBooks | Articles | Videos & Images | Databases | Websites | Grey Literature
Step 3. Evaluate and analyze information Evaluate Sources | Primary vs Secondary | Types of Periodicals
Step 4. Write, organize, and communicate information Take Notes | Outline the Paper | Incorporate Source Material
Step 5. Cite sources Avoid Plagiarism | Zotero & MyBib | MLA | APA | Chicago Style | Annotated Bibliographies
For research help, use one of the following options:
Ask the GTL

- Next: Step 1: Develop a Topic >>
- Last Updated: May 29, 2024 1:53 PM
- URL: https://libguides.elmira.edu/research
What Is Research, and Why Do People Do It?
- Open Access
- First Online: 03 December 2022
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- James Hiebert 6 ,
- Jinfa Cai 7 ,
- Stephen Hwang 7 ,
- Anne K Morris 6 &
- Charles Hohensee 6
Part of the book series: Research in Mathematics Education ((RME))
17k Accesses
Abstractspiepr Abs1
Every day people do research as they gather information to learn about something of interest. In the scientific world, however, research means something different than simply gathering information. Scientific research is characterized by its careful planning and observing, by its relentless efforts to understand and explain, and by its commitment to learn from everyone else seriously engaged in research. We call this kind of research scientific inquiry and define it as “formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses.” By “hypotheses” we do not mean the hypotheses you encounter in statistics courses. We mean predictions about what you expect to find and rationales for why you made these predictions. Throughout this and the remaining chapters we make clear that the process of scientific inquiry applies to all kinds of research studies and data, both qualitative and quantitative.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Part I. What Is Research?
Have you ever studied something carefully because you wanted to know more about it? Maybe you wanted to know more about your grandmother’s life when she was younger so you asked her to tell you stories from her childhood, or maybe you wanted to know more about a fertilizer you were about to use in your garden so you read the ingredients on the package and looked them up online. According to the dictionary definition, you were doing research.
Recall your high school assignments asking you to “research” a topic. The assignment likely included consulting a variety of sources that discussed the topic, perhaps including some “original” sources. Often, the teacher referred to your product as a “research paper.”
Were you conducting research when you interviewed your grandmother or wrote high school papers reviewing a particular topic? Our view is that you were engaged in part of the research process, but only a small part. In this book, we reserve the word “research” for what it means in the scientific world, that is, for scientific research or, more pointedly, for scientific inquiry .
Exercise 1.1
Before you read any further, write a definition of what you think scientific inquiry is. Keep it short—Two to three sentences. You will periodically update this definition as you read this chapter and the remainder of the book.
This book is about scientific inquiry—what it is and how to do it. For starters, scientific inquiry is a process, a particular way of finding out about something that involves a number of phases. Each phase of the process constitutes one aspect of scientific inquiry. You are doing scientific inquiry as you engage in each phase, but you have not done scientific inquiry until you complete the full process. Each phase is necessary but not sufficient.
In this chapter, we set the stage by defining scientific inquiry—describing what it is and what it is not—and by discussing what it is good for and why people do it. The remaining chapters build directly on the ideas presented in this chapter.
A first thing to know is that scientific inquiry is not all or nothing. “Scientificness” is a continuum. Inquiries can be more scientific or less scientific. What makes an inquiry more scientific? You might be surprised there is no universally agreed upon answer to this question. None of the descriptors we know of are sufficient by themselves to define scientific inquiry. But all of them give you a way of thinking about some aspects of the process of scientific inquiry. Each one gives you different insights.

Exercise 1.2
As you read about each descriptor below, think about what would make an inquiry more or less scientific. If you think a descriptor is important, use it to revise your definition of scientific inquiry.
Creating an Image of Scientific Inquiry
We will present three descriptors of scientific inquiry. Each provides a different perspective and emphasizes a different aspect of scientific inquiry. We will draw on all three descriptors to compose our definition of scientific inquiry.
Descriptor 1. Experience Carefully Planned in Advance
Sir Ronald Fisher, often called the father of modern statistical design, once referred to research as “experience carefully planned in advance” (1935, p. 8). He said that humans are always learning from experience, from interacting with the world around them. Usually, this learning is haphazard rather than the result of a deliberate process carried out over an extended period of time. Research, Fisher said, was learning from experience, but experience carefully planned in advance.
This phrase can be fully appreciated by looking at each word. The fact that scientific inquiry is based on experience means that it is based on interacting with the world. These interactions could be thought of as the stuff of scientific inquiry. In addition, it is not just any experience that counts. The experience must be carefully planned . The interactions with the world must be conducted with an explicit, describable purpose, and steps must be taken to make the intended learning as likely as possible. This planning is an integral part of scientific inquiry; it is not just a preparation phase. It is one of the things that distinguishes scientific inquiry from many everyday learning experiences. Finally, these steps must be taken beforehand and the purpose of the inquiry must be articulated in advance of the experience. Clearly, scientific inquiry does not happen by accident, by just stumbling into something. Stumbling into something unexpected and interesting can happen while engaged in scientific inquiry, but learning does not depend on it and serendipity does not make the inquiry scientific.
Descriptor 2. Observing Something and Trying to Explain Why It Is the Way It Is
When we were writing this chapter and googled “scientific inquiry,” the first entry was: “Scientific inquiry refers to the diverse ways in which scientists study the natural world and propose explanations based on the evidence derived from their work.” The emphasis is on studying, or observing, and then explaining . This descriptor takes the image of scientific inquiry beyond carefully planned experience and includes explaining what was experienced.
According to the Merriam-Webster dictionary, “explain” means “(a) to make known, (b) to make plain or understandable, (c) to give the reason or cause of, and (d) to show the logical development or relations of” (Merriam-Webster, n.d. ). We will use all these definitions. Taken together, they suggest that to explain an observation means to understand it by finding reasons (or causes) for why it is as it is. In this sense of scientific inquiry, the following are synonyms: explaining why, understanding why, and reasoning about causes and effects. Our image of scientific inquiry now includes planning, observing, and explaining why.

We need to add a final note about this descriptor. We have phrased it in a way that suggests “observing something” means you are observing something in real time—observing the way things are or the way things are changing. This is often true. But, observing could mean observing data that already have been collected, maybe by someone else making the original observations (e.g., secondary analysis of NAEP data or analysis of existing video recordings of classroom instruction). We will address secondary analyses more fully in Chap. 4 . For now, what is important is that the process requires explaining why the data look like they do.
We must note that for us, the term “data” is not limited to numerical or quantitative data such as test scores. Data can also take many nonquantitative forms, including written survey responses, interview transcripts, journal entries, video recordings of students, teachers, and classrooms, text messages, and so forth.

Exercise 1.3
What are the implications of the statement that just “observing” is not enough to count as scientific inquiry? Does this mean that a detailed description of a phenomenon is not scientific inquiry?
Find sources that define research in education that differ with our position, that say description alone, without explanation, counts as scientific research. Identify the precise points where the opinions differ. What are the best arguments for each of the positions? Which do you prefer? Why?
Descriptor 3. Updating Everyone’s Thinking in Response to More and Better Information
This descriptor focuses on a third aspect of scientific inquiry: updating and advancing the field’s understanding of phenomena that are investigated. This descriptor foregrounds a powerful characteristic of scientific inquiry: the reliability (or trustworthiness) of what is learned and the ultimate inevitability of this learning to advance human understanding of phenomena. Humans might choose not to learn from scientific inquiry, but history suggests that scientific inquiry always has the potential to advance understanding and that, eventually, humans take advantage of these new understandings.
Before exploring these bold claims a bit further, note that this descriptor uses “information” in the same way the previous two descriptors used “experience” and “observations.” These are the stuff of scientific inquiry and we will use them often, sometimes interchangeably. Frequently, we will use the term “data” to stand for all these terms.
An overriding goal of scientific inquiry is for everyone to learn from what one scientist does. Much of this book is about the methods you need to use so others have faith in what you report and can learn the same things you learned. This aspect of scientific inquiry has many implications.
One implication is that scientific inquiry is not a private practice. It is a public practice available for others to see and learn from. Notice how different this is from everyday learning. When you happen to learn something from your everyday experience, often only you gain from the experience. The fact that research is a public practice means it is also a social one. It is best conducted by interacting with others along the way: soliciting feedback at each phase, taking opportunities to present work-in-progress, and benefitting from the advice of others.
A second implication is that you, as the researcher, must be committed to sharing what you are doing and what you are learning in an open and transparent way. This allows all phases of your work to be scrutinized and critiqued. This is what gives your work credibility. The reliability or trustworthiness of your findings depends on your colleagues recognizing that you have used all appropriate methods to maximize the chances that your claims are justified by the data.
A third implication of viewing scientific inquiry as a collective enterprise is the reverse of the second—you must be committed to receiving comments from others. You must treat your colleagues as fair and honest critics even though it might sometimes feel otherwise. You must appreciate their job, which is to remain skeptical while scrutinizing what you have done in considerable detail. To provide the best help to you, they must remain skeptical about your conclusions (when, for example, the data are difficult for them to interpret) until you offer a convincing logical argument based on the information you share. A rather harsh but good-to-remember statement of the role of your friendly critics was voiced by Karl Popper, a well-known twentieth century philosopher of science: “. . . if you are interested in the problem which I tried to solve by my tentative assertion, you may help me by criticizing it as severely as you can” (Popper, 1968, p. 27).
A final implication of this third descriptor is that, as someone engaged in scientific inquiry, you have no choice but to update your thinking when the data support a different conclusion. This applies to your own data as well as to those of others. When data clearly point to a specific claim, even one that is quite different than you expected, you must reconsider your position. If the outcome is replicated multiple times, you need to adjust your thinking accordingly. Scientific inquiry does not let you pick and choose which data to believe; it mandates that everyone update their thinking when the data warrant an update.
Doing Scientific Inquiry
We define scientific inquiry in an operational sense—what does it mean to do scientific inquiry? What kind of process would satisfy all three descriptors: carefully planning an experience in advance; observing and trying to explain what you see; and, contributing to updating everyone’s thinking about an important phenomenon?
We define scientific inquiry as formulating , testing , and revising hypotheses about phenomena of interest.
Of course, we are not the only ones who define it in this way. The definition for the scientific method posted by the editors of Britannica is: “a researcher develops a hypothesis, tests it through various means, and then modifies the hypothesis on the basis of the outcome of the tests and experiments” (Britannica, n.d. ).

Notice how defining scientific inquiry this way satisfies each of the descriptors. “Carefully planning an experience in advance” is exactly what happens when formulating a hypothesis about a phenomenon of interest and thinking about how to test it. “ Observing a phenomenon” occurs when testing a hypothesis, and “ explaining ” what is found is required when revising a hypothesis based on the data. Finally, “updating everyone’s thinking” comes from comparing publicly the original with the revised hypothesis.
Doing scientific inquiry, as we have defined it, underscores the value of accumulating knowledge rather than generating random bits of knowledge. Formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses is an ongoing process, with each revised hypothesis begging for another test, whether by the same researcher or by new researchers. The editors of Britannica signaled this cyclic process by adding the following phrase to their definition of the scientific method: “The modified hypothesis is then retested, further modified, and tested again.” Scientific inquiry creates a process that encourages each study to build on the studies that have gone before. Through collective engagement in this process of building study on top of study, the scientific community works together to update its thinking.
Before exploring more fully the meaning of “formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses,” we need to acknowledge that this is not the only way researchers define research. Some researchers prefer a less formal definition, one that includes more serendipity, less planning, less explanation. You might have come across more open definitions such as “research is finding out about something.” We prefer the tighter hypothesis formulation, testing, and revision definition because we believe it provides a single, coherent map for conducting research that addresses many of the thorny problems educational researchers encounter. We believe it is the most useful orientation toward research and the most helpful to learn as a beginning researcher.
A final clarification of our definition is that it applies equally to qualitative and quantitative research. This is a familiar distinction in education that has generated much discussion. You might think our definition favors quantitative methods over qualitative methods because the language of hypothesis formulation and testing is often associated with quantitative methods. In fact, we do not favor one method over another. In Chap. 4 , we will illustrate how our definition fits research using a range of quantitative and qualitative methods.
Exercise 1.4
Look for ways to extend what the field knows in an area that has already received attention by other researchers. Specifically, you can search for a program of research carried out by more experienced researchers that has some revised hypotheses that remain untested. Identify a revised hypothesis that you might like to test.
Unpacking the Terms Formulating, Testing, and Revising Hypotheses
To get a full sense of the definition of scientific inquiry we will use throughout this book, it is helpful to spend a little time with each of the key terms.
We first want to make clear that we use the term “hypothesis” as it is defined in most dictionaries and as it used in many scientific fields rather than as it is usually defined in educational statistics courses. By “hypothesis,” we do not mean a null hypothesis that is accepted or rejected by statistical analysis. Rather, we use “hypothesis” in the sense conveyed by the following definitions: “An idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved” (Cambridge University Press, n.d. ), and “An unproved theory, proposition, or supposition, tentatively accepted to explain certain facts and to provide a basis for further investigation or argument” (Agnes & Guralnik, 2008 ).
We distinguish two parts to “hypotheses.” Hypotheses consist of predictions and rationales . Predictions are statements about what you expect to find when you inquire about something. Rationales are explanations for why you made the predictions you did, why you believe your predictions are correct. So, for us “formulating hypotheses” means making explicit predictions and developing rationales for the predictions.
“Testing hypotheses” means making observations that allow you to assess in what ways your predictions were correct and in what ways they were incorrect. In education research, it is rarely useful to think of your predictions as either right or wrong. Because of the complexity of most issues you will investigate, most predictions will be right in some ways and wrong in others.
By studying the observations you make (data you collect) to test your hypotheses, you can revise your hypotheses to better align with the observations. This means revising your predictions plus revising your rationales to justify your adjusted predictions. Even though you might not run another test, formulating revised hypotheses is an essential part of conducting a research study. Comparing your original and revised hypotheses informs everyone of what you learned by conducting your study. In addition, a revised hypothesis sets the stage for you or someone else to extend your study and accumulate more knowledge of the phenomenon.
We should note that not everyone makes a clear distinction between predictions and rationales as two aspects of hypotheses. In fact, common, non-scientific uses of the word “hypothesis” may limit it to only a prediction or only an explanation (or rationale). We choose to explicitly include both prediction and rationale in our definition of hypothesis, not because we assert this should be the universal definition, but because we want to foreground the importance of both parts acting in concert. Using “hypothesis” to represent both prediction and rationale could hide the two aspects, but we make them explicit because they provide different kinds of information. It is usually easier to make predictions than develop rationales because predictions can be guesses, hunches, or gut feelings about which you have little confidence. Developing a compelling rationale requires careful thought plus reading what other researchers have found plus talking with your colleagues. Often, while you are developing your rationale you will find good reasons to change your predictions. Developing good rationales is the engine that drives scientific inquiry. Rationales are essentially descriptions of how much you know about the phenomenon you are studying. Throughout this guide, we will elaborate on how developing good rationales drives scientific inquiry. For now, we simply note that it can sharpen your predictions and help you to interpret your data as you test your hypotheses.

Hypotheses in education research take a variety of forms or types. This is because there are a variety of phenomena that can be investigated. Investigating educational phenomena is sometimes best done using qualitative methods, sometimes using quantitative methods, and most often using mixed methods (e.g., Hay, 2016 ; Weis et al. 2019a ; Weisner, 2005 ). This means that, given our definition, hypotheses are equally applicable to qualitative and quantitative investigations.
Hypotheses take different forms when they are used to investigate different kinds of phenomena. Two very different activities in education could be labeled conducting experiments and descriptions. In an experiment, a hypothesis makes a prediction about anticipated changes, say the changes that occur when a treatment or intervention is applied. You might investigate how students’ thinking changes during a particular kind of instruction.
A second type of hypothesis, relevant for descriptive research, makes a prediction about what you will find when you investigate and describe the nature of a situation. The goal is to understand a situation as it exists rather than to understand a change from one situation to another. In this case, your prediction is what you expect to observe. Your rationale is the set of reasons for making this prediction; it is your current explanation for why the situation will look like it does.
You will probably read, if you have not already, that some researchers say you do not need a prediction to conduct a descriptive study. We will discuss this point of view in Chap. 2 . For now, we simply claim that scientific inquiry, as we have defined it, applies to all kinds of research studies. Descriptive studies, like others, not only benefit from formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses, but also need hypothesis formulating, testing, and revising.
One reason we define research as formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses is that if you think of research in this way you are less likely to go wrong. It is a useful guide for the entire process, as we will describe in detail in the chapters ahead. For example, as you build the rationale for your predictions, you are constructing the theoretical framework for your study (Chap. 3 ). As you work out the methods you will use to test your hypothesis, every decision you make will be based on asking, “Will this help me formulate or test or revise my hypothesis?” (Chap. 4 ). As you interpret the results of testing your predictions, you will compare them to what you predicted and examine the differences, focusing on how you must revise your hypotheses (Chap. 5 ). By anchoring the process to formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses, you will make smart decisions that yield a coherent and well-designed study.
Exercise 1.5
Compare the concept of formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses with the descriptions of scientific inquiry contained in Scientific Research in Education (NRC, 2002 ). How are they similar or different?
Exercise 1.6
Provide an example to illustrate and emphasize the differences between everyday learning/thinking and scientific inquiry.
Learning from Doing Scientific Inquiry
We noted earlier that a measure of what you have learned by conducting a research study is found in the differences between your original hypothesis and your revised hypothesis based on the data you collected to test your hypothesis. We will elaborate this statement in later chapters, but we preview our argument here.
Even before collecting data, scientific inquiry requires cycles of making a prediction, developing a rationale, refining your predictions, reading and studying more to strengthen your rationale, refining your predictions again, and so forth. And, even if you have run through several such cycles, you still will likely find that when you test your prediction you will be partly right and partly wrong. The results will support some parts of your predictions but not others, or the results will “kind of” support your predictions. A critical part of scientific inquiry is making sense of your results by interpreting them against your predictions. Carefully describing what aspects of your data supported your predictions, what aspects did not, and what data fell outside of any predictions is not an easy task, but you cannot learn from your study without doing this analysis.

Analyzing the matches and mismatches between your predictions and your data allows you to formulate different rationales that would have accounted for more of the data. The best revised rationale is the one that accounts for the most data. Once you have revised your rationales, you can think about the predictions they best justify or explain. It is by comparing your original rationales to your new rationales that you can sort out what you learned from your study.
Suppose your study was an experiment. Maybe you were investigating the effects of a new instructional intervention on students’ learning. Your original rationale was your explanation for why the intervention would change the learning outcomes in a particular way. Your revised rationale explained why the changes that you observed occurred like they did and why your revised predictions are better. Maybe your original rationale focused on the potential of the activities if they were implemented in ideal ways and your revised rationale included the factors that are likely to affect how teachers implement them. By comparing the before and after rationales, you are describing what you learned—what you can explain now that you could not before. Another way of saying this is that you are describing how much more you understand now than before you conducted your study.
Revised predictions based on carefully planned and collected data usually exhibit some of the following features compared with the originals: more precision, more completeness, and broader scope. Revised rationales have more explanatory power and become more complete, more aligned with the new predictions, sharper, and overall more convincing.
Part II. Why Do Educators Do Research?
Doing scientific inquiry is a lot of work. Each phase of the process takes time, and you will often cycle back to improve earlier phases as you engage in later phases. Because of the significant effort required, you should make sure your study is worth it. So, from the beginning, you should think about the purpose of your study. Why do you want to do it? And, because research is a social practice, you should also think about whether the results of your study are likely to be important and significant to the education community.
If you are doing research in the way we have described—as scientific inquiry—then one purpose of your study is to understand , not just to describe or evaluate or report. As we noted earlier, when you formulate hypotheses, you are developing rationales that explain why things might be like they are. In our view, trying to understand and explain is what separates research from other kinds of activities, like evaluating or describing.
One reason understanding is so important is that it allows researchers to see how or why something works like it does. When you see how something works, you are better able to predict how it might work in other contexts, under other conditions. And, because conditions, or contextual factors, matter a lot in education, gaining insights into applying your findings to other contexts increases the contributions of your work and its importance to the broader education community.
Consequently, the purposes of research studies in education often include the more specific aim of identifying and understanding the conditions under which the phenomena being studied work like the observations suggest. A classic example of this kind of study in mathematics education was reported by William Brownell and Harold Moser in 1949 . They were trying to establish which method of subtracting whole numbers could be taught most effectively—the regrouping method or the equal additions method. However, they realized that effectiveness might depend on the conditions under which the methods were taught—“meaningfully” versus “mechanically.” So, they designed a study that crossed the two instructional approaches with the two different methods (regrouping and equal additions). Among other results, they found that these conditions did matter. The regrouping method was more effective under the meaningful condition than the mechanical condition, but the same was not true for the equal additions algorithm.
What do education researchers want to understand? In our view, the ultimate goal of education is to offer all students the best possible learning opportunities. So, we believe the ultimate purpose of scientific inquiry in education is to develop understanding that supports the improvement of learning opportunities for all students. We say “ultimate” because there are lots of issues that must be understood to improve learning opportunities for all students. Hypotheses about many aspects of education are connected, ultimately, to students’ learning. For example, formulating and testing a hypothesis that preservice teachers need to engage in particular kinds of activities in their coursework in order to teach particular topics well is, ultimately, connected to improving students’ learning opportunities. So is hypothesizing that school districts often devote relatively few resources to instructional leadership training or hypothesizing that positioning mathematics as a tool students can use to combat social injustice can help students see the relevance of mathematics to their lives.
We do not exclude the importance of research on educational issues more removed from improving students’ learning opportunities, but we do think the argument for their importance will be more difficult to make. If there is no way to imagine a connection between your hypothesis and improving learning opportunities for students, even a distant connection, we recommend you reconsider whether it is an important hypothesis within the education community.
Notice that we said the ultimate goal of education is to offer all students the best possible learning opportunities. For too long, educators have been satisfied with a goal of offering rich learning opportunities for lots of students, sometimes even for just the majority of students, but not necessarily for all students. Evaluations of success often are based on outcomes that show high averages. In other words, if many students have learned something, or even a smaller number have learned a lot, educators may have been satisfied. The problem is that there is usually a pattern in the groups of students who receive lower quality opportunities—students of color and students who live in poor areas, urban and rural. This is not acceptable. Consequently, we emphasize the premise that the purpose of education research is to offer rich learning opportunities to all students.
One way to make sure you will be able to convince others of the importance of your study is to consider investigating some aspect of teachers’ shared instructional problems. Historically, researchers in education have set their own research agendas, regardless of the problems teachers are facing in schools. It is increasingly recognized that teachers have had trouble applying to their own classrooms what researchers find. To address this problem, a researcher could partner with a teacher—better yet, a small group of teachers—and talk with them about instructional problems they all share. These discussions can create a rich pool of problems researchers can consider. If researchers pursued one of these problems (preferably alongside teachers), the connection to improving learning opportunities for all students could be direct and immediate. “Grounding a research question in instructional problems that are experienced across multiple teachers’ classrooms helps to ensure that the answer to the question will be of sufficient scope to be relevant and significant beyond the local context” (Cai et al., 2019b , p. 115).
As a beginning researcher, determining the relevance and importance of a research problem is especially challenging. We recommend talking with advisors, other experienced researchers, and peers to test the educational importance of possible research problems and topics of study. You will also learn much more about the issue of research importance when you read Chap. 5 .
Exercise 1.7
Identify a problem in education that is closely connected to improving learning opportunities and a problem that has a less close connection. For each problem, write a brief argument (like a logical sequence of if-then statements) that connects the problem to all students’ learning opportunities.
Part III. Conducting Research as a Practice of Failing Productively
Scientific inquiry involves formulating hypotheses about phenomena that are not fully understood—by you or anyone else. Even if you are able to inform your hypotheses with lots of knowledge that has already been accumulated, you are likely to find that your prediction is not entirely accurate. This is normal. Remember, scientific inquiry is a process of constantly updating your thinking. More and better information means revising your thinking, again, and again, and again. Because you never fully understand a complicated phenomenon and your hypotheses never produce completely accurate predictions, it is easy to believe you are somehow failing.
The trick is to fail upward, to fail to predict accurately in ways that inform your next hypothesis so you can make a better prediction. Some of the best-known researchers in education have been open and honest about the many times their predictions were wrong and, based on the results of their studies and those of others, they continuously updated their thinking and changed their hypotheses.
A striking example of publicly revising (actually reversing) hypotheses due to incorrect predictions is found in the work of Lee J. Cronbach, one of the most distinguished educational psychologists of the twentieth century. In 1955, Cronbach delivered his presidential address to the American Psychological Association. Titling it “Two Disciplines of Scientific Psychology,” Cronbach proposed a rapprochement between two research approaches—correlational studies that focused on individual differences and experimental studies that focused on instructional treatments controlling for individual differences. (We will examine different research approaches in Chap. 4 ). If these approaches could be brought together, reasoned Cronbach ( 1957 ), researchers could find interactions between individual characteristics and treatments (aptitude-treatment interactions or ATIs), fitting the best treatments to different individuals.
In 1975, after years of research by many researchers looking for ATIs, Cronbach acknowledged the evidence for simple, useful ATIs had not been found. Even when trying to find interactions between a few variables that could provide instructional guidance, the analysis, said Cronbach, creates “a hall of mirrors that extends to infinity, tormenting even the boldest investigators and defeating even ambitious designs” (Cronbach, 1975 , p. 119).
As he was reflecting back on his work, Cronbach ( 1986 ) recommended moving away from documenting instructional effects through statistical inference (an approach he had championed for much of his career) and toward approaches that probe the reasons for these effects, approaches that provide a “full account of events in a time, place, and context” (Cronbach, 1986 , p. 104). This is a remarkable change in hypotheses, a change based on data and made fully transparent. Cronbach understood the value of failing productively.
Closer to home, in a less dramatic example, one of us began a line of scientific inquiry into how to prepare elementary preservice teachers to teach early algebra. Teaching early algebra meant engaging elementary students in early forms of algebraic reasoning. Such reasoning should help them transition from arithmetic to algebra. To begin this line of inquiry, a set of activities for preservice teachers were developed. Even though the activities were based on well-supported hypotheses, they largely failed to engage preservice teachers as predicted because of unanticipated challenges the preservice teachers faced. To capitalize on this failure, follow-up studies were conducted, first to better understand elementary preservice teachers’ challenges with preparing to teach early algebra, and then to better support preservice teachers in navigating these challenges. In this example, the initial failure was a necessary step in the researchers’ scientific inquiry and furthered the researchers’ understanding of this issue.
We present another example of failing productively in Chap. 2 . That example emerges from recounting the history of a well-known research program in mathematics education.
Making mistakes is an inherent part of doing scientific research. Conducting a study is rarely a smooth path from beginning to end. We recommend that you keep the following things in mind as you begin a career of conducting research in education.
First, do not get discouraged when you make mistakes; do not fall into the trap of feeling like you are not capable of doing research because you make too many errors.
Second, learn from your mistakes. Do not ignore your mistakes or treat them as errors that you simply need to forget and move past. Mistakes are rich sites for learning—in research just as in other fields of study.
Third, by reflecting on your mistakes, you can learn to make better mistakes, mistakes that inform you about a productive next step. You will not be able to eliminate your mistakes, but you can set a goal of making better and better mistakes.
Exercise 1.8
How does scientific inquiry differ from everyday learning in giving you the tools to fail upward? You may find helpful perspectives on this question in other resources on science and scientific inquiry (e.g., Failure: Why Science is So Successful by Firestein, 2015).
Exercise 1.9
Use what you have learned in this chapter to write a new definition of scientific inquiry. Compare this definition with the one you wrote before reading this chapter. If you are reading this book as part of a course, compare your definition with your colleagues’ definitions. Develop a consensus definition with everyone in the course.
Part IV. Preview of Chap. 2
Now that you have a good idea of what research is, at least of what we believe research is, the next step is to think about how to actually begin doing research. This means how to begin formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses. As for all phases of scientific inquiry, there are lots of things to think about. Because it is critical to start well, we devote Chap. 2 to getting started with formulating hypotheses.
Agnes, M., & Guralnik, D. B. (Eds.). (2008). Hypothesis. In Webster’s new world college dictionary (4th ed.). Wiley.
Google Scholar
Britannica. (n.d.). Scientific method. In Encyclopaedia Britannica . Retrieved July 15, 2022 from https://www.britannica.com/science/scientific-method
Brownell, W. A., & Moser, H. E. (1949). Meaningful vs. mechanical learning: A study in grade III subtraction . Duke University Press..
Cai, J., Morris, A., Hohensee, C., Hwang, S., Robison, V., Cirillo, M., Kramer, S. L., & Hiebert, J. (2019b). Posing significant research questions. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 50 (2), 114–120. https://doi.org/10.5951/jresematheduc.50.2.0114
Article Google Scholar
Cambridge University Press. (n.d.). Hypothesis. In Cambridge dictionary . Retrieved July 15, 2022 from https://dictionary.cambridge.org/us/dictionary/english/hypothesis
Cronbach, J. L. (1957). The two disciplines of scientific psychology. American Psychologist, 12 , 671–684.
Cronbach, L. J. (1975). Beyond the two disciplines of scientific psychology. American Psychologist, 30 , 116–127.
Cronbach, L. J. (1986). Social inquiry by and for earthlings. In D. W. Fiske & R. A. Shweder (Eds.), Metatheory in social science: Pluralisms and subjectivities (pp. 83–107). University of Chicago Press.
Hay, C. M. (Ed.). (2016). Methods that matter: Integrating mixed methods for more effective social science research . University of Chicago Press.
Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Explain. In Merriam-Webster.com dictionary . Retrieved July 15, 2022, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/explain
National Research Council. (2002). Scientific research in education . National Academy Press.
Weis, L., Eisenhart, M., Duncan, G. J., Albro, E., Bueschel, A. C., Cobb, P., Eccles, J., Mendenhall, R., Moss, P., Penuel, W., Ream, R. K., Rumbaut, R. G., Sloane, F., Weisner, T. S., & Wilson, J. (2019a). Mixed methods for studies that address broad and enduring issues in education research. Teachers College Record, 121 , 100307.
Weisner, T. S. (Ed.). (2005). Discovering successful pathways in children’s development: Mixed methods in the study of childhood and family life . University of Chicago Press.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Education, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA
James Hiebert, Anne K Morris & Charles Hohensee
Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA
Jinfa Cai & Stephen Hwang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Hiebert, J., Cai, J., Hwang, S., Morris, A.K., Hohensee, C. (2023). What Is Research, and Why Do People Do It?. In: Doing Research: A New Researcher’s Guide. Research in Mathematics Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19078-0_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19078-0_1
Published : 03 December 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-19077-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-19078-0
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Methodology
Definition:
Research Methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to conduct research, investigate problems, and gather data and information for a specific purpose. It involves the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect , analyze , and interpret data to answer research questions or solve research problems . Moreover, They are philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process.
Structure of Research Methodology
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section:
I. Introduction
- Provide an overview of the research problem and the need for a research methodology section
- Outline the main research questions and objectives
II. Research Design
- Explain the research design chosen and why it is appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Discuss any alternative research designs considered and why they were not chosen
- Describe the research setting and participants (if applicable)
III. Data Collection Methods
- Describe the methods used to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations)
- Explain how the data collection methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or instruments used for data collection
IV. Data Analysis Methods
- Describe the methods used to analyze the data (e.g., statistical analysis, content analysis )
- Explain how the data analysis methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or software used for data analysis
V. Ethical Considerations
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise from the research and how they were addressed
- Explain how informed consent was obtained (if applicable)
- Detail any measures taken to ensure confidentiality and anonymity
VI. Limitations
- Identify any potential limitations of the research methodology and how they may impact the results and conclusions
VII. Conclusion
- Summarize the key aspects of the research methodology section
- Explain how the research methodology addresses the research question(s) and objectives
Research Methodology Types
Types of Research Methodology are as follows:
Quantitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data using statistical methods. This type of research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Qualitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Mixed-Methods Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research. This approach can be particularly useful for studies that aim to explore complex phenomena and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Case Study Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves in-depth examination of a single case or a small number of cases. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and anthropology to gain a detailed understanding of a particular individual or group.
Action Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves a collaborative process between researchers and practitioners to identify and solve real-world problems. Action research is often used in education, healthcare, and social work.
Experimental Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the manipulation of one or more independent variables to observe their effects on a dependent variable. Experimental research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Survey Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection of data from a sample of individuals using questionnaires or interviews. Survey research is often used to study attitudes, opinions, and behaviors.
Grounded Theory Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the development of theories based on the data collected during the research process. Grounded theory is often used in sociology and anthropology to generate theories about social phenomena.
Research Methodology Example
An Example of Research Methodology could be the following:
Research Methodology for Investigating the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Reducing Symptoms of Depression in Adults
Introduction:
The aim of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. To achieve this objective, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach.
Research Design:
The study will follow a pre-test and post-test design with two groups: an experimental group receiving CBT and a control group receiving no intervention. The study will also include a qualitative component, in which semi-structured interviews will be conducted with a subset of participants to explore their experiences of receiving CBT.
Participants:
Participants will be recruited from community mental health clinics in the local area. The sample will consist of 100 adults aged 18-65 years old who meet the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder. Participants will be randomly assigned to either the experimental group or the control group.
Intervention :
The experimental group will receive 12 weekly sessions of CBT, each lasting 60 minutes. The intervention will be delivered by licensed mental health professionals who have been trained in CBT. The control group will receive no intervention during the study period.
Data Collection:
Quantitative data will be collected through the use of standardized measures such as the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7). Data will be collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at a 3-month follow-up. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a subset of participants from the experimental group. The interviews will be conducted at the end of the intervention period, and will explore participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-tests, and mixed-model analyses of variance (ANOVA) to assess the effectiveness of the intervention. Qualitative data will be analyzed using thematic analysis to identify common themes and patterns in participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Ethical Considerations:
This study will comply with ethical guidelines for research involving human subjects. Participants will provide informed consent before participating in the study, and their privacy and confidentiality will be protected throughout the study. Any adverse events or reactions will be reported and managed appropriately.
Data Management:
All data collected will be kept confidential and stored securely using password-protected databases. Identifying information will be removed from qualitative data transcripts to ensure participants’ anonymity.
Limitations:
One potential limitation of this study is that it only focuses on one type of psychotherapy, CBT, and may not generalize to other types of therapy or interventions. Another limitation is that the study will only include participants from community mental health clinics, which may not be representative of the general population.
Conclusion:
This research aims to investigate the effectiveness of CBT in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. By using a randomized controlled trial and a mixed-methods approach, the study will provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the relationship between CBT and depression. The results of this study will have important implications for the development of effective treatments for depression in clinical settings.
How to Write Research Methodology
Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It’s an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are the steps to write a research methodology:
- Start by explaining your research question: Begin the methodology section by restating your research question and explaining why it’s important. This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods.
- Describe your research design: Explain the overall approach you used to conduct research. This could be a qualitative or quantitative research design, experimental or non-experimental, case study or survey, etc. Discuss the advantages and limitations of the chosen design.
- Discuss your sample: Describe the participants or subjects you included in your study. Include details such as their demographics, sampling method, sample size, and any exclusion criteria used.
- Describe your data collection methods : Explain how you collected data from your participants. This could include surveys, interviews, observations, questionnaires, or experiments. Include details on how you obtained informed consent, how you administered the tools, and how you minimized the risk of bias.
- Explain your data analysis techniques: Describe the methods you used to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, content analysis, thematic analysis, or discourse analysis. Explain how you dealt with missing data, outliers, and any other issues that arose during the analysis.
- Discuss the validity and reliability of your research : Explain how you ensured the validity and reliability of your study. This could include measures such as triangulation, member checking, peer review, or inter-coder reliability.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your research: Discuss any limitations of your study, including any potential threats to validity or generalizability. This helps readers understand the scope of your findings and how they might apply to other contexts.
- Provide a summary: End the methodology section by summarizing the methods and techniques you used to conduct your research. This provides a clear overview of your research methodology and helps readers understand the process you followed to arrive at your findings.
When to Write Research Methodology
Research methodology is typically written after the research proposal has been approved and before the actual research is conducted. It should be written prior to data collection and analysis, as it provides a clear roadmap for the research project.
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
The methodology should be written in a clear and concise manner, and it should be based on established research practices and standards. It is important to provide enough detail so that the reader can understand how the research was conducted and evaluate the validity of the results.
Applications of Research Methodology
Here are some of the applications of research methodology:
- To identify the research problem: Research methodology is used to identify the research problem, which is the first step in conducting any research.
- To design the research: Research methodology helps in designing the research by selecting the appropriate research method, research design, and sampling technique.
- To collect data: Research methodology provides a systematic approach to collect data from primary and secondary sources.
- To analyze data: Research methodology helps in analyzing the collected data using various statistical and non-statistical techniques.
- To test hypotheses: Research methodology provides a framework for testing hypotheses and drawing conclusions based on the analysis of data.
- To generalize findings: Research methodology helps in generalizing the findings of the research to the target population.
- To develop theories : Research methodology is used to develop new theories and modify existing theories based on the findings of the research.
- To evaluate programs and policies : Research methodology is used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies by collecting data and analyzing it.
- To improve decision-making: Research methodology helps in making informed decisions by providing reliable and valid data.
Purpose of Research Methodology
Research methodology serves several important purposes, including:
- To guide the research process: Research methodology provides a systematic framework for conducting research. It helps researchers to plan their research, define their research questions, and select appropriate methods and techniques for collecting and analyzing data.
- To ensure research quality: Research methodology helps researchers to ensure that their research is rigorous, reliable, and valid. It provides guidelines for minimizing bias and error in data collection and analysis, and for ensuring that research findings are accurate and trustworthy.
- To replicate research: Research methodology provides a clear and detailed account of the research process, making it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings.
- To advance knowledge: Research methodology enables researchers to generate new knowledge and to contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. It provides a means for testing hypotheses, exploring new ideas, and discovering new insights.
- To inform decision-making: Research methodology provides evidence-based information that can inform policy and decision-making in a variety of fields, including medicine, public health, education, and business.
Advantages of Research Methodology
Research methodology has several advantages that make it a valuable tool for conducting research in various fields. Here are some of the key advantages of research methodology:
- Systematic and structured approach : Research methodology provides a systematic and structured approach to conducting research, which ensures that the research is conducted in a rigorous and comprehensive manner.
- Objectivity : Research methodology aims to ensure objectivity in the research process, which means that the research findings are based on evidence and not influenced by personal bias or subjective opinions.
- Replicability : Research methodology ensures that research can be replicated by other researchers, which is essential for validating research findings and ensuring their accuracy.
- Reliability : Research methodology aims to ensure that the research findings are reliable, which means that they are consistent and can be depended upon.
- Validity : Research methodology ensures that the research findings are valid, which means that they accurately reflect the research question or hypothesis being tested.
- Efficiency : Research methodology provides a structured and efficient way of conducting research, which helps to save time and resources.
- Flexibility : Research methodology allows researchers to choose the most appropriate research methods and techniques based on the research question, data availability, and other relevant factors.
- Scope for innovation: Research methodology provides scope for innovation and creativity in designing research studies and developing new research techniques.
Research Methodology Vs Research Methods
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...


Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Neurol Res Pract

How to use and assess qualitative research methods
Loraine busetto.
1 Department of Neurology, Heidelberg University Hospital, Im Neuenheimer Feld 400, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany
Wolfgang Wick
2 Clinical Cooperation Unit Neuro-Oncology, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany
Christoph Gumbinger
Associated data.
Not applicable.
This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions, and focussing on intervention improvement. The most common methods of data collection are document study, (non-) participant observations, semi-structured interviews and focus groups. For data analysis, field-notes and audio-recordings are transcribed into protocols and transcripts, and coded using qualitative data management software. Criteria such as checklists, reflexivity, sampling strategies, piloting, co-coding, member-checking and stakeholder involvement can be used to enhance and assess the quality of the research conducted. Using qualitative in addition to quantitative designs will equip us with better tools to address a greater range of research problems, and to fill in blind spots in current neurological research and practice.
The aim of this paper is to provide an overview of qualitative research methods, including hands-on information on how they can be used, reported and assessed. This article is intended for beginning qualitative researchers in the health sciences as well as experienced quantitative researchers who wish to broaden their understanding of qualitative research.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is defined as “the study of the nature of phenomena”, including “their quality, different manifestations, the context in which they appear or the perspectives from which they can be perceived” , but excluding “their range, frequency and place in an objectively determined chain of cause and effect” [ 1 ]. This formal definition can be complemented with a more pragmatic rule of thumb: qualitative research generally includes data in form of words rather than numbers [ 2 ].
Why conduct qualitative research?
Because some research questions cannot be answered using (only) quantitative methods. For example, one Australian study addressed the issue of why patients from Aboriginal communities often present late or not at all to specialist services offered by tertiary care hospitals. Using qualitative interviews with patients and staff, it found one of the most significant access barriers to be transportation problems, including some towns and communities simply not having a bus service to the hospital [ 3 ]. A quantitative study could have measured the number of patients over time or even looked at possible explanatory factors – but only those previously known or suspected to be of relevance. To discover reasons for observed patterns, especially the invisible or surprising ones, qualitative designs are needed.
While qualitative research is common in other fields, it is still relatively underrepresented in health services research. The latter field is more traditionally rooted in the evidence-based-medicine paradigm, as seen in " research that involves testing the effectiveness of various strategies to achieve changes in clinical practice, preferably applying randomised controlled trial study designs (...) " [ 4 ]. This focus on quantitative research and specifically randomised controlled trials (RCT) is visible in the idea of a hierarchy of research evidence which assumes that some research designs are objectively better than others, and that choosing a "lesser" design is only acceptable when the better ones are not practically or ethically feasible [ 5 , 6 ]. Others, however, argue that an objective hierarchy does not exist, and that, instead, the research design and methods should be chosen to fit the specific research question at hand – "questions before methods" [ 2 , 7 – 9 ]. This means that even when an RCT is possible, some research problems require a different design that is better suited to addressing them. Arguing in JAMA, Berwick uses the example of rapid response teams in hospitals, which he describes as " a complex, multicomponent intervention – essentially a process of social change" susceptible to a range of different context factors including leadership or organisation history. According to him, "[in] such complex terrain, the RCT is an impoverished way to learn. Critics who use it as a truth standard in this context are incorrect" [ 8 ] . Instead of limiting oneself to RCTs, Berwick recommends embracing a wider range of methods , including qualitative ones, which for "these specific applications, (...) are not compromises in learning how to improve; they are superior" [ 8 ].
Research problems that can be approached particularly well using qualitative methods include assessing complex multi-component interventions or systems (of change), addressing questions beyond “what works”, towards “what works for whom when, how and why”, and focussing on intervention improvement rather than accreditation [ 7 , 9 – 12 ]. Using qualitative methods can also help shed light on the “softer” side of medical treatment. For example, while quantitative trials can measure the costs and benefits of neuro-oncological treatment in terms of survival rates or adverse effects, qualitative research can help provide a better understanding of patient or caregiver stress, visibility of illness or out-of-pocket expenses.
How to conduct qualitative research?
Given that qualitative research is characterised by flexibility, openness and responsivity to context, the steps of data collection and analysis are not as separate and consecutive as they tend to be in quantitative research [ 13 , 14 ]. As Fossey puts it : “sampling, data collection, analysis and interpretation are related to each other in a cyclical (iterative) manner, rather than following one after another in a stepwise approach” [ 15 ]. The researcher can make educated decisions with regard to the choice of method, how they are implemented, and to which and how many units they are applied [ 13 ]. As shown in Fig. 1 , this can involve several back-and-forth steps between data collection and analysis where new insights and experiences can lead to adaption and expansion of the original plan. Some insights may also necessitate a revision of the research question and/or the research design as a whole. The process ends when saturation is achieved, i.e. when no relevant new information can be found (see also below: sampling and saturation). For reasons of transparency, it is essential for all decisions as well as the underlying reasoning to be well-documented.

Iterative research process
While it is not always explicitly addressed, qualitative methods reflect a different underlying research paradigm than quantitative research (e.g. constructivism or interpretivism as opposed to positivism). The choice of methods can be based on the respective underlying substantive theory or theoretical framework used by the researcher [ 2 ].
Data collection
The methods of qualitative data collection most commonly used in health research are document study, observations, semi-structured interviews and focus groups [ 1 , 14 , 16 , 17 ].
Document study
Document study (also called document analysis) refers to the review by the researcher of written materials [ 14 ]. These can include personal and non-personal documents such as archives, annual reports, guidelines, policy documents, diaries or letters.
Observations
Observations are particularly useful to gain insights into a certain setting and actual behaviour – as opposed to reported behaviour or opinions [ 13 ]. Qualitative observations can be either participant or non-participant in nature. In participant observations, the observer is part of the observed setting, for example a nurse working in an intensive care unit [ 18 ]. In non-participant observations, the observer is “on the outside looking in”, i.e. present in but not part of the situation, trying not to influence the setting by their presence. Observations can be planned (e.g. for 3 h during the day or night shift) or ad hoc (e.g. as soon as a stroke patient arrives at the emergency room). During the observation, the observer takes notes on everything or certain pre-determined parts of what is happening around them, for example focusing on physician-patient interactions or communication between different professional groups. Written notes can be taken during or after the observations, depending on feasibility (which is usually lower during participant observations) and acceptability (e.g. when the observer is perceived to be judging the observed). Afterwards, these field notes are transcribed into observation protocols. If more than one observer was involved, field notes are taken independently, but notes can be consolidated into one protocol after discussions. Advantages of conducting observations include minimising the distance between the researcher and the researched, the potential discovery of topics that the researcher did not realise were relevant and gaining deeper insights into the real-world dimensions of the research problem at hand [ 18 ].
Semi-structured interviews
Hijmans & Kuyper describe qualitative interviews as “an exchange with an informal character, a conversation with a goal” [ 19 ]. Interviews are used to gain insights into a person’s subjective experiences, opinions and motivations – as opposed to facts or behaviours [ 13 ]. Interviews can be distinguished by the degree to which they are structured (i.e. a questionnaire), open (e.g. free conversation or autobiographical interviews) or semi-structured [ 2 , 13 ]. Semi-structured interviews are characterized by open-ended questions and the use of an interview guide (or topic guide/list) in which the broad areas of interest, sometimes including sub-questions, are defined [ 19 ]. The pre-defined topics in the interview guide can be derived from the literature, previous research or a preliminary method of data collection, e.g. document study or observations. The topic list is usually adapted and improved at the start of the data collection process as the interviewer learns more about the field [ 20 ]. Across interviews the focus on the different (blocks of) questions may differ and some questions may be skipped altogether (e.g. if the interviewee is not able or willing to answer the questions or for concerns about the total length of the interview) [ 20 ]. Qualitative interviews are usually not conducted in written format as it impedes on the interactive component of the method [ 20 ]. In comparison to written surveys, qualitative interviews have the advantage of being interactive and allowing for unexpected topics to emerge and to be taken up by the researcher. This can also help overcome a provider or researcher-centred bias often found in written surveys, which by nature, can only measure what is already known or expected to be of relevance to the researcher. Interviews can be audio- or video-taped; but sometimes it is only feasible or acceptable for the interviewer to take written notes [ 14 , 16 , 20 ].
Focus groups
Focus groups are group interviews to explore participants’ expertise and experiences, including explorations of how and why people behave in certain ways [ 1 ]. Focus groups usually consist of 6–8 people and are led by an experienced moderator following a topic guide or “script” [ 21 ]. They can involve an observer who takes note of the non-verbal aspects of the situation, possibly using an observation guide [ 21 ]. Depending on researchers’ and participants’ preferences, the discussions can be audio- or video-taped and transcribed afterwards [ 21 ]. Focus groups are useful for bringing together homogeneous (to a lesser extent heterogeneous) groups of participants with relevant expertise and experience on a given topic on which they can share detailed information [ 21 ]. Focus groups are a relatively easy, fast and inexpensive method to gain access to information on interactions in a given group, i.e. “the sharing and comparing” among participants [ 21 ]. Disadvantages include less control over the process and a lesser extent to which each individual may participate. Moreover, focus group moderators need experience, as do those tasked with the analysis of the resulting data. Focus groups can be less appropriate for discussing sensitive topics that participants might be reluctant to disclose in a group setting [ 13 ]. Moreover, attention must be paid to the emergence of “groupthink” as well as possible power dynamics within the group, e.g. when patients are awed or intimidated by health professionals.
Choosing the “right” method
As explained above, the school of thought underlying qualitative research assumes no objective hierarchy of evidence and methods. This means that each choice of single or combined methods has to be based on the research question that needs to be answered and a critical assessment with regard to whether or to what extent the chosen method can accomplish this – i.e. the “fit” between question and method [ 14 ]. It is necessary for these decisions to be documented when they are being made, and to be critically discussed when reporting methods and results.
Let us assume that our research aim is to examine the (clinical) processes around acute endovascular treatment (EVT), from the patient’s arrival at the emergency room to recanalization, with the aim to identify possible causes for delay and/or other causes for sub-optimal treatment outcome. As a first step, we could conduct a document study of the relevant standard operating procedures (SOPs) for this phase of care – are they up-to-date and in line with current guidelines? Do they contain any mistakes, irregularities or uncertainties that could cause delays or other problems? Regardless of the answers to these questions, the results have to be interpreted based on what they are: a written outline of what care processes in this hospital should look like. If we want to know what they actually look like in practice, we can conduct observations of the processes described in the SOPs. These results can (and should) be analysed in themselves, but also in comparison to the results of the document analysis, especially as regards relevant discrepancies. Do the SOPs outline specific tests for which no equipment can be observed or tasks to be performed by specialized nurses who are not present during the observation? It might also be possible that the written SOP is outdated, but the actual care provided is in line with current best practice. In order to find out why these discrepancies exist, it can be useful to conduct interviews. Are the physicians simply not aware of the SOPs (because their existence is limited to the hospital’s intranet) or do they actively disagree with them or does the infrastructure make it impossible to provide the care as described? Another rationale for adding interviews is that some situations (or all of their possible variations for different patient groups or the day, night or weekend shift) cannot practically or ethically be observed. In this case, it is possible to ask those involved to report on their actions – being aware that this is not the same as the actual observation. A senior physician’s or hospital manager’s description of certain situations might differ from a nurse’s or junior physician’s one, maybe because they intentionally misrepresent facts or maybe because different aspects of the process are visible or important to them. In some cases, it can also be relevant to consider to whom the interviewee is disclosing this information – someone they trust, someone they are otherwise not connected to, or someone they suspect or are aware of being in a potentially “dangerous” power relationship to them. Lastly, a focus group could be conducted with representatives of the relevant professional groups to explore how and why exactly they provide care around EVT. The discussion might reveal discrepancies (between SOPs and actual care or between different physicians) and motivations to the researchers as well as to the focus group members that they might not have been aware of themselves. For the focus group to deliver relevant information, attention has to be paid to its composition and conduct, for example, to make sure that all participants feel safe to disclose sensitive or potentially problematic information or that the discussion is not dominated by (senior) physicians only. The resulting combination of data collection methods is shown in Fig. 2 .

Possible combination of data collection methods
Attributions for icons: “Book” by Serhii Smirnov, “Interview” by Adrien Coquet, FR, “Magnifying Glass” by anggun, ID, “Business communication” by Vectors Market; all from the Noun Project
The combination of multiple data source as described for this example can be referred to as “triangulation”, in which multiple measurements are carried out from different angles to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon under study [ 22 , 23 ].
Data analysis
To analyse the data collected through observations, interviews and focus groups these need to be transcribed into protocols and transcripts (see Fig. 3 ). Interviews and focus groups can be transcribed verbatim , with or without annotations for behaviour (e.g. laughing, crying, pausing) and with or without phonetic transcription of dialects and filler words, depending on what is expected or known to be relevant for the analysis. In the next step, the protocols and transcripts are coded , that is, marked (or tagged, labelled) with one or more short descriptors of the content of a sentence or paragraph [ 2 , 15 , 23 ]. Jansen describes coding as “connecting the raw data with “theoretical” terms” [ 20 ]. In a more practical sense, coding makes raw data sortable. This makes it possible to extract and examine all segments describing, say, a tele-neurology consultation from multiple data sources (e.g. SOPs, emergency room observations, staff and patient interview). In a process of synthesis and abstraction, the codes are then grouped, summarised and/or categorised [ 15 , 20 ]. The end product of the coding or analysis process is a descriptive theory of the behavioural pattern under investigation [ 20 ]. The coding process is performed using qualitative data management software, the most common ones being InVivo, MaxQDA and Atlas.ti. It should be noted that these are data management tools which support the analysis performed by the researcher(s) [ 14 ].

From data collection to data analysis
Attributions for icons: see Fig. Fig.2, 2 , also “Speech to text” by Trevor Dsouza, “Field Notes” by Mike O’Brien, US, “Voice Record” by ProSymbols, US, “Inspection” by Made, AU, and “Cloud” by Graphic Tigers; all from the Noun Project
How to report qualitative research?
Protocols of qualitative research can be published separately and in advance of the study results. However, the aim is not the same as in RCT protocols, i.e. to pre-define and set in stone the research questions and primary or secondary endpoints. Rather, it is a way to describe the research methods in detail, which might not be possible in the results paper given journals’ word limits. Qualitative research papers are usually longer than their quantitative counterparts to allow for deep understanding and so-called “thick description”. In the methods section, the focus is on transparency of the methods used, including why, how and by whom they were implemented in the specific study setting, so as to enable a discussion of whether and how this may have influenced data collection, analysis and interpretation. The results section usually starts with a paragraph outlining the main findings, followed by more detailed descriptions of, for example, the commonalities, discrepancies or exceptions per category [ 20 ]. Here it is important to support main findings by relevant quotations, which may add information, context, emphasis or real-life examples [ 20 , 23 ]. It is subject to debate in the field whether it is relevant to state the exact number or percentage of respondents supporting a certain statement (e.g. “Five interviewees expressed negative feelings towards XYZ”) [ 21 ].
How to combine qualitative with quantitative research?
Qualitative methods can be combined with other methods in multi- or mixed methods designs, which “[employ] two or more different methods [ …] within the same study or research program rather than confining the research to one single method” [ 24 ]. Reasons for combining methods can be diverse, including triangulation for corroboration of findings, complementarity for illustration and clarification of results, expansion to extend the breadth and range of the study, explanation of (unexpected) results generated with one method with the help of another, or offsetting the weakness of one method with the strength of another [ 1 , 17 , 24 – 26 ]. The resulting designs can be classified according to when, why and how the different quantitative and/or qualitative data strands are combined. The three most common types of mixed method designs are the convergent parallel design , the explanatory sequential design and the exploratory sequential design. The designs with examples are shown in Fig. 4 .

Three common mixed methods designs
In the convergent parallel design, a qualitative study is conducted in parallel to and independently of a quantitative study, and the results of both studies are compared and combined at the stage of interpretation of results. Using the above example of EVT provision, this could entail setting up a quantitative EVT registry to measure process times and patient outcomes in parallel to conducting the qualitative research outlined above, and then comparing results. Amongst other things, this would make it possible to assess whether interview respondents’ subjective impressions of patients receiving good care match modified Rankin Scores at follow-up, or whether observed delays in care provision are exceptions or the rule when compared to door-to-needle times as documented in the registry. In the explanatory sequential design, a quantitative study is carried out first, followed by a qualitative study to help explain the results from the quantitative study. This would be an appropriate design if the registry alone had revealed relevant delays in door-to-needle times and the qualitative study would be used to understand where and why these occurred, and how they could be improved. In the exploratory design, the qualitative study is carried out first and its results help informing and building the quantitative study in the next step [ 26 ]. If the qualitative study around EVT provision had shown a high level of dissatisfaction among the staff members involved, a quantitative questionnaire investigating staff satisfaction could be set up in the next step, informed by the qualitative study on which topics dissatisfaction had been expressed. Amongst other things, the questionnaire design would make it possible to widen the reach of the research to more respondents from different (types of) hospitals, regions, countries or settings, and to conduct sub-group analyses for different professional groups.
How to assess qualitative research?
A variety of assessment criteria and lists have been developed for qualitative research, ranging in their focus and comprehensiveness [ 14 , 17 , 27 ]. However, none of these has been elevated to the “gold standard” in the field. In the following, we therefore focus on a set of commonly used assessment criteria that, from a practical standpoint, a researcher can look for when assessing a qualitative research report or paper.
Assessors should check the authors’ use of and adherence to the relevant reporting checklists (e.g. Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR)) to make sure all items that are relevant for this type of research are addressed [ 23 , 28 ]. Discussions of quantitative measures in addition to or instead of these qualitative measures can be a sign of lower quality of the research (paper). Providing and adhering to a checklist for qualitative research contributes to an important quality criterion for qualitative research, namely transparency [ 15 , 17 , 23 ].
Reflexivity
While methodological transparency and complete reporting is relevant for all types of research, some additional criteria must be taken into account for qualitative research. This includes what is called reflexivity, i.e. sensitivity to the relationship between the researcher and the researched, including how contact was established and maintained, or the background and experience of the researcher(s) involved in data collection and analysis. Depending on the research question and population to be researched this can be limited to professional experience, but it may also include gender, age or ethnicity [ 17 , 27 ]. These details are relevant because in qualitative research, as opposed to quantitative research, the researcher as a person cannot be isolated from the research process [ 23 ]. It may influence the conversation when an interviewed patient speaks to an interviewer who is a physician, or when an interviewee is asked to discuss a gynaecological procedure with a male interviewer, and therefore the reader must be made aware of these details [ 19 ].
Sampling and saturation
The aim of qualitative sampling is for all variants of the objects of observation that are deemed relevant for the study to be present in the sample “ to see the issue and its meanings from as many angles as possible” [ 1 , 16 , 19 , 20 , 27 ] , and to ensure “information-richness [ 15 ]. An iterative sampling approach is advised, in which data collection (e.g. five interviews) is followed by data analysis, followed by more data collection to find variants that are lacking in the current sample. This process continues until no new (relevant) information can be found and further sampling becomes redundant – which is called saturation [ 1 , 15 ] . In other words: qualitative data collection finds its end point not a priori , but when the research team determines that saturation has been reached [ 29 , 30 ].
This is also the reason why most qualitative studies use deliberate instead of random sampling strategies. This is generally referred to as “ purposive sampling” , in which researchers pre-define which types of participants or cases they need to include so as to cover all variations that are expected to be of relevance, based on the literature, previous experience or theory (i.e. theoretical sampling) [ 14 , 20 ]. Other types of purposive sampling include (but are not limited to) maximum variation sampling, critical case sampling or extreme or deviant case sampling [ 2 ]. In the above EVT example, a purposive sample could include all relevant professional groups and/or all relevant stakeholders (patients, relatives) and/or all relevant times of observation (day, night and weekend shift).
Assessors of qualitative research should check whether the considerations underlying the sampling strategy were sound and whether or how researchers tried to adapt and improve their strategies in stepwise or cyclical approaches between data collection and analysis to achieve saturation [ 14 ].
Good qualitative research is iterative in nature, i.e. it goes back and forth between data collection and analysis, revising and improving the approach where necessary. One example of this are pilot interviews, where different aspects of the interview (especially the interview guide, but also, for example, the site of the interview or whether the interview can be audio-recorded) are tested with a small number of respondents, evaluated and revised [ 19 ]. In doing so, the interviewer learns which wording or types of questions work best, or which is the best length of an interview with patients who have trouble concentrating for an extended time. Of course, the same reasoning applies to observations or focus groups which can also be piloted.
Ideally, coding should be performed by at least two researchers, especially at the beginning of the coding process when a common approach must be defined, including the establishment of a useful coding list (or tree), and when a common meaning of individual codes must be established [ 23 ]. An initial sub-set or all transcripts can be coded independently by the coders and then compared and consolidated after regular discussions in the research team. This is to make sure that codes are applied consistently to the research data.
Member checking
Member checking, also called respondent validation , refers to the practice of checking back with study respondents to see if the research is in line with their views [ 14 , 27 ]. This can happen after data collection or analysis or when first results are available [ 23 ]. For example, interviewees can be provided with (summaries of) their transcripts and asked whether they believe this to be a complete representation of their views or whether they would like to clarify or elaborate on their responses [ 17 ]. Respondents’ feedback on these issues then becomes part of the data collection and analysis [ 27 ].
Stakeholder involvement
In those niches where qualitative approaches have been able to evolve and grow, a new trend has seen the inclusion of patients and their representatives not only as study participants (i.e. “members”, see above) but as consultants to and active participants in the broader research process [ 31 – 33 ]. The underlying assumption is that patients and other stakeholders hold unique perspectives and experiences that add value beyond their own single story, making the research more relevant and beneficial to researchers, study participants and (future) patients alike [ 34 , 35 ]. Using the example of patients on or nearing dialysis, a recent scoping review found that 80% of clinical research did not address the top 10 research priorities identified by patients and caregivers [ 32 , 36 ]. In this sense, the involvement of the relevant stakeholders, especially patients and relatives, is increasingly being seen as a quality indicator in and of itself.
How not to assess qualitative research
The above overview does not include certain items that are routine in assessments of quantitative research. What follows is a non-exhaustive, non-representative, experience-based list of the quantitative criteria often applied to the assessment of qualitative research, as well as an explanation of the limited usefulness of these endeavours.
Protocol adherence
Given the openness and flexibility of qualitative research, it should not be assessed by how well it adheres to pre-determined and fixed strategies – in other words: its rigidity. Instead, the assessor should look for signs of adaptation and refinement based on lessons learned from earlier steps in the research process.
Sample size
For the reasons explained above, qualitative research does not require specific sample sizes, nor does it require that the sample size be determined a priori [ 1 , 14 , 27 , 37 – 39 ]. Sample size can only be a useful quality indicator when related to the research purpose, the chosen methodology and the composition of the sample, i.e. who was included and why.
Randomisation
While some authors argue that randomisation can be used in qualitative research, this is not commonly the case, as neither its feasibility nor its necessity or usefulness has been convincingly established for qualitative research [ 13 , 27 ]. Relevant disadvantages include the negative impact of a too large sample size as well as the possibility (or probability) of selecting “ quiet, uncooperative or inarticulate individuals ” [ 17 ]. Qualitative studies do not use control groups, either.
Interrater reliability, variability and other “objectivity checks”
The concept of “interrater reliability” is sometimes used in qualitative research to assess to which extent the coding approach overlaps between the two co-coders. However, it is not clear what this measure tells us about the quality of the analysis [ 23 ]. This means that these scores can be included in qualitative research reports, preferably with some additional information on what the score means for the analysis, but it is not a requirement. Relatedly, it is not relevant for the quality or “objectivity” of qualitative research to separate those who recruited the study participants and collected and analysed the data. Experiences even show that it might be better to have the same person or team perform all of these tasks [ 20 ]. First, when researchers introduce themselves during recruitment this can enhance trust when the interview takes place days or weeks later with the same researcher. Second, when the audio-recording is transcribed for analysis, the researcher conducting the interviews will usually remember the interviewee and the specific interview situation during data analysis. This might be helpful in providing additional context information for interpretation of data, e.g. on whether something might have been meant as a joke [ 18 ].
Not being quantitative research
Being qualitative research instead of quantitative research should not be used as an assessment criterion if it is used irrespectively of the research problem at hand. Similarly, qualitative research should not be required to be combined with quantitative research per se – unless mixed methods research is judged as inherently better than single-method research. In this case, the same criterion should be applied for quantitative studies without a qualitative component.
The main take-away points of this paper are summarised in Table Table1. 1 . We aimed to show that, if conducted well, qualitative research can answer specific research questions that cannot to be adequately answered using (only) quantitative designs. Seeing qualitative and quantitative methods as equal will help us become more aware and critical of the “fit” between the research problem and our chosen methods: I can conduct an RCT to determine the reasons for transportation delays of acute stroke patients – but should I? It also provides us with a greater range of tools to tackle a greater range of research problems more appropriately and successfully, filling in the blind spots on one half of the methodological spectrum to better address the whole complexity of neurological research and practice.
Take-away-points
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations, authors’ contributions.
LB drafted the manuscript; WW and CG revised the manuscript; all authors approved the final versions.
no external funding.
Availability of data and materials
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
How to Do Market Research: The Complete Guide
Learn how to do market research with this step-by-step guide, complete with templates, tools and real-world examples.
Access best-in-class company data
Get trusted first-party funding data, revenue data and firmographics
What are your customers’ needs? How does your product compare to the competition? What are the emerging trends and opportunities in your industry? If these questions keep you up at night, it’s time to conduct market research.
Market research plays a pivotal role in your ability to stay competitive and relevant, helping you anticipate shifts in consumer behavior and industry dynamics. It involves gathering these insights using a wide range of techniques, from surveys and interviews to data analysis and observational studies.
In this guide, we’ll explore why market research is crucial, the various types of market research, the methods used in data collection, and how to effectively conduct market research to drive informed decision-making and success.
What is market research?
Market research is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing and interpreting information about a specific market or industry. The purpose of market research is to offer valuable insight into the preferences and behaviors of your target audience, and anticipate shifts in market trends and the competitive landscape. This information helps you make data-driven decisions, develop effective strategies for your business, and maximize your chances of long-term growth.

Why is market research important?
By understanding the significance of market research, you can make sure you’re asking the right questions and using the process to your advantage. Some of the benefits of market research include:
- Informed decision-making: Market research provides you with the data and insights you need to make smart decisions for your business. It helps you identify opportunities, assess risks and tailor your strategies to meet the demands of the market. Without market research, decisions are often based on assumptions or guesswork, leading to costly mistakes.
- Customer-centric approach: A cornerstone of market research involves developing a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences. This gives you valuable insights into your target audience, helping you develop products, services and marketing campaigns that resonate with your customers.
- Competitive advantage: By conducting market research, you’ll gain a competitive edge. You’ll be able to identify gaps in the market, analyze competitor strengths and weaknesses, and position your business strategically. This enables you to create unique value propositions, differentiate yourself from competitors, and seize opportunities that others may overlook.
- Risk mitigation: Market research helps you anticipate market shifts and potential challenges. By identifying threats early, you can proactively adjust their strategies to mitigate risks and respond effectively to changing circumstances. This proactive approach is particularly valuable in volatile industries.
- Resource optimization: Conducting market research allows organizations to allocate their time, money and resources more efficiently. It ensures that investments are made in areas with the highest potential return on investment, reducing wasted resources and improving overall business performance.
- Adaptation to market trends: Markets evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancements, cultural shifts and changing consumer attitudes. Market research ensures that you stay ahead of these trends and adapt your offerings accordingly so you can avoid becoming obsolete.
As you can see, market research empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions, cater to customer needs, outperform competitors, mitigate risks, optimize resources and stay agile in a dynamic marketplace. These benefits make it a huge industry; the global market research services market is expected to grow from $76.37 billion in 2021 to $108.57 billion in 2026 . Now, let’s dig into the different types of market research that can help you achieve these benefits.
Types of market research
- Qualitative research
- Quantitative research
- Exploratory research
- Descriptive research
- Causal research
- Cross-sectional research
- Longitudinal research
Despite its advantages, 23% of organizations don’t have a clear market research strategy. Part of developing a strategy involves choosing the right type of market research for your business goals. The most commonly used approaches include:
1. Qualitative research
Qualitative research focuses on understanding the underlying motivations, attitudes and perceptions of individuals or groups. It is typically conducted through techniques like in-depth interviews, focus groups and content analysis — methods we’ll discuss further in the sections below. Qualitative research provides rich, nuanced insights that can inform product development, marketing strategies and brand positioning.
2. Quantitative research
Quantitative research, in contrast to qualitative research, involves the collection and analysis of numerical data, often through surveys, experiments and structured questionnaires. This approach allows for statistical analysis and the measurement of trends, making it suitable for large-scale market studies and hypothesis testing. While it’s worthwhile using a mix of qualitative and quantitative research, most businesses prioritize the latter because it is scientific, measurable and easily replicated across different experiments.
3. Exploratory research
Whether you’re conducting qualitative or quantitative research or a mix of both, exploratory research is often the first step. Its primary goal is to help you understand a market or problem so you can gain insights and identify potential issues or opportunities. This type of market research is less structured and is typically conducted through open-ended interviews, focus groups or secondary data analysis. Exploratory research is valuable when entering new markets or exploring new product ideas.
4. Descriptive research
As its name implies, descriptive research seeks to describe a market, population or phenomenon in detail. It involves collecting and summarizing data to answer questions about audience demographics and behaviors, market size, and current trends. Surveys, observational studies and content analysis are common methods used in descriptive research.
5. Causal research
Causal research aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It investigates whether changes in one variable result in changes in another. Experimental designs, A/B testing and regression analysis are common causal research methods. This sheds light on how specific marketing strategies or product changes impact consumer behavior.
6. Cross-sectional research
Cross-sectional market research involves collecting data from a sample of the population at a single point in time. It is used to analyze differences, relationships or trends among various groups within a population. Cross-sectional studies are helpful for market segmentation, identifying target audiences and assessing market trends at a specific moment.
7. Longitudinal research
Longitudinal research, in contrast to cross-sectional research, collects data from the same subjects over an extended period. This allows for the analysis of trends, changes and developments over time. Longitudinal studies are useful for tracking long-term developments in consumer preferences, brand loyalty and market dynamics.
Each type of market research has its strengths and weaknesses, and the method you choose depends on your specific research goals and the depth of understanding you’re aiming to achieve. In the following sections, we’ll delve into primary and secondary research approaches and specific research methods.
Primary vs. secondary market research
Market research of all types can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: primary research and secondary research. By understanding the differences between these approaches, you can better determine the most appropriate research method for your specific goals.
Primary market research
Primary research involves the collection of original data straight from the source. Typically, this involves communicating directly with your target audience — through surveys, interviews, focus groups and more — to gather information. Here are some key attributes of primary market research:
- Customized data: Primary research provides data that is tailored to your research needs. You design a custom research study and gather information specific to your goals.
- Up-to-date insights: Because primary research involves communicating with customers, the data you collect reflects the most current market conditions and consumer behaviors.
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive: Despite its advantages, primary research can be labor-intensive and costly, especially when dealing with large sample sizes or complex study designs. Whether you hire a market research consultant, agency or use an in-house team, primary research studies consume a large amount of resources and time.
Secondary market research
Secondary research, on the other hand, involves analyzing data that has already been compiled by third-party sources, such as online research tools, databases, news sites, industry reports and academic studies.

Here are the main characteristics of secondary market research:
- Cost-effective: Secondary research is generally more cost-effective than primary research since it doesn’t require building a research plan from scratch. You and your team can look at databases, websites and publications on an ongoing basis, without needing to design a custom experiment or hire a consultant.
- Leverages multiple sources: Data tools and software extract data from multiple places across the web, and then consolidate that information within a single platform. This means you’ll get a greater amount of data and a wider scope from secondary research.
- Quick to access: You can access a wide range of information rapidly — often in seconds — if you’re using online research tools and databases. Because of this, you can act on insights sooner, rather than taking the time to develop an experiment.
So, when should you use primary vs. secondary research? In practice, many market research projects incorporate both primary and secondary research to take advantage of the strengths of each approach.
One rule of thumb is to focus on secondary research to obtain background information, market trends or industry benchmarks. It is especially valuable for conducting preliminary research, competitor analysis, or when time and budget constraints are tight. Then, if you still have knowledge gaps or need to answer specific questions unique to your business model, use primary research to create a custom experiment.
Market research methods
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Online research tools
- Experiments
- Content analysis
- Ethnographic research
How do primary and secondary research approaches translate into specific research methods? Let’s take a look at the different ways you can gather data:
1. Surveys and questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are popular methods for collecting structured data from a large number of respondents. They involve a set of predetermined questions that participants answer. Surveys can be conducted through various channels, including online tools, telephone interviews and in-person or online questionnaires. They are useful for gathering quantitative data and assessing customer demographics, opinions, preferences and needs. On average, customer surveys have a 33% response rate , so keep that in mind as you consider your sample size.
2. Interviews
Interviews are in-depth conversations with individuals or groups to gather qualitative insights. They can be structured (with predefined questions) or unstructured (with open-ended discussions). Interviews are valuable for exploring complex topics, uncovering motivations and obtaining detailed feedback.
3. Focus groups
The most common primary research methods are in-depth webcam interviews and focus groups. Focus groups are a small gathering of participants who discuss a specific topic or product under the guidance of a moderator. These discussions are valuable for primary market research because they reveal insights into consumer attitudes, perceptions and emotions. Focus groups are especially useful for idea generation, concept testing and understanding group dynamics within your target audience.
4. Observational research
Observational research involves observing and recording participant behavior in a natural setting. This method is particularly valuable when studying consumer behavior in physical spaces, such as retail stores or public places. In some types of observational research, participants are aware you’re watching them; in other cases, you discreetly watch consumers without their knowledge, as they use your product. Either way, observational research provides firsthand insights into how people interact with products or environments.
5. Online research tools
You and your team can do your own secondary market research using online tools. These tools include data prospecting platforms and databases, as well as online surveys, social media listening, web analytics and sentiment analysis platforms. They help you gather data from online sources, monitor industry trends, track competitors, understand consumer preferences and keep tabs on online behavior. We’ll talk more about choosing the right market research tools in the sections that follow.
6. Experiments
Market research experiments are controlled tests of variables to determine causal relationships. While experiments are often associated with scientific research, they are also used in market research to assess the impact of specific marketing strategies, product features, or pricing and packaging changes.
7. Content analysis
Content analysis involves the systematic examination of textual, visual or audio content to identify patterns, themes and trends. It’s commonly applied to customer reviews, social media posts and other forms of online content to analyze consumer opinions and sentiments.
8. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research immerses researchers into the daily lives of consumers to understand their behavior and culture. This method is particularly valuable when studying niche markets or exploring the cultural context of consumer choices.
How to do market research
- Set clear objectives
- Identify your target audience
- Choose your research methods
- Use the right market research tools
- Collect data
- Analyze data
- Interpret your findings
- Identify opportunities and challenges
- Make informed business decisions
- Monitor and adapt
Now that you have gained insights into the various market research methods at your disposal, let’s delve into the practical aspects of how to conduct market research effectively. Here’s a quick step-by-step overview, from defining objectives to monitoring market shifts.
1. Set clear objectives
When you set clear and specific goals, you’re essentially creating a compass to guide your research questions and methodology. Start by precisely defining what you want to achieve. Are you launching a new product and want to understand its viability in the market? Are you evaluating customer satisfaction with a product redesign?
Start by creating SMART goals — objectives that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. Not only will this clarify your research focus from the outset, but it will also help you track progress and benchmark your success throughout the process.
You should also consult with key stakeholders and team members to ensure alignment on your research objectives before diving into data collecting. This will help you gain diverse perspectives and insights that will shape your research approach.
2. Identify your target audience
Next, you’ll need to pinpoint your target audience to determine who should be included in your research. Begin by creating detailed buyer personas or stakeholder profiles. Consider demographic factors like age, gender, income and location, but also delve into psychographics, such as interests, values and pain points.
The more specific your target audience, the more accurate and actionable your research will be. Additionally, segment your audience if your research objectives involve studying different groups, such as current customers and potential leads.
If you already have existing customers, you can also hold conversations with them to better understand your target market. From there, you can refine your buyer personas and tailor your research methods accordingly.
3. Choose your research methods
Selecting the right research methods is crucial for gathering high-quality data. Start by considering the nature of your research objectives. If you’re exploring consumer preferences, surveys and interviews can provide valuable insights. For in-depth understanding, focus groups or observational research might be suitable. Consider using a mix of quantitative and qualitative methods to gain a well-rounded perspective.
You’ll also need to consider your budget. Think about what you can realistically achieve using the time and resources available to you. If you have a fairly generous budget, you may want to try a mix of primary and secondary research approaches. If you’re doing market research for a startup , on the other hand, chances are your budget is somewhat limited. If that’s the case, try addressing your goals with secondary research tools before investing time and effort in a primary research study.
4. Use the right market research tools
Whether you’re conducting primary or secondary research, you’ll need to choose the right tools. These can help you do anything from sending surveys to customers to monitoring trends and analyzing data. Here are some examples of popular market research tools:
- Market research software: Crunchbase is a platform that provides best-in-class company data, making it valuable for market research on growing companies and industries. You can use Crunchbase to access trusted, first-party funding data, revenue data, news and firmographics, enabling you to monitor industry trends and understand customer needs.
- Survey and questionnaire tools: SurveyMonkey is a widely used online survey platform that allows you to create, distribute and analyze surveys. Google Forms is a free tool that lets you create surveys and collect responses through Google Drive.
- Data analysis software: Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets are useful for conducting statistical analyses. SPSS is a powerful statistical analysis software used for data processing, analysis and reporting.
- Social listening tools: Brandwatch is a social listening and analytics platform that helps you monitor social media conversations, track sentiment and analyze trends. Mention is a media monitoring tool that allows you to track mentions of your brand, competitors and keywords across various online sources.
- Data visualization platforms: Tableau is a data visualization tool that helps you create interactive and shareable dashboards and reports. Power BI by Microsoft is a business analytics tool for creating interactive visualizations and reports.
5. Collect data
There’s an infinite amount of data you could be collecting using these tools, so you’ll need to be intentional about going after the data that aligns with your research goals. Implement your chosen research methods, whether it’s distributing surveys, conducting interviews or pulling from secondary research platforms. Pay close attention to data quality and accuracy, and stick to a standardized process to streamline data capture and reduce errors.
6. Analyze data
Once data is collected, you’ll need to analyze it systematically. Use statistical software or analysis tools to identify patterns, trends and correlations. For qualitative data, employ thematic analysis to extract common themes and insights. Visualize your findings with charts, graphs and tables to make complex data more understandable.
If you’re not proficient in data analysis, consider outsourcing or collaborating with a data analyst who can assist in processing and interpreting your data accurately.

7. Interpret your findings
Interpreting your market research findings involves understanding what the data means in the context of your objectives. Are there significant trends that uncover the answers to your initial research questions? Consider the implications of your findings on your business strategy. It’s essential to move beyond raw data and extract actionable insights that inform decision-making.
Hold a cross-functional meeting or workshop with relevant team members to collectively interpret the findings. Different perspectives can lead to more comprehensive insights and innovative solutions.
8. Identify opportunities and challenges
Use your research findings to identify potential growth opportunities and challenges within your market. What segments of your audience are underserved or overlooked? Are there emerging trends you can capitalize on? Conversely, what obstacles or competitors could hinder your progress?
Lay out this information in a clear and organized way by conducting a SWOT analysis, which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Jot down notes for each of these areas to provide a structured overview of gaps and hurdles in the market.
9. Make informed business decisions
Market research is only valuable if it leads to informed decisions for your company. Based on your insights, devise actionable strategies and initiatives that align with your research objectives. Whether it’s refining your product, targeting new customer segments or adjusting pricing, ensure your decisions are rooted in the data.
At this point, it’s also crucial to keep your team aligned and accountable. Create an action plan that outlines specific steps, responsibilities and timelines for implementing the recommendations derived from your research.
10. Monitor and adapt
Market research isn’t a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing process. Continuously monitor market conditions, customer behaviors and industry trends. Set up mechanisms to collect real-time data and feedback. As you gather new information, be prepared to adapt your strategies and tactics accordingly. Regularly revisiting your research ensures your business remains agile and reflects changing market dynamics and consumer preferences.
Online market research sources
As you go through the steps above, you’ll want to turn to trusted, reputable sources to gather your data. Here’s a list to get you started:
- Crunchbase: As mentioned above, Crunchbase is an online platform with an extensive dataset, allowing you to access in-depth insights on market trends, consumer behavior and competitive analysis. You can also customize your search options to tailor your research to specific industries, geographic regions or customer personas.
- Academic databases: Academic databases, such as ProQuest and JSTOR , are treasure troves of scholarly research papers, studies and academic journals. They offer in-depth analyses of various subjects, including market trends, consumer preferences and industry-specific insights. Researchers can access a wealth of peer-reviewed publications to gain a deeper understanding of their research topics.
- Government and NGO databases: Government agencies, nongovernmental organizations and other institutions frequently maintain databases containing valuable economic, demographic and industry-related data. These sources offer credible statistics and reports on a wide range of topics, making them essential for market researchers. Examples include the U.S. Census Bureau , the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the Pew Research Center .
- Industry reports: Industry reports and market studies are comprehensive documents prepared by research firms, industry associations and consulting companies. They provide in-depth insights into specific markets, including market size, trends, competitive analysis and consumer behavior. You can find this information by looking at relevant industry association databases; examples include the American Marketing Association and the National Retail Federation .
- Social media and online communities: Social media platforms like LinkedIn or Twitter (X) , forums such as Reddit and Quora , and review platforms such as G2 can provide real-time insights into consumer sentiment, opinions and trends.
Market research examples
At this point, you have market research tools and data sources — but how do you act on the data you gather? Let’s go over some real-world examples that illustrate the practical application of market research across various industries. These examples showcase how market research can lead to smart decision-making and successful business decisions.
Example 1: Apple’s iPhone launch
Apple ’s iconic iPhone launch in 2007 serves as a prime example of market research driving product innovation in tech. Before the iPhone’s release, Apple conducted extensive market research to understand consumer preferences, pain points and unmet needs in the mobile phone industry. This research led to the development of a touchscreen smartphone with a user-friendly interface, addressing consumer demands for a more intuitive and versatile device. The result was a revolutionary product that disrupted the market and redefined the smartphone industry.
Example 2: McDonald’s global expansion
McDonald’s successful global expansion strategy demonstrates the importance of market research when expanding into new territories. Before entering a new market, McDonald’s conducts thorough research to understand local tastes, preferences and cultural nuances. This research informs menu customization, marketing strategies and store design. For instance, in India, McDonald’s offers a menu tailored to local preferences, including vegetarian options. This market-specific approach has enabled McDonald’s to adapt and thrive in diverse global markets.
Example 3: Organic and sustainable farming
The shift toward organic and sustainable farming practices in the food industry is driven by market research that indicates increased consumer demand for healthier and environmentally friendly food options. As a result, food producers and retailers invest in sustainable sourcing and organic product lines — such as with these sustainable seafood startups — to align with this shift in consumer values.
The bottom line? Market research has multiple use cases and is a critical practice for any industry. Whether it’s launching groundbreaking products, entering new markets or responding to changing consumer preferences, you can use market research to shape successful strategies and outcomes.
Market research templates
You finally have a strong understanding of how to do market research and apply it in the real world. Before we wrap up, here are some market research templates that you can use as a starting point for your projects:
- Smartsheet competitive analysis templates : These spreadsheets can serve as a framework for gathering information about the competitive landscape and obtaining valuable lessons to apply to your business strategy.
- SurveyMonkey product survey template : Customize the questions on this survey based on what you want to learn from your target customers.
- HubSpot templates : HubSpot offers a wide range of free templates you can use for market research, business planning and more.
- SCORE templates : SCORE is a nonprofit organization that provides templates for business plans, market analysis and financial projections.
- SBA.gov : The U.S. Small Business Administration offers templates for every aspect of your business, including market research, and is particularly valuable for new startups.
Strengthen your business with market research
When conducted effectively, market research is like a guiding star. Equipped with the right tools and techniques, you can uncover valuable insights, stay competitive, foster innovation and navigate the complexities of your industry.
Throughout this guide, we’ve discussed the definition of market research, different research methods, and how to conduct it effectively. We’ve also explored various types of market research and shared practical insights and templates for getting started.
Now, it’s time to start the research process. Trust in data, listen to the market and make informed decisions that guide your company toward lasting success.
Related Articles

- Entrepreneurs
- 15 min read
What Is Competitive Analysis and How to Do It Effectively
Rebecca Strehlow, Copywriter at Crunchbase
17 Best Sales Intelligence Tools for 2024

- Market research
- 10 min read
How to Do Market Research for a Startup: Tips for Success
Jaclyn Robinson, Senior Manager of Content Marketing at Crunchbase
Search less. Close more.
Grow your revenue with Crunchbase, the all-in-one prospecting solution. Start your free trial.
Implementation research: what it is and how to do it
Affiliation.
- 1 Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health, Department of International Health, 615 N Wolfe St, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA.
- PMID: 24259324
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.f6753
- Delivery of Health Care / methods*
- Evidence-Based Medicine
- Program Development / methods*
- Translational Research, Biomedical*
Cookie Acceptance Needed
This website would like to use cookies to collect information to improve your browsing experience. Please review our Privacy Statement for more information. Do you accept?
accept deny
College of Sciences and Mathematics Homepage
- Toggle Search
- Find People
COSAM News Articles 2024 05 Virtual lab meetings improve undergraduate research experience and foster diversity in academia
Virtual lab meetings improve undergraduate research experience and foster diversity in academia
Published: 05/29/2024
By: Maria Gebhardt
Moisés A. Bernal , assistant professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at Auburn University, is collaborating with researchers Kathleen Lotterhos (Northeast University), Megan Phifer-Rixey (Drexel University), and Torrance Hanley , (Sacred Heart University) to evaluate the effectiveness of virtual lab meetings in demystifying the hidden curriculum in academia, incentivize primary research among students without previous experience, and foster participation of underrepresented groups in STEM.
The “Biological Practices” article entitled A virtual lab meeting training program mutually benefits mentees and host labs was recently published in Proceedings B, dives into the specific details that are needed to develop a virtual meetings program from scratch, and reports on the experiences by both mentors and mentees. The first step on the NSF-funded Virtual Lab Meeting Program (LaMP) was to match research mentors (i.e. faculty in research intensive institutions) with students in STEM fields (i.e. at institutions with limited research support), Bernal indicated.
“The program matched mentors and mentees based on affinity of research topics, and mentees were provided with a $500 stipend if they participated in at least 10 meetings,” Bernal said. “This is important because the students had an incentive to participate at the meetings and actively exchange ideas with a research lab.”
The team collected data that shared insight of the value of the LaMP experience.
“When we analyzed the data, we saw a gap that exists between the current mentors and the mentees,” he said. “The mentees were a much more diverse group then the mentors.”
The data included racial and sexual diversity among mentees participating. However, the faculty did not exhibit as much diversity, which highlights the need for this type of program among undergraduate and graduate students.
"Our results clearly show that this program worked to extend the professional networks of traditionally under-represented groups in the sciences, with little extra time commitment on the part of the participating labs,” said Lotterhos. “We hope these results will stimulate similar efforts across STEM disciplines."
And those efforts can be easily integrated into a lab.
“For faculty, this is a small-time investment, because we are already conducting regular lab meetings and we can simply bring on a new mentee into this experience” Bernal added. The results from the study show that the mentees learned new information on specific techniques and study systems, while developing a broader network of personal connections in academia. Further, the mentees learned how to discuss and present research as well as how to discuss a manuscript and the overall writing process. Meanwhile, mentors indicated it was beneficial to gain novel perspectives on how to discuss peer-reviewed manuscripts, and gain knowledge on other study systems presented by the mentees. Overall, the survey results indicate that the program was useful for staff and students in the mentor’s lab as well as the mentees, and participants strongly recommend this program to future participants.
Bernal spoke about his time with a virtual student in his lab.
“It was a positive experience because I was able to have someone in my lab with a novel perspective on how to discuss manuscripts and to look at research problems from a new angle” he explained. “This program helps to develop and expand professional networks for participants. It also helps them prepare to apply to graduate school and learn how to build their CVs over time.”
Overall, the LaMP initiative represents an effective way of connecting researchers with students in STEM, while fostering the participation of underrepresented groups in academia.

Latest Headlines
- Auburn alumnus bridges Auburn University and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in DOE's Energy Earthshots Initiative 05/28/2024
- Auburn hosts CBMS Conference: Mathematical Methods for Novel Metamaterials 05/28/2024
- Auburn biologists publish first work on avian migration conducted in the AU MitoMobile 05/21/2024
- 2024 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry awards honor faculty, staff and students 04/27/2024
- Department of Geosciences celebrates Earth Day 04/23/2024
Stay Connected
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Is College Worth It?
1. labor market and economic trends for young adults, table of contents.
- Labor force trends and economic outcomes for young adults
- Economic outcomes for young men
- Economic outcomes for young women
- Wealth trends for households headed by a young adult
- The importance of a four-year college degree
- Getting a high-paying job without a college degree
- Do Americans think their education prepared them for the workplace?
- Is college worth the cost?
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
- Current Population Survey methodology
- Survey of Consumer Finances methodology
A majority of the nation’s 36 million workers ages 25 to 34 have not completed a four-year college degree. In 2023, there were 19 million young workers who had some college or less education, including those who had not finished high school.
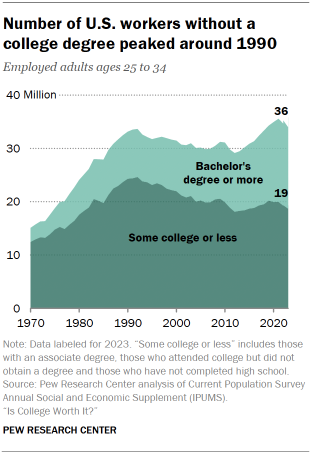
The overall number of employed young adults has grown over the decades as more young women joined the workforce. The number of employed young adults without a college degree peaked around 1990 at 25 million and then started to fall, as more young people began finishing college .
This chapter looks at the following key labor market and economic trends separately for young men and young women by their level of education:
Labor force participation
- Individual earnings
Household income
- Net worth 1
When looking at how young adults are doing in the job market, it generally makes the most sense to analyze men and women separately. They tend to work in different occupations and have different career patterns, and their educational paths have diverged in recent decades.
In 1970, almost all young men whose highest educational attainment was a high school diploma (98%) were in the labor force, meaning they were working or looking for work. By 2013, only 88% of high school-educated young men were in the labor force. Today, that share is 87%.
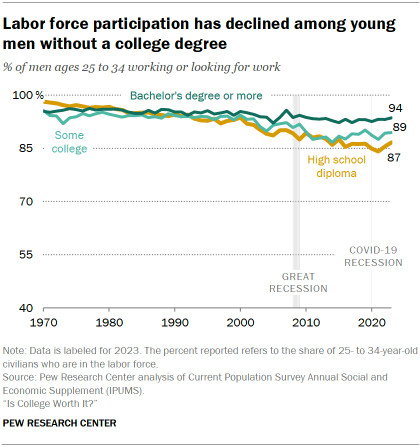
Similarly, 96% of young men whose highest attainment was some college education were in the labor force in 1970. Today, the share is 89%.
By comparison, labor force participation among young men with at least a bachelor’s degree has remained relatively stable these past few decades. Today, 94% of young men with at least a bachelor’s degree are in the labor force.
The long-running decline in the labor force participation of young men without a bachelor’s degree may be due to several factors, including declining wages , the types of jobs available to this group becoming less desirable, rising incarceration rates and the opioid epidemic . 2
Looking at labor force and earnings trends over the past several decades, it’s important to keep in mind broader forces shaping the national job market.
The Great Recession officially ended in June 2009, but the national job market recovered slowly . At the beginning of the Great Recession in the fourth quarter of 2007, the national unemployment rate was 4.6%. Unemployment peaked at 10.4% in the first quarter of 2010. It was not until the fourth quarter of 2016 that unemployment finally returned to its prerecession level (4.5%).
Studies suggest that things started to look up for less-skilled workers around 2014. Among men with less education, hourly earnings began rising in 2014 after a decade of stagnation. Wage growth for low-wage workers also picked up in 2014. The tightening labor markets in the last five years of the expansion after the Great Recession improved the labor market prospects of “vulnerable workers” considerably.
The COVID-19 pandemic interrupted the tight labor market, but the COVID-19 recession and recovery were quite different from the Great Recession in their job market impact. The more recent recession was arguably more severe, as the national unemployment rate reached 12.9% in the second quarter of 2020. But it was short – officially lasting two months, compared with the 18-month Great Recession – and the labor market bounced back much quicker. Unemployment was 3.3% before the COVID-19 recession; three years later, unemployment had once again returned to that level.
Full-time, full-year employment
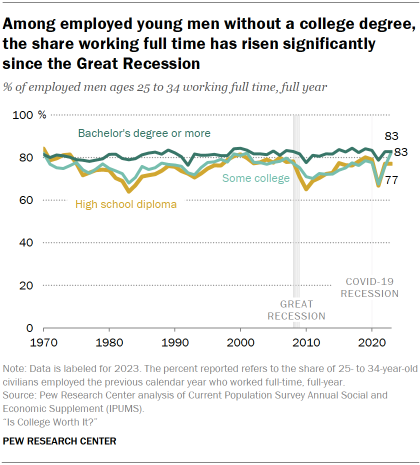
Since the Great Recession of 2007-09, young men without a four-year college degree have seen a significant increase in the average number of hours they work.
- Today, 77% of young workers with a high school education work full time, full year, compared with 69% in 2011.
- 83% of young workers with some college education work full time, full year, compared with 70% in 2011.
The share of young men with a college degree who work full time, year-round has remained fairly steady in recent decades – at about 80% – and hasn’t fluctuated with good or bad economic cycles.
Annual earnings
Annual earnings for young men without a college degree were on a mostly downward path from 1973 until roughly 10 years ago (with the exception of a bump in the late 1990s). 3
Earnings have been increasing modestly over the past decade for these groups.
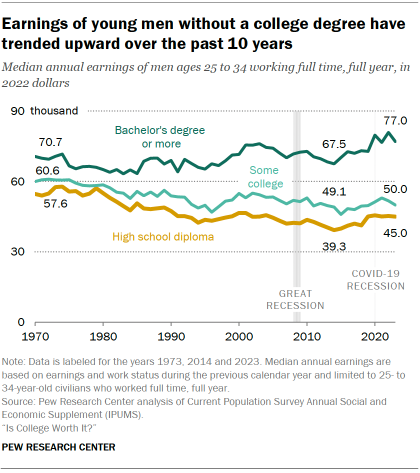
- Young men with a high school education who are working full time, full year have median earnings of $45,000 today, up from $39,300 in 2014. (All figures are in 2022 dollars.)
- The median earnings of young men with some college education who are working full time, full year are $50,000 today, similar to their median earnings in 2014 ($49,100).
It’s important to note that median annual earnings for both groups of noncollege men remain below their 1973 levels.
Median earnings for young men with a four-year college degree have increased over the past 10 years, from $67,500 in 2014 to $77,000 today.
Unlike young men without a college degree, the earnings of college-educated young men are now above what they were in the early 1970s. The gap in median earnings between young men with and without a college degree grew significantly from the late 1970s to 2014. In 1973, the typical young man with a degree earned 23% more than his high school-educated counterpart. By 2014, it was 72% more. Today, that gap stands at 71%. 4
Household income has also trended up for young men in the past 10 years, regardless of educational attainment.
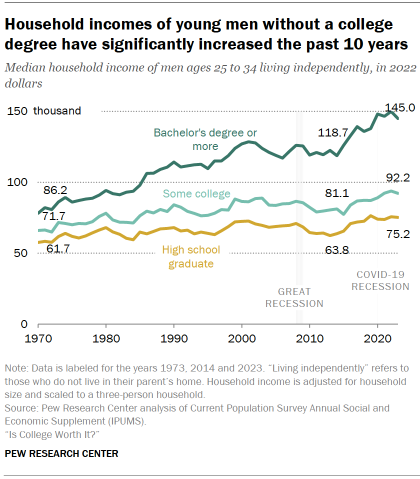
This measure takes into account the contributions of everyone in the household. For this analysis, we excluded young men who are living in their parents’ home (about 20% of 25- to 34-year-old men in 2023).
- The median household income of young men with a high school education is $75,200 today, up from $63,800 in 2014. This is slightly lower than the highpoint reached around 2019.
- The median household income of young men with some college education is $92,200 today, up from $81,100 in 2014. This is close to the 2022 peak of $93,800.
The median household income of young men with at least a bachelor’s degree has also increased from a low point of $118,700 in 2014 after the Great Recession to $145,000 today.
The gap in household income between young men with and without a college degree grew significantly between 1980 and 2014. In 1980, the median household income of young men with at least a bachelor’s degree was about 38% more than that of high school graduates. By 2014, that gap had widened to 86%.
Over the past 10 years, the income gap has fluctuated. In 2023, the typical college graduate’s household income was 93% more than that of the typical high school graduate.
The 2001 recession and Great Recession resulted in a large increase in poverty among young men without a college degree.
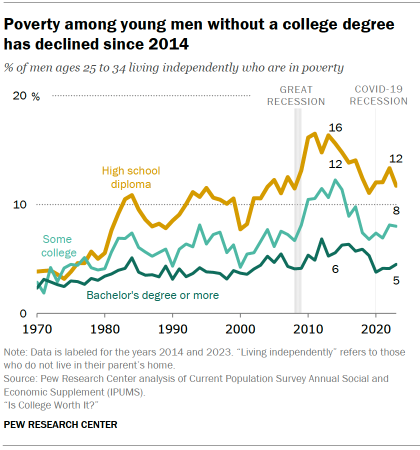
- In 2000, among young men living independently of their parents, 8% of those with a high school education were in poverty. Poverty peaked for this group at 17% around 2011 and has since declined to 12% in 2023.
- Among young men with some college education, poverty peaked at 12% around 2014, up from 4% in 2000. Poverty has fallen for this group since 2014 and stands at 8% as of 2023.
- Young men with a four-year college degree also experienced a slight uptick in poverty during the 2001 recession and Great Recession. In 2014, 6% of young college graduates were in poverty, up from 4% in 2000. Poverty among college graduates stands at 5% in 2023.
Labor force trends for young women are very different than for young men. There are occupational and educational differences between young women and men, and their earnings have followed different patterns.
Unlike the long-running decline for noncollege young men, young women without a college degree saw their labor force participation increase steadily from 1970 to about 1990.
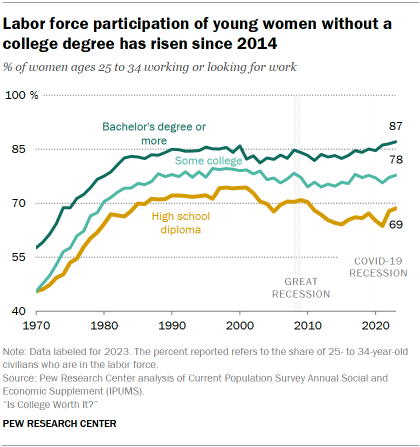
By 2000, about three-quarters of young women with a high school diploma and 79% of those with some college education were in the labor force.
Labor force participation has also trended upward for college-educated young women and has consistently been higher than for those with less education.
After rising for decades, labor force participation for young women without a college degree fell during the 2001 recession and the Great Recession. Their labor force participation has increased slightly since 2014.
As of 2023, 69% of young women with a high school education were in the labor force, as were 78% of young women with some college education. Today’s level of labor force participation for young women without a college degree is slightly lower than the level seen around 2000.
The decline in labor force participation for noncollege women partly reflects the declining labor force participation for mothers with children under 18 years of age . Other research has suggested that without federal paid parental and family leave benefits for parents, some women with less education may leave the labor force after having a baby.
In contrast, labor force participation for young women with a college degree has fully recovered from the recessions of the early 2000s. Today, 87% of college-educated young women are in the labor force, the highest estimate on record.
Young women without a college degree have steadily increased their work hours over the decades. The past 10 years in particular have seen a significant increase in the share of employed noncollege women working full time, full year (with the exception of 2021).
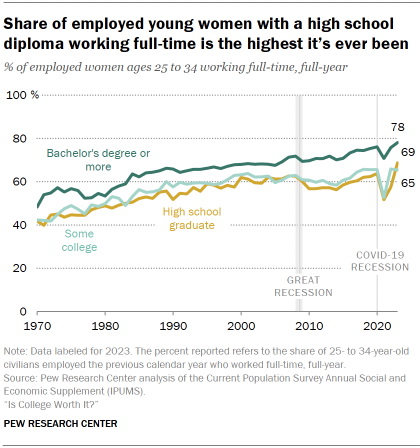
- In 2023, 69% of employed young women with a high school education worked full time, full year, up from 56% in 2014. This share is the highest it’s ever been.
- In 2023, 65% of employed women with some college worked full time, full year, up from 58% in 2014. This is among the highest levels ever.
The trend in the share working full time, full year has been similar for young women with college degrees. By 2023, 78% of these women worked full time, full year, the highest share it’s ever been.
Unlike young men, young women without a college education did not see their earnings fall between 1970 and 2000.
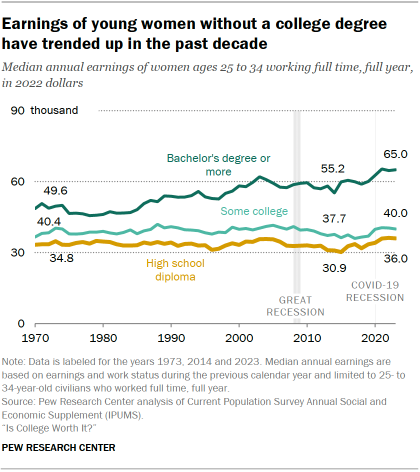
The 2001 recession and Great Recession also did not significantly impact the earnings of noncollege young women. In the past 10 years, their median earnings have trended upward.
- For young women with a high school diploma, median earnings reached $36,000 in 2023, up from $30,900 in 2014.
- For those with some college, median earnings rose to $40,000 in 2023 from $37,700 in 2014.
For young women with a college degree, median earnings rose steadily from the mid-1980s until the early 2000s. By 2003, they reached $62,100, but this declined to $55,200 by 2014. In the past 10 years, the median earnings of college-educated young women have risen, reaching $65,000 in 2023.
In the mid-1980s, the typical young woman with a college degree earned about 48% more than her counterpart with a high school diploma. The pay gap among women has widened since then, and by 2014, the typical college graduate earned 79% more than the typical high school graduate. The gap has changed little over the past 10 years.
Noncollege young women living independently from their parents have experienced large household income gains over the past 10 years, measured at the median.
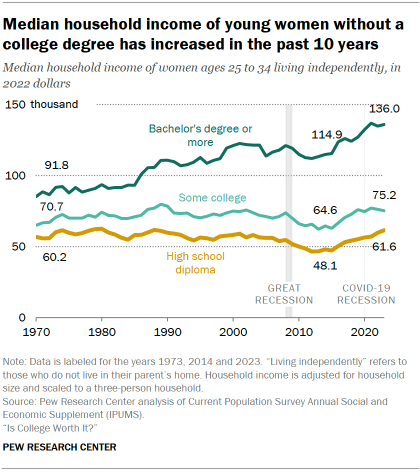
- In 2023, young women with a high school diploma had a median household income of $61,600, up from $48,100 in 2014.
- The pattern is similar for young women with some college education. Their median income rose to $75,200 in 2023 from $64,600 in 2014.
The median household income for young women with a four-year college degree is significantly higher than it is for their counterparts without a degree. College-educated young women have made substantial gains in the past 10 years.
The income gap between young women with and without a college degree has widened over the decades. In 1980, the median household income of young women with a college degree was 50% higher than that of high school-educated women. By 2014, the income gap had grown to 139%. Today, the household income advantage of college-educated women stands at 121% ($136,000 vs. $61,600).
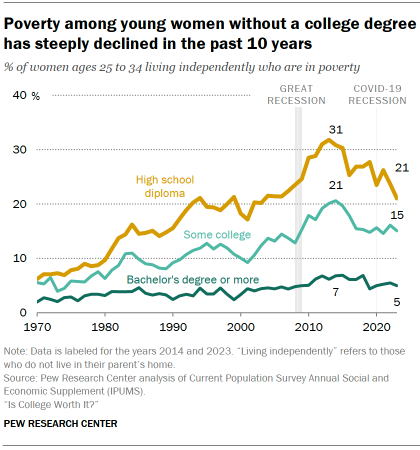
Poverty trends for young women mirror those for young men, although young women are overall more likely to be in poverty than young men. The past 10 years have resulted in a steep reduction in the share of noncollege women in poverty.
- Today, 21% of young women with a high school diploma are living in poverty. This is down from 31% in 2014.
- 15% of young women with some college education live in poverty, compared with 21% in 2014.
- Young women with a college degree are consistently far less likely than either group to be living in poverty (5% in 2023).
Along with young adults’ rising incomes over the past 10 years, there’s been a substantial increase in their wealth. This part of our analysis does not look at men and women separately due to limitations in sample size.
In 2022, households headed by a young high school graduate had a median net worth of $30,700, up from $12,700 in 2013. Those headed by a young adult with some college education had a median net worth of $52,900, up from $15,700 in 2013.
The typical wealth level of households headed by a young college graduate was $120,200 in 2022, up from $46,600 in 2013.
There has not been any significant narrowing of the wealth gap between young high school graduate and young college graduate households since 2013.
Wealth increased for Americans across age groups over this period due to several factors. Many were able to save money during the pandemic lockdowns. In addition, home values increased, and the stock market surged.
- Most of the analysis in this chapter is based on the Annual Social and Economic Supplement collected by the U.S. Census Bureau. Information on net worth is based on a Federal Reserve survey, which interviews fewer households. Due to this smaller sample size, the net worth of households headed by a young adult cannot be broken out by gender and education. ↩
- Bureau of Labor Statistics data indicates that the labor force participation rate for men ages 25 to 54 has been declining since 1953. ↩
- This analysis looks at the earnings of employed adults working full time, full year. This measure of earnings is not uncommon. For example, the National Center for Education Statistics publishes a series on the annual earnings of 25- to 34-year-olds working full time, full year. ↩
- Other studies using hourly wages rather than annual earnings find that the college wage premium has narrowed. For example, researchers at the San Francisco Federal Reserve report that the college wage gap peaked in the mid-2010s but declined by just 4 percentage points to about 75% in 2022. ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Business & Workplace
- Economic Conditions
- Higher Education
- Income & Wages
- Recessions & Recoveries
- Student Loans
Half of Latinas Say Hispanic Women’s Situation Has Improved in the Past Decade and Expect More Gains
From businesses and banks to colleges and churches: americans’ views of u.s. institutions, fewer young men are in college, especially at 4-year schools, key facts about u.s. latinos with graduate degrees, private, selective colleges are most likely to use race, ethnicity as a factor in admissions decisions, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

I want to keep my child safe from abuse − but research tells me I’m doing it wrong
Founder and Executive Director, Center for Violence Prevention Research; Affiliate Faculty with the Crimes Against Children Research Center, University of New Hampshire
Disclosure statement
Melissa Bright receives funding from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Childhood Foundation (via work with Stop it Now!).
View all partners
Child sexual abuse is uncomfortable to think about, much less talk about. The idea of an adult engaging in sexual behaviors with a child feels sickening. It’s easiest to believe that it rarely happens, and when it does, that it’s only to children whose parents aren’t protecting them.
This belief stayed with me during my early days as a parent. I kept an eye out for creepy men at the playground and was skeptical of men who worked with young children, such as teachers and coaches. When my kids were old enough, I taught them what a “good touch” was, like a hug from a family member, and what a “bad touch” was, like someone touching their private parts.
But after nearly a quarter-century of conducting research – 15 years on family violence, another eight on child abuse prevention, including sexual abuse – I realized that many people, including me, were using antiquated strategies to protect our children .
As the founder of the Center for Violence Prevention Research , I work with organizations that educate their communities and provide direct services to survivors of child sexual abuse. From them, I have learned much about the everyday actions all of us can take to help keep our children safe. Some of it may surprise you.
Wrong assumptions
First, my view of what constitutes child sexual abuse was too narrow. Certainly, all sexual activities between adults and children are a form of abuse.
But child sexual abuse also includes nonconsensual sexual contact between two children. It includes noncontact offenses such as sexual harassment, exhibitionism and using children to produce imagery of sexual abuse. Technology-based child sexual abuse is rising quickly with the rapid evolution of internet-based games, social media, and content generated by artificial intelligence. Reports to the National Center for Missing & Exploited Children of online enticements increased 300% from 2021 to 2023 .
My assumption that child sexual abuse didn’t happen in my community was wrong too. The latest data shows that at least 1 in 10 children, but likely closer to 1 in 5, experience sexual abuse . Statistically, that’s at least two children in my son’s kindergarten class.
Child sexual abuse happens across all ethnoracial groups, socioeconomic statuses and all gender identities. Reports of female victims outnumber males , but male victimization is likely underreported because of stigma and cultural norms about masculinity .
I’ve learned that identifying the “creepy man” at the playground is not an effective strategy. At least 90% of child sexual abusers know their victims or the victims’ family prior to offending. Usually, the abuser is a trusted member of the community; sometimes, it’s a family member .
In other words, rather than search for a predator in the park, parents need to look at the circle of people they invite into their home.
To be clear, abuse by strangers does happen, and teaching our kids to be wary of strangers is necessary. But it’s the exception, not the norm , for child sexual abuse offenses.
Most of the time, it’s not even adults causing the harm. The latest data shows more than 70% of self-reported child sexual abuse is committed by other juveniles . Nearly 1 in 10 young people say they caused some type of sexual harm to another child . Their average age at the time of causing harm is between 14 and 16.
Now for a bit of good news: The belief that people who sexually abuse children are innately evil is an oversimplification. In reality, only about 13% of adults and approximately 5% of adolescents who sexually harm children commit another sexual offense after five years . The recidivism rate is even lower for those who receive therapeutic help .
By contrast, approximately 44% of adults who commit a felony of any kind will commit another offense within a year of prison release .
What parents can do
The latest research says uncomfortable conversations are necessary to keep kids safe. Here are some recommended strategies:
Avoid confusing language. “Good touches” and “bad touches” are no longer appropriate descriptors of abuse . Harmful touches can feel physically good, rather than painful or “bad.” Abusers can also manipulate children to believe their touches are acts of love.
The research shows that it’s better to talk to children about touches that are “OK” or “not OK,” based on who does the touching and where they touch. This dissipates the confusion of something being bad but feeling good.
These conversations require clear identification of all body parts, from head and shoulders to penis and vagina. Using accurate anatomical labels teaches children that all body parts can be discussed openly with safe adults. Also, when children use accurate labels to disclose abuse, they are more likely to be understood and believed.
Encourage bodily autonomy. Telling my children that hugs from family members were universally good touches was also wrong . If children think they have to give hugs on demand, it conveys the message they do not have authority over their body.
Instead, I watch when my child is asked for a hug at family gatherings – if he hesitates, I advocate for him. I tell family members that physical touch is not mandatory and explain why – something like: “He prefers a bit more personal space, and we’re working on teaching him that he can decide who touches him and when. He really likes to give high-fives to show affection.” A heads-up: Often, the adults are put off, at least initially.
In my family, we also don’t allow the use of guilt to encourage affection. That includes phrases like: “You’ll make me sad if you don’t give me a hug.”
Promote empowerment. Research on adult sexual offenders found the greatest deterrence to completing the act was a vocal child – one who expressed their desire to stop, or said they would tell others.
Monitor your child’s social media. Multiple studies show that monitoring guards against sexting or viewing of pornography , both of which are risk factors for child sexual abuse. Monitoring can also reveal permissive or dangerous sexual attitudes the child might have.
Talk to the adults in your circle. Ask those watching your child how they plan to keep your child safe when in their care. Admittedly, this can be an awkward conversation. I might say, “Hey, I have a few questions that might sound weird, but I think they’re important for parents to ask. I’m sure my child will be safe with you, but I’m trying to talk about these things regularly, so this is good practice for me.” You may need to educate them on what the research shows.
Ask your child’s school what they’re doing to educate students and staff about child sexual abuse. Many states require schools to provide prevention education; recent research suggests these programs help children protect themselves from sexual abuse .
Talk to your child’s sports or activity organization. Ask what procedures are in place to keep children safe . This includes their screening and hiring practices, how they train and educate staff, and their guidelines for reporting abuse. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides a guide for organizations on keeping children safe .
Rely on updated research. Finally, when searching online for information, look for research that’s relatively recent – dated within the past five years. These studies should be published in peer-reviewed journals .
And then be prepared for a jolt. You may discover the conventional wisdom you’ve clung to all these years may be based on outdated – and even harmful – information.
- Child sexual abuse
- Child sexual abuse prevention
- Child safety

Head, School of Psychology

Lecturer In Arabic Studies - Teaching Specialist

Senior Research Fellow - Women's Health Services

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship
The world’s benchmark climate monitoring station passes a major milestone
- May 20, 2024
- Download Cover Image
On May 17, 1974, staff of the new National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration’s Geophysical Monitoring for Climatic Change program took their first atmospheric measurements for what would become one of the most scientifically significant records of humanity’s impact on Earth’s climate.
Since then, NOAA’s Global Monitoring Laboratory’s continuous measurements of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) at the Mauna Loa Observatory have contributed to the longest modern datasets of this important greenhouse gas. NOAA’s daily measurements provide independent observations that complement measurements taken by the University of California San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography, which started sampling in 1958. The sustained, collaborative effort has helped educate scientists and the public about the relentless rise of CO 2 caused primarily by fossil fuel pollution.
The concentration of carbon dioxide, or CO 2 , in that first sample was 333.46 parts per million (ppm). This month, as the annual CO 2 cycle peaks, concentrations have been averaging 427 ppm, more than 90 ppm above the 1974 level.
“The long-term measurements at Mauna Loa have given us an accurate and unmistakable record of humans’ impact on the only atmosphere we have,” said Vanda Grubišić, director of the Global Monitoring Laboratory (GML).
This graph shows the full record of monthly mean carbon dioxide measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, by NOAA and the Scripps Institution of Oceanography. Credit: NOAA Global Monitoring Laboratory
Perched high on the barren slopes of the Mauna Loa volcano in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, the observatory protrudes through the strong marine boundary layer temperature inversion that separates the more polluted lower portions of the atmosphere from the much cleaner free troposphere. The 11,135-foot elevation above sea level is ideal for sampling well-mixed air undisturbed by the influence of local pollution sources or vegetation, producing measurements that represent the average state of the atmosphere in the northern hemisphere.
The characteristics that make the site ideal for measuring CO 2 also provide ideal conditions for a wide variety of other atmospheric research efforts. The observatory’s 10 buildings house instruments that collected up to 250 climatological measurements for NOAA and partner agency scientists and engineers every day before the eruption of the volcano cut off access to the site in November 2022.
In the beginning
The Mauna Loa Observatory was established by the U.S. Weather Bureau , the precursor to NOAA’s National Weather Service, on June 28th, 1956, but not to monitor climate. Instead, scientists made routine weather observations and studied atmospheric circulation. They also made observations of solar radiation, cosmic radiation, fallout from atomic tests, snow crystals, meteors, the Sun’s corona, even the atmosphere of Mars.
Charles David Keeling was the first to observe that CO 2 levels rose and fell every year in concert with the seasons, a dynamic which is now known as the Keeling Curve . The highest monthly mean CO 2 value of the year occurs in May, just before plants in the northern hemisphere start to remove large amounts of CO 2 from the atmosphere during the growing season. In the northern fall, winter, and early spring, plants and soils give off CO 2, causing levels to rise through May.
Keeling was also the first to recognize that despite the seasonal fluctuation, average CO 2 levels were increasing every year. Not only has that trend continued, but the rate of the annual increase has also risen – sharply – in recent decades. (Keeling’s son, geochemist Ralph Keeling, runs the Scripps program at Mauna Loa.)

This aerial photograph shows the dominant fissure erupting on the Northeast Rift Zone of Mauna Loa, taken at approximately 8 a.m. Hawaii Standard Time on November 29, 2022. Lava fountains were up to 25 m (82 ft) that morning as the vent was feeding the main lava flow to the northeast. Credit: M. Patrick/USGS photo
The volcano awakes
On Nov. 27, 2022, lava flows from the erupting Mauna Loa volcano buried more than a mile of the access road and destroyed power poles, temporarily interrupting all scientific activity at the observatory. NOAA and Scripps scientists were able to quickly set up alternative sampling sites for some measurements, including CO 2 , at Maunakea.
In 2023, MLO staff visiting the site once a week via helicopter restored limited power to four key observatory buildings by augmenting existing solar generation and adding battery systems. Approximately 33 percent of the atmospheric measurements on the mountain site have been restored, including consistent measurements for greenhouse gases, halocarbons and trace gases, ozone, aerosols and global radiation. Reconstruction of the access road to the observatory is anticipated in 2025.
The Mauna Loa Observatory is one of four NOAA atmospheric baseline observatories strategically situated from the Arctic to the South Pole, each of which collects numerous daily in situ and remote atmospheric and solar measurements. Continuous measurements of atmospheric CO 2 at the Barrow Observatory near the village of Utqiaġvik, Alaska began in July 1973, at the South Pole Atmospheric Research Observatory in January 1975, and at the American Samoa Atmospheric Baseline Observatory in January 1976.
To explore more information about the CO 2 record at Mauna Loa Observatory, visit the GML website’s Trends in CO2 page.
For more information, contact Theo Stein, NOAA Communications: [email protected] .

Perseverance in the North Pacific: picturing a scientist’s life at sea

Measuring pollution levels in the Port of Baltimore after the bridge collapse

In hot water: exploring marine heatwaves

Cascade of extreme events transforming Bering Sea, challenging communities
Popup call to action.
A prompt with more information on your call to action.

Lose Weight with Pasta: Here's How It Works According to Research
When you think about losing weight, pasta probably isn’t the first thing that comes to mind.
However, a Canadian study suggests that enjoying pasta might actually help with weight loss.
Researchers at St. Michael's Hospital in Toronto conducted a study in 2018 to explore the impact of pasta consumption on weight loss, as reported by Freundin .
The study involved 2,500 participants divided into two groups.
Group A ate pasta dishes at least three times a week, while Group B consumed other carbohydrate sources like rice, bread, and potatoes.
The results were unexpected: participants who ate pasta lost more weight than those who ate other carbs.
The study measured factors such as body weight, BMI, waist circumference, and body fat percentage.
Do You Pour Pasta Water Down the Sink? Here's What You Should Do Instead
Breakthrough in Cancer Research: Blood Test Can Predict Cancer Years in Advance
The Pasta Diet Secret
The key to the pasta diet's success lies in combining pasta with vegetables.
Vegetables are low in calories, nutritious, and filling.
When pasta is paired with vegetables, it forms a balanced meal that fits well into a diet plan. For example, adding bell peppers, broccoli, spinach, and fresh tomatoes to a simple tomato sauce makes the dish more nutritious and lower in calories.
Portion control is essential.
We often tend to eat portions that are too large. As a rule of thumb, 100 grams of dry pasta is enough for a main meal.
The choice of sauce also matters: lighter sauces like tomato sauce are much lower in calories compared to heavy cheese sauces with bacon.
Practical Tips
Incorporate Vegetables : Add a variety of vegetables to your pasta dishes to increase their nutritional value.
Watch Portion Sizes : Stick to about 100 grams of dry pasta per meal to avoid overeating.
Choose Light Sauces : Opt for tomato-based sauces instead of creamy or cheese-heavy options to keep the calorie count low.
By following these tips, you can enjoy pasta while still working towards your weight loss goals. The study shows that pasta, when eaten in moderation and paired with healthy ingredients, doesn't have to be off-limits in a weight loss diet.
Got a Wet Phone? This App Clears Water from Speakers
Iconic "Home Alone" House for Sale: Take a Look Inside
F-35 Fighter Jet Crashes Near International Airport

Russian disinformation sites linked to former Florida deputy sheriff, research finds

More than 150 fake local news websites pushing Russian propaganda to U.S. audiences are connected to John Mark Dougan, an American former law enforcement officer living in Moscow, according to a research report published Wednesday by NewsGuard, a firm that monitors misinformation.
The websites, with names like DC Weekly, New York News Daily and Boston Times, look similar to those of legitimate local news outlets and have already succeeded in spreading a number of false stories surrounding the war in Ukraine. Experts warn they could be used to launder disinformation about the 2024 election.
In an interview over WhatsApp, Dougan denied involvement with the websites. “Never heard of them,” he said.
Dougan, a former Marine and police officer, fled his home in Florida in 2016 to evade criminal charges related to a massive doxxing campaign he was accused of launching against public officials and was given asylum by the Russian government. Most recently, Dougan has posed as a journalist in Ukraine’s Donbas region, testifying at Russian public hearings and making frequent appearances on Russian state TV .
He’s now part of a small club of Western expats who have become purveyors of English-language propaganda for Russia. Researchers and cybersecurity companies had previously linked Dougan to the sites. The NewsGuard report published Wednesday is the latest to implicate him in the fake news ring.
Academic research from Clemson University linked Dougan to the network of fake news websites last year after one of them was found to share an IP address with other sites he ran, including his personal website.
In an interview, Darren Linvill, co-director of the Watt Family Innovation Center Media Forensics Hub at Clemson, called Dougan “a tool of the broader Russian disinformation machine” whose websites “are just one of several mechanisms by which these narratives are distributed.”
Linvill noted the fake news websites had lately veered away from the narrow focus of undermining support for Ukraine. Recent fake articles include the false claims that the FBI wiretapped former President Donald Trump’s office at Mar-a-Lago, his estate in Florida, and that the CIA backed a Ukrainian plot to rig the election against Trump.
“There is no question we are beginning to see a shift in focus toward the U.S. election,” Linvill said.
Posing as local news, the sites host articles about crime, politics and sports, most of which seem to have been generated with artificial intelligence tools and are attributed to journalists who do not exist . Interspersed within the general news are articles that disparage the U.S., exalt Russia and spread disinformation about topics from the wars in Ukraine and Gaza to Covid vaccines.
Researchers say sites attributed to Dougan are marred with telltale signs of his signature, including early website registration records, IP addresses, similar image headers and layouts, being built with WordPress software, seemingly AI-generated prompts mistakenly left in copy and error messages at the ends of articles.
The reach of the campaigns varies. Some of the sites remained active for just weeks with little to no pickup in the wider media. But some fake news stories have gained traction, including several recent posts using forged documents that falsely claimed Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy was improperly using foreign aid to enrich himself. Last month, a story on the fake news site The London Crier said Zelenskyy had spent 20 million pounds on a mansion previously owned by King Charles III.
It followed a story posted to DC Weekly in November that falsely claimed Zelenskyy had used American aid money to buy two yachts.
Both rumors relied, as the network often does, on videos posted to YouTube by newly created accounts. A site like DC Weekly will publish fake news stories using videos of seemingly AI-generated “leaks” or examples of whistleblowing, and Russian influencers and bot networks will then spread those articles, according to the Clemson researchers. Ultimately, the fake articles are reported as fact by pro-Kremlin media outlets and, in some of the most successful cases, by Western politicos and pundits.
The rumor about Zelenskyy’s buying yachts was later promoted by Republican members of Congress , including Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene of Georgia and Sen. JD Vance of Ohio.
The author of the new report, McKenzie Sadeghi, NewsGuard’s editor, pointed to the network’s sophisticated use of AI to produce content and make narratives seem credible.
“In the wrong hands, this technology can be used to spread disinformation at scale,” Sadeghi said. “With this network, we’re seeing that play out exactly.”
What specific support Dougan receives from Russia is unclear. In May, the cybersecurity company Recorded Future reported a “realistic possibility” that the network receives strategic guidance, support or oversight from the Russian government. In March, The New York Times reported that the fake local news ring “appears to involve remnants” of the Internet Research Agency, the troll factory created by the late Putin associate Yevgeny Prigozhin to influence the 2016 presidential election. Previous reporting on Dougan and his more dubious claims — including that he was in possession of leaked documents from murdered Democratic National Committee staffer Seth Rich and secret tapes belonging to Jeffrey Epstein — suggests Dougan may be pursuing wealth, clout or operating from some other motive in addition to a state-sanctioned political agenda.
Dougan was an early creator of fake websites. After he resigned from his job as a sheriff’s deputy in Palm Beach County, Florida, and was fired months later from a subsequent one in Windham, Maine, over sexual harassment claims , he built a network of websites that focused on what he claimed was widespread corruption in Windham, naming local police and town officials in articles. He also reportedly launched a campaign doxxing thousands of federal agents, judges and law enforcement officers, posting their home addresses and salacious allegations online. By 2015 he was operating several websites with official-sounding names like DCWeekly.com and DCPost.org, which hosted made-up articles. In 2016, he fled to Russia following an FBI raid of his home to evade charges linked to his doxxing efforts.
YouTube banned Dougan last year. On Telegram, he attributed the ban to videos he uploaded alleging a Russian mission to destroy U.S.-run bioweapons labs in Ukraine, a false narrative that would take hold as a justification for Russia’s invasion. Dougan’s ban came on the heels of a report from NewsGuard that highlighted the pro-Russian propaganda on his channel.
According to co-CEO Steven Brill, NewsGuard’s earlier report and Dougan’s subsequent ban led to a harassment campaign against him. Brill says in a coming book that Dougan impersonated an FBI officer in phone calls to him, left threatening messages and posted YouTube videos showing aerial shots of Brill’s home.
Over WhatsApp, Dougan defended his videos about Brill, citing NewsGuard’s “partnership with the US government” to have his content removed.
There is no evidence NewsGuard acted in concert with or on behalf of the U.S. government when it investigated Dougan. Asked for proof of such a partnership, Dougan sent a link to his own video, a 31-minute monologue laden with conspiracy theories. He’d reposted it to YouTube.
Brandy Zadrozny is a senior reporter for NBC News. She covers misinformation, extremism and the internet.
Are you moving? What to know to protect your belongings and have a smooth experience

After 25 years in their Long Island, New York, house, Michael and Deirdre Kupka decided to move to Charleston, South Carolina, to be closer to their youngest grandchildren.
The lifelong New York residents thought they did everything right when shopping for a mover for their life’s belongings, including a large number of family antiques.
But instead of a smooth moving experience out of their four-bedroom house, the Kupkas’ move is a cautionary tale for others to protect themselves. Many pieces of their antique furniture were cracked or severely damaged and the couple had to pay nearly $5,000 above their original agreement when the moving company refused to deliver their furniture, instead drastically changing the price from their original “flat-rate booking" fee.
Since the couple refused to sign a document presented by the moving company after they saw all the damage to their furniture, the movers are now saying they have no claim to insurance to cover what the Kupkas estimate would take thousands of dollars to fix and refurbish.
Though USA TODAY made multiple attempts to reach the Kupkas' moving company, and it said via email that it would respond, USA TODAY never received a comment.
How to find a good mover
May is not only National Moving Month, it’s also the start of the busy summer moving season, said Ryan Bowley, the American Trucking Associations’ moving and storage executive director.
Most moving companies book 70% of their business between May and September, said Bowley. The trucking association is the largest national trade association for the trucking industry with more than 34,000 trucking and moving company members.
While a majority of those moves go smoothly and most professional moving companies are reputable, consumers do run into problems, he said,
More than 6,200 complaints were filed with the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration’s National Consumer Complaint Database in 2023. It is important to properly research a moving company, make sure you have a contract and understand your rights, said Bowley. The complaint database also has educational information on its website, www.protectyourmove.gov
There are unscrupulous companies who bait and switch consumers with low-ball estimates, then raise the prices, holding furniture until consumers pay, in what the industry calls a "hostage shipment." he said. Some scammers never deliver the goods and instead auction them off, he added.
There are also fraudulent companies that put up fancy websites or use a name that is similar to a long-standing, reputable company, posting what looks like legitimate reviews and endorsements, Bowley said.
But “if you look a little bit closer ... it doesn’t quite look right,” he said. Photos of trucks may be photoshopped or the promises by the company don’t line up with standard practices of reputable businesses, Bowley said.
Any company that moves goods over state lines must have a registration number with the Department of Transportation. That can be found on the www.protectyourmove.gov site, said Bowley.
Bowley said it did not appear that the Kupka’s moving company, Call My Mover, was registered with the DOT.
What happened to the Kupkas?
The Kupkas had a short window of time to coordinate the closing dates of their New York house and one being built in South Carolina. They were looking for a company that could store their furniture on the truck and not mingle their goods with those of another family.
They called four moving companies. Michael Kupka also received a cold call from a local moving company, Call My Mover.
Michael said he assumed the company got his contact information from listings of recent home sales.
The moving estimates from the other companies were about $13,500 while Call My Mover came in with a “flat booking price” of $8,603.75 after a salesperson came out to the house to see their belongings.
While price played a role in choosing the company, Deirdre said, it wasn’t the only reason.
The other movers said the couple would have to pay for storage while Call My Mover said it would be free and they did not need an exact closing date. The movers also said they would wrap all of the couple’s fragile mirrors and pictures.
“It sort of all fell into place with this wonderful salesman that we had with Call My Mover,” Deirdre Kupka said. “Everything I asked him, he said yes, and I believed him.”
The Kupkas now say they should have done some internet research on the company. They would have seen negative customer reviews and an F rating with the local Better Business Bureau for Call My Mover in Plainview, New York, which also does business as Tri-State Relocation Inc.
“That would be the first thing I would tell everybody,” Michael Kupka said. “These people prey mainly on older people that don’t have the knowledge of going on the internet and investigating these people.”
He also went to the office of the local mover twice to pick up boxes and sat down with the owner, who said “don’t worry about anything." That in-person connection helped him feel better about the upcoming move.
The couple agreed to use Call My Mover. They now know they didn’t sign a contract, but rather a spreadsheet of their home's contents that the salesperson put together.
What happened on moving day
When the foreman arrived on moving day, he said in 22 years, he’d never once had the quoted price be what the customer would ultimately pay. Usually, it was more, he said.
That was not what the Kupkas expected.
One of the movers also had Deirdre Kupka sign her name on a phone, saying it was to confirm the insurance plan she chose and that there were movers on site to complete the move. There was nothing for her to review, but with the stress of moving day, she signed.
By the end of the day, there would be two truckloads and a van that came for excess items though their original verbal agreement was that all of their belongings would be on one truck and not transferred,
“That’s when they started shoving things into the truck, which is when I’m sure half of it broke,” Deirdre Kupka said.
The foreman then showed her husband five written pages listing furniture not on the original spreadsheet. He signed but said there was no indication that there would be extra charges. The moving truck left.
A few days later as the truck was in transit, the Kupkas were told the new total was $13,763.59 – over $5,000 more than what the couple originally agreed to pay. They were also told the payment must be by certified check, not a credit card like the original $100 deposit the couple put down.
Michael Kupka argued with the company, saying he wanted to see a detailed report. He then received what he said were several threatening phone calls from the company saying the truck would not arrive unless the full amount was paid and that the truck’s driver would be told to return to New York with the Kupkas financially responsible for the fuel and additional storage.
The Kupkas finally gave the company a certified check for $885.85 as "a good faith gesture.” The company wasn't satisfied.
That evening, Michael Kupka said he got a phone call from a woman at the company using “language that a truck driver couldn’t even imagine.” She was upset that the full amount had not been paid. When he hung up, he was unsure if the truck would arrive the next morning.
It did, but the driver said he could not unload until the remaining $4,273.99 was paid.
The Kupkas were shown a contract with Deirdre’s signature on it, though she said the couple had never seen a copy of it. It also had a signature certifying “no damage had been done to any of the furniture.”
After more verbal threats during a phone call with the moving company, the couple felt they had no choice but to pay the money.
“They were holding our furniture hostage,” Deirdre Kupka said.
The furniture finally began to be unloaded, after about a 2 ½ hour delay. That's when she noticed that many of her family’s antique heirlooms were damaged.
“I’m crying because my antique furniture has got dents that it’s never had,” she said. Some furniture was more than 150 years old.
The damage included a China cabinet with the legs broken off and her dining room chairs, one of which was completely destroyed. A couch Deirdre's mother bought her at an antique store has broken legs and arms.
“You can’t sit on the couch on either end without it falling,” she said.
“Every single piece of furniture they packaged up had something wrong with it,” including screws loose, scratches, or broken," added Michael.
The driver wanted the Kupkas to sign a document after the truck was emptied, but they refused. They complained about the damaged items and the driver took pictures before leaving.
“There was too much emotion at that point to argue with him or do anything more,” Michael Kupka said.
An hour later, the Kupkas received an email saying since they refused to sign the document, they had no claim to the insurance they'd originally agreed to – $250,000.
Adult daughter tries to help resolve issues
The Kupkas' daughter, Rebecca Overton, tried to communicate with the company on behalf of her parents after she found out what happened.
The family has sent a letter from an attorney demanding the $5,159.84 they say they were forced to overpay and full reimbursement for their repairs or they will seek relief from the courts. The family has received no return communication.
How to make a safe move: Don't want to lug that couch down the stairs yourself? Here's how to find safe movers
Call My Mover did not respond with comment to three requests by USA TODAY. A phone message was left with an employee who answered the phone on a Tuesday and an email was sent. USA TODAY received a reply saying the company would respond by the end of the day Wednesday, but the company sent no follow-up to that email or another sent the following Monday.
The Kupkas don’t know how much the final cost to repair the damaged antiques will be, though they estimate it to be thousands of dollars. Deirdre Kupka said she has glued together as many of the cracked pieces as she can.
“A lot of this stuff is irreplaceable,” her husband said.
Housing report: Want to live near your state's top schools? Prepare to pay $300,000 more for your house.
Do your research before moving, couple advises
The Kupkas are the victims, said BBB spokeswoman Melanie McGovern.
“It sounds like they asked all of the questions they needed to ask, but they (the company) knew how to answer them” telling the Kupkas what they wanted to hear McGovern said.
“A lot of people would have been in the same situation," McGovern said.
Neither Bowley nor McGovern had ever heard of a moving company cold-calling a new home seller. Both said that concerned them and they would be alerting their organizations about the potential new tactic.
The cold-calling itself isn’t troublesome, they said, unless the company is then not following up with good customer service. They worry that the practice could become like “storm chasers” who go door-to-door in neighborhoods after storms offering new roofs or “extra asphalt” and other materials and not providing consumers with quality workmanship.
It’s difficult once a move is happening to do much to resolve issues if things go south, said Bowley. Consumers who call the local police will probably be told it’s a contract dispute and something the police can’t intercede in, he said. Consumers would then need to go to the state attorney general or the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration.
So do your research and follow these tips before you make a deal, Bowley said.
Betty Lin-Fisher is a consumer reporter for USA TODAY. Reach her at [email protected] or follow her on X, Facebook, or Instagram @blinfisher . Sign up for our free The Daily Money newsletter, which will include consumer news on Fridays, here.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 4: Create a research design. The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you'll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research. There are often many possible paths you can take to answering ...
How to Research: 5 Steps in the Research Process. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Mar 18, 2022 • 3 min read. Research is an essential process to keep yourself informed on any topic with reliable sources of information. Research is an essential process to keep yourself informed on any topic with reliable sources of information.
Preparing for research is an extensive step in itself. You must: Choose a topic or carefully analyze the assignment given to you. Craft a research question and hypothesis. Plan out your research. Create a research log. Transform your hypothesis into a working thesis. 2. Understand and Evaluate Sources.
Start writing the middle, or body, of your paper. Get your ideas down, then see if you need to do any research. Since your introduction and conclusion summarize your paper, it's best to write those last. [8] Include an in-text citation for everything that needs one, even in your initial rough draft.
Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist. Free lecture slides.
Research: Where to Begin. Research isn't something that only scientists and professors do. Any time you use sources to investigate claims or reach new conclusions, you are performing research. Research happens in virtually all fields, so it's vitally important to know how to conduct research and navigate through source material regardless of ...
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
Step 8: Proofread. The final step in the process is to proofread the paper you have created. Read through the text and check for any errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Make sure the sources you used are cited properly. Make sure the message that you want to get across to the reader has been thoroughly stated.
Explanation. 1. Exploratory. A problem that hasn't been investigated before and isn't clearly defined requires exploratory research. This is the first step in laying the foundation for future, in-depth study. It requires an unstructured approach and posits several questions for the researchers to answer. 2.
Promote your brand. Build up a great reputa- tion for yourself. • Cultivate your strengths and play to those strengths. Some possible strengths: being broad; creative; a great implementer; great at doing theory. Figure 4: Nurture your research brand. • Please don't report to me, "This instance doesn't work".
For research help, use one of the following options: Ask the GTL General Information & Research Help Phone: (607) 735-1862 Research Help Email: [email protected] For help registering a device, password reset and more: EC IT Resources and Services
🔥Join me for my Certification Course on 'A-Z of Research Writing & Presentation' 😃: https://wiseupcommunications.com/course/research-writing/If you are ner...
Abstractspiepr Abs1. Every day people do research as they gather information to learn about something of interest. In the scientific world, however, research means something different than simply gathering information. Scientific research is characterized by its careful planning and observing, by its relentless efforts to understand and explain ...
Research Methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to conduct research, investigate problems, and gather data and information for a specific purpose. It involves the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect, analyze, and interpret data to answer research questions or solve research problems.
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
Monitor and adapt. Now that you have gained insights into the various market research methods at your disposal, let's delve into the practical aspects of how to conduct market research effectively. Here's a quick step-by-step overview, from defining objectives to monitoring market shifts. 1. Set clear objectives.
Judge the scope of the project. Reevaluate the research question based on the nature and extent of information available and the parameters of the research project. Select the most appropriate investigative methods (surveys, interviews, experiments) and research tools (periodical indexes, databases, websites). Plan the research project.
MeSH terms. Delivery of Health Care / methods*. Evidence-Based Medicine. Humans. Program Development / methods*. Translational Research, Biomedical*. Implementation research: what it is and how to do it.
The results from the study show that the mentees learned new information on specific techniques and study systems, while developing a broader network of personal connections in academia. Further, the mentees learned how to discuss and present research as well as how to discuss a manuscript and the overall writing process.
Other research has suggested that without federal paid parental and family leave benefits for parents, some women with less education may leave the labor force after having a baby. In contrast, labor force participation for young women with a college degree has fully recovered from the recessions of the early 2000s. Today, 87% of college ...
Research on adult sexual offenders found the greatest deterrence to completing the act was a vocal child - one who expressed their desire to stop, or said they would tell others.
The characteristics that make the site ideal for measuring CO 2 also provide ideal conditions for a wide variety of other atmospheric research efforts. The observatory's 10 buildings house instruments that collected up to 250 climatological measurements for NOAA and partner agency scientists and engineers every day before the eruption of the ...
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Breakthrough in Cancer Research: Blood Test Can Predict Cancer Years in Advance. The Pasta Diet Secret. The key to the pasta diet's success lies in combining pasta with vegetables.
New research commissioned by SAP Insights identifies macro trends affecting finance organizations. One of the primary goals of this research was to gain a deeper understanding of AI's impact on ...
Russian disinformation sites linked to former Florida deputy sheriff, research finds . A new report from a media watchdog connects John Mark Dougan, who now lives in Russia, to scores of fake news ...
In short, make sure you're actually ready to give the card up before calling the company. 2. Get an update on your credit score. If you're not quite sure where your credit score stands these days ...
Lam Research isn't an exciting growth play, but it will warm up again as the PC market recovers, new smartphones arrive, and the expanding AI market drives more companies to upgrade their data ...
How to Improve Your Research Skills: 6 Research Tips. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Aug 18, 2021 • 3 min read. Whether you're writing a blog post or a short story, you'll likely reach a point in your first draft where you don't have enough information to go forward—and that's where research comes in. Whether you're writing ...
It is important to properly research a moving company, make sure you have a contract and understand your rights, said Bowley. The complaint database also has educational information on its website ...