Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.

The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
Why I Think All Schools Should Abolish Homework

H ow long is your child’s workweek? Thirty hours? Forty? Would it surprise you to learn that some elementary school kids have workweeks comparable to adults’ schedules? For most children, mandatory homework assignments push their workweek far beyond the school day and deep into what any other laborers would consider overtime. Even without sports or music or other school-sponsored extracurriculars, the daily homework slog keeps many students on the clock as long as lawyers, teachers, medical residents, truck drivers and other overworked adults. Is it any wonder that,deprived of the labor protections that we provide adults, our kids are suffering an epidemic of disengagement, anxiety and depression ?
With my youngest child just months away from finishing high school, I’m remembering all the needless misery and missed opportunities all three of my kids suffered because of their endless assignments. When my daughters were in middle school, I would urge them into bed before midnight and then find them clandestinely studying under the covers with a flashlight. We cut back on their activities but still found ourselves stuck in a system on overdrive, returning home from hectic days at 6 p.m. only to face hours more of homework. Now, even as a senior with a moderate course load, my son, Zak, has spent many weekends studying, finding little time for the exercise and fresh air essential to his well-being. Week after week, and without any extracurriculars, Zak logs a lot more than the 40 hours adults traditionally work each week — and with no recognition from his “bosses” that it’s too much. I can’t count the number of shared evenings, weekend outings and dinners that our family has missed and will never get back.
How much after-school time should our schools really own?
In the midst of the madness last fall, Zak said to me, “I feel like I’m working towards my death. The constant demands on my time since 5th grade are just going to continue through graduation, into college, and then into my job. It’s like I’m on an endless treadmill with no time for living.”
My spirit crumbled along with his.
Like Zak, many people are now questioning the point of putting so much demand on children and teens that they become thinly stretched and overworked. Studies have long shown that there is no academic benefit to high school homework that consumes more than a modest number of hours each week. In a study of high schoolers conducted by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), researchers concluded that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance.”
In elementary school, where we often assign overtime even to the youngest children, studies have shown there’s no academic benefit to any amount of homework at all.
Our unquestioned acceptance of homework also flies in the face of all we know about human health, brain function and learning. Brain scientists know that rest and exercise are essential to good health and real learning . Even top adult professionals in specialized fields take care to limit their work to concentrated periods of focus. A landmark study of how humans develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work only about four hours per day .
Yet we continue to overwork our children, depriving them of the chance to cultivate health and learn deeply, burdening them with an imbalance of sedentary, academic tasks. American high school students , in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found.
It’s time for an uprising.
Already, small rebellions are starting. High schools in Ridgewood, N.J. , and Fairfax County, Va., among others, have banned homework over school breaks. The entire second grade at Taylor Elementary School in Arlington, Va., abolished homework this academic year. Burton Valley Elementary School in Lafayette, Calif., has eliminated homework in grades K through 4. Henry West Laboratory School , a public K-8 school in Coral Gables, Fla., eliminated mandatory, graded homework for optional assignments. One Lexington, Mass., elementary school is piloting a homework-free year, replacing it with reading for pleasure.
More from TIME
Across the Atlantic, students in Spain launched a national strike against excessive assignments in November. And a second-grade teacher in Texas, made headlines this fall when she quit sending home extra work , instead urging families to “spend your evenings doing things that are proven to correlate with student success. Eat dinner as a family, read together, play outside and get your child to bed early.”
It is time that we call loudly for a clear and simple change: a workweek limit for children, counting time on the clock before and after the final bell. Why should schools extend their authority far beyond the boundaries of campus, dictating activities in our homes in the hours that belong to families? An all-out ban on after-school assignments would be optimal. Short of that, we can at least sensibly agree on a cap limiting kids to a 40-hour workweek — and fewer hours for younger children.
Resistance even to this reasonable limit will be rife. Mike Miller, an English teacher at Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology in Alexandria, Va., found this out firsthand when he spearheaded a homework committee to rethink the usual approach. He had read the education research and found a forgotten policy on the county books limiting homework to two hours a night, total, including all classes. “I thought it would be a slam dunk” to put the two-hour cap firmly in place, Miller said.
But immediately, people started balking. “There was a lot of fear in the community,” Miller said. “It’s like jumping off a high dive with your kids’ future. If we reduce homework to two hours or less, is my kid really going to be okay?” In the end, the committee only agreed to a homework ban over school breaks.
Miller’s response is a great model for us all. He decided to limit assignments in his own class to 20 minutes a night (the most allowed for a student with six classes to hit the two-hour max). His students didn’t suddenly fail. Their test scores remained stable. And they started using their more breathable schedule to do more creative, thoughtful work.
That’s the way we will get to a sane work schedule for kids: by simultaneously pursuing changes big and small. Even as we collaboratively press for policy changes at the district or individual school level, all teachers can act now, as individuals, to ease the strain on overworked kids.
As parents and students, we can also organize to make homework the exception rather than the rule. We can insist that every family, teacher and student be allowed to opt out of assignments without penalty to make room for important activities, and we can seek changes that shift practice exercises and assignments into the actual school day.
We’ll know our work is done only when Zak and every other child can clock out, eat dinner, sleep well and stay healthy — the very things needed to engage and learn deeply. That’s the basic standard the law applies to working adults. Let’s do the same for our kids.
Vicki Abeles is the author of the bestseller Beyond Measure: Rescuing an Overscheduled, Overtested, Underestimated Generation, and director and producer of the documentaries “ Race to Nowhere ” and “ Beyond Measure. ”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- How Far Trump Would Go
- Scenes From Pro-Palestinian Encampments Across U.S. Universities
- Saving Seconds Is Better Than Hours
- Why Your Breakfast Should Start with a Vegetable
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Ryan Gosling
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework
A Stanford researcher found that students in high-achieving communities who spend too much time on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, a lack of balance and even alienation from society. More than two hours of homework a night may be counterproductive, according to the study.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
• Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
• Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
• Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
share this!
August 16, 2021
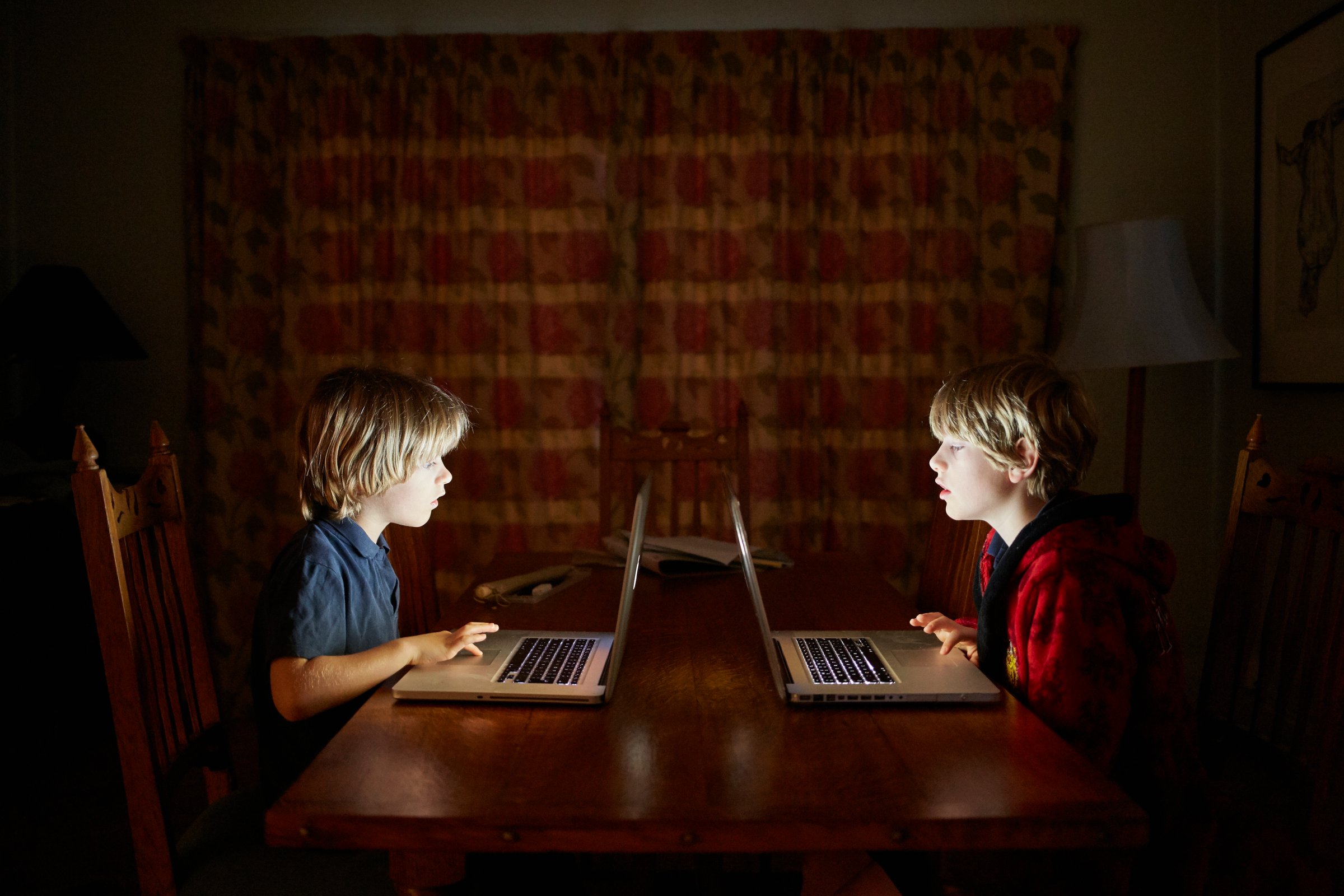
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Study finds human noise negatively impacts cricket survival and reproduction
27 minutes ago

New eco-friendly lubricant additives protect turbine equipment, waterways

Nanotubes, nanoparticles and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl

Bigger brains allow cliff-nesting seagull species to survive and thrive in urban environments

Oil palm plantations are driving massive downstream impact to watershed

Centipedes used in traditional Chinese medicine offer leads for kidney treatment

Physicists arrange atoms in close proximity, paving way for exploring exotic states of matter

For microscopic organisms, ocean currents act as 'expressway' to deeper depths, study finds

Targeting friends to induce social contagion can benefit the world, says new research
2 hours ago
Mice navigating a virtual reality environment reveal that walls, not floors, define space
Relevant physicsforums posts, physics instructor minimum education - community college.
11 hours ago
Studying "Useful" vs. "Useless" Stuff in School
Apr 30, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Apr 29, 2024
Plagiarism & ChatGPT: Is Cheating with AI the New Normal?
Apr 28, 2024
Digital oscilloscope for high school use
Apr 25, 2024
Motivating high school Physics students with Popcorn Physics
Apr 3, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

Investigation reveals varied impact of preschool programs on long-term school success
3 hours ago

Training of brain processes makes reading more efficient
Apr 18, 2024

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
Apr 17, 2024

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024

More than money, family and community bonds prep teens for college success: Study
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Credit: August de Richelieu
Does homework still have value? A Johns Hopkins education expert weighs in
Joyce epstein, co-director of the center on school, family, and community partnerships, discusses why homework is essential, how to maximize its benefit to learners, and what the 'no-homework' approach gets wrong.
By Vicky Hallett
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein , co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work," Epstein says.
But after decades of researching how to improve schools, the professor in the Johns Hopkins School of Education remains certain that homework is essential—as long as the teachers have done their homework, too. The National Network of Partnership Schools , which she founded in 1995 to advise schools and districts on ways to improve comprehensive programs of family engagement, has developed hundreds of improved homework ideas through its Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program. For an English class, a student might interview a parent on popular hairstyles from their youth and write about the differences between then and now. Or for science class, a family could identify forms of matter over the dinner table, labeling foods as liquids or solids. These innovative and interactive assignments not only reinforce concepts from the classroom but also foster creativity, spark discussions, and boost student motivation.
"We're not trying to eliminate homework procedures, but expand and enrich them," says Epstein, who is packing this research into a forthcoming book on the purposes and designs of homework. In the meantime, the Hub couldn't wait to ask her some questions:
What kind of homework training do teachers typically get?
Future teachers and administrators really have little formal training on how to design homework before they assign it. This means that most just repeat what their teachers did, or they follow textbook suggestions at the end of units. For example, future teachers are well prepared to teach reading and literacy skills at each grade level, and they continue to learn to improve their teaching of reading in ongoing in-service education. By contrast, most receive little or no training on the purposes and designs of homework in reading or other subjects. It is really important for future teachers to receive systematic training to understand that they have the power, opportunity, and obligation to design homework with a purpose.
Why do students need more interactive homework?
If homework assignments are always the same—10 math problems, six sentences with spelling words—homework can get boring and some kids just stop doing their assignments, especially in the middle and high school years. When we've asked teachers what's the best homework you've ever had or designed, invariably we hear examples of talking with a parent or grandparent or peer to share ideas. To be clear, parents should never be asked to "teach" seventh grade science or any other subject. Rather, teachers set up the homework assignments so that the student is in charge. It's always the student's homework. But a good activity can engage parents in a fun, collaborative way. Our data show that with "good" assignments, more kids finish their work, more kids interact with a family partner, and more parents say, "I learned what's happening in the curriculum." It all works around what the youngsters are learning.
Is family engagement really that important?
At Hopkins, I am part of the Center for Social Organization of Schools , a research center that studies how to improve many aspects of education to help all students do their best in school. One thing my colleagues and I realized was that we needed to look deeply into family and community engagement. There were so few references to this topic when we started that we had to build the field of study. When children go to school, their families "attend" with them whether a teacher can "see" the parents or not. So, family engagement is ever-present in the life of a school.
My daughter's elementary school doesn't assign homework until third grade. What's your take on "no homework" policies?
There are some parents, writers, and commentators who have argued against homework, especially for very young children. They suggest that children should have time to play after school. This, of course is true, but many kindergarten kids are excited to have homework like their older siblings. If they give homework, most teachers of young children make assignments very short—often following an informal rule of 10 minutes per grade level. "No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play.
Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with higher student achievement . However, as we discussed, some students stop doing homework. This leads, statistically, to results showing that doing homework or spending more minutes on homework is linked to higher student achievement. If slow or struggling students are not doing their assignments, they contribute to—or cause—this "result."
Teachers need to design homework that even struggling students want to do because it is interesting. Just about all students at any age level react positively to good assignments and will tell you so.
Did COVID change how schools and parents view homework?
Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling—teachers were still working hard to provide daily lessons. But if a child was learning at home in the living room, parents were more aware of what they were doing in school. One of the silver linings of COVID was that teachers reported that they gained a better understanding of their students' families. We collected wonderfully creative examples of activities from members of the National Network of Partnership Schools. I'm thinking of one art activity where every child talked with a parent about something that made their family unique. Then they drew their finding on a snowflake and returned it to share in class. In math, students talked with a parent about something the family liked so much that they could represent it 100 times. Conversations about schoolwork at home was the point.
How did you create so many homework activities via the Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program?
We had several projects with educators to help them design interactive assignments, not just "do the next three examples on page 38." Teachers worked in teams to create TIPS activities, and then we turned their work into a standard TIPS format in math, reading/language arts, and science for grades K-8. Any teacher can use or adapt our prototypes to match their curricula.
Overall, we know that if future teachers and practicing educators were prepared to design homework assignments to meet specific purposes—including but not limited to interactive activities—more students would benefit from the important experience of doing their homework. And more parents would, indeed, be partners in education.
Posted in Voices+Opinion
You might also like
News network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram
Homework could have an impact on kids’ health. Should schools ban it?
Professor of Education, Penn State
Disclosure statement
Gerald K. LeTendre has received funding from the National Science Foundation and the Spencer Foundation.
Penn State provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation US.
View all partners

Reformers in the Progressive Era (from the 1890s to 1920s) depicted homework as a “sin” that deprived children of their playtime . Many critics voice similar concerns today.
Yet there are many parents who feel that from early on, children need to do homework if they are to succeed in an increasingly competitive academic culture. School administrators and policy makers have also weighed in, proposing various policies on homework .
So, does homework help or hinder kids?
For the last 10 years, my colleagues and I have been investigating international patterns in homework using databases like the Trends in Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) . If we step back from the heated debates about homework and look at how homework is used around the world, we find the highest homework loads are associated with countries that have lower incomes and higher social inequality.
Does homework result in academic success?
Let’s first look at the global trends on homework.
Undoubtedly, homework is a global phenomenon ; students from all 59 countries that participated in the 2007 Trends in Math and Science Study (TIMSS) reported getting homework. Worldwide, only less than 7% of fourth graders said they did no homework.
TIMSS is one of the few data sets that allow us to compare many nations on how much homework is given (and done). And the data show extreme variation.
For example, in some nations, like Algeria, Kuwait and Morocco, more than one in five fourth graders reported high levels of homework. In Japan, less than 3% of students indicated they did more than four hours of homework on a normal school night.
TIMSS data can also help to dispel some common stereotypes. For instance, in East Asia, Hong Kong, Taiwan and Japan – countries that had the top rankings on TIMSS average math achievement – reported rates of heavy homework that were below the international mean.
In the Netherlands, nearly one out of five fourth graders reported doing no homework on an average school night, even though Dutch fourth graders put their country in the top 10 in terms of average math scores in 2007.
Going by TIMSS data, the US is neither “ A Nation at Rest” as some have claimed, nor a nation straining under excessive homework load . Fourth and eighth grade US students fall in the middle of the 59 countries in the TIMSS data set, although only 12% of US fourth graders reported high math homework loads compared to an international average of 21%.
So, is homework related to high academic success?
At a national level, the answer is clearly no. Worldwide, homework is not associated with high national levels of academic achievement .
But, the TIMSS can’t be used to determine if homework is actually helping or hurting academic performance overall , it can help us see how much homework students are doing, and what conditions are associated with higher national levels of homework.
We have typically found that the highest homework loads are associated with countries that have lower incomes and higher levels of social inequality – not hallmarks that most countries would want to emulate.
Impact of homework on kids
TIMSS data also show us how even elementary school kids are being burdened with large amounts of homework.
Almost 10% of fourth graders worldwide (one in 10 children) reported spending multiple hours on homework each night. Globally, one in five fourth graders report 30 minutes or more of homework in math three to four times a week.
These reports of large homework loads should worry parents, teachers and policymakers alike.
Empirical studies have linked excessive homework to sleep disruption , indicating a negative relationship between the amount of homework, perceived stress and physical health.

What constitutes excessive amounts of homework varies by age, and may also be affected by cultural or family expectations. Young adolescents in middle school, or teenagers in high school, can study for longer duration than elementary school children.
But for elementary school students, even 30 minutes of homework a night, if combined with other sources of academic stress, can have a negative impact . Researchers in China have linked homework of two or more hours per night with sleep disruption .
Even though some cultures may normalize long periods of studying for elementary age children, there is no evidence to support that this level of homework has clear academic benefits . Also, when parents and children conflict over homework, and strong negative emotions are created, homework can actually have a negative association with academic achievement.
Should there be “no homework” policies?
Administrators and policymakers have not been reluctant to wade into the debates on homework and to formulate policies . France’s president, Francois Hollande, even proposed that homework be banned because it may have inegaliatarian effects.
However, “zero-tolerance” homework policies for schools, or nations, are likely to create as many problems as they solve because of the wide variation of homework effects. Contrary to what Hollande said, research suggests that homework is not a likely source of social class differences in academic achievement .
Homework, in fact, is an important component of education for students in the middle and upper grades of schooling.
Policymakers and researchers should look more closely at the connection between poverty, inequality and higher levels of homework. Rather than seeing homework as a “solution,” policymakers should question what facets of their educational system might impel students, teachers and parents to increase homework loads.
At the classroom level, in setting homework, teachers need to communicate with their peers and with parents to assure that the homework assigned overall for a grade is not burdensome, and that it is indeed having a positive effect.
Perhaps, teachers can opt for a more individualized approach to homework. If teachers are careful in selecting their assignments – weighing the student’s age, family situation and need for skill development – then homework can be tailored in ways that improve the chance of maximum positive impact for any given student.
I strongly suspect that when teachers face conditions such as pressure to meet arbitrary achievement goals, lack of planning time or little autonomy over curriculum, homework becomes an easy option to make up what could not be covered in class.
Whatever the reason, the fact is a significant percentage of elementary school children around the world are struggling with large homework loads. That alone could have long-term negative consequences for their academic success.
- Trends in Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS)
- Elementary school
- Academic success

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Program Development Officer - Business Processes

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/71970990/05_nohomework_Jiayue_Li.0.jpg)
Filed under:
- The Highlight
Nobody knows what the point of homework is
The homework wars are back.
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Twitter
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Nobody knows what the point of homework is
As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework. But whether or not students could complete it at home varied. For some, schoolwork became public-library work or McDonald’s-parking-lot work.
Luis Torres, the principal of PS 55, a predominantly low-income community elementary school in the south Bronx, told me that his school secured Chromebooks for students early in the pandemic only to learn that some lived in shelters that blocked wifi for security reasons. Others, who lived in housing projects with poor internet reception, did their schoolwork in laundromats.
According to a 2021 Pew survey , 25 percent of lower-income parents said their children, at some point, were unable to complete their schoolwork because they couldn’t access a computer at home; that number for upper-income parents was 2 percent.
The issues with remote learning in March 2020 were new. But they highlighted a divide that had been there all along in another form: homework. And even long after schools have resumed in-person classes, the pandemic’s effects on homework have lingered.
Over the past three years, in response to concerns about equity, schools across the country, including in Sacramento, Los Angeles , San Diego , and Clark County, Nevada , made permanent changes to their homework policies that restricted how much homework could be given and how it could be graded after in-person learning resumed.
Three years into the pandemic, as districts and teachers reckon with Covid-era overhauls of teaching and learning, schools are still reconsidering the purpose and place of homework. Whether relaxing homework expectations helps level the playing field between students or harms them by decreasing rigor is a divisive issue without conclusive evidence on either side, echoing other debates in education like the elimination of standardized test scores from some colleges’ admissions processes.
I first began to wonder if the homework abolition movement made sense after speaking with teachers in some Massachusetts public schools, who argued that rather than help disadvantaged kids, stringent homework restrictions communicated an attitude of low expectations. One, an English teacher, said she felt the school had “just given up” on trying to get the students to do work; another argued that restrictions that prohibit teachers from assigning take-home work that doesn’t begin in class made it difficult to get through the foreign-language curriculum. Teachers in other districts have raised formal concerns about homework abolition’s ability to close gaps among students rather than widening them.
Many education experts share this view. Harris Cooper, a professor emeritus of psychology at Duke who has studied homework efficacy, likened homework abolition to “playing to the lowest common denominator.”
But as I learned after talking to a variety of stakeholders — from homework researchers to policymakers to parents of schoolchildren — whether to abolish homework probably isn’t the right question. More important is what kind of work students are sent home with and where they can complete it. Chances are, if schools think more deeply about giving constructive work, time spent on homework will come down regardless.
There’s no consensus on whether homework works
The rise of the no-homework movement during the Covid-19 pandemic tapped into long-running disagreements over homework’s impact on students. The purpose and effectiveness of homework have been disputed for well over a century. In 1901, for instance, California banned homework for students up to age 15, and limited it for older students, over concerns that it endangered children’s mental and physical health. The newest iteration of the anti-homework argument contends that the current practice punishes students who lack support and rewards those with more resources, reinforcing the “myth of meritocracy.”
But there is still no research consensus on homework’s effectiveness; no one can seem to agree on what the right metrics are. Much of the debate relies on anecdotes, intuition, or speculation.
Researchers disagree even on how much research exists on the value of homework. Kathleen Budge, the co-author of Turning High-Poverty Schools Into High-Performing Schools and a professor at Boise State, told me that homework “has been greatly researched.” Denise Pope, a Stanford lecturer and leader of the education nonprofit Challenge Success, said, “It’s not a highly researched area because of some of the methodological problems.”
Experts who are more sympathetic to take-home assignments generally support the “10-minute rule,” a framework that estimates the ideal amount of homework on any given night by multiplying the student’s grade by 10 minutes. (A ninth grader, for example, would have about 90 minutes of work a night.) Homework proponents argue that while it is difficult to design randomized control studies to test homework’s effectiveness, the vast majority of existing studies show a strong positive correlation between homework and high academic achievement for middle and high school students. Prominent critics of homework argue that these correlational studies are unreliable and point to studies that suggest a neutral or negative effect on student performance. Both agree there is little to no evidence for homework’s effectiveness at an elementary school level, though proponents often argue that it builds constructive habits for the future.
For anyone who remembers homework assignments from both good and bad teachers, this fundamental disagreement might not be surprising. Some homework is pointless and frustrating to complete. Every week during my senior year of high school, I had to analyze a poem for English and decorate it with images found on Google; my most distinct memory from that class is receiving a demoralizing 25-point deduction because I failed to present my analysis on a poster board. Other assignments really do help students learn: After making an adapted version of Chairman Mao’s Little Red Book for a ninth grade history project, I was inspired to check out from the library and read a biography of the Chinese ruler.
For homework opponents, the first example is more likely to resonate. “We’re all familiar with the negative effects of homework: stress, exhaustion, family conflict, less time for other activities, diminished interest in learning,” Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, which challenges common justifications for homework, told me in an email. “And these effects may be most pronounced among low-income students.” Kohn believes that schools should make permanent any moratoria implemented during the pandemic, arguing that there are no positives at all to outweigh homework’s downsides. Recent studies , he argues , show the benefits may not even materialize during high school.
In the Marlborough Public Schools, a suburban district 45 minutes west of Boston, school policy committee chair Katherine Hennessy described getting kids to complete their homework during remote education as “a challenge, to say the least.” Teachers found that students who spent all day on their computers didn’t want to spend more time online when the day was over. So, for a few months, the school relaxed the usual practice and teachers slashed the quantity of nightly homework.
Online learning made the preexisting divides between students more apparent, she said. Many students, even during normal circumstances, lacked resources to keep them on track and focused on completing take-home assignments. Though Marlborough Schools is more affluent than PS 55, Hennessy said many students had parents whose work schedules left them unable to provide homework help in the evenings. The experience tracked with a common divide in the country between children of different socioeconomic backgrounds.
So in October 2021, months after the homework reduction began, the Marlborough committee made a change to the district’s policy. While teachers could still give homework, the assignments had to begin as classwork. And though teachers could acknowledge homework completion in a student’s participation grade, they couldn’t count homework as its own grading category. “Rigorous learning in the classroom does not mean that that classwork must be assigned every night,” the policy stated . “Extensions of class work is not to be used to teach new content or as a form of punishment.”
Canceling homework might not do anything for the achievement gap
The critiques of homework are valid as far as they go, but at a certain point, arguments against homework can defy the commonsense idea that to retain what they’re learning, students need to practice it.
“Doesn’t a kid become a better reader if he reads more? Doesn’t a kid learn his math facts better if he practices them?” said Cathy Vatterott, an education researcher and professor emeritus at the University of Missouri-St. Louis. After decades of research, she said it’s still hard to isolate the value of homework, but that doesn’t mean it should be abandoned.
Blanket vilification of homework can also conflate the unique challenges facing disadvantaged students as compared to affluent ones, which could have different solutions. “The kids in the low-income schools are being hurt because they’re being graded, unfairly, on time they just don’t have to do this stuff,” Pope told me. “And they’re still being held accountable for turning in assignments, whether they’re meaningful or not.” On the other side, “Palo Alto kids” — students in Silicon Valley’s stereotypically pressure-cooker public schools — “are just bombarded and overloaded and trying to stay above water.”
Merely getting rid of homework doesn’t solve either problem. The United States already has the second-highest disparity among OECD (the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) nations between time spent on homework by students of high and low socioeconomic status — a difference of more than three hours, said Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University and author of No More Mindless Homework .
When she interviewed teachers in Boston-area schools that had cut homework before the pandemic, Bempechat told me, “What they saw immediately was parents who could afford it immediately enrolled their children in the Russian School of Mathematics,” a math-enrichment program whose tuition ranges from $140 to about $400 a month. Getting rid of homework “does nothing for equity; it increases the opportunity gap between wealthier and less wealthy families,” she said. “That solution troubles me because it’s no solution at all.”
A group of teachers at Wakefield High School in Arlington, Virginia, made the same point after the school district proposed an overhaul of its homework policies, including removing penalties for missing homework deadlines, allowing unlimited retakes, and prohibiting grading of homework.
“Given the emphasis on equity in today’s education systems,” they wrote in a letter to the school board, “we believe that some of the proposed changes will actually have a detrimental impact towards achieving this goal. Families that have means could still provide challenging and engaging academic experiences for their children and will continue to do so, especially if their children are not experiencing expected rigor in the classroom.” At a school where more than a third of students are low-income, the teachers argued, the policies would prompt students “to expect the least of themselves in terms of effort, results, and responsibility.”
Not all homework is created equal
Despite their opposing sides in the homework wars, most of the researchers I spoke to made a lot of the same points. Both Bempechat and Pope were quick to bring up how parents and schools confuse rigor with workload, treating the volume of assignments as a proxy for quality of learning. Bempechat, who is known for defending homework, has written extensively about how plenty of it lacks clear purpose, requires the purchasing of unnecessary supplies, and takes longer than it needs to. Likewise, when Pope instructs graduate-level classes on curriculum, she asks her students to think about the larger purpose they’re trying to achieve with homework: If they can get the job done in the classroom, there’s no point in sending home more work.
At its best, pandemic-era teaching facilitated that last approach. Honolulu-based teacher Christina Torres Cawdery told me that, early in the pandemic, she often had a cohort of kids in her classroom for four hours straight, as her school tried to avoid too much commingling. She couldn’t lecture for four hours, so she gave the students plenty of time to complete independent and project-based work. At the end of most school days, she didn’t feel the need to send them home with more to do.
A similar limited-homework philosophy worked at a public middle school in Chelsea, Massachusetts. A couple of teachers there turned as much class as possible into an opportunity for small-group practice, allowing kids to work on problems that traditionally would be assigned for homework, Jessica Flick, a math coach who leads department meetings at the school, told me. It was inspired by a philosophy pioneered by Simon Fraser University professor Peter Liljedahl, whose influential book Building Thinking Classrooms in Mathematics reframes homework as “check-your-understanding questions” rather than as compulsory work. Last year, Flick found that the two eighth grade classes whose teachers adopted this strategy performed the best on state tests, and this year, she has encouraged other teachers to implement it.
Teachers know that plenty of homework is tedious and unproductive. Jeannemarie Dawson De Quiroz, who has taught for more than 20 years in low-income Boston and Los Angeles pilot and charter schools, says that in her first years on the job she frequently assigned “drill and kill” tasks and questions that she now feels unfairly stumped students. She said designing good homework wasn’t part of her teaching programs, nor was it meaningfully discussed in professional development. With more experience, she turned as much class time as she could into practice time and limited what she sent home.
“The thing about homework that’s sticky is that not all homework is created equal,” says Jill Harrison Berg, a former teacher and the author of Uprooting Instructional Inequity . “Some homework is a genuine waste of time and requires lots of resources for no good reason. And other homework is really useful.”
Cutting homework has to be part of a larger strategy
The takeaways are clear: Schools can make cuts to homework, but those cuts should be part of a strategy to improve the quality of education for all students. If the point of homework was to provide more practice, districts should think about how students can make it up during class — or offer time during or after school for students to seek help from teachers. If it was to move the curriculum along, it’s worth considering whether strategies like Liljedahl’s can get more done in less time.
Some of the best thinking around effective assignments comes from those most critical of the current practice. Denise Pope proposes that, before assigning homework, teachers should consider whether students understand the purpose of the work and whether they can do it without help. If teachers think it’s something that can’t be done in class, they should be mindful of how much time it should take and the feedback they should provide. It’s questions like these that De Quiroz considered before reducing the volume of work she sent home.
More than a year after the new homework policy began in Marlborough, Hennessy still hears from parents who incorrectly “think homework isn’t happening” despite repeated assurances that kids still can receive work. She thinks part of the reason is that education has changed over the years. “I think what we’re trying to do is establish that homework may be an element of educating students,” she told me. “But it may not be what parents think of as what they grew up with. ... It’s going to need to adapt, per the teaching and the curriculum, and how it’s being delivered in each classroom.”
For the policy to work, faculty, parents, and students will all have to buy into a shared vision of what school ought to look like. The district is working on it — in November, it hosted and uploaded to YouTube a round-table discussion on homework between district administrators — but considering the sustained confusion, the path ahead seems difficult.
When I asked Luis Torres about whether he thought homework serves a useful part in PS 55’s curriculum, he said yes, of course it was — despite the effort and money it takes to keep the school open after hours to help them do it. “The children need the opportunity to practice,” he said. “If you don’t give them opportunities to practice what they learn, they’re going to forget.” But Torres doesn’t care if the work is done at home. The school stays open until around 6 pm on weekdays, even during breaks. Tutors through New York City’s Department of Youth and Community Development programs help kids with work after school so they don’t need to take it with them.
As schools weigh the purpose of homework in an unequal world, it’s tempting to dispose of a practice that presents real, practical problems to students across the country. But getting rid of homework is unlikely to do much good on its own. Before cutting it, it’s worth thinking about what good assignments are meant to do in the first place. It’s crucial that students from all socioeconomic backgrounds tackle complex quantitative problems and hone their reading and writing skills. It’s less important that the work comes home with them.
Jacob Sweet is a freelance writer in Somerville, Massachusetts. He is a frequent contributor to the New Yorker, among other publications.
Will you support Vox today?
Millions rely on Vox’s journalism to understand the coronavirus crisis. We believe it pays off for all of us, as a society and a democracy, when our neighbors and fellow citizens can access clear, concise information on the pandemic. But our distinctive explanatory journalism is expensive. Support from our readers helps us keep it free for everyone. If you have already made a financial contribution to Vox, thank you. If not, please consider making a contribution today from as little as $3.
We accept credit card, Apple Pay, and Google Pay. You can also contribute via
We can make birth safer for Black mothers. Here’s how.
How to be enough, america is full of abandoned malls. what if we turned them into housing, sign up for the newsletter today, explained, thanks for signing up.
Check your inbox for a welcome email.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Win Big in Our Teacher Appreciation Giveaway 🎁!
Should We Ban Homework?
The cons of homework are starting to outweigh the pros.

Recent research shows that teenagers have doubled the amount of time they spend on homework since the 1990s. This is in spite of other, well-documented research that calls the efficacy of homework into question, albeit in the younger grades. Why are students spending so much time on homework if the impact is zero (for younger kids) or moderate (for older ones)? Should we ban homework? These are the questions teachers, parents, and lawmakers are asking.
Bans proposed and implemented in the U.S. and abroad
The struggle of whether or not to assign homework is not a new one. In 2017, a Florida superintendent banned homework for elementary schools in the entire district, with one very important exception: reading at home. The United States isn’t the only country to question the benefits of homework. Last August, the Philippines proposed a bill to ban homework completely, citing the need for rest, relaxation, and time with family. Another bill there proposed no weekend homework, with teachers running the risk of fines or two years in prison. (Yikes!) While a prison sentence may seem extreme, there are real reasons to reconsider homework.
Refocus on mental health and educate the “whole child”
Prioritizing mental health is at the forefront of the homework ban movement. Leaders say they want to give students time to develop other hobbies, relationships, and balance in their lives.
This month two Utah elementary schools gained national recognition for officially banning homework. The results are significant, with psychologist referrals for anxiety decreasing by 50 percent. Many schools are looking for ways to refocus on wellness, and homework can be a real cause of stress.
[contextly_auto_sidebar]
Research supports a ban for elementary schools
Supporters of a homework ban often cite research from John Hattie, who concluded that elementary school homework has no effect on academic progress. In a podcast he said, “Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?'”
In the upper grades, Hattie’s research shows that homework has to be purposeful, not busy work. And the reality is, most teachers don’t receive training on how to assign homework that is meaningful and relevant to students.
Parents push back, too
In October this Washington Post article made waves in parenting and education communities when it introduced the idea that, even if homework is assigned, it doesn’t have to be completed for the student to pass the class. The writer explains how her family doesn’t believe in homework, and doesn’t participate. In response, other parents started “opting out” of homework, citing research that homework in elementary school doesn’t further intelligence or academic success.
Of course, homework has its defenders, especially in the upper grades
“I think some homework is a good idea,” says Darla E. in our WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook. “Ideally, it forces the parents to take some responsibility for their child’s education. It also reinforces what students learn and instills good study habits for later in life.”
Jennifer M. agrees. “If we are trying to make students college-ready, they need the skill of doing homework.”
And the research does support some homework in middle and high school, as long as it is clearly tied to learning and not overwhelming.
We’d love to hear your thoughts—do you think schools should ban homework? Come and share in our WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, why you should stop assigning reading homework.

You Might Also Like
What Teachers Need to Know About Dyscalculia
2+2 = confusion and anxiety. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Watch CBS News
Are schools across the country going too far by banning homework?
December 14, 2018 / 1:37 PM EST / CBS News
Are schools across the country going too far by banning homework? According to child and adolescent family therapist Darby Fox, yes.
"It's like an ultimate reaction. There is a point to homework and the right amount really is age appropriate," Fox said Friday on "CBS This Morning."
Elementary school students have an average of around 4.5 hours of homework a week, while high schoolers get an average of about 7.5 hours, according to the Wall Street Journal and Department of Education. The National Institute of Mental Health says more than 30 percent of teenagers experience some kind of anxiety, and homework is a major contributing factor.
"I think the current thing about getting rid of homework is about anxiety and trying reduce that. It should be about learning. We should be able to hit a medium," Fox said.
"Very young kids really – sometimes they like the idea that they have something industrious to do at home, and there's no harm in that. But they need time to just play and explore and become kind of curious," Fox added. "As we get older, fourth grade, you can have 45 minutes, an hour – up in through high school, 2.5 hours is appropriate, 3 hours. But schools have really taken it way too far."
She blamed the "race to get amazing resumes, the best test scores."
"But that has escalated almost directly with mental health problems, anxiety, depression," Fox said.
While parents might see sports or socializing as an important part of students' lives, Fox pointed out that's still a scheduled activity.
"What I'd really love to see is more time for kids to have nothing to do, unstructured time so that they have to figure it out on their own. And that's the most important thing they should be exploring," Fox said.
If your child is overwhelmed, Fox advised parents to let schools and teachers know.
"If there's not an appropriate response, follow it to the next level. Is it the principal or whoever is the next in command. Usually that might issue – that might alarm us that there's some kind of learning disability or processing problem if it's really overwhelming or the teachers are just simply giving too much work," she said.
More from CBS News

Walker Hayes shares his battle with addiction in new album

Want an easy way to relieve stress? Try this doctor-approved method.

Doctor explains why mammograms should start at age 40

Where pro-Palestinian university protests are happening around the world
Does homework really work?
by: Leslie Crawford | Updated: December 12, 2023
Print article

You know the drill. It’s 10:15 p.m., and the cardboard-and-toothpick Golden Gate Bridge is collapsing. The pages of polynomials have been abandoned. The paper on the Battle of Waterloo seems to have frozen in time with Napoleon lingering eternally over his breakfast at Le Caillou. Then come the tears and tantrums — while we parents wonder, Does the gain merit all this pain? Is this just too much homework?
However the drama unfolds night after night, year after year, most parents hold on to the hope that homework (after soccer games, dinner, flute practice, and, oh yes, that childhood pastime of yore known as playing) advances their children academically.
But what does homework really do for kids? Is the forest’s worth of book reports and math and spelling sheets the average American student completes in their 12 years of primary schooling making a difference? Or is it just busywork?
Homework haterz
Whether or not homework helps, or even hurts, depends on who you ask. If you ask my 12-year-old son, Sam, he’ll say, “Homework doesn’t help anything. It makes kids stressed-out and tired and makes them hate school more.”
Nothing more than common kid bellyaching?
Maybe, but in the fractious field of homework studies, it’s worth noting that Sam’s sentiments nicely synopsize one side of the ivory tower debate. Books like The End of Homework , The Homework Myth , and The Case Against Homework the film Race to Nowhere , and the anguished parent essay “ My Daughter’s Homework is Killing Me ” make the case that homework, by taking away precious family time and putting kids under unneeded pressure, is an ineffective way to help children become better learners and thinkers.
One Canadian couple took their homework apostasy all the way to the Supreme Court of Canada. After arguing that there was no evidence that it improved academic performance, they won a ruling that exempted their two children from all homework.
So what’s the real relationship between homework and academic achievement?
How much is too much?
To answer this question, researchers have been doing their homework on homework, conducting and examining hundreds of studies. Chris Drew Ph.D., founder and editor at The Helpful Professor recently compiled multiple statistics revealing the folly of today’s after-school busy work. Does any of the data he listed below ring true for you?
• 45 percent of parents think homework is too easy for their child, primarily because it is geared to the lowest standard under the Common Core State Standards .
• 74 percent of students say homework is a source of stress , defined as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss, and stomach problems.
• Students in high-performing high schools spend an average of 3.1 hours a night on homework , even though 1 to 2 hours is the optimal duration, according to a peer-reviewed study .
Not included in the list above is the fact many kids have to abandon activities they love — like sports and clubs — because homework deprives them of the needed time to enjoy themselves with other pursuits.
Conversely, The Helpful Professor does list a few pros of homework, noting it teaches discipline and time management, and helps parents know what’s being taught in the class.
The oft-bandied rule on homework quantity — 10 minutes a night per grade (starting from between 10 to 20 minutes in first grade) — is listed on the National Education Association’s website and the National Parent Teacher Association’s website , but few schools follow this rule.
Do you think your child is doing excessive homework? Harris Cooper Ph.D., author of a meta-study on homework , recommends talking with the teacher. “Often there is a miscommunication about the goals of homework assignments,” he says. “What appears to be problematic for kids, why they are doing an assignment, can be cleared up with a conversation.” Also, Cooper suggests taking a careful look at how your child is doing the assignments. It may seem like they’re taking two hours, but maybe your child is wandering off frequently to get a snack or getting distracted.
Less is often more
If your child is dutifully doing their work but still burning the midnight oil, it’s worth intervening to make sure your child gets enough sleep. A 2012 study of 535 high school students found that proper sleep may be far more essential to brain and body development.
For elementary school-age children, Cooper’s research at Duke University shows there is no measurable academic advantage to homework. For middle-schoolers, Cooper found there is a direct correlation between homework and achievement if assignments last between one to two hours per night. After two hours, however, achievement doesn’t improve. For high schoolers, Cooper’s research suggests that two hours per night is optimal. If teens have more than two hours of homework a night, their academic success flatlines. But less is not better. The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in a class with no homework.
Many schools are starting to act on this research. A Florida superintendent abolished homework in her 42,000 student district, replacing it with 20 minutes of nightly reading. She attributed her decision to “ solid research about what works best in improving academic achievement in students .”
More family time
A 2020 survey by Crayola Experience reports 82 percent of children complain they don’t have enough quality time with their parents. Homework deserves much of the blame. “Kids should have a chance to just be kids and do things they enjoy, particularly after spending six hours a day in school,” says Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth . “It’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.”
By far, the best replacement for homework — for both parents and children — is bonding, relaxing time together.
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How families of color can fight for fair discipline in school

Dealing with teacher bias

The most important school data families of color need to consider
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
25 Reasons Homework Should Be Banned (Busywork Arguments)

As students across the globe plow through heaps of homework each night, one question lingers in the minds of educators, parents, and students alike: should homework be banned?
This question is not new, yet it continues to spark lively debate as research findings, anecdotal evidence, and personal experiences paint a complex picture of the pros and cons of homework.
On one hand, proponents of homework argue that it reinforces classroom learning, encourages a disciplined work ethic, and provides teachers with valuable insight into student comprehension. They see homework as an extension of classroom instruction that solidifies and enriches learning while fostering important skills like time management and self-discipline. It also offers an opportunity for parents to be involved in their children's education.
However, some people say there are a lot of downsides. They argue that excessive homework can lead to stress and burnout, reduce time for extracurricular activities and family interactions, exacerbate educational inequalities, and even negatively impact students' mental health.

This article presents 25 reasons why we might need to seriously consider this radical shift in our educational approach. But first, lets share some examples of what homework actually is.
Examples of Homework
These examples cover a wide range of subjects and complexity levels, reflecting the variety of homework assignments students might encounter throughout their educational journey.
- Spelling lists to memorize for a test
- Math worksheets for practicing basic arithmetic operations
- Reading assignments from children's books
- Simple science projects like growing a plant
- Basic geography assignments like labeling a map
- Art projects like drawing a family portrait
- Writing book reports or essays
- Advanced math problems
- Research projects on various topics
- Lab reports for science experiments
- Reading and responding to literature
- Preparing presentations on various topics
- Advanced math problems involving calculus or algebra
- Reading classic literature and writing analytical essays
- Research papers on historical events
- Lab reports for advanced science experiments
- Foreign language exercises
- Preparing for standardized tests
- College application essays
- Extensive research papers
- In-depth case studies
- Advanced problem-solving in subjects like physics, engineering, etc.
- Thesis or dissertation writing
- Extensive reading and literature reviews
- Internship or practicum experiences
Lack of proven benefits

Homework has long been a staple of traditional education, dating back centuries. However, the actual efficacy of homework in enhancing learning outcomes remains disputed. A number of studies indicate that there's no conclusive evidence supporting the notion that homework improves academic performance, especially in primary education . In fact, research suggests that for younger students, the correlation between homework and academic achievement is weak or even negative .
Too much homework can often lead to increased stress and decreased enthusiasm for learning. This issue becomes particularly pressing when considering the common 'more is better' approach to homework, where the quantity of work given to students often outweighs the quality and effectiveness of the tasks. For instance, spending countless hours memorizing facts for a history test may not necessarily translate to better understanding or long-term retention of the subject matter.
However, it's worth noting that homework isn't completely devoid of benefits. It can help foster self-discipline, time management skills, and the ability to work independently. But, these positive outcomes are usually more pronounced in older students and when homework assignments are thoughtfully designed and not excessive in volume.
When discussing the merits and drawbacks of homework, it's critical to consider the nature of the assignments. Routine, repetitive tasks often associated with 'drill-and-practice' homework, such as completing rows of arithmetic problems or copying definitions from a textbook, rarely lead to meaningful learning. On the other hand, assignments that encourage students to apply what they've learned in class, solve problems, or engage creatively with the material can be more beneficial.
Increased stress

Homework can often lead to a significant increase in stress levels among students. This is especially true when students are burdened with large volumes of homework, leaving them with little time to relax or pursue other activities. The feeling of constantly racing against the clock to meet deadlines can contribute to anxiety, frustration, and even burnout.
Contrary to popular belief, stress does not necessarily improve performance or productivity. In fact, high levels of stress can negatively impact memory, concentration, and overall cognitive function. This counteracts the very purpose of homework, which is intended to reinforce learning and improve academic outcomes.
However, one might argue that homework can teach students about time management, organization, and how to handle pressure. These are important life skills that could potentially prepare them for future responsibilities. But it's essential to strike a balance. The pressure to complete homework should not come at the cost of a student's mental wellbeing.
Limited family time
Homework often infringes upon the time students can spend with their families. After spending the entire day in school, children come home to yet more academic work, leaving little room for quality family interactions. This limited family time can hinder the development of important interpersonal skills and familial bonds.
Moreover, family time isn't just about fun and relaxation. It also plays a crucial role in the social and emotional development of children. Opportunities for unstructured play, family conversations, and shared activities can contribute to children's well-being and character building.
Nonetheless, advocates of homework might argue that it can be a platform for parental involvement in a child's education. While this may be true, the involvement should not transform into parental control or cause friction due to differing expectations and pressures.
Reduced physical activity
Homework can often lead to reduced physical activity by eating into the time students have for sports, recreation, and simply being outdoors. Physical activity is essential for children's health, well-being, and even their academic performance. Research suggests that physical activity can enhance cognitive abilities, improve concentration, and reduce symptoms of ADHD .
Homework, especially when it's boring and repetitive, can deter students from engaging in physical activities, leading to a sedentary lifestyle. This lack of balance between work and play can contribute to physical health problems such as obesity, poor posture, and related health concerns.
Homework proponents might point out that disciplined time management could allow students to balance both work and play. However, given the demanding nature of many homework assignments, achieving this balance is often easier said than done.
Negative impact on sleep

A significant concern about homework is its impact on students' sleep patterns. Numerous studies have linked excessive homework to sleep deprivation in students. Children often stay up late to complete assignments, reducing the amount of sleep they get. Lack of sleep can result in a host of issues, from poor academic performance and difficulty concentrating to physical health problems like weakened immunity.
Even the quality of sleep can be affected. The stress and anxiety from a heavy workload can lead to difficulty falling asleep or restless nights. And let's not forget that students often need to wake up early for school, compounding the negative effects of late-night homework sessions.
On the other hand, some argue that homework can teach children time management skills, suggesting that effective organization could help prevent late-night work. However, when schools assign excessive amounts of homework, even the best time management might not prevent encroachment on sleep time.
Homework can exacerbate existing educational inequalities. Not all students have access to a conducive learning environment at home, necessary resources, or support from educated family members. For these students, homework can become a source of stress and disadvantage rather than an opportunity to reinforce learning.
Children from lower socio-economic backgrounds might need to contribute to household chores or part-time work, limiting the time they have for homework. This can create a gap in academic performance and grades, reflecting not on the students' abilities but their circumstances.
While homework is meant to level the playing field by providing additional learning time outside school, it often does the opposite. It's worth noting that students from privileged backgrounds can often access additional help like tutoring, further widening the gap.
Reduced creativity and independent thinking
Homework, particularly when it involves rote learning or repetitive tasks, can stifle creativity and independent thinking. Students often focus on getting the "right" answers to please teachers rather than exploring different ideas and solutions. This can hinder their ability to think creatively and solve problems independently, skills that are increasingly in demand in the modern world.
Homework defenders might claim that it can also promote independent learning. True, when thoughtfully designed, homework can encourage this. But, voluminous or repetitive tasks tend to promote compliance over creativity.
Diminished interest in learning
Overburdening students with homework can diminish their interest in learning. After long hours in school followed by more academic tasks at home, learning can begin to feel like a chore. This can lead to a decline in intrinsic motivation and an unhealthy association of learning with stress and exhaustion.
In theory, homework can deepen interest in a subject, especially when it involves projects or research. Yet, an excess of homework, particularly routine tasks, might achieve the opposite, turning learning into a source of stress rather than enjoyment.
Inability to pursue personal interests
Homework can limit students' ability to pursue personal interests. Hobbies, personal projects, and leisure activities are crucial for personal development and well-being. With heavy homework loads, students may struggle to find time for these activities, missing out on opportunities to discover new interests and talents.
Supporters of homework might argue that it teaches students to manage their time effectively. However, even with good time management, an overload of homework can crowd out time for personal interests.
Excessive workload
The issue of excessive workload is a common complaint among students. Spending several hours on homework after a full school day can be mentally and physically draining. This workload can lead to burnout, decreased motivation, and negative attitudes toward school and learning.
While homework can help consolidate classroom learning, too much can be counterproductive. It's important to consider the overall workload of students, including school, extracurricular activities, and personal time, when assigning homework.
Limited time for reflection
Homework can limit the time students have for reflection. Reflection is a critical part of learning, allowing students to digest and integrate new information. With the constant flow of assignments, there's often little time left for this crucial process. Consequently, the learning becomes superficial, and the true understanding of subjects can be compromised.
Although homework is meant to reinforce what's taught in class, the lack of downtime for reflection might hinder deep learning. It's important to remember that learning is not just about doing, but also about thinking.
Increased pressure on young children
Young children are particularly vulnerable to the pressures of homework. At an age where play and exploration are vital for cognitive and emotional development, too much homework can create undue pressure and stress. This pressure can instigate a negative relationship with learning from an early age, potentially impacting their future attitude towards education.
Advocates of homework often argue that it prepares children for the rigors of their future academic journey. However, placing too much academic pressure on young children might overshadow the importance of learning through play and exploration.

Lack of alignment with real-world skills
Traditional homework often lacks alignment with real-world skills. Assignments typically focus on academic abilities at the expense of skills like creativity, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence. These are crucial for success in the modern workplace and are often under-emphasized in homework tasks.
Homework can be an opportunity to develop these skills when properly structured. However, tasks often focus on memorization and repetition, rather than cultivating skills relevant to the real world.
Loss of motivation
Excessive homework can lead to a loss of motivation. The constant pressure to complete assignments and meet deadlines can diminish a student's intrinsic motivation to learn. This loss of motivation might not only affect their academic performance but also their love of learning, potentially having long-term effects on their educational journey.
Some believe homework instills discipline and responsibility. But, it's important to balance these benefits against the potential for homework to undermine motivation and engagement.
Disruption of work-life balance
Maintaining a healthy work-life balance is as important for students as it is for adults. Overloading students with homework can disrupt this balance, leaving little time for relaxation, socializing, and extracurricular activities. All of these are vital for a student's overall development and well-being.
Homework supporters might argue that it prepares students for the workloads they'll face in college and beyond. But it's also crucial to ensure students have time to relax, recharge, and engage in non-academic activities for a well-rounded development.
Impact on mental health
There's a growing body of evidence showing the negative impact of excessive homework on students' mental health. The stress and anxiety from heavy homework loads can contribute to issues like depression, anxiety, and even thoughts of suicide. Student well-being should be a top priority in education, and the impact of homework on mental health cannot be ignored.
While some might argue that homework helps students develop resilience and coping skills, it's important to ensure these potential benefits don't come at the expense of students' mental health.
Limited time for self-care
With excessive homework, students often find little time for essential self-care activities. These can include physical exercise, proper rest, healthy eating, mindfulness, or even simple leisure activities. These activities are critical for maintaining physical health, emotional well-being, and cognitive function.
Some might argue that managing homework alongside self-care responsibilities teaches students valuable life skills. However, it's important that these skills don't come at the cost of students' health and well-being.
Decreased family involvement
Homework can inadvertently lead to decreased family involvement in a child's learning. Parents often feel unqualified or too busy to help with homework, leading to missed opportunities for family learning interactions. This can also create stress and conflict within the family, especially when parents have high expectations or are unable to assist.
Some believe homework can facilitate parental involvement in education. But, when it becomes a source of stress or conflict, it can discourage parents from engaging in their child's learning.
Reinforcement of inequalities
Homework can unintentionally reinforce inequalities. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds might lack access to resources like private tutors or a quiet study space, placing them at a disadvantage compared to their more privileged peers. Additionally, these students might have additional responsibilities at home, further limiting their time to complete homework.
While the purpose of homework is often to provide additional learning opportunities, it can inadvertently reinforce existing disparities. Therefore, it's essential to ensure that homework doesn't favor students who have more resources at home.
Reduced time for play and creativity
Homework can take away from time for play and creative activities. These activities are not only enjoyable but also crucial for the cognitive, social, and emotional development of children. Play allows children to explore, imagine, and create, fostering innovative thinking and problem-solving skills.
Some may argue that homework teaches discipline and responsibility. Yet, it's vital to remember that play also has significant learning benefits and should be a part of every child's daily routine.
Increased cheating and academic dishonesty
The pressure to complete homework can sometimes lead to increased cheating and academic dishonesty. When faced with a large volume of homework, students might resort to copying from friends or searching for answers online. This undermines the educational value of homework and fosters unhealthy academic practices.
While homework is intended to consolidate learning, the risk of promoting dishonest behaviors is a concern that needs to be addressed.
Strained teacher-student relationships
Excessive homework can strain teacher-student relationships. If students begin to associate teachers with stress or anxiety from homework, it can hinder the development of a positive learning relationship. Furthermore, if teachers are perceived as being unfair or insensitive with their homework demands, it can impact the overall classroom dynamic.
While homework can provide an opportunity for teachers to monitor student progress, it's important to ensure that it doesn't negatively affect the teacher-student relationship.
Negative impact on family dynamics
Homework can impact family dynamics. Parents might feel compelled to enforce homework completion, leading to potential conflict, stress, and tension within the family. These situations can disrupt the harmony in the household and strain relationships.
Homework is sometimes seen as a tool to engage parents in their child's education. However, it's crucial to ensure that this involvement doesn't turn into a source of conflict or pressure.
Cultural and individual differences
Homework might not take into account cultural and individual differences. Education is not a one-size-fits-all process, and what works for one student might not work for another. Some students might thrive on hands-on learning, while others prefer auditory or visual learning methods. By standardizing homework, we might ignore these individual learning styles and preferences.
Homework can also overlook cultural differences. For students from diverse cultural backgrounds, certain types of homework might seem irrelevant or difficult to relate to, leading to disengagement or confusion.
Encouragement of surface-level learning
Homework often encourages surface-level learning instead of deep understanding. When students are swamped with homework, they're likely to rush through assignments to get them done, rather than taking the time to understand the concepts. This can result in superficial learning where students memorize information to regurgitate it on assignments and tests, instead of truly understanding and internalizing the knowledge.
While homework is meant to reinforce classroom learning, the quality of learning is more important than the quantity. It's important to design homework in a way that encourages deep, meaningful learning instead of mere rote memorization.
Related posts:
- Diathesis-Stress Model (Definition + Examples)
- HPA Axis (Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis)
- General Adaptation Syndrome Theory
- Careers in Psychology
- The Stress Response (General Adaptation Syndome)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test

Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters
Should homework be banned?
Social media has sparked into life about whether children should be given homework - should students be freed from this daily chore? Dr Gerald Letendre, a professor of education at Pennsylvania State University, investigates.
We’ve all done it: pretended to leave an essay at home, or stayed up until 2am to finish a piece of coursework we’ve been ignoring for weeks. Homework, for some people, is seen as a chore that’s ‘wrecking kids’ or ‘killing parents’, while others think it is an essential part of a well-rounded education. The problem is far from new: public debates about homework have been raging since at least the early-1900s, and recently spilled over into a Twitter feud between Gary Lineker and Piers Morgan.
Ironically, the conversation surrounding homework often ignores the scientific ‘homework’ that researchers have carried out. Many detailed studies have been conducted, and can guide parents, teachers and administrators to make sensible decisions about how much work should be completed by students outside of the classroom.
So why does homework stir up such strong emotions? One reason is that, by its very nature, it is an intrusion of schoolwork into family life. I carried out a study in 2005, and found that the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school, from nursery right up to the end of compulsory education, has greatly increased over the last century . This means that more of a child’s time is taken up with education, so family time is reduced. This increases pressure on the boundary between the family and the school.
Plus, the amount of homework that students receive appears to be increasing, especially in the early years when parents are keen for their children to play with friends and spend time with the family.
Finally, success in school has become increasingly important to success in life. Parents can use homework to promote, or exercise control over, their child’s academic trajectory, and hopefully ensure their future educational success. But this often leaves parents conflicted – they want their children to be successful in school, but they don’t want them to be stressed or upset because of an unmanageable workload.

However, the issue isn’t simply down to the opinions of parents, children and their teachers – governments also like to get involved. In the autumn of 2012, French president François Hollande hit world headlines after making a comment about banning homework, ostensibly because it promoted inequality. The Chinese government has also toyed with a ban, because of concerns about excessive academic pressure being put on children.
The problem is, some politicians and national administrators regard regulatory policy in education as a solution for a wide array of social, economic and political issues, perhaps without considering the consequences for students and parents.
Does homework work?
Homework seems to generally have a positive effect for high school students, according to an extensive range of empirical literature. For example, Duke University’s Prof Harris Cooper carried out a meta-analysis using data from US schools, covering a period from 1987 to 2003. He found that homework offered a general beneficial impact on test scores and improvements in attitude, with a greater effect seen in older students. But dig deeper into the issue and a complex set of factors quickly emerges, related to how much homework students do, and exactly how they feel about it.
In 2009, Prof Ulrich Trautwein and his team at the University of Tübingen found that in order to establish whether homework is having any effect, researchers must take into account the differences both between and within classes . For example, a teacher may assign a good deal of homework to a lower-level class, producing an association between more homework and lower levels of achievement. Yet, within the same class, individual students may vary significantly in how much homework improves their baseline performance. Plus, there is the fact that some students are simply more efficient at completing their homework than others, and it becomes quite difficult to pinpoint just what type of homework, and how much of it, will affect overall academic performance.
Over the last century, the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school has greatly increased
Gender is also a major factor. For example, a study of US high school students carried out by Prof Gary Natriello in the 1980s revealed that girls devote more time to homework than boys, while a follow-up study found that US girls tend to spend more time on mathematics homework than boys. Another study, this time of African-American students in the US, found that eighth grade (ages 13-14) girls were more likely to successfully manage both their tasks and emotions around schoolwork, and were more likely to finish homework.
So why do girls seem to respond more positively to homework? One possible answer proposed by Eunsook Hong of the University of Nevada in 2011 is that teachers tend to rate girls’ habits and attitudes towards work more favourably than boys’. This perception could potentially set up a positive feedback loop between teacher expectations and the children’s capacity for academic work based on gender, resulting in girls outperforming boys. All of this makes it particularly difficult to determine the extent to which homework is helping, though it is clear that simply increasing the time spent on assignments does not directly correspond to a universal increase in learning.
Can homework cause damage?
The lack of empirical data supporting homework in the early years of education, along with an emerging trend to assign more work to this age range, appears to be fuelling parental concerns about potential negative effects. But, aside from anecdotes of increased tension in the household, is there any evidence of this? Can doing too much homework actually damage children?
Evidence suggests extreme amounts of homework can indeed have serious effects on students’ health and well-being. A Chinese study carried out in 2010 found a link between excessive homework and sleep disruption: children who had less homework had better routines and more stable sleep schedules. A Canadian study carried out in 2015 by Isabelle Michaud found that high levels of homework were associated with a greater risk of obesity among boys, if they were already feeling stressed about school in general.
For useful revision guides and video clips to assist with learning, visit BBC Bitesize . This is a free online study resource for UK students from early years up to GCSEs and Scottish Highers.
It is also worth noting that too much homework can create negative effects that may undermine any positives. These negative consequences may not only affect the child, but also could also pile on the stress for the whole family, according to a recent study by Robert Pressman of the New England Centre for Pediatric Psychology. Parents were particularly affected when their perception of their own capacity to assist their children decreased.
What then, is the tipping point, and when does homework simply become too much for parents and children? Guidelines typically suggest that children in the first grade (six years old) should have no more that 10 minutes per night, and that this amount should increase by 10 minutes per school year. However, cultural norms may greatly affect what constitutes too much.
A study of children aged between 8 and 10 in Quebec defined high levels of homework as more than 30 minutes a night, but a study in China of children aged 5 to 11 deemed that two or more hours per night was excessive. It is therefore difficult to create a clear standard for what constitutes as too much homework, because cultural differences, school-related stress, and negative emotions within the family all appear to interact with how homework affects children.
Should we stop setting homework?
In my opinion, even though there are potential risks of negative effects, homework should not be banned. Small amounts, assigned with specific learning goals in mind and with proper parental support, can help to improve students’ performance. While some studies have generally found little evidence that homework has a positive effect on young children overall, a 2008 study by Norwegian researcher Marte Rønning found that even some very young children do receive some benefit. So simply banning homework would mean that any particularly gifted or motivated pupils would not be able to benefit from increased study. However, at the earliest ages, very little homework should be assigned. The decisions about how much and what type are best left to teachers and parents.
As a parent, it is important to clarify what goals your child’s teacher has for homework assignments. Teachers can assign work for different reasons – as an academic drill to foster better study habits, and unfortunately, as a punishment. The goals for each assignment should be made clear, and should encourage positive engagement with academic routines.

Parents should inform the teachers of how long the homework is taking, as teachers often incorrectly estimate the amount of time needed to complete an assignment, and how it is affecting household routines. For young children, positive teacher support and feedback is critical in establishing a student’s positive perception of homework and other academic routines. Teachers and parents need to be vigilant and ensure that homework routines do not start to generate patterns of negative interaction that erode students’ motivation.
Likewise, any positive effects of homework are dependent on several complex interactive factors, including the child’s personal motivation, the type of assignment, parental support and teacher goals. Creating an overarching policy to address every single situation is not realistic, and so homework policies tend to be fixated on the time the homework takes to complete. But rather than focusing on this, everyone would be better off if schools worked on fostering stronger communication between parents, teachers and students, allowing them to respond more sensitively to the child’s emotional and academic needs.
- Five brilliant science books for kids
- Will e-learning replace teachers?
Follow Science Focus on Twitter , Facebook , Instagram and Flipboard
Share this article

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
California bill to ban large loads of homework in public schools considered
(FOX40.COM) — A new bill introduced in the legislature is taking aim at banning excessive homework in California public schools.
“Homework is exhausting. It’s overwhelming, ” said sixth-grade student Sofia Johnson. “It’s depressing that my whole day- from when I wake up to when I go to bed- is nearly all taken up with schoolwork.”
Several scams circulate in California
That’s why Johnson’s mother, Assembly Member Pilar Schiavo says she authored AB 2999, also known as “The Healthy Homework Act.”
AB 2999 would not ban homework, however, the proposal would mandate local school boards and educational agencies to establish homework policies that consider impacts on students’ physical and mental health all with input from parents, teachers, and students themselves.
How does ‘burnout culture’ affect our bodies, minds?
While many Californians can remember spending hours after school at their desk bogged down in homework, Schiavo hopes to change that for the next generation.
“I think this is going to make a huge impact for students,” Schiavo said. “The times have changed and our homework policies don’t always change with the times, so we need to make sure we are addressing issues that are effective and also don’t harm kids.”
Her proposal comes as a survey of more than 300,000 American students conducted by Stanford University and the nonprofit organization Challenge Success found that 45% of students say workload and homework is their #1 source of stress. 13,000 California high school students who took the survey report an average of 2.5 hours of homework every night.
“If it’s such a source of stress for kids, and we know taking stress off kids’ plates will make a difference in their mental health, this is something that can practically impact kids’ mental health overnight,” Schiavo said.
The bill is also reported to be tailored around equity since some lower socioeconomic backgrounds may not have access to resources at home like high speed internet.
“A child’s grade should not be dependent on the resources they have at home to do the homework,” said California Teacher of the Year, Casey Cuny. “I truly believe the resources should be dependent on the learning that takes place in the classroom with the professional. That’s why I support this bill – because in the end, it will be what’s best for kids.”
The bill unanimously passed the assembly education committee with bipartisan support. It has no formal opposition.
For the latest news, weather, sports, and streaming video, head to FOX40.
Recommended Stories
Microsoft bans u.s. police departments from using enterprise ai tool for facial recognition.
Microsoft has changed its policy to ban U.S. police departments from using generative AI for facial recognition through the Azure OpenAI Service, the company's fully managed, enterprise-focused wrapper around OpenAI technologies. Language added Wednesday to the terms of service for Azure OpenAI Service prohibits integrations with Azure OpenAI Service from being used "by or for" police departments for facial recognition in the U.S., including integrations with OpenAI's text- and speech-analyzing models. A separate new bullet point covers "any law enforcement globally," and explicitly bars the use of "real-time facial recognition technology" on mobile cameras, like body cameras and dashcams, to attempt to identify a person in "uncontrolled, in-the-wild" environments.
'Saved our battered backs': This portable seat wants to be your bleacher bestie, and it's on sale for $38
Take it from 4,800 five-star fans: It's in a different league than most stadium cushions.
Hubble Network makes Bluetooth connection with a satellite for the first time
Hubble Network has become the first company in history to establish a Bluetooth connection directly to a satellite — a critical technology validation for the company, potentially opening the door to connecting millions more devices anywhere in the world.
Flagstar Bank mortgage review 2024
Flagstar Bank is a great mortgage lender for FHA loans, but it has many other types of home loans, too. Learn whether Flagstar Bank is the right lender for you.
Rookie WR expectations post-NFL Draft: Just how good will Marvin Harrison Jr. be?
Fantasy football analyst Matt Harmon lays out Year 1 expectations for the talented class of rookie wide receivers entering the 2024 season.
Microsoft’s latest Windows security updates might break your VPN
Microsoft says the April security updates for Windows may break your VPN. Oops!
Georgia gives Kirby Smart a raise to make him the highest-paid coach in college football
Smart is set to make $13 million in 2024 and his contract now goes through 2033.
Kelley O'Hara, 2-time World Cup champion and Olympic gold medalist, to retire after 2024 NWSL season
O'Hara was part of a golden era for USWNT.
What is the typical minimum balance required for savings accounts and CDs?
Some types of savings accounts come with minimum balance requirements. Here’s a look at the typical minimum balance needed to open a traditional savings accounts or CD.
Dry, brittle nails? This dermatologist-approved $10 cuticle oil is the secret to a lasting manicure
'Just like your skin, your nails need hydration to maintain their health,' says Miami-based board-certified dermatologist Anna Chacon, MD.
EU plan to force messaging apps to scan for CSAM risks millions of false positives, experts warn
A controversial push by European Union lawmakers to legally require messaging platforms to scan citizens' private communications for child sexual abuse material (CSAM) could lead to millions of false positives per day, hundreds of security and privacy experts warned in an open letter Thursday. Concern over the EU proposal has been building since the Commission proposed the CSAM-scanning plan two years ago -- with independent experts, lawmakers across the European Parliament and even the bloc's own Data Protection Supervisor among those sounding the alarm.
Two of our top Anker power banks are back on sale at all-time low prices
Two of our top Anker power banks are back on sale at all-time low prices, including the 20,000mAh Prime portable charger. The sale extends to the Nano charger.
April jobs report preview: Wages, job gains set to slow while unemployment holds steady
After a strong winter for the US labor market, economists expect hiring to have slowed in April.
I'm a shopping editor, and here's what I'm grabbing from Lululemon's We Made Too Much section
Don't miss this rare chance to scoop up fantastic finds for up to 50% off.
What is maternal sepsis and why are Black women twice as likely to develop it? Here's what you need to know.
Sepsis is a life-threatening infection and is considered a major cause of maternal death.
TikTok expands its premium ad slots despite potential US ban
In an effort to capture more ad dollars, despite the looming U.S. ban, TikTok is introducing new advertising products and opportunities that will allow marketers to better control what sort of content their ads appear against. The company says it will use generative AI to curate trending, brand-safe content; expand its selection of "tentpole" moments, like the Paris Olympics and Met Gala; and allow advertisers to buy slots with specific networks and content offerings. The company introduced the "Pulse Premiere" ad slot last year, and it is now adding new partners to it.
10 'life-changing and fabulous' caftans that are easy, breezy and great for summer sunshine — from just $15
Dreamy '70s elegance is having a moment. These caftans are the ideal dresses for soaking up the sun.
Cheers to Mother's Day! This elegant glass mug set — down to $13 at Amazon — arrives just in time
Clearly better than that 'No. 1 Mom' mug you gifted her last year — she'll even get two pretty gold spoons to stir in her sugar!
Jaylen Warren says Steelers' special teams coordinator has talked about Justin Fields returning kicks
The new NFL kickoff rules might see the Steelers get creative when it comes to returns.
NBA playoffs: Bucks' Giannis Antetokounmpo and Damian Lillard are game-time decisions for Game 6 vs. Pacers
The Bucks face a 3-2 deficit against the Pacers heading into Thursday's Game 6.
11 Surprising Homework Statistics, Facts & Data

The age-old question of whether homework is good or bad for students is unanswerable because there are so many “ it depends ” factors.
For example, it depends on the age of the child, the type of homework being assigned, and even the child’s needs.
There are also many conflicting reports on whether homework is good or bad. This is a topic that largely relies on data interpretation for the researcher to come to their conclusions.
To cut through some of the fog, below I’ve outlined some great homework statistics that can help us understand the effects of homework on children.
Homework Statistics List
1. 45% of parents think homework is too easy for their children.
A study by the Center for American Progress found that parents are almost twice as likely to believe their children’s homework is too easy than to disagree with that statement.
Here are the figures for math homework:
- 46% of parents think their child’s math homework is too easy.
- 25% of parents think their child’s math homework is not too easy.
- 29% of parents offered no opinion.
Here are the figures for language arts homework:
- 44% of parents think their child’s language arts homework is too easy.
- 28% of parents think their child’s language arts homework is not too easy.
- 28% of parents offered no opinion.
These findings are based on online surveys of 372 parents of school-aged children conducted in 2018.
2. 93% of Fourth Grade Children Worldwide are Assigned Homework
The prestigious worldwide math assessment Trends in International Maths and Science Study (TIMSS) took a survey of worldwide homework trends in 2007. Their study concluded that 93% of fourth-grade children are regularly assigned homework, while just 7% never or rarely have homework assigned.
3. 17% of Teens Regularly Miss Homework due to Lack of High-Speed Internet Access
A 2018 Pew Research poll of 743 US teens found that 17%, or almost 2 in every 5 students, regularly struggled to complete homework because they didn’t have reliable access to the internet.
This figure rose to 25% of Black American teens and 24% of teens whose families have an income of less than $30,000 per year.
4. Parents Spend 6.7 Hours Per Week on their Children’s Homework
A 2018 study of 27,500 parents around the world found that the average amount of time parents spend on homework with their child is 6.7 hours per week. Furthermore, 25% of parents spend more than 7 hours per week on their child’s homework.
American parents spend slightly below average at 6.2 hours per week, while Indian parents spend 12 hours per week and Japanese parents spend 2.6 hours per week.
5. Students in High-Performing High Schools Spend on Average 3.1 Hours per night Doing Homework
A study by Galloway, Conner & Pope (2013) conducted a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California.
Across these high-performing schools, students self-reported that they did 3.1 hours per night of homework.
Graduates from those schools also ended up going on to college 93% of the time.
6. One to Two Hours is the Optimal Duration for Homework
A 2012 peer-reviewed study in the High School Journal found that students who conducted between one and two hours achieved higher results in tests than any other group.
However, the authors were quick to highlight that this “t is an oversimplification of a much more complex problem.” I’m inclined to agree. The greater variable is likely the quality of the homework than time spent on it.
Nevertheless, one result was unequivocal: that some homework is better than none at all : “students who complete any amount of homework earn higher test scores than their peers who do not complete homework.”
7. 74% of Teens cite Homework as a Source of Stress
A study by the Better Sleep Council found that homework is a source of stress for 74% of students. Only school grades, at 75%, rated higher in the study.
That figure rises for girls, with 80% of girls citing homework as a source of stress.
Similarly, the study by Galloway, Conner & Pope (2013) found that 56% of students cite homework as a “primary stressor” in their lives.
8. US Teens Spend more than 15 Hours per Week on Homework
The same study by the Better Sleep Council also found that US teens spend over 2 hours per school night on homework, and overall this added up to over 15 hours per week.
Surprisingly, 4% of US teens say they do more than 6 hours of homework per night. That’s almost as much homework as there are hours in the school day.
The only activity that teens self-reported as doing more than homework was engaging in electronics, which included using phones, playing video games, and watching TV.
9. The 10-Minute Rule
The National Education Association (USA) endorses the concept of doing 10 minutes of homework per night per grade.
For example, if you are in 3rd grade, you should do 30 minutes of homework per night. If you are in 4th grade, you should do 40 minutes of homework per night.
However, this ‘rule’ appears not to be based in sound research. Nevertheless, it is true that homework benefits (no matter the quality of the homework) will likely wane after 2 hours (120 minutes) per night, which would be the NEA guidelines’ peak in grade 12.
10. 21.9% of Parents are Too Busy for their Children’s Homework
An online poll of nearly 300 parents found that 21.9% are too busy to review their children’s homework. On top of this, 31.6% of parents do not look at their children’s homework because their children do not want their help. For these parents, their children’s unwillingness to accept their support is a key source of frustration.
11. 46.5% of Parents find Homework too Hard
The same online poll of parents of children from grades 1 to 12 also found that many parents struggle to help their children with homework because parents find it confusing themselves. Unfortunately, the study did not ask the age of the students so more data is required here to get a full picture of the issue.
Get a Pdf of this article for class
Enjoy subscriber-only access to this article’s pdf
Interpreting the Data
Unfortunately, homework is one of those topics that can be interpreted by different people pursuing differing agendas. All studies of homework have a wide range of variables, such as:
- What age were the children in the study?
- What was the homework they were assigned?
- What tools were available to them?
- What were the cultural attitudes to homework and how did they impact the study?
- Is the study replicable?
The more questions we ask about the data, the more we realize that it’s hard to come to firm conclusions about the pros and cons of homework .
Furthermore, questions about the opportunity cost of homework remain. Even if homework is good for children’s test scores, is it worthwhile if the children consequently do less exercise or experience more stress?
Thus, this ends up becoming a largely qualitative exercise. If parents and teachers zoom in on an individual child’s needs, they’ll be able to more effectively understand how much homework a child needs as well as the type of homework they should be assigned.
Related: Funny Homework Excuses
The debate over whether homework should be banned will not be resolved with these homework statistics. But, these facts and figures can help you to pursue a position in a school debate on the topic – and with that, I hope your debate goes well and you develop some great debating skills!

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Homework Ban
- X (formerly Twitter)
NAT: Hey, Nat here, let's see what's making news. Poland has just banned homework. Yes, that's right no homework ever. For lower primary students anyway. Here's Wren.
DAKOTA: Are you thinking what I'm thinking?
JACK: Yeah. Let's move to Poland.
DAKOTA: No, let's make a mind control device so we can make the Prime Minister ban homework in Australia.
JACK: Okay.
Yep, over here in Poland, kids are here living the dream. Homework is now banned for students in years 1 to 3 and for students in years 4 to 8, it's optional and won't count towards grades.
OLA: I am happy because this homework, I did not like it too much and it didn't really make much sense because most people in my class, in the morning would copy it from someone who has done the homework.
JUILAN: It's a little bit uncool that there is no more homework. But when there is no homework, that's also rather cool.
The Polish government decided to make the big move. After a moment that went viral at a campaign rally in the lead up to the parliamentary elections were a 14-year-old decided to make a stand for all Polish kids.
MACIEK, PRIMARY SCHOOL STUDENT: This is a general problem of Polish schools that children's rights are being violated. For example, the right to take some rest. There is homework to be done during weekends, tests on Mondays, and so much homework is given us that we find no time for rest.
A lot of people agreed with Maciek. Before the ban, Polish kids spent around 1.7 hours per day on homework, which is more than a lot of other countries, and some experts questioned whether or not it was doing any good.
BARBARA NOWACKA, POLISH EDUCATION MINISTER: When I read research regarding the mental health of children, their overload with learning, the reasons of depression, of tensions, stress, or loss of interest in learning, one of the factors, the one that could be removed fastest, was the burden of homework.
Some studies have shown that while homework can be handy for high school students in primary school it doesn't necessarily help you learn and it takes up time that could be better spent doing things like hanging out with friends, playing sport, or doing other creative stuff.
STUDENT: I don't mind it but I still feel like it's a waste of time.
STUDENT: Because you could do everything else? Like you could do exercise? You could, like, play games.
On the flipside, fans of homework say, it can be a good way of making sure all the stuff you've learnt at school sticks in your head, and getting your parents involved in your learning. It can also teach you how to work independently, and to help you get ready for high school and university.
STUDENT: You can research more, and you have more time to catch up.
STUDENT: My grades have gone up a lot because of doing homework.
Some parents and teachers in Poland aren't on board with the ban, which they say happened too quickly and without enough consultation. So, could something like this happen here? Well, right now it's not on the cards and it's up to schools to decide their own homework policies. Unless of course…
DAKOTA: Three, two, one. JACK: Did it work? DAKOTA: Probably not.
Recently the Polish government decided to ban homework in lower primary and make it optional in upper primary. It’s a move that’s been welcomed by many kids although not all adults think it’s a good idea. We find out more about the debate over homework and whether or not it helps kids to learn.
- Justina Ward, Reporter
BTN Classroom Episode 10, 2024
In this episode
Kokoda Track
China Athlete Doping Claims
Should Homework Be Banned?
Homework Debate
Should Homework be banned? Newsround
- Close Menu Search
- Book Reviews
- Music Reviews
- Co-Curricular Clubs
- Campus Ministry

- The Disproportionate Rates of Homelessness Among Minorities
- Anti-Racism
- Artistic Expressions of Social Justice and Racial Equality
Why (Most) Homework Should Be Banned
The 30-minute rule is there to justify giving a lot of homework
Anthony Malcolm ‘23 , Staff Writer December 8, 2022
There are plenty of reasons why (most) homework should be banned. I’ll start out with some general facts and look at homework in general, then go into some detail about our school.
Stanford conducted a study surveying over 4,300 students in 10 high performing high schools in California. More than 70% of the students said they were “often or always stressed over schoolwork,” with 56% claiming that homework was the main stressor. But here’s the kicker: Less than 1% said homework was not a stressor.
The researchers then asked the students if they had exhibited symptoms of stress like headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss, and stomach problems. More than 80% of the students reported at least one stress related symptom recently and 44% claimed they experienced 3 or more symptoms. The study also found that students who spend a lot of time working on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, and a lack of balance in their lives. The study claimed that any more than 2 hours of homework per night was counterproductive, and that the students who spent too much time on homework were more likely to not participate in activities and hobbies, and stop seeing friends and family.
A smaller NYU study claimed that students at elite high schools are susceptible to chronic stress, emotional exhaustion, and alcohol and drug abuse. About half of the students said they received at least 3 hours of homework a night on top of being pressured to take college level classes and participate in extracurricular activities (sound familiar?). The study claims that many of the students felt they were being worked as hard as adults, and they said that their workload seemed inappropriate for their development level. The study reported that the students felt that they had little time for relaxing and hobbies. More than two thirds of students said they used alcohol or drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with the stress.
Back to the Stanford study for a second; many of the students claimed that the homework was “pointless” or “mindless.” The study argues that homework should have a purpose and benefit, which should be to cultivate learning. One of the main reasons is that school feels like a full-time job at this point. We, as in BC High students, are in school from 8:25 till 2:40; most of us have some sort of extracurricular activity on top of that, and most of us have significant commutes, which means we are getting home much later. On top of a rigorous day at school, an afterschool activity, and a commute, we have to deal with a varying amount of homework every night. Sometimes it is 2 hours, sometimes 3, sometimes even 4. I will give you an example of a day in my life last year to provide a specific example, because we are not a one size fits all community.
I live in Middleboro and Bridgewater, so I ride the train to school which takes 50 minutes to an hour. A spring day last year would start by waking up at 5:30 and then leaving my house to get to the train at 6:30-6:35, getting on the train at 6:50, getting off the train at 7:50, and arriving at the school before classes started at 8:20. I would go through the school day and stay after for track practice. After track, I would most likely get on the train at 5:00 and get home at 6:15. I would eat dinner, shower, and then start my homework around 7:30-8, and usually I would finish somewhere between 10:30ish to 11:30ish. Can you see how that can be misconstrued as a full-time job?
Some of you might be thinking (especially any teacher reading this), why didn’t you use the 30-minute rule? Well, because most (and I mean MOST) of the time the 30-minute rule is an ineffective rule that justifies giving students a lot of homework. If you use the 30-minute rule and don’t finish a homework assignment, it still has to be completed sometime, and you’ll be behind in class. It is only effective when a teacher plans for the 30-minute rule and tells you to stop at 30 minutes to get an idea of how long an assignment takes their students. The 30-minute rule is there to justify giving a lot of homework because if you say in class that the homework took a long time, you will probably be told about the 30-minute rule. But if you used the 30-minute rule, you would have an unfinished homework assignment which means, depending on the class, you would be lost and behind, and you would still have to do it at some point. If you should have to justify giving a lot of homework, then it is probably too much.
Parker, Clifton B. “Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework.” Stanford University , 10 Mar. 2014, http://news.stanford.edu/news/2014/march/too-much-homework-031014.html .
Communications, NYU Web. NYU Study Examines Top High School Students’ Stress and Coping Mechanisms . http://www.nyu.edu/content/nyu/en/about/news-publications/news/2015/august/nyu
-study-examines-top-high-school-students-stress-and-coping-mechanisms .
Sex Scene Discourse
Why Can’t You Get into College?
Behind the Commencement Speaker Selection Process
Be Worried?
Is the House System worth it?
Why JUG will Never Change
Should Parents Check Our Phones?
Hoodies in BC High?
Toll Booths: A Rebuttal
Why Do We Chase Success?
The Eyes and Ears of BC High.
Comments (0)
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Study Skills
No More Homework: 12 Reasons We Should Get Rid of It Completely
Last Updated: February 16, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Finn Kobler . Finn Kobler graduated from USC in 2022 with a BFA in Writing for Screen/Television. He is a two-time California State Champion and record holder in Original Prose/Poetry, a 2018 finalist for the Los Angeles Youth Poet Laureate, and he's written micro-budget films that have been screened in over 150 theaters nationwide. Growing up, Finn spent every summer helping his family's nonprofit arts program, Showdown Stage Company, empower people through accessible media. He hopes to continue that mission with his writing at wikiHow. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 129,057 times. Learn more...
The amount of homework students are given has increased dramatically in the 21st century, which has sparked countless debates over homework’s overall value. While some have been adamant that homework is an essential part of a good education, it’s been proven that too much homework negatively affects students’ mood, classroom performance, and overall well-being. In addition, a heavy homework load can stress families and teachers. Here are 12 reasons why homework should be banned (or at least heavily reduced).
School is already a full-time job.

- For years, teachers have followed the “10-minute rule” giving students roughly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. However, recent studies have shown students are completing 3+ hours of homework a night well before their senior years even begin. [2] X Trustworthy Source American Psychological Association Leading scientific and professional organization of licensed psychologists Go to source
Homework negatively affects students’ health.

Homework interferes with student’s opportunities to socialize.

Homework hinders students’ chances to learn new things.

Homework lowers students’ enthusiasm for school.

Homework can lower academic performance.

Homework cuts into family time.

Homework is stressful for teachers.

Homework is often irrelevant and punitive.

- There are even studies that have shown homework in primary school has no correlation with classroom performance whatsoever. [9] X Research source
Homework encourages cheating.

Homework is inequitable.

Other countries have banned homework with great results.

- There are even some U.S. schools that have adopted this approach with success. [13] X Research source
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.edutopia.org/no-proven-benefits
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/monitor/2016/03/homework
- ↑ https://healthier.stanfordchildrens.org/en/health-hazards-homework/
- ↑ https://teensneedsleep.files.wordpress.com/2011/04/galloway-nonacademic-effects-of-homework-in-privileged-high-performing-high-schools.pdf
- ↑ https://time.com/4466390/homework-debate-research/
- ↑ https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00220485.2022.2075506?role=tab&scroll=top&needAccess=true&journalCode=vece20
- ↑ https://kappanonline.org/teacher-stress-balancing-demands-resources-mccarthy/
- ↑ https://www.chicagotribune.com/lifestyles/ct-life-homework-pros-cons-20180807-story.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6294446/
- ↑ https://www.theatlantic.com/business/archive/2016/06/homework-inequality-parents-schedules-grades/485174/
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/news/education-37716005
- ↑ https://www.wsj.com/articles/no-homework-its-the-new-thing-in-u-s-schools-11544610600
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Anonymous ..
Did this article help you?

Leonardo F.

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
We need your help now
Support from readers like you keeps The Journal open.
You are visiting us because we have something you value. Independent, unbiased news that tells the truth. Advertising revenue goes some way to support our mission, but this year it has not been enough.
If you've seen value in our reporting, please contribute what you can, so we can continue to produce accurate and meaningful journalism. For everyone who needs it.
- Temperature Check
- The Stardust Inquests
- Inside The Newsroom
- Climate Crisis
- International

'Why I believe homework should be banned', by one primary school student
As the discussion around state exams through the Covid-19 shutdown continues, a separate debate about the very need for homework itself rumbles on. Over the years, many have argued that homework for students in busy modern-day family structures is no longer workable.
This year, the Green Party sought to open a discussion about the banning of homework in future. Here, primary school pupil Misha McEnaney, a fifth class student from Dublin, outlines why he believes homework is more of a hindrance than a help.
IRISH CHILDREN SPEND around 274.5 hours on homework in a year. Is it a waste of time? Generally speaking, homework does not improve academic performance among children, although it may improve academic skills among older students especially lower-achieving kids. Homework also creates stress among students who could be doing other things.
I think it is a waste of time. Here’s why I think so.
Many students think homework is extremely boring and hard so it increases our stress levels. You might fight with your family or friends and that gives the impression you are angry and irritated when often it’s just because your homework is increasing your stress.
Also, a study by scholar Denise Pope at Stanford shows that out of 4,300 students at high-performance schools, 60% stated that their homework was their primary source of stress.
Movement is more important
I believe that homework eliminates time when you could be exercising, playing sports, carrying out hobbies, reading etc. So when your friends are playing outside or something exciting or important is happening you can’t go out because you’re stuck inside doing your homework.
Homework messes up your sleep cycles and it causes you to be more tired. After school when you’re tired from working you still have to do your homework, so you don’t deliver your full concentration and that makes your performance not as acceptable as it should be. This can cause your grade to go down and so that defeats the whole point of education to become better and smarter.
A study from teenink.com shows that students perform best in school when they receive 10–12 hours of sleep each night, while only 15% of teenagers in America reported themselves sleeping eight hours or more on school nights, according to the national sleep foundation of America. Sleep disruption is very bad for our health.
Teacher trust
If you’re completely booked up for the day doing sports or other activities you have no time to do your homework. Your teachers start to trust you less and less and this develops a bad view of you when it’s not entirely your fault.
It’s also repetitive so you’re doing the same work at school and there’s no effectiveness, it’s not going in. So all that homework becomes a waste because you have already completed it at school. You can also easily get distracted.
Homework takes away revision time for tests and that can affect the test scores. That develops a bad reputation for the student and for the school. The parents then assume that the teaching at the school is bad and they might move school. So the kid might lose friends and over time the school becomes less liked and popular.
All because there is too much homework.
Bad for the mood
If you don’t sleep enough it can cause mood swings which can affect students’ performance and relationships. To think we can stop all of this by just banning homework makes me wonder why schools still give out homework at all.
People who believe that homework should not be banned have reasonable points and arguments. They believe that doing homework at home can be better for the students and they would receive higher results.
They also think the parents of the students will have an idea of what type of work they are doing in the classroom, at what scale the student is doing their work and how the student is doing that work. There is absolutely no reason why parents shouldn’t know what the student’s work is like.
Some people believe that homework boosts interaction between a student and his or her teacher. Homework might develop their presentation skills. They believe that homework is “a remedy against weaknesses”. These can all be done at school. They believe it teaches the students responsibility because they have to make sure that they do their work and not lose it or destroy it.
They think the students learn much more new information as well as in school. So people think it teaches the students important life skills. They also think it keeps the students busy and entertained. I would argue that these should all be the responsibility of parents, not school.
A shift in the debate
The Green Party in Ireland has promised to explore the banning of homework for primary school children. They also vow to review primary and secondary schools curriculum “to meet the needs of the 21st century”. Catherine Martin, deputy leader of the Green Party, said that “the phasing out of homework is something that definitely should be explored”.
“This isn’t new, this has been on our policy for the past several years. And I think we really need to have a conversation on how best to develop the creative juices of our children, or really change how we do homework, homework could be, ‘go home and draw a picture of something that means a lot to you’,” she said.

“They’re so young, especially up to the age of seven or eight, it’s a conversation that we need to have”.
She used the example of Loreto Primary School in Rathfarnham, Dublin, which is currently trialling a “no-homework” programme for all classes except sixth. Ms Martin said that they had found the pilot scheme “amazing” and children were spending a lot more time with their families as a result.
Mental health considerations
Psychotherapist Mary McHugh believes that we are reducing children’s natural “curious, imaginative and creative” tendencies by “pressuring them to conform”.
“Our children from the age of three, are being trained to sit still and from five upwards, it’s expected that this is the norm.” McHugh also says that “stress is showing up at an alarming scale and we’re still applying more pressure academically younger and younger”.
Let’s look at Finland. In Finland, there is no homework in all schools. Finland agrees that there should be no homework because it increases stress, it wastes time etc. Finnish students regularly top the charts on global education metric systems.
Some 93% of Finnish students graduate from secondary school compared to 75% in the USA and 78% in Canada. About two in every three students in Finland go to college which is the highest rate in Europe. The students’ test scores dominate everyone else. These are the scores for the PISA test (Program for International Student Assessment) 2006. There are other reasons why Finland’s education system is so good but no homework is definitely an important one.
Homework increases stress levels among students. It replaces time for hobbies and sports. It messes up your sleep. It can’t always be done and that causes trouble. It’s repetitive. You can develop health problems from lack of sleep.
It takes away time for studying and also when you don’t get enough sleep you can get mood swings and that can affect performance and relationships. There are reasonable arguments for why people who believe that homework shouldn’t be banned are wrong.
We have seen that the Green Party also thinks that homework should be banned and that some schools have already trialled it. We have looked at Finland banning homework and we have seen the impact it has made compared to other countries. This is why I think homework should be banned, not just in my school but in all schools.
Misha McEnaney is a fifth class student at St Mary’s College, Rathmines, Dublin.

Making a difference
A mix of advertising and supporting contributions helps keep paywalls away from valuable information like this article. over 5,000 readers like you have already stepped up and support us with a monthly payment or a once-off donation..
For the price of one cup of coffee each week you can make sure we can keep reliable, meaningful news open to everyone regardless of their ability to pay.
To embed this post, copy the code below on your site
600px wide <iframe width="600" height="460" frameborder="0" style="border:0px;" src="https://www.thejournal.ie/https://www.thejournal.ie/readme/homework-5086000-May2020/?embedpost=5086000&width=600&height=460" ></iframe>
400px wide <iframe width="600" height="460" frameborder="0" style="border:0px;" src="https://www.thejournal.ie/https://www.thejournal.ie/readme/homework-5086000-May2020/?embedpost=5086000&width=400&height=460" ></iframe>
300px wide <iframe width="600" height="460" frameborder="0" style="border:0px;" src="https://www.thejournal.ie/https://www.thejournal.ie/readme/homework-5086000-May2020/?embedpost=5086000&width=300&height=460" ></iframe>
Create an email alert based on the current article
- Entertainment
- London / Europe
- Border / Cartel Chronicles
- Israel / Middle East
- Latin America
- On the Hill Articles
- On The Hill Exclusive Video
- Breitbart News Daily
- Newsletters
- Trump Trial
- Anti-Israel Campus Protests
- Ukraine Funding Betrayal
- Wide Open Border
- Bidenomics Bust
California Lawmaker Introduces Bill Banning Excessive Homework: ‘Homework Is Exhausting’

A lawmaker in California introduced a bill that would ban teachers from being able to assign students an excessive amount of homework.
California State Assembly member Pilar Schiavo (D) introduced The Healthy Homework Act, also known as AB 2999, in February, noting in an interview with Fox40 that it would have a “huge impact” on the students.
Under AB 2999 , educational agencies, local school board officials, and school administration officials would need to “develop, adopt, and update” homework policies “at least once every five years,” and take into account research available regarding the impacts of homework on students’ physical and mental health.
Educational agencies, school board, and school administration officials would also need to take into account the reasonable amount of time that students should spend on homework and take into account learning disabilities and how some students might lack “access to the internet, computers, and learning tools.”
“I think this is going to make a huge impact for the students,” Schiavo said. “The times have changed and our homework policies don’t always change with the times, so we need to make sure we are addressing issues that are effective and also don’t harm kids.”
📚 The Healthy Homework Act (AB 2999) Advances! 🌟 With local control and input from teachers, students, and parents, #AB2999 aims to create supportive, equitable homework policies for our kids' mental and physical health. Let's make homework more supportive and less stressful! pic.twitter.com/4JawwuztZ0 — Assemblymember Pilar Schiavo (@AsmPilarSchiavo) April 24, 2024
Schiavo’s daughter, Sofia Johnson, who is in sixth grade, told the outlet that “homework is exhausting” and “overwhelming.”
“It’s depressing that my whole day — from when I wake up to when I go to bed — is nearly all taken up with schoolwork,” Johnson added.
While homework can be good, “there is a limit to how much kids can benefit from home study,” said Harris Cooper , a Professor Emeritus of Psychology and Neuroscience at Duke University, according to the American Psychological Association.
Cooper added that he agreed with the rule of thumb that students should be doing no more than 10 minutes of homework for each grade.
However, one of the downfalls of homework can also be associated with the lack of resources available to students at home.
The American Psychological Association wrote:
Yet homework can be a problem at the other end of the socioeconomic spectrum as well. Kids from wealthier homes are more likely to have resources such as computers, Internet connections, dedicated areas to do schoolwork and parents who tend to be more educated and more available to help them with tricky assignments. Kids from disadvantaged homes are more likely to work at afterschool jobs, or to be home without supervision in the evenings while their parents work multiple jobs, says Lea Theodore, PhD, a professor of school psychology at the College of William and Mary in Williamsburg, Virginia. They are less likely to have computers or quiet place to do homework in peace.
Schiavo’s bill comes after Standford University and Challenge Success , an organization that “partners with school communities to elevate student voice and implement research-based, equity-centered strategies that improve student well-being,” reportedly conducted a survey of more than 300,000 students.
The survey found that 45 percent of students said homework was their number one source of stress.
“If it’s such a source of stress for kids, and we know taking stress off kids’ plates will make a difference in their mental health, this is something that can practically impact kids’ mental health overnight,” Schiavo told the outlet.
Breitbart News reached out to Challenge Success for a statement but did not receive a response by the time of publication.
Please let us know if you're having issues with commenting.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

Campus protests over the Gaza war
As student protesters get arrested, they risk being banned from campus too.
Rachel Treisman

Jaclyn Diaz
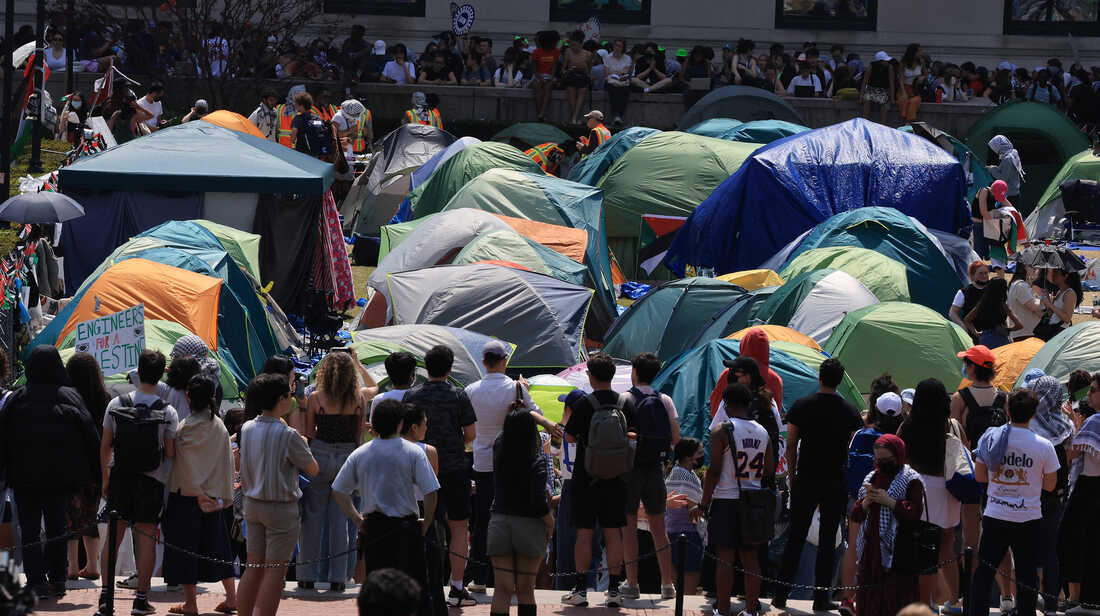

Dozens of tents are seen on a lawn inside the Columbia University Campus after students refused to take down the encampment by the 2 p.m. EDT deadline given to students protesting by Columbia President Minouche Shafik. Luiz C. Ribeiro/Tribune News Service/Getty Images hide caption
Dozens of tents are seen on a lawn inside the Columbia University Campus after students refused to take down the encampment by the 2 p.m. EDT deadline given to students protesting by Columbia President Minouche Shafik.
Pro-Palestinian demonstrators continue to turn out at schools across the country despite the risk of detention and suspension, with nearly 300 more protesters arrested over the weekend .
At Columbia University, where a pro-Palestinian encampment has catalyzed dozens of similar demonstrations across the nation, student protesters face threats of punishment, with some students already receiving word of their suspension.
On Monday morning, Columbia University President Minouche Shafik announced that in, negotiations over the encampment, faculty leaders and student organizers were not able to reach an agreement .
The university gave students until 2 p.m. ET to disperse and abandon the encampments or else face suspension pending further investigation, according to flyers it distributed on campus .
Columbia University spokesman Ben Chang confirmed to reporters that some students taking part in the pro-Palestinian encampment who refused to leave at that deadline were suspended. It's unclear how many students will receive that punishment.
Chang said the move is required to preserve campus safety.

Hundreds of students at a pro-Palestinian demonstration at Columbia University's campus. Brian Mann hide caption
Hundreds of students at a pro-Palestinian demonstration at Columbia University's campus.
Students who voluntarily left the encampment and signed a copy of a form committing to abide by university policies will be on academic probation through June 2025, according to the flyers. Those who remained past the deadline were told they will be restricted from all Columbia campuses and property and ineligible to participate in classes and academic or extracurricular activities.
"You are not permitted to complete the Spring 2024 semester, including participate in classes or exams in-person or remotely or otherwise submit assignments or engage in any activities affiliated with Columbia University," the notice dispersed on campus reads. "You may lose the semester. If you are scheduled to graduate, you are no longer eligible."
Dozens of New York police officers gathered outside the campus gates about an hour ahead of the deadline.
Many students remained despite the threats, saying they have no plans to leave unless the university meets its demand to divest from companies they say are aiding Israel's war in Gaza. After the flyers were distributed, Columbia Students for Justice in Palestine posted on X urging students not to sign anything.

Roughly 100 officers in uniform gathered at Columbia University's campus in the leadup to its 2 p.m. deadline for students to disperse from the encampment that's been up for nearly two weeks. Brian Mann/NPR hide caption
Roughly 100 officers in uniform gathered at Columbia University's campus in the leadup to its 2 p.m. deadline for students to disperse from the encampment that's been up for nearly two weeks.
"We will not be moved by these intimidation tactics. You can see the students are mobilized. There's hundreds of them here today. They will not be moved. We demand divestment, we will not be moved unless by force," Seuda Polat, a Columbia University graduate student, said during a press conference Monday.
Polat continued, "There has been no violence on this encampment. Students from diverse backgrounds have shared their religious observances together. We've celebrated Passover, we've celebrated shabbat twice. This is a place of community, of community learning, not violence."
Police continue to arrest protesters across the country
On Sunday, pro-Palestinian protesters and pro-Israeli protesters clashed at the University of California, Los Angeles, leading to what university leaders described as "physical altercations" and prompting them to increase security measures on campus.

Nearly 300 people arrested at campus protests against the war in Gaza this weekend
At Virginia Tech University, police arrested scores of protesters in the early hours of Monday morning. Virginia Tech Police confirmed early Monday evening that 82 individuals, 53 of whom are current students at the university, were arrested and all were charged with trespassing.
The school had warned of "heavy police activity around the Graduate Life Center" in a series of posts on X (formerly Twitter) starting just after 10 p.m. ET on Sunday, and announced around 3:30 a.m. that the incident " had stabilized ." Social media footage shows protesters chanting at police as they lead people into multiple white vans.
Elsewhere in the state, 12 protesters — including nine students — were arrested at the University of Mary Washington on Saturday evening after refusing to vacate an encampment on its Fredericksburg, Va., campus. University President Troy Paino said in a statement that health and safety concerns had emerged on Saturday after protestors invited the off-campus public to join the encampment.

A man holds up a Palestinian flag as activists and students surround piled barricades at an encampment at at George Washington University early Monday. Kent Nishimura/Getty Images hide caption
A man holds up a Palestinian flag as activists and students surround piled barricades at an encampment at at George Washington University early Monday.
Meanwhile, protests at George Washington University in D.C. are stretching into their fifth day on Monday — the last day of class for the semester — after a tense weekend, culminating in a clash between protesters and police.
Students first set up an encampment on University Yard on Thursday and later launched a second one on nearby H Street after the school put up barricades to restrict access.

The Picture Show
Photos: take a look at campus protests around the country.
Shortly before midnight on Sunday, protesters knocked down the barricades — piling them in a stack in the middle of the lawn — and flooded the lawn, with people remaining there overnight in some 85 tents, the GW Hatchet reports .
GW officials said in a statement early Monday that a group of "approximately 200 protesters from across [D.C., Maryland and Virginia], including professional organizers, activists, and university students, have joined the unauthorized encampment on our campus."
"This is an egregious violation of community trust and goes far beyond the boundaries of free expression and the right to protest," they added. "The university will use every avenue available to ensure those involved are held accountable for their actions."
Schools are alternately threatening and disavowing disciplinary action

Students arrested at Emerson College last week won't face disciplinary action from the school, its president announced. Joseph Prezioso/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Students arrested at Emerson College last week won't face disciplinary action from the school, its president announced.
One question on the minds of many is what, if any, disciplinary action student protesters might face from their schools, especially with finals and graduation fast approaching.
Some universities have suspended — or threatened to suspend — students who have been arrested for protesting, while others have said they will not.
Students have been suspended for protesting at George Washington University , Princeton University , Washington University in St. Louis , Pomona College and Vanderbilt University , according to reports.
Barnard College officials announced Friday that it will allow most of the 53 students who were arrested and suspended after protesting at Columbia University to return to campus. The New York Times reports that suspended students who reached agreements with the college have their access to residence halls, dining facilities and classrooms restored, while others are still working to reach agreements.

Middle East crisis — explained
Across the u.s., pro-palestinian campus protesters risk arrest and suspension.
On Sunday, Jay Bernhardt, the president of Emerson College in Boston — where more than 100 protesters were arrested at an encampment early Thursday morning — said the college will not bring disciplinary charges against protesters, and will "encourage the district attorney not to pursue charges related to encampment violations."
He said it is also taking steps to support students who were arrested, including posting bail for them and providing housing support to those who are required to stay local for court appearances after the closing of their dorms.
"The College has done its best to keep all community members safe every day during these challenging times, but we recognize that we must do more," he added.
In Texas, the Travis County district attorney has dropped misdemeanor trespassing charges against all 57 people arrested during a protest at UT-Austin last week, after a judge found insufficient evidence to proceed.

Law enforcement arrest a pro-Palestinian protestor on April 29, 2024, at the University of Texas at Austin. Michael Minasi/KUT hide caption
Law enforcement arrest a pro-Palestinian protestor on April 29, 2024, at the University of Texas at Austin.
But on Monday, around 100 protesters gathered at UT-Austin and set up a new encampment on the campus' south lawn, according to NPR member station KUT. By mid-afternoon, state, city and university police were on hand, breaking up the gathering.
Elsewhere, some schools are threatening disciplinary action for students who don't comply with directives to leave encampments that they say violate their policies.
Officials at the University of Florida, where students began protesting on Wednesday, said Friday that demonstrators could face suspension and a three-year ban from campus if they violate specific protest rules, reports member station WUFT .
They are prohibited from using bullhorns or speakers to amplify their voices, possessing weapons and protesting inside campus buildings — but also face more vague prohibitions like "no disruption," according to a list circulated late Thursday.
"They also included 'no sleeping' on a campus where students often doze in the sun between classes," per WUFT.

Mass arrests roil college campuses amid pro-Palestinian protests
At Cal Poly Humboldt, officials closed campus to the public on Saturday, several days after student protesters first occupied two academic and administrative buildings. They had previously given protesters until 5 p.m. on Friday to leave with a guarantee of no immediate arrest — but said they would still face consequences.
"This does not, however, eliminate University conduct-related sanctions or legal implications," officials said in a release. "In addition, voluntarily departing in this way will be considered as a mitigating factor in University conduct processes and may reduce the severity of sanctions imposed."
The campus will remain closed until May 10, with work and classes remote through the end of the semester. Officials say they are planning for "various scenarios" for commencement.
At Massachusetts Institute of Technology, president Sally Kornbluth said in a Sunday message to students that their growing encampment violates policies around registering for campus demonstrations and creates a "potential magnet for disruptive outside protestors."
She said rules have been broken, and those who break them — "including rules around the time, place and manner of protest" — will face disciplinary action.
"We are open to further discussion about the means of ending the encampment," she added. "But this particular form of expression needs to end soon."
Northwestern reaches a deal with protesters

Signs are displayed outside a tent encampment at Northwestern University on Friday in Evanston, Illinois. Students and the university reached a deal Monday, allowing the demonstrations to continue, but that mandated the removal of all but one of these tents. Teresa Crawford/AP hide caption
Signs are displayed outside a tent encampment at Northwestern University on Friday in Evanston, Illinois. Students and the university reached a deal Monday, allowing the demonstrations to continue, but that mandated the removal of all but one of these tents.
Northwestern University reached an agreement Monday with students and faculty protesting against the war, as demonstrations continued at other campuses across the country.
The deal was struck five days after students erected an encampment on Deering Meadow, a common area on the university's Evanston campus.
The agreement allows demonstrations to continue until the end of spring quarter classes on June 1, "provided all such activity immediately and continuously complies with University policies," Northwestern officials said in a statement.
The school will allow one aid tent to remain at the encampment on Deering Meadow but is demanding all other tents and sound systems be taken down.
"This agreement also addresses our commitment to protect the safety of our entire community and to ensure the ongoing academic operations of our campus while adhering to our support for free expression," Northwestern President Michael Schill wrote in an announcement posted on the school's website. "The agreement includes support for our Muslim, Arab and Palestinian students. Some of the actions have been discussed for years and some are new. Together, they will strengthen our community."
As part of the agreement, the university has promised to fund two Palestinian faculty members per year for two years and to provide scholarships for five Palestinian undergraduates.
Some faculty are calling for amnesty
Students and faculty at some universities are calling on their administrations not to discipline protesters. Arrested protesters face uncertainty about not only their legal records but the status of campus housing, financial aid and graduation eligibility.
At the University of Pennsylvania , officials say a campus statue was vandalized with antisemitic graffiti and are calling on demonstrators — from Penn and other area schools — to disband.
A group of Penn faculty and Philadelphia-area elected officials signed a letter last week urging university leaders to "respect students' rights to engage in nonviolent protest" by refraining from calling in law enforcement to make arrests and from filing disciplinary and criminal charges against peaceful protesters at the encampment.
"Protesters nationwide face police violence and severe discipline, and the safety and wellbeing of Philadelphia students exercising their rights are among our foremost concerns," they wrote.

In Columbia University's protests of 1968 and 2024, what's similar — and different
Nearly 300 faculty members at Yale University, where 48 protesters were arrested last week, signed a letter condemning what they called "the criminalization of Yale students engaged in recent acts of peaceful protest." They demanded that the university take no further disciplinary action and called on authorities to drop all charges against them.
They said the protesters arrested face Class A misdemeanors under Connecticut law, which carry possible penalties of up to 364 days in jail.
"Threatening students with sanctions of this kind is unconscionable and should not be the means by which Yale responds to peaceful protest," they added.
In a further sign of discontent, faculty members at universities in California, Georgia and Texas have either initiated or passed largely symbolic votes of no confidence in their leadership, according to the Associated Press .
- campus protests
- student protests
- Israel-Hamas war
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Campus Protests Aren’t Going Away. Colleges Need to Draw Lines.
By David French and Sarah Wildman
Produced by Vishakha Darbha and Jillian Weinberger
Student protests across the country continue to escalate, leading to mass arrests and police action.
In this conversation with politics editor Sarah Wildman, the Times Opinion columnist David French argues that while free speech needs to be upheld and even encouraged on campuses, there’s a line between civil disobedience and lawlessness, and universities need to clearly articulate where that line is.
Below is a lightly edited transcript of the audio piece. To listen to this piece, click the play button below.
Sarah Wildman: I’m Sarah Wildman , a staff editor and writer for Times Opinion.
Newsreel: (Protest chants)
Campus protests and rallies have been percolating since Oct. 8, but in the past week, something shifted.
Newsreel: New York City police used force last night to zip-tie the hands of dozens of student protests and hauled them away in buses. Newsreel: Protests against Israel’s assault on Gaza have rocked campuses from coast to coast over the past week. Newsreel: The ongoing demonstrations have stirred debate about the line between free speech for the protesters and open harassment of Jewish students.
Sarah Wildman: It seems on and off campus, the idea of what kind of protest should and should not be allowed is an open question. So I wanted to talk to my colleague David French . He recently wrote about this dilemma and what universities should be doing.
David is an opinion columnist. He’s a lawyer who spent most of his career defending free speech and religious freedom. He’s defended countless protesters, and he has been the subject of protest himself.
David, thank you so much for joining me.
David French: Well, thanks so much for having me, Sarah.
Sarah Wildman: In your recent column , you note that universities are meant to be the “sponsor of critics … not … the critic.” What does that mean?
David French: Schools that are bound by the First Amendment or adopt First Amendment-like principles as many private universities do should be neutral towards the expression of the protesters on campus.
They should be focused on granting equal access, equal rights to various sides of campus disputes. And one of the dangers you see with many of these encampments is their very existence crowds out other voices, and that’s one of the reasons why universities have implemented “time, place and manner restrictions” so that everyone has equal access to the quad, for example, or everyone has equal access to the public forums on campus.
Sarah Wildman: Does that mean you would support forcibly removing the encampments?
David French: Well, there are circumstances in which removing the encampments is necessary to ensure equal access to campus. These are legal responsibilities that the university has.
For example, if one set of students are occupying part of the campus that is normally open to other students as well, and other students are seeking to use that — as they have a right to do under the law — if the university is allowing the encampment to maintain, it can actually be violating the law itself.
Then if the encampment becomes a home of, for example, some vicious antisemitic speech, then it starts to get into the neighborhood of potential civil rights violations. And so, in some circumstances, I don’t think the law gives them much choice but to remove some of these encampments.
Sarah Wildman: Before we go deeper into this moment and the specificities of what’s happening on campuses across the country, I wanted you to take us back to your first experience with campus protest.
David French: Absolutely. It was my first year of law school. I went to a small Christian college in Nashville. And although a lot of my classmates had a lot of political feelings, it was just not a culture given to protest at all. And so I had never encountered it.
And I remember I’m studying in one of my first weeks of law school and I heard drums outside and I had no idea why. And I went out and I saw my first campus protest. It was a protest over faculty diversity at Harvard Law School in 1991. This was an issue that had really divided the campus. I watched a group of students get together and have a pretty raucous protest in front of our library, lots of angry speeches. There was dancing, there was chanting, there was drumming. People were angry, but it was all clearly just a free speech activity. It was all quite clearly exactly the kind of conduct that would be encompassed by the First Amendment.
And I remember being fascinated by it all and interested in quite a few of the campus protests. But they also took a much darker turn at times where the protests would get more aggressive, that protest movements would extend to the classroom to the extent that you would shout down other students to prevent them from being heard. There were disruptive occupations of the administration building.
So I saw the good, the bad and the ugly of campus protesting during my time in law school. And that experience helped launch my free speech career.
Sarah Wildman: In your most recent column, you identify the moment we’re in as one of lawlessness versus civil disobedience. That, to me, seems pretty gray. How are we defining lawlessness versus civil disobedience?
David French: One of the elements of civil disobedience is the person who participates in the act of civil disobedience accepts the consequences of the act.
In other words, things like we saw at Columbia, where people are trying to block access to the police that are trying to clear an encampment that is no longer lawful, or when you are masking and covering your face and perhaps breaking into buildings or blocking access so that students cannot go to classes — when civil disobedience starts to interfere with the rights of others, it is transgressing the bounds. When individuals are refusing to accept the consequences of breaking the law, it is transgressing the bounds.
So civil disobedience is not a license to do what I want, to whom and however I want, as long as it’s for a good cause. That’s not what civil disobedience is.
Sarah Wildman: It seems to me, though, that protests throughout time and certainly within the last 50 years of American history have often had the goal to disrupt. How does that fit into an idea of civility as you describe it?
David French: What I go back to when I think about protests — that is destructive versus protest that is constructive — is protests should not violate other people’s rights. When you’re violating other people’s rights through your protest, you are crossing red lines at that point.
And what I have seen many people do is, if they have sympathy for the underlying cause that the protesters are pursuing, they’ll often make a lot of excuses for the violation of other people’s rights. They’re more sympathetic to it.
But then if they strongly disagree with that cause, then they’re able to see with quite extreme clarity how much that protest is destructive and disruptive. And so one thing that I would ask people to do when they’re evaluating protests is immediately ask, how would you react to that protest if it was coming from somebody with whom you had strong disagreements? Would you see this as constructive, or would you see this as extremely destructive?
I prefer to take a wider look and say, “Is this protest violating other people’s rights?” And if so, it is this responsibility of the government to ensure that we all can exercise our rights.
Sarah Wildman: Are the lines drawn differently when protest is so closely aligned with student identities? You’ve mentioned antisemitism. We haven’t really dug in on why you have. Does it change the nature of how we see this protest if it’s aligned with specific student identities?
David French: So there are really two separate sort of legal strands here. One is, are there identity-based attacks on Jewish students on campus to such an extent that it arises to the level of harassment under federal law, is one set of questions.
Then there’s another set of questions that says, does occupying this quad, does the nature, the time, or the place or the manner of the protest that I’m engaged in, is it actually violating the free expression rights or the equal access rights of other students, regardless of their identity?
So, identity does matter as a matter of federal law, but when it comes to First Amendment analysis, it doesn’t matter as much.
Sarah Wildman: Is this about a failure of control?
David French: Well, it’s about a failure to enforce reasonable time, place and manner restrictions. I don’t know if you would call that control so much as rule of law.
The reasonable time, place and manner restrictions are designed to allow all members of a community to have the same rights within the community. And so, one of the problems that you have is a lot of campus administrators don’t want to do the hard thing. And so they hope the problem goes away, but it doesn’t. It becomes a much harder thing and then a much harder thing until it becomes almost an impossible thing to deal with.
Whereas by taking decisive action early when you see the first violations of these time, place and manner restrictions, you can prevent a problem from escalating to the extent that we’ve seen at Columbia and other schools.
Sarah Wildman: You mentioned Columbia — there you’re seeing some professors outwardly supporting, speaking out about, even protesting themselves, and the administration seen as suppressing. Does that tension create chaos?
David French: The university members of the faculty, they have their own academic freedom rights. They have their own free speech rights. But they also have their own legal obligations, both as members of the community and members of the faculty. And so, one of the things you want to protect when you are talking about free speech on campus is faculty free speech on campus. But if faculty engages in civil disobedience, it should accept the consequences. If faculty participates in protest that violates the rights of others, then it should accept the consequences of that as well.
Sarah Wildman: This goes back to this question of what a university’s role should be in campus activism. I was thinking about this in terms of words like neutral, supportive, incorporating, even promoting activism in some way. Is there a role the university plays other than providing a forum where both sides or many sides can discuss?
David French: Universities have their own institutional academic freedom. So a university does have the academic freedom to say, “OK, we’re going to fly a Palestinian flag. We’re going to condemn Israel’s incursion into Gaza.” A university institutionally can engage in boycotts and divestment. But if they take a single dime of federal dollars, they cannot refuse to protect any identity group from harassment covered by federal anti-discrimination law.
Sarah Wildman: You wrap up your piece by noting that the issues aren’t going away.
David French: No.
Sarah Wildman: And next fall, we may, unfortunately, still be seeing conflict in the Middle East. What’s the best-case scenario for campuses going forward?
David French: I think that a lot of campus administrators need to read some of the statements that I have seen come out of, for example, University of Chicago, where lines are clearly drawn: We will protect free speech. We will permit all voices to protest. We will protect faculty academic freedom. But the instant that your protest violates the rights of others is when it is too far. That language has to be clearly, clearly communicated from Day 1 of the fall semester, and then the university has to walk the talk.
So when the encampments come up, the message has to be “Zero disruptions are permitted, discipline will commence.” And that kind of approach, you’re protecting the rights of free speech, but you’re also protecting the rights of others to access the campus.
Sarah Wildman: David, thank you so much for joining us today.
David French: Thanks so much, Sarah. Really appreciated the conversation.

Thoughts? Email us at [email protected] .
This episode of “The Opinions” was produced by Vishakha Darbha and Jillian Weinberger. It was edited by Alison Bruzek and Kaari Pitkin. Mixing and original music by Sonia Herrero. Fact-checking by Mary Marge Locker. Audience strategy by Kristina Samulewski and Shannon Busta.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
David French is an Opinion columnist, writing about law, culture, religion and armed conflict. He is a veteran of Operation Iraqi Freedom and a former constitutional litigator. His most recent book is “Divided We Fall: America’s Secession Threat and How to Restore Our Nation .” You can follow him on Threads ( @davidfrenchjag ).

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies' Home Journal, decried homework's negative impact on children's physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but ...
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right. Students, read the entire article, then tell us ...
Why I Think All Schools Should Abolish Homework. 7 minute read. ... the daily homework slog keeps many students on the clock as long as lawyers, teachers, medical residents, truck drivers and ...
Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and ...
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
That report cited findings from a 2012 survey of first-year college students in which 38.4 percent reported spending six hours or more per week on homework during their last year of high school. That was down from 49.5 percent in 1986 ( The Brown Center Report on American Education , 2014).
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein, co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work ...
Undoubtedly, homework is a global phenomenon; students from all 59 countries that participated in the 2007 Trends in Math and Science Study reported getting homework. Worldwide, only less than 7% ...
The homework wars are back. By Jacob Sweet Updated Feb 23, 2023, 6:04am EST. As the Covid-19 pandemic began and students logged into their remote classrooms, all work, in effect, became homework ...
Jan 24, 2020. Recent research shows that teenagers have doubled the amount of time they spend on homework since the 1990s. This is in spite of other, well-documented research that calls the efficacy of homework into question, albeit in the younger grades. Why are students spending so much time on homework if the impact is zero (for younger kids ...
Elementary school students have an average of around 4.5 hours of homework a week, while high schoolers get an average of about 7.5 hours, according to the Wall Street Journal and Department of ...
The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in a class with no homework. Many schools are starting to act on this research. A Florida superintendent abolished homework in her 42,000 student district, replacing it with 20 minutes of nightly reading.
By Kyle Spencer. April 25, 2017. Last spring, when Public School 11, a prekindergarten through fifth-grade school in Manhattan's Chelsea neighborhood, banned mandatory traditional homework ...
Excessive workload. The issue of excessive workload is a common complaint among students. Spending several hours on homework after a full school day can be mentally and physically draining. This workload can lead to burnout, decreased motivation, and negative attitudes toward school and learning.
While some students used smartphones to help them complete homework - and got good grades on their assignments as a result - there was a big dip in performance when it came to exams. On the contrary, students who didn't use the internet to help them with their homework performed better on exams.
Should homework be banned? - BBC Science Focus Magazine
Reasons Why Homework Should Be Banned. 1. It Contributes to Increased Anxiety. If there's one word that describes middle-school and high-school students, it's anxiety. In my homework statistics article, I cite research showing that 74% of students cite homework as a source of stress. They have so much to juggle, from the novelty of ...
Her proposal comes as a survey of more than 300,000 American students conducted by Stanford University and the nonprofit organization Challenge Success found that 45% of students say workload and homework is their #1 source of stress. 13,000 California high school students who took the survey report an average of 2.5 hours of homework every night.
A 2018 Pew Research poll of 743 US teens found that 17%, or almost 2 in every 5 students, regularly struggled to complete homework because they didn't have reliable access to the internet. This figure rose to 25% of Black American teens and 24% of teens whose families have an income of less than $30,000 per year. 4.
A big report for the Department for Education, published in 2014, concluded that students in Year 9 who spent between two and three hours on homework on an average week night were almost 10 times ...
Before the ban, Polish kids spent around 1.7 hours per day on homework, which is more than a lot of other countries, and some experts questioned whether or not it was doing any good.
More than 80% of the students reported at least one stress related symptom recently and 44% claimed they experienced 3 or more symptoms. The study also found that students who spend a lot of time working on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, and a lack of balance in their lives. The study claimed that any more than 2 ...
Homework negatively affects students' health. Download Article. Homework takes a toll physically. Recent studies have demonstrated that too much homework can disrupt a student's sleep cycle, and cause stress headaches, stomach problems, and depression. [3] 3.
This is why I think homework should be banned, not just in my school but in all schools. Misha McEnaney is a fifth class student at St Mary's College, Rathmines, Dublin. Making a difference
Students who feel strongly about the Palestinian cause feel like the point is disruption, that something so big, and immediate, and urgent is happening that they need to get in the faces of their ...
A lawmaker in California introduced a bill that would ban teachers from being able to assign students an excessive amount of homework. California State Assembly member Pilar Schiavo (D) introduced The Healthy Homework Act, also known as AB 2999, in February, noting in an interview with Fox40 that it would have a "huge impact" on the students. ...
Earlier this year, an 18-year-old high school senior from New York City had planned to enroll at Columbia University's sister school Barnard College in Manhattan as an early decision student.
As student protesters get arrested, they risk being banned from campus too Updated April 29, 2024 6:59 PM ET Originally published April 29, 2024 10:00 AM ET By
David French: I think that a lot of campus administrators need to read some of the statements that I have seen come out of, for example, University of Chicago, where lines are clearly drawn: We ...