- Micro-Entreprise
- Association
- Choix Statut
- Services B2B
- SASU et EURL
- Bilan et liasse fiscale
- Déclarations de TVA
- Devis et Facturation
- Services Conseils
- Synchoronisation bancaire
- Tableau de bord et pilotage
- Domiciliation Entreprise Votre adresse prestigieuse à Paris
- Modifications de Statuts Procédure 100% en ligne
- Dissolution d'entreprise Traitement sous 24h
- Agent commercial
- Agent immobilier
- Bâtiments et Travaux Publics
- Boulanger, pâtissier, biscuitier
- Chauffeur de taxi et VTC
- Coach sportif et fitness
- Développeur web
- Métiers de la santé
- Restauration
- Services à la personne
- Transport de marchandises
- Webdesigner
- Autres activités
- 100 conseils pour créer
- La création d’entreprise
- Réflexion préalable
- Idée de création
- Business model
- Construire son projet
- Analyser l’entreprise
- Négocier le rachat
- Location-gérance
- Commerce organisé
- Se faire accompagner
- Étude de marché
- Préparer son business plan
- Prévisionnel financier
- Valider son Business Plan
- Faire son Business Plan en ligne
- Préparer son dossier
- Aides à la création
- Apports en capital
- Compte courant d’associé
- Financements bancaires
- Outils de trésorerie
- Investisseurs
- La micro-entreprise
- L’entreprise individuelle
- L’EURL
- L’association
- Régimes fiscaux
- Sécurité sociale
- Choix du statut juridique
- Local professionnel
- Autres choix de création
- Statuts de société
- Annonces légales
- Dépôt du capital social
- Immatriculation
- Création en ligne
- S’implanter en France
- Contrats commerciaux
- Conditions commerciales
- Communication
- Comptabilité
- Facturation
- Gestion financière
- Comptes annuels
- Assemblées générales
- Modification de capital
- Transfert de siège
- Transformations
- Autres modifications
- L’impôt sur le revenu
- L’impôt sur les sociétés
- Les crédits d’impôts
- La CFE et la CVAE
- Autres impôts et taxes
- L’embauche du salarié
- Les contrats de travail
- La gestion de la paie
- La mutuelle d’entreprise
- La rémunération du dirigeant
- La rupture du contrat de travail
- Groupes de sociétés
- Cession de fonds
- Cession de titres
- Fiscalité des cessions
- Fermer son entreprise

Combien de pages faut-il pour faire un bon business plan ?
Un business plan est un document écrit. Il comporte donc plusieurs pages . Cela dit, le nombre de pages ne présage en rien de la qualité du document. C’est pourquoi, en réalité, il importe peu. Il n’existe pas de standard en la matière et le nombre de pages d’un business plan dépend essentiellement de son destinataire et de ses objectifs . Voici les informations importantes à retenir à ce sujet.

Quelques pages seulement peuvent former un bon business plan
Lorsque le destinataire du business plan est le porteur de projet , le document peut ne compter que quelques pages . En effet, dans ce cas de figure, la partie explicative (volet rédactionnel) n’a pas forcément lieu d’être. Le business plan peut se limiter au prévisionnel financier . Il conviendra, par exemple, d’y présenter un compte de résultat prévisionnel , un bilan prévisionnel et un plan de trésorerie . Ces états suffiront car ils vous permettent de mesurer la rentabilité de votre projet et de vous assurer de sa pérennité. Vous y traduirez également les sorties de ressources (salaires et/ou dividendes) afin d’estimer votre rémunération probable. Le business plan ne contient alors que trois pages .
Autrement, lorsque le lecteur de votre business plan est une banque , il faut ajouter plusieurs autres parties. Le document comptera donc naturellement plus de pages . Les tableaux financiers s’enrichissent avec la présentation d’un plan de financement prévisionnel et le calcul de divers ratios financiers . La partie rédactionnelle , quant à elle, doit être écrite. Sa taille dépend de l’ampleur du projet et du risque associé. Au plus votre projet est ambitieux et le risque élevé, au plus vous devrez détailler votre projet. Vous aurez, à minima, à vous présenter (parcours, expérience professionnelle), à dévoiler votre offre (produits/services) et votre business model. Par ailleurs, il vous faudra chiffrer clairement votre besoin de financement . Ici, le nombre de pages du business plan peut aller jusqu’à 10 .
Un business plan dépasse rarement les trente pages
Les business plans les plus étoffés sont ceux proposés à des investisseurs . En effet, ces interlocuteurs demandent généralement beaucoup plus de détails avant d’investir de l’argent dans des projets. Leur engagement est, bien évidemment, plus important que celui d’une banque par exemple car ils vont entrer au capital de votre société et peuvent tout perdre si votre projet périclite.
Ainsi, la partie explicative doit être complète . Elle doit comprendre, non seulement tous les volets « traditionnels » (présentation de l’offre, de l’environnement, du marché, des concurrents, de la stratégie, du modèle économique) mais également des aspects plus techniques régissant la relation, prévus dans les statuts :
- Titres alloués en quantité et nature des droits attachés (droits de vote simples ou doubles, dividendes prioritaires…),
- Modalités de sortie de l’actionnariat (clause d’agrément, de préemption, d’exclusion, de sortie conjointe…),
La partie financière comprend, elle aussi, plus de tableaux financiers . Le seuil de rentabilité est une donnée susceptible d’intéresser les investisseurs, au même titre que la plus-value qu’ils peuvent potentiellement réaliser. L’accent doit être mis sur la croissance de la future entreprise, sur la rentabilité de son activité et sur le retour sur investissement que le projet va générer. Le besoin de financement doit aussi figurer distinctement.
Les business plans présentés aux investisseurs comptent généralement une vingtaine de pages . Leur nombre dépasse rarement trente.

Poster un commentaire
Nous ferons de notre mieux pour vous répondre dans des délais raisonnables. Vous pouvez demander à tout moment la rectification ou la suppression de vos informations à caractère personnel : Nous contacter
Prénom (obligatoire)
Mail (non affiché) (obligatoire)
XHTML: You can use these tags: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
Avertissez-moi de la publication de nouveaux commentaires par mail. Vous pouvez également souscrire sans laisser de commentaire.

- Création d’entreprise, les étapes clés
- Réaliser son étude de marché
- Faire son business plan
- Le guide de l’EURL
- Le guide de la SARL
- Le guide de la SASU
- Le guide de la SAS

- Construire son projet d’entreprise en ligne
- Création d’entreprise en ligne
- Comparateur de statut juridique
- Outil de business plan en ligne
- Prévisionnel financier sur Excel
- Evaluer et tester son idée de création
- Bien préparer son projet de création
- Faire un business model canvas
- Valider son projet de création d’entreprise
- Tout comprendre sur le business plan
- Bien préparer son business plan
- Établir les tableaux financiers
- Faire un prévisionnel financier
- Créer une EURL : tout ce qu’il faut savoir
- Créer une SARL : tout ce qu’il faut savoir
- Créer une SASU : tout ce qu’il faut savoir
- Créer une SAS : tout ce qu’il faut savoir
- Tableau comparatif des statuts juridiques
- Choix d’un statut juridique pour l’entreprise
- Choix du régime fiscal de l’entreprise
- Choix d’un statut social pour le dirigeant
- Formalités à accomplir pour créer son entreprise
- Procédure à suivre pour immatriculer sa société
- Solutions pour créer son entreprise
- Créer son entreprise en ligne, choisir et comparer
Navigation :
- Partenariats et publicité
- Nous contacter
- Mentions légales et CGU
- Politique de confidentialité
- Plan de site
- Notre politique de protection des Données à caractère personnel
- Plan du site
Nos autres sites :
- Notre application
- Entreprises et Droit
- Compta-Facile
Le coin des entrepreneurs :
Le coin des entrepreneurs est un média online de référence pour les créateurs d'entreprise, les repreneurs d'entreprises et les chefs d'entreprises. Nous vous proposons sur notre site internet des centaines de dossiers sur les thèmes de la création, la reprise et la gestion d'entreprise, dans le but de vous informer et de vous conseiller dans toutes les étapes de votre projet entrepreneurial (de l'idée de projet jusqu'au lancement de votre nouvelle activité).
En plus du média, Le Coin des Entrepreneurs vous propose également une application digitale pour vous accompagner dans vos projets entrepreneuriaux. Notre application vous propose une multitude de fonctionnalités pour vous guider dans votre projet de création ou de reprise d'entreprise
Notre mission est simple : proposer aux entrepreneurs un éco-système complet qui leur permet de construire leur projet et de se lancer dans leur nouvelle activité
How to Write a One-Page Business Plan

Noah Parsons
5 min. read
Updated January 30, 2024
What’s the most challenging part of writing a business plan? Getting started. That’s why you should create a one-page plan as a starting point.
The one-page business plan is simple to create, easy to update, and built for adaptation. It includes all of the essential components of a traditional plan but is far briefer and more focused.
Think of it like you’re tweeting about your business. You have a limited number of characters to work with and are intentionally making it easy to digest. If you need additional support, try downloading our free one-page plan template .
- What is a one-page business plan?
The one-page business plan is a simplified version of traditional operational plans that focuses on the core aspects of your business. While it may be a shorter business plan, it still follows the structure of a standard business plan and serves as a beefed-up pitch document.
There’s really not a lot of difference between a single-page business plan and a good executive summary. In fact, as you create a more detailed plan you may even be able to use it as your executive summary .
- What to include in your one-page plan
Here are the eight necessary sections to include when developing your one-page business plan.
Try and keep each section limited to 1-2 sentences or 3-4 bullet points to ensure that you stay within one page. It’s always easier to add more later rather than cutting back from lengthy sections.

The problem
A description of the problem or need your customers have and any relevant data that supports your claim.
The solution
Your product or service and how it solves the problem.
Business model
How you will make money—including the costs of production and selling, and the price that customers will pay.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Target market
Who is your customer and how many of them are there? Define your ideal customer by starting with a broad audience and narrowing it down. This provides investors with a clear picture of your thought process and understanding of the greater consumer market.
Competitive advantage
What makes you different from the competition? Explain how this will lead to greater success, customer loyalty, etc.
Management team
The management structure of your business, including currently filled roles, ideal candidates, and any management gaps.
Financial summary
Key financial metrics include your profit and loss, cash flow, balance sheet, and sales forecast. This section may be the most difficult part to condense, so try and focus on visualization and standard business ratios to get the point across. You can always share broader financial information if requested.
Funding required
Have what funding total you need front and center to clearly display what you are asking from investors.
Why you should start with a one-page plan
There are plenty of good reasons to write a business plan . There are even more reasons why your first step should be writing a one-page plan.
1. It’s faster
Instead of slogging away for hours, days, or even weeks tackling a formal business plan—the one-page format helps you get your ideas down much faster. It removes the complex formatting,
2. A great format for feedback
Need quick feedback from business partners, colleagues, potential customers, or your spouse? Provide them with a one-page plan instead of a lengthy in-depth version for better results.
The one-page plan is more likely to be read and reviewed. And since all of your business information is available at a glance, you’ll receive far more valuable and timely feedback.
3. Easy to update
Entrepreneurs never get things right the first time. You’ll constantly be learning and receiving feedback—requiring you to iterate and revise your business concept. Instead of updating a large document every time, you can do it in minutes with a one-page plan.
4. Direct and to-the-point
Learning to communicate your ideas clearly and directly is critical. You need to be sure that anyone can really understand the essence of your business. Delivering your entire business concept on a single page is a great way to practice this, as it forces you to be succinct.
5. Works as an idea validation tool
Initially, your business is just a set of assumptions that you need to validate. Do your potential customers have the problem you assume they have? Do they like your solution and are they willing to pay for it? What marketing and sales tactics will work?
As you validate these assumptions, you leave them in your plan. But, assumptions that end up being wrong will quickly fall off the page.
6. Becomes an outline for your detailed plan
By “detailed” we don’t mean “long.” If you do need to create a detailed business plan document for investors or business partners, you can use your one-page plan as your core outline. You will just expand and provide more details for each section.
7. No one really reads long business plans
A common problem with traditional business plans is that they are simply too long and overly complex. Even when investors ask for a detailed document, chances are that they won’t actually read every word. They may read certain sections, but often just want to see if you’ve thought through the details of your business, how it will operate, and how it will grow.
8. Useful for any business stage
A one-page plan is useful for business owners that are mulling over ideas, just starting, actively managing, or looking to grow a business. It can help validate a business idea, work as an internal strategy document, or as a flexible management tool that can be adapted over time.
Resources to help write your one-page plan
Check out our guide for quickly writing a one-page plan and download our free one-page plan template to kickstart the writing process.
How to write your one-page plan in under an hour
Still feeling a bit overwhelmed about creating a business plan? Check out this step-by-step guide to write a useful one-page business plan in as little as 30 minutes.

One-page business plan template
Download a free one-page business plan template to make the plan writing process simple and easy.
Download Template

Write your plan faster with LivePlan
Try the business planning and growth tool trusted by over 1-million business owners.
Start your plan
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Why start with a one-page plan
Related Articles

5 Min. Read
How to Write a Growth-Oriented Business Plan

11 Min. Read
Fundamentals of Lean Planning Explained

14 Min. Read
How to Write a Five-Year Business Plan

8 Min. Read
What Type of Business Plan Do You Need?
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

- Frequently Asked Questions
- Business Credit Cards
- Talk to Us 1-800-496-1056

How Many Pages Should a Business Plan be
One of the questions that many entrepreneurs face when writing a business plan is: how long should it be? There is no definitive answer to this question, as different types of businesses and investors may have different expectations and preferences. However, there are some general guidelines that can help you craft a business plan that is clear, concise and compelling.
Need a business plan writer?
Get a professional business plan now!
- Keep These Guidelines in Mind When Choosing Your Business Plan
Avoiding Extremes: Length Pitfalls to Watch For
Striking the balance: ideal length for a business plan, flexibility in length: tailoring your plan to your idea, quality over quantity: crafting a compelling business plan.
A common mistake that some entrepreneurs make is to write a business plan that is too long or too short. A very long business plan may include unnecessary details, repetitions, or irrelevant information that can bore or confuse the reader. A very short business plan may lack essential information, evidence, or analysis that can convince the reader of the feasibility and potential of the business idea.
Get our 14 Free Business Plan Examples
A good rule of thumb is to aim for a business plan that is between 15 and 25 pages long, excluding appendices. This length allows you to cover the main aspects of your business, such as the problem you are solving, the solution you are offering, the market opportunity, the competitive advantage, the revenue model, the marketing strategy, the financial projections, and the team. You can also include a summary or an executive summary at the beginning of your business plan that highlights the key points and captures the reader’s attention.
Of course, this rule of thumb is not set in stone, and you may need to adjust the length of your business plan depending on your specific situation. For example, if you are writing a business plan for a very complex or innovative business idea, you may need more pages to explain it clearly and convincingly. On the other hand, if you are writing a business plan for a very simple or straightforward business idea, you may be able to communicate it effectively in fewer pages.
The most important thing to remember is that the quality of your business plan matters more than the quantity. A well-written business plan that covers all the essential aspects of your business in a clear, concise and compelling way will have a better chance of attracting investors and customers than a poorly-written business plan that is either too long or too short. Therefore, focus on writing a business plan that showcases your value proposition, demonstrates your market potential, and proves your financial viability.
Need a Business Plan Writer? Hire our business plan experts now!
The length of a business plan can vary greatly depending on its purpose. For a lean startup plan, it can be as short as one page, provided it contains all the essential information.
The key components of a business plan include the executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization and management, service or product line, marketing and sales strategy, funding request, and financial projections. These components work together to create a comprehensive and informative plan.
To make your business plan more engaging, use clear and simple language that is easily understandable. Tailor the plan to suit your specific audience, addressing their needs and expectations. Additionally, incorporate visual elements such as graphs, charts, and infographics to present information in a visually appealing manner.
No, the success of a business plan does not solely depend on its length. Instead, the content, clarity, and effectiveness of presenting and justifying the business idea play a more significant role in determining its success.
Yes, a business plan can become too long if it includes unnecessary details or goes off on tangents. It is essential to keep the plan concise, focused, and to the point, ensuring that every section contributes directly to the overall purpose of the plan.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

- 212 best farm names
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
May 24, 2021
Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”

If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand

A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:
When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples

Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:

Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.

The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?
80% of businesses fail... Learn how not to.
Learn from business failures and successes in 5 min or less. The stories, frameworks, and tactics that will make you a 10x better founder.
Brandon Boushy
Related articles
520 Candle Company Names (for 2024)
Candle company names are one of the core ways people recognize a candle brand. That’s why you have to find the best candle business names for your candle business.
There are two main naming conventions you need to think about when you start your own candle company:
- Candle business name ideas
- Names for candles or scents
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"] We’ll discuss both of these types of candle company names to help you find an idea that works for you. You can jump to any of the sections by clicking the links below.
50 Candle Business Name Ideas
50 candle company name ideas, 48 luxury candle business names, 50 catchy names for candle business, 46 unique candle business names, 78 names for candle businesses, 52 unique candle names, 46 funny candle company names, 50 scent name ideas, 50 scented candle names.
- What to Do After Choosing a Candle Company Name [/su_note]

Create a name that sets you apart and is something you’ll want to stick with for the long haul. There are many different types of names you can go with, but your candle business name should be true to your shop and what your offering is. What do you want people to think of when they hear your name?
1. Wick-edly Scent-sational 2. Whispering Wick 3. Glow and Behold Candles 4. Moonbeam & Ember 5. Wax Poetic Candles 6. The Fragrant Alchemist 7. Bright and Bubbly Candles 8. Candlelight Sanctuary 9. Flicker of Joy Candles 10. Enchanted Aroma 11. Scent-sational Serenity Candles 12. Glow Getter Candles 13. A Scentsational Journey 14. Waxing Euphoria Candles 15. Wildflower Glow Co. 16. Flame and Fortune Candles 17. Kissed by Fragrance 18. Twinkle in Time Candles 19. The Gilded Wick 20. Gleeful Glow Candles 21. The Cozy Candle Co. 22. Waxen Whimsy Candles 23. Flame & Fortune 24. Blissful Beams Candles 25. The Luminous Muse
26. Flame Frolics Candles 27. Waxing Poetic 28. Candlelit Capers Candles 29. Scentual Escape 30. Waxen Whoopee Candles 31. Mystic Bazaar 32. Lustrous Laughs Candles 33. Whisper of Aroma 34. Soothing Smiles Candles 35. Emberglow Lights 36. Dazzling Delights Candles 37. Moonlight & Jasmine 38. Twilight Titters Candles 39. Serene Flame 40. Luminary Larks Candles 41. The Unforgettable Flame 42. Radiant Revels Candles 43. The Scentualist 44. Luminous Larks Candles 45. Candleabra Tales 46. Wick Winks Candles 47. Bliss & Bloom 48. Gleaming Guffaws Candles 49. Enchanted Fireside 50. Wick Wit
Pro Tip: Make sure your candle business name sounds appealing and memorable. You want your customers to remember where to go when they need more fabulous scents.
Short or long, your name should tell the story of what your shop offers, who you are, where you’re from, or what kind of experience customers will have when they shop with you. Online or brick and mortar, your name is the first thing they’ll see and hopefully something they’ll remember.
1. Candle Sense 2. Glistening Glow Candle Creations 3. Wax and Relax 4. Waxen Wonderlands Candle Co. 5. Candle Magic 6. Flame Fables Candles 7. Glow and Grow 8. Illuminated Illusions Co. 9. Candle Delight 10. Luminous Lullabies Candles 11. Spark and Scent 12. Wick Wonders Candle Co. 13. Wax Art
14. Glistening Gardens Candles 15. Candle Lab 16. Candlelit Canopies Candles 17. Glow Time 18. Waxen Waterfalls Candles 19. Wax and Glow 20. Lustrous Lagoons Candles 21. Candle Dream 22. Twilight Truffles Candles 23. Spark and Splendor 24. Glowing Groves Candles 25. Wax Appeal
Pro Tip: Your business name will last the length of the business, unless you decide to change your DBA (doing business as name) or update your brand entirely. Make sure you love your name. Don’t settle for “okay”—you should love it!
Luxury candle business names can bring you high-end, bougie buyers who are willing to spend more money because your shop has the “wow factor.”
Consider some of these luxurious candle business name ideas perfect for selling expensive aromatherapy candles, scented candles, or even beeswax candles.
1. Aroma Path 2. Ember & Co. 3. Glow & Co. 4. Gilded Wick Candle Co. 5. Aroma Bloom 6. Moonlight Sonata 7. Zenith Candles 8. Amethyst Flame 9. Glow Haven 10. Silk & Sillage 11. Spark & Scent 12. Emberlight Alchemy 13. Lumena Ignite 14. Velvet Wick 15. Scent Fusion 16. Moonstone Muse 17. Pheroma Memento 18. Whispering Embers 19. Flame Fest 20. Starlight Sanctuary 21. Petal Glow 22. Opulent Glow 23. Scent Sation 24. Golden Nectar
25. Luxe Light 26. Clandestine Embers 27. Flame Bright 28. Seraph's Sconce 29. Zodiac Flames 30. Damask & Dusk Candle Co. 31. Glow Makers 32. Emberlit Soiree 33. Moonstone Candles 34. Whispers of Oud 35. Celestial Scents 36. Gilded Alchemy 37. Eco Flame 38. Starlit Lace Candle Co. 39. Glow & Grow 40. Velvet & Ember 41. Pure Illuminate 42. Luminous Indigo 43. Gilded Haven 44. Seraphim's Ember 45. Luxe Luminance Candle Co. 46. Enchanted Candle Company 47. Custom Candles by Coco 48. The Candle Maker
Pro Tip: Who is your target customer? A good luxury candle business name can help you to target a higher-paying demographic. It’s more appealing to those who have the money to spend. Regardless of whether you will have an Etsy store, Shopify site, or brick-and-mortar store, you need to identify your target customer before you finalize a name.

Make your candle business name sticky…so buyers come back time and again. Using catchy phrases or sayings can really help keep your name top of mind.
1. Wick’d Wonders Candles 2. Soy Much Fun Soy Wax Candles 3. Radiant Flames 4. Waxing Poetic 5. Fabulous Flame Candle Co. 6. Flick Candles 7. Aromatic Artistry 8. The Flickering Flamingo 9. The Illuminated Co. 10. Scentsational Shenanigans 11. Soothing Scentsations 12. Litty & Witty Candles 13. The Candle Connoisseur 14. The Wacky Wickery 15. Illuminated Atelier 16. Candle Capers 17. Candle Conservatory 18. Grin & Glow Candles 19. Illuminated Gallery 20. Laughing Flames Candle Company 21. Candle Emporium Co. 22. Flame On, Funny Bone 23. Candle Artisan Co. 24. The Illuminaughty 25. Illuminated Haven
26. Scents & Sensibility 27. Heavenly Candle Co 28. Wickid Good Scents 29. Scented Studio Co. 30. Wax On, Wax Off 31. Candle Artistry Studio 32. The Melty Misfits Candle Company 33. Illuminated Studio Candles 34. Wickology 101 35. The Scented Atelier 36. Wax Flame Candy Candle 37. Candleabracadabra 38. Illuminated Boutique 39. Sniff & Giggle Candle Co. 40. Candle Emporium Studio 41. Wick It or Quit It Candle Company 42. Illuminated Suite 43. Glow-rious Meetings 44. Scented Emporium Candle Company 45. The Illuminating Co. 46. Scent-sational Humor 47. Lights All the Way Candle Co. 48. Waxing Lyrical 49. Cute Candles, Inc. 50. Love & Life Candles
Pro Tip: What’s your favorite commercial? Is it funny and catchy? It’s obviously memorable! The catchier the name, the better. You want to be remembered—just like that commercial that came to mind for you—even if a customer has lost your web address, can’t find an emailed receipt, and no longer has their candle jar.
What differentiates you from your competitors? Use those identifying factors when selecting your unique business name. You don’t want to sound like everyone else—you want your business name to be descriptive of who you are.
1. Candlelight Glow 2. Candle With Care 3. The Wick & Flame 4. Light My Fire 5. Waxing Poetic 6. Melt Your Heart 7. Sisters’ Soap & Candle Co. 8. Illuminate Creations 9. Glow and Tell Candle Company 10. Scentimental Memories 11. Candle in the Wind 12. Flaming Inspirations 13. Spark Joy Candle Company 14. The Candle Cove 15. Candle Crush 16. The Candle Lab 17. Glow Getter 18. Luminous Expressions 19. Scent From Heaven 20. The Candle Parlour 21. Candle Me Crazy 22. Flicker & Flame Candle Company 23. Ember & Muse
24. The Candle Bar 25. Flicker & Fable 26. The Aromatic Hearth 27. The Hushed Flame 28. The Candle Aisle 29. The Wax Alchemist Candle Company 30. The Candle Cottage 31. Cozy Flicker Co. 32. The Wickery 33. The Candle Conjurer 34. The Candelier 35. The Wandering Wick 36. Scented Wick 37. Flickering Folklore Candle Company 38. Whispers of Flame 39. Candlelight Concoctions 40. The Wickery Embers 41. The Wick Weaver 42. The Flickering Phoenix 43. Aromasmith & Co. 44. Emberlight Alchemy Candle Company 45. My Gentle Glow 46. Sillage Muse
Pro Tip: This is one time when you don’t want to follow the crowd. Be unique so you aren’t battling over a URL and 50 other eCommerce sites with a similar name.

Candle company names can be one or more words, and if you’re in doubt, add the word Candles , Company , or Shop to the end, and Bam! you have a business name!
1. Wick & Whimsy 2. Ember & Oak Co. 3. Radiant Flames 4. Luminescence Atelier 5. The Candle Collective 6. Candlemaker Scents & Pours 7. Wick & Wander Shop 8. The Candle Connoisseur 9. The Wax Emporium 10. Candle Artisan 11. The Gilded Flame Co. 12. The Illuminated Atelier 13. Moonlit Glow LLC 14. The Scented Salon 15. Whisper & Wisp Atelier 16. The Candle Artistry Co. 17. Cinder & Co. 18. The Candle Emporium Co. 19. The Flickering Muse Shop 20. Illuminated Haven Candle Co. 21. The Dancing Ember Atelier 22. The Scented Atelier 23. Nocturne Lumens Shop 24. The Candle Emporium Studio 25. The Alchemist's Candle Co. 26. The Scented Workshop 27. The Glimmering Grotto Shop 28. The Candle Conservatory StudioEmberlight 29. Apothecary Co. 30. The Scented Emporium Candle Company 31. Candlewick & Co. 32. Primitive Candle Company 33. The Flickering Lantern Emporium 34. Pure Light Candle Studios 35. Moonlit Muse Atelier 36. Fragrant Jewels Candle Company 37. The Candle Whisperer, LLC 38. Heaven Scent 39. Aurora Lumens Atelier
40. KC Candle Company 41. The Dancing Flame Emporium 42. Candleberry Studios 43. Candlewick & Whisper Shop 44. Darling Candles 45. Luminescence Alchemy Atelier 46. Enchanted Candle Atelier 47. The Glimmering Path 48. Homefront Candles House 49. Candle in the Wind Emporium 50. Berry Candles 51. Light My Fire, LLC 52. Decorative Candles 53. Scent of a Woman Atelier 54. Flaming Candle Co 55. Burn, Baby Burn Company 56. Country Candle Company 57. Rainbow Earth Gifts 58. Flame of Love Co. 59. None of Your Beeswax 60. Scents and Sensibility Atelier 61. Luxury Candles Co 62. Fire and Ice Co. 63. Scents Illuminated Candle Company 64. Scent From Heaven Atelier 65. Glorious Candles 66. Wick It Shop 67. The Candle Guy 68. Firefly Co. 69. Warwick Candles 70. Candle Magic, LLC 71. Ceremony Dreams Co. 72. Scent of the Sea Atelier 73. Fire Starter Co. 74. Candle Therapy, LLC 75. Wick and Mortar Shop 76. Mickey’s Creative Candles 77. Candleberry Candle Company 78. San Francisco Candle Making Collective
Pro Tip: Are you an LLC, S-Corp, or Sole Proprietorship? If you are an incorporation, you can include that in your name. For example, [Your Candle Business Name], LLC.
If you’d want to eat it, make it, or serve it, it’s likely a good name for a candle. Especially if it’s a dessert, drink, or fruit-scented candle.
1. Almond Bark Chocolate 2. Bergamot Delight 3. Blueberries and Whipped Cream 4. Brown Sugar Sizzle 5. Buttercream Sausage 6. Toasted Campfire 7. Caramel Coffee Cookie 8. Musky Cedarwood 9. Chamomile Snooze 10. Chocolate Chip Pancakes 11. Clementine Orange Zest 12. Clove Spice Warmth 13. Cotton Candy Fantasy 14. Cucumber Melon Splash 15. Fig and Olive 16. Frangipani Tropical Flower 17. Just Cut Suburban Lawn 18. Gardenia White Blossom 19. Ginger Lime Fizz 20. Green Tea Jasmine 21. Hyacinth Spring Breeze 22. Key Lime Pie 23. Kiwi Strawberry Smoothie 24. Fragrant Jewels, Heaven Scent 25. Lavender Lemonade Relax 26. Macaron Sweet Treat
27. Magnolia Pink Petal 28. Marshmallow Vanilla Fluff 29. Mint Chocolate Chip 30. Mistletoe Holiday Cheer 31. Nutmeg Spice Cake 32. Oatmeal Double Raisin Cookie 33. Orange Blossom Citrus + Sea Salt 34. Patchouli Earth 35. Peach Cobbler Yum 36. Peony Floral Bouquet 37. Pina Colada Vacation 38. Plum Wine Sangria 39. Popcorn Movie Night 40. Rain Fresh Clean 41. Red Velvet Cupcake 42. Salted Caramel Swirl 43. Smoky Quartz Crystal 44. Sunflower Sunny Day 45. Toasted Marshmallow Cozy 46. Toffee Nut Crunch 47. Vanilla Orchid Exotic 48. Vetiver Woody Aroma 49. Violet Purple Passion 50. Waffle Breakfast Time 51. Walnut Brownie Delish 52. The Woodland Homestead
Pro Tip: Name your candle scents something fun and unique. If you’re an online retailer, the customer will rely on your naming conventions to decide if they’ll like the smell of the candle. So, be unique and descriptive!

Customers will appreciate your sense of humor and know they can expect good-natured customer service when you use a funny candle company name.
1. Wickety Wacky Wonders 2. Light My Fire 3. Scents So Silly, They're Snort-Worthy 4. The Aromatherapy Absurdity Co. 5. The Illuminated Improbability Shop 6. Hilarity & Hygge, LLC 7. Wick-edly Good Scents Atelier 8. The Scents of Wit 9. Sniff & Giggles Galore 10. Flame on, Funny Bone! 11. The Snicker & Sizzle Shop 12. Punny Sentiments 13. Aromas Gone Wild 14. The Wick-edly Creative Waxers 15. Flame On, Fun On! 16. The Candle Cauldron 17. Scents So Silly, They're Scandalous 18. The Illuminating Insanity Atelier 19. Scents That Make You Chuckle 20. The Giggle & Glow Glow-Up Co. 21. Punny Wick Emporium 22. Wick-edly Weird Waxes 23. Scented Silliness Galore Shop
24. Aromas of Absurdity Atelier 25. Burnt Out Candles 26. Scent-sational Candles 27. Candle-icious 28. Wax-tastic Candles 29. Flame Game 30. Candle-ry of the Odd 31. Wick-er Man Company 32. Wick-edly Good Candles 33. Waxing Philosophical 34. Waxing Lyrical Candles 35. Scentsational Silliness, LLC 36. The Humerus Fragrance Co. 37. The Light Chuckle Atelier 38. Scentsational Shenanigans Shop 39. Of Laughters and Illumination 40. You Light Me Up 41. Candle in the Sky 42. Scentsational Wickers 43. The Chuckle Wax 44. Sniff Me Good 45. The Wick-ed Atelier 46. The OG Candle Brand
Pro Tip: Humor is memorable and humor sells. Whether you’re naming your candle business or your candle scents, humor is almost always a good way to go.
Scent names can evoke tastes and smells for the buyer. Make it heavenly and delicious. Something you’d maybe want to eat, but definitely want to smell!
1. Cinnamon Swirl 2. Pumpkin Spice Latte 3. Caramel Apple 4. Cranberry Bliss 5. Peppermint Mocha 6. Gingerbread House 7. Winter Wonderland 8. Sugar Plum Fairy 9. Frosty the Snowman 10. Mistletoe Kisses 11. Candy Lane 12. Sleigh Ride 13. Fireside Chat 14. Warm and Cozy 15. Chestnuts Roasting 16. Mulled Wine 17. Spiced Cider 18. Hot Cocoa 19. Vanilla Bean 20. Lavender Fields 21. Tea Rose Garden 22. Jasmine Dreams 23. Sandalwood Serenade 24. Citrus Grove 25. Ocean Breeze
26. Rainforest Retreat 27. Mountain Air 28. Desert Oasis 29. Tropical Paradise 30. Island Escape 31. Crispy Autumn Leaves 32. Harvest Moon 33. Pumpkin Patch 34. Apple Orchard in Fall 35. Crisp Fall Air 36. Maple Butter and Syrup 37. Cedarwood Forest 38. Pine Needle Forest 39. Eucalyptus-y Mint 40. Peppermint Twist 41. Lemon Verbena 42. Grapefruit Grove 43. Cherry Blossom Farm 44. Magnolia Bloom 45. Honeysuckle Heaven 46. Wildflower Meadow 47. Butterfly Garden 48. Hummingbird Haven 49. Dragonfly Dreams 50. Ladybug Lane
Pro Tip: Most candles are scented, and scents need names to sell. Be creative and imagine what visuals and scents a person might imagine when they read your names.

Your candle labels will need to specify what scent you're selling. Think of feeling-invoking scents that will make your customers want to buy them as gifts or a treat for themselves.
1. Winter Wonderland 2. Cozy Cabin 3. Pumpkin Spiced Chai 4. Lavender Dreams 5. Appley Pear Orchard 6. Caramel Popcorn 7. Ocean Breeze 8. Decadent Chocolate Cake 9. Lemonade Stand 10. Woody Fire 11. Cotton Candy 12. Gingerbread House 13. Rose, No Thorns 14. Banana Bread 15. Tropical Vacation 16. Vanilla and Cream 17. Fresh Laundry 18. Mulled Wine 19. Birthday Cake and Sprinkles 20. Hazelnut Coffee Shop 21. Autumn Leaves with Clove 22. Strawberry Shortcake 23. Rainforest and Fern 24. Maple Syrup and Brown Sugar 25. Cucumber Melon Mint
26. Snickerdoodle Cookie 27. Cherry Blossom Spring 28. Hot Chocolate with Marshmallows 29. Sunflowers and Honey 30. Campfire and S’mores 31. Juicy Peach Cobbler 32. Soothing Jasmine Tea 33. Warm Cinnamon Roll 34. Honeycomb Summer 35. Sandalwood and Vanilla 36. Sweet Blueberry Muffin 37. Refreshing Eucalyptus and Mint 38. Apple Pie Crust 39. Luscious Lilac 40. Tropical Coconut Lime 41. Cozy Oatmeal Cookie 42. Gardenia and Jasmine 43. Cranberry Orange Spice 44. Almond Biscotti 45. Lemongrass and Basil 46. Pumpkin Pie Delight 47. Vanilla Orchid 48. Spicy Ginger Ale 49. Sugar Plum Fairy 50. Earl Grey AM
Pro Tip: Naming candles after food is always a hit because people can imagine what they will taste and smell like.
What to Do After Choosing a Candle Company Name
After you choose a candle company name, you’ll want to make sure it’s available according to the:
- Secretary of State website
- United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO)
- A domain name
- Social media accounts
As long as the candle company names you are considering are available across the board, you are good to register your candle business name and start your business.
What candle business name ideas appeal to you?
How to Create a Marketing Budget (for 2024)
Are you struggling to find the right balance for your marketing budget? Maybe you don’t know which marketing strategy to use. We have the information you need to improve your overall marketing performance.
We surveyed business owners to understand how small businesses approach marketing. More than 1,800 people responded, and we’ve used their insights, as well as data gathered for our average marketing budget report to provide a guide for creating marketing budgets.
We’ll explain what a marketing budget is, how much experts suggest spending, and how much marketing teams spend, then we'll discuss how to create a marketing plan. We’ll even show you how to promote a company on a tight budget so you can become a marketing leader without spending thousands on ads.
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"]Click on any of the links below to jump ahead.
What is a marketing budget?
What is the average marketing budget for a small business, how does having a budget help you avoid the traps of digital marketing, how to create a marketing budget, why you need an integrated marketing strategy, how to promote your business on a limited marketing budget.
- What is your experience with marketing budgets? [/su_note]
A marketing budget outlines the costs a company spends on marketing its products or services. Your marketing budget should cover a specific duration, usually a quarter or a year. Your budget may also have periods for particular marketing campaigns.
Your marketing budget should include all expenses related to spreading the word about your business. Your marketing budget allocation will estimate costs for various line items, including:
- Marketing team
- Paid advertisements
- Marketing software
- Outsourced marketing services
Expect your company marketing spending to be approximately equal in all four categories.

We asked how much business owners spend on marketing strategies. We found that two-thirds spend less than $1,000 per year marketing their small business, while 15% spend over $10K and another 19% spend between $1K and $10K.
Meanwhile, the Small Business Administration suggests a marketing budget allocation of 8% of company revenue. That means two-thirds of businesses are only marketing enough to make $12,500 in revenue annually.
To make $100K in revenue, you should be spending around $8,000. Meanwhile, if you want $100K in after-tax profit, you’ll want to spend $32K to $400K on marketing each year, based on 2% to 25% profit margins .
A digital marketing budget makes tracking performance against goals and industry benchmarks easier when comparing marketing channels. The budgets for each channel can also be set in most advertisers’ software, preventing marketing from running rampant.
You can also limit wasted expenses on Google Ads by narrowing your spending to only high-performing keywords.
You can also use the high-performing keywords to guide other marketing team efforts by focusing social media ads, video marketing, and search engine optimization on subjects that actually contribute to your company’s success.
Author’s No-Nonsense Note About Marketing Budgets

There are two ways to go about marketing: Spending time or spending money. Every hour you spend marketing is one you can’t spend providing services or creating custom products. Of course, eCommerce stores, content creators, and marketing agencies are marketing during all work hours.
If you have virtually no marketing budget or want to do it all yourself, I suggest assuming you will spend 20 hours per week promoting your business and 20 billable hours per week serving customers. You’ll need to calculate your service rates (or product prices) based on these reduced weekly hours.

Creating a marketing budget involves careful planning, analysis, and allocation of resources to ensure that marketing activities align with business goals. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you create a marketing budget:
- Understand customer needs.
- Examine your business goals.
- Review past marketing budget management.
- Measure the average cost per lead.
- Calculate the average conversion rate.
- Establish how many leads you need.
- Define your marketing objectives.
- Create your marketing budget.
- Regularly monitor and adjust your marketing spend.
Understand customer needs
Your marketing strategies should focus on showing you understand your target customers. To succeed, you’ll want to use research and marketing analytics data to gain deeper insights into what existing and potential customers want and need.
Without market research, marketing teams may have a difficult time identifying the marketing channels to reach their target audience best.
Explore demographic and psychographic factors like age, gender, income level, location, and brand loyalty to learn more about what your target audience cares about.
Examine your business goals
You’ll want to consider the overlying business strategy and goals before you create a marketing plan and budget. You might need to talk to executives, investors, and other team members to establish what the business goals are, then create a marketing plan that helps you achieve those goals.
Your business strategy will also impact the marketing team's goals because the marketing budget needs to be high enough to accomplish the business goals.
Throughout this piece, we’ll assume you are trying to make $250K across 1,000 customers. We’ll use these numbers to help illustrate some of the concepts you’ll use to avoid common marketing budget mistakes.
Review past marketing budget management
Before you create a marketing budget plan, review previous years’ marketing budgets and marketing campaigns. Identify what worked well and what didn't. Look for indicators like:
- Which marketing channels were under budget or over budget?
- Which marketing campaigns had a higher or lower return on ad spend?
- Did you overestimate or underestimate the previous year’s marketing budget?
- Did you add new products or services that impacted marketing costs?
- How does your cost per lead, cost per click, clickthrough rate, and conversion rate compare to industry averages?
This data will help you make more informed decisions for the upcoming budget.
Wordstream is a good source for these metrics if you do not have information from previous marketing campaigns. It will provide you with a good benchmark to compare your performance.
This is Wordstream’s data regarding cost per click, cost per lead, click-through rate, and conversion rate for Google Ads.
Measure the average cost per lead
Cost per lead (CPL) is a marketing metric that compares what you spend on lead generation to the actual number of leads you generate. This helps you understand how much it will cost for a marketing campaign.
The CPL formula is:
CPL = Amount spent on leads / Number of leads
Ideally, marketing investments would use your current numbers, but for those just implementing marketing tactics, use the benchmarks in the table above.
Calculate the average conversion rate
Conversion rate (CVR) measures the percentage of leads you turn into paying customers. Use the formula below to calculate the average conversion rate:
CVR = Number of Sales / Number of Leads
Establish how many leads you need
Now that you're familiar with some of the terms used in a digital marketing strategy, you’ll want to calculate the number of leads you need to hit $250K in gross revenue.
You’ll need to use the formula:
Desired Customers / CVR = Leads to Meet Goal
Let’s assume you’re in the home improvement field, which has a 10.22% CVR. That means you’ll divide:
1,000 Customers / 10.22% = 9,785 leads
Taking it a step further, your marketing plan needs to calculate how much marketing projects cost by multiplying the leads needed by the CPL ($66.02) .
9,785 x $66.02 = $646,005.70
As you can see, this is way higher than the $250K revenue you’re hoping to make. That’s because marketing leaders like Google and Facebook tend to charge based on an estimated lifetime customer value. Effectively, you’re paying a percentage of the revenue that you expect to make over the life of the customer relationship.
This is why a marketing budget includes a budget allocated to increasing the earnings from each paying customer through remarketing, loyalty programs, and other strategies that are less costly than paid advertising.
Define your marketing objectives
Next, you’ll want to define your marketing goals and align them with your business goals. Let’s look at some business goals and corresponding goals to include in your marketing budget.
You could tie marketing goals to other business goals, like:
- Raise brand awareness by X%
- Limit discounting current customers' bills to under Y%
These are just a few examples of how your business goals should impact your marketing strategy. Want to know more about tying marketing goals to business goals? Check out this blog .
Create your marketing budget
First, you’ll want to establish the total funds available for marketing. This may be based on a percentage of revenue, a fixed amount set by the company, or other financial considerations.
We suggest using the marketing budget of 12.3% that was mentioned in this CMO study . A startup marketing budget may need to be even higher. MaidThis CEO Neel Parekh told us:
[su_quote]When you first start a business, you may need to spend 20% to get clients faster.[/su_quote]
Check out our interview with him below.
Use a marketing budget template
Whether you’re a small business owner or work with them, you can use the information in this report and our marketing budget template to create a balanced small business budget.
The template lets you choose your industry and your revenue goal. Then it suggests a sample marketing budget amount.
Once you know how much your marketing budget should be, you can use the other tabs to set the budgets for specific aspects of your marketing strategy. Then add the actual expenses for an entirely new way of budgeting.
Pro Tip: Seriously, this marketing budget template is probably the tool I am most proud of during my seven years of consulting.
Allocate budget by channel
Decide how much of your budget will be allocated to the marketing channels outlined below.
As you go, you’ll notice that some budget-based initiatives make advertising small business products and services easier than others do. Start limiting your marketing spend on the ineffective channels and transfer it to the ones that are performing better.
Marketing spending as a percentage of revenue ranges from 0% to as high as 38.57%, with an average of 12.3% and a median of 10%. In addition, the average marketing budget dedicates 53.4% of its marketing dollars to its digital marketing budget, while the rest is spent on traditional advertising.
Marketing Budget Distribution

Once you’ve decided how much to spend on marketing, you’ll want to break your marketing budget down to the costs for all marketing campaigns. Marketing costs for small businesses will include:
- Content marketing budget: Expect to spend a minimum of $29 per piece, but some of the best content creators have content marketing budgets that cost up to $1,000 per piece. You may also find content creators that charge $.05 to $1 per word.
- Paid digital advertising budget: Small businesses should expect to spend $2.59 per click, $3.12 per 1,000 impressions, $.66 to $1.23 on remarketing, $15 to $800 on tools, and a minimum of $350 per month for the monthly ad budget, according to WebFX .
- Ad monitoring budget: To pay someone to monitor ads for your small business, include a marketing spend of $350 to $5K per month or 12-30% of monthly ad spend—whichever is more.
- Email marketing budget: Your email marketing budget will vary based on the number of email addresses on your list and the features you need, but you should expect to spend around $18 per month for up to 1,000 people on your email list. As you grow, costs may increase up to $540 per month, plus related labor costs.
- Social media marketing budget: Social media marketing in 2023 is expected to reach $72.33B in spending, or $2,178.62 per business (calculated by dividing $72.33B by the number of U.S. businesses).
- Sales funnel automation budget: Automation systems might be included in your email marketing, social media marketing, or other marketing channel budgets.
- Marketing tools and software: You might include these costs in other categories or put them in a dedicated category. On average, 25.5% of marketing budgets are spent on tech. Depending on the size of your company and the number of customers, necessary tools and software could be free or cost thousands per month.
- Outsourced marketing expenses: Some companies will outsource all or part of their marketing. As you’ll see in the chart below, approximately 23.5% of marketing costs go to marketing services and agencies.
- Traditional advertising budget: Traditional marketing budgets are expected to decrease by 2.6%, according to the CMO report. This includes print ads, outdoor advertising, radio spots, and more.
For social media, paid ads, and traditional advertising, you may want to break the promotional budget into specific marketing channels. We recommend utilizing this marketing budget template .
Small Business Allocation: How It’s Different
Professional marketers who responded to the CMO Survey said they spend approximately equal portions of their marketing budgets on marketing labor, paid media, technology, and outsourcing.
Meanwhile, our surveys show that small business owners think about their marketing efforts and spend their marketing budgets differently. The primary form of marketing most small business owners use is social media (60%), followed by Google Ads (17%), SEO (10%), print (7%), and content marketing (6%).
In addition, 44% of small business owners state that print advertising has not worked for their business, while just 24% did not find social media effective. Google Ads and SEO were tied at 13% for perceived ineffectiveness, while content marketing is the channel small business owners find most effective.
Interestingly, small business owners focus least on the strategy that has the most perceived effectiveness. If you’re looking for ways to grow your business, consider creating more content.
Include a contingency
However you think you’ll allocate your marketing dollars, it’s always best to give yourself some wiggle room when creating a marketing budget plan. Most budgets for marketing tend to be approximately 20% higher than companies actually spend.
Make sure you include a contingency in your budget that is up to 10% so you have some extra room if you need it as you manage your small business.
Regularly monitor and adjust your marketing spend

Continuously monitor the performance of your marketing activities against your budget. Make adjustments as needed to optimize performance and maximize return on investment (ROI).
The most commonly used marketing analytics software is Google Analytics . The most common metrics to measure marketing performance are:
- Sales, revenues: 69.9%
- Digital, web, and mobile performance: 55.6%
- Content engagement: 43.4%
- Lead generation: 40.3%
- Lead conversion: 36.9%
- Campaign costs, efficiency (e.g., production, content reuse): 34.8%
- Campaign effectiveness (e.g., gross rating points, reach, frequency): 34.7%
- Customer satisfaction: 32.7%
- Campaign ROI: 30.7%
- Customer churn, retention rate, loyalty: 28.6%
When a company integrates its marketing strategy, it makes sure every marketing channel pulls from the same playbook.
An integrated marketing strategy is crucial for businesses and organizations for several key reasons:
- Consistency: An integrated marketing strategy ensures that your brand messaging and visuals are consistent across all channels. This consistency helps you create a cohesive brand identity that earns trust and credibility with your audience.
- Maximized Reach and Exposure: Different people consume information through different channels. By integrating various marketing channels (such as social media, email, content marketing, traditional advertising, etc.), you can increase your audience and visibility.
- Improved Customer Experience: An integrated approach allows for a seamless and unified customer experience. When customers encounter a consistent message and experience across different touchpoints, it makes for a smoother and more enjoyable interaction with your brand.
- Increased Efficiency: Coordinating different marketing efforts can lead to increased efficiency. For example, when your social media efforts align with your content marketing strategy, you can repurpose content for both channels, saving time and resources.
- Better Data and Analytics: Integrating different channels will help you get a better picture of your audience and their preferences. This allows for better tracking, measurement, and analysis of marketing efforts, leading to better-informed decision-making.
- Adaptability and Agility: An integrated strategy enables you to pivot when market conditions or consumer preferences change. If one channel isn't performing as expected, you can adjust your approach across multiple channels more easily.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies that successfully integrate their marketing efforts often gain a competitive edge. This is because they're able to deliver a more cohesive and compelling message than competitors with a disjointed or inconsistent approach.
- Alignment with Business Goals: An integrated strategy ensures that all marketing efforts are aligned with overall business goals and objectives. This means that every campaign and initiative is contributing to the broader mission of the company.
- Optimized Budget Allocation: Integrated marketing allows for better allocation of resources. By understanding which channels are most effective for your specific audience, you can allocate your budget and staff to maximize return on investment.
- Long-term Growth and Sustainability: An integrated approach sets the foundation for sustainable growth. By building a strong and consistent brand presence, you're more likely to retain customers and attract new ones, leading to long-term success.
In today's highly competitive and fast-paced business environment, having a well-thought-out and unified marketing plan is essential for staying relevant, reaching your target audience, and achieving your business objectives.
Promoting your business on a limited budget requires creativity, strategic planning, and a focus on cost-effective methods. Here are some practical steps to help you get started:
- Define your target audience.
- Leverage social media.
- Optimize your website.
- Invest in content marketing.
- Be consistent with email marketing.
- Collaborate with influencers or partners.
- Utilize free marketing tools.
- Network in your industry.
- Offer referral incentives.
- Leverage user-generated content.
- Do your own graphic design.
- Perform local SEO.
- Run giveaways and contests.
- Measure and adjust.
Keep reading to learn more about small business marketing methods on a small budget.
Define your target audience
You need to understand your target market to tailor your marketing efforts toward the people who are most likely to be interested in your products or services. Your target market should be as narrowly defined as is reasonable.
Some of the demographics and data points you can use to narrow your target market and reduce your online advertising expenditures include:
- Other demographics
The more narrow your budget, the less cost involved.
Leverage social media

Most small businesses that are operating on a small marketing budget will focus on social media posts. You can get a lot of free marketing when you:
- Choose the Right Platforms: Focus on the social media platforms where your target audience is most active.
- Join Facebook Groups: There are groups for everything on Facebook. Join your local groups to network and attract customers.
- Post Regularly: Regular and engaging content can help build a community around your brand.
- Utilize Hashtags: They can expand the reach of your posts to a wider audience.
- Engage with Your Audience: Respond to comments, answer questions, and foster a sense of community.
Optimize your website
Try using a free website builder to start. Ensure your site is user-friendly and responsive on mobile. Once you’ve set up your website, use SEO techniques to improve your site’s visibility on search engines.
As you grow, you’ll gain more functionality from a paid website.
Invest in content marketing
As we mentioned earlier, content marketing is one of the least used but most effective types of marketing small businesses can do. Businesses should create valuable, relevant, and informative content that resonates with their target audiences. Blog posts, videos, infographics, and e-books are all great options.
Be consistent with email marketing

Collect email addresses through your website and social media. Then send out regular newsletters with updates, promotions, and valuable content.
Collaborate with influencers or partners
Partnering with influencers in your niche can expose your business to a broader audience. You can also collaborate with complementary businesses for joint promotions or events.
Utilize free marketing tools
Free tools, like Google Analytics, Google Business Profile, and onsite social media analytics, help you monitor performance and make data-driven decisions. There are many other free apps to use as a small business, too.
Network in your industry

Attend industry seminars, conferences, and other events to make connections and spread the word about your business. These are great places to meet potential customers and people who can refer you to customers.
Offer referral incentives
Encourage your existing customers to refer friends and family by offering discounts or special deals. It doesn’t have to be much—people will appreciate 5% to 10% discounts.
Leverage user-generated content
Encourage customers to share their experiences with your products or services on social media. You can feature their content on your platforms and share them with your followers on social.
Do your own graphic design
Use free or low-cost tools, like Canva , to create eye-catching visuals for your marketing materials. Canva makes it easy to create content and doesn’t require design experience.
Perform local SEO

Optimize your business for local searches so people in your area can easily find you. To do this, you need to:
- Make sure your name, phone number, and address are consistent across the internet.
- Sign up for Google Business Profile.
- Improve your online listings.
- Share updates, like new locations or hours, with Google.
- Request Google reviews.
- Optimize URLs, title tags, headers, meta descriptions, and content on your website.
- Add a Google map with your location in your site’s footer.
- Create localized content.
- Improve your site’s mobile friendliness.
- Participate in the community. When people see your company interacting with the local community, it builds trust, and search engines may take notice.
Run contests and giveaways
Engage your audience by offering prizes in exchange for social media engagement or email sign-ups. The point here is to get more followers and more emails to contact. You’ll want to:
- Establish your goals.
- Choose a contest to run.
- Build the contest.
- Promote the contest.
- Track the results.
- Follow up after the contest.
- Improve the next contest.
Check out Wishpond’s blog for a more extensive guide on hosting contests .
Measure and adjust
Keep track of what works and what doesn't. Focus on the strategies that give you the best ROI. This will help you avoid falling into the category of small business owners unsatisfied with their marketing results.
These small business marketing statistics can help you create an informed marketing budget, especially when you remember that online marketing is steadily gaining traction over traditional marketing channels, like print and radio.
What is your experience with marketing budgets?
We’ve discussed the importance of creating a marketing budget, provided you with marketing budget allocation best practices, and shared tips on how to use marketing budget templates whether you have an established business or are just starting one.
Whether you have a marketing department or not, take the time to make a marketing budget. It will help increase sales and reduce wasted spending.
Based on years’ worth of UpFlip interviews, I can tell you that marketing automation software and content marketing have some of the best returns.
Have you ever created a marketing budget? What was the biggest pain point in creating it, and what new marketing strategy will you try next?
How to Open a $2M/Year Restaurant (2024)
- Creating a successful restaurant concept
- Funding your business
- The importance of the restaurant menu
- Choosing a commercial space
- And other keys for restaurant endurance
- Learn About Restaurants
- Ideas for Your Own Restaurant Concept
- Identify Your Ideal Target Market
- Create a Restaurant Business Plan
- Fund Your Restaurant Business
- Consider Restaurant Names
- What Do You Need to Open Restaurant?
- How to Open a Restaurant
- How to Advertise a Restaurant
Step 1. Learn About Restaurants
- Customer Service
- Financial Management
- Time Management
- People Management
Step 2. Ideas for Your Own Restaurant Concept
- Quick Service Restaurants
- Food Truck Business
- Fast Food Restaurants
- Casual Dining
- Delivery Service
- Fine Dining
- Bar and Grill
- Restaurant Franchises
- Restaurants Focused on Specific Foods
- Make something no one else has.
- Do it better than anyone else.[/su_quote]
What Is the Restaurant Industry Outlook?

Who Are the Major Players in the Restaurant Industry?
- Darden : The parent company of Olive Garden and Longhorn Steakhouse makes nearly $9 billion per year and nearly 10% profit margin. Figure out how to open a restaurant that emulates their business strategy and you’ll be a happy restaurant owner.
- Chipotle : The leader in the fast food industry has made a lot of gains over the years. It has surpassed both McDonald’s and Chick-Fil-A to have 2.2% market share. Chipotle makes around $7 billion and keeps growing, but their profit margin slightly lags the fast food industry .
- Hakkasan Group : A nightclub and bar operator that owns multiple Vegas hotspots earns more than $360 million dollars but has a lousy 2.4% profit margin.
Step 3. Identify Your Ideal Target Market

- Generation : Understanding which generations are more likely to eat at a restaurant can be helpful. For instance, getting younger generations to try new cuisines might be easy, while asking them to spend $200 on fine dining might not be.
- Gender : Women tend to be more likely to view food-based social media and blogs. If you can get them interested, you have a good chance of getting their significant other to try your food.
- Location : Do people tend to travel to eat at a restaurant or do they want something closer to their house? Depending on the location and type of restaurant, the answer varies.
- Wealth : If you’re trying to sell a premium experience, you’ll need to be in a premium neighborhood and market your restaurant opening to those that can afford it.
- Buying Preferences : You’ll want data like frequency of eating out, preferred means of payment, time of day more likely to eat, and what social media influencers they follow.
Why Do Restaurants Fail?
Step 4. opening a restaurant business plan.
- An Executive Summary
- Restaurant Type
- Startup Costs
- Operating Costs for 5+ Years
- Marketing Plan
- Organizational Chart
- Funding Needs
- One-page business plan template
- Our Blog: How to Write A Business Plan (Plus Examples and Templates)
Steps to Opening a Restaurant Checklist
Step 5. fund your restaurant business, how much does it cost to open a restaurant.
- Construction Costs : $70,000 to $472,500
- Kitchen and Bar Equipment Costs : $40,000 to $196,250
- Pre-Opening Costs : $10,000 to $50,000
How Much Do Restaurant Owners Make?

- Costs associated with business licensing
- Costs of the space, equipment, utilities, and food
- Costs of liability insurance to protect your business if something goes wrong
- Employee costs
- Cost of accepting credit cards
- Software for running the business
- Fees to delivery apps
- Paying yourself
Budgeting Resources:
- A complete guide to creating your business budget and managing expenses
- A breakdown of the necessary restaurant costs
How to Get Restaurant Funding
- Personal funds: Almost every owner will invest some of their own money when starting a restaurant. Bootstrapping is the most common way of starting a business.
- Government programs : Check the SBA site to see if there are grants for opening a restaurant. Then apply to see if you qualify.
- Small business loans : You might qualify for a small business loan especially if you are a franchise. Try our preferred lender, National Business Capital .
- Home equity loan : A home equity loan is a great way to get enough funds to start your restaurant, but many restaurants fail. If yours fails, you lose your home.
- Business partner: Many amazing chefs open their first restaurant because they were approached by a business partner.
- Friends and family : People who trust you and believe in your mission may be willing to help you get started.
- Crowdfunding : See if you can get retail investors to fund your company.
- Credit cards : You might use credit cards to fund part of a small restaurant, but most people don’t have a half a million credit line on their card. You’ll probably need other ways to fund your new restaurant in addition to a credit card.
How to Open a Restaurant with No Money?
How to open a restaurant with no experience, step 6. consider restaurant names.

- Using a family name: Huber’s Cafe is named after the original owner.
- Creating a pun : Many Asian restaurants use this strategy. I once went to a Pho restaurant named Pho King Pho Nomenal.
- Include the name of the food : This is common when someone considers opening a BBQ restaurant.
- Evoke emotions : Raising Cane’s is named after the owner’s dog Cane.
- Get Creative : You don’t have to stick with conventional names.
Don’t Forget to Register a Domain
Step 7. what do you need to open restaurant.
- Create a business entity.
- Get an Employer Identification Number (EIN).
- Get restaurant licensing.
- Buy a liquor license (if applicable).
- Get a food permit.
- Get a sales tax permit.
- Set up unemployment insurance.
- Buy business insurance.
Create a Business Entity

- Tax specialist
Corporation
Limited liability company.
- Worker injuries
- Guests getting food poisoning
- Serving a drunk driver
Every Restaurant Needs an EIN

- Open a business bank account.
- File tax returns.
- Apply for business licenses.
Get Your Restaurant License
Buy your liquor license, apply for a food permit.

Get a Sales Tax Permit
Set up unemployment insurance, buy business insurance and liability insurance.
- Business General Liability Insurance : For when costly damage occurs to a person or their property.
- Professional Liability Insurance : Protect the business in case something happens that causes injury or death.
- Cybersecurity insurance : Protects the restaurant should credit card information get stolen.
Step 8. How to Open a Restaurant

- Create a menu.
- Find a location.
- Purchase equipment.
- Establish a pricing structure.
- Implement the business systems.
- Hire employees.
- Control the cost of food.
- Follow safety and ethical business practices.
Create a Menu
- Build your menu around your masterpieces.
- Add appetizers that compliment the meal.
- Then add desserts and drinks.
- Don’t forget soups and salads.
- Add the items that every restaurant in your category is expected to have. You don’t need more than 15 entrees.
- Limit each category to less than 10 items.
- Use the menu within your marketing plan to help drive the dining experience to your unique selling point.
Huber’s Cafe Menu

Best Selling Drink: Spanish Coffee

Find a Location for Your Restaurant
- Lots of foot traffic
- Good parking
- A good fit for your service style (Service style can vary from buffets, pickup, dine-in, delivery, drive through, full-service, and more.)
Purchase Restaurant Equipment and Furniture

- Tables and chairs
- Hostess podium
- Drink machines
- Dishwashing machines
- Ice machines
- Prep tables
- Kitchen equipment (varies based on restaurant type)
- Vent hoods (remove heat)
- Dishes, cups, and utensils
- Combi-oven (steamer + convection oven)
- Double stacking convection ovens
- Groin pot (with soup stock and gravy)
How to Calculate Food Pricing

- Use the cost of goods (COGS) sold divided by industry benchmarks.
- Developing pricing similar to other restaurants.
- Use the cost of food divided by industry benchmarks.
Calculate Menu Prices with Cost of Goods Sold
- All employees make $10 per hour
- 5 minutes of prep time
- 10 minutes of cooking time
- 5 minutes of serving time
- The cost of the plate is $5
Price Similar to Other Restaurants
Use ingredient costs to calculate menu pricing, note about external delivery services, implement restaurant systems .

- Sales System: Huber’s uses Aloha from NCR .
- Inventory System: Huber uses FoodTrak .
- Payroll System: ADP is Huber’s preferred payroll provider, but you can check out other payroll providers , too.
- Accounting System: James told us they have a bookkeeper and an accountant but are looking at Quickbooks or PeachTree .
Hire Employees
Pay the employees .
- Cooks : $14.43 per hour or $ 30,010 annually
- Restaurant Managers : $28.58 per hour or $59,440 annually
- Bartenders : $12.67 per hour or $26,350 annually

Follow Tax Laws

Follow Federal Employment and Labor Laws
Other requirements.
- The Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) requires any business with employees to pay a payroll tax.
- Employment Eligibility Verification (Form I-9) allows business owners to verify the identity and employment clearance of every person they hire.
- Meeting Occupational Health and Safety Administration ( OSHA ) standards define workplace safety requirements and are necessary for any business (and highly relevant in an industry as physical as a restaurant).
- Worker’s Compensation Insurance is a must for restaurants, as it helps businesses avoid the cost of an employee’s medical bills and lost wages following a workplace injury.
Follow Safety Regulations for Restaurants

- Food poisoning
- Food allergies
- Serving intoxicated customers
- Injuries from slipping or falling
- Develop and implement written safety and emergency response procedures.
- Provide worker orientation and training on safety procedures.
- Follow a process to identify, control, and mitigate workplace safety hazards.
- Regularly inspect your workplace to help identify any potential hazards.
- Investigate and document accidents (or close calls) to prevent a future occurrence.
- Hold safety and health refreshers regularly.
- Keep records of workplace health and safety for review during internal or external investigations.
- Keep a first aid kit available and well-stocked in your restaurant.
Step 9. How to Advertise a Restaurant

- Create a Website: Learn how to build a website . Make sure to include your menu and a way to order.
- Start Social Media Profiles: Creating social media channels creates easy backlinks to your website and makes it easy for your customers to share pictures of your food.
- Create a Google Business Profile: Get found on Google Search and Google Maps by creating a profile and keeping it up to date on Google Business Profile .
- Partner with Other Businesses : James told us: “God sent UpFlip here to help us promote our business.”
- Start a Rewards Program : James uses the “Birthday Club” to build a mailing list and provides a free meal on your birthday.
- Consider a Soft Opening : We’ll discuss this more below.
- Advertise Your Grand Opening : We’ll also discuss this more below.
What Is a Soft Opening for a Restaurant?
- Work out kinks before serving the general public.
- Get good pictures for marketing.
- Help identify top performing employees.
- Get feedback on menu items early.
How Should I Advertise My Grand Opening?

Are You Ready for the Restaurant Industry?
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
Become a business owner in less than 90 days
Start your 10-day free trial of the UpFlip Academy and learn how to start your own business from scratch.
Get business advice straight to your Inbox

Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » startup, how to write a one-page business plan.
Need to pitch your idea on the spot? This quick one-page business plan outline can help you get your foot in the door with investors and incubators.

A complete, thoughtful business plan can help you recruit executive leaders, pitch investors and win grants. But sometimes you just need a one-page business plan to get your foot in the door. A condensed business plan can act as an elevator pitch to pique the interest of a startup incubator, bank or other business partner. Here’s what should go into your one-page business plan.
[ Read more: The Definitive Guide to Writing a Startup Business Plan ]
Section 1: The demand
Start by establishing the problem, need or demand for your product or service. Why should an investor back your business idea? This section establishes opportunity: why you’ve come up with this idea in the first place, and why other consumers will see your idea as valuable. There must be a demand in the market for which you are supplying a solution.
Note that “demand” is different than “market size.” “Start your pitch with the demand in your market, not how big the market is. It doesn't matter how big the market is if no one wants your product or service,” explains Sweta Patel in Forbes .
Try to keep each of these sections to two to three sentences . Treat this first section as the bait to get someone interested in reading the following sections, and to inevitably ask for a longer pitch.
Section 2: Your solution
Some experts consider this your company’s mission statement. Others treat it as an opportunity to describe the intricacies of your product or service. Overall, this section should describe your solution to the problem identified in Section 1. How is your solution distinctive from other companies tackling the same problem?
“You can even think of this section like a book headline,” wrote one expert . “The first part is the eye catching and very clear statement on what the book is about. And then the actual book text talks in more detail about the ‘bread and butter’ of the story.”
Make sure this section focuses on the things that make your idea unique: The details of why a customer will buy from you instead of any other company will provoke an investor to ask for more information.
Section 3: Business model
How will you make money? This section should cover your pricing strategy. “Briefly describe how your pricing will be competitive enough to attract customers but be high enough to generate a profit after subtracting expenses,” recommends The Balance .
Patel also writes about the importance of identifying multiple revenue streams for your new company. “The next step in crafting a one-page business plan is to ensure there is more than one way of making revenue in your business. If there isn't, investors might think your company isn't innovative enough. They might hold back on funding because they want to invest in an organization that is going to have several ways of making money,” she said .
Save the detailed financial information for the longer business plan, and focus on how your idea will generate revenue while keeping costs low.
Start your pitch with the demand in your market, not how big the market is.
Sweta Patel, Forbes Business Council
Section 4: Management team
Business incubators and investors often give more consideration to business ideas presented with a strong leadership team attached. The reason for this is that investors realize that an initial idea may go through a few iterations before launching to the market. Therefore, an investor will look for a talented, motivated founding team with whom they can refine a business idea until it works.
You may not have your executive team in place yet, but make sure you showcase the qualifications of yourself and any business partners you have. If you haven’t started hiring, demonstrate the profile of who you wish to bring on board to help your network put you in touch with the right people.
Section 5: Action plan
Use your remaining space to outline your goals, next steps and call to action. What is your big “ask”? If it’s funding, demonstrate what you will do with the amount of money you need. Try to outline specific targets with deadlines. For instance, you may write a sentence stating, “By ‘x date’ we will have the business premises chosen and lease signed.” Give potential partners a little taste of where their investment will make a difference.
You may also want to include a line that offers a more complete business plan with financial projections, marketing, distribution and competitive analysis available on request. Hopefully, your one-page plan will have given enough of a taste of your idea to encourage investors to seek more information.
[ Read more: 5 Business Plan Templates to Help You Plan for Success ]
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners’ stories.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .

Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more startup tips
How to change your ein, or how to fix an incorrect ein, micro-business vs. startup: what’s the difference, micro businesses: what are they and how do you start one.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Template Lists
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business What is A Business Plan & How To Design It?
What is A Business Plan & How To Design It?
Written by: Midori Nediger Jul 11, 2023

A business plan outlines the goals of your business and how it plans to achieve them.
Real important – because without it, it’s like running a business in the dark. It’s like a roadmap that guides your company’s direction and helps everyone stay on track.
Gone are the days when designing a business plan from scratch was a time-consuming and challenging task. Today, business plan templates offer a convenient solution by providing pre-designed layouts that simplify the process.
In this blog, I’m going to break it down for you. I’ll share the six things you need to know to put together a compelling, engaging business plan. Ready to get started now? Venngage’s online Business Plan Maker lets anyone create a winning business plan quickly and easily.
Click to jump ahead:
- How to format your business plan
Startup business plan templates
Simple business plan templates.
- How to write your business plan
- How to design an engaging executive summary
- How to use charts and graphs to present data
- How to communicate growth strategies in your business plan
How to present financial data in your business plan
How to format your business plan.
To format your business plan:
- Start with a clear title page.
- Include an executive summary.
- Provide a company description.
- Conduct a market analysis.
- Describe your product or service offering.
- Outline your marketing and sales strategy.
- Include organizational or business structure and management information.
A typical business plan is an in-depth document and covers every facet of your business (present and future). Creating a traditional business plan makes sense when you have a clear growth plan for the next three to five years, are in need of major funding, or want to attract long-term partners.
A professional business plan typically has the following sections:
- Table of Contents
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis
- Organization and management
- Service or product line
- Marketing and sales
- Funding request
- Financial projections
- An appendix
A business plan can span a dozen or more pages because it presents the big picture, as complete as possible, to reassure others to invest in you. Investment can mean a few different things – usually financial, but also as partners or employees.
The sections that can take a lot of research and add to the bulk of your business plan are your market analysis, marketing and sales plans, and financial projections.
These are the sections that demonstrate your business acumen, your long-term vision, and your accountability. Whereas, sections like the executive summary are meant to grab attention, inspire and get people excited about your business.
Start with a business plan template
To get started on your business plan, save yourself some time and use a template.
Most business plan templates will include things like a cover page, table of contents and the main sections you need. It will also have pre-formatted pages with placeholder text and charts that you can swap out.

It takes time to do market research, present growth plans, put together financial projections, analyze your customer base, create competitor breakdowns…the list goes on.
The last thing you want to do is spend precious time formatting the resulting document.
Save time by building your business plan from an existing business plan template, and customize it with your own content.
With a clean, consistent structure and clear headings, this template is the perfect starting point:

Then you’re free to customize the template with helpful visual elements like charts, tables, and diagrams, that will make your business pitch impossible to resist.
A Venngage business plan template is designed to help you communicate visually and explain complex ideas easily. The right business plan template for you depends on the length and detail of your business plan, your brand and style, and the different sections you want to cover.
If your small business doesn’t have a dedicated design team, but you still need to learn how to write a business plan to present to investors–build off of a pre-designed business plan template:

There are just a handful of our business plan templates that can be customized in the Venngage editor. Browse more business plan templates, choose one that’s best for you and start editing right away.
Structuring your startup business plan involves organizing it into sections such as executive summary, company description, market analysis, product/service offering, marketing and sales strategy, financial projections, and operational plan.
Here are some business plan template examples:

Short Business Plan Template
Number your pages and include a table of contents
A table of contents is crucial to help readers navigate your document and quickly find specific sections that are of interest to them.
It’s a good idea to include page numbers, main section headings, and section subheadings here for easy reference.

Keeping these tips in mind will ensure that your business plan design feels clean and professional and doesn’t distract from your content. You want your information, not your formatting, to be the focus!
How to write your business plan
Here are three tips for writing your business plan to ensure it’s easy to read, appears professional and is memorable.
Use bulleted lists, bold text, and a clear type hierarchy for ‘skimmability’
Business plans need to be understandable at a glance to attract funding . Investors are looking for information that will help them understand your business quickly and without much effort.
Take a look at this snippet of the business plan template from above:

What stands out to you?
To me, the large green headers pop out first, making it easy to scan through the sections to find what I want to focus on.
This is because there’s a defined type hierarchy, giving more visual weight to the headers over the body text.

Next, the unique selling points of this business–superior quality products, unique glass carving and brass inlays, and excellent service–jump out. Because they’re presented in an indented list , they’re easier to see at a glance, which will likely make them more memorable.
Finally, I’m drawn to the bolded stats–“top 30% of the industry” and “4 out of 5 households spent money on renovation”.
Key statistics like these can go a long way towards convincing your investors that you’re worth their time and money. If you’re going to include them within larger paragraphs, make sure they stand out by increasing their font weight.
To sum up: make your report skimmable. Draw attention to important takeaways with indented lists, bolded text, and a clear type hierarchy.
Consider using a one-column or two-column grid

If your business plan contains only text, stick with a single-column layout that reinforces the linear flow of the document. If your business plan includes some supporting data in the form of charts and tables, use a two-column layout to juxtapose text with its corresponding data.
Maintain page margins that set text at a readable line length
When we read long passages of text, the ease at which we read depends on how the text flows on the page. Something called line length (the number of characters in a horizontal line of text) plays a huge role in readability, and is something you should consider when formatting your business plan.
To dictate line length, designers and typesetters play with the width of page margins (the edges of a document that don’t contain any text or images) with the aim of maximizing readability.
It’s generally accepted that the ideal line length sits somewhere between 40 and 90 characters per line. Any longer or shorter and you’ll find that something feels “off” about your document.
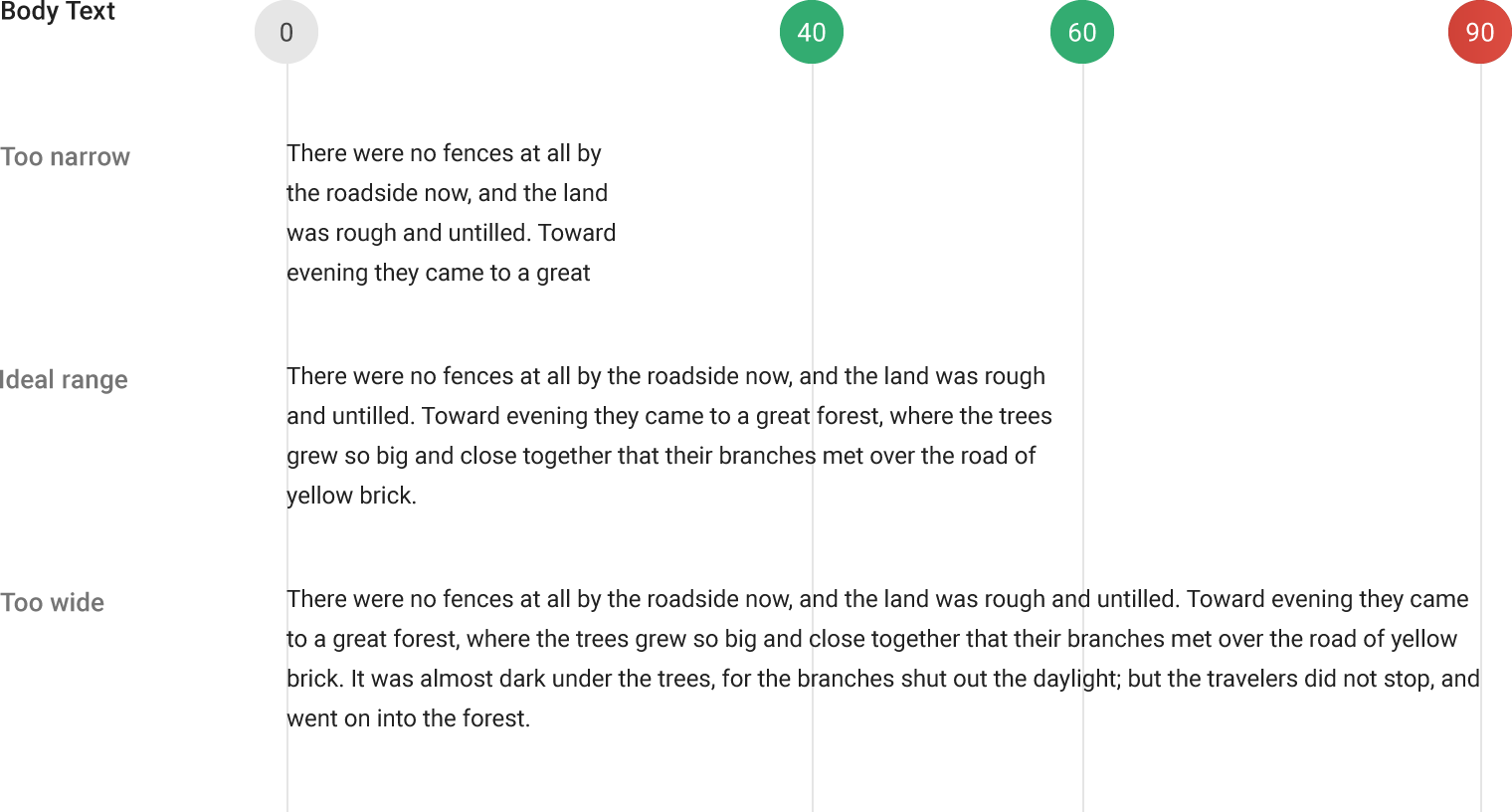
How do you achieve this in your business plan?
If you use a single-column layout, use nice wide margins (1 ½ to 2 inches) to limit your text to less than 90 characters per line.
With a two-column layout, you might need to use narrower margins (possibly as little as ½ an inch on either side) to make sure there’s enough space for at least 40 characters per line of text.
The last thing to remember about margins and line length–don’t play around with them from page to page. Use consistent margins across your whole document.
How to design an executive summary
An executive summary is a snapshot of your business plan. It should be concise and hook your readers. It should reassure stakeholders that your business plan will be a worthwhile read.
How you choose to structure your executive summary is key. You can deliver a lot of excellent information that simply gets lost in a sea of text and paragraphs. Even if someone reads through it entirely, they may have missed something.
To make key information stand out, use vibrant headings, incorporate visuals throughout, and break up the layout of your text.

Not every investor looks for the same thing. Some will care more about who you or your executive team are, while another is interested solely in the financials of the business. Identifying each section makes it easy for readers to find exactly what they’re looking for.
You can also list out the key takeaways, briefly explaining them in the executive summary. If your reader finds everything they needed to know in the executive summary, they’ll happily move onto the rest of the business plan.

Use one feature color to tie your business plan together
Color should be used with restraint in professional documents like business plans. Instead of adding color solely for aesthetic purposes, think of color selection as another tool to highlight information you want your reader to focus on and to tie the document together.
You shouldn’t need more than a single color (ideally one of your brand colors ) to achieve this in a business plan.
In business plan charts, color should be used only to clarify trends and relationships. Use color to emphasize single important data points, differentiate between real and projected values, or group related data:

In the rest of your business plan, keep color to a minimum. At most, use it to make headers stand out or to highlight key points in long-form text, diagrams, or tables.
The nice thing about keeping document colors this simple? It’s hard to mess up, and without any complex design work, it creates a sense of cohesion and unity within a document.
How to use charts and graphs to present your data
Since your business plan should be backed by solid data, you might want to include some of that data as evidence, in the form of charts, tables or diagrams . Even simple visuals can communicate better than long paragraphs of text.
I’ll touch on some specific types of charts commonly used in business plans next, but first let’s review a few general chart design tactics.
Use descriptive titles and annotations to spell out chart takeaways
Avoid generic headers whenever possible. Maximize your chart’s value and impact by providing takeaway messages right in the title.
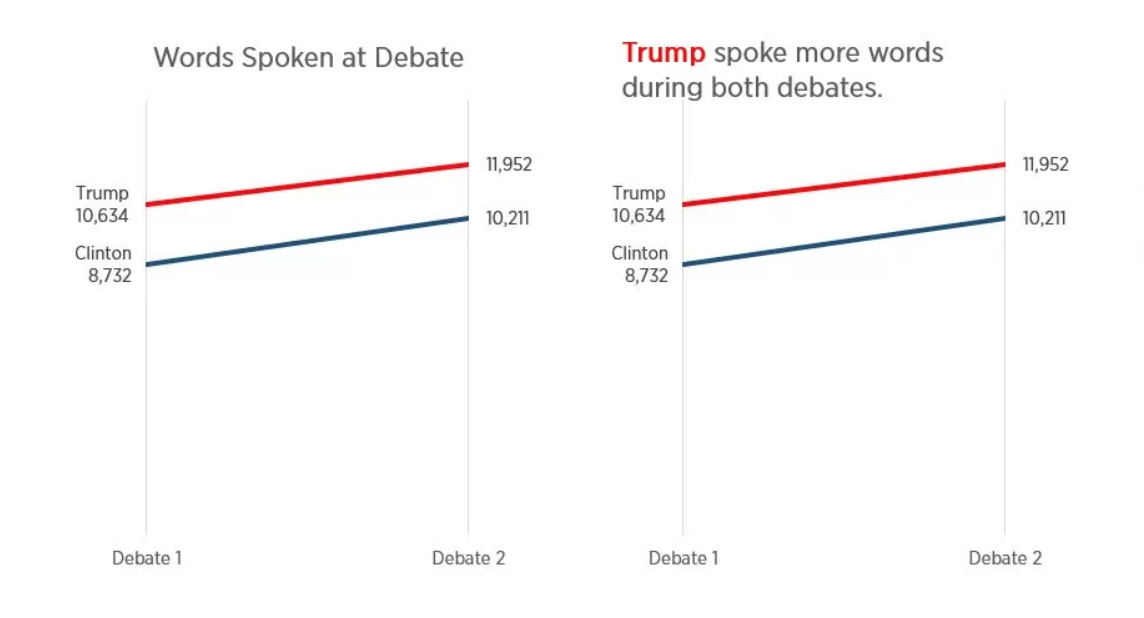
In the same vein, add direct annotations to data points or trends that support your case.

Repeating key messages within a chart, in the title, annotations, and captions, may improve viewers understanding and recall of those messages .
Aid understanding of market size and market share with area charts and pie charts
A market potential analysis is a fundamental pillar of your business plan. Market size and market share are two major components of a market potential analysis.
These numbers are typically in the millions and billions (the bigger the better, really), but most people have trouble grasping the meaning of such big numbers . At a surface level we can understand that one billion is one thousand times larger than one million, but we often struggle to comprehend what that really means.
This is the perfect opportunity to add some visual aids to your business plan.
Use bubble charts to represent market size
Bubble charts are useful for showing general proportions among numbers. Check out this one from our redesigned version of AirBnb’s first pitch deck :

Without having to think about the absolute values of these very large numbers, we can quickly see how they relate to one another.
While bubble charts are good for making quick, general comparisons, they’re less useful when it comes to precise measurements. To help readers make slightly more accurate judgements of proportion:
Use pie or donut charts to represent market share and market composition
Pie and donut charts are the industry standard for showing market share and market composition, since they’re the most widely understood method for representing part-to-whole relationships.
The way Uber breaks down their market with a simple donut chart makes their biggest segment (a key takeaway) really stand out, while the subtler differences between the smaller segments are still evident.
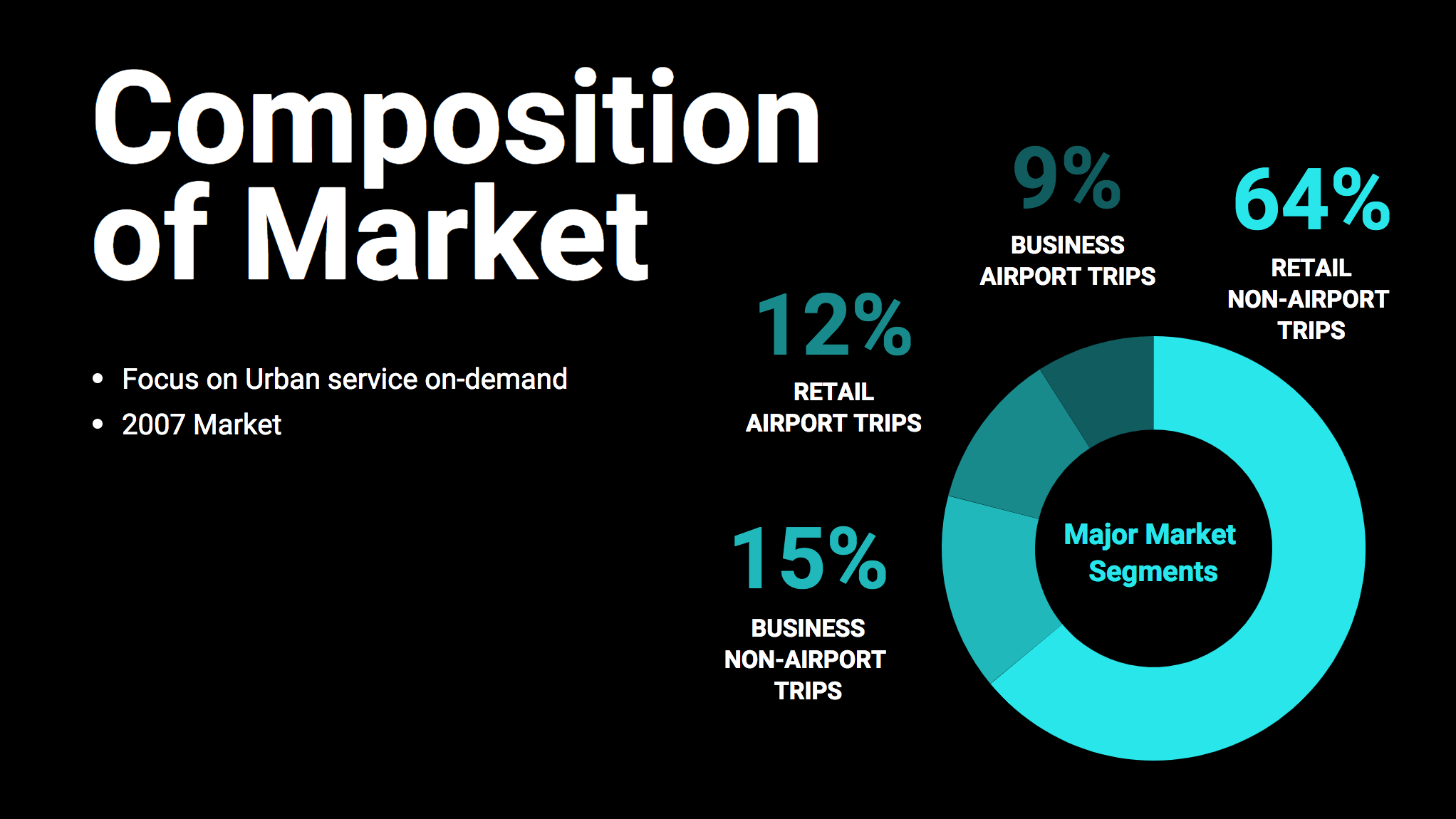
When you present a market analysis, use pie charts, donut charts, or bubble charts to aid the reader understanding proportions and part-to-whole relationships.
Use histograms and bar charts to represent demographic distributions in market segmentation summaries
Another part of analyzing market potential is about identifying and understanding target customers. This means segmenting customers by geography, interests, demographics…really anything that might affect purchasing behaviour.
Two standard metrics that most businesses include in a market segmentation summary are customer age and gender. These data are easily summarized in a histogram, with bars that represent age group distribution.
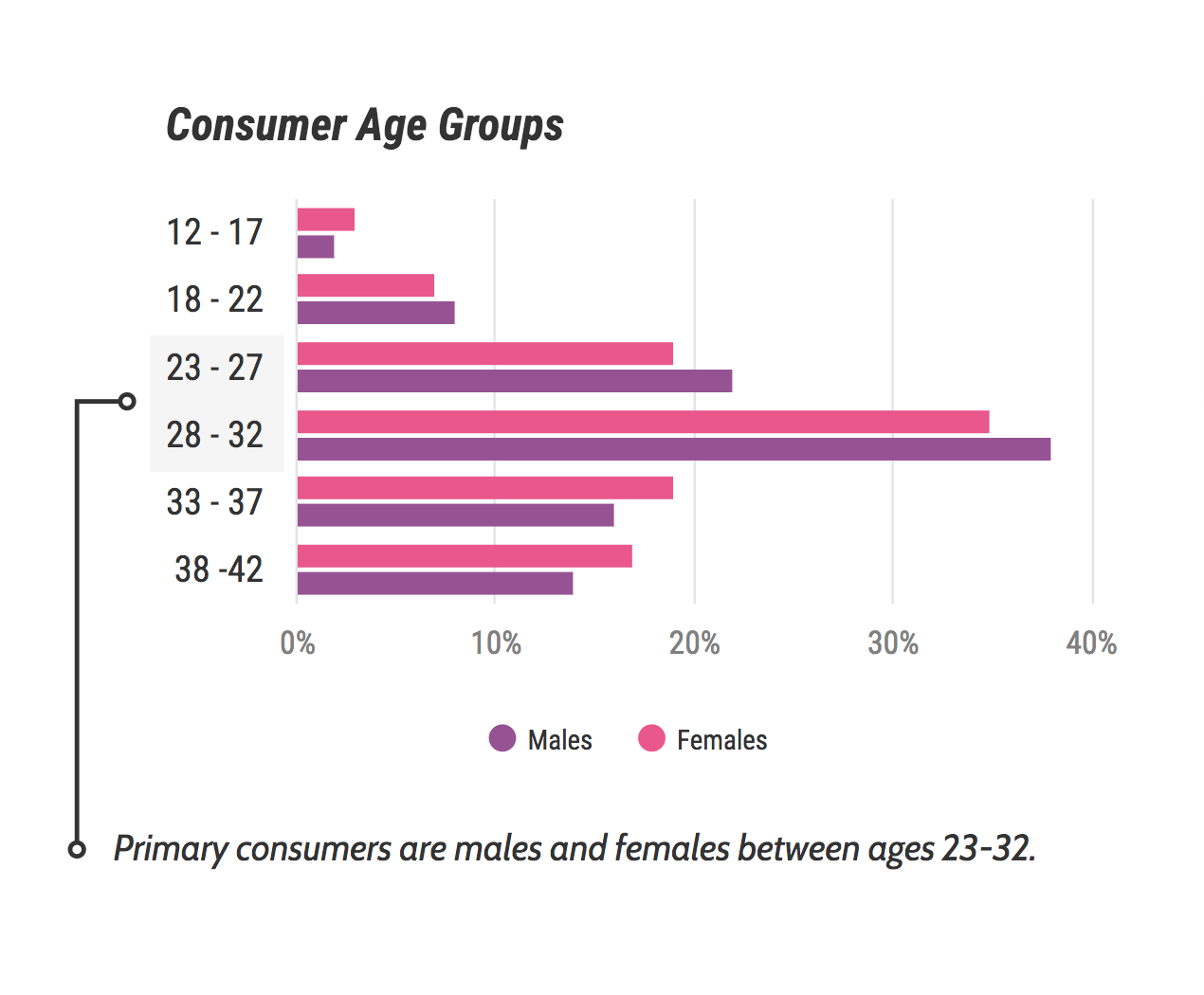
Bar charts can then be used to contrast the key behaviors and lifestyle choices of the top consumer segments.
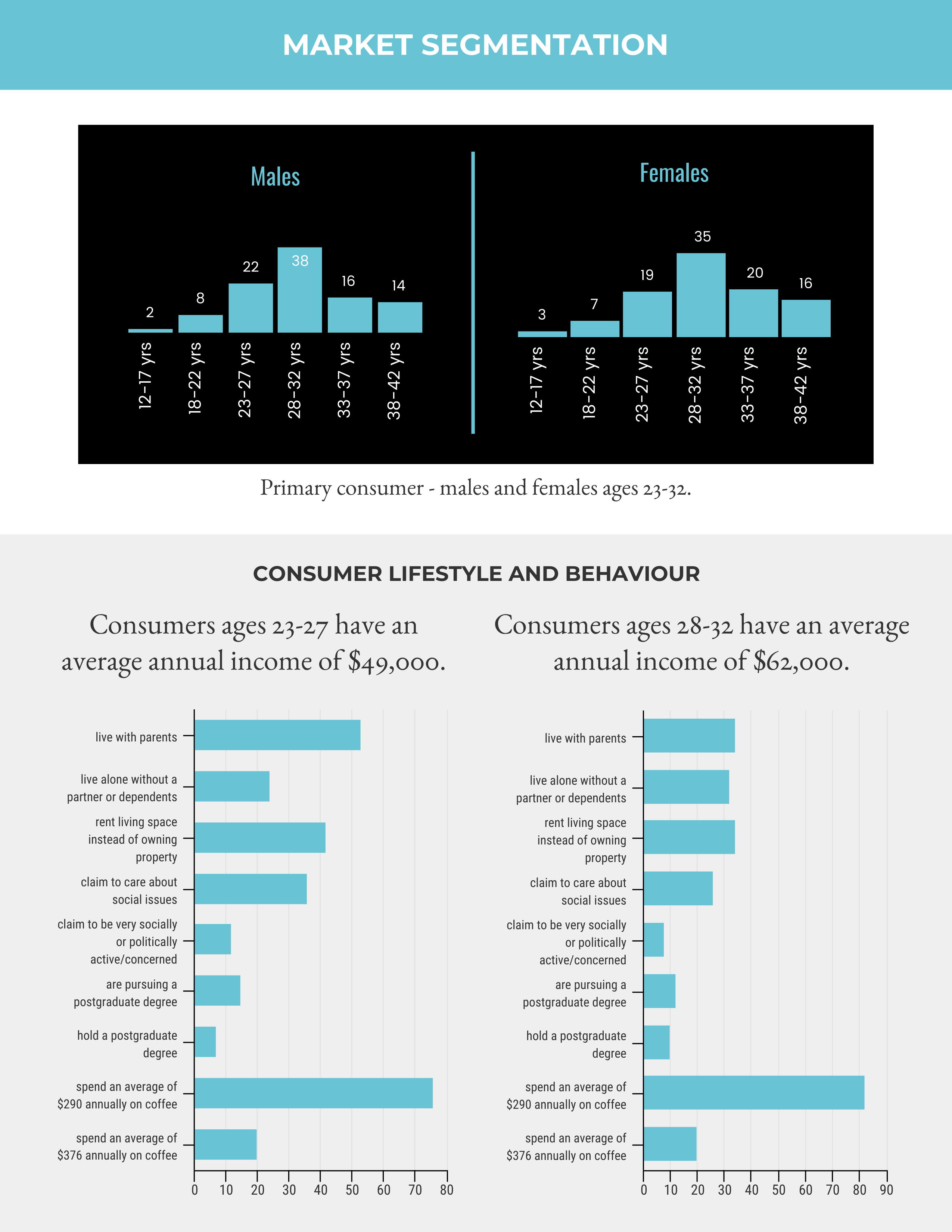
Histograms and bar charts are standard features of a market segmentation summary. Use them together to identify and present information about top customer segments.
Outline major milestones with a Gantt chart
Stakeholders will want to see that you have a concrete plan in place to help you reach your revenue goals. When formulating your goals, use the SMART principle to provide your stakeholders with a very clear vision of how you intend to achieve them.
Use a Gantt chart (a sort of modified bar chart) to outline the major milestones and phases of your business strategy. Try to include a multi-year plan, broken down by quarter and by project or department.
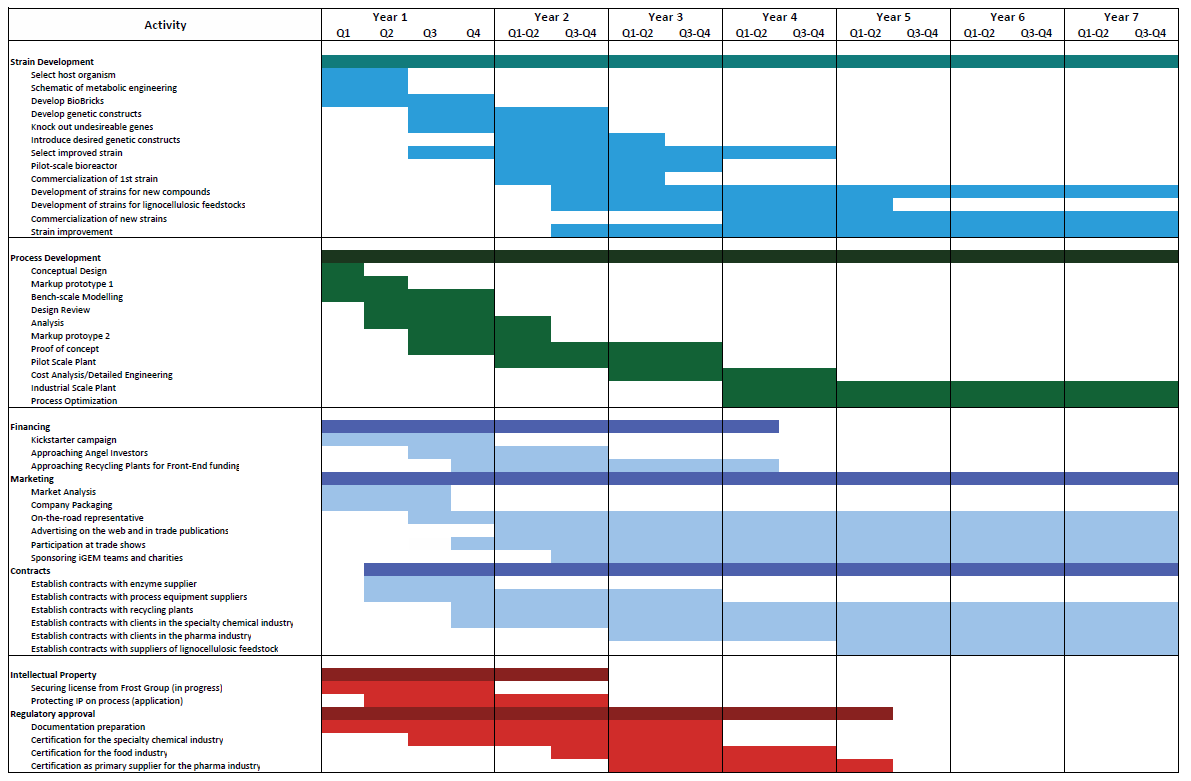
You can create your own Gantt chart with Venngage.
How to communicate growth strategies in your business plan
No matter how impressive your product line or services, your business won’t just magically grow. You concrete marketing and sales plans in place, and effectively communicate strategies to your stakeholders.
Start by acknowledging your target market – who are you going after? This is what your marketing and sales efforts will revolve around after all.
Demonstrate an understanding of the competitor landscape. You will always have direct or indirect competition, and showing how your planning accounts for it is key. Then you can talk about actual plans and strategies you wish to implement.
Present your target audience with persona guides
A product may great on its own. But its value is determined when there is a clear and obvious market for it. You can point out shortcomings of your competition, but you also need to show that your target audience exists and how you’re serving them.
A persona guide provides a great deal of context to readers of your business plan. It’s the best way for them to understand who cares about your product or service, how it aligns with their lifestyle and needs, and why your marketing and sales tactics will work.
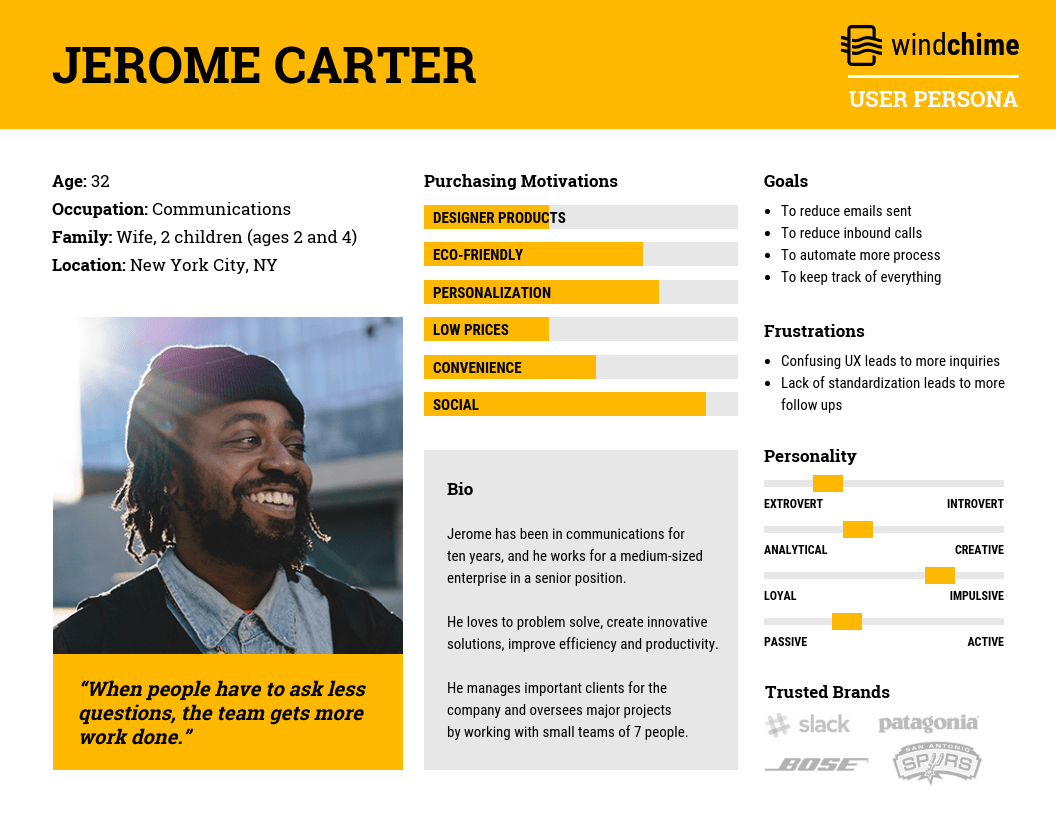
A persona guide needs to be detailed, and share an intimate understanding of your target audience. The more you can divulge, the more reassuring your research and overall business plan will be.
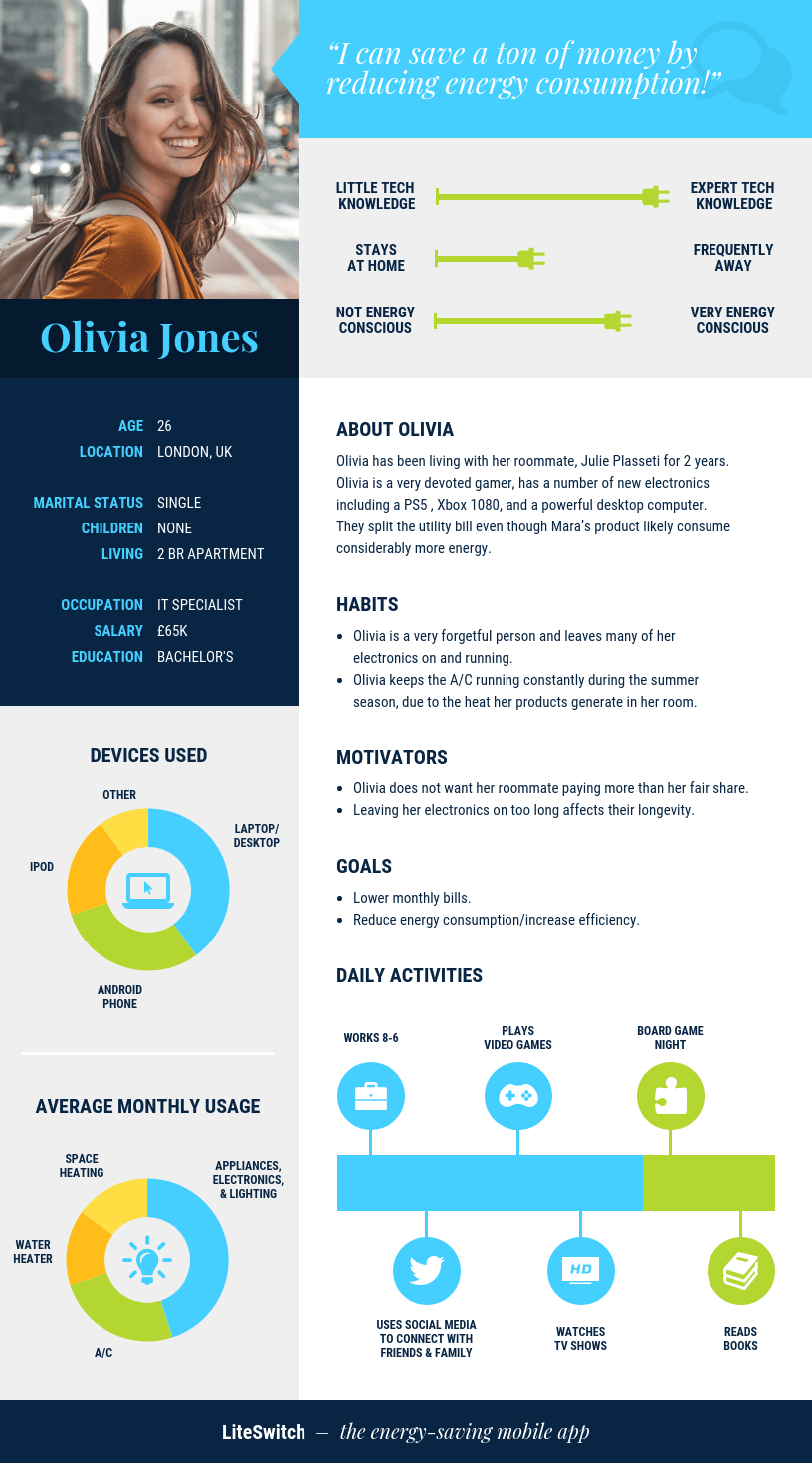
Even if you don’t have a substantial customer base, you can still create an ideal persona guide to show who you’re pursuing.
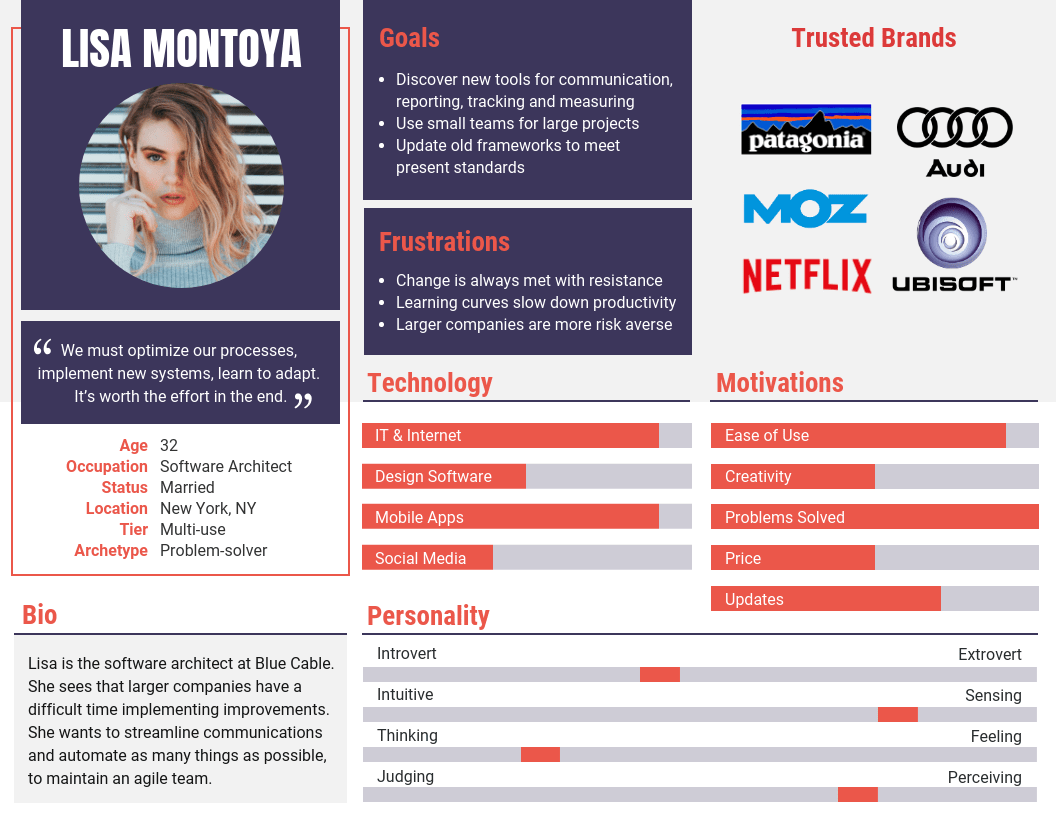
Highlight competitors and differentiate yourself with a SWOT analysis
Every business plan should include an analysis of the competitive landscape–an assessment of the strengths and weaknesses of competitive businesses.
In terms of visuals, this competitive analysis is typically summarized in a SWOT analysis matrix .

You can also present the SWOT analysis as a table or a list. The layout is up to you, but you want to focus on strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats in relation to your competition.

While the SWOT analysis framework provides valuable insights, it’s not the entire reflection of your competitive landscape. For example, it doesn’t make it easy to see at a glance the qualities that differentiate your business from your competitors.
To highlight those offerings that set you apart from your competitors, a comparison matrix is more effective. Take a look at these two templates:
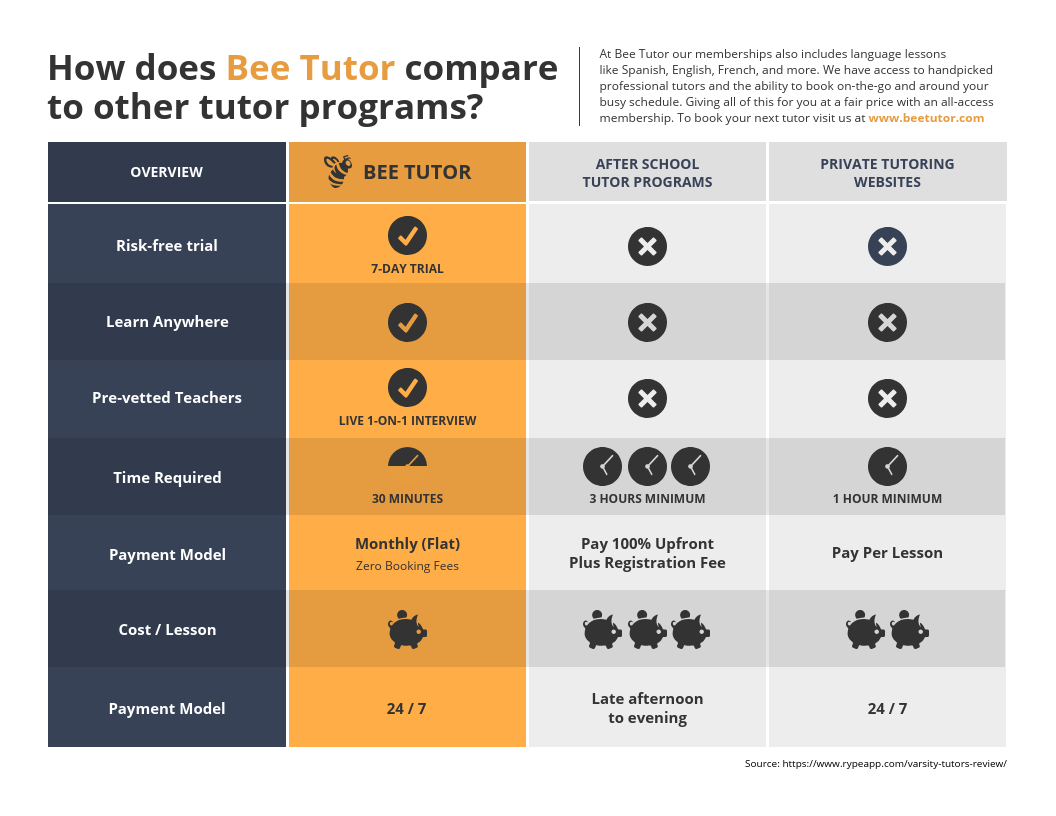
With a direct competitor comparison, it’s easy to present the key differentiators between the existing options for a product or service, and your business.
Alternatively, a “ Magic Quadrant ” can be useful when you’re focused on comparing across two main metrics ( key differentiators ):
Finally, in a competitive market, there are going to be a lot of players who compete directly or indirectly with you. A breakdown of them all may not be necessary. Instead, you can point visually to the space that you will address, that has been so far ignored up to now.
To do that, a prioritization chart can be used. By plotting competing businesses on a prioritization chart, you highlight experiences existing competitors focus on, and where your business falls.
Use roadmaps to present your marketing and sales plans
To explain any long-term marketing or sales plan, you want visuals. It’s easier to break down strategies you’ll be deploying every month or each quarter, when you can actually show what you’re talking about.
Keep in mind, those reading your business plan may not be marketers or sales executives. Being able to lay out your approach in a way that’s organized, shows how much thought you’ve given to your growth strategies.
You can design a simple roadmap that points to what you’ll be doing throughout the year. The more detailed you can get, the better.
You can also present your product roadmap , with your marketing roadmap how the business will be growing overall.

You don’t need to use a traditional roadmap layout, either. Experiment with different formats as you may find one easier to work with than another. As long as the time period for different strategies is clear, your roadmap will be easy to understand.
Presenting financial data isn’t easy. You have to crunch a lot of numbers before you can share projections with confidence. You’ll also need to explain how you arrived at the numbers and prepare for your answers.
Understanding how to organize your information is key to walking potential investors and other stakeholders through your projections.
Use organizational flow charts and summary tables for budget breakdowns and financial summaries
The financials section of your business plan will get a lot of attention from stakeholders. Simple bar charts and pie charts won’t suffice, as they can’t present financial data in very much detail.
If your business has already been operating for some time, stakeholders will expect a detailed report of revenues and expenses. Tables are usually the best choice for this kind of financial summary, as they provide an unbiased view of the numbers and allow stakeholders to look up specific values.

If you’re interested in highlighting a particular trend, however, you may want to include a line chart featuring a smaller snapshot of your financial data:
If you’re just starting your business and you don’t have any detailed revenue data, you can still provide useful information about your budget. Outline higher-level budget allocation with an organizational flow chart .
Use line or bar graphs to visualize financial trends
You can use different types of graphs to also show how your business has performed thus far.
You can share results over the course of a year with a line graph. This is effective to show an overall set of trends and growth rates.

You can also compare previous years to highlight how your business has grown.
Your audience should be able to draw conclusions from your data within seconds. If there is simply too much information, or it’s hard to find important information, they will lose interest.

Looking for a business plan software to help save time and reduce errors? Pick from one of these 7 best business plan software to get started.
A quick summary
A business plan is the one key document that every young business needs to present their vision to potential investors and other stakeholders.
The quality of a business plan can make or break a young business Here’s a quick recap of what we covered for you to keep in mind:
- Get started with a template
- Use a table of contents and numbered pages
- Use lists, bold headings and aim for skimmability
- Consider using a one-column or two-column
- Maintain page margins
- Use headings to identify the most important information
- Use one thematic color palette for your design
- Use descriptive titles and annotations
- Use area and pie charts to explain market size and market share
- Use pie/donut charts to visualize marketing share and market composition
- Use bar charts and histograms to capture demographics data
- Highlight major milestones with a gantt chart
- Identify your target audience using persona guides
- Differentiate yourself with a SWOT analysis/competitor chart
- Use roadmaps to visualize your marketing and sales plans
- Use flow charts and summary tables for financial breakdowns
- Use line or bar graphs for financial trends and projection
You can always reference this post as you work on your business plan. I’ve also included additional blog posts you can reference for specific areas of your business plan.
More Resources for business planning and growth:
- Growth Strategy Checklist: Plan Your Business Goals With These 5 Templates
- What is a Marketing Plan & How to Create One [with Examples]
- How to Communicate Strategy To Your Team Effectively
- 50+ Essential Business Report Examples with Templates
Discover popular designs

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Découvrez MerciApp Assist, votre nouvel assistant ! Essayer maintenant ↗
1/ Qu’est-ce qu’un Business Plan ?
On pourrait traduire l’expression par “ plan d’affaires ” en français. En voici la définition.
Le Business Plan est un document qui rassemble plusieurs éléments essentiels du projet d’entreprise.
Il contient les points clés de votre projet de reprise ou de création d’entreprise .
Il permet d’expliquer les étapes de mise en œuvre votre projet du point de vue stratégique et opérationnel. Concrètement, il explique comment votre organisation va gagner de l’argent et se développer.
Il joue un rôle clé dans la finalisation d’un projet. Il est l’ aboutissement du montage de ce dernier. Sa rédaction intervient donc après avoir mené l’étude de marché, établi le modèle économique, et choisi la structure juridique de l’entreprise.
Point d’attention : un Business Plan est d’abord et avant tout outil de communication . Le rôle du Business Plan est de vendre le projet à d’autres. Il sert à convaincre des partenaires potentiels de rejoindre ou de soutenir celui-ci. Il est donc souvent utilisé pour :
- trouver un partenaire ;
- obtenir un financement ;
- vendre une entreprise ;
- solliciter un investisseur.
On parle d’un CV financier.
En complément de son rôle externe, cet outil revêt une utilité interne essentielle. Il aide à superviser le développement de l’entreprise et à identifier tout écart par rapport aux projections initiales.

Le meilleur de votre expression écrite.
MerciApp analyse et corrige en temps réel tout ce que vous écrivez pour vous garantir de faire bonne impression à l’écrit.
Fonctionne avec tous vos outils préférés

2/ L’importance du Business Plan pour votre projet d’entreprise
Est-ce que le Business Plan est obligatoire ?
Oui, il est indispensable si vous avez besoin de recueillir des financements pour votre entreprise . Il doit convaincre vos interlocuteurs de la valeur de votre idée.
Il s’adresse tout particulièrement à des :
- Partenaires,
- Investisseurs,
- Fournisseurs,
- Distributeurs.
C’est la raison pour laquelle il va comporter des tableaux et des estimations comptables. C’est ce qui peut séduire ce type d’interlocuteurs.
Ils doivent ressentir une certaine vision à long terme. Le Business Plan doit donner le sentiment que le projet est scalable, c’est-à-dire qu’il a un véritable potentiel de croissance. Il transmet le sentiment que vous avez une vision stable et confiante qui fera la différence.
Cependant, le Business Plan présente un grand intérêt pour les entrepreneurs eux-mêmes.
Il permet de faire le point sur la maturité et le niveau d’aboutissement de votre projet de création d’entreprise. Vous allez l’examiner sous toutes ses coutures. Vous allez prendre en compte des détails que vous auriez pu négliger autrement.
Par exemple, l’étude de marché requiert de regarder à la loupe vos concurrents ainsi que leurs offres. C’est l’occasion d’affiner vos propres offres et de trouver de nouvelles opportunités à travers les lacunes des entreprises existantes.
Toute la partie financière va vous permettre de préciser la gestion de l’entreprise, de savoir si votre grille de prix est cohérente avec le montant de vos dépenses, etc.
Rédiger ce document va vous amener à vous poser les bonnes questions. Il permet de :
- faire une véritable mise au point,
- vous aider à structurer votre projet,
- questionner sa faisabilité et examiner sa rentabilité.
C’est le rôle de la partie économique qui requiert souvent l’aide d’un cabinet comptable ou d’un logiciel adapté.
En effet, vous devez rassembler des informations comme :
- Le chiffre d’affaires,
- Les dépenses et vos salaires,
- Les investissements,
- Les financements,
- Les impôts et les taxes.

Vous pouvez atteindre un niveau de détails intéressants et identifier des problèmes auxquels vous n’aviez pas pensé auparavant.
Pour le créateur d’entreprise, le Business Plan offre une planification précise sur les premières années d’existence de l’entreprise .
Il offre aussi une meilleure visibilité au projet d’entreprise.
Il va aider au pilotage de l’entreprise grâce aux différents tableaux financiers.
Il permet enfin de disposer d’un document synthétique, cohérent et complet du projet d’entreprise.
C’est pourquoi il est d’autant plus important de le soigner.
3/ Comment faire un bon Business Plan : 10 règles d’or
1 – ne pas externaliser la rédaction du business plan.
Certes, il existe des organismes qui peuvent le faire à votre place. Vous perdrez alors tous les bénéfices de l’exercice, notamment celui de challenger votre vision.
Encore une fois, c’est le CV de votre entreprise , votre projet. Vous n’auriez pas l’idée de faire rédiger votre CV professionnel par quelqu’un d’autre. Le but de cet article est de vous aider à le rédiger, étape par étape. Vous trouverez aussi à la fin de l’article un modèle à suivre.
Face à des investisseurs, vous devez connaître votre plan d’affaire afin de pouvoir le défendre.
Vous pouvez bien évidemment faire appel à un expert-comptable pour la rédaction du volet financier. Il vous aidera dans le calcul du budget prévisionnel, la présentation des tableaux comptables, etc.
Mais nous vous recommandons de ne pas déléguer à 100% la rédaction du document.
2 – Rédiger l’executive summary en dernier
À la fin de l’article, nous détaillons chaque partie du Business Plan. Disons pour l’instant que l’ executive summary est le résumé du plan d’affaire .
Même si c’est le premier document, nous vous recommandons de l’écrire à la fin. Vous devez avoir une vision claire du projet et une maîtrise de l’argumentation.
Il s’agit d’un document de synthèse. En fait , il reprend en une phrase chaque partie du Business Plan.
La première ligne donne la proposition de valeur. Ainsi, le lecteur comprend tout de suite :
- Ce que fait l’entreprise,
- Ce qu’elle vend,
- Et pourquoi.
Pour vous aider, voici la structure de la proposition de valeur : mon entreprise (nom de la société) propose (une offre claire) pour aider (une audience cible précise) à résoudre (un problème) avec (un avantage unique).
L’avantage unique est votre spécificité, ce que l’on appelle aussi l’avantage concurrentiel. C’est ce que vous faites de différent dans votre activité.
Par exemple : la société la Marque en Moins propose des produits constitués de composants naturels, 100 % biodégradables et livrés directement aux clients (en boîte aux lettres) dans des cartons recyclés (lessive en capsule, tablettes pour lave-vaisselle, etc.). Vous pouvez les commander en ligne.
Elle s’affranchit des emballages plastiques à usage unique et propose de livrer à domicile.

3/ Raconter une histoire
Une histoire offre d’innombrables avantages, notamment lorsqu’il s’agit d’agrémenter un document très factuel par ailleurs. Une bonne histoire permet de capter l’attention du lecteur, de susciter des émotions et de marquer les esprits. Le lecteur se projette plus facilement au travers d’une histoire.
Comment faire ?
Vous avez la possibilité de raconter l’histoire de la création de l’entreprise ou de celle du fondateur.
C’est ce qu’a fait Justine Hutteau. Elle a raconté le jour où un médecin lui a diagnostiqué une tumeur bénigne à la poitrine. Elle s’est alors intéressée à la composition des déodorants et a décidé de créer un produit 100 % naturel avec sa marque Respire .

Vous pouvez aussi raconter l’histoire de votre public cible. C’est l’occasion de montrer, avec une mise en scène, comment votre produit ou votre service résout un réel problème.
Le storytelling donne corps à votre rédaction.
4/ Être intraitable sur la qualité
Le Business Plan doit être un document soigné. Il est le reflet de votre future gestion d’entreprise.
Ce dernier doit donc communiquer une image de professionnalisme et de rigueur . La forme du document doit être irréprochable. Il atterrira dans les mains de banquiers ou d’investisseurs que vous sollicitez pour des centaines de milliers, voire des millions d’euros.
Vous vous en doutez, une faute d’orthographe n’est pas la bienvenue !
Vous pouvez faire appel à un relecteur. Mais c’est le moment d’utiliser un outil qui ôtera le doute de votre esprit : un correcteur orthographique .
5/ Se glisser constamment dans la peau du lecteur
Nous vous invitons à vous mettre constamment à la place de l’investisseur ou du banquier qui lit votre Business Plan.
- Est-ce que c’est compréhensible ?
- Est-ce qu’on comprend tout de suite quel est le produit ou le service ? Ce que fait l’entreprise ?
- Est-ce qu’on voit bien la valeur ajoutée du produit ou du service ?
Vous pouvez aussi faire lire le document à des personnes qui ne connaissent pas votre activité et leur demander ce qu’ils ont compris.
La lisibilité du document est aussi cruciale. Vous devriez offrir un confort de lecture maximum.
À ne pas oublier :
- Évitez les pavés de textes taille de caractère 9 austère. Préférez un texte aéré, agrémenté de quelques visuels.
- Utilisez des titres clairs pour chaque partie.
- Mettez les mots importants en gras.
- Lorsque vous faites une énumération, utilisez des bullet points .
Vous voulez que le document soit lu en intégralité. Il doit faire envie au premier coup d’œil, de la première à la dernière ligne.
Utiliser le jargon ou les termes techniques avec parcimonie. Si vous pouvez vous en passer, faites-le.
Enfin, pensez à créer un sommaire pour faciliter la lecture.
6/ Mettre en avant les forces de l’équipe
Dans la présentation de l’équipe (voir notre modèle de Business Plan plus bas), vous avez l’occasion de mettre en avant vos forces et les forces du ou des entrepreneurs. Vous pouvez également parler des employés clés.
Voici les éléments qui devraient y figurer :
- Les dernières expériences professionnelles des membres de l’équipe,
- Les compétences de chacun,
- L’histoire du ou des porteurs de projet.
Qui êtes-vous ? Pourquoi êtes-vous bien placé pour mener à bien ce projet ?
Ce n’est pas le moment de faire preuve d’une excessive humilité. Vous voulez convaincre le lecteur que vous êtes la meilleure équipe pour mener à bien ce projet entrepreneurial.
Insistez donc sur vos accomplissements et vos réussites. Mettez en valeurs vos compétences de gestionnaire. Démontrez votre capacité à vous adapter en fonction des circonstances.
Si vous êtes seul, vous pouvez parler de votre réseau professionnel, en particulier si vous avez des mentors, des conseillers ou des entrepreneurs chevronnés. Vous prouvez ainsi que vous êtes bien entouré.

7/ Ne pas cacher les lacunes
Soyez transparent. S’il y a des lacunes, des manques, n’essayez pas de le cacher sous le tapis.
Au contraire, montrez que vous savez identifier les axes d’amélioration.
Expliquer comment vous voulez combler ces manques. Si vous avez besoin de développer votre productivité et votre gestion du temps, vous pouvez indiquer que vous avez prévu de suivre une formation.
Vous donnez plus de crédibilité à votre projet et à vous en tant que dirigeant.
Pour vous aider à mieux anticiper tout le travail à effectuer, nous vous recommandons de lire notre article sur le Pitch Deck ou l’art de présenter votre projet ! Si le business plan vous intéresse, le pitch deck vous intéressera aussi !
8/ Prendre le temps maintenant pour en gagner plus tard
Même si ces étapes vous semblent laborieuses (elles le sont), prenez le temps d’ approfondir l’étude de marché et la stratégie commerciale .
Elles vont vous permettre de connaître à fond votre marché et vos concurrents. Vous pourrez aussi montrer comment vous allez prendre des parts de marché.
Faire à fond chaque étape permet de gagner du temps par la suite.
9/ Adopter la concision d’un poète japonais
Un Business Plan fait entre 10 et 30 pages en moyenne. Au-delà de 30 pages, vous risquez de perdre votre lecteur.
Allez à l’essentiel. Débarrassez-vous des fioritures ou du blabla non essentiel.
Pensez qu’un banquier ou un investisseur peut lire une vingtaine de Business Plans dans une journée !

10/ Estimer correctement les efforts
“La plupart des entreprises font faillite parce qu’elles visent la moyenne. Quelques personnes se réunissent, ont une idée géniale, rédigent un Business Plan, lancent une entreprise et fondent leur prédiction sur tout ce qui peut jouer en leur faveur.” Grant Cardone, La Règle du 10 X
Nous avons une tendance naturelle à l’optimisme même quand on choisit un “scénario pessimiste”.
“Imaginez que votre entreprise consiste à porter un sac à dos de 500 kilos tous les jours, avec des rafales de vent à 100 km/h sur une pente ascendante de 20 degrés.” Grant Cardone
Le remède que préconise Cardone ? C’est d’avoir de grandes ambitions, de s’entourer de personnes exceptionnelles et d’envisager une stratégie commerciale ambitieuse.
11/ Déterminer la typologie de votre interlocuteur
En raison de l’objectif attribué au busines plan, l’interlocuteur peut varier. Et, en fonction de sa nature et de sa relation vis-à-vis de votre entreprise, les objectifs de votre interlocuteur peuvent également être différents.
Vous devez donc mettre en avant des informations différentes après avoir déterminé les moteurs et les freins de décision du destinataire. Pour cela il faut comprendre sa perspective et sa logique .
Par exemple, un fond de capital-risque met l’accent sur la rentabilité, tandis qu’un business angel aspire à prendre part à une aventure, certes lucrative, mais qui l’enthousiasme.
Une institution analyse la valeur qu’elle apporte à une société, là ou un organisme d’accompagnement à la création se focalise sur l’alignement entre la personne et son projet.
Pour que le business plan soit convaincant , il doit expliciter pourquoi l’interlocuteur a été sélectionné et comment on s’attele à répondre à ses aspirations spécifiques .
4/ Le modèle d’un Business Plan
Le Business Plan possède une structure précise avec des éléments incontournables. Nous vous présentons chaque élément. Suivez le guide !
A) Executive summary
C’est le “résumé pour les dirigeants” ou “sommaire de gestion” en français.
Il s’agit d’un résumé du projet sur une ou deux pages. C’est la première chose que l’investisseur ou le banquier va lire.
C’est la bande-annonce. Ce texte doit donner envie de lire la suite.
Il comporte les éléments suivants :
- L’activité et l’offre , c’est-à-dire les produits et/ou les services proposés.
- L’entreprise , soit la date de création, la forme juridique, les ressources humaines, l’historique, le stade de développement, etc.
- L’équipe : les membres fondateurs et leurs forces
- Le marché et la vision : le positionnement, le public cible, la taille du marché, les concurrents.
- La stratégie : la traduction de la vision dans les opérations. La définition des objectifs. Les actions à mener pour le développement technique et le développement commercial.
- Les perspectives financières : un tableau indiquant le chiffre d’affaires et la rentabilité.
- La demande : le besoin en capital pour mener à bien le projet et la valorisation envisagée, ainsi que les perspectives de sortie prévues.
B) La présentation du projet
Cette partie explique l’idée initiale. D’où vient-elle ? Quelles sont les motivations des fondateurs ? C’est le pourquoi.
Elle doit comprendre :
- Le produit ou service que vous vendez,
- Le besoin auquel il répond,
- Le public cible,
- Le Business model,
- La façon dont il est distribué.
C) La présentation de l’entrepreneur et de l’équipe
Dans cette partie, vous présentez le parcours des membres fondateurs et les éléments pertinents de leur CV.
D) La partie économique du projet
Celle-ci comporte :
- La présentation du produit ou du service
- Le modèle économique ou business model : comment l’entreprise délivre et partage de la valeur. En clair, comment elle gagne de l’argent. Il existe aujourd’hui des business models basés sur une formule d’abonnement comme la Marque en Moins dont nous parlions plus haut ou MerciApp. Vous avez également le business model qui repose sur les précommandes effectuées en ligne. C’est celui de la marque de vêtements Asphalte ou encore Bonne Gueule.
- L’étude de marché : dans quel marché l’entreprise évolue, avec quels clients potentiels et quels concurrents.
- La stratégie commerciale : la façon dont l’entreprise s’y prend pour développer une proposition commerciale de qualité afin d’atteindre les objectifs commerciaux. Les prix du produit ou des services, etc.
- Le chiffre d’affaires prévisionnel
E) La partie financière
Celle-ci comporte :
- Le plan d’investissement : il s’agit d’un tableau qui répertorie les investissements à faire, leurs prix, et la durée d’amortissement comptable (perte de la valeur d’un bien du fait de son usage, de l’évolution technique ou de la durée).
- Le plan de financement initial : le montant des fonds minimum à réunir pour pouvoir lancer le projet.
- Le compte de résultat prévisionnel : l’ensemble des produits et des charges d’une société durant les trois premières années d’existence de l’entreprise
- Le bilan comptable : le document qui décrit l’état de la trésorerie de l’entreprise en répertoriant notamment ce qu’elle possède (les actifs) et ce qu’elle doit (les passifs).
- Le plan de trésorerie sur 12 mois : un document prévisionnel pour identifier tous les flux financiers, les encaissements et les décaissements prévisibles d’une entreprise.
- Le seuil de rentabilité : les objectifs de chiffre d’affaires que l’entreprise doit remplir pour couvrir ses charges. L’objectif est de faire un calcul afin d’estimer le moment où ce seuil de rentabilité sera atteint.
- Le plan de financement à 3 ans : il donne l’évolution prévisionnelle de la structure financière de l’entreprise. Il rend compte des besoins et ressources de financement durant les 3 premières années.
- L’annuité de crédits : pour préciser la décomposition des remboursements des emprunts.

F) Le dossier annexe
Nous vous recommandons de constituer un dossier annexe dédié aux pièces justificatives et documents annexes.
Cela évite de gêner la lecture du Business Plan par une surabondance de documents. Cependant, les investisseurs ou le banquier peuvent s’y reporter au besoin.
Dans ce dossier, vous pourrez mettre par exemple votre CV et les CV des autres membres de l’équipe fondatrice.
Modèle de Business Plan Canva
De nombreux sites comme canva.com proposent des modèles de business plan préconçus. Tout comme le template d’un site internet, ce genre de document peuvent vous faire gagner beaucoup de temps sur la partie esthétique de votre Business Plan.
Modèle de Business Plan Gratuit de BPI France
La BPI France propose aussi sur son site un modèle de Business Plan gratuit. Il peut servir de base à votre réflexion. Il reprend les éléments présentés dans cet article dans un autre légèrement différent. Retrouvez le ici !

5/ Les meilleurs outils pour créer son business plan
Previ’start.
Conçu pour les chefs d’entreprise , PREVI’START est un logiciel qui facilite la rédaction de tableaux financiers pour un business plan prévisionnel. Ce logiciel vous permet entre autres de profiter de calculs financiers et sociaux automatisés et de rapports prévisionnels personnalisables .
Il est simple d’utilisation et ne requiert pas de connaissances approfondies en comptabilité ou gestion.
PREVI’START est disponible à partir de 29€/mois pour 1 business plan et 1 utilisateur.
Créer mon business plan
Destinée aux futurs entrepreneurs , « Créer mon business plan » est une plateforme en ligne offrant une variété de services pour soutenir le démarrage de votre entreprise. Que ce soit sur son site web ou via sa plateforme, elle propose des modèles ajustable s, une analyse de projet, un suivi financier et plus encore. De plus, elle intègre une intelligence artificielle pour assister dans la rédaction.
Un chatbot alimenté par l’IA est à votre disposition pour répondre à vos interrogations liées à la croissance de votre entreprise.
« Créer mon business plan » est disponible à partir de 45€ pour 3 projets .
Que vous soyez une PME, un incubateur ou un expert-comptable, LivePlan est adapté à vos besoins, qu’il s’agisse de recherche de financement ou d’une refonte stratégique . Parmi ses atouts, citons sa bibliothèque de modèles , ses tableaux financiers générés automatiquement , sa page de résumé, sa base de données concurrentielle, ses fonctionnalités de collaboration, ses options d’exportation et son intégration facile .
Pour simplifier au maximum son utilisation, l’outil propose des instructions pour vous guider à chaque étape de réalisation de votre business plan.
LivePlan propose des abonnements à partir de 20€/mois .
Enloop facilite la création de business plans en tirant directement parti de vos données d’entreprise. Grâce à son environnement collaboratif , il permet un travail d’équipe en temps réel. Les fonctionnalités phares sont les prévisions financières automatisées , l’évaluation via 16 ratios financiers et un score prédictif pour évaluer la viabilité de votre plan.
Son mode de fonctionnement est simple : entrez les données, et Enloop construit les sections de votre plan , en y ajoutant des composants visuels.
Enloop propose une version d’essai et une version payante à partir de 19,95€/mois .
Les experts qui peuvent vous accompagner pour la rédaction de votre business plan
La rédaction d’un business plan est une étape cruciale qui peut être complexe en fonction de l’ envergure du projet et des connaissances spécifiques y étant liés. Pour vous assurer que celui-ci soit à la fois complet et convaincant, vous pouvez faire appel à différents experts et structures pour vous accompagner.
Les chambres consulaires
Les entités telles que les CCI ( Chambre de Commerce et d’Industrie) et CMA (Chambre des Métiers et de l’Artisanat) ont pour mission de soutenir le développement économique de la zone où elles sont situées. Dans cette optique, elles déploient diverses initiatives, dont certaines sont spécifiquement conçues pour aider les entrepreneurs , notamment dans l’élaboration de leur business plan.
Les formations y occupent une place prépondérante. Par exemple, toutes les CCI et CMA offrent une formation payante sur la rédaction de plans d’affaire . C’est l’occasion d’acquérir les compétences fondamentales pour élaborer votre business plan, tels que :
- la réalisation du prévisionnel financier ;
- la réalisation du plan de trésorerie ;
- la formalisation du business plan ;
Des conseillers spécialisés sont également présents pour accompagner. Ils peuvent régulièrement vous guider pour améliorer votre business plan .
Les associations d’accompagnement de créateurs
En France, de nombreuses structures sont dédiées à soutenir les futurs entrepreneurs de diverses manières. De la formation à l’accompagnement en passant par le financement.
Initiative France, avec sa notoriété et ses antennes partout en France, en est un exemple phare. Elle propose des prêts non rémunérés et des subventions .
Elle offre également l’opportunité d’être guidé par un chef d’entreprise à la retraite , expert dans les domaines du marketing et de la finance.
Faire appel à un expert dédié
Pour la rédaction de votre business plan, vous pouvez également solliciter l’aide d’un professionnel spécialisé . Que ce soit un expert-comptable ou un coach spécialisé, ces experts vous guideront pas à pas pour élaborer votre business plan conformément aux standards professionnels .
L’avantage de passer par un expert est que celui-ci sera entièrement consacré à votre projet et s’impliquera davantage dans votre initiative. Un expert rémunéré pour la tâche veillera à la justesse du travail . Il mise sur la réussite de votre business plan pour asseoir sa réputation.
La rédaction du Business Plan est un peu comme la préparation d’un voyage à l’étranger.
Vous préparez à l’avance les étapes. Vous planifiez votre trajet. Vous posez un cadre pour avoir une vision et un contrôle sur ce qui va se passer. Cela vous permettra ensuite de profiter de l’aventure au mieux.
Bien sûr, tout ne va pas se passer comme prévu. Mais le fait d’avoir fait cette préparation vous donnera plus de latitude pour vous adapter à l’impondérable.
Votre Business Plan est fin prêt ! Passez-le dans la machine MerciApp pour vous assurer qu’il soit crédible et sans fautes.
Et maintenant ? Découvrez notre article pour comprendre comment déposer une marque !
Aidez vos amis à parfaire leur français
Partagez-leur cette page
- Partager sur Facebook
- Partager sur X
- Partager sur LinkedIn
- Partager sur Pinterest
Arthur Ollier
Passionné par les nouvelles technologies et toutes les opportunités qu’elles représentent, ma fibre pour l’entrepreneuriat m’a amené à créer 3 sociétés avant l’aventure MerciApp. La première a rapidement échoué, la seconde et la troisième ont toutes les deux été rachetées. Je suis aujourd’hui cofondateur et CEO de MerciApp. Nous avons l’ambition de créer la solution d’aide à la rédaction indispensable et leader incontesté dans la sphère francophone.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

Javascript est desactivé dans votre navigateur.
République Française
Entreprendre .Service-Public.fr
Le site officiel d'information administrative pour les entreprises
- Accéder au site pour les particuliers
Sélectionnez une commune dans la liste des suggestions
Une erreur est survenue pendant la recherche, merci de réessayer.
Partager la page
Votre abonnement a bien été pris en compte
Vous serez alerté(e) par email dès que la page « Projet de création d'entreprise : comment faire un business plan » sera mise à jour significativement.
Vous pouvez à tout moment supprimer votre abonnement dans votre compte service-public.fr .
Votre abonnement n’a pas pu être pris en compte.
Vous devez vous connecter à votre espace personnel afin de vous abonner à la mise à jour de cette page.
Être alerté(e) en cas de changement
Ce sujet vous intéresse ? Connectez-vous à votre compte et recevez une alerte par email dès que l’information de la page « Projet de création d'entreprise : comment faire un business plan » est mise à jour.
Pour vous abonner aux mises à jour des pages service-public.fr, vous devez activer votre espace personnel .
Vous serez alerté(e) par courriel dès que la page « Projet de création d'entreprise : comment faire un business plan » sera mise à jour significativement.
ACTIVER MON ESPACE PERSONNEL
Projet de création d'entreprise : comment faire un business plan
Vérifié le 26 septembre 2023 - Direction de l'information légale et administrative (Premier ministre)
Personne qui investit de l'argent dans une entreprise innovante à fort potentiel. Elle est expérimentée et apporte des contacts, conseils. Elle espère faire une plus-value.
Autres cas ?
Reprise d’entreprise : bâtir un business plan
Vous avez un projet de création d'entreprise ? Le business plan (ou plan d'affaires) est un document écrit qui présente en détail votre projet de création entreprise. Le business plan sera l'outil pour convaincre les banques et les investisseurs . Nous vous expliquons comment faire un business plan étape par étape .
La démarche par étapes
1 Ce qu'il faut savoir avant de faire votre business plan
À quoi sert le business plan , un guide et un outil vendeur.
Le business plan doit être vendeur , rassurant , c'est-à-dire réaliste.
Vous devez le construire à partir du terrain , de vos recherches et de votre analyse .
Il doit prouver que votre projet de création d'entreprise est sérieux .
Le business plan doit être à la fois synthétique et très précis avec des prévisions chiffrées .
Un outil adapté à chaque investisseur
Votre business plan est l' outil pour convaincre les investisseurs et tous ceux qui soutiendront votre projet.
Il s'adresse donc aux investisseurs suivants :
- Collectivités locales
- Business angels : titleContent
- Futurs associés
- Tous ceux auprès de qui vous cherchez des fonds
À savoir
En fonction de l'investisseur à qui vous vous adressez, vous mettez certaines informations en avant.
Vous devez donc faire plusieurs versions de votre business plan selon chaque destinataire .
Les étapes du business plan
Le business plan est un document qui se construit en 5 étapes :
- Introduction ou pitch de présentation
- Présentation de votre produit (ou service)
- Présentation de votre business model (appelé aussi stratégie commerciale )
- Votre étude de marché (synthèse)
- Votre prévisionnel financier (synthèse)
2 Préparer un pitch de présentation
À quoi sert un pitch de présentation .
Le pitch de présentation du business plan est aussi appelé executive summary .
Il s'agit de la présentation de votre projet de création d'entreprise.
Il doit être condensé .
Son objectif est de convaincre un interlocuteur.
Vous devez convaincre dans un temps court .
L' objectif de cette synthèse est de prouver :
- Votre capacité à créer et diriger une entreprise
- Votre adéquation avec le projet
- Votre sérieuse préparation du projet
- Si vous êtes plusieurs associés, votre cohésion d'équipe
Il est conseillé de rédiger plusieurs versions de cette présentation selon chaque investisseur à convaincre.
- Pour convaincre un investisseur public, vous insisterez davantage sur le service que vous rendez à la société.
- Pour convaincre un business angel : titleContent , vous insisterez sur le caractère innovant de votre offre.
Ces informations doivent permettre de comprendre quelles sont vos idées , vos valeurs , ce qui vous motive , donc le sens de votre projet .
Si vous êtes plusieurs à porter le projet de création, on doit sentir la cohésion de l' équipe et la complémentarité des membres.
Cette présentation doit prouver votre capacité à créer et diriger une entreprise sur le court et le long terme .
Quel est le contenu du pitch ?
Cette présentation doit permettre de répondre aux questions suivantes :
- Qui êtes-vous et quels sont les membres de votre équipe (collaborateurs, associés) ?
- Quel est votre projet ? Il s'agit du nom de votre entreprise, sa forme juridique, sa domiciliation, la nature de l'activité, l'histoire du projet.
- Quelle est votre cible ? Il s'agit de montrer que vous avez identifié vos futurs clients.
- Quel est l' environnement ? Il s'agit de montrer que vous avez identifié la concurrence, les contraintes, les risques, les tendances de votre marché, etc.
- Quelles sont vos ambitions de développement ? Il s'agit de montrer que vous avez une vision du projet à court , moyen et long terme .
La présentation du business plan est en partie un résumé de l' étude de marché .
3 Expliquer quel est votre produit ou service
Vous décrivez ce que vous allez vendre .
Cette description doit être précise, concise, claire.
Il faut éviter d'employer des termes trop techniques.
Vous devez être compris par des personnes qui ne connaissent rien à votre domaine d'activité.
Vous pouvez faire des schémas, dessins, etc. pour accompagner cette description du produit.
4 Définir la stratégie marketing ou business model
Qu'est-ce que le business model d'une entreprise .
Vous devez présenter comment vous allez vendre votre produit ou votre service.
Le business model s'appelle de différentes façons : une stratégie marketing , une stratégie commerciale, un " mix-marketing " ou encore un modèle économique .
Le business model de votre entreprise doit répondre aux questions suivantes :
- De quelle façon allez-vous faire la promotion et la publicité de votre entreprise, de votre produit ou service ?
- Quels seront vos tarifs ?
- Quels seront vos fournisseurs ?
- Par qui sera fabriqué votre produit ou service ?
- Quels seront vos canaux de distribution , où sera vendu votre produit ou service (internet, réseaux professionnels, boutiques etc.) ?
- Quelle sera la relation avec vos clients, comment les fidéliser ?
- Où seront stockés vos produits ?
- Quelles seront les pistes de développement de votre activité (internet, national, international, etc.) ?
Avez-vous analysé les contraintes ?
Il s'agit de prévoir ce qui peut freiner votre activité .
Vous devez identifier ce qui peut faire grimper vos coûts : stockage, production, distribution, communication.
- Le cours fluctuant des matières premières influe-t-il sur votre production ?
- Les fournisseurs du secteur ont-ils un monopole ?
- La demande vis-à-vis de votre produit est-elle saisonnière ?
Vous devez prouver que vous avez réfléchi aux solutions suivantes :
- Comment dépasser les contraintes
- Comment faire face à des pertes de bénéfices, à une hausse de vos charges, à de nouveaux concurrents, etc.
5 Rédiger la synthèse de votre étude de marché
L'objectif de l'étude de marché et de sa synthèse est d'expliquer :
- Quels sont vos futurs clients ?
- Quelle plus-value votre produit apporte-t-il sur le marché ?
- Dans quel environnement s'insère votre future activité ?
Nous vous expliquons en détail comment faire une étude de marché dans notre fiche sur l'étude de marché .
6 Rédiger la synthèse du prévisionnel financier
L'objectif d'un prévisionnel financier est de montrer que votre entreprise sera rentable .
Il est aussi appelé plan de financements ou budget prévisionnel .
Le prévisionnel financier (ou budget prévisionnel) fait partie de votre étude de marché. Il s'agit de la dernière partie de votre étude de marché.
Vous devez construire ce budget sur les 3 années à venir .
Vous devez chiffrer :
- Vos charges, les dépenses nécessaires
- Vos recettes (chiffre d'affaires)
- Vos besoins de financements
- Les fluctuations de votre activité et celles du marché
Il se déroule en 4 parties :
- Compte de résultat
- Plan de financement
- Budget ou plan de trésorerie
Ces 4 parties correspondent à 4 tableaux chiffrés.
Nous vous expliquons en détail les 4 étapes d'un budget prévisionnel dans notre fiche sur l'étude de marché .
Services en ligne et formulaires
Trouver un accompagnement adapté à la création de votre entreprise
Service en ligne
Lister vos concurrents
Outil de recherche
Insee : portrait économique d'un territoire
Projet de création d’entreprise : comment faire une étude de marché
Recherche de financements pour créer ou reprendre une entreprise
Réseau entreprendre : des entrepreneurs vous aident à créer
Réseau entreprendre
Cette page vous a-t-elle été utile ?
- 1 Pas du tout Cette page ne pas m'a pas du tout été utile
- 2 Un peu Cette page m'a été un peu utile
- 3 Moyen Cette page m'a été moyennement utile
- 4 Beaucoup Cette page m'a été très utile
- 5 Parfait ! Cette page m'a été parfaitement utile
Pas du tout
L’équipe entreprendre.Service-Public.fr vous remercie
Je vais sur la page d’accueil
Vous avez noté 1 sur 5 : Pas du tout
Vous avez noté 2 sur 5 : Un peu
Vous avez noté 3 sur 5 : Moyen
Vous avez noté 4 sur 5 : Beaucoup
Vous avez noté 5 sur 5 : Parfait !
Je fais une remarque sur cette page
L’équipe entreprendre.Service-Public.fr vous remercie pour vos remarques utiles à l'amélioration du site.
Pour des raisons de sécurité, nous ne pouvons valider ce formulaire suite à une trop longue période d’inactivité. Merci de recharger la page si vous souhaitez le soumettre à nouveau.
Une erreur technique s'est produite. Merci de réessayer ultérieurement.
Vos remarques pour améliorer la page
La page est-elle facile à comprendre , l’information a-t-elle été utile .

Waza Business
Meilleur blog de conseils pour démarrer une entreprise commerciale au Congo – Kinshasa
Combien de pages un plan d’affaires doit-il comporter ? 10, 25, 50 ou 100 pages ?
Combien de pages un business plan doit-il comporter 10, 25, 50, 100 ou plus de pages voici une comparaison rapide des types de business plans disponibles et de leur durée optimale..
Beaucoup de nouveaux entrepreneurs se demandent souvent combien de temps est trop long pour un plan d’affaires. La plupart des experts et conseillers en affaires disent qu’il devrait y avoir au minimum 30 à 50 pages, tandis que d’autres donnent un nombre plus ou moins grand que celui mentionné ci-dessus.
Une chose que vous devez comprendre, c’est qu’il n’y a pas de chiffre précis qu’un plan d’affaires devrait être avant qu’il ne soit considéré comme parfait. Tout dépend de votre public et de ce pour quoi vous comptez utiliser le business plan.
Selon la Small Business Association des États-Unis, «un plan d’affaires doit être de la longueur requise pour exciter la source de financement, prouver que la direction comprend vraiment le marché et détailler la stratégie d’exécution».
À partir de divers sondages effectués par de nombreuses organisations et professionnels, il a été conclu qu’un plan d’affaires réalisable devrait être de l’ordre de 25 à 100 pages, selon les divers facteurs impliqués dans la rédaction du plan. Certains de ces facteurs peuvent inclure; marchés ciblés, hypothèses difficiles ou données non sectorielles, risque sectoriel, facteurs de crédit médiocres qui nécessitent une explication ou une documentation supplémentaire, source de financement, etc.
En utilisant le modèle SBA, un plan d’affaires peut aller de 38 à 50 pages pour un plan de base jusqu’à 80 à 100 pages pour des plans complexes. D’un autre côté, les concours d’entreprise sont arrivés à la conclusion qu’un plan d’affaires efficace devrait compter environ 30 pages, parfois 40, mais rarement 50 – et cela inclut des données financières détaillées dans les annexes.
Attente de longueur de page pour divers types de plans d’affaires
Les différents types de plans d’affaires existants ont leur propre attente de longueur de page selon les experts. Ils font généralement partie de ces indices;
Pour les petits rapports internes, la longueur de la page est généralement de dix à quinze pages
Pour les plans d’affaires d’entreprise, la longueur de page autorisée peut aller jusqu’à cent et même plus
Les plans de démarrage et d’expansion utilisés pour les investisseurs potentiels, les fournisseurs ou d’autres partenaires commerciaux peuvent comporter de 20 à 40 pages.
Les concours d’entreprise limitent la longueur des pages (y compris l’annexe contenant les informations financières), à un minimum de 30 pages et, dans certains cas rares, jusqu’à 50 pages.
Une répartition des pages d’un business plan
Le modèle SBA permet aux plans d’affaires de s’étendre de 38 pages à une centaine de pages selon le type de plan en question. Les pages du business plan type sont réparties comme suit;
Partie 1: Introduction (3 à 5 pages)
Partie 2: Analyse de marché (9 à 22 pages)
La section analyse de marché illustre les connaissances sur l’industrie particulière en question. Il présente les faits saillants généraux et les conclusions de toutes les données de recherche marketing qui ont été collectées; cependant, les détails spécifiques des études de recherche marketing devraient être déplacés dans la section annexe du plan d’affaires.
Partie 3: Description de l’entreprise (1 à 2 pages)
Sans entrer dans les détails, cette section comprend généralement un examen de haut niveau de la façon dont tous les différents éléments de l’entreprise s’articulent. La section de description de l’entreprise doit inclure des informations sur la nature de l’entreprise ainsi que la liste des principaux facteurs qui, selon eux, feront de l’entreprise un succès.
Partie 4: Organisation et gestion (3 à 5 pages)
Cette section doit inclure la structure organisationnelle de l’entreprise, des détails sur la propriété de l’entreprise, les profils de l’équipe de direction et les qualifications du conseil d’administration.
Partie 5: Stratégies de marketing et de vente (4 à 6 pages)
Le marketing est le processus de création de clients, et les clients sont la pierre angulaire d’une entreprise. Dans cette section, la première chose à faire est de définir la stratégie marketing de l’entreprise. Il n’y a pas de manière unique d’aborder une stratégie marketing; la stratégie doit faire partie d’un processus d’auto-évaluation continu et unique à l’entreprise.
Partie 6: Produit ou service (4 à 10 pages)
Que vend l’entreprise ? Quel est leur service ? Dans cette section, décrivez le service ou le produit, en insistant sur les avantages pour les clients potentiels et actuels. Concentrez-vous sur les domaines où il a un avantage distinct. Identifiez le problème de votre marché cible pour lequel votre service ou produit apporte une solution. Donnez au lecteur des preuves tangibles que les gens sont ou seront prêts à payer pour votre solution.
Partie 7: Investissement en actions et demande de financement (2 à 4 pages)
Dans cette section, vous identifierez combien vous prévoyez ou avez déjà investi dans l’entreprise. Identifiez le montant exact de financement dont vous aurez besoin pour démarrer et assurez-vous qu’il est spécifiquement lié à votre plan financier.
Si nécessaire, vous pouvez inclure différents scénarios de financement, tels que le meilleur et le pire des scénarios, mais n’oubliez pas que plus tard, dans la section financière, vous devez être en mesure de sauvegarder ces demandes et scénarios avec les états financiers et les projections correspondants.
Partie 8: Informations financières (12 à 25 pages)
Cette section est considérée comme la partie la plus importante de votre plan d’affaires et nécessite un effort considérable. Assurez-vous que vos informations financières sont examinées par un professionnel tel que votre comptable. Les données financières doivent être élaborées après avoir analysé le marché et défini des objectifs clairs. C’est à ce moment-là que vous pouvez allouer efficacement les ressources.

Accueil » Inclassable » Faire un Business Plan

Qu’est ce qu’un Business Plan ? (contenu, canvas, astuces)
- Mise à jour :
Business Plan est un document qui réunit les éléments de réflexion indispensables pour lancer votre projet d'entreprise. Voici comment le faire.
Vous avez une idée créative ? Un projet innovant ? Vous voulez être votre propre boss, vous l’êtes déjà ? Restez agile ! Aussi visionnaire que vous puissiez l’être, votre projet finalisé est rarement celui que vous avez imaginé au départ. Faites le point sur vos motivations. On crée par passion, pour gagner plus ou obtenir de la reconnaissance sociale. Mais aucun projet n’est jamais à 100% passionnel, financier ou sociétal ; envisagez l’avenir avec un Business Plan .
Qu’est ce qu’un Business Plan ?
Un Business Plan est un document qui réunit les éléments de réflexion indispensables pour lancer votre projet d’entreprise (comme dans le cadre du business model ). Il permet ainsi le reengineering d’un processus défaillant d’une entreprise déjà créée ou pour qu’un investisseur et/ou partenaire accède à votre requête. Aujourd’hui, sans lui, plus personne ne vous suivra. En effet, il s’agit d’un des éléments les plus importants dans la réalisation de tout projet.
Comment rédiger son Business plan ?
Même si cela constitue un excellent exercice en soit, faites-le avec un spécialiste qui aura l’art de poser les questions qui fâchent, autrement dit les bonnes questions que vous vous devrez de répondre. Un Business Plan (BP) réalisé il y a 10 ou 20 ans ne se construit plus de la même manière aujourd’hui. Et surtout ne se lit plus la même chose !
Ainsi, pour faire comprendre votre projet à un large auditoire, votre Business Plan devra être structuré.
Le Business Model Canvas
Pour commencer votre business plan, vous pouvez vous baser sur le Business Model Canvas . Celui-ic vous permettra de définir clairement les éléments essentiels à inclure dans votre business plan. Utilisez notre outil Business modèle canvas en ligne ou utiliser le canvas fourni ci-dessous pour cela. Télécharger la version PDF imprimable du canvas

Vous pouvez télécharger ce canvas et commencer à vous exercer dessus. Essayez donc de faire cet exercice dès maintenant. Faites le sérieusement et vous verrez clairement les forces et les faiblesses de votre idée. Votre business plan est un document assez complet et contient normalement des informations plus poussées que le business model canvas. Cependant, le business model canvas peut être un excellent exercice préliminaire. Une fois fait, vous pourriez alors rédiger plus facilement votre business plan.
Que doit contenir votre Business Plan ?
Le canvas ci-dessus contient les explications pour chaque section, mais il est important que vous gardiez en tête que votre Business Plan doit être en mesure de répondre à ces 9 questions :
- Où est votre marché ? Est-ce qu’il est régional, national ou international ? (Segmentation de la clientèle et relations clientes que vous aurez).
- Votre offre est-elle en phase avec les attentes du marché ? (Positionnement, local, etc.)
- Pouvez-vous vous différencier ? (Plus-value, value proposition du business model).
- Qui sont les nouveaux concurrents qui peuvent apparaître à brève échéance ? (Pénurie ou excès d’offre).
- Votre activité est-elle B2B, B2C, M2M ou sous-traitance en relation avec la grande distribution ?
- Votre savoir-faire vous donne-t-il un réel avantage face à vos concurrents ?
- Quel est le poids des différents stakeholders : clients, consultants, sous-traitants, autorités réglementaires ?
- Qui sont vos fournisseurs ? Auront-ils un pouvoir d’influence sur la qualité et le coût de votre offre ?
- Avez-vous le soutien de votre famille, amis (FFF) ? Cet écosystème peut-il faciliter la réalisation de votre projet ?
D’autres questions peuvent vous aider à monter pas à pas votre business plan :
- Combien de contacts professionnel et personnel pouvez-vous mobiliser ? (Possédez-vous un réseau que vous pouvez activer en cas de besoin).
- Êtes-vous prêt à ‘rouler’ pour 2 jobs (au début au moins) et faire des sacrifices ?
- Pouvez-vous vous appuyer sur une équipe dont les compétences clés pour la réussite de votre projet y sont représentées ?
- Comment allez-vous organiser votre force de vente et vos canaux de distribution ? (Processus de commercialisation).
- Avez-vous prévu un système de veille technologique, de reporting, de mesure des métriques (KPI’s) ?
- Avez-vous chiffré votre budget de communication ?
- Votre technologie peut-elle faire l’objet d’une protection juridique ? (IP)
- Votre innovation risque-t-elle d’être rapidement obsolète ?
- Quel est votre besoin en argent cash ? (+ calcul du break-even point)
- Quelle répartition entre capitaux propres et dette étrangère ?
- Au bout de combien de temps vos flux de trésorerie seront-ils, de manière récurrents, positifs ? (break even…).
Quand se lancer ?
Dans un premier temps, et une fois que votre Business Model est prêt, vous pouvez alors vous lancer dans la création de votre entreprise. Cependant faites cela seulement si :
- l’originalité de votre offre, son adéquation avec les attentes des clients doivent vous permettre de vite vous imposer ( Blue Ocean Strategy );
- vous êtes prêt à travailler plus et à gagner moins (au début). Avoir une équipe motivée et un entourage qui accepte les risques;
- vous avez chiffré les moyens à mettre en œuvre et vous avez compris que votre capacité à innover et à trouver des partenaires renforce la dimension opérationnelle de votre projet.
Comment détecter les faiblesses d’un business plan
Premièrement, il existe des cas où votre business plan pourrait vous indiquer que votre idée n’est pas aussi bonne qu’elle ne le paraissait. En effet le business plan sert aussi à identifier les faiblesses de votre idée. Dans ce cas il faut penser à rectifier votre business plan (ou à l’extrême le laisser tomber).
Les faiblesses à détecter
Voici donc les faiblesses que vous pourrez éventuellement détecter :
- vous êtes enthousiasmé par la réussite de certains et vous voulez les imiter;
- il serait intéressant d’opérer sur un marché très concurrentiel où les prix sont quasi systématiquement revus à la baisse;
- vous aurez beaucoup à perdre et peu à gagner;
- vous n’êtes pas prêt et votre marché ne vous suivra pas;
- les problèmes de fin de mois difficile vous angoissent;
- vous n’avez jamais dirigé d’équipe;
- vous souhaitez profiter de vos week-ends. Restez salarié !;
- vous êtes un génie de la technique, mais vous n’avez pas la moindre idée de comment vous allez commercialiser votre produit ni même s’il est vendable. Dans ce cas, vous ne pourrez jamais convaincre un Ange investisseur ou un banquier de vous suivre sur ce terrain miné !
Quelques astuces
➡ Astuce : Personnellement j’utilise un petit truc dans le cadre de ma société pour être au taquet 😀 , je vous recommande de suivre ce processus en 3 points :
- Tester : Dans votre Business Model (BM), après étude de marché avec votre MVP (Minimum Value Product), si il n’y pas d’achat de clients et de partenaires à vos côtés, changez d’idée ! Love me, Hate me, Buy me ! (en français cela donne : Aime moi, déteste moi, achète moi 😀 )
- Intégrer : Le(s) BM font parties intégrantes du BP c’est à dire BM global + BP details = idée !
- Viabiliser : Enfin , s i besoin dans un concours, présentation devant un Business Angel, Venture Capital Risquer ou votre banquier, aujourd’hui, sans BP, vous n’aurez aucune chance. Augmenter les chances d’un partenariat; le BP n’est pas que financier et on ne l’enferme plus dans un coffre où l’on jette la clé !
Laisser un commentaire Annuler la réponse
Votre adresse e-mail ne sera pas publiée. Les champs obligatoires sont indiqués avec *
A propos de l'auteur
Sandro Tronnolone
Sandro Tronnolone est co-fondateur de la startup TiKi4 (coaching et mentoring), il est expert en gestion d'entreprise avec 26 années dans l'industrie, les banques, les hôpitaux et dans les services tertiaires. En savoir plus sur Sandro
À lire ensuite

Discussions en cours sur des sujet similaires
Structure d'un business plan
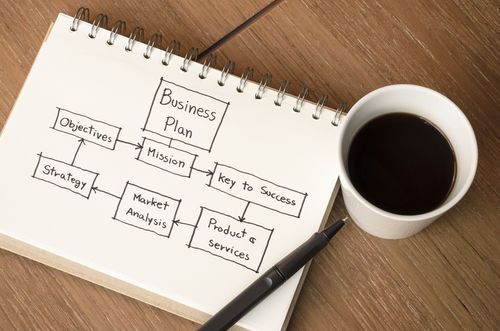
Cet article contient un plan détaillé de business plan ainsi que des conseils sur la rédaction de chacune des parties du plan.
Cet article fait partie de notre série d'articles sur comment faire un business plan .
Vous trouverez ci-dessous le plan que nous recommandons. Chaque projet d'entreprise étant différent, il convient naturellement d'ajuster ce plan en fonction de votre projet.
La structure de business plan que nous recommandons présente l'avantage de répondre à plusieurs questions que se posent les investisseurs dans chaque section, et d'offrir une progression naturelle, ce qui la rend adaptée à une lecture complète ou sélective de votre plan.
Sommaire du business plan :
- Chiffres Clés
Structure et Actionnariat
Emplacement.
- Produits et Services
Démographie et Segmentation
Marché cible, concurrence, barrières à l'entrée, réglementation, avantage concurrentiel, plan commercial, etapes de développement, plan de personnel, ressources clés, fournisseurs, emplois et ressources, prévisionnel de ventes, structure de coûts.
Parcourons maintenant en détail chacune des sections.
La première section est la plus importante, car c'est seulement s'ils la jugent suffisamment attractive que les investisseurs liront la suite de votre business plan.
Comme cette section est un résumé de votre plan c'est également la dernière que vous écrirez.
L'objectif de cette section est d'attirer l'attention du lecteur en 5 minutes et de lui donner envie d'en savoir plus. N'essayez surtout pas de tout couvrir, soyez concis et précis.
Il y a 4 points qu'il vous faut absolument couvrir:
- qui vous êtes
- ce que vous vendez
- le potentiel en terme de taille et de rentabilité
- de combien vous avez besoin
Cette section a pour but d'introduire la société ainsi que son équipe de direction. Le contenu variera légèrement suivant que vous écrivez un plan pour une nouvelle entreprise ou pour une entreprise déjà existante.
Cette partie est purement descriptive, vous devez répondre aux questions suivantes :
- qui sont les actionnaires : les investisseurs ont une obligation légale de vérifier l'identité des actionnaires d'une société avant d'investir. Leur fournir une liste complète leur permet de faire une rapide première vérification et leur donne l'opportunité de soulever un potentiel problème. Si vous adressez votre plan à un investisseur en fonds propres, cela lui permet également de savoir qui seront ses coactionnaires. Si vous avez des actionnaires qui apportent plus que juste du capital (par exemple un expert dans un domaine vous apportant de la crédibilité) il est important que vous le mentionniez ici.
- le siège social de la société ainsi que sa forme juridique : ceci permet au lecteur de se faire une idée de la taille et du régime fiscal de l'entreprise. Certains investisseurs ont également des restrictions géographiques sur leurs investissements, cela leur permet donc de vérifier que vous êtes éligible.
Si vous écrivez votre business plan pour une entreprise déjà en activité, vous pouvez utiliser cette section pour présenter les principales étapes franchies jusqu'à présent. L'idée ici est de construire votre capital confiance auprès de l'investisseur en montrant que vous avez une activité pérenne. Nous vous recommandons d'aborder les points suivants :
- le nombre d'années d'existence : ceci est un vrai facteur de confiance pour l'investisseur et démontre la solidité de votre entreprise.
- étapes clés dans le développement : expliquez ici les principaux succès en matière de croissance, lancement de produits, internationalisation. Si vous cherchez à lever des fonds pour financer un plan de croissance cela vous aidera à démontrer la crédibilité de votre plan.
Si l'emplacement joue un rôle important dans votre secteur (par exemple pour un restaurant ou une boutique) ou si vous dirigez une entreprise qui a plusieurs sites, vous pouvez les présenter ici (idéalement à l'aide d'une carte).
Cette section est l'une des plus importantes : vous devez démontrer que votre équipe possède l'expertise du secteur et les compétences requises pour mettre en place le business plan.
S'il vous manque certaines compétences clés dans l'équipe, vous devez expliquer comment vous comptez pallier ce manque. Il se peut qu'un recrutement soit en cours ou que l'un des membre de votre conseil d'administration possède cette compétence.
Essayez de mettre des photos si possible. Cela donnera un visage à votre équipe et permettra à vos investisseurs de vous reconnaitre lorsque vous les rencontrerez.
Vous vous êtes présenté, maintenant il est temps d'expliquer ce que vous faites.
3. Produits et Services
Le secret pour écrire une bonne section sur vos produits et services est d'être très précis sur les produits et services que vous vendez, le client cible et le réseau de distribution utilisé.
Après cette section, votre lecteur va commencer à réfléchir à la taille, la pression concurrentielle, et à la rentabilité potentielle du marché et essayer de deviner quelle va être votre stratégie. Vous voulez l'orienter dans la bonne direction! Donc soyez très précis, par exemple ne dites pas : "je vend des chaussures" mais "je vends des bottes en cuirs et cible le marché des femmes de 16 à 25 ans qui achètent sur internet".
Si possible essayez d'inclure des photos de vos produits.
A présent votre lecteur sait qui vous êtes et ce que vous faites, il est temps de lui montrer le potentiel du marché.
4. Etude de Marché
Cette partie est un résumé de notre article dédié à l'étude de marché dans le business plan .
L'objectif ici est de montrer à l'investisseur que :
- le marché est suffisamment large pour y bâtir une entreprise pérenne
- vous savez qui sont vos clients et pourquoi ils achètent
- malgré la concurrence, il existe une opportunité dans le marché vous permettant d'y réussir
La première étape consiste à estimer la taille du marché.
L'approche à employer dépend du type d'opportunité que vous essayez de vendre aux investisseurs. Si vous écrivez un business plan pour un restaurant indépendant, vous devez évaluer le marché autour de votre commerce. En revanche, si votre plan est pour une chaine de magasins, il vous faut évaluer le marché au niveau national.
Il y a deux facteurs que vous devez prendre en compte lorsque vous cherchez à évaluer la taille de votre marché : le nombre de clients potentiels et la valeur du marché.
L'idée ici consiste à déterminer le degré d'atomicité du marché. Si vous êtes dans un marché où un petit nombre de clients à forte valeur ajoutée il peut s'avérer compliqué de rentrer en concurrence avec des acteurs mieux implantés sur le marché, et votre entreprise risque d'être dépendante d'une poignée de clients pour sa survie.
Maintenant si vous êtes dans un marché avec un grand nombre de consommateurs à faible valeur ajoutée il se peut qu'il soit coûteux d'établir un réseau de distribution suffisamment large pour parvenir à toucher un nombre suffisant de clients pour atteindre votre seuil de rentabilité.
Idéalement vous voulez être dans un marché avec un nombre suffisant de clients potentiels pour permettre à plusieurs entreprises de coexister et où chaque client rapporte une somme d'argent suffisante pour vous permettre d'atteindre rapidement votre seuil de rentabilité.
Une fois que vous avez estimé la taille du marché, il vous faut expliquer à votre investisseur potentiel quel(s) segment(s) vous visez au sein du marché et pourquoi.
Le marché cible regroupe l'ensemble des types de clients que vous comptez cibler sur votre marché. Vous devez identifier les différents segments au sein de votre marché et expliquer lesquels vous ciblez.
Une façon d'identifier les segments consiste à grouper les consommateurs par caractéristique démographique ou par habitude d'achat.
Par exemple sur le marché de la mode vous pourriez avoir :
- hommes / femmes
- bas prix / marques
- achat en ligne / achat en magasin
Cette section est cruciale, car elle vous permet de démontrer à votre investisseur que vous êtes un expert de votre secteur : vous savez pourquoi les clients achètent!
Ici vous devez rentrer dans le détail des facteurs influençant la demande pour vos produits et services. Qu'est ce qui déclenche l'acte d'achat? S'agit-t-il d'un besoin comme pour la nourriture? Est-ce la valeur associée au produit ou la perception de la marque?
Plus tard dans votre business plan vous vous servirez de cette analyse pour justifier votre positionnement marketing.
L'objectif de cette section est de donner à l'investisseur un panorama complet des forces en présence sur votre marché. Vous devez expliquer qui sont vos concurrents, quel est leur positionnement et quelles sont leurs forces et faiblesses.
Voici quelques-uns des points que vous devez couvrir :
- qui sont ils? (nom, marque, emplacement)
- quel est leur taille? (chiffre d'affaires, nombre d'employés, etc.)
- quels consommateurs visent ils? (segments)
- quelles sont les principales caractéristiques de leur offre? (prix, services associés, etc.)
L'idée ici est d'analyser l'angle d'attaque de vos concurrents sur le marché afin d'identifier les faiblesses que vous allez pouvoir exploiter dans votre positionnement.
L'objectif ici est de montrer aux investisseurs que le risque d'un nouvel entrant sur le marché est limité. De fait si vous écrivez cette section dans le cadre d'une création d'entreprise la situation est assez délicate puisque vous devez expliquer pourquoi vous allez réussir là où les autres échoueront.
Dans section vous devez expliquer quelle est la réglementation applicable à votre activité et comment vous allez vous y conformer.
Vous l'avez vu les premières parties de notre structure de business plan sont plutôt descriptives. Nous allons maintenant rentrer dans le détail de l'implémentation de votre business plan.
5. Stratégie
Stratégie est un grand mot, il s'agit ici d'expliquer simplement votre vision du marché, votre angle d'attaque et pourquoi vous pensez que cette approche est la bonne.
Ici vous devez répondre à la question préférée des investisseurs : "qu'est-ce qui vous différencie de vos concurrents?"
Si vous avez suivi mes conseils, vous avez déjà préparé votre lecteur à accepter votre positionnement dans l'étude de marché. Il vous suffit alors de réitérer les facteurs influençant la demande qui constituent le coeur de votre positionnement et montrer que ceux-ci on été délaissés par la concurrence laissant une place pour un nouvel acteur sur le marché.
Afin d'expliquer et de justifier votre politique tarifaire, vous devez couvrir les points suivants :
- Comparer vos prix à ceux de vos concurrents
- Montrer que vous êtes rentables à ce niveau
- Expliquer pourquoi vous avez choisi ce niveau de prix
Je ne vais pas rentrer dans le détails des deux premiers points qui ne présentent pas de difficulté majeure. Le troisième en revanche mérite un peu plus d'explications. Fixer un prix n'est pas facile mais il existe un certain nombre de techniques que vous pouvez utiliser.
La première chose à faire est de déterminer si vous avez le contrôle sur vos prix. Si vous êtes dans un marché où tout le monde facture 9,90 € il peut être compliqué de faire accepter un prix supérieur à vos clients.
Si vous avez le contrôle sur votre politique tarifaire, il y a deux approches que nous vous recommandons d'utiliser pour fixer votre prix :
- Coût de revient majoré : cette technique consiste à ajouter une marge au coût de revient des produits. L'avantage de cette méthode est que vous connaissez de façon certaine la marge que vous réaliserez sur chaque vente. L'inconvénient est que ce prix peut être inférieur à ce que vos clients seraient prêts à payer pour vos produits.
- Tarification axée sur les avantages : cette méthode consiste à estimer la valeur du bénéfice que votre produit apporte au client et à facturer une fraction de ce gain. Cette technique est plus facile à appliquer lorsque vous pouvez quantifier le gain monétaire réalisé par votre client que lorsque votre produit procure un bénéfice intangible tel qu'un gain de temps par exemple. L'avantage de cette approche est qu'elle permet de maximiser le prix de vos produits et services. L'inconvénient est que vous devrez sûrement tester différents niveaux de prix pour déterminer le prix de marché optimal.
Il est toujours bon de tester différents niveaux de prix. Faites une semaine avec un prix A et une semaine avec un prix B et comparez les résultats.
L'investisseur connait maintenant votre positionnement et votre prix, il est temps de lui expliquer comment vous allez atteindre vos clients.
Jusqu'à présent vous avez montré à votre investisseur que vous connaissez votre marché. Il s'agit maintenant de démontrer que votre plan est réalisable.
Pour cela vous devez rentrer dans le détail de l'exécution de votre stratégie commerciale. L'idée est de lui montrer que vous êtes prêt et qu'il lui suffit d'appuyer sur un bouton (ou de vous écrire un chèque) pour que tout se mette en action.
Vous devez démontrer que vous avez identifié les meilleurs réseaux de distribution (site marchant, magasins propres, distributeur tiers, porte à porte, etc.) et de communication (dépliant, affichage, marketing web, etc.) pour toucher votre public.
Pour ce faire vous pouvez commencer par lister les différentes options et justifier vos choix sur la base des critères suivants :
- portée : pourquoi ce réseau permet d'atteindre un nombre considérable de clients potentiels?
- coût : pourquoi ce réseau est-il optimal? Quel est le budget alloué?
- concurrence : pourquoi avez-vous une meilleure chance face à la concurrence en utilisant ce réseau?
- implémentation : qui sera responsable de l'exécution? En quoi cette personne est-elle qualifiée?
Dans cette partie vous devez définir les objectifs pour votre entreprise au cours des prochains mois.
Il s'agit d'un engagement que vous prenez envers votre investisseur et vous serez jugé sur votre capacité à atteindre ces objectifs. Il est donc important que vous preniez le temps d'identifier des objectifs qui :
- sont pertinents : c'est-à-dire des objectifs qui auront un réel impact sur la performance financière de l'entreprise.
- sont atteignables : vous voulez montrer à vos investisseurs que vous êtes capable de réaliser votre plan
- sont mesurables : vous voulez pouvoir revenir vers votre investisseur en lui disant "je vous avais promis qu'on aurait 1 000 clients cette année, on en a eu 1 200!".
Du point de vue de la gestion de la relation avec votre investisseur, votre capacité à atteindre et à dépasser vos objectifs jouera un rôle important lorsque (et si) vous lui demanderez de réinvestir dans l'entreprise.
Cette section a un seul objectif : vous permettre d'anticiper et de désamorcer tout doute que votre investisseur pourrait avoir concernant votre plan ou votre capacité à l'exécuter. Utilisez-la pour préempter toute critique en montrant que :
- vous savez que "x" est un risque dans votre plan,
- vous y avez réfléchi,
- vous avez un plan B ou un moyen de l'atténuer.
Vous devez vous montrer extrêmement transparent dans cette section. Si le lecteur découvre un risque majeur que vous n'avez pas identifié, il va douter de votre connaissance du secteur et votre capacité à mener à bien votre projet.
6. Opérations
Dans cette section vous devez détailler la façon dont votre entreprise va fonctionner. La première partie est généralement le plan de personnel.
Ici vous devez expliquer combien de personnes la société emploiera, leurs rôles et les coûts associés. S'il est prévu que l'effectif augmente massivement sur la durée du plan, il est recommandé d'expliquer quel en sera l'élément déclencheur.
Il peut être question d'augmenter le nombre de personnes au SAV en fonction des ventes ou cela peut être lié à des ouvertures prévues de magasins par exemple.
Si vous avez un magasin ou un restaurant, il est également utile de mettre le plan de personnel en parallèle avec les horaires d'ouvertures.
L'idée ici est d'identifier ou d'écarter tout risque opérationnel lié à des actifs.
Vous devez lister les actifs sans lesquels la société ne pourrait pas fonctionner (un camion de livraison ou une licence par exemple) et expliquer les démarches que vous avez effectuées pour les protéger ou les renouveler.
Il s'agit ici pour l'investisseur de vérifier que vous n'êtes pas dépendant d'un fournisseur unique et que vous traitez avec des partenaires respectables. Vous devez donc lister vos principaux fournisseurs, la nature de la relation, et un potentiel remplaçant en cas de besoin.
Vous devez également mentionner les principaux termes que vous avez négocié avec vos fournisseurs (délais de paiement, prix, fréquence des livraisons, volume minimum, etc.).
Maintenant que vous avez expliqué comment l'entreprise va fonctionner, il est temps de se pencher sur les chiffres.
7. Plan Financier
Voici une autre partie clé d'un business plan. Si vous avez lu notre article sur comment les investisseurs évaluent les business plans , vous savez que l'interprétation de cette section va dépendre de si votre lecteur est un investisseur en dette ou un investisseur en fonds propres :
- S'il s'agit d'une banque, vous devez montrer que votre activité va être pérenne, rentable, et génératrice de trésorerie et que vous n'allez pas prendre trop de risques.
- S'il s'agit d'un investisseur en fonds propres vous devez montrer que l'entreprise a le potentiel de croitre et de devenir suffisamment génératrice de trésorerie pour lui permettre de vendre ses parts et d'atteindre ses objectifs de retour sur investissement.
Au minimum vous devez montrer des états financiers (compte de résultat, bilan, tableau des flux de trésorerie) sur 3 ans ainsi qu'un tableau des flux de trésorerie mensuel pour la 1ère année. Il est également recommandé de montrer un compte de résultat et un bilan mensuel pour la première année.
Les investisseurs veulent voir des chiffres mensuels pour la 1ère année car :
- c'est l'année où vous êtes le plus vulnérable
- tout retard ou sous performance cette année-là aura des impacts sur les années 2 et 3
Si vous n'avez pas de bonnes notions en comptabilité et en finance, vous pouvez faire appel à un logiciel spécialisé pour vous aider à établir les états financiers prévisionnels.
The Business Plan Shop propose un outil en ligne avec lequel vous pouvez facilement réaliser votre plan financier. Le logiciel vous aidera également à rédiger les autres parties de votre business plan, et vous permet d'exporter le plan final au format PDF ou Word. Vous trouverez plus d'informations sur notre solution ici .
Le tableau d'emplois-ressources n'est rien de plus qu'une liste des apports de fonds (les ressources) et leur usage (les emplois).
Les investisseurs regarderont combien d'argent est nécessaire au démarrage du projet ainsi que le pourcentage de fonds apporté par les actionnaires.
Si vous adressez votre business plan à une banque il est important que vous listiez l'ensemble des actifs dont vous avez besoin, et que vous isoliez les stocks et la TVA sur une ligne dédiée, car ces éléments font souvent l'objet d'un financement spécifique.
Dans cette section vous devez détailler les hypothèses sur lesquelles reposent vos prévisions financières. Les investisseurs testeront ces hypothèses sous différents scénarios afin de quantifier le risque financier.
Prenons l'exemple d'un site de e-commerce.
La rentabilité d'un site de e-commerce dépend généralement de 2 "drivers" :
- le panier moyen : qui représente la valeur moyenne d'une vente
- le coût d'acquisition d'un client : qui représente les frais de marketing nécessaires pour attirer un client sur le site
La première hypothèse est liée aux ventes, elle aura donc un impact supérieur à 1x sur le résultat. La seconde est liée aux coûts, mais est également très importante, car elle impacte directement la vitesse de croissance du site.
Regardons tout de suite un exemple chiffré afin de mieux comprendre la sensibilité du profit à ces 2 hypothèses :
Comme vous pouvez le voir dans le tableau ci-dessus, une déviation de 10% du panier moyen entraine une baisse du profit de 30%, un écart de 10% dans le coût d'acquisition entraine une baisse de 20% du profit et un cumul des 2 impacts divise le profit par 2 !
Et ces écarts ne sont pas improbables. Admettons que les coûts d'acquisition soient liés à de la publicité sur internet et que le coût moyen d'un clic soit de 0,4 €.
Un coût d'acquisition de 8,00 € implique un taux de conversion de 5% : il faut donc 20 clics pour réaliser une vente. Maintenant un coût d'acquisition de 8,80 € signifie qu'il faut 22 clics pour faire une vente. 2 clics peuvent vous couter 20% du profit!
Si vous avez identifié ces moteurs, vous êtes en mesure de suivre de près la valeur de ces coûts. Il est fort probable que ces coûts soient mal évalués dans votre business plan initial, mais après quelque temps vous aurez une idée plus précise de leur vraie valeur.
Si vous maintenez votre modèle de prévisions financières à jour, vous pourrez rapidement rafraichir ces hypothèses dans le modèle et obtenir une prévision de trésorerie plus fiable vous permettant de prendre des décisions financières.
Notez que dans mon exemple je n'ai pas inclus le nombre de clients parmi les hypothèses clés. J'ai fait ici l'hypothèse que 100% du trafic du site était issu de la publicité.
Cette hypothèse est spécifique à l'e-commerce. Un site dans sa première année d'exploitation n'est généralement pas très bien classé dans les résultats de recherche et peut donc difficilement générer du trafic de façon naturel.
La section de prévision du chiffre d'affaires est extrêmement importante. Cette section est en rapport direct avec l'étude de marché, votre positionnement, votre plan commercial et votre politique tarifaire. L'objectif ici est de construire et justifier vos prévisions de ventes pour les 3 prochaines années.
Construire un prévisionnel de ventes est un double exercice : vous devez tout d'abord construire le chiffre en utilisant la méthode ascendante, puis valider ce chiffre à l'aide de la méthode descendante. La prévision des ventes fait partie d'un article à part entière que vous trouverez ici .
Après avoir construit un prévisionnel de ventes réalistes, il vous faut détailler votre structure de coûts.
L'objectif de cette partie consiste à analyser le risque opérationnel de l'entreprise. L'analyse réside dans deux notions : levier opérationnel et point mort.
Commençons par le point mort qui est le niveau de ventes requis pour atteindre l'équilibre financier. Toute entreprise à deux types de coûts :
- Les coûts fixes comme leur nom l'indique sont des coûts qui existent indépendamment du niveau d'activité. Par exemple le loyer d'une boutique.
- Les coûts variables au contraire sont des coûts dont le niveau est directement proportionnel au niveau d'activité. Par exemple le coût des marchandises vendues dans une boutique.
Le point mort se calcule en divisant le total des coûts fixes par la marge sur coûts variables.
Prenons un exemple. Si une boutique a pour unique coût fixe son loyer de 2 000 € par mois et qu'on y vend des marchandises achetées 30 €/article à un prix de 50 €/article.
La boutique réalise alors une marge sur coûts variables de 50 - 30 = 20 € par article. Ce qui signifie qu'il faut vendre 2 000 / 20 = 100 articles par mois pour couvrir le loyer. Le point mort de cette boutique est donc de 100 articles ou 5 000 € de ventes.
La conclusion directe de cela est que plus les coûts fixes sont élevés plus le niveau de ventes requis pour atteindre l'équilibre financier est important. Le risque de l'entreprise est donc proportionnel au niveau de coûts fixes.
Levier opérationnel
Voyons maintenant le levier opérationnel. Le levier opérationnel est une mesure de l'élasticité des ventes sur le résultat d'exploitation, c'est-à-dire l'impact d'une variation de 1% des ventes sur le résultat opérationnel. Cela parait complexe, mais c'est en réalité très simple.
Il y a deux dimensions autour du levier opérationnel : le niveau de coûts fixes par rapport au niveau de coûts variables, et le niveau de marge sur coûts variables.
Comme nous l'avons vu précédemment plus les coûts fixes sont élevés plus le niveau de ventes requis pour atteindre le point mort est important. Mais ce n'est pas tout.
Comparons 2 entreprises dans le même secteur. L'entreprise A fabrique elle même ses biens tandis que l'entreprise B sous-traite la fabrication à un partenaire. En conséquence l'entreprise A a un niveau de coûts fixes supérieur à l'entreprise B (le coût de l'usine qui fabrique les biens).
L'entreprise A bénéficie également d'une marge supérieure sur chaque vente par rapport à B (l'entreprise B doit payer une marge à son partenaire). Une entreprise à fort levier opérationnel (coûts fixes importants, A ici) est donc plus rentable qu'une entreprise utilisant moins de levier (B ici). Le risque supplémentaire est donc compensé par une rentabilité plus élevée.
Le deuxième aspect du levier opérationnel est lié au niveau de marge sur coûts variables. Si la marge sur coûts variables est élevée, alors il suffit d'un nombre limité de ventes pour couvrir les coûts fixes, ce qui est positif. En revanche cela signifie aussi que chaque erreur dans les prévisions de ventes aura un impact important sur la rentabilité.
Ce qu'il faut retenir est que les investisseurs examineront la structure de coûts et le niveau de coûts fixes afin d'évaluer le niveau de risque associé à l'entreprise. Ils s'attendront également à voir un calcul de point mort dans cette partie.
Les investisseurs vous jugeront sur votre capacité à utiliser le levier opérationnel à votre avantage. Si votre projet est une création d'entreprise dans une niche où le marché est incertain ils s'attendront à ce que vous externalisiez le plus de services possible.
Votre marge sera plus faible, mais il vous faudra infiniment moins de ventes pour atteindre le point mort compensant ainsi le risque sur les ventes par une diminution du risque sur les coûts.
A l'inverse, si votre entreprise est mature, les investisseurs s'attendront à ce que vous n'externalisiez des services que lorsque cela permet d'en réduire le coût afin d'optimiser votre marge.
Etats Financiers
L'objectif de cette section est de présenter vos états financiers.
Vous devez guider le lecteur à travers les éléments principaux de chacun des états :
- Compte de résultat : ventes, croissance, EBE, marge d'EBE
- Flux de trésorerie : flux de trésorerie opérationnel, ratio conversion du flux de trésorerie opérationnel (% de l'EBE), principaux investissements, principales échéances d'emprunt.
- Flux de trésorerie mensuels : mouvement de BFR saisonnier
- Bilan : trésorerie, dette et fonds propres
Votre financement doit être équilibré (trésorerie positive) et vous devez atteindre votre point mort au cours des 3 ans. Vous pouvez également détailler quelques ratios financiers supplémentaires, en particulier si votre entreprise a un important besoin de fonds de roulement : vous pouvez expliquer le niveau de BFR / ventes, créances clients en jour de CA, créances fournisseurs en jour de CA, et stocks en jour de CA.
Mettez ici toutes les données pouvant servir à l'investisseur pendant sa due diligence.
Félicitations vous êtes maintenant prêt à écrire votre business plan! Nous espérons que la structure de business plan et les conseils proposés dans cet article vous on été utiles. N'hésitez pas à nous faire part de vos remarques ou questions dans les commentaires.
A voir aussi sur The Business Plan Shop :
- Le plan financier du business plan en 7 questions
- Les questions de l'étude de marché du business plan
- Rédiger l'executive summary du business plan
Cet article intéresserait l'une de vos connaissances ? N'hésitez pas à le lui partager !

Fondateur & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster est un entrepreneur et un financier chevronné.
Guillaume est entrepreneur depuis plus de dix ans et possède une expérience directe en création, gestion et développement d'une entreprise prospère.
Avant d'être dirigeant d'entreprise, Guillaume a travaillé en banque d'affaires et en capital-investissement, où il a passé la plupart de son temps à créer des prévisions financières complexes, à rédiger des plans d'affaires et à analyser des états financiers pour prendre des décisions en matière de financement et d'investissement.
Guillaume est titulaire d'un Master en Finance de l'ESCP Business School et d'une Maîtrise des Sciences en Gestion de l'Université de Paris Dauphine.
Vous voulez écrire facilement votre business plan ?
Essayez gratuitement notre logiciel de business plan .
Vérifiez que votre projet peut-être rentable et obtenez un business plan professionnel pour votre recherche de financement
Ne partez pas d'une page blanche !
La version complète de The Business Plan Shop donne accès à plus de 50 modèles de business plan.

Besoin d'un business plan professionnel ? Découvrez notre solution
Créez facilement votre business plan !

Réaliser un business plan convaincant est facile avec The Business Plan Shop
Pas prêt à essayer notre outil en ligne ? Obtenez plus d'informations
Danser sur la toile | UX design - Création de site Internet - SEO

- Prestations
- Formation web à domicile
- Cas clients

Exemple de business plan pour start-up et créateur d’entreprise
31 mars 2016 Développer son activité
Comment bien présenter votre projet à des investisseurs ou futurs partenaires ? Voici un modèle de dossier de demande de financement (business plan) à compléter, avec idées de présentation originale et bons conseils, pour ne pas avoir à rougir de vous. Installez-vous confortablement sur Word (ou autre logiciel de traitement de texte), et complétez chaque partie.
Questions préliminaires :
- Combien de temps pour la réalisation du business plan ? Un bon business plan se travaille dans la durée . Comptez trois semaines à un mois pour réunir tous les éléments et approfondir votre idée.
- Quand le rédiger ? En début de projet pour vous aider à affiner votre idée, ou après une première phase de test réussie pour une demande de financement.
- Combien de pages ? Il faut synthétiser plusieurs jours de recherche (et plusieurs nuits de conception cérébrale) en quelques pages. Limitez-vous à 20 ou 30 pages grand max.
Page de couverture
C’est la porte d’entrée, celle qui doit donner envie d’ouvrir votre dossier. En prenant soin à sa mise en page, il faut faire figurer :
- Le nom du projet , accompagné d’une éventuelle « baseline » évocatrice. (ex : Qui Troque Tout / pour troquer tous vos objets sans avoir à vous déplacer). Vous pouvez utiliser le travail fait sur la proposition de valeur (cf. plus bas)
- Le logo s’il existe déjà, ou une image véhiculant l’idée principale
- Vos informations de contact
- La date à laquelle le business plan est rédigé
Le petit plus : ajouter toute autre information utile, appuyant la légitimité de votre projet (mentionnez vos soutiens s’ils sont reconnus, une adresse de site web si une visibilité existe déjà, une photo représentant un évènement autour de votre projet qui a attiré beaucoup de monde, …).

I. Présentation succincte du projet
Entraînez vous dès maintenant à présenter votre projet en une demi-page max. Vous devez faire comprendre rapidement de quoi il s’agit. On parle souvent de « l’exercice de l’ascenseur » ou de « l’elevator pitch « . Imaginez expliquer votre projet à un investisseur, dans un temps très court (le temps de prendre l’ascenseur). C’est un exercice difficile, mais qui permet de travailler sur l’essentiel (ce qu’on oublie quand on cogite trop longtemps sur ses idées).
Répondez aux interrogations suivantes :
- À quels besoins le projet répond-il?
- À qui, comment, où ?
- Quels sont vos besoins, que demandez-vous via ce business plan ?
Exemple de pitch pour présenter rapidement votre projet :
Avez-vous déjà essayé de trouver un cours de danse sur Paris, pour vous, vos enfants, votre mariage ? Si oui, vous devez certainement connaître la difficulté que c’est de trouver un bon cours sur Internet. Le site Onydanse.com offre la solution : trouvez votre cours de danse, à côté de chez vous, aux horaires qui vous conviennent, en suivant les avis des autres utilisateurs.
Le petit plus, c’est le module de billetterie, qui permet de réserver et de payer son cours à l’avance, à des tarifs préférentiels.
Avec déjà plus de 5000 utilisateurs quotidiens, et un chiffre d’affaires de 1000€/mois le site est en ligne depuis 6 mois.
Accompagnée d’un développeur web chevronné, je suis à la recherche d’un financement de 15 000€ pour augmenter la visibilité du site et le développer sur toute la France.
II. Présentation du créateur et de son idée
Portrait du créateur.
Synthétisez votre CV, avec les informations utiles (compétences, formations, expériences professionnelles) qui peuvent servir au projet.
Le petit plus : insérez une photo de vous, dans l’environnement de votre projet. Mettez-vous en scène.

Présentation du créateur
Autres membres de l’équipe
Décrivez les autres membres de l’équipe et leur rôle. Mettez en avant ce qui peut rassurer vos investisseurs : la complémentarité des compétences , des liens de longue date, une expérience professionnelle déjà partagée.
Genèse de l’idée
Comment l’idée vous est-elle venue ? Vous avez le droit d’enjoliver un peu pour livrer à votre lecteur un scénario captivant.
Forces et faiblesses
Terminez par un aperçu de vos points forts et points faibles pour mener le projet. C’est une manière de mieux vous faire connaître auprès de votre lecteur. Retenez que la personnalité du créateur/des associés est un des deux axes (avec la viabilité du projet) qui retiennent l’attention des investisseurs .
III. Étude du marché
Il vous faut faire de nombreuses recherches documentaires pour alimenter cette partie. Aidez-vous des ressources en ligne (études INSEE, Sofres, …) et pensez à aller faire un tour dans les principaux centres de documentation (ex : BNF, Cité des Sciences, …).
Environnement
Dans quel environnement s’inscrit le projet ?
Le petit plus : pour reprendre une notion fidèle au marketing, vous pouvez aborder l’environnement selon le modèle PESTEL (politique, économique, socio-culturel, technologique, écologique, légal). Faites ressortir les opportunités à saisir et les menaces à contrer.

Cliquer pour agrandir. (Notez que l’aspect environnemental n’a pas été traité car non pertinent pour ce cas précis.)
Présentez les grandes tendances, les catégories de consommateurs, les évolutions (nombre d’acheteurs, budget consacré), les évènements marquant. Illustrez vos propos de données chiffrées et graphiques, toujours en citant vos sources.
Le petit plus : faire parler les graphiques, en indiquant ce qui est important.

Concurrence
Qui sont les concurrents ? Comment se positionnent-ils ? Quelles sont leurs forces et leurs faiblesses ? Sachez que vous n’êtes jamais complètement seul (même si vous avez eu l’idée de génie qui n’existe pas encore). Il suffit de taper dans Google la requête qui correspond au besoin que vous vous apprêtez à combler pour identifier des concurrents de taille : ceux en première page du moteur de recherche .
Vous pouvez distinguer :
- Les concurrents directs : ceux qui proposent le même produit/service
- Les concurrents indirects : ceux qui offrent une alternative (ex : les applications numériques de visite guidée dans les musées représentent une concurrence indirecte pour les guides conférenciers).
L’enjeu est ici d’entrevoir la maturité du marché (les entreprises sont-elles plutôt jeunes ou bien existe-t-il déjà de gros mastodontes ?), le positionnement et les parts de marché des différents acteurs.
IV. Évaluation du projet
Etat d’avancement.
Définir les grandes étapes passées et à venir pour situer le projet aujourd’hui.

Proposition de valeur
À quel besoin principal répond votre projet ? Vous pouvez vous amuser à trouver la phrase qui fera mouche pour vos cibles : à la fois courte et claire sur ce que vous proposez. Il est important de mettre en avant une seule proposition (unique selling proposition) , qui sera plus facile à comprendre de vos utilisateurs que si vous les perdez dans tout ce que vous avez imaginé pour eux (faites-vous adopter étape par étape). Pour des exemples, inspirez-vous des affiches dans le métro ou rendez-vous sur les sites Internet des grandes start-ups.
Regardez comment ces enseignes, qui proposent toutes le même service, communiquent différemment sur leur proposition de valeur. Leur point commun : on comprend tout de suite ce qu’elles proposent.

Positionnement par rapport à la concurrence
Précisez comment vous vous démarquez.
Le petit plus : identifiez deux axes pour positionner visuellement vos concurrents les uns par rapport aux autres, et situez votre future entreprise.
Facteur de différenciation
Quelle est cette originalité qui vous fera préférer des autres ?
Définir 1 à 5 cibles (particuliers, professionnels, …), et décrivez leurs besoins.
Le petit plus : présenter les cibles selon le modèle des personas (utilisé en UX design). Donnez-leur un prénom et faites leur portrait, comme si vous les connaissiez intimement. Le mieux est de se baser sur des données réelles, glanées via des études sur Internet (reprenez votre étude du marché) ou des questionnaires que vous aurez préalablement administrés.
Voici quelques informations que vous pouvez rapporter :
- Importance de la cible pour vous (très forte, forte, moyenne)
- Profession, âge, situation familial
- Besoin principal, attentes
- Questions et points de stress
Exemple de persona pour une agence immobilière souhaitant capter une nouvelle clientèle sur Internet :

Produits et services
La réflexion sur la proposition de valeur (cf. plus haut) peut être frustrante. Ici, c’est le moment de vous libérer en décrivant l’étendue de votre offre . Vous pouvez détailler tous vos produits et services selon les « 4p » du marketing mix :
- Product (produit) : détails du produit/service, à quels besoins répond-il, comment ?
- Price (prix) : quel est le prix affiché ? le prix de départ ? le prix en promotion (sous quelles conditions) ?
- Place (lieu) : où peut-il s’acheter (lieu physique, site Internet, …)
- Promotion (publicité) : comment est-il promu, connu des clients ?
Fournisseurs
Si le projet nécessite l’achat de matière première, services ou produits, faites une liste des types de fournisseurs. Vous pouvez déjà identifier (marque, adresse, coût) les fournisseurs que vous êtes sûr de solliciter.
Business model
Décrivez ce qui vous fera gagner de l’argent (commission, marge, …).
Communication
Décrire les actions de communication à engager, comment vont-elles être mises en place, quand, sur quels médias (presse, distribution de flyers, réseaux sociaux, site Internet, …). Budgétez-les.
Objectifs et perspectives de développement
Même si l’aventure fera que dans un an, vous serez là où vous n’auriez jamais imaginé être, faites entrevoir à votre investisseur l’évolution souhaitée pour le projet et les objectifs que vous vous fixez à un an, voire trois ans :
- Chiffre d’affaires
- Nombre de clients / visiteurs
- Évolution du périmètre géographique, de la cible
- Ajout d’une technologie, d’un produit/service, …
- Prévision d’embauches
Il s’agira de juger si votre modèle est réaliste.
Test de l’idée
Définir comment tester le projet dans un premier temps avec un minimum de moyens (ex : proposer une première prestation chez un client sans avoir à engager de coûts de communication, aller toquer à la porte de votre voisin pour lui proposer un système de troc avant de développer un service sur Internet, …). Cette démarche est identifiée comme un « mode guerilla » ou un MVP (minimum viable product) , notion très utilisée en lean start-up (méthodologie pour la création d’entreprise).
Cette étape est primordiale pour tester votre idée en engageant un minimum d’argent. Elle vous donnera de bonnes leçons sur la compréhension de votre marché.
Le très grand plus : avoir testé l’idée avant de présenter votre business plan. Racontez dans cette partie les résultats de l’expérience.
V. Étude financière et juridique
C’est une des parties les plus complexes pour qui n’est pas à l’aise avec les chiffres. Même s’il peut paraître absurde d’envisager les ventes alors que l’idée est encore à un stade prématuré, l’exercice est fort apprenant. Il permet de montrer aux investisseurs que vous maîtrisez les notions importantes de gestion : compte de résultat, bilan, trésorerie .
Intentionnellement, nous ne nous attardons pas sur les façons de bâtir chaque élément financier, car ce sera l’objet d’un futur article (la comptabilité pour ceux qui croient qu’ils n’y comprendront jamais rien).
Plan de financement
Décrire tous les postes à budgéter, nécessaires au démarrage de l’activité . Estimer leurs coûts, et envisager les sources de financements (deniers personnels, aide des proches, aides publiques, aides privées, …).
Le petit plus : mettre en avant la somme demandée à l’investisseur à qui vous présentez ce business plan, en précisant bien ce qu’elle vient financer : l’achat de la matière première, le site Internet, …
Compte de résultat prévisionnel
Estimer les premières ventes et coûts récurrents la première année.
Structure juridique
Précisez la structure juridique pour le projet : SAS, SARL, EURL, Association, …
VI. Synthèse
Terminez en beauté en listant :
- Les forces et faiblesses du projet, les opportunités et menaces du marché. Vous utiliserez ainsi la notion marketing d’ analyse SWOT (Strenghts, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats).
- Les facteurs clés de succès .
Pour bien finir, n’oubliez pas :
- La table des matières
- La numérotation des pages
- De corriger les fautes et de vous faire relire
- D’enregistrer le dossier en pdf si vous souhaitez l’envoyer par email
- D’imprimer et relier vos pages si vous préférez présenter une version papier (chez Copytop, par exemple, ils font cela très bien pour quelques euros…tout dépend de la grosseur de votre dossier).
Vous avez des questions ou des idées pour compléter cet article ? N’hésitez pas à nous en faire part dans les commentaires.
Vous aimerez aussi :
- Trouvez des financements publics pour vos projets associatifs : les bonnes méthodes pour y arriver
- Apprenez à créer un flyer en moins de 10 minutes avec Word
- Comment référencer ses activités sur Google Maps pour gagner en visibilité
- Inbound Marketing : changez votre façon de communiquer
À propos de l'auteur
- Partenaires
- Stratégie commerciale
- Documents et rapports
- Ressources humaines
- Marketing et ventes
- Gestion de produit
- Productivité
- Planification de projet
- Développement de logiciels/Informatique
- Travail d'équipe
Modèle de business plan en une page
Définissez votre stratégie (et respectez-la) à l'aide d'un plan court et simple
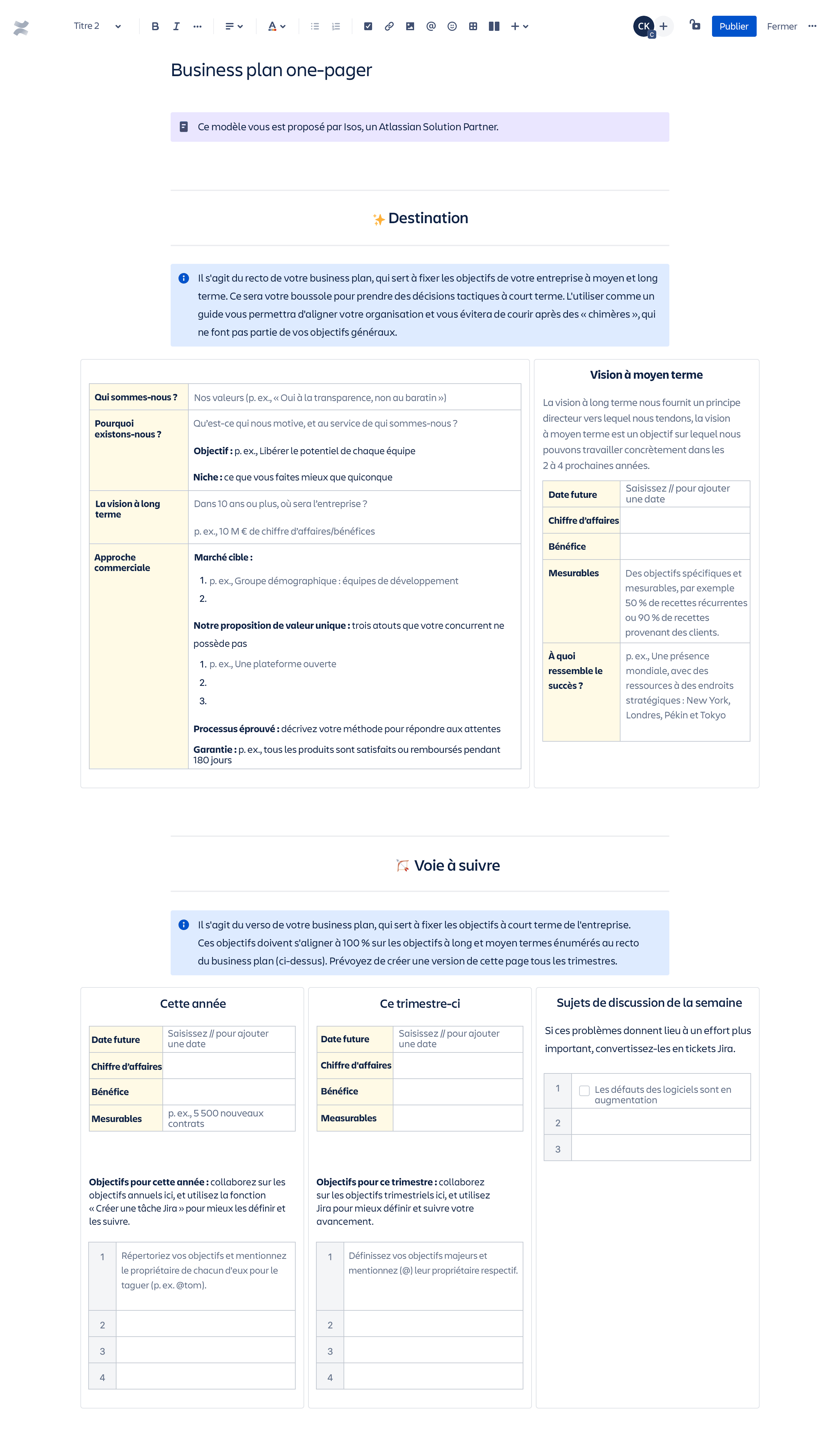
Les plans stratégiques sont difficiles à créer, et encore plus à revoir. La quantité d'informations est effroyable, et la vision de votre entreprise peut se retrouver perdue au milieu de toutes ces pages. Isos Technology sait comment réaliser de grandes choses et ne jure que par ce modèle de business plan en une page, qui vous permet d'esquisser une idée de manière simplifiée et de la présenter dans un format exploitable par votre équipe.
Comment utiliser le modèle Business plan en une page ?
Étape 1 : résumez qui vous êtes.
Votre entreprise dispose probablement de documents qui décrivent votre activité et vos objectifs. L'une des choses les plus utiles pour l'ensemble de votre équipe est de les résumer en énoncés concis. C'est ce que vous ferez dans les deux premières sections du tableau Destination de ce modèle. Indiquez qui vous êtes et quelle est votre raison d'être afin que tout le monde soit sur la même longueur d'onde en ce qui concerne ces éléments essentiels.
Étape 2 : Précisez votre stratégie à long terme
La partie supérieure du modèle est appelée Destination pour une raison : elle permet de définir vos objectifs à moyen et à long terme. Utilisez le reste du tableau pour déterminer où se trouvera votre entreprise dans les dix prochaines années environ. Avez-vous l'intention de réaliser un certain profit ? D'atteindre une taille d'équipe spécifique ? Une position de leader dans le secteur ? Notez ces objectifs ici. Vous disposez également d'espace pour définir votre approche du marché, y compris des informations sur vos objectifs, votre proposition de valeur et le processus que vous utilisez pour apporter cette valeur à vos clients.
Étape 3 : Définissez votre vision à moyen terme
Les stratégies à long terme peuvent vous donner l'impression que vous avez beaucoup trop à faire, alors la section Vision à moyen terme vous permet d'identifier ce sur quoi vous allez travailler dans les deux à quatre prochaines années. Bien entendu, ces tâches à moyen terme doivent soutenir les objectifs plus larges que vous vous fixez : elles ne feront que rendre le processus de réalisation plus accessible. Dans cette section, vous pouvez également fixer une date, et noter vos recettes et vos bénéfices, les mesures que vous contrôlerez et une définition claire de la réussite.
Étape 4 : Définissez vos objectifs à court terme
Voie à suivre vous permet de fixer vos objectifs pour l'année, le trimestre, et même les sujets à aborder durant la semaine en cours. Pour vos objectifs annuels et trimestriels, vous renseignerez également vos recettes, vos bénéfices et vos métriques. Contrairement à vos stratégies à long terme, prévoyez de créer cette page tous les trimestres afin de suivre l'avancement et de rester à jour.

Isos Technology est un Atlassian Platinum Solution Partner qui fournit des conseils, des formations et une expertise en processus pour aider les clients à exploiter la gamme de produits Atlassian afin de favoriser la transformation métier.
Plus de modèles Stratégie d'entreprise Tout afficher
Rétrospective des « 4 l ».
Utilisez ce modèle pour réaliser une rétrospective des « 4 L » avec votre équipe.
Analyse des 5 pourquoi
Utilisez ce modèle pour effectuer une analyse des Cinq pourquoi et découvrir les sources des problèmes de l'équipe.
Réunion générale
Partagez les mises à jour métier, les réussites, les points forts des employés et bien plus encore avec votre équipe dans son ensemble.
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Un business plan est un document écrit. Il comporte donc plusieurs pages.Cela dit, le nombre de pages ne présage en rien de la qualité du document. C'est pourquoi, en réalité, il importe peu. Il n'existe pas de standard en la matière et le nombre de pages d'un business plan dépend essentiellement de son destinataire et de ses objectifs.Voici les informations importantes à retenir ...
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Here are the key elements of a one-page business plan: The executive summary, business opportunity, value proposition, team members, industry analysis, target market, marketing plan, revenue model, implementation time, financial summary, funding requirements and contact information. To design a startup one pager, you should create an outline ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
4. Direct and to-the-point. Learning to communicate your ideas clearly and directly is critical. You need to be sure that anyone can really understand the essence of your business. Delivering your entire business concept on a single page is a great way to practice this, as it forces you to be succinct. 5.
Striking the Balance: Ideal Length for a Business Plan. A good rule of thumb is to aim for a business plan that is between 15 and 25 pages long, excluding appendices. This length allows you to cover the main aspects of your business, such as the problem you are solving, the solution you are offering, the market opportunity, the competitive ...
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
Whether you want to launch a side gig, a solo operation or a small business, you need a simple business plan template to guide you. Forbes Advisor offers you a comprehensive and easy-to-follow ...
A complete, thoughtful business plan can help you recruit executive leaders, pitch investors and win grants. But sometimes you just need a one-page business plan to get your foot in the door. A condensed business plan can act as an elevator pitch to pique the interest of a startup incubator, bank or other business partner.
A business plan outlines the goals of your business and how it plans to achieve them. Real important - because without it, it's like running a business in the dark. It's like a roadmap that guides your company's direction and helps everyone stay on track. Gone are the days when designing a business plan from scratch was a time-consuming ...
Un Business Plan fait entre 10 et 30 pages en moyenne. Au-delà de 30 pages, vous risquez de perdre votre lecteur. Allez à l'essentiel. Débarrassez-vous des fioritures ou du blabla non essentiel. Pensez qu'un banquier ou un investisseur peut lire une vingtaine de Business Plans dans une journée !
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Vous avez un projet de création d'entreprise ? Le business plan (ou plan d'affaires) est un document écrit qui présente en détail votre projet de création entreprise. Le business plan sera l'outil pour convaincre les banques et les investisseurs. Nous vous expliquons comment faire un business plan étape par étape.
Combien de pages un business plan doit-il comporter ? 10, 25, 50, 100 ou plus de pages ? Voici une comparaison rapide des types de business plans disponibles et de leur durée optimale. Beaucoup de nouveaux entrepreneurs se demandent souvent combien de temps est trop long pour un plan d'affaires. La plupart des experts et conseillers en ...
Un Business Plan est un document qui réunit les éléments de réflexion indispensables pour lancer votre projet d'entreprise (comme dans le cadre du business model ). Il permet ainsi le reengineering d'un processus défaillant d'une entreprise déjà créée ou pour qu'un investisseur et/ou partenaire accède à votre requête.
La structure de business plan que nous recommandons présente l'avantage de répondre à plusieurs questions que se posent les investisseurs dans chaque section, et d'offrir une progression naturelle, ce qui la rend adaptée à une lecture complète ou sélective de votre plan. Sommaire du business plan :
Installez-vous confortablement sur Word (ou autre logiciel de traitement de texte), et complétez chaque partie. Questions préliminaires : Combien de temps pour la réalisation du business plan ? Un bon business plan se travaille dans la durée. Comptez trois semaines à un mois pour réunir tous les éléments et approfondir votre idée.
706 templates. Create a blank Business Plan. Beige Aesthetic Modern Business Plan A4 Document. Document by Rise & Roar Design. Green Professional Strategic Business Plan Executive Summary. Document by Antler. Startup Business Plan. Document by Maea Studio. Blue White Corporate Business Plan Cover Document.
Analyse des 5 pourquoi. Utilisez ce modèle pour effectuer une analyse des Cinq pourquoi et découvrir les sources des problèmes de l'équipe. La planification stratégique peut être décourageante. Utilisez ce modèle de business plan en une page pour simplifier le processus, et mettre en évidence les objectifs et les chiffres qui comptent ...
Pages offer several benefits and features that can help your business. Learn about which benefits are most important for your business. Pages provide free tools to help you communicate with customers and achieve your business goals. See which tools can work best for your business. Pages keep your business presence and personal profile separate.
Everything included in Plus. Higher message caps on GPT-4 and tools like DALL·E, Browsing, Advanced Data Analysis, and more. Create and share GPTs with your workspace. Admin console for workspace management. Team data excluded from training by default. Learn more. $25 per user/month, billed annually. $30 per user/month, billed monthly.
Bloomberg Technology. The only daily news program focused exclusively on technology, innovation and the future of business from San Francisco. Hosted by Emily Chang. More episodes and clips. 02:31.
Treasury to Start Buyback Program May 29. Bloomberg Surveillance. TV Shows. May 1st, 2024, 10:20 AM PDT. Bonds held gains after the US Treasury kept its quarterly debt sales steady and said it ...