- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Poetry Worksheet Bundle! Perfect for National Poetry Month.

40 Philosophy of Education Examples, Plus How To Write Your Own
Learn how to define and share your teaching philosophy.

These days, it’s become common for educators to be asked what their personal teaching philosophy is. Whether it’s for a job interview, a college class, or to share with your principal, crafting a philosophy of education can seem like a daunting task. So set aside some time to consider your own teaching philosophy (we’ll walk you through it), and be sure to look at philosophy of education examples from others (we’ve got those too!).
What is a philosophy of education?
Before we dive into the examples, it’s important to understand the purpose of a philosophy of education. This statement will provide an explanation of your teaching values and beliefs. Your teaching philosophy is ultimately a combination of the methods you studied in college and any professional experiences you’ve learned from since. It incorporates your own experiences (negative or positive) in education.
Many teachers have two versions of their teaching philosophy: a long form (a page or so of text) and a short form. The longer form is useful for job application cover letters or to include as part of your teacher portfolio. The short form distills the longer philosophy into a couple of succinct sentences that you can use to answer teacher job interview questions or even share with parents.
What’s the best teaching philosophy?
Here’s one key thing to remember: There’s no one right answer to “What’s your teaching philosophy?” Every teacher’s will be a little bit different, depending on their own teaching style, experiences, and expectations. And many teachers find that their philosophies change over time, as they learn and grow in their careers.
When someone asks for your philosophy of education, what they really want to know is that you’ve given thought to how you prepare lessons and interact with students in and out of the classroom. They’re interested in finding out what you expect from your students and from yourself, and how you’ll apply those expectations. And they want to hear examples of how you put your teaching philosophy into action.
What’s included in strong teaching philosophy examples?
Depending on who you ask, a philosophy of education statement can include a variety of values, beliefs, and information. As you build your own teaching philosophy statement, consider these aspects, and write down your answers to the questions.
Purpose of Education (Core Beliefs)
What do you believe is the purpose of teaching and learning? Why does education matter to today’s children? How will time spent in your classroom help prepare them for the future?
Use your answers to draft the opening statement of your philosophy of education, like these:
- Education isn’t just about what students learn, but about learning how to learn.
- A good education prepares students to be productive and empathetic members of society.
- Teachers help students embrace new information and new ways of seeing the world around them.
- A strong education with a focus on fundamentals ensures students can take on any challenges that come their way.
- I believe education is key to empowering today’s youth, so they’ll feel confident in their future careers, relationships, and duties as members of their community.
- Well-educated students are open-minded, welcoming the opinions of others and knowing how to evaluate information critically and carefully.
Teaching Style and Practices
Do you believe in student-led learning, or do you like to use the Socratic method instead? Is your classroom a place for quiet concentration or sociable collaboration? Do you focus on play-based learning, hands-on practice, debate and discussion, problem-solving, or project-based learning? All teachers use a mix of teaching practices and styles, of course, but there are some you’re likely more comfortable with than others. Possible examples:
- I frequently use project-based learning in my classrooms because I believe it helps make learning more relevant to my students. When students work together to address real-world problems, they use their [subject] knowledge and skills and develop communication and critical thinking abilities too.
- Play-based learning is a big part of my teaching philosophy. Kids who learn through play have more authentic experiences, exploring and discovering the world naturally in ways that make the process more engaging and likely to make a lasting impact.
- In my classroom, technology is key. I believe in teaching students how to use today’s technology in responsible ways, embracing new possibilities and using technology as a tool, not a crutch.
- While I believe in trying new teaching methods, I also find that traditional learning activities can still be effective. My teaching is mainly a mix of lecture, Socratic seminar, and small-group discussions.
- I’m a big believer in formative assessment , taking every opportunity to measure my students’ understanding and progress. I use tools like exit tickets and Kahoot! quizzes, and watch my students closely to see if they’re engaged and on track.
- Group work and discussions play a major role in my instructional style. Students who learn to work cooperatively at a young age are better equipped to succeed in school, in their future careers, and in their communities.
Students and Learning Styles
Why is it important to recognize all learning styles? How do you accommodate different learning styles in your classroom? What are your beliefs on diversity, equity, and inclusion? How do you ensure every student in your classroom receives the same opportunities to learn? How do you expect students to behave, and how do you measure success?
Sample teaching philosophy statements about students might sound like this:
- Every student has their own unique talents, skills, challenges, and background. By getting to know my students as individuals, I can help them find the learning styles that work best for them, now and throughout their education.
- I find that motivated students learn best. They’re more engaged in the classroom and more diligent when working alone. I work to motivate students by making learning relevant, meaningful, and enjoyable.
- We must give every student equal opportunities to learn and grow. Not all students have the same support outside the classroom. So as a teacher, I try to help bridge gaps when I see them and give struggling students a chance to succeed academically.
- I believe every student has their own story and deserves a chance to create and share it. I encourage my students to approach learning as individuals, and I know I’m succeeding when they show a real interest in showing up and learning more every day.
- In my classroom, students take responsibility for their own success. I help them craft their own learning goals, then encourage them to evaluate their progress honestly and ask for help when they need it.
- To me, the best classrooms are those that are the most diverse. Students learn to recognize and respect each other’s differences, celebrating what each brings to the community. They also have the opportunity to find common ground, sometimes in ways that surprise them.
How do I write my philosophy of education?
Think back to any essay you’ve ever written and follow a similar format. Write in the present tense; your philosophy isn’t aspirational, it’s something you already live and follow. This is true even if you’re applying for your first teaching job. Your philosophy is informed by your student teaching, internships, and other teaching experiences.
Lead with your core beliefs about teaching and learning. These beliefs should be reflected throughout the rest of your teaching philosophy statement.
Then, explain your teaching style and practices, being sure to include concrete examples of how you put those practices into action. Transition into your beliefs about students and learning styles, with more examples. Explain why you believe in these teaching and learning styles, and how you’ve seen them work in your experiences.
A long-form philosophy of education statement usually takes a few paragraphs (not generally more than a page or two). From that long-form philosophy, highlight a few key statements and phrases and use them to sum up your teaching philosophy in a couple of well-crafted sentences for your short-form teaching philosophy.
Still feeling overwhelmed? Try answering these three key questions:
- Why do you teach?
- What are your favorite, tried-and-true methods for teaching and learning?
- How do you help students of all abilities and backgrounds learn?
If you can answer those three questions, you can write your teaching philosophy!
Short Philosophy of Education Examples
We asked real educators in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook to share their teaching philosophy examples in a few sentences . Here’s what they had to say:
I am always trying to turn my students into self-sufficient learners who use their resources to figure it out instead of resorting to just asking someone for the answers. —Amy J.

My philosophy is that all students can learn. Good educators meet all students’ differentiated learning needs to help all students meet their maximum learning potential. —Lisa B.
I believe that all students are unique and need a teacher that caters to their individual needs in a safe and stimulating environment. I want to create a classroom where students can flourish and explore to reach their full potential. My goal is also to create a warm, loving environment, so students feel safe to take risks and express themselves. —Valerie T.
In my classroom, I like to focus on the student-teacher relationships/one-on-one interactions. Flexibility is a must, and I’ve learned that you do the best you can with the students you have for however long you have them in your class. —Elizabeth Y
I want to prepare my students to be able to get along without me and take ownership of their learning. I have implemented a growth mindset. —Kirk H.
My teaching philosophy is centered around seeing the whole student and allowing the student to use their whole self to direct their own learning. As a secondary teacher, I also believe strongly in exposing all students to the same core content of my subject so that they have equal opportunities for careers and other experiences dependent upon that content in the future. —Jacky B.

All children learn best when learning is hands-on. This works for the high students and the low students too, even the ones in between. I teach by creating experiences, not giving information. —Jessica R.
As teachers, it’s our job to foster creativity. In order to do that, it’s important for me to embrace the mistakes of my students, create a learning environment that allows them to feel comfortable enough to take chances, and try new methods. —Chelsie L.
I believe that every child can learn and deserves the best, well-trained teacher possible who has high expectations for them. I differentiate all my lessons and include all learning modalities. —Amy S.
All students can learn and want to learn. It is my job to meet them where they are and move them forward. —Holli A.
I believe learning comes from making sense of chaos. My job is to design work that will allow students to process, explore, and discuss concepts to own the learning. I need to be part of the process to guide and challenge perceptions. —Shelly G.

I want my students to know that they are valued members of our classroom community, and I want to teach each of them what they need to continue to grow in my classroom. —Doreen G.
Teach to every child’s passion and encourage a joy for and love of education and school. —Iris B.
I believe in creating a classroom culture of learning through mistakes and overcoming obstacles through teamwork. —Jenn B.
It’s our job to introduce our kids to many, many different things and help them find what they excel in and what they don’t. Then nurture their excellence and help them figure out how to compensate for their problem areas. That way, they will become happy, successful adults. —Haley T.
Longer Philosophy of Education Examples
Looking for longer teaching philosophy examples? Check out these selections from experienced teachers of all ages and grades.
- Learning To Wear the Big Shoes: One Step at a Time
- Nellie Edge: My Kindergarten Teaching Philosophy
- Faculty Focus: My Philosophy of Teaching
- Robinson Elementary School: My Teaching Philosophy
- David Orace Kelly: Philosophy of Education
- Explorations in Higher Education: My Teaching Philosophy Statement
- University of Washington Medical School Faculty Teaching Philosophy Statements
Do you have any philosophy of education examples? Share them in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE Group on Facebook!
Want more articles and tips like this be sure to subscribe to our newsletters to find out when they’re posted..

You Might Also Like
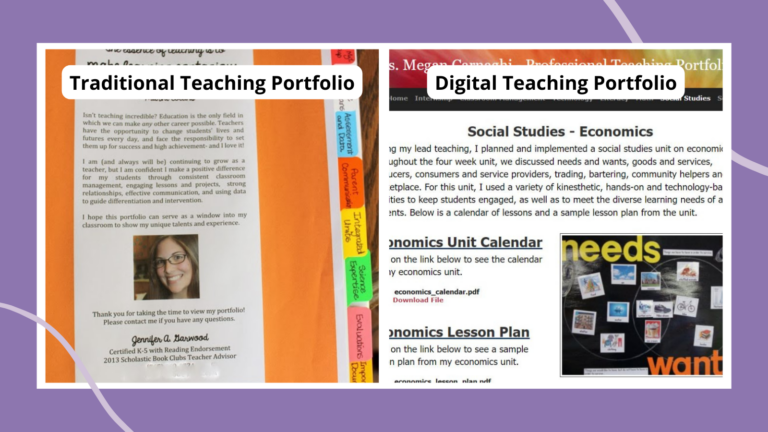
15 Inspiring Teaching Portfolio Examples (Plus How To Create Your Own)
Show them what you've got. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Skip to Content
Other ways to search:
- Events Calendar
How to write your philosophy of education statement

The Philosophy of Education Statement is an important piece in your educator portfolio. It may be requested by hiring personnel at schools to be included with a cover letter and resume. Your teaching philosophy should be thoughtful, organized and well-written. The summary should be between 1-2 pages and should document and support your core educational principles.
- First, state your objectives as a teacher. These need to be achievable through some form of assessment.
- Second, you will want to outline the methods by which you will achieve your teaching objectives.
- Third, you will need to have demonstrated evidence of your achievements. This may take the form of standardized assessments or evaluations.
- Forth, allude to the factors that motivate you to be in the teaching profession. This is where you can be cerebral. State what motivates you to be in the teaching profession.
Some Important Considerations
Your core values and beliefs.
The statement should reflect your core values and beliefs in terms of teaching. Consider your thoughts regarding the nature of students, the purpose of education and how people learn, and the role of teacher. As you develop your educational philosophy, think about completing the following statements:
- I believe the purposes of education are ...
- I believe that students learn best when...
- I believe that the following curriculum basics will contribute to the social, emotional, intellectual and physical development of my students ...
- I believe that a good learning environment is one in which ...
- I believe that all students have the following basic needs ...
- In order to further the growth and learning of my students, these basic needs will be met in my classroom through ...
- I believe that teachers should have the following qualities ...
Why You Teach
- What is the purpose of education?
- What is your role as an educator?
Whom You Teach
- How will you reach the diverse students in your classroom?
- How do you define your community of learners?
How and What You Teach
- What are your beliefs about how students learn?
- How will your beliefs affect your teaching? Think about management, instructional strategies, curriculum design and assessment.
- How do you balance the needs of the individual learner with the needs of the classroom community?
- What are your goals for students?
Where You Teach
- How will you bring a global awareness to your classroom?
- What will be your relationship with the community, parents, teaching colleagues and administration?
Completing the Application
Don't cut corners! As you are completing your applications, keep in mind that they are as important to your job search as your resume, letter of interest and other documents in your application packet. You are encouraged not to rush through completing your applications. Regional applications may be required instead of or in addition to the employer’s individual application.
- Be consistent with the information you provide on the application and on your resume. Make sure there are no contradictions of dates and places of employment and education.
- Do not make up an answer. Be honest. If you embellish, it will eventually catch up with you and you will leave a negative impression on the employer.
- Extra-curricular activities, which you may be willing to sponsor or coach, may be listed on most applications. Your willingness to sponsor activities can sometimes enhance your consideration for positions.
- Follow the application directions exactly. The directions may be different for each application you complete, so read all the directions carefully. Enter the correct information in the correct fields.
- Grammatical rules should be followed at all times. Teachers are held to high standards. Errors are unacceptable.
- Humor in your responses on an application can come across as sarcastic or flippant.
- Remember, an application may be a prospective employer’s first introduction to you; make it a professional one.
- Incomplete applications give the appearance of poor attention to detail. It is always best to respond to each question posed on an application whenever possible. An employer would not ask it if s/he did not want an answer.
- Never answer a question with “See my resume.”

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4 Chapter 4: Foundational Philosophies of Education

A philosophy is often defined as the foundation upon which knowledge is based. However, when you break apart the actual word, a much different meaning emerges. Derived from the Greek “philos,” which means love , and “sophos,” which means wisdom , the actual meaning of the word philosophy is love of wisdom (Johnson et. al., 2011).
In this chapter, we will explore how traditional philosophies have evolved over time by briefly looking at three key branches of philosophy. Then, the schools of philosophy and their influence on education will be presented. Finally, you will hear from educators in the field and see how they put their “philosophies” of education into practice.
Section I: Schools of Philosophy
4.1 Essential Questions
At the end of this section, the following essential questions will be answered:
- What are the four main schools of philosophy?
- Who were the key philosophers within each school of philosophy?
- What are the key implications of each school of philosophy on education today?
There are four broad schools of thought that reflect the key philosophies of education that we know today. These schools of thought are: Idealism, Realism, Pragmatism, and Existentialism. It is important to note that idealism and realism, otherwise known as general or world philosophies, have their roots in the work of the ancient Greek philosophers: Plato and Aristotle. Whereas pragmatism and existentialism are much more contemporary schools of thought.
It is important to study each school of thought because they shape the way we approach education today. Specifically, each school of thought directly impacts how curriculum is developed, implemented, and assessed.
Idealism is a school of philosophy that emphasizes that “ideas or concepts are the essence of all that is worth knowing” (Johnson et. al., 2011, p. 87). In other words, the only true reality is that of ideas. Based on the writings of Plato, this school of philosophy encourages conscious reasoning in the mind. Furthermore, idealists look for, and value, universal or absolute truths and ideas. Consequently, idealists believe that ideas should remain constant throughout the centuries.
Key Philosophers
Plato (ca. 427 – ca. 347 BCE):

4.2 A Closer Look
- How does the Allegory of the Cave give us insight into Plato’s conception of reality?
- What are some other examples of “cave-like” thinking?
- Do you agree with Plato’s premise? Why or why not?
Socrates (ca. 470 – ca. 399 BCE):

4.3 A Closer Look
- In what ways does the Socratic Method actively engage students in the learning process?
- Do you think this method improves students understanding?
- How does this method promote higher-order thinking?
- Elementary Example: Socratic Seminar Strategies for the Second Grade Classroom
- Secondary Example: Scaffolding Discussion Skills with a Socratic Circle
Kant (1724 – 1804):

Educational Implications of Idealism
When translated to the classroom, teachers with an Idealist school of though would emphasize being role models of these absolute truths, ideas, and values. Curriculum would focus on broad ideas, particularly those contained in great works of literature and/or scriptures. Teaching methods used within idealism include: lecture, discussion, and Socratic dialogue. Essential to these teaching methods is posing questions that generate thoughts and spark connections.
Paul (n/d) suggests the following six types of Socratic questions:
- How does this relate to our discussion?

- What would be an example?
- What is another way to look at it?
- What are the consequences of that assumption?
- What was the point of this question?
Realism is a school of philosophy with origins in the work of Aristotle. This philosophy emphasizes that “reality, knowledge, and value exist independent of the human mind” (Johnson, 2011, p. 89). Realists argue for the use of the senses and scientific investigation in order to discover truth. The application of the scientific method also allows individuals to classify things into different groups based on their essential differences.
Aristotle (384 – 322 BCE):

4.4 A Closer Look
- Scientific Method Clip
Locke (1632 – 1704):
John Locke believed in the tabula rasa, or blank tablet, view of the mind. According to this view, a child’s mind is a blank slate when they are born. All the sensory experiences they have after birth fill up the slate through the impressions that are made upon the mind.
4.5 A Closer Look
- Do you agree with Locke’s claim that “at birth our minds are like a sheet of white paper?” Why or why not?
- How is this idea more similar to “nature” vs. “nurture?”
Educational Implications of Realism
Within a realist educational philosophy, the curricular focus is on scientific research and development as Realists’ consider education a matter of reality rather than speculation. The teacher role is to teach students about the world they live in. Realists view the subject expert as the source and authority for determining the curriculum.
Outcomes of this thinking in classrooms today include the appearance of standardized tests, serialized textbooks, and specialized curriculum (Johnson et. al., 2011). Teaching methods used in realism include:

- Critical thinking
- Observation
- Experimentation
Pragmatism is “a process philosophy that stresses evolving and change rather than being” (Johnson et. al., 2011, p. 91). In other words, pragmatists believe that reality is constantly changing so we learn best through experience.

According to pragmatists, the learner is constantly conversing and being changed by the environment with whom he or she is interacting. There is “no absolute and unchanging truth, but rather, truth is what works” (Cohen, 1999, p.1). Based on what is learned at any point and time, the learner or the world in which he or she is interacting can be changed.
Peirce (1839 – 1914):
Charles Sanders Peirce is one of the first pragmatic thinkers. He introduced the pragmatic method in which students are supplied a procedure for constructing and clarifying meanings. In addition, this system helps to facilitate communication among students.
Dewey (1859 – 1952):

Dewey also believed that the application of the “scientific method” could solve an array of problems. He saw ideas as the instruments to solving problems and advocated for the application of the following steps to meet this goal:
- Recognize that the problem exists.
- Clearly define the problem.
- Suggest possible solutions.
- Consider the potential consequences of the possible solutions.
- Carry out further observation and experiment leading to the solution’s acceptance or rejection. (Timm, 2020)
4.6 A Closer Look
- What did the “new” or “Romantic” side believe about education? What did the “old” or “traditional” side believe about education? Which side(s) did Dewey lean toward and why?
- What else did Dewey think we should take into account? Why is this so important to Dewey?
- Why did Dewey want to connect education with society?
- What is the question of education according to Dewey? Do you agree? Why or why not?
Educational Implications of Pragmatism
According to a Pragmatic school of thought, curriculum should be so planned in such a way that it teaches the learner how to think critically rather than what to think. Teaching should, therefore, be more exploratory in nature than explanatory. To promote this approach to teaching, students should be actively engaged in the learning process and be challenged to solve problems. The teachers job is to help support students learning by promoting questioning and problem-solving during the natural course of lesson delivery.
The curriculum is also interdisciplinary. Teaching methods used in pragmatism include:
- Hands-on problem solving
- Experimenting
- Cooperative Learning
Existentialism
Existentialism is a school of philosophy that “focuses on the importance of the individual rather than on external standards” (Johnson et. al., 2011, p. 93). Existentialists believe that our reality is made up of nothing more than our lived experiences, therefore our final realities reside within each of us as individuals. As such, the physical world has no real meaning outside our human experience and there is no objective, authoritative truth about metaphysics, epistemology, and ethics.

Kierkegaard (1813-1855):

Soren Kierkegaard was a Danish minister and philosopher. He is
considered to be the founder of existentialism.
4.7 A Closer Look
- Kierkegaard’s Philosophy
Nietzsche (1844-1900):
Friedrich Nietzcshe stressed the importance of the individuality of each person. According to Johnson et. al. (2011), his work provided a “strategy to liberate people from the oppression of feeling inferior within themselves, and a teaching of how not to judge what one is in relation to what one should be” (p. 95).

Educational Implications of Existentialism
Within an existentialist classroom, subject matter takes second place to helping the students understand and appreciate themselves for who they are as individuals. The teacher’s role is to help students accept individual responsibility for their personal thoughts, feelings, and actions. To do this, the teacher is responsible for creating an environment in which student may freely choose their own preferred way of learning by giving students latitude in their choice of subject matter.
Furthermore, answers come from within the individual in an existential classroom, not from the teacher. For this reason, Existentialists strongly oppose standardized assessments which measure or track student learning. Instead, they want the educational experience of the student to focus on creating opportunities for self-direction and self-actualization of the whole person, not just the mind (Cohen, 1999).
In an Existentialist classroom, curriculum is structured to provide students with experiences that will help unleash their own creativity and self-expression through an emphasis on teaching humanities. For example, rather than emphasizing historical events, existentialists focus upon the actions of historical individuals, each of whom provides possible models for the students’ own behavior. Math and science may be de-emphasized because their subject matter would be considered “cold,” “dry,” “objective,” and therefore less fruitful to self-awareness. In teaching art, existentialism encourages individual creativity and imagination more than copying and imitating established models.
As described above, Existentialist methods focus on the individual. Learning is self-paced, self directed, and includes a great deal of individual contact with the teacher, who relates to each student openly and honestly. Although elements of existentialism occasionally appear in public schools, this philosophy has found wider acceptance in private schools and in alternative public schools founded in the late 1960s and early 1970s.
4.8 A Closer Look
Now that you have learned about the four main schools of thought, let’s find out which one you most align to right now. In order to do this, you are going to take the quiz below. Note: Make sure to write down which school of thought you are based on your quiz results.
- What school of thought were you?
- Do you agree that you align with the school of thought identified by the quiz? Why or why not?
- What are some specific implications for you as a future teacher given the school of thought you were identified as from the quiz?
Section II: Defining your own philosophy
4.9 Essential Questions
- What is a philosophy?
- What elements do you consider to be most important to include in your philosophy of education?
- Think about the elements identified in this section, do you think all of them are essential to include when writing a philosophy of education? Why or why not?

As discussed in section one, there are several key schools of thought that reflect key philosophies of education. In this section, we are going to look at the “definition” of a philosophy. We will also explore the importance of defining your own education philosophy as a future teacher. Finally, we will identify essential elements that should be considered when writing your educational philosophy.
What is a Philosophy?
When asked to think about the following question, what comes to mind: What is a Philosophy?
Common responses include:

• A set of beliefs
• A personal platform
• Our personal thoughts
A philosophy is indeed all of these things, and so much more! According to the New Oxford American Dictionary (2005), a philosophy is “the study of the fundamental nature of knowl- edge, reality, and existence” (p. 1278).
When it comes to our educational philosophy, Webb et. al. (2010) state that our “philosophy of education enables us to recognize certain educational principles that define our views about the learner, the teacher, and the school” (p. 50). As such, it critical to determine what school of thought you most align to as this will shape the way you see the students, curriculum and educational setting.
Articulating Your Philosophy of Education
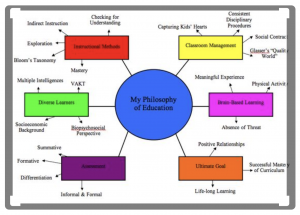
When articulating your philosophy of education, it is essential to reflect on the multiple dimension of teaching that would impact your philosophy. As demonstrated by the diagram, there are a lot of factors to consider. Take a moment to reflect on the diagram, are there any elements you feel are more important than the others? Are there elements missing that you would include? If so, what are they and why do you feel they are important?
When approaching the writing of your philosophy of education, we recommend using the following key elements to ensure that your philosophy of education is well thought out and supported, no matter which school of thought it is based upon.
- Why do you teach?
- Why have you chosen to teach elementary, secondary, or a particular content area?
- What are your values as a teacher?
- FOUNDATIONS OF EDUCATION
- What philosophy of education do you MOST align with and why (revisit Ch. 4 – Ch. 9 of your iBook)?
- How has education changed historically in the last 50/60 years (revisit Ch. 2 & Ch. 3 of your iBook)?
- What impact have movements like the civil rights had on schools (revisit Ch. 2 of your iBook)?
- How have educational policies like NCLB and the standardized testing movement impacted educators and instructional decisions/programming?
- In what ways has the increased diversity in our educational settings impacted the need for teachers to be prepared to address the needs of linguistically and culturally diverse students in their classrooms now more than ever before?
3. UNDERSTANDING OF TEACHING AND LEARNING
- What approaches, methods, pedagogy do you use and why and how are these influenced by the philosophy you MOST aligned with (revisit Ch. 4 – Ch. 9 of your iBook)?
- Which elements of effective instruction do you think are most important to apply to support ALL students learning?
- What strategies do you apply to actively engage ALL your students throughout the lesson?
- How do you motivate your students to learn?
- How do you motivate yourself to be the teacher your students need you to be?
4. CLASSROOM ENVIRONMENT
- How do you create a community of learners (revisit Ch. 1 of your iBook)?
- What is your “code of conduct” (revisit Ch. 1 of your iBook)?
- How do you engage students to limit disruptions and time off task?
- If disruptions do occur, what do you do?
5. INCLUSIVENESS
- Do you understand your own bias and how this impacts your teaching (revisit Ch. 2 of your iBook)?
- How are you effective with ALL students (revisit Ch. 2 of your iBook)?
- How do you create a culturally responsive class room environment (revisit Ch. 1 of your iBook)?
- How do you teach UNCONDITIONALLY so that all your students get the best education possible and you demonstrate respect for the customs and beliefs of the diverse student groups represented in your classroom?
- What specific strategies do you use to support diverse learners?
- In what ways do you act as an advocate for your students, their families, and the community?

Take a moment to reflect on all the information you read about educational philosophies. Your challenge is to write at least a one-page, single-spaced philosophy of education paper that summarizes your current philosophy of education.
Section III: The importance of student voices
4.10 Essential Questions
By the end of this section, the following essential questions will be answered.
- What can we learn from student voices?
- What insights might you gain from the student quotes?
- What did you learn from watching the video clips?
- What links did you make between the what the speakers shared in the video clips and the different schools of thought discussed in this chapter?
To best understand the power of an educational philosophy in practice, this section is going to provide you with two different sets of evidence. The first set of evidence comes from KSU students. The second set comes from a student and two educators in the field. As you read and listen to the information being shared, please reflect on the questions to consider. Although you do not need to document your responses to each of the questions, they have been provided to help you critical reflect on the information being presented.
4.11 Student Voices
- “My philosophical belief is that I want to prepare my children, not for the next grade or college; but for their future in society through tools learned in the classroom.” ASU16
- “I feel that after studying several popular philosophies of education my personal philosophy is a medley of all of them, making it completely mine.” DP U16
- “Every experience I have impacts the way I look at the world and I will continue to strive to keep my teaching the same while as the same time adapting to the needs of my students.” MLU16
4.12 A Closer Look
The following video provides and more in-depth look the importance of having a solid philosophy of education from a student’s point of view. As you watch this video, consider the following questions:
- What insights did you gain from the video?
- Based on the information shared, what school of thought(s) do you think influenced prior educational experiences of this student?
- What school of thought do you think this student is advocating for in the future? Why?
As demonstrated in the student voices, and video by Adora Avitak, being able to articulate your philosophy of education is essential as a future educator. For your philosophy of education shapes your delivery of academic content, but more importantly guides your beliefs when it comes to working with students. To learn more about the importance of how educators view students, let’s watch Rita Pierson.
4.7 A Closer Look
As you listen to Rita Pierson, consider the following questions:
- Based on the information shared, what school of thought(s) do you think influence this teacher?
- How might you apply what you learned from Rita Pierson to your own future practice?
Rita Pierson is such a powerful educator and advocate for students. I hope you learned a lot from her TedTalk! As we wrap up this chapter, I leave you with one final question: How will you be a champion for your future students?!
Media Attributions
- Socrates Aristotle Shakespeare Flintstone © esmemes
- Plato Quote © TraumaAndDissociation
- Socrates Quote © obscuredreamer
- Kant Quote © Butrous Foundation
- Socratic Circle © Samantha Bush
- Aristotle Quote © Mountaingoat Seventeen
- Standardized Test © Alberto G.
- Pragmatism Pic © Kristian Bjornard
- Dewey Quote © PetiteFamily93
- Existentialist Snoopy © Rob S
- Kierkegaard Quote © Max Lagace
- Nietzcshe Quote © SnD Quotes
- Glass half full © Geralt
- Thinking © GlobalUppal
- My Philosophy of Education © Kelsey F. Hawkins
To the extent possible under law, Della Perez has waived all copyright and related or neighboring rights to Social Foundations of K-12 Education , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Philosophy of Education
All human societies, past and present, have had a vested interest in education; and some wits have claimed that teaching (at its best an educational activity) is the second oldest profession. While not all societies channel sufficient resources into support for educational activities and institutions, all at the very least acknowledge their centrality—and for good reasons. For one thing, it is obvious that children are born illiterate and innumerate, and ignorant of the norms and cultural achievements of the community or society into which they have been thrust; but with the help of professional teachers and the dedicated amateurs in their families and immediate environs (and with the aid, too, of educational resources made available through the media and nowadays the internet), within a few years they can read, write, calculate, and act (at least often) in culturally-appropriate ways. Some learn these skills with more facility than others, and so education also serves as a social-sorting mechanism and undoubtedly has enormous impact on the economic fate of the individual. Put more abstractly, at its best education equips individuals with the skills and substantive knowledge that allows them to define and to pursue their own goals, and also allows them to participate in the life of their community as full-fledged, autonomous citizens.
But this is to cast matters in very individualistic terms, and it is fruitful also to take a societal perspective, where the picture changes somewhat. It emerges that in pluralistic societies such as the Western democracies there are some groups that do not wholeheartedly support the development of autonomous individuals, for such folk can weaken a group from within by thinking for themselves and challenging communal norms and beliefs; from the point of view of groups whose survival is thus threatened, formal, state-provided education is not necessarily a good thing. But in other ways even these groups depend for their continuing survival on educational processes, as do the larger societies and nation-states of which they are part; for as John Dewey put it in the opening chapter of his classic work Democracy and Education (1916), in its broadest sense education is the means of the “social continuity of life” (Dewey, 1916, 3). Dewey pointed out that the “primary ineluctable facts of the birth and death of each one of the constituent members in a social group” make education a necessity, for despite this biological inevitability “the life of the group goes on” (Dewey, 3). The great social importance of education is underscored, too, by the fact that when a society is shaken by a crisis, this often is taken as a sign of educational breakdown; education, and educators, become scapegoats.
It is not surprising that such an important social domain has attracted the attention of philosophers for thousands of years, especially as there are complex issues aplenty that have great philosophical interest. Even a cursory reading of these opening paragraphs reveals that they touch on, in nascent form, some but by no means all of the issues that have spawned vigorous debate down the ages; restated more explicitly in terms familiar to philosophers of education, the issues the discussion above flitted over were: education as transmission of knowledge versus education as the fostering of inquiry and reasoning skills that are conducive to the development of autonomy (which, roughly, is the tension between education as conservative and education as progressive, and also is closely related to differing views about human “perfectibility”—issues that historically have been raised in the debate over the aims of education); the question of what this knowledge, and what these skills, ought to be—part of the domain of philosophy of the curriculum; the questions of how learning is possible, and what is it to have learned something—two sets of issues that relate to the question of the capacities and potentialities that are present at birth, and also to the process (and stages) of human development and to what degree this process is flexible and hence can be influenced or manipulated; the tension between liberal education and vocational education, and the overlapping issue of which should be given priority—education for personal development or education for citizenship (and the issue of whether or not this is a false dichotomy); the differences (if any) between education and enculturation; the distinction between educating versus teaching versus training versus indoctrination; the relation between education and maintenance of the class structure of society, and the issue of whether different classes or cultural groups can—justly—be given educational programs that differ in content or in aims; the issue of whether the rights of children, parents, and socio-cultural or ethnic groups, conflict—and if they do, the question of whose rights should be dominant; the question as to whether or not all children have a right to state-provided education, and if so, should this education respect the beliefs and customs of all groups and how on earth would this be accomplished; and a set of complex issues about the relation between education and social reform, centering upon whether education is essentially conservative, or whether it can be an (or, the ) agent of social change.
It is impressive that most of the philosophically-interesting issues touched upon above, plus additional ones not alluded to here, were addressed in one of the early masterpieces of the Western intellectual tradition—Plato's Republic . A.N. Whitehead somewhere remarked that the history of Western philosophy is nothing but a series of footnotes to Plato, and if the Meno and the Laws are added to the Republic , the same is true of the history of educational thought and of philosophy of education in particular. At various points throughout this essay the discussion shall return to Plato, and at the end there shall be a brief discussion of the two other great figures in the field—Rousseau and Dewey. But the account of the field needs to start with some features of it that are apt to cause puzzlement, or that make describing its topography difficult. These include, but are not limited to, the interactions between philosophy of education and its parent discipline.
1.1 The open nature of philosophy and philosophy of education
1.2 the different bodies of work traditionally included in the field, 1.3 paradigm wars the diversity of, and clashes between, philosophical approaches, 2.1 the early work: c.d. hardie, 2.2 the dominant years: language, and clarification of key concepts, 2.3 countervailing forces, 2.4 a new guise contemporary social, political and moral philosophy, 3.1 philosophical disputes concerning empirical education research, 3.2 the content of the curriculum, and the aims and functions of schooling, 3.3 rousseau, dewey, and the progressive movement, 4. concluding remarks, bibliography, other internet resources, related entries, 1. problems in delineating the field.
There is a large—and ever expanding—number of works designed to give guidance to the novice setting out to explore the domain of philosophy of education; most if not all of the academic publishing houses have at least one representative of this genre on their list, and the titles are mostly variants of the following archetypes: The History and Philosophy of Education , The Philosophical Foundations of Education , Philosophers on Education , Three Thousand Years of Educational Wisdom , A Guide to the Philosophy of Education , and Readings in Philosophy of Education . The overall picture that emerges from even a sampling of this collective is not pretty; the field lacks intellectual cohesion, and (from the perspective taken in this essay) there is a widespread problem concerning the rigor of the work and the depth of scholarship—although undoubtedly there are islands, but not continents, of competent philosophical discussion of difficult and socially-important issues of the kind listed earlier. On the positive side—the obverse of the lack of cohesion—there is, in the field as a whole, a degree of adventurousness in the form of openness to ideas and radical approaches, a trait that is sometimes lacking in other academic fields. This is not to claim, of course, that taken individually philosophers of education are more open-minded than their philosophical cousins!
Part of the explanation for this diffuse state-of-affairs is that, quite reasonably, most philosophers of education have the goal (reinforced by their institutional affiliation with Schools of Education and their involvement in the initial training of teachers) of contributing not to philosophy but to educational policy and practice. This shapes not only their selection of topics, but also the manner in which the discussion is pursued; and this orientation also explains why philosophers of education—to a far greater degree, it is to be suspected, than their “pure” cousins—publish not in philosophy journals but in a wide range of professionally-oriented journals (such as Educational Researcher , Harvard Educational Review , Teachers College Record , Cambridge Journal of Education, Journal of Curriculum Studies , and the like). Some individuals work directly on issues of classroom practice, others identify as much with fields such as educational policy analysis, curriculum theory, teacher education, or some particular subject-matter domain such as math or science education, as they do with philosophy of education. It is still fashionable in some quarters to decry having one's intellectual agenda shaped so strongly as this by concerns emanating from a field of practice; but as Stokes (1997) has made clear, many of the great, theoretically-fruitful research programs in natural science had their beginnings in such practical concerns—as Pasteur's grounbreaking work illustrates. It is dangerous to take the theory versus practice dichotomy too seriously.
However, there is another consequence of this institutional housing of the vast majority of philosphers of education that is worth noting—one that is not found in a comparable way in philosophers of science, for example, who almost always are located in departments of philosophy—namely, that experience as a teacher, or in some other education-related role, is a qualification to become a philosopher of education that in many cases is valued at least as much as depth of philosophical training. (The issue is not that educational experience is irrelevant—clearly it can be highly pertinent—but it is that in the tradeoff with philosophical training, philosophy often loses.) But there are still other factors at work that contribute to the field's diffuseness, that all relate in some way to the nature of the discipline of philosophy itself.
In describing the field of philosophy, and in particular the sub-field that has come to be identified as philosophy of education, one quickly runs into a difficulty not found to anything like the same degree in other disciplines. For example, although there are some internal differences in opinion, nevertheless there seems to be quite a high degree of consensus within the domain of quantum physics about which researchers are competent members of the field and which ones are not, and what work is a strong contribution (or potential contribution). The very nature of philosophy, on the other hand, is “essentially contested”; what counts as a sound philosophical work within one school of thought, or socio-cultural or academic setting, may not be so-regarded (and may even be the focus of derision) in a different one. Coupled with this is the fact that the borders of the field are not policed, so that the philosophically-untrained can cross into it freely—indeed, over the past century or more a great many individuals from across the spectrum of real and pseudo disciplines have for whatever reason exercised their right to self-identify as members of this broad and loosely defined category of “philosophers” (as a few minutes spent browsing in the relevant section of a bookstore will verify).
In essence, then, there are two senses of the term “philosopher” and its cognates: a loose but common sense in which any individual who cogitates in any manner about such issues as the meaning of life, the nature of social justice, the essence of sportsmanship, the aims of education, the foundations of the school curriculum, or relationship with the Divine, is thereby a philosopher; and there is a more technical sense referring to those who have been formally trained or have acquired competence in one or more areas such as epistemology, metaphysics, moral philosophy, logic, philosophy of science, and the like. If this bifurcation presents a problem for adequately delineating the field of philosophy, the difficulties grow tenfold or more with respect to philosophy of education.
This essay offers a description and assessment of the field as seen by a scholar rooted firmly in the formal branch of “philosophy of education”, and moreover this branch as it has developed in the English-speaking world (some of which, of course, has been inspired by Continental philosophy); but first it is necessary to say a little more about the difficulties that confront the individual who sets out, without presuppositions, to understand the topography of “philosophy of education”.
It will not take long for a person who consults several of the introductory texts alluded to earlier to encounter a number of different bodies of work (loosely bounded to be sure) that have by one source or another been regarded as part of the domain of philosophy of education; the inclusion of some of these as part of the field is largely responsible for the diffuse topography described earlier. What follows is an informal and incomplete accounting.
First, there are works of advocacy produced by those non-technical, self-identified “philosophers” described above, who often have an axe to grind; they may wish to destroy (or to save) common schooling, support or attack some innovation or reform, shore-up or destroy the capitalist mode of production, see their own religion (or none at all) gain a foothold in the public schools, strengthen the place of “the basics” in the school curriculum, and so forth. While these topics certainly can be, and have been, discussed with due care, often they have been pursued in loose but impressive language where exhortation substitutes for argumentation—and hence sometimes they are mistaken for works of philosophy of education! In the following discussion this genre shall be passed over in silence.
Second, there is a corpus of work somewhat resembling the first, but where the arguments are tighter, and where the authors usually are individuals of some distinction whose insights are thought-provoking—possibly because they have a degree of familiarity with some branch of educational activity, having been teachers (or former teachers), school principals, religious leaders, politicians, journalists, and the like. While these works frequently touch on philosophical issues, they are not pursued to any philosophical depth and can hardly be considered as contributions to the scholarship of the discipline. However, some works in this genre are among the classics of “educational thought”—a more felicitous label than “philosophy of education”; cases in point would be the essays, pamphlets and letters of Thomas Arnold (headmaster of Rugby school), John Wesley (the founder of Methodism), J.H. (Cardinal) Newman, T.H. Huxley, and the writings on progressive schooling by A.S. Neill (of Summerhill school). Some textbooks even include extracts from the writings or recorded sayings of such figures as Thomas Jefferson, Ben Franklin, and Jesus of Nazareth (for the latter three, in works spanning more than half a century, see Ulich, 1950, and Murphy, 2006). Books and extracts in this genre—which elsewhere I have called “cultured reflection on education”—are often used in teacher-training courses that march under the banner of “educational foundations”, “introduction to educational thought”, or “introduction to philosophy of education”.
Third, there are a number of educational theorists and researchers, whose field of activity is not philosophy but—for example—might be human development or learning theory, who in their technical work and sometimes in their non-technical books and reflective essays explicitly raise philosophical issues or adopt philosophical modes of argumentation—and do so in ways worthy of careful study. If philosophy (including philosophy of education) is defined so as to include analysis and reflection at an abstract or “meta-level”, which undoubtedly is a domain where many philosophers labor, then these individuals should have a place in the annals of philosophy or philosophy of education; but too often, although not always, accounts of the field ignore them. Their work might be subjected to scrutiny for being educationally important, but their conceptual or philosophical contributions are rarely focused upon. (Philosophers of the physical and biological sciences are far less prone to make this mistake about the meta-level work of reflective scientists in these domains.)
The educational theorists and researchers I have in mind as exemplars here are the behaviorist psychologist B.F. Skinner (who among other things wrote about the fate of the notions of human freedom and dignity in the light of the development of a “science of behavior”, and who developed a model of human action and also of learning that eschewed the influence of mental entities such as motives, interests, and ideas and placed the emphasis instead upon “schedules of reinforcement”); the foundational figure in modern developmental psychology with its near-fixation on stage theories, Jean Piaget (who developed in an abstract and detailed manner a “genetic epistemology” that was related to his developmental research); and the social psychologist Lev Vygotsky (who argued that the development of the human youngster was indelibly shaped by social forces, so much so that approaches which focused on the lone individual and that were biologically-oriented—he had Piaget in mind here—were quite inadequate).
Fourth, and in contrast to the group above, there is a type of work that is traditionally but undeservedly given a prominent place in the annals of philosophy of education, and which thereby generates a great deal of confusion and misunderstanding about the field. These are the books and reflective essays on educational topics that were written by mainstream philosophers, a number of whom are counted among the greatest in the history of the discipline. The catch is this: Even great philosophers do not always write philosophy! The reflections being referred-to contain little if any philosophical argumentation, and usually they were not intended to be contributions to the literature on any of the great philosophical questions. Rather, they expressed the author's views (or even prejudices) on educational rather than philosophical problems, and sometimes—as in the case of Bertrand Russell's rollicking pieces defending progressive educational practices—they explicitly were “potboilers” written to make money. (In Russell's case the royalties were used to support a progressive school he was running with his current wife.) Locke, Kant, and Hegel also are among those who produced work of this genre.
John Locke is an interesting case in point. He had been requested by a cousin and her husband—possibly in part because of his medical training—to give advice on the upbringing of their son and heir; the youngster seems to have troubled his parents, most likely because he had learning difficulties. Locke, then in exile in Europe, wrote the parents a series of letters in which alongside sensible advice about such matters as the priorities in the education of a landed gentleman, and about making learning fun for the boy, there were a few strange items such as the advice that the boy should wear leaky shoes in winter so that he would be toughened-up! The letters eventually were printed in book form under the title Some Thoughts Concerning Education (1693), and seem to have had enormous influence down the ages upon educational practice; after two centuries the book had run through some 35 English editions and well over thirty foreign editions, and it is still in print and is frequently excerpted in books of readings in philosophy of education. In stark contrast, several of Locke's major philosophical writings—the Essay Concerning Human Understanding , and the Letter on Toleration —have been overlooked by most educational theorists over the centuries, even though they have enormous relevance for educational philosophy, theory, policy, and practice. It is especially noteworthy that the former of these books was the foundation for an approach to psychology—associationism—that thrived during the nineteenth century. In addition it stimulated interest in the processes of child development and human learning; Locke's model of the way in which the “blank tablet” of the human mind became “furnished” with simple ideas that were eventually combined or abstracted in various ways to form complex ideas, suggested to some that it might be fruitful to study this process in the course of development of a young child (Cleverley and Phillips, 1986).
Fifth, and finally, there is a large body of work that clearly falls within the more technically-defined domain of philosophy of education. Three historical giants of the field are Plato, Rousseau, and Dewey, and there are a dozen or more who would be in competition for inclusion along with them; the short-list of leading authors from the second-half of the 20 th century would include Richard Peters, Paul Hirst, and Israel Scheffler, with many jostling for the next places—but the choices become cloudy as we approach the present-day, for schisms between philosophical schools have to be negotiated.
It is important to note, too, that there is a sub-category within this domain of literature that is made-up of work by philosophers who are not primarily identified as philosophers of education, and who might or might not have had much to say directly about education, but whose philosophical work has been drawn upon by others and applied very fruitfully to educational issues. (A volume edited by Amelie Rorty contains essays on the education-related thought, or relevance, of many historically-important philosophers; significantly the essays are almost entirely written by philosophers rather than by members of the philosophy of education community. This is both their strength and weakness. See Rorty, 1998.)
The discussion will turn briefly to the difficulty in picturing the topography of the field that is presented by the influence of these philosophers.
As sketched earlier, the domain of education is vast, the issues it raises are almost overwhelmingly numerous and are of great complexity, and the social significance of the field is second to none. These features make the phenomena and problems of education of great interest to a wide range of socially-concerned intellectuals, who bring with them their own favored conceptual frameworks—concepts, theories and ideologies, methods of analysis and argumentation, metaphysical and other assumptions, criteria for selecting evidence that has relevance for the problems that they consider central, and the like. No wonder educational discourse has occasionally been likened to Babel, for the differences in backgrounds and assumptions means that there is much mutual incomprehension. In the midst of the melee sit the philosophers of education.
It is no surprise, then, to find that the significant intellectual and social trends of the past few centuries, together with the significant developments in philosophy, all have had an impact on the content and methods of argument in philosophy of education—Marxism, psycho-analysis, existentialism, phenomenology, positivism, post-modernism, pragmatism, neo-liberalism, the several waves of feminism, analytic philosophy in both its ordinary language and more formal guises, are merely the tip of the iceberg. It is revealing to note some of the names that were heavily-cited in a pair of recent authoritative handbooks in the field (according to the indices of the two volumes, and in alphabetical order): Adorno, Aristotle, Derrida, Descartes, Dewey, Habermas, Hegel, Horkheimer, Kant, Locke, Lyotard, Marx, Mill, Nietzsche, Plato, Rawls, Richard Rorty, Rousseau, and Wittgenstein (Curren 2003; Blake, Smeyers, Smith, and Standish 2003). Although this list conveys something of the diversity of the field, it fails to do it complete justice, for the influence of feminist philosophers is not adequately represented.
No one individual can have mastered work done by such a range of figures, representing as they do a number of quite different frameworks or approaches; and relatedly no one person stands as emblematic of the entire field of philosophy of education, and no one type of philosophical writing serves as the norm, either. At professional meetings, peace often reigns because the adherents of the different schools go their separate ways; but occasionally there are (intellectually) violent clashes, rivaling the tumult that greeted Derrida's nomination for an honorary degree at Cambridge in 1992. It is sobering to reflect that only a few decades have passed since practitioners of analytic philosophy of education had to meet in individual hotel rooms, late at night, at annual meetings of the Philosophy of Education Society in the USA, because phenomenologists and others barred their access to the conference programs; their path to liberation was marked by discord until, eventually, the compromise of “live and let live” was worked out (Kaminsky, 1996). Of course, the situation has hardly been better in the home discipline; an essay in Time magazine in 1966 on the state of the discipline of philosophy reported that adherents of the major philosophical schools “don't even understand one another”, and added that as a result “philosophy today is bitterly segregated. Most of the major philosophy departments and scholarly journals are the exclusive property of one sect or another” ( Time , reprinted in Lucas, 1969, 32). Traditionally there has been a time-lag for developments in philosophy to migrate over into philosophy of education, but in this respect at least the two fields have been on a par.
Inevitably, however, traces of discord remain, and some groups still feel disenfranchised, but they are not quite the same groups as a few decades ago—for new intellectual paradigms have come into existence, and their adherents are struggling to have their voices heard; and clearly it is the case that—reflecting the situation in 1966—many analytically-trained philosophers of education find postmodern writings incomprehensible while scholars in the latter tradition are frequently dismissive if not contemptuous of work done by the former group. In effect, then, the passage of time has made the field more—and not less—diffuse. All this is evident in a volume published in 1995 in which the editor attempted to break-down borders by initiating dialogue between scholars with different approaches to philosophy of education; her introductory remarks are revealing:
Philosophers of education reflecting on the parameters of our field are faced not only with such perplexing and disruptive questions as: What counts as Philosophy of Education and why?; but also Who counts as a philosopher of education and why?; and What need is there for Philosophy of Education in a postmodern context? Embedded in these queries we find no less provocative ones: What knowledge, if any, can or should be privileged and why?; and Who is in a position to privilege particular discursive practices over others and why? Although such questions are disruptive, they offer the opportunity to take a fresh look at the nature and purposes of our work and, as we do, to expand the number and kinds of voices participating in the conversation. (Kohli, 1995, xiv).
There is an inward-looking tone to the questions posed here: Philosophy of education should focus upon itself, upon its own contents, methods, and practitioners. And of course there is nothing new about this; for one thing, almost forty years ago a collection of readings—with several score of entries—was published under the title What is Philosophy of Education? (Lucas, 1969). It is worth noting, too, that the same attitude is not unknown in philosophy; Simmel is reputed to have said a century or so ago that philosophy is its own first problem.
Having described the general topography of the field of philosophy of education, the focus can change to pockets of activity where from the perspective of this author interesting philosophical work is being, or has been, done—and sometimes this work has been influential in the worlds of educational policy or practice. It is appropriate to start with a discussion of the rise and partial decline—but lasting influence of—analytic philosophy of education This approach (often called “APE” by both admirers and detractors) dominated the field in the English-speaking world for several decades after the second world war, and its eventual fate throws light on the current intellectual climate.
2. Analytic philosophy of education, and its influence
Conceptual analysis, careful assessment of arguments, the rooting out of ambiguity, the drawing of clarifying distinctions—which make up part at least of the philosophical analysis package—have been respected activities within philosophy from the dawn of the field. But traditionally they stood alongside other philosophical activities; in the Republic , for example, Plato was sometimes analytic, at other times normative, and on occasion speculative/metaphysical. No doubt it somewhat over-simplifies the complex path of intellectual history to suggest that what happened in the twentieth century—early on, in the home discipline itself, and with a lag of a decade or more in philosophy of education—is that philosophical analysis came to be viewed by some scholars as being the major philosophical activity (or set of activities), or even as being the only viable or reputable activity (for metaphysics was judged to be literally vacuous, and normative philosophy was viewed as being unable to provide compelling warrants for whatever moral and ethical positions were being advocated).
So, although analytic elements in philosophy of education can be located throughout intellectual history back to the ancient world, the pioneering work in the modern period entirely in an analytic mode was the short monograph by C.D. Hardie, Truth and Fallacy in Educational Theory (1941; reissued in 1962). In his Introduction, Hardie (who had studied with C.D. Broad and I.A. Richards) made it clear that he was putting all his eggs into the ordinary-language-analysis basket:
The Cambridge analytical school, led by Moore, Broad and Wittgenstein, has attempted so to analyse propositions that it will always be apparent whether the disagreement between philosophers is one concerning matters of fact, or is one concerning the use of words, or is, as is frequently the case, a purely emotive one. It is time, I think, that a similar attitude became common in the field of educational theory. (Hardie, 1962, xix)
The first object of his analytic scrutiny in the book was the view that “a child should be educated according to Nature”; he teased apart and critiqued various things that writers through the ages could possibly have meant by this, and very little remained standing by the end of the chapter. Then some basic ideas of Herbart and Dewey were subjected to similar treatment. Hardie's hard-nosed approach can be illustrated by the following: One thing that educationists mean by “education according to Nature” (later he turns to other things they might mean) is that “the teacher should thus act like a gardener” who fosters natural growth of his plants and avoids doing anything “unnatural”(Hardie, 1962, 3). He continues:
The crucial question for such a view of education is how far does this analogy hold? There is no doubt that there is some analogy between the laws governing the physical development of the child and the laws governing the development of a plant, and hence there is some justification for the view if applied to physical education. But the educationists who hold this view are not generally very much concerned with physical education, and the view is certainly false if applied to mental education. For some of the laws that govern the mental changes which take place in a child are the laws of learning …. [which] have no analogy at all with the laws which govern the interaction between a seed and its environment. (Hardie, 1962, 4)
About a decade after the end of the Second World War the floodgates opened and a stream of work in the analytic mode appeared; the following is merely a sample. D.J. O'Connor published An Introduction to Philosophy of Education (1957) in which, among other things, he argued that the word “theory” as it is used in educational contexts is merely a courtesy title, for educational theories are nothing like what bear this title in the natural sciences; Israel Scheffler, who became the paramount philosopher of education in North America, produced a number of important works including The Language of Education (1960), that contained clarifying and influential analyses of definitions (he distinguished reportive, stipulative, and programmatic types) and the logic of slogans (often these are literally meaningless, and should be seen as truncated arguments); Smith and Ennis edited the volume Language and Concepts in Education (1961); and R.D. Archambault edited Philosophical Analysis and Education (1965), consisting of essays by a number of British writers who were becoming prominent—most notably R.S. Peters (whose status in Britain paralleled that of Scheffler in the USA), Paul Hirst, and John Wilson. Topics covered in the Archambault volume were typical of those that became the “bread and butter” of analytic philosophy of education throughout the English-speaking world—education as a process of initiation, liberal education, the nature of knowledge, types of teaching, and instruction versus indoctrination.
Among the most influential products of APE was the analysis developed by Hirst and Peters (1970), and Peters (1973), of the concept of education itself. Using as a touchstone “normal English usage”, it was concluded that a person who has been educated (rather than instructed or indoctrinated) has been (i) changed for the better; (ii) this change has involved the acquisition of knowledge and intellectual skills, and the development of understanding; and (iii) the person has come to care for, or be committed to, the domains of knowledge and skill into which he or she has been initiated. The method used by Hirst and Peters comes across clearly in their handling of the analogy with the concept of “reform”, one they sometimes drew upon for expository purposes. A criminal who has been reformed has changed for the better, and has developed a commitment to the new mode of life (if one or other of these conditions does not hold, a speaker of standard English would not say the criminal has been reformed). Clearly the analogy with reform breaks down with respect to the knowledge and understanding conditions. Elsewhere Peters developed the fruitful notion of “education as initiation”.
The concept of indoctrination was also of great interest to analytic philosophers of education, for—it was argued—getting clear about precisely what constitutes indoctrination also would serve to clarify the border that demarcates it from acceptable educational processes. Unfortunately, ordinary language analysis did not lead to unanimity of opinion about where this border was located, and rival analyses of the concept were put forward (Snook, 1972). Thus, whether or not an instructional episode was a case of indoctrination was determined by: the content that had been taught; or by the intention of the instructor; or by the methods of instruction that had been used; or by the outcomes of the instruction; or, of course, by some combination of these. Adherents of the different analyses used the same general type of argument to make their case, namely, appeal to normal and aberrant usage. Two examples will be sufficient to make the point: (i) The first criterion mentioned above—the nature of the content being imparted—was supported by an argument that ran roughly as follows: “If some students have learned, as factual, some material that is patently incorrect (like ‘The capital city of Canada is Washington D.C.’), then they must have been indoctrinated. This conclusion is reinforced by the consideration that we would never say students must have been indoctrinated if they believe an item that is correct!” However, both portions of this argument have been challenged. (ii) The method criterion—how the knowledge was imparted to the students—usually was supported by an argument that, while different, clearly paralleled the previous one in its logic. It ran roughly like this: “We never would say that students had been indoctrinated by their teacher if he or she had fostered open inquiry and discussion, encouraged exploration in the library and on the net, allowed students to work in collaborative groups, and so on. However, if the teacher did not allow independent inquiry, quashed classroom questions, suppressed dissenting opinions, relied heavily on rewards and punishments, used repetition and fostered rote memorization, and so on, then it is likely we would say the students were being indoctrinated”. (The deeper issue in this second example is that the first method of teaching allows room for the operation of the learners' rationality, while the second method does not. Siegel, 1988, stresses this in his discussion of indoctrination.)
After a period of dominance, for a number of important reasons the influence of APE went into decline. First, there were growing criticisms that the work of analytic philosophers of education had become focused upon minutiae and in the main was bereft of practical import; I can offer as illustration a presidential address at a US Philosophy of Education Society annual meeting that was an hour-long discourse on the various meanings of the expression “I have a toothache”. (It is worth noting that the 1966 article in Time , cited earlier, had put forward the same criticism of mainstream philosophy.) Second, in the early 1970's radical students in Britain accused the brand of linguistic analysis practiced by R.S. Peters of conservatism, and of tacitly giving support to “traditional values”—they raised the issue of whose English usage was being analyzed?
Third, criticisms of language analysis in mainstream philosophy had been mounting for some time, and finally after a lag of many years were reaching the attention of philosophers of education. There even had been a surprising degree of interest in this arcane topic on the part of the general reading public in the UK as early as 1959, when Gilbert Ryle, editor of the journal Mind , refused to commission a review of Ernest Gellner's Words and Things (1959)—a detailed and quite acerbic critique of Wittgenstein's philosophy and its espousal of ordinary language analysis. (Ryle argued that Gellner's book was too insulting, a view that drew Bertrand Russell into the fray on Gellner's side—in the daily press, no less; Russell produced examples of insulting remarks drawn from the work of great philosophers of the past. See Mehta, 1963)
Richard Peters had been given warning that all was not well with APE at a conference in Canada in 1966; after delivering a paper on “The aims of education: A conceptual inquiry” that was based on ordinary language analysis, a philosopher in the audience (William Dray) asked Peters “ whose concepts do we analyze?” Dray went on to suggest that different people, and different groups within society, have different concepts of education. Five years before the radical students raised the same issue, Dray pointed to the possibility that what Peters had presented under the guise of a “logical analysis” was nothing but the favored usage of a certain class of persons—a class that Peters happened to identify with. (See Peters, 1973, where to the editor's credit the interaction with Dray is reprinted.)
Fourth, during the decade of the seventies when these various critiques of analytic philosophy were in the process of eroding its luster, a spate of translations from the Continent stimulated some philosophers of education in Britain and North America to set out in new directions, and to adopt a new style of writing and argumentation. Key works by Gadamer, Foucault, and Derrida appeared in English, and these were followed in 1984 by Lyotard's foundational work on The Postmodern Condition . The classic works of Heidegger and Husserl also found new admirers; and feminist philosophers of education were finding their voices—Maxine Greene published a number of pieces in the 1970s; the influential book by Nel Noddings, Caring: A Feminine Approach to Ethics and Moral Education , appeared the same year as the work by Lyotard, followed a year later by Jane Roland Martin's Reclaiming a Conversation . APE was no longer the center of interest.
By the 1980s, the rather simple if not simplistic ordinary language analysis practiced in philosophy of education, was reeling under the attack from the combination of forces sketched above, but the analytic spirit lived on in the form of rigorous work done in other specialist areas of philosophy—work that trickled out and took philosophy of education in rich new directions. Technically-oriented epistemology, philosophy of science, and even metaphysics, flourished; as did the interrelated fields of social, political and moral philosophy. John Rawls published A Theory of Justice in 1971; a decade later MacIntyre's After Virtue appeared; and in another decade or so there was a flood of work on individualism, communitarianism, democratic citizenship, inclusion, exclusion, rights of children versus rights of parents, rights of groups (such as the Amish) versus rights of the larger polity. From the early 1990s philosophers of education have contributed significantly to the debates on these and related topics—indeed, this corpus of work illustrates that good philosophy of education flows seamlessly into work being done in mainstream areas of philosophy. Illustrative examples are Creating Citizens: Political Education and Liberal Democracy , Callan (1997); The Demands of Liberal Education , Levinson (1999); Social Justice and School Choice , Brighouse (2000); and Bridging Liberalism and Multiculturalism in American Education , Reich (2002). These works stand shoulder-to-shoulder with semi-classics on the same range of topics by Gutmann, Kymlicka, Macedo, and others. An excerpt from the book by Callan nicely illustrates that the analytic spirit lives on in this body of work; the broader topic being pursued is the status of the aims of education in a pluralistic society where there can be deep fundamental disagreements:
… the distinction must be underlined between the ends that properly inform political education and the extent to which we should tolerate deviations from those ends in a world where reasonable and unreasonable pluralism are entangled and the moral costs of coercion against the unreasonable variety are often prohibitive. Our theoretical as well as our commonsense discourse do not always respect the distinction…. If some of the teachings of the Roman Catholic Church conflict with our best theory of the ends of civic education, it does not follow that we have any reason to revise our theory; but neither does it mean we have any reason to impose these ends on Catholic schools and the families that they serve. (Callan, 1997, 44)
Callan and White (2003) have given an analysis of why the topics described above have become such a focus of attention. “What has been happening in philosophy of education in recent years”, they argue, mirrors “a wider self-examination in liberal societies themselves”. World events, from the fall of communism to the spread of ethnic conflicts “have all heightened consciousness of the contingency of liberal politics”. A body of work in philosophy, from the early Rawls on, has systematically examined (and critiqued) the foundations of liberalism, and philosophy of education has been drawn into the debates. Callan and White mention communitarianism as offering perhaps “the most influential challenge” to liberalism, and they write:
The debate between liberals and communitarians is far more than a theoretical diversion for philosophers and political scientists. At stake are rival understandings of what makes human lives and the societies in which they unfold both good and just, and derivatively, competing conceptions of the education needed for individual and social betterment. (Callan and White, 2003, 95-96)
It should be appended here that it is not only “external” world events that have stimulated this body of work; events internal to a number of democratic societies also have been significant. To cite one example that is prominent in the literature in North America at least, the US Supreme Court issued a ruling ( Wisconsin v. Yoder ) in which members of the Amish sect were allowed to withdraw their children from public schools before they had reached the age of sixteen—for, it had been argued, any deeper education would endanger the existence of the group and its culture. In assessing this decision—as of course philosophers have frequently done (see, for example, Kymlicka, 1995)—a balance has to be achieved between (i) the interest of civic society in having an informed, well-educated, participatory citizenry; (ii) the interest of the Amish as a group in preserving their own culture; and (iii) the interests of the Amish children, who have a right to develop into autonomous individuals who can make reflective decisions for themselves about the nature of the life they wish to lead. These are issues that fall squarely in the domain covered by the works mentioned above.
So much work is being produced on the complex and interrelated issues just outlined, that in a different context it seemed fair for me to remark (descriptively, and not judgmentally) that a veritable cottage industry had sprung up in post-Rawlsian philosophy of education. There are, of course, other areas of activity, where interesting contributions are being made, and the discusion will next turn to a sampling of these.
3. Other areas of contemporary activity
As was stressed at the outset, and illustrated with a cursory listing of examples, the field of education is huge and contains within it a virtually inexhaustible number of issues that are of philosophical interest. To attempt comprehensive coverage of how philosophers of education have been working within this thicket would be a quixotic task for a large single volume, and is out of the question for a solitary encyclopedia entry. Nevertheless, a valiant attempt to give an overview was made in the recent A Companion to the Philosophy of Education (Curren, 2003), which contained more than six-hundred pages divided into fourty-five chapters each of which surveyed a subfield of work. The following random selection of chapter topics gives a sense of the enormous scope of the field: Sex education, special education, science education, aesthetic education, theories of teaching and learning, religious education, knowledge and truth in learning, cultivating reason, the measurement of learning, multicultural education, education and the politics of identity, education and standards of living, motivation and classroom management, feminism, critical theory, postmodernism, romanticism, purposes of universities in a fluid age, affirmative action in higher education, and professional education.
There is no non-arbitrary way to select a small number of topics for further discussion, nor can the topics that are chosen be pursued in great depth. The choice of those below has been made with an eye to filling out—and deepening—the topographical account of the field that was presented in the preceding sections. The discussion will open with a topic that was not included in the Companion , despite it being one that is of great concern across the academic educational community, and despite it being one where adherents of some of the rival schools of philosophy (and philosophy of education) have had lively exchanges.
The educational research enterprise has been criticized for a century or more by politicians, policymakers, administrators, curriculum developers, teachers, philosophers of education, and by researchers themselves—but the criticisms have been contradictory. Charges of being “too ivory tower and theory-oriented” are found alongside “too focused on practice and too atheoretical”; but particularly since publication of the book by Stokes mentioned earlier, and also in light of the views of John Dewey and William James that the function of theory is to guide intelligent practice and problem-solving, it is becoming more fashionable to hold that the “theory v. practice” dichotomy is a false one.
A similar trend can be discerned with respect to the long warfare between two rival groups of research methods—on one hand quantitative/statistical approaches to research, and on the other hand the qualitative/ethnographic family. (The choice of labels here is its not entirely risk-free, for they have been contested; furthermore the first approach is quite often associated with “experimental” studies, and the latter with “case studies”, but this is an over-simplification.) For several decades these two rival methodological camps were treated by researchers and a few philosophers of education as being rival paradigms (Kuhn's ideas, albeit in a very loose form, have been influential in the field of educational research), and the dispute between them was commonly referred-to as “the paradigm wars”. In essence the issue at stake was epistemolgical: members of the quantitative/experimental camp believed that only their methods could lead to well-warranted knowledge claims, especially about the causal factors at play in educational phenomena, and on the whole they regarded qualitative methods as lacking in rigor; on the other hand the adherents of qualitative/ethnographic approaches held that the other camp was too “positivistic” and was operating with an inadequate view of causation in human affairs—one that ignored the role of motives and reasons, possession of relevant background knowledge, awareness of cultural norms, and the like. Few if any commentators in the “paradigm wars” suggested that there was anything prohibiting the use of both approaches in the one research program—provided that if both were used, they only were used sequentially or in parallel, for they were underwritten by different epistemologies and hence could not be blended together. But recently the trend has been towards rapprochement, towards the view that the two methodological families are, in fact, compatible and are not at all like paradigms in the Kuhnian sense(s) of the term; the melding of the two approaches is often called “mixed methods research”, and it is growing in popularity. (For more detailed discussion of these “wars” see Howe, 2003, and Phillips, 2008.)
The most lively contemporary debates about education research, however, were set in motion around the turn of the millenium when the US Federal Government moved in the direction of funding only rigorously scientific educational research—the kind that could establish causal factors which could then guide the development of practically effective policies. (It was held that such a causal knowledge base was available for medical decisionmaking.) The definition of “rigorously scientific”, however, was decided by politicans and not by the research community, and it was given in terms of the use of a specific research method—the net effect being that the only research projects to receive Federal funding were those that carried out randomized controlled experiments or field trials (RFTs). It has beome common over the last decade to refer to the RFT as the “gold standard” methodology.
The National Research Council (NRC)—an arm of the U.S. National Academies of Science—issued a report, influenced by postpostivistic philosophy of science (NRC, 2002), that argued this criterion was far too narrow. Numerous essays have appeared subsequently that point out how the “gold standard” account of scientific rigor distorts the history of science, how the complex nature of the relation between evidence and policy-making has been distorted and made to appear overly simple (for instance the role of value-judgments in linking empirical findings to policy directives is often overlooked), and qualitative researchers have insisted upon the scientific nature of their work.
Nevertheless, and possibly because it tried to be balanced and supported the use of RFTs in some research contexts, the NRC report has been the subject of symposia in four journals, where it has been supported by a few and attacked from a variety of philosophical fronts: Its authors were positivists, they erroneously believed that educational inquiry could be value-neutral and that it could ignore the ways in which exercise of power constrains the research process, they misunderstood the nature of educational phenomena, they were guilty of advocating “your father's paradigm”(clearly this was not intended as a compliment). One critic with postmodernist leanings asserted that educational research should move “toward a Nietzschean sort of ‘unnatural science’ that leads to greater health by fostering ways of knowing that escape normativity”—a suggestion that evokes the reaction discussed in Section 1.3 above, namely, one of incomprehension on the part of most researchers and those philosophers of education who work within a different tradition where a “way of knowing”, in order to be a “way”, must inevitably be normative.
The final complexity in the debates over the nature of educational research is that there are some respected members of the philosophy of education community who claim, along with Carr, that “the forms of human association characteristic of educational engagement are not really apt for scientific or empirical study at all” (Carr, 2003, 54-5). His reasoning is that educational processes cannot be studied empirically because they are processes of “normative initiation”—a position that as it stands begs the question by not making clear why such processes cannot be studied empirically.
The issue of what should be taught to students at all levels of education—the issue of curriculum content—obviously is a fundamental one, and it is an extraordinarily difficult one with which to grapple. In tackling it, care needs to be taken to distinguish between education and schooling—for although education can occur in schools, so can mis-education (as Dewey pointed out), and many other things can take place there that are educationally orthogonal (such as the provision of free or subsidized lunches, or the development of social networks); and it also must be recognized that education can occur in the home, in libraries and museums, in churches and clubs, in solitary interaction with the public media, and the like.
In developing a curriculum (whether in a specific subject area, or more broadly as the whole range of offerings in an educational institution or in a system), a number of difficult decisions need to be made. Issues such as the proper ordering or sequencing of topics in the chosen subject, the time to be allocated to each topic, the lab work or excursions or projects that are appropriate for particular topics, can all be regarded as technical issues best resolved either by educationists who have a depth of experience with the target age group or by experts in the psychology of learning and the like. But there are deeper issues, ones concerning the validity of the justifications that have been given for including particular subjects or topics in the offerings of formal educational institutions. (Why is evolution included, or excluded, as a topic within the standard high school subject Biology? Why is Driver Education part of the high school curriculum, and methods of birth control usually not—even though sex has an impact on the life of teenagers that at least is comparable to the impact of car-driving? Is the justification that is given for teaching Economics in some schools coherent and convincing? Does the justification for not including the Holocaust or the phenomenon of wartime atrocities in the curriculum in some countries stand up to critical scrutiny?)
The different justifications for particular items of curriculum content that have been put forward by philosophers and others since Plato's brilliant pioneering efforts all draw upon, explicitly or implicitly, the positions that the respective theorists hold about at least three sets of issues. First, what are the aims and/or functions of education (aims and functions are not necessarily the same), or alternatively, what constitutes the good life and human flourishing. These two formulations are related, for presumably our educational institutions should aim to equip individuals to pursue this good life. Thus, for example, if our view of human flourishing includes the capacity to act rationally and/or autonomously, then the case can be made that educational institutions—and their curricula—should aim to prepare, or help to prepare, autonomous individuals. How this is to be done, of course, is not immediately obvious, and much philosophical ink has been spilled on the matter. One influential line of argument was developed by Paul Hirst, who argued that knowledge is essential for developing a conception of the good life, and then for pursuing it; and because logical analysis shows—he argued—that there are seven basic forms of knowledge, the case can be made that the function of the curriculum is to introduce students to each of these forms. Luckily for Hirst, the typical British high school day was made up of seven instructional periods. (Hirst, 1965; for a critique see Phillips, 1987, ch.11.)
Second, is it justifiable to treat the curriculum of an educational institution as vehicle for furthering the socio-political interests and goals of a ruler or ruling class; and relatedly, is it justifiable to design the curriculum so that it serves as a medium of control or of social engineering? In the closing decades of the twentieth century there were numerous discussions of curriculum theory, particularly from Marxist and postmodern perspectives, that offered the sobering analysis that in many educational systems, including those in Western democracies, the curriculum did indeed reflect, and serve, the interests of the ruling class. Michael Apple is typical:
… the knowledge that now gets into schools is already a choice from a much larger universe of possible social knowledge and principles. It is a form of cultural capital that comes from somewhere, that often reflects the perspectives and beliefs of powerful segments of our social collectivity. In its very production and dissemination as a public and economic commodity—as books, films, materials, and so forth—it is repeatedly filtered through ideological and economic commitments. Social and economic values, hence, are already embedded in the design of the institutions we work in, in the ‘formal corpus of school knowledge’ we preserve in our curricula….(Apple, 1990, 8-9)
Third, should educational programs at the elementary and secondary levels be made up of a number of disparate offerings, so that individuals with different interests and abilities and affinities for learning can pursue curricula that are suitable? Or should every student pursue the same curriculum as far as each is able—a curriculum, it should be noted, that in past cases nearly always was based on the needs or interests of those students who were academically inclined or were destined for elite social roles. Mortimer Adler and others in the late twentieth century (who arguably were following Plato's lead in the Republic ), sometimes used the aphorism “the best education for the best is the best education for all”.
The thinking here can be explicated in terms of the analogy of an out-of-control virulent disease, for which there is only one type of medicine available; taking a large dose of this medicine is extremely beneficial, and the hope is that taking only a little—while less effective—is better than taking none at all! Medically, this probably is dubious, while the educational version—forcing students to work, until they exit the system, on topics that do not interest them and for which they have no facility or motivation—has even less merit. (For a critique of Adler and his Paideia Proposal , see Noddings, 2007.) It is interesting to compare the modern “one curriculum track for all” position with Plato's system outlined in the Republic , according to which all students—and importantly this included girls—set out on the same course of study. Over time, as they moved up the educational ladder it would become obvious that some had reached the limit imposed upon them by nature, and they would be directed off into appropriate social roles in which they would find fulfillment, for their abilities would match the demands of these roles. Those who continued on with their education would eventually be able to contemplate the metaphysical realm of the “forms”, thanks to their advanced training in mathematics and philosophy. Having seen the form of the Good, they would be eligible after a period of practical experience to become members of the ruling class of Guardians.
Plato's educational scheme was guided, presumably, by the understanding he thought he had achieved of the transcendental realm of fixed “forms”. John Dewey, ever a strong critic of positions that were not naturalistic, or that incorporated a priori premises, commented as follows:
Plato's starting point is that the organization of society depends ultimately upon knowledge of the end of existence. If we do not know its end, we shall be at the mercy of accident and caprice…. And only those who have rightly trained minds will be able to recognize the end, and ordering principle of things. (Dewey, 1916, 102-3)
Furthermore, as Dewey again put it, Plato “had no perception of the uniqueness of individuals…. they fall by nature into classes”, which masks the “infinite diversity of active tendencies” which individuals harbor (104). In addition, Plato tended to talk of learning using the passive language of seeing, which has shaped our discourse down to the present (witness “Now I see it!” when a difficult point has become clear).
In contrast, for Dewey each individual was an organism situated in a biological and social environment in which problems were constantly emerging, forcing the individual to reflect and act, and learn. Dewey, following William James, held that knowledge arises from reflection upon our actions; and the worth of a putative item of knowledge is directly correlated with the problem-solving success of the actions performed under its guidance. Thus Dewey, sharply disagreeing with Plato, regarded knowing as an active rather than a passive affair—a strong theme in his writings is his opposition to what is sometimes called “the spectator theory of knowledge”. All this is made clear enough in a passage containing only a thinly-veiled allusion to Plato's famous analogy of the prisoners in the cave whose eyes are turned to the light by education:
In schools, those under instruction are too customarily looked upon as acquiring knowledge as theoretical spectators, minds which appropriate knowledge by direct energy of intellect. The very word pupil has almost come to mean one who is engaged not in having fruitful experiences but in absorbing knowledge directly. Something which is called mind or consciousness is severed from the physical organs of activity. (164)
This passage also illuminates a passage that many have found puzzling: “philosophy is the theory of education” (387). For in the sentences above it is easy to see the tight link between Dewey's epistemology and his views on education—his anti-spectator epistemology morphs directly into advocacy for anti-spectator learning by students in school—students learn by being active inquirers. Over the past few decades this view of learning has inspired a major tradition of research by educational psychologists, and related theory-development (the “situated cognition” framework); and these bodies of work have in turn led to innovative efforts in curriculum development. (For a discussion of these, see Phillips, 2003.)
The final important difference with Plato is that, for Dewey, each student is an individual who blazes his or her unique trail of growth; the teacher has the task of guiding and facilitating this growth, without imposing a fixed end upon the process. Dewey sometimes uses the term “curriculum” to mean “the funded wisdom of the human race”, the point being that over the course of human history an enormous stock of knowledge and skills has accumulated and the teacher has the task of helping the student to make contact with this repertoire—but helping by facilitating rather than by imposing. (All this, of course, has been the subject of intense discussion among philosophers of education: Does growth imply a direction? Is growth always good—can't a plant end up misshapen, and can't a child develop to become bad? Is Dewey some type of perfectionist? Is his philosophy too vague to offer worthwhile educational guidance? Isn't it possible for a “Deweyan” student to end up without enough relevant knowledge and skills to be able to make a living in the modern world?)
Dewey's work was of central importance for the American progressive education movement in its formative years, although there was a fair degree of misunderstanding of his ideas as progressives interpreted his often extremely dense prose to be saying what they personally happened to believe. Nevertheless, Dewey became the “poster child” or the “house philosopher” of progressive education, and if he didn't make it onto many actual posters he certainly made it onto a postage stamp.
His popularity, however, sharply declined after the Soviets launched Sputnik, for Dewey and progressive education were blamed for the USA losing the race into space (illustrating the point about scapegoating made at the start of this essay). But he did not remain in disgrace for long; and for some time has been the focus of renewed interest—although it is still noticeable that commentators interpret Dewey to be holding views that mirror their own positions or interests. And interestingly, there now is slightly more interest in Dewey on the part of philosophers of education in the UK than there was in earlier years, and there is growing interest by philosophers from the Continent (see, for example, Biesta and Burbules, 2003).
To be a poster child for progressivism, however, is not to be the parent. Rather than to Dewey, that honor must go to Jean-Jacques Rousseau, and to his educational novel written in soaring prose, Emile (1762). Starting with the premise that “God makes all things good; man meddles with them and they become evil” (Rousseau, 1955, 5), Rousseau held that contemporary man has been misshapen by his education; the “crushing force” of social conventions has stifled the “Nature within him”. The remedy adopted in the novel is for the young Emile to be taken to his family estate in the country where, away from the corrupting influence of society, and under the watchful eye of his tutor, “everything should … be brought into harmony with these natural tendencies”. (This idea of education according to nature, it will be recalled, was the object of Hardie's analytic attention almost two centuries later.)
Out in the countryside, rather than having a set curriculum that he is forced to follow, Emile learns when some natural stimulus or innate interest motivates him—and under these conditions learning comes easily. He is allowed to suffer the natural consequences of his actions (if he breaks a window, he gets cold; if he takes the gardener's property, the gardener will no longer do him favors), and experiences such as these lead to the development of his moral system. Although Rousseau never intended these educational details to be taken literally as a blueprint (he saw himself as developing and illustrating the basic principles), over the ages there have been attempts to implement them, one being the famous British “free school”, A.S. Neill's Summerhill. (It is worth noting that Neill claimed not to have read Rousseau; but he was working in a milieu in which Rousseau's ideas were well-known—intellectual influence can follow a less than direct path.) Furthermore, over the ages these principles also have proven to be fertile soil for philosophers of education to till.
Even more fertile ground for comment, in recent years, has been Rousseau's proposal for the education of girls, developed in a section of the novel (Book V) that bears the name of the young woman who is destined to be Emile's soul-mate, Sophy. The puzzle has been why Rousseau—who had been so far-sighted in his discussion of Emile's education—was so hide-bound if not retrograde in his thinking about her education. One short quotation is sufficient to illustrate the problem: “If woman is made to please and to be in subjection to man, she ought to make herself pleasing in his eyes and not provoke him …her strength is in her charms” (324).
The educational principles developed by Rousseau and Dewey, and numerous educational theorists and philosophers in the interregnum, are alive and well in the twenty-first century. Of particular contemporary interest is the evolution that has occurred of the progressive idea that each student is an active learner who is pursuing his or her own individual educational path. By incorporating elements of the classical empiricist epistemology of John Locke, this progressive principle has become transformed into the extremely popular position known as constructivism, according to which each student in a classroom constructs his or her own individual body of understandings even when all in the group are given what appears to be the same stimulus or educational experience. (A consequence of this is that a classroom of thirty students will have thirty individually-constructed, and possibly different, bodies of “knowledge”, in addition to that of the teacher!) There is also a solipsistic element here, for constructivists also believe that none of us—teachers included—can directly access the bodies of understandings of anyone else; each of us is imprisoned in a world of our own making. It is an understatement to say that this poses great difficulties for the teacher. The education journals of the past two decades contain many thousands of references to discussions of this position, which elsewhere I claimed has become a type of educational “secular religion”; for reasons that are hard to discern it is particularly influential in mathematics and science education. (For a discussion of the underlying philosophical ideas in constructivism, and for an account of some of its varieties, see the essays in Phillips, ed., 2000.)
As stressed earlier, it is impossible to do justice the whole field of philosophy of education in a single encyclopedia entry. Different countries around the world—France, Germany, the Netherlands, Japan, to mention only a few—have their own intellectual traditions, and their own ways of institutionalizing philosophy of education into the academic universe, and no discussion of any of this appears in the present essay. But even in the Anglo-American world, there is such a diversity of approaches to the discipline that any author attempting to produce a synoptic account will quickly run into the borders of his or her areas of competence. Clearly this has happened in the present case.
Fortunately, in the last twenty years or so resources have become available that significantly alleviate these problems. There has been a flood of encyclopedia entries, commenting on the field as a whole or on many specific topics not well-covered in the present essay (see, as a sample, Burbules, 1994; Chambliss, 1996; Phillips, 1985; Siegel, 2007; Smeyers, 1994); two large volumes—a “Guide” (Blake, Smeyers, Smith and Standish, 2003) and a “Companion” (Curren, 2003)—have been produced by Blackwell in their well-known philosophy series; and the same publisher recently released an anthology, with 60 papers considered to be important in the field, and which also are representative of the range of work that is being done (Curren, 2007). Several encyclopedias of philosophy of education have been published or are in the works (for example, Chambliss, 1996; Siegel, 2008); there is a dictionary of key concepts in the field (Winch and Gingell, 1999), and a good textbook or two (see Noddings, 2007); in addition there are numerous volumes both of reprinted selections and of specially commissioned essays on specific topics, some of which were given short shrift in the present work (for another sampling see A. Rorty, 1998; Smeyers and Marshall, 1995; Stone, 1994); and several international journals appear to be flourishing— Educational Philosophy and Theory , Educational Theory , Journal of Philosophy of Education , Studies in Philosophy and Education , Theory and Research in Education . Thus there is enough material available to keep the interested reader busy, and to provide alternative assessments to the ones presented in this present essay.
- Apple, M., 1990, Ideology and Curriculum , New York: Routledge, 2 nd . Editon.
- Archambault, R., (ed.), 1965, Philosophical Analysis and Education , London: Routledge.
- Biesta, G., and Burbules, N., 2003, Pragmatism and Educational Research , Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
- Blake, N., Smeyers, P., Smith, R., and Standish, P., (eds.), 2003, The Blackwell Guide to the Philosophy of Education , Oxford: Blackwell.
- Brighouse, H., 2000, Social Justice and School Choice , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Burbules, N., 1994, “Marxism and Educational Thought”, in The International Encyclopedia of Education , (Volume 6), T. Husen and N. Postlethwaite (eds.), Oxford: Pergamon, 2 nd . Edition, pp. 3617-22.
- Callan, E., 1997, Creating Citizens: Political Education and Liberal Democracy , Oxford: Clarendon Press, Oxford.
- Callan, E., and White, J., 2003, “Liberalism and Communitarianism”, in The Blackwell Guide to the Philosophy of Education , N. Blake, P. Smeyers, R. Smith and P. Standish (eds.), Oxford: Blackwell, pp.95-109.
- Carr, D., 2003, Making Sense of Education: An Introduction to the Philosophy and Theory of Education and Teaching , London: RoutledgeFalmer.
- Chambliss, J., 1996, “History of Philosophy of Education”, in Philosophy of Education: An Encyclopedia , J. Chambliss (ed.), New York: Garland, pp.461-72.
- Cleverley, J., and Phillips, D.C., 1986, Visions of Childhood , New York: Teachers College Press.
- Curren, R., (ed.), 2003, A Companion to the Philosophy of Education , Oxford: Blackwell.
- Curren, R., (ed.), 2007, Philosophy of Education: An Anthology , Oxford: Blackwell.
- Dewey, J., 1916, Democracy and Education: An Introduction to the Philosophy of Education , New York: Macmillan.
- Gellner, E., 1959, Words and Things , London: Gollancz.
- Hardie, C., 1962, Truth and Fallacy in Educational Theory , New York: Teachers College Bureau of Publications.
- Hirst, P., 1965, “Liberal Education and the Nature of Knowledge”, in Philosophical Analysis and Education , R. Archambault, (ed.), London: Routledge, pp. 113-138.
- Hirst, P., and Peters, R., 1970, The Logic of Education , London: Routledge.
- Howe, K., 2003, Closing Methodological Divides: Toward Democratic Educational Research . Dordrecht: Kluwer.
- Kaminsky, J., 1996, “Philosophy of Education: Professional Organizations In”, in Philosophy of Education: An Encyclopedia , J. Chambliss, (ed.), New York: Garland, pp. 475-79.
- Kohli, W., (ed.), 1995, Critical Conversations in Philosophy of Education , New York: Routledge.
- Kymlicka, W., 1995, Multicultural Citizenship , Oxford: Clarendon Press, Oxford.
- Levinson, M., 1999, The Demands of Liberal Education , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Lucas, C., (ed.), 1969, What is Philosophy of Education? London: Macmillan.
- Martin, J., 1985, Reclaiming a Conversation , New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press.
- Mehta, V., 1963, Fly and the Fly-Bottle : London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson.
- Murphy, M., (ed.), 2006, The History and Philosophy of Education: Voices of Educational Pioneers , New Jersey: Pearson.
- Noddings, N., 1984, Caring: A Feminine Approach to Ethics and Moral Education , Berkeley: University of California Press.
- –––, 2007, Philosophy of Education , Boulder, CO: Westview, 2 nd . Edition.
- National Research Council (NRC), 2002, Scientific Research in Education , Washington, DC: National Academies Press.
- O'Connor, D., 1957, An Introduction to Philosophy of Education , London: Routledge.
- Peters, R., (ed.), 1973, The Philosophy of Education , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Phillips, D.C., 1985, “Philosophy of Education”, in International Encyclopedia of Education, T. Husen and N. Postletwaite, (eds.), pp.3859-3877.
- –––, 1987, Philosophy, Science, and Social Inquiry , Oxford: Pergamon.
- –––, (ed.), 2000, Constructivism in Education: Opinions and Second Opinions on Controversial Issues , (Series: 99 th . Yearbook of the National Society for the Study of Education), Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- –––, 2003, “Theories of Teaching and Learning”, in A Companion to the Philosophy of Education , R. Curren, (ed.), Oxford: Blackwell, pp. 232-245.
- –––, 2008, “Empirical Educational Research: Charting Philosophical Disagreements in an Undisciplined Field”, in The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Education , H. Siegel (ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, in press.
- Reich, R., 2002, Bridging Liberalism and Multiculturalism in American Education , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Rorty, A., (ed.), 1998, Philosophers on Education: New Historical Perspectives , New York: Routledge.
- Rousseau, J-J., 1955, Emile , B. Foxley, (tr.), London: Dent/Everyman.
- Scheffler, I., 1960, The Language of Education , Illinois: Thomas.
- Siegel, H., 1988, Educating Reason: rationality, Critical Thinking, and Education , New York: Routledge.
- –––, 2007, “Philosophy of Education”, in Britannica Online Encyclopedia , [ Available online ].
- –––, (ed.), 2008, The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Education , Oxford: Oxford University Press, in press.
- Smeyers, P., 1994, “Philosophy of Education: Western European Perspectives”, in The International Encyclopedia of Education , (Volume 8), T. Husen and N. Postlethwaite, (eds.), Oxford: Pergamon, 2 nd . Edition, pp. 4456-61.
- Smeyers, P., and Marshall, J., (eds.), 1995, Philosophy and Education: Accepting Wittgenstein's Challenge , Dordrecht: Kluwer.
- Smith, B., and Ennis, R., (eds.), 1961, Language and Concepts in Education , Chicago: Rand McNally.
- Snook, I., 1972, Indoctrination and Education , London: Routledge.
- Stokes, D., 1997, Pasteur's Quadrant: Basic Science and Technological Innovation , Washington, DC: Brookings.
- Stone, L., (ed.), 1994, The Education Feminism Reader , New York: Routledge.
- Ulich, R., 1954, Three Thousand Years of Educational Wisdom , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, Revised Ed.
- Winch, C., and Gingell, J., 1999, Key Concepts in the Philosophy of Education , London: Routledge.
- PES (Philosophy of Education Society, North America)
- PESA (Philosophy of Education Society of Australasia)
- PESGB (Philosophy of Education Society of Great Britain)
- INPE (International Network of Philosophers of Education)
- UNESCO/International Bureau of Education: Thinkers on Education
autonomy: personal | -->Dewey, John --> | feminist (interventions): ethics | feminist (interventions): liberal feminism | feminist (interventions): political philosophy | -->feminist (topics): perspectives on autonomy --> | feminist (topics): perspectives on disability | Foucault, Michel | Gadamer, Hans-Georg | liberalism | Locke, John | -->Lyotard, Jean François --> | -->ordinary language --> | Plato | postmodernism | Rawls, John | rights: of children | -->Rousseau, Jean Jacques -->
2.6 Writing Philosophy Papers
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify and characterize the format of a philosophy paper.
- Create thesis statements that are manageable and sufficiently specific.
- Collect evidence and formulate arguments.
- Organize ideas into a coherent written presentation.
This section will provide some practical advice on how to write philosophy papers. The format presented here focuses on the use of an argumentative structure in writing. Different philosophy professors may have different approaches to writing. The sections below are only intended to give some general guidelines that apply to most philosophy classes.
Identify Claims
The key element in any argumentative paper is the claim you wish to make or the position you want to defend. Therefore, take your time identifying claims , which is also called the thesis statement. What do you want to say about the topic? What do you want the reader to understand or know after reading your piece? Remember that narrow, modest claims work best. Grand claims are difficult to defend, even for philosophy professors. A good thesis statement should go beyond the mere description of another person’s argument. It should say something about the topic, connect the topic to other issues, or develop an application of some theory or position advocated by someone else. Here are some ideas for creating claims that are perfectly acceptable and easy to develop:
- Compare two philosophical positions. What makes them similar? How are they different? What general lessons can you draw from these positions?
- Identify a piece of evidence or argument that you think is weak or may be subject to criticism. Why is it weak? How is your criticism a problem for the philosopher’s perspective?
- Apply a philosophical perspective to a contemporary case or issue. What makes this philosophical position applicable? How would it help us understand the case?
- Identify another argument or piece of evidence that might strengthen a philosophical position put forward by a philosopher. Why is this a good argument or piece of evidence? How does it fit with the philosopher’s other claims and arguments?
- Consider an implication (either positive or negative) that follows from a philosopher’s argument. How does this implication follow? Is it necessary or contingent? What lessons can you draw from this implication (if positive, it may provide additional reasons for the argument; if negative, it may provide reasons against the argument)?
Think Like a Philosopher
The following multiple-choice exercises will help you identify and write modest, clear philosophical thesis statements. A thesis statement is a declarative statement that puts forward a position or makes a claim about some topic.
- How does Aristotle think virtue is necessary for happiness?
- Is happiness the ultimate goal of human action?
- Whether or not virtue is necessary for happiness.
- Aristotle argues that happiness is the ultimate good of human action and virtue is necessary for happiness.
- René Descartes argues that the soul or mind is the essence of the human person.
- Descartes shows that all beliefs and memories about the external world could be false.
- Some people think that Descartes is a skeptic, but I will show that he goes beyond skepticism.
- In the meditations, Descartes claims that the mind and body are two different substances.
- Descartes says that the mind is a substance that is distinct from the body, but I disagree.
- Contemporary psychology has shown that Descartes is incorrect to think that human beings have free will and that the mind is something different from the brain.
- Thomas Hobbes’s view of the soul is materialistic, whereas Descartes’s view of the soul is nonphysical. In this paper, I will examine the differences between these two views.
- John Stuart Mill reasons that utilitarian judgments can be based on qualitative differences as well as the quantity of pleasure, but ultimately any qualitative difference must result in a difference in the quantity of pleasure.
- Mill’s approach to utilitarianism differs from Bentham’s by introducing qualitative distinctions among pleasures, where Bentham only considers the quantitative aspects of pleasure.
- J. S. Mill’s approach to utilitarianism aligns moral theory with the history of ethics because he allows qualitative differences in moral judgments.
- Rawls’s liberty principle ensures that all people have a basic set of freedoms that are important for living a full life.
- The US Bill of Rights is an example of Rawls’s liberty principle because it lists a set of basic freedoms that are guaranteed for all people.
- While many people may agree that Rawls’s liberty principle applies to all citizens of a particular country, it is much more controversial to extend those same basic freedoms to immigrants, including those classified by the government as permanent residents, legal immigrants, illegal immigrants, and refugees.
[ANS: 1.d 2.c 3.c 4.a 5.c]
Write Like a Philosopher
Use the following templates to write your own thesis statement by inserting a philosopher, claim, or contemporary issue:
- [Name of philosopher] holds that [claim], but [name of another philosopher] holds that [another claim]. In this paper, I will identify reasons for thinking [name of philosopher]’s position is more likely to be true.
- [Name of philosopher] argues that [claim]. In this paper, I will show how this claim provides a helpful addition to [contemporary issue].
- When [name of philosopher] argues in favor of [claim], they rely on [another claim] that is undercut by contemporary science. I will show that if we modify this claim in light of contemporary science, we will strengthen or weaken [name of philosopher]’s argument.
Collect Evidence and Build Your Case
Once you have identified your thesis statement or primary claim, collect evidence (by returning to your readings) to compose the best possible argument. As you assemble the evidence, you can think like a detective or prosecutor building a case. However, you want a case that is true, not just one that supports your position. So you should stay open to modifying your claim if it does not fit the evidence . If you need to do additional research, follow the guidelines presented earlier to locate authoritative information.
If you cannot find evidence to support your claim but still feel strongly about it, you can try to do your own philosophical thinking using any of the methods discussed in this chapter or in Chapter 1. Imagine counterexamples and thought experiments that support your claim. Use your intuitions and common sense, but remember that these can sometimes lead you astray. In general, common sense, intuitions, thought experiments, and counterexamples should support one another and support the sources you have identified from other philosophers. Think of your case as a structure: you do not want too much of the weight to rest on a single intuition or thought experiment.
Consider Counterarguments
Philosophy papers differ from typical argumentative papers in that philosophy students must spend more time and effort anticipating and responding to counterarguments when constructing their own arguments. This has two important effects: first, by developing counterarguments, you demonstrate that you have sufficiently thought through your position to identify possible weaknesses; second, you make your case stronger by taking away a potential line of attack that an opponent might use. By including counterarguments in your paper, you engage in the kind of dialectical process that philosophers use to arrive at the truth.
Accurately Represent Source Material
It is important to represent primary and secondary source material as accurately as possible. This means that you should consider the context and read the arguments using the principle of charity. Make sure that you are not strawmanning an argument you disagree with or misrepresenting a quote or paraphrase just because you need some evidence to support your argument. As always, your goal should be to find the most rationally compelling argument, which is the one most likely to be true.
Organize Your Paper
Academic philosophy papers use the same simple structure as any other paper and one you likely learned in high school or your first-year composition class.
Introduce Your Thesis
The purpose of your introduction is to provide context for your thesis. Simply tell the reader what to expect in the paper. Describe your topic, why it is important, and how it arises within the works you have been reading. You may have to provide some historical context, but avoid both broad generalizations and long-winded historical retellings. Your context or background information should not be overly long and simply needs to provide the reader with the context and motivation for your thesis. Your thesis should appear at the end of the introduction, and the reader should clearly see how the thesis follows from the introductory material you have provided. If you are writing a long paper, you may need several sentences to express your thesis, in which you delineate in broad terms the parts of your argument.
Make a Logical and Compelling Case Using the Evidence
The paragraphs that follow the introduction lay out your argument. One strategy you can use to successfully build paragraphs is to think in terms of good argument structure. You should provide adequate evidence to support the claims you want to make. Your paragraphs will consist of quotations and paraphrases from primary and secondary sources, context and interpretation, novel thoughts and ideas, examples and analogies, counterarguments, and replies to the counterarguments. The evidence should both support the thesis and build toward the conclusion. It may help to think architecturally: lay down the foundation, insert the beams of your strongest support, and then put up the walls to complete the structure. Or you might think in terms of a narrative: tell a story in which the evidence leads to an inevitable conclusion.
Connections
See the chapter on logic and reasoning for a developed account of different types of philosophical arguments.
Summarize Your Argument in the Conclusion
Conclude your paper with a short summary that recapitulates the argument. Remind the reader of your thesis and revisit the evidence that supports your argument. You may feel that the argument as written should stand on its own. But it is helpful to the reader to reinforce the argument in your conclusion with a short summary. Do not introduce any new information in the conclusion; simply summarize what you have already said.
The purpose of this chapter has been to provide you with basic tools to become a successful philosophy student. We started by developing a sophisticated picture of how the brain works, using contemporary neuroscience. The brain represents and projects a picture of the world, full of emotional significance, but this image may contain distortions that amount to a kind of illusion. Cognitive illusions produce errors in reasoning, called cognitive biases. To guard against error, we need to engage in effortful, reflective thinking, where we become aware of our biases and use logical strategies to overcome them. You will do well in your philosophy class if you apply the good habits of mind discussed in this chapter and apply the practical advice that has been provided about how to read and write about philosophy.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-philosophy/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Nathan Smith
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introduction to Philosophy
- Publication date: Jun 15, 2022
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-philosophy/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-philosophy/pages/2-6-writing-philosophy-papers
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.6: Writing Philosophy Papers
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 162139

- Nathan Smith et al.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify and characterize the format of a philosophy paper.
- Create thesis statements that are manageable and sufficiently specific.
- Collect evidence and formulate arguments.
- Organize ideas into a coherent written presentation.
This section will provide some practical advice on how to write philosophy papers. The format presented here focuses on the use of an argumentative structure in writing. Different philosophy professors may have different approaches to writing. The sections below are only intended to give some general guidelines that apply to most philosophy classes.
Identify Claims
The key element in any argumentative paper is the claim you wish to make or the position you want to defend. Therefore, take your time identifying claims, which is also called the thesis statement. What do you want to say about the topic? What do you want the reader to understand or know after reading your piece? Remember that narrow, modest claims work best. Grand claims are difficult to defend, even for philosophy professors. A good thesis statement should go beyond the mere description of another person’s argument. It should say something about the topic, connect the topic to other issues, or develop an application of some theory or position advocated by someone else. Here are some ideas for creating claims that are perfectly acceptable and easy to develop:
- Compare two philosophical positions. What makes them similar? How are they different? What general lessons can you draw from these positions?
- Identify a piece of evidence or argument that you think is weak or may be subject to criticism. Why is it weak? How is your criticism a problem for the philosopher’s perspective?
- Apply a philosophical perspective to a contemporary case or issue. What makes this philosophical position applicable? How would it help us understand the case?
- Identify another argument or piece of evidence that might strengthen a philosophical position put forward by a philosopher. Why is this a good argument or piece of evidence? How does it fit with the philosopher’s other claims and arguments?
- Consider an implication (either positive or negative) that follows from a philosopher’s argument. How does this implication follow? Is it necessary or contingent? What lessons can you draw from this implication (if positive, it may provide additional reasons for the argument; if negative, it may provide reasons against the argument)?
Think Like A Philosopher
The following multiple-choice exercises will help you identify and write modest, clear philosophical thesis statements. A thesis statement is a declarative statement that puts forward a position or makes a claim about some topic.
- How does Aristotle think virtue is necessary for happiness?
- Is happiness the ultimate goal of human action?
- Whether or not virtue is necessary for happiness.
- Aristotle argues that happiness is the ultimate good of human action and virtue is necessary for happiness.
- René Descartes argues that the soul or mind is the essence of the human person.
- Descartes shows that all beliefs and memories about the external world could be false.
- Some people think that Descartes is a skeptic, but I will show that he goes beyond skepticism.
- In the meditations, Descartes claims that the mind and body are two different substances.
- Descartes says that the mind is a substance that is distinct from the body, but I disagree.
- Contemporary psychology has shown that Descartes is incorrect to think that human beings have free will and that the mind is something different from the brain.
- Thomas Hobbes’s view of the soul is materialistic, whereas Descartes’s view of the soul is nonphysical. In this paper, I will examine the differences between these two views.
- John Stuart Mill reasons that utilitarian judgments can be based on qualitative differences as well as the quantity of pleasure, but ultimately any qualitative difference must result in a difference in the quantity of pleasure.
- Mill’s approach to utilitarianism differs from Bentham’s by introducing qualitative distinctions among pleasures, where Bentham only considers the quantitative aspects of pleasure.
- J. S. Mill’s approach to utilitarianism aligns moral theory with the history of ethics because he allows qualitative differences in moral judgments.
- Rawls’s liberty principle ensures that all people have a basic set of freedoms that are important for living a full life.
- The US Bill of Rights is an example of Rawls’s liberty principle because it lists a set of basic freedoms that are guaranteed for all people.
- While many people may agree that Rawls’s liberty principle applies to all citizens of a particular country, it is much more controversial to extend those same basic freedoms to immigrants, including those classified by the government as permanent residents, legal immigrants, illegal immigrants, and refugees.
1.d 2.c 3.c 4.a 5.c

Write Like A Philosopher
Use the following templates to write your own thesis statement by inserting a philosopher, claim, or contemporary issue:
- [Name of philosopher] holds that [claim], but [name of another philosopher] holds that [another claim]. In this paper, I will identify reasons for thinking [name of philosopher]’s position is more likely to be true.
- [Name of philosopher] argues that [claim]. In this paper, I will show how this claim provides a helpful addition to [contemporary issue].
- When [name of philosopher] argues in favor of [claim], they rely on [another claim] that is undercut by contemporary science. I will show that if we modify this claim in light of contemporary science, we will strengthen or weaken [name of philosopher]’s argument.
Collect Evidence and Build Your Case
Once you have identified your thesis statement or primary claim, collect evidence (by returning to your readings) to compose the best possible argument. As you assemble the evidence, you can think like a detective or prosecutor building a case. However, you want a case that is true, not just one that supports your position. So you should stay open to modifying your claim if it does not fit the evidence. If you need to do additional research, follow the guidelines presented earlier to locate authoritative information.
If you cannot find evidence to support your claim but still feel strongly about it, you can try to do your own philosophical thinking using any of the methods discussed in this chapter or in Chapter 1. Imagine counterexamples and thought experiments that support your claim. Use your intuitions and common sense, but remember that these can sometimes lead you astray. In general, common sense, intuitions, thought experiments, and counterexamples should support one another and support the sources you have identified from other philosophers. Think of your case as a structure: you do not want too much of the weight to rest on a single intuition or thought experiment.
Consider Counterarguments
Philosophy papers differ from typical argumentative papers in that philosophy students must spend more time and effort anticipating and responding to counterarguments when constructing their own arguments. This has two important effects: first, by developing counterarguments, you demonstrate that you have sufficiently thought through your position to identify possible weaknesses; second, you make your case stronger by taking away a potential line of attack that an opponent might use. By including counterarguments in your paper, you engage in the kind of dialectical process that philosophers use to arrive at the truth.
Accurately Represent Source Material
It is important to represent primary and secondary source material as accurately as possible. This means that you should consider the context and read the arguments using the principle of charity. Make sure that you are not strawmanning an argument you disagree with or misrepresenting a quote or paraphrase just because you need some evidence to support your argument. As always, your goal should be to find the most rationally compelling argument, which is the one most likely to be true.
Organize Your Paper
Academic philosophy papers use the same simple structure as any other paper and one you likely learned in high school or your first-year composition class.
Introduce Your Thesis
The purpose of your introduction is to provide context for your thesis. Simply tell the reader what to expect in the paper. Describe your topic, why it is important, and how it arises within the works you have been reading. You may have to provide some historical context, but avoid both broad generalizations and long-winded historical retellings. Your context or background information should not be overly long and simply needs to provide the reader with the context and motivation for your thesis. Your thesis should appear at the end of the introduction, and the reader should clearly see how the thesis follows from the introductory material you have provided. If you are writing a long paper, you may need several sentences to express your thesis, in which you delineate in broad terms the parts of your argument.
Make a Logical and Compelling Case Using the Evidence
The paragraphs that follow the introduction lay out your argument. One strategy you can use to successfully build paragraphs is to think in terms of good argument structure. You should provide adequate evidence to support the claims you want to make. Your paragraphs will consist of quotations and paraphrases from primary and secondary sources, context and interpretation, novel thoughts and ideas, examples and analogies, counterarguments, and replies to the counterarguments. The evidence should both support the thesis and build toward the conclusion. It may help to think architecturally: lay down the foundation, insert the beams of your strongest support, and then put up the walls to complete the structure. Or you might think in terms of a narrative: tell a story in which the evidence leads to an inevitable conclusion.
CONNECTIONS
See the chapter on logic and reasoning for a developed account of different types of philosophical arguments.
Summarize Your Argument in the Conclusion
Conclude your paper with a short summary that recapitulates the argument. Remind the reader of your thesis and revisit the evidence that supports your argument. You may feel that the argument as written should stand on its own. But it is helpful to the reader to reinforce the argument in your conclusion with a short summary. Do not introduce any new information in the conclusion; simply summarize what you have already said.
The purpose of this chapter has been to provide you with basic tools to become a successful philosophy student. We started by developing a sophisticated picture of how the brain works, using contemporary neuroscience. The brain represents and projects a picture of the world, full of emotional significance, but this image may contain distortions that amount to a kind of illusion. Cognitive illusions produce errors in reasoning, called cognitive biases. To guard against error, we need to engage in effortful, reflective thinking, where we become aware of our biases and use logical strategies to overcome them. You will do well in your philosophy class if you apply the good habits of mind discussed in this chapter and apply the practical advice that has been provided about how to read and write about philosophy.
/images/cornell/logo35pt_cornell_white.svg" alt="how to write a philosophy paper on education"> Cornell University --> Graduate School
Teaching philosophy statement, what is a teaching philosophy statement.
A teaching philosophy statement is a narrative that includes:
- your conception of teaching and learning.
- a description of how you teach.
- justification for why you teach that way.
The statement can:
- demonstrate that you have been reflective and purposeful about your teaching.
- communicate your goals as an instructor and your corresponding actions in the classroom.
- point to and tie together the other sections of your portfolio.
What is the purpose of a teaching philosophy statement?
You generally need a teaching statement to apply for an academic position. A teaching statement:
- conveys your teaching values, beliefs, and goals to a broader audience.
- provides a set of criteria and/or standards to judge the quality of your teaching.
- provides evidence of your teaching effectiveness.
Components of a teaching philosophy statement
- educational purpose and learning goals for students
- your teaching methods
- methods for assessing students’ learning
- assessment of teaching
You also may include:
- a list of courses you have taught.
- samples of course syllabi.
- teaching evaluations.
- letters of recommendation.
- a video of a class you have taught (asked for by some universities).
Teaching values, beliefs, and goals
You should consider what you believe is the end goal or purpose of education:
- content mastery
- engaged citizenry
- individual fulfillment
- critical thinking
- problem solving
- discovery and knowledge generation
- self-directed learning
- experiential learning
What criteria are used to judge your teaching?
- student-teaching roles and responsibilities
- student-teacher interaction
- inclusiveness
- teaching methods
- assessment of learning
How do you provide evidence of your teaching effectiveness?
- peer review
- students’ comments
- teaching activities
Writing guidelines:
- There is no required content, set format, or right or wrong way to write a teaching statement. That is why writing one can be challenging.
- Make the length suit the context. Generally, they are one to two pages.
- Use present tense and the first person, in most cases.
- Avoid technical terms and use broadly understood language and concepts, in most cases. Write with the audience in mind. Have someone from your field guide you on discipline-specific jargon and issues to include or exclude.
- Include teaching strategies and methods to help people “see” you in the classroom. Include specific examples of your teaching strategies, assignments, discussions, etc. Help them to visualize the learning environment you create and the exchanges between you and your students.
- Make it memorable and unique. The search committee is seeing many of these documents—What is going to set you apart? What will they remember? Your teaching philosophy will come to life if you create a vivid portrait of yourself as a person who is intentional about teaching practices and committed to your career.
“Own” your philosophy
Don’t make general statements such as “students don’t learn through lecture” or “the only way to teach is with class discussion.” These could be detrimental, appearing as if you have all of the answers. Instead, write about your experiences and your beliefs. You “own” those statements and appear more open to new and different ideas about teaching. Even in your own experience, you make choices about the best teaching methods for different courses and content: sometimes lecture is most appropriate; other times you may use service-learning, for example.
Teaching philosophy statement dos and don’ts:
- Don’t give idyllic but empty concepts.
- Don’t repeat your CV.
- Do research on the teaching institution and disciplinary trends.
- Do keep it short (one to two pages).
- Do provide concrete examples and evidence of usefulness of teaching concepts.
- Do discuss impact of methods, lessons learned, challenges, and innovations—how did students learn?
- Do discuss connections between teaching, research, and service.
Answer these questions to get started:
- The purpose of education is to________.
- Why do you want to teach your subject?
- Students learn best by______________.
- When you are teaching your subject, what are your goals?
- The most effective methods for teaching are___________.
- I know this because__________________.
- The most important aspects of my teaching are______________.
More information on teaching philosophy statements
An excellent guide for writing your teaching philosophy statement is Occasional Paper number 23, “Writing a Statement of Teaching Philosophy for the Academic Job Search,” from the University of Michigan’s Center for Research on Learning and Teaching, which you can find at this page on The Teaching Philosophy and Statement .
Articles on Teaching Statements:
- “Writing the Teaching Statement” by Rachel Narehood Austin, Science Magazine
- “How to Write a Statement of Teaching Philosophy” by Gabriela Montell, The Chronicle of Higher Education
- “What’s Your Philosophy on Teaching, and Does it Matter?” by Gabriela Montell, The Chronicle of Higher Education
- “A Teaching Statement” by Jeffrey Marcus, The Chronicle of Higher Education
- “Everything But the Teaching Statement” by Jeremy S. Clay, The Chronicle of Higher Education
- “Writing a Teaching Philosophy Statement” by Helen G. Grundman, Notices of the American Mathematical Society
Additional Resources:
- From Cornell’s Center for Teaching Innovation
- From the University of Michigan
- From University of California Berkeley
- From University of Pennsylvania
Electronic portfolios
The electronic portfolio is a way to showcase your accomplishments, skills, and philosophy on the internet. You can write a personal profile; post your CV, resume, research statement, teaching philosophy statement; give links to published articles, work samples, etc.; and post photos and other images. You can continually update it as you progress through your studies and your career. It is readably available for potential employers to see.
Sites that Host Electronic Portfolios:
- Digication (Cornell-supported option)
- Interfolio (fee-based)
- Google Sites (free)
Help at the Center for Teaching Innovation (CTI)
Coursework involving teaching portfolio development.
The course ALS 6015, “ Teaching in Higher Education ,” guides graduate students in how to prepare teaching portfolios and provides opportunity for peer and instructor feedback.
Individual Advice
By enrolling in the CTI’s new Teaching Portfolio Program , you will have access to consultations and advice on helping prepare elements of a teaching portfolio such as a teaching philosophy statement.
Workshops and Institutes
For graduate teaching assistants and postdocs considering academic positions in higher education, you could attend a teaching statement workshop as part of the Graduate School’s Academic Job Search Series , or a day-long Teaching Portfolio Institute offered by the CTI to help refine and document your teaching for the job search.
How to Write a Philosophy of Education for Elementary Teachers
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.S., Education, Buffalo State College
- B.S., Education, Buffalo State College
A philosophy of education statement, sometimes called a teaching statement, should be a staple in every teacher's portfolio. For elementary school teachers, the statement is an opportunity to define what teaching means to you and allows you to describe how and why you teach as you do at the early stages of learning. The following tips and philosophy of education examples for elementary teachers can help you write an essay that you'll be proud to have.
A philosophy of education statement is an opportunity to define what teaching means to you, and to describe how and why you teach as you do. Articulating this statement in the first person and using a traditional essay format (introduction, body, conclusion) will help you craft an enduring and inspiring personal statement.
Structure of a Teaching Philosophy
Unlike other kinds of writing, educational statements are frequently written in the first person because these are personal essays on your chosen profession. In general, they should be one to two pages long, though they can be longer if you've had an extensive career. Like other essays, a good educational philosophy should have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Here is a sample structure.
Introduction
Use this paragraph to describe your views on teaching in a general sense. State your thesis (for example, "My philosophy of education is that every child should have the right to learn and get a quality education.") and discuss your ideals. Be brief; you'll use the following paragraphs to explain the details. Think about aspects of early education that are unique to elementary teachers, and introduce these ideals into your writing.
Use the following three to five paragraphs (or more, if needed) to elaborate on your introductory statement. For example, you could discuss the ideal elementary classroom environment and how it makes you a better teacher, addresses student needs, and facilitates parent/child interactions.
Build on these ideals in the following paragraphs by discussing how you keep your classes aware and engaged, how you facilitate age-appropriate learning , and how you involve students in the assessment process . Whatever your approach, remember to focus on what you value most as an educator and to cite examples of how you've put these ideals into practice.
Go beyond simply restating your educational philosophy in your closing. Instead, talk about your goals as a teacher, how you have been able to meet them in the past, and how you can build on these to meet future challenges.
Philosophy of education documents for elementary teachers are very personal and unique to the individual. While some may have similarities, your own philosophy should focus on your personal approach to pedagogy and classroom management. Focus on what makes you unique as an educator, and how you wish to advance your career to further support elementary education.
Writing Prompts
As with any writing, take the time to outline your ideas before you begin. The following tips can help you craft your teaching philosophy statement:
- Brainstorm about your educational philosophy and your views of education, making notes on those principles you value most. This can help you articulate your philosophy as you organize your essay.
- Demonstrate how you have put your educational philosophy into practice in the classroom by citing specific examples and outcomes with students, parents, or fellow teachers and administrators.
- Reflect on your experience over your career. Most likely, your teaching philosophy has changed over time. Reflect on the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead, and how you intend to meet them.
- Connect with others and talk to your peers in the field, as well as mentors. Ask them about how they crafted their essays and ask them to review yours once you complete it. Having people who know you and your teaching style well review your work can help you craft a truly representative statement.
- Review a few sample essays to help you as you begin writing your own.
Career Advancement
Applying for a brand new job isn't the only time you need an educational philosophy. If you're seeking a promotion or are applying for tenure, you'll need to craft or update your educational philosophy statement. As time goes on, your approach to education and classroom management will likely evolve, and so will your beliefs. Updating your philosophy allows you to articulate your professional motivations and goals, as well as your approach to educating others so that observers can have a better sense of who you are, even without observing you in the classroom. Consider reviewing your philosophy every few years.
- 10 Questions to Ask Yourself to Design Your Educational Philosophy
- Educational Philosophy Basics
- 4 Teaching Philosophy Statement Examples
- Top Tips for Acing a Teacher Interview
- Common Interview Questions in Education
- An Educational Leadership Philosophy for School Leaders
- What is a Waldorf School?
- How to Write a Homeschooling Philosophy Statement
- 5 Types of Report Card Comments for Elementary Teachers
- Seven Strategies to Provide Help for Teachers
- Teacher Interview Questions and Suggested Answers
- Perfecting Your Professional Portfolio
- Important Daily Teaching Tasks
- Strategies for Teachers: The Power of Preparation and Planning
- An Overview of Early Childhood Education
- 10 New Year's Resolutions for Teachers

How to Write a Philosophy Paper
- Develop a Thesis
- Formulate an Argument
- Structure & Outline
- Grammar & Style
Getting Started
Writing a Paper in Philosophy Part 1 -- Getting Started from LMU ITS on Vimeo .
When & Where to Begin
Unsure of when to begin? Or what to do? The University of Minnesota has constructed a research paper navigator that'll construct a tailored research paper timeline based on your start and due dates. It also provides excellent information on the steps you need to complete to produce a successful research paper--but be aware that it will be pointing you to Tufts University resources, some of which LVC may or may not own.
" Lengthy introductions
These are entirely unnecessary and of no interest to the informed reader. There is no need to point out that your topic is an iimportant one, and one that has interested philosophers for hundreds of years. Introductions should be as brief as possible...

Lengthy quotations
Inexperienced writers rely too heavily on quotations and paraphrases. Direct quotation is best restricted to those cases where it is essential to establish another writer's exact selection of words. Even paraphrasing should be kept to a minimum. After all, it is your paper. It is your thoughts that the instructor is concerned with...
Fence sitting
Do not present a number of positions in your paper and then end by saying that you are not qualified to settle the matter. In particular, do not close by saying that philosophers have been divided over this issue for as long as humans have been keeping record and you cannot be expected to resolve the dispute in a few short pages. Your instructor knows that. But you can be expected to take a clear stand based on an evaluation of the argument(s) presented. Go out on a limb. If you have argued well, it will support you.
Cuteness .
Good philosophical writing usually has an air of simple dignity about it. Your topic is no joke. No writers whose views you have been asked to read are idiots. (If you think they are, then you have not understood them.) Name calling is inappropriate and could never substitute for careful argumentation anyway.
Begging the question
You are guilty of begging the question (or circular reasoning) on a particular issue if you somehow presuppose the truth of whatever it is that you are trying to show in the course of arguing for it. Here is a quick example. If Smith argues that abortion is morally wrong on the grounds that it amounts to murder, Smith begs the question. Smith presupposes a particular stand on the moral status of abortion -- the stand represented by the conclusion of the argument. To see that this is so, notice that the person who denies the conclusion -- that abortion is morally wrong -- will not accept Smith's premise that it amounts to murder, since murder is, by definition, morally wrong.
[Claiming overall conclusions are false]
When arguing against other positions, it is important to realize that you cannot show that your opponents are mistaken just by claiming that their overall conclusions are false. Nor will it do simply to claim that at least one of their premises is false. You must demonstrate these sorts of things, and in a fashion that does not presuppose that your position is correct."
Source: Horban, Peter. Writing a Philosophy Paper . Simon Fraser University. 1993.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Develop a Thesis >>
- Last Updated: Jan 22, 2024 10:48 AM
- URL: https://libguides.lvc.edu/philosophypaper
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
- Academic Leaders
- Faculty and Instructors
- Graduate Students and Postdocs
Center for Educational Innovation
- Campus and Collegiate Liaisons
- Pedagogical Innovations Journal Club
- Teaching Enrichment Series
- Recorded Webinars
- Video Series
- All Services
- Teaching Consultations
- Student Feedback Facilitation
- Instructional Media Production
- Curricular and Educational Initiative Consultations
- Educational Research and Evaluation
- Thank a Teacher
- All Teaching Resources
- Aligned Course Design
- Active Learning
- Team Projects
- Active Learning Classrooms
- Leveraging the Learning Sciences
- Inclusive Teaching at a Predominantly White Institution
- Assessments
- Online Teaching and Design
- AI and ChatGPT in Teaching
- Documenting Growth in Teaching
- Early Term Feedback
- Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
- Writing Your Teaching Philosophy
- All Programs
- Assessment Deep Dive
- Designing and Delivering Online Learning
- Early Career Teaching and Learning Program
- International Teaching Assistant (ITA) Program
- Preparing Future Faculty Program
- Teaching with Access and Inclusion Program
- Teaching for Student Well-Being Program
- Teaching Assistant and Postdoc Professional Development Program
Your teaching philosophy is a self-reflective statement of your beliefs about teaching and learning. It's a one to two page narrative that conveys your core ideas about being an effective teacher in the context of your discipline. It develops these ideas with specific, concrete examples of what the teacher and learners will do to achieve those goals. Importantly, your teaching philosophy statement also explains why you choose these options.
+ Getting Started
Your reasons for writing a teaching philosophy may vary. You might be writing it as an exercise in concisely documenting your beliefs so that you can easily articulate them to your students, peers, or a search committee. It might serve as the introduction to your teaching portfolio. Or, it can serve as a means of professional growth as it requires you to give examples of how you enact your philosophy, thus requiring you to consider the degree to which your teaching is congruent with your beliefs.
Generating ideas
Teaching philosophies express your values and beliefs about teaching. They are personal statements that introduce you, as a teacher, to your reader. As such, they are written in the first person and convey a confident, professional tone. When writing a teaching philosophy, use specific examples to illustrate your points. You should also discuss how your values and beliefs about teaching fit into the context of your discipline.
Below are categories you might address with prompts to help you begin generating ideas. Work through each category, spending time thinking about the prompts and writing your ideas down. These notes will comprise the material you’ll use to write the first draft of your teaching philosophy statement. It will help if you include both general ideas (‘I endeavor to create lifelong learners’) as well as specifics about how you will enact those goals. A teaching philosophy template is also available to help you get started.
Questions to prompt your thinking
Your concept of learning.
What do you mean by learning? What happens in a successful learning situation? Note what constitutes "learning" or "mastery" in your discipline.
Your concept of teaching
What are your values, beliefs, and aspirations as a teacher? Do you wish to encourage mastery, competency, transformational learning, lifelong learning, general transference of skills, critical thinking? What does a perfect teaching situation look like to you and why? How are the values and beliefs realized in classroom activities? You may discuss course materials, lesson plans, activities, assignments, and assessment instruments.
Your goals for students
What skills should students obtain as a result of your teaching? Think about your ideal student and what the outcomes of your teaching would be in terms of this student's knowledge or behavior. Address the goals you have for specific classes or curricula and that rational behind them (i.e., critical thinking, writing, or problem solving).
Your teaching methods
What methods will you consider to reach these goals and objectives? What are your beliefs regarding learning theory and specific strategies you would use, such as case studies, group work, simulations, interactive lectures? You might also want to include any new ideas or strategies you want to try.
Your interaction with students
What are you attitudes towards advising and mentoring students? How would an observer see you interact with students? Why do you want to work with students?
Assessing learning
How will you assess student growth and learning? What are your beliefs about grading? Do you grade students on a percentage scale (criterion referenced) or on a curve (norm referenced)? What different types of assessment will you use (i.e. traditional tests, projects, portfolios, presentations) and why?
Professional growth
How will you continue growing as a teacher? What goals do you have for yourself and how will you reach them? How have your attitudes towards teaching and learning changed over time? How will you use student evaluations to improve your teaching? How might you learn new skills? How do you know when you've taught effectively?
+ Creating a Draft
Two ways of organizing your draft.
Now that you've written down your values, attitudes, and beliefs about teaching and learning, it's time to organize those thoughts into a coherent form. Perhaps the easiest way of organizing this material would be to write a paragraph covering each of the seven prompts you answered in the Getting Started section. These would then become the seven major sections of your teaching philosophy.
Another way of knitting your reflections together—and one that is more personal—is to read through your notes and underscore ideas or observations that come up more than once. Think of these as "themes" that might point you toward an organizational structure for the essay. For example, you read through your notes and realize that you spend a good deal of time writing about your interest in mentoring students. This might become one of the three or four major foci of your teaching philosophy. You should then discuss what it says about your attitudes toward teaching, learning, and what's important in your discipline.
No matter which style you choose, make sure to keep your writing succinct. Aim for two double-spaced pages. And don't forget to start with a "hook." Your job is to make your readers want to read more; their level of engagement is highest when they read your opening line. Hook your readers by beginning with a question, a statement, or even an event from your past.
Using specific examples
Remember to provide concrete examples from your teaching practice to illustrate the general claims you make in your teaching philosophy. The following general statements about teaching are intended as prompts to help you come up with examples to illustrate your claims about teaching. For each statement, how would you describe what happens in your classroom? Is your description specific enough to bring the scene to life in a teaching philosophy?
"I value helping my students understand difficult information. I am an expert, and my role is to model for them complex ways of thinking so that they can develop the same habits of mind as professionals in the medical field."
"I enjoy lecturing, and I'm good at it. I always make an effort to engage and motivate my students when I lecture."
"It is crucial for students of geology to learn the techniques of field research. An important part of my job as a professor of geology is to provide these opportunities."
"I believe that beginning physics students should be introduced to the principles of hypothesis generation, experimentation, data collection, and analysis. By learning the scientific method, they develop critical thinking skills they can apply to other areas of their lives. Small group work is a crucial tool for teaching the scientific method."
"As a teacher of writing, I am committed to using peer review in my classes. By reading and commenting on other students' work in small cooperative groups, my students learn to find their voice, to understand the important connection between writer and audience, and to hone their editing skills. Small group work is indispensible in the writing classroom."
Go back to the notes you made when getting started and underline the general statements you’ve made about teaching and learning. As you start drafting, make sure to note the specific approaches, methods, or products you use to realize those goals.
+ Assessing Your Draft
Assessing your draft teaching philosophy.
According to a survey of search committee chairs by the University of Michigan Center for Research on Learning and Teaching, there are five elements that are shared by strong teaching philosophy statements:
- They offer evidence of practice (specific examples)
- They are student-centered
- They demonstrate reflectiveness
- They demonstrate that the writer values teaching
- They are well written, clear, and readable
Now that you’ve completed an initial draft, ask whether your statement captures these elements and how well you articulate them.
You might find it useful to compare your draft to other teaching philosophies in your discipline. It can also be useful to have a colleague review your draft and offer recommendations for revision. Consider printing out a teaching philosophy rubric from our “Rubrics and Samples” tab to provide your reviewer with guidelines to assess your draft. These exercises will give you the critical distance necessary to see your teaching philosophy objectively and revise it accordingly.
+ Rubrics and Samples
Rubrics and sample teaching philosophies.
Here are links to three teaching philosophy rubrics to help you assess your statement. We have included four different rubrics for you to choose from. These rubrics cover similar elements, and one is not necessarily better than the other. Your choice of which to use should be guided by how comfortable you feel with the particular instrument and how usable you find it.
- Teaching Philosophy Rubric 1 This rubric allows a reader to rate several elements of persuasiveness and format on a scale of 1 to 5.
- Teaching Philosophy Rubric 2 This rubric contains prompts for assessing purpose and audience, voice, beliefs and support, and conventions.
- Teaching Philosophy Rubric 3 This rubric contains prompts for assessing content, format, and writing quality.
- Rubric for Statements of Teaching Philosophy This rubric was developed by Kaplan et. al. from the University of Michigan.
- Marisol Brito – philosophy
- Benjamin Harrison – biology
- Jamie Peterson – psychology
- The University of Michigan has a wide variety of samples organized by field of study.
- Research and Resources
- Why Use Active Learning?
- Successful Active Learning Implementation
- Addressing Active Learning Challenges
- Why Use Team Projects?
- Project Description Examples
- Project Description for Students
- Team Projects and Student Development Outcomes
- Forming Teams
- Team Output
- Individual Contributions to the Team
- Individual Student Understanding
- Supporting Students
- Wrapping up the Project
- Addressing Challenges
- Course Planning
- Working memory
- Retrieval of information
- Spaced practice
- Active learning
- Metacognition
- Definitions and PWI Focus
- A Flexible Framework
- Class Climate
- Course Content
- An Ongoing Endeavor
- Align Assessments
- Multiple Low Stakes Assessments
- Authentic Assessments
- Formative and Summative Assessments
- Varied Forms of Assessments
- Cumulative Assessments
- Equitable Assessments
- Essay Exams
- Multiple Choice Exams and Quizzes
- Academic Paper
- Skill Observation
- Alternative Assessments
- Assessment Plan
- Grade Assessments
- Prepare Students
- Reduce Student Anxiety
- SRT Scores: Interpreting & Responding
- Student Feedback Question Prompts
- Research Questions and Design
- Gathering data
- Publication
- GRAD 8101: Teaching in Higher Education
- Finding a Practicum Mentor
- GRAD 8200: Teaching for Learning
- Proficiency Rating & TA Eligibility
- Schedule a SETTA
- TAPD Webinars
Sam Berstler's Teaching Page
How do i write a philosophy paper.
Here are some excellent guides from around the web.
Guidelines on Writing a Philosophy Paper , Jim Pryor (NYU)
A Brief Guide to Writing the Philosophy Paper , Simon Rippon (Harvard)
Tackling the Philosophical Essay: A Student Guide, Claire Benn et al (Cambridge)
Here is a sample paper that I wrote for Introduction to Ethics.
Educational Philosophy Paper Information
This first set of items are required reading for the course and should be reviewed before beginning the assignment:
_ How to Write the Educational Philosophy Paper _ A Bibliography of Sources for Principles of Teaching and Learning _ Self-Evaluation/Peer-Evaluation Feedback Sheet (review these questions before you hand in a draft of your paper) _ A Sample Educational Philosophy Paper posted to GoogleDocs. Note that the proper format for naming the file should include both your name and the name of the specific document or assignment. For example, "Student Name - Educational Philosophy Paper." Also remember to attach and fill-out the self-evaluation rubric (link above).
These items explain the basics of APA style and plagiarism. (Also see links below for automated assistance in formatting your references.) _ APA Basics _ APA Publications Manual Cribsheet How To CIte Sources and Avoid Plagerism APA Format Template and Scoring Rubric (Make a copy of this GoogleDoc template and use it to format your paper in APA. Fill out the scoring rubric when you hand in the final draft of your paper)
About Your Statement of Educational Philosophy and Practice : In order to assist you in critically analyzing and applying the different theories of education to which you have been exposed during your teacher preparation, you will write a statement of your educational philosophy. This paper will be an integration and explanation of your educational philosophy and its implications on your teaching practice. You should not need to invent your own theory of education. This paper should focus on an integration of traditional Western educational philosophy (i.e., progressivism, existentialism, perennialism, and essentialism) and your personal application of this theory in your classroom. But remember, this is not a paper about the historic philosophical schools, it is a paper about your philosophy.
An alternate paper might develop the rationale for a new school. This new school proposal needs to be thoroughly grounded in a philosophical perspective and explained in great detail. The document must be primarily text/prose (not bulleted points) and be at least 10-14 pages in length. This translates to a word count of between 3,500-5,500 words (using 12-point Arial font, double spaced). This refers to the body of the paper only. It would not include the title page, abstract, or references.
The paper must be documented (the same as the philosophy paper) in APA style. The school proposal should include: the school's mission statement or vision, curriculum overview, approach to student motivation, approaches to parent and community involvement, approach to assessment and evaluation, and a plan for professional educator development. The plan should also include an annotated budget including both projected revenue and expenses. If you chose this option, please schedule a one-on-one meeting with the course instructor to review the expectations for the assignment.
Whichever paper you write, it should be approached as a summative critical integration of your teacher preparation program. This paper (if done well) could be the centerpiece of your teaching portfolio. It should display the professionalism and clarity you would like to project in a job interview.
Your theories of education will undoubtedly change as you become more experienced, but this experience will force you to make some choices and take a stand. Your continued investigation of education will be enhanced by this road map.
This paper should conform to American Psychological Association (APA) style . APA is the standard professional format for educators. The APA Publication Manual is available in the reference section of the library. The paper must conform to APA format for bibliographic research, inclusive language, documentation, and professional style.
Portions or drafts of the paper will be handed-in several times during the term to provide opportunities for feedback at the pre-writing, drafting, revising and editing stages of the writing process. It will be graded in two parts. First your paper will be assessed with regards to its completeness and the clarity of the ideas presented (20 points). Then the paper will be evaluated with regards to its style (correct English usage, thematic focus, APA style, etc., 10 points). Overall, the paper is worth 30 points.
Because this class fulfills a required university writing graduation skill, you must pass the writing assignment in order to pass this course (whether or not you are completing your bachelor's degree at Augsburg University).
This paper will be posted electronically on Google Drive for feedback and review.
Several documents which discuss how to develop your paper will be distributed in class or are available on this webpage. Several in-class activities will also assist you in identifying and developing your educational philosophy.
- A.P.A. (2020, 7th edition). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association. Washington, D.C.: A.P.A.
- Baron, B. (1998). Philosophy applied to education. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill.
- Frankena, W. (1965). Three historical philosophies of education. Chicago: Scott, Foresman, and Co.
- Gutek, G. (1997). Historical and philosophical foundations of education. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill.
- Kneller, G. (1971, 2nd ed.). Introduction to the philosophy of education. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
- Ozmon, H. & Cramer, S. (1992, 5th ed.). Philosophical foundations of education. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, Inc.
- Strouse, J. (1996). Themes of social justice in education. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill.
- My UCalgary
- Class Schedule
- UCalgary Directory
- Continuing Education
- Active Living
- Academic Calendar
- UCalgary Maps
- Close Faculty Websites List Viewing: Faculty Websites
- Cumming School of Medicine
- Faculty of Arts
- Faculty of Graduate Studies
- Faculty of Kinesiology
- Faculty of Law
- Faculty of Nursing
- Faculty of Nursing (Qatar)
- Faculty of Science
- Faculty of Social Work
- Faculty of Veterinary Medicine
- Haskayne School of Business
- School of Architecture, Planning and Landscape
- School of Public Policy
- Schulich School of Engineering
- Werklund School of Education
- Taylor Institute for Teaching and Learning
- Resource Library
- Academic integrity
- Artificial Intelligence
- Blended and online learning
- Curriculum review and development
- Designing learning
- Educational leadership and mentorship
- Equity, diversity, inclusion and accessibility
- Experiential learning
- Indigenous Ways of Knowing
- Mental health and wellness
- Scholarship of teaching and learning
- Teaching assistants
- Teaching continuity
- Teaching dossiers
- Search the catalogue
- Learning modules
Writing an Educational Leadership Philosophy Statement
Dr. natasha kenny, phd, & dr. carol berenson, phd, taylor institute for teaching and learning .
December 2016
We often support instructors in creating teaching philosophy statements, and various resources exist to support their development (e.g. Chism, 1998; Kenny, Jeffs, and Berenson, 2015; Schonwetter et al., 2002). However, few resources are available to help faculty in preparing educational leadership philosophy statements.
We recently created a resource to help faculty preparing educational leadership philosophy statements as part of their nomination dossiers for institutional and national awards, such as the University of Calgary Teaching Award for Educational Leadership and the 3M National Teaching Fellowship .
Similar in format to a teaching philosophy statement, an educational leadership philosophy statement “clearly communicate[s] what our beliefs are about educational leadership, why we hold these beliefs and how we translate our beliefs into practice” (Berenson and Kenny, 2015). An example structure for an educational leadership philosophy statement and guiding questions to help those preparing a statement are presented in Table 1 below. While every statement will uniquely articulate the educational leadership beliefs and practices of each author, these questions provide a foundational guide for helping to support faculty in creating an educational leadership philosophy statement.
Dr. Ken MacMillan, 3M National Teaching Fellow, and the 2015 recipient of the UCalgary Award for Educational Leadership has shared an example educational leadership philosophy statement here .
Philosophy statement components
Developing an educational leadership philosophy statement provides an opportunity for individuals to reflect on their own leadership beliefs and activities. This process also makes visible the many ways in which leadership is formally and informally enacted by individuals on our campus.
Beliefs about educational leadership
What are my beliefs about educational leadership in post-secondary education? Why do I hold these beliefs? Who or what has most informed my leadership approaches? How have my beliefs been influenced by my experiences postsecondary educator and/or scholarly literature related to leadership? What difference do I hope to make as a leader? What does it mean to be a good leader in a post-secondary context?
Educational leadership activities and initiatives
What educational leadership activities, practices and initiatives have I implemented? How do these align with my beliefs? When have I felt most engaged and affirmed as an educational leader? What are my key strengths and skills as a leader? What am I most proud of? What sets me apart? What are some of my accomplishments as a post-secondary leader?
Impact and influence
What difference have I made, and how do I know? What has been the impact and influence of my educational leadership (on me, on students, on colleagues, on my department, on my faculty, on the institution and beyond)? What have others learned from my leadership approaches?
Future aspirations
How will I continue to develop, grow, and improve as a leader? What interests me most about teaching and learning in post-secondary education? What changes do I most hope to see and inspire? What are my future goals and aspirations as a leader in post-secondary education?
Guiding questions adapted from: Kearns, K.D. & Sullivan, C.S. (2011); Kenny, Jeffs & Berenson (2015); Stavros & Hinrichs (2011); Schonwetter et al. (2002); Seldin, P., Miller, J. E., & Seldin, C. A. (2010).
Related content
Sample teaching philosophy statements .
Read more >>
What Makes a Great Teaching Award Nomination Dossier?
Berenson, C. & Kenny, N.A. (2016). Preparing an Educational Leadership Philosophy Statement . Calgary, AB: Taylor Institute for Teaching and Learning.
Chism, Nancy. (1998). Developing a philosophy of teaching statement. Essays on Teaching Excellence: Toward the Best in the Academy, 9, 1-3. Retrieved from http://podnetwork.org/content/uploads/V9-N3-Chism.pdf
Kearns, K.D. and Sullivan, C.S. (2011). Resources and practices to help graduate students and postdoctoral fellows write statements of teaching philosophy. Advances in Physiology Education , 35, 136-145.
Kenny, N.A., Jeffs, C., & Berenson, C. (2015). Preparing a Teaching Philosophy Statement. Calgary, AB: Taylor Institute for Teaching and Learning.
Schonwetter, D.J., Sokal, L., Friesen, M., & Taylor, L.K. (2002). Teaching philosophies reconsidered: A conceptual model for the development and evaluation of teaching philosophy statements. International Journal for Academic Development, 7(1), 83-97
Seldin, P., Miller, J. E., & Seldin, C. A. (2010). The teaching portfolio: A practical guide to improved performance and promotion/tenure decisions. John Wiley & Sons.
Stavros, Jacqueline M, & Hinrichs, Gina. (2011). The Thin Book Of SOAR: Building Strengths-Based Strategy: Thin Book Publishing.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Your teaching philosophy should be 2-3 pages in length and written in first person and in present tense. It should state your goal of education and several ideas you have about how to reach that goal. You will want to include examples and descriptions so your reader can "see" you in your classroom—these may be specific teaching strategies ...
GOOD WRITING EXAMPLE Jen was an excellent philosophy writer who received the following assignment: Evaluate Smith's argument for the claim that people lack free will. Jen decided before she began writing her paper that Smith's argument ultimately fails because it trades on an ambiguity. Accordingly, she began her paper with the following ...
Play-based learning is a big part of my teaching philosophy. Kids who learn through play have more authentic experiences, exploring and discovering the world naturally in ways that make the process more engaging and likely to make a lasting impact. In my classroom, technology is key.
The statement should reflect your core values and beliefs in terms of teaching. Consider your thoughts regarding the nature of students, the purpose of education and how people learn, and the role of teacher. As you develop your educational philosophy, think about completing the following statements: I believe the purposes of education are ...
Chapter 4: Foundational Philosophies of Education. A philosophy is often defined as the foundation upon which knowledge is based. However, when you break apart the actual word, a much different meaning emerges. Derived from the Greek "philos," which means love, and "sophos," which means wisdom, the actual meaning of the word philosophy ...
Philosophy of education is the branch of applied or practical philosophy concerned with the nature and aims of education and the philosophical problems arising from educational theory and practice. Because that practice is ubiquitous in and across human societies, its social and individual manifestations so varied, and its influence so profound ...
3. How philosophy papers will be evaluated, and how this might differ from what you are used to. This short guide will provide step-by-step guidance to each step of the process. How you use it is up to you. For example, your instructor may recommend that you read this guide in its entirety, either before you write a paper, or
How to Write a Philosophy Paper. Shelly Kagan Department of Philosophy. 1. Every paper you write for me will be based on the same basic assignment: state a thesis and defend it. That is, you must stake out a position that you take to be correct, and then you must offer arguments for that view, consider objections, and reply to those objections.
This is a file in the archives of the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Philosophy of Education. First published Mon Jun 2, 2008. All human societies, past and present, have had a vested interest in education; and some wits have claimed that teaching (at its best an educational activity) is the second oldest profession.
Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit. Give today and help us reach more students. Help. OpenStax. This free textbook is an OpenStax resource written to increase student access to high-quality, peer-reviewed learning materials.
Examples of Teaching Philosophy Statements. Sample 1. This passage is an example of a strong statement of teaching philosophy because it puts students where they belong in education: at the front and center of a teacher's focus. An author who writes such as a statement is likely to continuously examine and verify this philosophy by always ...
In this paper, I will identify reasons for thinking [name of philosopher]'s position is more likely to be true. [Name of philosopher] argues that [claim]. In this paper, I will show how this claim provides a helpful addition to [contemporary issue]. When [name of philosopher] argues in favor of [claim], they rely on [another claim] that is ...
The title and abstract should give your reader a quick overview of your paper to decide if they wish to read the article itself, and to prepare them for the key issues you want to raise. A well written title and abstract makes your paper easier to read. A recommended length for a title is 6-12 words.
Some additional virtues of a good philosophy paper: First, the paper should be well-organized; That is, its structure should reflect a logical progression of ideas. Second, the paper should contain only material relevant to the direct objective of the paper. The idea of the paper is to state and defend a central thesis.
A teaching philosophy statement is a narrative that includes: your conception of teaching and learning. a description of how you teach. justification for why you teach that way. The statement can: demonstrate that you have been reflective and purposeful about your teaching. communicate your goals as an instructor and your corresponding actions ...
State your thesis (for example, "My philosophy of education is that every child should have the right to learn and get a quality education.") and discuss your ideals. Be brief; you'll use the following paragraphs to explain the details. Think about aspects of early education that are unique to elementary teachers, and introduce these ideals ...
Your instructor knows that. But you can be expected to take a clear stand based on an evaluation of the argument (s) presented. Go out on a limb. If you have argued well, it will support you. Cuteness . Good philosophical writing usually has an air of simple dignity about it. Your topic is no joke.
Writing Your Teaching Philosophy. Your teaching philosophy is a self-reflective statement of your beliefs about teaching and learning. It's a one to two page narrative that conveys your core ideas about being an effective teacher in the context of your discipline. It develops these ideas with specific, concrete examples of what the teacher and ...
Here are some excellent guides from around the web. Guidelines on Writing a Philosophy Paper, Jim Pryor (NYU) A Brief Guide to Writing the Philosophy Paper, Simon Rippon (Harvard) Tackling the Philosophical Essay: A Student Guide, Claire Benn et al (Cambridge) Here is a sample paper that I wrote for Introduction to Ethics.
An obstacle you overcame in your educational career ... Carl Wieman Science Education Initiative -papers and presentations (can be used to support any STEM education at the undergraduate level): ... Writing your teaching philosophy statement Author: Barb Created Date:
This paper will be an integration and explanation of your educational philosophy and its implications on your teaching practice. You should not need to invent your own theory of education. This paper should focus on an integration of traditional Western educational philosophy (i.e., progressivism, existentialism, perennialism, and essentialism ...
Follow these seven steps to write your teaching philosophy statement: 1. Consider your audience. Before you begin writing your teaching philosophy statement, begin by considering your audience and what may be of greatest importance to them. If you're writing for a hiring committee, know that they may be interested in both the internal and ...
Similar in format to a teaching philosophy statement, an educational leadership philosophy statement "clearly communicate[s] what our beliefs are about educational leadership, why we hold these beliefs and how we translate our beliefs into practice" (Berenson and Kenny, 2015).