- Privacy Policy

Home » Variables in Research – Definition, Types and Examples

Variables in Research – Definition, Types and Examples
Table of Contents

Variables in Research
Definition:
In Research, Variables refer to characteristics or attributes that can be measured, manipulated, or controlled. They are the factors that researchers observe or manipulate to understand the relationship between them and the outcomes of interest.
Types of Variables in Research
Types of Variables in Research are as follows:
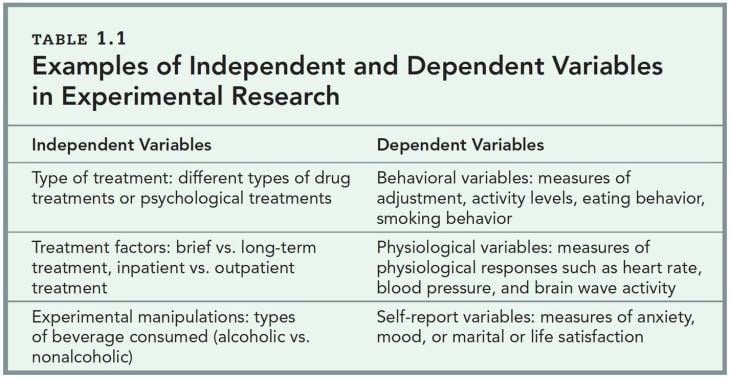
Independent Variable
This is the variable that is manipulated by the researcher. It is also known as the predictor variable, as it is used to predict changes in the dependent variable. Examples of independent variables include age, gender, dosage, and treatment type.
Dependent Variable
This is the variable that is measured or observed to determine the effects of the independent variable. It is also known as the outcome variable, as it is the variable that is affected by the independent variable. Examples of dependent variables include blood pressure, test scores, and reaction time.
Confounding Variable
This is a variable that can affect the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. It is a variable that is not being studied but could impact the results of the study. For example, in a study on the effects of a new drug on a disease, a confounding variable could be the patient’s age, as older patients may have more severe symptoms.
Mediating Variable
This is a variable that explains the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. It is a variable that comes in between the independent and dependent variables and is affected by the independent variable, which then affects the dependent variable. For example, in a study on the relationship between exercise and weight loss, the mediating variable could be metabolism, as exercise can increase metabolism, which can then lead to weight loss.
Moderator Variable
This is a variable that affects the strength or direction of the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. It is a variable that influences the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. For example, in a study on the effects of caffeine on cognitive performance, the moderator variable could be age, as older adults may be more sensitive to the effects of caffeine than younger adults.
Control Variable
This is a variable that is held constant or controlled by the researcher to ensure that it does not affect the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. Control variables are important to ensure that any observed effects are due to the independent variable and not to other factors. For example, in a study on the effects of a new teaching method on student performance, the control variables could include class size, teacher experience, and student demographics.
Continuous Variable
This is a variable that can take on any value within a certain range. Continuous variables can be measured on a scale and are often used in statistical analyses. Examples of continuous variables include height, weight, and temperature.
Categorical Variable
This is a variable that can take on a limited number of values or categories. Categorical variables can be nominal or ordinal. Nominal variables have no inherent order, while ordinal variables have a natural order. Examples of categorical variables include gender, race, and educational level.
Discrete Variable
This is a variable that can only take on specific values. Discrete variables are often used in counting or frequency analyses. Examples of discrete variables include the number of siblings a person has, the number of times a person exercises in a week, and the number of students in a classroom.
Dummy Variable
This is a variable that takes on only two values, typically 0 and 1, and is used to represent categorical variables in statistical analyses. Dummy variables are often used when a categorical variable cannot be used directly in an analysis. For example, in a study on the effects of gender on income, a dummy variable could be created, with 0 representing female and 1 representing male.
Extraneous Variable
This is a variable that has no relationship with the independent or dependent variable but can affect the outcome of the study. Extraneous variables can lead to erroneous conclusions and can be controlled through random assignment or statistical techniques.
Latent Variable
This is a variable that cannot be directly observed or measured, but is inferred from other variables. Latent variables are often used in psychological or social research to represent constructs such as personality traits, attitudes, or beliefs.
Moderator-mediator Variable
This is a variable that acts both as a moderator and a mediator. It can moderate the relationship between the independent and dependent variables and also mediate the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Moderator-mediator variables are often used in complex statistical analyses.
Variables Analysis Methods
There are different methods to analyze variables in research, including:
- Descriptive statistics: This involves analyzing and summarizing data using measures such as mean, median, mode, range, standard deviation, and frequency distribution. Descriptive statistics are useful for understanding the basic characteristics of a data set.
- Inferential statistics : This involves making inferences about a population based on sample data. Inferential statistics use techniques such as hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis to draw conclusions from data.
- Correlation analysis: This involves examining the relationship between two or more variables. Correlation analysis can determine the strength and direction of the relationship between variables, and can be used to make predictions about future outcomes.
- Regression analysis: This involves examining the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. Regression analysis can be used to predict the value of the dependent variable based on the value of the independent variable, and can also determine the significance of the relationship between the two variables.
- Factor analysis: This involves identifying patterns and relationships among a large number of variables. Factor analysis can be used to reduce the complexity of a data set and identify underlying factors or dimensions.
- Cluster analysis: This involves grouping data into clusters based on similarities between variables. Cluster analysis can be used to identify patterns or segments within a data set, and can be useful for market segmentation or customer profiling.
- Multivariate analysis : This involves analyzing multiple variables simultaneously. Multivariate analysis can be used to understand complex relationships between variables, and can be useful in fields such as social science, finance, and marketing.
Examples of Variables
- Age : This is a continuous variable that represents the age of an individual in years.
- Gender : This is a categorical variable that represents the biological sex of an individual and can take on values such as male and female.
- Education level: This is a categorical variable that represents the level of education completed by an individual and can take on values such as high school, college, and graduate school.
- Income : This is a continuous variable that represents the amount of money earned by an individual in a year.
- Weight : This is a continuous variable that represents the weight of an individual in kilograms or pounds.
- Ethnicity : This is a categorical variable that represents the ethnic background of an individual and can take on values such as Hispanic, African American, and Asian.
- Time spent on social media : This is a continuous variable that represents the amount of time an individual spends on social media in minutes or hours per day.
- Marital status: This is a categorical variable that represents the marital status of an individual and can take on values such as married, divorced, and single.
- Blood pressure : This is a continuous variable that represents the force of blood against the walls of arteries in millimeters of mercury.
- Job satisfaction : This is a continuous variable that represents an individual’s level of satisfaction with their job and can be measured using a Likert scale.
Applications of Variables
Variables are used in many different applications across various fields. Here are some examples:
- Scientific research: Variables are used in scientific research to understand the relationships between different factors and to make predictions about future outcomes. For example, scientists may study the effects of different variables on plant growth or the impact of environmental factors on animal behavior.
- Business and marketing: Variables are used in business and marketing to understand customer behavior and to make decisions about product development and marketing strategies. For example, businesses may study variables such as consumer preferences, spending habits, and market trends to identify opportunities for growth.
- Healthcare : Variables are used in healthcare to monitor patient health and to make treatment decisions. For example, doctors may use variables such as blood pressure, heart rate, and cholesterol levels to diagnose and treat cardiovascular disease.
- Education : Variables are used in education to measure student performance and to evaluate the effectiveness of teaching strategies. For example, teachers may use variables such as test scores, attendance, and class participation to assess student learning.
- Social sciences : Variables are used in social sciences to study human behavior and to understand the factors that influence social interactions. For example, sociologists may study variables such as income, education level, and family structure to examine patterns of social inequality.
Purpose of Variables
Variables serve several purposes in research, including:
- To provide a way of measuring and quantifying concepts: Variables help researchers measure and quantify abstract concepts such as attitudes, behaviors, and perceptions. By assigning numerical values to these concepts, researchers can analyze and compare data to draw meaningful conclusions.
- To help explain relationships between different factors: Variables help researchers identify and explain relationships between different factors. By analyzing how changes in one variable affect another variable, researchers can gain insight into the complex interplay between different factors.
- To make predictions about future outcomes : Variables help researchers make predictions about future outcomes based on past observations. By analyzing patterns and relationships between different variables, researchers can make informed predictions about how different factors may affect future outcomes.
- To test hypotheses: Variables help researchers test hypotheses and theories. By collecting and analyzing data on different variables, researchers can test whether their predictions are accurate and whether their hypotheses are supported by the evidence.
Characteristics of Variables
Characteristics of Variables are as follows:
- Measurement : Variables can be measured using different scales, such as nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio scales. The scale used to measure a variable can affect the type of statistical analysis that can be applied.
- Range : Variables have a range of values that they can take on. The range can be finite, such as the number of students in a class, or infinite, such as the range of possible values for a continuous variable like temperature.
- Variability : Variables can have different levels of variability, which refers to the degree to which the values of the variable differ from each other. Highly variable variables have a wide range of values, while low variability variables have values that are more similar to each other.
- Validity and reliability : Variables should be both valid and reliable to ensure accurate and consistent measurement. Validity refers to the extent to which a variable measures what it is intended to measure, while reliability refers to the consistency of the measurement over time.
- Directionality: Some variables have directionality, meaning that the relationship between the variables is not symmetrical. For example, in a study of the relationship between smoking and lung cancer, smoking is the independent variable and lung cancer is the dependent variable.
Advantages of Variables
Here are some of the advantages of using variables in research:
- Control : Variables allow researchers to control the effects of external factors that could influence the outcome of the study. By manipulating and controlling variables, researchers can isolate the effects of specific factors and measure their impact on the outcome.
- Replicability : Variables make it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and test its findings. By defining and measuring variables consistently, other researchers can conduct similar studies to validate the original findings.
- Accuracy : Variables make it possible to measure phenomena accurately and objectively. By defining and measuring variables precisely, researchers can reduce bias and increase the accuracy of their findings.
- Generalizability : Variables allow researchers to generalize their findings to larger populations. By selecting variables that are representative of the population, researchers can draw conclusions that are applicable to a broader range of individuals.
- Clarity : Variables help researchers to communicate their findings more clearly and effectively. By defining and categorizing variables, researchers can organize and present their findings in a way that is easily understandable to others.
Disadvantages of Variables
Here are some of the main disadvantages of using variables in research:
- Simplification : Variables may oversimplify the complexity of real-world phenomena. By breaking down a phenomenon into variables, researchers may lose important information and context, which can affect the accuracy and generalizability of their findings.
- Measurement error : Variables rely on accurate and precise measurement, and measurement error can affect the reliability and validity of research findings. The use of subjective or poorly defined variables can also introduce measurement error into the study.
- Confounding variables : Confounding variables are factors that are not measured but that affect the relationship between the variables of interest. If confounding variables are not accounted for, they can distort or obscure the relationship between the variables of interest.
- Limited scope: Variables are defined by the researcher, and the scope of the study is therefore limited by the researcher’s choice of variables. This can lead to a narrow focus that overlooks important aspects of the phenomenon being studied.
- Ethical concerns: The selection and measurement of variables may raise ethical concerns, especially in studies involving human subjects. For example, using variables that are related to sensitive topics, such as race or sexuality, may raise concerns about privacy and discrimination.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Control Variable – Definition, Types and Examples

Moderating Variable – Definition, Analysis...

Categorical Variable – Definition, Types and...

Independent Variable – Definition, Types and...

Ratio Variable – Definition, Purpose and Examples

Ordinal Variable – Definition, Purpose and...
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Definitions
Dependent Variable The variable that depends on other factors that are measured. These variables are expected to change as a result of an experimental manipulation of the independent variable or variables. It is the presumed effect.
Independent Variable The variable that is stable and unaffected by the other variables you are trying to measure. It refers to the condition of an experiment that is systematically manipulated by the investigator. It is the presumed cause.
Cramer, Duncan and Dennis Howitt. The SAGE Dictionary of Statistics . London: SAGE, 2004; Penslar, Robin Levin and Joan P. Porter. Institutional Review Board Guidebook: Introduction . Washington, DC: United States Department of Health and Human Services, 2010; "What are Dependent and Independent Variables?" Graphic Tutorial.
Identifying Dependent and Independent Variables
Don't feel bad if you are confused about what is the dependent variable and what is the independent variable in social and behavioral sciences research . However, it's important that you learn the difference because framing a study using these variables is a common approach to organizing the elements of a social sciences research study in order to discover relevant and meaningful results. Specifically, it is important for these two reasons:
- You need to understand and be able to evaluate their application in other people's research.
- You need to apply them correctly in your own research.
A variable in research simply refers to a person, place, thing, or phenomenon that you are trying to measure in some way. The best way to understand the difference between a dependent and independent variable is that the meaning of each is implied by what the words tell us about the variable you are using. You can do this with a simple exercise from the website, Graphic Tutorial. Take the sentence, "The [independent variable] causes a change in [dependent variable] and it is not possible that [dependent variable] could cause a change in [independent variable]." Insert the names of variables you are using in the sentence in the way that makes the most sense. This will help you identify each type of variable. If you're still not sure, consult with your professor before you begin to write.
Fan, Shihe. "Independent Variable." In Encyclopedia of Research Design. Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2010), pp. 592-594; "What are Dependent and Independent Variables?" Graphic Tutorial; Salkind, Neil J. "Dependent Variable." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2010), pp. 348-349;
Structure and Writing Style
The process of examining a research problem in the social and behavioral sciences is often framed around methods of analysis that compare, contrast, correlate, average, or integrate relationships between or among variables . Techniques include associations, sampling, random selection, and blind selection. Designation of the dependent and independent variable involves unpacking the research problem in a way that identifies a general cause and effect and classifying these variables as either independent or dependent.
The variables should be outlined in the introduction of your paper and explained in more detail in the methods section . There are no rules about the structure and style for writing about independent or dependent variables but, as with any academic writing, clarity and being succinct is most important.
After you have described the research problem and its significance in relation to prior research, explain why you have chosen to examine the problem using a method of analysis that investigates the relationships between or among independent and dependent variables . State what it is about the research problem that lends itself to this type of analysis. For example, if you are investigating the relationship between corporate environmental sustainability efforts [the independent variable] and dependent variables associated with measuring employee satisfaction at work using a survey instrument, you would first identify each variable and then provide background information about the variables. What is meant by "environmental sustainability"? Are you looking at a particular company [e.g., General Motors] or are you investigating an industry [e.g., the meat packing industry]? Why is employee satisfaction in the workplace important? How does a company make their employees aware of sustainability efforts and why would a company even care that its employees know about these efforts?
Identify each variable for the reader and define each . In the introduction, this information can be presented in a paragraph or two when you describe how you are going to study the research problem. In the methods section, you build on the literature review of prior studies about the research problem to describe in detail background about each variable, breaking each down for measurement and analysis. For example, what activities do you examine that reflect a company's commitment to environmental sustainability? Levels of employee satisfaction can be measured by a survey that asks about things like volunteerism or a desire to stay at the company for a long time.
The structure and writing style of describing the variables and their application to analyzing the research problem should be stated and unpacked in such a way that the reader obtains a clear understanding of the relationships between the variables and why they are important. This is also important so that the study can be replicated in the future using the same variables but applied in a different way.
Fan, Shihe. "Independent Variable." In Encyclopedia of Research Design. Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2010), pp. 592-594; "What are Dependent and Independent Variables?" Graphic Tutorial; “Case Example for Independent and Dependent Variables.” ORI Curriculum Examples. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Research Integrity; Salkind, Neil J. "Dependent Variable." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2010), pp. 348-349; “Independent Variables and Dependent Variables.” Karl L. Wuensch, Department of Psychology, East Carolina University [posted email exchange]; “Variables.” Elements of Research. Dr. Camille Nebeker, San Diego State University.
- << Previous: Design Flaws to Avoid
- Next: Glossary of Research Terms >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 4:39 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Research Variables 101
Independent variables, dependent variables, control variables and more
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Kerryn Warren (PhD) | January 2023
If you’re new to the world of research, especially scientific research, you’re bound to run into the concept of variables , sooner or later. If you’re feeling a little confused, don’t worry – you’re not the only one! Independent variables, dependent variables, confounding variables – it’s a lot of jargon. In this post, we’ll unpack the terminology surrounding research variables using straightforward language and loads of examples .
Overview: Variables In Research
What (exactly) is a variable.
The simplest way to understand a variable is as any characteristic or attribute that can experience change or vary over time or context – hence the name “variable”. For example, the dosage of a particular medicine could be classified as a variable, as the amount can vary (i.e., a higher dose or a lower dose). Similarly, gender, age or ethnicity could be considered demographic variables, because each person varies in these respects.
Within research, especially scientific research, variables form the foundation of studies, as researchers are often interested in how one variable impacts another, and the relationships between different variables. For example:
- How someone’s age impacts their sleep quality
- How different teaching methods impact learning outcomes
- How diet impacts weight (gain or loss)
As you can see, variables are often used to explain relationships between different elements and phenomena. In scientific studies, especially experimental studies, the objective is often to understand the causal relationships between variables. In other words, the role of cause and effect between variables. This is achieved by manipulating certain variables while controlling others – and then observing the outcome. But, we’ll get into that a little later…
The “Big 3” Variables
Variables can be a little intimidating for new researchers because there are a wide variety of variables, and oftentimes, there are multiple labels for the same thing. To lay a firm foundation, we’ll first look at the three main types of variables, namely:
- Independent variables (IV)
- Dependant variables (DV)
- Control variables
What is an independent variable?
Simply put, the independent variable is the “ cause ” in the relationship between two (or more) variables. In other words, when the independent variable changes, it has an impact on another variable.
For example:
- Increasing the dosage of a medication (Variable A) could result in better (or worse) health outcomes for a patient (Variable B)
- Changing a teaching method (Variable A) could impact the test scores that students earn in a standardised test (Variable B)
- Varying one’s diet (Variable A) could result in weight loss or gain (Variable B).
It’s useful to know that independent variables can go by a few different names, including, explanatory variables (because they explain an event or outcome) and predictor variables (because they predict the value of another variable). Terminology aside though, the most important takeaway is that independent variables are assumed to be the “cause” in any cause-effect relationship. As you can imagine, these types of variables are of major interest to researchers, as many studies seek to understand the causal factors behind a phenomenon.
Need a helping hand?
What is a dependent variable?
While the independent variable is the “ cause ”, the dependent variable is the “ effect ” – or rather, the affected variable . In other words, the dependent variable is the variable that is assumed to change as a result of a change in the independent variable.
Keeping with the previous example, let’s look at some dependent variables in action:
- Health outcomes (DV) could be impacted by dosage changes of a medication (IV)
- Students’ scores (DV) could be impacted by teaching methods (IV)
- Weight gain or loss (DV) could be impacted by diet (IV)
In scientific studies, researchers will typically pay very close attention to the dependent variable (or variables), carefully measuring any changes in response to hypothesised independent variables. This can be tricky in practice, as it’s not always easy to reliably measure specific phenomena or outcomes – or to be certain that the actual cause of the change is in fact the independent variable.
As the adage goes, correlation is not causation . In other words, just because two variables have a relationship doesn’t mean that it’s a causal relationship – they may just happen to vary together. For example, you could find a correlation between the number of people who own a certain brand of car and the number of people who have a certain type of job. Just because the number of people who own that brand of car and the number of people who have that type of job is correlated, it doesn’t mean that owning that brand of car causes someone to have that type of job or vice versa. The correlation could, for example, be caused by another factor such as income level or age group, which would affect both car ownership and job type.
To confidently establish a causal relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable (i.e., X causes Y), you’ll typically need an experimental design , where you have complete control over the environmen t and the variables of interest. But even so, this doesn’t always translate into the “real world”. Simply put, what happens in the lab sometimes stays in the lab!
As an alternative to pure experimental research, correlational or “ quasi-experimental ” research (where the researcher cannot manipulate or change variables) can be done on a much larger scale more easily, allowing one to understand specific relationships in the real world. These types of studies also assume some causality between independent and dependent variables, but it’s not always clear. So, if you go this route, you need to be cautious in terms of how you describe the impact and causality between variables and be sure to acknowledge any limitations in your own research.

What is a control variable?
In an experimental design, a control variable (or controlled variable) is a variable that is intentionally held constant to ensure it doesn’t have an influence on any other variables. As a result, this variable remains unchanged throughout the course of the study. In other words, it’s a variable that’s not allowed to vary – tough life 🙂
As we mentioned earlier, one of the major challenges in identifying and measuring causal relationships is that it’s difficult to isolate the impact of variables other than the independent variable. Simply put, there’s always a risk that there are factors beyond the ones you’re specifically looking at that might be impacting the results of your study. So, to minimise the risk of this, researchers will attempt (as best possible) to hold other variables constant . These factors are then considered control variables.
Some examples of variables that you may need to control include:
- Temperature
- Time of day
- Noise or distractions
Which specific variables need to be controlled for will vary tremendously depending on the research project at hand, so there’s no generic list of control variables to consult. As a researcher, you’ll need to think carefully about all the factors that could vary within your research context and then consider how you’ll go about controlling them. A good starting point is to look at previous studies similar to yours and pay close attention to which variables they controlled for.
Of course, you won’t always be able to control every possible variable, and so, in many cases, you’ll just have to acknowledge their potential impact and account for them in the conclusions you draw. Every study has its limitations, so don’t get fixated or discouraged by troublesome variables. Nevertheless, always think carefully about the factors beyond what you’re focusing on – don’t make assumptions!

Other types of variables
As we mentioned, independent, dependent and control variables are the most common variables you’ll come across in your research, but they’re certainly not the only ones you need to be aware of. Next, we’ll look at a few “secondary” variables that you need to keep in mind as you design your research.
- Moderating variables
- Mediating variables
- Confounding variables
- Latent variables
Let’s jump into it…
What is a moderating variable?
A moderating variable is a variable that influences the strength or direction of the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. In other words, moderating variables affect how much (or how little) the IV affects the DV, or whether the IV has a positive or negative relationship with the DV (i.e., moves in the same or opposite direction).
For example, in a study about the effects of sleep deprivation on academic performance, gender could be used as a moderating variable to see if there are any differences in how men and women respond to a lack of sleep. In such a case, one may find that gender has an influence on how much students’ scores suffer when they’re deprived of sleep.
It’s important to note that while moderators can have an influence on outcomes , they don’t necessarily cause them ; rather they modify or “moderate” existing relationships between other variables. This means that it’s possible for two different groups with similar characteristics, but different levels of moderation, to experience very different results from the same experiment or study design.
What is a mediating variable?
Mediating variables are often used to explain the relationship between the independent and dependent variable (s). For example, if you were researching the effects of age on job satisfaction, then education level could be considered a mediating variable, as it may explain why older people have higher job satisfaction than younger people – they may have more experience or better qualifications, which lead to greater job satisfaction.
Mediating variables also help researchers understand how different factors interact with each other to influence outcomes. For instance, if you wanted to study the effect of stress on academic performance, then coping strategies might act as a mediating factor by influencing both stress levels and academic performance simultaneously. For example, students who use effective coping strategies might be less stressed but also perform better academically due to their improved mental state.
In addition, mediating variables can provide insight into causal relationships between two variables by helping researchers determine whether changes in one factor directly cause changes in another – or whether there is an indirect relationship between them mediated by some third factor(s). For instance, if you wanted to investigate the impact of parental involvement on student achievement, you would need to consider family dynamics as a potential mediator, since it could influence both parental involvement and student achievement simultaneously.

What is a confounding variable?
A confounding variable (also known as a third variable or lurking variable ) is an extraneous factor that can influence the relationship between two variables being studied. Specifically, for a variable to be considered a confounding variable, it needs to meet two criteria:
- It must be correlated with the independent variable (this can be causal or not)
- It must have a causal impact on the dependent variable (i.e., influence the DV)
Some common examples of confounding variables include demographic factors such as gender, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, age, education level, and health status. In addition to these, there are also environmental factors to consider. For example, air pollution could confound the impact of the variables of interest in a study investigating health outcomes.
Naturally, it’s important to identify as many confounding variables as possible when conducting your research, as they can heavily distort the results and lead you to draw incorrect conclusions . So, always think carefully about what factors may have a confounding effect on your variables of interest and try to manage these as best you can.
What is a latent variable?
Latent variables are unobservable factors that can influence the behaviour of individuals and explain certain outcomes within a study. They’re also known as hidden or underlying variables , and what makes them rather tricky is that they can’t be directly observed or measured . Instead, latent variables must be inferred from other observable data points such as responses to surveys or experiments.
For example, in a study of mental health, the variable “resilience” could be considered a latent variable. It can’t be directly measured , but it can be inferred from measures of mental health symptoms, stress, and coping mechanisms. The same applies to a lot of concepts we encounter every day – for example:
- Emotional intelligence
- Quality of life
- Business confidence
- Ease of use
One way in which we overcome the challenge of measuring the immeasurable is latent variable models (LVMs). An LVM is a type of statistical model that describes a relationship between observed variables and one or more unobserved (latent) variables. These models allow researchers to uncover patterns in their data which may not have been visible before, thanks to their complexity and interrelatedness with other variables. Those patterns can then inform hypotheses about cause-and-effect relationships among those same variables which were previously unknown prior to running the LVM. Powerful stuff, we say!

Let’s recap
In the world of scientific research, there’s no shortage of variable types, some of which have multiple names and some of which overlap with each other. In this post, we’ve covered some of the popular ones, but remember that this is not an exhaustive list .
To recap, we’ve explored:
- Independent variables (the “cause”)
- Dependent variables (the “effect”)
- Control variables (the variable that’s not allowed to vary)
If you’re still feeling a bit lost and need a helping hand with your research project, check out our 1-on-1 coaching service , where we guide you through each step of the research journey. Also, be sure to check out our free dissertation writing course and our collection of free, fully-editable chapter templates .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

Very informative, concise and helpful. Thank you
Helping information.Thanks
practical and well-demonstrated
Very helpful and insightful
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Variables in Research | Types, Definiton & Examples

Introduction
What is a variable, what are the 5 types of variables in research, other variables in research.
Variables are fundamental components of research that allow for the measurement and analysis of data. They can be defined as characteristics or properties that can take on different values. In research design , understanding the types of variables and their roles is crucial for developing hypotheses , designing methods , and interpreting results .
This article outlines the the types of variables in research, including their definitions and examples, to provide a clear understanding of their use and significance in research studies. By categorizing variables into distinct groups based on their roles in research, their types of data, and their relationships with other variables, researchers can more effectively structure their studies and achieve more accurate conclusions.

A variable represents any characteristic, number, or quantity that can be measured or quantified. The term encompasses anything that can vary or change, ranging from simple concepts like age and height to more complex ones like satisfaction levels or economic status. Variables are essential in research as they are the foundational elements that researchers manipulate, measure, or control to gain insights into relationships, causes, and effects within their studies. They enable the framing of research questions, the formulation of hypotheses, and the interpretation of results.
Variables can be categorized based on their role in the study (such as independent and dependent variables ), the type of data they represent (quantitative or categorical), and their relationship to other variables (like confounding or control variables). Understanding what constitutes a variable and the various variable types available is a critical step in designing robust and meaningful research.
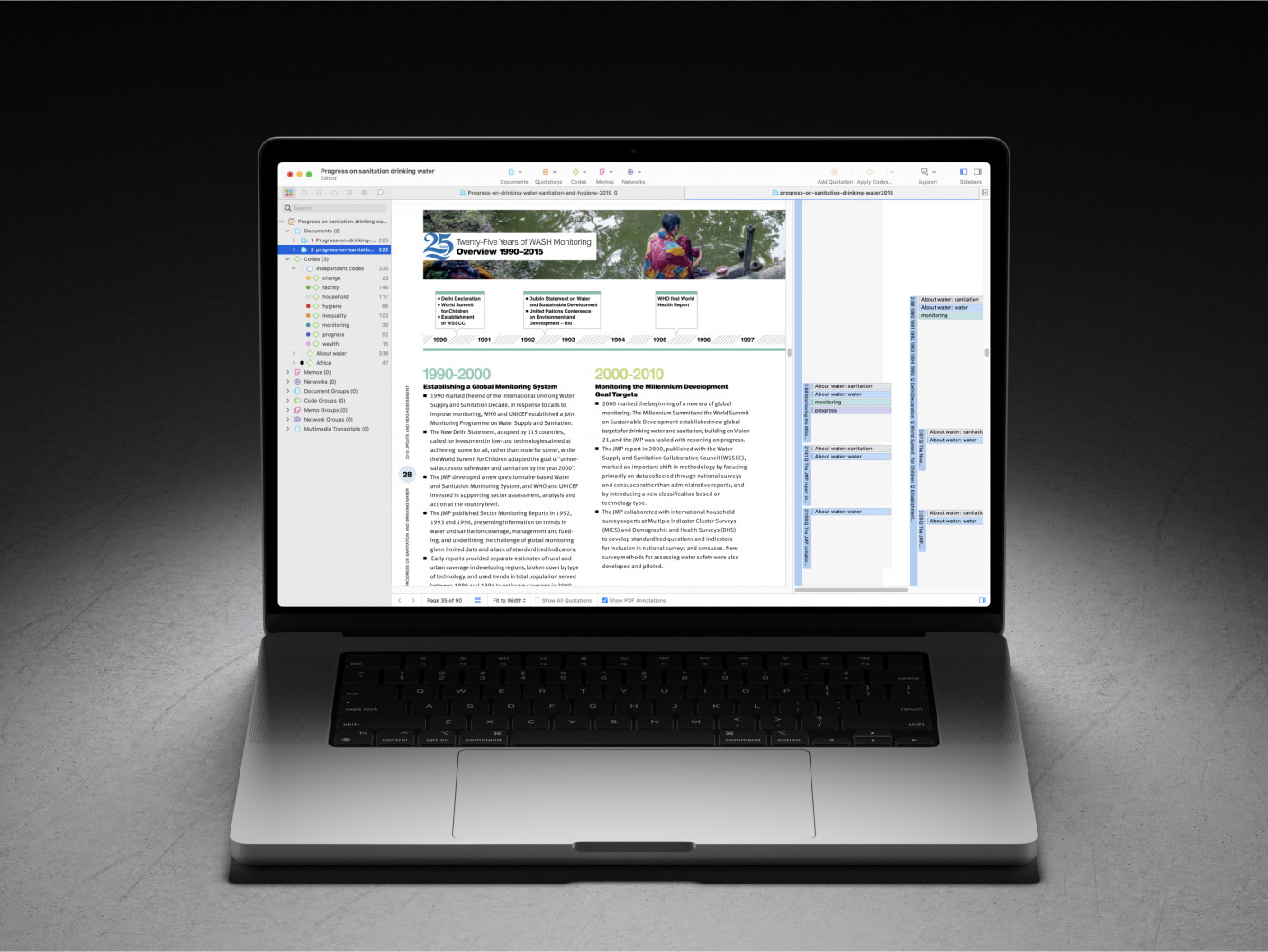
ATLAS.ti makes complex data easy to understand
Turn to our powerful data analysis tools to make the most of your research. Get started with a free trial.
Variables are crucial components in research, serving as the foundation for data collection , analysis , and interpretation . They are attributes or characteristics that can vary among subjects or over time, and understanding their types is essential for any study. Variables can be broadly classified into five main types, each with its distinct characteristics and roles within research.
This classification helps researchers in designing their studies, choosing appropriate measurement techniques, and analyzing their results accurately. The five types of variables include independent variables, dependent variables, categorical variables, continuous variables, and confounding variables. These categories not only facilitate a clearer understanding of the data but also guide the formulation of hypotheses and research methodologies.
Independent variables
Independent variables are foundational to the structure of research, serving as the factors or conditions that researchers manipulate or vary to observe their effects on dependent variables. These variables are considered "independent" because their variation does not depend on other variables within the study. Instead, they are the cause or stimulus that directly influences the outcomes being measured. For example, in an experiment to assess the effectiveness of a new teaching method on student performance, the teaching method applied (traditional vs. innovative) would be the independent variable.
The selection of an independent variable is a critical step in research design, as it directly correlates with the study's objective to determine causality or association. Researchers must clearly define and control these variables to ensure that observed changes in the dependent variable can be attributed to variations in the independent variable, thereby affirming the reliability of the results. In experimental research, the independent variable is what differentiates the control group from the experimental group, thereby setting the stage for meaningful comparison and analysis.
Dependent variables
Dependent variables are the outcomes or effects that researchers aim to explore and understand in their studies. These variables are called "dependent" because their values depend on the changes or variations of the independent variables.
Essentially, they are the responses or results that are measured to assess the impact of the independent variable's manipulation. For instance, in a study investigating the effect of exercise on weight loss, the amount of weight lost would be considered the dependent variable, as it depends on the exercise regimen (the independent variable).
The identification and measurement of the dependent variable are crucial for testing the hypothesis and drawing conclusions from the research. It allows researchers to quantify the effect of the independent variable , providing evidence for causal relationships or associations. In experimental settings, the dependent variable is what is being tested and measured across different groups or conditions, enabling researchers to assess the efficacy or impact of the independent variable's variation.
To ensure accuracy and reliability, the dependent variable must be defined clearly and measured consistently across all participants or observations. This consistency helps in reducing measurement errors and increases the validity of the research findings. By carefully analyzing the dependent variables, researchers can derive meaningful insights from their studies, contributing to the broader knowledge in their field.
Categorical variables
Categorical variables, also known as qualitative variables, represent types or categories that are used to group observations. These variables divide data into distinct groups or categories that lack a numerical value but hold significant meaning in research. Examples of categorical variables include gender (male, female, other), type of vehicle (car, truck, motorcycle), or marital status (single, married, divorced). These categories help researchers organize data into groups for comparison and analysis.
Categorical variables can be further classified into two subtypes: nominal and ordinal. Nominal variables are categories without any inherent order or ranking among them, such as blood type or ethnicity. Ordinal variables, on the other hand, imply a sort of ranking or order among the categories, like levels of satisfaction (high, medium, low) or education level (high school, bachelor's, master's, doctorate).
Understanding and identifying categorical variables is crucial in research as it influences the choice of statistical analysis methods. Since these variables represent categories without numerical significance, researchers employ specific statistical tests designed for a nominal or ordinal variable to draw meaningful conclusions. Properly classifying and analyzing categorical variables allow for the exploration of relationships between different groups within the study, shedding light on patterns and trends that might not be evident with numerical data alone.
Continuous variables
Continuous variables are quantitative variables that can take an infinite number of values within a given range. These variables are measured along a continuum and can represent very precise measurements. Examples of continuous variables include height, weight, temperature, and time. Because they can assume any value within a range, continuous variables allow for detailed analysis and a high degree of accuracy in research findings.
The ability to measure continuous variables at very fine scales makes them invaluable for many types of research, particularly in the natural and social sciences. For instance, in a study examining the effect of temperature on plant growth, temperature would be considered a continuous variable since it can vary across a wide spectrum and be measured to several decimal places.
When dealing with continuous variables, researchers often use methods incorporating a particular statistical test to accommodate a wide range of data points and the potential for infinite divisibility. This includes various forms of regression analysis, correlation, and other techniques suited for modeling and analyzing nuanced relationships between variables. The precision of continuous variables enhances the researcher's ability to detect patterns, trends, and causal relationships within the data, contributing to more robust and detailed conclusions.
Confounding variables
Confounding variables are those that can cause a false association between the independent and dependent variables, potentially leading to incorrect conclusions about the relationship being studied. These are extraneous variables that were not considered in the study design but can influence both the supposed cause and effect, creating a misleading correlation.
Identifying and controlling for a confounding variable is crucial in research to ensure the validity of the findings. This can be achieved through various methods, including randomization, stratification, and statistical control. Randomization helps to evenly distribute confounding variables across study groups, reducing their potential impact. Stratification involves analyzing the data within strata or layers that share common characteristics of the confounder. Statistical control allows researchers to adjust for the effects of confounders in the analysis phase.
Properly addressing confounding variables strengthens the credibility of research outcomes by clarifying the direct relationship between the dependent and independent variables, thus providing more accurate and reliable results.
Beyond the primary categories of variables commonly discussed in research methodology , there exists a diverse range of other variables that play significant roles in the design and analysis of studies. Below is an overview of some of these variables, highlighting their definitions and roles within research studies:
- Discrete variables : A discrete variable is a quantitative variable that represents quantitative data , such as the number of children in a family or the number of cars in a parking lot. Discrete variables can only take on specific values.
- Categorical variables : A categorical variable categorizes subjects or items into groups that do not have a natural numerical order. Categorical data includes nominal variables, like country of origin, and ordinal variables, such as education level.
- Predictor variables : Often used in statistical models, a predictor variable is used to forecast or predict the outcomes of other variables, not necessarily with a causal implication.
- Outcome variables : These variables represent the results or outcomes that researchers aim to explain or predict through their studies. An outcome variable is central to understanding the effects of predictor variables.
- Latent variables : Not directly observable, latent variables are inferred from other, directly measured variables. Examples include psychological constructs like intelligence or socioeconomic status.
- Composite variables : Created by combining multiple variables, composite variables can measure a concept more reliably or simplify the analysis. An example would be a composite happiness index derived from several survey questions .
- Preceding variables : These variables come before other variables in time or sequence, potentially influencing subsequent outcomes. A preceding variable is crucial in longitudinal studies to determine causality or sequences of events.

Master qualitative research with ATLAS.ti
Turn data into critical insights with our data analysis platform. Try out a free trial today.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Independent vs Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples
Independent vs Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples
Published on 4 May 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 17 October 2022.
In research, variables are any characteristics that can take on different values, such as height, age, temperature, or test scores.
Researchers often manipulate or measure independent and dependent variables in studies to test cause-and-effect relationships.
- The independent variable is the cause. Its value is independent of other variables in your study.
- The dependent variable is the effect. Its value depends on changes in the independent variable.
Your independent variable is the temperature of the room. You vary the room temperature by making it cooler for half the participants, and warmer for the other half.
Table of contents
What is an independent variable, types of independent variables, what is a dependent variable, identifying independent vs dependent variables, independent and dependent variables in research, visualising independent and dependent variables, frequently asked questions about independent and dependent variables.
An independent variable is the variable you manipulate or vary in an experimental study to explore its effects. It’s called ‘independent’ because it’s not influenced by any other variables in the study.
Independent variables are also called:
- Explanatory variables (they explain an event or outcome)
- Predictor variables (they can be used to predict the value of a dependent variable)
- Right-hand-side variables (they appear on the right-hand side of a regression equation).
These terms are especially used in statistics , where you estimate the extent to which an independent variable change can explain or predict changes in the dependent variable.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
There are two main types of independent variables.
- Experimental independent variables can be directly manipulated by researchers.
- Subject variables cannot be manipulated by researchers, but they can be used to group research subjects categorically.
Experimental variables
In experiments, you manipulate independent variables directly to see how they affect your dependent variable. The independent variable is usually applied at different levels to see how the outcomes differ.
You can apply just two levels in order to find out if an independent variable has an effect at all.
You can also apply multiple levels to find out how the independent variable affects the dependent variable.
You have three independent variable levels, and each group gets a different level of treatment.
You randomly assign your patients to one of the three groups:
- A low-dose experimental group
- A high-dose experimental group
- A placebo group
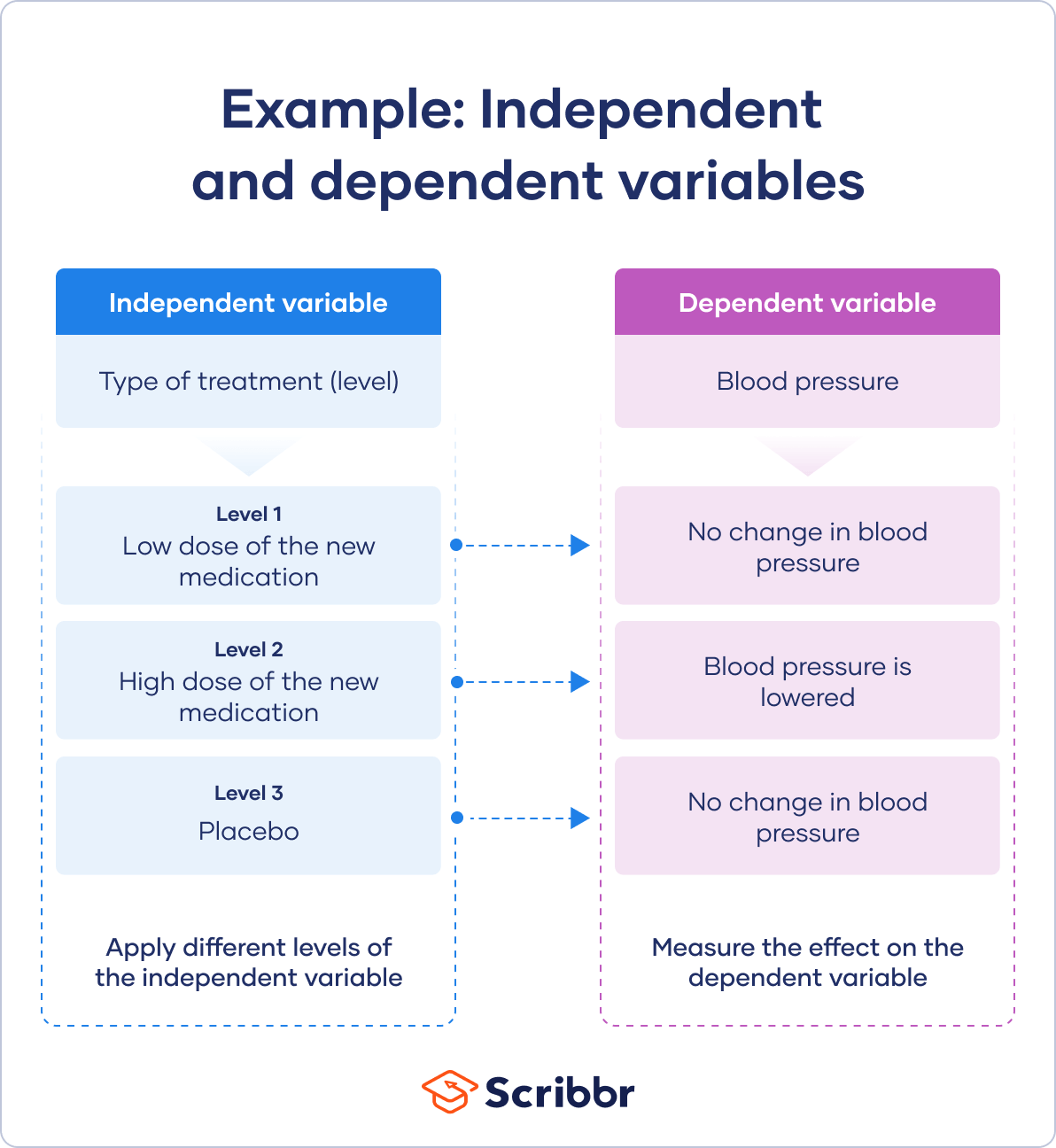
A true experiment requires you to randomly assign different levels of an independent variable to your participants.
Random assignment helps you control participant characteristics, so that they don’t affect your experimental results. This helps you to have confidence that your dependent variable results come solely from the independent variable manipulation.
Subject variables
Subject variables are characteristics that vary across participants, and they can’t be manipulated by researchers. For example, gender identity, ethnicity, race, income, and education are all important subject variables that social researchers treat as independent variables.
It’s not possible to randomly assign these to participants, since these are characteristics of already existing groups. Instead, you can create a research design where you compare the outcomes of groups of participants with characteristics. This is a quasi-experimental design because there’s no random assignment.
Your independent variable is a subject variable, namely the gender identity of the participants. You have three groups: men, women, and other.
Your dependent variable is the brain activity response to hearing infant cries. You record brain activity with fMRI scans when participants hear infant cries without their awareness.
A dependent variable is the variable that changes as a result of the independent variable manipulation. It’s the outcome you’re interested in measuring, and it ‘depends’ on your independent variable.
In statistics , dependent variables are also called:
- Response variables (they respond to a change in another variable)
- Outcome variables (they represent the outcome you want to measure)
- Left-hand-side variables (they appear on the left-hand side of a regression equation)
The dependent variable is what you record after you’ve manipulated the independent variable. You use this measurement data to check whether and to what extent your independent variable influences the dependent variable by conducting statistical analyses.
Based on your findings, you can estimate the degree to which your independent variable variation drives changes in your dependent variable. You can also predict how much your dependent variable will change as a result of variation in the independent variable.
Distinguishing between independent and dependent variables can be tricky when designing a complex study or reading an academic paper.
A dependent variable from one study can be the independent variable in another study, so it’s important to pay attention to research design.
Here are some tips for identifying each variable type.
Recognising independent variables
Use this list of questions to check whether you’re dealing with an independent variable:
- Is the variable manipulated, controlled, or used as a subject grouping method by the researcher?
- Does this variable come before the other variable in time?
- Is the researcher trying to understand whether or how this variable affects another variable?
Recognising dependent variables
Check whether you’re dealing with a dependent variable:
- Is this variable measured as an outcome of the study?
- Is this variable dependent on another variable in the study?
- Does this variable get measured only after other variables are altered?
Independent and dependent variables are generally used in experimental and quasi-experimental research.
Here are some examples of research questions and corresponding independent and dependent variables.
For experimental data, you analyse your results by generating descriptive statistics and visualising your findings. Then, you select an appropriate statistical test to test your hypothesis .
The type of test is determined by:
- Your variable types
- Level of measurement
- Number of independent variable levels
You’ll often use t tests or ANOVAs to analyse your data and answer your research questions.
In quantitative research , it’s good practice to use charts or graphs to visualise the results of studies. Generally, the independent variable goes on the x -axis (horizontal) and the dependent variable on the y -axis (vertical).
The type of visualisation you use depends on the variable types in your research questions:
- A bar chart is ideal when you have a categorical independent variable.
- A scatterplot or line graph is best when your independent and dependent variables are both quantitative.
To inspect your data, you place your independent variable of treatment level on the x -axis and the dependent variable of blood pressure on the y -axis.
You plot bars for each treatment group before and after the treatment to show the difference in blood pressure.
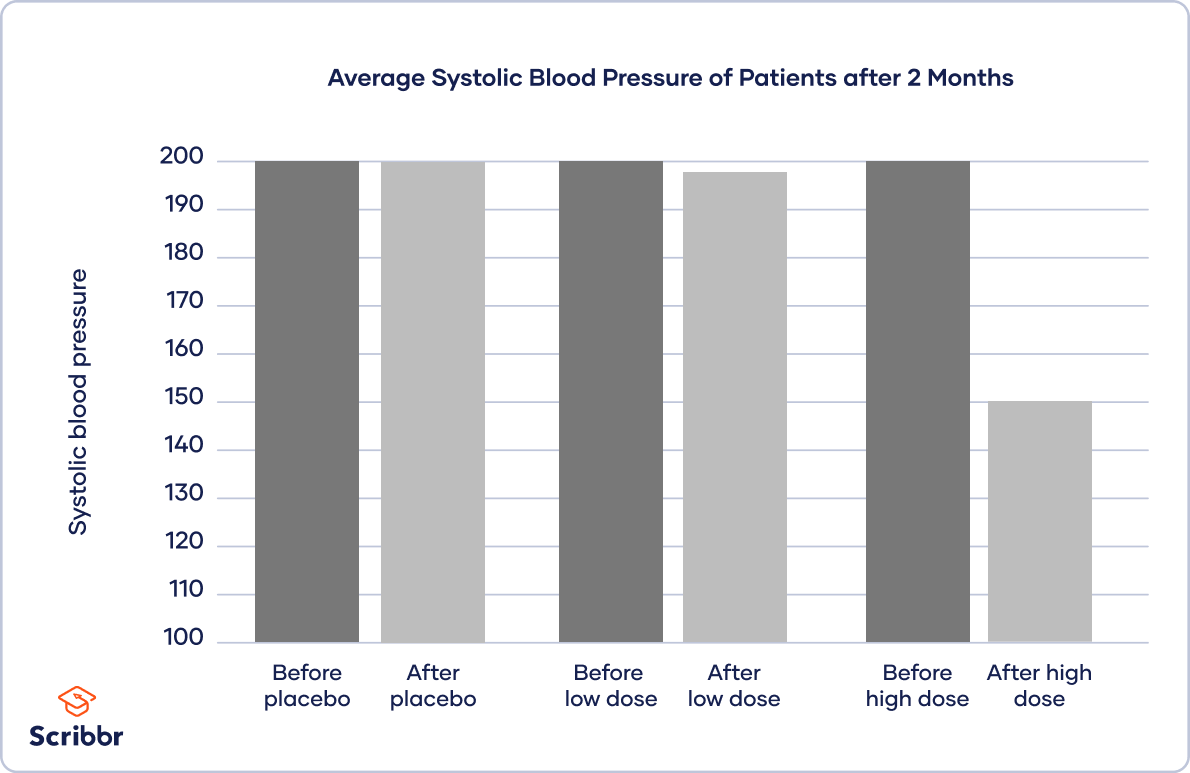
An independent variable is the variable you manipulate, control, or vary in an experimental study to explore its effects. It’s called ‘independent’ because it’s not influenced by any other variables in the study.
- Right-hand-side variables (they appear on the right-hand side of a regression equation)
A dependent variable is what changes as a result of the independent variable manipulation in experiments . It’s what you’re interested in measuring, and it ‘depends’ on your independent variable.
In statistics, dependent variables are also called:
Determining cause and effect is one of the most important parts of scientific research. It’s essential to know which is the cause – the independent variable – and which is the effect – the dependent variable.
You want to find out how blood sugar levels are affected by drinking diet cola and regular cola, so you conduct an experiment .
- The type of cola – diet or regular – is the independent variable .
- The level of blood sugar that you measure is the dependent variable – it changes depending on the type of cola.
Yes, but including more than one of either type requires multiple research questions .
For example, if you are interested in the effect of a diet on health, you can use multiple measures of health: blood sugar, blood pressure, weight, pulse, and many more. Each of these is its own dependent variable with its own research question.
You could also choose to look at the effect of exercise levels as well as diet, or even the additional effect of the two combined. Each of these is a separate independent variable .
To ensure the internal validity of an experiment , you should only change one independent variable at a time.
No. The value of a dependent variable depends on an independent variable, so a variable cannot be both independent and dependent at the same time. It must be either the cause or the effect, not both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, October 17). Independent vs Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/independent-vs-dependent-variables/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, quasi-experimental design | definition, types & examples, types of variables in research | definitions & examples.
Independent and Dependent Variables
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
In research, a variable is any characteristic, number, or quantity that can be measured or counted in experimental investigations . One is called the dependent variable, and the other is the independent variable.
In research, the independent variable is manipulated to observe its effect, while the dependent variable is the measured outcome. Essentially, the independent variable is the presumed cause, and the dependent variable is the observed effect.
Variables provide the foundation for examining relationships, drawing conclusions, and making predictions in research studies.
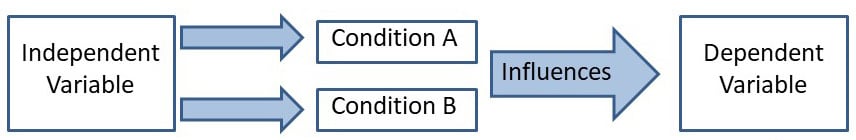
Independent Variable
In psychology, the independent variable is the variable the experimenter manipulates or changes and is assumed to directly affect the dependent variable.
It’s considered the cause or factor that drives change, allowing psychologists to observe how it influences behavior, emotions, or other dependent variables in an experimental setting. Essentially, it’s the presumed cause in cause-and-effect relationships being studied.
For example, allocating participants to drug or placebo conditions (independent variable) to measure any changes in the intensity of their anxiety (dependent variable).
In a well-designed experimental study , the independent variable is the only important difference between the experimental (e.g., treatment) and control (e.g., placebo) groups.
By changing the independent variable and holding other factors constant, psychologists aim to determine if it causes a change in another variable, called the dependent variable.
For example, in a study investigating the effects of sleep on memory, the amount of sleep (e.g., 4 hours, 8 hours, 12 hours) would be the independent variable, as the researcher might manipulate or categorize it to see its impact on memory recall, which would be the dependent variable.
Dependent Variable
In psychology, the dependent variable is the variable being tested and measured in an experiment and is “dependent” on the independent variable.
In psychology, a dependent variable represents the outcome or results and can change based on the manipulations of the independent variable. Essentially, it’s the presumed effect in a cause-and-effect relationship being studied.
An example of a dependent variable is depression symptoms, which depend on the independent variable (type of therapy).
In an experiment, the researcher looks for the possible effect on the dependent variable that might be caused by changing the independent variable.
For instance, in a study examining the effects of a new study technique on exam performance, the technique would be the independent variable (as it is being introduced or manipulated), while the exam scores would be the dependent variable (as they represent the outcome of interest that’s being measured).
Examples in Research Studies
For example, we might change the type of information (e.g., organized or random) given to participants to see how this might affect the amount of information remembered.
In this example, the type of information is the independent variable (because it changes), and the amount of information remembered is the dependent variable (because this is being measured).
For the following hypotheses, name the IV and the DV.
1. Lack of sleep significantly affects learning in 10-year-old boys.
IV……………………………………………………
DV…………………………………………………..
2. Social class has a significant effect on IQ scores.
DV……………………………………………….…
3. Stressful experiences significantly increase the likelihood of headaches.
4. Time of day has a significant effect on alertness.
Operationalizing Variables
To ensure cause and effect are established, it is important that we identify exactly how the independent and dependent variables will be measured; this is known as operationalizing the variables.
Operational variables (or operationalizing definitions) refer to how you will define and measure a specific variable as it is used in your study. This enables another psychologist to replicate your research and is essential in establishing reliability (achieving consistency in the results).
For example, if we are concerned with the effect of media violence on aggression, then we need to be very clear about what we mean by the different terms. In this case, we must state what we mean by the terms “media violence” and “aggression” as we will study them.
Therefore, you could state that “media violence” is operationally defined (in your experiment) as ‘exposure to a 15-minute film showing scenes of physical assault’; “aggression” is operationally defined as ‘levels of electrical shocks administered to a second ‘participant’ in another room.
In another example, the hypothesis “Young participants will have significantly better memories than older participants” is not operationalized. How do we define “young,” “old,” or “memory”? “Participants aged between 16 – 30 will recall significantly more nouns from a list of twenty than participants aged between 55 – 70” is operationalized.
The key point here is that we have clarified what we mean by the terms as they were studied and measured in our experiment.
If we didn’t do this, it would be very difficult (if not impossible) to compare the findings of different studies to the same behavior.
Operationalization has the advantage of generally providing a clear and objective definition of even complex variables. It also makes it easier for other researchers to replicate a study and check for reliability .
For the following hypotheses, name the IV and the DV and operationalize both variables.
1. Women are more attracted to men without earrings than men with earrings.
I.V._____________________________________________________________
D.V. ____________________________________________________________
Operational definitions:
I.V. ____________________________________________________________
2. People learn more when they study in a quiet versus noisy place.
I.V. _________________________________________________________
D.V. ___________________________________________________________
3. People who exercise regularly sleep better at night.
Can there be more than one independent or dependent variable in a study?
Yes, it is possible to have more than one independent or dependent variable in a study.
In some studies, researchers may want to explore how multiple factors affect the outcome, so they include more than one independent variable.
Similarly, they may measure multiple things to see how they are influenced, resulting in multiple dependent variables. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the topic being studied.
What are some ethical considerations related to independent and dependent variables?
Ethical considerations related to independent and dependent variables involve treating participants fairly and protecting their rights.
Researchers must ensure that participants provide informed consent and that their privacy and confidentiality are respected. Additionally, it is important to avoid manipulating independent variables in ways that could cause harm or discomfort to participants.
Researchers should also consider the potential impact of their study on vulnerable populations and ensure that their methods are unbiased and free from discrimination.
Ethical guidelines help ensure that research is conducted responsibly and with respect for the well-being of the participants involved.
Can qualitative data have independent and dependent variables?
Yes, both quantitative and qualitative data can have independent and dependent variables.
In quantitative research, independent variables are usually measured numerically and manipulated to understand their impact on the dependent variable. In qualitative research, independent variables can be qualitative in nature, such as individual experiences, cultural factors, or social contexts, influencing the phenomenon of interest.
The dependent variable, in both cases, is what is being observed or studied to see how it changes in response to the independent variable.
So, regardless of the type of data, researchers analyze the relationship between independent and dependent variables to gain insights into their research questions.
Can the same variable be independent in one study and dependent in another?
Yes, the same variable can be independent in one study and dependent in another.
The classification of a variable as independent or dependent depends on how it is used within a specific study. In one study, a variable might be manipulated or controlled to see its effect on another variable, making it independent.
However, in a different study, that same variable might be the one being measured or observed to understand its relationship with another variable, making it dependent.
The role of a variable as independent or dependent can vary depending on the research question and study design.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.2: Concepts, Constructs, and Variables
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 26212

- Anol Bhattacherjee
- University of South Florida via Global Text Project
We discussed in Chapter 1 that although research can be exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory, most scientific research tend to be of the explanatory type in that they search for potential explanations of observed natural or social phenomena. Explanations require development of concepts or generalizable properties or characteristics associated with objects, events, or people. While objects such as a person, a firm, or a car are not concepts, their specific characteristics or behavior such as a person’s attitude toward immigrants, a firm’s capacity for innovation, and a car’s weight can be viewed as concepts.
Knowingly or unknowingly, we use different kinds of concepts in our everyday conversations. Some of these concepts have been developed over time through our shared language. Sometimes, we borrow concepts from other disciplines or languages to explain a phenomenon of interest. For instance, the idea of gravitation borrowed from physics can be used in business to describe why people tend to “gravitate” to their preferred shopping destinations. Likewise, the concept of distance can be used to explain the degree of social separation between two otherwise collocated individuals. Sometimes, we create our own concepts to describe a unique characteristic not described in prior research. For instance, technostress is a new concept referring to the mental stress one may face when asked to learn a new technology.
Concepts may also have progressive levels of abstraction. Some concepts such as a person’s weight are precise and objective, while other concepts such as a person’s personality may be more abstract and difficult to visualize. A construct is an abstract concept that is specifically chosen (or “created”) to explain a given phenomenon. A construct may be a simple concept, such as a person’s weight , or a combination of a set of related concepts such as a person’s communication skill , which may consist of several underlying concepts such as the person’s vocabulary , syntax , and spelling . The former instance (weight) is a unidimensional construct , while the latter (communication skill) is a multi-dimensional construct (i.e., it consists of multiple underlying concepts). The distinction between constructs and concepts are clearer in multi-dimensional constructs, where the higher order abstraction is called a construct and the lower order abstractions are called concepts. However, this distinction tends to blur in the case of unidimensional constructs.
Constructs used for scientific research must have precise and clear definitions that others can use to understand exactly what it means and what it does not mean. For instance, a seemingly simple construct such as income may refer to monthly or annual income, before-tax or after-tax income, and personal or family income, and is therefore neither precise nor clear. There are two types of definitions: dictionary definitions and operational definitions. In the more familiar dictionary definition, a construct is often defined in terms of a synonym. For instance, attitude may be defined as a disposition, a feeling, or an affect, and affect in turn is defined as an attitude. Such definitions of a circular nature are not particularly useful in scientific research for elaborating the meaning and content of that construct. Scientific research requires operational definitions that define constructs in terms of how they will be empirically measured. For instance, the operational definition of a construct such as temperature must specify whether we plan to measure temperature in Celsius, Fahrenheit, or Kelvin scale. A construct such as income should be defined in terms of whether we are interested in monthly or annual income, before-tax or after-tax income, and personal or family income. One can imagine that constructs such as learning , personality , and intelligence can be quite hard to define operationally.
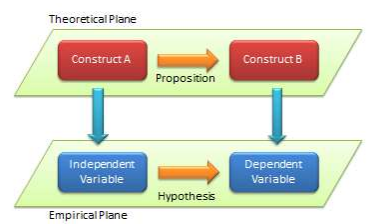
A term frequently associated with, and sometimes used interchangeably with, a construct is a variable. Etymologically speaking, a variable is a quantity that can vary (e.g., from low to high, negative to positive, etc.), in contrast to constants that do not vary (i.e., remain constant). However, in scientific research, a variable is a measurable representation of an abstract construct. As abstract entities, constructs are not directly measurable, and hence, we look for proxy measures called variables. For instance, a person’s intelligence is often measured as his or her IQ ( intelligence quotient ) score , which is an index generated from an analytical and pattern-matching test administered to people. In this case, intelligence is a construct, and IQ score is a variable that measures the intelligence construct. Whether IQ scores truly measures one’s intelligence is anyone’s guess (though many believe that they do), and depending on whether how well it measures intelligence, the IQ score may be a good or a poor measure of the intelligence construct. As shown in Figure 2.1, scientific research proceeds along two planes: a theoretical plane and an empirical plane. Constructs are conceptualized at the theoretical (abstract) plane, while variables are operationalized and measured at the empirical (observational) plane. Thinking like a researcher implies the ability to move back and forth between these two planes.
Depending on their intended use, variables may be classified as independent, dependent, moderating, mediating, or control variables. Variables that explain other variables are called independent variables , those that are explained by other variables are dependent variables , those that are explained by independent variables while also explaining dependent variables are mediating variables (or intermediate variables), and those that influence the relationship between independent and dependent variables are called moderating variables . As an example, if we state that higher intelligence causes improved learning among students, then intelligence is an independent variable and learning is a dependent variable. There may be other extraneous variables that are not pertinent to explaining a given dependent variable, but may have some impact on the dependent variable. These variables must be controlled for in a scientific study, and are therefore called control variables .
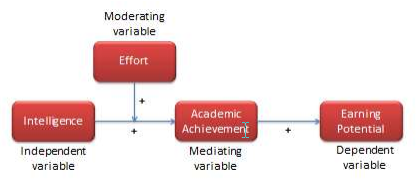
To understand the differences between these different variable types, consider the example shown in Figure 2.2. If we believe that intelligence influences (or explains) students’ academic achievement, then a measure of intelligence such as an IQ score is an independent variable, while a measure of academic success such as grade point average is a dependent variable. If we believe that the effect of intelligence on academic achievement also depends on the effort invested by the student in the learning process (i.e., between two equally intelligent students, the student who puts is more effort achieves higher academic achievement than one who puts in less effort), then effort becomes a moderating variable. Incidentally, one may also view effort as an independent variable and intelligence as a moderating variable. If academic achievement is viewed as an intermediate step to higher earning potential, then earning potential becomes the dependent variable for the independent variable academic achievement , and academic achievement becomes the mediating variable in the relationship between intelligence and earning potential. Hence, variable are defined as an independent, dependent, moderating, or mediating variable based on their nature of association with each other. The overall network of relationships between a set of related constructs is called a nomological network (see Figure 2.2). Thinking like a researcher requires not only being able to abstract constructs from observations, but also being able to mentally visualize a nomological network linking these abstract constructs.
Variables: Definition, Examples, Types of Variables in Research

What is a Variable?
Within the context of a research investigation, concepts are generally referred to as variables. A variable is, as the name applies, something that varies.
Examples of Variable
These are all examples of variables because each of these properties varies or differs from one individual to another.
- income and expenses,
- family size,
- country of birth,
- capital expenditure,
- class grades,
- blood pressure readings,
- preoperative anxiety levels,
- eye color, and
- vehicle type.
What is Variable in Research?
A variable is any property, characteristic, number, or quantity that increases or decreases over time or can take on different values (as opposed to constants, such as n , that do not vary) in different situations.
When conducting research, experiments often manipulate variables. For example, an experimenter might compare the effectiveness of four types of fertilizers.
In this case, the variable is the ‘type of fertilizers.’ A social scientist may examine the possible effect of early marriage on divorce. Her early marriage is variable.
A business researcher may find it useful to include the dividend in determining the share prices . Here, the dividend is the variable.
Effectiveness, divorce, and share prices are variables because they also vary due to manipulating fertilizers, early marriage, and dividends.
11 Types of Variables in Research
Qualitative variables.
An important distinction between variables is the qualitative and quantitative variables.
Qualitative variables are those that express a qualitative attribute, such as hair color, religion, race, gender, social status, method of payment, and so on. The values of a qualitative variable do not imply a meaningful numerical ordering.
The value of the variable ‘religion’ (Muslim, Hindu.., etc..) differs qualitatively; no ordering of religion is implied. Qualitative variables are sometimes referred to as categorical variables.
For example, the variable sex has two distinct categories: ‘male’ and ‘female.’ Since the values of this variable are expressed in categories, we refer to this as a categorical variable.
Similarly, the place of residence may be categorized as urban and rural and thus is a categorical variable.
Categorical variables may again be described as nominal and ordinal.
Ordinal variables can be logically ordered or ranked higher or lower than another but do not necessarily establish a numeric difference between each category, such as examination grades (A+, A, B+, etc., and clothing size (Extra large, large, medium, small).
Nominal variables are those that can neither be ranked nor logically ordered, such as religion, sex, etc.
A qualitative variable is a characteristic that is not capable of being measured but can be categorized as possessing or not possessing some characteristics.
Quantitative Variables
Quantitative variables, also called numeric variables, are those variables that are measured in terms of numbers. A simple example of a quantitative variable is a person’s age.
Age can take on different values because a person can be 20 years old, 35 years old, and so on. Likewise, family size is a quantitative variable because a family might be comprised of one, two, or three members, and so on.
Each of these properties or characteristics referred to above varies or differs from one individual to another. Note that these variables are expressed in numbers, for which we call quantitative or sometimes numeric variables.
A quantitative variable is one for which the resulting observations are numeric and thus possess a natural ordering or ranking.
Discrete and Continuous Variables
Quantitative variables are again of two types: discrete and continuous.
Variables such as some children in a household or the number of defective items in a box are discrete variables since the possible scores are discrete on the scale.
For example, a household could have three or five children, but not 4.52 children.
Other variables, such as ‘time required to complete an MCQ test’ and ‘waiting time in a queue in front of a bank counter,’ are continuous variables.
The time required in the above examples is a continuous variable, which could be, for example, 1.65 minutes or 1.6584795214 minutes.
Of course, the practicalities of measurement preclude most measured variables from being continuous.
Discrete Variable
A discrete variable, restricted to certain values, usually (but not necessarily) consists of whole numbers, such as the family size and a number of defective items in a box. They are often the results of enumeration or counting.
A few more examples are;
- The number of accidents in the twelve months.
- The number of mobile cards sold in a store within seven days.
- The number of patients admitted to a hospital over a specified period.
- The number of new branches of a bank opened annually during 2001- 2007.
- The number of weekly visits made by health personnel in the last 12 months.
Continuous Variable
A continuous variable may take on an infinite number of intermediate values along a specified interval. Examples are:
- The sugar level in the human body;
- Blood pressure reading;
- Temperature;
- Height or weight of the human body;
- Rate of bank interest;
- Internal rate of return (IRR),
- Earning ratio (ER);
- Current ratio (CR)
No matter how close two observations might be, if the instrument of measurement is precise enough, a third observation can be found, falling between the first two.
A continuous variable generally results from measurement and can assume countless values in the specified range.

Dependent Variables and Independent Variable
In many research settings, two specific classes of variables need to be distinguished from one another: independent variable and dependent variable.
Many research studies aim to reveal and understand the causes of underlying phenomena or problems with the ultimate goal of establishing a causal relationship between them.
Look at the following statements:
- Low intake of food causes underweight.
- Smoking enhances the risk of lung cancer.
- Level of education influences job satisfaction.
- Advertisement helps in sales promotion.
- The drug causes improvement of health problems.
- Nursing intervention causes more rapid recovery.
- Previous job experiences determine the initial salary.
- Blueberries slow down aging.
- The dividend per share determines share prices.
In each of the above queries, we have two independent and dependent variables. In the first example, ‘low intake of food’ is believed to have caused the ‘problem of being underweight.’
It is thus the so-called independent variable. Underweight is the dependent variable because we believe this ‘problem’ (the problem of being underweight) has been caused by ‘the low intake of food’ (the factor).
Similarly, smoking, dividend, and advertisement are all independent variables, and lung cancer, job satisfaction, and sales are dependent variables.
In general, an independent variable is manipulated by the experimenter or researcher, and its effects on the dependent variable are measured.
Independent Variable
The variable that is used to describe or measure the factor that is assumed to cause or at least to influence the problem or outcome is called an independent variable.
The definition implies that the experimenter uses the independent variable to describe or explain its influence or effect of it on the dependent variable.
Variability in the dependent variable is presumed to depend on variability in the independent variable.
Depending on the context, an independent variable is sometimes called a predictor variable, regressor, controlled variable, manipulated variable, explanatory variable, exposure variable (as used in reliability theory), risk factor (as used in medical statistics), feature (as used in machine learning and pattern recognition) or input variable.
The explanatory variable is preferred by some authors over the independent variable when the quantities treated as independent variables may not be statistically independent or independently manipulable by the researcher.
If the independent variable is referred to as an explanatory variable, then the term response variable is preferred by some authors for the dependent variable.
Dependent Variable
The variable used to describe or measure the problem or outcome under study is called a dependent variable.
In a causal relationship, the cause is the independent variable, and the effect is the dependent variable. If we hypothesize that smoking causes lung cancer, ‘smoking’ is the independent variable and cancer the dependent variable.
A business researcher may find it useful to include the dividend in determining the share prices. Here dividend is the independent variable, while the share price is the dependent variable.
The dependent variable usually is the variable the researcher is interested in understanding, explaining, or predicting.
In lung cancer research, the carcinoma is of real interest to the researcher, not smoking behavior per se. The independent variable is the presumed cause of, antecedent to, or influence on the dependent variable.
Depending on the context, a dependent variable is sometimes called a response variable, regressand, predicted variable, measured variable, explained variable, experimental variable, responding variable, outcome variable, output variable, or label.
An explained variable is preferred by some authors over the dependent variable when the quantities treated as dependent variables may not be statistically dependent.
If the dependent variable is referred to as an explained variable, then the term predictor variable is preferred by some authors for the independent variable.
Levels of an Independent Variable
If an experimenter compares an experimental treatment with a control treatment, then the independent variable (a type of treatment) has two levels: experimental and control.
If an experiment were to compare five types of diets, then the independent variables (types of diet) would have five levels.
In general, the number of levels of an independent variable is the number of experimental conditions.
Background Variable
In almost every study, we collect information such as age, sex, educational attainment, socioeconomic status, marital status, religion, place of birth, and the like. These variables are referred to as background variables.
These variables are often related to many independent variables, so they indirectly influence the problem. Hence they are called background variables.
The background variables should be measured if they are important to the study. However, we should try to keep the number of background variables as few as possible in the interest of the economy.
Moderating Variable
In any statement of relationships of variables, it is normally hypothesized that in some way, the independent variable ’causes’ the dependent variable to occur.
In simple relationships, all other variables are extraneous and are ignored.
In actual study situations, such a simple one-to-one relationship needs to be revised to take other variables into account to explain the relationship better.
This emphasizes the need to consider a second independent variable that is expected to have a significant contributory or contingent effect on the originally stated dependent-independent relationship.
Such a variable is termed a moderating variable.
Suppose you are studying the impact of field-based and classroom-based training on the work performance of health and family planning workers. You consider the type of training as the independent variable.
If you are focusing on the relationship between the age of the trainees and work performance, you might use ‘type of training’ as a moderating variable.
Extraneous Variable
Most studies concern the identification of a single independent variable and measuring its effect on the dependent variable.
But still, several variables might conceivably affect our hypothesized independent-dependent variable relationship, thereby distorting the study. These variables are referred to as extraneous variables.
Extraneous variables are not necessarily part of the study. They exert a confounding effect on the dependent-independent relationship and thus need to be eliminated or controlled for.
An example may illustrate the concept of extraneous variables. Suppose we are interested in examining the relationship between the work status of mothers and breastfeeding duration.
It is not unreasonable in this instance to presume that the level of education of mothers as it influences work status might have an impact on breastfeeding duration too.
Education is treated here as an extraneous variable. In any attempt to eliminate or control the effect of this variable, we may consider this variable a confounding variable.
An appropriate way of dealing with confounding variables is to follow the stratification procedure, which involves a separate analysis of the different levels of lies in confounding variables.
For this purpose, one can construct two crosstables for illiterate mothers and the other for literate mothers.
Suppose we find a similar association between work status and duration of breastfeeding in both the groups of mothers. In that case, we conclude that mothers’ educational level is not a confounding variable.
Intervening Variable
Often an apparent relationship between two variables is caused by a third variable.
For example, variables X and Y may be highly correlated, but only because X causes the third variable, Z, which in turn causes Y. In this case, Z is the intervening variable.
An intervening variable theoretically affects the observed phenomena but cannot be seen, measured, or manipulated directly; its effects can only be inferred from the effects of the independent and moderating variables on the observed phenomena.
We might view motivation or counseling as the intervening variable in the work-status and breastfeeding relationship.
Thus, motive, job satisfaction, responsibility, behavior, and justice are some of the examples of intervening variables.
Suppressor Variable
In many cases, we have good reasons to believe that the variables of interest have a relationship, but our data fail to establish any such relationship. Some hidden factors may suppress the true relationship between the two original variables.
Such a factor is referred to as a suppressor variable because it suppresses the relationship between the other two variables.
The suppressor variable suppresses the relationship by being positively correlated with one of the variables in the relationship and negatively correlated with the other. The true relationship between the two variables will reappear when the suppressor variable is controlled for.
Thus, for example, low age may pull education up but income down. In contrast, a high age may pull income up but education down, effectively canceling the relationship between education and income unless age is controlled for.
4 Relationships Between Variables

In dealing with relationships between variables in research, we observe a variety of dimensions in these relationships.
Positive and Negative Relationship
Symmetrical relationship, causal relationship, linear and non-linear relationship.
Two or more variables may have a positive, negative, or no relationship. In the case of two variables, a positive relationship is one in which both variables vary in the same direction.
However, they are said to have a negative relationship when they vary in opposite directions.
When a change in the other variable does not accompany the change or movement of one variable, we say that the variables in question are unrelated.
For example, if an increase in wage rate accompanies one’s job experience, the relationship between job experience and the wage rate is positive.
If an increase in an individual’s education level decreases his desire for additional children, the relationship is negative or inverse.
If the level of education does not have any bearing on the desire, we say that the variables’ desire for additional children and ‘education’ are unrelated.
Strength of Relationship
Once it has been established that two variables are related, we want to ascertain how strongly they are related.
A common statistic to measure the strength of a relationship is the so-called correlation coefficient symbolized by r. r is a unit-free measure, lying between -1 and +1 inclusive, with zero signifying no linear relationship.
As far as the prediction of one variable from the knowledge of the other variable is concerned, a value of r= +1 means a 100% accuracy in predicting a positive relationship between the two variables, and a value of r = -1 means a 100% accuracy in predicting a negative relationship between the two variables.
So far, we have discussed only symmetrical relationships in which a change in the other variable accompanies a change in either variable.
This relationship does not indicate which variable is the independent variable and which variable is the dependent variable.
In other words, you can label either of the variables as the independent variable.
Such a relationship is a symmetrical relationship. In an asymmetrical relationship, a change in variable X (say) is accompanied by a change in variable Y, but not vice versa.
The amount of rainfall, for example, will increase productivity, but productivity will not affect the rainfall. This is an asymmetrical relationship.
Similarly, the relationship between smoking and lung cancer would be asymmetrical because smoking could cause cancer, but lung cancer could not cause smoking.
Indicating a relationship between two variables does not automatically ensure that changes in one variable cause changes in another.
It is, however, very difficult to establish the existence of causality between variables. While no one can ever be certain that variable A causes variable B , one can gather some evidence that increases our belief that A leads to B.
In an attempt to do so, we seek the following evidence:
- Is there a relationship between A and B? When such evidence exists, it indicates a possible causal link between the variables.
- Is the relationship asymmetrical so that a change in A results in B but not vice-versa? In other words, does A occur before B? If we find that B occurs before A, we can have little confidence that A causes.
- Does a change in A result in a change in B regardless of the actions of other factors? Or, is it possible to eliminate other possible causes of B? Can one determine that C, D, and E (say) do not co-vary with B in a way that suggests possible causal connections?
A linear relationship is a straight-line relationship between two variables, where the variables vary at the same rate regardless of whether the values are low, high, or intermediate.
This is in contrast with the non-linear (or curvilinear) relationships, where the rate at which one variable changes in value may differ for different values of the second variable.
Whether a variable is linearly related to the other variable or not can simply be ascertained by plotting the K values against X values.
If the values, when plotted, appear to lie on a straight line, the existence of a linear relationship between X and Y is suggested.
Height and weight almost always have an approximately linear relationship, while age and fertility rates have a non-linear relationship.
Frequently Asked Questions about Variable
What is a variable within the context of a research investigation.
A variable, within the context of a research investigation, refers to concepts that vary. It can be any property, characteristic, number, or quantity that can increase or decrease over time or take on different values.
How is a variable used in research?
In research, a variable is any property or characteristic that can take on different values. Experiments often manipulate variables to compare outcomes. For instance, an experimenter might compare the effectiveness of different types of fertilizers, where the variable is the ‘type of fertilizers.’
What distinguishes qualitative variables from quantitative variables?
Qualitative variables express a qualitative attribute, such as hair color or religion, and do not imply a meaningful numerical ordering. Quantitative variables, on the other hand, are measured in terms of numbers, like a person’s age or family size.
How do discrete and continuous variables differ in terms of quantitative variables?
Discrete variables are restricted to certain values, often whole numbers, resulting from enumeration or counting, like the number of children in a household. Continuous variables can take on an infinite number of intermediate values along a specified interval, such as the time required to complete a test.
What are the roles of independent and dependent variables in research?
In research, the independent variable is manipulated by the researcher to observe its effects on the dependent variable. The independent variable is the presumed cause or influence, while the dependent variable is the outcome or effect that is being measured.
What is a background variable in a study?
Background variables are information collected in a study, such as age, sex, or educational attainment. These variables are often related to many independent variables and indirectly influence the main problem or outcome, hence they are termed background variables.
How does a suppressor variable affect the relationship between two other variables?
A suppressor variable can suppress or hide the true relationship between two other variables. It does this by being positively correlated with one of the variables and negatively correlated with the other. When the suppressor variable is controlled for, the true relationship between the two original variables can be observed.

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
Neag School of Education
Educational Research Basics by Del Siegle
Each person/thing we collect data on is called an OBSERVATION (in our work these are usually people/subjects. Currently, the term participant rather than subject is used when describing the people from whom we collect data).
OBSERVATIONS (participants) possess a variety of CHARACTERISTICS .
If a CHARACTERISTIC of an OBSERVATION (participant) is the same for every member of the group (doesn’t vary) it is called a CONSTANT .
If a CHARACTERISTIC of an OBSERVATION (participant) differs for group members it is called a VARIABLE . In research we don’t get excited about CONSTANTS (since everyone is the same on that characteristic); we’re more interested in VARIABLES. Variables can be classified as QUANTITATIVE or QUALITATIVE (also known as CATEGORICAL).
QUANTITATIVE variables are ones that exist along a continuum that runs from low to high. Ordinal, interval, and ratio variables are quantitative. QUANTITATIVE variables are sometimes called CONTINUOUS VARIABLES because they have a variety (continuum) of characteristics. Height in inches and scores on a test would be examples of quantitative variables.
QUALITATIVE variables do not express differences in amount, only differences. They are sometimes referred to as CATEGORICAL variables because they classify by categories. Nominal variables such as gender, religion, or eye color are CATEGORICAL variables. Generally speaking, categorical variables
A special case of a CATEGORICAL variable is a DICHOTOMOUS VARIABLE. DICHOTOMOUS variables have only two CHARACTERISTICS (male or female). When naming QUALITATIVE variables, it is important to name the category rather than the levels (i.e., gender is the variable name, not male and female).
Variables have different purposes or roles…
Independent (Experimental, Manipulated, Treatment, Grouping) Variable- That factor which is measured, manipulated, or selected by the experimenter to determine its relationship to an observed phenomenon. “In a research study, independent variables are antecedent conditions that are presumed to affect a dependent variable. They are either manipulated by the researcher or are observed by the researcher so that their values can be related to that of the dependent variable. For example, in a research study on the relationship between mosquitoes and mosquito bites, the number of mosquitoes per acre of ground would be an independent variable” (Jaeger, 1990, p. 373)
While the independent variable is often manipulated by the researcher, it can also be a classification where subjects are assigned to groups. In a study where one variable causes the other, the independent variable is the cause. In a study where groups are being compared, the independent variable is the group classification.
Dependent (Outcome) Variable- That factor which is observed and measured to determine the effect of the independent variable, i.e., that factor that appears, disappears, or varies as the experimenter introduces, removes, or varies the independent variable. “In a research study, the independent variable defines a principal focus of research interest. It is the consequent variable that is presumably affected by one or more independent variables that are either manipulated by the researcher or observed by the researcher and regarded as antecedent conditions that determine the value of the dependent variable. For example, in a study of the relationship between mosquitoes and mosquito bites, the number of mosquito bites per hour would be the dependent variable” (Jaeger, 1990, p. 370). The dependent variable is the participant’s response.
The dependent variable is the outcome. In an experiment, it may be what was caused or what changed as a result of the study. In a comparison of groups, it is what they differ on.
Moderator Variable- That factor which is measured, manipulated, or selected by the experimenter to discover whether it modifies the relationship of the independent variable to an observed phenomenon. It is a special type of independent variable.
The independent variable’s relationship with the dependent variable may change under different conditions. That condition is the moderator variable. In a study of two methods of teaching reading, one of the methods of teaching reading may work better with boys than girls. Method of teaching reading is the independent variable and reading achievement is the dependent variable. Gender is the moderator variable because it moderates or changes the relationship between the independent variable (teaching method) and the dependent variable (reading achievement).
Suppose we do a study of reading achievement where we compare whole language with phonics, and we also include students’ social economic status (SES) as a variable. The students are randomly assigned to either whole language instruction or phonics instruction. There are students of high and low SES in each group.
Let’s assume that we found that whole language instruction worked better than phonics instruction with the high SES students, but phonics instruction worked better than whole language instruction with the low SES students. Later you will learn in statistics that this is an interaction effect. In this study, language instruction was the independent variable (with two levels: phonics and whole language). SES was the moderator variable (with two levels: high and low). Reading achievement was the dependent variable (measured on a continuous scale so there aren’t levels).
With a moderator variable, we find the type of instruction did make a difference, but it worked differently for the two groups on the moderator variable. We select this moderator variable because we think it is a variable that will moderate the effect of the independent on the dependent. We make this decision before we start the study.
If the moderator had not been in the study above, we would have said that there was no difference in reading achievement between the two types of reading instruction. This would have happened because the average of the high and low scores of each SES group within a reading instruction group would cancel each other an produce what appears to be average reading achievement in each instruction group (i.e., Phonics: Low—6 and High—2; Whole Language: Low—2 and High—6; Phonics has an average of 4 and Whole Language has an average of 4. If we just look at the averages (without regard to the moderator), it appears that the instruction types produced similar results).
Extraneous Variable- Those factors which cannot be controlled. Extraneous variables are independent variables that have not been controlled. They may or may not influence the results. One way to control an extraneous variable which might influence the results is to make it a constant (keep everyone in the study alike on that characteristic). If SES were thought to influence achievement, then restricting the study to one SES level would eliminate SES as an extraneous variable.
Here are some examples similar to your homework:
Null Hypothesis: Students who receive pizza coupons as a reward do not read more books than students who do not receive pizza coupon rewards. Independent Variable: Reward Status Dependent Variable: Number of Books Read
High achieving students do not perform better than low achieving student when writing stories regardless of whether they use paper and pencil or a word processor. Independent Variable: Instrument Used for Writing Moderator Variable: Ability Level of the Students Dependent Variable: Quality of Stories Written When we are comparing two groups, the groups are the independent variable. When we are testing whether something influences something else, the influence (cause) is the independent variable. The independent variable is also the one we manipulate. For example, consider the hypothesis “Teachers given higher pay will have more positive attitudes toward children than teachers given lower pay.” One approach is to ask ourselves “Are there two or more groups being compared?” The answer is “Yes.” “What are the groups?” Teachers who are given higher pay and teachers who are given lower pay. Therefore, the independent variable is teacher pay (it has two levels– high pay and low pay). The dependent variable (what the groups differ on) is attitude towards school.
We could also approach this another way. “Is something causing something else?” The answer is “Yes.” “What is causing what?” Teacher pay is causing attitude towards school. Therefore, teacher pay is the independent variable (cause) and attitude towards school is the dependent variable (outcome).
Research Questions and Hypotheses
The research question drives the study. It should specifically state what is being investigated. Statisticians often convert their research questions to null and alternative hypotheses. The null hypothesis states that no relationship (correlation study) or difference (experimental study) exists. Converting research questions to hypotheses is a simple task. Take the questions and make it a positive statement that says a relationship exists (correlation studies) or a difference exists (experiment study) between the groups and we have the alternative hypothesis. Write a statement that a relationship does not exist or a difference does not exist and we have the null hypothesis.
Format for sample research questions and accompanying hypotheses:
Research Question for Relationships: Is there a relationship between height and weight? Null Hypothesis: There is no relationship between height and weight. Alternative Hypothesis: There is a relationship between height and weight.
When a researcher states a nondirectional hypothesis in a study that compares the performance of two groups, she doesn’t state which group she believes will perform better. If the word “more” or “less” appears in the hypothesis, there is a good chance that we are reading a directional hypothesis. A directional hypothesis is one where the researcher states which group she believes will perform better. Most researchers use nondirectional hypotheses.
We usually write the alternative hypothesis (what we believe might happen) before we write the null hypothesis (saying it won’t happen).
Directional Research Question for Differences: Do boys like reading more than girls? Null Hypothesis: Boys do not like reading more than girls. Alternative Hypothesis: Boys do like reading more than girls.
Nondirectional Research Question for Differences: Is there a difference between boys’ and girls’ attitude towards reading? –or– Do boys’ and girls’ attitude towards reading differ? Null Hypothesis: There is no difference between boys’ and girls’ attitude towards reading. –or– Boys’ and girls’ attitude towards reading do not differ. Alternative Hypothesis: There is a difference between boys’ and girls’ attitude towards reading. –or– Boys’ and girls’ attitude towards reading differ.
Del Siegle, Ph.D. Neag School of Education – University of Connecticut [email protected] www.delsiegle.com

- Foundations
- Write Paper
Search form
- Experiments
- Anthropology
- Self-Esteem
- Social Anxiety

Research Variables
The research variables, of any scientific experiment or research process, are factors that can be manipulated and measured.
This article is a part of the guide:
- Experimental Research
- Pretest-Posttest
- Third Variable
- Research Bias
- Independent Variable
Browse Full Outline
- 1 Experimental Research
- 2.1 Independent Variable
- 2.2 Dependent Variable
- 2.3 Controlled Variables
- 2.4 Third Variable
- 3.1 Control Group
- 3.2 Research Bias
- 3.3.1 Placebo Effect
- 3.3.2 Double Blind Method
- 4.1 Randomized Controlled Trials
- 4.2 Pretest-Posttest
- 4.3 Solomon Four Group
- 4.4 Between Subjects
- 4.5 Within Subject
- 4.6 Repeated Measures
- 4.7 Counterbalanced Measures
- 4.8 Matched Subjects
Any factor that can take on different values is a scientific variable and influences the outcome of experimental research .
Most scientific experiments measure quantifiable factors, such as time or weight, but this is not essential for a component to be classed as a variable.
As an example, most of us have filled in surveys where a researcher asks questions and asks you to rate answers. These responses generally have a numerical range, from ‘1 - Strongly Agree’ through to ‘5 - Strongly Disagree’. This type of measurement allows opinions to be statistically analyzed and evaluated.

Dependent and Independent Variables
The key to designing any experiment is to look at what research variables could affect the outcome.
There are many types of variable but the most important, for the vast majority of research methods, are the independent and dependent variables.
The independent variable is the core of the experiment and is isolated and manipulated by the researcher. The dependent variable is the measurable outcome of this manipulation, the results of the experimental design . For many physical experiments , isolating the independent variable and measuring the dependent is generally easy.
If you designed an experiment to determine how quickly a cup of coffee cools, the manipulated independent variable is time and the dependent measured variable is temperature.
In other fields of science, the variables are often more difficult to determine and an experiment needs a robust design. Operationalization is a useful tool to measure fuzzy concepts which do not have one obvious variable.

The Difficulty of Isolating Variables
In biology , social science and geography, for example, isolating a single independent variable is more difficult and any experimental design must consider this.
For example, in a social research setting, you might wish to compare the effect of different foods upon hyperactivity in children. The initial research and inductive reasoning leads you to postulate that certain foods and additives are a contributor to increased hyperactivity. You decide to create a hypothesis and design an experiment , to establish if there is solid evidence behind the claim.
The type of food is an independent variable, as is the amount eaten, the period of time and the gender and age of the child. All of these factors must be accounted for during the experimental design stage. Randomization and controls are generally used to ensure that only one independent variable is manipulated.
To eradicate some of these research variables and isolate the process, it is essential to use various scientific measurements to nullify or negate them.
For example, if you wanted to isolate the different types of food as the manipulated variable, you should use children of the same age and gender.
The test groups should eat the same amount of the food at the same times and the children should be randomly assigned to groups. This will minimize the physiological differences between children. A control group , acting as a buffer against unknown research variables, might involve some children eating a food type with no known links to hyperactivity.
In this experiment, the dependent variable is the level of hyperactivity, with the resulting statistical tests easily highlighting any correlation . Depending upon the results , you could try to measure a different variable, such as gender, in a follow up experiment.
Converting Research Variables Into Constants
Ensuring that certain research variables are controlled increases the reliability and validity of the experiment, by ensuring that other causal effects are eliminated. This safeguard makes it easier for other researchers to repeat the experiment and comprehensively test the results.
What you are trying to do, in your scientific design, is to change most of the variables into constants, isolating the independent variable. Any scientific research does contain an element of compromise and inbuilt error , but eliminating other variables will ensure that the results are robust and valid .
- Psychology 101
- Flags and Countries
- Capitals and Countries
Martyn Shuttleworth (Aug 9, 2008). Research Variables. Retrieved May 03, 2024 from Explorable.com: https://explorable.com/research-variables
You Are Allowed To Copy The Text
The text in this article is licensed under the Creative Commons-License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) .
This means you're free to copy, share and adapt any parts (or all) of the text in the article, as long as you give appropriate credit and provide a link/reference to this page.
That is it. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).
Want to stay up to date? Follow us!
Get all these articles in 1 guide.
Want the full version to study at home, take to school or just scribble on?
Whether you are an academic novice, or you simply want to brush up your skills, this book will take your academic writing skills to the next level.

Download electronic versions: - Epub for mobiles and tablets - For Kindle here - For iBooks here - PDF version here
Save this course for later
Don't have time for it all now? No problem, save it as a course and come back to it later.
Footer bottom
- Privacy Policy

- Subscribe to our RSS Feed
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
Sciencing_Icons_Science SCIENCE
Sciencing_icons_biology biology, sciencing_icons_cells cells, sciencing_icons_molecular molecular, sciencing_icons_microorganisms microorganisms, sciencing_icons_genetics genetics, sciencing_icons_human body human body, sciencing_icons_ecology ecology, sciencing_icons_chemistry chemistry, sciencing_icons_atomic & molecular structure atomic & molecular structure, sciencing_icons_bonds bonds, sciencing_icons_reactions reactions, sciencing_icons_stoichiometry stoichiometry, sciencing_icons_solutions solutions, sciencing_icons_acids & bases acids & bases, sciencing_icons_thermodynamics thermodynamics, sciencing_icons_organic chemistry organic chemistry, sciencing_icons_physics physics, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-physics fundamentals, sciencing_icons_electronics electronics, sciencing_icons_waves waves, sciencing_icons_energy energy, sciencing_icons_fluid fluid, sciencing_icons_astronomy astronomy, sciencing_icons_geology geology, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geology fundamentals, sciencing_icons_minerals & rocks minerals & rocks, sciencing_icons_earth scructure earth structure, sciencing_icons_fossils fossils, sciencing_icons_natural disasters natural disasters, sciencing_icons_nature nature, sciencing_icons_ecosystems ecosystems, sciencing_icons_environment environment, sciencing_icons_insects insects, sciencing_icons_plants & mushrooms plants & mushrooms, sciencing_icons_animals animals, sciencing_icons_math math, sciencing_icons_arithmetic arithmetic, sciencing_icons_addition & subtraction addition & subtraction, sciencing_icons_multiplication & division multiplication & division, sciencing_icons_decimals decimals, sciencing_icons_fractions fractions, sciencing_icons_conversions conversions, sciencing_icons_algebra algebra, sciencing_icons_working with units working with units, sciencing_icons_equations & expressions equations & expressions, sciencing_icons_ratios & proportions ratios & proportions, sciencing_icons_inequalities inequalities, sciencing_icons_exponents & logarithms exponents & logarithms, sciencing_icons_factorization factorization, sciencing_icons_functions functions, sciencing_icons_linear equations linear equations, sciencing_icons_graphs graphs, sciencing_icons_quadratics quadratics, sciencing_icons_polynomials polynomials, sciencing_icons_geometry geometry, sciencing_icons_fundamentals-geometry fundamentals, sciencing_icons_cartesian cartesian, sciencing_icons_circles circles, sciencing_icons_solids solids, sciencing_icons_trigonometry trigonometry, sciencing_icons_probability-statistics probability & statistics, sciencing_icons_mean-median-mode mean/median/mode, sciencing_icons_independent-dependent variables independent/dependent variables, sciencing_icons_deviation deviation, sciencing_icons_correlation correlation, sciencing_icons_sampling sampling, sciencing_icons_distributions distributions, sciencing_icons_probability probability, sciencing_icons_calculus calculus, sciencing_icons_differentiation-integration differentiation/integration, sciencing_icons_application application, sciencing_icons_projects projects, sciencing_icons_news news.
- Share Tweet Email Print
- Home ⋅
- Math ⋅
- Probability & Statistics ⋅
- Independent/Dependent Variables
What Is the Meaning of Variables in Research?

Science Projects to Learn if an Ice Cube Melts Faster in Air or Water
In scientific research, scientists, technicians and researchers utilize a variety of methods and variables when conducting their experiments. In simple terms, a variable represents a measurable attribute that changes or varies across the experiment whether comparing results between multiple groups, multiple people or even when using a single person in an experiment conducted over time. In all, there are six common variable types.
TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read)
Variables represents the measurable traits that can change over the course of a scientific experiment. In all there are six basic variable types: dependent, independent, intervening, moderator, controlled and extraneous variables.
Independent and Dependent Variables
In general, experiments purposefully change one variable, which is the independent variable. But a variable that changes in direct response to the independent variable is the dependent variable. Say there’s an experiment to test whether changing the position of an ice cube affects its ability to melt. The change in an ice cube's position represents the independent variable. The result of whether the ice cube melts or not is the dependent variable.
Intervening and Moderator Variables
Intervening variables link the independent and dependent variables, but as abstract processes, they are not directly observable during the experiment. For example, if studying the use of a specific teaching technique for its effectiveness, the technique represents the independent variable, while the completion of the technique's objectives by the study participants represents the dependent variable, while the actual processes used internally by the students to learn the subject matter represents the intervening variables.
By modifying the effect of the intervening variables -- the unseen processes -- moderator variables influence the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Researchers measure moderator variables and take them into consideration during the experiment.
Constant or Controllable Variable
Sometimes certain characteristics of the objects under scrutiny are deliberately left unchanged. These are known as constant or controlled variables. In the ice cube experiment, one constant or controllable variable could be the size and shape of the cube. By keeping the ice cubes' sizes and shapes the same, it's easier to measure the differences between the cubes as they melt after shifting their positions, as they all started out as the same size.
Extraneous Variables
A well-designed experiment eliminates as many unmeasured extraneous variables as possible. This makes it easier to observe the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. These extraneous variables, also known as unforeseen factors, can affect the interpretation of experimental results. Lurking variables, as a subset of extraneous variables represent the unforeseen factors in the experiment.
Another type of lurking variable includes the confounding variable, which can render the results of the experiment useless or invalid. Sometimes a confounding variable could be a variable not previously considered. Not being aware of the confounding variable’s influence skews the experimental results. For example, say the surface chosen to conduct the ice-cube experiment was on a salted road, but the experimenters did not realize the salt was there and sprinkled unevenly, causing some ice cubes to melt faster. Because the salt affected the experiment's results, it's both a lurking variable and a confounding variable.
Related Articles
Science projects to learn if an ice cube melts faster..., what is a constant in a science fair project, what is the purpose of factor analysis, the definition of an uncontrolled variable, what is the difference between a control & a controlled..., what is a constant in the scientific method, differences between within & between subjects design, why should you only test for one variable at a time..., how to write a summary on a science project, five characteristics of the scientific method, science project: the effects of temperature on liquids, how to eliminate bias in qualitative research, 5 components of a well-designed scientific experiment, experiments with salt melting ice, what are constants & controls of a science project..., how to calculate logit, distinguishing between descriptive & causal studies, difference between manipulative & responding variable.
- Arizona State University: Developing Hypothesis and Research Questions
- University of Massachusetts, Amherst: How to Do Case Research Study
- University of California, Berkeley: Lurking Variable
About the Author
Mariecor Agravante earned a Bachelor of Science in biology from Gonzaga University and has completed graduate work in Organizational Leadership. She's been published on USA Today, Medium, Red Tricycle, and other online media venues.
Find Your Next Great Science Fair Project! GO
- How it works
Types of Variables – A Comprehensive Guide
Published by Carmen Troy at August 14th, 2021 , Revised On October 26, 2023
A variable is any qualitative or quantitative characteristic that can change and have more than one value, such as age, height, weight, gender, etc.
Before conducting research, it’s essential to know what needs to be measured or analysed and choose a suitable statistical test to present your study’s findings.
In most cases, you can do it by identifying the key issues/variables related to your research’s main topic.
Example: If you want to test whether the hybridisation of plants harms the health of people. You can use the key variables like agricultural techniques, type of soil, environmental factors, types of pesticides used, the process of hybridisation, type of yield obtained after hybridisation, type of yield without hybridisation, etc.
Variables are broadly categorised into:
- Independent variables
- Dependent variable
- Control variable
Independent Vs. Dependent Vs. Control Variable
The research includes finding ways:
- To change the independent variables.
- To prevent the controlled variables from changing.
- To measure the dependent variables.
Note: The term dependent and independent is not applicable in correlational research as this is not a controlled experiment. A researcher doesn’t have control over the variables. The association and between two or more variables are measured. If one variable affects another one, then it’s called the predictor variable and outcome variable.
Example: Correlation between investment (predictor variable) and profit (outcome variable)
What data collection best suits your research?
- Find out by hiring an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Despite how challenging the subject may be, we are here to help you.
Types of Variables Based on the Types of Data
A data is referred to as the information and statistics gathered for analysis of a research topic. Data is broadly divided into two categories, such as:
Quantitative/Numerical data is associated with the aspects of measurement, quantity, and extent.
Categorial data is associated with groupings.
A qualitative variable consists of qualitative data, and a quantitative variable consists of a quantitative variable.
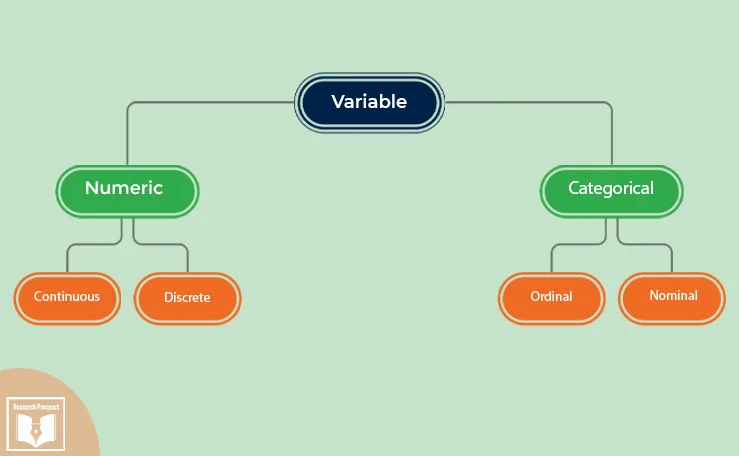
Quantitative Variable
The quantitative variable is associated with measurement, quantity, and extent, like how many . It follows the statistical, mathematical, and computational techniques in numerical data such as percentages and statistics. The research is conducted on a large group of population.
Example: Find out the weight of students of the fifth standard studying in government schools.
The quantitative variable can be further categorised into continuous and discrete.
Categorial Variable
The categorical variable includes measurements that vary in categories such as names but not in terms of rank or degree. It means one level of a categorical variable cannot be considered better or greater than another level.
Example: Gender, brands, colors, zip codes
The categorical variable is further categorised into three types:
Note: Sometimes, an ordinal variable also acts as a quantitative variable. Ordinal data has an order, but the intervals between scale points may be uneven.
Example: Numbers on a rating scale represent the reviews’ rank or range from below average to above average. However, it also represents a quantitative variable showing how many stars and how much rating is given.
Not sure which statistical tests to use for your data?
Let the experts at researchprospect do the daunting work for you..
Using our approach, we illustrate how to collect data, sample sizes, validity, reliability, credibility, and ethics, so you won’t have to do it all by yourself!
Other Types of Variables
It’s important to understand the difference between dependent and independent variables and know whether they are quantitative or categorical to choose the appropriate statistical test.
There are many other types of variables to help you differentiate and understand them.
Also, read a comprehensive guide written about inductive and deductive reasoning .
- Entertainment
- Online education
- Database management, storage, and retrieval
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 10 types of variables in research.
The 10 types of variables in research are:
- Independent
- Confounding
- Categorical
- Extraneous.
What is an independent variable?
An independent variable, often termed the predictor or explanatory variable, is the variable manipulated or categorized in an experiment to observe its effect on another variable, called the dependent variable. It’s the presumed cause in a cause-and-effect relationship, determining if changes in it produce changes in the observed outcome.
What is a variable?
In research, a variable is any attribute, quantity, or characteristic that can be measured or counted. It can take on various values, making it “variable.” Variables can be classified as independent (manipulated), dependent (observed outcome), or control (kept constant). They form the foundation for hypotheses, observations, and data analysis in studies.
What is a dependent variable?
A dependent variable is the outcome or response being studied in an experiment or investigation. It’s what researchers measure to determine the effect of changes in the independent variable. In a cause-and-effect relationship, the dependent variable is presumed to be influenced or caused by the independent variable.
What is a variable in programming?
In programming, a variable is a symbolic name for a storage location that holds data or values. It allows data storage and retrieval for computational operations. Variables have types, like integer or string, determining the nature of data they can hold. They’re fundamental in manipulating and processing information in software.
What is a control variable?
A control variable in research is a factor that’s kept constant to ensure that it doesn’t influence the outcome. By controlling these variables, researchers can isolate the effects of the independent variable on the dependent variable, ensuring that other factors don’t skew the results or introduce bias into the experiment.
What is a controlled variable in science?
In science, a controlled variable is a factor that remains constant throughout an experiment. It ensures that any observed changes in the dependent variable are solely due to the independent variable, not other factors. By keeping controlled variables consistent, researchers can maintain experiment validity and accurately assess cause-and-effect relationships.
How many independent variables should an investigation have?
Ideally, an investigation should have one independent variable to clearly establish cause-and-effect relationships. Manipulating multiple independent variables simultaneously can complicate data interpretation.
However, in advanced research, experiments with multiple independent variables (factorial designs) are used, but they require careful planning to understand interactions between variables.
You May Also Like
Action research for my dissertation?, A brief overview of action research as a responsive, action-oriented, participative and reflective research technique.
Disadvantages of primary research – It can be expensive, time-consuming and take a long time to complete if it involves face-to-face contact with customers.
Descriptive research is carried out to describe current issues, programs, and provides information about the issue through surveys and various fact-finding methods.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Types of Variables in Psychology Research
Examples of Independent and Dependent Variables
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
James Lacy, MLS, is a fact-checker and researcher.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/James-Lacy-1000-73de2239670146618c03f8b77f02f84e.jpg)
Dependent and Independent Variables
- Intervening Variables
- Extraneous Variables
- Controlled Variables
- Confounding Variables
- Operationalizing Variables
Frequently Asked Questions
Variables in psychology are things that can be changed or altered, such as a characteristic or value. Variables are generally used in psychology experiments to determine if changes to one thing result in changes to another.
Variables in psychology play a critical role in the research process. By systematically changing some variables in an experiment and measuring what happens as a result, researchers are able to learn more about cause-and-effect relationships.
The two main types of variables in psychology are the independent variable and the dependent variable. Both variables are important in the process of collecting data about psychological phenomena.
This article discusses different types of variables that are used in psychology research. It also covers how to operationalize these variables when conducting experiments.
Students often report problems with identifying the independent and dependent variables in an experiment. While this task can become more difficult as the complexity of an experiment increases, in a psychology experiment:
- The independent variable is the variable that is manipulated by the experimenter. An example of an independent variable in psychology: In an experiment on the impact of sleep deprivation on test performance, sleep deprivation would be the independent variable. The experimenters would have some of the study participants be sleep-deprived while others would be fully rested.
- The dependent variable is the variable that is measured by the experimenter. In the previous example, the scores on the test performance measure would be the dependent variable.
So how do you differentiate between the independent and dependent variables? Start by asking yourself what the experimenter is manipulating. The things that change, either naturally or through direct manipulation from the experimenter, are generally the independent variables. What is being measured? The dependent variable is the one that the experimenter is measuring.
Intervening Variables in Psychology
Intervening variables, also sometimes called intermediate or mediator variables, are factors that play a role in the relationship between two other variables. In the previous example, sleep problems in university students are often influenced by factors such as stress. As a result, stress might be an intervening variable that plays a role in how much sleep people get, which may then influence how well they perform on exams.
Extraneous Variables in Psychology
Independent and dependent variables are not the only variables present in many experiments. In some cases, extraneous variables may also play a role. This type of variable is one that may have an impact on the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
For example, in our previous example of an experiment on the effects of sleep deprivation on test performance, other factors such as age, gender, and academic background may have an impact on the results. In such cases, the experimenter will note the values of these extraneous variables so any impact can be controlled for.
There are two basic types of extraneous variables:
- Participant variables : These extraneous variables are related to the individual characteristics of each study participant that may impact how they respond. These factors can include background differences, mood, anxiety, intelligence, awareness, and other characteristics that are unique to each person.
- Situational variables : These extraneous variables are related to things in the environment that may impact how each participant responds. For example, if a participant is taking a test in a chilly room, the temperature would be considered an extraneous variable. Some participants may not be affected by the cold, but others might be distracted or annoyed by the temperature of the room.
Other extraneous variables include the following:
- Demand characteristics : Clues in the environment that suggest how a participant should behave
- Experimenter effects : When a researcher unintentionally suggests clues for how a participant should behave
Controlled Variables in Psychology
In many cases, extraneous variables are controlled for by the experimenter. A controlled variable is one that is held constant throughout an experiment.
In the case of participant variables, the experiment might select participants that are the same in background and temperament to ensure that these factors don't interfere with the results. Holding these variables constant is important for an experiment because it allows researchers to be sure that all other variables remain the same across all conditions.
Using controlled variables means that when changes occur, the researchers can be sure that these changes are due to the manipulation of the independent variable and not caused by changes in other variables.
It is important to also note that a controlled variable is not the same thing as a control group . The control group in a study is the group of participants who do not receive the treatment or change in the independent variable.
All other variables between the control group and experimental group are held constant (i.e., they are controlled). The dependent variable being measured is then compared between the control group and experimental group to see what changes occurred because of the treatment.
Confounding Variables in Psychology
If a variable cannot be controlled for, it becomes what is known as a confounding variable. This type of variable can have an impact on the dependent variable, which can make it difficult to determine if the results are due to the influence of the independent variable, the confounding variable, or an interaction of the two.
Operationalizing Variables in Psychology
An operational definition describes how the variables are measured and defined in the study. Before conducting a psychology experiment , it is essential to create firm operational definitions for both the independent variable and dependent variables.
For example, in our imaginary experiment on the effects of sleep deprivation on test performance, we would need to create very specific operational definitions for our two variables. If our hypothesis is "Students who are sleep deprived will score significantly lower on a test," then we would have a few different concepts to define:
- Students : First, what do we mean by "students?" In our example, let’s define students as participants enrolled in an introductory university-level psychology course.
- Sleep deprivation : Next, we need to operationally define the "sleep deprivation" variable. In our example, let’s say that sleep deprivation refers to those participants who have had less than five hours of sleep the night before the test.
- Test variable : Finally, we need to create an operational definition for the test variable. For this example, the test variable will be defined as a student’s score on a chapter exam in the introductory psychology course.
Once all the variables are operationalized, we're ready to conduct the experiment.
Variables play an important part in psychology research. Manipulating an independent variable and measuring the dependent variable allows researchers to determine if there is a cause-and-effect relationship between them.
A Word From Verywell
Understanding the different types of variables used in psychology research is important if you want to conduct your own psychology experiments. It is also helpful for people who want to better understand what the results of psychology research really mean and become more informed consumers of psychology information .
Independent and dependent variables are used in experimental research. Unlike some other types of research (such as correlational studies ), experiments allow researchers to evaluate cause-and-effect relationships between two variables.
Researchers can use statistical analyses to determine the strength of a relationship between two variables in an experiment. Two of the most common ways to do this are to calculate a p-value or a correlation. The p-value indicates if the results are statistically significant while the correlation can indicate the strength of the relationship.
In an experiment on how sugar affects short-term memory, sugar intake would be the independent variable and scores on a short-term memory task would be the independent variable.
In an experiment looking at how caffeine intake affects test anxiety, the amount of caffeine consumed before a test would be the independent variable and scores on a test anxiety assessment would be the dependent variable.
Just as with other types of research, the independent variable in a cognitive psychology study would be the variable that the researchers manipulate. The specific independent variable would vary depending on the specific study, but it might be focused on some aspect of thinking, memory, attention, language, or decision-making.
American Psychological Association. Operational definition . APA Dictionary of Psychology.
American Psychological Association. Mediator . APA Dictionary of Psychology.
Altun I, Cınar N, Dede C. The contributing factors to poor sleep experiences in according to the university students: A cross-sectional study . J Res Med Sci . 2012;17(6):557-561. PMID:23626634
Skelly AC, Dettori JR, Brodt ED. Assessing bias: The importance of considering confounding . Evid Based Spine Care J . 2012;3(1):9-12. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1298595
- Evans, AN & Rooney, BJ. Methods in Psychological Research. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications; 2014.
- Kantowitz, BH, Roediger, HL, & Elmes, DG. Experimental Psychology. Stamfort, CT: Cengage Learning; 2015.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Advertisement
The Independent Variable vs. Dependent Variable in Research
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email

In any scientific research, there are typically two variables of interest: independent variables and dependent variables. In forming the backbone of scientific experiments , they help scientists understand relationships, predict outcomes and, in general, make sense of the factors that they're investigating.
Understanding the independent variable vs. dependent variable is so fundamental to scientific research that you need to have a good handle on both if you want to design your own research study or interpret others' findings.
To grasp the distinction between the two, let's delve into their definitions and roles.
What Is an Independent Variable?
What is a dependent variable, research study example, predictor variables vs. outcome variables, other variables, the relationship between independent and dependent variables.
The independent variable, often denoted as X, is the variable that is manipulated or controlled by the researcher intentionally. It's the factor that researchers believe may have a causal effect on the dependent variable.
In simpler terms, the independent variable is the variable you change or vary in an experiment so you can observe its impact on the dependent variable.
The dependent variable, often represented as Y, is the variable that is observed and measured to determine the outcome of the experiment.
In other words, the dependent variable is the variable that is affected by the changes in the independent variable. The values of the dependent variable always depend on the independent variable.
Let's consider an example to illustrate these concepts. Imagine you're conducting a research study aiming to investigate the effect of studying techniques on test scores among students.
In this scenario, the independent variable manipulated would be the studying technique, which you could vary by employing different methods, such as spaced repetition, summarization or practice testing.
The dependent variable, in this case, would be the test scores of the students. As the researcher following the scientific method , you would manipulate the independent variable (the studying technique) and then measure its impact on the dependent variable (the test scores).
You can also categorize variables as predictor variables or outcome variables. Sometimes a researcher will refer to the independent variable as the predictor variable since they use it to predict or explain changes in the dependent variable, which is also known as the outcome variable.
When conducting an experiment or study, it's crucial to acknowledge the presence of other variables, or extraneous variables, which may influence the outcome of the experiment but are not the focus of study.
These variables can potentially confound the results if they aren't controlled. In the example from above, other variables might include the students' prior knowledge, level of motivation, time spent studying and preferred learning style.
As a researcher, it would be your goal to control these extraneous variables to ensure you can attribute any observed differences in the dependent variable to changes in the independent variable. In practice, however, it's not always possible to control every variable.
The distinction between independent and dependent variables is essential for designing and conducting research studies and experiments effectively.
By manipulating the independent variable and measuring its impact on the dependent variable while controlling for other factors, researchers can gain insights into the factors that influence outcomes in their respective fields.
Whether investigating the effects of a new drug on blood pressure or studying the relationship between socioeconomic factors and academic performance, understanding the role of independent and dependent variables is essential for advancing knowledge and making informed decisions.
Correlation vs. Causation
Understanding the relationship between independent and dependent variables is essential for making sense of research findings. Depending on the nature of this relationship, researchers may identify correlations or infer causation between the variables.
Correlation implies that changes in one variable are associated with changes in another variable, while causation suggests that changes in the independent variable directly cause changes in the dependent variable.
Control and Intervention
In experimental research, the researcher has control over the independent variable, allowing them to manipulate it to observe its effects on the dependent variable. This controlled manipulation distinguishes experiments from other types of research designs.
For example, in observational studies, researchers merely observe variables without intervention, meaning they don't control or manipulate any variables.
Context and Analysis
Whether it's intentional or unintentional, independent, dependent and other variables can vary in different contexts, and their effects may differ based on various factors, such as age, characteristics of the participants, environmental influences and so on.
Researchers employ statistical analysis techniques to measure and analyze the relationships between these variables, helping them to draw meaningful conclusions from their data.
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a HowStuffWorks editor.
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:
- Skip to main content
- Skip to FDA Search
- Skip to in this section menu
- Skip to footer links

The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Search
- Menu
- Science & Research
- Science and Research Special Topics
- Advancing Regulatory Science
Statistical methods to improve precision and reduce the required sample size in many phase 2 and 3 clinical trials, including COVID-19 trials, by covariate adjustment
CERSI Collaborators: Michael Rosenblum, PhD; Joshua Betz, MS; Kelly Van Lancker, PhD; Bingkai Wang, PhD
FDA Collaborators: Daniel Rubin, PhD, CDER; Greg Levin, PhD, CDER; Boguang Zhen, PhD, CBER; Gene Pennello, PhD, CDRH
CERSI Subcontractors: Weill Cornell Medicine Art Sedrakyan, MD, PhD; Jim C. Hu, MD, MPH; Jialin Mao, MD, MS; Miko Yu, MA; Sendong Zhao, PHD, Vahan Simonyan, PhD
Project Start Date: March 1, 2020
Regulatory Science Challenge
Investigators are addressing the following FDA research priority: “Developing methods and tools to improve and streamline clinical and post-market evaluation of FDA-regulated products.”
Project Description and Goals
Clinical trials are often conducted to learn whether new medical treatments are safe and effective. Data collected when participants first enter a trial are called baseline variables. Examples of baseline variables include age, sex, and disease severity. Sometimes, due to chance, there are imbalances in these variables between those assigned to the experimental treatment arm (or group) and those assigned to the control arm (or group). For example, in some trials participants in the treatment arm may have higher or lower baseline disease severity compared with participants in the control arm.
When baseline variables (e.g., older age as a risk factor for worse outcome among those with COVID-19 infection) are related to the outcome, (e.g., one intended to support effectiveness of a treatment), taking the baseline variables into account in the data analysis of a trial’s results can lead to more precise estimates of treatment effectiveness (i.e., smaller standard errors for the estimates). More precise estimation means that at the planning stage, trials could be conducted with fewer participants than when baseline variables are not considered in the data analysis. Unfortunately, in many clinical trials information in baseline variables is not considered, leading to a greater chance that the trial will fail due to greater uncertainty regarding conclusions that can be drawn, potentially wasting resources. At the planning stage, not accounting for baseline information may lead to the planning of a larger trial size and longer trial duration than is necessary.
A major barrier to using baseline variables (called covariate adjustment) is that for many common types of clinical trial outcomes, such as binary, ordinal, and time-to-event outcomes, confusion remains as to what statistical approach is appropriate. The results of this project will help to overcome this barrier by demonstrating how to appropriately adjust for baseline variables to improve precision of treatment effect estimates for outcomes of these types. The statistical adjustments will be demonstrated on case studies in several disease areas as examples of best practices for the use of baseline variables in clinical trial data analysis. Investigators plan to disseminate these case studies to the public through a free, online tutorial on the FDA public website.
Publications
Williams, N., Rosenblum, M. & Díaz, I. (2022) Optimising precision and power by machine learning in randomised trials with ordinal and time-to-event outcomes with an application to COVID-19. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A (Statistics in Society) , 1– 23. https://doi.org/10.1111/rssa.12915
Wang, B., Susukida, R., Mojtabai, R., Amin-Esmaeili, M., and Rosenblum, M. (2021) Model-Robust Inference for Clinical Trials that Improve Precision by Stratified Randomization and Adjustment for Additional Baseline Variables. Journal of the American Statistical Association, Theory and Methods Section. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/01621459.2021.1981338
Kelly Van Lancker, Joshua Betz, Michael Rosenblum. Combining Covariate Adjustment with Group Sequential, Information Adaptive Designs to Improve Randomized Trial Efficiency. Under review: https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.12921
Putting science to work for the health of women
Gender and Health Scientific Workshop
On October 26, 2022, the NIH Office of Research on Women’s Health (ORWH) and Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) hosted a scientific workshop titled Gender & Health: Impacts of Structural Sexism, Gender Norms, Relational Power Dynamics, and Gender Inequities . This virtual workshop was held in partnership with the National Institute of Aging (NIA), the National institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease (NIAID), the National Cancer Institute (NCI), the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), the National Institute of Drug Abuse (NIDA), and the NIH Office of Behavioral and Social Sciences Research (OBSSR).
The overarching goal of the workshop was to convene NIH staff, the external scientific community, and the public to discuss methods, measurement, modifiable factors, interventions, and best practices in health research on gender as a social and cultural variable.
Workshop Objectives
- Review definitions and conceptual frameworks commonly used to study structural sexism, gender norms, relational power dynamics, and gender inequities in health. Examine issues in measurement and methods to evaluate structural sexism, gender norms, relational power dynamics, and gender inequities.
- Identify modifiable factors and points of intervention to mitigate health disparities based in structural sexism, gender norms, relational power dynamics, and gender inequities.
- Highlight interventions (evidence-based practices, promising practices, etc.) and targeting different levels (e.g., socioecological, multilevel frameworks) aimed at mitigating health disparities based in structural sexism, gender norms, relational power dynamics, and gender inequities.
- Identify opportunities to advance research and foster collaborations on health impacts of structural sexism, gender norms, relational power dynamics, and gender inequities.
Speaker Biographies
Click the title to view a PDF of the poster and the abstract number for the poster video presentation. For more details on the featured poster presentations, please view the Poster Abstract Booklet . You can also view the full poster video presentation playlist.
Main Session Agenda
Concurrent Session: Measurement and Methods Agenda
Concurrent Session: Modifiable Factors & Clinical Interventions Agenda
Concurrent Session Modifiable Factors & Social Determinants of Health Agenda
- Sex & Gender
- ORWH MISSION AREA: Sex & Gender in Research
- What are Sex & Gender?
- Sex and Gender in Health and Disease
- Methods and Techniques for Integrating Sex into Research
- NIH Policy on Sex as a Biological Variable
- Related ORWH Programs & Initiatives
- Program Summaries, Fiscal Year 2014
- Program Summaries, Fiscal Year 2013
- Specialized Centers of Research Excellence (SCORE) on Sex Differences
- Sex, Gender, and Intersectionality (SG&I) Innovations Collaborative
- Gender and Health Scientific Workshop (2022)
- ORWH E-Learning Courses
Director’s Messages
April 30, 2024
March 27, 2024
February 27, 2024
January 25, 2024
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
This article is part of the research topic.
Towards Sustainable Development Goal of Zero Hunger: Exploring the Dynamic Relationships between Food Pricing, Agriculture, and Food Security
Impact of Zero Tillage Maize Production on Yield, Income, and Resource Utilization in Peninsular India: An Action-Based Quasi-Experimental Research Provisionally Accepted

- 1 Dr. Reddy's Foundation, India
- 2 Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
The present study aims to identify the crucial determinants of the widespread adoption of zerotillage (ZT) technology in maize production. The study also measures the impact of ZT adoption on maize yield, income generation, and the expenses associated with different agricultural operations.The study used multi-stage stratified random sampling and conducted a face-to-face questionnaire survey to collect primary data from 1189 maize farmers. Initially, the study employed probit regression analysis to identify the ZT adoption determinants. Subsequently, using the Propensity Score Matching (PSM) approach, the study measures the impact of ZT adoption over conventional tillage in terms of yield, income, and cost management. Finally, the Endogenous Switch Regression (ESR) method was implemented to mitigate unobserved heterogeneity and sample selection bias. Additionally, ESR assessed the robustness of PSM results.The probit model identifies that variables like education, institutional credit adoption, crop insurance, visit of extension agent, landholding size, and prior experience of new technology adoption positively influence ZT adoption. The PSM and ESR approach results suggest that ZT adoption positively impacts farmers' yield and net income while reducing the cultivation cost and labor use. Results show that ZT adoption decreases the cost of land preparation, weed, pest management, and harvesting, thereby decreasing the cultivation cost by INR8376 acre -1 . Moreover, adopting ZT improves maize yield by 2.53quintal acre -1 and minimizes 9.56 persondays acre -1 .The study findings may support policymakers in designing suitable agricultural policies to improve technology adoption and motivate farmers for sustainable production.
Keywords: Conservation tillage, impact assessment, economic analysis, Propensity score matching (PSM) approach, Endogenous Switch Regression, Peninsular India
Received: 28 Dec 2023; Accepted: 02 May 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Dey, Abbhishek, Saraswathibatla, Singh, Sreedhar, Bommaraboyina, Raj, Kaliki, Choubey, Rongali and Upamaka. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Dr. Kumar Abbhishek, Dr. Reddy's Foundation, Hyderabad, India
People also looked at
Proceedings of the International Conference on Business, Management, Accounting and Sustainable Economy (ICBMASE 2023)
The Effect of E-Filing, Tax Socialization, and Taxpayer Awareness on MSME Taxpayer Compliance with Tax Sanctions as Variable Moderation
This research purpose is to investigate the effect of E-Filing Implementation, Taxation Socialization, and Taxpayer Awareness on the Compliance of SMEs Taxpayers, with Tax Sanctions acting as a Moderating Variable. The primary data for this study were obtained from respondents’ answers to the questionnaire used in the research. The research sample consists of 100 SME taxpayers holding a Taxpayer Identification Number (NPWP) in Depok City. Methodology sampling technique employed is purposive sampling. The data analysis methods include Descriptive Statistics, Data Quality Test, Classical Assumption Test, and Hypothesis Testing, which includes Moderation Regression Analysis, Coefficient of Determination, F-test, and T-test. Findings indicate that E-Filing Implementation, Socialization and Taxpayer Awareness have a positive and significant impact on Taxpayer Compliance. Regarding the hypothesis testing results for the moderation variable, Tax Sanctions and Taxation Socialization can positively moderate the relationship between E-Filing Implementation and Taxpayer Compliance. Tax Sanctions have negatively moderated the association between Taxpayer Awareness and Taxpayer Compliance. Suggestion is that the government and relevant institutions enhance the implementation of a more user-friendly E-Filing system and provide clear guidelines for SMEs. Taxation socialization should be intensified through various media to enhance taxpayers’ understanding. Moreover, encouraging unpaid awareness through tax education programs is crucial. Additionally, the proportional application of tax sanctions can serve as an effective tool in promoting SMEs’ tax compliance.
Download article (PDF)
Cite this article
Explaining the Department of Labor’s new overtime rule that will benefit 4.3 million workers
The U.S. Department of Labor issued a final rule today making changes to the regulations about who is eligible for overtime pay. Here’s why this matters:
How the overtime threshold works
Overtime pay protections are included in the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) to ensure that most workers who put in more than 40 hours a week get paid 1.5 times their regular pay for the extra hours they work. Almost all hourly workers are automatically eligible for overtime pay. But workers who are paid on a salary basis are only automatically eligible for overtime pay if they earn below a certain salary. Above that level, employers can claim that workers are “exempt” from overtime pay protection if their job duties are considered executive, administrative, or professional (EAP) —essentially managers or highly credentialed professionals.
The current overtime salary threshold is too low to protect many workers
The pay threshold determining which salaried workers are automatically eligible for overtime pay has been eroded both by not being updated using a proper methodology, and by inflation. Currently, workers earning $684 per week (the equivalent of $35,568 per year for a full-time, full-year employee) can be forced to work 60-70 hours a week for no more pay than if they worked 40 hours. The extra 20-30 hours are completely free to the employer, allowing employers to exploit workers with no consequences.
The Department of Labor’s new final rule will phase in the updated salary threshold in two steps over the next eight months, and automatically update it every three years thereafter.
- This is the equivalent of $43,888 per year for a full-time, full-year worker.
- In 2019, the Department updated the salary threshold to a level that was inappropriately low. Further, that threshold has eroded substantially in the last 4+ years as wages and prices have risen over that period, leaving roughly one million workers without overtime protections who would have received those protections under the methodology of even that inappropriately weak rule. This first step essentially adjusts the salary threshold set in the 2019 rule for inflation.
- This is the equivalent of $58,656 per year for a full-time, full-year worker.
- This level appropriately sets the threshold at the 35th percentile of weekly wages for full-time, salaried workers in the lowest-wage Census region, currently the South.
- The salary threshold will automatically update every three years thereafter, based on the methodology laid out in the rule, to ensure that the strength of the rule does not erode over time as prices and wages rise.
The final rule will benefit 4.3 million workers
- 2.4 million of these workers (56%) are women
- 1.0 million of these workers (24%) are workers of color
- The largest numbers of impacted workers are in professional and business services, health care and social services, and financial activities.
- The 4.3 million represents 3.0% of workers subject to the FLSA.
Expanding overtime protections is good for workers and manageable for employers
- The final rule will result in a transfer of $1.5 billion annually from employers to workers in increased pay.
- While that increase in wages will be enormously impactful to affected workers, it represents well under one-tenth of one-percent of total wages and salaries in the U.S. economy. Employers will be more than able to adjust to the rule without negatively impacting the overall economy.
- In addition to increasing pay for many workers, the overtime rule will also reduce excessive hours of unpaid work. Before this update to the salary threshold, the cost to employers of overworking salaried EAP workers who make more than $684 weekly was effectively zero. The concept of overtime pay is designed to protect workers’ most valuable asset—their time—and to push employers to value it too.
- Automatic updating is a smart and easy way to simply maintain the labor standard established in the proposal. If the threshold is not updated automatically over time, it will steadily weaken as a labor standard until the next rulemaking, covering fewer and fewer workers as the salary distribution naturally rises over time with inflation and productivity growth.
- With automatic updating, employers will know exactly what to expect and when to expect it. They will also be able to get a reasonable sense well in advance of what the next threshold will be, because they will be able to track on a dedicated Bureau of Labor Statistics website how the 35th percentile of full-time salaried worker earnings in the lowest-wage Census region is evolving over time.
Enjoyed this post?
Sign up for EPI's newsletter so you never miss our research and insights on ways to make the economy work better for everyone.
Track us on Twitter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Types of Variables in Research. Types of Variables in Research are as follows: Independent Variable. This is the variable that is manipulated by the researcher. It is also known as the predictor variable, as it is used to predict changes in the dependent variable. Examples of independent variables include age, gender, dosage, and treatment type ...
In research, variables are any characteristics that can take on different values, such as height, age, temperature, or test scores. Researchers often manipulate or measure independent and dependent variables in studies to test cause-and-effect relationships. The independent variable is the cause.
Types of Variables in Research & Statistics | Examples. Published on September 19, 2022 by Rebecca Bevans. Revised on June 21, 2023. In statistical research, a variable is defined as an attribute of an object of study. Choosing which variables to measure is central to good ...
Types of Variables in Research | Definitions & Examples. Published on 19 September 2022 by Rebecca Bevans. Revised on 28 November 2022. In statistical research, a variable is defined as an attribute of an object of study. Choosing which variables to measure is central to good experimental design.
The Role of Variables in Research. In scientific research, variables serve several key functions: Define Relationships: Variables allow researchers to investigate the relationships between different factors and characteristics, providing insights into the underlying mechanisms that drive phenomena and outcomes. Establish Comparisons: By manipulating and comparing variables, scientists can ...
A variable in research simply refers to a person, place, thing, or phenomenon that you are trying to measure in some way. The best way to understand the difference between a dependent and independent variable is that the meaning of each is implied by what the words tell us about the variable you are using. You can do this with a simple exercise ...
While the independent variable is the " cause ", the dependent variable is the " effect " - or rather, the affected variable. In other words, the dependent variable is the variable that is assumed to change as a result of a change in the independent variable. Keeping with the previous example, let's look at some dependent variables ...
Examples of categorical variables include gender (male, female, other), type of vehicle (car, truck, motorcycle), or marital status (single, married, divorced). These categories help researchers organize data into groups for comparison and analysis. Categorical variables can be further classified into two subtypes: nominal and ordinal.
Variables in Research. The definition of a variable in the context of a research study is some feature with the potential to change, typically one that may influence or reflect a relationship or ...
In research, variables are any characteristics that can take on different values, such as height, age, temperature, or test scores. Researchers often manipulate or measure independent and dependent variables in studies to test cause-and-effect relationships. The independent variable is the cause.
In research, the independent variable is manipulated to observe its effect, while the dependent variable is the measured outcome. Essentially, the independent variable is the presumed cause, and the dependent variable is the observed effect. Variables provide the foundation for examining relationships, drawing conclusions, and making ...
As shown in Figure 2.1, scientific research proceeds along two planes: a theoretical plane and an empirical plane. Constructs are conceptualized at the theoretical (abstract) plane, while variables are operationalized and measured at the empirical (observational) plane. Thinking like a researcher implies the ability to move back and forth ...
Quantitative Variables. Quantitative variables, also called numeric variables, are those variables that are measured in terms of numbers. A simple example of a quantitative variable is a person's age. Age can take on different values because a person can be 20 years old, 35 years old, and so on.
The definition of a variable changes depending on the context. Typically, a letter represents them, and it stands in for a numerical value. In algebra, a variable represents an unknown value that you need to find. For mathematical functions and equations, you input their values to calculate the output. In an equation, a coefficient is a fixed ...
Categorical variables are groups…such as gender or type of degree sought. Quantitative variables are numbers that have a range…like weight in pounds or baskets made during a ball game. When we analyze data we do turn the categorical variables into numbers but only for identification purposes…e.g. 1 = male and 2 = female.
Research Variables. The research variables, of any scientific experiment or research process, are factors that can be manipulated and measured. Any factor that can take on different values is a scientific variable and influences the outcome of experimental research. Gender, color and country are all perfectly acceptable variables, because they ...
In scientific research, scientists, technicians and researchers utilize a variety of methods and variables when conducting their experiments. In simple terms, a variable represents a measurable attribute that changes or varies across the experiment whether comparing results between multiple groups, multiple people or even when using a single person in an experiment conducted over time.
A control variable in research is a factor that's kept constant to ensure that it doesn't influence the outcome. By controlling these variables, researchers can isolate the effects of the independent variable on the dependent variable, ensuring that other factors don't skew the results or introduce bias into the experiment. ...
By systematically changing some variables in an experiment and measuring what happens as a result, researchers are able to learn more about cause-and-effect relationships. The two main types of variables in psychology are the independent variable and the dependent variable. Both variables are important in the process of collecting data about ...
The independent variable, often denoted as X, is the variable that is manipulated or controlled by the researcher intentionally. It's the factor that researchers believe may have a causal effect on the dependent variable. In simpler terms, the independent variable is the variable you change or vary in an experiment so you can observe its impact ...
So, it is usual for research protocols to include many independent variables and many dependent variables in the generation of many hypotheses, as shown in Table 1. Pairing each variable in the "independent variable" column with each variable in the "dependent variable" column would result in the generation of these hypotheses.
The purpose of research is to describe and explain variance in the world, that is, variance that. occurs naturally in the world or chang e that we create due to manipulation. Variables are ...
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
When baseline variables (e.g., older age as a risk factor for worse outcome among those with COVID-19 infection) are related to the outcome, (e.g., one intended to support effectiveness of a ...
The given code initializes three variables: a, b, and t, with the values 3, 7, and 0 respectively.The purpose of the code is to swap the values of a and b without using any direct arithmetic operations or additional variables. To achieve this, the value of a is first stored in the temporary variable t.Then, the value of b is assigned to a, effectively overwriting a original value.
The overarching goal of the workshop was to convene NIH staff, the external scientific community, and the public to discuss methods, measurement, modifiable factors, interventions, and best practices in health research on gender as a social and cultural variable.
May 2 2024 Duke University. Duke researchers have opened a new avenue in the attack against influenza viruses by creating a vaccine that encourages the immune system to target a portion of the ...
The present study aims to identify the crucial determinants of the widespread adoption of zerotillage (ZT) technology in maize production. The study also measures the impact of ZT adoption on maize yield, income generation, and the expenses associated with different agricultural operations.The study used multi-stage stratified random sampling and conducted a face-to-face questionnaire survey ...
This research purpose is to investigate the effect of E-Filing Implementation, Taxation Socialization, and Taxpayer Awareness on the Compliance of SMEs Taxpayers, with Tax Sanctions acting as a Moderating Variable. The primary data for this study were obtained from respondents' answers to the questionnaire used in the research. The research sample consists...
EPI is an independent, nonprofit think tank that researches the impact of economic trends and policies on working people in the United States. EPI's research helps policymakers, opinion leaders, advocates, journalists, and the public understand the bread-and-butter issues affecting ordinary Americans. Follow EPI. 1225 Eye St. NW, Suite 600