(92) 336 3216666
Here’s a brief but on-point “Of Studies Summary and Analysis” for you from LitPriest.

Of Studies by Francis Bacon Summary
“Studies serve for delight, ornament, and for ability”.
Francis Bacon gives account of three chief uses of studies. The first use is that they serve for delight. This delight may come in solitude or in leisure after retirement from active life. Secondly, they serve for ornament in communication, conversation and discourse. A person who is well read can talk more attractively than an uneducated person. The third use of studies is they help in the judgement, and disposition of business.
An expert man can judge matters one by one when they come face by face to him and he executes them according to his experience. However, this is not the case with an educated man. He can give counsels at any situation according to his knowledge and thus, learned men are best at marshalling of affairs.
Studies, however, have their limitations. If too much time is spent at studies it nothing more than sloth. If they are used excessively in conversation, they show exaggeration and posing of a person. And if a scholar makes each and every judgement of his life with the help of his knowledge, it is just foolish and humorous behavior of the scholar.
Studies perfect nature. Furthermore, they are perfected by experience. Bacon compares natural abilities of a man with a natural tree that needs proyning that comes by study. Studies have a vast scope, it is icing on the cake if experience is also added with them.
Bacon says,
“Crafty men contemn studies, simple men admire them, and wise men use them”.
The men who are hard workers or primitive men hate or contemn studies. However, the men who have simple wits admire them. Moreover, the men who are wise use them practically. Studies do not teach their own use. It is the wisdom of a person that teaches him their usage. Bacon is of the view that a man should not read to contradict and confute others; he should not believe and rely wholly on words; nor to find a point of discussion in conversation; but he should read to weigh them their value and use them. The writer further supports this argument in the following statement,
“Some books are to be tasted, others to be swallowed, and some few to be chewed and digested”.
There are some books that are to be read only in parts because they are useful for a person only at some places. It is not worthy to read them word by word. On contrary, there are some books that are to be read not with curiosity; and some are to be read completely with attention and diligence because they require the full attention of the reader. Moreover, this category of books has treasures hidden in them that can be found only by reader’s diligence. There is another category ‘like common distilled waters’ i.e ‘distilled books’, these books are extracts made from other books and compiled in another book. These are the meaner sort of books.
Bacon says a million dollars verses,
“Reading maketh a full man; conference a ready man; and writing an exact man”.
It is reading that adds to the knowledge of a man and makes him complete in a sense of his wit. Undoubtedly, it is conversation with others that makes a man ready for any sort of step to be taken practically on behalf of his knowledge. Furthermore, it is the skill of comprehensive or innovative writing that makes a full man because man is created to do wonders, make innovations and generate new ideas.
Moreover, the writer describes some facts about studies. He says if a man writes little than he needs to have a great memory to remember all the learned things. If a man interacts little he needs to have a present and sharp wit; and if a man read little, he should be cunning to know what he does not.
Bacon impresses reader through his comprehensive and great sayings. He says,
“Histories make men wise; pots witty; the mathematics subtile; natural philosophy deep; moral grave; logic and rhetoric able to contend”.
The about stated couple of lines contains an ocean of meaning in it. Bacon says that it is history of ancients that makes new generations wise and witty. These are rules and laws stated by the ancients that make mathematics subtile in its nature. It is because of histories that philosophy has deeper meanings and logic and rhetoric are able to defend through arguments.
Bacon is of the view that any impediment or stond in the wit can be wrought out by fit studies. If a person considers oneself dull, he can make him better through studies. Clearly, ‘bowling is good for the stone and reins; shooting for the lungs and breast; gentle walking for the stomach; riding for the head’, similarly, studies also have a physical role in mortals’ life. If a man’s wit is unable to focus at a point and it keeps wandering, let him study mathematics so that he may learn to demonstrate rationally. If his wit is unable to find differences let him study the schoolmen. If a man is not able to call up one thing to prove and illustrate another, he should study the lawyers’ cases.
Bacon encloses the essay by saying,
“So every defect of the mind may have a special receipt”.
Of Studies Frequently Asked Questions
What are the views of francis bacon regarding studies in his essay “of studies”.
Bacon’s view regarding studies is that it “serve for Delight, for Ornament, and for Ability”. Here Delight refers to the personal and private education, similarly, Ornament refers to the conversation among people that Bacon tags as Discourse. Whereas, studies for Ability tips and individual for the better interpretation of trade and commercial pursuit. According to Bacon, the worldly experience can lead men to carry out plans and interpret particular circumstances, however, the study makes men to better recognize the various dogmatic matters and how to act in various circumstances realizing its severity i.e. rationalizing of affairs.
Bacon also encourages studies and warns the readers that sometimes too much studying may lead to the sluggishness; moreover, the excessive and irrelevant use of knowledge by men in conversation indicates the showing off of knowledge; likewise, if one only takes guidance from studies disregard of practical experiences, he only becomes a scholar. Bacon argues that the only way to use studies appropriately is to modernize it i.e. studies are only effective if it is influenced by experience as this will enhance the natural abilities of a man; however, studies without the influence of experience may lead to a great misperception in communication with the world around.
Bacon illustrates that corrupt men denounce education; imprudent men approve education; however the wise men utilize education according to the command of the real-world. He also warns the educated men not to indulge himself in an unnecessarily argument with people, likewise, educated men must not suppose that education can always cause the correct conduct or interpretation; moreover, educated men should not use purely to emphasize on their conversation with others. Rather, Bacon illustrates, some books must only be read, some must be ignored completely, while few books must be “Chewed and digested”, i.e. should be understood and interpreted completely. Furthermore, he advises that some books are read by other and they take notes out of it, and these notes are good enough substitute of a book to be read, however, this category mustn’t include the books with sublime subject matters.
Bacon, by returning to the previous argument, addresses the consequences of reading, writing, and conversation by illustrating the reading crafts an all-rounder man; conversation makes a man sharp and fast thinker; while writing makes a man rational. Furthermore, Bacon says that if an individual doesn’t write must, he must have a good memory to compensate for his writing; similarly, if he doesn’t have a good conversation, he should compensate it with a wit; and an individual has to pretend that he knows more than he does in order to fake his reading that he never does much.
Bacon, by pointing out the various subject, argues that the studying history makes men wise; mathematics makes them intellectually sharp, while logic and rhetoric skilled men in arguments. Moreover, thinking is not problematic if it cannot be established by the proper study. Every mind disorder has a treatment just like every physical illness. For instance, a man should study law, if he cannot utilizes the proofs to demonstrate the certainty of unrelated facts. By studying other forms, any defect in the brain can be cured.
Explain the line “Some books are to be tasted, others to be swallowed, and some few to be chewed and digested” in reference to the context of Bacon’s essay “Of Studies”?
The notion with which Bacon opens his essay “Studies serve for delight, for ornament, and for ability” parallels the line quoted in the question. The simplest interpretation of the statement implies that the studies which delight are intended for personal observation, pleasure, and understanding; the studies which are for ornament are intended to improve discourse, communication, and inscription; those that are intended for ability are meant for the “argument and judgment of business”. However, one may also assume that one by reading, for amusement or pleasure, can also grasp a thoughtful understanding that could be utilized in serious learning.
Hence, among the books that delight are tend to be the ones that are only to be tasted. As one doesn’t surely take in the philosophical knowledge, so one simple tastes it. The books that contain some wisdom and deep thoughts need to be swallowed. However, the books that contain a real sociological, philosophical, or psychological perception, and that necessarily becomes a part of one’s mental being, are to be chewed and digested. Nutrients are absorbed when one chew and digest the food and these nutrients become a part of the body. Similarly, the books that are useful, truthful, and worthier, Bacon says, must be chewed and digested. However, if they lack truth and wisdom, they must only be tasted.
What are the three main benefits of studies did Bacon mention in his essay Of Studies? And what are dangers associated with each benefit?
Bacon’s essays contain practical, religious, and moral subjects that, according to him, would direct a man to a valuable and successful life in both business and politics. Most of his essay deals with the manners, behavior, and conduct of a man and guides him how should one act and to adopt moderation in everything. In simple words, one should neither exceed nor fall short of anything as it can lead to an unstable life, with devastating results.
Bacon, in the essay Of Studies, illustrates both the benefits and the drawbacks of studying and reading books. 1st of all he argues that “studies serve for Delight, for Ornament, and for Ability. Delight is intended for private and personal affairs; Ornament for communication; the ability for logical judgment and outlook for the business.
He argues that one study for delight as it allows an individual to be contented in himself. In short, studies make a man relax when he is away from social life. Studies also make one skillful to analyze and discuss a variety of topics in a prudent way and allow him to convince other with strong facts and arguments. Moreover, in business life that also includes politics, one’s judgmental qualities increases by thorough study.
Bacon, however, simultaneously discuss the pitfall of excessive studying, more importantly, if one is studying with wrong intentions. He says that spending time only on studying makes man idle; moreover, studying for ornament is showing-off; and a scholar seems to be silly if he makes his judgment solely by rules.
Bacon depicts his practical nature in the essay when he argues that a man should have concerns for both public and private business. He mustn’t only spend his time in studying as by this he may neglect his business. Similarly, if the purpose of study for a man is only to show-off his articulating skill, then he is embarrassed with affectation. For Bacon, showing-off is not merely a waste of time but also a moral degradation. The last disadvantage of only acquiring bookish knowledge and neglecting real world experience is it may make a person “book smart” but not “street smart”. In short, study without experience is useless.
The main purpose of Bacon’s essay is to guide people in experiences they might come across as they live in the world. He encourages the readers to bring their bookish knowledge in practical use.
Explain Francis Bacon’s perspective in the line “Writing makes an exact man” with reference to the essay “Of Studies”?
This line is extracted from Bacon’s essay “Of Studies”. The whole statement reads “Reading makes a full man; Conference a ready man; and Writing an exact man.” Through this line, Bacon argues that writing makes man perfect. This statement is immediately followed by another statement in which he states that if a man doesn’t write much, he must have a good memory to remember. Inscription aids a person to understand various composite problems as it is inclined to stamp on the mind.
Bacon also links writing with compactness and preciseness. It is well said that if a person is unable to write about a subject clearly, his thinking is about the subject is also vague.
More From Francis Bacon
- Of Adversity
- Of Ambition
- Of Discourse
- Of Followers and Friends
- Of Friendship
- Of Great Place
- Of Marriage and Single Life
- Of Nobility
- Of Parents and Children
- Of Simulation and Dissimulation
- Of Superstition
- Of Goodness and Goodness of Nature

English Charity
Let’s write good English
Of Studies – Francis Bacon – Complete Explanation
by Francis Bacon
Complete explanation of the essay alongside the original text
Studies serve for delight, for ornament, and for ability.
Explanation
Study as an activity, in whatever form, brings us joy and enhances our thinking, speaking and writing ability adding charm to our personality.
Their chief use for delight is in privateness and retiring; for ornament, is in discourse; and for ability, is in the judgment and disposition of business.
Study is always a private activity which people engage in when they are alone or in the privacy of their homes. It helps them in relaxation after a strenuous routine, when the body and mind need to slow down. It sharpens our intellect helping us to judge things soundly. It helps us to go about our life’s business in a more capable way.
For expert men can execute, and perhaps judge of particulars, one by one; but the general counsels, and the plots and marshalling of affairs, come best from those that are learned.
It enables the learned men, who have studied extensively, to critically examine issues, and arrive at the right conclusion. They can garner data, facts and arguments or against a particular view rationally. Such intelligent analysis of facts improves the soundness and quality of their judgment.
To spend too much time in studies is sloth; to use them too much for ornament, is affectation; to make judgment wholly by their rules, is the humor of a scholar.
However, over-indulgence in studies leads to undesirable consequences. Setting aside long hours in a day to study will make a man indolent. Overuse of the wisdom to analyze ordinary commonplace issues may make the man appear pretentious and vainglorious. Sticking too much to rules to asses situations and decide on action may invite derision from others.
They perfect nature, and are perfected by experience: for natural abilities are like natural plants, that need pruning, by study; and studies themselves do give forth directions too much at large, except they be bounded in by experience.
Studying adds finesse and perfection to human nature. Experiences in life supplements such honing of nature. A person’s abilities inherited by birth are raw. Only when they are carefully worked upon and honed, the in-born abilities yield the best benefits to us. Studying is the whetstone that we use to sharpen our abilities. But inferences from study may lead to imprecise and misleading conclusions. In such situations, one’s experience in life comes in handy to arrive at the right conclusion. So, experience is very valuable as it supplements studies.
Crafty men condemn studies, simple men admire them, and wise men use them; for they teach not their own use; but that is a wisdom without them, and above them, won by observation.
People who are cunning and deceitful have no appreciation for studies as they accomplish their objectives through many crooked ways. Simple folks, however, greatly value the role of studies in human life. Wise people inherently draw upon the ideas obtained from their studies while solving life’s myriad problems.
Read not to contradict and confute; nor to believe and take for granted; nor to find talk and discourse; but to weigh and consider.
The aim of reading and acquiring knowledge must not be to aggressively refute other’s views or accept the writer’s views as gospel truth. It should also not be to engage in pointless discussion and argumentation. Studying should enable us to weigh facts and analyze them rationally.
Some books are to be tasted, others to be swallowed, and some few to be chewed and digested; that is, some books are to be read only in parts; others to be read, but not curiously; and some few to be read wholly, and with diligence and attention.
Books of varying content and genre are to be made use of differently. Some may be given a cursory reading, some others can be quickly sifted through. Other important books are to be read slowly and minutely so as to truly fathom the meaning and underlying sense.
Some books also may be read by deputy, and extracts made of them by others; but that would be only in the less important arguments, and the meaner sort of books, else distilled books are like common distilled waters, flashy things.
One can ask an assistant to read a book and prepare a short summary of it. But such practice should be followed for obtaining guidance on matters of lesser importance. There are some books which are, in fact, shortened already.
Reading maketh a full man; conference a ready man; and writing an exact man. Reading adds perfection to a man’s personality.
Discussing with others about the contents of a book imparts special practical skills to the reader. Writing removes all the residual weaknesses and ignorance from the person and enables him to remember the contents of a book.
And therefore, if a man write little, he had need have a great memory; if he confer little, he had need have a present wit: and if he read little, he had need have much cunning, to seem to know that he doth not.
So, writing helps to memorize facts. If a person is bashful so as not to discuss his reading with others, he will not be able to improve his wit. If he does not read, he will remain a somewhat stupid person.
Histories make men wise; poets witty; the mathematics subtle; natural philosophy deep; moral grave; logic and rhetoric able to contend.
Studying history makes a man wiser, studying poetry makes a man wittier: mathematics gives sound logical sense, and philosophy imparts valuable lessons on morality.
Abeunt studia in mores [Studies pass into and influence manners]. Nay, there is no stond or impediment in the wit but may be wrought out by fit studies; like as diseases of the body may have appropriate exercises.
Wit is a god-given gift. It is present in everybody. However, it can be sharpened by selective studying. This is akin to the way certain weaknesses of the human body are cured by appropriate physical exercises.
Bowling is good for the stone and reins; shooting for the lungs and breast; gentle walking for the stomach; riding for the head; and the like. They cure many ailments.
So if a man’s wit be wandering, let him study the mathematics; for in demonstrations, if his wit be called away never so little, he must begin again.
If a person is unable to concentrate, he will do well to study mathematics to focus his wavering mind. In mathematics, a slight loss of concentration leads to grave error.This makes the man to start all over again to do it. Thus, studying mathematics restrains the mind from darting off elsewhere.
If his wit be not apt to distinguish or find differences, let him study the Schoolmen; for they are cymini sectores [splitters of hairs].
If a person does not have the ability to discern, he will be benefited by studying Schoolmen as it trains mental ability and develops the art of expression.
If he be not apt to beat over matters, and to call up one thing to prove and illustrate another, let him study the lawyers’ cases.So every defect of the mind may have a special receipt.
If a person is unable to garner facts and manipulate them to put across his views convincingly, studying law will help him. Thus, every deficiency of mind can be addressed by appropriate reading.
Click here for explanations of more essays by Francis Bacon.
——————————————————————-END———————————————————–
Dear Readers,
If you are a student or a teacher living in Pakistan, Bangladesh, The Philippines, or the UAE, and want me to write notes on any English lesson from Class 10 till M.A, please make a request attaching either the lesson as a Word document or giving me its link for browsing on the internet. I will do my best to write and post those. Thanks
Elsewhere in the blog
La Belle Dame sans Merci: A Ballad by John Keats
Click: https://www.englishcharity.com/la-belle-dame-sans-merci-a-ballad-by-john-keats/
On His Blindness by John Milton
Click: https://www.englishcharity.com/on-his-blindness-by-john-milton/
The Fall of the House of Usher by Edgar Allan Poe
Click: https://www.englishcharity.com/the-fall-of-the-house-of-usher-by-edgar-allan-poe/
A Happy Man by W. Somerset Maugham
Click: https://www.englishcharity.com/the-happy-man-by-w-somerset-maugham/
Related Posts
- Of Unity In Religion – Francis Bacon – Complete Explanation
- Of Envy – Francis Bacon – Complete Explanation
- Of Friendship – Francis Bacon – Complete Explanation
- Of Ambition – Francis Bacon – Complete Explanation
- Of Marriage and Single Life – Francis Bacon – Complete Explanation
- Of Anger – Francis Bacon – Complete Explanation
- Of Death – Francis Bacon – Complete Explanation
- Of Wisdom for a Man’s Self – Francis Bacon – Complete Explanation
- Of Travel – Francis Bacon – Complete Explanation
- Of Revenge – Francis Bacon – Complete Explanation
[…] http://www.englishcharity.com/francis-bacon-essays-of-studies-explanation/ […]
Very helpful …..lot of thanks
Thank you for your kind comment.
This way of explanation is very useful
Thank you, Nageswari.
It’s too helpful Thanks for this… Small request Plz do upload ‘of friendship’ by Bacon
Click on this. https://www.englishcharity.com/of-friendship-by-bacon/
Where is simulation and dissimulation
very helpful…….thank you.
Is great. Thanks a lot
How according to francis bacon studies provide wisdom won by obserwation
Question for all essays sir ji prose subject ka subjective paper kia type ka hota h mid term ka or final ka
It is amazing the way you explained the way I am now a follower of this website
Literary Yog
Of Studies by Francis Bacon: Easiest Summary, Line by Line Explanation, and Theme
In this blog post on “Of Studies”, I will discuss the following points:
Table of Contents
Of Studies Summary
Studies here mean the collective studies that a person does. The main idea of “ Of Studies ” by Francis Bacon is the benefits of studies. Reading helps readers to cope with diverse situations.
Reading also enhances intellect and cures restraints on the minds of readers.
The essay provides the proper method for reading different subjects and discusses their benefits. For instance, history makes men wise; poetry witty; the mathematics subtle; philosophy deep, etc.
In short, the theme of “Of Studies” is how books benefit a reader tremendously in different ways.
Line by Line Explanation
Three important uses of studies.
At the outset, Francis Bacon states the three beneficial purposes of studies : delight, ornament, and ability.
The first utility is reading delights the reader. Reading in privateness and retiring is worthwhile, since it provides immense pleasure.
For instance, if a reader enjoys fiction like Paulo Coelho’s The Alchemist . Then the quest for treasure would entertain him. The journey of Santiago from Andalusia to the pyramid is quite delightful. Thus, studies not only compensate for boredom but also provide enormous pleasure to the reader.
The second purpose is it adds ornament to discourse. In a written or spoken discussion, studies help a well-read person to exhibit his knowledge more efficiently than an average person does .
For instance, in Of Truth , Of Love , and Of Friendship , Bacon heavily uses Latin phrases in these essays. It shows his excellence in Latin. Therefore, Bacon uses it for ornament in his writing.
Studies also improve the judgment ability of a reader and the arrangement of things. One can be an expert without studies. However, there is a distinction between an expert and a learned man. An expert can execute his plan and even judge a situation, but a learned man can perform better by giving advice, making plans, and managing things. Therefore, a learned man is better than an expert.
I have discussed an example in the video below.
The Effect of Excessive Studies
In these three ways, studies serve a reader. However, too much study is dangerous. The reason is excessive readers lead a sedentary lifestyle. When a reader sits for long, the immobility makes the body sluggish.
Similarly, using decorated words and knowledge excessively in discourse does the opposite. Too much use of ornaments would show a learned man ostentatious. Bacon also states that making judgments based on bookish knowledge is the humor of a scholar.
Consideration and application of the learning without understanding the practical world are inaccurate. A reader must be able to distinguish between theory and practical application while judging.
In each situation, Bacon emphasizes excess of anything is unwelcome. Therefore, a learner must maintain an equilibrium between studying and other activities, ornament and argument, and theory and practical.
Bacon repeats his principal argument that studies hone human nature and experience perfects it. Bacon draws an analogy between natural plants and the natural abilities of a person.
We cut the plants, which could grow in any direction, for growth.
Studies nurture the natural abilities of man. It enhances the comprehension of the reader. But that remains unfulfilled until the person gains experience related to the subject of study. It means knowledge and experience make reading complete.
Views of Studies
Studies benefit a reader in diverse ways. However, not all men admire it. For instance, crafty men contempt studies. They think it does not help individuals. They deal with different situations of life without studies. Therefore, for them, studies are of no use.
On the contrary, simple men admire studies. The simple men are aware of the benefits of studies and are amazed to see a knowledgeable man.
On the other hand, wise men take the best out of their studies by using theoretical knowledge practically. Books do not tell readers about their pragmatic aspects. One gains the ability to implement knowledge in learning through observation. Bacon emphasizes that having bookish knowledge is not enough. Our theoretical information is complete only when we use it in real life.
Real Method of Studies
To get the most out of books, Francis Bacon suggests one method of study. One should not read to prove others wrong. The reader looks for points that he can use in an argument. While reading with this motive, the reader loses what the book offers.
The reader must not also believe what the book says or take everything every word for granted. This approach is also problematic because instead of using his mind, the reader does nothing except imbibe the knowledge theoretically.
A reader should not also read just for discourse. He will be concerned about the points that he can use in the discussion. As a result, learning becomes superficial.
Contrary to these approaches, a reader should try to comprehend the message or argument/s of the writer. For example, while reading Essays (1597) by Francis Bacon, we should not read it to confuse someone, blindly follow it, and read it wholly for discourse. The best approach would be to consider what Bacon says on different subjects in Essays .
I would like to add here that the best practice of reading is syntopical reading. Mortimer Adler states, in How to Read a Book , syntopical reading or comparative reading is analyzing a subject based on a man’s studies of books on the same topic.
Not Every Book is Same
However, Bacon reminds us we cannot follow this method everywhere. He says,
“Some books are to be tasted, others to be swallowed, and some few to be chewed and digested.” Bacon 209
We need to read some books (for entertainment) partially. We can skim the parts of these books.
We need to read some other books plainly. They are necessary for memorization so that we can use them in real life.
There are only a few books that need our complete attention. We need to read the book with constant focus and effort. In these cases, analytical reading is critical.
Bacon also suggests that we can study abridged versions and summaries of unimportant books. These books are like distilled water, which has no significance for later use. Therefore, it is up to the reader to decide the correct method.
Benefits of Studies
Bacon also discusses the effects of reading, discussion, and writing. He says,
“reading makes a full man; conference leads to a ready man while writing makes an exact man .” (Bacon 1)
Reading provides a reader with knowledge. When one reads books one after the other, knowledge expands. In this way, it fills the reader with wisdom.
Like reading, continuous engagement in the discussion makes a well-read person good at the discourse. In conferences, the practice of using knowledge instantly and constant practice makes one prepared for any topic to talk about.
Furthermore, if the reader notes down his thought or opinion on a book, he can revisit them later without pressuring the memory.
If one does not do any of them, he needs to pretend to know things if he reads little. Otherwise, his lack of knowledge will become apparent. Moreover, if one does not know the topic, he needs to have a presence of mind.
And if a person does not write much, he needs to have significant memory because he must rely on his memory for everything he thinks.
Benefits of studying different subjects
Francis Bacon restates the benefits of reading diverse fields of knowledge. Francis Bacon mentions,
Histories make Men Wise; Poets Witty; The Mathematics Subtill; Natural Philosophy Deepe; Morall Grave; Logick and Rhetorick Able to Contend. (Bacon 210)
For an explanation, watch the video below.
Further, Bacon says that the way a particular physical exercise is appropriate for a distinct disease of the body, similarly proper studies can improve intelligence.
For instance, for a distracted mind, mathematics would be fit to improve concentration. While doing mathematics, we need to focus. If the mind wanders at the moment, then it would spoil everything. Thus, it is a practice to do a particular task with focus.
If the mind finds it hard to differentiate between matters, then studying the philosophers and theologians of the Middle Ages would be beneficial as we consider them for their logical distinctions.
Studying lawyers’ cases would be the right thing to do if one wants to improve their reasoning skills. So, for such flaws of mind, reading has the solution.
Buy The Alchemist on Amazon
Of Studies Theme
The theme of “Of Studies” is the benefits of reading . I have made a video where I have focused on the theme of the essay. You can watch the video below.
In the essay, Bacon mainly discusses the benefits of reading. He also discusses the benefits of reading different subjects. However, he does not support idle sitting. He makes his arguments balanced by focusing on the experience. For Bacon, we complete studies only with experience.
Bibliography
- Adler, Mortimer J and Charles Van Doren. How to Read a Book . Simon & Schuster, 2014.
- Bacon, Francis. “Of Truth.” Francis Bacon: The Essays , edited by John Pitcher, Penguin Books, 1985, pp. 209, 210.
- Coelho, Paulo. The Alchemist . Harper Collins, 2012.
I'm a PhD research scholar & MPhil degree holder from DU, Assam and also a budding blogger. I have cracked CBSE NET (July 2018), NE-SLET (July 2018), and UGC-NTA-NET (June 2019).
41 Comments
Understood very well. The way of analysis is nice. Thank you.
You’re welcome Bulen. Thanks 😊😊😊
Thank u dear God bless you
You have provided a very deep, and short summary of it.
#Rajendra Singh Nagar, you are welcome 😊😊😊
Thanks it was very helpful for me to make a perfect presentation.🤗
I’m thrilled to hear that the blog post was helpful for you in creating your presentation.🤗🤗🤗
You have explained it so beautifully. Thanks a lot. Stay safe.
Thank you Pranami. You too stay safe😊😊😊
I have read Bacon years ago, i only read text now by your critical analysis, i really catch many ideas many references even in simple it makes me clear. No words to praise you have done such a splendid job.
Glad to know that my work has helped you. Shukriya! 😊😊😊
It is a very good work. Jazak Allah
nice and educative
thank you for the appreciation 😊😊😊
I am very thankful to you….❤️🙏🏻
Thank you Bishakha 💛💛💛
It’s a very good work…. I understood very well🤗 The way of analysis is very good 👍 Thankyou soooo muchhh 🤗😊
Hi Krupa. Glad to know that my effort has brought a smile to your face. Keep reading💛💛💛
It’s a very good work… Thankyou soooo muchhh 🤗😊
Very nice readers
Thank you so much 🤗😊😊
Best explanation in simple and logical way…. Weldon! Good job👌
Thank you Maria for the acknowledgement 😊😊😊
Thankyou for this analysis. It was very helpful.
I’m so glad to know that Shivani! 😊😊😊
You explained it very well😊 Thank you so much 🤗❤🙏
Thank you, Akanksha 🙏🙏🙏. You are welcome 😊😊😊
Thank you so much sir, it’s held me a lot…. Thank you so very much 🙏
Thank you Puja 😊😊😊
It’s too much usefull for me , all the things you describe with easy way .
Glad to know that, Subhash😊
Thank uhh sir, it help aa lot to prepare my exam 🤩 thank uhh very much sir🙏
Glad to know that, Snehitha😊😊😊 You are welcome.
Well written and very helpful for new blogger
Thank you, Mir Hassan 😊😊😊
I have read it .Well written and very helpful for new blogger
Thank uhh sir, it help a lot to prepare for my exam
Glad to know that, Varsha😊😊😊
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Of Studies | Summary and Analysis
Summary and analysis of of studies by francis bacon.

Of Studies by Sir Francis Bacon, written in 1597 and enlarged in 1625, is an essay written in didactic style – it is intended to inform, or teach a lesson. Here, Bacon discusses the importance of studies, highlighting three main reasons to convince his readers of its necessity. In the end, we are told that merely studying a subject isn’t enough. What’s needed to perfect one’s study is the exercise and practice of the studied subject matter. On the whole, Of Studies is an engaging read from “ The Father of English Essays”.
Of Studies | Summary
Bacon begins the essay by listing the three central reasons that studies are important for: delight , ornament and ability . He says that a man can deal with his problems one at a time based on experience, but it is only informed men who can give counsels according to any situation, whether or not they have directly trained in it. In the next paragraph, he hastens to add that too much of anything is not good- and that includes studies. Spending an excess amount of time on it will make one a sloth , while displaying too much in conversation will make one seem affected . And living life solely based on book-learned knowledge is plainly foolish. One has in-born natural talents which are honed by studying and embellished by experiences.
Naturally clever men view studies with contempt , those with average wits admire i t, and wise men learn from it. Because studies do not teach how one should use the information- it simply provides it, it is up to the person’s wisdom to utilise it well. One should not study with the intention of contradicting or disproving others, nor should they entirely believe and rely upon everything they read- books should be read to understand and apply, to weigh and consider .
Bacon then says that some books are meant to be read in snippets, as only a few parts are necessary. Others are meant to be ‘swallowed’ as they are important in their entirety. And some are meant to be analysed and understood thoroughly, as they present principal information. Some books may be made up of excerpts from other books- but only excerpts of less important arguments may be read in this fashion. Removing key points from a book and reading it out of context is as good as not reading it at all.
Together, it is reading, writing and discussion that makes a man truly wise. If he only has little of one of these elements, then he must have an overflowing abundance of the other. There are different academic subjects which provide different aspects of intelligence to a person – history for wisdom, poetry for wit, morals for gravity, philosophy for depth. And it is the presence of one that aids the improvement of the other. Bacon then makes a connection between intellectual improvement and physical improvement. Like how bowling is good for the stone and reins, and shooting for the lung and breast and so forth- which each sport aiding a different part of the body- each subject aids a different part of their intellectual capacity. If a man wants to learn to focus, let him study mathematics. If his wit is not up to par, let him study Schoolmen. If he is not up to par in his reasoning and analytical strength, let him study law. Every intellectual capability which one’s mind lacks has an apt solution in the form of a subject of study.
Of Studies | Analysis
Sir Francis Bacon employs an informative, lesson-oriented structure to his essay. The vocabulary and context are fit to the late 1500s and early 1600s, as we can see by several references such as the reference to shooting and riding, which was especially popular in that time, and the use of a Latin phrase in the piece. The theme of the essay is the intelligent application of studies , rather than merely the concept of studying. Sir Bacon emphasises on the importance of knowing how to use what one has learnt .
In order to convey the importance of studying in a more efficient manner, he created three main reasons – to read for enjoyment , to read for merit , and to read for knowledge . However, it is interesting to note that he also inserts bits of advice, suggestions and explanations which elaborate his statements. Such an essay is termed ‘ didactic ’, as it is written with the intention of conveying a lesson or a point.
He points out in the first paragraph the difference between experts and learned men . Here, he draws a comparison between experience and book-based knowledge. Experience can make one an expert only in that particular subject matter, while reading can be done on several different topics- this may be likened to the modern, on-going debate of ‘book-smart versus street smart’ . Rather than choosing one, Sir Bacon underlines the importance of having both. A point to note is that despite advocating for the importance of studies, it is stressed that an excess of anything is harmful:
“ To spend too much time in studies is sloth; to use them too much for ornament, is affectation; to make judgment wholly by their rules, is the humor of a scholar. ”
This is a cleverly strung sentence, drawing a firm boundary between necessity and imprudence. It also places weight on the significance of balance.
He also proceeds to reiterate the link between studied knowledge and experiential knowledge, saying that one embellishes the other . We may understand from this, as well as his emphasis on using what the book teaches, that his idea of studying gives value to the ability to apply it in the real world. He regards studying as a tool, something one should be able to connect to real-world scenarios and consequently use. The following sentence gives an insight to how a person may observe studying based on their natural intellectual capacity:
“ Crafty men contemn studies, simple men admire them, and wise men use them; for they teach not their own use; but that is a wisdom without them, and above them, won by observation.”
Studies are scorned by the shrewd, admired by the simple and observed by the wise.
Sir Bacon follows this with another aspect of studying a subject: intention . It must be acknowledged that one’s reason for performing a certain task plays a great role in how well it is accomplished. Consider the line below:
“R ead not to contradict and confute; nor to believe and take for granted; nor to find talk and discourse; but to weigh and consider. ”
One will not receive the same amount of knowledge if their intention is simply to disprove others. This may be because it is not a genuine desire to learn for oneself, but out of pure ambition, and therefore the motivation can disappear quickly. Similarly, Bacon also warns readers against naivety and quick relaxation. Believing everything immediately is equally as dangerous as learning without sincerity. The advice to “ weigh and consider” once more links back to Sir Bacon’s accentuation of application . One must understand what they study, when and how to use it, and the reason behind it. They must consider which information is valid for a given situation. It is only with this ability to think critically and use their book-learned information that they can say they are truly learned.
Sir Bacon also discusses how to study- sometimes it is better to read mere chapters of the books, while certain other books are meant to be thoroughly inspected. This may be symbolic of ‘smart learning’ over ‘rote learning’ in more contemporary language. It is important to know how to make use of one’s time and energy, that is the only way not to waste effort on unnecessary information. He likens books which contain collections of important excerpts without context to “common distilled waters, flashy things. ” because it is a plateau. There is no further learning that can be done from such books, because we can only learn many things superficially, rather than one thing deeply. Not having context prevents us from understanding the true meaning behind the argument.
Another theme of Sir Bacon’s essay is balance . Multiple times, he mentions the importance of being well-versed in more than one area . We may compare this to his earlier lesson of “too much of anything will cause harm.” Having too much of one strength and none of the other will cause an imbalance of the mind- for example, the ability to memorize quickly, but the inability to focus does not lead to a learned man. Bacon’s vision of an ideal learned man is one who can study, write and discuss.
As this is a didactic essay, Sir Bacon ends it in a rather prescriptive manner- he tells the readers of the importance of different academic subjects, and how they may improve one’s skill and temperament. This advice is put forth in the form of information, with the idea of inspiring curiosity and willpower. He says :
“Histories make men wise; poets witty; the mathematics subtile; natural philosophy deep; moral grave; logic and rhetoric able to contend.”
He goes on to elaborate that each subject can be seen as a ‘remedy’ to a lack of ability . For example, if one suffers a lack of wit, the remedy is learning poetry. In order to make the explanation more relatable to his readers, he brings in the example of physical sports:
“ Bowling is good for the stone and reins; shooting for the lungs and breast; gentle walking for the stomach; riding for the head; and the like. ”
This is in a similar format of listing which physical activities will heal and help which parts of the body.
Bacon’s main point in his essay Of Studies, is that there is a subject for every aspect of intellectual temperament , and becoming well versed in it will confirm personal growth and improvement. He ends the essay with “So every defect of the mind, may have a special receipt. ” However, as he makes clear throughout the essay, it is crucial to maintain a balance. Too much is harmful, too little is purposeless. Too much of one and not enough of the other will work in contradiction. Intent is key, and most importantly, the experience and application of what one has read is what truly proves if they have understood their lesson.
Poem of the Week : Metamorphosis
Dr. heidegger’s experiment | summary and analysis, related articles, departure | summary and analysis, beyond the bayou | summary & analysis, comparison by sylvia plath | summary and analysis, a village after dark summary, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- The Indian Burying Ground Analysis December 28, 2023
Adblock Detected
Search Suggest

Class with Mason - School of Literary Studies
- Full Courses
- Poetry Analysis
- Notes on Novels
- Drama Notes
- Prose Notes
- Biographies
- Literary Terms
- Literary Theory
- Bridge of Faiths
- Mobile-First Slides
- Sub Menu 03
- Sub Menu 04
- Sub Menu 05
Of Studies, Francis Bacon: Summary & Analysis
"Of Studies" stands as one of the most widely quoted essays by the renowned philosopher Sir Francis Bacon. Within its pages, Bacon meticulously dissects the profound importance of acquiring knowledge, endeavoring to persuade his readers of its inherent vitality. His discourse extends beyond mere bookish knowledge, acknowledging the crucial role that experience plays in conjunction with scholarly pursuits.
Bacon distinguishes between studies and education, asserting that they are distinct yet intertwined. While education encompasses the assimilation of both book knowledge and life experiences, studies delve specifically into the acquisition of knowledge. Bacon deftly addresses common queries that pervade the minds of individuals, offering insights into the reasons behind reading books, the transformative impact of studies on one's life, and the futility of pursuing knowledge without the accompanying richness of experiential wisdom.
Throughout the essay, Bacon bolsters his assertions with references and illustrative examples, lending credence to his arguments. His writing style is marked by simplicity, yet the potency of his arguments remains palpable. Bacon employs concise sentences, similes, and Latin phrases to fortify his stance, lending further weight to his persuasive discourse.
"Of Studies" serves as a timeless repository of wisdom, inspiring individuals across generations to recognize and embrace the profound significance of knowledge. Bacon's compelling arguments, accompanied by his adept use of rhetoric, continue to resonate, reinforcing the indelible impact that studies and experiential learning have on personal growth and intellectual development.
The Threefold Significance of Studies: Insights from Sir Francis Bacon
Within his essay, Sir Francis Bacon classifies studies into three distinct categories, each offering unique benefits and serving a specific purpose. Bacon asserts that studies fulfill the roles of "delight," "ornament," and "ability." While these designations were particularly pertinent in Bacon's era, their relevance can still be observed in contemporary times.
In Bacon's time, the stage was banned, leaving books as the sole medium of entertainment. Consequently, books assumed the role of providing delight, offering a substitute for the forbidden drama. Even from a modern perspective, there are individuals who derive great pleasure and delight from the pages of a book, finding solace and entertainment within their captivating narratives, rivaling the allure of movies and plays.
Bacon further expands upon the notion of "delight," explaining that the chief purpose of books in providing delight lies in their ability to be enjoyed privately and in moments of solitude. Thus, although the terminology may differ, the essence remains the same: studies, whether in the form of books or other sources, continue to offer entertainment and personal enjoyment.
By delineating the multifaceted significance of studies, Bacon underscores their pivotal role in enriching our lives, both intellectually and emotionally. Whether through providing delight, enhancing our knowledge and intellectual capabilities, or adorning our persona with the "ornament" of wisdom, studies remain an invaluable pursuit for personal growth and fulfillment.
The Ornamental and Professional Aspects of Studies: Insights from Sir Francis Bacon
Bacon asserts that studies serve a second purpose: "ornament." Through the acquisition of knowledge, individuals are able to present themselves in a favorable manner, acquiring a refined demeanor and social grace. Studies enable individuals to cultivate etiquettes and manners that leave a lasting impression on society, bestowing upon them a perception of wisdom and sophistication in the eyes of others. While Bacon employs the term "discourse" to explain this purpose, it warrants further exploration.
Discourse, in this context, encompasses various forms of communication, such as professional, religious, romantic, motivational, or debate-oriented. By engaging in studies, individuals enhance their ability to communicate effectively in different spheres of life. They develop the power to express themselves eloquently, whether in their profession, their religious beliefs, or their personal relationships.
Furthermore, studies also serve the third purpose identified by Bacon: the development of judgment and the ability to handle business matters. This aspect aligns more closely with a professional context. By engaging in studies, individuals acquire the necessary knowledge and skills to navigate complex business situations. Studies strengthen their mental acuity, allowing them to make swift and accurate decisions, while also honing their overall judgment and business acumen.
In summary, studies not only enhance a person's ornamental qualities, elevating their social presence and communication skills, but also equip them with the discernment and competence needed to excel in professional endeavors. Bacon's insights highlight the profound impact that studies can have on shaping an individual's intellectual growth and their ability to succeed in various aspects of life.
The Role of Experience in the Pursuit of Knowledge: Insights from Sir Francis Bacon
"The natural abilities are like natural plants, that need pruning by study; and studies themselves do give forth directions too much at large, except they be bounded in by experience." - Sir Francis Bacon
Bacon emphasizes the indispensability of experience in conjunction with studies, asserting that without it, the three purposes previously discussed become futile. Excessive pursuit of studies for "delight" can lead to laziness, as the individual may become engrossed in the pleasure derived from knowledge acquisition without applying it to practical endeavors. Similarly, focusing solely on ornamentation can result in a mere display of learned knowledge, devoid of genuine understanding and critical thinking. Merely memorizing an array of rules and facts from books does not enhance one's abilities or contribute to the development of their cognitive capacities.
According to Bacon, every individual possesses natural abilities, akin to plants in need of pruning through study. While studies provide valuable directions and guidance, their full potential can only be realized when complemented by the guidance of experience. Experience serves as a guiding force, allowing individuals to discern the most suitable path among the multitude of options that studies present.
Furthermore, Bacon acknowledges that individuals perceive studies differently. Some disregard their value, while others appreciate their significance. However, the truly wise are those who skillfully integrate studies into their lives, harnessing their power to achieve personal growth and success.
In conclusion, studies offer a plethora of paths for individuals to explore, but it is the wisdom gained through experience that enables them to make informed choices and effectively apply their knowledge. Bacon's insights underscore the importance of combining theoretical knowledge with practical experience in order to fully benefit from the pursuit of education and intellectual growth.
The Purpose and Selection of Books: Insights from Sir Francis Bacon
According to Sir Francis Bacon, the act of reading should go beyond mere consumption. He emphasizes that the primary objective of reading should be to weigh and consider the ideas presented in books, rather than using them solely as ammunition in debates or blindly accepting everything written within their pages. The discerning reader engages with books to distinguish between right and wrong, developing a critical mindset.
Bacon further classifies books into three categories: "tasted," "swallowed," and "chewed and digested." "Tasted" books require minimal attention, with the reader simply skimming through their contents. "Swallowed" books demand a bit more attention and engagement from the reader. Finally, "chewed and digested" books necessitate the utmost concentration and thorough examination. Such books demand that every word and line be meticulously chewed, contemplated, and thoroughly digested.
By categorizing books in this manner, Bacon underscores the importance of discernment in choosing what to read. Not all books hold the same value or require the same level of engagement. Readers must exercise judgment to select books that align with their interests, intellectual pursuits, and desired depth of understanding.
In summary, Bacon encourages readers to approach books with a critical mindset, seeking to distinguish between right and wrong. He advises discerning readers to carefully select books that warrant their full attention, recognizing that different books may require varying levels of engagement and contemplation. By engaging with books in this thoughtful manner, individuals can derive the greatest benefit from their reading endeavors.
Subjects and Their Benefits: A Guide by Sir Francis Bacon
Sir Francis Bacon recognizes that different subjects of study offer unique benefits and contribute to the development of an individual's intellectual faculties. By engaging with specific subjects, one can enhance various aspects of their mental capacity and broaden their intellectual horizons.
Here is a list of subjects highlighted by Bacon and their corresponding benefits:
History Studying history increases wisdom, providing valuable insights into past events, human behavior, and the consequences of actions. Poetry Engaging with poetry nurtures and enhances the imagination, allowing one to explore the depths of creativity and appreciate the power of language and artistic expression. Mathematics Delving into mathematics develops the mind's subtlety, sharpening logical reasoning, problem-solving abilities, and analytical thinking. Philosophy Exploring philosophy deepens one's capacity for critical thinking, abstract reasoning, and contemplation of fundamental questions about life, knowledge, and existence. Logic and Rhetoric Engaging with logic and rhetoric cultivates the ability to argue effectively, present ideas persuasively, and engage in logical reasoning, enabling individuals to contend with complex concepts and effectively communicate their thoughts.
It is essential for individuals to choose subjects based on their personal interests, goals, and areas of improvement. By focusing on relevant subjects, one can actively pursue the specific benefits they seek to acquire. Bacon's underlying message is that through the diligent study of various subjects, individuals can strive for continuous self-improvement, exercising and nourishing their minds just as physical exercise strengthens the body.
Conclusion of "Of Studies" by Sir Francis Bacon:
The whole essay exemplifies the remarkable intellectuality of Sir Francis Bacon. It is imbued with profound wisdom, and each line bears the mark of philosophical depth. Bacon's philosophy, encapsulated within this essay, is undeniably praiseworthy. Moreover, his mastery of language and style has earned him the title of the father of English prose. In "Of Studies," he employs precise and concise words to succinctly summarize his viewpoints. The essay is masterfully crafted, showcasing Bacon's unique intellectual prowess. It is an exemplary work that solidifies Bacon's position as the father of English prose.
Ad-Blocker Detected!
Sorry, we detected that you have activated Ad-Blocker. Please consider supporting us by disabling your Ad-Blocker, it helps us in developing this Website. Thank you!
Of Studies – Summary and Analysis
Fresh Reads
In his essay, Of Studies , Francis Bacon explains how and why study is important.
Studies are a source of pleasure. They have an ornamental value and also add to one’s ability.
This essay deals with some of the uses of study and offers some sound ideas relating to this theme. The pleasure of study can best be enjoyed by a man leading a life of aloofness and retirement. The ornamental value of study lies in enabling a man to become a good talker. He who spends too much time in studies is temporarily lazy. He who makes too much use of reading for purposes of conversation, is trying to make a vain display of his learning. If a man’s judgment is governed wholly by rules, he has learned from books,it shows his eccentricity.
Studies makes one develop one’s abilities with ease Studies by themselves provide guidance, but without practical experience this is abstract. Men who are cunning, do not approve of the studies, but those who are simple, feel an admiration for studies. Men who are basically wise, make use of studies for their progress.
One should not read books only to contradict others. All things written in books should not be followed in life. One should ponder over what he read sand how he uses it.
Some books are to be read in parts only. Some may be read quickly and hastily. There are only a small number of books that are worth close and detailed study. In the case of some books, a man may engage somebody else to read them and then tell him what they contain and also give him extracts from them. But this method should be adopted in the case of the meaner sort of books only. No man can be satisfied with a mere summary or synopsis of a good book.
Reading develops the whole personality of a man. Conversation makes a man witty. Different kinds of books have different effects upon the reader.History man a man wise, Poetry makes a man imaginative, Mathematics develops subtlety in a man, Natural science enables a man to look, deep into the things, Logic and art of public speaking develop a person’s communicative skills.
Various capabilities are developed by effective and useful reading. If a man’s mind wonders too much, he should be made to study Mathematics to develop concentration; if a man is unable to make distinctions amongst things, he should study the literature produced in the Middle Ages.
Studies are a cure for mental deficiency. Just as bowling is good for kidneys,shooting for the lungs, walking for digestion and riding for the head, so also mathematics is good for wondering wits. Every defect of a man’s mind can be cured through studies.
This essay deals with different kinds of books and their effect on the reader.The uses of studies are classified by Bacon under three heads – the use of studies for delight; the use of studies for ornament and the use of studies for ability. Bacon also gives us some excellent advice as to why or how one should read. He tells us that different studies have varied effects on the human mind.
Various mental defects can be remedied by various kinds of studies. The need of experience to supplement and perfect studies has duly been emphasized in the essay. Bacon would not be satisfied with more bookish knowledge. The wisdom won by experience is as necessary as the wisdom gained from books.
But it is not only the ideas that are so important in this essay. We find Bacon displaying his talent for using the maximum economy of words in order to express his ideas. The essay is a masterpiece of brevity and terseness. Some of his sentences read like proverbs.
Bacon’s essays abound in very appropriate and original similes. We have one such simile here when Bacon says that “distilled books are, like common distilled waters, flashy things”.
We could say, without any exaggeration, that it is one of the finest essays in English prose. It gives us a number of sound maxims and a number of sentences that we can use as quotations when occasion demands. Some of the sentences, indeed, cling to our memory without any mental effort on our part to memorise them. This is one of the best known essays from the pen of Bacon.
The Elizabethan Age is the most creative period in English Literature. The foreign wars were over and the Englishmen had for the first time the leisure to devote their energies to interests other than war upon their neighbours.
Fortunately, just at this time, the great wave of the Renaissance, the new birth of letters, having spent itself in Italy and crossing over France and Spain reached the shores of England.
With Francis Bacon begins philosophical reflections upon life, in the style of Plutarch’s “Morals” and the “Essays” of Montaigne. Bacon’s mind was catholic in its range, but the subjects of moral thought that interest him are comparatively few and generalized.
The method used by Bacon is to reduce reflection to the lowest terms to try to discover the fundamental principles of conduct, the influence and the actions of men. His essays reflects his experiences of learning. His observations do not clear his likes or dislikes. They are austere, brief to the point of crudeness.
In the essay Of Studies, a life-long student, Bacon describes his craft. He was no plodder upon books though he read much and that with great judgment. The subject of this essay was the one that revolved longest in the edition of his “Essays”.
One peculiarity of this essay which deserves notice is the frequency with which Bacon repeats himself. Thus essay has each sentence carefully selected and strung together, Bacon has gems of thought and language, but he does not scatter them about with un calculating profusion of a Shakespeare, non‘like wealthy men who care not how they give, but rather like those who are spending their story with care’.
Bacon is not an optimist. He has no sentiment to lead the reader astray. He writes with brevity and compactness. To the careless reader much of what he has written will seem common-place enough. But to the serious reader,his thoughts are universal. The sentences are compact and simple.
The passage is compressed, bold, full of condensed thought and utterly devoid of ornamentation. The sentences run smooth. Force and precision are its main characteristics. The sustained passage has easy eloquence, and sentences here and there are of singular and unaffected beauty and not thrust in but flowing continuously with the rest. Bacon writes with an air of modesty.His passages bear the mark of a grand and confident self-esteem sometimes directly assertive, sometimes condescending, sometimes scornful, sometimes disguised under a transparent affectation of modesty.
There is one special characteristic of Bacon’s manner which does not admit of being illustrated except at a prohibitive length, his long magnificent roll of sentence after sentence. Each falling into its place, each adding new weight to what has gone before it, and all together uniting to complete the entire effect.
His style has simplicity, strength, brevity, clearness and precision. Simplicity cannot be said to be a characteristics in its strict sense, of his style. His passage is simple in the sense of being free from all affection, free from any studied elegance in the choice of words and in the structure of sentences.He avoids with equal care both pedantry and vulgarity, though he has no scruple in using homely illustrations, where such illustrations would be more telling.
That the quality of strength in Bacon’s style is intellectual rather than emotional.
Related posts:
- On the Choice of a Profession – Summary
- Children’s Literature: Theory and Practice – Summary
- On the Dignity of Man – Summary
- When We Dead Awaken: Writing as Re-Vision – Summary
Why I Write by George Orwell
What is fascism by george orwell, the shoemaker and the devil by anton chekhov.
Try aiPDF , our new AI assistant for students and researchers

Of Studies By Francis Bacon | Of Studies Summary & Analysis

Table of Contents
Introduction
Of Studies is the masterpiece essay nicely written by Francis Bacon. This essay is one of the most attractive essays, which was written on the behalf of Study. In the essay Of Studies, the writer Francis Bacon describes the importance of studies in human life. The essay Of Studies is the first essay in a series of ten essays published in 1597. The title of this essay collection is Essays or Counsels: Civil and Moral . In this essay, the writer has highlighted the importance of reading, writing, and learning in One’s life with experience, reinforcing the three purposes of studies – for delight, for ornament, and for ability.
Francis Bacon is popularly known as an eminent essayist, thinker, scholar, and philosopher. He belongs to the Elizabethan age. So far as Francis Bacon is concerned, he was one of the greatest men of Literature and is popularly known as the Father of English Essays . Being the essayist of the Elizabethan age, he wrote a galaxy of essays on different issues. His world-famous essay is – Of Studies, Of Love, Of Friendship, Of Hatred, Of Death, Of Truth, Of Philosophy, Of Beauty, Of Ambition, and Of Custom and Education.
Analysis of “Of Studies”
The writer begins this essay by enlisting three purposes of studies which are as follows:
- Studies for delight : Studies for gaining delight or happiness in one’s life.
- Studies for ability : Studies for improving one’s ability in life.
- Studies for Ornament : Studies for ornamenting one’s life.
The first use of studies is that they serve for delight or pleasure. This delight can be found in solitude or leisure after retirement from active life. Secondly, studies serve as an ornament in communication, conversation, and discourse. An educated person talks more attractively than an illiterate person. The third help in decision-making or judgment and disposition of business.
However, the studies have their own limitation. If too much time, is spent on studies, it is nothing but laziness. If these are used excessively in conversation, they tend to exaggerate and pose a person and if a scholar makes every decision of his life with his knowledge then it is foolish and humorous behavior of the scholar.
According to Bacon “ Crafty men condemn studies, simple men admire them, and wise men use them.”
Men who are hardworking or primitive men hate or condemn studies. However, men with simple intellect admire them. Moreover, intelligent men use them practically . Studies do not teach their own uses. It is the wisdom of a person that teaches him to use them. The author says:
“Some books are to be tasted others to be swallowed, and some few to be chewed and digested.”
There are some books which have to be read – only in parts because they are useful to a person only in a certain place. It is not proper to read them word by word. On the contrary. Some books should not be read out of curiosity and some must be read with full attention and diligence as they require the full attention of the reader. Moreover, there are hidden treasures in this category of books that can only be found through the diligence of the reader.
Bacon says a useful line in favor of reading, and according to him, “Reading maketh a Full Man; conference a ready man; and writing an exact man.”
It is reading that adds to a man’s knowledge and makes him complete in the sense of his wisdom. Undoubtedly, it is interaction with others that prepares a person practically. Furthermore, it is the skill of extensive or innovative writing that makes a complete person.
In addition, the author describes some facts about studies. He says that if a man writes less, he needs a great memory to remember all the learned things. If a person interacts less he needs a present and sharp intellect and if one reads a little he must be clever in knowing what he does not.
Bacon impresses the reader through his comprehensive and great sayings. He says,
“Histories make men wise; Poets, witty; the mathematics subtle; natural philosophy, deep; moral grave; logic and rhetoric, able to contend.”
Bacon says that it is the history of the ancestors that makes the new generation wise and witty. These are the rules and regulations laid down by the ancients that make mathematics subtle. It is because of history that philosophy has deep meaning and can be defended through logic and rhetorical arguments. Bacon encloses the essay by saying;
“So every defect of the mind may have a special receipt.”
Bacon’s Of Studies essay deals with the benefits of the study to individuals in their daily lives. From reading books to writing papers, study plays an important role in a person’s life, making him learn, wise and experienced.
Francis Bacon ‘s essay is rich in intellectual wisdom, practical approach, and practical wisdom. Hence, it is considered the most beneficial essay for students and young people.
Are you struggling to keep up with your English Literature Coursework? Do you need detailed, customized notes to help you better understand the texts you’re studying? “Look no further! Our customized paid notes will help you achieve your study goals quickly.
– varsha singh, related posts.

War Poetry In English Literature | Fight during World War 1st | War Poets

I Know Why The Caged Bird Sings Summary & Analysis | I Know Why The Caged Bird Sings Poem Explanation

French Borrowing Words & French Loan Words | French loan Words In English Literature

New Criticism in literature | 20th Century Criticism | Modern Criticism
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

UNDERSTANDING FRANCIS BACON'S 'OF STUDIES'

Explanation of Francis Bacon's 'Of Studies'
Related Papers
Doina-Cristina Rusu
The general aim of Francis Bacon's philosophy was the reformation of human knowledge, with the intent to put it into practice and use it for the benefit of humankind. He criticized Aristotelian-Scholastic philosophy on the grounds that its method was unable to bring about progress. Bacon's method of induction was the antidote to the idleness of previous philosophies, and it had a twofold function. First, it was supposed to eradicate the errors and idols from human mind, so that this could become like a polished mirror in which the nature could reflect itself, leading to the cultivation of virtues and elimination of vices. Second , it was supposed to discover the inner structure of matter and its activity. This was done by gradual abstraction and, most important , with the help of experiments. Bacon's emphasis on experience and the use of experiments as the right tools to be employed in the study of nature was an idea that influenced future generations of philosophers, and it is considered a building stone in the establishment of the societies of knowledge founded in the second half of the seventeenth century. Bacon contended that his method of induction should be employed beyond the study of nature into other disciplines, such as ethics. This enterprise, he believed, would bring about not only knowledge, but also welfare and happiness.
Vladimir Moss
An Account of the Nature of the Conflict between Science and Religion in the Seventeenth Century
Dana Jalobeanu
British journal for the history of philosophy
Silvia Manzo
The aim of this article is to examine how Bacon proposed to replace the older patterns of authority and freedom in science. I hope that this textual exegesis will contribute to the reflection on freedom and power in modernity. In doing this I have in mind three important considerations. First, Bacon deals with authority and freedom in different fields: theology, law, politics and science. Second, the psychological conditions of scientists are relevant in order to examine the extent of the scientific freedom. Third, Bacon thought of science as part of a political network. Sections I and II expose Bacon’s approach to authority in theology, law and politics by contrasting his ideas on authority and science. Section III deals with the psychological aspects of the freedom of the scientist. Sections IV and V are concerned with authority in science considered both as an institution of the state and as the inquisition of nature.
Perspectives on Science
This article is an investigation into the rationale and the structure of order of Francis Bacon's natural and experimental histories. My aim is to show that these natural histories are mainly composed of experimental series, ie methodologically organized recordings of experimental inquiries. Bacon's experimental series have a double purpose: heuristic and pedagogical. They direct and encode the “good” experimental practices, while also teaching the neophyte how to become a Baconian experimenter.
Nikolaus Egel
Canadian Journal of Political Science
Heidi Studer
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Of Studies | Francis Bacon |Summary and Analysis | Questions
Table of Contents
Of Studies – Summary
Francis Bacon’s classic essay “Of Studies” explains how and why study—knowledge—is important. In this essay, he discusses some of the benefits of studying and offers some sound ideas on the subject.
Bacon is regarded as the “Father of the English Essay”. Bacon envisioned the essay as an opportunity to offer advice. The title of his essay collection: “Essays or Counsels: Civil and Moral,” suggests that didactic intent.
OUR LATEST VIDEOS
Please enable JavaScript
In “Of Studies,” Bacon explains the practical value of knowledge. Bacon considers how studies might be put to use. He is more interested in their practical utility than in their theoretical promise, a proclivity that is perhaps more English than French. In “Of Studies,” Bacon’s writing is direct and pointed. It avoids Montaigne’s essays’ meandering, find-your-own-way free form. Bacon gets right to the point in his first sentence: “Studies serve for delight, ornament, and ability.” He then goes on to explain how studies can help in these three ways. And he doesn’t mince words when describing the use of “studies” for a Renaissance gentleman.
One of the essay’s main draws is Bacon’s skillful use of parallel sentence structure, which is evident in the opening sentence and throughout “Of Studies.” This stylistic technique adds clarity and order to the writing, as in “crafty men condemn studies, simple men admire them, and wise men use them,” which demonstrates confidence and elegance in addition to clarity and emphasis through its straightforward assertiveness.
Studies are a source of pleasure. They have ornamental value and also improve one’s ability.
A man who lives a life of aloofness and retirement is best suited to enjoy the pleasures of study. Study has a ornamental value in that it enables a man to become a good talker. A student who devotes too much time to his studies becomes temporarily sluggish. Whoever tries to make a show of his knowledge by reading excessively for conversational purposes is wasting his time. It reveals a man’s eccentricity if his judgement is entirely based on rules he has learned from books.
Studies allow you to easily develop your skills and abilities. Studies provide guidance on their own, but this is abstract without practical experience. The studies are disliked by cunning men, but they are admired by simple men. Men who are fundamentally wise use studies to advance in life.
One should not read books solely to contradict others. Everything written in a book should not be followed in real life. One should think about what he reads and how he applies it.
Studies are a treatment for mental illness. Mathematics is good for wondering wits in the same way that bowling is good for kidneys, shooting is good for lungs, walking is good for digestion, and riding is good for the head. Every mental defect in a man can be cured through studies
Critical Analysis
This essay discusses various types of books and their effects on the reader. Bacon divides the uses of studies into three categories: the use of studies for delight, the use of studies for ornament, and the use of studies for ability. Bacon also provides some excellent advice on why and how to read. He claims that different studies have different effects on the human mind.
Various kinds of studies can help to correct a variety of mental flaws. The importance of experience in supplementing and perfecting studies is duly emphasised in the essay. Bacon would not be satisfied with more bookish knowledge. The wisdom gained through experience is just as important as the wisdom gained through reading books.
But ideas aren’t the only thing that matters in this essay. Bacon demonstrates his talent for expressing his ideas with the least amount of words possible. The essay is a masterwork of concision and brevity. His sentences have a proverbial feel to them.
Bacon’s essays abound in very appropriate and original similes. We have one such simile here when Bacon says that “distilled books are, like common distilled waters, flashy things”.
It is, without a doubt, one of the best English prose essays ever written. It provides us with a number of sound maxims and sentences that we can quote when the situation calls for it. Some of the sentences do, in fact, stick in our heads without any conscious effort on our part. Bacon’s essay is one of his most well-known works.
Questions and Answers
You must have understood Bacon’s ideas about studies. You must have understood the uses and disadvantages of study. You have also come to know about rules and modes of study.
Exercise – 1
Now answer the following questions by choosing the correct answer from the three alternatives given below each question.
1. Bacon’s essay entitled Of Studies is a passage to be:
(i) chewed and digested
(ii) read with main points
(iii) studied thoroughly Answer: i) chewed and digested
2. One who makes too much use of his readings for conversational purposes makes:
(i) things haphazard
(ii) vain display of his learnings
(iii) proper use of books Answer: (ii) vain display of his learning
3. One should take extracts from :
(i) books of high value
(ii) meaner sort of books
(iii) remedial books Answer: (ii) meaner sort of books
4. Books worth a closer and thorough reading :
(i) are smaller in number
(ii) are written by famous writers
(iii) are text books Answer: (i) are smaller in number
5. Logic and rhetoric develops :
(i) man’s debating powers
(ii) man’s thinking power
(iii) man’s power to interact Answer: (i) man’s debating powers
Exercise – 2
Now try to answer the following questions in sentences of your own :
1. What type of books are to be chewed and digested? Answer: The books which have knowledgeable contents should be read thoroughly and understood properly.
2. What do you think is the proper use of study? Answer: We study for personal enjoyment and for cultivation of social charm through the cultivation of the power of exposition in speech and to develop ability for judgment of facts and circumstances.
3. What is the use of the study of natural philosophy? Answer: It enables the reader to understand things in a better way and reach to the depth of subject matter.
4. How can a man acquire ability to perfection? Answer: It can be acquired when knowledge gained from books is supplemented with practical experience.
5. For what we should not read books? Answer: One should not read books to contradict others.
Now try to answer the following questions :
1. How did Bacon classify the books? Answer: Bacon classified books under three major categories. Some books are for personal enjoyment, others are to be read to develop conversational qualities and some others are to develop power of judgment.
2. What are special qualities of this essay? Answer: Some of these qualities are maximum economy of words, straight forward presentation, brevity, terseness and use of sentences as proverbs.
3. Comment on the theme of this essay. Answer: Bacon tries to discover fundamental principles of conduct influence and actions of men.
4. Discuss the peculiarity of structure of this essay. Answer: Each sentence is carefully selected and strung together. The essay shows brevity and compactness.
5. Discuss the main qualities of Bacon’s style. Answer: The essay of Bacon is compressed, full of condensed thought and utterly devoid of ornamentation. The sentences in the paragraph run smooth.
Discover more from Smart English Notes
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Premium Content

- Republic Policy

Constitutional Law

Criminal Law

International Law

Civil Service Law

Recruitment

Appointment

Civil Services Reforms

Legislature

Fundamental Rights

Civil & Political Rights

Economic, Social & Cultural Rights

Focused Rights

Political Philosophy


Political Economy

International Relations

National Politics
- Organization
Tariq Mahmood Awan
As a literature student, Francis Bacon has always inspired me. Therefore, reading him is a privilege. The best thing about his literary endeavors is his clarity of thought and persuasive expression.
Francis Bacon’s essay “Of Studies” provides multifaceted benefits of learning while offering cautions against potential pitfalls. Bacon argues that studies serve three primary purposes: delight, ornament, and ability. In private moments, studies provide intellectual pleasure and the satisfaction of acquiring new knowledge. They also enhance one’s communication ability, adding depth and richness to conversations through a broader knowledge base. Ultimately, their ability to improve judgment and decision-making is the most significant benefit. While experts excel at specific tasks, those with a more comprehensive understanding gained from studies can effectively manage complex situations and formulate strategic plans.
However, Bacon warns against taking studies to extremes. Dedicating an excessive amount of time solely to studies can be a form of idleness, neglecting the practical application of knowledge. Similarly, using studies purely for show, to impress others with one’s erudition, is seen as affectation. True wisdom lies not just in accumulating facts but in applying them effectively. Studies are best viewed as tools that refine our natural abilities, just as pruning cultivates a plant’s growth. However, studies can provide overly broad guidance without the grounding of practical experience.
The essay explores how different people perceive the value of studies. Cunning individuals may dismiss their importance, while the naive may overestimate their impact. The truly wise, however, recognize studies as a valuable resource but not a substitute for practical wisdom gained through observation. Bacon emphasizes approaching reading with a critical mind. Effective reading is not about passively accepting information, arguing about contradicting or simply finding conversation topics. It’s about careful analysis, weighing evidence, and forming well-considered opinions. The essay suggests different strategies for various types of books. Some deserve a thorough, in-depth reading, while others may only require skimming or relying on summaries for key points.
Writing refines one’s thoughts and expressions, leading to greater precision. Engaging in discussions helps one think on one’s feet and articulate ideas clearly. The essay concludes by highlighting how different disciplines contribute to intellectual development. History imparts wisdom, poetry fosters wit, mathematics sharpens logic, and various fields cultivate valuable mental faculties. By studying these diverse areas, one can achieve a well-rounded mind.
Critical evaluation of the essay is essential. An essay will always remain subjective despite how much it is written objectively. Francis Bacon’s essay “Of Studies” is a thought-provoking exploration of the importance of learning and the pursuit of knowledge. Bacon argues that studies offer three distinct benefits. The act of learning itself can be a source of enjoyment. Whether one dives into scholarly pursuits during quiet moments or seeks intellectual stimulation as a respite from a busy life, the process of acquiring knowledge can be inherently pleasurable. Studies enhance our communication skills. A well-read individual can draw upon a broader knowledge base to enrich conversations, making them more engaging and insightful.
Ultimately, the most significant benefit of studies lies in their ability to improve our judgment and decision-making capabilities. While experts excel in specific areas based on experience, those with a broader understanding gained through studies can effectively handle complex situations and formulate strategic plans.
While advocating for the importance of studies, Bacon warns against taking them to extremes. Devoting an excessive amount of time solely to studies can be a form of laziness. Without applying the acquired knowledge to real-world problems or situations, one is essentially neglecting the practical value of learning. Using studies purely for ornamental purposes, to impress others with one’s erudition, is seen as a form of pretentiousness. True wisdom lies not just in accumulating facts but in utilizing them effectively. Furthermore, relying solely on theoretical knowledge acquired through studies to make life decisions can be unwise. Experience and practical application are crucial for sound judgment.
Bacon uses a metaphor to illustrate the relationship between natural abilities and studies. He compares natural abilities to a tree that thrives with proper pruning. Studies serve as the pruning tool, refining and shaping our natural talents. However, studies by themselves can provide overly broad guidance. Experience acts as the grounding force, ensuring that theoretical knowledge is applied effectively in the real world.
Furthermore, the essay explores how different people perceive the value of studies. Crafty Men focused solely on practical matters may dismiss the importance of studies, viewing them as unnecessary. Simple Men may overestimate the impact of studies, believing that knowledge alone is sufficient for success. Wise Men truly recognize studies as a valuable resource but not a substitute for practical wisdom gained through observation and experience. Then, Bacon emphasizes the importance of approaching reading with a critical and active mind. Effective reading is not about passive acceptance of information. More importantly, one should not read solely to contradict others or take everything at face value. Instead, the focus should be critically evaluating the presented information, weighing evidence, and forming well-considered opinions.
The essay suggests different strategies for various types of books. Some books may not require a deep dive. Skimming or sampling key passages may be sufficient to grasp the main ideas. Certain books, particularly those rich in content or seminal works in a field, deserve a thorough and attentive reading. Then, hidden treasures may lie within complex texts that demand in-depth exploration and analysis. Careful study and reflection are crucial to extracting such books’ full value. Bacon cautions against relying solely on “distilled books,” essentially compilations of other works’ extracts. These summaries often lack the depth of the original sources and can provide a superficial understanding of complex topics. Therefore, readers need to be wiser in selecting books that could provide substantive information and compelling persuasion to the imagination.
Bacon’s “Of Studies” is a powerful endorsement of the pursuit of knowledge. However, he emphasizes the importance of balance and discernment. Studies, when combined with experience and practical application, lead to true wisdom. As readers, we must engage actively with texts, critically evaluating information and extracting the essence of what they offer.
Please, subscribe to the YouTube channel of republicpolicy.com
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Search the Blog

Investigation of allegations of over-billing of electricity by distribution companies

World Water Day: A Call for Cooperation and Harmony

International Nowruz Day21 March: Celebrating Renewal and Harmony

A Case of Women Empowerment in Pakistan
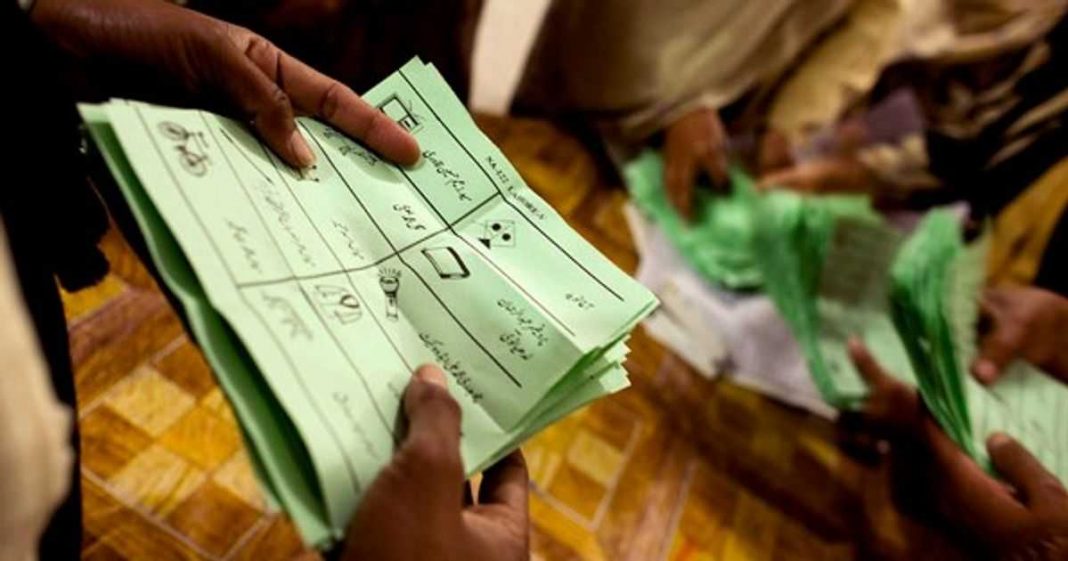

The People’s Will is Undeniable: Lesson from the Elections, 2024

The Importance of Transforming the Primary Education in Pakistan

Fixing the Economy of Pakistan

The Duality of Likes and Links: Social Media’s Power and the Urgent Need for Regulation
Human Rights and the Pakistani State and Society: An Analysis

Reforming the Local Governments in Pakistan: A Complete Analysis
Support our cause.
"Republic Policy Think Tank, a team of dedicated volunteers, is working tirelessly to make Pakistan a thriving republic. We champion reforms, advocate for good governance, and fight for human rights, the rule of law, and a strong federal system. Your contribution, big or small, fuels our fight. Donate today and help us build a brighter future for all."
Qiuck Links
- Op Ed columns
Contact Details

- Editor: +923006650789
- Lahore Office: +923014243788
- E-mail: [email protected]
- Lahore Office: 143-Gull-e-Daman, College Road, Lahore
- Islamabad Office: Zafar qamar and Co. Office No. 7, 1st Floor, Qasim Arcade, Street 124, G-13/4 Mini Market, Adjacent to Masjid Ali Murtaza, Islamabad
- Submission Guidelines
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy & Policy
Copyright © 2024 Republic Policy
| Developed and managed by Abdcorp.co
Of Studies by Francis Bacon
STUDIES serve for delight, for ornament, and for ability. Their chief use for delight is in privateness and retiring; for ornament, is in discourse; and for ability, is in the judgment and disposition of business. For expert men can execute, and perhaps judge of particulars, one by one; but the general counsels, and the plots and marshalling of affairs, come best from those that are learned. To spend too much time in studies is sloth; to use them too much for ornament, is affectation; to make judgment wholly by their rules, is the humor of a scholar. They perfect nature, and are perfected by experience: for natural abilities are like natural plants, that need proyning, 1 by study; and studies themselves do give forth directions too much at large, except they be bounded in by experience. Crafty men contemn studies, simple men admire them, and wise men use them; for they teach not their own use; but that is a wisdom without them, and above them, won by observation. Read not to contradict and confute; nor to believe and take for granted; nor to find talk and discourse; but to weigh and consider. Some books are to be tasted, others to be swallowed, and some few to be chewed and digested; that is, some books are to be read only in parts; others to be read, but not curiously; and some few to be read wholly, and with diligence and attention. Some books also may be read by deputy, and extracts made of them by others; but that would be only in the less important arguments, and the meaner sort of books, else distilled books are like common distilled waters, flashy 2 things. Reading maketh a full man; conference a ready man; and writing an exact man. And therefore, if a man write little, he had need have a great memory; if he confer little, he had need have a present wit: and if he read little, he had need have much cunning, to seem to know that he doth not. Histories make men wise; poets witty; the mathematics subtile; natural philosophy deep; moral grave; logic and rhetoric able to contend. Abeunt studia in mores [Studies pass into and influence manners]. Nay, there is no stond or impediment in the wit but may be wrought out by fit studies; like as diseases of the body may have appropriate exercises. Bowling is good for the stone and reins; 3 shooting for the lungs and breast; gentle walking for the stomach; riding for the head; and the like. So if a man’s wit be wandering, let him study the mathematics; for in demonstrations, if his wit be called away never so little, he must begin again. If his wit be not apt to distinguish or find differences, let him study the Schoolmen; for they are cymini sectores [splitters of hairs]. If he be not apt to beat over matters, and to call up one thing to prove and illustrate another, let him study the lawyers’ cases. So every defect of the mind may have a special receipt.
More from Francis Bacon :
- Of Vicissitude of Things
- Of Judicature
- Of Honor and Reputation
- Of Vain-glory
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
51 Francis Bacon: Essays
Introduction.
by Mary Larivee and Rithvik Saravanan
Francis Bacon (1561-1626), the English philosopher, was instrumental in the development of the Scientific Revolution in the late 18th century even though he had passed away centuries before. The “Scientific Revolution” was an important movement that emphasized Europe’s shift toward modernized science in fields such as mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology, and chemistry (Grant). It was an extension of the Renaissance period, which then led to the Enlightenment which brought advances across all areas of human endeavor. Francis Bacon, in particular, is remembered today primarily for the “scientific method” as a way of establishing what is true from what is false perception (a method that still lies at the heart of modern science). Bacon’s primary focus in his writings revolved around the practice of inductive reasoning, which he believed to be a complement to practical observation (Grant). Most people before this period followed the Aristotelian methodology for scientific arguments. This idea maintained that “if sufficiently clever men discussed a subject long enough, the truth would eventually be discovered” (“History – Francis Bacon.”). However irrational this sounds, the Scientific Revolution helped replace this outdated system of thinking with Bacon’s scientific method. Bacon argued that any proper argument required “evidence from the real world” (“History – Francis Bacon.”). His revolutionary ideas about empirical information helped propel him toward political and societal importance and fame.
Literary Context
Francis Bacon had a passion for metaphors, analogies, and vivid imagery. He was a rhetorical writer and his essays highlight his wisdom and incisive mind. His first book was released in 1597 followed by later editions with added essays that were released in 1612 and 1625. Each essay that Bacon wrote reveals his knowledge of Latin and draws on ancient Roman wisdom through axioms and proverbs. Additionally, Bacon uses wit as a way of getting his point across to his audience and this indeed causes the reader to reflect on his or her own beliefs and values. A key aspect of Bacon’s literature is its “terseness and epigrammatic force” (De). By managing to pack all of his thoughts and ideas into quick, brief statements, Bacon deepens the reach and impact of his work. His writing deviated from the typical Ciceronian style of the time, which was characterized by “melodious language, clarity, and forcefulness of presentation” (“Ciceronian.”). His statements are meaningful particularly because they are straight and to the point. The brevity of his ideas also facilitates the communication of his arguments, which is significant because, at the time, a solid, meaningful education was hard to come by. As such, Bacon’s work helped spread the notions that would eventually bear fruit with the discoveries of the Scientific Revolution.
Historical Context
Francis Bacon’s Essays cover a wide variety of topics and styles, ranging from individual to societal issues and from commonplace to existential. Another important aspect of the appeal of Bacon’s essays are that they weigh the argument at hand with multiple points of view. Bacon’s essays were received at the time with great praise, adoration, and reverence (Potter). He was noted for borrowing ideas from the works of historical writers such as Aristotle (Harmon), and, as such, he represents a continuation of this philosophical school of thought. Another important impact of the Scientific Revolution and Bacon’s literature is that it allowed common people of the era to question old, traditional beliefs. They began to consider everything with reason, which led to a greater sense of self as well as moral and ethical standards. By having the opportunity to judge for themselves, the people were able to advance society a step closer to a form of democracy.
Francis Bacon Essays is a collection of eight of the famous philosopher’s many essays. Each dissertation contains words of wisdom that have proven to be enlightening for many generations that followed. From “Truth” to “Of Superstition” and “Marriage and Single Life”, Bacon covers a wide range of intriguing topics in order to challenge the human mind to think deeply; as he himself writes: “Read not to contradict and confute, nor to believe and take for granted, nor to find talk and discourse, but to weigh and consider” (Bacon). The philosopher not only provides a framework for the genre of the modern essay but also provides his readers a code to live by.
Works Cited
“Ciceronian.” Dictionary.com , n.d., www.dictionary.com/browse/ciceronian. 23 Oct. 2020.
De, Ardhendu. “Rhetorical Devices as Used by Francis Bacon in His Essays.” A.D.’s English Literature: Notes and Guide , 07 Apr. 2011, ardhendude.blogspot.com/2011/04/rhetorical-devices-used-by-francis.html. Accessed 23 Oct. 2020.
Grant, Edward. The Foundations of Modern Science in the Middle Ages: Their Religious, Institutional, and Intellectual Contexts . Cambridge University Press, 1996.
Harmon, William. The Oxford Book of American Light Verse. Oxford University Press, 1979.
“History – Francis Bacon.” History , British Broadcasting Corporation, 2014, www.bbc.co.uk/history/historic_figures/bacon_francis.shtml. Accessed 24 Oct. 2020.
Potter, Vincent G. Readings in Epistemology: from Aquinas, Bacon, Galileo, Descartes, Locke, Berkeley, Hume, Kant. Fordham University Press, 1993.
Discussion Questions
- Why do you think Francis Bacon chose to enlighten and inspire his readers as opposed to other writers of his time who focused more on classic folklore tales?
- Why do you think Francis Bacon choose the topics that he did? Who or what do you think had a major influence on his writings?
- What are the goals and intentions behind Bacon’s use of rhetorical questioning?
- What are some common themes and ideas from Francis Bacon’s Essays that can be applied to general situations and contemporary society?
- From the ideas presented in this reading, how do you think Francis Bacon’s work affected government policies throughout history, including modern day governmental standards?
Further Resources
- Detailed biography of Franics Bacon’s life
- Analytical article of Francis Bacon’s impact on the Scientific Revolution
- List of Francis Bacon’s most significant accomplishments
- Compilation of Francis Bacon’s literature
- Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy entry on Francis Bacon
- Discussion video of Francis Bacon’s “Of Studies”
Reading: From Essayes
I. of truth..
What is truth? said jesting Pilate; and would not stay for an answer. Certainly there be that delight in giddiness; and count it a bondage to fix a belief; affecting free-will in thinking, as well as in acting. And though the sects of philosophers of that kind be gone, yet there remain certain discoursive wits, which are of the same veins, though there be not so much blood in them as was in those of the ancients. But it is not only the difficulty and labour which men take in finding out of truth, nor again, that when it is found, it imposeth upon men’s thoughts, that doth bring lies in favour, but a natural though corrupt love of the lie itself. One of the later schools of the Grecians examineth the matter, and is at a stand to think what should be in it, that men should love lies; where neither they make for pleasure, as with poet; nor for advantage, as with the mer chant, but for the lie’s sake. But I cannot tell: this same truth is a naked and open daylight, that doth not show the masks, and mummeries, and triumphs of the world, half so stately and daintily as candlelights. Truth may perhaps come to the price of a pearl, that showeth best by day, but it will not rise to the price of a diamond or carbuncle, that showeth best in varied lights. A mixture of a lie doth ever add pleasure. Doth any man doubt, that if there were taken out of men’s minds, vain opinions, flattering hopes, false valuations, imaginations as one would, and the like, but it would leave the minds of a number of men, poor shrunken things, full of melancholy and indisposition, and unpleasing to themselves? One of the fathers, in great severity, called poesy “vinum dæmonum,”; because it filleth the imagination, and yet it is but with the shadow of a lie. But it is not the lie that passeth through the mind, but the lie that sinketh in, and settleth in it, that doth the hurt, such as we spake of before. But howsoever these things are thus in men’s depraved judgments and affections, yet truth, which only doth judge itself, teacheth, that the inquiry of truth, which is the love-making, or wooing of it, the knowledge of truth, which is the presence of it, and the belief of truth, which is the enjoying of it, is the sovereign good of human nature. The first creature of God, in the works of the days, was the light of the sense: the last was the light of reason; and his Sabbath work ever since, is the illumination of his Spirit. First, he breathed light upon the face of the matter, or chaos; then he breathed light into the face of man; and still he breatheth and inspireth light into the face of his chosen. The poet that beautified the sect, that was otherwise inferior to the rest, saith yet excellently well: “It is a pleasure to stand upon the shore, and to see ships tossed upon the sea: a pleasure to stand in the window of a castle, and to see a battle, and the adventures thereof below: but no pleasure is comparable to the standing upon the vantage ground of truth, (a hill not to be commanded, and where the air is always clear and serene,) and to see the errors, and wanderings, and mists, and tempests in the vale below:” so always that this prospect be with pity, and not with swelling or pride. Certainly, it is heaven upon earth, to have a man’s mind move in charity, rest in providence, and turn upon the poles of truth.
To pass from theological and philosophical truth, to the truth of civil business; it will be acknowledged even by those that practise it not, that clean and round dealing is the honour of man’s nature, and that mixture of falsehood is like alloy in coin of gold and silver, which may make the metal work the better, but it embaseth it. For these winding and crooked courses are the goings of the serpent; which goeth basely upon the belly, and not upon the feet. There is no vice that doth so cover a man with shame as to be found false and perfidious; and therefore Montaigne saith prettily, when he inquired the reason, why the word of the lie should be such a disgrace, and such an odious charge, saith he, “If it be well weighed, to say that a man lieth, is as much as to say, that he is brave towards God, and a coward towards men. For a lie faces God, and shrinks from man.” Surely the wickedness of falsehood and breach of faith cannot possibly be so highly expressed, as in that it shall be the last peal to call the judgments of God upon the generations of men: it being foretold, that when “Christ cometh,” he shall not “find faith upon the earth.”
VIII. OF MARRIAGE AND SINGLE LIFE.
He that hath wife and children hath given hostages to fortune; for they are impediments to great enterprises, either of virtue or mischief. Certainly the best works, and of greatest merit for the public, have proceeded from the unmarried or childless men; which, both in affection and means, have married and endowed the public. Yet it were great reason that those that have children should have greatest care of future times, unto which they know they must transmit their dearest pledges. Some there are, who, though they lead a single life, yet their thoughts do end with themselves, and account future times impertinences; nay, there are some other that account wife and children but as bills of charges; nay more, there are some foolish rich covetous men, that take a pride in having no children, because they may be thought so much the richer; for, perhaps, they have heard some talk, “Such an one’s a great rich man” and another except to it. “Yea, but he hath a great charge of children;” as if it were an abatement to his riches: but the most ordinary cause of a single life is liberty, especially in certain self-pleasing and humorous minds, which are so sensible of every restraint, as they will go near to think heir girdles and garters to be bonds and shackles. Unmarried men are best friends, best masters, best servants; but not always best subjects; for they are light to run away; and almost all fugitives are of that condition. A single life doth well with churchmen, for charity will hardly water the ground where it must first fill a pool. It is indifferent for judges and magistrates; for if they be facile and corrupt, you shall have a servant five times worse than a wife. For soldiers, I find the generals commonly, in their hortatives, put men in mind of their wives and children; and I think the despising of marriage among the Turks maketh the vulgar soldier more base. Certainly wife and children are a kind of discipline of humanity; and single men, though they may be many times more charitable, because their means are less exhaust, yet, on the other side, they are more cruel and hardhearted, (good to make severe inquisitors,) because their tenderness is not so oft called upon. Grave natures, led by custom, and therefore constant, are commonly loving husbands, as was said of Ulysses, “vetulam suam prætulit immortalitati.” Chaste women are often proud and froward, as presuming upon the merit of their chastity. It is one of the best bonds, both of chastity and obedience, in the wife, if she think her husband wise; which she will never do if she find him jealous. Wives are young men’s mistresses, companions for middle age, and old men’s nurses; so as a man may have a quarrel to marry when he will: but yet he was reputed one of the wise men, that made answer to the question when a man should marry:—”A young man not yet, an elder man not at all.” It is often seen, that bad husbands have very good wives; whether it be that it raiseth the price of their husband’s kindness when it comes, or that the wives take a pride in their patience; but this never fails, if the bad husbands were of their own choosing, against their friends consent, for then they will be sure to make good their own folly.
XI. OF GREAT PLACE.
Men in great place are thrice servants; servants of the sovereign or state, servants of fame, and servants of business; so as they have no freedom, neither in their persons, nor in their actions, nor in their times. It is a strange desire to seek power and to lose liberty; or to seek power over others, and to lose power over a man’s self. The rising unto place is laborious, and by pains men come to greater pains; and it is sometimes base, and by indignities men come to dignities. The standing is slippery, and the regress is either a downfall, or at least an eclipse, which is a melancholy thing: “Cum non sis qui fueris, non esse cur velis vivere.” Nay, retire men cannot when they would, neither will they when it were reason; but are impatient of privateness even in age and sickness, which require the shadow: like old townsmen, that will be still sitting at their street door, though thereby they offer age to scorn. Certainly great persons had need to borrow other men’s opinions to think themselves happy; for if they judge by their own feeling, they cannot find it: but if they think with themselves what other men think of them, and that other men would fain be as they are, then they are happy as it were by report, when, perhaps, they find the contrary within; for they are the first that find their own griefs, though they be the last that find their own faults. Certainly men in great fortunes are strangers to themselves, and while they are in the puzzle of business they have no time to tend their health either of body or mind: “Illi mors gravis incubat, qui notus nimis omnibus, ignotus moritur sibi.” In place there is license to do good and evil; whereof the latter is a curse: for in evil the best condition is not to will; the second not to can. But power to do good is the true and lawful end of aspiring; for good thoughts (though God accept them,) yet towards men are little better than good dreams, except they be put in act; and that cannot be without power and place, as the vantage and commanding ground. Merit and good works is the end of man’s motion; and conscience of the same is the accomplishment of man’s rest; for if a man can be partaker of God’s theatre, he shall likewise be partaker of God’s rest: “Et conversus Deus, ut aspiceret opera, quaæ fecerunt manus suæ, vidit quod omnia essent bona nimis;” and then the sabbath. In the discharge of the place set before thee the best examples; for imitation is a globe of precepts; and after a time set before thine own example; and examine thyself strictly whether thou didst not best at first. Neglect not also the examples of those that have carried themselves ill in the same place; not to set off thyself by taxing their memory, but to direct thyself what to avoid. Reform, therefore, without bravery or scandal of former times and persons; but yet set it down to thyself, as well to create good precedents as to follow them. Reduce things to the first institution, and observe wherein and how they have degenerated; but yet ask counsel of both times; of the ancienter time what is best; and of the latter time what is fittest. Seek to make thy course regular, that men may know be forehand what they may expect; but be not too positive and peremptory; and express thyself well when thou digressest from thy lure. Preserve the right of thy place, but stir not questions of jurisdiction; and rather assume thy right in silence, and “de facto,” than voice it with claims and challenges. Preserve likewise the rights of inferior places; and think it more honour to direct in chief than to be busy in all. Embrace and invite helps and advices touching the execution of thy place; and do not drive away such as bring thee information as meddlers, but accept of them in good part. The vices of authority are chiefly four; delays, corruption, roughness, and facility. For delays give easy access: keep times appointed; go through with that which is in hand, and interlace not business but of necessity. For corruption, do not only bind thine own hands or thy servant’s hands from taking, but bind the hands of suitors also from offering; for integrity used doth the one; but integrity professed, and with a manifest detestation of bribery, doth the other; and avoid not only the fault, but the suspicion. Whosoever is found variable, and changeth manifestly without manifest cause, giveth suspicion of corruption; therefore, always when thou changest thine opinion or course, profess it plainly, and declare it, together with the reasons that move thee to change, and do not think to steal it. A servant or a favourite, if he be inward, and no other apparent cause of esteem, is commonly thought but a by-way to close corruption. For roughness, it is a needless cause of discontent; severity breedeth fear, but roughness breedeth hate. Even reproofs from authority ought to be grave, and not taunting. As for facility, it is worse than bribery; for bribes come but now and then; but if importunity or idle respects lead a man, he shall never be without; as Solomon saith, “To respect persons is not good, for such a man will transgress for a piece of bread.” It is most true that was anciently spoken, “A place showeth the man; and it showeth some to the better and some to the worse;” “omnium consensu capax imperii, nisi imperasset,” saith Tacitus of Galba; but of Vespasian he saith, “solus imperantium, Vespasianus mutatus in melius;” though the one was meant of sufficiency, the other of manners and affection. It is an assured sign of a worthy and generous spirit, whom honour amends; for honour is, or should be, the place of virtue; and as in nature things move violently to their place and calmly in their place, so virtue in ambition is violent, in authority settled and calm. All rising to great place is by a winding stair; and if there be factions, it is good to side a man’s self whilst he is in the rising, and to balance himself when he is placed. Use the memory of thy predecessor fairly and tenderly; for if thou dost not, it is a debt will sure be paid when thou art gone. If thou have colleagues, respect them; and rather call them when they looked not for it, than exclude them when they have reason to look to be called. Be not too sensible or too remembering of thy place in conversation and private answers to suitors; but let it rather be said, “When he sits in place he is another man.”
XVII. OF SUPERSTITION.
It were better to have no opinion of God at all than such an opinion as is unworthy of him; for the one is unbelief, the other is contumely; and certainly superstition is the reproach of the Deity. Plutarch saith well to that purpose: “Surely,” saith he, “I had rather a great deal men should say there was no such man at all as Plutarch, than that they should say that there was one Plutarch, that would eat his children as soon as they were born:” as the poets speak of Saturn: and, as the contumely is greater towards God, so the danger is greater towards men. Atheism leaves a man to sense, to philosophy, to natural piety, to laws, to reputation: all which may be guides to an outward moral virtue, though religion were not; but superstition dismounts all these, and erecteth an absolute monarchy in the minds of men: therefore atheism did never perturb states; for it makes men wary of themselves, as looking no further, and we see the times inclined to atheism (as the time of Augustus Cæsar) were civil times: but superstition hath been the confusion of many states, and bringeth in a new “primum mobile,” that ravisheth all the spheres of government. The master of superstition is the people, and in all superstition wise men follow fools; and arguments are fitted to practice, in a reversed order. It was gravely said, by some of the prelates in the council of Trent, where the doctrine of the schoolmen bare great sway, that the schoolmen were like astronomers, which did feign eccentrics and epicycles, and such engines of orbs to save phenomena, though they knew there were no such things; and, in like manner, that the schoolmen had framed a number of subtle and intricate axioms and theorems, to save the practice of the church. The causes of superstition are, pleasing and sensual rites and ceremonies; excess of outward and pharisaical holiness; over great reverence of traditions, which cannot but load the church; the stratagems of prelates for their own ambition and lucre; the favouring too much of good intentions, which openeth the gate to conceits and novelties; the taking an aim at divine matters by human, which cannot but breed mixture of imaginations; and, lastly, barbarous times, especially joined with calamities and disasters. Superstition, without a veil, is a deformed thing: for as it addeth deformity to an ape to be so like a man, so the similitude of superstition to religion makes it the more deformed: and, as wholesome meat corrupteth to little worms, so good forms and orders corrupt into a number of petty observances. There is a superstition in avoiding superstition, when men think to do best if they go furthest from the superstition formerly received; therefore care would be had that (as it fareth in ill purgings) the good be not taken away with the bad, which commonly is done when the people is the reformer.
XXXIII. OF PLANTATIONS.
Plantations are amongst ancient, primitive, and heroical works. When the world was young, it begat more children; but now it is old, it begets fewer; for I may justly account new plantations to be the children of former kingdoms. I like a plantation in a pure soil; that is, where people are not displanted to the end to plant in others; for else it is rather an extirpation than a plantation. Planting of countries is like planting of woods; for you must make account to lose almost twenty years profit, and expect your recompense in the end: for the principal thing that hath been the destruction of most plantations, hath been the base and hasty drawing of profit in the first years. It is true, speedy profit is not to be neglected, as far as may stand with the good of the plantation, but no further. It is a shameful and unblessed thing to take the scum of people and wicked condemned men, to be the people with whom you plant; and not only so, but it spoileth the plantation; for they will ever live like rogues, and not fall to work, but be lazy, and do mischief, and spend victuals, and be quickly weary, and then certify over to their country to the discredit of the plantation. The people wherewith you plant ought to be gardeners, ploughmen, labourers, smiths, carpenters, joiners, fishermen, fowlers, with some few apothecaries, surgeons, cooks, and bakers. In a country of plantation, first look about what kind of victual the country yields of itself to hand; as chestnuts, walnuts, pineapples, olives, dates, plums, cherries, wild honey, and the like, and make use of them. Then consider what victual, or esculent things there are which grow speedily and within the year: as parsnips, carrots, turnips, onions, radish, artichokes of Jerusalem, maize, and the like: for wheat, barley, and oats, they ask too much labour; but with pease and beans you may begin, both because they ask less labour, and because they serve for meat as well as for bread; and of rice likewise cometh a great increase, and it is a kind of meat. Above all, there ought to be brought store biscuit, oatmeal, flour, meal, and the like, in the beginning, till bread may be had. For beasts, or birds, take chiefly such as are least subject to diseases, and multiply fastest; as swine, goats, cocks, hens, turkeys, geese, house-doves, and the like. The victual in plantations ought to be expended almost as in a besieged town; that is, with certain allowance: and let the main part of the ground employed to gardens or corn, be to a common stock; and to be laid in, and stored up, and then delivered out in proportion; besides some spots of ground that any particular person will manure for his own private use. Consider, likewise, what commodities the soil where the plantation is doth naturally yield, that they may some way help to defray the charge of the plantation; so it be not, as was said, to the untimely prejudice of the main business, as it hath fared with tobacco in Virginia. Wood commonly aboundeth but too much: and therefore timber is fit to be one. If there be iron ore, and streams whereupon to set the mills, iron is a brave commodity where wood aboundeth. Making of bay-salt, if the climate be proper for it, would be put in experience: growing silk likewise, if any be, is a likely commodity: pitch and tar, where store of firs and pines are, will not fail; so drugs and sweet woods, where they are, cannot but yield great profit; soap-ashes likewise, and other things that may be thought of; but moil not too much under ground, for the hope of mines is very uncertain and useth to make the planters lazy in other things. For government, let it be in the hands of one, assisted with some counsel; and let them have commission to exercise martial laws, with some limitation; and, above all, let men make that profit of being in the wilderness, as they have God always, and his service before their eyes; let not the government of the plantation depend upon too many counsellors and undertakers in the country that planteth, but upon a temperate number; and let those be rather noblemen and gentle men, than merchants; for they look ever to the present gain: let there be freedoms from custom, till the plantation be of strength; and not only freedom from custom, but freedom to carry their commodities where they may make their best of them, except there be some special cause of caution. Cram not in people, by sending too fast, company after company; but rather hearken how they waste, and send supplies proportionably; but so as the number may live well in the plantation, and not by surcharge be in penury. It hath been a great endangering to the health of some plantations, that they have built along the sea and rivers in marish and unwholesome grounds: therefore, though you begin there, to avoid carriage and other like discommodities, yet build still rather upwards from the stream, than along. It concerneth likewise the health of the plantation that they have good store of salt with them, that they may use it in their victuals when it shall be necessary. If you plant where savages are, do not only entertain them with trifles and gingles, but use them justly and graciously, with sufficient guard nevertheless; and do not win their favour by helping them to invade their enemies, but for their defence it is not amiss: and send oft of them over to the country that plants, that they may see a better condition than their own, and commend it when they return. When the plantation grows to strength, then it is time to plant with women as well as with men; that the plantation may spread into generations, and not be ever pieced from without. It is the sinfullest thing in the world to forsake or destitute a plantation once in forwardness; for, besides the dishonour, it is the guiltiness of blood of many commiserable persons.
XLVII. OF NEGOTIATING.
It is generally better to deal by speech than by letter; and by the mediation of a third than by a man’s self. Letters are good when a man would draw an answer by letter back again; or when it may serve for a man’s justification afterwards to produce his own letter; or where it may be danger to be interrupted, or heard by pieces. To deal in person is good, when a man’s face breedeth regard, as commonly with inferiors; or in tender cases, where a man’s eye upon the countenance of him with whom he speaketh, may give him a direction how far to go; and generally, where a man will reserve to himself liberty either to disavow or to expound. In choice of instruments, it is better to choose men of a plainer sort, that are like to do that that is committed to them, and to report back again faithfully the success, than those that are cunning to contrive out of ether men’s business somewhat to grace themselves, and will help the matter in report, for satisfaction sake. Use also such persons as affect the business wherein they are employed, for that quickeneth much; and such as are fit for the matter, as bold men for expostulation, fair-spoken men for persuasion, crafty men for inquiry and observation, froward and absurd men for business that doth not well bear out itself. Use also such as have been lucky and prevailed before in things wherein you have employed them; for that breeds confidence, and they will strive to maintain their prescription. It is better to sound a person with whom one deals afar off, than to fall upon the point at first; except you mean to surprise him by some short question. It is better dealing with men in appetite, than with those that are where they would be. If a man deal with another upon conditions, the start of first performance is all; which a man can reasonably demand, except either the nature of the thing be such, which must go before: or else a man can persuade the other party, that he shall still need him in some other thing; or else that he be counted the honester man. All practice is to discover, or to work. Men discover themselves in trust, in passion, at unawares; and of necessity, when they would have somewhat done, and cannot find an apt pretext, if you would work any man, you must either know his nature and fashions, and so lead him; or his ends, and so persuade him; or his weakness and disadvantages, and so awe him; or these that have interest in him, and so govern him. In dealing with cunning persons, we must ever consider their ends, to interpret their speeches; and it is good to say little to them, and that which they least look for. In all negotiations of difficulty, a man may not look to sow and reap at once; but must prepare business, and so ripen it by degrees.
XXXVII. OF MASQUES AND TRIUMPHS.
These things are but toys to come amongst such serious observations; but yet, since princes will have such things, it is better they should be graced with elegancy, than daubed with cost. Dancing to song, is a thing of great state and pleasure. I understand it that the song be inquire, placed aloft, and accompanied by some broken music; and the ditty fitted to the device. Acting in song, especially in dialogues, hath an extreme good grace; I say acting, not dancing, (for that is a mean and vulgar thing;) and the voices of the dialogue would be strong and manly, (a base and a tenor, no treble,) and the ditty high and tragical, not nice or dainty. Several quires placed one over against another, and taking the voice by catches anthem-wise, give great pleasure. Turning dances into figure is a childish curiosity; and generally let it be noted, that those things which I here set down are such as do naturally take the sense, and not respect petty wonderments. It is true, the alterations of scenes, so it be quietly and without noise, are things of great beauty and pleasure; for they feed and relieve the eye before it be full of the same object. Let the scenes abound with light, especially coloured and varied; and let the masquers, or any other that are to come down from the scene, have some motions upon the scene it self before their coining down; for it draws the eye strangely, and makes it with great pleasure to desire to see that it cannot perfectly discern. Let the songs be loud and cheerful, and not chirpings or pulings: let the music likewise be sharp and loud, and well placed. The colours that show best by candle-light, are white, carnation, and a kind of sea-water green and ouches, or spangs, as they are of no great cost, so they are of most glory. As for rich embroidery, it is lost and not discerned. Let the suits of the masquers be graceful, and such as become the person when the vizards are off; not after examples of known attires; Turks, soldiers, mariners, and the like. Let anti-masques not be long; they have been commonly of fools, satyrs, baboons, wild men antics, beasts, spirits, witches, Ethiopes, pigmies turquets, nymphs, rustics, Cupids, statues moving and the like. As for angels, it is not comical enough to put them in anti-masques; and any thing that is hideous, as devils, giants, is, on the other side as unfit; but chiefly, let the music of them be recreative, and with some strange changes. Some sweet odours suddenly coming forth, without any drops falling, are, in such a company as there is steam and heat, things of great pleasure and refreshment. Double masques, one of men another of ladies, addeth state and variety; but all is nothing except the room be kept clean and neat.
For jousts, and tourneys, and barriers, the glories of them are chiefly in the chariots, wherein the challengers make their entry; especially if they be drawn with strange beasts; as lions, bears camels, and the like; or in the devices of their entrance, or in bravery of their liveries, or in the goodly furniture of their horses and armour. But enough of these toys.
L. OF STUDIES.
Studies serve for delight, for ornament and for ability. Their chief use for delight, is in privateness and retiring; for ornament, is in discourse; and for ability, is in the judgment and disposition of business; for expert men can execute, and perhaps judge of particulars, one by one: but the general counsels, and the plots and marshalling of affairs come best from those that are learned. To spend too much time in studies, is sloth; to use them too much for ornament, is affectation; to make judgment wholly by their rules, is the humour of a scholar: they perfect nature, and are perfected by experience: for natural abilities are like natural plants, that need pruning by study; and studies themselves do give forth directions too much at large, except they be bounded in by experience. Crafty men contemn studies, simple men admire them, and wise men use them; for they teach not their own use; but that is a wisdom without them, and above them, won by observation. Read not to contradict and confute, nor to believe and take for granted, nor to find talk and discourse, but to weigh and consider. Some books are to be tasted, others to be swallowed, and some few to be chewed and digested; that is, some books are to be read only in parts; others to be read, but not curiously; and some few to be read wholly, and with diligence and attention. Some books also may be read by deputy, and extracts made of them by others; but that would be only in the less important arguments, and the meaner sort of books; else distilled books are, like common distilled waters, flashy things. Reading maketh a full man; conference a ready man; and writing an exact man; and, therefore, if a man write little, he had need have a great memory; if he confer little, he had need have a present wit: and if he read little, he had need have much cunning, to seem to know that he doth not. Histories make men wise; poets witty; the mathematics subtile; natural philosophy deep; moral, grave; logic and rhetoric, able to contend “Abeunt studia in mores;” nay, there is no stond or impediment in the wit, but may be wrought out by fit studies: like as diseases of the body may have appropriate exercises; bowling is good for the stone and reins, shooting for the lungs and breast, gentle walking for the stomach, riding for the head, and the like; so, if a man’s wit be wandering, let him study the mathematics; for in demonstrations, if his wit be called away never so little, he must begin again; if his wit be no apt to distinguish or find differences, let him study the schoolmen, for they are “Cymini sectores;” if he be not apt to beat over matters, and to call upon one thing to prove and illustrate another, let him study the lawyer’s cases: so every defect of the mind may have a special receipt.
Source Text:
Bacon, Francis. Bacon’s Essays and Wisdom of the Ancients . Little, Brown, and Company, 1884, is licensed under no known copyright.

An Open Companion to Early British Literature Copyright © 2019 by Allegra Villarreal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Line By Line Explanation Of Francis Bacon’s ‘Of Studies’
1. studies serves……business..
In these lines of his famous essay ‘Of Studies’ Francis Bacon lays down the advantages of study.
There are three advantages of study. It gives pleasure, prestige and ability.
It gives pleasure to a person when he is leading a lonely life. Books are said to be the best companions. By reading books we are lost in the world created by the author. We talk to the characters of the books. And thus books help us to forget that we are alone. Further it gives prestige to a person when he is engaged in discussion. It is a fact that only that person can argue and discuss who is well-read. And as such study enables a person to acquire knowledge, which he uses during the discussion and thus gets prestige. And finally it gives the ability for performing business. Knowledge is a lamp which shows our path. And we get knowledge from books. A person who has to dispose of business and take decision on various matters, he must have sound knowledge. And this knowledge he gets from books only. Thus study gives ability.
2. For expert men……..learned.
In these lines of his famous essay ‘Of Studies’ Francis Bacon shows superiority of a learned person over a specialist.
Here learned stands for a person who has studied different branches of knowledge and gained a general view. On the other hand a specialist specializes himself in a particular branch of knowledge. A specialist’s knowledge is confined to his subject only. No doubt, he can give best judgment on any matter relating to his subject, but where a judgment which requires a general view, he fails utterly. In such cases a learned person comes successful. General advice in respect of planning and management of business can best be given by a well-read person only, because he possesses vast knowledge and large perspective.
Here we get the personal touch of the essayist. Of course Bacon was a versatile genius. He had studied different branches of the knowledge. And thus here he is speaking from his own experience.
3. To spend too much……scholar.
In these lines of his famous essay ‘Of Studies’ Francis Bacon points out the drawbacks which arises due to misuse of study.
No doubt, study can be a source of gaining, delight, prestige and ability. but excessive use of study for this above purpose, gives some adverse result.
Also Read :
- Compare Hamlet with Macbeth, Othello and other Tragedies
- “The Pardoner’s Tale” is the finest tale of Chaucer
- Prologue to Canterbury Tales – (Short Ques & Ans)
- Confessional Poetry – Definition & meaning
- Line By Line Explanation Of The Poem The Eve of St. Agnes
In retirement study can be used only as a means of entertainment. As such only a part of day’s life is devoted to it. But if a man devotes his entire time in study, he becomes lazy. Similarly if one employs too much ornamental language during the speech, it destroys the naturality. It hampers the natural flow, and everything looks artificial. And if a person uses only bookish knowledge in managing general affairs, keeping the practical knowledge aside, it becomes something humourous.
A man should not see everything through the eyes of books only. He should use the eyes of experience also. It means that theoretical knowledge should be supported by the practical experience.
4. Histories…….able to contend.
These lines are from Bacon’s ‘Of Studies. In these lines the author gives the different effects of different subjects upon human mind and nature. According to him we derive wisdom from the study of history. The study of poetry gives wit, for poetry is written in the best kind of language. The study of mathematics gives fineness. By the study of Philosophy we gain depth, The study of moral science gives gravity. The study of logic and rhetoric makes one in a position to quarrel or enter discussion. In this way we see that different subject have different duty to perform. Real perfection can be achieved by the study of all these different subjects. One should not depend upon a particular subject only if one has to achieve perfection.
5. Read not to…… weigh and consider.
In these lines of his famous essay ‘Of Studies’ Francis Bacon tells the reader the real purpose of study.
One should not read only with a view to prove others wrong. Some persons study only with an object to equip themselves with arguments for refuting others. But this is not the real use of study. Study should impart some permanent ability. But a man should not read to accept everything that is conveyed through books. The real object of study should be to cultivate understanding which may help in finding out the proper value of things. Thus study must impart wisdom to understand value of a thing, to distinguish right from wrong.
6. Some books……..diligence.
In these lines of his famous essay ‘Of Studies’ Francis Bacon categorises the books in three classes from the viewpoint of attention and diligence which their studies require.
All books are not of equal value and therefore equal labour and attention need not be devoted to all.
In order to make his point clear. Bacon compares books with food. Some books are like light food. They are just to be tasted. They are just to change the taste. Hence like light food they are tasted. Only a slight attention is devoted to them. On the other hand some books are such that their studies require some attention and labour. But only a slight labour on the part of the reader can serve the purpose.
As some foods are not required to be chewed slowly, but are swallowed hastily, so some books are also to be swallowed i.e. they are to be read in parts and with haste. But in case of our main diet we chew and digest them. So some foods are such that they can be neither tasted nor swallowed but must be chewed and digested. Similarly some books are such that they require much time, patience, labour and attention in order to grasp them. So these are three categories of books according to Bacon.
PLEASE HELP ME TO REACH 1000 SUBSCRIBER ON MY COOKING YT CHANNEL (CLICK HERE)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel
🔥 Don't Miss Out! Subscribe to Our YouTube Channel for Exclusive English Literature, Research Papers, Best Notes for UG, PG & UGC-NET!
🌟 Click Now! 👉
Recent Posts

Narrate briefly the story “An Astrologer’s Day”

Critical Analysis Of The Babus of Nayanjore by R.N. Tagore

The Fortune and Chance in Antony and Cleopatra

Describe The Happy Ending Of Play Antony and Cleopatra

The Politics of Antony and Cleopatra By Shakespeare

Some Explanation from Indian English Prose

Summary Of No Man’s An Island By John Donne

Ideas Contained In The Essay The Secret of Work by Swami Vivekanand

Education for New India By C. Rajagopalachari

Indian Civilization and Culture By M.K. Gandhi

Of Studies by Francis Bacon Summary and Analysis
Table of Contents
Introduction
The essay Of Studies by Sir Francis Bacon is the first essay in the series of ten essays published in 1597. Later, it was revised in 1612 with the addition of some more sentences and ideas in it along with the alteration in some vocabulary terms.
This essay is regarded as Bacon’s masterpiece enriched with stylised Latin vocabulary, fresh and new ideas, logical and relevant themes and wisdom of the world.
For these reasons, the essay is still popular among individuals of all ages. Adopting a didactic approach, the essay informs the readers about the benefits and uses of studies in one’s life.
Highlighting the importance of studies, Bacon’s essay illustrates the role studies play in an individual’s daily life. For Bacon, the study is always related to the application of knowledge in practical life.
At the beginning of his essay, Bacon describes the three main purposes of study including studying for gaining delight, studies done for ornamenting one’s life and studying in order to improve one’s ability.
The author is the notion that only learned and well-read men can execute plans effectively, manage their daily affairs with expertise and lead a healthy and stable life. He further states that reading makes a full man; conference leads to a ready man while writing makes an exact man.
While throwing light on the advantages and usefulness of studies, Bacon also puts forward some demerits of study as he thinks that studying for a prolonged period of time may lead to laziness.
He also condemns the act of studying from books solely without learning from nature around. The essay Of Studies further asserts the benefits of studies by considering this act as a medicine for the defects of the human mind and the source of enhancing one’s wit.
While discussing the importance of studying in an individual’s life, the essayist informs his readers about the benefits of reading good books.
For Bacon, some books are only meant to be tasted; others are there to swallow while some books are meant for chewing and digesting properly. Therefore, the readers must choose wisely before studying any book to enhance his/her knowledge about the world around.
Bacon concludes his essay by suggesting that studies assist an individual in removing the defects of his/her mind as every problem of the human mind carries special importance for the individual and the world.
Bacon’s essay Of Studies deals with the benefits of studies for the individuals in their daily lives. From reading books to writing papers, study plays a vital role in a man’s life making him learned, witty and experienced.
The essay by Bacon is enriched with intellectual wisdom, pragmatic approach and practical knowledge; therefore, it is considered to be the most beneficial essay for the students and young individuals.
Although the essay is devoid of any emotions and colourful expressions, it is; nevertheless, a wonderful effort of teaching the readers about the importance of studying. Here is the original essay .
Click here to play quiz on Of Studies
Related Posts:
- Howl Poem By Allen Ginsberg Summary, Notes and Line by Line Explanation in English
- Michael Poem by William Wordsworth Summary, Notes and Line by Line Explanation in English
- Goblin Market Poem by Christina Rossetti Summary, Notes and Line by Line Explanation in English
- Of Marriage and Single Life by Francis Bacon | Summary & Analysis
- The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock Poem By Thomas Stearns Eliot Summary, Notes And Line By Line Analysis In English
- Random Job Generator [List]
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions

Poets and Writers
Short stories, literary essays, india today english lit 1, francis bacon’s essay of studies—summary and critical analysis, introduction:.
The Renaissance influenced the people of Elizabethan Age so greatly that studies became an essential part of their daily life. In order to attain limitless knowledge so many of them began to adopt short - cut methods of reading books. In place of reading bulky books they liked to know about books by using notes, or extracts made from them by others. Bacon points out objects and proper ways of studies in the present essay. According to him the short - cut method should be used to study unimportant books only.
Bacon claims that studies serve not only the single purpose of increasing knowledge, but also they contribute to delight, to improve ability and to make our expression impressive. He warns against the excessive use of studies for in practical life the importance of natural abilities and practical experience cannot be ignored. This essay brings to light Bacon's good sense, wit and condensation of thought. It consists of those thoughts and ideas which Bacon has discussed in his great work “The Advancement of Learning” . It is Bacon's comprehensive approach to the subject that he points out the medical value as well as the disadvantages of studies.
Summary of the Essay:
Bacon deals with different modes of study and concludes with useful advice how some mental defects can be cured by appropriate studies. The essay is remarkable for apt illustrations and the wisdom it embodies. Bacon begins his essay by pointing out that there are three chief uses of studies. They provide delight in leisure and privacy. They serve as decorative ornaments in social gatherings and they give ability in practical business. They develop and perfect the natural faculties of the mind and are themselves perfected by the experience of real life. The disadvantages of studies are also there. Spending too much of time in studies and neglecting other affairs indicate sloth. Needless display of knowledge in season and out of season shows affectation. To decide everything by the help of bookish learning is the natural characteristic of a scholar.
Bacon gives valuable guidance to us by laying down some rules for study. He says that books should be studied dispassionately and not with a prejudiced mind. One should not blindly accept everything that is written in books; nor should one criticize and contradict everything. One should weigh, consider and accept only those things that convince one as true. There are also different kinds of books. Some books are to be read in parts only. There are some others which can be read entirely but hurriedly there are a few good books which must be read in details and very carefully. There are still some books which can be read in summaries and abstracts made by others.
There are different modes of study. Reading is meant to gather knowledge. Conversation helps the mind to acquire readiness and agility. The habit of writing helps to systematize thoughts and ideas and to obtain accuracy of expressions. Studies also exercise a profound influence on the development of character. The study of mathematics increases the subtlety of mind and that of philosophy enhance its gravity. The study of logic and rhetoric increases the power of debate and discussion.
Just as physical exercises cure physical defects and diseases, in the same way studies cure mental defects and diseases. Just as bowling is good for the kidneys, shooting for the lungs, gentle walking for the stomach and riding for the head, in the same way the study of mathematics in good for wandering wits, that of scholastic philosophy helps a confused mind and the study of law cases helps those who cannot recall reference and arrange arguments to prove their point. Thus, every mental defect can be removed by proper study.
Critical Analysis of the Essay:
Introduction: .
Bacon's “Of Studies” is one of his most popular essays. The Renaissance influenced the people of Elizabethan Age so greatly that studies became an essential part of their daily life. In order to attain limitless knowledge so many of them began to adopt short - cut methods of reading books. In place of reading bulky books they liked to know about books by using notes, or extracts made from them by others. Bacon points out objects and proper ways of studies in the present essay. According to him the short - cut method should be used to study unimportant books only. Bacon claims that studies serve not only the single purpose of increasing knowledge, but also they contribute to delight, to improve ability and to make our expression impressive. He warns against the excessive use of studies for in practical life the importance of natural abilities and practical experience cannot be ignored. This essay brings to light Bacon's good sense, wit and condensation of thought. It consists of those thoughts and ideas which Bacon has discussed in his great work “The Advancement of Learning” . It is Bacon's comprehensive approach to the subject that he points out the medical value as well as the disadvantages of studies. It is a representative essay by Bacon for it brings to light all of his qualities as an essayist. The essay is full of great ideas, clarity of thought and expression, practical wisdom, poetic images as well as for and against arguments. The poet uses some Latin expressions also.
Greatness of Ideas:
Bacon's "Of Studies" is an ideal essay that is full of great ideas. The Renaissance influenced the people of Elizabethan Age so greatly that studies became an essential part of their daily life. In order to attain limitless knowledge so many of them began to adopt short - cut methods of reading books. In place of reading bulky books they liked to know about books by using notes, or extracts made from them by others. Bacon points out objects and proper ways of studies in the present essay. According to him the short - cut method should be used to study unimportant books only. Bacon claims that studies serve not only the single purpose of increasing knowledge, but also they contribute to delight, to improve ability and to make our expression impressive.
“Studies serve for delight, for ornament, and for ability.”
He warns against the excessive use of studies for in practical life the importance of natural abilities and practical experience cannot be ignored.
“They perfect nature, and are perfected by experience.”
According to Bacon there should be a positive object of making studies. We should study not to contradict and challenge or accept whatever is present in books. It is better to judge and think over that.
“Read not to contradict and confute, nor to believe and take for granted, nor to find talk and discourse, but to weigh and consider.”
He warns against blind following of books. Besides, all books are not of equal standard. We should give importance to books according to their greatness. Only a few books are to be chewed and digested i.e., to read and understand attentively. All books are not to be read attentively with labour. It is practical wisdom to give time to books according to their importance. Mostly books may be read with the help of notes and guide books or selected pieces made of the subject by other writers. Books of lower standard may be read with notes. But it will be foolishness to read important books with the help of notes.
“Some books are to be tasted, others to be swallowed, and some few to be chewed and digested.”
Otherwise notes and guides are like purified water that is tasteless and devoid of depth. No man feels inclined to drink it more. The same may be said regarding notes, no reader wishes to read it again while original books amuse in spite of reading again and again. In this way, Bacon points out the great importance of original books.
“Some books also may be read by deputy, and extracts made of arguments, and the meaner sort of books; else distilled books are, like common distilled waters, flashy things.”
Bacon's greatness of ideas becomes remarkable when he points out how different subjects affect the character of a reader.
“Histories make man wise; poets witty; the mathematics subtle: natural philosophy deep; moral grave; logic and rhetoric able to contend.”
Bacon claims that all mental weaknesses can be removed by proper studies. Studies pass into human character and therefore, all the defects of mind can be cured by proper study just as proper physical exercise is useful to remove physical defects. Thus, there is proper treatment of every mental weakness.
Clear of Thought and Expression:
Bacon's belief in clarity of thought and expression is well exposed in this essay when he adopts the device of classification. He classifies purposes of studies in three parts:
He brings to light not only advantages of studies but also its disadvantages that appear when studies are used in excess. Too much study for delight develops idleness; for ornamentation develops artificiality; to take decision wholly by their rules is a bookish approach becomes the whim of a learned man. Studies mature natural talent that is perfected by practical knowledge. Natural talent too requires pruning or trimming. Books express confusing or contradictory ideas that should be limited by experience. Wicked people oppose studies, common or foolish people admire them while wise people use them.
“Crafty men condemn studies, simple men admire them, and wise men use them.”
Bacon's classification of books on the basis of their importance is remarkable. He advises the ways of studies according to the value of the book. He clearly points out that all books are not to be studies attentively.
“Some books are to be tasted, others to be swallowed, and some few to be of wed and digested.”
It makes a clear account of various subjects and their positive effect on human minds. According to him Histories develop wisdom, poetry wit, mathematics concentration, natural philosophy depth and moral gravity.
“Histories make man wise: poets witty; the mathematics subtle: natural philosophy deep; moral grave; logic and rhetoric able to contend.”
Poetic Images:
Bacon uses poetic images to give a poetic touch to his style. In “Of Studies”, he introduces nature imagery when he claims that natural abilities are like natural plants that should be ordered by study.
“For natural abilities are like natural plants that need pruning by study.”
Likewise to classify books on the basis of their importance he uses the food imagery.
“Some books are to be tasted, others to be swallowed, and some few to be chewed and digested.”
Proverbial Style:
Bacon's great wisdom enables him to express thoughts of universal importance. When he expresses these thoughts in aphoristic style so many sentences of the novel seem proverbial. It encourages him to make proverbial statements. The essay, “Of Studies” for example opens with a proverbial statement:
If anybody talks about studies, he refers to this statement necessarily. The essay is full of such statements that express a general thought which is true to all.
“To spend too much time in studies is sloth.
For natural abilities are like natural plants, that need pruning by study: They perfect nature, and are perfected by experience.
Crafty men condemn studies, simple men admire them, and wise men use them.
Some books are to be tasted, others to be swallowed, and some few to be chewed and digested.”
Bacon uses water imagery for notes and guides;
Compendium of Practical Wisdom and Comprehensiveness:
Throughout the essay, Bacon shows his practical wisdom and comprehensiveness. Generally people give unimportance to either technical knowledge or practical experience but Bacon recognizes importance to both and advises to consult an experienced man if the work is at a small scale, and technically trained or learned man for managing a work at a large scale. Generally people think studies are always useful but Bacon advises to avoid excess of studies. He recognises importance of natural talent, training and practical experience. Generally people think all books are equally important but Bacon advises to study books according to their importance. He recognises importance of original texts and notes. Generally people think that reading is the only way of learning but Bacon advises to give importance to conference and writing also. Bacon shows how different subjects affect our mind also.
Comprehensive Arguments:
Bacon is a practical philosopher who does not believe in imposing his thoughts on others. He gives arguments for and against the subject and leaves it to the reader to conclude according to his requirement. For example, he points out advantages as well as disadvantages of studies and its three purposes.
Studies provide amusement; help in improving effectiveness of speech: and improve skill and perfection; their main purpose of giving amusement is when we are alone or taking rest. They give effectiveness to conversation or discussion. They make perfect in deciding or managing things. According to Bacon experienced man perform well in special parts. But suggestions of universal importance, details and management of business are done best by trained persons. But his discussion does not end here for incoming lines he warns against the disadvantages of making excessive use of studies. Bacon points out disadvantages of studies if done unwisely. Too much study for delight develops idleness; for ornamentation develops artificiality; to take decision wholly by their rules is a bookish approach becomes the whim of a learned man. Studies mature natural talent that is perfected by practical knowledge, Natural talent too requires pruning or trimming. Books express confusing or contradictory ideas that should be limited by experience. Wicked people oppose studies, common or foolish people admire them while wise people use them. How to use studies is a more important art that is attained by practical experience. Likewise on the one hand suggests reading of books and on the others pleads for natural talent. He points out advantages as well as disadvantages of experienced man. He suggests reading some books with the help of notes or extracts made by others.
Use of Latin Expressions:
Bacon used to think that his Latin works should prove immortal and the English works would disappear with the passing of time. It shows his love for Latin . In this essay also he uses a few Latin expressions like:
Abeunt studia in mores (studies pass into character)
Cymni Sectores (hair - splitters)
Thus, Bacon's “Of Studies” is a representative essay that brings to light all the qualities of the essayist with a comprehensive discussion on the subject.
Saurabh Gupta
You may like these posts, social plugin, popular posts.

Francis Bacon, the Father of English Essays—His Prose Style

Joseph Addison’s Female Orators—Summary and Critical Analysis

Bacon’s Essay Of Regiment of Health: A Critical Study

Walt Whitman’s Poem On the Beach at Night—Summary and Critical Analysis

- Charles Dickens
- Francis Bacon
- Jack London
- Jane Austen
- John Galsworthy
- Joseph Addison
- Walt Whitman
- William Shakespeare
- William Somerset Maugham
- O Captain! My Captain!
- Ode on A Grecian Urn
- On the Beach at Night
- Oliver Twist
- Pride and Prejudice
- The Family Reunion
- The Tempest
- Female Orators
- Popular Superstitions
- To Build A Fire
- Charles Dickens 4
- English Novels 7
- English Plays 12
- English Poetry 5
- English Short Stories 9
- Female Orators 1
- Francis Bacon 3
- Jack London 3
- Jane Austen 3
- John Galsworthy 5
- John Keats 2
- Joseph Addison 4
- Literary Essays 7
- O Captain! My Captain! 1
- Ode on A Grecian Urn 2
- Of Regiment of Health 1
- Of Studies 1
- Oliver Twist 4
- On the Beach at Night 1
- Poets and Writers 32
- Popular Superstitions 1
- Pride and Prejudice 2
- Salvatore 3
- T S Eliot 2
- The Family Reunion 2
- The Tempest 4
- To Build A Fire 3
- Walt Whitman 3
- William Shakespeare 8
- William Somerset Maugham 3
Most Recent

Footer Copyright
Contact form.
Of Truth, by Francis Bacon
De Agostini Picture Library / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
"Of Truth" is the opening essay in the final edition of the philosopher, statesman and jurist Francis Bacon 's "Essays or Counsels, Civil and Moral" (1625). In this essay, as associate professor of philosophy Svetozar Minkov points out, Bacon addresses the question of "whether it is worse to lie to others or to oneself--to possess truth (and lie, when necessary, to others) or to think one possesses the truth but be mistaken and hence unintentionally convey falsehoods to both oneself and to others" ("Francis Bacon's 'Inquiry Touching Human Nature,'" 2010). In "Of Truth," Bacon argues that people have a natural inclination to lie to others: "a natural though corrupt love, of the lie itself."
"What is truth?" said jesting Pilate, and would not stay for an answer. Certainly, there be that delight in giddiness, and count it a bondage to fix a belief, affecting free-will in thinking as well as in acting. And though the sects of philosophers of that kind be gone, yet there remain certain discoursing wits which are of the same veins, though there be not so much blood in them as was in those of the ancients. But it is not only the difficulty and labor which men take in finding out of truth, nor again that when it is found it imposeth upon men's thoughts, that doth bring lies in favor, but a natural though corrupt love of the lie itself. One of the later school of the Grecians examineth the matter, and is at a stand to think what should be in it, that men should love lies where neither they make for pleasure, as with poets, nor for advantage, as with the merchant; but for the lie's sake. But I cannot tell: this same truth is a naked and open daylight that doth not show the masques and mummeries and triumphs of the world half so stately and daintily as candle-lights. Truth may perhaps come to the price of a pearl that showeth best by day; but it will not rise to the price of a diamond or carbuncle, that showeth best in varied lights. A mixture of a lie doth ever add pleasure. Doth any man doubt that if there were taken out of men's minds vain opinions, flattering hopes, false valuations, imaginations as one would, and the like, but it would leave the minds of a number of men poor shrunken things, full of melancholy and indisposition, and unpleasing to themselves? One of the fathers, in great severity, called poesy vinum daemonum [the wine of devils] because it filleth the imagination, and yet it is but with the shadow of a lie. But it is not the lie that passeth through the mind, but the lie that sinketh in and settleth in it that doth the hurt, such as we spake of before. But howsoever these things are thus in men's depraved judgments and affections, yet truth, which only doth judge itself, teacheth that the inquiry of truth, which is the love-making or wooing of it; the knowledge of truth, which is the presence of it; and the belief of truth, which is the enjoying of it, is the sovereign good of human nature. The first creature of God in the works of the days was the light of the sense; the last was the light of reason; and his Sabbath work ever since is the illumination of his spirit. First he breathed light upon the face of the matter, or chaos; then he breathed light into the face of man; and still he breatheth and inspireth light into the face of his chosen. The poet that beautified the sect that was otherwise inferior to the rest, saith yet excellently well, "It is a pleasure to stand upon the shore, and to see ships tossed upon the sea; a pleasure to stand in the window of a castle, and to see a battle and the adventures thereof below; but no pleasure is comparable to the standing upon the vantage ground of truth (a hill not to be commanded, and where the air is always clear and serene), and to see the errors and wanderings and mists and tempests in the vale below"*; so always that this prospect be with pity, and not with swelling or pride. Certainly it is heaven upon earth to have a man's mind move in charity, rest in providence, and turn upon the poles of truth.
To pass from theological and philosophical truth to the truth of civil business: it will be acknowledged, even by those that practice it not, that clear and round dealing is the honor of man's nature, and that mixture of falsehood is like alloy in coin of gold and silver, which may make the metal work the better, but it embaseth it. For these winding and crooked courses are the goings of the serpent, which goeth basely upon the belly and not upon the feet. There is no vice that doth so cover a man with shame as to be found false and perfidious; and therefore Montaigne saith prettily, when he inquired the reason why the word of the lie should be such a disgrace and such an odious charge. Saith he, "If it be well weighed, to say that a man lieth, is as much as to say that he is brave towards God, and a coward towards man." For a lie faces God, and shrinks from man. Surely the wickedness of falsehood and breach of faith cannot possibly be so highly expressed as in that it shall be the last peal to call the judgments of God upon the generations of men: it being foretold that when Christ cometh, "He shall not find faith upon the earth."
*Bacon's paraphrase of the opening lines of Book II of "On the Nature of Things" by Roman poet Titus Lucretius Carus.
- On Rhetoric, or the Art of Eloquence, by Francis Bacon
- Virginia Woolf Quotes
- 'Of Studies' by Francis Bacon
- Atlas Shrugged by Ayn Rand Quotes
- The Pleasures of Ignorance by Robert Lynd
- The Power and Pleasure of Metaphor
- A Guide to Wordsworth's Themes of Memory and Nature in 'Tintern Abbey'
- Writers on Words
- Classic British and American Essays and Speeches
- Best Speeches From Shakespeare's Henry V
- Thinking About Reading
- By the Railway Side, by Alice Meynell
- The Paradox of Tragedy
- What Is Enlightenment Rhetoric?
- Myth and Explanations for Creation
- Elizabeth Cady Stanton Quotes

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Francis Bacon gives account of three chief uses of studies. The first use is that they serve for delight. This delight may come in solitude or in leisure after retirement from active life. Secondly, they serve for ornament in communication, conversation and discourse. A person who is well read can talk more attractively than an uneducated person.
Explanation. It enables the learned men, who have studied extensively, to critically examine issues, and arrive at the right conclusion. They can garner data, facts and arguments or against a particular view rationally. Such intelligent analysis of facts improves the soundness and quality of their judgment.
Studies serve three purposes, says Sir Francis Bacon, "delight", "ornament" and "ability". In Bacon's times, the drama was banned; drama may have a moral purpose but it is certainly a source of entertainment. It was forbidden in that era; therefore, people had no other option except to rely upon books; thus, books replaced stage.
Francis Bacon, the first major English essayist, comments forcefully in Of Studies on the value of reading, writing, and learning. Notice Bacon's reliance on parallel structures (in particular, tricolons) throughout this concise, aphoristic essay. Then, compare the essay to Samuel Johnson 's treatment of the same theme more than a century later ...
The title "Of Studies" means the collective studies that a person does in his life. The main idea of "Of Studies" by Francis Bacon is the benefits of reading. Reading helps the readers to cope up with diverse situations. Reading also enhances readers' intellect and cures restraints of the mind. The essay provides the right method to read different branches of knowledge and discusses ...
Summary and Analysis of Of Studies by Francis Bacon. Of Studies by Sir Francis Bacon, written in 1597 and enlarged in 1625, is an essay written in didactic style - it is intended to inform, or teach a lesson. Here, Bacon discusses the importance of studies, highlighting three main reasons to convince his readers of its necessity.
Francis Bacon. Of Studies, Francis Bacon: Summary & Analysis. "Of Studies" stands as one of the most widely quoted essays by the renowned philosopher Sir Francis Bacon. Within its pages, Bacon meticulously dissects the profound importance of acquiring knowledge, endeavoring to persuade his readers of its inherent vitality.
Analysis. This essay deals with different kinds of books and their effect on the reader.The uses of studies are classified by Bacon under three heads - the use of studies for delight; the use of studies for ornament and the use of studies for ability. Bacon also gives us some excellent advice as to why or how one should read.
Of Studies is the masterpiece essay nicely written by Francis Bacon. This essay is one of the most attractive essays, which was written on the behalf of Study. In the essay Of Studies, the writer Francis Bacon describes the importance of studies in human life. The essay Of Studies is the first essay in a series of ten essays published in 1597.
Of Studies: Analysis. In the essay, Of Studies, Francis Bacon expresses that studies "serve for Delight, for Ornament and for Ability". For delight he means once personal private education; for ornament he means in conversation between and among others, which Bacon labels as " discourse ". Studies for ability lead one to judgement in ...
The general aim of Francis Bacon's philosophy was the reformation of human knowledge, with the intent to put it into practice and use it for the benefit of humankind. He criticized Aristotelian-Scholastic philosophy on the grounds that its method was unable to bring about progress. Bacon's method of induction was the antidote to the idleness of ...
Of Studies - Summary. Francis Bacon's classic essay "Of Studies" explains how and why study—knowledge—is important. In this essay, he discusses some of the benefits of studying and offers some sound ideas on the subject. Bacon is regarded as the "Father of the English Essay". Bacon envisioned the essay as an opportunity to offer ...
Francis Bacon's argument about the value of studies is that studies are wonderful only if influenced by experience because a person's natural abilities are enhanced by studies, but studies without experience lead to confusion. According to Francis Bacon's tricky man condemn education; stupid man admire education; but wise men use education as ...
The best reason to study is because you have a guanine interest in the material. Bacon's essay is a diatribe on studying, the ways and purposes, and categories. As mentioned in reply #2, the ...
An essay will always remain subjective despite how much it is written objectively. Francis Bacon's essay "Of Studies" is a thought-provoking exploration of the importance of learning and the pursuit of knowledge. Bacon argues that studies offer three distinct benefits. The act of learning itself can be a source of enjoyment.
Of Studies by Francis Bacon. Of Studies. STUDIES serve for delight, for ornament, and for ability. Their chief use for delight is in privateness and retiring; for ornament, is in discourse; and for ability, is in the judgment and disposition of business. For expert men can execute, and perhaps judge of particulars, one by one; but the general ...
Introduction. by Mary Larivee and Rithvik Saravanan. Francis Bacon (1561-1626), the English philosopher, was instrumental in the development of the Scientific Revolution in the late 18th century even though he had passed away centuries before. The "Scientific Revolution" was an important movement that emphasized Europe's shift toward ...
In these lines of his famous essay 'Of Studies' Francis Bacon points out the drawbacks which arises due to misuse of study. No doubt, study can be a source of gaining, delight, prestige and ability. but excessive use of study for this above purpose, gives some adverse result.
An analysis of Francis Bacon's popular essay 'Of Studies'.The prose style of Francis Bacon : https://youtu.be/GKtti2E9ReQ
Critical reception. Though Bacon considered the Essays "but as recreation of my other studies", he was given high praise by his contemporaries, even to the point of crediting him with having invented the essay form. Later researches made clear the extent of Bacon's borrowings from the works of Montaigne, Aristotle and other writers, but the Essays have nevertheless remained in the highest repute.
The essay Of Studies by Sir Francis Bacon is the first essay in the series of ten essays published in 1597. Later, it was revised in 1612 with the addition of some more sentences and ideas in it along with the alteration in some vocabulary terms. This essay is regarded as Bacon's masterpiece enriched with stylised Latin vocabulary, fresh and ...
Bacon points out objects and proper ways of studies in the present essay. According to him the short - cut method should be used to study unimportant books only. Francis Bacon's Essay Of Studies—Summary and Critical Analysis. Bacon claims that studies serve not only the single purpose of increasing knowledge, but also they contribute to ...
Updated on January 24, 2019. "Of Truth" is the opening essay in the final edition of the philosopher, statesman and jurist Francis Bacon 's "Essays or Counsels, Civil and Moral" (1625). In this essay, as associate professor of philosophy Svetozar Minkov points out, Bacon addresses the question of "whether it is worse to lie to others or to ...