

The Evolution Of Computer | Generations of Computer
The development of computers has been a wonderful journey that has covered several centuries and is defined by a number of inventions and advancements made by our greatest scientists. Because of these scientists, we are using now the latest technology in the computer system.
Now we have Laptops , Desktop computers , notebooks , etc. which we are using today to make our lives easier, and most importantly we can communicate with the world from anywhere around the world with these things.
So, In today’s blog, I want you to explore the journey of computers with me that has been made by our scientists.
Note: If you haven’t read our History of Computer blog then must read first then come over here
let’s look at the evolution of computers/generations of computers
COMPUTER GENERATIONS
Computer generations are essential to understanding computing technology’s evolution. It divides computer history into periods marked by substantial advancements in hardware, software, and computing capabilities. So the first period of computers started from the year 1940 in the first generation of computers. let us see…
Table of Contents
Generations of computer
The generation of classified into five generations:
- First Generation Computer (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computer (1956-1963)
- Third Generation Computer(1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computer(1971-Present)
- Fifth Generation Computer(Present and Beyond)
1. FIRST GENERATION COMPUTER: Vacuum Tubes (1940-1956)
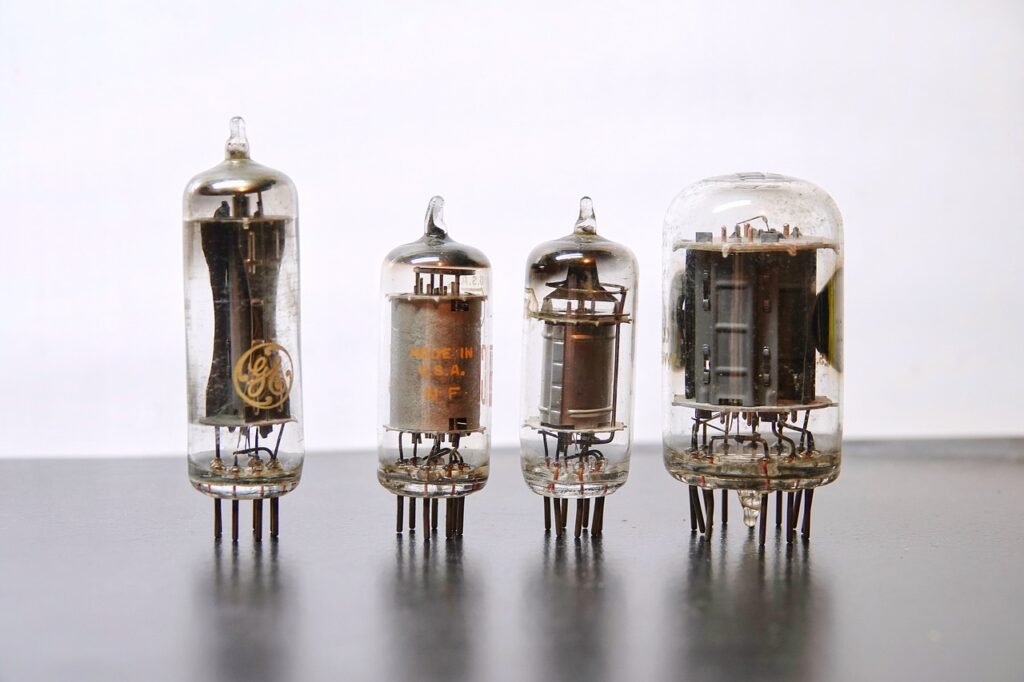

The first generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Vacuum tubes” It was developed in 1904 by the British engineer “John Ambrose Fleming” . A vacuum tube is an electronic device used to control the flow of electric current in a vacuum. It is used in CRT(Cathode Ray Tube) TV , Radio , etc.

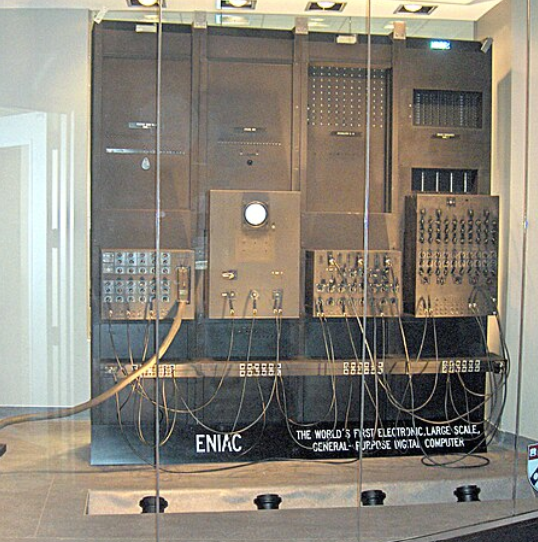
The first general-purpose programmable electronic computer was the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) which was completed in 1945 and introduced on Feb 14, 1946, to the public. It was built by two American engineers “J. Presper Eckert” and “John V Mauchly” at the University of Pennsylvania.

The ENIAC was 30-50 feet long, 30 tons weighted, contained 18000 vacuum tubes, 70,000 registers, and 10,000 capacitors, and it required 150000 watts of electricity, which makes it very expensive.
Later, Eckert and Mauchly developed the first commercially successful computer named UNIVAC(Univeral Automatic Computer) in 1952 .
Examples are ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer), UNIVAC-1 (Univeral Automatic Computer-1)

- These computers were designed by using vacuum tubes.
- These generations’ computers were simple architecture.
- These computers calculate data in a millisecond.
- This computer is used for scientific purposes.
DISADVANTAGES
- The computer was very costly.
- Very large.
- It takes up a lot of space and electricity
- The speed of these computers was very slow
- It is used for commercial purposes.
- It is very expensive.
- These computers heat a lot.
- Cooling is needed to operate these types of computers because they heat up very quickly.
2. SECOND GENERATION COMPUTER: Transistors (1956-1963)
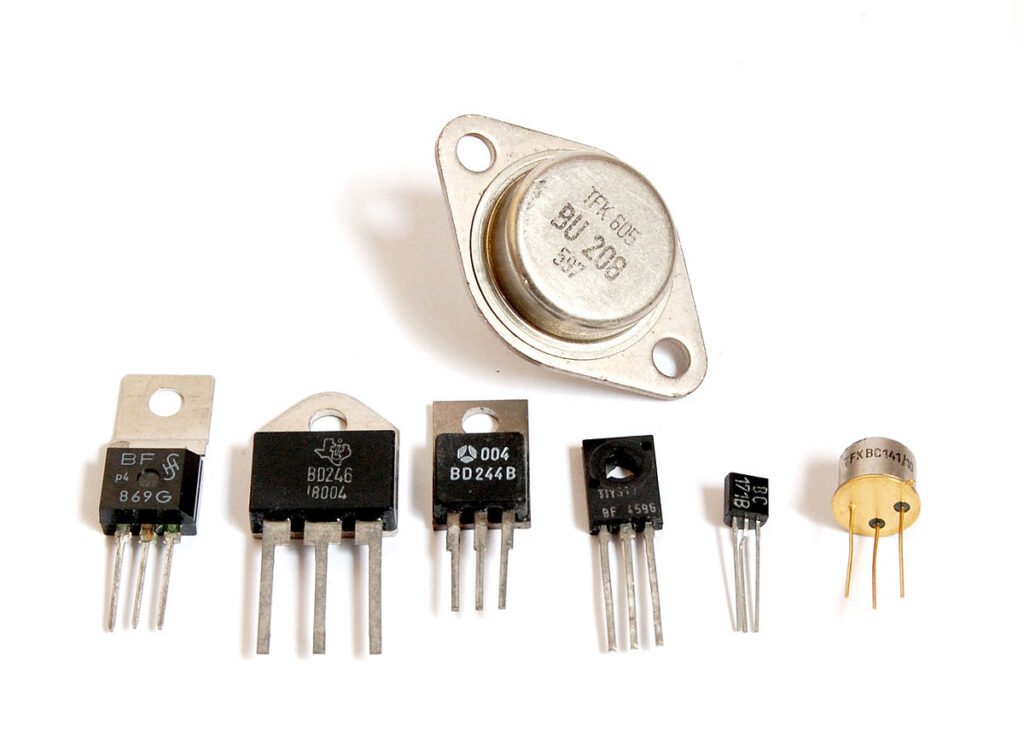
The second generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Transistors” and it was developed in 1947 by three American physicists “John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley” .

A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals or open or close a circuit. It was invented in Bell labs, The transistors became the key ingredient of all digital circuits, including computers.
The invention of transistors replaced the bulky electric tubes from the first generation of computers.
Transistors perform the same functions as a Vacuum tube , except that electrons move through instead of through a vacuum. Transistors are made of semiconducting materials and they control the flow of electricity.
It is smaller than the first generation of computers, it is faster and less expensive compared to the first generation of computers. The second-generation computer has a high level of programming languages, including FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1958), and COBOL (1959).
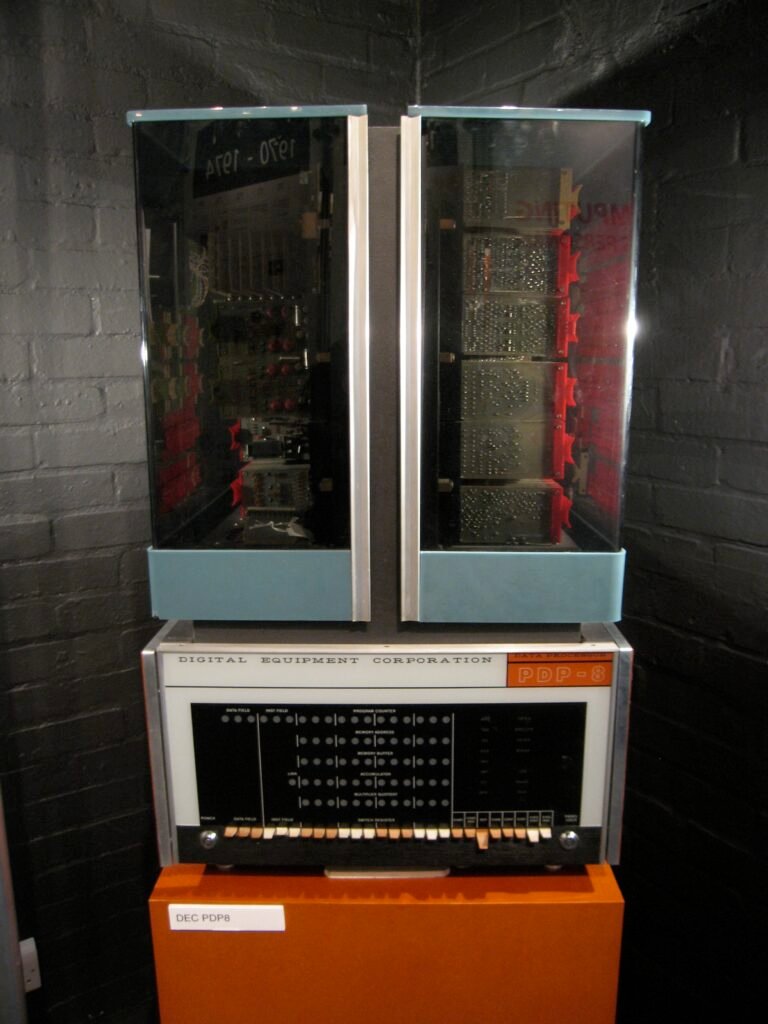
Examples are PDP-8 (Programmed Data Processor-8), IBM1400 (International business machine 1400 series), IBM 7090 (International business machine 7090 series), CDC 3600 ( Control Data Corporation 3600 series)

ADVANTAGES:
- It is smaller in size as compared to the first-generation computer
- It used less electricity
- Not heated as much as the first-generation computer.
- It has better speed
DISADVANTAGES:
- It is also costly and not versatile
- still, it is expensive for commercial purposes
- Cooling is still needed
- Punch cards were used for input
- The computer is used for a particular purpose
3. THIRD GENERATION COMPUTER: Integrated Circuits (1964-1971)
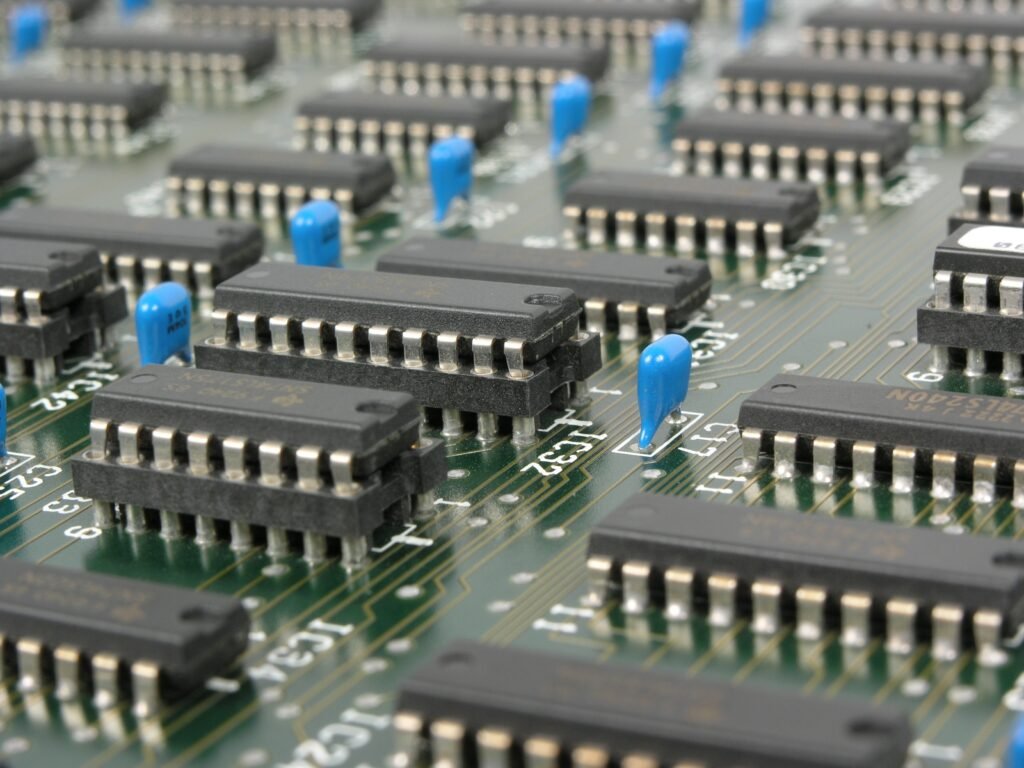
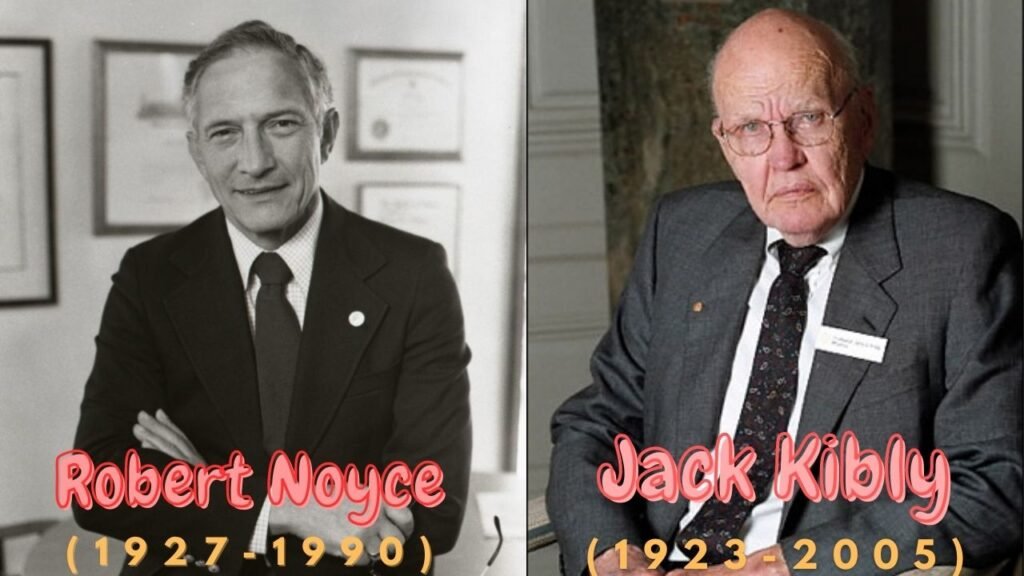
The Third generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Integrated Circuits” It was developed in 1958 by two American engineers “Robert Noyce” & “Jack Kilby” . The integrated circuit is a set of electronic circuits on small flat pieces of semiconductor that is normally known as silicon. The transistors were miniaturized and placed on silicon chips which are called semiconductors, which drastically increased the efficiency and speed of the computers.
These ICs (integrated circuits) are popularly known as chips. A single IC has many transistors, resistors, and capacitors built on a single slice of silicon.
This development made computers smaller in size, low cost, large memory, and processing. The speed of these computers is very high and it is efficient and reliable also.
These generations of computers have a higher level of languages such as Pascal PL/1, FORTON-II to V, COBOL, ALGOL-68, and BASIC(Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) was developed during these periods.
Examples are NCR 395 (National Cash Register), IBM 360,370 series, B6500

- These computers are smaller in size as compared to previous generations
- It consumed less energy and was more reliable
- More Versatile
- It produced less heat as compared to previous generations
- These computers are used for commercial and as well as general-purpose
- These computers used a fan for head discharge to prevent damage
- This generation of computers has increased the storage capacity of computers
- Still, a cooling system is needed.
- It is still very costly
- Sophisticated Technology is required to manufacture Integrated Circuits
- It is not easy to maintain the IC chips.
- The performance of these computers is degraded if we execute large applications.
4. FOURTH GENERATION OF COMPUTER: Microprocessor (1971-Present)
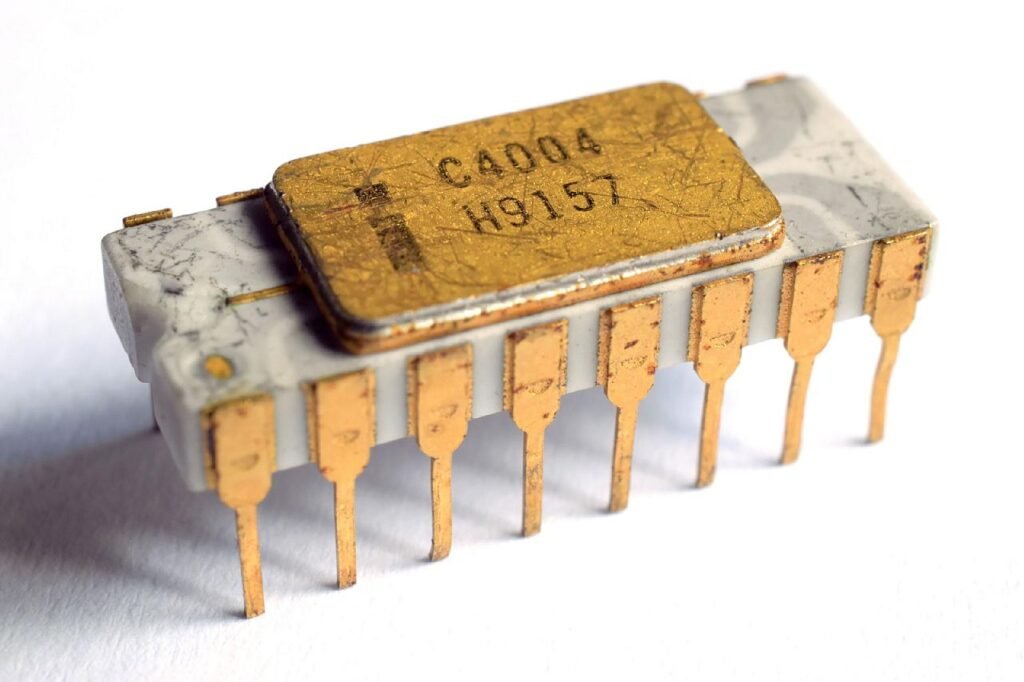
The fourth generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Microprocessor”. It was invented in the 1970s and It was developed by four inventors named are “Marcian Hoff, Masatoshi Shima, Federico Faggin, and Stanley Mazor “. The first microprocessor named was the “Intel 4004” CPU, it was the first microprocessor that was invented.

A microprocessor contains all the circuits required to perform arithmetic, logic, and control functions on a single chip. Because of microprocessors, fourth-generation includes more data processing capacity than equivalent-sized third-generation computers. Due to the development of microprocessors, it is possible to place the CPU(central processing unit) on a single chip. These computers are also known as microcomputers. The personal computer is a fourth-generation computer. It is the period when the evolution of computer networks takes place.
Examples are APPLE II, Alter 8800

- These computers are smaller in size and much more reliable as compared to other generations of computers.
- The heating issue on these computers is almost negligible
- No A/C or Air conditioner is required in a fourth-generation computer.
- In these computers, all types of higher languages can be used in this generation
- It is also used for the general purpose
- less expensive
- These computers are cheaper and portable
- Fans are required to operate these kinds of computers
- It required the latest technology for the need to make microprocessors and complex software
- These computers were highly sophisticated
- It also required advanced technology to make the ICs(Integrated circuits)
5. FIFTH GENERATION OF COMPUTERS (Present and beyond)
These generations of computers were based on AI (Artificial Intelligence) technology. Artificial technology is the branch of computer science concerned with making computers behave like humans and allowing the computer to make its own decisions currently, no computers exhibit full artificial intelligence (that is, can simulate human behavior).

In the fifth generation of computers, VLSI technology and ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology are used and the speed of these computers is extremely high. This generation introduced machines with hundreds of processors that could all be working on different parts of a single program. The development of a more powerful computer is still in progress. It has been predicted that such a computer will be able to communicate in natural spoken languages with its user.
In this generation, computers are also required to use a high level of languages like C language, c++, java, etc.
Examples are Desktop computers, laptops, notebooks, MacBooks, etc. These all are the computers which we are using.

- These computers are smaller in size and it is more compatible
- These computers are mighty cheaper
- It is obviously used for the general purpose
- Higher technology is used
- Development of true artificial intelligence
- Advancement in Parallel Processing and Superconductor Technology.
- It tends to be sophisticated and complex tools
- It pushes the limit of transistor density.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many computer generations are there.
Mainly five generations are there:
First Generation Computer (1940-1956) Second Generation Computer (1956-1963) Third Generation Computer(1964-1971) Fourth Generation Computer(1971-Present) Fifth Generation Computer(Present and Beyond)
Which things were invented in the first generation of computers?
Vacuum Tubes
What is the fifth generation of computers?
The Fifth Generation of computers is entirely based on Artificial Intelligence. Where it predicts that the computer will be able to communicate in natural spoken languages with its user.
What is the latest computer generation?
The latest generation of computers is Fifth which is totally based on Artificial Intelligence.
Who is the inventor of the Integrated Circuit?
“Robert Noyce” and “Jack Bily”
What is the full form of ENIAC ?
ENIAC Stands for “Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer” .
Related posts:
- The History of Computer Systems and its Generations
- Basic Components of Computer Systems and its Functions
- What is a computer? How is it a useful device?
- 10 Limitations Of Computers System|And its Capabilities?
- Different Applications of Computer Systems in Various Fields | Top 12 Fields
- Explain Von Neumann Architecture?
- What are the input and Output Devices of Computer System with Examples
- What is Unicode and ASCII Code
- What is RAM and its Types?
- What is the difference between firmware and driver? | What are Firmware and Driver?
2 thoughts on “The Evolution Of Computer | Generations of Computer”
It is really useful thanks
Glad to see
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Unit 7. Evolution of computers
Topic A: Computer generations
Click play on the following audio player to listen along as you read this section.
Basic Terms

Vacuum tube – an electronic device that controls the flow of electrons in a vacuum. It used as a switch, amplifier, or display screen in many older model radios, televisions, computers, etc.

Transistor – an electronic component that can be used as an amplifier or as a switch. It is used to control the flow of electricity in radios, televisions, computers, etc.
Integrated circuit (IC) – a small electronic circuit printed on a chip (usually made of silicon) that contains many its own circuit elements (e.g. transistors, diodes , resistors, etc.).

Microprocessor – an electronic component held on an integrated circuit that contains a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) and other associated circuits.

CPU (central processing unit) – It is often referred to as the brain or engine of a computer where most of the processing and operations take place (CPU is part of a microprocessor).

Magnetic drum – a cylinder coated with magnetic material, on which data and programs can be stored.
Magnetic core – uses arrays of small rings of magnetized material called cores to store information.

Machine language – a low-level programming language comprised of a collection of binary digits (ones and zeros) that the computer can read and understand.
Assembly language is like the machine language that a computer can understand, except that assembly language uses abbreviated words (e.g. ADD, SUB, DIV…) in place of numbers (0s and 1s).

Artificial intelligence (AI) – an area of computer science that deals with the simulation and creation of intelligent machines or intelligent behave in computers (they think, learn, work, and react like humans).
First Generation of Computers
Classification of generations of computers.
The evolution of computer technology is often divided into five generations.
The main characteristics of first generation of computers (1940s-1950s)

- Main memory – magnetic drums and magnetic tapes
- Programming language – machine language

- Speed and size – very slow and very large in size (often taking up entire room).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and paper tape.
- Examples – ENIAC, UNIVAC1, IBM 650, IBM 701, etc.
- Quantity – there were about 100 different vacuum tube computers produced between 1942 and1963.
Second Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of second generation of computers (1950s-1960s).
- Memory – magnetic core and magnetic tape / disk

- Power and size – low power consumption, generated less heat, and smaller in size (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and magnetic tape.
- Examples – IBM 1401, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107, etc.
Third Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of third generation of computers (1960s-1970s).
- Memory – large magnetic core, magnetic tape / disk

- Size – smaller, cheaper, and more efficient than second generation computers (they were called minicomputers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the second generation computers).

- Examples – IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, UNIVAC 1108, etc.
Fourth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fourth generation of computers (1970s-present).

- VLSI– thousands of transistors on a single microchip.
- RAM (random-access memory) – a type of data storage (memory element) used in computers that temporary stores of programs and data (volatile: its contents are lost when the computer is turned off).

- A mix of both third- and fourth-generation languages
- Size – smaller, cheaper and more efficient than third generation computers.
- Speed – improvement of speed, accuracy, and reliability (in comparison with the third generation computers).

- Network – a group of two or more computer systems linked together.
- Examples – IBM PC, STAR 1000, APPLE II, Apple Macintosh, etc.

Fifth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fifth generation of computers (the present and the future).

- ULSI – millions of transistors on a single microchip
- Parallel processing method – use two or more microprocessors to run tasks simultaneously.
- Language – understand natural language (human language).
- Power – consume less power and generate less heat.
- Speed – remarkable improvement of speed, accuracy and reliability (in comparison with the fourth generation computers).
- Size – portable and small in size, and have a huge storage capacity.

- Example – desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.

The computer – this amazing technology went from a government/business-only technology to being everywhere from people’s homes, work places, to people’s pockets in less than 100 years.

an electronic device that controls the flow of electrons in a vacuum. It used as a switch, amplifier, or display screen in many older model radios, televisions, computers, etc.
an electronic component that can be used as an amplifier or as a switch. It is used to control the flow of electricity in radios, televisions, computers, etc.
a small electronic circuit printed on a chip (usually made of silicon) that contains many its own circuit elements (e.g. transistors, diodes, resistors, etc.).
an electronic component held on an integrated circuit that contains a computer's central processing unit (CPU) and other associated circuits.
The brain or engine of a computer, where most of the processing and operations take place.
a cylinder coated with magnetic material, on which data and programs can be stored.
uses arrays of small rings of magnetized material called cores to store information.
a low-level programming language comprised of a collection of binary digits (ones and zeros) that the computer can read and understand.
a physical device that is used to store data, information, and programs in a computer.
an area of computer science that deals with the simulation and creation of intelligent machines or intelligent behave in computers (they think, learn, work, and react like humans).
Key Concepts of Computer Studies Copyright © 2020 by Meizhong Wang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Generations of Computers
The section on computer awareness is a fairly new section of banking exams. So from this section, the topic on generations of computers is of prime importance. Here in this article, we will discuss the various generations of computers and the reasons that are important. Let us see!
Suggested Videos
A computer is basically an electronic machine that can process information. However, the “ process ” could be anything. For example, it could be the addition or any other arithmetic operation . Otherwise, it could be just the instruction to group a given set of data or to ungroup it. Today’s computers have the power to carry out billions of calculations in a second and return results that are very accurate and reliable. How did it all happen? Where did it all start?
Click here to learn everything you need to know about the English Language .
The computers of today find their roots in the second half of the twentieth century. Later as time progressed, we saw many technological improvements in physics and electronics . This has eventually led to revolutionary developments in the hardware and software of computers. In other words, soon the computer started to evolve. Each such technological advancement marks a generation of computers. Let us begin with the first one.

First Generation Of Computers
Computers developed between 1946 – 1959, are the first generation of computers. They were large and limited to basic calculations. They consisted of large devices like the vacuum tubes. The input method of these computers was a machine language known as the 1GL or the first generation language. The physical methods of using punch cards, paper tape, and magnetic tape were used to enter data into these computers.
Be updated and don’t get stuck in an exam. Prepare your General Awareness topics here.
Examples of the first generation computers include ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, IBM-701, and IBM-650. These computers were large and very unreliable. They would heat up and frequently shut down and could only be used for very basic computations.
Second Generation Of Computers
Computers developed between 1959-1965 the second generation computers. These computers were more reliable and in place of vacuum tubes, used transistors. This made them far more compact than the first generation computers. The input for these computers were higher level languages like COBOL, FORTRAN etc. In these computers, primary memory was stored on the magnetic cores and magnetic tape and they used magnetic disks as secondary storage devices.
Examples of the second generation computers include IBM 1620, IBM 7094, CDC 1604, CDC 3600, UNIVAC 1108. As a result, they worked on AC and therefore were faster than their predecessors.
Having trouble with concepts like DBMS? Have an important exam soon? Click here and start your preparations now!
Third Generation Of Computers
Computers developed during the period of 1965 – 1971, the third generation of computers. These computers differed from the first and the second generations simply by the fact that a new circuit element like IC’s (Integrated Circuits) was used. An integrated circuit is a small device that can contain thousands and thousands of devices like transistors, resistances and other circuit elements that make up a computer. Jack Kilby is credited with the invention of the Integrated Circuit or the IC chips. With the invention of IC’s, it became possible to fit thousands of circuit elements into a small region and hence the size of the computers eventually became smaller and smaller.
Another salient feature of these computers was that they were much more reliable and consumed far less power. The input languages for such computers were COBOL, FORTRAN-II up to FORTRAN-IV, PASCAL, ALGOL-68, BASIC, etc. These languages were much better and could represent more information. Consequently more and more complex calculations are possible
Examples of the third generation computers include IBM-360 series, Honeywell-6000 series, PDP (Personal Data Processor), and IBM-370/168.
Find all the topics of Reasoning Ability here!
Fourth Generation Of Computers
Fourth Generation of computers was between 1971 – 1980. These computers used the VLSI technology or the Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits technology. Therefore they were also known as the microprocessors. Intel was the first company to develop a microprocessor. The first “personal computer” or PC developed by IBM, belonged to this generation. VLSI circuits had almost about 5000 transistors on a very small chip and were capable of performing many high-level tasks and computations. These computers were thus very compact and thereby required a small amount of electricity to run.
Examples are STAR 1000, CRAY-X-MP(Super Computer), DEC 10, PDP 11, CRAY-1. This generation of computers had the first “supercomputers” that could perform many calculations accurately. They were also used in networking and also used higher and more complicated languages as their inputs. The computer languages like languages like C, C+, C++, DBASE etc. were the input for these computers.
Want to see how smart you are? Want to exercise your brain? Click here for a wonderfully explained and lucid section of Reasoning Ability.
Fifth Generation Of Computers
This is the present generation of computers and is the most advanced one. The generation began somewhere around 1981 and is the present generation of computers. The methods of input include the modern high-level languages like Python, R, C#, Java etc. These are extremely reliable and employ the ULSI or the Ultra Large Scale Integration technology. These computers are at the frontiers of the modern scientific calculations and are used to develop the Artificial Intelligence or AI components that will have the ability to think for themselves.
Examples include: Intel P 4, i 3 – i10, AMD Athlon, etc.
We have the most complete syllabus of quantitative aptitude in one place for you! Click here
Check Your Awareness
Q 1: The language used in ENIAC:
A) C B) C++ C) 1 GL D) Python
Ans: Basically ENIAC was a first generation computer and therefore the correct option is 1 GL.
Q 2: Which among these will have VLSI?
A) DEC 10 B) PDP 11 C) CRAY-1 D) All of these.
Ans: Earlier VLSI or the very large scale integration was employed in the fourth generation of computers. All of these above examples are from the fourth generation and therefore the answer is D.
Practice Questions
Q 1: You can use Java in which of these following generations:
Ans: D is the correct option.
Q 2: The ULSI technology is present in which generation of computers:
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Basics of Computers
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Basic Computer Terminology
- Computer Abbreviations
- Computer Languages
- Basic Internet Knowledge and Protocols
- History of Computers
- Basic Computer Knowledge – Practice Problems
- Computer Organization
- Input and Output (I/O) Devices
- Hardware and Software
One response to “Hardware and Software”
THANKS ,THIS IS THE VERY USEFUL KNOWLEDGE
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Provide details on what you need help with along with a budget and time limit. Questions are posted anonymously and can be made 100% private.

Studypool matches you to the best tutor to help you with your question. Our tutors are highly qualified and vetted.

Your matched tutor provides personalized help according to your question details. Payment is made only after you have completed your 1-on-1 session and are satisfied with your session.

- Homework Q&A
- Become a Tutor
All Subjects
Mathematics
Programming
Health & Medical
Engineering
Computer Science
Foreign Languages
Access over 20 million homework & study documents
Generations of computer (1 - 5) complete guide and assignment.
Sign up to view the full document!

24/7 Homework Help
Stuck on a homework question? Our verified tutors can answer all questions, from basic math to advanced rocket science !

Similar Documents
working on a homework question?
Studypool is powered by Microtutoring TM
Copyright © 2024. Studypool Inc.
Studypool is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university.
Ongoing Conversations

Access over 20 million homework documents through the notebank
Get on-demand Q&A homework help from verified tutors
Read 1000s of rich book guides covering popular titles

Sign up with Google
Sign up with Facebook
Already have an account? Login
Login with Google
Login with Facebook
Don't have an account? Sign Up
Generation of Computers 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th
The Generation of Computer tells about the evolution of technology to distinguish the computers in terms of varying hardware and software. Know everything about the Generation of Computers 1st to 5th.

Table of Contents
For many decades we have relied on computers and now they have become an inseparable part of our lives. We cannot imagine our lives without computers are they have made our work easier. These computers have gone through changes over time and have you ever really wondered what a computer actually is? Today we use Laptops for our office work, and tablets for day-to-day calculations or entertainment purposes. These indicate that computers have evolved and undergone changes in their structure, functions and speed over time.
What is the Evolution of the computer?
The evolution of computers started around the 16th century. The evolution of the computer is the process of which transformation of the oldest vacuum tube-based system to the current model system of today’s computers. Long ago, the early primitive people were trailblazers in the use of counting tools, making use of objects like sticks, stones, and bones for their counting needs. The computer we see today has faced many changes, for the betterment via history of computers . It has continuously improved itself in terms of speed, accuracy, size, and price to urge the form of the computer we have today. Here we have discussed the 5 generations of computers and their characteristics.
Generation of Computer
In computers, we use the term “generation” to show the evolution of technology. Earlier, the generation term was used to distinguish the computers in terms of varying hardware but now it all together includes the hardware and software which makes up a computer system. After centuries of evolution that began in the 16th century, the contemporary computer has taken its current form. There are 5 Generations of computers and all of them have been discussed below along with their features.
- First Generation Computers (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computers (1956-1963)
- Third Generation Computers (1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computers (1971-Present)
- Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Beyond)

1. First Generation Computers
The 1st Generation Computers were introduced using the technology of vacuum tubes which can control the flow of electronics in a vacuum. These tubes are usually used in switches, amplifiers, radios, televisions, etc. The First Generation of Computer was very heavy and large and were not ideal for programming. They used basic programming and didn’t have an operating system, which made it tough for users to do programming on them. The 1st Generation Computers required a big room dedicated to them and also consumed a lot of electricity.
Some examples of main first-generation computers are-
- ENIAC: Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, built by J. Presper Eckert and John V. Mauchly which contained 18,000 vacuum tubes.
- EDVAC: Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer, designed by Von Neumann.
- UNIVAC: Universal Automatic Computer, developed by Eckert and Mauchly in 1952.
Characteristics of 1st Generation Computers
- These computers were designed using vacuum tubes.
- Programming in these computers was done using machine languages.
- The main memory of 1st Generation Computers consisted of magnetic tapes and magnetic drums.
- Paper tapes and Punched cards were used as input/output devices in these computers.
- These computers were very huge but worked very slowly.
- Examples of 1st Generation Computers are IBM 650, IBM 701, ENIAC, UNIVAC1, etc.

2. Second Generation Computers
The Second Generation of Computers revolutionized as it started using the technology of transistors instead of bulky vacuum tubes. Transistors are devices made of semiconductor materials that open or close a circuit. These transistors were invented in the Bell Labs which made the Second Generation Computer powerful and faster than the previous ones. Transistors made these computers smaller and generated less heat compared to the vacuum tubes they replaced. The Second Generation of Computers also introduced the use of CPU, memory and input/output units. The programming languages used for the second-generation computers were FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1958), and COBOL (1959).

Characteristics of Second-Generation Computers
- The Second Generation computers used the technology of Transistors.
- Machine language and Assembly Languages were used for these computers.
- Magnetic core and magnetic tape/disk were used for memory storage.
- The Second Generation Computers were smaller in size, consumed less power and generated less heat.
- Magnetic tape and punched cards were used as input/output devices.
- Some of the examples are PDP-8, IBM1400 series, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107, CDC 3600, etc.

3. Third Generation Computers
The evolution of Third Generation Computers took place with a shift from transistors to integrated circuits also called IC. The Third Generation of Computer was very fast and reliable. The ICs used in these computers were made from silicons and were called silicon chips. A single IC has many transistors, registers, and capacitors built on one thin slice of silicon. This generation of computers has increased memory space and efficiency. Higher-level languages like BASIC (Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) were used and the Minicomputers were introduced in this era.
Characteristics of Third-Generation Computers
- These computers were built using Integrated Circuits (ICs).
- High-level programming languages were used for programming on these computers.
- Large magnetic core and magnetic tape/disk were used for memory storage.
- Magnetic tape, monitor, keyboard, printer, etc were used as input/ output devices .
- Some of the examples of Third Generation Computers are IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, NCR 395, B6500, UNIVAC 1108, etc.

4. Fourth Generation Computers
The period from 1972 to 2010 is considered the period of the fourth generation of computers. Microprocessor technology was used to develop the Fourth Generation of Computers. The foremost advantage of these computers is that the microprocessor can contain all the circuits required to perform arithmetic, logic, and control functions on one chip. In the Fourth Generation, computers became very small in size and also became portable.
Technologies like multiprocessing, multiprogramming, time-sharing, operating speed, and virtual memory were also introduced by then. During the fourth generation, private computers and computer networks became a reality.
Characteristics of Fourth-Generation Computers
- The Fourth Generation Computers have been developed using the technology of Very-large-scale integration (VLSI) and the microprocessor (VLSI has thousands of transistors on a single microchip).
- Semiconductor memory such as RAM, ROM , etc was used for memory storage.
- Input/output devices such as pointing devices, optical scanning, keyboard, monitor, printer, etc were introduced.
- Some examples of Fourth Generation Computers are IBM PC, STAR 1000, APPLE II, Apple Macintosh, Alter 8800, etc.

5. Fifth Generation Of Computers
The Fifth Generation of Computers has been built using the technology called Artificial Intelligence (AI). This technology encourages computers to behave like humans. Some of the applications of AI have been seen in features like voice recognition, entertainment, etc. The speed of the Fifth Generation of Computers is the highest while the sizes are the smallest. A big improvement has been noticed so far over the years in the various generations of computers in the aspect of speed, accuracy dimensions, etc.
Characteristics of Fifth Generation of Computers
- The 5th Generation Computers have been built based on artificial intelligence, use the Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) technology and parallel processing method (ULSI has millions of transistors on a single microchip and the Parallel processing method uses two or more microprocessors to run tasks simultaneously).
- These computers understand natural language (human language).
- The Fifth-generation computers are portable and smaller in size.
- Trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (recognize voice/speech), light scanner, printer, keyboard, monitor, mouse, etc are used as Input/Output devices.
- Examples of 5th Generation Computers are Desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.

History of Computer Generation
The word ‘computer’ was first used in the 16th century for a person who used to do calculations until the 20th century. Women were hired as human computers to carry out all forms of calculations and computations. By the end of the 19th century, the word ‘computer’ was used for the machines that did calculations. Nowadays we use the word for the programmable digital devices that run on electricity.
Before computers were invented, sticks, stones, and bones were used as counting tools. With the evolution of human intellect and the advancement of technology, more computing devices were produced. There are mechanical calculators used by humans before computers. Some of the most famous mechanical calculators are:
- Pascal’s Calculator
- Stepped Reckoner
- Arithmometer
- Comptometer & Comptograph
Difference Engine
Analytical engine.
- The Millionaire
Below we have discussed briefly the early-age computing devices used by mankind.
The Chinese are said to have discovered the Abacus some 4,000 years ago. The abacus was built using a wooden rack having metal rods with beads mounted on them. To perform the arithmetic calculations, beads were moved by the abacus operator according to some rules.
Napier’s Bones
John Napier invented Napier’s Bones which was a manually operated calculating device. John used 9 different ivory strips or bones marked with numbers to multiply and divide with the help of this calculating tool. The Napier’s Bone was also the first calculating tool to use decimal points.
A French mathematician-philosopher Biaise Pascal invented the Pascaline between 1642 and 1644. This tool was also called the Arithmetic Machine or Adding Machine and is believed to be the first mechanical and automatic calculator.
Stepped Reckoner or Leibnitz wheel
A German mathematician-philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibnitz developed the Stepped Reckoner or Leibnitz wheel in 1673. This machine was technically an upgrade of Pascal’s invention. The Stepped Reckoner or Leibnitz wheel was a digital mechanical calculator that was made of fluted drums instead of gears.
Charles Babbage, known as the “Father of Modern Computer designed the Difference engine in the early 1820s. The Difference Engine was a mechanical computer that could perform simple calculations. It was a steam-driven calculating machine designed to solve tables of numbers like logarithm tables.
The Analytical Engine was also developed by Charles Babbage in the 1830s. This calculating machine was a mechanical computer that used punch cards as input. These machines were capable of solving any mathematical problem and storing information as a permanent memory.
Tabulating Machine
Herman Hollerith, an American statistician invented the Tabulating Machine in the 1890s which was a mechanical tabulator based on punch cards that was capable of tabulating statistics and recording or sorting data or information.
Differential Analyzer
The Differential Analyzer was the first electronic computer introduced in the United States in 1930. It was an analog device invented by Vannevar Bush. This machine could perform 25 calculations in a few minutes.
The major changes in the history of computers began in 1937 when Howard Aiken aimed to invent a machine that could perform calculations of larger numbers. In 1944, IBM and Harvard partnered to build the Mark I computer. The Mark 1 was the first programmable digital computer.
Sharing is caring!
Generation of Computers- FAQs
Q1. what is a generation.
In computers, we use the term "generation" to show the evolution of technology. Earlier, the generation term was used to distinguish the computers in terms of varying hardware but now it all together includes the hardware and software which makes up a computer system.
Q2. How many generations of computer are there?
There are a total of 5 generation of computer that exist in the world.
Q3. What technology is used behind the Fifth Generation of Computers?
Artificial Intelligence is used to build the Fifth Generation of Computers.
Q4. Who invented Vacuum Tubes?
The Vacuum Tubes were invented by Lee De Forest.
Q5. Who invented 2nd generation computer?
The 2nd generation computer were invented by Walter H. Brattain (1902-1987), John Bardeen (1908-1991), and William B at at Bell Labs. The second generation computers are based upon transistors, not on vacuum tubes.
Q6. Which computer introduced the concept of the mouse and graphical user interface (GUI)?
Apple Macintosh introduced the concept of the mouse and graphical user interface (GUI)
Q7. Which computer is considered the first true personal computer?
Altair 8800 the first true personal computer.
As Team Lead- Content Writer, I take on leadership within our content creation team, overseeing the development of error-free educational content. My primary responsibility is to produce and analyse high-quality content educating and informing the aspirants about upcoming government exams published on our website. I have more than 6 years experience in content writing wherein 3.5 years of experience in ed-tech content writing.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Board Result 2024
- Karnataka 2nd PUC Result 2024
- CBSE 10th Result 2024
- UP Board 10th Result 2024
- MP Board 12th Result 2024
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 English Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus
CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 10 English Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 SST Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Hindi Syllabus
Exam Date 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- NEET Exam Date 2024
- JEE Mains Exam Date 2024
Latest Posts
Important exams.
- JEE Mains 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- NIMCET 2024
- AP EAMCET 2024
- TS EAMCET 2024
- AP ECET 2024
- TS ECET 2024
- TS PGECET 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- AP Polycet 2024
- TS Polycet 2024
- JEECUP 2024
- Bihar Polytechnic 2024
- Jharkhand Polytechnic 2024
- Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Prof. Eric Grimson
- Prof. John Guttag
Departments
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
As Taught In
- Programming Languages
Introduction to Computer Science and Programming
Assignments.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
Computer Fundamental Tutorial
What is computer, introduction to computer fundamentals, history and evolution of computers, components of a computer system, computer hardware, computer software, data storage and memory.
- Computer Memory
Basics of Operating System
Computer networks and internet, introduction to programming, computer security and privacy, functionalities of computer, the evolution of computers, applications of computer fundamentals, faqs on computer fundamentals.
This Computer Fundamental Tutorial covers everything from basic to advanced concepts, including computer hardware, software, operating systems, peripherals, etc. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, this tutorial is designed to enhance your computer skills and take them to the next level.

The computer is a super-intelligent electronic device that can perform tasks, process information, and store data. It takes the data as an input and processes that data to perform tasks under the control of a program and produces the output. A computer is like a personal assistant that follows instructions to get things done quickly and accurately. It has memory to store information temporarily so that the computer can quickly access it when needed.
Prerequisites: No prerequisites or prior knowledge required. This article on Computer Fundamentals is designed for absolute beginners.
Computer Fundamentals Index
- What are Computer Fundamentals?
- Importance of Computer Fundamentals in Digital Age
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer
- Classification of Computers
- Application area of Computer
- History of Computers
- The Origins of Computing
- Generations of Computer
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Memory Units
- Input Devices
- Output Devices
- Motherboard
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
- Solid State Drives (SSD)
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
- Power Supply Unit (PSU)
- Computer Peripherals (Keyboard, Mouse, Monitor, etc.)
- Introduction to Software
- Types of Software
- Application Software
- System Software
- What is a Storage Device?
- Types of Data Storage
- Optical Storage ( CDs , DVDs, Blu-rays )
- Flash Drives and Memory Cards
- Cloud Storage
- Register Memory
- Cache Memory
- Primary Memory
- Secondary Memory
- What is Operating System?
- Evolution of Operating System
- Types of Operating Systems
- Operating System Services
- Functions of Operating System
- Introduction to Computer Networks
- Types of Networks (LAN, WAN, MAN)
- Network Topologies (Star, Bus, Ring)
- Network Protocols (TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP)
- Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)
- World Wide Web
- What is Programming?
- A Categorical List of programming languages
- Language Processors: Assembler, Compiler and Interpreter
- Variables ( C , C++ , Java )
- Data Types ( C , C++ , Java )
- Operators ( C , C++ , Java )
- Control Structures (Conditionals, Loops)
- Functions and Procedures
- Importance of Computer Security
- Common Security Threats
- Malware (Viruses, Worms, Trojans)
- Network Security Measures (Firewalls, Encryption)
- Access Control
- User Authentication
- Privacy Concerns and Data Protection
Any digital computer performs the following five operations:
- Step 1 − Accepts data as input.
- Step 2 − Saves the data/instructions in its memory and utilizes them as and when required.
- Step 3 − Execute the data and convert it into useful information.
- Step 4 − Provides the output.
- Step 5 − Have control over all the above four steps
A journey through the history of computers. We’ll start with the origins of computing and explore the milestones that led to the development of electronic computers.
- Software Development: Computer fundamentals are fundamental to software development. Understanding programming languages, algorithms, data structures, and software design principles are crucial for developing applications, websites, and software systems. It forms the basis for creating efficient and functional software solutions.
- Network Administration : Computer fundamentals are essential for network administrators. They help set up and manage computer networks, configure routers and switches, troubleshoot network issues, and ensure reliable connectivity. Knowledge of computer fundamentals enables network administrators to maintain and optimize network performance.
- Cybersecurity : Computer fundamentals are at the core of cybersecurity. Understanding the basics of computer networks, operating systems, encryption techniques, and security protocols helps professionals protect systems from cyber threats. It enables them to identify vulnerabilities, implement security measures, and respond effectively to security incidents.
- Data Analysis : Computer fundamentals are necessary for data analysis and data science. Knowledge of programming, statistical analysis, and database management is essential to extract insights from large datasets. Understanding computer fundamentals helps in processing and analyzing data efficiently, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning : Computer fundamentals provide the foundation for AI and machine learning. Concepts such as algorithms, data structures, and statistical modelling are vital in training and developing intelligent systems. Understanding computer fundamentals allows professionals to create AI models, train them on large datasets, and apply machine learning techniques to solve complex problems.
Q.1 How long does it take to learn computer fundamentals?
The time required to learn computer fundamentals can vary depending on your prior knowledge and the depth of understanding you aim to achieve. With consistent effort and dedication, one can grasp the basics within a few weeks or months. However, mastering computer fundamentals is an ongoing process as technology evolves.
Q.2 Are computer fundamentals only for technical professionals?
No, computer fundamentals are not limited to technical professionals. They are beneficial for anyone who uses computers in their personal or professional life. Basic computer skills are increasingly essential in various careers and everyday tasks.
Q.3 Can I learn computer fundamentals without any prior technical knowledge?
Absolutely! Computer fundamentals are designed to be beginner-friendly. You can start learning without any prior technical knowledge. There are numerous online tutorials, courses, and resources available that cater to beginners.
Q.4 How can computer fundamentals improve my job prospects?
Computer skills are highly sought after in today’s job market. Proficiency in computer fundamentals can enhance your employability by opening up job opportunities in various industries. It demonstrates your adaptability, problem-solving abilities, and ability to work with digital tools.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Computer Subject
- How to Use ChatGPT with Bing for Free?
- 7 Best Movavi Video Editor Alternatives in 2024
- How to Edit Comment on Instagram
- 10 Best AI Grammar Checkers and Rewording Tools
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

TrendyDigests
In 2024, The U.S. Army Plans To Provide Its Troops With State-of-the-art Sig Sauer Rifles And Optics
Posted: April 10, 2024 | Last updated: April 10, 2024
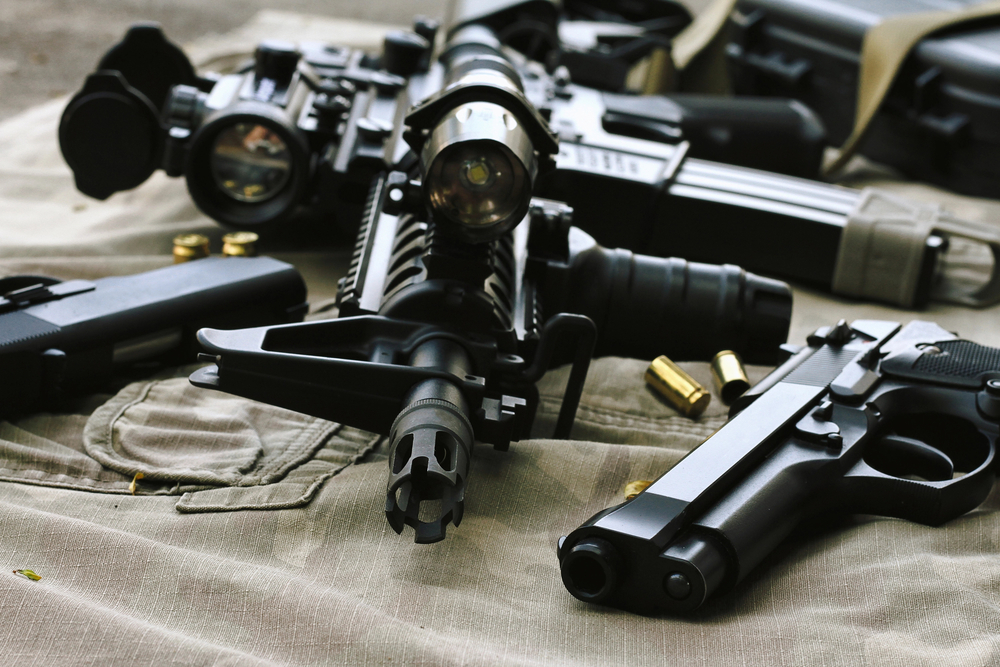

The Army has commenced a new chapter in small arms capabilities, choosing Sig Sauer to manufacture the Next Generation Squad Weapon (NGSW), which will significantly enhance the firepower of close combat forces. In a contract that could potentially reach $2.7 billion over the next decade, Sig Sauer will provide both the rifle and automatic rifle variants that utilize the more potent 6.8mm cartridges, aiming to revolutionize the effectiveness, range, and accuracy of the soldiers' weapons.
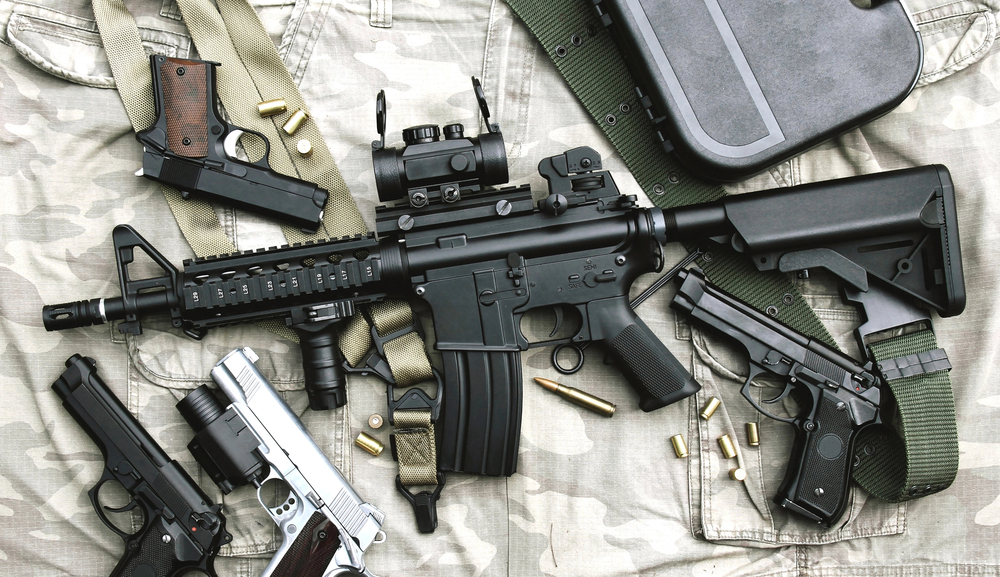

This transformational step forward in combat lethality originated from an April 2022 decision when the Army awarded Sig Sauer the contract to replace the M4A1 Carbine and the M249 Squad Automatic Weapon within close combat forces. The decision underscores the Army's determined effort to respond to evolving threats and to keep its weaponry at the forefront of technology and capability.
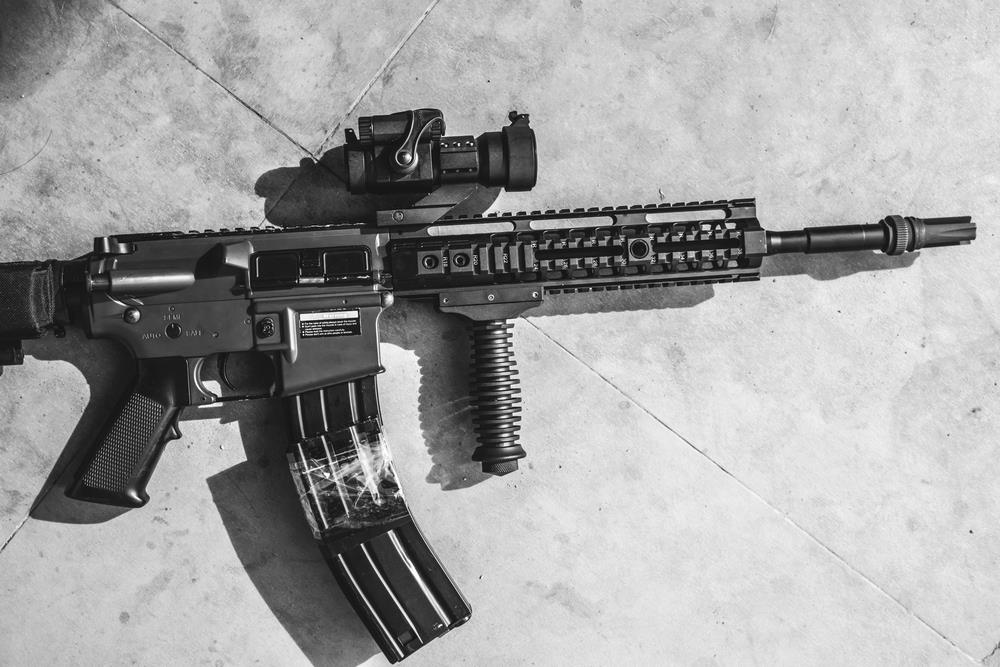

The Army delivered the XM7 rifle and the XM250 automatic rifle, along with the advanced XM157 fire control optics, to a platoon in the 101st Airborne Division at Fort Campbell, Kentucky in late September for testing. The sophisticated fire control system, developed by Vortex Optics/Sheltered Wings, integrates computer-aided ballistics, range-finding, and environmental sensors that dramatically improve accuracy and allow for rapid adjustment of fire. It's a partnership that could yield up to 250,000 optics produced over the next decade, with a cost ceiling set at $2.7 billion.

The XM7 will ultimately replace the M4 for units such as infantry, scouts, combat engineers, and special operations forces, while the XM250 will take over the duties of the M249 Squad Automatic Weapon for these same units. The new systems are intended to be fielded to a yet-to-be-identified unit in the 101st by the second quarter of fiscal year 2024.
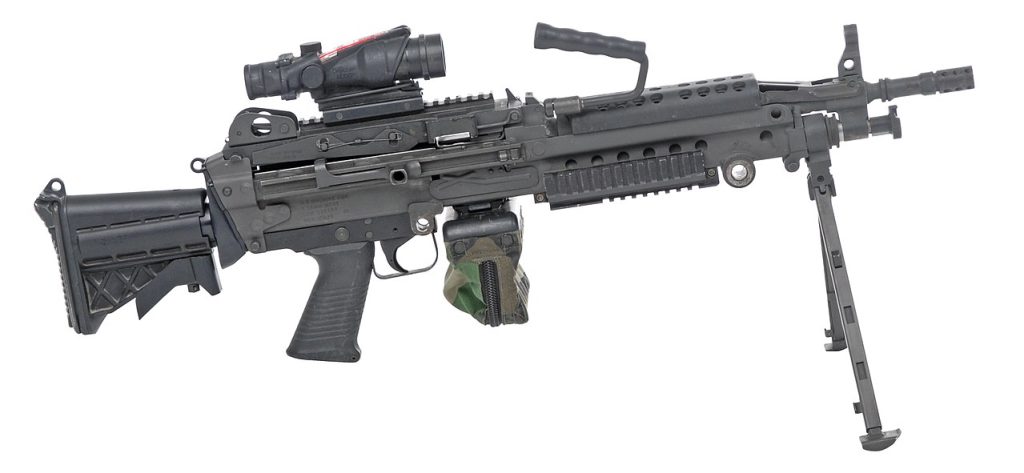

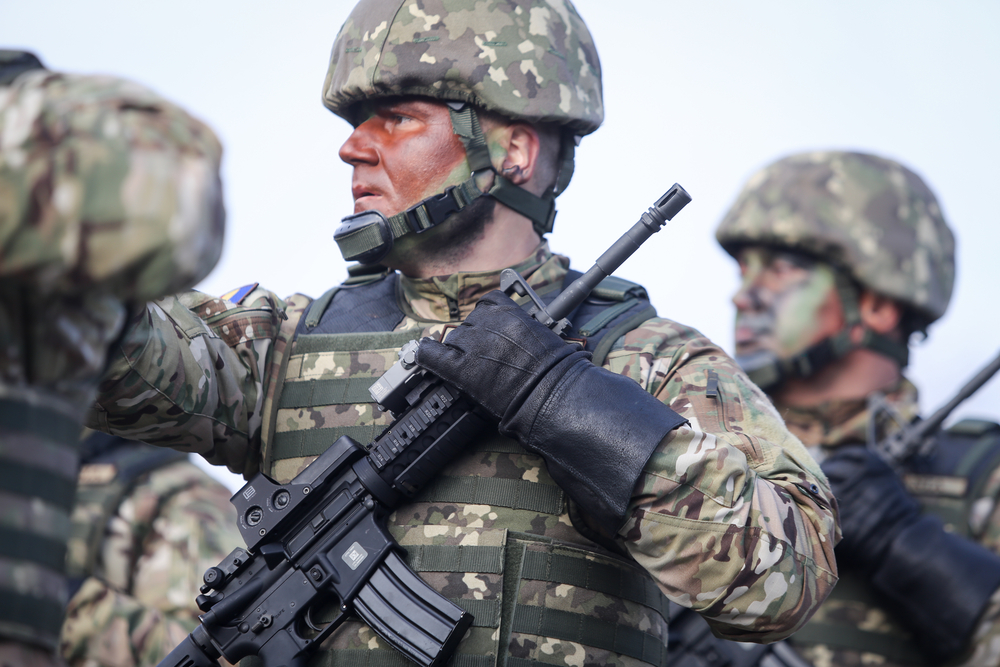
It is important to note that the non-close combat units will continue to carry the M4 and M249 for the foreseeable future. The switch to the 6.8mm cartridge comes as part of the Army's dedication to defeating enemy body armor more effectively and maintaining an edge in lethality and accuracy at increased ranges. Such ammunition advancements not only penetrate hard targets with greater ease but also maintain the capability of reaching and affecting soft targets at extended distances.
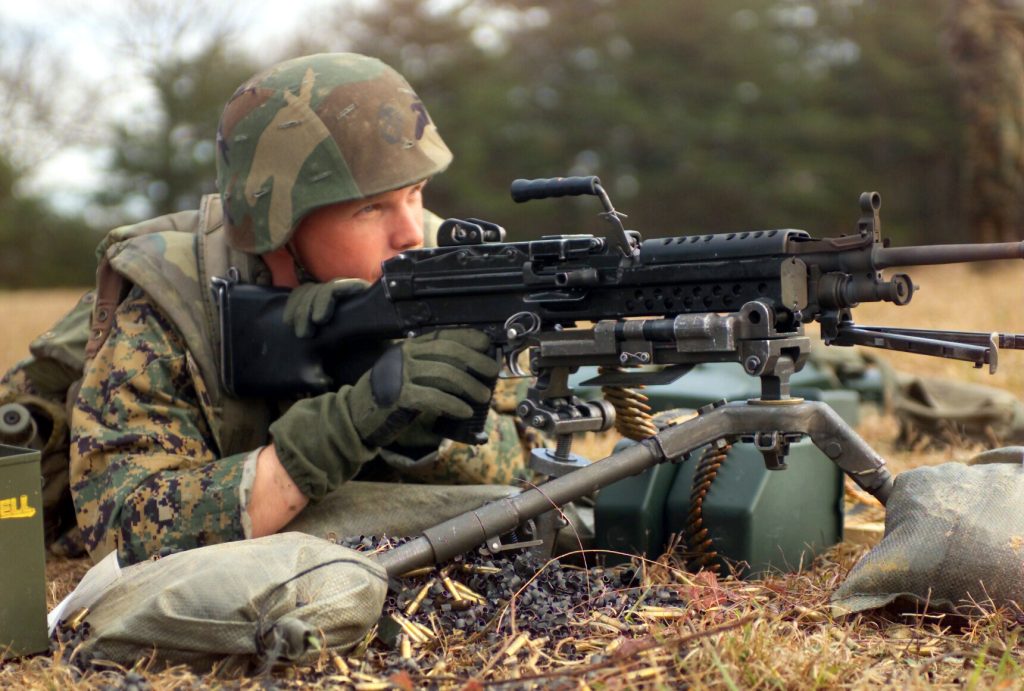

Test demonstrations have illustrated the superior performance of the 6.8mm rounds compared to the existing 5.56mm, particularly in their ability to convert cover into mere concealment for enemy forces. The advanced XM157 optics paired with the new firearms are designed to not only enhance lethality but also maintain the essential fundamentals of marksmanship training.
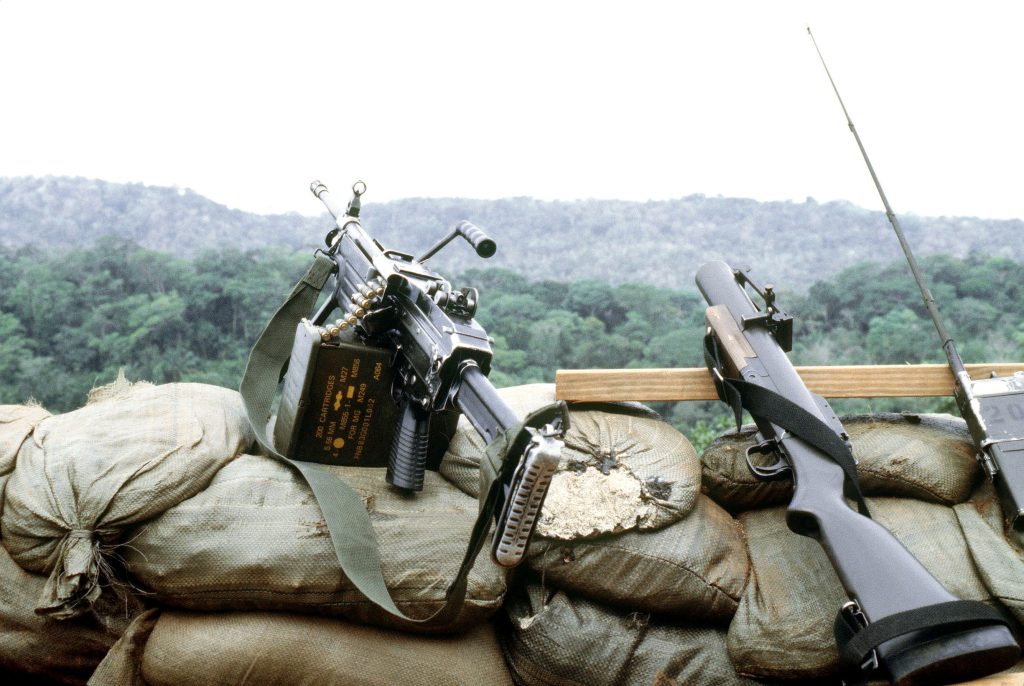

The Army's selection of Sig Sauer for this significant upgrade also reflects the high confidence in the vendor, which was affirmed by rigorous technical tests, including over 1.5 million rounds of 6.8mm ammunition fired and extensive user acceptance assessments by soldiers.

The NGSW program marks a pivotal advancement, as it's the first major replacement of small arms and ammunition in six decades. Soldiers will get a more powerful, accurate, and versatile weapon system, which will transform the dynamics of close combat engagements and potentially alter the infantry's tactical operations.
related images you might be interested.

More for You
Women Are Working Longer Hours From Home Than Men
Naeher penalty heroics as USA win SheBelieves Cup
Conan O'Brien's Return to ‘The Tonight Show' Was Melancholy, Powerful TV
'Joker' pairs up with Gaga as sequel hype hits CinemaCon
Celtics make bizarre history in loss against Bucks as they go entire game without shooting free throw
Monopoly Go: How to Increase Net Worth Faster
D&D Building landlord faces $966 million debt lawsuit, layoffs at MillerKnoll and more
A period piece, a contemporary drama, and a speculative sci-fi movie all in one
Is maple syrup a superfood? What to know about its health benefits
9 Insider Secrets You Should Know From a Goodwill Employee
13 Menu Items McDonald's Employees Refuse To Order
A father with children born via surrogacy rejects the Vatican's view that condemns the practice
$90,000 colleges, the toolbelt generation, and why high schools need a three-track system
These Are The World’s Best Nude Beaches
This type of supplement may increase heart disease risk, new study finds
As bans spread, fluoride in drinking water divides communities across the US
Here's What Happens When You Keep a Car For Over a Decade
I’m a nutritionist from Japan, home to the world’s longest-living people—here are 6 American foods I never eat
Toy Company Launches Life-Sized M3GAN Doll Replica
4-Year-Old Living With One of the Rarest Disorders in the World
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: animatezoo: zero-shot video generation of cross-species animation via subject alignment.
Abstract: Recent video editing advancements rely on accurate pose sequences to animate subjects. However, these efforts are not suitable for cross-species animation due to pose misalignment between species (for example, the poses of a cat differs greatly from that of a pig due to differences in body structure). In this paper, we present AnimateZoo, a zero-shot diffusion-based video generator to address this challenging cross-species animation issue, aiming to accurately produce animal animations while preserving the background. The key technique used in our AnimateZoo is subject alignment, which includes two steps. First, we improve appearance feature extraction by integrating a Laplacian detail booster and a prompt-tuning identity extractor. These components are specifically designed to capture essential appearance information, including identity and fine details. Second, we align shape features and address conflicts from differing subjects by introducing a scale-information remover. This ensures accurate cross-species animation. Moreover, we introduce two high-quality animal video datasets featuring a wide variety of species. Trained on these extensive datasets, our model is capable of generating videos characterized by accurate movements, consistent appearance, and high-fidelity frames, without the need for the pre-inference fine-tuning that prior arts required. Extensive experiments showcase the outstanding performance of our method in cross-species action following tasks, demonstrating exceptional shape adaptation capability. The project page is available at this https URL .
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Third Generation Computers (1964-1971) Fourth Generation Computers (1971-Present) Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Beyond) Generations of Computer. Time-Period. Evolving Hardware. First Generation. 1940s - 1950s. Vacuum Tube Based.
Second-generation computers moved from cryptic binary machine language to symbolic, or assembly, languages, which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words. High-level programming languages were also being developed at this time, such as early versions of COBOL and FORTRAN.
Here are the five generations of computers: First Generation (1940s-1950s): The first computers used vacuum tubes for processing and magnetic drums for storage. They were large, expensive, and unreliable. Second Generation (1950s-1960s): The second generation of computers replaced vacuum tubes with transistors, making them smaller, faster, and ...
Fifth-generation computer technology, based on artificial intelligence, is still in development, though there are some applications, such as voice recognition, that are being used today. The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality.
Generations of computer. The generation of classified into five generations: 1. FIRST GENERATION COMPUTER: Vacuum Tubes (1940-1956) The first generation of computers is characterized by the use of "Vacuum tubes" It was developed in 1904 by the British engineer "John Ambrose Fleming".
The Third Generation, 1964-1979. The third generation officially began in April 1964 with IBM's announcement of its System/360 family of computers. Hardware technology began to use integrated circuits (ICs) which yielded significant advantages in both speed and economy. Operating System development continued with the introduction and ...
The main characteristics of first generation of computers (1940s-1950s) Main electronic component - vacuum tube. Main memory - magnetic drums and magnetic tapes. Programming language - machine language. Power - consume a lot of electricity and generate a lot of heat. Speed and size - very slow and very large in size (often taking up ...
Fifth generation computers are in developmental stage which is based on the artificial intelligence. The goal of the fifth generation is to develop the device which could respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization. Quantum computation and molecular and nanotechnology will be used in this technology.
computer, which gets its power by variable programs, with the ability to calculate rapidly, hold lots of information and even learn. We mark computer generations by the logic technology they're built from. We're currently in the fourth generation, called large scale integrated circuit technology. The first generation began
5 Generations of Computers. Generations of computers have seen changes based on evolving technologies. With each new generation, computer circuitry, size, and parts have been miniaturized, the processing and speed doubled, memory got larger, and usability and reliability improved.
Generations of Computer - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. A simple pdf document about the five generations of computer.
and more powerful and more efficient and reliable devices, characterizes each generation of computer. According to the technology used, there are five generations of computers, which are discussed in the following sections. 1.4.1 FIRST GENERATION (1940-56): VACUUM TUBES First generation computers were vacuum tubes/thermionic valve based machines.
In these computers, primary memory was stored on the magnetic cores and magnetic tape and they used magnetic disks as secondary storage devices. Examples of the second generation computers include IBM 1620, IBM 7094, CDC 1604, CDC 3600, UNIVAC 1108. As a result, they worked on AC and therefore were faster than their predecessors.
In comparison to first generation computers, the second generation computer had the following favorable features. 1. Smaller in size as compared to first generation computers 2. More reliable 3. Less heat generated 4. Faster computational speed Disadvantages: Some unfavorable features can also be seen in this generation. 1. Air conditioning ...
The size of computer is also reduced with the passage of time. Types of Generations of Computers: There are five types of generations of computers which are described below: 1. First Generation Computers (1940-1956): A va cuum-tube compute r, also known as a first - generation computer, uses vacuum. tubes for logi c circuitry.
The Fifth-generation computers are portable and smaller in size. Trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (recognize voice/speech), light scanner, printer, keyboard, monitor, mouse, etc are used as Input/Output devices. Examples of 5th Generation Computers are Desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.
Second generation computers were slow The third generation computer is very fast as compared to the second generation computer. Second generation were of small memory the third generation is large memory as compared to the second generation computer. Comparison of third and forth generation : Third generation Forth generation
The history of computer dated back to the period of scientific revolution (i.e. 1543 - 1678). The calculating machine invented by Blaise Pascal in 1642 and. that of Goffried Liebnits marked the ...
Assignments. pdf. 98 kB Getting Started: Python and IDLE. file. 193 B shapes. file. 3 kB subjects. file. 634 kB words. pdf. 52 kB ... Computer Science. Programming Languages; Download Course. Over 2,500 courses & materials Freely sharing knowledge with learners and educators around the world.
Computer Concepts INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY 3 Fig. 1.1.1: Different Computer Operations Input: A computer accepts data that is provided by means of an input device, such as a keyboard. Processing: A computer performs operations on the data to transform it in some way. Output: A computer produces output on a device, such as a printer or a monitor, that shows
assignment topic: generation of computer submitted to: sir attaulah submitted by: shams ullah roll no: 44 subject: computer science semester: bs 2 nd semester session: 2020-department of political science university of balochistan quetta table of content: 1: introduction 2: history of computer 3: characteristices of computer 4: generations of ...
Generations of Computer •The computer has evolved from a large-sized simple calculating machine to a smaller but much more powerful machine. •The evolution of computer to the current state is defined in terms of the generations of computer. •Each generation of computer is designed based on a new technological development, resulting in better, cheaper and
Functionalities of Computer. Any digital computer performs the following five operations: Step 1 − Accepts data as input. Step 2 − Saves the data/instructions in its memory and utilizes them as and when required. Step 3 − Execute the data and convert it into useful information. Step 4 − Provides the output.
Firefighter Type 1 (FFT1) Helicopter Crewmember (HECM) Incident Commander Type 3 (ICT3) Incident Commander Type 4 (ICT4) Incident Commander Type 5 (ICT5) Intermediate Faller (FAL2) Operations Section Chief Type 3, Wildland Fire (OPS3) Prescribed Fire Burn Boss Type 1 (RXB1) Prescribed Fire Burn Boss Type 2 (RXB2)
The Army has commenced a new chapter in small arms capabilities, choosing Sig Sauer to manufacture the Next Generation Squad Weapon (NGSW), which will significantly enhance the firepower of close ...
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) and IBM officially unveiled the world's first-ever IBM quantum computer on a university campus. Building on RPI's bicentennial celebration of 200 years of firsts, IBM Quantum System One will significantly enhance educational and research opportunities for the university, as well as with other academic institutions and organizations across the New York ...
Photo courtesy of IBM. A former chapel at Troy, New York's Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) is now home to the world's first IBM quantum computer on a college campus. Why it matters: It's an opportunity to start training a new generation of quantum-focused students, researchers and workers, IBM and RPI reps told Axios at Friday's ...
STUTTGART, GERMANY and WATERLOO, CANADA - April 10, 2024 - ETAS GmbH, a leading solution provider for the development of automotive software and BlackBerry QNX, a business unit of BlackBerry Limited (NYSE: BB; TSX: BB), have signed a contract to jointly sell and market software solutions accelerating the development of safety-critical functions for next generation software-defined vehicles ...
Visual Autoregressive Modeling: Scalable Image Generation via Next-Scale Prediction. Keyu Tian, Yi Jiang, Zehuan Yuan, Bingyue Peng, Liwei Wang. We present Visual AutoRegressive modeling (VAR), a new generation paradigm that redefines the autoregressive learning on images as coarse-to-fine "next-scale prediction" or "next-resolution prediction ...
In this paper, we present AnimateZoo, a zero-shot diffusion-based video generator to address this challenging cross-species animation issue, aiming to accurately produce animal animations while preserving the background. The key technique used in our AnimateZoo is subject alignment, which includes two steps. First, we improve appearance feature ...