

1 Introduction to Critical Thinking
I. what is c ritical t hinking [1].
Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally about what to do or what to believe. It includes the ability to engage in reflective and independent thinking. Someone with critical thinking skills is able to do the following:
- Understand the logical connections between ideas.
- Identify, construct, and evaluate arguments.
- Detect inconsistencies and common mistakes in reasoning.
- Solve problems systematically.
- Identify the relevance and importance of ideas.
- Reflect on the justification of one’s own beliefs and values.
Critical thinking is not simply a matter of accumulating information. A person with a good memory and who knows a lot of facts is not necessarily good at critical thinking. Critical thinkers are able to deduce consequences from what they know, make use of information to solve problems, and to seek relevant sources of information to inform themselves.
Critical thinking should not be confused with being argumentative or being critical of other people. Although critical thinking skills can be used in exposing fallacies and bad reasoning, critical thinking can also play an important role in cooperative reasoning and constructive tasks. Critical thinking can help us acquire knowledge, improve our theories, and strengthen arguments. We can also use critical thinking to enhance work processes and improve social institutions.
Some people believe that critical thinking hinders creativity because critical thinking requires following the rules of logic and rationality, whereas creativity might require breaking those rules. This is a misconception. Critical thinking is quite compatible with thinking “out-of-the-box,” challenging consensus views, and pursuing less popular approaches. If anything, critical thinking is an essential part of creativity because we need critical thinking to evaluate and improve our creative ideas.
II. The I mportance of C ritical T hinking
Critical thinking is a domain-general thinking skill. The ability to think clearly and rationally is important whatever we choose to do. If you work in education, research, finance, management or the legal profession, then critical thinking is obviously important. But critical thinking skills are not restricted to a particular subject area. Being able to think well and solve problems systematically is an asset for any career.
Critical thinking is very important in the new knowledge economy. The global knowledge economy is driven by information and technology. One has to be able to deal with changes quickly and effectively. The new economy places increasing demands on flexible intellectual skills, and the ability to analyze information and integrate diverse sources of knowledge in solving problems. Good critical thinking promotes such thinking skills, and is very important in the fast-changing workplace.
Critical thinking enhances language and presentation skills. Thinking clearly and systematically can improve the way we express our ideas. In learning how to analyze the logical structure of texts, critical thinking also improves comprehension abilities.
Critical thinking promotes creativity. To come up with a creative solution to a problem involves not just having new ideas. It must also be the case that the new ideas being generated are useful and relevant to the task at hand. Critical thinking plays a crucial role in evaluating new ideas, selecting the best ones and modifying them if necessary.
Critical thinking is crucial for self-reflection. In order to live a meaningful life and to structure our lives accordingly, we need to justify and reflect on our values and decisions. Critical thinking provides the tools for this process of self-evaluation.
Good critical thinking is the foundation of science and democracy. Science requires the critical use of reason in experimentation and theory confirmation. The proper functioning of a liberal democracy requires citizens who can think critically about social issues to inform their judgments about proper governance and to overcome biases and prejudice.
Critical thinking is a metacognitive skill . What this means is that it is a higher-level cognitive skill that involves thinking about thinking. We have to be aware of the good principles of reasoning, and be reflective about our own reasoning. In addition, we often need to make a conscious effort to improve ourselves, avoid biases, and maintain objectivity. This is notoriously hard to do. We are all able to think but to think well often requires a long period of training. The mastery of critical thinking is similar to the mastery of many other skills. There are three important components: theory, practice, and attitude.
III. Improv ing O ur T hinking S kills
If we want to think correctly, we need to follow the correct rules of reasoning. Knowledge of theory includes knowledge of these rules. These are the basic principles of critical thinking, such as the laws of logic, and the methods of scientific reasoning, etc.
Also, it would be useful to know something about what not to do if we want to reason correctly. This means we should have some basic knowledge of the mistakes that people make. First, this requires some knowledge of typical fallacies. Second, psychologists have discovered persistent biases and limitations in human reasoning. An awareness of these empirical findings will alert us to potential problems.
However, merely knowing the principles that distinguish good and bad reasoning is not enough. We might study in the classroom about how to swim, and learn about the basic theory, such as the fact that one should not breathe underwater. But unless we can apply such theoretical knowledge through constant practice, we might not actually be able to swim.
Similarly, to be good at critical thinking skills it is necessary to internalize the theoretical principles so that we can actually apply them in daily life. There are at least two ways to do this. One is to perform lots of quality exercises. These exercises don’t just include practicing in the classroom or receiving tutorials; they also include engaging in discussions and debates with other people in our daily lives, where the principles of critical thinking can be applied. The second method is to think more deeply about the principles that we have acquired. In the human mind, memory and understanding are acquired through making connections between ideas.
Good critical thinking skills require more than just knowledge and practice. Persistent practice can bring about improvements only if one has the right kind of motivation and attitude. The following attitudes are not uncommon, but they are obstacles to critical thinking:
- I prefer being given the correct answers rather than figuring them out myself.
- I don’t like to think a lot about my decisions as I rely only on gut feelings.
- I don’t usually review the mistakes I have made.
- I don’t like to be criticized.
To improve our thinking we have to recognize the importance of reflecting on the reasons for belief and action. We should also be willing to engage in debate, break old habits, and deal with linguistic complexities and abstract concepts.
The California Critical Thinking Disposition Inventory is a psychological test that is used to measure whether people are disposed to think critically. It measures the seven different thinking habits listed below, and it is useful to ask ourselves to what extent they describe the way we think:
- Truth-Seeking—Do you try to understand how things really are? Are you interested in finding out the truth?
- Open-Mindedness—How receptive are you to new ideas, even when you do not intuitively agree with them? Do you give new concepts a fair hearing?
- Analyticity—Do you try to understand the reasons behind things? Do you act impulsively or do you evaluate the pros and cons of your decisions?
- Systematicity—Are you systematic in your thinking? Do you break down a complex problem into parts?
- Confidence in Reasoning—Do you always defer to other people? How confident are you in your own judgment? Do you have reasons for your confidence? Do you have a way to evaluate your own thinking?
- Inquisitiveness—Are you curious about unfamiliar topics and resolving complicated problems? Will you chase down an answer until you find it?
- Maturity of Judgment—Do you jump to conclusions? Do you try to see things from different perspectives? Do you take other people’s experiences into account?
Finally, as mentioned earlier, psychologists have discovered over the years that human reasoning can be easily affected by a variety of cognitive biases. For example, people tend to be over-confident of their abilities and focus too much on evidence that supports their pre-existing opinions. We should be alert to these biases in our attitudes towards our own thinking.
IV. Defining Critical Thinking
There are many different definitions of critical thinking. Here we list some of the well-known ones. You might notice that they all emphasize the importance of clarity and rationality. Here we will look at some well-known definitions in chronological order.
1) Many people trace the importance of critical thinking in education to the early twentieth-century American philosopher John Dewey. But Dewey did not make very extensive use of the term “critical thinking.” Instead, in his book How We Think (1910), he argued for the importance of what he called “reflective thinking”:
…[when] the ground or basis for a belief is deliberately sought and its adequacy to support the belief examined. This process is called reflective thought; it alone is truly educative in value…
Active, persistent and careful consideration of any belief or supposed form of knowledge in light of the grounds that support it, and the further conclusions to which it tends, constitutes reflective thought.
There is however one passage from How We Think where Dewey explicitly uses the term “critical thinking”:
The essence of critical thinking is suspended judgment; and the essence of this suspense is inquiry to determine the nature of the problem before proceeding to attempts at its solution. This, more than any other thing, transforms mere inference into tested inference, suggested conclusions into proof.
2) The Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (1980) is a well-known psychological test of critical thinking ability. The authors of this test define critical thinking as:
…a composite of attitudes, knowledge and skills. This composite includes: (1) attitudes of inquiry that involve an ability to recognize the existence of problems and an acceptance of the general need for evidence in support of what is asserted to be true; (2) knowledge of the nature of valid inferences, abstractions, and generalizations in which the weight or accuracy of different kinds of evidence are logically determined; and (3) skills in employing and applying the above attitudes and knowledge.
3) A very well-known and influential definition of critical thinking comes from philosopher and professor Robert Ennis in his work “A Taxonomy of Critical Thinking Dispositions and Abilities” (1987):
Critical thinking is reasonable reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe or do.
4) The following definition comes from a statement written in 1987 by the philosophers Michael Scriven and Richard Paul for the National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking (link), an organization promoting critical thinking in the US:
Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action. In its exemplary form, it is based on universal intellectual values that transcend subject matter divisions: clarity, accuracy, precision, consistency, relevance, sound evidence, good reasons, depth, breadth, and fairness. It entails the examination of those structures or elements of thought implicit in all reasoning: purpose, problem, or question-at-issue, assumptions, concepts, empirical grounding; reasoning leading to conclusions, implications and consequences, objections from alternative viewpoints, and frame of reference.
The following excerpt from Peter A. Facione’s “Critical Thinking: A Statement of Expert Consensus for Purposes of Educational Assessment and Instruction” (1990) is quoted from a report written for the American Philosophical Association:
We understand critical thinking to be purposeful, self-regulatory judgment which results in interpretation, analysis, evaluation, and inference, as well as explanation of the evidential, conceptual, methodological, criteriological, or contextual considerations upon which that judgment is based. CT is essential as a tool of inquiry. As such, CT is a liberating force in education and a powerful resource in one’s personal and civic life. While not synonymous with good thinking, CT is a pervasive and self-rectifying human phenomenon. The ideal critical thinker is habitually inquisitive, well-informed, trustful of reason, open-minded, flexible, fairminded in evaluation, honest in facing personal biases, prudent in making judgments, willing to reconsider, clear about issues, orderly in complex matters, diligent in seeking relevant information, reasonable in the selection of criteria, focused in inquiry, and persistent in seeking results which are as precise as the subject and the circumstances of inquiry permit. Thus, educating good critical thinkers means working toward this ideal. It combines developing CT skills with nurturing those dispositions which consistently yield useful insights and which are the basis of a rational and democratic society.
V. Two F eatures of C ritical T hinking
A. how not what .
Critical thinking is concerned not with what you believe, but rather how or why you believe it. Most classes, such as those on biology or chemistry, teach you what to believe about a subject matter. In contrast, critical thinking is not particularly interested in what the world is, in fact, like. Rather, critical thinking will teach you how to form beliefs and how to think. It is interested in the type of reasoning you use when you form your beliefs, and concerns itself with whether you have good reasons to believe what you believe. Therefore, this class isn’t a class on the psychology of reasoning, which brings us to the second important feature of critical thinking.
B. Ought N ot Is ( or Normative N ot Descriptive )
There is a difference between normative and descriptive theories. Descriptive theories, such as those provided by physics, provide a picture of how the world factually behaves and operates. In contrast, normative theories, such as those provided by ethics or political philosophy, provide a picture of how the world should be. Rather than ask question such as why something is the way it is, normative theories ask how something should be. In this course, we will be interested in normative theories that govern our thinking and reasoning. Therefore, we will not be interested in how we actually reason, but rather focus on how we ought to reason.
In the introduction to this course we considered a selection task with cards that must be flipped in order to check the validity of a rule. We noted that many people fail to identify all the cards required to check the rule. This is how people do in fact reason (descriptive). We then noted that you must flip over two cards. This is how people ought to reason (normative).
- Section I-IV are taken from http://philosophy.hku.hk/think/ and are in use under the creative commons license. Some modifications have been made to the original content. ↵
Critical Thinking Copyright © 2019 by Brian Kim is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- LEARNING SKILLS
- Study Skills
- Critical Thinking
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Learning Skills:
- A - Z List of Learning Skills
- What is Learning?
- Learning Approaches
- Learning Styles
- 8 Types of Learning Styles
- Understanding Your Preferences to Aid Learning
- Lifelong Learning
- Decisions to Make Before Applying to University
- Top Tips for Surviving Student Life
- Living Online: Education and Learning
- 8 Ways to Embrace Technology-Based Learning Approaches
Critical Thinking Skills
- Critical Thinking and Fake News
- Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories
- Critical Analysis
- Top Tips for Study
- Staying Motivated When Studying
- Student Budgeting and Economic Skills
- Getting Organised for Study
- Finding Time to Study
- Sources of Information
- Assessing Internet Information
- Using Apps to Support Study
- What is Theory?
- Styles of Writing
- Effective Reading
- Critical Reading
- Note-Taking from Reading
- Note-Taking for Verbal Exchanges
- Planning an Essay
- How to Write an Essay
- The Do’s and Don’ts of Essay Writing
- How to Write a Report
- Academic Referencing
- Assignment Finishing Touches
- Reflecting on Marked Work
- 6 Skills You Learn in School That You Use in Real Life
- Top 10 Tips on How to Study While Working
- Exam Skills
- Writing a Dissertation or Thesis
- Research Methods
- Teaching, Coaching, Mentoring and Counselling
- Employability Skills for Graduates
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally, understanding the logical connection between ideas. Critical thinking has been the subject of much debate and thought since the time of early Greek philosophers such as Plato and Socrates and has continued to be a subject of discussion into the modern age, for example the ability to recognise fake news .
Critical thinking might be described as the ability to engage in reflective and independent thinking.
In essence, critical thinking requires you to use your ability to reason. It is about being an active learner rather than a passive recipient of information.
Critical thinkers rigorously question ideas and assumptions rather than accepting them at face value. They will always seek to determine whether the ideas, arguments and findings represent the entire picture and are open to finding that they do not.
Critical thinkers will identify, analyse and solve problems systematically rather than by intuition or instinct.
Someone with critical thinking skills can:
Understand the links between ideas.
Determine the importance and relevance of arguments and ideas.
Recognise, build and appraise arguments.
Identify inconsistencies and errors in reasoning.
Approach problems in a consistent and systematic way.
Reflect on the justification of their own assumptions, beliefs and values.
Critical thinking is thinking about things in certain ways so as to arrive at the best possible solution in the circumstances that the thinker is aware of. In more everyday language, it is a way of thinking about whatever is presently occupying your mind so that you come to the best possible conclusion.
Critical Thinking is:
A way of thinking about particular things at a particular time; it is not the accumulation of facts and knowledge or something that you can learn once and then use in that form forever, such as the nine times table you learn and use in school.
The Skills We Need for Critical Thinking
The skills that we need in order to be able to think critically are varied and include observation, analysis, interpretation, reflection, evaluation, inference, explanation, problem solving, and decision making.
Specifically we need to be able to:
Think about a topic or issue in an objective and critical way.
Identify the different arguments there are in relation to a particular issue.
Evaluate a point of view to determine how strong or valid it is.
Recognise any weaknesses or negative points that there are in the evidence or argument.
Notice what implications there might be behind a statement or argument.
Provide structured reasoning and support for an argument that we wish to make.
The Critical Thinking Process
You should be aware that none of us think critically all the time.
Sometimes we think in almost any way but critically, for example when our self-control is affected by anger, grief or joy or when we are feeling just plain ‘bloody minded’.
On the other hand, the good news is that, since our critical thinking ability varies according to our current mindset, most of the time we can learn to improve our critical thinking ability by developing certain routine activities and applying them to all problems that present themselves.
Once you understand the theory of critical thinking, improving your critical thinking skills takes persistence and practice.
Try this simple exercise to help you to start thinking critically.
Think of something that someone has recently told you. Then ask yourself the following questions:
Who said it?
Someone you know? Someone in a position of authority or power? Does it matter who told you this?
What did they say?
Did they give facts or opinions? Did they provide all the facts? Did they leave anything out?
Where did they say it?
Was it in public or in private? Did other people have a chance to respond an provide an alternative account?
When did they say it?
Was it before, during or after an important event? Is timing important?
Why did they say it?
Did they explain the reasoning behind their opinion? Were they trying to make someone look good or bad?
How did they say it?
Were they happy or sad, angry or indifferent? Did they write it or say it? Could you understand what was said?
What are you Aiming to Achieve?
One of the most important aspects of critical thinking is to decide what you are aiming to achieve and then make a decision based on a range of possibilities.
Once you have clarified that aim for yourself you should use it as the starting point in all future situations requiring thought and, possibly, further decision making. Where needed, make your workmates, family or those around you aware of your intention to pursue this goal. You must then discipline yourself to keep on track until changing circumstances mean you have to revisit the start of the decision making process.
However, there are things that get in the way of simple decision making. We all carry with us a range of likes and dislikes, learnt behaviours and personal preferences developed throughout our lives; they are the hallmarks of being human. A major contribution to ensuring we think critically is to be aware of these personal characteristics, preferences and biases and make allowance for them when considering possible next steps, whether they are at the pre-action consideration stage or as part of a rethink caused by unexpected or unforeseen impediments to continued progress.
The more clearly we are aware of ourselves, our strengths and weaknesses, the more likely our critical thinking will be productive.
The Benefit of Foresight
Perhaps the most important element of thinking critically is foresight.
Almost all decisions we make and implement don’t prove disastrous if we find reasons to abandon them. However, our decision making will be infinitely better and more likely to lead to success if, when we reach a tentative conclusion, we pause and consider the impact on the people and activities around us.
The elements needing consideration are generally numerous and varied. In many cases, consideration of one element from a different perspective will reveal potential dangers in pursuing our decision.
For instance, moving a business activity to a new location may improve potential output considerably but it may also lead to the loss of skilled workers if the distance moved is too great. Which of these is the more important consideration? Is there some way of lessening the conflict?
These are the sort of problems that may arise from incomplete critical thinking, a demonstration perhaps of the critical importance of good critical thinking.
Further Reading from Skills You Need

The Skills You Need Guide for Students

Develop the skills you need to make the most of your time as a student.
Our eBooks are ideal for students at all stages of education, school, college and university. They are full of easy-to-follow practical information that will help you to learn more effectively and get better grades.
In Summary:
Critical thinking is aimed at achieving the best possible outcomes in any situation. In order to achieve this it must involve gathering and evaluating information from as many different sources possible.
Critical thinking requires a clear, often uncomfortable, assessment of your personal strengths, weaknesses and preferences and their possible impact on decisions you may make.
Critical thinking requires the development and use of foresight as far as this is possible. As Doris Day sang, “the future’s not ours to see”.
Implementing the decisions made arising from critical thinking must take into account an assessment of possible outcomes and ways of avoiding potentially negative outcomes, or at least lessening their impact.
- Critical thinking involves reviewing the results of the application of decisions made and implementing change where possible.
It might be thought that we are overextending our demands on critical thinking in expecting that it can help to construct focused meaning rather than examining the information given and the knowledge we have acquired to see if we can, if necessary, construct a meaning that will be acceptable and useful.
After all, almost no information we have available to us, either externally or internally, carries any guarantee of its life or appropriateness. Neat step-by-step instructions may provide some sort of trellis on which our basic understanding of critical thinking can blossom but it doesn’t and cannot provide any assurance of certainty, utility or longevity.
Continue to: Critical Thinking and Fake News Critical Reading
See also: Analytical Skills Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories Introduction to Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP)

- Schools & departments

Critical thinking
Advice and resources to help you develop your critical voice.
Developing critical thinking skills is essential to your success at University and beyond. We all need to be critical thinkers to help us navigate our way through an information-rich world.
Whatever your discipline, you will engage with a wide variety of sources of information and evidence. You will develop the skills to make judgements about this evidence to form your own views and to present your views clearly.
One of the most common types of feedback received by students is that their work is ‘too descriptive’. This usually means that they have just stated what others have said and have not reflected critically on the material. They have not evaluated the evidence and constructed an argument.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the art of making clear, reasoned judgements based on interpreting, understanding, applying and synthesising evidence gathered from observation, reading and experimentation. Burns, T., & Sinfield, S. (2016) Essential Study Skills: The Complete Guide to Success at University (4th ed.) London: SAGE, p94.
Being critical does not just mean finding fault. It means assessing evidence from a variety of sources and making reasoned conclusions. As a result of your analysis you may decide that a particular piece of evidence is not robust, or that you disagree with the conclusion, but you should be able to state why you have come to this view and incorporate this into a bigger picture of the literature.
Being critical goes beyond describing what you have heard in lectures or what you have read. It involves synthesising, analysing and evaluating what you have learned to develop your own argument or position.
Critical thinking is important in all subjects and disciplines – in science and engineering, as well as the arts and humanities. The types of evidence used to develop arguments may be very different but the processes and techniques are similar. Critical thinking is required for both undergraduate and postgraduate levels of study.
What, where, when, who, why, how?
Purposeful reading can help with critical thinking because it encourages you to read actively rather than passively. When you read, ask yourself questions about what you are reading and make notes to record your views. Ask questions like:
- What is the main point of this paper/ article/ paragraph/ report/ blog?
- Who wrote it?
- Why was it written?
- When was it written?
- Has the context changed since it was written?
- Is the evidence presented robust?
- How did the authors come to their conclusions?
- Do you agree with the conclusions?
- What does this add to our knowledge?
- Why is it useful?
Our web page covering Reading at university includes a handout to help you develop your own critical reading form and a suggested reading notes record sheet. These resources will help you record your thoughts after you read, which will help you to construct your argument.
Reading at university
Developing an argument
Being a university student is about learning how to think, not what to think. Critical thinking shapes your own values and attitudes through a process of deliberating, debating and persuasion. Through developing your critical thinking you can move on from simply disagreeing to constructively assessing alternatives by building on doubts.
There are several key stages involved in developing your ideas and constructing an argument. You might like to use a form to help you think about the features of critical thinking and to break down the stages of developing your argument.
Features of critical thinking (pdf)
Features of critical thinking (Word rtf)
Our webpage on Academic writing includes a useful handout ‘Building an argument as you go’.
Academic writing
You should also consider the language you will use to introduce a range of viewpoints and to evaluate the various sources of evidence. This will help your reader to follow your argument. To get you started, the University of Manchester's Academic Phrasebank has a useful section on Being Critical.
Academic Phrasebank
Developing your critical thinking
Set yourself some tasks to help develop your critical thinking skills. Discuss material presented in lectures or from resource lists with your peers. Set up a critical reading group or use an online discussion forum. Think about a point you would like to make during discussions in tutorials and be prepared to back up your argument with evidence.
For more suggestions:
Developing your critical thinking - ideas (pdf)
Developing your critical thinking - ideas (Word rtf)
Published guides
For further advice and more detailed resources please see the Critical Thinking section of our list of published Study skills guides.
Study skills guides
This article was published on 2024-02-26
- Our Mission
Helping Students Hone Their Critical Thinking Skills
Used consistently, these strategies can help middle and high school teachers guide students to improve much-needed skills.

Critical thinking skills are important in every discipline, at and beyond school. From managing money to choosing which candidates to vote for in elections to making difficult career choices, students need to be prepared to take in, synthesize, and act on new information in a world that is constantly changing.
While critical thinking might seem like an abstract idea that is tough to directly instruct, there are many engaging ways to help students strengthen these skills through active learning.
Make Time for Metacognitive Reflection
Create space for students to both reflect on their ideas and discuss the power of doing so. Show students how they can push back on their own thinking to analyze and question their assumptions. Students might ask themselves, “Why is this the best answer? What information supports my answer? What might someone with a counterargument say?”
Through this reflection, students and teachers (who can model reflecting on their own thinking) gain deeper understandings of their ideas and do a better job articulating their beliefs. In a world that is go-go-go, it is important to help students understand that it is OK to take a breath and think about their ideas before putting them out into the world. And taking time for reflection helps us more thoughtfully consider others’ ideas, too.
Teach Reasoning Skills
Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
One way to teach reasoning is to use problem-solving activities that require students to apply their skills to practical contexts. For example, give students a real problem to solve, and ask them to use reasoning skills to develop a solution. They can then present their solution and defend their reasoning to the class and engage in discussion about whether and how their thinking changed when listening to peers’ perspectives.
A great example I have seen involved students identifying an underutilized part of their school and creating a presentation about one way to redesign it. This project allowed students to feel a sense of connection to the problem and come up with creative solutions that could help others at school. For more examples, you might visit PBS’s Design Squad , a resource that brings to life real-world problem-solving.
Ask Open-Ended Questions
Moving beyond the repetition of facts, critical thinking requires students to take positions and explain their beliefs through research, evidence, and explanations of credibility.
When we pose open-ended questions, we create space for classroom discourse inclusive of diverse, perhaps opposing, ideas—grounds for rich exchanges that support deep thinking and analysis.
For example, “How would you approach the problem?” and “Where might you look to find resources to address this issue?” are two open-ended questions that position students to think less about the “right” answer and more about the variety of solutions that might already exist.
Journaling, whether digitally or physically in a notebook, is another great way to have students answer these open-ended prompts—giving them time to think and organize their thoughts before contributing to a conversation, which can ensure that more voices are heard.
Once students process in their journal, small group or whole class conversations help bring their ideas to life. Discovering similarities between answers helps reveal to students that they are not alone, which can encourage future participation in constructive civil discourse.
Teach Information Literacy
Education has moved far past the idea of “Be careful of what is on Wikipedia, because it might not be true.” With AI innovations making their way into classrooms, teachers know that informed readers must question everything.
Understanding what is and is not a reliable source and knowing how to vet information are important skills for students to build and utilize when making informed decisions. You might start by introducing the idea of bias: Articles, ads, memes, videos, and every other form of media can push an agenda that students may not see on the surface. Discuss credibility, subjectivity, and objectivity, and look at examples and nonexamples of trusted information to prepare students to be well-informed members of a democracy.
One of my favorite lessons is about the Pacific Northwest tree octopus . This project asks students to explore what appears to be a very real website that provides information on this supposedly endangered animal. It is a wonderful, albeit over-the-top, example of how something might look official even when untrue, revealing that we need critical thinking to break down “facts” and determine the validity of the information we consume.
A fun extension is to have students come up with their own website or newsletter about something going on in school that is untrue. Perhaps a change in dress code that requires everyone to wear their clothes inside out or a change to the lunch menu that will require students to eat brussels sprouts every day.
Giving students the ability to create their own falsified information can help them better identify it in other contexts. Understanding that information can be “too good to be true” can help them identify future falsehoods.
Provide Diverse Perspectives
Consider how to keep the classroom from becoming an echo chamber. If students come from the same community, they may have similar perspectives. And those who have differing perspectives may not feel comfortable sharing them in the face of an opposing majority.
To support varying viewpoints, bring diverse voices into the classroom as much as possible, especially when discussing current events. Use primary sources: videos from YouTube, essays and articles written by people who experienced current events firsthand, documentaries that dive deeply into topics that require some nuance, and any other resources that provide a varied look at topics.
I like to use the Smithsonian “OurStory” page , which shares a wide variety of stories from people in the United States. The page on Japanese American internment camps is very powerful because of its first-person perspectives.
Practice Makes Perfect
To make the above strategies and thinking routines a consistent part of your classroom, spread them out—and build upon them—over the course of the school year. You might challenge students with information and/or examples that require them to use their critical thinking skills; work these skills explicitly into lessons, projects, rubrics, and self-assessments; or have students practice identifying misinformation or unsupported arguments.
Critical thinking is not learned in isolation. It needs to be explored in English language arts, social studies, science, physical education, math. Every discipline requires students to take a careful look at something and find the best solution. Often, these skills are taken for granted, viewed as a by-product of a good education, but true critical thinking doesn’t just happen. It requires consistency and commitment.
In a moment when information and misinformation abound, and students must parse reams of information, it is imperative that we support and model critical thinking in the classroom to support the development of well-informed citizens.

Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking
(10 reviews)
Matthew Van Cleave, Lansing Community College
Copyright Year: 2016
Publisher: Matthew J. Van Cleave
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by "yusef" Alexander Hayes, Professor, North Shore Community College on 6/9/21
Formal and informal reasoning, argument structure, and fallacies are covered comprehensively, meeting the author's goal of both depth and succinctness. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
Formal and informal reasoning, argument structure, and fallacies are covered comprehensively, meeting the author's goal of both depth and succinctness.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The book is accurate.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
While many modern examples are used, and they are helpful, they are not necessarily needed. The usefulness of logical principles and skills have proved themselves, and this text presents them clearly with many examples.
Clarity rating: 5
It is obvious that the author cares about their subject, audience, and students. The text is comprehensible and interesting.
Consistency rating: 5
The format is easy to understand and is consistent in framing.
Modularity rating: 5
This text would be easy to adapt.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The organization is excellent, my one suggestion would be a concluding chapter.
Interface rating: 5
I accessed the PDF version and it would be easy to work with.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
The writing is excellent.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This is not an offensive text.
Reviewed by Susan Rottmann, Part-time Lecturer, University of Southern Maine on 3/2/21
I reviewed this book for a course titled "Creative and Critical Inquiry into Modern Life." It won't meet all my needs for that course, but I haven't yet found a book that would. I wanted to review this one because it states in the preface that it... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
I reviewed this book for a course titled "Creative and Critical Inquiry into Modern Life." It won't meet all my needs for that course, but I haven't yet found a book that would. I wanted to review this one because it states in the preface that it fits better for a general critical thinking course than for a true logic course. I'm not sure that I'd agree. I have been using Browne and Keeley's "Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking," and I think that book is a better introduction to critical thinking for non-philosophy majors. However, the latter is not open source so I will figure out how to get by without it in the future. Overall, the book seems comprehensive if the subject is logic. The index is on the short-side, but fine. However, one issue for me is that there are no page numbers on the table of contents, which is pretty annoying if you want to locate particular sections.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
I didn't find any errors. In general the book uses great examples. However, they are very much based in the American context, not for an international student audience. Some effort to broaden the chosen examples would make the book more widely applicable.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
I think the book will remain relevant because of the nature of the material that it addresses, however there will be a need to modify the examples in future editions and as the social and political context changes.
Clarity rating: 3
The text is lucid, but I think it would be difficult for introductory-level students who are not philosophy majors. For example, in Browne and Keeley's "Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking," the sub-headings are very accessible, such as "Experts cannot rescue us, despite what they say" or "wishful thinking: perhaps the biggest single speed bump on the road to critical thinking." By contrast, Van Cleave's "Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking" has more subheadings like this: "Using your own paraphrases of premises and conclusions to reconstruct arguments in standard form" or "Propositional logic and the four basic truth functional connectives." If students are prepared very well for the subject, it would work fine, but for students who are newly being introduced to critical thinking, it is rather technical.
It seems to be very consistent in terms of its terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 4
The book is divided into 4 chapters, each having many sub-chapters. In that sense, it is readily divisible and modular. However, as noted above, there are no page numbers on the table of contents, which would make assigning certain parts rather frustrating. Also, I'm not sure why the book is only four chapter and has so many subheadings (for instance 17 in Chapter 2) and a length of 242 pages. Wouldn't it make more sense to break up the book into shorter chapters? I think this would make it easier to read and to assign in specific blocks to students.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The organization of the book is fine overall, although I think adding page numbers to the table of contents and breaking it up into more separate chapters would help it to be more easily navigable.
Interface rating: 4
The book is very simply presented. In my opinion it is actually too simple. There are few boxes or diagrams that highlight and explain important points.
The text seems fine grammatically. I didn't notice any errors.
The book is written with an American audience in mind, but I did not notice culturally insensitive or offensive parts.
Overall, this book is not for my course, but I think it could work well in a philosophy course.
Reviewed by Daniel Lee, Assistant Professor of Economics and Leadership, Sweet Briar College on 11/11/19
This textbook is not particularly comprehensive (4 chapters long), but I view that as a benefit. In fact, I recommend it for use outside of traditional logic classes, but rather interdisciplinary classes that evaluate argument read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
This textbook is not particularly comprehensive (4 chapters long), but I view that as a benefit. In fact, I recommend it for use outside of traditional logic classes, but rather interdisciplinary classes that evaluate argument
To the best of my ability, I regard this content as accurate, error-free, and unbiased
The book is broadly relevant and up-to-date, with a few stray temporal references (sydney olympics, particular presidencies). I don't view these time-dated examples as problematic as the logical underpinnings are still there and easily assessed
Clarity rating: 4
My only pushback on clarity is I didn't find the distinction between argument and explanation particularly helpful/useful/easy to follow. However, this experience may have been unique to my class.
To the best of my ability, I regard this content as internally consistent
I found this text quite modular, and was easily able to integrate other texts into my lessons and disregard certain chapters or sub-sections
The book had a logical and consistent structure, but to the extent that there are only 4 chapters, there isn't much scope for alternative approaches here
No problems with the book's interface
The text is grammatically sound
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
Perhaps the text could have been more universal in its approach. While I didn't find the book insensitive per-se, logic can be tricky here because the point is to evaluate meaningful (non-trivial) arguments, but any argument with that sense of gravity can also be traumatic to students (abortion, death penalty, etc)
No additional comments
Reviewed by Lisa N. Thomas-Smith, Graduate Part-time Instructor, CU Boulder on 7/1/19
The text covers all the relevant technical aspects of introductory logic and critical thinking, and covers them well. A separate glossary would be quite helpful to students. However, the terms are clearly and thoroughly explained within the text,... read more
The text covers all the relevant technical aspects of introductory logic and critical thinking, and covers them well. A separate glossary would be quite helpful to students. However, the terms are clearly and thoroughly explained within the text, and the index is very thorough.
The content is excellent. The text is thorough and accurate with no errors that I could discern. The terminology and exercises cover the material nicely and without bias.
The text should easily stand the test of time. The exercises are excellent and would be very helpful for students to internalize correct critical thinking practices. Because of the logical arrangement of the text and the many sub-sections, additional material should be very easy to add.
The text is extremely clearly and simply written. I anticipate that a diligent student could learn all of the material in the text with little additional instruction. The examples are relevant and easy to follow.
The text did not confuse terms or use inconsistent terminology, which is very important in a logic text. The discipline often uses multiple terms for the same concept, but this text avoids that trap nicely.
The text is fairly easily divisible. Since there are only four chapters, those chapters include large blocks of information. However, the chapters themselves are very well delineated and could be easily broken up so that parts could be left out or covered in a different order from the text.
The flow of the text is excellent. All of the information is handled solidly in an order that allows the student to build on the information previously covered.
The PDF Table of Contents does not include links or page numbers which would be very helpful for navigation. Other than that, the text was very easy to navigate. All the images, charts, and graphs were very clear
I found no grammatical errors in the text.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
The text including examples and exercises did not seem to be offensive or insensitive in any specific way. However, the examples included references to black and white people, but few others. Also, the text is very American specific with many examples from and for an American audience. More diversity, especially in the examples, would be appropriate and appreciated.
Reviewed by Leslie Aarons, Associate Professor of Philosophy, CUNY LaGuardia Community College on 5/16/19
This is an excellent introductory (first-year) Logic and Critical Thinking textbook. The book covers the important elementary information, clearly discussing such things as the purpose and basic structure of an argument; the difference between an... read more
This is an excellent introductory (first-year) Logic and Critical Thinking textbook. The book covers the important elementary information, clearly discussing such things as the purpose and basic structure of an argument; the difference between an argument and an explanation; validity; soundness; and the distinctions between an inductive and a deductive argument in accessible terms in the first chapter. It also does a good job introducing and discussing informal fallacies (Chapter 4). The incorporation of opportunities to evaluate real-world arguments is also very effective. Chapter 2 also covers a number of formal methods of evaluating arguments, such as Venn Diagrams and Propositional logic and the four basic truth functional connectives, but to my mind, it is much more thorough in its treatment of Informal Logic and Critical Thinking skills, than it is of formal logic. I also appreciated that Van Cleave’s book includes exercises with answers and an index, but there is no glossary; which I personally do not find detracts from the book's comprehensiveness.
Overall, Van Cleave's book is error-free and unbiased. The language used is accessible and engaging. There were no glaring inaccuracies that I was able to detect.
Van Cleave's Textbook uses relevant, contemporary content that will stand the test of time, at least for the next few years. Although some examples use certain subjects like former President Obama, it does so in a useful manner that inspires the use of critical thinking skills. There are an abundance of examples that inspire students to look at issues from many different political viewpoints, challenging students to practice evaluating arguments, and identifying fallacies. Many of these exercises encourage students to critique issues, and recognize their own inherent reader-biases and challenge their own beliefs--hallmarks of critical thinking.
As mentioned previously, the author has an accessible style that makes the content relatively easy to read and engaging. He also does a suitable job explaining jargon/technical language that is introduced in the textbook.
Van Cleave uses terminology consistently and the chapters flow well. The textbook orients the reader by offering effective introductions to new material, step-by-step explanations of the material, as well as offering clear summaries of each lesson.
This textbook's modularity is really quite good. Its language and structure are not overly convoluted or too-lengthy, making it convenient for individual instructors to adapt the materials to suit their methodological preferences.
The topics in the textbook are presented in a logical and clear fashion. The structure of the chapters are such that it is not necessary to have to follow the chapters in their sequential order, and coverage of material can be adapted to individual instructor's preferences.
The textbook is free of any problematic interface issues. Topics, sections and specific content are accessible and easy to navigate. Overall it is user-friendly.
I did not find any significant grammatical issues with the textbook.
The textbook is not culturally insensitive, making use of a diversity of inclusive examples. Materials are especially effective for first-year critical thinking/logic students.
I intend to adopt Van Cleave's textbook for a Critical Thinking class I am teaching at the Community College level. I believe that it will help me facilitate student-learning, and will be a good resource to build additional classroom activities from the materials it provides.
Reviewed by Jennie Harrop, Chair, Department of Professional Studies, George Fox University on 3/27/18
While the book is admirably comprehensive, its extensive details within a few short chapters may feel overwhelming to students. The author tackles an impressive breadth of concepts in Chapter 1, 2, 3, and 4, which leads to 50-plus-page chapters... read more
While the book is admirably comprehensive, its extensive details within a few short chapters may feel overwhelming to students. The author tackles an impressive breadth of concepts in Chapter 1, 2, 3, and 4, which leads to 50-plus-page chapters that are dense with statistical analyses and critical vocabulary. These topics are likely better broached in manageable snippets rather than hefty single chapters.
The ideas addressed in Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking are accurate but at times notably political. While politics are effectively used to exemplify key concepts, some students may be distracted by distinct political leanings.
The terms and definitions included are relevant, but the examples are specific to the current political, cultural, and social climates, which could make the materials seem dated in a few years without intentional and consistent updates.
While the reasoning is accurate, the author tends to complicate rather than simplify -- perhaps in an effort to cover a spectrum of related concepts. Beginning readers are likely to be overwhelmed and under-encouraged by his approach.
Consistency rating: 3
The four chapters are somewhat consistent in their play of definition, explanation, and example, but the structure of each chapter varies according to the concepts covered. In the third chapter, for example, key ideas are divided into sub-topics numbering from 3.1 to 3.10. In the fourth chapter, the sub-divisions are further divided into sub-sections numbered 4.1.1-4.1.5, 4.2.1-4.2.2, and 4.3.1 to 4.3.6. Readers who are working quickly to master new concepts may find themselves mired in similarly numbered subheadings, longing for a grounded concepts on which to hinge other key principles.
Modularity rating: 3
The book's four chapters make it mostly self-referential. The author would do well to beak this text down into additional subsections, easing readers' accessibility.
The content of the book flows logically and well, but the information needs to be better sub-divided within each larger chapter, easing the student experience.
The book's interface is effective, allowing readers to move from one section to the next with a single click. Additional sub-sections would ease this interplay even further.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
Some minor errors throughout.
For the most part, the book is culturally neutral, avoiding direct cultural references in an effort to remain relevant.
Reviewed by Yoichi Ishida, Assistant Professor of Philosophy, Ohio University on 2/1/18
This textbook covers enough topics for a first-year course on logic and critical thinking. Chapter 1 covers the basics as in any standard textbook in this area. Chapter 2 covers propositional logic and categorical logic. In propositional logic,... read more
This textbook covers enough topics for a first-year course on logic and critical thinking. Chapter 1 covers the basics as in any standard textbook in this area. Chapter 2 covers propositional logic and categorical logic. In propositional logic, this textbook does not cover suppositional arguments, such as conditional proof and reductio ad absurdum. But other standard argument forms are covered. Chapter 3 covers inductive logic, and here this textbook introduces probability and its relationship with cognitive biases, which are rarely discussed in other textbooks. Chapter 4 introduces common informal fallacies. The answers to all the exercises are given at the end. However, the last set of exercises is in Chapter 3, Section 5. There are no exercises in the rest of the chapter. Chapter 4 has no exercises either. There is index, but no glossary.
The textbook is accurate.
The content of this textbook will not become obsolete soon.
The textbook is written clearly.
The textbook is internally consistent.
The textbook is fairly modular. For example, Chapter 3, together with a few sections from Chapter 1, can be used as a short introduction to inductive logic.
The textbook is well-organized.
There are no interface issues.
I did not find any grammatical errors.
This textbook is relevant to a first semester logic or critical thinking course.
Reviewed by Payal Doctor, Associate Professro, LaGuardia Community College on 2/1/18
This text is a beginner textbook for arguments and propositional logic. It covers the basics of identifying arguments, building arguments, and using basic logic to construct propositions and arguments. It is quite comprehensive for a beginner... read more
This text is a beginner textbook for arguments and propositional logic. It covers the basics of identifying arguments, building arguments, and using basic logic to construct propositions and arguments. It is quite comprehensive for a beginner book, but seems to be a good text for a course that needs a foundation for arguments. There are exercises on creating truth tables and proofs, so it could work as a logic primer in short sessions or with the addition of other course content.
The books is accurate in the information it presents. It does not contain errors and is unbiased. It covers the essential vocabulary clearly and givens ample examples and exercises to ensure the student understands the concepts
The content of the book is up to date and can be easily updated. Some examples are very current for analyzing the argument structure in a speech, but for this sort of text understandable examples are important and the author uses good examples.
The book is clear and easy to read. In particular, this is a good text for community college students who often have difficulty with reading comprehension. The language is straightforward and concepts are well explained.
The book is consistent in terminology, formatting, and examples. It flows well from one topic to the next, but it is also possible to jump around the text without loosing the voice of the text.
The books is broken down into sub units that make it easy to assign short blocks of content at a time. Later in the text, it does refer to a few concepts that appear early in that text, but these are all basic concepts that must be used to create a clear and understandable text. No sections are too long and each section stays on topic and relates the topic to those that have come before when necessary.
The flow of the text is logical and clear. It begins with the basic building blocks of arguments, and practice identifying more and more complex arguments is offered. Each chapter builds up from the previous chapter in introducing propositional logic, truth tables, and logical arguments. A select number of fallacies are presented at the end of the text, but these are related to topics that were presented before, so it makes sense to have these last.
The text is free if interface issues. I used the PDF and it worked fine on various devices without loosing formatting.
1. The book contains no grammatical errors.
The text is culturally sensitive, but examples used are a bit odd and may be objectionable to some students. For instance, President Obama's speech on Syria is used to evaluate an extended argument. This is an excellent example and it is explained well, but some who disagree with Obama's policies may have trouble moving beyond their own politics. However, other examples look at issues from all political viewpoints and ask students to evaluate the argument, fallacy, etc. and work towards looking past their own beliefs. Overall this book does use a variety of examples that most students can understand and evaluate.
My favorite part of this book is that it seems to be written for community college students. My students have trouble understanding readings in the New York Times, so it is nice to see a logic and critical thinking text use real language that students can understand and follow without the constant need of a dictionary.
Reviewed by Rebecca Owen, Adjunct Professor, Writing, Chemeketa Community College on 6/20/17
This textbook is quite thorough--there are conversational explanations of argument structure and logic. I think students will be happy with the conversational style this author employs. Also, there are many examples and exercises using current... read more
This textbook is quite thorough--there are conversational explanations of argument structure and logic. I think students will be happy with the conversational style this author employs. Also, there are many examples and exercises using current events, funny scenarios, or other interesting ways to evaluate argument structure and validity. The third section, which deals with logical fallacies, is very clear and comprehensive. My only critique of the material included in the book is that the middle section may be a bit dense and math-oriented for learners who appreciate the more informal, informative style of the first and third section. Also, the book ends rather abruptly--it moves from a description of a logical fallacy to the answers for the exercises earlier in the text.
The content is very reader-friendly, and the author writes with authority and clarity throughout the text. There are a few surface-level typos (Starbuck's instead of Starbucks, etc.). None of these small errors detract from the quality of the content, though.
One thing I really liked about this text was the author's wide variety of examples. To demonstrate different facets of logic, he used examples from current media, movies, literature, and many other concepts that students would recognize from their daily lives. The exercises in this text also included these types of pop-culture references, and I think students will enjoy the familiarity--as well as being able to see the logical structures behind these types of references. I don't think the text will need to be updated to reflect new instances and occurrences; the author did a fine job at picking examples that are relatively timeless. As far as the subject matter itself, I don't think it will become obsolete any time soon.
The author writes in a very conversational, easy-to-read manner. The examples used are quite helpful. The third section on logical fallacies is quite easy to read, follow, and understand. A student in an argument writing class could benefit from this section of the book. The middle section is less clear, though. A student learning about the basics of logic might have a hard time digesting all of the information contained in chapter two. This material might be better in two separate chapters. I think the author loses the balance of a conversational, helpful tone and focuses too heavily on equations.
Consistency rating: 4
Terminology in this book is quite consistent--the key words are highlighted in bold. Chapters 1 and 3 follow a similar organizational pattern, but chapter 2 is where the material becomes more dense and equation-heavy. I also would have liked a closing passage--something to indicate to the reader that we've reached the end of the chapter as well as the book.
I liked the overall structure of this book. If I'm teaching an argumentative writing class, I could easily point the students to the chapters where they can identify and practice identifying fallacies, for instance. The opening chapter is clear in defining the necessary terms, and it gives the students an understanding of the toolbox available to them in assessing and evaluating arguments. Even though I found the middle section to be dense, smaller portions could be assigned.
The author does a fine job connecting each defined term to the next. He provides examples of how each defined term works in a sentence or in an argument, and then he provides practice activities for students to try. The answers for each question are listed in the final pages of the book. The middle section feels like the heaviest part of the whole book--it would take the longest time for a student to digest if assigned the whole chapter. Even though this middle section is a bit heavy, it does fit the overall structure and flow of the book. New material builds on previous chapters and sub-chapters. It ends abruptly--I didn't realize that it had ended, and all of a sudden I found myself in the answer section for those earlier exercises.
The simple layout is quite helpful! There is nothing distracting, image-wise, in this text. The table of contents is clearly arranged, and each topic is easy to find.
Tiny edits could be made (Starbuck's/Starbucks, for one). Otherwise, it is free of distracting grammatical errors.
This text is quite culturally relevant. For instance, there is one example that mentions the rumors of Barack Obama's birthplace as somewhere other than the United States. This example is used to explain how to analyze an argument for validity. The more "sensational" examples (like the Obama one above) are helpful in showing argument structure, and they can also help students see how rumors like this might gain traction--as well as help to show students how to debunk them with their newfound understanding of argument and logic.
The writing style is excellent for the subject matter, especially in the third section explaining logical fallacies. Thank you for the opportunity to read and review this text!
Reviewed by Laurel Panser, Instructor, Riverland Community College on 6/20/17
This is a review of Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking, an open source book version 1.4 by Matthew Van Cleave. The comparison book used was Patrick J. Hurley’s A Concise Introduction to Logic 12th Edition published by Cengage as well as... read more
This is a review of Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking, an open source book version 1.4 by Matthew Van Cleave. The comparison book used was Patrick J. Hurley’s A Concise Introduction to Logic 12th Edition published by Cengage as well as the 13th edition with the same title. Lori Watson is the second author on the 13th edition.
Competing with Hurley is difficult with respect to comprehensiveness. For example, Van Cleave’s book is comprehensive to the extent that it probably covers at least two-thirds or more of what is dealt with in most introductory, one-semester logic courses. Van Cleave’s chapter 1 provides an overview of argumentation including discerning non-arguments from arguments, premises versus conclusions, deductive from inductive arguments, validity, soundness and more. Much of Van Cleave’s chapter 1 parallel’s Hurley’s chapter 1. Hurley’s chapter 3 regarding informal fallacies is comprehensive while Van Cleave’s chapter 4 on this topic is less extensive. Categorical propositions are a topic in Van Cleave’s chapter 2; Hurley’s chapters 4 and 5 provide more instruction on this, however. Propositional logic is another topic in Van Cleave’s chapter 2; Hurley’s chapters 6 and 7 provide more information on this, though. Van Cleave did discuss messy issues of language meaning briefly in his chapter 1; that is the topic of Hurley’s chapter 2.
Van Cleave’s book includes exercises with answers and an index. A glossary was not included.
Reviews of open source textbooks typically include criteria besides comprehensiveness. These include comments on accuracy of the information, whether the book will become obsolete soon, jargon-free clarity to the extent that is possible, organization, navigation ease, freedom from grammar errors and cultural relevance; Van Cleave’s book is fine in all of these areas. Further criteria for open source books includes modularity and consistency of terminology. Modularity is defined as including blocks of learning material that are easy to assign to students. Hurley’s book has a greater degree of modularity than Van Cleave’s textbook. The prose Van Cleave used is consistent.
Van Cleave’s book will not become obsolete soon.
Van Cleave’s book has accessible prose.
Van Cleave used terminology consistently.
Van Cleave’s book has a reasonable degree of modularity.
Van Cleave’s book is organized. The structure and flow of his book is fine.
Problems with navigation are not present.
Grammar problems were not present.
Van Cleave’s book is culturally relevant.
Van Cleave’s book is appropriate for some first semester logic courses.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Reconstructing and analyzing arguments
- 1.1 What is an argument?
- 1.2 Identifying arguments
- 1.3 Arguments vs. explanations
- 1.4 More complex argument structures
- 1.5 Using your own paraphrases of premises and conclusions to reconstruct arguments in standard form
- 1.6 Validity
- 1.7 Soundness
- 1.8 Deductive vs. inductive arguments
- 1.9 Arguments with missing premises
- 1.10 Assuring, guarding, and discounting
- 1.11 Evaluative language
- 1.12 Evaluating a real-life argument
Chapter 2: Formal methods of evaluating arguments
- 2.1 What is a formal method of evaluation and why do we need them?
- 2.2 Propositional logic and the four basic truth functional connectives
- 2.3 Negation and disjunction
- 2.4 Using parentheses to translate complex sentences
- 2.5 “Not both” and “neither nor”
- 2.6 The truth table test of validity
- 2.7 Conditionals
- 2.8 “Unless”
- 2.9 Material equivalence
- 2.10 Tautologies, contradictions, and contingent statements
- 2.11 Proofs and the 8 valid forms of inference
- 2.12 How to construct proofs
- 2.13 Short review of propositional logic
- 2.14 Categorical logic
- 2.15 The Venn test of validity for immediate categorical inferences
- 2.16 Universal statements and existential commitment
- 2.17 Venn validity for categorical syllogisms
Chapter 3: Evaluating inductive arguments and probabilistic and statistical fallacies
- 3.1 Inductive arguments and statistical generalizations
- 3.2 Inference to the best explanation and the seven explanatory virtues
- 3.3 Analogical arguments
- 3.4 Causal arguments
- 3.5 Probability
- 3.6 The conjunction fallacy
- 3.7 The base rate fallacy
- 3.8 The small numbers fallacy
- 3.9 Regression to the mean fallacy
- 3.10 Gambler's fallacy
Chapter 4: Informal fallacies
- 4.1 Formal vs. informal fallacies
- 4.1.1 Composition fallacy
- 4.1.2 Division fallacy
- 4.1.3 Begging the question fallacy
- 4.1.4 False dichotomy
- 4.1.5 Equivocation
- 4.2 Slippery slope fallacies
- 4.2.1 Conceptual slippery slope
- 4.2.2 Causal slippery slope
- 4.3 Fallacies of relevance
- 4.3.1 Ad hominem
- 4.3.2 Straw man
- 4.3.3 Tu quoque
- 4.3.4 Genetic
- 4.3.5 Appeal to consequences
- 4.3.6 Appeal to authority
Answers to exercises Glossary/Index
Ancillary Material
About the book.
This is an introductory textbook in logic and critical thinking. The goal of the textbook is to provide the reader with a set of tools and skills that will enable them to identify and evaluate arguments. The book is intended for an introductory course that covers both formal and informal logic. As such, it is not a formal logic textbook, but is closer to what one would find marketed as a “critical thinking textbook.”
About the Contributors
Matthew Van Cleave , PhD, Philosophy, University of Cincinnati, 2007. VAP at Concordia College (Moorhead), 2008-2012. Assistant Professor at Lansing Community College, 2012-2016. Professor at Lansing Community College, 2016-
Contribute to this Page
Module 5: Thinking and Analysis
Introduction to critical thinking skills, what you’ll learn to do: d efine critical thinking and its role in your education.

The essence of the independent mind lies not in what it thinks, but in how it thinks. —Christopher Hitchens, author and journalist
By the end of this section, you will be able to explain critical thinking, describe the role that logic plays in critical thinking, and identify how critical thinking skills can be used to evaluate information. You’ll also define information literacy and describe how critical thinking skills can be used to solve problems by identifying strategies for developing yourself as a critical thinker.
- Outcome: Critical Thinking Skills. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of three students. Authored by : PopTech. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/8tXtQp . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike

- Professional
- International
Select a product below:
- Connect Math Hosted by ALEKS
- My Bookshelf (eBook Access)
Sign in to Shop:
My Account Details
- My Information
- Security & Login
- Order History
Log In to My PreK-12 Platform
- AP/Honors & Electives
- my.mheducation.com
- Open Learning Platform
Log In to My Higher Ed Platform
- Connect Math Hosted by Aleks
Business and Economics
Accounting Business Communication Business Law Business Mathematics Business Statistics & Analytics Computer & Information Technology Decision Sciences & Operations Management Economics Finance Keyboarding Introduction to Business Insurance and Real Estate Management Information Systems Management Marketing Student Success
Humanities, Social Science and Language
American Government Anthropology Art Career Development Communication Criminal Justice Developmental English Education Film Composition Health and Human Performance
History Humanities Music Philosophy and Religion Psychology Sociology Student Success Theater World Languages
Science, Engineering and Math
Agriculture and Forestry Anatomy & Physiology Astronomy and Physical Science Biology - Majors Biology - Non-Majors Chemistry Cell/Molecular Biology and Genetics Earth & Environmental Science Ecology Engineering/Computer Science Engineering Technologies - Trade & Tech Health Professions Mathematics Microbiology Nutrition Physics Plants and Animals
Digital Products
Connect® Course management , reporting , and student learning tools backed by great support .
McGraw Hill GO Greenlight learning with the new eBook+
ALEKS® Personalize learning and assessment
ALEKS® Placement, Preparation, and Learning Achieve accurate math placement
SIMnet Ignite mastery of MS Office and IT skills
McGraw Hill eBook & ReadAnywhere App Get learning that fits anytime, anywhere
Sharpen: Study App A reliable study app for students
Virtual Labs Flexible, realistic science simulations
Inclusive Access Reduce costs and increase success
LMS Integration Log in and sync up
Math Placement Achieve accurate math placement
Content Collections powered by Create® Curate and deliver your ideal content
Custom Courseware Solutions Teach your course your way
Professional Services Collaborate to optimize outcomes
Remote Proctoring Validate online exams even offsite
Institutional Solutions Increase engagement, lower costs, and improve access for your students
General Help & Support Info Customer Service & Tech Support contact information
Online Technical Support Center FAQs, articles, chat, email or phone support
Support At Every Step Instructor tools, training and resources for ALEKS , Connect & SIMnet
Instructor Sample Requests Get step by step instructions for requesting an evaluation, exam, or desk copy
Platform System Check System status in real time

Critical Thinking: A Students Introduction , 7th Edition
Format options:.
Lowest Price!
- Print from $70.00
- Connect from $100.10
- GO from $68.33
McGraw Hill eBook
- Highlight, take notes, and search
- Download the free ReadAnywhere app for offline and mobile access
Watch to learn more about the eBook
Textbook Rental (150 Days Access)
- Rent for a fraction of the printed textbook price
- Complete text bound in hardcover or softcover
Loose-Leaf Purchase
Unbound loose-leaf version of full text
Shipping Options
- Next-day air
- 2nd-day air
Orders within the United States are shipped via FedEx or UPS Ground. For shipments to locations outside of the U.S., only standard shipping is available. All shipping options assume the product is available and that processing an order takes 24 to 48 hours prior to shipping.
Note: Connect can only be used if assigned by your instructor.
Connect (180 Days Access)
- Digital access to a comprehensive online learning platform
- Includes homework , study tools , eBook, and adaptive assignments
- Download the free ReadAnywhere app to access the eBook offline
Connect + Loose-Leaf
- Comprehensive online learning platform + unbound loose-leaf print text package
- Connect includes homework , study tools, eBook, and adaptive assignments
McGraw Hill GO (180 Days Access)
- Digital access to eBook+ embedded in your school's Learning Management System (LMS)
- Includes full eBook and chapter questions
- Download the free ReadAnywhere app for offline and mobile access
* The estimated amount of time this product will be on the market is based on a number of factors, including faculty input to instructional design and the prior revision cycle and updates to academic research-which typically results in a revision cycle ranging from every two to four years for this product. Pricing subject to change at any time.
Instructor Information
Quick Actions ( Only for Validated Instructor Accounts ):
- Table of Contents
- Digital Platform
- Author Bios
- Accessibility
Affordability
Critical Thinking: A Student’s Introduction provides the skills and attitudes needed to become a skilled thinker, an effective problem solver, and a sound decision-maker. Students will learn—step by step—how to understand complex texts, analyze issues, think logically, and argue effectively. They will hone the thinking skills needed to succeed in college, in their career and in life. It is written to provide a versatile and comprehensive introduction to critical thinking through a student-centered approach that covers all the basics of critical thinking—and more—in reader-friendly language.
Main Features
- LMS Integration
- Print/Loose-Leaf Book Add-On Availability
- Presentation Slides & Instructor Resources
- Question & Test Banks
- Adaptive Assignments
- Student Progress Reporting & Analytics
- Essay Prompts
- Prebuilt Courses
- Interactive Exercises
- eBook Access (ReadAnywhere App)
- Remote Proctoring (Proctorio)
- Subject-Specific Tools
- Quick Setup
- Lives within the LMS
- Assignable Readings
- Auto-Graded Chapter Questions
About the Author
Gregory Bassham
William Irwin
Henry Nardone
James Wallace
Creating accessible products is a priority for McGraw Hill. We make accessibility and adhering to WCAG AA guidelines a part of our day-to-day development efforts and product roadmaps.
For more information, visit our accessibility page , or contact us at [email protected]
Reduce course material costs for your students while still providing full access to everything they need to be successful. It isn't too good to be true - it's Inclusive Access.
Need support? We're here to help - Get real-world support and resources every step of the way.
Company Info
- Contact & Locations
- Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
- Social Responsibility
- Investor Relations
- Social Media Directory
- Place an Order
- Get Support
- Contact Customer Service
- Contact Sales Rep
- Check System Status
Additional Resources
- Permissions
- Author Support
- International Rights
- Purchase Order
Follow McGraw Hill:
©2024 McGraw Hill. All Rights Reserved.

Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
Integrating Critical Thinking Into the Classroom

- Share article
(This is the second post in a three-part series. You can see Part One here .)
The new question-of-the-week is:
What is critical thinking and how can we integrate it into the classroom?
Part One ‘s guests were Dara Laws Savage, Patrick Brown, Meg Riordan, Ph.D., and Dr. PJ Caposey. Dara, Patrick, and Meg were also guests on my 10-minute BAM! Radio Show . You can also find a list of, and links to, previous shows here.
Today, Dr. Kulvarn Atwal, Elena Quagliarello, Dr. Donna Wilson, and Diane Dahl share their recommendations.
‘Learning Conversations’
Dr. Kulvarn Atwal is currently the executive head teacher of two large primary schools in the London borough of Redbridge. Dr. Atwal is the author of The Thinking School: Developing a Dynamic Learning Community , published by John Catt Educational. Follow him on Twitter @Thinkingschool2 :
In many classrooms I visit, students’ primary focus is on what they are expected to do and how it will be measured. It seems that we are becoming successful at producing students who are able to jump through hoops and pass tests. But are we producing children that are positive about teaching and learning and can think critically and creatively? Consider your classroom environment and the extent to which you employ strategies that develop students’ critical-thinking skills and their self-esteem as learners.
Development of self-esteem
One of the most significant factors that impacts students’ engagement and achievement in learning in your classroom is their self-esteem. In this context, self-esteem can be viewed to be the difference between how they perceive themselves as a learner (perceived self) and what they consider to be the ideal learner (ideal self). This ideal self may reflect the child that is associated or seen to be the smartest in the class. Your aim must be to raise students’ self-esteem. To do this, you have to demonstrate that effort, not ability, leads to success. Your language and interactions in the classroom, therefore, have to be aspirational—that if children persist with something, they will achieve.
Use of evaluative praise
Ensure that when you are praising students, you are making explicit links to a child’s critical thinking and/or development. This will enable them to build their understanding of what factors are supporting them in their learning. For example, often when we give feedback to students, we may simply say, “Well done” or “Good answer.” However, are the students actually aware of what they did well or what was good about their answer? Make sure you make explicit what the student has done well and where that links to prior learning. How do you value students’ critical thinking—do you praise their thinking and demonstrate how it helps them improve their learning?
Learning conversations to encourage deeper thinking
We often feel as teachers that we have to provide feedback to every students’ response, but this can limit children’s thinking. Encourage students in your class to engage in learning conversations with each other. Give as many opportunities as possible to students to build on the responses of others. Facilitate chains of dialogue by inviting students to give feedback to each other. The teacher’s role is, therefore, to facilitate this dialogue and select each individual student to give feedback to others. It may also mean that you do not always need to respond at all to a student’s answer.
Teacher modelling own thinking
We cannot expect students to develop critical-thinking skills if we aren’t modeling those thinking skills for them. Share your creativity, imagination, and thinking skills with the students and you will nurture creative, imaginative critical thinkers. Model the language you want students to learn and think about. Share what you feel about the learning activities your students are participating in as well as the thinking you are engaging in. Your own thinking and learning will add to the discussions in the classroom and encourage students to share their own thinking.
Metacognitive questioning
Consider the extent to which your questioning encourages students to think about their thinking, and therefore, learn about learning! Through asking metacognitive questions, you will enable your students to have a better understanding of the learning process, as well as their own self-reflections as learners. Example questions may include:
- Why did you choose to do it that way?
- When you find something tricky, what helps you?
- How do you know when you have really learned something?

‘Adventures of Discovery’
Elena Quagliarello is the senior editor of education for Scholastic News , a current events magazine for students in grades 3–6. She graduated from Rutgers University, where she studied English and earned her master’s degree in elementary education. She is a certified K–12 teacher and previously taught middle school English/language arts for five years:
Critical thinking blasts through the surface level of a topic. It reaches beyond the who and the what and launches students on a learning journey that ultimately unlocks a deeper level of understanding. Teaching students how to think critically helps them turn information into knowledge and knowledge into wisdom. In the classroom, critical thinking teaches students how to ask and answer the questions needed to read the world. Whether it’s a story, news article, photo, video, advertisement, or another form of media, students can use the following critical-thinking strategies to dig beyond the surface and uncover a wealth of knowledge.
A Layered Learning Approach
Begin by having students read a story, article, or analyze a piece of media. Then have them excavate and explore its various layers of meaning. First, ask students to think about the literal meaning of what they just read. For example, if students read an article about the desegregation of public schools during the 1950s, they should be able to answer questions such as: Who was involved? What happened? Where did it happen? Which details are important? This is the first layer of critical thinking: reading comprehension. Do students understand the passage at its most basic level?
Ask the Tough Questions
The next layer delves deeper and starts to uncover the author’s purpose and craft. Teach students to ask the tough questions: What information is included? What or who is left out? How does word choice influence the reader? What perspective is represented? What values or people are marginalized? These questions force students to critically analyze the choices behind the final product. In today’s age of fast-paced, easily accessible information, it is essential to teach students how to critically examine the information they consume. The goal is to equip students with the mindset to ask these questions on their own.
Strike Gold
The deepest layer of critical thinking comes from having students take a step back to think about the big picture. This level of thinking is no longer focused on the text itself but rather its real-world implications. Students explore questions such as: Why does this matter? What lesson have I learned? How can this lesson be applied to other situations? Students truly engage in critical thinking when they are able to reflect on their thinking and apply their knowledge to a new situation. This step has the power to transform knowledge into wisdom.
Adventures of Discovery
There are vast ways to spark critical thinking in the classroom. Here are a few other ideas:
- Critical Expressionism: In this expanded response to reading from a critical stance, students are encouraged to respond through forms of artistic interpretations, dramatizations, singing, sketching, designing projects, or other multimodal responses. For example, students might read an article and then create a podcast about it or read a story and then act it out.
- Transmediations: This activity requires students to take an article or story and transform it into something new. For example, they might turn a news article into a cartoon or turn a story into a poem. Alternatively, students may rewrite a story by changing some of its elements, such as the setting or time period.
- Words Into Action: In this type of activity, students are encouraged to take action and bring about change. Students might read an article about endangered orangutans and the effects of habitat loss caused by deforestation and be inspired to check the labels on products for palm oil. They might then write a letter asking companies how they make sure the palm oil they use doesn’t hurt rain forests.
- Socratic Seminars: In this student-led discussion strategy, students pose thought-provoking questions to each other about a topic. They listen closely to each other’s comments and think critically about different perspectives.
- Classroom Debates: Aside from sparking a lively conversation, classroom debates naturally embed critical-thinking skills by asking students to formulate and support their own opinions and consider and respond to opposing viewpoints.
Critical thinking has the power to launch students on unforgettable learning experiences while helping them develop new habits of thought, reflection, and inquiry. Developing these skills prepares students to examine issues of power and promote transformative change in the world around them.

‘Quote Analysis’
Dr. Donna Wilson is a psychologist and the author of 20 books, including Developing Growth Mindsets , Teaching Students to Drive Their Brains , and Five Big Ideas for Effective Teaching (2 nd Edition). She is an international speaker who has worked in Asia, the Middle East, Australia, Europe, Jamaica, and throughout the U.S. and Canada. Dr. Wilson can be reached at [email protected] ; visit her website at www.brainsmart.org .
Diane Dahl has been a teacher for 13 years, having taught grades 2-4 throughout her career. Mrs. Dahl currently teaches 3rd and 4th grade GT-ELAR/SS in Lovejoy ISD in Fairview, Texas. Follow her on Twitter at @DahlD, and visit her website at www.fortheloveofteaching.net :
A growing body of research over the past several decades indicates that teaching students how to be better thinkers is a great way to support them to be more successful at school and beyond. In the book, Teaching Students to Drive Their Brains , Dr. Wilson shares research and many motivational strategies, activities, and lesson ideas that assist students to think at higher levels. Five key strategies from the book are as follows:
- Facilitate conversation about why it is important to think critically at school and in other contexts of life. Ideally, every student will have a contribution to make to the discussion over time.
- Begin teaching thinking skills early in the school year and as a daily part of class.
- As this instruction begins, introduce students to the concept of brain plasticity and how their brilliant brains change during thinking and learning. This can be highly motivational for students who do not yet believe they are good thinkers!
- Explicitly teach students how to use the thinking skills.
- Facilitate student understanding of how the thinking skills they are learning relate to their lives at school and in other contexts.
Below are two lessons that support critical thinking, which can be defined as the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgment.
Mrs. Dahl prepares her 3rd and 4th grade classes for a year of critical thinking using quote analysis .
During Native American studies, her 4 th grade analyzes a Tuscarora quote: “Man has responsibility, not power.” Since students already know how the Native Americans’ land had been stolen, it doesn’t take much for them to make the logical leaps. Critical-thought prompts take their thinking even deeper, especially at the beginning of the year when many need scaffolding. Some prompts include:
- … from the point of view of the Native Americans?
- … from the point of view of the settlers?
- How do you think your life might change over time as a result?
- Can you relate this quote to anything else in history?
Analyzing a topic from occupational points of view is an incredibly powerful critical-thinking tool. After learning about the Mexican-American War, Mrs. Dahl’s students worked in groups to choose an occupation with which to analyze the war. The chosen occupations were: anthropologist, mathematician, historian, archaeologist, cartographer, and economist. Then each individual within each group chose a different critical-thinking skill to focus on. Finally, they worked together to decide how their occupation would view the war using each skill.
For example, here is what each student in the economist group wrote:
- When U.S.A. invaded Mexico for land and won, Mexico ended up losing income from the settlements of Jose de Escandon. The U.S.A. thought that they were gaining possible tradable land, while Mexico thought that they were losing precious land and resources.
- Whenever Texas joined the states, their GDP skyrocketed. Then they went to war and spent money on supplies. When the war was resolving, Texas sold some of their land to New Mexico for $10 million. This allowed Texas to pay off their debt to the U.S., improving their relationship.
- A detail that converged into the Mexican-American War was that Mexico and the U.S. disagreed on the Texas border. With the resulting treaty, Texas ended up gaining more land and economic resources.
- Texas gained land from Mexico since both countries disagreed on borders. Texas sold land to New Mexico, which made Texas more economically structured and allowed them to pay off their debt.
This was the first time that students had ever used the occupations technique. Mrs. Dahl was astonished at how many times the kids used these critical skills in other areas moving forward.

Thanks to Dr. Auwal, Elena, Dr. Wilson, and Diane for their contributions!
Please feel free to leave a comment with your reactions to the topic or directly to anything that has been said in this post.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email (The RSS feed for this blog, and for all Ed Week articles, has been changed by the new redesign—new ones won’t be available until February). And if you missed any of the highlights from the first nine years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagement in Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1: Introduction to Critical Thinking, Reasoning, and Logic
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 29580

- Golden West College via NGE Far Press
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
What is thinking? It may seem strange to begin a logic textbook with this question. ‘Thinking’ is perhaps the most intimate and personal thing that people do. Yet the more you ‘think’ about thinking, the more mysterious it can appear. It is the sort of thing that one intuitively or naturally understands, and yet cannot describe to others without great difficulty. Many people believe that logic is very abstract, dispassionate, complicated, and even cold. But in fact the study of logic is nothing more intimidating or obscure than this: the study of good thinking.
- 1.1: Prelude to Chapter
- 1.2: Introduction and Thought Experiments- The Trolley Problem
- 1.3: Truth and Its Role in Argumentation - Certainty, Probability, and Monty Hall Only certain sorts of sentences can be used in arguments. We call these sentences propositions, statements or claims.
- 1.4: Distinction of Proof from Verification; Our Biases and the Forer Effect
- 1.5: The Scientific Method The procedure that scientists use is also a standard form of argument. Its conclusions only give you the likelihood or the probability that something is true (if your theory or hypothesis is confirmed), and not the certainty that it’s true. But when it is done correctly, the conclusions it reaches are very well-grounded in experimental evidence.
- 1.6: Diagramming Thoughts and Arguments - Analyzing News Media
- 1.7: Creating a Philosophical Outline
Critical Thinking Definition, Skills, and Examples
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ADHeadshot-Cropped-b80e40469d5b4852a68f94ad69d6e8bd.jpg)
- Indiana University, Bloomington
- State University of New York at Oneonta
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze information objectively and make a reasoned judgment. It involves the evaluation of sources, such as data, facts, observable phenomena, and research findings.
Good critical thinkers can draw reasonable conclusions from a set of information, and discriminate between useful and less useful details to solve problems or make decisions. These skills are especially helpful at school and in the workplace, where employers prioritize the ability to think critically. Find out why and see how you can demonstrate that you have this ability.
Examples of Critical Thinking
The circumstances that demand critical thinking vary from industry to industry. Some examples include:
- A triage nurse analyzes the cases at hand and decides the order by which the patients should be treated.
- A plumber evaluates the materials that would best suit a particular job.
- An attorney reviews the evidence and devises a strategy to win a case or to decide whether to settle out of court.
- A manager analyzes customer feedback forms and uses this information to develop a customer service training session for employees.

Why Do Employers Value Critical Thinking Skills?
Employers want job candidates who can evaluate a situation using logical thought and offer the best solution.
Someone with critical thinking skills can be trusted to make decisions independently, and will not need constant handholding.
Hiring a critical thinker means that micromanaging won't be required. Critical thinking abilities are among the most sought-after skills in almost every industry and workplace. You can demonstrate critical thinking by using related keywords in your resume and cover letter and during your interview.
How to Demonstrate Critical Thinking in a Job Search
If critical thinking is a key phrase in the job listings you are applying for, be sure to emphasize your critical thinking skills throughout your job search.
Add Keywords to Your Resume
You can use critical thinking keywords (analytical, problem solving, creativity, etc.) in your resume. When describing your work history, include top critical thinking skills that accurately describe you. You can also include them in your resume summary, if you have one.
For example, your summary might read, “Marketing Associate with five years of experience in project management. Skilled in conducting thorough market research and competitor analysis to assess market trends and client needs, and to develop appropriate acquisition tactics.”
Mention Skills in Your Cover Letter
Include these critical thinking skills in your cover letter. In the body of your letter, mention one or two of these skills, and give specific examples of times when you have demonstrated them at work. Think about times when you had to analyze or evaluate materials to solve a problem.
Show the Interviewer Your Skills
You can use these skill words in an interview. Discuss a time when you were faced with a particular problem or challenge at work and explain how you applied critical thinking to solve it.
Some interviewers will give you a hypothetical scenario or problem, and ask you to use critical thinking skills to solve it. In this case, explain your thought process thoroughly to the interviewer. He or she is typically more focused on how you arrive at your solution rather than the solution itself. The interviewer wants to see you analyze and evaluate (key parts of critical thinking) the given scenario or problem.
Of course, each job will require different skills and experiences, so make sure you read the job description carefully and focus on the skills listed by the employer.
Top Critical Thinking Skills
Keep these in-demand skills in mind as you refine your critical thinking practice —whether for work or school.
Part of critical thinking is the ability to carefully examine something, whether it is a problem, a set of data, or a text. People with analytical skills can examine information, understand what it means, and properly explain to others the implications of that information.
- Asking Thoughtful Questions
- Data Analysis
- Interpretation
- Questioning Evidence
- Recognizing Patterns
Communication
Often, you will need to share your conclusions with your employers or with a group of classmates or colleagues. You need to be able to communicate with others to share your ideas effectively. You might also need to engage in critical thinking in a group. In this case, you will need to work with others and communicate effectively to figure out solutions to complex problems.
- Active Listening
- Collaboration
- Explanation
- Interpersonal
- Presentation
- Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
Critical thinking often involves creativity and innovation. You might need to spot patterns in the information you are looking at or come up with a solution that no one else has thought of before. All of this involves a creative eye that can take a different approach from all other approaches.
- Flexibility
- Conceptualization
- Imagination
- Drawing Connections
- Synthesizing
Open-Mindedness
To think critically, you need to be able to put aside any assumptions or judgments and merely analyze the information you receive. You need to be objective, evaluating ideas without bias.
- Objectivity
- Observation
Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is another critical thinking skill that involves analyzing a problem, generating and implementing a solution, and assessing the success of the plan. Employers don’t simply want employees who can think about information critically. They also need to be able to come up with practical solutions.
- Attention to Detail
- Clarification
- Decision Making
- Groundedness
- Identifying Patterns
More Critical Thinking Skills
- Inductive Reasoning
- Deductive Reasoning
- Noticing Outliers
- Adaptability
- Emotional Intelligence
- Brainstorming
- Optimization
- Restructuring
- Integration
- Strategic Planning
- Project Management
- Ongoing Improvement
- Causal Relationships
- Case Analysis
- Diagnostics
- SWOT Analysis
- Business Intelligence
- Quantitative Data Management
- Qualitative Data Management
- Risk Management
- Scientific Method
- Consumer Behavior
Key Takeaways
- Demonstrate you have critical thinking skills by adding relevant keywords to your resume.
- Mention pertinent critical thinking skills in your cover letter, too, and include an example of a time when you demonstrated them at work.
- Finally, highlight critical thinking skills during your interview. For instance, you might discuss a time when you were faced with a challenge at work and explain how you applied critical thinking skills to solve it.
University of Louisville. " What is Critical Thinking ."
American Management Association. " AMA Critical Skills Survey: Workers Need Higher Level Skills to Succeed in the 21st Century ."
- Questions for Each Level of Bloom's Taxonomy
- Critical Thinking in Reading and Composition
- Bloom's Taxonomy in the Classroom
- 6 Skills Students Need to Succeed in Social Studies Classes
- Introduction to Critical Thinking
- Higher-Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) in Education
- Creativity & Creative Thinking
- How To Become an Effective Problem Solver
- 2020-21 Common Application Essay Option 4—Solving a Problem
- The Horse Problem: A Math Challenge
- College Interview Tips: "Tell Me About a Challenge You Overcame"
- How Depth of Knowledge Drives Learning and Assessment
- How to Facilitate Learning and Critical Thinking
- What to Do When the Technology Fails in Class
- Types of Medical School Interviews and What to Expect
- A Guide to Business Letters Types
- [email protected]
- Login / Register
Teach Critical, Creative, and Independent Thinking
Article 26 May 2024 119 0

Introduction
In an ever-evolving world, the ability to think critically, creatively, and independently is more crucial than ever. These skills empower individuals to navigate complex problems, innovate solutions, and make informed decisions. This article explores various methods and techniques to teach these essential thinking skills, providing educators, parents, and learners with practical strategies to foster a thinking mindset.
Definitions and Importance
Critical thinking.
Critical thinking involves analyzing information objectively, evaluating evidence, and reasoning logically. It’s essential for problem-solving, decision-making, and understanding complex issues. In today’s information-rich age, critical thinking helps discern credible sources from misinformation, making it a vital skill for both personal and professional success.
Creative Thinking
Creative thinking is the ability to generate new ideas, see connections between seemingly unrelated concepts, and think outside the box. This skill drives innovation and is crucial in fields ranging from the arts to science and business. Creative thinkers can adapt to new situations and find unique solutions to challenges.
Independent Thinking
Independent thinking refers to the ability to form one’s own opinions and make decisions without undue influence from others. It involves self-reflection, confidence, and the courage to stand by one’s beliefs. Independent thinkers are better equipped to lead, innovate, and contribute meaningfully to society.
Educational Approaches
Socratic questioning.
Socratic questioning is a method of teaching that encourages critical thinking through dialogue. By asking probing questions, educators can help students explore complex ideas and develop their reasoning skills. This approach fosters deep understanding and helps learners become more thoughtful and reflective.
Problem-Based Learning (PBL)
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) is an educational strategy where students learn by solving real-world problems. This method promotes critical thinking, creativity, and independent learning as students must research, collaborate, and apply their knowledge to find solutions.
Brainstorming Sessions
Brainstorming sessions are a popular technique for fostering creative thinking. By encouraging free-flowing ideas in a judgment-free environment, educators can help students think expansively and explore multiple possibilities. This method is especially effective in group settings, where diverse perspectives can spark innovative solutions.
Practical Tips for Educators and Parents
Use open-ended questions.
Open-ended questions stimulate critical and creative thinking by requiring more than a yes-or-no answer. Questions like “What do you think will happen if...?” or “How might we solve this problem?” encourage students to think deeply and explore different angles.
Encourage Curiosity
Fostering a sense of curiosity is fundamental to developing thinking skills. Encourage students to ask questions, explore new topics, and seek out information. Create a learning environment that celebrates inquiry and values the process of discovery.
Promote Self-Reflection
Self-reflection helps students develop independent thinking by encouraging them to consider their own thoughts and feelings. Activities like journaling or discussing personal experiences can help learners understand their thought processes and build confidence in their ideas.
Cognitive Strategies
Mind mapping.
Mind mapping is a visual tool that helps organize thoughts and ideas. By creating a diagram that connects related concepts, students can see the relationships between different pieces of information and think more holistically. This technique is particularly useful for brainstorming and organizing complex subjects.
Analogical Reasoning
Analogical reasoning involves drawing comparisons between similar situations to understand new concepts. By relating unfamiliar ideas to known experiences, students can grasp complex ideas more easily and develop creative solutions.
Thinking Routines
Thinking routines are structured approaches that guide students through the thinking process. Routines like “See-Think-Wonder” or “Claim-Support-Question” provide a framework for exploring ideas deeply and systematically. These routines can be used across various subjects to promote critical and creative thinking.
Real-Life Applications
Problem-solving skills.
Critical and creative thinking skills are essential for effective problem-solving. Whether in personal life or professional settings, the ability to analyze situations, generate solutions, and make decisions is invaluable. Teaching these skills equips learners to handle challenges confidently and competently.
Decision-Making Abilities
Independent thinking enhances decision-making by fostering self-reliance and confidence. By teaching students to evaluate options, consider consequences, and trust their judgment, we prepare them to make informed choices that align with their values and goals.
Innovation and Creativity
Creative thinking drives innovation, which is crucial in today’s fast-paced, competitive world. By encouraging students to think creatively, we cultivate a mindset that embraces change, seeks out new opportunities, and continuously strives for improvement.
Resources and Tools
- “Thinking, Fast and Slow” by Daniel Kahneman : This book explores the two systems of thought and how they shape our judgments and decisions.
- “The Art of Thinking Clearly” by Rolf Dobelli : A practical guide to avoiding cognitive errors and thinking more effectively.
- “Creative Confidence” by Tom Kelley and David Kelley : A book that encourages readers to unleash their creativity and apply it in their daily lives.
Online Courses
- Coursera’s “Learning How to Learn” : This course offers techniques to help learners master complex subjects and develop effective thinking strategies.
- edX’s “Critical Thinking & Problem-Solving” : A course designed to enhance critical thinking skills through practical exercises and real-world applications.
- Udemy’s “Creative Thinking Techniques and Tools for Success” : A course that provides tools and methods to boost creative thinking and innovation.
- MindMeister : An online mind mapping tool that helps visualize and organize ideas.
- Evernote : A note-taking app that supports organizing thoughts and tracking creative ideas.
- Coggle : A collaborative mind mapping tool that is ideal for group brainstorming sessions.
Teaching someone how to think critically, creatively, and independently is one of the most valuable gifts we can offer. These skills not only enhance academic and professional success but also enrich personal growth and lifelong learning. By employing the educational approaches, cognitive strategies, and practical tips discussed in this blog, educators and parents can cultivate a thinking mindset in learners, empowering them to navigate an increasingly complex world with confidence and creativity.
Whether through Socratic questioning, problem-based learning, or encouraging self-reflection, the journey to developing these essential skills is both challenging and rewarding. Let us commit to fostering environments that celebrate curiosity, promote deep thinking, and inspire the next generation of critical, creative, and independent thinkers.
- Latest Articles
How Psychology Shapes Decision-Making
10 unwritten social rules you should know, overview of nepal's education budget for the fiscal year 2081-2082, the curse of knowledge: risks of overstudying, why read the science of getting rich: key benefits & insights, 7 rules for happiness: your guide to a joyful life, best tips for students to improve their study, essential improvements for nepali students' education, facilitating foreign students by u.s. government, how does reading affect your brain, why there are 60 seconds in a minute: the historical reason, buddha was born in nepal: discover lumbini’s significance, 20 essential life lessons to learn early, 20 life lessons i wish i knew at 20: wisdom from 40, 20 reading rules that transformed my life, how bill gates reads: tips every reader can learn, what actually matters in your 20s: key life lessons, 20 daily life hacks to transform your routine, apply online.

Find Detailed information on:
- Top Colleges & Universities
- Popular Courses
- Exam Preparation
- Admissions & Eligibility
- College Rankings
Sign Up or Login
Not a Member Yet! Join Us it's Free.
Already have account Please Login
Admissions Visit Opportunities
The Charger Blog
Peterson Library's Unique Program Trains Students to Be Research Experts
The student workers who are part of the Marvin K. Peterson Library's Researcher 2 Researcher Program serve the Charger community, offering support to students and faculty members while also building their own research, interpersonal, and critical thinking skills.
May 28, 2024
By Renee Chmiel, Office of Marketing and Communications

As a Charger, Ethan Reeder '24 enjoyed working at the circulation desk in the University's Marvin K. Peterson Library , where he helped students and faculty members find the materials they were seeking for their research. Whether they'd stopped by in-person, called the library, or reached out via email or through the library's online chat program, Reeder offered them a friendly source of support.
A new graduate of the University's homeland security and emergency management program , Reeder was a student worker for the library's Researcher 2 Researcher (R2R) Program. He and his fellow student workers, who received a comprehensive training before beginning their positions, are committed to making sure members of the Charger community find exactly what they are looking for.
"I've loved being able to help students with their research and to have academic conversations with faculty about research topics," he said. "I wouldn't have been able to gain such an understanding of research without the help of the amazing faculty in the library. Through this position, I have come to call the library a second home, and many of the faculty I regard as friends and mentors."
Reeder was one of the program's four student workers during the Spring semester. R2R was developed in 2019 by Joe Scollo, MLS, M.A., an information literacy librarian at the Peterson Library, and he continues to oversee the program. The idea was to provide students with an experiential opportunity to learn in-depth and advanced research strategies and techniques. They also gain a robust knowledge of the library's database and resources, and help their fellow Chargers learn what's available to them and how to find it.

At its core, the student positions are focused on customer service, enabling them to build their interpersonal skills. While interacting with faculty, staff, and students, they learn to professionally address challenging questions, whether verbally or in writing. They understand what questions to ask as they serve their fellow Chargers.
"To see them excel means so much to me personally," said Scollo, who also serves as associate director of the University's award-winning Model United Nations program . "My role as an information literacy librarian allows me to be an educator. This program is one of those opportunities in which I get see students learn, develop, and apply my teaching to get ahead in life.
"Not only does this help them find better jobs, but it also helps them become lifelong learners," he continued. "It is extremely rewarding when former students reach out to me to talk about their new job, or just to catch up. It makes me very proud."
Scollo says that research supports the benefits of the program, and that many students who may be reluctant to interact with a staff librarian are more comfortable asking a fellow student for assistance. The student workers help foster a friendly and comfortable environment in which all students can feel comfortable seeking support.
Lauren Slingluff, M.S. , the University librarian, says the program's success is a testament to Scollo's leadership and training, as well as the students' commitment to the program.
"Having students provide research assistance in this way is unique for academic libraries," she said. "I'm constantly struck by their skill, their creativity, and their commitment to supporting other students. Some of our best ideas for program enhancements have come from our wonderful researcher-to-researcher team as they blend their knowledge of the student experience with their advanced library training."

For Allison Mahr '24, who recently accepted her bachelor's degree in international affairs , the opportunity to collaborate with her fellow Chargers in the library was her favorite part of being a part of the R2R program.
Mahr, who recently earned a prestigious Boren Fellowship Award and will soon travel to the Republic of Georgia to continue her own research , says R2R was an incredible way for her to learn how to explain complex topics in a way that is understandable – a skill that she believes will be crucial as she completes her fellowship and begins graduate school.
"This program has been a remarkable opportunity to enhance my research skills and to learn from Joe Scollo about information literacy," she said. "I've also worked behind the scenes to help create some posters and graphics to help advertise library services, and I've been helping Joe and the other R2Rs revamp the library website and other key materials."
Scollo envisions the program helping students in all majors develop their own ability to learn – and teach others – as well as their critical thinking skills. Student workers become research experts, of sorts, and that's a skill that he believes will serve them well as they begin their careers or continue their education.
For Reeder, the new homeland security and emergency management grad, the program was a great way to serve the University community while also developing his own abilities. He's now applying for analytical positions with federal agencies such as the U.S. Secret Service, and he also plans to pursue his master's degree. He believes the program was a great way for him to develop the skills he'll need to excel.
"Through this program I have gained an advanced understanding of research methods, as well as a wide understanding of research databases across a variety of academic fields," he explains. "I've been able to use these skills from this position to benefit my personal research as a student and as a developing professional in the field of homeland and national security."
Recent News

Seniors Share Art and Design Projects with Charger Community
A group of art and design majors recently displayed their senior capstone projects as part of an exhibition in the University's Seton Gallery.

Unique Program Introduces Middle School Students to Math and Coding
The University’s Excellence in Math and Coding Chargers (E = MC2) was a fun after-school program for Engineering and Science University Magnet School students, offering them a sampling of math, coding, and life as a college student.

New Grad Receives Prestigious Public Health Award
Krupa Ann Mathew ’24 MPH is one of only three students in the country to receive the Vivian Drenckhahn Student Scholarship from the Society for Public Health Education (SOPHE). She’s the fourth Charger to receive the award, which is one of the highest honors the organization bestows on students.
- MBA/MPA Program - University of New Haven
- Arts & Sciences: Art & Design | University of...
- Make Your Gift
- Open access
- Published: 24 May 2024
Integration of case-based learning and three-dimensional printing for tetralogy of fallot instruction in clinical medical undergraduates: a randomized controlled trial
- Jian Zhao 1 na1 ,
- Xin Gong 1 na1 ,
- Jian Ding 1 ,
- Kepin Xiong 2 ,
- Kangle Zhuang 3 ,
- Rui Huang 1 ,
- Shu Li 4 &
- Huachun Miao 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 571 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
164 Accesses
Metrics details
Case-based learning (CBL) methods have gained prominence in medical education, proving especially effective for preclinical training in undergraduate medical education. Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart disease characterized by four malformations, presenting a challenge in medical education due to the complexity of its anatomical pathology. Three-dimensional printing (3DP), generating physical replicas from data, offers a valuable tool for illustrating intricate anatomical structures and spatial relationships in the classroom. This study explores the integration of 3DP with CBL teaching for clinical medical undergraduates.
Sixty senior clinical medical undergraduates were randomly assigned to the CBL group and the CBL-3DP group. Computed tomography imaging data from a typical TOF case were exported, processed, and utilized to create four TOF models with a color 3D printer. The CBL group employed CBL teaching methods, while the CBL-3DP group combined CBL with 3D-printed models. Post-class exams and questionnaires assessed the teaching effectiveness of both groups.
The CBL-3DP group exhibited improved performance in post-class examinations, particularly in pathological anatomy and TOF imaging data analysis ( P < 0.05). Questionnaire responses from the CBL-3DP group indicated enhanced satisfaction with teaching mode, promotion of diagnostic skills, bolstering of self-assurance in managing TOF cases, and cultivation of critical thinking and clinical reasoning abilities ( P < 0.05). These findings underscore the potential of 3D printed models to augment the effectiveness of CBL, aiding students in mastering instructional content and bolstering their interest and self-confidence in learning.
The fusion of CBL with 3D printing models is feasible and effective in TOF instruction to clinical medical undergraduates, and worthy of popularization and application in medical education, especially for courses involving intricate anatomical components.
Peer Review reports
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is the most common cyanotic congenital heart disease(CHD) [ 1 ]. Characterized by four structural anomalies: ventricular septal defect (VSD), pulmonary stenosis (PS), right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), and overriding aorta (OA), TOF is a focal point and challenge in medical education. Understanding anatomical spatial structures is pivotal for learning and mastering TOF [ 2 ]. Given the constraints of course duration, medical school educators aim to provide students with a comprehensive and intuitive understanding of the disease within a limited timeframe [ 3 ].
The case-based learning (CBL) teaching model incorporates a case-based instructional approach that emphasizes typical clinical cases as a guide in student-centered and teacher-facilitated group discussions [ 4 ]. The CBL instructional methods have garnered widespread attention in medical education as they are particularly appropriate for preclinical training in undergraduate medical education [ 5 , 6 ]. The collection of case data, including medical records and examination results, is essential for case construction [ 7 ]. The anatomical and hemodynamic consequences of TOF can be determined using ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging techniques. However, understanding the anatomical structures from imaging data is a slow and challenging psychological reconstruction process for undergraduate medical students [ 8 ]. Three-dimensional (3D) visualization is valuable for depicting anatomical structures [ 9 ]. 3D printing (3DP), which creates physical replicas based on data, facilitates the demonstration of complex anatomical structures and spatial relationships in the classroom [ 10 ].
During the classroom session, 3D-printed models offer a convenient means for hands-on demonstration and communication, similar to facing a patient, enhancing the efficiency and specificity of intra-team communication and discussion [ 11 ]. In this study, we printed TOF models based on case imaging data, integrated them into CBL teaching, and assessed the effectiveness of classroom instruction.
Research participants
The study employed a prospective, randomized controlled design which received approval from the institutional ethics committee. Senior undergraduate students majoring in clinical medicine at Wannan Medical College were recruited for participation based on predefined inclusion criteria. The researchers implemented recruitment according to the recruitment criteria by contacting the class leaders of the target classes they had previously taught. Notably, these students were in their third year of medical education, with anticipation of progressing to clinical courses in the fourth year, encompassing Internal Medicine, Surgery, Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Pediatrics. Inclusion criteria for participants encompassed the following: (1) proficient communication and comprehension abilities, (2) consistent attendance without absenteeism or truancy, (3) absence of failing grades in prior examinations, and (4) capability to conscientiously fulfill assigned learning tasks. Exclusion criteria were (1) absence from lectures, (2) failure to complete pre-and post-tests, and (3) inadequate completion of questionnaires. For their participation in the study, Students were provided access to the e-book “Localized Anatomy,” authored by the investigators, as an incentive for their participation. Voluntary and anonymous participation was emphasized, with participants retaining the right to withdraw from the study at any time without providing a reason.
The study was conducted between May 1st, 2023, and June 30, 2023, from recruitment to completion of data collection. Drawing upon insights gained from a previous analogous investigation which yielded an effect size of 0.95 [ 10 ]. Sample size was computed, guided by a statistical consultant, with the aim of 0.85 power value, predicated on an effect size of 0.8 and a margin of error set at 0.05. A minimum of 30 participants per group was calculated using G*Power software (latest ver. 3.1.9.7; Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf, Düsseldorf, Germany), resulting in the recruitment of a total of 60 undergraduate students. Each participant was assigned an identification number, with codes placed in boxes. Codes drawn from the boxes determined allocation to either the CBL group or the CBL-3DP group. Subsequently, participants were randomly assigned to either the CBL group, receiving instruction utilizing the CBL methodology, or the CBL-3DP group, which received instruction integrating both CBL and 3D Printed models.
Printing of TOF models
Figure 1 A shows the printing flowchart of the TOF models. A typical TOF case was collected from the Yijishan Hospital of Wannan Medical College. The CT angiography imaging data of the case was exported. Mimics Research 20.0 software (Mimics Innovation Suite version 20, Materialize, Belgium) was used for data processing. The cardiovascular module of the CT-Heart tool was employed to adjust the threshold range, independently obtain the cardiac chambers and vessels, post-process the chambers and vessels to generate a hollow blood pool, and merge it with the myocardial volume to construct a complete heart model. The file was imported into Magics 24.0 software (version 24.0; Materialize, Belgium) for correction using the Shell tool page. After repairs, the model entered the smoothing page, where tools such as triangular surface simplification, local smoothing, refinement and smoothing, subdivision of components, and mesh painting were utilized to achieve varying degrees of smoothness. Finally, optimized data were obtained and exported as stereolithography (STL) files. An experienced cardiothoracic surgeon validated the anatomical accuracy of the digital model.
The STL files were imported into a 3D printer (J401Pro; Sailner 3D Technology, China) for model printing. This printer can produce full-color medical models using different materials. The models were fabricated using two distinct materials: rigid and flexible. Both materials are suitable for the observational discussion of the teaching objectives outlined in our study. From the perspective of observing pathological changes in the TOF, there is no significant difference between the two materials.
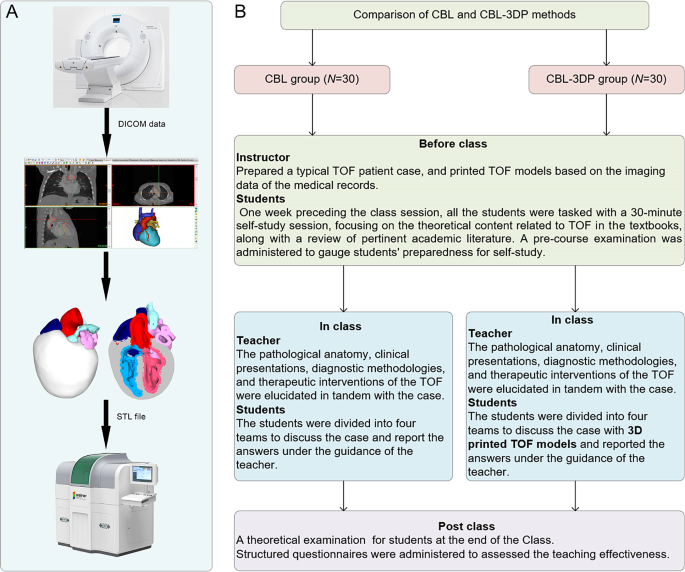
Experimental flow chart of this study. A TOF model printing flow chart. B The instructional framework
Teaching implementation
Figure 1 B illustrates the instructional framework employed in this study. One week preceding the class session, all the students were tasked with a 30-minute self-study session, focusing on the theoretical content related to TOF as outlined in the Pediatrics and Surgery textbooks, along with a review of pertinent academic literature. Both groups received co-supervision from two basic medicine lecturers boasting over a decade of teaching experience, alongside a senior cardiothoracic surgeon. Teaching conditions remained consistent across groups, encompassing uniform assessment criteria and adherence to predefined teaching time frames, all conducted in a Project-Based Learning (PBL) classroom at Wannan Medical College. Additionally, a pre-course examination was administered to gauge students’ preparedness for self-study.
In adherence to the curriculum guidelines, the teaching objectives aimed to empower students to master TOF’s clinical manifestations, diagnostic modalities, and differential diagnoses, while acquainting them with treatment principles and surgical methodologies. Additionally, the objectives sought to cultivate students’ clinical reasoning abilities and problem-solving skills. the duration of instruction for the TOF theory session was standardized to 25 min. The didactic content was integrated with the TOF case study to construct a coherent pedagogical structure.
During the instructional session, both groups underwent teaching utilizing the CBL methodology. Clinical manifestations and case details of TOF cases were presented to stimulate students’ interest and curiosity. Subsequently, the theory of TOF, including its etiology, pathogenesis, pathologic anatomy, clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, and therapeutic interventions, was briefly elucidated. Emphasis was then placed on the case, wherein selected typical TOF cases were explained, guiding students in analysis and discussion. Students were organized into four teams under the instructors’ supervision, fostering cooperative learning and communication, thereby deepening their understanding of the disease through continuous inquiry and exploration (Fig. 2 L). In the routinely equipped PBL classroom with standard heart models (Fig. 2 J, K), all students had prior exposure to human anatomy and were familiar with these models. Both groups were provided with four standard heart models for reference, while the CBL-3DP group received additional four 3D-printed models depicting TOF anomalies, enriching their learning experience (Fig. 2 D, G). After the lesson, summarization, and feedback sessions were conducted to consolidate group discussions’ outcomes, evaluate teaching effectiveness, and assess learning outcomes.
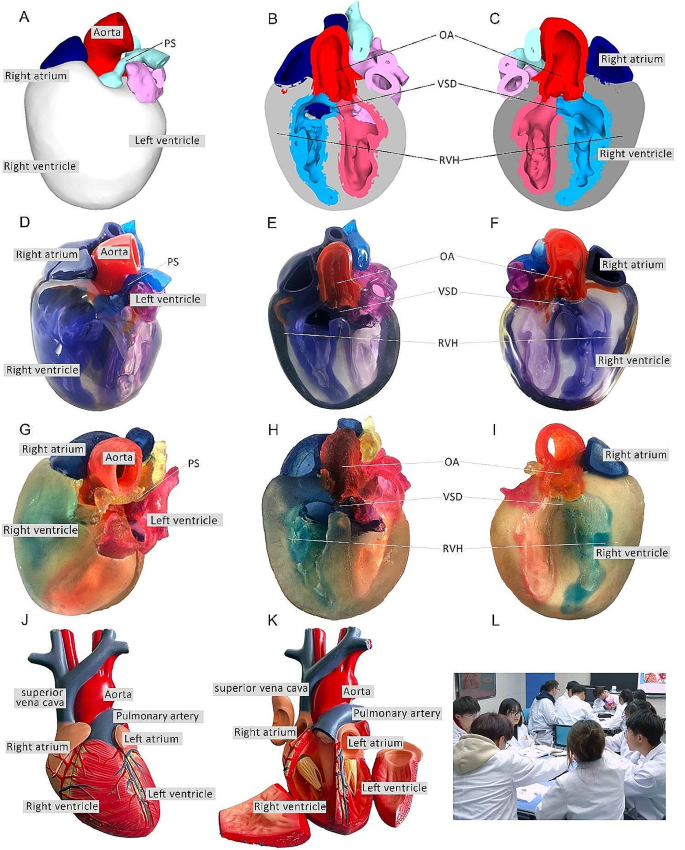
Heart models utilized in instructional sessions. A External perspective of 3D digital models. B, C Cross-sectional views following trans-septal sagittal dissection of the 3D digital model (PS: Pulmonary Stenosis; OA: Overriding Aorta; VSD: Ventricular Septal Defect; RVH: Right Ventricular Hypertrophy). D External depiction of rigid 3D printed model. E, F Sagittal sections of the rigid 3D printed model. G External portrayal of flexible 3D printed model. H, I Sagittal sections of the flexible 3D printed model. J, K The normal heart model employed in the instruction of the CBL group. L Ongoing classroom session
Teaching effectiveness assessment
Following the instructional session, participants from the two groups underwent a theoretical examination to assess their comprehension of the taught material. This assessment covered domains such as pathological anatomy, clinical manifestations, imaging data interpretation, diagnosis, and treatment relevant to TOF. Additionally, structured questionnaires were administered to evaluate the efficacy of the pedagogical approach employed. The questionnaire consisted of six questions designed to gauge participants’ understanding of the teaching content, enhancement of diagnostic skills, cultivation of critical thinking and clinical reasoning abilities, bolstering of confidence in managing TOF cases, satisfaction with the teaching mode, and satisfaction with the CBL methodology.
The questionnaire employed a 5-point Likert scale to gauge responses, with 5 indicating “strongly satisfied/agree,” 4 for “satisfied/agree,” 3 denoting “neutral,” 2 reflecting “dissatisfied/disagree,” and 1 indicating “strongly dissatisfied/disagree.” It comprised six questions, with the initial two probing participants’ knowledge acquisition, questions 3 and 4 exploring satisfaction regarding enhanced competence, and the final two assessing satisfaction with teaching methods and modes. Additionally, participants were encouraged to provide suggestions at the end of the questionnaire. To ensure the questionnaire’s validity, five esteemed lecturers in basic medical sciences with more than 10 years of experience verified its content and assessed its Content Validity Ratio and Content Validity Index to ensure alignment with the study’s objectives.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted utilizing GraphPad Prism 9.0 software. Aggregate score data for both groups were presented as mean ± standard deviation (x ± s). The gender comparisons were analyzed with the chi-square (χ2) test, while the other variables were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test. The threshold for determining statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
Three-dimensional printing models
After configuring the structural colors of each component (Fig. 2 A, B, C), we printed four color TOF models using both rigid and flexible materials, resulting in four life-sized TOF models. Two color TOF models were created using rigid materials (Fig. 2 D, E, F). These models, exhibiting resistance to deformation, and with a firm texture, smooth and glossy surface, and good transparency, allowing visibility of the internal structures, were deemed conducive to teaching and observation. We also fabricated two color TOF models using flexible materials (Fig. 2 G, H, I), characterized by soft texture, opacity, and deformability, allowing for easy manipulation and cutting. It has potential utility beyond observational purposes. It can serve as a valuable tool for simulating surgical interventions and may be employed to create tomographic anatomical specimens. In this study, both material models were suitable for observation in the classroom. The participants were able to discern the four pathological changes characteristic of TOF from surface examination or cross-sectional analysis.
Baseline characteristics of the students
In total, 60 students were included in this study. The CBL group comprised 30 students (14 males and 16 females), with an average age of (21.20 ± 0.76) years. The CBL-3DP group consisted of 30 students (17 males and 13 females) with an average age of 20.96 years. All the students completed the study procedures. There were no significant differences in age, sex ratio, or pre-class exam scores between the two groups ( P > 0.05), indicating that the baseline scores between the two groups were comparable (Table 1 ).
Theoretical examination results
All students completed the research procedures as planned. The post-class theoretical examination encompassed assessment of pathological anatomy, clinical presentations, imaging data interpretation, diagnosis, and treatment pertinent to TOF. Notably, no statistically significant disparities were observed in the scores on clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment components between the cohorts, as delineated in Table 2 . Conversely, discernible distinctions were evident whereby the CBL-3DP group outperformed the CBL group notably in pathological anatomy, imaging data interpretation, and overall aggregate scores ( P < 0.05).
Results of the questionnaires
All the 60 participants submitted the questionnaire. Comparing the CBL and CBL-3DP groups, the scores from the CBL-3DP group showed significant improvements in many areas. This included satisfaction with the teaching mode, promotion of diagnostic skills, bolstering of self-assurance in managing TOF cases, and cultivation of critical thinking and clinical reasoning abilities (Fig. 3 B, C, D, E). All of which improved significantly ( P < 0.05 for the first aspects and P < 0.01 for the rest). However, the two groups were not comparable ( P > 0.05) in terms of understanding of the teaching content and Satisfaction with the CBL methodology (Fig. 3 A, F).
Upon completion of the questionnaires, participants were invited to proffer recommendations. Notably, in the CBL group, seven students expressed challenges in comprehending TOF and indicated a need for additional time for consolidation to enhance understanding. Conversely, within the CBL-3DP group, twelve students advocated for the augmentation of model repertoire and the expansion of disease-related data collection to bolster pedagogical efficacy across other didactic domains.
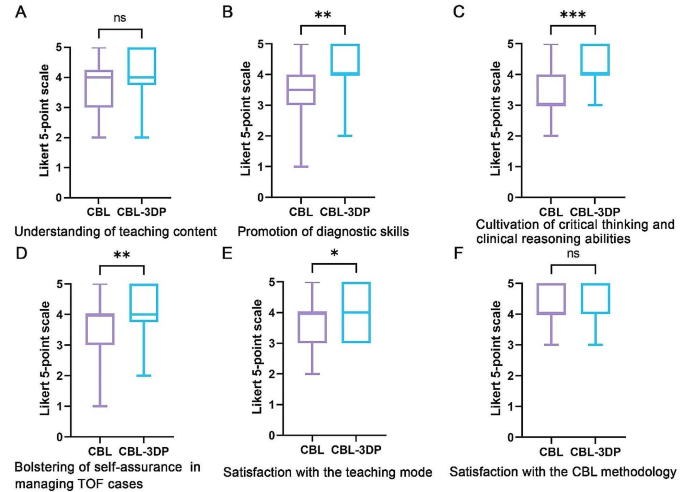
Five-point Likert scores of students’ attitudes in CBL ( n = 30) and CBL-3DP ( n = 30) groups. A Understanding of teaching content. B Promotion of diagnostic skills. C Cultivation of critical thinking and clinical reasoning abilities. D Bolstering of self-assurance in managing TOF cases. E Satisfaction with the teaching mode. F Satisfaction with the CBL methodology. ns No significant difference, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001
TOF presents a significant challenge in clinical practice, necessitating a comprehensive understanding for effective diagnosis and treatment [ 12 ]. Traditional teaching methods in medical schools have relied on conventional resources such as textbooks, 2D illustrations, cadaver dissections, and radiographic materials to impart knowledge about complex conditions like TOF [ 13 ]. However, the limitations of these methods in fully engaging students and bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application have prompted a need for innovative instructional approaches.
CBL has emerged as a valuable tool in medical education, offering students opportunities to engage with authentic clinical cases through group discussions and inquiry-based learning [ 14 ]. By actively involving students in problem-solving and decision-making processes, CBL facilitates the application of theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, thus better-preparing students for future clinical practice [ 15 ]. Our investigation revealed that both groups of students exhibited comparable levels of satisfaction with the CBL methodology, devoid of discernible disparities.
CHD presents a formidable challenge due to the intricate nature of anatomical anomalies, the diverse spectrum of conditions, and individual variations [ 16 ]. Utilizing 3D-printed physical models, derived from patient imaging data, can significantly enhance comprehension of complex anatomical structures [ 17 ]. These models have proven invaluable in guiding surgical planning, providing training for junior or inexperienced pediatric residents, and educating healthcare professionals and parents of patients [ 18 ]. Studies indicate that as much as 50% of pediatric surgical decisions can be influenced by the insights gained from 3D printed models [ 19 ]. By providing tangible, anatomically accurate models, 3D printing offers a unique opportunity for people to visualize complex structures and enhance their understanding of anatomical intricacies. Our study utilized full-color, to-scale 3D printed models to illustrate the structural abnormalities associated with TOF, thereby enriching classroom sessions and facilitating a deeper comprehension of the condition.
Comparative analysis between the CBL-3DP group and the CBL group revealed significant improvements in post-test performance, particularly in pathological anatomy and imaging data interpretation. Additionally, questionnaire responses indicated higher levels of satisfaction and confidence among students in the CBL-3DP group, highlighting the positive impact of incorporating 3D printed models into the learning environment, improving the effectiveness of CBL classroom instruction. Despite the merits, our study has limitations. Primarily, participants were exclusively drawn from the same grade level within a single college, possibly engendering bias owing to shared learning backgrounds. Future research could further strengthen these findings by expanding the sample size and including long-term follow-up to assess the retention of knowledge and skills. Additionally, the influence of the 3D models depicting a normal heart on the learning process and its potential to introduce bias into the results warrants consideration, highlighting a need for scrutiny in subsequent studies.
As medical science continues to advance, the need for effective teaching methods becomes increasingly paramount. Our study underscores the potential of combining active learning approaches like CBL with innovative technologies such as 3D printing to enhance teaching effectiveness, improve knowledge acquisition, and foster students’ confidence and enthusiasm in pursuing clinical careers. Moving forward, further research and integration of such methodologies are essential for meeting the evolving demands of medical education, especially in areas involving complex anatomical understanding.
Conclusions
Integrating 3D-printed models with the CBL method is feasible and effective in TOF instruction. The demonstrated success of this method warrants broad implementation in medical education, particularly for complex anatomical topics.
Data availability
All data supporting the conclusions of this research are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Apitz C, Webb GD, Redington AN. Tetralogy of Fallot. Lancet. 2009;374:1462–71.
Article Google Scholar
Ghosh RM, Jolley MA, Mascio CE, Chen JM, Fuller S, Rome JJ, et al. Clinical 3D modeling to guide pediatric cardiothoracic surgery and intervention using 3D printed anatomic models, computer aided design and virtual reality. 3D Print Med. 2022;8:11.
Chakrabarti R, Wardle K, Wright T, Bennie T, Gishen F. Approaching an undergraduate medical curriculum map: challenges and expectations. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21:341.
Donkin R, Yule H, Fyfe T. Online case-based learning in medical education: a scoping review. BMC Med Educ. 2023;23:564.
Novack JP. Designing cases for case-based immunology teaching in large medical school classes. Front Immunol. 2020;11:995.
Chen HC, Van Den Broek WES, Ten Cate O. The case for use of entrustable professional activities in undergraduate medical education. Acad Med. 2015;90:431–6.
Wang M, Sun Z, Jia M, Wang Y, Wang H, Zhu X, et al. Intelligent virtual case learning system based on real medical records and natural language processing. BMC Med Inf Decis Mak. 2022;22:60.
Yoo S-J, Thabit O, Kim EK, Ide H, Yim D, Dragulescu A, et al. 3D printing in medicine of congenital heart diseases. 3D Print Med. 2015;2:3.
Yammine K, Violato C. A meta-analysis of the educational effectiveness of three-dimensional visualization technologies in teaching anatomy. Anat Sci Educ. 2015;8:525–38.
Miao H, Ding J, Gong X, Zhao J, Li H, Xiong K, et al. Application of 3D-printed pulmonary segment specimens in experimental teaching of sectional anatomy. BMC Surg. 2023;23:109.
Sun Z, Wong YH, Yeong CH. Patient-specific 3D-printed low-cost models in medical education and clinical practice. Micromachines (Basel). 2023;14:464.
Downing TE, Kim YY. Tetralogy of Fallot: general principles of management. Cardiol Clin. 2015;33:531–41. vii–viii.
Jia X, Zeng W, Zhang Q. Combined administration of problem- and lecture-based learning teaching models in medical education in China: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Med (Baltim). 2018;97:e11366.
McLean SF. Case-based learning and its application in medical and health-care fields: a review of worldwide literature. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2016;3:JMECD.S20377.
Zeng N, Lu H, Li S, Yang Q, Liu F, Pan H, et al. Application of the combination of CBL teaching method and SEGUE framework to improve the doctor-patient communication skills of resident physicians in otolaryngology department. Bmc Med Educ. 2024;24:201.
Sun Z. Patient-specific 3D-printed models in pediatric congenital heart disease. Children. 2023;10:319.
Meyer-Szary J, Luis MS, Mikulski S, Patel A, Schulz F, Tretiakow D, et al. The role of 3D printing in planning complex medical procedures and training of medical professionals—cross-sectional multispecialty review. IJERPH. 2022;19:3331.
Sun Z, Wee C. 3D printed models in cardiovascular disease: an exciting future to deliver personalized medicine. Micromachines-basel. 2022;13:1575.
Valverde I, Gomez-Ciriza G, Hussain T, Suarez-Mejias C, Velasco-Forte MN, Byrne N, et al. Three-dimensional printed models for surgical planning of complex congenital heart defects: an international multicentre study. Eur J Cardio-thorac. 2017;52:1139–48.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We extend our sincere appreciation to the instructors and students whose invaluable participated in this study.
This paper received support from the Education Department of Anhui Province, China (Grant Numbers 2022jyxm1693, 2022jyxm1694, 2022xskc103, 2018jyxm1280).
Author information
Jian Zhao and Xin Gong are joint first authors.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Human Anatomy, Wannan Medical College, No.22 West Wenchang Road, Wuhu, 241002, China
Jian Zhao, Xin Gong, Jian Ding, Rui Huang & Huachun Miao
Department of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, Yijishan Hospital of Wannan Medical College, Wuhu, China
Kepin Xiong
Zhuhai Sailner 3D Technology Co., Ltd., Zhuhai, China
Kangle Zhuang
School of Basic Medical Sciences, Wannan Medical College, Wuhu, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Jian Zhao and Huachun Miao designed the research. Jian Zhao, Xin Gong, Jian Ding, Kepin Xiong designed the tests and questionnaires. Kangle Zhuang processed the imaging data and printed the models. Xing Gong and Kepin Xiong implemented the teaching. Jian Zhao and Rui Huang collected the data and performed the statistical analysis. Jian Zhao and Huachun Miao prepared the manuscript. Shu Li and Huachun Miao revised the manuscript. Shu Li provided the Funding acquisition. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Shu Li or Huachun Miao .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This investigation received ethical approval from the Ethical Committee of School of Basic Medical Sciences, Wannan Medical College (ECBMSWMC2022-1-12). All methodologies adhered strictly to established protocols and guidelines. Written informed consent was obtained from the study participants to take part in the study.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the individuals for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zhao, J., Gong, X., Ding, J. et al. Integration of case-based learning and three-dimensional printing for tetralogy of fallot instruction in clinical medical undergraduates: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Med Educ 24 , 571 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05583-z
Download citation
Received : 03 March 2024
Accepted : 21 May 2024
Published : 24 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05583-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Medical education
- Case-based learning
- 3D printing
- Tetralogy of fallot
- Medical undergraduates
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally about what to do or what to believe. It includes the ability to engage in reflective and independent thinking. Someone with critical thinking skills is able to do the following: Understand the logical connections between ideas. Identify, construct, and evaluate arguments.
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [ 1 ]: Universal. Crucial for the economy. Essential for improving language and presentation skills. Very helpful in promoting creativity. Important for self-reflection.
The kind of thinking which seeks to explore questions about existing knowledge for issues which are not clearly defined and for which there are no clear-cut answers. . In order to display critical thinking, students need to develop skills in. ♦ interpreting: understanding the significance of data and to clarify its meaning.
The Skills We Need for Critical Thinking. The skills that we need in order to be able to think critically are varied and include observation, analysis, interpretation, reflection, evaluation, inference, explanation, problem solving, and decision making. Specifically we need to be able to: Think about a topic or issue in an objective and ...
Critical thinking is the art of making clear, reasoned judgements based on interpreting, understanding, applying and synthesising evidence gathered from observation, reading and experimentation. Essential Study Skills: The Complete Guide to Success at University (4th ed.) London: SAGE, p94. Being critical does not just mean finding fault.
Teach Reasoning Skills. Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
This is an introductory textbook in logic and critical thinking. The goal of the textbook is to provide the reader with a set of tools and skills that will enable them to identify and evaluate arguments. The book is intended for an introductory course that covers both formal and informal logic. As such, it is not a formal logic textbook, but is closer to what one would find marketed as a ...
The concept of critical thinking has been defined in many complex ways, but for young students new to the concept, it can best be summed up as thinking and judging for yourself . When you develop critical thinking skills, you will learn to evaluate information that you hear and process information that you collect while recognizing your ...
Geoff Pynn (Northern Illinois University) gets you started on the critical thinking journey. He tells you what critical thinking is, what an argument is, and...
Introduction to Critical Thinking Critical thinking is an important and vital topic in modern education. All educators are interested in teaching critical thinking to their students. Many academic departments hope that its professors and instructors will become informed about the strategy of teaching critical thinking skills, identify areas in
The essence of the independent mind lies not in what it thinks, but in how it thinks. —Christopher Hitchens, author and journalist. By the end of this section, you will be able to explain critical thinking, describe the role that logic plays in critical thinking, and identify how critical thinking skills can be used to evaluate information.
INTRODUCTION. Critical thinking is a common course in college and uni-versity settings today. Frequently taught as a way to "im- ... Students who develop critical thinking skills often prac-tice those skills well into latter life. These skills may, in fact, literally change their lives forever. Developing criti-
Critical Thinking: A Student's Introduction provides the skills and attitudes needed to become a skilled thinker, an effective problem solver, and a sound decision-maker. Students will learn—step by step—how to understand complex texts, analyze issues, think logically, and argue effectively.
Students grappled with ideas and their beliefs and employed deep critical-thinking skills to develop arguments for their claims. Embedding critical-thinking skills in curriculum that students care ...
Critical thinking has the power to launch students on unforgettable learning experiences while helping them develop new habits of thought, reflection, and inquiry. Developing these skills prepares ...
It may seem strange to begin a logic textbook with this question. 'Thinking' is perhaps the most intimate and personal thing that people do. Yet the more you 'think' about thinking, the more mysterious it can appear. It is the sort of thing that one intuitively or naturally understands, and yet cannot describe to others without great ...
1 INTRODUCTION. Critical thinking has become key to the skillset that people should develop to have better prospects in the labour market but also for a better personal and civic life. ... These comprise conceptual rubrics that help teachers and students identify the critical thinking sub-skills students should develop, and teachers to reflect ...
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze information objectively and make a reasoned judgment. It involves the evaluation of sources, such as data, facts, observable phenomena, and research findings. Good critical thinkers can draw reasonable conclusions from a set of information, and discriminate between useful and less useful ...
Critical Thinkers can analyse situations and make balanced decisions. This is a key skill looked for by employers. However, many Critical Thinking processes are involved implicitly in other activities, so many students are unaware of their ability to think critically. Students need to be able to demonstrate these skills, in order to show how ...
It is: Critical thinking is that mode of thinking - about any subject, content or problem - in which the thinker improves the quality of his or her thinking by skilfully taking charge of the structures. Question 1.3. 4Critical thinking. inherent in thinking and imposing intellectual standards upon them.
Introduction. Critical thinking skills generally are seen as very important in equipping individuals to participate in a rapidly changing democratic society and economy (e.g. Davies Citation 2015).Critical thinking skills tend to be highly valued in education, especially in university education where their promotion is a key objective around the world (see, e.g. Universities UK Citation 2015 ...
Teach Critical, Creative, and Independent Thinking Introduction. In an ever-evolving world, the ability to think critically, creatively, and independently is more crucial than ever. ... Fostering a sense of curiosity is fundamental to developing thinking skills. Encourage students to ask questions, explore new topics, and seek out information ...
In recent decades, approaches to critical thinking have generally taken a practical turn, pivoting away from more abstract accounts - such as emphasizing the logical relations that hold between statements (Ennis, 1964) - and moving toward an emphasis on belief and action.According to the definition that Robert Ennis (2018) has been advocating for the last few decades, critical thinking is ...
Project-based learning offers alternatives that can potentially improve students' critical thinking skills. This study examines the effect of project-based learning models and creativity on the critical thinking of students in ecosystem learning in class V SDN Kaloy Tamiang Hulu Aceh Tamiang. The quantitative research approach uses the quasi ...
The student workers who are part of the Marvin K. Peterson Library's Researcher 2 Researcher Program serve the Charger community, offering support to students and faculty members while also building their own research, interpersonal, and critical thinking skills.
Comparing the CBL and CBL-3DP groups, the scores from the CBL-3DP group showed significant improvements in many areas. This included satisfaction with the teaching mode, promotion of diagnostic skills, bolstering of self-assurance in managing TOF cases, and cultivation of critical thinking and clinical reasoning abilities (Fig. 3B, C, D