Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an introduction paragraph , how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction paragraph about the importance of education:
Education is often viewed as a fundamental human right and a key social and economic development driver. As Nelson Mandela once famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” It is the key to unlocking a wide range of opportunities and benefits for individuals, societies, and nations. In today’s constantly evolving world, education has become even more critical. It has expanded beyond traditional classroom learning to include digital and remote learning, making education more accessible and convenient. This essay will delve into the importance of education in empowering individuals to achieve their dreams, improving societies by promoting social justice and equality, and driving economic growth by developing a skilled workforce and promoting innovation.
This introduction paragraph example includes a hook (the quote by Nelson Mandela), provides some background information on education, and states the thesis statement (the importance of education).
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.

Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
Similarity Checks: The Author’s Guide to Plagiarism and Responsible Writing
Types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , what is academic writing: tips for students, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &....

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write an introduction paragraph in 3 steps.
General Education

It’s the roadmap to your essay, it’s the forecast for your argument, it’s...your introduction paragraph, and writing one can feel pretty intimidating. The introduction paragraph is a part of just about every kind of academic writing , from persuasive essays to research papers. But that doesn’t mean writing one is easy!
If trying to write an intro paragraph makes you feel like a Muggle trying to do magic, trust us: you aren’t alone. But there are some tips and tricks that can make the process easier—and that’s where we come in.
In this article, we’re going to explain how to write a captivating intro paragraph by covering the following info:
- A discussion of what an introduction paragraph is and its purpose in an essay
- An overview of the most effective introduction paragraph format, with explanations of the three main parts of an intro paragraph
- An analysis of real intro paragraph examples, with a discussion of what works and what doesn’t
- A list of four top tips on how to write an introduction paragraph
Are you ready? Let’s begin!

What Is an Introduction Paragraph?
An introduction paragraph is the first paragraph of an essay , paper, or other type of academic writing. Argumentative essays , book reports, research papers, and even personal essays are common types of writing that require an introduction paragraph. Whether you’re writing a research paper for a science course or an argumentative essay for English class , you’re going to have to write an intro paragraph.
So what’s the purpose of an intro paragraph? As a reader’s first impression of your essay, the intro paragraph should introduce the topic of your paper.
Your introduction will also state any claims, questions, or issues that your paper will focus on. This is commonly known as your paper’s thesis . This condenses the overall point of your paper into one or two short sentences that your reader can come back and reference later.
But intro paragraphs need to do a bit more than just introduce your topic. An intro paragraph is also supposed to grab your reader’s attention. The intro paragraph is your chance to provide just enough info and intrigue to make your reader say, “Hey, this topic sounds interesting. I think I’ll keep reading this essay!” That can help your essay stand out from the crowd.
In most cases, an intro paragraph will be relatively short. A good intro will be clear, brief, purposeful, and focused. While there are some exceptions to this rule, it’s common for intro paragraphs to consist of three to five sentences .
Effectively introducing your essay’s topic, purpose, and getting your reader invested in your essay sounds like a lot to ask from one little paragraph, huh? In the next section, we’ll demystify the intro paragraph format by breaking it down into its core parts . When you learn how to approach each part of an intro, writing one won’t seem so scary!

Once you figure out the three parts of an intro paragraph, writing one will be a piece of cake!
The 3 Main Parts of an Intro Paragraph
In general, an intro paragraph is going to have three main parts: a hook, context, and a thesis statement . Each of these pieces of the intro plays a key role in acquainting the reader with the topic and purpose of your essay.
Below, we’ll explain how to start an introduction paragraph by writing an effective hook, providing context, and crafting a thesis statement. When you put these elements together, you’ll have an intro paragraph that does a great job of making a great first impression on your audience!
Intro Paragraph Part 1: The Hook
When it comes to how to start an introduction paragraph, o ne of the most common approaches is to start with something called a hook.
What does hook mean here, though? Think of it this way: it’s like when you start a new Netflix series: you look up a few hours (and a few episodes) later and you say, “Whoa. I guess I must be hooked on this show!”
That’s how the hook is supposed to work in an intro paragrap h: it should get your reader interested enough that they don’t want to press the proverbial “pause” button while they’re reading it . In other words, a hook is designed to grab your reader’s attention and keep them reading your essay!
This means that the hook comes first in the intro paragraph format—it’ll be the opening sentence of your intro.
It’s important to realize that there are many different ways to write a good hook. But generally speaking, hooks must include these two things: what your topic is, and the angle you’re taking on that topic in your essay.
One approach to writing a hook that works is starting with a general, but interesting, statement on your topic. In this type of hook, you’re trying to provide a broad introduction to your topic and your angle on the topic in an engaging way .
For example, if you’re writing an essay about the role of the government in the American healthcare system, your hook might look something like this:
There's a growing movement to require that the federal government provide affordable, effective healthcare for all Americans.
This hook introduces the essay topic in a broad way (government and healthcare) by presenting a general statement on the topic. But the assumption presented in the hook can also be seen as controversial, which gets readers interested in learning more about what the writer—and the essay—has to say.
In other words, the statement above fulfills the goals of a good hook: it’s intriguing and provides a general introduction to the essay topic.
Intro Paragraph Part 2: Context
Once you’ve provided an attention-grabbing hook, you’ll want to give more context about your essay topic. Context refers to additional details that reveal the specific focus of your paper. So, whereas the hook provides a general introduction to your topic, context starts helping readers understand what exactly you’re going to be writing about
You can include anywhere from one to several sentences of context in your intro, depending on your teacher’s expectations, the length of your paper, and complexity of your topic. In these context-providing sentences, you want to begin narrowing the focus of your intro. You can do this by describing a specific issue or question about your topic that you’ll address in your essay. It also helps readers start to understand why the topic you’re writing about matters and why they should read about it.
So, what counts as context for an intro paragraph? Context can be any important details or descriptions that provide background on existing perspectives, common cultural attitudes, or a specific situation or controversy relating to your essay topic. The context you include should acquaint your reader with the issues, questions, or events that motivated you to write an essay on your topic...and that your reader should know in order to understand your thesis.
For instance, if you’re writing an essay analyzing the consequences of sexism in Hollywood, the context you include after your hook might make reference to the #metoo and #timesup movements that have generated public support for victims of sexual harassment.
The key takeaway here is that context establishes why you’re addressing your topic and what makes it important. It also sets you up for success on the final piece of an intro paragraph: the thesis statement.
Elle Woods' statement offers a specific point of view on the topic of murder...which means it could serve as a pretty decent thesis statement!
Intro Paragraph Part 3: The Thesis
The final key part of how to write an intro paragraph is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the backbone of your introduction: it conveys your argument or point of view on your topic in a clear, concise, and compelling way . The thesis is usually the last sentence of your intro paragraph.
Whether it’s making a claim, outlining key points, or stating a hypothesis, your thesis statement will tell your reader exactly what idea(s) are going to be addressed in your essay. A good thesis statement will be clear, straightforward, and highlight the overall point you’re trying to make.
Some instructors also ask students to include an essay map as part of their thesis. An essay map is a section that outlines the major topics a paper will address. So for instance, say you’re writing a paper that argues for the importance of public transport in rural communities. Your thesis and essay map might look like this:
Having public transport in rural communities helps people improve their economic situation by giving them reliable transportation to their job, reducing the amount of money they spend on gas, and providing new and unionized work .
The underlined section is the essay map because it touches on the three big things the writer will talk about later. It literally maps out the rest of the essay!
So let’s review: Your thesis takes the idea you’ve introduced in your hook and context and wraps it up. Think of it like a television episode: the hook sets the scene by presenting a general statement and/or interesting idea that sucks you in. The context advances the plot by describing the topic in more detail and helping readers understand why the topic is important. And finally, the thesis statement provides the climax by telling the reader what you have to say about the topic.
The thesis statement is the most important part of the intro. Without it, your reader won’t know what the purpose of your essay is! And for a piece of writing to be effective, it needs to have a clear purpose. Your thesis statement conveys that purpose , so it’s important to put careful thought into writing a clear and compelling thesis statement.

How To Write an Introduction Paragraph: Example and Analysis
Now that we’ve provided an intro paragraph outline and have explained the three key parts of an intro paragraph, let’s take a look at an intro paragraph in action.
To show you how an intro paragraph works, we’ve included a sample introduction paragraph below, followed by an analysis of its strengths and weaknesses.
Example of Introduction Paragraph
While college students in the U.S. are struggling with how to pay for college, there is another surprising demographic that’s affected by the pressure to pay for college: families and parents. In the face of tuition price tags that total more than $100,000 (as a low estimate), families must make difficult decisions about how to save for their children’s college education. Charting a feasible path to saving for college is further complicated by the FAFSA’s estimates for an “Expected Family Contribution”—an amount of money that is rarely feasible for most American families. Due to these challenging financial circumstances and cultural pressure to give one’s children the best possible chance of success in adulthood, many families are going into serious debt to pay for their children’s college education. The U.S. government should move toward bearing more of the financial burden of college education.
Example of Introduction Paragraph: Analysis
Before we dive into analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of this example intro paragraph, let’s establish the essay topic. The sample intro indicates that t he essay topic will focus on one specific issue: who should cover the cost of college education in the U.S., and why. Both the hook and the context help us identify the topic, while the thesis in the last sentence tells us why this topic matters to the writer—they think the U.S. Government needs to help finance college education. This is also the writer’s argument, which they’ll cover in the body of their essay.
Now that we’ve identified the essay topic presented in the sample intro, let’s dig into some analysis. To pin down its strengths and weaknesses, we’re going to use the following three questions to guide our example of introduction paragraph analysis:
- Does this intro provide an attention-grabbing opening sentence that conveys the essay topic?
- Does this intro provide relevant, engaging context about the essay topic?
- Does this intro provide a thesis statement that establishes the writer’s point of view on the topic and what specific aspects of the issue the essay will address?
Now, let’s use the questions above to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of this sample intro paragraph.
Does the Intro Have a Good Hook?
First, the intro starts out with an attention-grabbing hook . The writer starts by presenting an assumption (that the U.S. federal government bears most of the financial burden of college education), which makes the topic relatable to a wide audience of readers. Also note that the hook relates to the general topic of the essay, which is the high cost of college education.
The hook then takes a surprising turn by presenting a counterclaim : that American families, rather than students, feel the true burden of paying for college. Some readers will have a strong emotional reaction to this provocative counterclaim, which will make them want to keep reading! As such, this intro provides an effective opening sentence that conveys the essay topic.
Does the Intro Give Context?
T he second, third, and fourth sentences of the intro provide contextual details that reveal the specific focus of the writer’s paper . Remember: the context helps readers start to zoom in on what the paper will focus on, and what aspect of the general topic (college costs) will be discussed later on.
The context in this intro reveals the intent and direction of the paper by explaining why the issue of families financing college is important. In other words, the context helps readers understand why this issue matters , and what aspects of this issue will be addressed in the paper.
To provide effective context, the writer refers to issues (the exorbitant cost of college and high levels of family debt) that have received a lot of recent scholarly and media attention. These sentences of context also elaborate on the interesting perspective included in the hook: that American families are most affected by college costs.
Does the Intro Have a Thesis?
Finally, this intro provides a thesis statement that conveys the writer’s point of view on the issue of financing college education. This writer believes that the U.S. government should do more to pay for students’ college educations.
However, the thesis statement doesn’t give us any details about why the writer has made this claim or why this will help American families . There isn’t an essay map that helps readers understand what points the writer will make in the essay.
To revise this thesis statement so that it establishes the specific aspects of the topic that the essay will address, the writer could add the following to the beginning of the thesis statement:
The U.S. government should take on more of the financial burden of college education because other countries have shown this can improve education rates while reducing levels of familial poverty.
Check out the new section in bold. Not only does it clarify that the writer is talking about the pressure put on families, it touches on the big topics the writer will address in the paper: improving education rates and reduction of poverty. So not only do we have a clearer argumentative statement in this thesis, we also have an essay map!
So, let’s recap our analysis. This sample intro paragraph does an effective job of providing an engaging hook and relatable, interesting context, but the thesis statement needs some work ! As you write your own intro paragraphs, you might consider using the questions above to evaluate and revise your work. Doing this will help ensure you’ve covered all of your bases and written an intro that your readers will find interesting!

4 Tips for How To Write an Introduction Paragraph
Now that we’ve gone over an example of introduction paragraph analysis, let’s talk about how to write an introduction paragraph of your own. Keep reading for four tips for writing a successful intro paragraph for any essay.
Tip 1: Analyze Your Essay Prompt
If you’re having trouble with how to start an introduction paragraph, analyze your essay prompt! Most teachers give you some kind of assignment sheet, formal instructions, or prompt to set the expectations for an essay they’ve assigned, right? Those instructions can help guide you as you write your intro paragraph!
Because they’ll be reading and responding to your essay, you want to make sure you meet your teacher’s expectations for an intro paragraph . For instance, if they’ve provided specific instructions about how long the intro should be or where the thesis statement should be located, be sure to follow them!
The type of paper you’re writing can give you clues as to how to approach your intro as well. If you’re writing a research paper, your professor might expect you to provide a research question or state a hypothesis in your intro. If you’re writing an argumentative essay, you’ll need to make sure your intro overviews the context surrounding your argument and your thesis statement includes a clear, defensible claim.
Using the parameters set out by your instructor and assignment sheet can put some easy-to-follow boundaries in place for things like your intro’s length, structure, and content. Following these guidelines can free you up to focus on other aspects of your intro... like coming up with an exciting hook and conveying your point of view on your topic!
Tip 2: Narrow Your Topic
You can’t write an intro paragraph without first identifying your topic. To make your intro as effective as possible, you need to define the parameters of your topic clearly—and you need to be specific.
For example, let’s say you want to write about college football. “NCAA football” is too broad of a topic for a paper. There is a lot to talk about in terms of college football! It would be tough to write an intro paragraph that’s focused, purposeful, and engaging on this topic. In fact, if you did try to address this whole topic, you’d probably end up writing a book!
Instead, you should narrow broad topics to identify a specific question, claim, or issue pertaining to some aspect of NCAA football for your intro to be effective. So, for instance, you could frame your topic as, “How can college professors better support NCAA football players in academics?” This focused topic pertaining to NCAA football would give you a more manageable angle to discuss in your paper.
So before you think about writing your intro, ask yourself: Is my essay topic specific, focused, and logical? Does it convey an issue or question that I can explore over the course of several pages? Once you’ve established a good topic, you’ll have the foundation you need to write an effective intro paragraph .

Once you've figured out your topic, it's time to hit the books!
Tip 3: Do Your Research
This tip is tightly intertwined with the one above, and it’s crucial to writing a good intro: do your research! And, guess what? This tip applies to all papers—even ones that aren’t technically research papers.
Here’s why you need to do some research: getting the lay of the land on what others have said about your topic—whether that’s scholars and researchers or the mass media— will help you narrow your topic, write an engaging hook, and provide relatable context.
You don't want to sit down to write your intro without a solid understanding of the different perspectives on your topic. Whether those are the perspectives of experts or the general public, these points of view will help you write your intro in a way that is intriguing and compelling for your audience of readers.
Tip 4: Write Multiple Drafts
Some say to write your intro first; others say write it last. The truth is, there isn’t a right or wrong time to write your intro—but you do need to have enough time to write multiple drafts .
Oftentimes, your professor will ask you to write multiple drafts of your paper, which gives you a built-in way to make sure you revise your intro. Another approach you could take is to write out a rough draft of your intro before you begin writing your essay, then revise it multiple times as you draft out your paper.
Here’s why this approach can work: as you write your paper, you’ll probably come up with new insights on your topic that you didn’t have right from the start. You can use these “light bulb” moments to reevaluate your intro and make revisions that keep it in line with your developing essay draft.
Once you’ve written your entire essay, consider going back and revising your intro again . You can ask yourself these questions as you evaluate your intro:
- Is my hook still relevant to the way I’ve approached the topic in my essay?
- Do I provide enough appropriate context to introduce my essay?
- Now that my essay is written, does my thesis statement still accurately reflect the point of view that I present in my essay?
Using these questions as a guide and putting your intro through multiple revisions will help ensure that you’ve written the best intro for the final draft of your essay. Also, revising your writing is always a good thing to do—and this applies to your intro, too!

What's Next?
Your college essays also need great intro paragraphs. Here’s a guide that focuses on how to write the perfect intro for your admissions essays.
Of course, the intro is just one part of your college essay . This article will teach you how to write a college essay that makes admissions counselors sit up and take notice.
Are you trying to write an analytical essay? Our step-by-step guide can help you knock it out of the park.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

Introductions
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain the functions of introductions, offer strategies for creating effective introductions, and provide some examples of less effective introductions to avoid.
The role of introductions
Introductions and conclusions can be the most difficult parts of papers to write. Usually when you sit down to respond to an assignment, you have at least some sense of what you want to say in the body of your paper. You might have chosen a few examples you want to use or have an idea that will help you answer the main question of your assignment; these sections, therefore, may not be as hard to write. And it’s fine to write them first! But in your final draft, these middle parts of the paper can’t just come out of thin air; they need to be introduced and concluded in a way that makes sense to your reader.
Your introduction and conclusion act as bridges that transport your readers from their own lives into the “place” of your analysis. If your readers pick up your paper about education in the autobiography of Frederick Douglass, for example, they need a transition to help them leave behind the world of Chapel Hill, television, e-mail, and The Daily Tar Heel and to help them temporarily enter the world of nineteenth-century American slavery. By providing an introduction that helps your readers make a transition between their own world and the issues you will be writing about, you give your readers the tools they need to get into your topic and care about what you are saying. Similarly, once you’ve hooked your readers with the introduction and offered evidence to prove your thesis, your conclusion can provide a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. (See our handout on conclusions .)
Note that what constitutes a good introduction may vary widely based on the kind of paper you are writing and the academic discipline in which you are writing it. If you are uncertain what kind of introduction is expected, ask your instructor.
Why bother writing a good introduction?
You never get a second chance to make a first impression. The opening paragraph of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions of your argument, your writing style, and the overall quality of your work. A vague, disorganized, error-filled, off-the-wall, or boring introduction will probably create a negative impression. On the other hand, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will start your readers off thinking highly of you, your analytical skills, your writing, and your paper.
Your introduction is an important road map for the rest of your paper. Your introduction conveys a lot of information to your readers. You can let them know what your topic is, why it is important, and how you plan to proceed with your discussion. In many academic disciplines, your introduction should contain a thesis that will assert your main argument. Your introduction should also give the reader a sense of the kinds of information you will use to make that argument and the general organization of the paragraphs and pages that will follow. After reading your introduction, your readers should not have any major surprises in store when they read the main body of your paper.
Ideally, your introduction will make your readers want to read your paper. The introduction should capture your readers’ interest, making them want to read the rest of your paper. Opening with a compelling story, an interesting question, or a vivid example can get your readers to see why your topic matters and serve as an invitation for them to join you for an engaging intellectual conversation (remember, though, that these strategies may not be suitable for all papers and disciplines).
Strategies for writing an effective introduction
Start by thinking about the question (or questions) you are trying to answer. Your entire essay will be a response to this question, and your introduction is the first step toward that end. Your direct answer to the assigned question will be your thesis, and your thesis will likely be included in your introduction, so it is a good idea to use the question as a jumping off point. Imagine that you are assigned the following question:
Drawing on the Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass , discuss the relationship between education and slavery in 19th-century America. Consider the following: How did white control of education reinforce slavery? How did Douglass and other enslaved African Americans view education while they endured slavery? And what role did education play in the acquisition of freedom? Most importantly, consider the degree to which education was or was not a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
You will probably refer back to your assignment extensively as you prepare your complete essay, and the prompt itself can also give you some clues about how to approach the introduction. Notice that it starts with a broad statement and then narrows to focus on specific questions from the book. One strategy might be to use a similar model in your own introduction—start off with a big picture sentence or two and then focus in on the details of your argument about Douglass. Of course, a different approach could also be very successful, but looking at the way the professor set up the question can sometimes give you some ideas for how you might answer it. (See our handout on understanding assignments for additional information on the hidden clues in assignments.)
Decide how general or broad your opening should be. Keep in mind that even a “big picture” opening needs to be clearly related to your topic; an opening sentence that said “Human beings, more than any other creatures on earth, are capable of learning” would be too broad for our sample assignment about slavery and education. If you have ever used Google Maps or similar programs, that experience can provide a helpful way of thinking about how broad your opening should be. Imagine that you’re researching Chapel Hill. If what you want to find out is whether Chapel Hill is at roughly the same latitude as Rome, it might make sense to hit that little “minus” sign on the online map until it has zoomed all the way out and you can see the whole globe. If you’re trying to figure out how to get from Chapel Hill to Wrightsville Beach, it might make more sense to zoom in to the level where you can see most of North Carolina (but not the rest of the world, or even the rest of the United States). And if you are looking for the intersection of Ridge Road and Manning Drive so that you can find the Writing Center’s main office, you may need to zoom all the way in. The question you are asking determines how “broad” your view should be. In the sample assignment above, the questions are probably at the “state” or “city” level of generality. When writing, you need to place your ideas in context—but that context doesn’t generally have to be as big as the whole galaxy!
Try writing your introduction last. You may think that you have to write your introduction first, but that isn’t necessarily true, and it isn’t always the most effective way to craft a good introduction. You may find that you don’t know precisely what you are going to argue at the beginning of the writing process. It is perfectly fine to start out thinking that you want to argue a particular point but wind up arguing something slightly or even dramatically different by the time you’ve written most of the paper. The writing process can be an important way to organize your ideas, think through complicated issues, refine your thoughts, and develop a sophisticated argument. However, an introduction written at the beginning of that discovery process will not necessarily reflect what you wind up with at the end. You will need to revise your paper to make sure that the introduction, all of the evidence, and the conclusion reflect the argument you intend. Sometimes it’s easiest to just write up all of your evidence first and then write the introduction last—that way you can be sure that the introduction will match the body of the paper.
Don’t be afraid to write a tentative introduction first and then change it later. Some people find that they need to write some kind of introduction in order to get the writing process started. That’s fine, but if you are one of those people, be sure to return to your initial introduction later and rewrite if necessary.
Open with something that will draw readers in. Consider these options (remembering that they may not be suitable for all kinds of papers):
- an intriguing example —for example, Douglass writes about a mistress who initially teaches him but then ceases her instruction as she learns more about slavery.
- a provocative quotation that is closely related to your argument —for example, Douglass writes that “education and slavery were incompatible with each other.” (Quotes from famous people, inspirational quotes, etc. may not work well for an academic paper; in this example, the quote is from the author himself.)
- a puzzling scenario —for example, Frederick Douglass says of slaves that “[N]othing has been left undone to cripple their intellects, darken their minds, debase their moral nature, obliterate all traces of their relationship to mankind; and yet how wonderfully they have sustained the mighty load of a most frightful bondage, under which they have been groaning for centuries!” Douglass clearly asserts that slave owners went to great lengths to destroy the mental capacities of slaves, yet his own life story proves that these efforts could be unsuccessful.
- a vivid and perhaps unexpected anecdote —for example, “Learning about slavery in the American history course at Frederick Douglass High School, students studied the work slaves did, the impact of slavery on their families, and the rules that governed their lives. We didn’t discuss education, however, until one student, Mary, raised her hand and asked, ‘But when did they go to school?’ That modern high school students could not conceive of an American childhood devoid of formal education speaks volumes about the centrality of education to American youth today and also suggests the significance of the deprivation of education in past generations.”
- a thought-provoking question —for example, given all of the freedoms that were denied enslaved individuals in the American South, why does Frederick Douglass focus his attentions so squarely on education and literacy?
Pay special attention to your first sentence. Start off on the right foot with your readers by making sure that the first sentence actually says something useful and that it does so in an interesting and polished way.
How to evaluate your introduction draft
Ask a friend to read your introduction and then tell you what they expect the paper will discuss, what kinds of evidence the paper will use, and what the tone of the paper will be. If your friend is able to predict the rest of your paper accurately, you probably have a good introduction.
Five kinds of less effective introductions
1. The placeholder introduction. When you don’t have much to say on a given topic, it is easy to create this kind of introduction. Essentially, this kind of weaker introduction contains several sentences that are vague and don’t really say much. They exist just to take up the “introduction space” in your paper. If you had something more effective to say, you would probably say it, but in the meantime this paragraph is just a place holder.
Example: Slavery was one of the greatest tragedies in American history. There were many different aspects of slavery. Each created different kinds of problems for enslaved people.
2. The restated question introduction. Restating the question can sometimes be an effective strategy, but it can be easy to stop at JUST restating the question instead of offering a more specific, interesting introduction to your paper. The professor or teaching assistant wrote your question and will be reading many essays in response to it—they do not need to read a whole paragraph that simply restates the question.
Example: The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass discusses the relationship between education and slavery in 19th century America, showing how white control of education reinforced slavery and how Douglass and other enslaved African Americans viewed education while they endured. Moreover, the book discusses the role that education played in the acquisition of freedom. Education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
3. The Webster’s Dictionary introduction. This introduction begins by giving the dictionary definition of one or more of the words in the assigned question. Anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and copy down what Webster says. If you want to open with a discussion of an important term, it may be far more interesting for you (and your reader) if you develop your own definition of the term in the specific context of your class and assignment. You may also be able to use a definition from one of the sources you’ve been reading for class. Also recognize that the dictionary is also not a particularly authoritative work—it doesn’t take into account the context of your course and doesn’t offer particularly detailed information. If you feel that you must seek out an authority, try to find one that is very relevant and specific. Perhaps a quotation from a source reading might prove better? Dictionary introductions are also ineffective simply because they are so overused. Instructors may see a great many papers that begin in this way, greatly decreasing the dramatic impact that any one of those papers will have.
Example: Webster’s dictionary defines slavery as “the state of being a slave,” as “the practice of owning slaves,” and as “a condition of hard work and subjection.”
4. The “dawn of man” introduction. This kind of introduction generally makes broad, sweeping statements about the relevance of this topic since the beginning of time, throughout the world, etc. It is usually very general (similar to the placeholder introduction) and fails to connect to the thesis. It may employ cliches—the phrases “the dawn of man” and “throughout human history” are examples, and it’s hard to imagine a time when starting with one of these would work. Instructors often find them extremely annoying.
Example: Since the dawn of man, slavery has been a problem in human history.
5. The book report introduction. This introduction is what you had to do for your elementary school book reports. It gives the name and author of the book you are writing about, tells what the book is about, and offers other basic facts about the book. You might resort to this sort of introduction when you are trying to fill space because it’s a familiar, comfortable format. It is ineffective because it offers details that your reader probably already knows and that are irrelevant to the thesis.
Example: Frederick Douglass wrote his autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, An American Slave , in the 1840s. It was published in 1986 by Penguin Books. In it, he tells the story of his life.
And now for the conclusion…
Writing an effective introduction can be tough. Try playing around with several different options and choose the one that ends up sounding best to you!
Just as your introduction helps readers make the transition to your topic, your conclusion needs to help them return to their daily lives–but with a lasting sense of how what they have just read is useful or meaningful. Check out our handout on conclusions for tips on ending your paper as effectively as you began it!
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Douglass, Frederick. 1995. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself . New York: Dover.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Excellent Essay Introduction

3-minute read
- 27th September 2022
Love it or hate it, essay writing is a big part of student life. Writing a great essay might seem like a daunting task, especially when you’re staring at a blank document, but there are formulas you can follow to make sure your paper hits the mark.
When you plan your essays , don’t neglect your introduction! It might seem like a trivial part of the paper, but it can make it or break it. A badly written introduction can leave your reader feeling confused about the topic and what to expect from your essay.
To help your writing reach its full potential, we’ve put together a guide to writing an excellent essay introduction.
How to Write an Essay Introduction
An essay introduction has four main steps:
● Hook your reader
● Provide context
● Present your thesis statement
● Map your essay
Hook Your Reader
The first part of your introduction should be the hook. This is where you introduce the reader to the topic of the essay. A great hook should be clear, concise, and catchy. It doesn’t need to be long; a hook can be just one sentence.
Provide Context
In this section, introduce your reader to key definitions, ideas, and background information to help them understand your argument.
Present Your Thesis Statement
A thesis statement tells the reader the main point or argument of the essay. This can be just one sentence, or it can be a few sentences.
Map Your Essay
Before you wrap up your essay introduction, map it! This means signposting sections of your essay. The key here is to be concise. The purpose of this part of the introduction is to give your reader a sense of direction.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction:
Hook: Suspense is key for dramatic stories, and Shakespeare is well-known and celebrated for writing suspenseful plays.
Context: While there are many ways in which Shakespeare created suspension for his viewers, two techniques he used effectively were foreshadowing and dramatic irony. Foreshadowing is a literary device that hints at an event or situation that is yet to happen. Dramatic irony is a literary technique, originally used in Greek tragedy, by which the full significance of a character’s words or actions is clear to the audience or reader, although it is unknown to the character.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Thesis statement: Foreshadowing and dramatic irony are two powerful techniques that Shakespeare used to create suspense in literature. These methods have been used to keep the reader intrigued, excited, or nervous about what is to come in many of his celebrated works.
Essay mapping: In this essay, I will be detailing how Shakespeare uses foreshadowing and dramatic irony to create suspense, with examples from Romeo and Juliet and Othello.
Pro tip: Essays take twists and turns. We recommend changing your introduction as necessary while you write the main text to make sure it fully aligns with your final draft.
Proofread and Editing
Proofreading is an essential part of delivering a great essay. We offer a proofreading and editing service for students and academics that will provide you with expert editors to check your work for any issues with:
● Grammar
● Spelling
● Formatting
● Tone
● Audience
● Consistency
● Accuracy
● Clarity
Want 500 words of your work proofread completely free of charge?
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
How to insert a text box in a google doc.
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Introduce Evidence: 41 Effective Phrases & Examples
Research requires us to scrutinize information and assess its credibility. Accordingly, when we think about various phenomena, we examine empirical data and craft detailed explanations justifying our interpretations. An essential component of constructing our research narratives is thus providing supporting evidence and examples.
The type of proof we provide can either bolster our claims or leave readers confused or skeptical of our analysis. Therefore, it’s crucial that we use appropriate, logical phrases that guide readers clearly from one idea to the next. In this article, we explain how evidence and examples should be introduced according to different contexts in academic writing and catalog effective language you can use to support your arguments, examples included.
When to Introduce Evidence and Examples in a Paper
Evidence and examples create the foundation upon which your claims can stand firm. Without proof, your arguments lack credibility and teeth. However, laundry listing evidence is as bad as failing to provide any materials or information that can substantiate your conclusions. Therefore, when you introduce examples, make sure to judiciously provide evidence when needed and use phrases that will appropriately and clearly explain how the proof supports your argument.
There are different types of claims and different types of evidence in writing. You should introduce and link your arguments to evidence when you
- state information that is not “common knowledge”;
- draw conclusions, make inferences, or suggest implications based on specific data;
- need to clarify a prior statement, and it would be more effectively done with an illustration;
- need to identify representative examples of a category;
- desire to distinguish concepts; and
- emphasize a point by highlighting a specific situation.
Introductory Phrases to Use and Their Contexts
To assist you with effectively supporting your statements, we have organized the introductory phrases below according to their function. This list is not exhaustive but will provide you with ideas of the types of phrases you can use.
Although any research author can make use of these helpful phrases and bolster their academic writing by entering them into their work, before submitting to a journal, it is a good idea to let a professional English editing service take a look to ensure that all terms and phrases make sense in the given research context. Wordvice offers paper editing , thesis editing , and dissertation editing services that help elevate your academic language and make your writing more compelling to journal authors and researchers alike.
For more examples of strong verbs for research writing , effective transition words for academic papers , or commonly confused words , head over to the Wordvice Academic Resources website.
How To Write An Essay
Essay Introduction

Writing an Essay Introduction - Step by Step Guide
Published on: Dec 26, 2020
Last updated on: Jan 30, 2024

People also read
How To Write An Essay - "The Secret To Craft an A+ Essay"
Learn How to Title an Essay Like a Professional Writer
How to Write an Essay Outline Like a Pro
Essay Format - An Easy Guide & Examples
What is a Thesis Statement, and How is it Written? - Know Here
Arguable and Strong Thesis Statement Examples for Your Essay
200+ Creative Hook Examples: Ready, Set, Hook
A Guide to Writing a 1000 Word Essay for School or College
All You Need to Know About a 500-word Essay
Different Types of Essay: Definition With Best Examples
Transition Words for Essays - An Ultimate List
Jumpstart Your Writing with These Proven Strategies on How to Start an Essay
Learn How to Write a Topic Sentence that Stands Out
A Guide to Crafting an Impactful Conclusion for Your Essay
Amazing Essay Topics & Ideas for Your Next Project (2024)
Explore the Different Types of Sentences with Examples
Share this article
Many students struggle with writing essay introductions that grab the reader's attention and set the stage for a strong argument.
It's frustrating when your well-researched essay doesn't get the recognition it deserves because your introduction falls flat. You deserve better results for your hard work!
In this guide, you’ll learn how to create engaging essay introductions that leave a lasting impression. From catchy opening lines to clear thesis statements, you'll learn techniques to hook your readers from the very beginning.
So, read on and learn how to write the perfect catchy introduction for your essay.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Good Essay Introduction?
An introduction is good if it gives a clear idea of what an essay is about. It tells the reader what to expect from the type of academic writing you are presenting.
However, it should strike a balance between being informative and engaging, avoiding excessive detail that may lead to confusion.
A strong introduction is engaging, attractive, and also informative. Itâs important to note that an essay introduction paragraph should not be too short or too long.
Remember, the introduction sets the stage for the body of your essay. So, keep it concise and focused while hinting at the critical elements you'll explore in more depth later.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How to Write an Essay Introduction?
Crafting an effective essay introduction is essential for capturing your reader's attention and setting the tone for your entire piece of writing. To ensure your introduction is engaging and impactful, you can follow an introduction format.
Here is the essay introduction format that will help you write an introduction for your essay easily.
1. Hook Sentence
A hook sentence is a must for the introductory part of an essay. It helps to keep the reader engaged in your content and seek the readerâs attention. It is an attention-grabbing sentence that develops the interest of the reader. It develops the anxiousness of reading the complete essay.
You can use the following as the hook sentence in your essay introduction:
- A famous quotation
- An interesting fact
- An anecdote
All of the above are attention-grabbing things that prove to be perfect for a hook sentence.
Not sure how to create an attention-grabbing hook statement? Check out these hook statement examples to get a better idea!
2. Background Information
Once you have provided an interesting hook sentence, it's time that you provide a little background information related to your essay topic.
The background information should comprise two or three sentences. The information should include the reason why you chose the topic and what is the expected scope of the topic.
Also, clarify the theme and nature of your essay.
3. Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a significant element of not just the introduction but also the whole essay. It is a statement that gives an overview of your complete essay.
It should be written in such a way that the reader can have an idea about the whole purpose of your essay.
Before you write a thesis statement for your essay, try looking into some thesis statement examples. It will help you write a meaningful statement for your essay.
A thesis statement is mentioned after the background information and before the last sentence of the introductory paragraph. The last sentence of the introduction is a transitional sentence.
Need more information on crafting an impactful thesis statement? Read this insightful guide on writing a thesis statement to get started!
4. Transition Sentence
To end the introduction paragraph in a good way, a transition sentence is used. This sentence helps to relate the introduction to the rest of the essay.
In such a sentence, we mention a hint about the elements that we will be discussing next.
Check out this list of transition words to write a good transition sentence.
Essay Introduction Template
Essay Introduction Starters
The introduction of your essay plays a crucial role in captivating your readers and setting the tone for the rest of your paper.
To help you craft an impressive introduction, here are some effective essay introduction phrases that you can use:
- "In today's society, [topic] has become an increasingly significant issue."
- "From [historical event] to [current trend], [topic] has shaped our world in numerous ways."
- "Imagine a world where [scenario]. This is the reality that [topic] addresses."
- "Have you ever wondered about [question]? In this essay, we will explore the answers and delve into [topic]."
- "Throughout history, humanity has grappled with the complexities of [topic]."
Here are some more words to start an introduction paragraph with:
- "Throughout"
- "In today's"
- "With the advent of"
- "In recent years"
- "From ancient times"
Remember, these words are just tools to help you begin your introduction. Choose the words that best fit your essay topic and the tone you want to set.
Essay Introduction Examples
To help you get started, here are some examples of different essay types:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Examples
In an argumentative essay, we introduce an argument and support the side that we think is more accurate. Here is a short example of the introduction of a short argumentative essay.
Reflective Essay Introduction Examples
A writer writes a reflective essay to share a personal real-life experience. It is a very interesting essay type as it allows you to be yourself and speak your heart out.
Here is a well-written example of a reflective essay introduction.
Controversial Essay Introduction Examples
A controversial essay is a type of expository essay. It is written to discuss a topic that has controversy in it.
Below is a sample abortion essay introduction
Here are some more examples:
Essay introduction body and conclusion
Heritage Day essay introduction
Covid-19 essay introduction body conclusion
Tips for Writing an Essay Introduction
The following are some tips for what you should and should not do to write a good and meaningful essay introduction.
- Do grab the reader's attention with a captivating opening sentence.
- Do provide a clear and concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument of your essay.
- Do give a brief overview of the key points you will discuss in the body paragraphs.
- Do use relevant and engaging examples or anecdotes to support your introduction.
- Do consider the tone and style that best suits your essay topic and audience.
- Do revise and edit your introduction to ensure it flows smoothly with the rest of your essay.
- Don't use clichés or overused phrases as your opening line.
- Don't make your introduction overly lengthy or complex .
- Don't include unnecessary background information that doesn't contribute to the main idea.
- Don't introduce new information or arguments in the introduction that will be discussed later in the body paragraphs.
- Don't use informal language or slang unless it aligns with the essay's purpose and audience.
- Don't forget to proofread your introduction for grammar and spelling errors before finalizing it.
Remember to follow the do's and avoid the don'ts to create an impactful opening that hooks your readers from the start.
Now you know the steps and have the tips and tools to get started on creating your essayâs introduction. However, if you are a beginner, it can be difficult for you to do this task on your own.
This is what our professional essay writing service is for! We have a team of professional writers who can help you with all your writing assignments. Also, we have a customer support team available 24/7 to assist you.
Place your order now, and our customer support representative will get back to you right away. Try our essay writer ai today!
Barbara P (Literature, Marketing)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
How to write an Essay Introduction (5-Step Formula)

One of my friends – a high-up professor in an English university – told me he can tell the grade a student will get within the first 90 seconds of reading a paper.
This makes the introduction the most important paragraph in your whole paper.
The introduction orients your reader to how well you understand academic writing, your skills in critical thinking, your ability to write professionally with minimal errors, and the depth of knowledge you have on the topic.
All in one fantastic paragraph! No pressure.
No wonder introductions are so difficult to write. If you’re like me, you find that you can sit and stare at a blank page as the moments tick by. You’re just not sure how to write an introduction!
After reading the top 30 online articles on how to write an essay introduction, I synthesized the five most common steps that universities give on how to write an introduction.
The five steps I am going to introduce to you in this paragraph are from my I.N.T.R.O. method. The intro method provides an easy-to-use acronym for how to write an introduction that the top universities recommend.
The INTRO method’s steps are:
- [I] Interest: Provide an opening sentence that shows why the topic is of interest to everyday human beings
- [N] Notify: Notify the reader of background or contextual information
- [T] Translate: Translate the essay topic or question by paraphrasing it
- [R] Report: Report on your position or argument
- [O] Outline: Provide an outline of the essay structure
Below, I go through each step one by one. Each step is designed to be written in order, although you may feel free to mix them up after you’ve written each sentence to make it feel and read just the way you like.
Use the INTRO method as a guide for how to write an introduction and get words down on paper. As I often argue on this website, just writing something is often the hardest part .
You may also find that some essay introductions work better without one or more of these 5 steps. That is okay, too. Use these 5 steps as advice on points to include in an introduction and adjust them as you need. You may find in your specific area of study you need to add or remove other sentences. Play around with your introduction until you feel comfortable with it.
So don’t be too hard on yourself: have a go at a draft of your introduction with no pressure to use it in the end. You’ll find by the time you’ve written these five sentences you’ll have the creative juices flowing and a compelling introduction will be down on paper in no time.
1. Interest
Provide an opening sentence that shows why the topic is interesting to everyday human beings
Nearly every source on how to write an introduction that I found online recommended that your first sentence be an engaging ‘hook’ . Most sources highlight that the ‘hook’ sentence should draw in the reader’s interest in order to make your piece stand out.
The marker wants to see if you understand why this topic is of interest is in the first place. They want to see if you ‘get it’ from the very start.
I also recommend that you view the hook as an opportunity to show why the topic is interesting to everyday human beings . This makes it relevant to your reader.
To show you understand why the topic is of interest in the first place, aim to do one of the following things:
- Show what makes the topic worth discussing. Your ‘Interest’ sentence might help show why someone should care about the topic. Will it affect our livelihoods? Will it harm us? Make our work lives easier? The more relatable this point is to real human lives, the better.
- Highlight the single most interesting point in the essay. You might notice that you have already pointed out this interesting ‘hook’ somewhere in your essay. Find that interesting, relatable point and make it the opening sentence of your introduction.
- Use an interesting fact or figure to show the topic’s importance. Percentages or real numbers about how many people are or would be impacted by the issue help to show the topic’s importance. This will create reader interest with a ‘wow’ factor.
- Show how the essay topic is relevant to today’s world. If you’re struggling to identify this interesting ‘hook’, go onto google and find news reports related to your topic. How has the topic made it into the news recently? The news report will help you to brainstorm why this topic is of interest to the everyday lives of real human beings.
However, do not overstate the issue. You should provide a clear, reasonable perspective in this first sentence rather than an over-the-top claim. For example, aim to avoid hyperbolic or overly emotional phrases:
To find out more about retracting over-the-top emotion and hyperbole, we have put together a guide on academic language that you may like to read.
To summarize, I recommend that your first step in how to write an introduction is to write a ‘hook’ sentence that focuses on why the topic is interesting to everyday human beings . Use sober, clear facts about the importance of the topic to real human lives to get yourself started.
Read Also: My Suggested Best Words to Start a Paragraph
Notify the reader of background or contextual information
Nearly every source I found also recommended that you provide brief ‘background’ or ‘contextual’ information.
‘Background’ or ‘contextual’ information shows your depth of knowledge and understanding of the topic.
Here are some examples of ‘context’ for a few topics:
Hopefully, you can see here that giving ‘context’ is a way of showing that you have a really strong or deep knowledge of the history or background story of the topic. This is your chance to differentiate your depth of knowledge from other students. A sentence or two giving some of this context also helps to show off your knowledge right from the start.
Most sources recommend only providing one or two sentences of background information. This will help you to show off your knowledge without stealing content from the body of your essay. The body of the essay will add depth and detail to your points in the introduction, so feel free to leave out examples and explanations beyond your engaging sentence or two: you will have time in the body of the essay to elaborate.
3. Translate
Translate the essay topic or question
This point was mentioned by more than half the websites I found giving advice on how to write an introduction.
Many universities recommend re-stating the essay topic or question in your own words. This helps your marker to see that you understand the topic and are directly addressing it.
Here are some examples of essay questions and ways you can re-state the essay question in your introduction:
Something to keep in mind is that you do not want to appear to be re-stating the essay question simply to take up extra words. We call this ‘padding’. An example of padding is when a student drops the essay question in as a question, word-for-word:
- How can knowledge about history help us to improve our lives in the future? This is the question that will be answered in this essay.
- This essay will answer the question “What is the lasting impact of European Colonisation in the 21 st Century?”
Do not drop the essay question into the introduction without paraphrasing or surrounding explanation. If you do this, your marker will think you’re just trying to add words to the introduction because you’re not sure of anything interesting to say
Report your position or argument
Most essays do not require you to take a stance on an issue.
Essays that do require you to take a stance are called either ‘argumentative essays’ or ‘persuasive essays’.
If you are writing a persuasive essay, you will need to include Step 4: Report. For this step, you’ll need to state where you stand on the issue:
Keep in mind that essays should never leave a reader confused. Essay writing is not like creative writing: your reader must always know what’s going to be said right from the start. When reading to gather information, readers don’t like to be surprised. They want the facts up-front. Therefore, your marker will expect to know what your stance is on the issue right from the introduction onwards.
Provide an outline of the Essay Structure
This last point on how to write an introduction is important and separates average students from top students.
Introductions should always highlight the key points that will be made in an essay. Academic writing should never surprise the reader.
The fact that steps 4 and 5 both highlight that you should orient your marker reinforces the importance of this. Always, always, guide your marker’s reading experience.
Your essay should signpost all key concepts, theories, and main sections that make up your essay. If an important point is made in the essay but not signposted in the introduction, you are likely to confuse your marker. A confused marker very rapidly lowers your mark.
Too often, students fail to outline key points of their essays in the introduction. Make a habit of signposting your key ideas, points, theories, or concepts you will cover in the introduction in order to gain marks.
It is always easier to write this outline once the essay plan is written. You will then be able to gather together the key points that you listed in your essay plan and include them in the introduction.
The outline of the essay structure can only be one or two sentences long. You can state as your last sentence in your introduction:
- “Firstly, this essay … then, …, and finally …”
- “The essay opens with …, then, …, and then closes with …”
- “After exploring …, … and …, this essay will conclude with …”
Try to outline the issues you will cover in order. Providing an orderly outline of your essay is very helpful for your reader.
Now, I know that some people don’t like this method. Let me reassure you with this study from Theresa Thonney in 2016. Thonney examined 600 top-ranking articles in fields including Literature, Music, Environmental Sciences, Nutrition, Inter-Cultural Studies, and more to see how many articles used this method. In other words, she completed a comprehensive study of whether professional, published authors use this method of orientating the reader to the structure of the article.
Thonney found that 100% of top-ranking articles she looked at in the Astronomy field used this method. 98% of articles in Sociology journals used this method. In fact, the field with the lowest amount of authors who use this method is Art, which had 76% of authors use this method. In other words, even the lowest result she found showed that three in every four professional authors use this method.
So, you should too.
Let’s sum point 5 up by reinforcing this very important rule: your marker should always be very clear about what they will read, and in what order, to improve their reading experience.
A short list of things to Avoid in Introductions
I want to conclude this post with an outline of some of the worst things you can do in an introduction. The introduction sets the scene, so you want to make a good impression. You don’t want your marker taking away marks due to one of these top mistakes:
- Rhetorical Questions.
- Vague padding.
- Dictionary definitions.
Sometimes, teachers also recommend avoiding referencing in introductions. I have colleagues who absolutely refuse to let students include references in their introductions. Personally, I think that’s absurd – if a reference is required, include it! However, check with your teacher on their personal preferences here as I know this is a point of contention in faculty lounges.

The introduction is important for creating a strong first impression, especially since markers often make up their mind about your grade very early on in the marking process.
Introductions are best written last. That way, you will be able to include all the signposting you need to do (step 5), have a good understanding of the context (step 2), and be more certain about what your stance is on the issue (step 4).
Here’s the five INTRO steps I’d encourage you to use every time:
Once you have written your introduction, it is a good idea to put it away for a few days and then come back to edit it with fresh eyes . Remember that grammar and punctuation are important in the introduction. You want to leave a good impression.
If you have a friend who can read the draft for you and give you tips, or if your teacher has drop-in hours, use them to get some tips on how to write an introduction, what sounds right, want sounds off, and how you might be able to improve your introduction.
Once you have written your introduction, you might want to have a look at our guidance on how to write conclusions in order to end your piece as strongly as you started! People often think conclusions are just like introductions. That’s not true. Conclusions are unique paragraphs, so head over to our guidance on conclusions now to get the support you need on writing the best conclusion you can.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Essay Writing Guide
Writing An Essay Introduction
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
15 min read
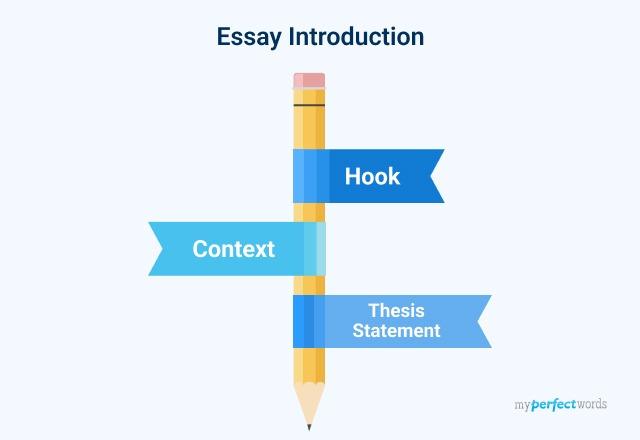
People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
Learn How to Write An Essay in Simple Steps
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 500+ Essay Topics for Students
Explore Different Types of Essays, their Purpose, and Sub-types
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
Learn How to Create a Perfect Essay Outline
How to Start an Essay- A Step-by-Step Guide
Learn How to Write an Essay Hook, With Examples
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
How to Make an Essay Longer: 14 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay - A Detailed Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
Essay introductions are the first impression that your reader will have of your paper.
You want to draw in your readers with an interesting opening that sets the tone for the rest of your work. So, it's important to make sure they're well-written and engaging.
In this blog, you will learn how to write an effective introduction to grab your reader’s attention from the very beginning. With the help of tips and examples below, you can craft an incredible essay introduction to set the tone for a powerful paper.
So let's begin!

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers
- 1. What is an Essay Introduction?
- 2. How To Write An Essay Introduction?
- 3. The Essay Introduction Structure
- 4. Essay Introduction Examples
- 5. Tips for Writing Better Essay Introductions
What is an Essay Introduction?
An essay introduction is the first paragraph of your It provides a roadmap for the rest of your paper and tells the reader what to expect from your work.
Purpose of the Essay Introduction
The main purpose of an essay introduction is to set the stage for what the reader can expect from your essay. It aims to catch the readers’ interest, provide necessary background information, and introduce them to the central argument.
How To Write An Essay Introduction?
Now that you know what an introduction is supposed to be, let’s move on to how to write an effective one.
There are four essential elements of an effective introduction:
- Engaging Hook
- Context and Background Information
- Overview of the Main Points and Essay Structure
- Thesis Statement
Let’s go over them step by step:
Step 1: Start With a Hook
Start your essay introduction with an interesting hook statement that grabs your readers’ attention. The goal of the hook is to make your reader interested in reading your essay and keep them engaged until the end.
Hooks can have several different forms; it can be a quote, an anecdote, or an interesting fact. Here are some types of hooks you can use:
- Anecdote: Share a relevant and interesting story or personal experience related to your topic.
- Rhetorical Question: Pose a thought-provoking question that encourages readers to think about the subject.
- Quotation: Begin with a compelling quote from a reputable source or a well-known figure.
- Surprising Fact or Statistic: Present a surprising or startling piece of information that relates to your topic.
- Vivid Description: Use descriptive language to paint a vivid picture that draws the reader into your essay.
The key to a successful hook is relevance. Ensure that your hook relates directly to the topic of your essay and sets the stage for what follows. You can also refer to other catchy hook examples for writing a captivating start.
Step 2: Discuss Context Background Information
After grabbing your reader's attention with a hook, it's crucial to provide context and background information about your topic.
This can include facts, definitions, and historical information. Knowing this information, your reader will be better equipped to understand the rest of your essay.
Depending on your topic, you can include these aspects to establish context:
- Historical Context: Explain the historical significance or evolution of the topic if relevant.
- Definitions: Provide a clear definition of key terms or concepts central to your essay.
- Explain Relevant Developments: Briefly mention important facts or developments related to your topic.
- Why It Matters: Explain why the topic is important or relevant to your readers or the society at large.
Here's an example:
Step 3: Overview of the Main Points and Essay Structure
Once you've engaged your reader and provided the necessary context, it's time to introduce the topic and overall argument. This part of the introduction serves as a preview of what to expect in the body of the essay.
You can achieve this by outlining the main points or arguments you will discuss and briefly mentioning the structure of the essay. This helps your reader navigate the content and understand the logical flow of your ideas.
Here's a demonstration of it.

Step 4: Write the Thesis Statement
The last part of the introduction is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the central point or argument of your essay. It conveys the main idea you will explore and defend in the following paragraphs.
A well-constructed thesis statement is specifically debatable and provides a road map for the entire essay. The thesis statement is written at the end of the introduction paragraph.
Here's a thesis statement example:
Now, if we put all these elements together step-by-step, we will have an excellent essay introduction. Here's an example of a strong introduction:
The Essay Introduction Structure
The structure of an essay introduction includes a hook, contextual information, and a thesis statement. In other words, the introduction moves from the general to the specific.

Check out these essay introduction samples that demonstrate the structure of an introduction.
Essay Introduction Outline
Essay Introduction Sample
Essay Introduction Examples
Here are some interesting introduction examples for different types of essays . Read these examples to understand what a powerful start looks like for various kinds of essays.
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing where the author takes a stance on a particular issue, presents arguments to support that stance, and aims to persuade the reader of the validity of their viewpoint.
To write an effective argumentative essay introduction, you should hook the reader's attention, provide context, present your thesis statement, and outline your main arguments.
Here is an example for you to understand how to write an argumentative essay introduction.
Persuasive Essay Introduction Example
A persuasive essay is a type of academic writing that seeks to convince the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action. The writing process of a persuasive essay introduction is similar to what is described above.
Below is a perfect example of a persuasive essay introduction.
Compare and Contrast Essay Introduction Example
The compare and contrast essay analyzes the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. A compare and contrast essay introduction has to introduce two elements. Otherwise, it has a similar structure to introductions in general.
The following is a great introduction for a compare and contrast essay that you can refer to.
Synthesis Essay Introduction Example
A synthesis essay is a form of writing that challenges you to explore information from multiple sources to form a coherent and original perspective on a given topic.
Here is a good essay introduction example for a synthesis essay.
Narrative Essay Introduction Example
A narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that allows writers to share personal experiences, memories, or events in a creative and engaging way.
The content of narrative essay introductions is a bit different. They require you to set the scene, introduce the protagonist, and present the upcoming conflict. Here is an example:
Expository Essay Introduction Example
An expository essay is a common type of academic writing that aims to provide a clear and concise explanation or analysis of a specific topic, concept, or idea.
Here’s an example of how you can start an expository essay.
Abortion Essay Introduction Example
The abortion debate remains one of the most controversial topics in modern society.
Pro-choice and pro-life advocates have been debating this issue for decades, with no end in sight. Writing an essay on this topic requires thoughtful research and a clear understanding of both sides.
Here's an example of how to write an abortion essay introduction.
Tips for Writing Better Essay Introductions
Crafting an effective essay introduction is an art that can significantly influence how readers engage with your writing. Here are some valuable tips to help you create engaging and impactful introductions.
- Be Clear and Concise: Keep your introduction clear and concise. Avoid unnecessary jargon or complex language that might confuse your readers. Present your ideas in a straightforward way.
- State Your Thesis Clearly: Your thesis statement is the core of your introduction. Clearly state your main argument or the purpose of your essay. It should be specific and debatable, giving readers a roadmap of what to expect in the essay.
- Transition Smoothly: Ensure a smooth transition from your introduction to the body of the essay. Your introduction should provide a logical segue into the main points or arguments you will explore.
- Avoid Clichés and Overused Phrases: Try to avoid clichés or overused phrases in your introduction. Readers appreciate fresh and original language that piques their interest.
- Tailor the Introduction to the Essay Type: Consider the type of essay you're writing (e.g., persuasive, expository, narrative) and adapt your introduction accordingly. Each type may require a different approach to engage the reader effectively.
- Revise and Edit: Don't hesitate to revise and edit your introduction as needed. It's often helpful to write the introduction after completing the rest of the essay, as this allows you to better align it with the content.
- Consider the Audience: Think about your target audience and their expectations. Tailor your introduction to resonate with your specific readership.
- Seek Feedback: Before finalizing your introduction, seek feedback from peers, professors, or writing tutors. Fresh perspectives can help you refine your introduction for maximum impact.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Essay Introductions
Here are some common mistakes that you should avoid to write compelling introductions:
- Try to avoid writing a vague introduction of irrelevant details about the topic.
- Do not provide too much information and facts in the introduction. Simply present the topic with sufficient information for the reader’s understanding.
- Avoid using informal language or slang terms in the introduction. Essay introductions should be written in formal and academic language.
- Do not make assumptions about the reader’s knowledge of the topic. Provide only basic background information to fill any gaps in understanding.
- Finally, do not introduce any new information in the introduction. The introduction should only provide an overview of what will be discussed in the essay, not dive into details.
By avoiding these mistakes, you can ensure that your essay introduction is clear and concise. It will help readers easily understand the topic and follow your argument throughout the paper.
Moreover, you can watch this video that introduces an easy method and helpful method for writing effective introductions.
To conclude,
By using the steps and tips discussed above, you can become a skilled essayist who leaves a lasting impression, one introduction at a time.
Just remember that writing is a process of constant refinement, and your introductions will evolve as your skills grow. So, the next time you sit down to write, take the time to craft it with care, for it holds the promise of what lies ahead.
However, if you are struggling to make your essay introduction engaging, don’t stress over it. MyPerfectWords.com is here to back you up!
You can get essay help online at our professional writing service. Our experienced and skilled writers can provide you with a perfect introduction and write a compelling story from start to finish!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

How to write an essay: Introduction
- What's in this guide
- Introduction
- Essay structure
- Additional resources
The Introduction
An in troduction generally does three things. The first part is usually a general comment that shows the reader why the topic is important, gets their interest, and leads them into the topic. It isn’t actually part of your argument. The next part of the introduction is the thesis statement . This is your response to the question; your final answer. It is probably the most important part of the introduction. Finally, the introduction tells the reader what they can expect in the essay body. This is where you briefly outline your arguments .
Here is an example of the introduction to the question - Discuss how media can influence children. Use specific examples to support your view.

Pathways and Academic Learning Support

- << Previous: Essay structure
- Next: Body >>
- Last Updated: Nov 29, 2023 1:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Introduce a Journal Article in an Essay
Last Updated: February 9, 2024
This article was co-authored by Noah Taxis and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Noah Taxis is an English Teacher based in San Francisco, California. He has taught as a credentialed teacher for over four years: first at Mountain View High School as a 9th- and 11th-grade English Teacher, then at UISA (Ukiah Independent Study Academy) as a Middle School Independent Study Teacher. He is now a high school English teacher at St. Ignatius College Preparatory School in San Francisco. He received an MA in Secondary Education and Teaching from Stanford University’s Graduate School of Education. He also received an MA in Comparative and World Literature from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and a BA in International Literary & Visual Studies and English from Tufts University. This article has been viewed 35,132 times.
Using a journal article in your essay can add to your credibility and make your points more persuasive. When you introduce an article to your readers, you help them understand why you're using it as a source. We've gathered a number of different ways you can introduce the journal article and transition between your thoughts and those of the other author. Pick the one that works best for you and your personal writing style.
List the title and the author.

- For example, you might write: "Albus Dumbledore describes the origin of the four Hogwarts houses in his article 'Separating Hogwarts Fact and Fiction.'"
- Put the title of the article in double-quotation marks in your text. [1] X Research source
- If you're quoting directly from the source, include the author's full name the first time you quote them. [2] X Research source
Summarize the article.

- For example, you might write: "The history of Hogwarts makes clear that the houses were never intended to be seen as 'good' or 'evil.' Rather, each house emphasizes and nurtures specific traits students have—how they use those traits is up to them."
- Paraphrasing from the article is similar to summarizing. However, when you summarize, you're covering the entire article in a sentence or two. A paraphrase typically only covers a small portion of the article.
Provide any necessary background.

- For example, you might write: "Professor Slughorn was one of the longest-serving teachers at Hogwarts, schooling generations of students in potions until his retirement."
- You might also include some background if the author of the article is controversial or the article's conclusions have been seriously questioned. If you're doing this, go on to explain why you're using the article in your essay.
Explain the purpose of the source in your essay.

- For example, you might write: "Although this essay doesn't discuss defenses against the dark arts, Gilderoy Lockhart's article provides an example of how you can't learn anything by plagiarizing the work of others."
Frame the source in the context of your own essay.

- For example, you might write: "This article demonstrates broad support for the idea that Hogwarts should continue to sort students into four houses."
Add a signal phrase to distinguish ideas from the source.

- For example, you might write: "McGonagall argues that Slytherin House should be disbanded after the Battle of Hogwarts."
Discuss the source's limitations.

- For example, you might write: "While McGonagall makes a compelling argument that Slytherin House should be disbanded, she was biased by her experiences. In this essay, I will show that the personality traits emphasized by Slytherin are positive traits that can be used for good."
Expert Q&A
- Remember to include an in-text citation for the source if required by your citation guide. You'll also need an entry for the source in your reference list at the end of your paper. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- In an academic essay, you typically introduce a journal article in the first sentence of a paragraph. Then, use the sentences that follow to show how the material from the article relates to the rest of your essay. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about academic writing, check out our in-depth interview with Noah Taxis .
- ↑ https://rasmussen.libanswers.com/faq/32501
- ↑ https://www.ursinus.edu/live/files/1160-integrating-quotespdf
- ↑ https://www.una.edu/writingcenter/docs/Writing-Resources/Source%20Integration.pdf
- ↑ https://www.stetson.edu/other/writing-center/media/Handout%20-%20Incorporating%20Sources%20Effectively.pdf
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Essay writing: Introductions
- Introductions
- Conclusions
- Analysing questions
- Planning & drafting
- Revising & editing
- Proofreading
- Essay writing videos
Jump to content on this page:
“A relevant and coherent beginning is perhaps your best single guarantee that the essay as a whole will achieve its object.” Gordon Taylor, A Student's Writing Guide
Your introduction is the first thing your marker will read and should be approximately 10% of your word count. Within the first minute they should know if your essay is going to be a good one or not. An introduction has several components but the most important of these are the last two we give here. You need to show the reader what your position is and how you are going to argue the case to get there so that the essay becomes your answer to the question rather than just an answer.
What an introduction should include:
- A little basic background about the key subject area (just enough to put your essay into context, no more or you'll bore the reader).
- Explanation of how you are defining any key terms . Confusion on this could be your undoing.
- A road-map of how your essay will answer the question. What is your overall argument and how will you develop it?
- A confirmation of your position .
Background information
It is good to start with a statement that fixes your essay topic and focus in a wider context so that the reader is sure of where they are within the field. This is a very small part of the introduction though - do not fall into the trap of writing a whole paragraph that is nothing but background information.
Beware though, this only has to be a little bit wider, not completely universal. That is, do not start with something like "In the whole field of nursing...." or "Since man could write, he has always...". Instead, simply situate the area that you are writing about within a slightly bigger area. For example, you could start with a general statement about a topic, outlining some key issues but explain that your essay will focus on only one. Here is an example:
The ability to communicate effectively and compassionately is a key skill within nursing. Communication is about more than being able to speak confidently and clearly, it is about effective listening (Singh, 2019), the use of gesture, body language and tone (Adebe et al., 2016) and the ability to tailor language and messaging to particular situations (Smith & Jones, 2015). This essay will explore the importance of non-verbal communication ...
The example introduction at the bottom of this page also starts with similar, short background information.

Defining key terms
This does not mean quoting dictionary definitions - we all have access to dictionary.com with a click or two. There are many words we use in academic work that can have multiple or nuanced definitions. You have to write about how you are defining any potentially ambiguous terms in relation to your essay topic. This is really important for your reader, as it will inform them how you are using such words in the context of your essay and prevent confusion or misunderstanding.

Stating your case (road mapping)
The main thing an introduction will do is...introduce your essay! That means you need to tell the reader what your conclusion is and how you will get there.
There is no need to worry about *SPOILER ALERTS* - this is not a detective novel you can give away the ending! Sorry, but building up suspense is just going to irritate the reader rather than eventually satisfy. Simply outline how your main arguments (give them in order) lead to your conclusion. In American essay guides you will see something described as the ‘thesis statement’ - although we don't use this terminology in the UK, it is still necessary to state in your introduction what the over-arching argument of your essay will be. Think of it as the mega-argument , to distinguish it from the mini-arguments you make in each paragraph. Look at the example introduction at the bottom of this page which includes both of these elements.

Confirming your position
To some extent, this is covered in your roadmap (above), but it is so important, it deserves some additional attention here. Setting out your position is an essential component of all essays. Brick et al. (2016:143) even suggest
"The purpose of an essay is to present a clear position and defend it"
It is, however, very difficult to defend a position if you have not made it clear in the first place. This is where your introduction comes in. In stating your position, you are ultimately outlining the answer to the question. You can then make the rest of your essay about providing the evidence that supports your answer. As such, if you make your position clear, you will find all subsequent paragraphs in your essay easier to write and join together. As you have already told your reader where the essay is going, you can be explicit in how each paragraph contributes to your mega-argument.
In establishing your position and defending it, you are ultimately engaging in scholarly debate. This is because your positions are supported by academic evidence and analysis. It is in your analysis of the academic evidence that should lead your reader to understand your position. Once again - this is only possible if your introduction has explained your position in the first place.

An example introduction
(Essay title = Evaluate the role of stories as pedagogical tools in higher education)
Stories have been an essential communication technique for thousands of years and although teachers and parents still think they are important for educating younger children, they have been restricted to the role of entertainment for most of us since our teenage years. This essay will claim that stories make ideal pedagogical tools, whatever the age of the student, due to their unique position in cultural and cognitive development. To argue this, it will consider three main areas: firstly, the prevalence of stories across time and cultures and how the similarity of story structure suggests an inherent understanding of their form which could be of use to academics teaching multicultural cohorts when organising lecture material; secondly, the power of stories to enable listeners to personally relate to the content and how this increases the likelihood of changing thoughts, behaviours and decisions - a concept that has not gone unnoticed in some fields, both professional and academic; and finally, the way that different areas of the brain are activated when reading, listening to or watching a story unfold, which suggests that both understanding and ease of recall, two key components of learning, are both likely to be increased . Each of these alone could make a reasoned argument for including more stories within higher education teaching – taken together, this argument is even more compelling.
Key: Background information (scene setting) Stating the case (r oad map) Confirming a position (in two places). Note in this introduction there was no need to define key terms.
Brick, J., Herke, M., and Wong, D., (2016) Academic Culture, A students guide to studying at university, 3rd edition. Victoria, Australia: Palgrave Macmillan.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Main body >>
- Last Updated: Nov 3, 2023 3:17 PM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/essays
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem
IELTS Preparation with Liz: Free IELTS Tips and Lessons, 2024
- Test Information FAQ
- Band Scores
- IELTS Candidate Success Tips
- Computer IELTS: Pros & Cons
- How to Prepare
- Useful Links & Resources
- Recommended Books
- Writing Task 1
- Writing Task 2
- Speaking Part 1 Topics
- Speaking Part 2 Topics
- Speaking Part 3 Topics
- 100 Essay Questions
- On The Day Tips
- Top Results
- Advanced IELTS
How to Put Examples in Your Essay
Learn the best way to add examples to your essay to support your ideas. You need to use a range of linking words in your essay and also use them flexibly in different locations in the sentence. See below for a list of useful linking words with sample sentences:
Linking Words for Giving Examples
- for example
- for instance
- to illustrate
- as an illustration
- to give a clear example
- take, for example,
Video Tutorial: How to Add Examples in an Essay
Sample Sentences with Supporting Examples
Please note that the linking words do not need to be at the start of the sentence. You can use them more flexibly by changing their location.
Global warming should be taken more serious as it can result in a number of disastrous consequences. To give a clear example , the melting polar ice caps have not only caused a loss of habitat for polar bears but are also threatening seas levels worldwide.
More and more women are choosing to start a family later in life. 20% of women giving birth to their first child, for instance , are over the age of 30 in the UK.
Crimes should not have the same punishment. Minor crimes, such as pick pocketing and traffic offences, should not have the same penalty as major crimes, namely murder and manslaughter.
Children often learn behaviour from the adults around them subconsciously. To illustrate , around 50% of children who are brought up by aggressive parents often use aggression to solve their own problems later in life.
Parents should be responsible for teaching their children right and wrong. If, for example , they see their child using bad language, they should spend time explaining to their child the serious consequences that can result from this type of behaviour.
More and more people are leading sedentary life styles due to work conditions. Take for example office workers in the UK who spend at least 8 hours a day, 5 days a week sitting in front of their computers.
All Linking Words for Essay Writing
You can find a list of all linking words that can be used in essay writing: Linking Words for Writing .
IELTS Essay Questions
- Over 100 IELTS Essay Questions
Main IELTS Pages Develop your IELTS skills with tips, model answers, lessons, free videos and more. IELTS Listening IELTS Reading IELTS Writing Task 1 IELTS Writing Task 2 IELTS Speaking Vocabulary for IELTS IELTS Test Information (FAQ) Home Page: IELTS Liz
Hi Liz, thank you for all the advices, I truly appreciate.
I have a minor question however, is it proper to use ‘e.g.’ (exempli gratia) when giving examples in IELTS writing? or it’s not recommended?
It’s definitely best to stick to usual English language linking words: for example, for instance, namely etc. You should avoid using “etc” or “eg” because you are being marked on the use of linking words and general vocabulary.
I see. Thanks!
I can say that you are on of my the best theachers I have ever met.I do not what to say ; ı wish you the best for all your life.
Thanks. That’s a kind comment
Thank you so much Liz for all the resources on your site. God bless you immensely.
You’re welcome 🙂
Dear Liz, In my example can I lie? For example, “the Times News once reported more than 50% of youths to prefer to use laptops”. This information was not actually written in the news.
You do not need to state the origin of examples in any IELTS essay. It does not help your score to do so. In fact, mentioning data in task 2 will not help your score either. It’s better to use language which will help your score: On average it can be said that around half of all youths prefer to access the internet using a laptop rather than any other kind of device. On average it can be said that an overwhelming majority of all youths use laptops to go online rather than any other device.
Your website is the best for learning IELTS techniques. It’s even better than the British Council courses
Thanks. I’m glad you find it useful 🙂
Thank you so much Liz for all this resources. God bless you immensely.
Hi Liz, is it okay if we make up the statistics in essay ( for we want to provide examples, but we know nothing about the topic).
As you don’t get extra points for stats anyway, there’s no point. It would be much better to boost your vocab score by saying “the overwhelming majority” or “only a mere fraction of” etc etc.
Hi Liz, I hope you are doing fine!
Is it acceptable to use a mix of American English and UK English while writing? I’m asking because there are few words that are spelled differently in both countries.
You should stick to one way of spelling for the writing test.
Alright! Thanks for the quick reply!
Hi Liz! Is it okay if the one main paragraph is bigger than other or should they be balanced? Does this affect my score? Thank you.
Yes, it affects your score. Body paragraphs should be equally developed.
thank you liz.
Thank you you Liz all I have never read a website as helpful as yours . Wishing you more successful feats in all your life endeavors Am Sameer Hassan Saleh
hi liz… I have seen your all paid essay vedios. These all are excellent. Thanks alot for all these lessons. I just want to know can we use personal examples in task 2. For instance, my younger brother eat noodels frequently as he finds it much delicious than conventional healthy food and vegitables. Pleass guide in this regard? Thanks alot..
It is best to continue writing about people in general for examples: “Many younger people prefer eating noodles because …”
Hello Liz Thank you very much for these very useful interesting lessons. I just want to now if the statistics that might be mentioned in the essay have to be generally “correct”; or the examiner may penalize you for giving statistics that are clearly not true and just made up in the exam room?
Putting statistics in your essay does not boost your score. The examiner is marking your English and your ideas, not facts or numbers in task 2.
Hi liz , thank you for you precious blog, it really helped me. I have a question! Is it ok to give false statistics?? I mean to fake one to support my idea????
Why would you want to give false statistics? Do you think examples should contain statistics? Do you think you get a better score because you use statistics? Statistics play no part in your score for writing task 2.
In case we don’t remember exact figures can we guess ie say around 5-6%, it’s not possible that examiner knows all exact statics.
You will not get a higher score because you put statistics in your task 2 essay. You do not need to give any numbers at all.
Hi, Liz, I have some doubt amout ‘your own experience’ 1. what actually does it mean? 2. can I state my own experience or commonly observation experience? 3. My own experience mean any EXAMPLE?
PEASE LET ME KNOW. THNAKS
It means your experience of the world in general. It does not need to be your own personal experience, but rather your experience of the world. As essays are formal, we don’t usually refer to ourselves or our family and friends.
Hi, Thank you for your great lessons. I have a question, in this video you wrote: “an increasing number of people are eating unhealthy food…” you used “increasing number of people” which means you used Gerund. that’s why you put “an” in front of it, however you used “are eating”, shouldn’t have you said “is eating”? Gerund consider as singular, right?
An increasing number = the word “increasing” is used as a adjective, not as a gerund. The noun = number of people Adjective = increasing. Don’t get your grammar confused.
Hello Liz! 🙂 I’m writing an academic research paper involving diabetes. I’m not sure, however, where to place the statistics surrounding the number of people with diabetes in my country in my introduction. Do I put it before my description of diabetes, or after it?
All my advice is for IELTS which is an English language test. It is not for academic writing at uni or college which is not testing language. IELTS has specific requirements which are not the same as any academic research. You will have to find sample research papers and use their structure.
Hi Liz, In General IELTS Task 2 essays, often it is asked that “Give examples from your own knowledge or experience” So my question is can I use “I”, “my”, “me” while quoting an example? Secondly i was reading some where that IELTS essays are persuasive essays so we have to use first person voice and should use “I”, “my”, “me” at least once in each paragraph. Please comment on this. Thanks
Essays are formal, so examples of your experience or knowledge should relate to “the majority of people …”. It is not actually about you or your friends but your experience of the world. GT writing is more marked as strictly as academic essays but even so I recommend you to use formal examples.
Can I use fake examples whic are grammatically correct?
Why – it won’t help your score.
Hi Liz, In your examples above, you have written “To illustrate, around 50% of children who are bought up by aggressive parents often use aggression to solve their own problems later in life” If we were to write such an example, does it have to be factual or just believable?
It is just as good to write “the majority of children..” or “about half of all children …”.
Good day to you madam, I would like to ask how many sentences are recommended to give an example in an essay. I would also like to know if it is okay to not mention the actual source of a statistic in an essay that writes about contemporary issues. Thank you.
1) You don’t need to use examples. So, if you use them, it’s your choice how many. 2) you should NEVER state the source of numbers in an IELTS essay. In fact, most examples are better given without numbers. This is an English language test, not a essay presenting data.
Hi Dear Liz My name’s Ghazale You cannot imagine how incredibly you have changed my world of learning English these few past weeks And i must confess your videos helped me too good What a wonderful teacher you are I keep watching your videos but unfortunately i couldn’t log into your website to be a member Thanks a lot
I have a burning question in mind about examples. Would it be alright to use ither languages in an essay. For example,in an essay about using English as the only language, I pointed out that language often go side by side with culture. My sentences: Japanese add “guzaimasu” after a phrase or “san” after a name to express politeness. In the Philippines, we say “bayanihan” to describe the value we place on our neighbors and community. There are no direct English translations for these words.
I do hope you see this question. I have been learning quite a lot from you. This is, in fact, a question I got from your site. Thank you very much!
Your aim in your essay is to provide clear, relevant main points which are well developed, explained and linked. Your other aim is to provide accurate grammar and vocabulary in English. Those examples might be appropriate to use one example but certainly not more than that. Once you make your point, move on – don’t become repetitive. Your Japanese example is confusing for people who don’t understand Japanese but your example from the Philippines is clearer. Remember this is not about filling your essay will all your ideas – it is about being selective and deciding what to include and what to exclude.
Thank you very much! Will try my very best!
Dear Liz, Is it ok to create statistical data as example for academic writing task 2?
Why? It won’t help your band score at all. It’s better to explain your ideas using English language and focus on accuracy of language.
In IELTS it is said : “Ideas should be supported by evidence, and examples may be drawn from the test takers’ own experience.” In many mock essays answers, there are no examples. Can an essay reach band score 9 without any examples? Thank you very much
The instructions mean that you must expand and explain your ideas – it does not means you must give examples. There are many ways to illustrate and explain ideas.
Is it okay to make up facts to use as examples?
You should not be thinking about memorising facts for your essay. It will not help your score at all. IELTS don’t expect you to do that. When are you asked to support your ideas, it means to explain them or give examples of situations – not figures, statistics or facts.
can i use personal pronoun in essay ?
See this page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2-expressing-your-opinion/
Hi Liz, All your videos are very useful, all those tips and tricks really boosted my confidence, thanks a lot for that:)
I have a doubt regarding the writing task2, when I was doing a sample writing task, I came across this “include any relevant examples from your knowledge or experience”. So, does this mean we can give real life examples while writing our essay?
Thank you, Hari, India.
Your writing task 2 essay deals with world issues. You can give examples but I advise you to use examples relating to the world in general: “For example, it is commonly known that ….” or “For example, the majority of people ….”. These are examples of your view of the world. If, however, you write “For example, my friend Dave …” your essay loses style and language content.
Thanks a lot, Liz:) that was a great example. I am taking my exam on 22 of this month, with all your videos and tips hoping to get a great score.
Can we you hypothetical statistics? For example, if I want to make my point strong, can i use any university name or any research journal?? I mean can i state in the essay that, “In a recent article published by ABC university, 70% of the people have found addicted to smartphones” Whereas in fact, there is no such article ever published stating this fact of 70%.
Yes, you can lie about stats but why? It won’t help your score at all. This phrase ““In a recent article published by ..” won’t boost your score. It’s a learn expression which is generic (it can be applied to any topic) and this means the examiner won’t count it towards examples of your natural language.
Thanks Liz for your reply. I have gone through a number of your advises and found them very useful.
But I saw in some of the articles that if you show some reference and support with research data, you will be able to reinforce your argument. Had I rephrased it but still lied about the fact, would it add value then to my task 2?
Regards Ahmed
The examiner does not give you a higher band score because you are presenting statistics. Statistics are irrelevant to your mark. The supporting points being assessed are relating to language, not figures. You can add all the stats you want, it won’t increase your score at all.
That’s really helpful. It relief some of the pressure of knowing statistical data related to the topic.
Thanks once again,
Wow, were you really trying to remember stats for your essay? You are not marked on your knowledge at all. Just think of some relevant main ideas and then explain them – nothing more is needed. It is essentially an English language test. Take a look at my band 9 model essays: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2/
I have a question regarding grammar. I am not in what case can we put Verb+ing after the word “to”
I always thought that we have to put the verb whit its original form, but I have noticed two examples and still didn’t understand the rule.
Here are the two examples I saw in your blog:
– resort to buying ( why not resort to buy?) – I am looking forward to hearing from you ( why not looking forward to hear from you soon?)
appreciate your always help.
You can use “to” as a preposition. If you haven’t seen this before, don’t use it. More mistakes will lower your score. Use the grammar you know well.
Hi .. can I add “example” form my own information or not ?
sorry i mean from
You can write anything you want. However, writing about the world in general usually produces a better level of English.
As long as it is in the allotted time, are we allowed to write our essays out in rough first, then transfer them onto the exam papers?
You will not have time. You need to spend at least 5 mins planning your essay which includes main ideas as well as supporting points. This means you can write your essay directly. Try timing yourself and you will see how difficult it is to do both task 1 and task 2 in one hour.
I can not buy your lesson which must be paid by paybal, because in Turkey there is not paybal. How I can bu these lessons? Please inform me.
Hi Liz! Thanks for the amazing tips! And I would like to ask whether I can make up facts as an example in my writing test? Thanks!
Sure, if you want. But it’s better to explain your ideas rather than just make up stats.
Hello Liz! I have to ask that is it possible to get 7 bands in writing? As I have never heard above 7 bands of any student. Why so?
You will find many students hit band 7 and above: https://ieltsliz.com/post-your-ielts-test-results/
Liz, Thanks a lot for your fantastic information. Your work is exceptional and highly recommendable for not only IELTS test takers but also first-year university students who use English as a second language.
I had a question about the use of “resort”. Is it “resort to doing” or “resort to do”?
In the last scene, I was two sentences:
1. This is exemplified by the 70% of working people in the UK, who resort to BUYING ready made meals for convenience. 2. This can be seen by the growing number of working people in the UK who resort to BUY ready made meals for convenience instead of cooking at home.
Is it a typo in the second sentence?
Many thanks for your tutoring videos. They are extremely helpful!
https://ieltsliz.com/liz-notice-2015-2016/
I wonder if it is possible to include false statistics in my writings?
It isn’t necessary. You don’t need to put in statistics at all. It’s best to explain your opinion.
Hi, Juliana. I post the explanation of the resort. “resort to sth to make use of sth, especially something bad, as a means of achieving sth, often because there is no other solution.”
E.g. They felt obliged to resort to violence We may have to resort to using untrained staff.
So, we should put doing after the resort to.
And you are right. there is a typo mistake in the second sentence. I think liz post that in the video.
Dear madam,
I need 6 bands in each tasks for IELTS General module.Still I’m worried about Speaking and Listening exam because I don’t get grip on this tasks compared to other tasks.Please suggest me a technique for practice to acquire a good score.I have next exam on 18th February.
Hi Liz, I just started to follow your blogs recently. As I read the topics above, I wonder if we could present or invent statistics in our own just to support our answers in essay 🙂 ? Thanks!
Hi liz ,hope u r doing fine..i would be very grateful if u cud give some advice about the ielts..recently i sat for the it,n i got an overall 6.5band, with 7 listening , 6.5 writing, 6.5 reading and 5.5 speaking.though its not enuf for my professional career,im wondering if i shud give it again and if yes ,will i be able to attain the requirement that is a total of 7.5 with a minimum of 7 in each section….honestly speaking i had only ten days for the exam and during the process i didnt practice at all,just read some sample essay on net n some passage reading..and i came to conclusion that the only way to succeed is practise because your only opponent on the day of exam is time.for instance for my case,i finish my essay just in time,cud not do proofreading and this apply for the reading as well…n it was my first experiece with ielts…is there a chance that i can reach the objective band nxt time?my essay was is should the private life of celebrity be respected by the media,to what extent u agree or disagree..thnk u,,waiting impatiently for ur reply…
You will need to improve your English and also get training for IELTS to get band 7 in each criterion. Liz
Task 2: Some people say that interview is a good way of selecting competent candidates. What are the other ways for selecting a good candidate What do you think is the best way to select a good candidate. How write intro this question and make paragraph
Hi Liz. Thank for this tip. it’s really helpful. But i have a question. How can i explain my idea in writing task 2? I always have a problem with this
The supporting points are only explanations of your ideas. Just more detail. It could be examples, consequences, exceptions, explanation, causes – anything you feel will explain what you mean. If you aim for three body paragraph, you will only need about two supporting sentences which is easier. Liz
what i am looking for is some questions that i need to question myself whenever i have an idea needed to explained. I found your video bout ideas. I have a lot of them now. but dont know how to expand it.
Ask yourself “why”. If you state “Firstly one of the best ways to tackle traffic congestion is to build wider roads.” Then you ask “why is this a good method? What does it do?”. You then add: “By doing this, traffic will be able to flow more easily and congestion will be reduced”. Then you choose your next sentence, either an example or an opposite: “If the roads are not widened, traffic will slowly grind to a halt as traffic is no longer able to flow along the streets because they are too narrow.”.
I strongly advice you to read all model essays online and make a note of what kind of information is given in the supporting points. Then you will have a range of ideas. Liz
This is a great way to illustrate how to expand ideas Liz. Very clear and concise.
Thank you very much.
Hello, Liz Could I write “As an example/illustration of something, …”?
If I’m not mistaken, it is “Cambridge IELTS 9” on the shelf on each video. Do you recommend this book? Thank you in advance! Julia
Yes, you can use those two ways to give examples. I have both Cambridge 9 and 10. They are the two most recent books published by IELTS. They contain 4 practice tests but not tips. They are good for practicing. No students should enter the test without doing a full practice test at least once. All the best Liz
Can we make up our own examples with fake dates and events.??
The examiner will not check factual information so you can use examples as you wish. But it is unnecessary to invest data – just describe it for a higher score. Liz
I will just use supporting examples, which will make sense by different Organization names.I have exam on 8 October, 2015.
I was wondering, it won t be considered ok to write 2 ideas in one paragraph? For instance 1 BP with 2 ideas explained or 2 causes etx. It would be more correct to have only one idea/solution/cause/advantage in each BP?
The organisation of ideas depends on the type of essay you have. You would need full training to understand more deeply: http://subscriptions.viddler.com/IELTSLizStore All the best Liz
Thanks Dear, I appreciate it.
that is the example, and I guess you are right.And where do you recommend I can write my opinion? computers are becoming an essential part of education. Discuss the advantages and the disadvantages and give your own opinion?
I’ve never seen those instructions before. However, to follow them, you must do exactly what they say: give the advantages, give the disadvantages and give your opinion. If your opinion agrees with one side, then include it in your body paragraph. If your opinion agrees with neither side, put it in a separate body paragraph. There’s no fixed rule. All the best Liz
Hi Liz, Regarding the advantage and disadvantage and giving your opinion question. where is the best place exactly to express my opinion?is it in the conclusion sentence or included in the introduction?
There is no question in IELTS that asks for the advantages, disadvantages and your opinion. Are you talking about the discussion essay? All the best Liz
Hi, For writing task 2, sometimes I don’t have relevant examples ? I start properly with a topic sentence and I explain it in detail, but I, sometimes, find difficulty of giving a clear example?
if there is any other way to state it ? thank you
You do not need to give examples unless you want to. Supporting points are any points which explain your idea further. All the best Liz
Thank you very much for the very useful article. I have some concern about the use of ‘i.e.’ and ‘e.g.’. Do you think they are formal enough to be used in IELTS writing?
Many thanks again,
Never use shortened forms in IELTS writing. All the best Liz
I would be so grateful if you could suggest me the perfect study plan in order to prepare for my second Ielts exam on 12 September. I need to improve each section with 0.5 or 1 score.
Thank you in advance, Genta
Sorry, I don’t provide study plans. Watch my video on my home page about preparing for IELTS and just cover the points mentioned. You know your weaknesses and you know the time you have available – you are the best one to make a study plan. Liz
Hi, Liz I want to use “Example” at the end of my essay. So, which one is correct 1. for example 2. in example 3. at example 4. on example
Examples are usually put in the body paragraphs to support your ideas, not at the end. See this page for correct linking words: https://ieltsliz.com/linking-words-for-writing/ . Then review all tips on the main writing task 2 page: https://ieltsliz.com/ielts-writing-task-2/
Dear Liz, I would be acknowledge by my heartfelt appreciation about your website and merits videos . I’m settling in Tehran and wand passing ielts strictly. In recent years , there has been hard rise in ielts examination . Let’s emphatically endorse to this fact that the band score 7 and upper goals are crucial for us to make the future by proper mentoring , extensive training and practicing . Hence , it’s important to be realistic about apprentices who need the band 6.5 in general training modules . With all this taken into account , I believe that I have some problems in reading to pass this examination . Another thing I should mention is how can I improve myself in listening module because I couldn’t accurately pass this . It has fluctuated on 5 to 6.5 in 3 mock examinations . This is often cited as a reason for practicing more but I can not fix my grade in 6.5 . It will make me feel happy if I solve this problem . Eventually, if you have leisure convenient, please, test us with some sample questions ( talking points ) by writing in both issues and make us as well . Let’s commonly apprentice about this website . I’m looking forward to knowing more from you . With warmest wishes, As ever, Hooman
I will be very direct with you. To get band score 7, you need to have a very strong level of English in which you have good use of English but with few errors. Your message above shows quite a lot of errors when you use vocabulary that is not appropriate. You clearly know a lot of vocabulary but not how to use it and what it really means. For example, “apprentice” is not a synonym for student. For this reason, you are not getting band 7 in your listening or reading etc. Of course, you will need to check your techniques and follow the right tips but at the end of the day, if your English is not band 7, it will be hard to get that score. Spend time developing your English. I don’t mean learning new words (you have a wide enough vocabulary) but learning more about the meaning of the words, collocations, paraphrasing correctly and how to use words appropriately. All the best Liz
Hlo Dear liz.. firstly i would like to you say thanku for your support. second of all, can you plz recommend me books of good authors for preparation of ielts? I am weak in speaking module due to lack of ideas.please help me. Thanks
You could try the Collins IELTS speaking book. That has good ideas and vocabulary for various topics. Liz
Hi Liz , u r ways of study fanatastic,I need ur guidance i live near border problem regarding internet, I can buy ur task 2 any book I need 6 GN plz help me
Unfortunately, I don’t have a book for IELTS at present. Possibly in the future. Liz
Dear Liz , I would like to buy your essay tips, please could you tell me as soon as possible ,I just booked my test for first of August . Beast regards Maria
At present, I have just opened my video course with in-depth lessons and tips for writing: http://subscriptions.viddler.com/IELTSLizStore I will add more lessons to my course in the coming months. All the best Liz
Hello liz. The linking words you presented to are very helpful. Hope to hear more from your post. Thank you.
I’m glad you find them useful. They are so important to use in your essay. Liz
Hi liz. .I want to seek help from you in doing my essay. I am really having a hard to put my ideas. I need a band score of 7 in all categories. Please help me.
Unfortunately, I don’t offer individual tuition to help you. You should go through topics and research ideas for your essays. You can find some ideas on my blog and others online. Then practice adapting the ideas to suit the essay question and the instructions. Liz
hi liz. .ok. .I will do as you said. .I will read your blog. .thank you for patiently replying my issues. Godbless. .
Im confused with the” to buy and to buying” from your examples
1. for example about 70% of people working in the UK resort to buying ready-made meals for convenience rather than doing home cooking
2. This can be seen by the growing number of working people who resort to buy ready-made meals for convenience instead of cooking at home
Could you please explain to me when should I use to buy and to buying ?
Thank you very much
Thanks for pointing it out. It’s a typo. I’ve put a comment in the video. All the best Liz
Hi Liz. Guys.
I just found this website yesterday when I was looking for some stuff for ielts self preparation. Yes, I would like to take an exam and also like to ask you how long you recommend a prepation before the exam date?
It really depends on a number of factors, one of which is your understanding of the test and requirements of the band scores. If your English is suitable for the band score you are aiming for, you will only need to focus on exam skills to make sure you reach your potential. The skills will help you understand how to approach questions and what the examiner is looking for in your writing and speaking. Once you feel comfortable with all that, you will have a clear idea of how long you want to practice before your test. Whatever you decide, make sure you are frequently getting the band score you want in practice tests. All the best Liz
Thank u for your reply. I need least band 6. What do u think about level B2 communicator. Is possible to get that band and of course with preparation bfr exam. Thanks in advance
See this chart: http://www.ielts.org/researchers/common_european_framework.aspx Liz
Thank you. Looks possibly
How should i start my preparation plz advice and accordlingly i will follow in Reading/Writing/Speaking/Listining
Regards, Mirza
You start in any way you want. I advise you to learn the content and question types of all skills and then start practicing. Then do practice tests to check your level. After that, start planning your development. Liz
Thanks for the useful lesson .
Hi Liz! I got overall 7.5 band score and the credit goes to you as well. Thankyou so much for being my virtual tutor. It’s my pleasure to study with you online. Preparation material and guidelines by you helped me a lot in achieving my target in first attempt. Goodluck to all the students who are preparing for IELTS ,”it’s not that much difficult” Thanks Liz for all your efforts, stay blessed always 🙂
Well done! It is an inspiration to all students 🙂
Too good again, I am going to give my GT on 1st Aug. Thanking you so much. I like those additional examples by using linking devices.
Hii ma’m! I am from Pakistan and I want to tell you that you are indeed a very great teacher. I’m gonna appear in coming IELTS on 1st August. I’m feeling really confident now after going through your very informative lectures here.
Thank you a lot for being so helpful! Need your prayers now 🙂
Regards, Madiha
Good luck !!
I got 5.5 band in first attempt R-4 L-5 W-5.5 S-6.5
Second attaempt R-4 W-4.5 L-4.5 S-5.5 Total band-4.5
Please advice me how i need to follow.I need 6 band in each module immigration.
Regards, Mirza Ehteshamulla Baig Kuwait
The key is probably your level of English. Your results are quite even so you will probably need to develop your English language to get a higher score. All the best Liz
Did you give third attempt? How much u got?
Dear Liz, When writing essays, we usually don’t have statistical data at hand. Is it OK to make up such information to give examples?
Sure, if you want. The examiner won’t know the difference. But you don’t need to give statistics. Examples can just be an example of a situation. Liz
Hello Liz! I also have a question about statistics… Do we have to mention where we got the information from?
You can give examples in any way you wish.
Dear Liz, Thank you so much for your very informative lesson here. It really helped me when I took the exam on 11th of July and I got a total band score of 7.5. You are indeed a blessing. God bless you more.
Regards, jen
Great news! Band 7.5 is a strong score. I hope you celebrated 🙂 Liz
Speak Your Mind Cancel reply
Notify me of new posts by email.
Advanced IELTS Lessons & E-books

Click Below to Learn:
- IELTS Test Information
Copyright Notice
Copyright © Elizabeth Ferguson, 2014 – 2024
All rights reserved.
Privacy Policy & Disclaimer
- Click here: Privacy Policy
- Click here: Disclaimer
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 · Prose on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in
Narrative Essays
Narrative: The spoken or written account of connected events; a story
Narrative Introductions
The introduction of a narrative essay sets the scene for the story that follows. Interesting introductions—for any kind of writing—engage and draw readers in because they want to know more.
Since narratives tell a story and involve events, the introduction of a narrative quite often starts in the middle of the action in order to bring the reader into the story immediately, as shown in examples 1, 3, and 5 below. Other effective introductions briefly provide background for the point of the story—often the lesson learned—as in 4 below and the first example on the reverse side.
Below are some strategies for writing effective openings. Remember your introduction should be interesting and draw your reader in. It should make your audience want to read more. If it's a person , begin with a description of the person and then say why that person mattered. If it's an event , begin with the action or begin by reflecting back on why the event mattered, then go into the narrative.
- "Potter...take off!" my coach yelled as I was cracking yet another joke during practice.
- Why do such a small percentage of high school athletes play Division One sports?
- It was a cold, rainy night, under the lights on the field. I lined up the ball on the penalty line under the wet grass. After glancing up at the tied score, I stared into the goalkeeper's eyes.
- My heart pounds in my chest. My stomach full of nervous butterflies. I hear the crowd talking and names being cheered.
- Slipping the red and white uniform over my head for the first time is a feeling I will never forget.
- "No football." Those words rang in my head for hours as I thought about what a stupid decision I had made three nights before.
- "SNAP!" I heard the startling sound of my left knee before I ever felt the pain.
- According to the NCAA, there are over 400,000 student-athletes in the United States.
Narrative Story
- Unified: Ensure all actions in your story develop a central idea or argument.
- Interesting: Draw your readers into your scene(s), making them feel as if they're experiencing them first-hand.
- Coherent: Indicate changes in time, location, and characters clearly (even if your story is not chronological).
- Climactic: Include a moment (the climax) when your ending is revealed or the importance of events is made clear.
- Remember the 5 W's : Who? What? When? Where? Why?
- Write vividly : Include significant sensory information in the scene (sight, sound, touch, smell, taste) to make readers feel they are there
- Develop " Thick Descriptions "
Clifford Geertz describes thick descriptions as accounts that include not only facts but also commentary and interpretation . The goal is to vividly describe an action or scene, often through the use of metaphors, analogies, and other forms of interpretation that can emote strong feelings and images in your readers' minds.
"The flatness of the Delta made the shack, the quarters, and the railroad tracks nearby seem like some tabletop model train set. Like many Mississippi shacks, this one looked as if no one had lived there since the birth of the blues. Four sunflowers leaned alongside a sagging porch. When the front door creaked open, cockroaches bigger than pecans scurried for cover [...] walls wept with mildew."
—from Bruce Watson's Freedom Summer
Narrative Checklist
- Does the story have a clear and unifying idea? If not, what could that idea be?
- If the story doesn't include a thesis sentence, is the unifying idea of the story clear without it?
- Is the story unified, with all the details contributing to the central idea?
- Is the story arranged chronologically? If not, is the organization of ideas and events still effective and clear?
- Do the transitions show the movement from idea to idea and scene to scene?
- Are there enough details?
- Is there dialogue at important moments?
- Is there a climax to the story—moment at which the action is resolved or a key idea is revealed?
501 E. High Street Oxford, OH 45056
- Online: Miami Online
- Main Operator 513-529-1809
- Office of Admission 513-529-2531
- Vine Hotline 513-529-6400
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/emergency
1601 University Blvd. Hamilton, OH 45011
- Online: E-Campus
- Main Operator 513-785-3000
- Office of Admission 513-785-3111
- Campus Status Line 513-785-3077
- Emergency Info https://miamioh.edu/regionals/emergency
4200 N. University Blvd. Middletown, OH 45042
- Main Operator 513-727-3200
- Office of Admission 513-727-3216
- Campus Status 513-727-3477
7847 VOA Park Dr. (Corner of VOA Park Dr. and Cox Rd.) West Chester, OH 45069
- Main Operator 513-895-8862
- From Middletown 513-217-8862
Chateau de Differdange 1, Impasse du Chateau, L-4524 Differdange Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
- Main Operator 011-352-582222-1
- Email [email protected]
- Website https://miamioh.edu/luxembourg
217-222 MacMillan Hall 501 E. Spring St. Oxford, OH 45056, USA
- Main Operator 513-529-8600
Initiatives
- Miami THRIVE Strategic Plan
- Miami Rise Strategic Plan
- Boldly Creative
- Annual Report
- Moon Shot for Equity
- Miami and Ohio
- Majors, Minors, and Programs
- Inclusive Excellence
- Employment Opportunities
- University Safety and Security
- Parking, Directions, and Maps
- Equal Opportunity
- Consumer Information
- Land Acknowledgement
- Privacy Statement
- Title IX Statement
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- Annual Security and Fire Safety Report
- Report a Problem with this Website
- Policy Library
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

Situation Essay
Situation essay generator.

Have you ever written an essay that involves topics that may not be as common as people perceive them to be? We know for a fact that the most common essay topics are friendship, love and success. However, there are also essays wherein the topics may not be the kind you would think some readers would enjoy. These essays can either touch the hearts of many, or can bring tears to those who read them. In literature and prose, they are called situation essays. What are situation essays and why are they important to learn and understand? Take a look at these examples of a situation essay, which topics like pandemic, ethics and family can be written.
10+ Situation Essay Examples
1. rhetorical situation essay.

Size: 202 KB
2. Pandemic Situation Essay

Size: 579 KB
3. Dangerous Situation Essay

Size: 60 KB
4. Covid 19 Situation Essay

Size: 76 KB
5. Family Situation Essay
6. situation ethics essay.

Size: 94 KB
7. Situational Essay on Crime Prevention

Size: 471 KB
8. Situation Essay on Leadership

Size: 530 KB
9. Situation Essay On Awareness

Size: 83 KB
10. Situation Essay on Poverty

11. Sample Situation Essay

Size: 26 KB
What Is a Situation Essay?
A situation essay is a kind of writing style that you use in order to adapt to what your essay topic is about. You often see this in any kind of essay you will write about. From informative essays , reflective essays , analytical essays , welcome speeches , This kind of writing style helps you adapt or understand the nature of your topic without having to go off topic or having to find a better way to write or address it. Situation essays can be used in just about any form of writing. Just like in emails, speeches, essays, and letters. The main purpose of the situation essay is to provide you the means to appeal to the person or people reading your writing.
How to Write a Situation Essay
Getting an idea on how to write a situation essay should not be that difficult or complicated. All you need to do is to follow simple steps to get there. The important thing to remember is you provide the means to appeal to your audience. Here’s how to do it.
Step 1: Your Introduction Must Catch Their Curiosity
Just like in writing any story, or an email, or even a speech, the most important thing you can do is to make an introduction that catches the reader’s attention and curiosity. Make your introduction something catchy but not too catchy they may lose interest after the introduction. In a way, give them a little taste of what they are going to expect.
Step 2: Add Something That Relates to the Topic
This is the second part or the second paragraph if you are writing a letter, an email, or even a speech. Think of something that relates to your topic. Not only does this continue to grab your audience’s attention, but it also shows you are able to correlate your introductory topic to your main topic.
Step 3: Be Clear and Concise with Your Writing
Since you are going to be writing about a topic for your essay, there are times that you may forget that you are writing for your audience to appeal to what you are saying. This however does not mean that you should forget to be clear and concise with your topic and your writing. Make sure that you stick to making it clear all the way.
Step 4: Review Your Essay
Before you hand it over to the respective audience, always be sure that every single detail is present in your essay. The topic, the introduction, the statement or purpose of your essay and the conclusion. In addition, part of your review should also be about the grammatical errors, spelling and punctuations.
What is a situation essay?
A situation essay is a kind of writing style that you use in order to adapt to what your essay topic is about. You often see this in any kind of essay you will write about.
What are other kinds of essays or works you can use for this writing style?
The other essays you can use for this writing style are:
- Reflective essay
- Narrative essay
- Formal essays
- Case studies
What are some common topics for a situation essay?
Any topic can be used for a situation essay. You can write about family, friends, romance, personal, business, etc.
Have you ever written an essay that involves topics that may not be as common as people perceive them to be? Situation essays are the type of writing format that gives your readers the opportunity to put themselves in the shoes of the person or character they are reading. This is often used in writing stories, essays or speeches.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Situation Essay on the impact of climate change on small island nations
Situation Essay on the ethical considerations of genetic engineering
- Hiring Advice
- Career Advice
- Hiring Platform
- Interview advice
- HR Insights
- Product Innovations
- Fresher advice
- Resume tips
- Hiring Guidelines
- City wise jobs

In a world of job interviews, the question “Tell me about yourself” is often an opening question that interviewers ask. Here, giving a self-introduction in an interview doesn’t simply mean telling your entire life story or listing everything you have achieved so far. Instead, a self-introduction in a job interview is a chance for you to present yourself in a professional light and talk about your key experiences, skills, and qualities that make you a perfect fit for the role you’re interviewing for.
Crafting the right answer to this question requires skills, preparation, and an understanding of what your interviewer is trying to find out about you. In this blog, we will take a look at the purpose, strategies, tips, and sample answers that will help you effectively answer the self-introduction question during the interview. Let’s quickly get started!
The question “Can you tell me about yourself?” is often regarded as an icebreaker during an interview. Its primary aim is to gain a comprehensive understanding of your background, experiences, skills, and overall personality. Interviewers use this question to assess how effectively you present yourself, evaluate your communication skills, and gauge your ability to articulate your strengths and qualifications. Moreover, a self-introduction in an interview serves as a means for the interviewer to ascertain how well you align with the job requirements and company culture.
Additionally, since the question usually is an opening question, it helps establish rapport between the interviewer and candidate, setting a tone for the rest of the interview.
- Interview Tips on How to Introduce Yourself

Tailor your answer to align with the job description. Talk about your experiences and skills that are directly relevant to the job role you are interviewing for.
To prepare an answer to introduce yourself during an interview, finding the perfect balance is crucial. It’s advisable to keep your introduction concise yet informative, providing a glimpse into your qualifications and background. Aim to craft an answer that lasts 2-3 minutes, effectively highlighting the key pointers.
Rather than listing job titles and responsibilities, focus on highlighting your most notable achievements. Share stories of challenges you’ve overcome, projects you’ve led, and outcomes you’ve achieved.
Show your passion in your introduction by expressing enthusiasm for the industry, company, and the job role. Employers or hiring managers hunt for candidates who are genuinely excited about the opportunity.
Prepare your self-introduction pitch very strategically. Highlight what makes you different from other candidates. Whether it’s your special skill, achievement, or perspective, highlighting and talking about your unique selling proposition can help you leave a positive impression.
To deliver a great introduction pitch during an interview, rehearse it well. Improve your delivery by practicing in front of a mirror, with a friend, or by recording yourself.
Related: How to Describe Yourself for an Interview – Sample Answers and Examples
- Self Introduction Samples for a Job Interview
Hi, I am [Name ], I recently graduated with a degree in [Your Field], and during my academic journey, I had the opportunity to intern at [Company Name] as [Job Role]. This experience was instrumental in shaping my skills in [relevant skills], and I’m eager to leverage them in a dynamic role like [Job Title]. I’m particularly drawn to [specific aspect of the industry], and I’m excited about the prospect of contributing to the innovative projects here at [Company Name].
Hello, my name is [Your Name], and I am thrilled to be here today. As a recent graduate with a degree in [Your Field], I am eager to kick-start my career in [Specific Industry or Job Role]. Throughout my academic journey, I have developed a strong foundation in [Key Skills or Knowledge Areas Relevant to the Job]. For instance, during my internship at [Company Name], I had the opportunity to [Briefly Describe Relevant Experience or Project]. This experience not only honed my technical skills but also taught me the importance of teamwork and effective communication in achieving project goals. I am excited about the opportunity to apply my knowledge and contribute to the innovative projects here at [Company Name]. Thank you for considering my candidacy.
Hi, My name is [Your Name], and I am excited to be interviewing for the [Job Title] position. With over [Number of Years] years of experience in [Industry or Field], I have developed a deep understanding of [Key Skills or Knowledge Areas Relevant to the Job]. Throughout my career, I have had the opportunity to [Briefly Describe Relevant Achievements or Projects], which has allowed me to refine my expertise in [Specific Area]. For example, in my previous role at [Previous Company], I spearheaded a project to [Briefly Describe Relevant Achievement or Initiative], resulting in [Quantifiable Result or Impact]. I am particularly drawn to the opportunity at [Company Name] because of [Specific Reason, such as Company’s Reputation, Innovative Projects, or Company Culture]. I am eager to leverage my skills and experience to contribute to the success of your team. Thank you for considering my application.
Sample 2:
Hello, [Interviewer’s Name]. My name is [Your Name], and I am delighted to be interviewing for the [Job Title] position. With a proven track record of success in [Industry or Field], I bring over [Number of Years] years of experience in [Specific Areas of Expertise]. Throughout my career, I have consistently delivered results by [Briefly Describe Relevant Achievements or Projects]. For instance, at [Previous Company], I led a team to [Briefly Describe Relevant Achievement or Initiative], resulting in [Quantifiable Result or Impact]. Additionally, my experience has equipped me with strong leadership, problem-solving, and communication skills, which I believe are essential for success in this role. I am drawn to the opportunity at [Company Name] because of [Specific Reason, such as Company’s Innovative Projects, Growth Opportunities, or Company Culture]. I am excited about the possibility of bringing my expertise to your team and making a meaningful impact. Thank you for considering me for this opportunity.
In Conclusion, A great opening introduction is a mix of creativity and strategy. It requires thoughtful preparation, authenticity, and the ability to communicate your value proposition effectively. Follow these tips and sample answers to confidently approach the question “Tell me about yourself” in an interview.
Remember, your introduction sets the tone for the rest of the conversation, so make it count!
Read More: How to Answer “What Is Your Biggest Achievement?” With Samples
Kickstart your job search journey with Apna ! Apna is your one-stop solution for all your job needs. With the Apna app, you can take a step closer to finding your dream job. Apna allows you to build profiles, connect with HRs faster, create creative resumes , and prepare for interviews seamlessly.
Download the Apna App today and take the next step towards your career goals!
- Job Seekers
Looking for a new opportunity?
Get access to over 5000 new job openings everyday across India.
Related articles
How to answer “what is your biggest achievement” with samples, 20 popular group discussion topics with tips, how to skillfully answer the question: “what is your current ctc”.
Follow us on social media

COMMENTS
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
Learn how to write an effective introduction paragraph for any academic essay with four steps and examples. Hook your reader, give background information, present your thesis statement, and map your essay's structure. See how to introduce an example in an essay with a hook and a background.
Every good introduction needs a thesis statement, a sentence that plainly and concisely explains the main topic. Thesis statements are often just a brief summary of your entire paper, including your argument or point of view for personal essays. For example, if your paper is about whether viewing violent cartoons impacts real-life violence ...
aspect of the essay. For example, while it may be acceptable to write a two-paragraph (or longer) introduction for your papers in some courses, instructors in other disciplines, such as those in some Government courses, may expect a shorter introduction that includes a preview of the argument that will follow.
Intro Paragraph Part 3: The Thesis. The final key part of how to write an intro paragraph is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the backbone of your introduction: it conveys your argument or point of view on your topic in a clear, concise, and compelling way. The thesis is usually the last sentence of your intro paragraph.
Intriguing ways to start an essay. There are many different ways to write an essay introduction. Each has its benefits and potential drawbacks, and each is best suited for certain kinds of essays.Although these essay introductions use different rhetorical devices and prime the reader in different ways, they all achieve the same goal: hooking the reader and enticing them to keep reading.
Example: Since the dawn of man, slavery has been a problem in human history. 5. The book report introduction. This introduction is what you had to do for your elementary school book reports. It gives the name and author of the book you are writing about, tells what the book is about, and offers other basic facts about the book.
This example guides you through the structure of an essay. It shows how to build an effective introduction , focused paragraphs , clear transitions between ideas, and a strong conclusion . Each paragraph addresses a single central point, introduced by a topic sentence , and each point is directly related to the thesis statement .
Good example. I wiped the sweat from my head and tried to catch my breath. I was nearly there—just one more back tuck and a strong dismount and I'd have nailed a perfect routine. Some students choose to write more broadly about themselves and use some sort of object or metaphor as the focus.
One example that illustrates this is the fact that fires were more frequent than in past years." 3. Include multiple examples to make your argument even stronger. For each main point in your essay, try to use 2-3 examples to back it up. That will help the reader understand the importance of your point.
A thesis statement tells the reader the main point or argument of the essay. This can be just one sentence, or it can be a few sentences. Map Your Essay. Before you wrap up your essay introduction, map it! This means signposting sections of your essay. The key here is to be concise. The purpose of this part of the introduction is to give your ...
Wordvice KH. Research requires us to scrutinize information and assess its credibility. Accordingly, when we think about various phenomena, we examine empirical data and craft detailed explanations justifying our interpretations. An essential component of constructing our research narratives is thus providing supporting evidence and examples.
Essay Introduction Examples. To help you get started, here are some examples of different essay types: Argumentative Essay Introduction Examples. In an argumentative essay, we introduce an argument and support the side that we think is more accurate. Here is a short example of the introduction of a short argumentative essay.
Effective Ways to Introduce New Essay Topics. Introduce the topic with a transition word, like "Similarly" or "Likewise.". Use a contrasting transition word for clashing topics, like "However" or "Yet.". Give an overview of the topic you're discussing after the introductory sentence. Method 1.
Report your position or argument. Most essays do not require you to take a stance on an issue. Essays that do require you to take a stance are called either 'argumentative essays' or 'persuasive essays'. If you are writing a persuasive essay, you will need to include Step 4: Report.
Persuasive Essay Introduction Example. A persuasive essay is a type of academic writing that seeks to convince the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action. The writing process of a persuasive essay introduction is similar to what is described above. Below is a perfect example of a persuasive essay introduction.
An introduction generally does three things. The first part is usually a general comment that shows the reader why the topic is important, gets their interest, and leads them into the topic. It isn't actually part of your argument. The next part of the introduction is the thesis statement. This is your response to the question; your final answer.
In an academic essay, you typically introduce a journal article in the first sentence of a paragraph. Then, use the sentences that follow to show how the material from the article relates to the rest of your essay. Submit a Tip. All tip submissions are carefully reviewed before being published. Submit.
Essay writing: Introductions. "A relevant and coherent beginning is perhaps your best single guarantee that the essay as a whole will achieve its object.". Gordon Taylor, A Student's Writing Guide. Your introduction is the first thing your marker will read and should be approximately 10% of your word count. Within the first minute they ...
The essay writing process consists of three main stages: Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline. Writing: Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion. Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling ...
Learn the best way to add examples to your essay to support your ideas. You need to use a range of linking words in your essay and also use them flexibly in different locations in the sentence. See below for a list of useful linking words with sample sentences: Linking Words for Giving Examples. for example; for instance; to illustrate; as an ...
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis. For example, if you are analyzing ...
Narrative Introductions. The introduction of a narrative essay sets the scene for the story that follows. Interesting introductions—for any kind of writing—engage and draw readers in because they want to know more. Since narratives tell a story and involve events, the introduction of a narrative quite often starts in the middle of the ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
A compare and contrast essay is a type of analytical essay that explores the similarities and differences between two subjects. We guide you through one with some examples.
Step 1: Your Introduction Must Catch Their Curiosity. Just like in writing any story, or an email, or even a speech, the most important thing you can do is to make an introduction that catches the reader's attention and curiosity. Make your introduction something catchy but not too catchy they may lose interest after the introduction.
Integrating sources means incorporating another scholar's ideas or words into your work. It can be done by: Quoting. Paraphrasing. Summarizing. By integrating sources properly, you can ensure a consistent voice in your writing and ensure your text remains readable and coherent. You can use signal phrases to give credit to outside sources and ...
To deliver a great introduction pitch during an interview, rehearse it well. Improve your delivery by practicing in front of a mirror, with a friend, or by recording yourself. Related: How to Describe Yourself for an Interview - Sample Answers and Examples. Self Introduction Samples for a Job Interview Self Introduction for Freshers: Sample 1: