- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Additional menu
Khan Academy Blog
Free Math Worksheets — Over 100k free practice problems on Khan Academy
Looking for free math worksheets.
You’ve found something even better!
That’s because Khan Academy has over 100,000 free practice questions. And they’re even better than traditional math worksheets – more instantaneous, more interactive, and more fun!
Just choose your grade level or topic to get access to 100% free practice questions:
Kindergarten, basic geometry, pre-algebra, algebra basics, high school geometry.
- Trigonometry
Statistics and probability
High school statistics, ap®︎/college statistics, precalculus, differential calculus, integral calculus, ap®︎/college calculus ab, ap®︎/college calculus bc, multivariable calculus, differential equations, linear algebra.
- Addition and subtraction
- Place value (tens and hundreds)
- Addition and subtraction within 20
- Addition and subtraction within 100
- Addition and subtraction within 1000
- Measurement and data
- Counting and place value
- Measurement and geometry
- Place value
- Measurement, data, and geometry
- Add and subtract within 20
- Add and subtract within 100
- Add and subtract within 1,000
- Money and time
- Measurement
- Intro to multiplication
- 1-digit multiplication
- Addition, subtraction, and estimation
- Intro to division
- Understand fractions
- Equivalent fractions and comparing fractions
- More with multiplication and division
- Arithmetic patterns and problem solving
- Quadrilaterals
- Represent and interpret data
- Multiply by 1-digit numbers
- Multiply by 2-digit numbers
- Factors, multiples and patterns
- Add and subtract fractions
- Multiply fractions
- Understand decimals
- Plane figures
- Measuring angles
- Area and perimeter
- Units of measurement
- Decimal place value
- Add decimals
- Subtract decimals
- Multi-digit multiplication and division
- Divide fractions
- Multiply decimals
- Divide decimals
- Powers of ten
- Coordinate plane
- Algebraic thinking
- Converting units of measure
- Properties of shapes
- Ratios, rates, & percentages
- Arithmetic operations
- Negative numbers
- Properties of numbers
- Variables & expressions
- Equations & inequalities introduction
- Data and statistics
- Negative numbers: addition and subtraction
- Negative numbers: multiplication and division
- Fractions, decimals, & percentages
- Rates & proportional relationships
- Expressions, equations, & inequalities
- Numbers and operations
- Solving equations with one unknown
- Linear equations and functions
- Systems of equations
- Geometric transformations
- Data and modeling
- Volume and surface area
- Pythagorean theorem
- Transformations, congruence, and similarity
- Arithmetic properties
- Factors and multiples
- Reading and interpreting data
- Negative numbers and coordinate plane
- Ratios, rates, proportions
- Equations, expressions, and inequalities
- Exponents, radicals, and scientific notation
- Foundations
- Algebraic expressions
- Linear equations and inequalities
- Graphing lines and slope
- Expressions with exponents
- Quadratics and polynomials
- Equations and geometry
- Algebra foundations
- Solving equations & inequalities
- Working with units
- Linear equations & graphs
- Forms of linear equations
- Inequalities (systems & graphs)
- Absolute value & piecewise functions
- Exponents & radicals
- Exponential growth & decay
- Quadratics: Multiplying & factoring
- Quadratic functions & equations
- Irrational numbers
- Performing transformations
- Transformation properties and proofs
- Right triangles & trigonometry
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry (Advanced)
- Analytic geometry
- Conic sections
- Solid geometry
- Polynomial arithmetic
- Complex numbers
- Polynomial factorization
- Polynomial division
- Polynomial graphs
- Rational exponents and radicals
- Exponential models
- Transformations of functions
- Rational functions
- Trigonometric functions
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry
- Trigonometric equations and identities
- Analyzing categorical data
- Displaying and comparing quantitative data
- Summarizing quantitative data
- Modeling data distributions
- Exploring bivariate numerical data
- Study design
- Probability
- Counting, permutations, and combinations
- Random variables
- Sampling distributions
- Confidence intervals
- Significance tests (hypothesis testing)
- Two-sample inference for the difference between groups
- Inference for categorical data (chi-square tests)
- Advanced regression (inference and transforming)
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Scatterplots
- Data distributions
- Two-way tables
- Binomial probability
- Normal distributions
- Displaying and describing quantitative data
- Inference comparing two groups or populations
- Chi-square tests for categorical data
- More on regression
- Prepare for the 2020 AP®︎ Statistics Exam
- AP®︎ Statistics Standards mappings
- Polynomials
- Composite functions
- Probability and combinatorics
- Limits and continuity
- Derivatives: definition and basic rules
- Derivatives: chain rule and other advanced topics
- Applications of derivatives
- Analyzing functions
- Parametric equations, polar coordinates, and vector-valued functions
- Applications of integrals
- Differentiation: definition and basic derivative rules
- Differentiation: composite, implicit, and inverse functions
- Contextual applications of differentiation
- Applying derivatives to analyze functions
- Integration and accumulation of change
- Applications of integration
- AP Calculus AB solved free response questions from past exams
- AP®︎ Calculus AB Standards mappings
- Infinite sequences and series
- AP Calculus BC solved exams
- AP®︎ Calculus BC Standards mappings
- Integrals review
- Integration techniques
- Thinking about multivariable functions
- Derivatives of multivariable functions
- Applications of multivariable derivatives
- Integrating multivariable functions
- Green’s, Stokes’, and the divergence theorems
- First order differential equations
- Second order linear equations
- Laplace transform
- Vectors and spaces
- Matrix transformations
- Alternate coordinate systems (bases)
Frequently Asked Questions about Khan Academy and Math Worksheets
Why is khan academy even better than traditional math worksheets.
Khan Academy’s 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don’t need to be graded, and don’t require a printer.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets look like?
Here’s an example:
What are teachers saying about Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets?
“My students love Khan Academy because they can immediately learn from their mistakes, unlike traditional worksheets.”
Is Khan Academy free?
Khan Academy’s practice questions are 100% free—with no ads or subscriptions.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets cover?
Our 100,000+ practice questions cover every math topic from arithmetic to calculus, as well as ELA, Science, Social Studies, and more.
Is Khan Academy a company?
Khan Academy is a nonprofit with a mission to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere.
Want to get even more out of Khan Academy?
Then be sure to check out our teacher tools . They’ll help you assign the perfect practice for each student from our full math curriculum and track your students’ progress across the year. Plus, they’re also 100% free — with no subscriptions and no ads.
Get Khanmigo
The best way to learn and teach with AI is here. Ace the school year with our AI-powered guide, Khanmigo.
For learners For teachers For parents
Math and Logic Puzzles
If you REALLY like exercising your brain, figuring things 'round and 'round till you explode, then this is the page for you !
Whosoever shall solve these puzzles shall Rule The Universe!
... or at least they should ...

- Prodigy Math
- Prodigy English
- Is a Premium Membership Worth It?
- Promote a Growth Mindset
- Help Your Child Who's Struggling with Math
- Parent's Guide to Prodigy
- Assessments
- Math Curriculum Coverage
- English Curriculum Coverage
- Game Portal
120 Math Word Problems To Challenge Students Grades 1 to 8

Written by Marcus Guido
Hey teachers! 👋
Use Prodigy to spark a love for math in your students – including when solving word problems!
- Teaching Tools
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Mixed operations
- Ordering and number sense
- Comparing and sequencing
- Physical measurement
- Ratios and percentages
- Probability and data relationships
You sit at your desk, ready to put a math quiz, test or activity together. The questions flow onto the document until you hit a section for word problems.
A jolt of creativity would help. But it doesn’t come.
Whether you’re a 3rd grade teacher or an 8th grade teacher preparing students for high school, translating math concepts into real world examples can certainly be a challenge.
This resource is your jolt of creativity. It provides examples and templates of math word problems for 1st to 8th grade classes.
There are 120 examples in total.
The list of examples is supplemented by tips to create engaging and challenging math word problems.
120 Math word problems, categorized by skill
Addition word problems.

Best for: 1st grade, 2nd grade
1. Adding to 10: Ariel was playing basketball. 1 of her shots went in the hoop. 2 of her shots did not go in the hoop. How many shots were there in total?
2. Adding to 20: Adrianna has 10 pieces of gum to share with her friends. There wasn’t enough gum for all her friends, so she went to the store to get 3 more pieces of gum. How many pieces of gum does Adrianna have now?
3. Adding to 100: Adrianna has 10 pieces of gum to share with her friends. There wasn’t enough gum for all her friends, so she went to the store and got 70 pieces of strawberry gum and 10 pieces of bubble gum. How many pieces of gum does Adrianna have now?
4. Adding Slightly over 100: The restaurant has 175 normal chairs and 20 chairs for babies. How many chairs does the restaurant have in total?
5. Adding to 1,000: How many cookies did you sell if you sold 320 chocolate cookies and 270 vanilla cookies?
6. Adding to and over 10,000: The hobby store normally sells 10,576 trading cards per month. In June, the hobby store sold 15,498 more trading cards than normal. In total, how many trading cards did the hobby store sell in June?
7. Adding 3 Numbers: Billy had 2 books at home. He went to the library to take out 2 more books. He then bought 1 book. How many books does Billy have now?
8. Adding 3 Numbers to and over 100: Ashley bought a big bag of candy. The bag had 102 blue candies, 100 red candies and 94 green candies. How many candies were there in total?
Subtraction word problems
Best for: 1st grade, second grade
9. Subtracting to 10: There were 3 pizzas in total at the pizza shop. A customer bought 1 pizza. How many pizzas are left?
10. Subtracting to 20: Your friend said she had 11 stickers. When you helped her clean her desk, she only had a total of 10 stickers. How many stickers are missing?
11. Subtracting to 100: Adrianna has 100 pieces of gum to share with her friends. When she went to the park, she shared 10 pieces of strawberry gum. When she left the park, Adrianna shared another 10 pieces of bubble gum. How many pieces of gum does Adrianna have now?

Practice math word problems with Prodigy Math
Join millions of teachers using Prodigy to make learning fun and differentiate instruction as they answer in-game questions, including math word problems from 1st to 8th grade!
12. Subtracting Slightly over 100: Your team scored a total of 123 points. 67 points were scored in the first half. How many were scored in the second half?
13. Subtracting to 1,000: Nathan has a big ant farm. He decided to sell some of his ants. He started with 965 ants. He sold 213. How many ants does he have now?
14. Subtracting to and over 10,000: The hobby store normally sells 10,576 trading cards per month. In July, the hobby store sold a total of 20,777 trading cards. How many more trading cards did the hobby store sell in July compared with a normal month?
15. Subtracting 3 Numbers: Charlene had a pack of 35 pencil crayons. She gave 6 to her friend Theresa. She gave 3 to her friend Mandy. How many pencil crayons does Charlene have left?
16. Subtracting 3 Numbers to and over 100: Ashley bought a big bag of candy to share with her friends. In total, there were 296 candies. She gave 105 candies to Marissa. She also gave 86 candies to Kayla. How many candies were left?
Multiplication word problems

Best for: 2nd grade, 3rd grade
17. Multiplying 1-Digit Integers: Adrianna needs to cut a pan of brownies into pieces. She cuts 6 even columns and 3 even rows into the pan. How many brownies does she have?
18. Multiplying 2-Digit Integers: A movie theatre has 25 rows of seats with 20 seats in each row. How many seats are there in total?
19. Multiplying Integers Ending with 0: A clothing company has 4 different kinds of sweatshirts. Each year, the company makes 60,000 of each kind of sweatshirt. How many sweatshirts does the company make each year?
20. Multiplying 3 Integers: A bricklayer stacks bricks in 2 rows, with 10 bricks in each row. On top of each row, there is a stack of 6 bricks. How many bricks are there in total?
21. Multiplying 4 Integers: Cayley earns $5 an hour by delivering newspapers. She delivers newspapers 3 days each week, for 4 hours at a time. After delivering newspapers for 8 weeks, how much money will Cayley earn?
Division word problems
Best for: 3rd grade, 4th grade, 5th grade
22. Dividing 1-Digit Integers: If you have 4 pieces of candy split evenly into 2 bags, how many pieces of candy are in each bag?
23. Dividing 2-Digit Integers: If you have 80 tickets for the fair and each ride costs 5 tickets, how many rides can you go on?
24. Dividing Numbers Ending with 0: The school has $20,000 to buy new computer equipment. If each piece of equipment costs $50, how many pieces can the school buy in total?
25. Dividing 3 Integers: Melissa buys 2 packs of tennis balls for $12 in total. All together, there are 6 tennis balls. How much does 1 pack of tennis balls cost? How much does 1 tennis ball cost?
26. Interpreting Remainders: An Italian restaurant receives a shipment of 86 veal cutlets. If it takes 3 cutlets to make a dish, how many cutlets will the restaurant have left over after making as many dishes as possible?
Mixed operations word problems

27. Mixing Addition and Subtraction: There are 235 books in a library. On Monday, 123 books are taken out. On Tuesday, 56 books are brought back. How many books are there now?
28. Mixing Multiplication and Division: There is a group of 10 people who are ordering pizza. If each person gets 2 slices and each pizza has 4 slices, how many pizzas should they order?
29. Mixing Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction: Lana has 2 bags with 2 marbles in each bag. Markus has 2 bags with 3 marbles in each bag. How many more marbles does Markus have?
30. Mixing Division, Addition and Subtraction: Lana has 3 bags with the same amount of marbles in them, totaling 12 marbles. Markus has 3 bags with the same amount of marbles in them, totaling 18 marbles. How many more marbles does Markus have in each bag?
Ordering and number sense word problems
31. Counting to Preview Multiplication: There are 2 chalkboards in your classroom. If each chalkboard needs 2 pieces of chalk, how many pieces do you need in total?
32. Counting to Preview Division: There are 3 chalkboards in your classroom. Each chalkboard has 2 pieces of chalk. This means there are 6 pieces of chalk in total. If you take 1 piece of chalk away from each chalkboard, how many will there be in total?
33. Composing Numbers: What number is 6 tens and 10 ones?
34. Guessing Numbers: I have a 7 in the tens place. I have an even number in the ones place. I am lower than 74. What number am I?
35. Finding the Order: In the hockey game, Mitchell scored more points than William but fewer points than Auston. Who scored the most points? Who scored the fewest points?
Fractions word problems

Best for: 3rd grade, 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade
36. Finding Fractions of a Group: Julia went to 10 houses on her street for Halloween. 5 of the houses gave her a chocolate bar. What fraction of houses on Julia’s street gave her a chocolate bar?
37. Finding Unit Fractions: Heather is painting a portrait of her best friend, Lisa. To make it easier, she divides the portrait into 6 equal parts. What fraction represents each part of the portrait?
38. Adding Fractions with Like Denominators: Noah walks ⅓ of a kilometre to school each day. He also walks ⅓ of a kilometre to get home after school. How many kilometres does he walk in total?
39. Subtracting Fractions with Like Denominators: Last week, Whitney counted the number of juice boxes she had for school lunches. She had ⅗ of a case. This week, it’s down to ⅕ of a case. How much of the case did Whitney drink?
40. Adding Whole Numbers and Fractions with Like Denominators: At lunchtime, an ice cream parlor served 6 ¼ scoops of chocolate ice cream, 5 ¾ scoops of vanilla and 2 ¾ scoops of strawberry. How many scoops of ice cream did the parlor serve in total?
41. Subtracting Whole Numbers and Fractions with Like Denominators: For a party, Jaime had 5 ⅓ bottles of cola for her friends to drink. She drank ⅓ of a bottle herself. Her friends drank 3 ⅓. How many bottles of cola does Jaime have left?
42. Adding Fractions with Unlike Denominators: Kevin completed ½ of an assignment at school. When he was home that evening, he completed ⅚ of another assignment. How many assignments did Kevin complete?
43. Subtracting Fractions with Unlike Denominators: Packing school lunches for her kids, Patty used ⅞ of a package of ham. She also used ½ of a package of turkey. How much more ham than turkey did Patty use?
44. Multiplying Fractions: During gym class on Wednesday, the students ran for ¼ of a kilometre. On Thursday, they ran ½ as many kilometres as on Wednesday. How many kilometres did the students run on Thursday? Write your answer as a fraction.
45. Dividing Fractions: A clothing manufacturer uses ⅕ of a bottle of colour dye to make one pair of pants. The manufacturer used ⅘ of a bottle yesterday. How many pairs of pants did the manufacturer make?
46. Multiplying Fractions with Whole Numbers: Mark drank ⅚ of a carton of milk this week. Frank drank 7 times more milk than Mark. How many cartons of milk did Frank drink? Write your answer as a fraction, or as a whole or mixed number.
Decimals word problems
Best for: 4th grade, 5th grade
47. Adding Decimals: You have 2.6 grams of yogurt in your bowl and you add another spoonful of 1.3 grams. How much yogurt do you have in total?
48. Subtracting Decimals: Gemma had 25.75 grams of frosting to make a cake. She decided to use only 15.5 grams of the frosting. How much frosting does Gemma have left?
49. Multiplying Decimals with Whole Numbers: Marshall walks a total of 0.9 kilometres to and from school each day. After 4 days, how many kilometres will he have walked?
50. Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers: To make the Leaning Tower of Pisa from spaghetti, Mrs. Robinson bought 2.5 kilograms of spaghetti. Her students were able to make 10 leaning towers in total. How many kilograms of spaghetti does it take to make 1 leaning tower?
51. Mixing Addition and Subtraction of Decimals: Rocco has 1.5 litres of orange soda and 2.25 litres of grape soda in his fridge. Antonio has 1.15 litres of orange soda and 0.62 litres of grape soda. How much more soda does Rocco have than Angelo?
52. Mixing Multiplication and Division of Decimals: 4 days a week, Laura practices martial arts for 1.5 hours. Considering a week is 7 days, what is her average practice time per day each week?
Comparing and sequencing word problems

Best for: Kindergarten, 1st grade, 2nd grade
53. Comparing 1-Digit Integers: You have 3 apples and your friend has 5 apples. Who has more?
54. Comparing 2-Digit Integers: You have 50 candies and your friend has 75 candies. Who has more?
55. Comparing Different Variables: There are 5 basketballs on the playground. There are 7 footballs on the playground. Are there more basketballs or footballs?
56. Sequencing 1-Digit Integers: Erik has 0 stickers. Every day he gets 1 more sticker. How many days until he gets 3 stickers?
57. Skip-Counting by Odd Numbers: Natalie began at 5. She skip-counted by fives. Could she have said the number 20?
58. Skip-Counting by Even Numbers: Natasha began at 0. She skip-counted by eights. Could she have said the number 36?
59. Sequencing 2-Digit Numbers: Each month, Jeremy adds the same number of cards to his baseball card collection. In January, he had 36. 48 in February. 60 in March. How many baseball cards will Jeremy have in April?
Time word problems
66. Converting Hours into Minutes: Jeremy helped his mom for 1 hour. For how many minutes was he helping her?
69. Adding Time: If you wake up at 7:00 a.m. and it takes you 1 hour and 30 minutes to get ready and walk to school, at what time will you get to school?
70. Subtracting Time: If a train departs at 2:00 p.m. and arrives at 4:00 p.m., how long were passengers on the train for?
71. Finding Start and End Times: Rebecca left her dad’s store to go home at twenty to seven in the evening. Forty minutes later, she was home. What time was it when she arrived home?
Money word problems
Best for: 1st grade, 2nd grade, 3rd grade, 4th grade, 5th grade
60. Adding Money: Thomas and Matthew are saving up money to buy a video game together. Thomas has saved $30. Matthew has saved $35. How much money have they saved up together in total?
61. Subtracting Money: Thomas has $80 saved up. He uses his money to buy a video game. The video game costs $67. How much money does he have left?
62. Multiplying Money: Tim gets $5 for delivering the paper. How much money will he have after delivering the paper 3 times?
63. Dividing Money: Robert spent $184.59 to buy 3 hockey sticks. If each hockey stick was the same price, how much did 1 cost?
64. Adding Money with Decimals: You went to the store and bought gum for $1.25 and a sucker for $0.50. How much was your total?
65. Subtracting Money with Decimals: You went to the store with $5.50. You bought gum for $1.25, a chocolate bar for $1.15 and a sucker for $0.50. How much money do you have left?
67. Applying Proportional Relationships to Money: Jakob wants to invite 20 friends to his birthday, which will cost his parents $250. If he decides to invite 15 friends instead, how much money will it cost his parents? Assume the relationship is directly proportional.
68. Applying Percentages to Money: Retta put $100.00 in a bank account that gains 20% interest annually. How much interest will be accumulated in 1 year? And if she makes no withdrawals, how much money will be in the account after 1 year?
Physical measurement word problems

Best for: 1st grade, 2nd grade, 3rd grade, 4th grade
72. Comparing Measurements: Cassandra’s ruler is 22 centimetres long. April’s ruler is 30 centimetres long. How many centimetres longer is April’s ruler?
73. Contextualizing Measurements: Picture a school bus. Which unit of measurement would best describe the length of the bus? Centimetres, metres or kilometres?
74. Adding Measurements: Micha’s dad wants to try to save money on gas, so he has been tracking how much he uses. Last year, Micha’s dad used 100 litres of gas. This year, her dad used 90 litres of gas. How much gas did he use in total for the two years?
75. Subtracting Measurements: Micha’s dad wants to try to save money on gas, so he has been tracking how much he uses. Over the past two years, Micha’s dad used 200 litres of gas. This year, he used 100 litres of gas. How much gas did he use last year?
76. Multiplying Volume and Mass: Kiera wants to make sure she has strong bones, so she drinks 2 litres of milk every week. After 3 weeks, how many litres of milk will Kiera drink?
77. Dividing Volume and Mass: Lillian is doing some gardening, so she bought 1 kilogram of soil. She wants to spread the soil evenly between her 2 plants. How much will each plant get?
78. Converting Mass: Inger goes to the grocery store and buys 3 squashes that each weigh 500 grams. How many kilograms of squash did Inger buy?
79. Converting Volume: Shad has a lemonade stand and sold 20 cups of lemonade. Each cup was 500 millilitres. How many litres did Shad sell in total?
80. Converting Length: Stacy and Milda are comparing their heights. Stacy is 1.5 meters tall. Milda is 10 centimetres taller than Stacy. What is Milda’s height in centimetres?
81. Understanding Distance and Direction: A bus leaves the school to take students on a field trip. The bus travels 10 kilometres south, 10 kilometres west, another 5 kilometres south and 15 kilometres north. To return to the school, in which direction does the bus have to travel? How many kilometres must it travel in that direction?
Ratios and percentages word problems
Best for: 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade
82. Finding a Missing Number: The ratio of Jenny’s trophies to Meredith’s trophies is 7:4. Jenny has 28 trophies. How many does Meredith have?
83. Finding Missing Numbers: The ratio of Jenny’s trophies to Meredith’s trophies is 7:4. The difference between the numbers is 12. What are the numbers?
84. Comparing Ratios: The school’s junior band has 10 saxophone players and 20 trumpet players. The school’s senior band has 18 saxophone players and 29 trumpet players. Which band has the higher ratio of trumpet to saxophone players?
85. Determining Percentages: Mary surveyed students in her school to find out what their favourite sports were. Out of 1,200 students, 455 said hockey was their favourite sport. What percentage of students said hockey was their favourite sport?
86. Determining Percent of Change: A decade ago, Oakville’s population was 67,624 people. Now, it is 190% larger. What is Oakville’s current population?
87. Determining Percents of Numbers: At the ice skate rental stand, 60% of 120 skates are for boys. If the rest of the skates are for girls, how many are there?
88. Calculating Averages: For 4 weeks, William volunteered as a helper for swimming classes. The first week, he volunteered for 8 hours. He volunteered for 12 hours in the second week, and another 12 hours in the third week. The fourth week, he volunteered for 9 hours. For how many hours did he volunteer per week, on average?
Probability and data relationships word problems

Best for: 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, 7th grade
89. Understanding the Premise of Probability: John wants to know his class’s favourite TV show, so he surveys all of the boys. Will the sample be representative or biased?
90. Understanding Tangible Probability: The faces on a fair number die are labelled 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. You roll the die 12 times. How many times should you expect to roll a 1?
91. Exploring Complementary Events: The numbers 1 to 50 are in a hat. If the probability of drawing an even number is 25/50, what is the probability of NOT drawing an even number? Express this probability as a fraction.
92. Exploring Experimental Probability: A pizza shop has recently sold 15 pizzas. 5 of those pizzas were pepperoni. Answering with a fraction, what is the experimental probability that he next pizza will be pepperoni?
93. Introducing Data Relationships: Maurita and Felice each take 4 tests. Here are the results of Maurita’s 4 tests: 4, 4, 4, 4. Here are the results for 3 of Felice’s 4 tests: 3, 3, 3. If Maurita’s mean for the 4 tests is 1 point higher than Felice’s, what’s the score of Felice’s 4th test?
94. Introducing Proportional Relationships: Store A is selling 7 pounds of bananas for $7.00. Store B is selling 3 pounds of bananas for $6.00. Which store has the better deal?
95. Writing Equations for Proportional Relationships: Lionel loves soccer, but has trouble motivating himself to practice. So, he incentivizes himself through video games. There is a proportional relationship between the amount of drills Lionel completes, in x , and for how many hours he plays video games, in y . When Lionel completes 10 drills, he plays video games for 30 minutes. Write the equation for the relationship between x and y .
Geometry word problems
Best for: 4th grade, 5th grade, 6th grade, 7th grade, 8th grade
96. Introducing Perimeter: The theatre has 4 chairs in a row. There are 5 rows. Using rows as your unit of measurement, what is the perimeter?
97. Introducing Area: The theatre has 4 chairs in a row. There are 5 rows. How many chairs are there in total?
98. Introducing Volume: Aaron wants to know how much candy his container can hold. The container is 20 centimetres tall, 10 centimetres long and 10 centimetres wide. What is the container’s volume?
99. Understanding 2D Shapes: Kevin draws a shape with 4 equal sides. What shape did he draw?
100. Finding the Perimeter of 2D Shapes: Mitchell wrote his homework questions on a piece of square paper. Each side of the paper is 8 centimetres. What is the perimeter?
101. Determining the Area of 2D Shapes: A single trading card is 9 centimetres long by 6 centimetres wide. What is its area?
102. Understanding 3D Shapes: Martha draws a shape that has 6 square faces. What shape did she draw?
103. Determining the Surface Area of 3D Shapes: What is the surface area of a cube that has a width of 2cm, height of 2 cm and length of 2 cm?
104. Determining the Volume of 3D Shapes: Aaron’s candy container is 20 centimetres tall, 10 centimetres long and 10 centimetres wide. Bruce’s container is 25 centimetres tall, 9 centimetres long and 9 centimetres wide. Find the volume of each container. Based on volume, whose container can hold more candy?
105. Identifying Right-Angled Triangles: A triangle has the following side lengths: 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm. Is this triangle a right-angled triangle?
106. Identifying Equilateral Triangles: A triangle has the following side lengths: 4 cm, 4 cm and 4 cm. What kind of triangle is it?
107. Identifying Isosceles Triangles: A triangle has the following side lengths: 4 cm, 5 cm and 5 cm. What kind of triangle is it?
108. Identifying Scalene Triangles: A triangle has the following side lengths: 4 cm, 5 cm and 6 cm. What kind of triangle is it?
109. Finding the Perimeter of Triangles: Luigi built a tent in the shape of an equilateral triangle. The perimeter is 21 metres. What is the length of each of the tent’s sides?
110. Determining the Area of Triangles: What is the area of a triangle with a base of 2 units and a height of 3 units?
111. Applying Pythagorean Theorem: A right triangle has one non-hypotenuse side length of 3 inches and the hypotenuse measures 5 inches. What is the length of the other non-hypotenuse side?
112. Finding a Circle’s Diameter: Jasmin bought a new round backpack. Its area is 370 square centimetres. What is the round backpack’s diameter?
113. Finding a Circle's Area: Captain America’s circular shield has a diameter of 76.2 centimetres. What is the area of his shield?
114. Finding a Circle’s Radius: Skylar lives on a farm, where his dad keeps a circular corn maze. The corn maze has a diameter of 2 kilometres. What is the maze’s radius?
Variables word problems

Best for: 6th grade, 7th grade, 8th grade
115. Identifying Independent and Dependent Variables: Victoria is baking muffins for her class. The number of muffins she makes is based on how many classmates she has. For this equation, m is the number of muffins and c is the number of classmates. Which variable is independent and which variable is dependent?
116. Writing Variable Expressions for Addition: Last soccer season, Trish scored g goals. Alexa scored 4 more goals than Trish. Write an expression that shows how many goals Alexa scored.
117. Writing Variable Expressions for Subtraction: Elizabeth eats a healthy, balanced breakfast b times a week. Madison sometimes skips breakfast. In total, Madison eats 3 fewer breakfasts a week than Elizabeth. Write an expression that shows how many times a week Madison eats breakfast.
118. Writing Variable Expressions for Multiplication: Last hockey season, Jack scored g goals. Patrik scored twice as many goals than Jack. Write an expression that shows how many goals Patrik scored.
119. Writing Variable Expressions for Division: Amanda has c chocolate bars. She wants to distribute the chocolate bars evenly among 3 friends. Write an expression that shows how many chocolate bars 1 of her friends will receive.
120. Solving Two-Variable Equations: This equation shows how the amount Lucas earns from his after-school job depends on how many hours he works: e = 12h . The variable h represents how many hours he works. The variable e represents how much money he earns. How much money will Lucas earn after working for 6 hours?
How to easily make your own math word problems & word problems worksheets

Armed with 120 examples to spark ideas, making your own math word problems can engage your students and ensure alignment with lessons. Do:
- Link to Student Interests: By framing your word problems with student interests, you’ll likely grab attention. For example, if most of your class loves American football, a measurement problem could involve the throwing distance of a famous quarterback.
- Make Questions Topical: Writing a word problem that reflects current events or issues can engage students by giving them a clear, tangible way to apply their knowledge.
- Include Student Names: Naming a question’s characters after your students is an easy way make subject matter relatable, helping them work through the problem.
- Be Explicit: Repeating keywords distills the question, helping students focus on the core problem.
- Test Reading Comprehension: Flowery word choice and long sentences can hide a question’s key elements. Instead, use concise phrasing and grade-level vocabulary.
- Focus on Similar Interests: Framing too many questions with related interests -- such as football and basketball -- can alienate or disengage some students.
- Feature Red Herrings: Including unnecessary information introduces another problem-solving element, overwhelming many elementary students.
A key to differentiated instruction , word problems that students can relate to and contextualize will capture interest more than generic and abstract ones.
Final thoughts about math word problems
You’ll likely get the most out of this resource by using the problems as templates, slightly modifying them by applying the above tips. In doing so, they’ll be more relevant to -- and engaging for -- your students.
Regardless, having 120 curriculum-aligned math word problems at your fingertips should help you deliver skill-building challenges and thought-provoking assessments.
The result?
A greater understanding of how your students process content and demonstrate understanding, informing your ongoing teaching approach.
Open Middle®

Mastery-Aligned Maths Tutoring
“The best thing has been the increase in confidence and tutors being there to deal with any misunderstandings straight away."
FREE daily maths challenges
A new KS2 maths challenge every day. Perfect as lesson starters - no prep required!

The 21 Best Maths Challenges At KS2 To Really Stretch Your More Able Primary School Pupils
Emily Weston
It won’t be long in your teaching career before you’re seeking out maths challenges at KS2 to stretch your more able pupils. Particularly once you get to Year 6, the maths challenges that may have previously kept them busy will no longer be stretching them. At least this is what I found out recently.
Every child deserves maths challenges that stretch them
You are not alone looking for ks2 maths challenges for high attainers, 1. i see reasoning uks2 – gareth metcalfe, 3. third space learning, 4. peter dickinson – reasoning club, 5. royal institute of science – maths masterclass, 7. nace (national association for able children in education) , 8. maths bot , 9. craig barton – same surface different deep, 10. dr frost maths , 21. mastering mixed ability maths, 12. parallel maths, 13. ted airplane riddle, 14. times tables app, 15. fibonacci rabbit sequence , 16. open middle, 17. daily rigour articles, 18. total maths , 19. maths in sport, 20. wild maths, 11. white rose, maths challenge books, where this list of mathematical challenges for able pupils came from.
Usually, applying knowledge and using transferable skills is enough to keep a class ticking over; extending their understanding beyond number. But in some cohorts there will be a child who completes the ‘challenges’ we set with relative ease; they aren’t taken out of their comfort zone or rarely make mistakes.
Some children will readily grasp the concepts being shown to them and will be ready to apply their strategies and understanding to further reasoning and problem solving questions.
This year I had a child like this in my class, and I found stretching his abilities a struggle as I didn’t have access to enough resources to give me, or him, variety.
I’d be helping one child grasp long multiplication – or something similar – when a shadow would loom over my shoulder. Turning around, he’d be there, telling me he had finished. Often, he had finished a year 6 maths challenge which I was sure would last for the whole lesson. Looking at the clock, 40 minutes of the lesson remained.
His abilities stretched beyond any child I had previously had in my class. So, I reached out to Twitter to discover some new ways to include maths challenges for more able pupils in my lessons.I was especially looking for work which he could pick up and use independently, if he had managed to complete the tasks already set.
After the responses on Twitter, it was clear to see I wasn’t not the only person left scratching my head in this kind of situation, wondering what resources I can turn to.
So, to help you find even more challenges for your greater depth pupils quickly and easily, we’ve put together this list of activities, categorised for ease of use.
You can find the original tweet here . It’s worth a read; the thread is packed with lots more ideas than I was able to include on this blog!
Top 6 Maths Challenges For Primary School Pupils
Prep: Find the activity you want, photocopy (and maybe some guillotine-ing!)
Who it’s for: Although this is the Upper Key Stage 2 version, it is available for Lower Key Stage 2 too!
Cost: You will need to purchase the ‘I See Reasoning’ resources.
This resource is full of a huge range of activities which push children to think beyond numbers and begin to use mathematical language to explain.
Each activity requires children to display their understanding of what they have already learnt, and build upon their knowledge in order to describe what they notice or know.
This document covers the whole of the maths curriculum, including not only problems relating to number, but also geometry, shape and statistics.
I also love that this really clearly includes the answers, which makes it so simple to use!
Each activity has its merits, but the three I find particularly useful are:
Explain the Mistakes
Children are shown mistakes and are required to explain why the diagrams/calculations are wrong.
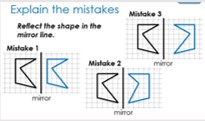
They must use mathematical language and previous knowledge to first understand, then explain their thinking to show what would need to change in order for there to be a correct solution.
‘I know…so…’
This activity models to children how to link ideas and get them reasoning, building on what they know already.
Once they have seen this model in ‘I See Reasoning’ they will then begin to use this phrase within the classroom, not only when speaking to the teacher but also to their peers.
Different Ways
This activity requires children to understand that their can be different variations. They can then explain how they know that these answers all work, and why.
Child Review: This was challenging as when you understand number so easily, it can be trickier to explain exactly how you know a fact is true. There was some element of challenge because of the range of different activities.
Link: I See Reasoning
Prep: Just print and go! (Unless they’ve already done the challenge in a previous year group…!)
Who it’s for: There are activities for all primary age ranges.
Cost: FREE!
I have to admit, this is my absolute go-to for mathematical challenges (as I’m sure it is for many of you out there!).
The huge range of challenges that are available can be easily searched so you can find the activity which is perfectly suited to the topic you’re doing,
They are also labelled with which age range the problem is most suited for (and can be adapted if you want to).
However, because Nrich is so popular I often find that the children have already accessed problems the previous year, meaning that inevitably they no longer pose any challenge to them, or it takes extra time to plan as you need to consult previous teachers.
My favourite challenge so far this year from Nrich is:

This activity really challenged my whole class. They worked in groups to discover the answer and there were cries of ‘noooo’ when we started running out of time for them to solve it (which inevitably led to another lesson being abandoned to let them have more time to work it out!)
This was an activity I thought would be completed quickly, but really challenged the all the children.
Child Review: This activity was really challenging as it used lots of logic. You had to use what you knew about number, use trial and error and really understand how the strategy works! I like these types of problems as they make me think.
Link: Nrich
Prep: Access to a computer and a headset.
Who it’s for: Years 2 to 7
Cost: Bespoke to each school, on average £15 per pupil per week.
Some of you might already be using Third Space Learning’s one-to-one online maths interventions with your lower attaining pupils or as part of your Pupil Premium budget. But these interventions can also be an excellent way of further stretching most able pupils.
Third Space’s highly targeted initial diagnostic assessment identifies maths strengths as well as weaknesses. With higher attaining pupils, Third Space tutors can create lesson plans aimed at engaging and developing these strengths, introducing them to concepts and topics that will challenge and motivate them.
Third Space also provides an online Maths Hub full of premium and free maths resources , such as the one below, that you can use in lessons to continue challenging your more able pupils.
Child Review: “ I enjoy coming here every Friday to do Third Space Learning! It makes me happy every time I come to school!” – Katie, Third Space pupil
Link: Find out about the maths interventions (or call 0203 771 0095)
108 Greater Depth Questions for KS2 Maths Mastery
Download our set of 108 Greater Depth Maths Mastery questions for some free additional stretch and challenge for your more able pupils.
Prep: Print and go!
Who it’s for: Year 5 and 6.
Cost: There is a cost for these resources. You will need to contact Peter directly to enquire.
Peter Dickinson has created a range of reasoning resources which really require children to think and apply their knowledge.
Each challenge explicitly targets a different aspect of maths, as well as requiring the children to transfer a range of different skills to help them solve the problem.
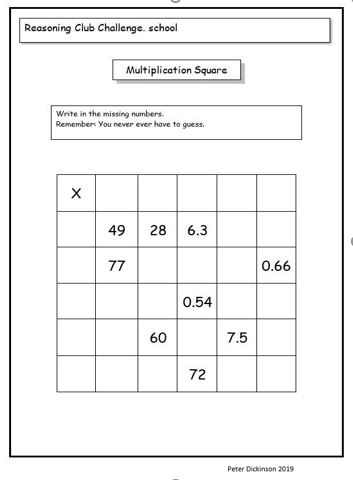
For example, in the ‘Multiplication Square’ children have to not only use multiplying knowledge, but also that of decimals and place value.
I’ve found that these reasoning word problems cover a lot of the curriculum, particularly number, which allow a really wide range of maths challenge for the class.
The best part of these, is that it’s really useful to laminate them within the classroom in order to use over and over again; because of the level of challenge, sometimes they don’t get finished and it enables the child to continue another time before passing them on to someone else.
Child Review: I really like that these are usually laid out in familiar ways and full of lots of different types of challenges. Some of them really make me think and use lots of logic – I enjoy that they actually challenge me!
Link: Peter can be found on Twitter at @2358Peter
Prep: There are quite a few downloads to prepare for the session, but they also have PowerPoints to help with you explanation.
Who it’s for: Year 5 and 6, although they may also link to some topic work in a lesser capacity lower down.

I was really disappointed I hadn’t come across these resources before (thanks for the suggestion @Glazgow/@racheldorris1)!
They cover a range of topics including (but not limited to!) fractions, shape, number patterns and reflections.
Each of these are also linked to a science element (and in some cases, some history or art too!) providing a range of curricular links you can also build into your lessons.
Each ‘off the shelf’ lesson is fully planned and resourced for you, which means it is easy to prep for the children (although I do recommend reading through it all first – some lessons have quite a few downloads you need to use whereas some need equipment!).
The topics are all very interesting and are some you may not come across or think of having not discovered them on the Royal Institute of Science site. One example of this is creating colours through using fractions and proportion.
These sorts of cross-curricular activities are also excellent evidence to show off during Ofsted inspections !
Child Review: These challenges are really interesting because they involve different parts of the curriculum too! We have only done one of these, but I really look forward to doing more!
Link: Royal Institution Maths Masterclasses
Prep: Some printing may be required!
Who it’s for: KS2 – there are a range of different challenges.
This resource was kindly suggested by @ianr73 and I am very glad it was! Transum has a range of features which are really useful to use in class.

Firstly, they have a range of daily challenges which are puzzles for the children to complete and challenge a different area of their maths knowledge each day.
In this example, it focuses on time and has a range of different examples for them to work on. I have this on my board at some point each day to expose the class to new ideas and maths puzzles!
Also, as you might expect, they have a range of maths challenges on their site too. There are a wide range of problems to choose from – I found them to be quite like Nrich in their style which meant they were easy to begin using in the classroom.
There were also the options of outdoor maths, riddles and a range of online maths games to use too!
Child Review: I really enjoy the daily maths puzzle that we can have as it shows lots of different types of maths I might not otherwise get to see. The challenges are fun, and can be done in different ways too.
Link: Transum
Favourite Maths Challenges Recommended By Primary School Teachers
Gone through all of the challenges above and still need more? These are some of the other maths challenges that were recommended on the Twitter thread:
What it is: An association which specifically focuses on how to challenge more able children in a range of different ways.
What it is: These are a range of maths challenges in different formats (including exam style questions) which can be used in different year groups (as well as going through Secondary).
What it is: These problems are based around the concept that children should be revisiting different areas of maths constantly. If they do problems based around just the topic being studied they aren’t effectively applying their knowledge.
A range of problem solving activities which children can use to extend their reasoning understanding.
What it is: A free Third Space Learning resource with 8 mastery-based maths activities, all designed to be ‘low threshold/high ceiling’ – relatively easy to pick up, but with lots of room to stretch more able pupils.
Link: Mastering Mixed Ability Maths Resource
What it is: These are challenges which are used to stretch children. They are aimed for Year 7 up, but might be used to stretch children in Year 6 as an extra ‘weekly challenge’ if the topic matches!
What is is: A riddle which children will need to apply their knowledge and maths logic to solve the problem.
What it is: A challenging app to speed up times table recall knowledge, which can be done on a phone or tablet.

What it is: This is using mathematical discovery (trial and error) rather than allocation of knowledge. It is a really good challenge for children (especially Year 5/6 )
What it is: A site that promotes problem solving over worksheets, allowing children to work in a more practical manner.
What it is: This is a free newspaper that puts maths problems into a real life context. It is full of interesting ideas to get children using challenge!
What it is: Tara Loughran (@MathsMummy) is a maths consultant who has created a range of problem sheets which stretch children across a range of topics in the maths curriculum.
What it is: A range of maths problems which are also linked to sport. Curated by University of Cambridge, it covers KS1 and KS2!
What it is: This is a similar site to Nrich which has a range of activities, stories and maths puzzles to challenge your children.
What it is: A scheme of work which moves from fluency to reasoning in all areas of the maths curriculum.
A few books were suggested for Maths Challenges too!
- Maths No Problem
- Kjartan Poskit books – Murderous Maths
- Alex’s Adventures in Numberland – Alex Bellos
- The Number Detective: 100 Number Puzzles to Test Your Logical Thinking
These KS2 maths challenges have really allowed me to go deeper with certain children within maths lessons (and even during particular topics!) within the classroom.
Having a wider range of maths challenge resources makes it much easier to ensure that you are deepening maths mastery in a way that is meaningful and encourages children to use logic.
To find more challenges you can use with the greater depth children in your class, check out these other TSL blogs:
- How To Stretch And Challenge More Able Pupils In KS2 Maths
- What Does Greater Depth Look Like In KS2 Maths?
- 108 Greater Depth Questions For Maths Mastery
- Ready To Progress Criteria
DO YOU HAVE STUDENTS WHO NEED MORE SUPPORT IN MATHS?
Every week Third Space Learning’s specialist online maths tutors support thousands of students across hundreds of schools with weekly online 1 to 1 maths lessons designed to plug gaps and boost progress.
Since 2013 these personalised one to 1 lessons have helped over 150,000 primary and secondary students become more confident, able mathematicians.
Learn how the programmes are aligned to maths mastery teaching or request a personalised quote for your school to speak to us about your school’s needs and how we can help.
Related articles

Maths Problem Solving: Engaging Your Students And Strengthening Their Mathematical Skills

Free Year 7 Maths Test With Answers And Mark Scheme: Mixed Topic Questions

What Is A Number Square? Explained For Primary School Teachers, Parents & Pupils
What Is Numicon? Explained For Primary School Teachers, Parents And Pupils
FREE Guide to Maths Mastery
All you need to know to successfully implement a mastery approach to mathematics in your primary school, at whatever stage of your journey.
Ideal for running staff meetings on mastery or sense checking your own approach to mastery.
Privacy Overview
Math Solver
Geogebra math solver.
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems, while enhancing your problem-solving skills!

- Home |
- About |
- Contact Us |
- Privacy |
- Newsletter |
- Shop |
- 🔍 Search Site
- Easter Color By Number Sheets
- Printable Easter Dot to Dot
- Easter Worksheets for kids
- Kindergarten
- All Generated Sheets
- Place Value Generated Sheets
- Addition Generated Sheets
- Subtraction Generated Sheets
- Multiplication Generated Sheets
- Division Generated Sheets
- Money Generated Sheets
- Negative Numbers Generated Sheets
- Fraction Generated Sheets
- Place Value Zones
- Number Bonds
- Addition & Subtraction
- Times Tables
- Fraction & Percent Zones
- All Calculators
- Fraction Calculators
- Percent calculators
- Area & Volume Calculators
- Age Calculator
- Height Calculator
- Roman Numeral Calculator
- Coloring Pages
- Fun Math Sheets
- Math Puzzles
- Mental Math Sheets
- Online Times Tables
- Online Addition & Subtraction
- Math Grab Packs
- All Math Quizzes
- 1st Grade Quizzes
- 2nd Grade Quizzes
- 3rd Grade Quizzes
- 4th Grade Quizzes
- 5th Grade Quizzes
- 6th Grade Math Quizzes
- Place Value
- Rounding Numbers
- Comparing Numbers
- Number Lines
- Prime Numbers
- Negative Numbers
- Roman Numerals
- Subtraction
- Add & Subtract
- Multiplication
- Fraction Worksheets
- Learning Fractions
- Fraction Printables
- Percent Worksheets & Help
- All Geometry
- 2d Shapes Worksheets
- 3d Shapes Worksheets
- Shape Properties
- Geometry Cheat Sheets
- Printable Shapes
- Coordinates
- Measurement
- Math Conversion
- Statistics Worksheets
- Bar Graph Worksheets
- Venn Diagrams
- All Word Problems
- Finding all possibilities
- Logic Problems
- Ratio Word Problems
- All UK Maths Sheets
- Year 1 Maths Worksheets
- Year 2 Maths Worksheets
- Year 3 Maths Worksheets
- Year 4 Maths Worksheets
- Year 5 Maths Worksheets
- Year 6 Maths Worksheets
- All AU Maths Sheets
- Kindergarten Maths Australia
- Year 1 Maths Australia
- Year 2 Maths Australia
- Year 3 Maths Australia
- Year 4 Maths Australia
- Year 5 Maths Australia
- Meet the Sallies
- Certificates
CHALLENGE ZONE 4th Grade Math Problems
Welcome to our 4th Grade Math Problems. Here you will find our range of challenging math problem worksheets which are designed to give children the opportunity to apply their skills and knowledge to solve a range of longer problems.
These problems are also a great way of developing perseverance and getting children to try different approaches in their math.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript.
Here are the instructions how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .
4th Grade Math Problems
Here you will find a range of problem solving worksheets.
The 4th grade math problems on the sheets are longer math problems designed to encourage children to use a range of math skills to solve them.
The skills the problems will help to develop include:
- systematic working
- logical thinking
- number fact knowledge
- fraction problems
- trial and improvement strategies
- working systematically
- searching for all possible answers.
At fourth grade, the problems are starting to become more advanced with children needing to become more systematic in their approach and experimenting using trial and improvement strategies.
Many of the problems have addition 'What if ...' questions with them to extend learning and get children looking for alternative solutions.
- 4th Grade Math Word Problems
Captain Salamander's Puzzling Problems
Captain Salamander's Puzzling Problems involves using thinking and reasoning skills to work out two math challenges. The challenges also involve an element of trial and improvement. This sheet is available in standard and metric units.
- Captain Salamander's Puzzling Problems - metric
- PDF version
- Captain Salamander's Puzzling Problems - standard
- Broken Calculator Problem 3
The Broken Calculator problem is a number problem involving using an imaginary broken calculator with only the 4, 7, +, - and = buttons working to make different totals.
There are 2 versions of the problem sheet, one with a pre-prepared template for filling in, and a second blank version for children to show their own recording system.
- Blank version
Quadra's Magic Bag Challenges
Quadra's Magic Bag Challenges involves using thinking and reasoning skills to work out two math challenges. The challenges also involve an element of trial and improvement, and also some addition.
- Quadra's Magic Bag Challenge
- Tyger's Fishy Problems
Tyger's Fishy Problems is a 4th grade math problem which involves using thinking and reasoning skills to solve two money challenges. This sheet is available in both dollars ( $ ) and pounds ( £ ).
- Tyger's Fishy Problems UK Version
- Bruno's Bones
Bruno's Bones is an activity to encourage children to work systematically to find the number of bones that a dog called Bruno has buried in his garden. This is a good problem for using lists/tables to solve and also counting in single digit steps.
- Don't Be Alarmed
Don't Be Alarmed is a sequencing problem where a burglar alarm is switching different lights on and off at different times. It is good for developing mathematical modeling and using lists/tables to help solve problems.
- Four Dogs Problem
Four Dogs Problem is a logic problem which involves using the clues to work out the owners for each of the four dogs.
Fox vs Rabbit
Fox vs Rabbit is an another mathematical modeling activity which involves looking at the routes of a fox and a rabbit and working out at if/when the rabbit is likely to get caught.
- Fox vs Rabbit #1 Standard Units
- Fox vs Rabbit #1 Metric Units
Frazer's Wall
Frazer's Wall is a trial and improvement activity which involves trying to work out the number of bricks that were laid in each day to make a set total of bricks. This problem can also be solved or modelled using algebra.
- Frazer's Wall #1
- Make Me 100
Make Me 100 is one of our 4th grade math problems designed to test children to find ways of making the numbers from 1 to 10 make 100 using different operators. It is good for developing perseverance and also for reinforcing the use of brackets of PEMDAS.
Sally's Fruit Punch
Sally's Fruit Punch is a money and scaling activity. The aim is to use the information to work out how much ingredients are needed. The ingredients then need to be priced to work out a total cost.
- Sally's Fruit Punch #2
- Sally's Fruit Punch #2 UK Version
- Share the Treasure #4
Share the Treasure is a fraction sharing activity where the aim is to work backwards to find out how many bars of treasure the pirates had before they shared them all out. It is a good activity for developing fraction problem solving and working backwards.
Something Fishy
Something Fishy is a money problem which involves working out exactly how many of each fish were bought in order to have spent $150 on the fish. It is a good activity for using lists and tables to find all possibilities.
- Something Fishy #1
- Something Fishy #1 UK Version

The Rock Race #2
The Rock Race is a 4th grade math problem which needs some perseverance to complete. The aim of the activity is to try different routes around the 6 rocks to determine which route is the shortest.
- The Rock Race #2 Metric version
- The Rock Race #2 Standard version
- Who Caught the Biggest Fish?
Who Caught the Biggest Fish is a logical number problem where you need to use trial and improvement strategies to work out the order of size of the fish from the clues given about their weights.
Looking for some easier math problems?
We have a range of easier word problems on our 3rd grade math problems page.
The problems on this page are at a simpler level than those here.
Many of the problems, e.g. Place It Right, Pick the Cards and Share the Treasure have easier versions on this page.
- 3rd grade Math Problems
Looking for some harder word problems
We have a range of more challenging word problems on our 5th grade problem solving page.
The problems on this page are at a trickier level than those here.
Some of the problems, e.g. The Rock Race and Sally's Fruit Punch and Frazer's Wall have harder versions on this page.
- 5th Grade Math Problems
Looking for some more fourth grade math word problems?
Here is our set of 4th grade math word problems to help your child with their problem solving skills.
Each problem sheet comes complete with answers, and is available in both standard and metric units where applicable.
Using these sheets will help your child to:
- apply their addition, subtraction and problem solving skills;
- apply their knowledge of rounding and place value;
- solve a range of 'real life' problems;
- attempt more challenging longer problems.
Using the problems in this section will help your child develop their problem solving and reasoning skills.
- Multiplication Word Problems 4th Grade
- 4th Grade Math Puzzles
Here you will find a range of printable 4th grade math puzzles for your child to enjoy.
The puzzles will help your child practice and apply their addition, subtraction, multiplication and division facts as well as developing their thinking and reasoning skills in a fun and engaging way.
Using these puzzles will help your child to:
- learn and practice their addition facts;
- practice adding both positive and negative numbers;
- practice their subtraction facts;
- practice multiplication and division facts;
- develop problem solving skills and reasoning.
All the puzzles support elementary math benchmarks for 4th grade.
- Math Games 4th Grade
Using games is a great way to learn Math facts and develop mental calculation skills in a fun and easy way.
The following games involve different 4th Grade Math activities which your child will enjoy playing.
Games include using negative numbers, decimal addition and subtraction, rounding, multiplying by 10s.
How to Print or Save these sheets 🖶
Need help with printing or saving? Follow these 3 steps to get your worksheets printed perfectly!
- How to Print support
Subscribe to Math Salamanders News
Sign up for our newsletter to get free math support delivered to your inbox each month. Plus, get a seasonal math grab pack included for free!

- Newsletter Signup
Return to 4th Grade Math Worksheets Hub
Return to Math Problem Worksheets Hub
Return from 4th Grade Math Problems to Math Salamanders Homepage
Math-Salamanders.com
The Math Salamanders hope you enjoy using these free printable Math worksheets and all our other Math games and resources.
We welcome any comments about our site or worksheets on the Facebook comments box at the bottom of every page.
New! Comments
TOP OF PAGE
© 2010-2024 Math Salamanders Limited. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
Welcome to Challenge Math Online
Challenge Math is designed to hone young students' mathematical problem-solving skills and logical reasoning skills.
Challenge Math gives out challenging word problem assignments weekly. Problems are non-routine problem-solving questions that are adapted to many math competitions, including the Noetic Learning Math Contest.
Challenge Math is primarily designed for gifted elementary students. Our unique program
- provides challenge beyond regular school curriculum,
- strengthens creative problem solving , and logical reasoning skills,
- further develops gifted students' intellect in math, and
- helps students excel in national math competitions.
- Detailed step-by-step instructions and solutions are provided for all assignments.
Problem Solving Strategies Covered
Topics Covered

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
- The Number System and Place Value
- Calculations and Numerical Methods
- Fractions, Decimals, Percentages, Ratio and Proportion
- Properties of Numbers
- Patterns, Sequences and Structure
- Algebraic expressions, equations and formulae
- Coordinates, Functions and Graphs
Geometry and measure
- Angles, Polygons, and Geometrical Proof
- 3D Geometry, Shape and Space
- Measuring and calculating with units
- Transformations and constructions
- Pythagoras and Trigonometry
- Vectors and Matrices
Probability and statistics
- Handling, Processing and Representing Data
- Probability
Working mathematically
- Thinking mathematically
- Mathematical mindsets
- Cross-curricular contexts
- Physical and digital manipulatives
For younger learners
- Early Years Foundation Stage
Advanced mathematics
- Decision Mathematics and Combinatorics
- Advanced Probability and Statistics
Problem Solving
Problem Solving and the New Curriculum Age 5 to 11
Developing a Classroom Culture That Supports a Problem-solving Approach to Mathematics Age 5 to 11
Developing Excellence in Problem Solving with Young Learners Age 5 to 11
Using NRICH Tasks to Develop Key Problem-solving Skills Age 5 to 11
Trial and Improvement at KS1 Age 5 to 7
Trial and Improvement at KS2 Age 7 to 11
Working Systematically - Primary Teachers Age 5 to 11
Number Patterns Age 5 to 11
Working Backwards at KS1 Age 5 to 7
Working Backwards at KS2 Age 7 to 11
Reasoning Age 5 to 11
Visualising at KS1 - Primary Teachers Age 5 to 7
Visualising at KS2 - Primary Teachers Age 7 to 11
Conjecturing and Generalising at KS1 - Primary Teachers Age 5 to 7
Conjecturing and Generalising at KS2 - Primary Teachers Age 7 to 11
- Mathematical Problem Solving in the Early Years
- Low Threshold High Ceiling - an Introduction
- What's All the Talking About?
- Group-worthy Tasks and Their Potential to Support Children to Develop Independent Problem-solving Skills
- Developing the Classroom Culture: Using the Dotty Six Activity as a Springboard for Investigation
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to help provide a better website experience for you, and help us to understand how people use our website. Our partners will also collect data and use cookies for ad personalisation and measurement.
Clicking "Accept" will allow us and our partners to use cookies, learn more in our cookie policy or to change your cookie preferences, click "Manage".
To find out more about cookies and the types of cookies we are setting please visit our cookie policy .
If you'd prefer that certain types of cookie are not saved on your browser when visiting our website, use the toggles below to adjust those preferences and click "Save choices".
Strictly Necessary
These cookies are necessary for the website to function and without them you would not be able to reliably use the website. For example, logging into your account or completing forms.
Analytics Cookies
A series of cookies that collect anonymised data on how users interact with our website. This anonymous data helps us improve the website with a focus on its users, for example, ensuring the most popular content is easier to access.
View associated providers +
Marketing Cookies
These cookies track your online activity to help advertisers deliver more relevant and personalised advertising or to limit how many times you see an ad. These cookies can share that information with other organisations or advertisers.
Watch CBS News
How two high school students solved a 2,000-year-old math puzzle
By Bill Whitaker , Aliza Chasan , Sara Kuzmarov, Mariah Campbell
May 5, 2024 / 7:00 PM EDT / CBS News
A high school math teacher at St. Mary's Academy in New Orleans, Michelle Blouin Williams, was looking for ingenuity when she and her colleagues set a school-wide math contest with a challenging bonus question. That bonus question asked students to create a new proof for the Pythagorean Theorem, a fundamental principle of geometry, using trigonometry. The teachers weren't necessarily expecting anyone to solve it, as proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem using trigonometry were believed to be impossible for nearly 2,000 years.
But then, in December 2022, Calcea Johnson and Ne'Kiya Jackson, seniors at St. Mary's Academy, stepped up to the challenge. The $500 prize money was a motivating factor.
After months of work, they submitted their innovative proofs to their teachers. With the contest behind them, their teachers encouraged the students to present at a mathematics conference, and then to seek to publish their work. And even today, they're not done. Now in college, they've been working on further proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem and believe they have found five more proofs. Amazingly, despite their impressive achievements, they insist they're not math geniuses.
"I think that's a stretch," Calcea said.
The St. Mary's math contest
When the pair started working on the math contest they were familiar with the Pythagorean Theorem's equation: A² + B² = C², which explains that by knowing the length of two sides of a right triangle, it's possible to figure out the length of the third side.
When Calcea and Ne'Kiya set out to create a new Pythagorean Theorem proof, they didn't know that for thousands of years, one using trigonometry was thought to be impossible. In 2009, mathematician Jason Zimba submitted one, and now Calcea and Ne'Kiya are adding to the canon.
Calcea and Ne'Kiya had studied geometry and some trigonometry when they started working on their proofs, but said they didn't feel math was easy. As the contest went on, they spent almost all their free time developing their ideas.

"The garbage can was full of papers, which she would, you know, work out the problems and if that didn't work, she would ball it up, throw it in the trash," Cal Johnson, Calcea's dad, said.
Neliska Jackson, Ne'Kiya's mother, says lightheartedly, that most of the time, her daughter's work was beyond her.
To document Calcea and Ne'Kiya's work, math teachers at St. Mary's submitted their proofs to an American Mathematical Society conference in Atlanta in March 2023.
"Well, our teacher approached us and was like, 'Hey, you might be able to actually present this,'" Ne'Kiya said. "I was like, 'Are you joking?' But she wasn't. So we went. I got up there. We presented and it went well, and it blew up."
Why Calcea' and Ne'kiya's work "blew up"
The reaction was insane and unexpected, Calcea said. News of their accomplishment spread around the world. The pair got a write-up in South Korea and a shoutout from former first lady Michelle Obama. They got a commendation from the governor and keys to the city of New Orleans.
Calcea and Ne'Kiya said they think there's several reasons why people found their work so impressive.
"Probably because we're African American, one," Ne'Kiya said. "And we're also women. So I think-- oh, and our age. Of course our ages probably played a big part."
Ne'Kiya said she'd like their accomplishment to be celebrated for what it is: "a great mathematical achievement."
In spite of the community's celebration of the students' work, St. Mary's Academy president and interim principal Pamela Rogers said that with recognition came racist calls and comments.
"[People said] 'they could not have done it. African Americans don't have the brains to do it.' Of course, we sheltered our girls from that," Rogers said. "But we absolutely did not expect it to come in the volume that it came."

Rogers said too often society has a vision of who can be successful.
"To some people, it is not always an African American female," Rogers said. "And to us, it's always an African American female."
Success at St. Marys
St. Mary's, a private Catholic elementary and high school, was started for young Black women just after the Civil War. Ne'Kiya and Calcea follow a long line of barrier-breaking graduates. Leah Chase , the late queen of Creole cuisine, was an alum. So was Michelle Woodfork, the first African American female New Orleans police chief, and Dana Douglas, a judge for the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals.
Math teacher Michelle Blouin Williams, who initiated the math contest, said Calcea and Ne'Kiya are typical St. Mary's students. She said if they're "unicorns," then every student who's matriculated through the school is a "beautiful, Black unicorn."
Students hear that message from the moment they walk in the door, Rogers said.
"We believe all students can succeed, all students can learn," the principal said. "It does not matter the environment that you live in."

About half the students at St. Mary's get scholarships, subsidized by fundraising to defray the $8,000 a year tuition. There's no test to get in, but expectations are high and rules are strict: cellphones are not allowed and modest skirts and hair in its natural color are required.
Students said they appreciate the rules and rigor.
"Especially the standards that they set for us," junior Rayah Siddiq said. "They're very high. And I don't think that's ever going to change."
What's next for Ne'Kiya and Calcea
Last year when Ne'Kiya and Calcea graduated, all their classmates were accepted into college and received scholarship offers. The school has had a 100% graduation rate and a 100% college acceptance rate for 17 years, according to Rogers.
Ne'Kiya got a full ride in the pharmacy department at Xavier University in New Orleans. Calcea, the class valedictorian, is studying environmental engineering at Louisiana State University. Neither one is pursuing a career in math, though Calcea said she may minor in math.
"People might expect too much out of me if I become a mathematician," Ne'Kiya said wryly.

Bill Whitaker is an award-winning journalist and 60 Minutes correspondent who has covered major news stories, domestically and across the globe, for more than four decades with CBS News.
More from CBS News

Teens come up with answer to problem that stumped math world for centuries

Can workers prosper with employee ownership?

Rep. Jeffries says House Democrats "governing as if we were in the majority"

Democratic leader Jeffries: "Pro-Putin faction" in GOP delayed Ukraine aid

Welcome to Problem Challenge!
Problem Challenge is a mathematics problem solving competition aimed primarily at children in years 7 and 8, and of interest to able children from Year 6.
It has been organised by John Curran and John Shanks, retired members of the Department of Mathematics and Statistics at the University of Otago, with extensive secretarial help from Leanne Kirk and Sarah Stewart, also of that Department. From 2024 it will be organised by John Shanks, with Sarah processing the book orders.
Children participating in the competition attempt to answer five questions in 30 minutes on each of five problem sheets, which are done about a month apart starting in April.
Competition Books

Teens come up with answer to problem that stumped math world for centuries
A s the school year ends, many students will be only too happy to see math classes in their rearview mirrors. It may seem to some of us non-mathematicians that geometry and trigonometry were created by the Greeks as a form of torture, so imagine our amazement when we heard two high school seniors had proved a mathematical puzzle that was thought to be impossible for 2,000 years.
We met Calcea Johnson and Ne'Kiya Jackson at their all-girls Catholic high school in New Orleans. We expected to find two mathematical prodigies.
Instead, we found at St. Mary's Academy , all students are told their possibilities are boundless.
Come Mardi Gras season, New Orleans is alive with colorful parades, replete with floats, and beads, and high school marching bands.
In a city where uniqueness is celebrated, St. Mary's stands out – with young African American women playing trombones and tubas, twirling batons and dancing - doing it all, which defines St. Mary's, students told us.
Junior Christina Blazio says the school instills in them they have the ability to accomplish anything.
Christina Blazio: That is kinda a standard here. So we aim very high - like, our aim is excellence for all students.
The private Catholic elementary and high school sits behind the Sisters of the Holy Family Convent in New Orleans East. The academy was started by an African American nun for young Black women just after the Civil War. The church still supports the school with the help of alumni.
In December 2022, seniors Ne'Kiya Jackson and Calcea Johnson were working on a school-wide math contest that came with a cash prize.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: I was motivated because there was a monetary incentive.
Calcea Johnson: 'Cause I was like, "$500 is a lot of money. So I-- I would like to at least try."
Both were staring down the thorny bonus question.
Bill Whitaker: So tell me, what was this bonus question?
Calcea Johnson: It was to create a new proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. And it kind of gave you a few guidelines on how would you start a proof.
The seniors were familiar with the Pythagorean Theorem, a fundamental principle of geometry. You may remember it from high school: a² + b² = c². in plain English, when you know the length of two sides of a right triangle, you can figure out the length of the third.
Both had studied geometry and some trigonometry, and both told us math was not easy. What no one told them was there had been more than 300 documented proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem using algebra and geometry, but for 2,000 years a proof using trigonometry was thought to be impossible, … and that was the bonus question facing them.
Bill Whitaker: When you looked at the question did you think, "Boy, this is hard"?
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Yeah.
Bill Whitaker: What motivated you to say, "Well, I'm going to try this"?
Calcea Johnson: I think I was like, "I started something. I need to finish it."
Bill Whitaker: So you just kept on going.
Calcea Johnson: Yeah.
For two months that winter, they spent almost all their free time working on the proof.
CeCe Johnson: She was like, "Mom, this is a little bit too much."
CeCe and Cal Johnson are Calcea's parents.
CeCe Johnson: So then I started looking at what she really was doing. And it was pages and pages and pages of, like, over 20 or 30 pages for this one problem.
Cal Johnson: Yeah, the garbage can was full of papers, which she would, you know, work out the problems and-- if that didn't work she would ball it up, throw it in the trash.
Bill Whitaker: Did you look at the problem?
Neliska Jackson is Ne'Kiya's mother.
Neliska Jackson: Personally I did not. 'Cause most of the time I don't understand what she's doing (laughter).
Michelle Blouin Williams: What if we did this, what if I write this? Does this help? ax² plus ….
Their math teacher, Michelle Blouin Williams, initiated the math contest.
Bill Whitaker: And did you think anyone would solve it?
Michelle Blouin Williams: Well, I wasn't necessarily looking for a solve. So, no, I didn't—
Bill Whitaker: What were you looking for?
Michelle Blouin Williams: I was just looking for some ingenuity, you know—
Calcea and Ne'Kiya delivered on that! They tried to explain their groundbreaking work to 60 Minutes. Calcea's proof is appropriately titled the Waffle Cone.
Calcea Johnson: So to start the proof, we start with just a regular right triangle where the angle in the corner is 90°. And the two angles are alpha and beta.
Bill Whitaker: Uh-huh
Calcea Johnson: So then what we do next is we draw a second congruent, which means they're equal in size. But then we start creating similar but smaller right triangles going in a pattern like this. And then it continues for infinity. And eventually it creates this larger waffle cone shape.
Calcea Johnson: Am I going a little too—
Bill Whitaker: You've been beyond me since the beginning. (laughter)
Bill Whitaker: So how did you figure out the proof?
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Okay. So you have a right triangle, 90° angle, alpha and beta.
Bill Whitaker: Then what did you do?
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Okay, I have a right triangle inside of the circle. And I have a perpendicular bisector at OP to divide the triangle to make that small right triangle. And that's basically what I used for the proof. That's the proof.
Bill Whitaker: That's what I call amazing.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Well, thank you.
There had been one other documented proof of the theorem using trigonometry by mathematician Jason Zimba in 2009 – one in 2,000 years. Now it seems Ne'Kiya and Calcea have joined perhaps the most exclusive club in mathematics.
Bill Whitaker: So you both independently came up with proof that only used trigonometry.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Yes.
Bill Whitaker: So are you math geniuses?
Calcea Johnson: I think that's a stretch.
Bill Whitaker: If not genius, you're really smart at math.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Not at all. (laugh)
To document Calcea and Ne'Kiya's work, math teachers at St. Mary's submitted their proofs to an American Mathematical Society conference in Atlanta in March 2023.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Well, our teacher approached us and was like, "Hey, you might be able to actually present this," I was like, "Are you joking?" But she wasn't. So we went. I got up there. We presented and it went well, and it blew up.
Bill Whitaker: It blew up.
Calcea Johnson: Yeah.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: It blew up.
Bill Whitaker: Yeah. What was the blowup like?
Calcea Johnson: Insane, unexpected, crazy, honestly.
It took millenia to prove, but just a minute for word of their accomplishment to go around the world. They got a write-up in South Korea and a shout-out from former first lady Michelle Obama, a commendation from the governor and keys to the city of New Orleans.
Bill Whitaker: Why do you think so many people found what you did to be so impressive?
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Probably because we're African American, one. And we're also women. So I think-- oh, and our age. Of course our ages probably played a big part.
Bill Whitaker: So you think people were surprised that young African American women, could do such a thing?
Calcea Johnson: Yeah, definitely.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: I'd like to actually be celebrated for what it is. Like, it's a great mathematical achievement.
Achievement, that's a word you hear often around St. Mary's academy. Calcea and Ne'Kiya follow a long line of barrier-breaking graduates.
The late queen of Creole cooking, Leah Chase , was an alum. so was the first African-American female New Orleans police chief, Michelle Woodfork …
And judge for the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals, Dana Douglas. Math teacher Michelle Blouin Williams told us Calcea and Ne'Kiya are typical St. Mary's students.
Bill Whitaker: They're not unicorns.
Michelle Blouin Williams: Oh, no no. If they are unicorns, then every single lady that has matriculated through this school is a beautiful, Black unicorn.
Pamela Rogers: You're good?
Pamela Rogers, St. Mary's president and interim principal, told us the students hear that message from the moment they walk in the door.
Pamela Rogers: We believe all students can succeed, all students can learn. It does not matter the environment that you live in.
Bill Whitaker: So when word went out that two of your students had solved this almost impossible math problem, were they universally applauded?
Pamela Rogers: In this community, they were greatly applauded. Across the country, there were many naysayers.
Bill Whitaker: What were they saying?
Pamela Rogers: They were saying, "Oh, they could not have done it. African Americans don't have the brains to do it." Of course, we sheltered our girls from that. But we absolutely did not expect it to come in the volume that it came.
Bill Whitaker: And after such a wonderful achievement.
Pamela Rogers: People-- have a vision of who can be successful. And-- to some people, it is not always an African American female. And to us, it's always an African American female.
Gloria Ladson-Billings: What we know is when teachers lay out some expectations that say, "You can do this," kids will work as hard as they can to do it.
Gloria Ladson-Billings, professor emeritus at the University of Wisconsin, has studied how best to teach African American students. She told us an encouraging teacher can change a life.
Bill Whitaker: And what's the difference, say, between having a teacher like that and a whole school dedicated to the excellence of these students?
Gloria Ladson-Billings: So a whole school is almost like being in Heaven.
Bill Whitaker: What do you mean by that?
Gloria Ladson-Billings: Many of our young people have their ceilings lowered, that somewhere around fourth or fifth grade, their thoughts are, "I'm not going to be anything special." What I think is probably happening at St. Mary's is young women come in as, perhaps, ninth graders and are told, "Here's what we expect to happen. And here's how we're going to help you get there."
At St. Mary's, half the students get scholarships, subsidized by fundraising to defray the $8,000 a year tuition. Here, there's no test to get in, but expectations are high and rules are strict: no cellphones, modest skirts, hair must be its natural color.
Students Rayah Siddiq, Summer Forde, Carissa Washington, Tatum Williams and Christina Blazio told us they appreciate the rules and rigor.
Rayah Siddiq: Especially the standards that they set for us. They're very high. And I don't think that's ever going to change.
Bill Whitaker: So is there a heart, a philosophy, an essence to St. Mary's?
Summer Forde: The sisterhood—
Carissa Washington: Sisterhood.
Tatum Williams: Sisterhood.
Bill Whitaker: The sisterhood?
Voices: Yes.
Bill Whitaker: And you don't mean the nuns. You mean-- (laughter)
Christina Blazio: I mean, yeah. The community—
Bill Whitaker: So when you're here, there's just no question that you're going to go on to college.
Rayah Siddiq: College is all they talk about. (laughter)
Pamela Rogers: … and Arizona State University (Cheering)
Principal Rogers announces to her 615 students the colleges where every senior has been accepted.
Bill Whitaker: So for 17 years, you've had a 100% graduation rate—
Pamela Rogers: Yes.
Bill Whitaker: --and a 100% college acceptance rate?
Pamela Rogers: That's correct.
Last year when Ne'Kiya and Calcea graduated, all their classmates went to college and got scholarships. Ne'Kiya got a full ride to the pharmacy school at Xavier University in New Orleans. Calcea, the class valedictorian, is studying environmental engineering at Louisiana State University.
Bill Whitaker: So wait a minute. Neither one of you is going to pursue a career in math?
Both: No. (laugh)
Calcea Johnson: I may take up a minor in math. But I don't want that to be my job job.
Ne'Kiya Jackson: Yeah. People might expect too much out of me if (laugh) I become a mathematician. (laugh)
But math is not completely in their rear-view mirrors. This spring they submitted their high school proofs for final peer review and publication … and are still working on further proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem. Since their first two …
Calcea Johnson: We found five. And then we found a general format that could potentially produce at least five additional proofs.
Bill Whitaker: And you're not math geniuses?
Bill Whitaker: I'm not buying it. (laughs)
Produced by Sara Kuzmarov. Associate producer, Mariah B. Campbell. Edited by Daniel J. Glucksman.

Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Artificial Intelligence
Title: gold: geometry problem solver with natural language description.
Abstract: Addressing the challenge of automated geometry math problem-solving in artificial intelligence (AI) involves understanding multi-modal information and mathematics. Current methods struggle with accurately interpreting geometry diagrams, which hinders effective problem-solving. To tackle this issue, we present the Geometry problem sOlver with natural Language Description (GOLD) model. GOLD enhances the extraction of geometric relations by separately processing symbols and geometric primitives within the diagram. Subsequently, it converts the extracted relations into natural language descriptions, efficiently utilizing large language models to solve geometry math problems. Experiments show that the GOLD model outperforms the Geoformer model, the previous best method on the UniGeo dataset, by achieving accuracy improvements of 12.7% and 42.1% in calculation and proving subsets. Additionally, it surpasses the former best model on the PGPS9K and Geometry3K datasets, PGPSNet, by obtaining accuracy enhancements of 1.8% and 3.2%, respectively.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Math puzzles are one of the best -- and oldest -- ways to encourage student engagement. Brain teasers, logic puzzles and math riddles give students challenges that encourage problem-solving and logical thinking. They can be used in classroom gamification, and to inspire students to tackle problems they might have previously seen as too difficult.
The NRICH weekly challenges are aimed at Post-16 students to provide an interesting, shorter challenge to try out each week which will fit around any usual course of study. Each challenge is designed to be simple to get into and to cover an important and intriguing area of mathematics. How many will you solve? The Challenges
Khan Academy's 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don't need to be graded, and don't require a printer. Math Worksheets. Khan Academy. Math worksheets take forever to hunt down across the internet. Khan Academy is your one-stop-shop for practice from arithmetic to calculus. Math worksheets can vary in quality from ...
The 5th grade math problems on the sheets are longer math problems designed to encourage children to use a range of math skills to solve them. The skills the problems will help to develop include: systematic working. logical thinking. number fact knowledge. fraction problems. trial and improvement strategies. working backwards.
Math and Logic Puzzles. If you REALLY like exercising your brain, figuring things 'round and 'round till you explode, then this is the page for you ! Whosoever shall solve these puzzles shall Rule The Universe!... or at least they should ... Starter Puzzles. Puzzle Games. Measuring Puzzles ...
Short problems for Starters, Homework and Assessment. The links below take you to a selection of short problems based on UKMT junior and intermediate mathematical challenge questions. We have chosen these problems because they are ideal for consolidating and assessing subject knowledge, mathematical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Art of Problem Solving offers two other multifaceted programs. Beast Academy is our comic-based online math curriculum for students ages 6-13. And AoPS Academy brings our methodology to students grades 2-12 through small, in-person classes at local campuses. Through our three programs, AoPS offers the most comprehensive honors math pathway ...
Feature Red Herrings: Including unnecessary information introduces another problem-solving element, overwhelming many elementary students. A key to differentiated instruction, word problems that students can relate to and contextualize will capture interest more than generic and abstract ones. Final thoughts about math word problems
CHALLENGING MATH PROBLEMS WORTH SOLVING DOWNLOAD OUR FAVORITE PROBLEMS FROM EVERY GRADE LEVEL Get Our Favorite Problems Take The Online Workshop WANT GOOGLE SLIDE VERSIONS OF ALL PROBLEMS? HERE'S OUR GROWING COLLECTION Get Google Slide Versions WANT TO SHARE OPEN MIDDLE WITH OTHERS? CHECK OUT THESE FREE WEBINARS TO HELP TEACHERS RETHINK CLASSWORK Elementary Version
Enriching mathematics for all learners. Turn on sound. We offer curriculum-linked resources for students aged 3-18, designed to nurture curious, resourceful and confident learners of school mathematics. All of our resources are free to use by everyone. We are based in the Faculty of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge.
Here are some general tips for answering short-answer Challenge Problems: Do not include units of measurement or dollar signs in your answers. Express probabilities, decimal values, and ratios as simplified common fractions unless told otherwise. Enter variable values without including the variable and an equals sign.
What it is: A site that promotes problem solving over worksheets, allowing children to work in a more practical manner. 17. Daily Rigour Articles. What it is: This is a free newspaper that puts maths problems into a real life context. It is full of interesting ideas to get children using challenge! 18. Total Maths
Problem Solving Strategies - Math Challenge. If you are interested in adopting Math Challenge program for your school, please contact [email protected] and we'll be happy to assist you or someone you appointed to start on-boarding Math Challenge program into your school and provide all the necessary details.
Weekly Problems. Age 11 to 16. Challenge Level. The short problems are easy to state and fascinating to solve. The content is aimed at the lower secondary level, but will give a dose of mathematical stimulation to solvers of all ages.
Check out BBC Bitesize KS2 maths for more activities, videos and guides for students. Maths game - Guardians: Defenders of Mathematica. Use your times tables and more maths skills to defeat ...
These math challenges cover problem solving strategies such as draw a picture or model, make an organized list, look for a pattern, working backward, and guess and check. Each challenge presents 10 to 18 problems ordered by level of difficulties which enables students from various grades to participate. Problems are suitable for grade 1 through 6.
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems with the free GeoGebra Math Solver. Enhance your problem-solving skills while learning how to solve equations on your own. Try it now!
The 4th grade math problems on the sheets are longer math problems designed to encourage children to use a range of math skills to solve them. The skills the problems will help to develop include: systematic working. logical thinking. number fact knowledge. fraction problems. trial and improvement strategies.
Welcome to Challenge Math Online. Challenge Math is designed to hone young students' mathematical problem-solving skills and logical reasoning skills.. Challenge Math gives out challenging word problem assignments weekly. Problems are non-routine problem-solving questions that are adapted to many math competitions, including the Noetic Learning Math Contest.
Developing Excellence in Problem Solving with Young Learners. Age 5 to 11. Becoming confident and competent as a problem solver is a complex process that requires a range of skills and experience. In this article, Jennie suggests that we can support this process in three principal ways. Using NRICH Tasks to Develop Key Problem-solving Skills.
Practice is crucial to maths success, and our questions are designed to support your daily routines. These problems can be used across Y1 and Y2 throughout the year. Download. Our maths problems of the day provide four problems across KS1, KS2 and Lower KS3 for pupils to solve. View our Maths resources from White Rose Maths.
Solve mathematical problems or puzzles. Know addition and subtraction facts up to 10. Snakes and ladders. Your counter is on 9. You roll a 1 to 6 dice. After two moves you land on 16. Find all the different ways you can do it. Now think of other questions you could ask.
A high school math teacher at St. Mary's Academy in New Orleans, Michelle Blouin Williams, was looking for ingenuity when she and her colleagues set a school-wide math contest with a challenging ...
Problem Challenge is a mathematics problem solving competition aimed primarily at children in years 7 and 8, and of interest to able children from Year 6. It has been organised by John Curran and John Shanks, retired members of the Department of Mathematics and Statistics at the University of Otago, with extensive secretarial help from Leanne ...
A high school teacher didn't expect a solution when she set a 2,000-year-old Pythagorean Theorem problem in front of her students. Then Calcea Johnson and Ne'Kiya Jackson stepped up to the challenge.
Addressing the challenge of automated geometry math problem-solving in artificial intelligence (AI) involves understanding multi-modal information and mathematics. Current methods struggle with accurately interpreting geometry diagrams, which hinders effective problem-solving. To tackle this issue, we present the Geometry problem sOlver with natural Language Description (GOLD) model. GOLD ...