Become a Bestseller
Follow our 5-step publishing path.

Fundamentals of Fiction & Story
Bring your story to life with a proven plan.
Market Your Book
Learn how to sell more copies.
Edit Your Book
Get professional editing support.
Author Advantage Accelerator Nonfiction
Grow your business, authority, and income.
Author Advantage Accelerator Fiction
Become a full-time fiction author.
Author Accelerator Elite
Take the fast-track to publishing success.
Take the Quiz
Let us pair you with the right fit.
Free Copy of Published.
Book title generator, nonfiction outline template, writing software quiz, book royalties calculator.
Learn how to write your book
Learn how to edit your book
Learn how to self-publish your book
Learn how to sell more books
Learn how to grow your business
Learn about self-help books
Learn about nonfiction writing
Learn about fiction writing
How to Get An ISBN Number
A Beginner’s Guide to Self-Publishing
How Much Do Self-Published Authors Make on Amazon?
Book Template: 9 Free Layouts
How to Write a Book in 12 Steps
The 15 Best Book Writing Software Tools
How to Write a Biography: 11 Step Guide + Book Template

Get a Free Copy of Published.
The proven path from blank page to 10,000 copies sold.
So you’d like to know how to write a biography. We can help with that! Learning how to write a biography doesn't have to be intimidating. In fact, it can be a lot of fun!
In this guide, we show you how to write a biography from the initial book idea all the way through to publishing your book , and we throw in a free template to help you on your way.
Ready to learn how to start a biography? Let’s jump right in.
Get Our 6″ x 9″ Pre-Formatted Book Template for Word or Mac
We will send you a Book Template for US Trade (standard paperback size).
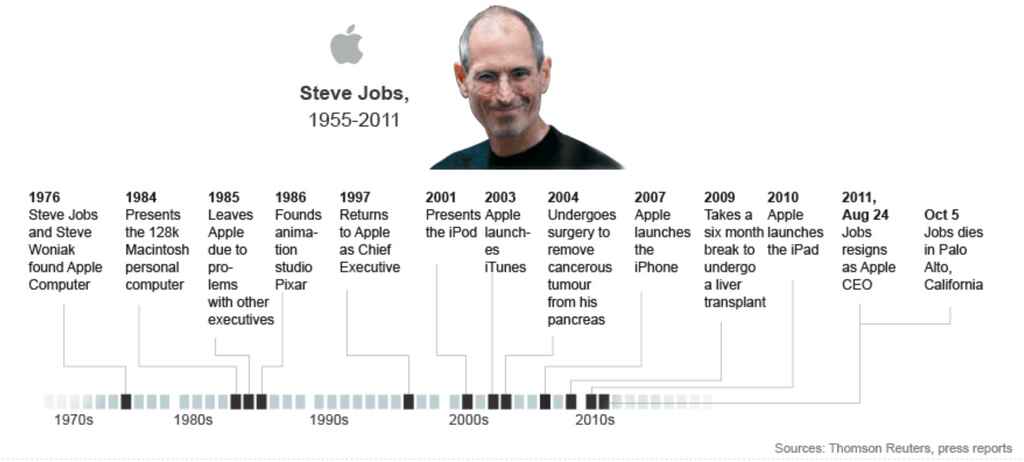
How to Write a Biography in 11 Simple Steps
Here are the steps you need to take to learn how to write a biography:
1. Read other biographies
Austin Kleon, Author of Steal Like an Artist , says “the writer tries to master words. All of these pursuits involve the study of those who have come before and the effort to build upon their work in some way.”
In other words, if you want to learn how to write a biography, you need to read the best biographies written by other excellent authors!
In this case, it would behoove you to read several biographies – whether historical or celebrity biographies is up to you and your sub-genre.
A good author to start with? Walter Isaacson . He’s written highly acclaimed biographies on everyone from Abraham Lincoln and Steve Jobs to Leonardo Da Vinci and Elon Musk.
Once you've read some well-crafted biographies, you'll have a better idea of how to start a biography of your own.
2. Identify your subject
In order to learn how to start a biography, you need to choose who you’d like to write about – if you don’t already have someone in mind.
The most important factor will be, of course, your interest in the person you’re planning to write about. You’ll spend months (or even years) deep-diving into this person’s history, so you want to choose someone who you’re unlikely to tire of.
When learning how to write a biography, here are few factors to consider:
- How impactful has your potential subject’s life been? In other words, will people care to learn more about this person?
- How readily available is information about your potential subject? Biographies require extensive research, so it’s critical to choose someone who has enough information out there to dig into! Consider whether your subject has done interviews, written journals, has family or a partner willing to speak with you, and more.
- Are there already books written about your potential subject? Just because there’s an existing biography about the person you’re interested in doesn’t (necessarily) mean you can’t write another one. But if there are two or three biographies, you may want to reconsider. If you do choose to write about someone who has already been well-documented, be mindful about approaching the topic with a new angle or perspective. For instance, there are several biographies about George Washington, but author Alexis Coe wrote one about how Washington isn’t “quite the man we remember.” This brilliant iteration has over 12,000 ratings on Goodreads .
- Is there a market demand for a book about your potential subject? If you’re learning how to write a biography, you need to be mindful of whether folks will want to read it. Do some research to determine if readers will be receptive to a book about the person you’re interested in.
Related: Is a Biography a Primary Source?
3. Get permission to write about your subject
We’ll start by stating the obvious. It’s a good idea to get permission to write about your subject, even if you’re not legally required to. For one thing, it’s just good manners. Plus, you’re much more likely to get unfettered access to the information and sources you need to write your book.
But do you have to get permission? It depends.
In some cases, if your subject is considered a “public figure,” permission may not be required. The definition of a public figure varies depending on your jurisdiction, so you should always consult a lawyer before writing a biography.
If you do decide to proceed without permission, be mindful of how your book will be received and any legal issues that may arise. That's why we always recommend asking permission from your subject when learning how to write a biography.
Related : Difference Between A Memoir and Biography
4. Create an outline
The next step of learning how to write a biography is to outline your story. It’s critical to outline your biography before you begin writing it. Among other things, it helps ensure you cover every topic you’d like to and get the book in the correct chronological order. It also helps you identify themes that emerge as you organize your ideas.

Need help creating your outline? Learn how to do it (and take advantage of free templates!) in our guide to outlining a book .
5. Select a working title (using a title generator)
Now is the fun part of learning how to write a biography! It’s time to create a working title for your book. A working title is just what it sounds like: it’s a title that works – for now.
Of course, it’s helpful to have something to call the book as you’re working on it. And it encourages you to think about the message you’d like your book to convey. When your biography is complete, you can always do a little more research on how to write book titles for your specific sub-genre and update your working title accordingly.
Or, you can decide you still love your initial title and publish your book with that one!
We’ve made it easy for you to develop a working title – or multiple – using our book title generator .
Don't like it?
6. Write a rough draft
Okay, now it’s time to start writing your rough draft. Don’t be intimidated; just focus on getting something down on the page. As experts on all things writing and self-publishing, we’ve got a rough draft writing guide to help you get through this phase of writing a biography.
Remember to be as balanced and objective as possible when learning how to write a biography.
Make good use of your primary and secondary sources, and double-check all of your facts. You’ve got this!
7. Self-edit
There are several different types of editing that we recommend each manuscript undergo. But before you give your rough draft to anyone else to review, you should edit it yourself.
The first step to self-editing?
Take a break! It’s essential to give your mind some time to recuperate before you go over your work. And never self-edit as you go!
After you’ve completed your break, here are a few things to consider as you edit:
- Grammar. This one is self-explanatory and usually the easiest. You can use an AI editor to make a first pass and quickly catch obvious spelling errors. Depending on prompts and your experience with the tool, you can also use AI to catch some grammar and syntax issues as well.
- Content and structure . This is the time to make sure the bones of your piece are good. Make sure your content flows logically (and in chronological order), no important pieces of information are missing, and there isn’t redundant or unhelpful information.
- Clarity and consistency. Keep an eye out for any confusing copy and ensure your tone is uniform throughout the book.
- Try reading your draft aloud. You’d be surprised at how many errors, shifts in tone, or other things you’d like to change that you don’t notice while reading in your head. Go ahead and do a read-through of your draft out loud.
8. Work with an editor
Once you’ve created the best draft you can, it’s time to hire an editor. As we mentioned, there are multiple types of book editing, so you’ll need to choose the one(s) that are best for you and your project when learning how to write a biography.
For instance, you can work with a developmental editor who helps with big-picture stuff. Think book structure, organization, and overall storytelling. Or you might work with a line editor who focuses on grammar, spelling, punctuation, and the like.
There are also specialized copy editors, content editors, fact-checkers, and more.
It’s in your best interest to do a substantial amount of research before choosing an editor since they’ll have a large impact on your book. Many editors are open to doing a paid trial so you can see their work before you sign them on for the entire book.
9. Hire a book cover designer
Once you’ve worked with your editor(s) to finalize your book, it’s time to get your book ready to go out into the world. So the nest step in learning how to write a biography is to hire a book cover designer to create a cover that grabs readers’ attention (pssst: did you know that all SelfPublishing authors get done-for-you professional book design? Ask us about it !).
10. Get an ISBN
The next step in learning how to write a biography is getting an ISBN number for your book – or an International Standard Book Number. It’s a unique way to identify your book and is critical for ordering, inventory tracking, and more.
Bear in mind that each rendition of your book – regardless of when you publish them – will need their own ISBN numbers. So if you initially publish as a softcover and hardcover book and then decide to publish an ebook with the same exact content, you'll need 3 total ISBN numbers.
To get an ISBN, head to ISBN.org and follow the steps they provide. Or reference our guide right here for step-by-step instructions (complete with photos) on how to get an ISBN number for self-published books.
11. Create a launch plan
Now is the most exciting part of learning how to write a biography. It’s time to get your book out into the world! You’ll need to map out your plan, schedule events , finalize your pricing strategy, and more.
And you can't just launch your book in a single day. When you go through all the work of learning how to write a biography, you want your book to succeed – and that requires a strategic marketing plan. Luckily, we have an entire guide to launching a book to help you figure it out.

Get your free book template!
Learning how to write a biography can be challenging, but when you have a clear plan and guidance, the process is much easier. We've helped thousands of aspiring authors just like you write and self-publish their own books. We know what works – and how to become a successfully published author faster.
Take the first step today and down the book template below!
And, if you need additional help with learning how to write a biography, remember that we’re standing by to assist you. Just schedule a book consultation and one of our team members will help answer any of your questions about the writing or self-publishing process.

Elite Author T. Lynette Yankson Teaches Perseverance in Her Children’s Book About a True Story
Children's Book, Non-Fiction

Elite Author Peder Tellefsdal Is On a Mission to Rebrand the Church with His New Book
Non-Fiction

Elite Author Lisa Bray Reawakens the American Dream in Her Debut Business Book
Join the community.
Join 100,000 other aspiring authors who receive weekly emails from us to help them reach their author dreams. Get the latest product updates, company news, and special offers delivered right to your inbox.
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Blog • Perfecting your Craft
Posted on Jun 30, 2023
How to Write a Biography: A 7-Step Guide [+Template]
From time to time, nonfiction authors become so captivated by a particular figure from either the present or the past, that they feel compelled to write an entire book about their life. Whether casting them as heroes or villains, there is an interesting quality in their humanity that compels these authors to revisit their life paths and write their story.
However, portraying someone’s life on paper in a comprehensive and engaging way requires solid preparation. If you’re looking to write a biography yourself, in this post we’ll share a step-by-step blueprint that you can follow.
How to write a biography:
1. Seek permission when possible
2. research your subject thoroughly, 3. do interviews and visit locations, 4. organize your findings, 5. identify a central thesis, 6. write it using narrative elements, 7. get feedback and polish the text.

FREE RESOURCE
Biography Outline Template
Craft a satisfying story arc for your biography with our free template.
While you technically don’t need permission to write about public figures (or deceased ones), that doesn't guarantee their legal team won't pursue legal action against you. Author Kitty Kelley was sued by Frank Sinatra before she even started to write His Way , a biography that paints Ol Blue Eyes in a controversial light. (Kelley ended up winning the lawsuit, however).

Whenever feasible, advise the subject’s representatives of your intentions. If all goes according to plan, you’ll get a green light to proceed, or potentially an offer to collaborate. It's a matter of common sense; if someone were to write a book about you, you would likely want to know about it well prior to publication. So, make a sincere effort to reach out to their PR staff to negotiate an agreement or at least a mutual understanding of the scope of your project.
At the same time, make sure that you still retain editorial control over the project, and not end up writing a puff piece that treats its protagonist like a saint or hero. No biography can ever be entirely objective, but you should always strive for a portrayal that closely aligns with facts and reality.
If you can’t get an answer from your subject, or you’re asked not to proceed forward, you can still accept the potential repercussions and write an unauthorized biography . The “rebellious act” of publishing without consent indeed makes for great marketing, though it’ll likely bring more headaches with it too.
✋ Please note that, like other nonfiction books, if you intend to release your biography with a publishing house , you can put together a book proposal to send to them before you even write the book. If they like it enough, they might pay you an advance to write it.

Book Proposal Template
Craft a professional pitch for your nonfiction book with our handy template.
Once you’ve settled (or not) the permission part, it’s time to dive deep into your character’s story.
Deep and thorough research skills are the cornerstone of every biographer worth their salt. To paint a vivid and accurate portrait of someone's life, you’ll have to gather qualitative information from a wide range of reliable sources.
Start with the information already available, from books on your subject to archival documents, then collect new ones firsthand by interviewing people or traveling to locations.
Browse the web and library archives

Put your researcher hat on and start consuming any piece on your subject you can find, from their Wikipedia page to news articles, interviews, TV and radio appearances, YouTube videos, podcasts, books, magazines, and any other media outlets they may have been featured in.
Establish a system to orderly collect the information you find 一 even seemingly insignificant details can prove valuable during the writing process, so be sure to save them.
Depending on their era, you may find most of the information readily available online, or you may need to search through university libraries for older references.

For his landmark biography of Alexander Hamilton, Ron Chernow spent untold hours at Columbia University’s library , reading through the Hamilton family papers, visiting the New York Historical Society, as well as interviewing the archivist of the New York Stock Exchange, and so on. The research process took years, but it certainly paid off. Chernow discovered that Hamilton created the first five securities originally traded on Wall Street. This finding, among others, revealed his significant contributions to shaping the current American financial and political systems, a legacy previously often overshadowed by other founding fathers. Today Alexander Hamilton is one of the best-selling biographies of all time, and it has become a cultural phenomenon with its own dedicated musical.
Besides reading documents about your subject, research can help you understand the world that your subject lived in.
Try to understand their time and social environment
Many biographies show how their protagonists have had a profound impact on society through their philosophical, artistic, or scientific contributions. But at the same time, it’s worth it as a biographer to make an effort to understand how their societal and historical context influenced their life’s path and work.
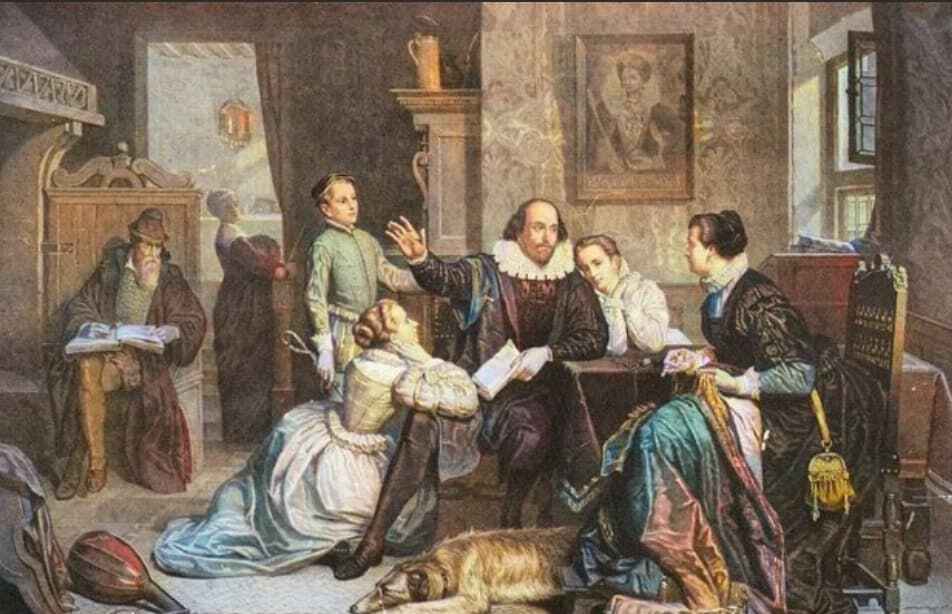
An interesting example is Stephen Greenblatt’s Will in the World . Finding himself limited by a lack of verified detail surrounding William Shakespeare's personal life, Greenblatt, instead, employs literary interpretation and imaginative reenactments to transport readers back to the Elizabethan era. The result is a vivid (though speculative) depiction of the playwright's life, enriching our understanding of his world.

Many readers enjoy biographies that transport them to a time and place, so exploring a historical period through the lens of a character can be entertaining in its own right. The Diary of Samuel Pepys became a classic not because people were enthralled by his life as an administrator, but rather from his meticulous and vivid documentation of everyday existence during the Restoration period.
Once you’ve gotten your hands on as many secondary sources as you can find, you’ll want to go hunting for stories first-hand from people who are (or were) close to your subject.
With all the material you’ve been through, by now you should already have a pretty good picture of your protagonist. But you’ll surely have some curiosities and missing dots in their character arc to figure out, which you can only get by interviewing primary sources.
Interview friends and associates
This part is more relevant if your subject is contemporary, and you can actually meet up or call with relatives, friends, colleagues, business partners, neighbors, or any other person related to them.
In writing the popular biography of Steve Jobs, Walter Isaacson interviewed more than one hundred people, including Jobs’s family, colleagues, former college mates, business rivals, and the man himself.
🔍 Read other biographies to get a sense of what makes a great one. Check out our list of the 30 best biographies of all time , or take our 30-second quiz below for tips on which one you should read next.
Which biography should you read next?
Discover the perfect biography for you. Takes 30 seconds!
When you conduct your interviews, make sure to record them with high quality audio you can revisit later. Then use tools like Otter.ai or Descript to transcribe them 一 it’ll save you countless hours.
You can approach the interview with a specific set of questions, or follow your curiosity blindly, trying to uncover revealing stories and anecdotes about your subject. Whatever your method, author and biography editor Tom Bromley suggests that every interviewer arrives prepared, "Show that you’ve done your work. This will help to put the interviewee at ease, and get their best answers.”
Bromley also places emphasis on the order in which you conduct interviews. “You may want to interview different members of the family or friends first, to get their perspective on something, and then go directly to the main interviewee. You'll be able to use that knowledge to ask sharper, more specific questions.”
Finally, consider how much time you have with each interviewee. If you only have a 30-minute phone call with an important person, make it count by asking directly the most pressing questions you have. And, if you find a reliable source who is also particularly willing to help, conduct several interviews and ask them, if appropriate, to write a foreword as part of the book’s front matter .
Sometimes an important part of the process is packing your bags, getting on a plane, and personally visiting significant places in your character’s journey.
Visit significant places in their life
A place, whether that’s a city, a rural house, or a bodhi tree, can carry a particular energy that you can only truly experience by being there. In putting the pieces together about someone’s life, it may be useful to go visit where they grew up, or where other significant events of their lives happened. It will be easier to imagine what they experienced, and better tell their story.
In researching The Lost City of Z , author David Grann embarked on a trek through the Amazon, retracing the steps of British explorer Percy Fawcett. This led Grann to develop new theories about the circumstances surrounding the explorer's disappearance.
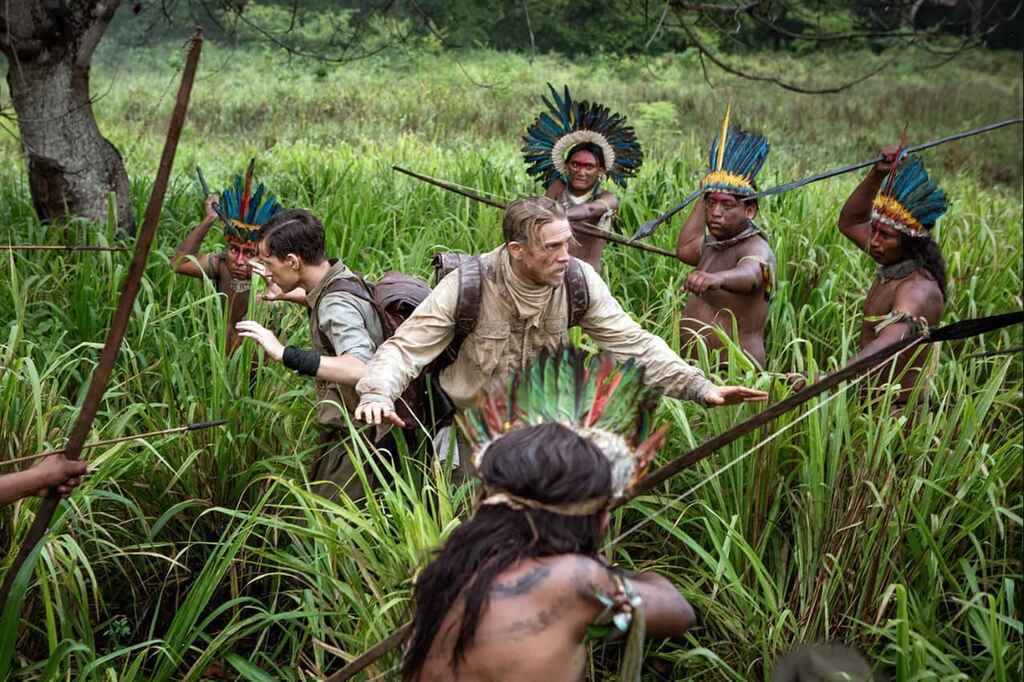

Hopefully, you won’t have to deal with jaguars and anacondas to better understand your subject’s environment, but try to walk into their shoes as much as possible.
Once you’ve researched your character enough, it’s time to put together all the puzzle pieces you collected so far.
Take the bulk of notes, media, and other documents you’ve collected, and start to give them some order and structure. A simple way to do this is by creating a timeline.
Create a chronological timeline
It helps to organize your notes chronologically 一 from childhood to the senior years, line up the most significant events of your subject’s life, including dates, places, names and other relevant bits.
You should be able to divide their life into distinct periods, each with their unique events and significance. Based on that, you can start drafting an outline of the narrative you want to create.
Draft a story outline
Since a biography entails writing about a person’s entire life, it will have a beginning, a middle, and an end. You can pick where you want to end the story, depending on how consequential the last years of your subject were. But the nature of the work will give you a starting character arc to work with.
To outline the story then, you could turn to the popular Three-Act Structure , which divides the narrative in three main parts. In a nutshell, you’ll want to make sure to have the following:
- Act 1. Setup : Introduce the protagonist's background and the turning points that set them on a path to achieve a goal.
- Act 2. Confrontation : Describe the challenges they encounter, both internal and external, and how they rise to them. Then..
- Act 3. Resolution : Reach a climactic point in their story in which they succeed (or fail), showing how they (and the world around them) have changed as a result.
Only one question remains before you begin writing: what will be the main focus of your biography?
Think about why you’re so drawn to your subject to dedicate years of your life to recounting their own. What aspect of their life do you want to highlight? Is it their evil nature, artistic genius, or visionary mindset? And what evidence have you got to back that up? Find a central thesis or focus to weave as the main thread throughout your narrative.

Or find a unique angle
If you don’t have a particular theme to explore, finding a distinct angle on your subject’s story can also help you distinguish your work from other biographies or existing works on the same subject.
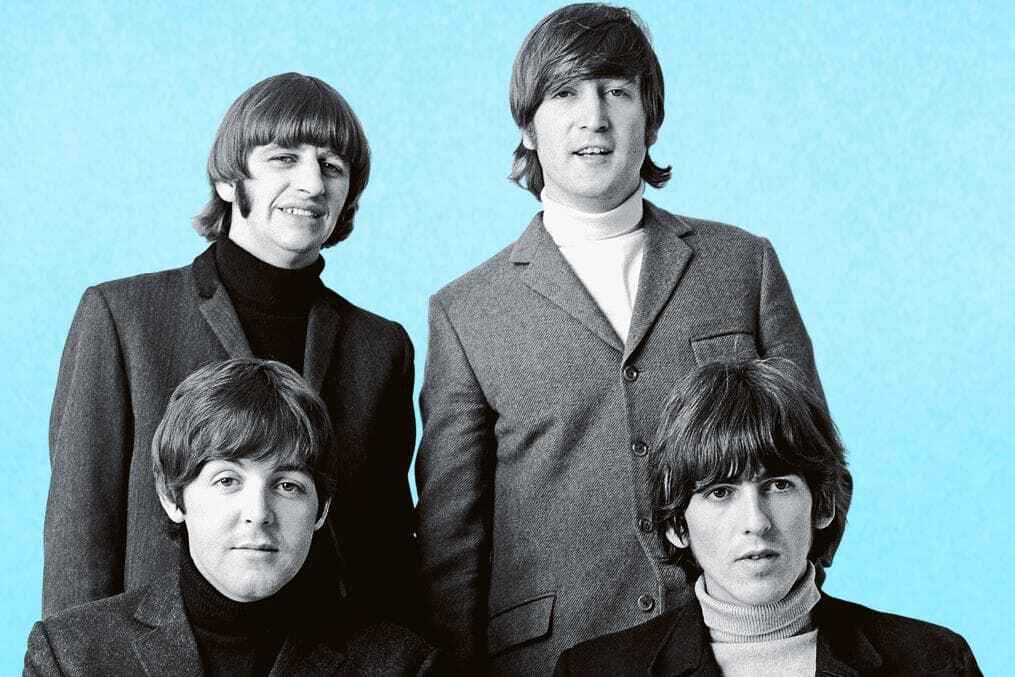
Plenty of biographies have been published about The Beatles 一 many of which have different focuses and approaches:
- Philip Norman's Shout is sometimes regarded as leaning more towards a pro-Lennon and anti-McCartney stance, offering insights into the band's inner dynamics.
- Ian McDonald's Revolution in the Head closely examines their music track by track, shifting the focus back to McCartney as a primary creative force.
- Craig Brown's One Two Three Four aims to capture their story through anecdotes, fan letters, diary entries, and interviews.
- Mark Lewisohn's monumental three-volume biography, Tune In , stands as a testament to over a decade of meticulous research, chronicling every intricate detail of the Beatles' journey.

Finally, consider that biographies are often more than recounting the life of a person. Similar to how Dickens’ Great Expectations is not solely about a boy named Pip (but an examination and critique of Britain’s fickle, unforgiving class system), a biography should strive to illuminate a broader truth — be it social, political, or human — beyond the immediate subject of the book.
Once you’ve identified your main focus or angle, it’s time to write a great story.

While biographies are often highly informative, they do not have to be dry and purely expository in nature . You can play with storytelling elements to make it an engaging read.
You could do that by thoroughly detailing the setting of the story , depicting the people involved in the story as fully-fledged characters , or using rising action and building to a climax when describing a particularly significant milestone of the subject’s life.
One common way to make a biography interesting to read is starting on a strong foot…
Hook the reader from the start
Just because you're honoring your character's whole life doesn't mean you have to begin when they said their first word. Starting from the middle or end of their life can be more captivating as it introduces conflicts and stakes that shaped their journey.
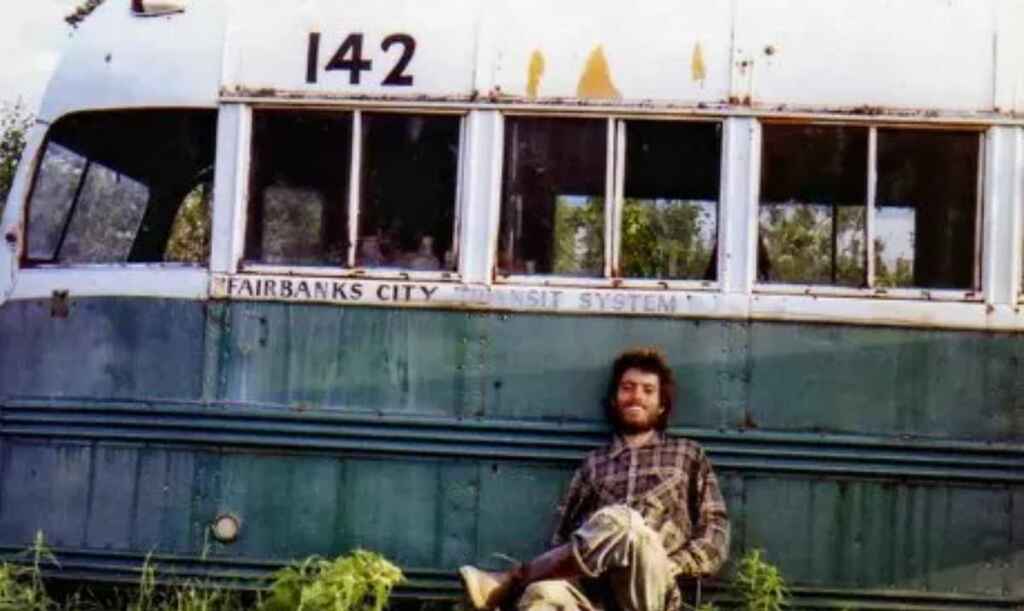
When he wrote about Christopher McCandless in Into the Wild , author Jon Krakauer didn’t open his subject’s childhood and abusive family environment. Instead, the book begins with McCandless hitchhiking his way into the wilderness, and subsequently being discovered dead in an abandoned bus. By starting in medias res , Krakauer hooks the reader’s interest, before tracing back the causes and motivations that led McCandless to die alone in that bus in the first place.

You can bend the timeline to improve the reader’s reading experience throughout the rest of the story too…
Play with flashback
While biographies tend to follow a chronological narrative, you can use flashbacks to tell brief stories or anecdotes when appropriate. For example, if you were telling the story of footballer Lionel Messi, before the climax of winning the World Cup with Argentina, you could recall when he was just 13 years old, giving an interview to a local newspaper, expressing his lifelong dream of playing for the national team.
Used sparsely and intentionally, flashbacks can add more context to the story and keep the narrative interesting. Just like including dialogue does…
Reimagine conversations
Recreating conversations that your subject had with people around them is another effective way to color the story. Dialogue helps the reader imagine the story like a movie, providing a deeper sensory experience.

One thing is trying to articulate the root of Steve Jobs’ obsession with product design, another would be to quote his father , teaching him how to build a fence when he was young: “You've got to make the back of the fence just as good looking as the front of the fence. Even though nobody will see it, you will know. And that will show that you're dedicated to making something perfect.”
Unlike memoirs and autobiographies, in which the author tells the story from their personal viewpoint and enjoys greater freedom to recall conversations, biographies require a commitment to facts. So, when recreating dialogue, try to quote directly from reliable sources like personal diaries, emails, and text messages. You could also use your interview scripts as an alternative to dialogue. As Tom Bromley suggests, “If you talk with a good amount of people, you can try to tell the story from their perspective, interweaving different segments and quoting the interviewees directly.”

FREE COURSE
How to Write Believable Dialogue
Master the art of dialogue in 10 five-minute lessons.
These are just some of the story elements you can use to make your biography more compelling. Once you’ve finished your manuscript, it’s a good idea to ask for feedback.
If you’re going to self-publish your biography, you’ll have to polish it to professional standards. After leaving your work to rest for a while, look at it with fresh eyes and self-edit your manuscript eliminating passive voice, filler words, and redundant adverbs.

Then, have a professional editor give you a general assessment. They’ll look at the structure and shape of your manuscript and tell you which parts need to be expanded on or cut. As someone who edited and commissioned several biographies, Tom Bromley points out that a professional “will look at the sources used and assess whether they back up the points made, or if more are needed. They would also look for context, and whether or not more background information is needed for the reader to understand the story fully. And they might check your facts, too.”
In addition to structural editing, you may want to have someone copy-edit and proofread your work.

MEET EDITORS
Polish your book with expert help
Sign up, meet 1500+ experienced editors, and find your perfect match.
Importantly, make sure to include a bibliography with a list of all the interviews, documents, and sources used in the writing process. You’ll have to compile it according to a manual of style, but you can easily create one by using tools like EasyBib . Once the text is nicely polished and typeset in your writing software , you can prepare for the publication process.
In conclusion, by mixing storytelling elements with diligent research, you’ll be able to breathe life into a powerful biography that immerses readers in another individual’s life experience. Whether that’ll spark inspiration or controversy, remember you could have an important role in shaping their legacy 一 and that’s something not to take lightly.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

How to Write an Autobiography: The Story of Your Life
Want to write your autobiography but aren’t sure where to start? This step-by-step guide will take you from opening lines to publishing it for everyone to read.

What is the Climax of a Story? Examples & Tips
The climax is perhaps a story's most crucial moment, but many writers struggle to stick the landing. Let's see what makes for a great story climax.

What is Tone in Literature? Definition & Examples
We show you, with supporting examples, how tone in literature influences readers' emotions and perceptions of a text.

Writing Cozy Mysteries: 7 Essential Tips & Tropes
We show you how to write a compelling cozy mystery with advice from published authors and supporting examples from literature.

Man vs Nature: The Most Compelling Conflict in Writing
What is man vs nature? Learn all about this timeless conflict with examples of man vs nature in books, television, and film.

The Redemption Arc: Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
Learn what it takes to redeem a character with these examples and writing tips.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

We made a writing app for you
Yes, you! Write. Format. Export for ebook and print. 100% free, always.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
How to Write a Biography in 8 Steps (The Non-Boring Way!)
Compelling biographies help us better connect with others while fostering empathy and understanding. Discover the steps to write one that captivates your audience!
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
Have you ever been captivated by someone’s life story? From the ancient tales of great conquerors to the modern accounts of influential figures, biographies have enchanted readers and viewers for centuries.
The stories of real people’s lives not only entertain and educate but also provide a unique window into the human experience. In fact, according to research 1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8796048/ , human stories like biographies can help us better connect with others while fostering empathy and understanding.
In this article, let’s dive into how to write a compelling biography, from the research phase to delivery.
What Are the Key Elements of a Biography?
The key elements of a well-written biography bring characters to life. They include thorough research, relevant interviews, clear structure, captivating prose, compelling themes, and a balance between objectivity and empathy.
- Thorough research: Helps create an accurate portrayal of your subject
- Relevant interviews: Insights help provide a deeper understanding of your subject
- Clear structure: Helps you outline your ideas for a compelling narrative
- Captivating prose: Provides descriptive language to paint a picture of your subject
- Compelling themes: Showcases the motivations and desires behind your subject
- A balance between objectivity and empathy: Keeps biases in check and allows your subject to shine for who they are
As you develop your biography, remember that these stories hold an enduring appeal because they offer people an opportunity to explore the depths of the human psyche, unravel extraordinary accomplishments, and discover the vulnerabilities and triumphs of individuals who have left their mark on the world.
Here are the topics a biography typically covers:
- Early life and background : Provide context about the subject’s upbringing, family, and cultural influences.
- Achievements and milestones: Highlight notable accomplishments, contributions, and significant events throughout their life.
- Challenges and struggles: Explore the obstacles they faced, the lessons learned, and how they overcame adversity.
- Personal characteristics: Describe their personality traits, values, beliefs, and motivations that shaped their actions and decisions.
- Impact and legacy: Discuss the lasting influence and contributions of the subject, both during their lifetime and beyond.
Ready to start crafting your biography? Find greater success with this helpful goal-setting resource!
How To Set Better Goals Using Science
Do you set the same goals over and over again? If you’re not achieving your goals – it’s not your fault! Let me show you the science-based goal-setting framework to help you achieve your biggest goals.
Let’s look at the six key elements of a well-written biography more closely and the steps you can follow to develop your own.
How to Write a Biography in 8 Steps Using Key Elements
Choose your presentation format.
Presenting your biography can take on various forms, the most traditional being written form. The basis for this article assumes you’re writing a conventional biography; however, this foundation can also help you create a multimedia presentation or website as well.
Consider these various formats to present your biography:
- Traditional Written Biographies: This classic approach provides a comprehensive account of a person’s life through the written word. Traditional biographies can be published in print or ebooks , allowing readers to engage deeply with the subject’s story.
- Multimedia Presentations: In the digital age, multimedia presentations offer a dynamic way to present biographies. Incorporate audio, video, photographs, and interactive elements to enhance the audience’s experience.
- Online Platforms: Online platforms, such as blogs or dedicated biography websites, provide accessible avenues for sharing biographies. They allow for easy updates, reader engagement, and the incorporation of multimedia elements.
Choose your subject and conduct research
To create a vivid and accurate portrayal of a person’s life, conduct extensive research. Dive into archives, read letters, examine diaries, explore photographs, and immerse yourself in the historical and cultural context surrounding your subject. This will help you unearth the small details that breathe life into your biography.
Whether you’re writing a biography about a historical figure, contemporary icon, or everyday individual, you’ll want to consider the different factors to focus on. Here are some examples of three types of individuals and the kind of research that will be most helpful.
- Historical Figures: When writing about historical figures, immerse yourself in their era. Understand the social, political, and cultural forces that shaped their lives. I recommend visiting your local library and connecting with a research librarian for support. Otherwise, other tools for historical research include Google Scholar. Analyze primary sources and multiple perspectives to present a well-rounded account.
- Contemporary Icons: Biographies of modern icons offer a chance to delve into their ongoing impact. Conduct interviews or gather insights from their close associates to understand their present-day influence. Stay current with the latest developments, and be prepared to update your work as the subject’s story unfolds.
- Everyday Individuals: Biographies need not be reserved for the famous. Every day individuals possess stories that can be just as compelling. Uncover the extraordinary within the ordinary, highlighting the struggles, triumphs, and personal growth of individuals who might otherwise remain unsung.
- Yourself! Want to write a biography on yourself? Autobiographies are a great way to explore who you are. Get ready to do some serious self-reflection with the steps below.
Pro Tip: Compile your research digitally using helpful cloud filings systems like Google Drive , OneDrive , or Dropbox . Organize your files by category, including information about their youth, family, achievements, and life lessons. You may also choose to write down research references or collect paper clippings on note cards, categorizing your physical files of research along the way.
Develop compelling themes and motifs
Identify overarching themes or motifs that emerge from the subject’s life. These could be resilience, ambition, love, or societal change. Weave these elements into the narrative, highlighting their significance and impact on the person’s journey. Here are some examples:
- Overcoming Adversity: These biographies feature perseverance, resilience, and determination. Examples include Helen Keller, Nelson Mandela, and Malala Yousafzai.
- Pursuit of Excellence: These biographies highlight people who have worked tirelessly to achieve their goals. Examples include Steve Jobs, Serena Williams, and Michael Jordan.
- Quest for Knowledge: These biographies focus on the curiosity that led to significant contributions to our world. Examples include Albert Einstein, Marie Curie, and Charles Darwin.
- Personal Transformation: These biographies explore a change in beliefs, values, or priorities. Examples include Malcolm X, Oprah Winfrey, and Maya Angelou.
- Legacy and Impact: These biographies examine a body of work that made a lasting contribution to society. Examples include Martin Luther King Jr., Mother Teresa, and Mahatma Gandhi.
Conduct relevant interviews
Whenever possible, seek firsthand accounts from those who knew or interacted with the subject. Conduct interviews with family members, friends, colleagues, or experts in the field. Their insights and anecdotes can provide a deeper understanding of the person’s character and experiences.
When conducting interviews for a biography, consider the following tips to ensure a productive and insightful conversation:
- Familiarize yourself with the interviewee’s background and accomplishments.
- Develop a list of well-thought-out questions that cover key aspects of their lives and experiences, including questions about your subject’s youth, family, achievements, and life transitions or struggles.
- Begin the interview by establishing a comfortable and friendly atmosphere to put the interviewee at ease.
- Show genuine interest in their story and listen actively to their responses.
- Ask open-ended questions encouraging detailed and reflective responses.
- Avoid yes/no questions and ask for their insights, memories, and personal perspectives.
- Some topics you might consider for your questions include early life, achievements, challenges, motivations, values, relationships, lessons learned, and advice.
- Pay close attention to the interviewee’s answers, body language, and tone of voice.
- Ask follow-up questions to clarify or delve deeper into specific topics.
- Show empathy and understanding, creating a safe space for the interviewee to share personal or sensitive information.
- Remain flexible during the interview, allowing the conversation to flow naturally.
- Be prepared to deviate from your prepared questions if unexpected but relevant topics arise.
- Respect the interviewee’s boundaries and be mindful of any topics they may not wish to discuss.
- Take thorough and organized notes during the interview to capture important details.
- Consider recording the interview (with permission) to ensure accurate quotes and references.
- Ask for permission to follow up with additional questions or for clarification.
- Doing a biography on yourself? Ask yourself deep questions to harvest new stories and anecdotes.
Remember, the goal of the interview is to gather valuable information and personal perspectives that will contribute to the authenticity and depth of your biography. Approach the interview process with sensitivity, respect, and genuine curiosity about the interviewee’s life and experiences.
Develop a clear structure
Outline your biography, ensuring a logical and engaging narrative flow. Consider the chronological order, significant milestones, and turning points in the subject’s life. Organize your gathered information to capture the essence of their journey while maintaining a compelling rhythm throughout.
A good outline for a biography can vary depending on the specific subject and the desired structure of the narrative. However, here’s a general outline that can serve as a starting point:
A. Introduction
a) Hook or engaging opening to capture the reader’s attention
b) Background information (birthplace, date, family, etc.)
c) A brief overview of the subject’s significance or why they are worth exploring
B. Early Life and Background
a) Childhood and upbringing
b) Influences, such as family, education, or cultural factors
c) Formative experiences or events that shaped the subject’s character or interests
C. Major Achievements and Milestones
a) A chronological exploration of the subject’s notable accomplishments, contributions, or milestones
b) Focus on key moments or achievements that highlight their impact or significance.
c) Provide context and details to paint a vivid picture of their achievements
D. Challenges and Obstacles
a) Discussion of the challenges, setbacks, or adversities the subject encountered
b) How they overcame obstacles or grew through difficult experiences
c) Insights into their resilience, determination, or problem-solving abilities
E. Personal Life and Relationships
a) Exploration of the subject’s relationships, such as family, friends, or romantic partners
b) Insights into their personal joys, struggles, or transformative experiences
c) How their personal life intersected with their professional or public achievements
F. Legacy and Impact
a) Examination of the subject’s lasting influence, contributions, or impact on society
b) Discuss how their work or actions continue to resonate or shape the world today
c) Reflection on their legacy and the lessons we can learn from their life story
G. Conclusion
a) Summarize the key aspects of the subject’s life and their significance
b) Provide a final reflection or insight on their overall journey or impact
c) Leave the reader with a lasting impression or call to action
Pro Tip: Looking for help drafting an outline to get you started? Use free tools like ChatGPT to jumpstart your outline by putting in a prompt request like, “Write an outline for a biography about X, including any relevant details on the subject that should be included.”
Craft captivating prose
Employ descriptive language to transport readers into the subject’s world. Paint vivid portraits of their physical appearance, mannerisms, and surroundings. Use sensory details to evoke emotions and create a strong connection between the reader and the subject.
Here are some examples:
- “She was a force of nature, with a fierce determination and an unwavering commitment to justice.” (Ruth Bader Ginsburg)
- “His piercing blue eyes seemed to look right through you, and his voice had a commanding presence that demanded attention.” (Winston Churchill)
- “She moved with a grace and elegance that belied her inner strength and resilience.” (Audrey Hepburn)
- “His rugged features and piercing gaze made him a natural leading man, but it was his depth and vulnerability that set him apart.” (Marlon Brando)
- “She had a contagious energy and a magnetic personality that drew people to her like a moth to a flame.” (Princess Diana)
- “His quiet intensity and unwavering dedication to his craft made him one of the greatest artists of his time.” (Leonardo da Vinci)
Action Step: While writing descriptive prose takes some practice, it’s an art you can master with little creative writing skills. To help you write descriptive prose, practice closing your eyes and imagining your subject.
- What expression is on their face?
- How are they dressed?
- What does their body language express?
- How do they smell?
- How do they make you feel?
- How do they make others feel?
- What’s in their surroundings?
- What are they doing with their hands?
- What do you imagine they’re thinking about?
With questions like these, you’ll start to use descriptive language to bring your subject to life.
Build a balance of objectivity and empathy
Strive for an objective portrayal while infusing empathy and understanding into your writing. Remain aware of biases and preconceived notions, giving your subject the space to shine in their unique light.
To check yourself, filter your writing and interviewing with these tips:
- Verify Information: Cross-reference information from various sources to ensure accuracy. Use tools like Fact Check Explorer to fact-check claims, dates, and events to avoid errors or inaccuracies that could skew the narrative.
- Multiple Perspectives: Seek out different viewpoints on the subject. This includes interviewing or reaching out to people with significant interactions or relationships with the subject. Incorporating diverse perspectives can counterbalance biases and provide a broader understanding.
- Empathetic Listening: During interviews or conversations, practice active listening and empathize with the interviewee’s experiences and emotions. This allows you to understand the subject’s perspective and incorporate their insights and feelings into the narrative.
- Contextualize Emotions: When sharing the subject’s emotional experiences or personal struggles, provide sufficient context and background. This helps readers understand the motivations and circumstances behind their actions and allows for empathetic understanding without veering into excessive sentimentality.
- Credible Interpretation: While interpreting the subject’s thoughts, motives, or intentions, be clear about what is factual and what is speculative. Clearly distinguish between evidence-based information and your interpretations to maintain objectivity.
- Respect Boundaries: Be mindful of the subject’s privacy and any requests they may have regarding sensitive or personal information. Respecting their boundaries shows empathy and allows for a respectful portrayal while maintaining the necessary level of objectivity.
- Acknowledge Limitations: Recognize that achieving complete objectivity in a biography is challenging. Biases can inadvertently seep into the narrative. However, by being aware of your biases and consciously presenting a fair and balanced account, you can mitigate their influence.
Respect truth, privacy, and sensitivity
Remember, writing biographies carries ethical responsibilities. It’s important to maintain accuracy through credible research and gain consent while being sensitive to controversial or difficult topics. Here are some considerations:
- Accuracy: Maintain a commitment to truth and accuracy. Verify facts and corroborate information from multiple sources to ensure the reliability of your narrative. Cite your sources and be transparent about any uncertainties or gaps in knowledge.
- Privacy and Consent: Respect the privacy of living individuals mentioned in your biography. Seek consent when sharing personal details or sensitive information. Balance the subject’s right to privacy with the importance of honesty and transparency.
- Sensitivity: Approach sensitive or controversial topics with care and empathy. Consider the potential impact of your words on the subject’s loved ones or affected communities—present differing perspectives without sensationalism or bias.
Writing a Biography FAQs
The length of a biography can vary greatly, depending on the subject and the depth of exploration. Some biographies span a few hundred pages, while others extend to multiple volumes. Focus on capturing the subject’s life’s essence rather than strictly adhering to a predetermined length.
Some common mistakes to avoid when writing a biography include the following: Lack of thorough research or reliance on a single source. Inaccurate or misleading information. Excessive personal bias or projection onto the subject. Neglecting to verify facts or failing to cite sources. Poor organization or a disjointed narrative flow. Neglecting to balance objectivity with empathy. Overloading the biography with irrelevant details or digressions. Failing to respect privacy or ethical considerations.
While chronological order is commonly used in biographies, it is not required. Some biographers employ a thematic approach or explore specific periods or events in the subject’s life. Experiment with different structures to find the most engaging way to tell your subject’s story.
The purpose of writing a biography is to capture and share an individual’s life story. Biographies provide insights into a person’s experiences, achievements, and challenges, offering readers inspiration, knowledge, and understanding. They preserve the legacy of individuals, contribute to historical records, and celebrate the diversity of human lives.
When choosing a subject for your biography, consider someone who inspires you, interests you, or has significantly impacted society. It could be a historical figure, a contemporary icon, or even an everyday individual with a remarkable story. Choose a subject with sufficient available information, access to primary sources or interviews, and a narrative that resonates with you and potential readers.
Key elements to include in a biography are: Early life and background: Provide context about the subject’s upbringing, family, and cultural influences. Achievements and milestones: Highlight notable accomplishments, contributions, and significant events throughout their life. Challenges and struggles: Explore the obstacles they faced, the lessons learned, and how they overcame adversity. Personal characteristics: Describe their personality traits, values, beliefs, and motivations that shaped their actions and decisions. Impact and legacy: Discuss the lasting influence and contributions of the subject, both during their lifetime and beyond.
Including personal anecdotes can add depth and humanize the subject of your biography. However, be selective and ensure that the stories are relevant, contribute to understanding the person’s character or experiences, and align with the overall narrative. Balancing personal anecdotes with factual information is critical to maintaining accuracy and credibility.
Conducting research for a biography involves exploring a variety of sources. Start with primary sources such as personal papers, letters, journals, and interviews with the subject or people who knew them. Secondary sources such as books, articles, and academic papers provide additional context and perspectives. Online databases, archives, libraries, and museums are valuable resources for finding relevant information.
Consult a wide range of sources to ensure a comprehensive and accurate biography. Primary sources, such as personal documents, letters, diaries, and interviews, offer firsthand accounts and unique insights. Secondary sources provide broader context and analysis, including books, articles, scholarly works, and historical records. Remember to evaluate the credibility and reliability of your sources critically.
Organize the information in your biography logically and engagingly. Consider using a chronological structure, starting with the subject’s early life and progressing through significant events and milestones. Alternatively, adopt a thematic approach, grouping related information based on themes or significant aspects of their life. Use clear headings, subheadings, and transitions to guide readers through the narrative flow.
Writing Biographies Key Takeaways
In summary, take note of these ideas and tips before you start writing your biography:
- Biographies hold enduring appeal, offering a glimpse into the human experience across time.
- Thorough research, interviews, and captivating prose are essential for crafting compelling biographies.
- Ethical considerations, such as accuracy, privacy, and sensitivity, are crucial when writing about real people’s lives.
- Choose subjects that genuinely inspire and resonate with you.
- Immerse yourself in the subject’s world to understand their motivations and challenges.
- Develop strong research skills and utilize a wide range of sources.
- Craft a compelling narrative that engages readers from the very first page.
- Seek feedback from trusted sources to refine your writing and storytelling abilities.
- Continuously explore new biographies to broaden your understanding of different styles and approaches.
- Embrace the unique voice and perspective you bring to the storytelling process.
Writing a biography book? Check out this helpful article, How to Write a Book: 10 Questions to Ask Before You Start Writing !
Article sources
Popular guides, how to deal with difficult people at work.
Do you have a difficult boss? Colleague? Client? Learn how to transform your difficult relationship. I’ll show you my science-based approach to building a strong, productive relationship with even the most difficult people.
Related Articles
Science of People offers over 1000+ articles on people skills and nonverbal behavior.
Get our latest insights and advice delivered to your inbox.
It’s a privilege to be in your inbox. We promise only to send the good stuff.
Is MasterClass right for me?
Take this quiz to find out.
Get 50% off this Father's Day.
Offer Ends Soon
How to Write a Biography: 6 Tips for Writing Biographical Texts
Written by MasterClass
Last updated: Aug 30, 2021 • 4 min read
Biographies are how we learn information about another human being’s life. Whether you want to start writing a biography about a famous person, historical figure, or an influential family member, it’s important to know all the elements that make a biography worth both writing and reading.


- Learn How to Write a Biography: A Step-by-Step Guide.
- Self Publishing Guide
Human lives are intricate tapestries woven with experiences, emotions, challenges, and triumphs. Biographies and autobiographies serve as windows into these remarkable stories, offering insight into the lives of individuals who have left their mark on history or those who wish to chronicle their own journeys.
I n this guide, we will explore the art of writing biographies and autobiographies, delving into the nuances of both genres and providing valuable tips on how to craft compelling narratives.
Understanding Biography and Autobiography
- Biography: Exploring Lives Beyond the Surface A biography is a literary exploration that unveils the intricate layers of a person’s existence, transcending the mere listing of events. It provides a comprehensive account of an individual’s life, offering insights into their achievements, struggles, societal impact, and distinct qualities that define them. These narratives serve as windows into history, allowing readers to traverse time and understand the legacy left by remarkable individuals. Biographies are usually crafted by biographers, individuals skilled in research and storytelling. They undertake a meticulous journey of gathering information from diverse sources, such as historical records, interviews, letters, and secondary literature. The biographer’s role is to curate these fragments of information into a coherent narrative, painting a vivid portrait of the subject. This comprehensive approach lends credibility and depth to the portrayal, enriching the reader’s understanding of the subject’s contributions and character. Example: Consider the biography of Mahatma Gandhi. A biographer compiling his life story would explore not only his role in India’s fight for independence but also his principles of nonviolence, his experiments with truth, and his impact on the world’s political landscape. By presenting a holistic view of Gandhi’s life, the biography reveals the nuances of his personality, beliefs, and the larger context in which he operated.
- Autobiography: The Intimate Dialogue of Self-Discovery An autobiography is a narrative journey undertaken by the subject themselves—a profound sharing of one’s life experiences, emotions, and reflections. This genre provides readers with an intimate insight into the subject’s psyche, allowing them to witness their life’s trajectory through personal recollections. Autobiographies carry a unique authenticity, as they are composed from the vantage point of the person who lived those moments, providing a firsthand account of their journey. Autobiographies draw from the subject’s reservoir of memories, emotions, and introspections. This self-exploration leads to a narrative that is often more than a linear chronicle; it becomes a tapestry woven with the threads of emotions, thoughts, and personal revelations. By directly communicating with the reader, the autobiographer creates a powerful connection, allowing readers to step into their shoes and experience their story from within. Example: A notable example of an autobiography is “The Diary of a Young Girl” by Anne Frank. Written during her time in hiding during World War II, the book offers a candid portrayal of Anne’s life, fears, hopes, and dreams. Through her own words, readers gain a deep understanding of the challenges faced by Jews during the Holocaust, as well as the resilience and humanity that Anne exudes even in the face of adversity.
Writing a Biography:
Research: The Foundation of a Compelling Biography Thorough research is the cornerstone of a captivating biography. Delve into reputable sources like books, articles, interviews, and archives to gather a comprehensive view of your subject’s life. By immersing yourself in these materials, you gain insights into their experiences, motivations, and contributions. Scrutinise the historical context to understand the era’s impact on their journey. Successful research forms the bedrock of your biography, enabling you to present an accurate and nuanced portrayal that resonates with readers. It’s through meticulous research that you uncover the hidden stories and connect the dots, allowing the subject’s essence to shine through the pages.
Selecting a Focus: Defining the Narrative Scope Choosing a focal point is essential for a well-structured biography. Decide whether to cover the subject’s entire life or concentrate on specific periods or achievements. This decision shapes the narrative’s trajectory, preventing it from becoming overwhelming or disjointed. A focused approach allows you to delve deeply into pivotal moments, providing a more profound understanding of the subject’s journey. By clarifying the scope, you enable readers to follow a coherent storyline, making it easier for them to engage with the subject’s life in a meaningful way.
Structuring the Biography: Chronology and Themes The organisation of your biography greatly impacts its readability. Structure your work into logical sections or chapters, employing either a chronological or thematic arrangement. Begin with an engaging introduction that captures readers’ attention and provides essential context. A chronological structure follows the subject’s life in sequential order, offering a clear timeline of events. Alternatively, a thematic structure groups events by themes, allowing you to explore different facets of the subject’s life. A well-structured biography guides readers smoothly through the subject’s experiences, fostering a deeper connection and understanding.
Show, Don’t Tell: Evocative Storytelling Vivid descriptions, anecdotes, and quotes breathe life into your biography. Rather than merely listing facts, employ descriptive language to recreate scenes and emotions, allowing readers to immerse themselves in the subject’s world. Use anecdotes to illustrate key moments, capturing the essence of the subject’s character and the impact of events on their journey. Integrating quotes from the subject, contemporaries, or relevant sources adds authenticity and depth. Through this technique, you transport readers into the subject’s experiences, enabling them to witness the moments that shaped their lives.
Balanced Perspective: Portraying Strengths and Flaws A balanced portrayal adds credibility and depth to your biography. While it’s tempting to focus solely on accomplishments, a well-rounded view includes the subject’s strengths and flaws. This authenticity humanises the subject, making it relatable and multidimensional. By acknowledging both successes and challenges, readers gain a more honest understanding of their journey. Balancing positives and negatives helps readers empathise with the subject, connecting them on a deeper level and offering a more genuine insight into their lives.
Engaging Emotions: Creating Emotional Resonance Emotions are a potent tool in biography writing. Delve into the subject’s feelings, struggles, and aspirations to create an emotional connection with readers. By tapping into their emotional experiences, you make the narrative relatable and engaging. Sharing personal challenges and triumphs allows readers to empathise and reflect on their own lives. This emotional resonance elevates the biography from a mere factual account to a compelling and moving story that lingers in readers’ minds, leaving a lasting impact.
Citing Sources: Ensuring Accuracy and Credibility Accurate information is vital in biography writing. Properly cite your sources to maintain credibility and integrity. Clear citations not only lend authority to your work but also provide readers with the opportunity to explore further if they desire. Accurate referencing safeguards against misinformation and ensures that your portrayal is based on reliable evidence. In addition to enhancing your credibility, thorough citations demonstrate your commitment to thorough research and ethical writing practises, contributing to the overall trustworthiness of your biography.

Complete Guide to Write a Biography. Start Writing Your Biography Now
Writing an Autobiography:
Reflecting on Significant Moments and Experiences Initiating an autobiography involves introspection into your life’s pivotal moments. Delve into memories that have influenced your journey, such as turning points, challenges, relationships, and achievements. Reflect on these experiences, dissecting their impact on your personal growth and development. By contemplating these key events, you gain insight into the narrative threads that weave your life story together. This reflective process sets the foundation for an authentic autobiography that resonates with readers on a profound level.
Developing Your Unique Voice and Tone Crafting an autobiography demands a consistent voice and tone that reflect your personality. Write in a way that feels true to you, capturing your unique perspective and emotions. Authenticity is key, as it allows readers to connect with your narrative on a personal level. Whether your tone is introspective, humorous, or contemplative, ensure it aligns with the essence of your experiences. By embracing your genuine voice, you create an autobiography that not only tells your story but also conveys the essence of who you are.
Structured Storytelling for Engagement While autobiographies can be more flexible in structure compared to biographies, organising your narrative into coherent sections or themes enhances its readability. By grouping related experiences together, you provide readers with a clearer understanding of the themes that have shaped your life. This structure helps maintain their engagement by guiding them through your journey in a logical and compelling manner. While allowing for creativity, a structured approach ensures that your autobiography remains focused and accessible.
Embracing honesty and authenticity Honesty is the bedrock of an impactful autobiography. Share not only your triumphs but also your mistakes and failures. Authenticity creates relatability, allowing readers to connect with your humanity and vulnerabilities. Your journey’s challenges and setbacks are just as integral to your story as your successes. By being candid about your experiences, you demonstrate resilience and growth, inspiring readers to reflect on their own paths. This level of authenticity fosters a deeper connection, making your autobiography a source of empathy and encouragement.
Adding Depth Through Reflection Incorporate reflection to imbue your autobiography with depth and meaning. Explore the lessons you’ve learned from your experiences and the transformations they’ve prompted. Delve into how these moments shaped your beliefs, values, and perspective on life. By offering insights gained from introspection, you provide readers with wisdom and a broader understanding of your journey. Reflection transforms your autobiography from a chronicle of events into a thoughtful exploration of personal growth and the profound impact of life’s moments.
Creating vivid details for immersion Immerse readers in your world by employing sensory details and vivid descriptions. Paint a picture with words, allowing readers to visualise the scenes and emotions you’re describing. By incorporating sensory elements like sights, sounds, smells, and feelings, you transport readers into the moments you’re recounting. This immersive experience draws them closer to your story, fostering a stronger connection. Vivid details not only make your autobiography more engaging but also enable readers to forge a deeper connection with your experiences and emotions.
In the realm of literature, biographies and autobiographies stand as powerful testaments to the diversity and richness of human existence. Whether you’re capturing the life of a historical figure or penning your own life story, the art of writing these genres involves meticulous research, introspection, and a keen understanding of human emotions.
Through carefully chosen words and evocative storytelling, biographers and autobiographers alike can craft narratives that resonate with readers and offer a deeper understanding of the human experience. So, whether you’re writing about the extraordinary or the everyday, embrace the challenge and privilege of narrating lives through the written word.
Publish your book with BlueRoseONE and become a bestselling author . Don’t let your dream of becoming an author fade away, grab the opportunity now and publish your book – be it fiction, non fiction, poetry or more.
- About The Author
- Latest Posts
Mansi Chauhan

You May Also Like

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How to write a biography: 7 life-writing ideas
Biography – literally ‘life writing’ – poses a variety of challenges. Balancing historical narration and day-to-day incident, for example. Or choosing what to include and what to leave out. Read 7 ideas on how to write a biography, with examples from biographical writing:
- Post author By Jordan
- 4 Comments on How to write a biography: 7 life-writing ideas

7 life-writing ideas:
- Create compelling voice
- Think about representation
- Decide on narrative style
- Use illustrative anecdotes
- Find interest in the mundane
- Avoid hagiography
- Fictionalize where necessary
First: What type of biography do you want to write?
There are many different types of biography, both in fiction and non-fiction.
Popular types of biographical books
If you want to write non-fiction, you may be working on either an autobiography (a book about your life) or memoir , or a biography of a public figure.
Biographies can straddle both fiction and non-fiction, too. Many authors have written semi-fictionalized biographical stories (such as Now Novel writing coach Hedi Lampert’s novel , The Trouble with My Aunt ) with the author themselves as a main or supporting character.
For example, in Ivan Vladislavic’s Portrait with Keys , the author invents a brother. This fictional addition allows for lively debates between him and this imaginary relative about urban spaces and race politics in the city of Johannesburg.
Novelized biographies (such as Charles Dickens’ David Copperfield or Charlotte Brontë’s Jane Eyre ) often follow a central character’s life arc in a linear way , from early life to later years or even death.
Other types of fictional biography include fictional letters and diaries. These allow you to play with other modes of representation.
For example, Sue Townsend’s popular Adrian Mole series (the first book being The Secret Diary of Adrian Mole, Aged 13¾ ), presented as a British teenage boy’s diary.
Let’s examine 7 ideas about how to write a biography:
1. Create compelling voice
You could say that voice is a crucial ingredient of any story , especially in first person (where the narrator is the character).
In autobiography, in particular, you want your reader to form a clear sense of who is telling the story. Are they funny? Serious? Angry? Inventive? Philosophical? Just a little bit insane?
Consider the comical, self-aware voice that comes through from page 1 of Townsend’s novel. The first chapter, under the heading ‘THURSDAY JANUARY 1ST’, begins:
These are my New Year’s resolutions: 1. I will help the blind across the road. 2. I will hang my trousers up. 3. I will put the sleeves back on my records. 4. I will not start smoking. 5. I will stop squeezing my spots. 6. I will be kind to the dog. 7. I will help the poor and ignorant. 8. After hearing the disgusting noises from downstairs last night, I have also vowed never to drink alcohol. Sue Townsend, The Secret Diary of Adrian Mole, Aged 13¾ (1982), p. 5.
Adrian Mole’s resolutions range from the virtuous to the droll (e.g. helping the ‘poor and ignorant’; scathing remarks on his parents’ drunken ‘disgusting noises’).
From the opening page there’s a clear sense of the voice of the subject of this diary-format biography. We form a sense of Mole’s desires, faults, attitudes and beliefs straight away.
2. Think about representation
Whether you’re writing fictional or non-fictional biography, how you represent events or tell the story is a creative decision.
Besides curating content (choosing what formative experiences, dramatic incidents, background details you include), there are different ways to approach representation , the way you tell the story.
As respected literary biographer Hermione Lee says, in an interview with James Rivington , there’s a difference between ‘autopsy’ and ‘portraiture’:
Autopsy, yes. There is a kind of biographical process that is, necessarily, cutting into the dead corpse, however ghoulish that can seem. You are as ruthlessly as possible trying to dissect and analyse the nature of the life. The other approach is more akin to portraiture: to see how the person looked from the outside, how they affected and influenced people, what their friendships were like, how they were one thing to one person and another thing to another person. I think you have get at both inside and outside if you can. Hermione Lee, interviewed by James Rivington for The British Academy
What Lee touches on is the issue of representation .
How will you mix biographical and historical facts (e.g. born here, raised there, had this key experience) with more painterly ways of revealing character ?

3. Decide on narrative style
Deciding how to write a biography means choosing between many available narrative modes or styles.
Will your story run from A to B to C, documenting each decade in a person’s life? Or will it be a crisscross portrait cutting back and forth in time?
A fragmentary style of narration may suit certain subjects and contexts better than a linear story. Says Lee:
I think that biography has to be watchful of making life seem too predictable, or determinist, or shaped, or ordered. Biographies go through fashions. There used to be a fashion for making the study run smoothly and look definitive – ‘this leads to this leads to this.’ I think life-stories are more bitty and piecemeal. Hermione Lee, interview for The British Academy
Example of inventive narrative style: Roland Barthes
As an example, Roland Barthes, a pioneer in semiotics (the study of signs and symbols and their interpretation), famously wrote an autobiography in fragments called Roland Barthes by Roland Barthes .
In this book, Barthes includes the preface ‘it must all be considered as if spoken by a character in a novel’.
What follows are captioned images from Barthes’ life, and then titled fragments where Barthes reflects on incidents, places, experiences and the development of his body of work.
For example, in a short section about the discomfort of writing called ‘Truth and Assertion’, Barthes refers to himself in third person , expressing discomfort in how words committed to paper express more than our original aims:
His (sometimes acute) discomfort—mounting some evenings, after writing the whole day, to a kind of fear—was generated by his sense of producing a double discourse, whose mode overreached its aim, somehow: for the aim of his discourse is not truth, and yet this discourse is assertive. (This kind of embarrassment started, for him, very early; he strives to master it — for otherwise he would have to stop writing — by reminding himself that it is language which is assertive, not he). Roland Barthes, Roland Barthes by Roland Barthes , p. 48, available here.
Fragments provide a fitting choice of narrative style for an unconventional autobiography that is as much a self-portrait of Barthes as a questioner of seemingly self-evident truths, as it is the representation of his life.
Barthes’ use of third-person and questioning reflections on the act of writing creates the ‘looking from the outside’ effect Hermione Lee describes as ‘portraiture’ in biography. Even as Barthes creates a self-portrait, he resists the idea of the ‘assertive’ author, the ‘completeness’ of the ‘final report’.
4. Use illustrative anecdotes
An English professor once asked his third year class ‘What is an anecdote?’
A girl put up her hand and answered, ‘It’s what you give someone when they’ve been bitten by a snake’, to which he replied ‘Please don’t ask someone for an anecdote if you’re ever bitten by a snake, for they will talk and talk and you will die.’
This is an anecdote. These usually short, often humorous stories about events involving a particular person are great fodder for biographies. They may illustrate a person’s quick wit or surly, non-communicative demeanor .
In biography, a brief anecdote may be all the reader needs to develop a sense of a key figure – a parent, friend, lover, rival or other.
Example of illustrative anecdotes: Dorothy Parker
The writer, poet and satirist Dorothy Parker is known for her witty comebacks and phrases.
One anecdote illustrating this character gives an alleged exchange between Parker and a snooty woman at an event, where both were trying to enter through a door at the same time:
It is recorded that Mrs. Parker and a snooty debutante were both going in to supper at a party: the debutante made elaborate way, saying sweetly “Age before beauty, Mrs. Parker.” “And pearls before swine,” said Mrs. Parker, sweeping in. Dorothy Parker, attributed. More on this anecdote at Quote Investigator.
Parker’s clever comeback to the woman’s quip about her being the older (and the implication she is less beautiful) evokes Jesus’s sermon on the Mount in which he said ‘Do not give what is holy to the dogs; nor cast your pearls before swine…’
The anecdote is a brilliant illustration of Parker as a quick-witted person with a sharp tongue and an ear for comedy. An anecdotal exchange here conveys a good sense of personality.
5. Find interest in the mundane
When we think about how a biography is written, we might think in terms of grand, important or scandalous events. Yet a biography is not a gossip column.
Lee makes this important point in her interview, regarding Virginia Woolf’s eventual suicide.
In writing the author’s biography, Lee describes the pitfalls of writing it as though Woolf was thinking about suicide every day.
It would possibly be sensationalizing (rather than allowing multiple ‘Woolfs’ to come through) to assume this linearity:
When, as in the case of Virginia Woolf, you have a very important, much-read woman writer who kills herself, there is a powerful desire to make the story move towards that point. You see that also in the life of Sylvia Plath – perhaps even more, because she was so much younger. It becomes all about the suicide. […] So one of my motives in writing about Virginia Woolf was to get away from the determinist sense of a story that had to end that way. Lee, interview for The British Academy
How do we make the repetitive, ‘boring’ parts of life interesting in life-writing?
- Skip over them (e.g. ‘For the next 5 years she was busy establishing the Hogarth Press. Then…’)
- Show their interesting place within a wider arc (e.g. ‘With every manuscript the Press put out, she gained a keener understanding of X that would lead to …’)

6. Avoid hagiography
Hagiography, the term for the writing of the lives of saints, also means ‘to display a subject undue reverence’ in writing.
The British statesman Arhtur Balfour is alleged to have said ‘Biography should be written by an acute enemy.’
There’s truth in this, since an enemy would dissect their rival’s life without mercy. Perform a thorough autopsy, and paint a colourful (even if unflattering) portrait.
In deciding how to write a biography, make sure you choose incidents that reflect multiple dimensions of the subject’s life. Their glorious and inglorious moments.
For example, to write the story of a now-revered author as the story of success after success may ring false for readers who know about the 12 rejections their first manuscript received.
Plan the scenes and incidents of a biography the way you would build a character profile. Ask, ‘What are the subject’s…’
- Impressive moments?
- Cringe moments?
7. Fictionalize where necessary
Author and essayist Geoff Dyer has written books in many forms, from travelogues blending fiction and non-fiction to books about writing biography ( Out of Sheer Rage: Wrestling with DH Lawrence ).
Dyer’s book But Beautiful: A Book about Jazz is an example of his genre-defying approach.
Part biography of renowned jazz musicians (including Duke Ellington and Thelonious Monk), part homage to the improvisational and playful language of jazz, it combines historical details, photography and discussion of music. Rather than tell a linear story of each musician’s life, Dyer captures fleeting moments and experiences in a manner evocative of jazz music’s ephemeral nature.
This approach naturally involves plenty of fictionalizing, filling in and describing unknown details.
For example, here Dyer imagines a road trip where Duke Ellington’s driver muses on their road-tripping and the impossibility of recording every detail:
He’d bought the car in ’49, intending just to hop around New York, but soon he was driving Duke all over the country. Several times he’d had an impulse to keep a notebook record of how far they’d traveled but always he came to thinking how he wished he’d done it right from the start and so, each time he thought of it, he gave up the idea and fell to calculating vaguely cumulative distances, remembering the countries and towns they had passed through. Geoff Dyer, But Beautiful: A Book about Jazz (1991), p. 4.
Adding fictionalized events, such as particular exchanges between Duke Ellington and a driver that may not have happened ‘exactly that way’, is a useful part of biography. Like the driver’s thought process, there are ‘vaguely cumulative distances’ you, the biographer, must calculate and recreate for your reader.
Writing a fiction or non-fiction (or semi-fictional) biographical novel? Get constructive, considere d feedback from a writing coach.
Related Posts:
- How to be inspired to write every day: 10 ideas
- How to write the first chapter of a book: 7 ideas
- How to write dystopian fiction: 9 core ideas
- Tags biography , life-writing , memoir
Jordan is a writer, editor, community manager and product developer. He received his BA Honours in English Literature and his undergraduate in English Literature and Music from the University of Cape Town.
4 replies on “How to write a biography: 7 life-writing ideas”
This article is brilliant, useful and educational which I admired the most and I can’t wait to read more. Thanks for the topic you’ve shared!
Thank you, Rosella. Thanks for reading our blog and sharing your feedback.
I would like to write a biography of someone who is a brother to me. Inorder to be remembered forever.
That sounds wonderful. Have you started writing or planning it?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Pin It on Pinterest

How to Write a Biography
Biographies are big business. Whether in book form or Hollywood biopics, the lives of the famous and sometimes not-so-famous fascinate us.
While it’s true that most biographies are about people who are in the public eye, sometimes the subject is less well-known. Primarily, though, famous or not, the person who is written about has led an incredible life.
In this article, we will explain biography writing in detail for teachers and students so they can create their own.
While your students will most likely have a basic understanding of a biography, it’s worth taking a little time before they put pen to paper to tease out a crystal-clear definition of one.

What Is a Biography?

A biography is an account of someone’s life written by someone else . While there is a genre known as a fictional biography, for the most part, biographies are, by definition, nonfiction.
Generally speaking, biographies provide an account of the subject’s life from the earliest days of childhood to the present day or, if the subject is deceased, their death.
The job of a biography is more than just to outline the bare facts of a person’s life.
Rather than just listing the basic details of their upbringing, hobbies, education, work, relationships, and death, a well-written biography should also paint a picture of the subject’s personality and experience of life.

Full Biographies
Teaching unit.
Teach your students everything they need to know about writing an AUTOBIOGRAPHY and a BIOGRAPHY.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ ( 26 reviews )
Features of a Biography
Before students begin writing a biography, they’ll need to have a firm grasp of the main features of a Biography. An excellent way to determine how well they understand these essential elements is to ask them to compile a checklist like the one-blow
Their checklists should contain the items below at a minimum. Be sure to help them fill in any gaps before moving on to the writing process.
The purpose of a biography is to provide an account of someone’s life.
Biography structure.
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Open your biography with a strong hook to grab the reader’s attention
SEQUENCING: In most cases, biographies are written in chronological order unless you are a very competent writer consciously trying to break from this trend.
COVER: childhood, upbringing, education, influences, accomplishments, relationships, etc. – everything that helps the reader to understand the person.
CONCLUSION: Wrap your biography up with some details about what the subject is doing now if they are still alive. If they have passed away, make mention of what impact they have made and what their legacy is or will be.
BIOGRAPHY FEATURES
LANGUAGE Use descriptive and figurative language that will paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read. Use time connectives to link events.
PERSPECTIVE Biographies are written from the third person’s perspective.
DETAILS: Give specific details about people, places, events, times, dates, etc. Reflect on how events shaped the subject. You might want to include some relevant photographs with captions. A timeline may also be of use depending upon your subject and what you are trying to convey to your audience.
TENSE Written in the past tense (though ending may shift to the present/future tense)
THE PROCESS OF WRITING A BIOGRAPHY
Like any form of writing, you will find it simple if you have a plan and follow it through. These steps will ensure you cover the essential bases of writing a biography essay.
Firstly, select a subject that inspires you. Someone whose life story resonates with you and whose contribution to society intrigues you. The next step is to conduct thorough research. Engage in extensive reading, explore various sources, watch documentaries, and glean all available information to provide a comprehensive account of the person’s life.
Creating an outline is essential to organize your thoughts and information. The outline should include the person’s early life, education, career, achievements, and any other significant events or contributions. It serves as a map for the writing process, ensuring that all vital information is included.
Your biography should have an engaging introduction that captivates the reader’s attention and provides background information on the person you’re writing about. It should include a thesis statement summarising the biography’s main points.
Writing a biography in chronological order is crucial . You should begin with the person’s early life and move through their career and achievements. This approach clarifies how the person’s life unfolded and how they accomplished their goals.
A biography should be written in a narrative style , capturing the essence of the person’s life through vivid descriptions, anecdotes, and quotes. Avoid dry, factual writing and focus on creating a compelling narrative that engages the reader.
Adding personal insights and opinions can enhance the biography’s overall impact, providing a unique perspective on the person’s achievements, legacy, and impact on society.
Editing and proofreading are vital elements of the writing process. Thoroughly reviewing your biography ensures that the writing is clear, concise, and error-free. You can even request feedback from someone else to ensure that it is engaging and well-written.
Finally, including a bibliography at the end of your biography is essential. It gives credit to the sources that were used during research, such as books, articles, interviews, and websites.
Tips for Writing a Brilliant Biography
Biography writing tip #1: choose your subject wisely.
There are several points for students to reflect on when deciding on a subject for their biography. Let’s take a look at the most essential points to consider when deciding on the subject for a biography:
Interest: To produce a biography will require sustained writing from the student. That’s why students must choose their subject well. After all, a biography is an account of someone’s entire life to date. Students must ensure they choose a subject that will sustain their interest throughout the research, writing, and editing processes.
Merit: Closely related to the previous point, students must consider whether the subject merits the reader’s interest. Aside from pure labors of love, writing should be undertaken with the reader in mind. While producing a biography demands sustained writing from the author, it also demands sustained reading from the reader.
Therefore, students should ask themselves if their chosen subject has had a life worthy of the reader’s interest and the time they’d need to invest in reading their biography.
Information: Is there enough information available on the subject to fuel the writing of an entire biography? While it might be a tempting idea to write about a great-great-grandfather’s experience in the war. There would be enough interest there to sustain the author’s and the reader’s interest, but do you have enough access to information about their early childhood to do the subject justice in the form of a biography?
Biography Writing Tip #2: R esearch ! Research! Research!
While the chances are good that the student already knows quite a bit about the subject they’ve chosen. Chances are 100% that they’ll still need to undertake considerable research to write their biography.
As with many types of writing , research is an essential part of the planning process that shouldn’t be overlooked. If students wish to give as complete an account of their subject’s life as possible, they’ll need to put in the time at the research stage.
An effective way to approach the research process is to:
1. Compile a chronological timeline of the central facts, dates, and events of the subject’s life
2. Compile detailed descriptions of the following personal traits:
- Physical looks
- Character traits
- Values and beliefs
3. Compile some research questions based on different topics to provide a focus for the research:
- Childhood : Where and when were they born? Who were their parents? Who were the other family members? What education did they receive?
- Obstacles: What challenges did they have to overcome? How did these challenges shape them as individuals?
- Legacy: What impact did this person have on the world and/or the people around them?
- Dialogue & Quotes: Dialogue and quotations by and about the subject are a great way to bring color and life to a biography. Students should keep an eagle eye out for the gems that hide amid their sources.
As the student gets deeper into their research, new questions will arise that can further fuel the research process and help to shape the direction the biography will ultimately go in.
Likewise, during the research, themes will often begin to suggest themselves. Exploring these themes is essential to bring depth to biography, but we’ll discuss this later in this article.
Research Skills:
Researching for biography writing is an excellent way for students to hone their research skills in general. Developing good research skills is essential for future academic success. Students will have opportunities to learn how to:
- Gather relevant information
- Evaluate different information sources
- Select suitable information
- Organize information into a text.
Students will have access to print and online information sources, and, in some cases, they may also have access to people who knew or know the subject (e.g. biography of a family member).
These days, much of the research will likely take place online. It’s crucial, therefore, to provide your students with guidance on how to use the internet safely and evaluate online sources for reliability. This is the era of ‘ fake news ’ and misinformation after all!
COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON INTERNET RESEARCH SKILLS USING GOOGLE SEARCH

Teach your students ESSENTIAL SKILLS OF THE INFORMATION ERA to become expert DIGITAL RESEARCHERS.
⭐How to correctly ask questions to search engines on all devices.
⭐ How to filter and refine your results to find exactly what you want every time.
⭐ Essential Research and critical thinking skills for students.
⭐ Plagiarism, Citing and acknowledging other people’s work.
⭐ How to query, synthesize and record your findings logically.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip #3: Find Your Themes In Biography Writing
Though predominantly a nonfiction genre, the story still plays a significant role in good biography writing. The skills of characterization and plot structuring are transferable here. And, just like in fiction, exploring themes in a biographical work helps connect the personal to the universal. Of course, these shouldn’t be forced; this will make the work seem contrived, and the reader may lose faith in the truthfulness of the account. A biographer needs to gain and maintain the trust of the reader.
Fortunately, themes shouldn’t need to be forced. A life well-lived is full of meaning, and the themes the student writer is looking for will emerge effortlessly from the actions and events of the subject’s life. It’s just a case of learning how to spot them.
One way to identify the themes in a life is to look for recurring events or situations in a person’s life. These should be apparent from the research completed previously. The students should seek to identify these patterns that emerge in the subject’s life. For example, perhaps they’ve had to overcome various obstacles throughout different periods of their life. In that case, the theme of overcoming adversity is present and has been identified.
Usually, a biography has several themes running throughout, so be sure your students work to identify more than one theme in their subject’s life.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip: #4 Put Something of Yourself into the Writing
While the defining feature of a biography is that it gives an account of a person’s life, students must understand that this is not all a biography does. Relating the facts and details of a subject’s life is not enough. The student biographer should not be afraid to share their thoughts and feelings with the reader throughout their account of their subject’s life.
The student can weave some of their personality into the fabric of the text by providing commentary and opinion as they relate the events of the person’s life and the wider social context at the time. Unlike the detached and objective approach we’d expect to find in a history textbook, in a biography, student-writers should communicate their enthusiasm for their subject in their writing.
This makes for a more intimate experience for the reader, as they get a sense of getting to know the author and the subject they are writing about.
Biography Examples For Students
- Year 5 Example
- Year 7 Example
- Year 9 Example
“The Rock ‘n’ Roll King: Elvis Presley”
Elvis Aaron Presley, born on January 8, 1935, was an amazing singer and actor known as the “King of Rock ‘n’ Roll.” Even though he’s been dead for nearly 50 years, I can’t help but be fascinated by his incredible life!
Elvis grew up in Tupelo, Mississippi, in a tiny house with his parents and twin brother. His family didn’t have much money, but they shared a love for music. Little did they know Elvis would become a music legend!
When he was only 11 years old, Elvis got his first guitar. He taught himself to play and loved singing gospel songs. As he got older, he started combining different music styles like country, blues, and gospel to create a whole new sound – that’s Rock ‘n’ Roll!
In 1954, at the age of 19, Elvis recorded his first song, “That’s All Right.” People couldn’t believe how unique and exciting his music was. His famous hip-swinging dance moves also made him a sensation!
Elvis didn’t just rock the music scene; he also starred in movies like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock.” But fame came with challenges. Despite facing ups and downs, Elvis kept spreading happiness through his music.

Tragically, Elvis passed away in 1977, but his music and charisma live on. Even today, people worldwide still enjoy his songs like “Hound Dog” and “Can’t Help Falling in Love.” Elvis Presley’s legacy as the King of Rock ‘n’ Roll will live forever.
Long Live the King: I wish I’d seen him.
Elvis Presley, the Rock ‘n’ Roll legend born on January 8, 1935, is a captivating figure that even a modern-day teen like me can’t help but admire. As I delve into his life, I wish I could have experienced the magic of his live performances.
Growing up in Tupelo, Mississippi, Elvis faced challenges but found solace in music. At 11, he got his first guitar, a symbol of his journey into the world of sound. His fusion of gospel, country, and blues into Rock ‘n’ Roll became a cultural phenomenon.
The thought of being in the audience during his early performances, especially when he recorded “That’s All Right” at 19, sends shivers down my spine. Imagining the crowd’s uproar and feeling the revolutionary energy of that moment is a dream I wish I could have lived.
Elvis wasn’t just a musical prodigy; he was a dynamic performer. His dance moves, the embodiment of rebellion, and his roles in films like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock” made him a true icon.
After watching him on YouTube, I can’t help but feel a little sad that I’ll never witness the King’s live performances. The idea of swaying to “Hound Dog” or being enchanted by “Can’t Help Falling in Love” in person is a missed opportunity. Elvis may have left us in 1977, but he was the king of rock n’ roll. Long live the King!
Elvis Presley: A Teen’s Take on the Rock ‘n’ Roll Icon”
Elvis Presley, born January 8, 1935, was a revolutionary force in the music world, earning his title as the “King of Rock ‘n’ Roll.” Exploring his life, even as a 16-year-old today, I’m captivated by the impact he made.
Hailing from Tupelo, Mississippi, Elvis grew up in humble beginnings, surrounded by the love of his parents and twin brother. It’s inspiring to think that, despite financial challenges, this young man would redefine the music scene.
At 11, Elvis got his first guitar, sparking a self-taught journey into music. His early gospel influences evolved into a unique fusion of country, blues, and gospel, creating the electrifying genre of Rock ‘n’ Roll. In 1954, at only 19, he recorded “That’s All Right,” marking the birth of a musical legend.
Elvis wasn’t just a musical innovator; he was a cultural phenomenon. His rebellious dance moves and magnetic stage presence challenged the norms. He transitioned seamlessly into acting, starring in iconic films like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock.”

However, fame came at a cost, and Elvis faced personal struggles. Despite the challenges, his music continued to resonate. Even now, classics like “Hound Dog” and “Can’t Help Falling in Love” transcend generations.
Elvis Presley’s impact on music and culture is undeniable. He was known for his unique voice, charismatic persona, and electrifying performances. He sold over one billion records worldwide, making him one of the best-selling solo artists in history. He received numerous awards throughout his career, including three Grammy Awards and the Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award.
Elvis’s influence can still be seen in today’s music. Many contemporary artists, such as Bruno Mars, Lady Gaga, and Justin Timberlake, have cited Elvis as an inspiration. His music continues to be featured in movies, TV shows, and commercials.
Elvis left us in 1977, but his legacy lives on. I appreciate his breaking barriers and fearlessly embracing his artistic vision. Elvis Presley’s impact on music and culture is timeless, a testament to the enduring power of his artistry. His music has inspired generations and will continue to do so for many years to come.

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING TEACHING IDEAS AND LESSONS
We have compiled a sequence of biography-related lessons or teaching ideas that you can follow as you please. They are straightforward enough for most students to follow without further instruction.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 1:
This session aims to give students a broader understanding of what makes a good biography.
Once your students have compiled a comprehensive checklist of the main features of a biography, allow them to use it to assess some biographies from your school library or on the internet using the feature checklist.
When students have assessed a selection of biographies, take some time as a class to discuss them. You can base the discussion around the following prompts:
- Which biographies covered all the criteria from their checklist?
- Which biographies didn’t?
- Which biography was the most readable in terms of structure?
- Which biography do you think was the least well-structured? How would you improve this?
Looking at how other writers have interpreted the form will help students internalize the necessary criteria before attempting to produce a biography. Once students have a clear understanding of the main features of the biography, they’re ready to begin work on writing a biography.
When the time does come to put pen to paper, be sure they’re armed with the following top tips to help ensure they’re as well prepared as possible.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 2:
This session aims to guide students through the process of selecting the perfect biography subject.
Instruct students to draw up a shortlist of three potential subjects for the biography they’ll write.
Using the three criteria mentioned in the writing guide (Interest, Merit, and Information), students award each potential subject a mark out of 5 for each of the criteria. In this manner, students can select the most suitable subject for their biography.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 3:
This session aims to get students into the researching phase, then prioritise and organise events chronologically.
Students begin by making a timeline of their subject’s life, starting with their birth and ending with their death or the present day. If the student has yet to make a final decision on the subject of their biography, a family member will often serve well for this exercise as a practice exercise.
Students should research and gather the key events of the person’s life, covering each period of their life from when they were a baby, through childhood and adolescence, right up to adulthood and old age. They should then organize these onto a timeline. Students can include photographs with captions if they have them.
They can present these to the class when they have finished their timelines.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 4:
Instruct students to look over their timeline, notes, and other research. Challenge them to identify three patterns that repeat throughout the subject’s life and sort all the related events and incidents into specific categories.
Students should then label each category with a single word. This is the thematic concept or the broad general underlying idea. After that, students should write a sentence or two expressing what the subject’s life ‘says’ about that concept.
This is known as the thematic statement . With the thematic concepts and thematic statements identified, the student now has some substantial ideas to explore that will help bring more profound meaning and wider resonance to their biography.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 5:
Instruct students to write a short objective account of an event in their own life. They can write about anyone from their past. It needn’t be more than a couple of paragraphs, but the writing should be strictly factual, focusing only on the objective details of what happened.
Once they have completed this, it’s time to rewrite the paragraph, but they should include some opinion and personal commentary this time.
The student here aims to inject some color and personality into their writing, to transform a detached, factual account into a warm, engaging story.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING BIOGRAPHIES

Teach your students to write AMAZING BIOGRAPHIES & AUTOBIOGRAPHIES using proven RESEARCH SKILLS and WRITING STRATEGIES .
- Understand the purpose of both forms of biography.
- Explore the language and perspective of both.
- Prompts and Challenges to engage students in writing a biography.
- Dedicated lessons for both forms of biography.
- Biographical Projects can expand students’ understanding of reading and writing a biography.
- A COMPLETE 82-PAGE UNIT – NO PREPARATION REQUIRED.
FREE Biography Writing Graphic Organizer
Use this valuable tool in the research and writing phases to keep your students on track and engaged.
WRITING CHECKLIST & RUBRIC BUNDLE

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
To Conclude
By this stage, your students should have an excellent technical overview of a biography’s essential elements.
They should be able to choose their subject in light of how interesting and worthy they are, as well as give consideration to the availability of information out there. They should be able to research effectively and identify emerging themes in their research notes. And finally, they should be able to bring some of their personality and uniqueness into their retelling of the life of another.
Remember that writing a biography is not only a great way to develop a student’s writing skills; it can be used in almost all curriculum areas. For example, to find out more about a historical figure in History, to investigate scientific contributions to Science, or to celebrate a hero from everyday life.
Biography is an excellent genre for students to develop their writing skills and to find inspiration in the lives of others in the world around them.
HOW TO WRITE A BIOGRAPHY TUTORIAL VIDEO

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO BIOGRAPHY WRITING

How to write an Autobiography

How to Write a Historical Recount Text

15 Awesome Recount & Personal Narrative Topics

Personal Narrative Writing Guide
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Write a Biography
Last Updated: May 28, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Stephanie Wong Ken, MFA . Stephanie Wong Ken is a writer based in Canada. Stephanie's writing has appeared in Joyland, Catapult, Pithead Chapel, Cosmonaut's Avenue, and other publications. She holds an MFA in Fiction and Creative Writing from Portland State University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,865,074 times.
Writing a biography can be a fun challenge, where you are sharing the story of someone’s life with readers. You may need to write a biography for a class or decide to write one as a personal project. Once you have identified the subject of the biography, do your research so you know as much about them as possible. Then, dive into the writing of the biography and revising it until it is at its finest.
Researching Your Subject

- If the subject does not give you permission to write the biography, you may want to choose a different subject. If you decide to publish the biography without the subject’s permission, you may be susceptible to legal action by the subject.
- If the subject is no longer alive, you obviously do not need to ask permission to write about them.

- You may create research questions to help focus your research of the subject, such as, What do I find interesting about the subject? Why is this subject important to readers? What can I say that is new about the subject? What would I like to learn more about?

- For in person interviews, record them with a tape recorder or a voice recorder on your computer or phone.
- You may need to interview the subject and others several times to get the material you need.

- You may also want to visit areas where the subject made a major decision or breakthrough in their life. Being physically in the area can give you a sense of how the subject might have felt and help you write their experiences more effectively.

- When researching the time period ask yourself: What were the social norms of that time? What was going on economically and politically? How did the social and political climate affect the subject?

- You may also include historical events or moments that affected the subject on the timeline. For example, maybe there was a conflict or civil war that happened during the person’s life that affected their life.
Writing the Biography

- You may end up focusing on particular areas of the person’s life. If you do this, work through a particular period in the person’s life chronologically.

- For example, you may have a thesis statement about focusing on how the person impacted the civil rights movement in America in the 1970s. You can then make sure all your content relates back to this thesis.

- Flashbacks should feel as detailed and real as present day scenes. Use your research notes and interviews with the subject to get a good sense of their past for the flashbacks.
- For example, you may jump from the person’s death in the present to a flashback to their favorite childhood memory.

- For example, you may focus on the person’s accomplishments in the civil rights movement. You may write a whole section about their contributions and participation in major civil rights marches in their hometown.

- For example, you may notice that the person’s life is patterned with moments of adversity, where the person worked hard and fought against larger forces. You can then use the theme of overcoming adversity in the biography.

- For example, you may note how you see parallels in the person’s life during the civil rights movement with your own interests in social justice. You may also commend the person for their hard work and positive impact on society.
Polishing the Biography

- Revise the biography based on feedback from others. Do not be afraid to cut or edit down the biography to suit the needs of your readers.

- Having a biography riddled with spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors can turn off your readers and result in a poor grade if you are handing in the text for a class.

- If the biography is for a class, use MLA , APA , or Chicago Style citations based on the preferences of your instructor.

Biography Help

Community Q&A
- Be careful when publishing private or embarrassing information, especially if the person is not a celebrity. You may violate their "Right of Privacy" or equivalent. Thanks Helpful 31 Not Helpful 5
- Have the sources to back up your statements about the subject's life. Untruthful written statements can lead to litigation. If it is your opinion, be clear that it is such and not fact (although you can support your opinion with facts). Thanks Helpful 16 Not Helpful 15

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://grammar.yourdictionary.com/writing/how-to-write-a-biography.html
- ↑ https://au.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-a-bio
- ↑ https://www.writersdigest.com/writing-articles/3-tips-for-writing-successful-flashbacks
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/how-to-write-bio/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ https://www.plagiarism.org/article/how-do-i-cite-sources
About This Article

Before you write a biography, gather as much information about the subject that you can from sources like newspaper articles, interviews, photos, existing biographies, and anything else you can find. Write the story of that person’s life, including as much supporting detail as you can, including information about the place and time where the person lived. Focus on major events and milestones in their life, including historical events, marriage, children, and events which would shape their path later in life. For tips from our reviewer on proofreading the biography and citing your sources, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jan 24, 2021
Did this article help you?

Janis Hendrick
Oct 10, 2018
Teresa Bradley
Sep 15, 2020
Apr 18, 2016
Latanya Foster
Apr 26, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

- Write for us
- Self-Publishing
Home → Writing
How to write a biography.
Writing biographies is a passion shared by some incredible writers. If you have decided that your next book will be a biography, you’re in good company. Some of the most famous biographers are Plutarch, Elizabeth Gaskell, and Thomas More. The following article explains how to write a biography.
Authorized or Unauthorized
An authorized biography is where the subject or their estate assists the writer and an unauthorized one is where they do not.
There are many benefits of an authorized biography. You will have access to the subject and the people who know them well; you may also have access to private letters, journals, and photographs. On the other hand, you may have to agree to share the royalties with your subject. However, It’s not always the case. This is based on negotiation. Remember that a biography will create publicity, so there is already a reward in the project for the subject.
If you can’t get authorization for your biography or don’t wish to share credit and financial rewards, consider writing an unauthorized biography. Your biography can still be written, published, and sold, although you may run into problems with the subject or their estate. There can be legal ramifications to publishing an unauthorized biography, more so if the person you’re writing about is not a public figure. As always, be wary of libel and defamation in your writing.
Research and Interview
Once you’ve got the legal stuff out of the way, you can dig into the research. You could dedicate a notebook or document to take notes and plan carefully in advance. You may benefit from a bullet journal to help you organize tasks.
Compile a list of questions you would like the answers to, and then arrange them into a more naturally-flowing interview. If you have a lot of questions, it is much better to set up multiple interviews. You will need the time to cover everything in detail, so don’t try to get it all into one session. While interviewing your subject, always consider their comfort. Ensure they have water on-hand, and let them take breaks, or finish, when they need to. You could also interview their family, friends, or colleagues, particularly if someone famous or prominent in their field knows your subject.
If your subject has a body of work behind them, you’ll need to dig into that. Read their books, watch their films, and ask questions about them. It’s also worth reading other biographies that have been written about them and find articles involving them.
Don’t forget to thank your interviewees.
Position Your Voice
The advice that it’s not about you is excellent advice as any media coverage will focus on the subject, not the author. However, it is your writing, and the authorial voice will be yours. It is acceptable to include your thoughts about something the subject did, and it can lend readability and entertainment value to the book. The book is your creative project, and you are the writer. Your subject may not understand the rules of writing as you do, and they may have their own ideas on how it should be produced, but stand your ground, but be polite.
Always keep in mind that you are writing to inform and entertain. That should be your priority, despite the added responsibility to stay true to the facts and not defame your subject.
There are many ways to structure a book, and they work for biographies too. You can write about your subject’s life chronologically (from beginning to end, in order), or you can even use the three-act structure favored by novelists. Some other methods of structuring a book are Freytag’s Pyramid , in media res (start at the end then explain how you got there), or the age-old Hero’s Journey method. There are some excellent biographies out there with creative narrative styles, but don’t try to reinvent the wheel.
However you decide to structure your biography, always start with an outline. Write up a chapter-by-chapter plan for your book, and try to keep yourself on track with it when you write. This is the best way to remain organized, and it will ensure your book reads well. An outline doesn’t have to be lengthy, although some writers choose to develop detailed outlines. A few lines per chapter works fine. An outline acts as a framework for research and to-do lists, breaking the book down into chapters.
Biographies are one of the most rewarding books to write, preserving human history for years to come. So now that you know how to write a biography, it’s time to contact your favorite role model and get started on writing one.
You May Also Like

How To Write a Short Story

How To Use Dictation Software To Write Your Book Fast

Writing Your Book Back Cover

How To Plan and Write Novels Using the Snowflake Method
Published In: Brief
How to Write a Biography (Examples & Templates)
A biography is a written account of a person’s life that details their life in chronological order. Another person usually writes this detailed account, and it contains reports of their childhood, career, major life events, relationships, and social impact. It also details their relationships with their family, children, and life accomplishments.
The best way to find out more about a popular figure is through reading their biographies, so you need to make sure you get the correct information. Before writing a biography, you need to do a lot of research and interviews to represent a person’s life accurately.
Types of Biography
A biography is the story of someone’s life as written by another writer. Most biographies of popular figures are written years, or even decades, after their deaths. Authors write biographies of popular figures due to either a lack of information on the subject or personal interest.
A biography aims to share a person’s story or highlight a part of their life.
There are different types of biographies, depending on the story. Some biographies are written true to the story, while some are written as fictional works. Biographies can give you true understanding of a person on an internal as well as external level along with a lot of life lessons.
Autobiography
An autobiography is different from a biography because it is written by the subject of the story, themselves. The author writes in the first-person narrative, and it flows step-by-step like a story of their life. Autobiographies contain personal accounts of the subject’s life, along with their perspectives and opinions on events in their life.
How To Write a Biography
Pick a subject.
Picking a subject is the first step in writing a biography. You can pick an already famous person or a relatively unknown person with a great life story. If you already have a few in mind, you can start by asking yourself some questions such as;
- What has the subject accomplished that makes them a good subject?
- Have they had an impact on society?
- Is the subject a celebrity or a well-known personality?
- Will the biography appeal to a wide audience?
Get Permission
When you pick a subject, the next thing to do is to get permission from them or their family or rights owners. Although, with some historical figures, there may not be any need for permission. Getting permission from your subject makes it easier for you to get stories to put into your book. You can get the chance to obtain additional personal stories and anecdotes that will make your book more interesting by doing so as well.
Do The Research
Research is the most important part of a biography’s process as the entire content of the book is dependent on it. Irrespective of what you know about the subject, you need to carry out as much research as possible to get the story’s facts precisely.
Biography research comes from various sources, depending on the book’s subject. Firsthand reports from family, friends, or personal accounts from the subjects are primary sources. They are usually the most accurate and reliable, and they are crucial for a biography. Secondary sources come from other sources like magazines or documentaries.
Pick a Format
Biographies come in various formats, with each of them having their pros and cons. A typical biography will start at the beginning, usually with the birth and childhood of the subject. Yet, if the biography’s theme involves a different event in their life, the author may want to explore the flashback option or one with concurrent events from different times.
Usually, biographies have a theme or a general life lesson at the center. The author’s role is to tell the subject’s story leading up to the major event.
Which-ever format you choose should place the theme at the center, with the other events detailing the journey.
Create a Timeline Of The Story
Since a biography takes place in chronological order, there needs to be a timeline of the events in the right order. The timeline should contain the key events in the subject’s life, in the order the author plans on revealing them. A great way to declutter the story and keep it interesting is to use flashbacks . This way, the author can introduce past events and explain later events excluding the element of monotony.
Add In Your Thoughts
The good thing about biographies is that you don’t have to stick to the hard facts only. As the author, you can share your opinions and emotions in writing. The author has the freedom to do this by commenting on a significant action by the subject in a manner that describes why they feel the subject may have done what they did.
The author can also include commentary on events depicted in the biography – how it was influenced society or its impact on the lives around them. Recounting these events through a different perspective can make the biography more relatable and interesting to read.
FAQ’s
Why is a biography template important.
A biography template has an outline that makes the writing easier for the author. Biography templates usually contain a sample timeline, format, and questions that provide more information about the subject. With a great biography template, you can cut your writing time in half and spend less time coming up with an outline.
How are biographies better in comparison to autobiographies
Since a different person writes biographies, they tend to be more objective and somewhat accurate than autobiographies. An autobiography tells things from the author’s perspective, so their views and perspective cloud it. Thus, a biography will likely tell a more factual story.
These are the important steps you need to take to help you write a great biography. Now, to make things easier for you, we have a free customizable autobiography and biography template that you can use to start your first book. Get the template and start writing today
What are some of the most important elements to keep in consideration while writing a biography?
Any author looking to write a biography must consider the factors below. They aren’t the only important factors, but a biography isn’t complete without them. • Date and place of their birth • Academic background • Professional expertise • Death, if deceased • Facts and anecdotes about the person • Main accomplishments • Detailed accounts of their child and adult life
Biographies tell the untold stories of some incredibly relevant people in the world. But biographies are not always strictly accurate. So, every biographer needs to follow the necessary steps to provide a biography with all the requirements.
Related Documents
- BookBub Partners Blog
Book Marketing & Publishing Tips
The BookBub Partners Blog
We love helping authors and publishers sell more books using data-driven best practices and inspiring case studies. Subscribe to get weekly book marketing ideas, publishing insights, and BookBub tips delivered to your inbox, or get started here:

The Ultimate Guide to Book Marketing
See our top posts in one comprehensive guide.

Book Marketing Tools from BookBub
See the tools available to authors and publishers.

How to Get More BookBub Followers
Read 14 ideas for getting more BookBub followers.
Writing Your Author Bio? Here Are 20 Great Examples. (Plus a Checklist!)
October 15, 2020 by Diana Urban

Writing your author bio can be a daunting task, but a well-crafted bio can help readers learn more about what makes you and your books so interesting. You should regularly maintain your bio on places like your BookBub Author Profile so fans and potential readers seeking you out can learn more about you and why they should pick up your latest book.
Stuck on what to include? While there is no one-size-fits-all formula, here are some examples of author bios we love so you can get some inspiration when crafting your own bio. We’ve also created an Author Biography Checklist with recommendations on what to include, as well as where to keep your author bio up to date online.

Download a printable checklist!
Subscribe to the BookBub Partners Blog to download this checklist as a printable PDF, and keep it handy any time you want to write or update your author bio!
DOWNLOAD NOW
1. Ramona Emerson
Ramona Emerson is a Diné writer and filmmaker originally from Tohatchi, New Mexico. She has a bachelor’s in Media Arts from the University of New Mexico and an MFA in Creative Writing from the Institute of American Indian Arts. After starting in forensic videography, she embarked upon a career as a photographer, writer, and editor. She is an Emmy nominee, a Sundance Native Lab Fellow, a Time-Warner Storyteller Fellow, a Tribeca All-Access Grantee and a WGBH Producer Fellow. In 2020, Emerson was appointed to the Governor’s Council on Film and Media Industries for the State of New Mexico. She currently resides in Albuquerque, New Mexico, where she and her husband, the producer Kelly Byars, run their production company Reel Indian Pictures. Shutter is her first novel.
Why we love it: Ramona makes a splash as a new author by detailing her extensive experience in both writing and filmmaking. Her background makes an effective setup for her debut novel about a forensic photographer.
2. Courtney Milan
Courtney Milan writes books about carriages, corsets, and smartwatches. Her books have received starred reviews in Publishers Weekly , Library Journal , and Booklist . She is a New York Times and a USA Today Bestseller. Courtney pens a weekly newsletter about tea, books, and basically anything and everything else. Sign up for it here: https://bit.ly/CourtneysTea Before she started writing romance, Courtney got a graduate degree in theoretical physical chemistry from UC Berkeley. After that, just to shake things up, she went to law school at the University of Michigan and graduated summa cum laude. Then she did a handful of clerkships. She was a law professor for a while. She now writes full-time. Courtney is represented by Kristin Nelson of the Nelson Literary Agency.
Why we love it: Courtney concisely leads with her accolades and bestseller status before diving into more personal information with a witty tone. She also includes a call-to-action for readers to sign up to Weekly Tea, one of her mailing lists.
3. Adam Silvera
Adam Silvera is the number one New York Times bestselling author of More Happy Than Not , History Is All You Left Me , They Both Die at the End , Infinity Son , Infinity Reaper , and—with Becky Albertalli— What If It’s Us . He was named a Publishers Weekly Flying Start for his debut. Adam was born and raised in the Bronx. He was a bookseller before shifting to children’s publishing and has worked at a literary development company and a creative writing website for teens and as a book reviewer of children’s and young adult novels. He is tall for no reason and lives in Los Angeles. Visit him online at www.adamsilvera.com .
Why we love it: Adam begins his bio with his bestseller accolades and a list of his popular titles. But we especially love how he also includes his previous experience in children’s literature. It’s a fantastic way an author can craft a unique and credible bio using information besides accolades or bestseller status.
4. Farrah Rochon
USA Today Bestselling author Farrah Rochon hails from a small town just west of New Orleans. She has garnered much acclaim for her Crescent City-set Holmes Brothers series and her Moments in Maplesville small town series. Farrah is a two-time finalist for the prestigious RITA Award from the Romance Writers of America and has been nominated for an RT BOOKReviews Reviewers Choice Award. In 2015, she received the Emma Award for Author of the Year. When she is not writing in her favorite coffee shop, Farrah spends most of her time reading, cooking, traveling the world, visiting Walt Disney World, and catching her favorite Broadway shows. An admitted sports fanatic, she feeds her addiction to football by watching New Orleans Saints games on Sunday afternoons. Keep in touch with Farrah via the web: Website: https://www.farrahrochon.com/ Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/farrahrochonauthor Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/FarrahRochon Instagram: https://instagram.com/farrahrochon/ Newsletter: http://bit.ly/2povjuZ Join my online Fan Club, the Rochonettes! https://www.facebook.com/groups/FarrahRochon/ Farrah’s Books In Order: The Holmes Brothers Deliver Me (Mar. 2007) Release Me (May 2008) Rescue Me (Jan. 2009) Chase Me (Jan. 2017) Trust Me (May 2017) Awaken Me (Jan. 2018) Cherish Me (Jun. 2018) Return To Me (Aug. 2019) New York Sabers Huddle With Me Tonight (Sept. 2010) I’ll Catch You (Mar. 2011) Field of Pleasure (Sept. 2011) Pleasure Rush (Mar. 2012) Bayou Dreams A Forever Kind of Love (Aug. 2012) Always and Forever (Jan. 2013) Yours Forever (Mar. 2014) Forever’s Promise (Apr. 2014) Forever With You (Feb. 2015) Stay With Me Forever (Aug. 2015) Moments in Maplesville A Perfect Holiday Fling (Nov. 2012) A Little Bit Naughty (Mar. 2013) Just A Little Taste (Jan. 2014) I Dare You! (Nov. 2014) All You Can Handle (June 2015) Any Way You Want It (Feb. 2016) Any Time You Need Me (June 2016) Standalones In Her Wildest Dreams (Jan. 2012) The Rebound Guy (July 2012) Delectable Desire (Apr. 2013) Runaway Attraction (Nov. 2013) A Mistletoe Affari (Nov. 2014) Passion’s Song (Feb. 2016) Mr. Right Next Door (Sept. 2016) Anthologies A Change of Heart (The Holiday Inn Anthology – Sept. 2008) No Ordinary Gift (Holiday Brides Anthology – Oct. 2009) Holiday Spice (Holiday Temptation Anthology – Sept. 2016) Christmas Kisses (Reissue–Contains Tuscan Nights and Second-Chance Christmas previously published by Harlequin Kimani
Why we love it: Farrah packs a lot of information into that first paragraph, elegantly describing the awards she’s received and has been nominated for. We also love how she makes it easy for readers to find her on whichever social media platform they prefer and to discover which book to start with for each series.
5. Angie Fox
New York Times bestselling author Angie Fox writes sweet, fun, action-packed mysteries. Her characters are clever and fearless, but in real life, Angie is afraid of basements, bees, and going up stairs when it is dark behind her. Let’s face it. Angie wouldn’t last five minutes in one of her books. Angie is best known for her Southern Ghost Hunter mysteries and for her Accidental Demon Slayer books. Visit her at www.angiefox.com
Why we love it: We love how Angie distinguishes herself from her characters, making herself relatable to readers. She also mentions her bestseller status and best-known works in a humble way.
6. Tiffany D. Jackson
Tiffany D. Jackson is the critically acclaimed author of Allegedly , Monday’s Not Coming , and Let Me Hear a Rhyme . A Walter Dean Myers Honor Book and Coretta Scott King–John Steptoe New Talent Award winner, she received her bachelor of arts in film from Howard University, earned her master of arts in media studies from the New School, and has over a decade in TV and film experience. The Brooklyn native still resides in the borough she loves. You can visit her at www.writeinbk.com .
Why we love it: This is an excellent example of a short, concise bio — a perfect snippet for journalists, bloggers, or event coordinators who need to grab Tiffany’s bio for their article or programming.
7. Kwame Alexander
Kwame Alexander is the New York Times Bestselling author of 32 books, including The Undefeated ; How to Read a Book ; Solo ; Swing ; Rebound , which was shortlisted for prestigious Carnegie Medal; and his Newbery medal-winning middle grade novel, The Crossover . He’s also the founding editor of Versify, an imprint that aims to Change the World One Word at a Time. Visit him at KwameAlexander.com
Why we love it: We adore how Kwame calls out his aim to “change the world one word at a time” along with a handful of his best-known books. Short and sweet!
8. Glynnis Campbell
For deals, steals, and new releases from Glynnis, click FOLLOW on this BookBub page! Glynnis Campbell is a USA Today bestselling author of over two dozen swashbuckling action-adventure historical romances, mostly set in Scotland, and a charter member of The Jewels of Historical Romance — 12 internationally beloved authors. She’s the wife of a rock star and the mother of two young adults, but she’s also been a ballerina, a typographer, a film composer, a piano player, a singer in an all-girl rock band, and a voice in those violent video games you won’t let your kids play. Doing her best writing on cruise ships, in Scottish castles, on her husband’s tour bus, and at home in her sunny southern California garden, Glynnis loves to play medieval matchmaker… transporting readers to a place where the bold heroes have endearing flaws, the women are stronger than they look, the land is lush and untamed, and chivalry is alive and well! Want a FREE BOOK? Sign up for her newsletter at https://www.glynnis.net Tag along on her latest adventures here: Website: https://www.glynnis.net Facebook: bit.ly/GCReadersClan Goodreads: bit.ly/GlynnisGoodreads Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/GlynnisCampbell Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/GlynnisCampbell Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/GlynnisCampbell BOOK LIST: The Warrior Maids of Rivenloch: THE SHIPWRECK A YULETIDE KISS LADY DANGER CAPTIVE HEART KNIGHT’S PRIZE The Warrior Daughters of Rivenloch: THE STORMING A RIVENLOCH CHRISTMAS BRIDE OF FIRE BRIDE OF ICE BRIDE OF MIST The Knights of de Ware: THE HANDFASTING MY CHAMPION MY WARRIOR MY HERO Medieval Outlaws: THE REIVER DANGER’S KISS PASSION’S EXILE DESIRE’S RANSOM Scottish Lasses: THE OUTCAST MacFARLAND’S LASS MacADAM’S LASS MacKENZIE’S LASS California Legends: THE STOWAWAY NATIVE GOLD NATIVE WOLF NATIVE HAWK
Why we love it: Like other authors, Glynnis leads with her bestseller status, but not before making sure readers know to follow her on BookBub! We like how her personality shines through in her all-caps calls to action and that she includes the characteristics of her books in a fun way so readers will know what to expect from her work.
9. Laurelin Paige
Laurelin Paige is the NY Times , Wall Street Journal , and USA Today bestselling author of the Fixed Trilogy . She’s a sucker for a good romance and gets giddy anytime there’s kissing, much to the embarrassment of her three daughters. Her husband doesn’t seem to complain, however. When she isn’t reading or writing sexy stories, she’s probably singing, watching edgy black comedy on Netflix or dreaming of Michael Fassbender. She’s also a proud member of Mensa International though she doesn’t do anything with the organization except use it as material for her bio. You can connect with Laurelin on Facebook at facebook.com/LaurelinPaige or on twitter @laurelinpaige. You can also visit her website, laurelinpaige.com , to sign up for emails about new releases. Subscribers also receive a free book from a different bestselling author every month.
Why we love it: We love Laurelin’s bio because she lets her fun personality shine through! She also includes information about a monthly giveaway she runs through her mailing list, which is enticing and unique.
10. Mia Sosa
Mia Sosa is a USA Today bestselling author of contemporary romance and romantic comedies. Her books have received starred reviews from Publishers Weekly , Kirkus Reviews , Booklist , and Library Journal , and have been praised by Cosmopolitan , The Washington Post , Buzzfeed , Entertainment Weekly , and more. Book Riot included her debut, Unbuttoning the CEO , in its list of 100 Must-Read Romantic Comedies, and Booklist recently called her “the new go-to author for fans of sassy and sexy contemporary romances.” A former First Amendment and media lawyer, Mia practiced for more than a decade before trading her suits for loungewear (okay, okay, they’re sweatpants). Now she strives to write fun and flirty stories about imperfect characters finding their perfect match. Mia lives in Maryland with her husband, their two daughters, and an adorable dog that rules them all. For more information about Mia and her books, visit www.miasosa.com .
Why we love it: This is such a well-constructed bio, with a paragraph for each (1) listing accolades and praise from trade reviews, (2) including a blurb about Mia’s overall author brand, (3) describing her previous work experience and how she became an author, and (4) sharing personal information and directing readers to where they could learn more.
11. Aiden Thomas
Aiden Thomas is a trans, Latinx, New York Times Bestselling Author with an MFA in Creative Writing from Mills College. Originally from Oakland, California, they now make their home in Portland, OR. Aiden is notorious for not being able to guess the endings of books and movies, and organizes their bookshelves by color. Their books include Cemetery Boys and Lost in the Never Woods .
Why we love it: A well-known advocate of diverse books, Aiden leads with their identity markers to connect right away with readers of similar identities. The rest of their concise bio fits information about their bestseller status, education, location, personality, and popular titles into just a few short sentences!
12. Wayne Stinnett
Wayne Stinnett is an American novelist and Veteran of the United States Marine Corps. Between those careers, he’s worked as a deckhand, commercial fisherman, divemaster, taxi driver, construction manager, and over the road truck driver, among many other things. He now lives on a sea island, in the South Carolina Lowcountry, with his wife and youngest daughter. They also have three grown children, five grand children, three dogs and a whole flock of parakeets. Stinnett grew up in Melbourne, Florida and has also lived in the Florida Keys, the Bahamas, and Cozumel, Mexico. His next dream is to one day visit and dive Cuba.
Why we love it: What better way to introduce an author of novels about travel, seafaring, and military adventures than to share his first-hand experiences! By weaving in relevant professional background and a glimpse of his home life by the sea, Wayne demonstrates deep knowledge of his subjects to his readers, as well as connecting with them on a personal level by describing his family and goals for the future.
13. June Hur
June Hur was born in South Korea and raised in Canada, except for the time when she moved back to Korea and attended high school there. She studied History and Literature at the University of Toronto. She began writing her debut novel after obsessing over books about Joseon Korea. When she’s not writing, she can be found wandering through nature or journaling at a coffee shop. June is the bestselling author of The Silence of Bones , The Forest of Stolen Girls , and The Red Palace , and currently lives in Toronto with her husband and daughter.
Why we love it: We love how June includes her background and what inspired her writing. Sharing a story’s origins is a wonderful way to meaningfully connect with readers.
14. Claire Delacroix
Bestselling author Claire Delacroix published her first medieval romance in 1993. Since then, she has published over seventy romance novels and numerous novellas, including time travel romances, contemporary romances and paranormal romances. The Beauty , part of her successful Bride Quest series, was her first book to land on the New York Times list of bestselling books. Claire has written under the name Claire Cross and continues to write as Deborah Cooke as well as Claire Delacroix. Claire makes her home in Canada with her family, a large undisciplined garden and a growing number of incomplete knitting projects. Sign up for Claire’s monthly medieval romance newsletter at: https://view.flodesk.com/pages/622ca9849b7136a9e313df83 Visit Claire’s website to find out more about her books at http://delacroix.net
Why we love it: While Claire has an extensive backlist, she succinctly describes her publishing success and subgenres. She also includes all of her pen names so readers can easily find her, no matter which name they’re looking for.
15. Vanessa Riley
Vanessa Riley writes Historical Fiction and Historical Romance (Georgian, Regency, & Victorian) featuring hidden histories, dazzling multi-culture communities, and strong sisterhoods. She promises to pull heart strings, offer a few laughs, and share tidbits of tantalizing history. This Southern, Irish, Trini (West Indies) girl holds a doctorate in mechanical engineering and a MS in industrial engineering and engineering management from Stanford University. She also earned a BS and MS in mechanical engineering from Penn State University. Yet, her love of history and lattes have overwhelmed her passion for math, leading to the publication of over 20+ titles. She loves writing on her southern porch with proper caffeine.
Why we love it: Vanessa launches into her bio by sharing the specific time periods she writes in, as well as the diverse characters and emotions her readers can look forward to, appealing directly to her ideal audience . She then shares a bit of personal info, leaving readers with an image of her in her element: writing on a porch while sipping tea.
16. April White
April White has been a film producer, private investigator, bouncer, teacher and screenwriter. She has climbed in the Himalayas, survived a shipwreck, and lived on a gold mine in the Yukon. She and her husband share their home in Southern California with two extraordinary boys and a lifetime collection of books. Her first novel, Marking Time , is the 2016 winner of the Library Journal Indie E-Book Award for YA Literature, and her contemporary romantic suspense, Code of Conduct , was a Next Generation Indie Award and RONE Award Finalist. All five books in the Immortal Descendants series are on the Amazon Top 100 lists in Time Travel Romance and Historical Fantasy. More information and her blog can be found at www.aprilwhitebooks.com .
Why we love it: April’s bio is short and sweet, but is packed with interesting information. She was a private investigator and survived a shipwreck? How can you not want to learn more about this author? She also elegantly includes her books’ status and subgenre in the last paragraph, along with a call-to-action for readers to learn more.
17. Julia Quinn
#1 New York Times bestselling author Julia Quinn loves to dispel the myth that smart women don’t read (or write) romance, and if you watch reruns of the game show The Weakest Link you might just catch her winning the $79,000 jackpot. She displayed a decided lack of knowledge about baseball, country music, and plush toys, but she is proud to say that she aced all things British and literary, answered all of her history and geography questions correctly, and knew that there was a Da Vinci long before there was a code. On December 25, 2020, Netflix premiered Bridgerton , based on her popular series of novels about the Bridgerton family. Find her on the web at www.juliaquinn.com .
Why we love it: Julia takes a unique approach, making her bio more voicey and focused on her interests. Yet she keeps it up to date, including her latest news in the last sentence (above the call-to-action).
18. Rick Mofina
USA Today bestselling author Rick Mofina is a former journalist who has interviewed murderers on death row, flown over L.A. with the LAPD and patrolled with the Royal Canadian Mounted Police near the Arctic. He’s also reported from the Caribbean, Africa and Kuwait’s border with Iraq. His books have been published in nearly 30 countries, including an illegal translation produced in Iran. His work has been praised by James Patterson, Dean Koontz, Michael Connelly, Lee Child, Tess Gerritsen, Jeffery Deaver, Sandra Brown, James Rollins, Brad Thor, Nick Stone, David Morrell, Allison Brennan, Heather Graham, Linwood Barclay, Peter Robinson, Håkan Nesser and Kay Hooper. The Crime Writers of Canada, The International Thriller Writers and The Private Eye Writers of America have listed his titles among the best in crime fiction. As a two-time winner of Canada’s Arthur Ellis Award, a four-time Thriller Award finalist and a two-time Shamus Award finalist, the Library Journal calls him, “One of the best thriller writers in the business.” Join Rick Mofina’s newsletter from his website and receive a free eBook! You can also find Rick Mofina’s new exclusive serialized thriller, The Dying Light , by subscribing to Radish Fiction com For more information please visit www.rickmofina.com https://www.facebook.com/rickmofina or follow Rick on Twitter @Rick Mofina
Why we love it: Including Rick’s first-hand experiences as a journalist lends him credibility in his genres of Crime Fiction and Thrillers. He also includes a list of well-known authors who have praised his work, and these endorsements may encourage those authors’ fans to give Rick a try. The free ebook offer effectively sweetens the deal!
19. J.T. Ellison
J.T. Ellison is the New York Times and USA Today bestselling author of more than 25 novels, and the EMMY® award winning co-host of the literary TV show A Word on Words . She also writes urban fantasy under the pen name Joss Walker. With millions of books in print, her work has won critical acclaim, prestigious awards, been optioned for television, and has been published in 28 countries. J.T. lives in Nashville with her husband and twin kittens, where she is hard at work on her next novel.
Why we love it: This is a great example of a concise bio suitable for use in any blog or publication. J.T. keeps to just the essential ingredients of a professional author bio: accolades, genres, experience, and a bit of what she’s up to today for a personal touch.
20. James S.A. Corey
James S.A. Corey is the pen name for a collaboration between Daniel Abraham and Ty Franck. James is Daniel’s middle name, Corey is Ty’s middle name, and S.A. are Daniel’s daughter’s initials. James’ current project is a series of science fiction novels called The Expanse Series. They are also the authors of Honor Among Thieves: Star Wars (Empire and Rebellion).
Why we love it: We love co-author bios that reveal how the duo came up with their pseudonym as a fun fact for readers! We also like that the reminder of this bio simply points readers straight to their buzziest works.
Want to share this post? Here are ready-made tweets:
Click to tweet: If you’re writing your author bio, these examples are so helpful! #writetip #pubtip http://bit.ly/1OSBcDO
Click to tweet: Make sure to keep your author bio updated! Here are some great bio examples, PLUS a printable checklist of what to include and where to keep it up to date. #amwriting http://bit.ly/1OSBcDO
This post was originally published on October 15 2015 and has been updated with new examples and a PDF checklist!
Free: The Ultimate Collection of Book Marketing Examples

Subscribe to the BookBub Partners Blog to get your free flipbook right away. You'll also get BookBub’s latest book marketing tips and insights delivered to your inbox each week.
About Diana Urban

- Featured Deals
- BookBub Ads
- Author Profiles
- Book Marketing Ideas
- Self-Pub Tips
- For the Press
- Privacy & Terms
- What is BookBub?
- In the News
- Free Ebooks
- Invite Your Friends
Publishers & Authors
- Partners Overview
- Submit New Deal
- Partner Dashboard
- Claim an Author Profile
- Partner FAQ
© 2021 BookBub. All rights reserved.

How to Write a Book From Start to Finish: A Proven Guide
So you want to write a book. Becoming an author can change your life—not to mention give you the ability to impact thousands, even millions, of people.
But writing a book isn’t easy. As a 21-time New York Times bestselling author, I can tell you: It’s far easier to quit than to finish.
You’re going to be tempted to give up writing your book when you run out of ideas, when your own message bores you, when you get distracted, or when you become overwhelmed by the sheer scope of the task.
But what if you knew exactly:
- Where to start…
- What each step entails…
- How to overcome fear, procrastination, a nd writer’s block…
- And how to keep from feeling overwhelmed?
You can write a book—and more quickly than you might think, because these days you have access to more writing tools than ever.
The key is to follow a proven, straightforward, step-by-step plan .
My goal here is to offer you that book-writing plan.
I’ve used the techniques I outline below to write more than 200 books (including the Left Behind series) over the past 50 years. Yes, I realize writing over four books per year on average is more than you may have thought humanly possible.
But trust me—with a reliable blueprint, you can get unstuck and finally write your book .
This is my personal approach on how to write a book. I’m confident you’ll find something here that can change the game for you. So, let’s jump in.
- How to Write a Book From Start to Finish
Part 1: Before You Begin Writing Your Book
- Establish your writing space.
- Assemble your writing tools.
Part 2: How to Start Writing a Book
- Break the project into small pieces.
- Settle on your BIG idea.
- Construct your outline.
- Set a firm writing schedule.
- Establish a sacred deadline.
- Embrace procrastination (really!).
- Eliminate distractions.
- Conduct your research.
- Start calling yourself a writer.
Part 3: The Book-Writing Itself
- Think reader-first.
- Find your writing voice.
- Write a compelling opener.
- Fill your story with conflict and tension.
- Turn off your internal editor while writing the first draft.
- Persevere through The Marathon of the Middle.
- Write a resounding ending.
Part 4: Editing Your Book
- Become a ferocious self-editor.
- Find a mentor.
- Part 5: Publishing Your Book
- Decide on your publishing avenue.
- Properly format your manuscript.
- Set up and grow your author platform.
- Pursue a Literary Agent
- Writing Your Query Letter
- Part One: Before You Begin Writing Your Book
You’ll never regret—in fact, you’ll thank yourself later—for investing the time necessary to prepare for such a monumental task.
You wouldn’t set out to cut down a huge grove of trees with just an axe. You’d need a chain saw, perhaps more than one. Something to keep them sharp. Enough fuel to keep them running.
You get the picture. Don’t shortcut this foundational part of the process.
Step 1. Establish your writing space.
To write your book, you don’t need a sanctuary. In fact, I started my career o n my couch facing a typewriter perched on a plank of wood suspended by two kitchen chairs.
What were you saying about your setup again? We do what we have to do.
And those early days on that sagging couch were among the most productive of my career.
Naturally, the nicer and more comfortable and private you can make your writing lair (I call mine my cave), the better.

Real writers can write anywhere .
Some authors write their books in restaurants and coffee shops. My first full time job was at a newspaper where 40 of us clacked away on manual typewriters in one big room—no cubicles, no partitions, conversations hollered over the din, most of my colleagues smoking, teletype machines clattering.
Cut your writing teeth in an environment like that, and anywhere else seems glorious.
Step 2. Assemble your writing tools.
In the newspaper business, there was no time to hand write our stuff and then type it for the layout guys. So I have always written at a keyboard and still write my books that way.
Most authors do, though some hand write their first drafts and then keyboard them onto a computer or pay someone to do that.
No publisher I know would even consider a typewritten manuscript, let alone one submitted in handwriting.
The publishing industry runs on Microsoft Word, so you’ll need to submit Word document files. Whether you prefer a Mac or a PC, both will produce the kinds of files you need.
And if you’re looking for a musclebound electronic organizing system, you can’t do better than Scrivener . It works well on both PCs and Macs, and it nicely interacts with Word files.
Just remember, Scrivener has a steep learning curve, so familiarize yourself with it before you start writing.
Scrivener users know that taking the time to learn the basics is well worth it.
Tons of other book-writing tools exist to help you. I’ve included some of the most well-known in my blog po st on here (for software) and here (for writing tools) fo r your reference.
So, what else do you need?
If you are one who handwrites your first drafts, don’t scrimp on paper, pencils, or erasers.
Don’t shortchange yourself on a computer either. Even if someone else is keyboarding for you, you’ll need a computer for research and for communicating with potential agents, edi tors, publishers.
Get the best computer you can afford, the latest, the one with the most capacity and speed.
Try to imagine everything you’re going to need in addition to your desk or table, so you can equip yourself in advance and don’t have to keep interrupting your work to find things like:
- Paper clips
- Pencil holders
- Pencil sharpeners
- Printing paper
- Paperweight
- Tape dispensers
- Cork or bulletin boards
- Reference works
- Space heaters
- Beverage mugs
- You name it
- Last, but most crucial, get the best, most ergonomic chair you can afford.
If I were to start my career again with that typewriter on a plank, I would not sit on that couch. I’d grab another straight-backed kitchen chair or something similar and be proactive about my posture and maintaining a healthy spine.
There’s nothing worse than trying to be creative and immerse yourself in writing while you’re in agony . The chair I work in today cost more than my first car!

If you’ve never used some of the items I listed above and can’t imagine needing them, fine. But make a list of everything you know you’ll need so when the actual writing begins, you’re already equipped.
As you grow as a writer and actually start making money at it, you can keep upgrading your writing space.
Where I work now is light years from where I started. But the point is, I didn’t wait to start writing until I could have a great spot in which to do it.
- Part Two: How to Start Writing a Book
Step 1. Break your book into small pieces.
Writing a book feels like a colossal project, because it is! Bu t your manuscript w ill be made up of many small parts .
An old adage says that the way to eat an elephant is one bite at a time .
Try to get your mind off your book as a 400-or-so-page monstrosity.
It can’t be written all at once any more than that proverbial elephant could be eaten in a single sitting.
See your book for what it is: a manuscript made up of sentences, paragraphs, pages. Those pages will begin to add up, and though after a week you may have barely accumulated double digits, a few months down the road you’ll be into your second hundred pages.
So keep it simple.
Start by distilling you r big book idea from a page or so to a single sentence— your premise . The more specific that one-sentence premise, the more it will keep you focused while you’re writing.
But let’s not get ahead of ourselves. Before you can turn your big idea into one sentence, which can then b e expanded to an outline, you have to settle on exactly what that big idea is.
Step 2. Settle on your BIG idea.
To be book-worthy, your idea has to be killer.
You need to write something about which you’re passionate , something that gets you up in the morning, draws you to the keyboard, and keeps you there. It should excite not only you, but also anyone you tell about it.
I can’t overstate the importance of this.
If you’ve tried and failed to finish your book before—maybe more than once—it could be that the basic premise was flawed. Maybe it was worth a blog post or an article but couldn’t carry an entire book.
Think The Hunger Games , Harry Potter , or How to Win Friends and Influence People . The market is crowded, the competition fierce. There’s no more room for run-of-the-mill ideas. Your premise alone should make readers salivate.
Go for the big concept book.
How do you know you’ve got a winner? Does it have legs? In other words, does it stay in your mind, growing and developing every time you think of it?
Run it past loved ones and others you trust.
Does it raise eyebrows? Elicit Wows? Or does it result in awkward silences?
The right concept simply works, and you’ll know it when you land on it. Most importantly, your idea must capture you in such a way that you’re compelled to write it . Otherwise you will lose interest halfway through and never finish.
Step 3. Construct your outline.
Writing your book without a clear vision of where you’re going usually ends in disaster.
Even if you ’re writing a fiction book an d consider yourself a Pantser* as opposed to an Outliner , you need at least a basic structure.
[*Those of us who write by the seat of our pants and, as Stephen King advises, pu t interesting characters i n difficult situations and write to find out what happens]
You don’t have to call it an outline if that offends your sensibilities. But fashion some sort of a directional document that provides structure for your book and also serves as a safety net.
If you get out on that Pantser highwire and lose your balance, you’ll thank me for advising you to have this in place.
Now if you’re writing a nonfiction book, there’s no substitute for an outline .
Potential agents or publishers require this in your proposal. T hey want to know where you’re going, and they want to know that you know. What do you want your reader to learn from your book, and how will you ensure they learn it?
Fiction or nonfiction, if you commonly lose interest in your book somewhere in what I call the Marathon of the Middle, you likely didn’t start with enough exciting ideas .
That’s why and outline (or a basic framework) is essential. Don’t even start writing until you’re confident your structure will hold up through the end.
You may recognize this novel structure illustration.
Did you know it holds up—with only slight adaptations—for nonfiction books too ? It’s self-explanatory for novelists; they list their plot twists and developments and arrange them in an order that best serves to increase tension .
What separates great nonfiction from mediocre? The same structure!
Arrange your points and evidence in the same way so you’re setting your reader up for a huge payoff, and then make sure you deliver.
If your nonfiction book is a memoir ( more scene based ), an autobiography ( more fact-based ), or a biography, structure it like a novel and you can’t go wrong.
But even if it’s a straightforward how-to book, stay as close to this structure as possible, and you’ll see your manuscript come alive.
Make promises early, triggering your reader to anticipate fresh ideas, secrets, inside information, something major that will make him thrilled with the finished product.

While a nonfiction book may not have as much action or dialogue or character development as a novel, you can inject tension by showing where people have failed before and how your reader can succeed.
You can even make the how-to project look impossible until you pay off that setup with your unique solution.
Keep your outline to a single page for now. But make sure every major point is represented, so you’ll always know where you’re going.
And don’t worry if you’ve forgotten the basics of classic outlining or have never felt comfortable with the concept.
Your outline must serve you. If that means Roman numerals and capital and lowercase letters and then Arabic numerals, you can certainly fashion it that way. But if you just want a list of sentences that synopsize your idea, that’s fine too.
Simply start with your working title, then your premise, then—for fiction, list all the major scenes that fit into the rough structure above.
For nonfiction, try to come up with chapter titles and a sentence or two of what each chapter will cover.
Once you have your one-page outline, remember it is a fluid document meant to serve you and your book. Expand it, change it, play with it as you see fit—even during the writing process .
Step 4. Set a firm writing schedule.
Ideally, you want to schedule at least six hours per week to write your book.
That may consist of three sessions of two hours each, two sessions of three hours, or six one-hour sessions—whatever works for you.
I recommend a regular pattern (same times, same days) that can most easily become a habit. But if that’s impossible, just make sure you carve out at least six hours so you can see real progress.
Having trouble finding the time to write a book? News flash—you won’t find the time. You have to make it.
I used the phrase carve out above for a reason. That’s what it takes.
Something in your calendar will likely have to be sacrificed in the interest of writing time .
Make sure it’s not your family—they should always be your top priority. Never sacrifice your family on the altar of your writing career.
But beyond that, the truth is that we all find time for what we really want to do.
Many writers insist they have no time to write, but they always seem to catch the latest Netflix original series, or go to the next big Hollywood feature. They enjoy concerts, parties, ball games, whatever.
How important is it to you to finally write your book? What will you cut from your calendar each week to ensure you give it the time it deserves?
- A favorite TV show?
- An hour of sleep per night? (Be careful with this one; rest is crucial to a writer.)
Successful writers make time to write.
When writing becomes a habit, you’ll be on your way.
Step 5. Establish a sacred deadline.
Without deadlines, I rarely get anything done. I need that motivation.
Admittedly, my deadlines are now established in my contracts from publishers.
If you’re writing your first book, you probably don’t have a contract yet. To ensure you finish your book, set your own deadline—then consider it sacred .
Tell your spouse or loved one or trusted friend. Ask that they hold you accountable.
Now determine—and enter in your calendar—the number of pages you need to produce per writing session to meet your deadline. If it proves unrealistic, change the deadline now.
If you have no idea how many pages or words you typically produce per session, you may have to experiment before you finalize those figures.
Say you want to finish a 400-page manuscript by this time next year.
Divide 400 by 50 weeks (accounting for two off-weeks), and you get eight pages per week.
Divide that by your typical number of writing sessions per week and you’ll know how many pages you should finish per session.
Now is the time to adjust these numbers, while setting your deadline and determining your pages per session.
Maybe you’d rather schedule four off weeks over the next year. Or you know your book will be unusually long.
Change the numbers to make it realistic and doable, and then lock it in. Remember, your deadline is sacred.
Step 6. Embrace procrastination (really!).
You read that right. Don’t fight it; embrace it.
You wouldn’t guess it from my 200+ published books, but I’m the king of procrastinators .
Don’t be. So many authors are procrastinators that I’ve come to wonder if it’s a prerequisite.
The secret is to accept it and, in fact, schedule it.
I quit fretting and losing sleep over procrastinating when I realized it was inevitable and predictable, and also that it was productive.
Sound like rationalization?
Maybe it was at first. But I learned that while I’m putting off the writing, my subconscious is working on my book. It’s a part of the process. When you do start writing again, you’ll enjoy the surprises your subconscious reveals to you.
So, knowing procrastination is coming, book it on your calendar .
Take it into account when you’re determining your page quotas. If you have to go back in and increase the number of pages you need to produce per session, do that (I still do it all the time).
But—and here’s the key—you must never let things get to where that number of pages per day exceeds your capacity.
It’s one thing to ratchet up your output from two pages per session to three. But if you let it get out of hand, you’ve violated the sacredness of your deadline.
How can I procrastinate and still meet more than 190 deadlines?
Because I keep the deadlines sacred.
Step 7. Eliminate distractions to stay focused.
Are you as easily distracted as I am?
Have you found yourself writing a sentence and then checking your email? Writing another and checking Facebook? Getting caught up in the pictures of 10 Sea Monsters You Wouldn’t Believe Actually Exist?
Then you just have to check out that precious video from a talk show where the dad surprises the family by returning from the war.
That leads to more and more of the same. Once I’m in, my writing is forgotten, and all of a sudden the day has gotten away from me.
The answer to these insidious timewasters?
Look into these apps that allow you to block your email, social media, browsers, game apps, whatever you wish during the hours you want to write. Some carry a modest fee, others are free.
- Freedom app
- FocusWriter
Step 8. Conduct your research.
Yes, research is a vital part of the process , whether you’re writing fiction or nonfiction.
Fiction means more than just making up a story.
Your details and logic and technical and historical details must be right for your novel to be believable.
And for nonfiction, even if you’re writing about a subject in which you’re an expert—as I’m doing here—getting all the facts right will polish your finished product.
In fact, you’d be surprised at how many times I’ve researched a fact or two while writing this blog post alone.

The last thing you want is even a small mistake due to your lack of proper research.
Regardless the detail, trust me, you’ll hear from readers about it.
Your credibility as an author and an expert hinges on creating trust with your reader . That dissolves in a hurry if you commit an error.
My favorite research resources:
- World Almanacs : These alone list almost everything you need for accurate prose: facts, data, government information, and more. For my novels, I often use these to come up with ethnically accurate character names.
- The Merriam-Webster Thesaurus : The online version is great, because it’s lightning fast. You couldn’t turn the pages of a hard copy as quickly as you can get where you want to onscreen. One caution: Never let it be obvious you’ve consulted a thesaurus. You’re not looking for the exotic word that jumps off the page. You’re looking for that common word that’s on the tip of your tongue.
- WorldAtlas.com : Here you’ll find nearly limitless information about any continent, country, region, city, town, or village. Names, monetary units, weather patterns, tourism info, and even facts you wouldn’t have thought to search for. I get ideas when I’m digging here, for both my novels and my nonfiction books.
Step 9. Start calling yourself a writer.
Your inner voice may tell you, “You’re no writer and you never will be. Who do you think you are, trying to write a book?”
That may be why you’ve stalled at writing your book in the past .
But if you’re working at writing, studying writing, practicing writing, that makes you a writer. Don’t wait till you reach some artificial level of accomplishment before calling yourself a writer.
A cop in uniform and on duty is a cop whether he’s actively enforced the law yet or not. A carpenter is a carpenter whether he’s ever built a house.
Self-identify as a writer now and you’ll silence that inner critic —who, of course, is really you.
Talk back to yourself if you must. It may sound silly, but acknowledging yourself as a writer can give you the confidence to keep going and finish your book.
Are you a writer? Say so.
- Part Three: The Book-Writing Itself
Step 1. Think reader-first.
This is so important that that you should write it on a sticky note and affix it to your monitor so you’re reminded of it every time you write.
Every decision you make about your manuscript must be run through this filter.
Not you-first, not book-first, not editor-, agent-, or publisher-first. Certainly not your inner circle- or critics-first.
Reader-first, last, and always .
If every decision is based on the idea of reader-first, all those others benefit anyway.
When fans tell me they were moved by one of my books, I think back to this adage and am grateful I maintained that posture during the writing.
Does a scene bore you? If you’re thinking reader-first, it gets overhauled or deleted.
Where to go, what to say, what to write next? Decide based on the reader as your priority.
Whatever your gut tells you your reader would prefer, that’s your answer.
Whatever will intrigue him, move him, keep him reading, those are your marching orders.
So, naturally, you need to know your reader. Rough age? General interests? Loves? Hates? Attention span?
When in doubt, look in the mirror .
The surest way to please your reader is to please yourself. Write what you would want to read and trust there is a broad readership out there that agrees.
Step 2. Find your writing voice.
Discovering your voice is nowhere near as complicated as some make it out to be.
You can find yours by answering these quick questions :
- What’s the coolest thing that ever happened to you?
- Who’s the most important person you told about it?
- What did you sound like when you did?
- That’s your writing voice. It should read the way you sound at your most engaged.
That’s all there is to it.
If you write fiction and the narrator of your book isn’t you, go through the three-question exercise on the narrator’s behalf—and you’ll quickly master the voice.
Here’s a blog I posted that’ll walk you through the process .
Step 3. Write a compelling opener.
If you’re stuck because of the pressure of crafting the perfect opening line for your book, you’re not alone.
And neither is your angst misplaced.
This is not something you should put off and come back to once you’ve started on the rest of the first chapter.

Oh, it can still change if the story dictates that. But settling on a good one will really get you off and running.
It’s unlikely you’ll write a more important sentence than your first one , whether you’re writing fiction or nonfiction. Make sure you’re thrilled with it and then watch how your confidence—and momentum—soars.
Most great first lines fall into one of these categories:
1. Surprising
Fiction : “It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen.” —George Orwell, Nineteen Eighty-Four
Nonfiction : “By the time Eustace Conway was seven years old, he could throw a knife accurately enough to nail a chipmunk to a tree.” —Elizabeth Gilbert, The Last American Man
2. Dramatic Statement
Fiction : “They shoot the white girl first.” —Toni Morrison, Paradise
Nonfiction : “I was five years old the first time I ever set foot in prison.” —Jimmy Santiago Baca, A Place to Stand
3. Philosophical
Fiction : “Happy families are all alike; every unhappy family is unhappy in its own way.” —Leo Tolstoy, Anna Karenina
Nonfiction : “It’s not about you.” —Rick Warren, The Purpose Driven Life
Fiction : “When I finally caught up with Abraham Trahearne, he was drinking beer with an alcoholic bulldog named Fireball Roberts in a ramshackle joint just outside of Sonoma, California, drinking the heart right out of a fine spring afternoon. —James Crumley, The Last Good Kiss
Nonfiction : “The village of Holcomb stands on the high wheat plains of western Kansas, a lonesome area that other Kansans call ‘out there.’” —Truman Capote, In Cold Blood
Great opening lines from other classics may give you ideas for yours. Here’s a list of famous openers .
Step 4. Fill your story with conflict and tension.
Your reader craves conflict, and yes, this applies to nonfiction readers as well.
In a novel, if everything is going well and everyone is agreeing, your reader will soon lose interest and find something else to do.
Are two of your characters talking at the dinner table? Have one say something that makes the other storm out.
Some deep-seeded rift in their relationship has surfaced—just a misunderstanding, or an injustice?
Thrust people into conflict with each other .
That’ll keep your reader’s attention.
Certain nonfiction genres won’t lend themselves to that kind of conflict, of course, but you can still inject tension by setting up your reader for a payoff in later chapters. Check out some of the current bestselling nonfiction works to see how writers accomplish this.
Somehow they keep you turning those pages, even in a simple how-to title.
Tension is the secret sauce that will propel your reader through to the end .
And sometimes that’s as simple as implying something to come.
Step 5. Turn off your internal editor while writing the first draft.
Many of us perfectionists find it hard to write a first draft—fiction or nonfiction—without feeling compelled to make every sentence exactly the way we want it.
That voice in your head that questions every word, every phrase, every sentence, and makes you worry you’re being redundant or have allowed cliches to creep in—well, that’s just your editor alter ego.
He or she needs to be told to shut up .

This is not easy.
Deep as I am into a long career, I still have to remind myself of this every writing day. I cannot be both creator and editor at the same time. That slows me to a crawl, and my first draft of even one brief chapter could take days.
Our job when writing that first draft is to get down the story or the message or the teaching—depending on your genre.
It helps me to view that rough draft as a slab of meat I will carve tomorrow .
I can’t both produce that hunk and trim it at the same time.
A cliche, a redundancy, a hackneyed phrase comes tumbling out of my keyboard, and I start wondering whether I’ve forgotten to engage the reader’s senses or aimed for his emotions.
That’s when I have to chastise myself and say, “No! Don’t worry about that now! First thing tomorrow you get to tear this thing up and put it back together again to your heart’s content!”
Imagine yourself wearing different hats for different tasks , if that helps—whatever works to keep you rolling on that rough draft. You don’t need to show it to your worst enemy or even your dearest love. This chore is about creating. Don’t let anything slow you down.
Some like to write their entire first draft before attacking the revision. As I say, whatever works.
Doing it that way would make me worry I’ve missed something major early that will cause a complete rewrite when I discover it months later. I alternate creating and revising.
The first thing I do every morning is a heavy edit and rewrite of whatever I wrote the day before. If that’s ten pages, so be it. I put my perfectionist hat on and grab my paring knife and trim that slab of meat until I’m happy with every word.
Then I switch hats, tell Perfectionist Me to take the rest of the day off, and I start producing rough pages again.
So, for me, when I’ve finished the entire first draft, it’s actually a second draft because I have already revised and polished it in chunks every day.
THEN I go back through the entire manuscript one more time, scouring it for anything I missed or omitted, being sure to engage the reader’s senses and heart, and making sure the whole thing holds together.
I do not submit anything I’m not entirely thrilled with .
I know there’s still an editing process it will go through at the publisher, but my goal is to make my manuscript the absolute best I can before they see it.
Compartmentalize your writing vs. your revising and you’ll find that frees you to create much more quickly.
Step 6. Persevere through The Marathon of the Middle.
Most who fail at writing a book tell me they give up somewhere in what I like to call The Marathon of the Middle.
That’s a particularly rough stretch for novelists who have a great concept, a stunning opener, and they can’t wait to get to the dramatic ending. But they bail when they realize they don’t have enough cool stuff to fill the middle.
They start padding, trying to add scenes just for the sake of bulk, but they’re soon bored and know readers will be too.
This actually happens to nonfiction writers too.
The solution there is in the outlining stage , being sure your middle points and chapters are every bit as valuable and magnetic as the first and last.
If you strategize the progression of your points or steps in a process—depending on nonfiction genre—you should be able to eliminate the strain in the middle chapters.
For novelists, know that every book becomes a challenge a few chapters in. The shine wears off, keeping the pace and tension gets harder, and it’s easy to run out of steam.
But that’s not the time to quit. Force yourself back to your structure, come up with a subplot if necessary, but do whatever you need to so your reader stays engaged.
Fiction writer or nonfiction author, The Marathon of the Middle is when you must remember why you started this journey in the first place.
It isn’t just that you want to be an author. You have something to say. You want to reach the masses with your message.
Yes, it’s hard. It still is for me—every time. But don’t panic or do anything rash, like surrendering. Embrace the challenge of the middle as part of the process. If it were easy, anyone could do it.
Step 7. Write a resounding ending.
This is just as important for your nonfiction book as your novel. It may not be as dramatic or emotional, but it could be—especially if you’re writing a memoir.
But even a how-to or self-help book needs to close with a resounding thud, the way a Broadway theater curtain meets the floor .
How do you ensure your ending doesn’t fizzle ?
- Don’t rush it . Give readers the payoff they’ve been promised. They’ve invested in you and your book the whole way. Take the time to make it satisfying.
- Never settle for close enough just because you’re eager to be finished. Wait till you’re thrilled with every word, and keep revising until you are.
- If it’s unpredictable, it had better be fair and logical so your reader doesn’t feel cheated. You want him to be delighted with the surprise, not tricked.
- If you have multiple ideas for how your book should end, go for the heart rather than the head, even in nonfiction. Readers most remember what moves them.
- Part Four: Rewriting Your Book
Step 1. Become a ferocious self-editor.
Agents and editors can tell within the first two pages whether your manuscript is worthy of consideration. That sounds unfair, and maybe it is. But it’s also reality, so we writers need to face it.
How can they often decide that quickly on something you’ve devoted months, maybe years, to?
Because they can almost immediately envision how much editing would be required to make those first couple of pages publishable. If they decide the investment wouldn’t make economic sense for a 300-400-page manuscript, end of story.
Your best bet to keep an agent or editor reading your manuscript?
You must become a ferocious self-editor. That means:
- Omit needless words
- Choose the simple word over one that requires a dictionary
- Avoid subtle redundancies , like “He thought in his mind…” (Where else would someone think?)
- Avoid hedging verbs like almost frowned, sort of jumped, etc.
- Generally remove the word that —use it only when absolutely necessary for clarity
- Give the reader credit and resist the urge to explain , as in, “She walked through the open door.” (Did we need to be told it was open?)
- Avoid too much stage direction (what every character is doing with every limb and digit)
- Avoid excessive adjectives
- S how, don’t tell
- And many more
For my full list and how to use them, click here . (It’s free.)
When do you know you’re finished revising? When you’ve gone from making your writing better to merely making it different. That’s not always easy to determine, but it’s what makes you an author.
Step 2. Find a mentor.
Get help from someone who’s been where you want to be.
Imagine engaging a mentor who can help you sidestep all the amateur pitfalls and shave years of painful trial-and-error off your learning curve.
Just make sure it’s someone who really knows the writing and publishing world. Many masquerade as mentors and coaches but have never really succeeded themselves.
Look for someone widely-published who knows how to work with agents, editors, and publishers .
There are many helpful mentors online . I teach writers through this free site, as well as in my members-only Writers Guild .
Step 1. Decide on your publishing avenue.
In simple terms, you have two options when it comes to publishing your book:
1. Traditional publishing
Traditional publishers take all the risks. They pay for everything from editing, proofreading, typesetting, printing, binding, cover art and design, promotion, advertising, warehousing, shipping, billing, and paying author royalties.
2. Self-publishing
Everything is on you. You are the publisher, the financier, the decision-maker. Everything listed above falls to you. You decide who does it, you approve or reject it, and you pay for it. The term self-publishing is a bit of a misnomer, however, because what you’re paying for is not publishing, but printing.
Both avenues are great options under certain circumstances.
Not sure which direction you want to take? Click here to read my in-depth guide to publishing a book. It’ll show you the pros and cons of each, what each involves, and my ultimate recommendation.
Step 2: Properly format your manuscript.
Regardless whether you traditionally or self-publish your book, proper formatting is critical.
Because poor formatting makes you look like an amateur .
Readers and agents expect a certain format for book manuscripts, and if you don’t follow their guidelines, you set yourself up for failure.
Best practices when formatting your book:
- Use 12-point type
- Use a serif font; the most common is Times Roman
- Double space your manuscript
- No extra space between paragraphs
- Only one space between sentences
- Indent each paragraph half an inch (setting a tab, not using several spaces)
- Text should be flush left and ragged right, not justified
- If you choose to add a line between paragraphs to indicate a change of location or passage of time, center a typographical dingbat (like ***) on the line
- Black text on a white background only
- One-inch margins on the top, bottom, and sides (the default in Word)
- Create a header with the title followed by your last name and the page number. The header should appear on each page other than the title page.
If you need help implementing these formatting guidelines, click here to read my in-depth post on formatting your manuscript.
Step 3. Set up your author website and grow your platform.
All serious authors need a website. Period.
Because here’s the reality of publishing today…
You need an audience to succeed.
If you want to traditionally publish, agents and publishers will Google your name to see if you have a website and a following.
If you want to self-publish, you need a fan base.
And your author website serves as a hub for your writing, where agents, publishers, readers, and fans can learn about your work.
Don’t have an author website yet? Click here to read my tutorial on setting this up.
Step 4. Pursue a Literary Agent.
There remain a few traditional publishers (those who pay you and take the entire financial risk of publishing your book rather than the other way around) who accept unsolicited submissions, but I do NOT recommend going that route.
Your submission will likely wind up in what is known in the business as the slush pile. That means some junior staff member will be assigned to get to it when convenient and determine whether to reject it out of hand (which includes the vast majority of the submissions they see) or suggest the publisher’s editorial board consider it.
While I am clearly on record urging you to exhaust all your efforts to traditionally publish before resorting to self-publishing (in other words, paying to be printed), as I say, I do not recommend submitting unsolicited material even to those publishers who say they accept such efforts.
Even I don’t try to navigate the publishing world by myself, despite having been an author, an editor, a publisher, and a writing coach over the last 50 years.
That’s why I have an agent and you need one too.
Many beginning writers naturally wonder why they should share any of their potential income with an agent (traditionally 15%). First, they don’t see any of that income unless you’re getting your 85% at the same time. And second, everyone I know in the business is happy to have someone in their corner, making an agent a real bargain.
I don’t want to have to personally represent myself and my work. I want to stay in my creative lane and let a professional negotiate every clause of the contract and win me the best advance and rights deal possible.
Once under contract, I work directly with the publishing house’s editor and proofreader, but I leave the financial business to my agent.
Ultimately, an agent’s job is to protect your rights and make you money. They profit only when you do.
That said, landing an agent can be as difficult and painstaking as landing a publisher. They know the market, they know the editors, they know what publishers want, and they can advise you how to put your best foot forward.
But how do you know who to trust? Credible, trustworthy agents welcome scrutiny. If you read a book in your genre that you like, check the Acknowledgments page for the agent’s name. If the author thinks enough of that person to mention them glowingly, that’s a great endorsement.
If you’re writing in the inspirational market, peruse agents listed in The Christian Writer’s Market Guide . If you’re writing for the general market, try The Writer’s Market . If you know any published authors, ask about their agents.
The guides that list agents also include what they’re looking for, what they specialize in, and sometimes even what they’re not interested in. Study these to determine potential agents who ply their trade in your genre. Visit their websites for their submission guidelines, and follow these to a T.
They may ask for a query letter, a synopsis, a proposal, or even sample chapters. Be sure not to send more or less than they suggest.
The best, and most logical place to start is by sending them a query letter. Query simply means question, and in essence the question your letter asks is whether you may send them more.
Step 5: Writing Your Query Letter.
It’s time to move from author to salesperson.
Your query letter will determine whether a literary agent asks to see more, sends you a cordial form letter to let you down easy, or simply doesn’t respond.
Sadly, many agents stipulate on their websites that if you hear nothing after a certain number of weeks, you should take that as an indication that they’re not interested. Frankly, to me, this is frustrating to the writer and lazy on the part of the agent. Surely, in this technological age, it should be easy to hit one button and send a note to someone who might otherwise wonder if the query reached the agent at all.
But that’s the reality we deal with.
So, the job of your one-page single-spaced email letter is to win a response—best case scenario: an invitation to send more: a proposal or even the manuscript.
Basically, you’re selling yourself and your work. Write a poor query letter and an agent will assume your book is also poorly written.
Without being gimmicky or cute, your letter must intrigue an agent.
Your query letter should:
- Be addressed to a specific person (not to the staff of the agency or “To Whom It May Concern”)*
- Present your book idea simply
- Evidence your style
- Show you know who your readers are
- Clarify your qualifications
- Exhibit flexibility and professionalism
*If you see a list of agents in a firm, choose one from the middle or bottom of the list. It could be that they get less personal mail than the person whose name is on the door. Who knows? That you single them out may make them see your query in a more favorable light.
For some great advice on writing a query letter, check this out: https://janefriedman.com/query-letters/
- You Have What It Takes to Write a Book
Writing a book is a herculean task, but that doesn’t mean it can’t be done.
You can do this .
Take it one step at a time and vow to stay focused. And who knows, maybe by this time next year you’ll be holding a published copy of your book. :)
I’ve created an exclusive writing guide called How to Maximize Your Writing Time that will help you stay on track and finish writing your book.
Get your FREE copy by clicking the button below.

Are You Making This #1 Amateur Writing Mistake?

Faith-Based Words and Phrases

What You and I Can Learn From Patricia Raybon

Before you go, be sure to grab my FREE guide:
How to Write a Book: Everything You Need to Know in 20 Steps
Just tell me where to send it:

Enter your email to instantly access the free PDF version of How to Write a Book: Everything You Need to Know in 20 Steps .

Enter your email to instantly access my ultimate guide:
How to maximize your writing time.
Suzanne Collins
American writer Suzanne Collins is the author of the best-selling The Hunger Games series and The Underland Chronicles .

1962-present
Latest News: Suzanne Collins Writing New Hunger Games Book
Author Suzanne Collins is expanding The Hunger Games universe.
The new title is set 40 years after the events of the most recent book in the series, The Ballad of Songbirds and Snakes , and focuses on themes of misinformation and government influence. “I was inspired by David Hume’s idea of implicit submission and, in his words, ‘the easiness with which the many are governed by the few,’” Collins said in a statement. “The story also lent itself to a deeper dive into the use of propaganda and the power of those who control the narrative. The question ‘Real or not real?’ seems more pressing to me every day.”
Quick Facts
Books: the hunger games and more, personal life, suzanne collins net worth, who is suzanne collins.
Suzanne Collins is an American author who published her debut book, Gregor the Overlander , the first of the five-part The Underland Chronicles , in 2003. Five years later, in 2008, her first book of The Hunger Games series was published. The best-selling trilogy was adapted into a blockbuster film series starring Jennifer Lawrence as Katniss Everdeen and later expanded to include a prequel book and film, The Ballad of Songbirds of Snakes , and a newly announced fifth novel in 2025.
FULL NAME: Suzanne Collins BORN: August 10, 1962 BIRTHPLACE: Hartford, Connecticut HUSBAND: Charles Pryor (m. 1992) CHILDREN: Charlie and Isabel ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Leo
The youngest of four children, Suzanne Collins was born on August 10, 1962, in Hartford, Connecticut. The daughter of an Air Force officer, Michael J. Collins, and his wife Jane, Suzanne moved considerably during her childhood, living in places like New York City and Brussels.
For the Collins family, history was a critical topic. Much of that was driven by Collins’ father, who taught history at the college level and was open with his kids about his military experience, including his deployment to Vietnam.
“I believe he felt a great responsibility and urgency about educating his children about war,” Collins said. “He would take us frequently to places like battlefields and war monuments. It would start back with whatever had precipitated the war and moved up through the battlefield you were standing in and through that and after that. It was a very comprehensive tour guide experience. So throughout our lives, we basically heard about war.”
Eventually, Collins and her family ended up in the South, where she graduated high school from the Alabama School of Fine Arts in 1980. Collins then enrolled at Indiana University, graduating in 1985 with a double major in theater and telecommunications. She then went on to earn a master’s degree in dramatic writing from New York University.
After graduating, Collins moved into television, writing for several children’s television programs, including Clarissa Explains It All and Little Bear . Her work for those shows soon caught the notice of James Proimos, creator of the WB children’s program Generation O! , who hired Collins as his head writer. A big fan of her writing, it was Proimos who urged Collins to try writing books.
In 2003, Collins published Gregor the Overlander , the first book of The Underland Chronicles . The book tells the tale of a boy who discovers a vast new world when he accidentally falls through the grate of the laundry room in his New York City apartment building.
Gregor received critical success and became a New York Times best seller. The Underland Chronicles series comprised four additional books: Gregor and the Prophecy Bane , Gregor and the Curse of the Warmbloods , Gregor and the Marks of Secret, and Gregor and the Code of Claw .
The Hunger Games Trilogy and Movies

While The Underland Chronicles made Collins a well-known author, her next series ratcheted up her celebrity status. As Collins later recalled, The Hunger Games trilogy was born while she watched television late one night. Flipping through the channels, Collins was suddenly struck by the lack of distinction between reality TV and coverage of the Iraq war: “We have so much programming coming at us all the time,” she says. “Is it too much? Are we becoming desensitized to the entire experience? ... I can’t believe a certain amount of that isn’t happening.”
The Hunger Games revolves around the series’ rebel heroine, Katniss Everdeen, who lives in the post-apocalyptic nation of Panem, formerly North America. In Panem, the Hunger Games are an annual event in which young boys and girls fight to the death in a televised battle.
For Collins, The Hunger Games and her other books touch on the subjects—necessary and unnecessary wars—that her father often discussed with her. “If we introduce kids to these ideas earlier, we could get a dialogue about war going earlier and possibly it would lead to more solutions,” she says. “I just feel it isn’t discussed, not the way it should be. ... I know from my experience that we are quite capable of understanding things and processing them at an early age.”
The series’ first book, The Hunger Games , was released in 2008. Its two sequels, Catching Fire and Mockingjay , were published in 2009 and 2010, respectively. The series became a huge success, selling more than 100 million copies worldwide.
A film version of The Hunger Games , with a screenplay written by Collins, was released in 2012. Starring Jennifer Lawrence as Katniss, Josh Hutcherson as Peeta Mellark, and Liam Hemsworth as Gale Hawthorne, the film grossed just under $700 million globally, paving the way for Catching Fire and the two-part Mockingjay over each of the next three years.
Prequel: The Ballad of Songbirds and Snakes
May 2020 brought the highly anticipated release of The Hunger Games prequel, The Ballad of Songbirds and Snakes . The book follows the rise of the series’ villain, Coriolanus Snow, his ambitions fueling the expansion of the Games from a minor curiosity into an all-consuming media spectacle.
The novel was adapted into a 2023 film, The Hunger Games: The Ballad of Songbirds and Snakes , starring Tom Blyth, Rachel Zegler, Hunter Schafer, and Peter Dinklage .
Other Books: Charlie McButton and Year of the Jungle
Just before the massive success of The Hunger Games , Collins wrote a children’s book about a computer-game-obsessed boy, When Charlie McButton Lost Power (2007). She followed with When Charlie McButton Gained Power (2009).
In 2013, Collins penned the autobiographical picture book Year of The Jungle . The book, aimed at children, talks about a parent leaving for war and how a young girl struggles to cope with his absence.
Collins married Charles “Cap” Pryor in 1992. They have two children, Charlie and Isabel. According to Collins’ IMDb profile , she and Pryor divorced in 2015; however, no details of their potential split have been made public.
According to Celebrity Net Worth , Collins’ total wealth is estimated at around $90 million as of May 2024.
- Destroying things is much easier than making them.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
Tyler Piccotti first joined the Biography.com staff as an Associate News Editor in February 2023, and before that worked almost eight years as a newspaper reporter and copy editor. He is a graduate of Syracuse University. When he's not writing and researching his next story, you can find him at the nearest amusement park, catching the latest movie, or cheering on his favorite sports teams.
Watch Next .css-smpm16:after{background-color:#323232;color:#fff;margin-left:1.8rem;margin-top:1.25rem;width:1.5rem;height:0.063rem;content:'';display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;}

Famous Authors & Writers

Agatha Christie

A Huge Shakespeare Mystery, Solved

9 Surprising Facts About Truman Capote

William Shakespeare

How Did Shakespeare Die?

Meet Stand-Up Comedy Pioneer Charles Farrar Browne
Francis Scott Key

Christine de Pisan

Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz

10 Famous Langston Hughes Poems
Why is Christian Science in our name?
Our name is about honesty. The Monitor is owned by The Christian Science Church, and we’ve always been transparent about that.
The Church publishes the Monitor because it sees good journalism as vital to progress in the world. Since 1908, we’ve aimed “to injure no man, but to bless all mankind,” as our founder, Mary Baker Eddy, put it.
Here, you’ll find award-winning journalism not driven by commercial influences – a news organization that takes seriously its mission to uplift the world by seeking solutions and finding reasons for credible hope.
Your subscription makes our work possible.
We want to bridge divides to reach everyone.

Deepen your worldview with Monitor Highlights.
Already a subscriber? Log in to hide ads .
Select free newsletters:
A thoughtfully curated selection of our most popular news stories and podcasts.
Every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday
Hear about special editorial projects, new product information, and upcoming events.
An update on major political events, candidates, and parties twice a week.
Twice a Week
Stay informed about the latest scientific discoveries & breakthroughs.
Every Tuesday
A weekly digest of Monitor views and insightful commentary on major events.
Every Thursday
Latest book reviews, author interviews, and reading trends.
Every Friday
A weekly update on music, movies, cultural trends, and education solutions.
The three most recent Christian Science articles with a spiritual perspective.
Every Monday
Ann Powers was writing Joni Mitchell’s life story. She found her own.
- Deep Read ( 4 Min. )
- By Stephen Humphries Staff writer @steve_humphries
June 10, 2024
Ann Powers, music critic for NPR, is renowned for writing about female artists such as Kate Bush and Tori Amos. Their songs have given voice to her feminist awakening. But due to a generational gap, Ms. Powers had resisted writing about another icon: Joni Mitchell. That changed when a publisher commissioned her to write a biography.
“I didn’t know that I needed Joni,” Ms. Powers says during a video call. “She really did set the bar and set the template for what so many others have done.”
Why We Wrote This
With her new biography about Joni Mitchell, NPR music critic Ann Powers says she wanted to challenge the idea that there’s only one definitive story of a life.
Ms. Powers’ book “Traveling: On the Path of Joni Mitchell,” available June 11, is about as conventional as her subject’s alternate guitar tunings. It not only retraces the seldom-explored paths of the musician’s travelogue, but also detours into Ms. Powers’ own experiences. The project offered a chance to explore Ms. Mitchell’s career – and rethink the form of biography.
“She’s the perfect subject to make this argument that biography needs to be even more fluid,” the author says. “That we need to look in surprising places for parts of the story.”
Early on, Ann Powers wasn’t a fan of Joni Mitchell. The music critic for NPR is renowned for writing about female artists such as Kate Bush and Tori Amos. Their songs had given voice to her feminist awakening. But due to a generational gap, Ms. Powers had resisted the iconic songwriter who once called Bob Dylan her pace runner. That all changed when a publisher commissioned her to write a biography.
Ms. Powers’ book “Traveling: On the Path of Joni Mitchell,” available June 11, is about as conventional as her subject’s alternate guitar tunings. It not only retraces the seldom-explored paths of the musician’s travelogue, but also detours into Ms. Powers’ own experiences. In a conversation with the Monitor, the author explains that music takes on additional meaning when we filter it through our own subjective perspectives. Ms. Powers’ autobiographical stories illustrate the universality of Ms. Mitchell’s songs. This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
What makes Joni Mitchell extraordinary?
It’s not that often that you have the combination of this restless mind that endlessly wants to move to a new place and this hyperbrilliant sui generis talent. She is both. Oftentimes, when you look at long careers, whether they’re musicians or painters or filmmakers, many great artists kind of do one thing or maybe two things very well and offer variations on that. But with Joni, there’s these distinct loops within loops within loops. As I say in the book, quoting Dan Wilson the songwriter, there’s just this way she moves and changes and it’s never unrecognizable, but is always requiring us to go somewhere maybe we don’t want to go with her.
I think another thing that’s very rare about Joni Mitchell is that her musicality and her skill at writing lyrics and her physical vocal talent are all at this pinnacle. Here’s someone who’s the whole package.
What’s your pitch for why “Traveling” isn’t a run-of-the-mill biography?
I really tried to confront the edifice of biography, in a sense. Now is a great time for people experimenting with biography. You see books like “My Autobiography of Carson McCullers” [by Jenn Shapland], which won the National Book Award. So it’s not like it was unprecedented, what I was doing. But I welcomed the chance to challenge the idea that there’s any definitive story of a life.
I had great help in that from my subject. Joni Mitchell is an artist who has told us her life story in many ways, from many perspectives, and ... constantly challenged her fans’ perceptions of what she can be as an artist and what her life means. I realized she’s the perfect subject to make this argument that biography needs to be even more fluid. That we need to look in surprising places for parts of the story. That we do need to recount the official story, but we also have to recognize both the kind of minor moments in people’s lives and the way that our lives as listeners intersect with and kind of help build the meaning of the story of the artist’s work.

“Traveling” isn’t just about Joni Mitchell. It’s also about you. Does that exemplify how Ms. Mitchell’s music perhaps invites listeners to see themselves in her songs?
One of her most famous early quotes is her saying, Don’t look for me in my songs. Look for yourself.
I guess my reflecting on how I interact with her work and life are wanting to be open about that. Yeah, it’s a little maverick as far as doing a biography. But I think we’re living in a time when the idea of objectivity has been exposed as an idea, as an ideal, and not an achievable goal. So in my writing, I try to always acknowledge my own presence and hopefully without having that be overweening.
You interviewed just about everybody who has worked with Joni Mitchell. But you deliberately avoided interviewing the artist. Why?
Partly because I have read the wonderful books that grow from interviews with her and time spent with her. And I know that once you’re in Joni’s story with Joni, that your perspective is fixed on that telling of the story. I didn’t want to get sucked into the vortex of her charisma. I didn’t want to feel obligated to an official story.
I treasure the distance between myself and my subject because that’s what all of us who are fans, who are music lovers, experience with artists we love the most. It’s in that distance between their human reality, and our perception of them, that understanding grows and that opinions grow. Many of the people she’s worked with, and people who were sort of on the path near her, did give me insight into who she is.
For someone who owns “Blue” but wants to go deeper into her catalog, what would you recommend?
I would recommend “Hejira” because while “Blue” is the entryway for so many people, for so many generations, I want people to hear Joni with a band. To show the richness of her musical intelligence. The heartbreak journey of “Blue” is really relatable. In some ways, the self-actualization journey or the journey into maturity of “Hejira” is one that speaks to me very deeply and also just speaks to our moment. It’s universal in a different way.
I’m very attached to “Night Ride Home.” It does have maybe her greatest anthem, “Come in From the Cold,” which is just a song we all need to listen to once a month as a cleanser.
Why is that her greatest song?
It’s the circularity of the song. It’s the tidal force of the song. It’s the way it goes from memories of adolescent or young love and heartbreak to ... a statement on human vulnerability and need. The way she builds it is, I think, what’s beautiful. She does it in other songs, too, like “Shine.” But “Come in From the Cold” has that perfect blend of intimacy and oracular wisdom that Joni can get to.
Help fund Monitor journalism for $11/ month
Already a subscriber? Login

Monitor journalism changes lives because we open that too-small box that most people think they live in. We believe news can and should expand a sense of identity and possibility beyond narrow conventional expectations.
Our work isn't possible without your support.
Unlimited digital access $11/month.

Digital subscription includes:
- Unlimited access to CSMonitor.com.
- CSMonitor.com archive.
- The Monitor Daily email.
- No advertising.
- Cancel anytime.

Related stories
The monitor's view songs of beauty amid war, women of the italian renaissance held their ground, review how the changing world affected mozart’s music, piece by piece, share this article.
Link copied.
Give us your feedback
We want to hear, did we miss an angle we should have covered? Should we come back to this topic? Or just give us a rating for this story. We want to hear from you.
Dear Reader,
About a year ago, I happened upon this statement about the Monitor in the Harvard Business Review – under the charming heading of “do things that don’t interest you”:
“Many things that end up” being meaningful, writes social scientist Joseph Grenny, “have come from conference workshops, articles, or online videos that began as a chore and ended with an insight. My work in Kenya, for example, was heavily influenced by a Christian Science Monitor article I had forced myself to read 10 years earlier. Sometimes, we call things ‘boring’ simply because they lie outside the box we are currently in.”
If you were to come up with a punchline to a joke about the Monitor, that would probably be it. We’re seen as being global, fair, insightful, and perhaps a bit too earnest. We’re the bran muffin of journalism.
But you know what? We change lives. And I’m going to argue that we change lives precisely because we force open that too-small box that most human beings think they live in.
The Monitor is a peculiar little publication that’s hard for the world to figure out. We’re run by a church, but we’re not only for church members and we’re not about converting people. We’re known as being fair even as the world becomes as polarized as at any time since the newspaper’s founding in 1908.
We have a mission beyond circulation, we want to bridge divides. We’re about kicking down the door of thought everywhere and saying, “You are bigger and more capable than you realize. And we can prove it.”
If you’re looking for bran muffin journalism, you can subscribe to the Monitor for $15. You’ll get the Monitor Weekly magazine, the Monitor Daily email, and unlimited access to CSMonitor.com.
Subscribe to insightful journalism
Subscription expired
Your subscription to The Christian Science Monitor has expired. You can renew your subscription or continue to use the site without a subscription.
Return to the free version of the site
If you have questions about your account, please contact customer service or call us at 1-617-450-2300 .
This message will appear once per week unless you renew or log out.
Session expired
Your session to The Christian Science Monitor has expired. We logged you out.
No subscription
You don’t have a Christian Science Monitor subscription yet.
Advertisement

- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
Elin Hilderbrand Says Goodbye to Nantucket Summers
The author discusses her new novel, “swan song,” which she says is the last beach read she intends to write..

- Share full article
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | Spotify | How to Listen
For decades, Elin Hilderbrand’s name has been synonymous with summer reading. Her novels set among the misbehaving moneyed class on Nantucket Island juggle romance and crime and a sun-kissed beach vibe that her fans soak up like coconut oil, some of them so fervently that they even make pilgrimages to Nantucket in the off-season .
Now, Hilderbrand is giving all of that up. She has announced that her new novel, the appropriately titled “Swan Song,” will be the last of her Nantucket summer novels, letting her catch her breath and pursue other plans. This week on the podcast, she discusses that decision and tells Gilbert Cruz how she feels about her impending semiretirement.
“Oh, I’m ecstatic. I couldn’t be any happier,” she says. “The business of publishing, the way I’ve been doing it, Gilbert, has put me constantly on deadline for the last 24 years. So there has never been a time when I have not been either starting a book, in the middle of a book, finishing a book, and then, really the part that I like the least, which is marketing the book. … I’d really rather be sitting home writing, or even better still, reading. So in my retirement I hope to be doing a lot more quiet work on projects that do not have a deadline.”
We would love to hear your thoughts about this episode, and about the Book Review’s podcast in general. You can send them to [email protected] .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. Create an outline. The next step of learning how to write a biography is to outline your story. It's critical to outline your biography before you begin writing it. Among other things, it helps ensure you cover every topic you'd like to and get the book in the correct chronological order.
Facebook. These are just some of the story elements you can use to make your biography more compelling. Once you've finished your manuscript, it's a good idea to ask for feedback. 7. Get feedback and polish the text. If you're going to self-publish your biography, you'll have to polish it to professional standards.
A good writing routine can make the process smoother and more enjoyable. Choose a Writing Space: Find a quiet, comfortable place free of distractions. Set a Time: Write at the same time each day to build a habit. Prepare Mentally: Take a few minutes before writing to clear your mind and focus on the task ahead.
8. Send a copy to your subject. Consider sending a copy of your manuscript to the person whose life you wrote about in your book. The copy may serve as a thank-you gift, but also, if you intend to publish your work, you will need them to approve, as well as fact check, everything you put into the story.
Conduct relevant interviews. Whenever possible, seek firsthand accounts from those who knew or interacted with the subject. Conduct interviews with family members, friends, colleagues, or experts in the field. Their insights and anecdotes can provide a deeper understanding of the person's character and experiences.
Biographies are how we learn information about another human being's life. Whether you want to start writing a biography about a famous person, historical figure, or an influential family member, it's important to know all the elements that make a biography worth both writing and reading.
Now let's look at the number of chapters in your biography and your word count. Laying out your chapters. Most nonfiction books have 6 to 12 chapters. Each chapter may be 5,000 to 10,000 words. In my view, 8 to 10 chapters is the sweet spot. Aim for a total word count of 60,000 to 100,000 words.
The organisation of your biography greatly impacts its readability. Structure your work into logical sections or chapters, employing either a chronological or thematic arrangement. Begin with an engaging introduction that captures readers' attention and provides essential context.
These allow you to play with other modes of representation. For example, Sue Townsend's popular Adrian Mole series (the first book being The Secret Diary of Adrian Mole, Aged 13¾ ), presented as a British teenage boy's diary. Let's examine 7 ideas about how to write a biography: 1. Create compelling voice.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip: #4 Put Something of Yourself into the Writing. While the defining feature of a biography is that it gives an account of a person's life, students must understand that this is not all a biography does. Relating the facts and details of a subject's life is not enough.
1. Go for a chronological structure. Start chronologically from the subject's birth to their death or later life. Use the timeline of the person's life to structure the biography. Start with birth and childhood. Then, go into young adulthood and adulthood.
2. Get clear on the basicfacts of the person's life. Reading a few short articles—Wikipedia- or encyclopedia-style articles, obituaries, feature articles, or academic articles, for example—should help you to form a short profile of your subject. 3. Start digging a little deeper to learn more about the person and their life.
This book is so comprehensive on elements of biography, it qualifies to be a definitive text for subject. It is a handy tool-kit for both readers and writers of biography and memoir. I came out of it much the wiser in the craft of writing biography. Biography is more than the chronology of a life, a mistake writers and readers make.
However you decide to structure your biography, always start with an outline. Write up a chapter-by-chapter plan for your book, and try to keep yourself on track with it when you write. This is the best way to remain organized, and it will ensure your book reads well. An outline doesn't have to be lengthy, although some writers choose to ...
A biography is the story of someone's life as written by another writer. Most biographies of popular figures are written years, or even decades, after their deaths. Authors write biographies of popular figures due to either a lack of information on the subject or personal interest. A biography aims to share a person's story or highlight a ...
Carole Angier has written biographies of Jean Rhys (winner of the Writers' Guild Non-Fiction Award) and Primo Levi. She is a regular critic for The Independent, The Spectat or and The Literary Review, and is a Fellow of the Royal Society of Literature, and teaches life writing at Birkbeck College, London University. Sally Cline, award-winning biographer, short story writer and winner of the ...
Hamilton invites the reader to join him on a fascinating journey through the art of biographical composition. Starting with personal motivation, he charts the making of a modern biography from the inside: from conception to fulfillment. He emphasizes the need to know one's audience, rehearses the excitement and perils of modern research ...
"For many scholars, historical biography occupies a kind of no man's land, between history and literature. This elegant collection, based upon a symposium held in 2000 on 'biography and historical analysis' both explains and undermines such a stereotype."—David Watson, Literature and History Published On: 2005-10-24 "These provocative essays contribute two useful points: biography is ...
12. The Lost City of Z: A Tale of Deadly Obsession in the Amazon by David Grann. Another mysterious explorer takes center stage in this gripping 2009 biography. Grann tells the story of Percy Fawcett, the archaeologist who vanished in the Amazon along with his son in 1925, supposedly in search of an ancient lost city.
J.T. keeps to just the essential ingredients of a professional author bio: accolades, genres, experience, and a bit of what she's up to today for a personal touch. 20. James S.A. Corey. James S.A. Corey is the pen name for a collaboration between Daniel Abraham and Ty Franck.
Dec 9, 2013. The most important thing that you as a biographer can do is to write from the heart. Write only about someone you have deep feelings for. If you care deeply about your subject, either positively or negatively, so will your readers. If you take on a biography about someone you couldn't care less about, possibly for the money, or ...
Once you have your one-page outline, remember it is a fluid document meant to serve you and your book. Expand it, change it, play with it as you see fit—even during the writing process. Step 4. Set a firm writing schedule. Ideally, you want to schedule at least six hours per week to write your book.
Get ready to learn about some extraordinary people. Via Amazon.com. 1. The Collected Autobiographies of Maya Angelou by Maya Angelou (2004) Maya Angelou's I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings is one ...
Suzanne Collins is an American author who published her debut book, Gregor the Overlander, the first of the five-part The Underland Chronicles, in 2003. In 2008, her first book of The Hunger Games ...
NPR music critic Ann Powers is the author of the new book "Traveling: On the path of Joni Mitchell.". Early on, Ann Powers wasn't a fan of Joni Mitchell. The music critic for NPR is renowned ...
Amazon.com: writing biography. Skip to main content.us. Delivering to Lebanon 66952 Update location All. Select the department you want to search in ...
Nonfiction. Nonfiction is an account or representation of a subject which is presented as fact. This presentation may be accurate or not; that is, it can give either a true or a false account of the subject in question. However, it is generally assumed that the authors of such accounts believe them to be truthful at the time of their composition.
She has announced that her new novel, the appropriately titled "Swan Song," will be the last of her Nantucket summer novels, letting her catch her breath and pursue other plans. This week on ...