

Food Testing Lab Business Plan [Sample Template]
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business Plans » Food Sector
Are you about starting a food testing business? If YES, here is a detailed sample food testing lab business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE .
Okay, so we have considered all the requirements for starting a food testing business. We also took it further by analyzing and drafting a sample food testing marketing plan template backed up by actionable guerrilla marketing ideas for food testing companies. So let’s proceed to the business planning section.
If you are a scientist and you intend starting your own business, you can decide to start a food testing lab business; this industry is open to certified lab scientists cum investors.
Starting a food testing lab business requires training, experience, creativity, reasonable startup capital, license and detailed business plan. The truth is that you can’t just wake up and launch your own food testing lab business; you must follow established protocols. This industry is highly regulated because of the potential risk involved.
Below is a sample food testing lab business plan template that will help you successfully write yours without much stress.
A Sample Food Testing Lab Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
Food testing labs engage in food testing, and food testing is a process used to check whether a food is safe and that it does not contain harmful contaminants, or that it contains only permitted additives at acceptable levels, or that it contains the right levels of key ingredients and its label declarations are correct, or to know the levels of nutrients present.
Food testing lab business is a subset of the Laboratory Testing Services industry and establishments that operate in the Laboratory Testing Services industry perform physical, chemical and other analytical testing for commercial purposes.
Such testing may occur in a laboratory or an on-site facility (i.e. where the product is manufactured or developed). Most results from industry-led tests are checked against government regulations and environmental, industrial and product standards. Please note that this industry does not include medical and veterinary testing labs.
In an increasingly regulated society, pressure on operators to ensure the safety and quality of their products is higher than ever. A greater number of government safety regulations and consumer lawsuits have led to rigorous testing of manufacturers’ goods prior to sale.
The industry has grown over the past five years, driven by renewed consumer spending and corporate investment in the development of new products. As companies accommodate stricter environmental regulations and invest in new products over the next five years, demand for laboratory testing services is expected to grow.
The Laboratory Testing Services Industry is indeed a thriving sector of the economy of countries like Israel, Japan, Canada, India, China, United Kingdom , Germany and the united states of America. Statistics has it that in the United States alone, the industry generates over $20 billion annually from more than 10,837 registered and licensed laboratory testing services companies (food testing labs included).
The industry is responsible for the employment of over 150,989 people. Experts project the industry to grow at a 2.0 percent annual rate from 2014 to 2019. Bureau Veritas, Intertek Group PLC and SGS SA are the companies with the lion shares of the Laboratory Testing Services industry in the United States of America.
A recent report published by IBISWORLD shows that capital expenditure in the Laboratory Testing Services is low. For every $1.00 spent on labor, an estimated $0.07 is allocated toward capital. The majority of work requires specialized, high-cost equipment to conduct certain types of tests. Additionally, depreciation expenditure is expected to account for 3.8 percent of industry revenue in 2018.
Nonetheless, the industry is heavily labor intensive. Industry employees perform a range of activities, from simple manual tasks and automated experimental procedures to high-tech testing. Since the industry requires a highly skilled labor force, wages are high. Labor costs account for about 50.7 percent of industry revenue in 2018 and have risen substantially over the past five years.
The bottom line is that the laboratory testing services industry is still very much open for new entrants; the competition within the industry is not as stiff as similar industries. If your food testing lab is well – staffed and equipped, it can gain fair share of the available market in any country or region you intend launching the business.
2. Executive Summary
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. is a licensed laboratory testing services company with bias in food testing that will be located in an industrial area in Bowling Green – Kentucky. We have been able to secure a long-term lease agreement for a facility in a strategic location with an option of long-term renewal on terms and conditions that are favorable to us.
The facility has government approval for the kind of business we want to run and the facility is easily accessible to our target market.
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. is in the laboratory testing industry to perform physical, chemical and other analytical food testing for commercial purposes. Such testing may occur in a laboratory or an on-site facility (i.e. where the food product is manufactured or developed). We are also in business to make profits at the same time to give our customers value for their money.
We are aware that there are several food testing labs scattered all around the United States, which is why we spent time and resources to conduct our feasibility studies and market survey so as to enable us locate the business in an area that can easily accept our services and brand.
Much more than offering highly regulated scientific services, our customer care is going to be second to none. We know that our customers are the reason why we are in business which is why we will go the extra mile to get them satisfied when they patronize our services.
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. will ensure that all our customers are given first class treatment whenever they bring their food items/products for testing in our food testing lab. We have a CRM software that will enable us manage a one on one relationship with our customers no matter how large they may grow to. We will ensure that we get our customers involved when making some business decisions that will directly or indirectly affect them.
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. will be owned and managed by Dr. Nicole Williams (PhD) and her immediate family members. Dr. Nicole Williams has a PhD in Molecular Science. She has over 20 years’ experience working in related industry as a senior research director prior to starting Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. She will be working with a team of professionals to grow the business.
3. Our Products and Services
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. is going to run a standard and licensed food testing lab whose services will not only be accepted in Bowling Green – Kentucky but also throughout the United States of America. We are in the Laboratory Testing Services industry to make profits and also to give our customers value for their money.
We will ensure that we do all that is permitted by the law in the United States of America to accomplish our business goal and objective. These are some of the services that we will be offering;
- Food allergen testing
- Food chemical analysis
- Food contact tests
- Food contaminant testing
- Nutritional analysis and testing
- GMO testing
- Melamine contamination testing
- Microbiological tests
- Spiral plating for bacterial count
- Pesticide residue testing
- Veterinary drug residue testing
- PCR food testing
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our vision is to establish a standard food testing lab whose services will be not only be accepted in Bowling Green – Kentucky, but also throughout the United States of America.
- Our mission is to establish a standard and world class food testing lab that in our own capacity will favorably compete with leaders in the industry. We want to build a business that will be listed amongst the top 20 food testing labs in the United States of America.
Our Business Structure
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. is established with the aim of competing favorably with other leading food testing labs in the industry. This is why we will ensure that we put the right structures in place that will support the kind of growth that we have in mind.
We will ensure that we only hire people that are qualified, honest, hardworking, customer centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all the stake holders. As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our senior management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of five years or more depending how fast we meet our set target.
In view of that, we have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions;
- Chief Executive Officer (Owner)
- Senior Research Fellow / Lab Scientist
Human Resources and Admin Manager
Sales and Marketing Manager
- Laboratory Assistant
- Accountants/Cashiers
- Customer Care Executive
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Executive Officer – CEO (Owner):
- Increases management’s effectiveness by recruiting, selecting, orienting, training, coaching, counseling, and disciplining managers; communicating values, strategies, and objectives; assigning accountabilities; planning, monitoring, and appraising job results
- Creating, communicating, and implementing the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Responsible for providing direction for the business
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization.
Senior Research Fellow/Lab Scientist
- Responsible for research and development in collaboration with others on projects. He or she makes detailed observations, analyzes data, and interprets results. Research associates prepare technical reports, summaries, protocols, and quantitative analyses.
- Responsible for identifying patentable inventions and acting as principal investigator in conducting his or her own experiments.
- Performs a variety of food testing research tasks and experiments. He or she may be required to make detailed observations, detecting food poisoning problems, and instituting corrective action.
- Determine optimal cultural requirements and perform tasks related to food related disease prevention; they often are required to collect, record, and analyze data, as well as interpret results.
- Participate in scientific conferences and contribute to scientific journals.
- Ensures operation of equipment by completing preventive maintenance requirements; calling for repairs.
- Ensures that the lab meets the expected safety and health standard at all times.
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Defining job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carrying out induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Oversee the smooth running of the daily office and chemical lab activities.
- Manages external research and coordinate all the internal sources of information to retain the organizations’ best customers and attract new ones
- Models demographic information and analyze the volumes of transactional data generated by customer purchases
- Identifies, prioritizes, and reaches out to new partners, and business opportunities et al
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Documents all customer contact and information
- Represents the company in strategic meetings
- Help increase sales and growth for the company
Accountant/Cashier
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Provides managements with financial analyses, development budgets, and accounting reports
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis.
- Performs cash management, general ledger accounting, and financial reporting
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensuring compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for the organization
- Serves as internal auditor for the organization
Client Service Executive
- Welcomes guests and clients by greeting them in person or on the telephone; answering or directing inquiries.
- Ensures that all contacts with clients (e-mail, walk-In center, SMS or phone) provides the client with a personalized customer service experience of the highest level
- Through interaction with clients on the phone, uses every opportunity to build client’s interest in the company’s products and services
- Manages administrative duties assigned by the manager in an effective and timely manner
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the company’s products, promotional campaigns etc. to ensure accurate and helpful information is supplied to clients
- Receives parcels/documents for the company
- Distribute mails in the organization
Laboratory Assistant:
- Responsible for performing a wide variety of research laboratory tasks and experiments, making detailed observations, analyzing data, and interpreting results. He or she maintains laboratory equipment and inventory levels for laboratory supplies. He or she may also write reports, summaries, and protocols regarding experiments.
- Performs limited troubleshooting and calibration of instruments.
- Responsible for handling agriculture and food testing, environmental testing, product performance and safety testing and product certification
- Responsible for handling food allergen testing, food chemical analysis, food contact tests, food contaminant testing, nutritional analysis and testing, GMO testing, Melamine contamination testing, microbiological tests, spiral plating for bacterial count, pesticide residue testing, veterinary drug residue testing and PCR food testing
- Performs routine maintenance of equipment and other related duties as required.
6. SWOT Analysis
We are quite aware that there are several food testing labs in the United States of America which is why we are following the due process of establishing a business. We know that if a proper SWOT analysis is conducted for our business, we will be able to position our business to maximize our strength, leverage on the opportunities that will be available to us, mitigate our risks and be equipped to confront our threats.
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. employed the services of an expert HR and Business Analyst with bias in startup business to help us conduct a thorough SWOT analysis and to help us create a Business model that will help us achieve our business goals and objectives. This is the summary of the SWOT analysis that was conducted for Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc.;
Part of what is going to count as positives for Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. is the vast experience of our management team, we have people on board who understand how to grow a business from the scratch to becoming a national phenomenon.
So also, our state of the art food testing lab machines and equipment, the wide varieties of food testing services we conduct, our large national network and of course our excellent customer service culture will definitely count as a strong strength for the business.
A major weakness that may count against us is the fact that we are a new food testing lab in the United States and we don’t have the financial capacity to engage in the kind of publicity that we intend giving the business especially when big names like AbbVie, Amgen Inc., Genentech Inc., Monsanto and Gilead et al are already determining the direction of the market both in the United States and in the global market.
- Opportunities:
The opportunities available to food testing labs cum laboratory testing services are enormous and this is anchored on the fact that it is compulsory for any chemical related products and food to undergo mandatory testing in the United States.
As a result of that, we were able to conduct a thorough market survey and feasibility studies so as to position our business to take advantage of the existing market for food testing services and also to create our own new market. We know that it is going to requires hard work, and we are determined to achieve it.
We are quite aware that just like any other business, one of the major threats that we are likely going to face are economic downturn and unfavorable government policies . It is a fact that economic downturn affects purchasing power. Another threat that may likely confront us is the arrival of a new food testing lab in same location where ours is located and where our target market exists.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
A close study of the trends in the Laboratory testing industry shows that the industry is growing rapidly, with revenue increase over the last five years driven by rising use of chemical based products. Even though the industry has grown, a consolidation trend has emerged as large laboratory testing companies have increasingly targeted industry firms for acquisition, to expand their services portfolios ahead of impending patent expirations.
Sustained spending on research and development, including by the federal government, will benefit the industry going forward, driving growth in revenue generation and of course profit. The fact that there are several fields that need the input of food testing services to boost production makes it an industry that is worth paying attention to.
The industry has thrived due to higher government regulation of consumer and food products, government regulation across a range of industries has stimulated demand and aided by the projected expansion of the economy, experts expect industry revenue to grow. Lastly, external factors such as research and development expenditure and consumer spending in the Laboratory Testing Services industry will impact industry performance.
Lastly, consumer and industrial manufacturers are major users of laboratory testing services, and a decline in corporate profit can lead to a reduction in R&D expenditures. As companies choose in-house product testing instead of outsourcing such services to laboratories, demand for this industry can also diminish. Corporate profit is expected to increase in 2019, representing an opportunity for the industry.
8. Our Target Market
When it comes to the services offered by food testing labs, there is indeed a wide range of available customers. In essence, our target market can’t be restricted to just an industry, but all the industries that manufacture food – based products.
In view of that, we have conducted our market research and we have ideas of what our target market would be expecting from us. Hence our target markets are;
- All manufacturing companies that manufacture food based products
- Food processing and preservation companies
- Medicine and pharmaceutical manufacturing companies
- Hybrid food processing and production companies
- Hybrids crop cultivators
- Hybrid animal breeders
- Hybrid bird/poultry farmers
- Hotels and restaurants
- Dormitories and schools where foods are served
Our competitive advantage
A close study of the laboratory testing industry reveals that the market has become much more intensely competitive over the last half decade. As a matter of fact, you have to be highly creative, customer centric and proactive if you must survive in this industry. We are aware of the competition and we are prepared to compete favorably with other laboratory testing services companies in Bowling Green – Kentucky and throughout the United States.
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. is launching a standard food testing lab that will indeed become the preferred choice for businesses in and around Bowling Green – Kentucky. We have easy access to highly skilled workforce, proximity to key markets and recommendation/accreditation from authoritative sources.
Part of what is going to count as competitive advantage for Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. is the vast experience of our management team, we have people on board who are highly experienced and understand how to grow a business from the scratch to becoming a national phenomenon. So also, our state of the art food testing machines and equipment (laboratory), the wide varieties of services that we offer, our large and far reaching national network and of course our excellent customer service culture will definitely count as a strong strength for the business.
Lastly, our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category (startups food testing labs) in the laboratory testing services industry, meaning that they will be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our objectives. We will also give good working conditions and commissions to freelance sales agents that we will recruit from time to time.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. is established with the aim of maximizing profits in the laboratory testing services industry in the United States of America and we are going to ensure that we do all it takes to offer our services to a wide range of customers.
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. will generate income by offering the following services;
10. Sales Forecast
One thing is assured when it comes to food testing lab, if your laboratory and services meet the expected industrial standard and if your laboratory is centrally positioned and easily accessible, you will always attract customers.
We are well positioned to take on the available market in Bowling Green – Kentucky and every city where our services will be offered and we are quite optimistic that we will meet our set target of generating enough income/profits from the first six months of operation and grow the business and our clientele base.
We have been able to examine the laboratory testing services industry, we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast. Below is the sales projection for Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc., it is based on the location of our business and other factors as it relates to small scale and medium scale food testing lab startups in the United States;
- First Fiscal Year (FY1): $250,000
- Second Fiscal Year (FY2): $550,000
- Third Fiscal Year (FY3): $950,000
N.B : This projection was done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown and there won’t be any major competitor offering same services as we do within same location. Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
Before choosing a location for Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. and also the kind of services we will offer, we conducted a thorough market survey and feasibility studies in order for us to penetrate the available market in our target market locations.
We have detailed information and data that we were able to utilize to structure our business to attract the number of customers we want to attract per time and also for our services to favorable compete with other leading laboratory testing brands in the United States of America.
We hired experts who have good understanding of the laboratory testing industry to help us develop marketing strategies that will help us achieve our business goal of winning a larger percentage of the available market in Bowling Green – Kentucky and other cities in the United States of America.
In summary, Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. will adopt the following sales and marketing approach to attract clients;
- Introduce our food testing lab brand by sending introductory letters to manufacturers of food – based products, hotels, boarding schools and other stakeholders in Bowling Green – Kentucky and other cities in the United States of America
- Advertise our services in community – based newspapers, local TV and radio stations
- List our business and products on yellow pages’ ads (local directories)
- Leverage on the internet to promote and market our food testing lab services – brands
- Engage in direct marketing and sales
- Encourage the use of Word of mouth marketing (referrals)
- Join local chambers of industry and commerce with the aim of networking and marketing our services.
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
In spite of the fact that our food testing lab is a standard one with a wide range of laboratory testing services that in few years from now will favorably compete with other leading brands in the industry. We will still go ahead to intensify publicity for all our brand. We are going to explore all available means to promote Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc.
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. has a long-term plan of attracting clients all around the United States of America which is why we will deliberately build our brand to be well accepted first in Bowling Green – Kentucky before venturing out. Here are the platforms we intend leveraging on to promote and advertise Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc.;
- Place adverts on both print (community – based newspapers and food science magazines) and electronic media platforms
- Sponsor relevant community programs
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like; Instagram, Facebook, twitter, et al to promote our food testing lab brand
- Install our billboards in strategic locations all around major cities in the United States of America
- Distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas
- Position our Flexi Banners at strategic positions in our target location
- Ensure that our staff members wear our customized clothes, and all our official cars are customized and well branded.
12. Our Pricing Strategy
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. will work towards ensuring that all our services are offered at highly competitive prices compared to what is obtainable in the United States of America.
In view of that, our prices will conform to what is obtainable in the industry but will ensure that within the first 6 to 12 months our services are offered a little bit below the average price of various laboratory testing services in the United States of America. We have put in place business strategies that will help us run on low profits for a period of 6 months; it is a way of encouraging people to buy into our brand.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. is all inclusive because we are quite aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. will make available to her clients;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment via credit cards / Point of Sale Machines (POS Machines)
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via mobile money transfer
- Payment via bank draft
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our client make payment for our services without any stress on their part.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
Starting a standard food testing lab is indeed capital intensive. The bulk of the startup capital will be sent on leasing or acquiring a facility, acquiring license and in purchasing chemical lab machines and equipment. Aside from that, you are not expected to spend much except for the purchase of chemical supplies, paying of your employees and utility bills.
These are the key areas where we will spend our startup capital;
- The total fee for registering the Business in the United States of America – $750.
- Legal expenses for obtaining licenses and permits as well as the accounting services (software, P.O.S machines and other software) – $1,300.
- Marketing promotion expenses for the grand opening of Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of – $3,580.
- The cost for hiring Business Consultant – $2,500.
- The cost for insurance (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) coverage at a total premium – $2,400.
- The cost for payment of rent for 12 months at $1.76 per square feet in the total amount of $76,600.
- The cost for construction of a standard chemical testing lab – $100,000.
- Other start-up expenses including stationery ($500) and phone and utility deposits ($2,500).
- Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $100,000
- The cost for start-up inventory (laboratory equipment, chemical supplies, and packaging materials et al) – $80,000
- The cost for store equipment (cash register, security, ventilation, signage) – $13,750
- The cost for the purchase of furniture and gadgets (Computers, Printers, Telephone, Fax Machines, tables and chairs et al) – $4,000.
- The cost of launching a website – $600
- Miscellaneous – $10,000
We would need an estimate of $500,000 to successfully set up our food testing lab in Bowling Green – Kentucky.
Generating Funds/Startup Capital for Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc.
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. is owned and financed by Dr. Nicole Williams (PhD) and her immediate family members. They do not intend to welcome any external business partner which is why she has decided to restrict the sourcing of the startup capital to 3 major sources.
- Generate part of the startup capital from personal savings and sell of stocks
- Source for soft loans from family members and friends
- Apply for loan from the bank
N.B: We have been able to generate about $200,000 (Personal savings $150,000 and soft loan from family members $50,000) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $300,000 from our bank. All the papers and documents have been signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited with the amount.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
The future of any business lies in the number of loyal customers that they have, the capacity and competence of their employees, their investment strategy and business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business, then it won’t be too long before the business closes shop.
One of our major goals of starting Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. is to build a business that will survive off its own cash flow without injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running. We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers over is to offer our food testing services a little bit cheaper than what is obtainable in the market and we are prepared to survive on lower profit margin for a while.
Nicole Williams® Food Testing Lab, Inc. will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner.
We know that if all these are put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry; they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List/Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check : Completed
- Business Registration: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts: Completed
- Securing Point of Sales (POS) Machines: Completed
- Opening Mobile Money Accounts: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Leasing of facility and construction of standard food testing lab: In Progress
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Generating capital from family members and friends: Completed
- Applications for Loan from the bank: In Progress
- writing of business plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Drafting of Contract Documents and other relevant Legal Documents: In Progress
- Design of the Company’s Logo: Completed
- Printing of Promotional Materials: In Progress
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of the needed food testing lab machines and equipment, furniture, racks, shelves, computers, electronic appliances, office appliances and CCTV: In progress
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business both online and around the community: In Progress
- Health and Safety and Fire Safety Arrangement (License): Secured
- Establishing business relationship with food manufacturing companies, and other related stakeholders: In Progress
Related Posts:
- Catering Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Snow Cone Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Shawarma Stand Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Frozen Food Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Bottled Water Distribution Business Plan [Sample Template]
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Laboratory Business Plan
Start your own laboratory business plan
Fargo Medical Laboratories
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Fargo Medical Laboratories (FML) is a start-up company committed to providing the most convenient, friendliest blood testing service to the physicians of the Main Street Professional Building and the surrounding area. Fargo Medical Laboratories has been founded as a single member L.L.C. registered in North Dakota by Dave Gigsted. Fargo Medical Laboratories will quickly gain market share serving the Fargo medical community.
Objectives Fargo Medical Laboratories has established three significant objectives to pursue. The first is securing 60% of the physicians in the Main Street Professional Building as customers. The second objective is to develop 20% of their revenue from physicians who practice in the nearby vicinity. The third objective is the desire to reach profitability with 12 months. This is especially important since Fargo Medical Laboratories will be using bank debt would like to see a positive ROI fairly soon.
Market Fargo Medical Laboratories has identified two market segments they will serve. First is the large number of physicians that have a practice in the Main Street Professional Building, where Fargo Medical Laboratories will lease space. This customer segment has 128 potential customers with a growth rate of 3%. The second group is physicians that have medical practices in other nearby facilities. There are 115 potential customers in this segment with a 5% annual growth rate.
Services Fargo Medical Laboratories offers a comprehensive battery of blood tests for physician’s patients. Several tests will be done in-house including:
- CBC- A complete test of red blood cell count, white blood count, and a platelet count. Each of these three can be ordered individually if needed.
- Blood sugar test- Frequently requested for diabetics or possible diabetics.
- Electrolyte testing- For patients who are on diuretics and there is concern that they may be losing too many of their electrolytes.
- Creatine- Often used to check kidney functioning or to determine if there is heart or kidney problems.
Other types of blood analysis can be done with the specimen sent to a central lab for testing.
Management Fargo Medical Laboratories has been founded and will be led by Dave Gigsted. Dave received an undergraduate degree in small business management. After graduation Dave got his laboratory technician certification and went to work for a laboratory. He was eventually elevated to lab manager, staying with the lab for five years.
Dave then moved with his wife to Fargo where he worked for a year in a lab. Surveying the business environment with the thought of opening up his own blood laboratory, he recognized the great need for a lab in the Main Street Professional Building, and developed a plan and secured financing for the venture.
1.1 Objectives
- To gain 60% of the Professional Building’s blood testing work.
- Develop 20% of the revenues from offices outside the Professional Building.
- Reach profitability within 12 months.
1.2 Mission
It is Fargo Medical Laboratories’ mission to serve local physicians with fast, accurate, private, reasonably priced blood testing services. Fargo Medical Laboratories exists to exceed all of their customer’s expectations.
1.3 Keys to Success
- Lease space in the Main Street Professional Building, the location of our primary target market.
- Set up a strong contract with a large local laboratory to outsource the more difficult tests, ensuring fast service and good rates.
- Follow a strict regime of accounting controls to help ensure profitability.

Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Fargo Medical Laboratories has been formed as an L.L.C., registered in North Dakota. Fargo Medical Laboratories is a single member entity owned by Dave Gigsted. Fargo Medical Laboratories will lease office space in the Main Street Professional Building. This building has over 120 offices, 93 of which are leased by medical professionals. Of the 93, a high percentage of those are primary care physicians or general practitioners. There currently is no laboratory within this professional building, and doctors are forced to send their patients across town to have blood drawn and analyzed.
2.1 Company Ownership
The owner of Fargo Medical Laboratories is Dave Gigsted. Dave has received bank debt financing and will have a long term loan to pay off.
2.2 Start-up Summary
Fargo Medical Laboratories will require the following equipment for the start up of the business:
- Waiting room furniture
- Two computers with QuickBooks Pro, Microsoft Office, and insurance billing software, sharing a laser printer and a broadband Internet connection.
- Five portable ice coolers.
- Four chairs for the blood drawing rooms.
- Latex gloves, syringes, needles.
- Autoanalyzer.
- Complete blood testing machine.
- Centrifuge.
- Refrigerator/freezer unit.

Fargo Medical Laboratories offers routine blood tests on-site and more complex blood tests outsourced to a central lab. FML will be located inside the Main Street Professional Building which is home to numerous physicians. Currently, when the doctors need blood work done, they have to send their patients to an off-site laboratory, a 15 minute drive from the doctor’s office.
Once Fargo Medical Laboratories is up an running the doctors will be able to send their patients to FML’s offices, within the building. For simple tests Fargo Medical Laboratories will do the analysis in-house, for more complex blood work the specimens will be sent to an outsourced central laboratory.
The advantages to the physicians and their patients include: convenience (blood can be drawn within the same building), and faster service (there is no driving or transportation time to get the blood drawn), and for the most commonly requested tests the analysis occurs in-house guaranteeing results within 24 hours.
Fargo Medical Laboratories will offer the following tests in-house:
- Red blood cell count- $15
- White blood cell count- $15
- CBC (a more complete test that counts platelets in addition to white and red blood cell counts)- $30
- Blood sugar (suited for diabetics or people who are trying to determine if they have a blood sugar problem)- $15
- Electrolytes (for people on diuretics)- $20
- Creatine (tests for heart or kidney difficulties)- $15
If more extensive blood work is needed, blood with be drawn in our offices and sent to a central laboratory. Fargo Medical Laboratories will use a courier service that transports the samples in an ice cooler. The specimens are tested within 24-36 hours of receipt at the central lab and the results are returned to FML via encrypted email.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
4.1 Market Segmentation
Fargo Medical Laboratories will provide services geared to two distinct customer segments.
- Main Street Professional Building physicians – This segment is made up of physicians that practice medicine in offices that are located within the Main Street Professional Building. There is a wide range of specialties represented, but predominantly primary care and general practitioners. Most types of doctors need blood work done on their patients with some regularity. The Main Street physicians have always just had to send their patients to another area of town to have blood drawn and analyzed. This is not convenient for their patients and is time consuming, so physicians in the building would generally be quite happy if there were a blood laboratory within the building.
- Nearby physicians – These physicians practice near the Main Street Professional Building. These doctors also have to send their patients out to a different location to have blood work done. Fargo Medical Laboratories’ services would be attractive to this group because FML would be located closer to their offices than the blood lab currently used. The advantage to this group of physicians would also be convenience.

4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
It is fairly intuitive as to why physicians within the Main Street Professional Building will be targeted, they are the customers who would have the most demand for Fargo Medical Laboratories’ services. Almost all types of doctors regularly have patients who need blood testing done. Assuming that the lab accepts most of the common types of medical insurance, the lab is generally chosen by being the most convenient for the patient since they are the ones who must travel to the lab to have the blood drawn.
For physicians who work within the Main Street Professional Building, Fargo Medical Laboratories would be the most convenient laboratory, being located within the same building as the physician’s offices. No longer would the doctor have to ask the patient to travel to have blood drawn. For the second target market, the nearby physicians, the reasoning is similar, convenience for the patients. While it is not quite as convenient as sending the patient to another office within the same building, Fargo Medical Laboratories would still be closer than the current lab.
4.3 Service Business Analysis
Blood laboratories all provide similar services. Most accept a wide range of insurance plans. Some do the tests in-house, others will outsource the tests. Where the tests are completed is not really that significant. To be competitive the labs need to have the tests completed within a couple of days at the most. This means it all comes down to convenience. Labs serve the physicians and doctors that are closest in terms of geographic proximity. In most cities/towns, you will see labs placed throughout the city serving the different clusters of physicians.
Fargo is different, or at least Main Street is. Main Street Professional Building has for years been trying to have a laboratory locate within the building to serve the large population of doctors. The trouble has been that South Dakota is experiencing an exodus of people. As college students have completed school, they have left the state. Fargo has had difficulty attracting qualified technical people, in this instance phlebotomists (blood drawing technicians) and chemical analyzers. This is the explanation for the absence of a blood laboratory in the Main Street Professional Building. The need has existed, just no one has “stepped up to the plate”, at least not until now.
4.3.1 Competition and Buying Patterns
In Fargo, there is a total of seven blood drawing laboratories. Of the seven, two only serve their specific clients and do not do work for other physicians. Of the remaining five, three offer basic tests done on-site, like Fargo Medical Laboratories, and the remaining two are full service laboratories that do work complex for the other labs.
The closest competitor to Fargo Medical Laboratories is Mednet, located four miles away. This is the facility that 95% of the physicians in the Main Street Professional Building currently use. It is used by these physicians because of convenience, it WAS the closest laboratory. As mentioned earlier, blood testing service providers are chosen based on convenience, how close they are to the patients. Hours of operation (i.e. longer hours/evening hours) are insignificant since physicians are only available during traditional daytime office hours.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
Fargo Medical Laboratories will leverage their competitive edge of a convenient location within a large medical facility to help it quickly gain market share. FML has developed a strategic marketing plan that will use several different methods to develop local awareness of itself and the benefits offered. Fargo Medical Laboratories has also developed a sales strategy to help turn the qualified leads into clients by emphasizing the significant benefits that physicians can offer their patients by sending them to Fargo Medical Laboratories. Sections 5.1-5.3 offers more detail regarding the competitive edge, marketing and sales strategies.
5.1 Competitive Edge
Fargo Medical Laboratories’ competitive edge is convenience. In the blood analysis industry it is hard to differentiate yourself from competitors assuming a few basic levels of care and performance:
- You accept several popular insurance plans, otherwise many patients could not use your service.
- You provide fast analysis, tests are completed and reported within 48-60 hours at the most.
- You provide accurate, precise results.
If these basic, foundational levels of performance are met, then you are competitive. This is why convenience is so important and why it is an effective way of distinguishing one lab from another. The physician is looking for a way to get a blood sample from a patient that is easiest from the patient’s perspective.
Other factors include maintaining a high level of customer satisfaction. If these were not met it would not “kill the deal” but would decrease sales. Here are some important customer service elements that all employees of Fargo Medical Laboratories will emphasize:
- The receptionists and phlebotomists are friendly.
- A satisfactory specimen is secured on the first try.
- Patient discomfort is minimized.
- The phlebotomist was able to personify the laboratory and promote a positive impression between the lab and the patient.
These customer service factors will certainly be taught to all employees to ensure the most positive patient experience.
5.2 Marketing Strategy
Fargo Medical Laboratories will undertake a marketing strategy employing three means of communicating its new service offering:
- Direct mail . Local physicians will receive a flyer announcing the opening of Fargo Medical Laboratories and detailing the services offered. A list of physicians is easily obtained through the local licensing board.
- Personal introductions to Main Street Professional Building tenants. A representative from Fargo Medical Laboratories will visit all of the medical offices within the building as a way of introducing FML to the doctors. This will provide FML with an opportunity to develop a personal relationship with doctors, something that is useful and valuable for service providers within a licensed industry.
- Advertisements . Ads will be placed in the regional flyer that all licensed physicians receive as members of their local chapter of the American Medical Association (AMA).
5.3 Sales Strategy
Fargo Medical Laboratories’ sales strategy will be used to convert a qualified lead into a client by emphasizing three important services:
- Most forms of insurance accepted – This is important because the vast number of patients that will have their blood tested will not be self-paying, they will be using insurance. FML would not be a viable alternative if they did not accept popular insurance plans.
- Quick turnaround – A doctor’s diagnosis and treatment is often based on the results of the test. It is not reasonable to expect the patient to wait an excessive period of time for the results. Fargo Medical Laboratories will deliver results fast.
- Convenience – There is no other alternative that is more convenient than sending the patients to an office within the building.
5.3.1 Sales Forecast
Fargo Medical Laboratories had developed a conservative sales forecast for the three years of this business plan. A conservative forecast was chosen because the venture is being funded by bank debt, which is fairly risk-averse, and therefore, it is in Fargo Medical Laboratories’ best interests if they are able to meet the monthly sales goals. If the forecast was more aggressive it would be far easier for FML to miss sales targets and find themselves hurting financially due to inaccurate assumptions and forecasts. This would then cast doubt on the survival of the business.
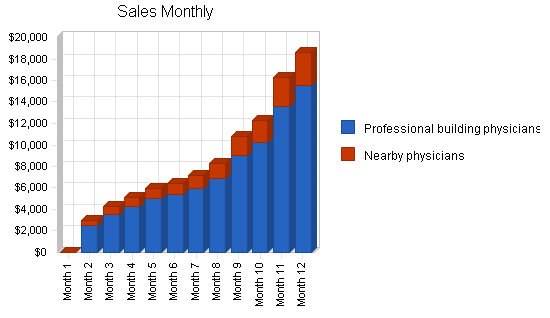
5.4 Milestones
Fargo Medical Laboratories has identified several milestones for the organization to achieve. The achievement of the milestones will be instrumental in the success of the the venture. By enumerating the milestones it provides the organization with clear goals that everyone can focus their energy on.

Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Dave Gigsted is the founder and manager of Fargo Medical Laboratories. Dave received his undergraduate degree in Small Business Management from the University of Illinois. While in college, Dave worked at a bicycle shop, initially as a mechanic, moving up to assistant manager by the time he graduated. This provided him with hands-on business experience to combine with his business degree.
Upon graduation, Dave began his job search, including opportunities in the medical profession. His mother and aunt are both registered nurses who shared with Dave that, at that time in Illinois, lab technicians were in short supply. So Dave enrolled in an eight-month program through the community college for a degree in Laboratory Technology. After completing this degree, Dave went to work at a laboratory. Within two years, he had been promoted to Lab Manager. Dave found this work challenging, enjoyed the medical aspect and worked hard in the business end of the job.
After five years, Dave and his wife moved to Fargo for a job opportunity for his wife. He immediately began working at a laboratory and worked there for a year. During this time Dave began looking into different business opportunities, recognizing that he had now developed sufficient business skills to operate his own business. Dave found there was a high concentration of physicians in a professional building with no nearby lab. In talking with people, he learned the physicians were looking for a lab to relocate to the building but but had been unable to find any. Armed with this information, Dave began to draft a business plan confident that with a solid strategy and comprehensive plan he would be able to find financing and begin his new venture.
6.1 Personnel Plan
- Dave will handle business development, sales, marketing, accounting, courier, customer service, and assorted lab tech work.
- Two phlebotomists on staff at any one time to draw blood
- One Lab technician will be responsible for doing onsite blood tests. This will be a part-time position. Dave will be able to fill in as needed in this capacity
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The following sections will outline important financial information.
7.1 Important Assumptions
The following table includes important financial assumptions.
7.2 Break-even Analysis
The Break-even Analysis indicates what will be needed in monthly revenue to reach the break even point.

7.3 Business Ratios
The following chart provides business ratios for Fargo Medical Laboratories as well as for the blood-related health industry, SIC Code 8099.01. Fargo Medical Laboratories’ ratios are consistent with the industry, with the exception of liabilities because it is a start-up organization that is relying on financing for its start-up costs.
7.4 Projected Profit and Loss
The following table will show annual projected profit and loss. A net loss will occur the first year, with well developed profit in year two and year three.

7.5 Projected Cash Flow
The following chart and table describe the projected cash flow. Because we will have a large starting balance because of our initial bank loan, our cash flow should be strong enough to cover our expenses as the business becomes established. The only concern will be to monitor the accounts receivable balances, since the majority of our revenue will be in receivables.

7.6 Projected Balance Sheet
The following table will indicate the projected balance sheet. We will achieve positive Net Worth in the second and third years.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Website Design & Development Services
- Startup Branding
- Paid Marketing
- Organic Marketing
- Market Research
- Business Plans
- Pitch Decks
- Financial Forecast
- Industry Market Research Reports
- Social Media & Website Guides
- Case Studies
- Services Marketing Website Design & Development Services Startup Branding Paid Marketing Organic Marketing Consulting Market Research Business Plans Pitch Decks Financial Forecast
- About Resources Articles Templates Industry Market Research Reports Social Media & Website Guides Case Studies Team
Food Testing Lab Business Plan Template
Explore Options to Get a Business Plan.

Are you interested in starting your own Food Testing Lab Business?

Introduction
Global market size, target market, business model, competitive landscape, legal and regulatory requirements, financing options, marketing and sales strategies, operations and logistics, human resources & management.
How to Start a Profitable Laboratory Testing Business [11 Steps]

By Nick Cotter Updated Feb 02, 2024

Business Steps:
1. perform market analysis., 2. draft a laboratory testing business plan., 3. develop a laboratory testing brand., 4. formalize your business registration., 5. acquire necessary licenses and permits for laboratory testing., 6. open a business bank account and secure funding as needed., 7. set pricing for laboratory testing services., 8. acquire laboratory testing equipment and supplies., 9. obtain business insurance for laboratory testing, if required., 10. begin marketing your laboratory testing services., 11. expand your laboratory testing business..
Starting a laboratory testing business requires a comprehensive understanding of the market dynamics. It's crucial to assess the demand for testing services, identify potential competitors, and understand customer needs. Here's how you can perform an effective market analysis:
- Research your target market to determine the size, growth trends, and demographic characteristics of potential clients.
- Analyze competitors by looking at their market share, strengths, and weaknesses to identify gaps in the market.
- Explore industry trends, such as regulatory changes or technological advancements, which can create new opportunities or challenges.
- Understand customer requirements by engaging with potential clients or conducting surveys to gather feedback on their needs and preferences.
- Assess the pricing strategies used by existing laboratories to establish a competitive yet profitable pricing model for your services.
- Identify potential barriers to entry, like high initial investments or stringent regulatory requirements, to prepare a risk mitigation strategy.

Are Laboratory Testing businesses profitable?
Yes, laboratory testing businesses can be very profitable. The size and scope of the laboratory business will determine how profitable it can be. Factors such as location, services offered, and the number of clients serviced may also affect the profitability of the business.
Starting a laboratory testing business requires careful planning and a well-thought-out strategy. A robust business plan is crucial for outlining your business goals, securing financing, and guiding your operations. Here’s a guide to drafting your laboratory testing business plan:
- Executive Summary: Begin with a concise overview of your business, including your mission statement, the testing services you will offer, and your target market.
- Market Analysis: Research your industry, identify your competitors, and understand your potential customers. Highlight the demand for laboratory testing services in your chosen niche.
- Organization and Management: Outline your business structure, detail the experience of your management team, and describe the operational workflow of your lab.
- Services Offered: Clearly define the types of tests and services you will provide, along with any unique selling propositions (USPs) or specialized capabilities.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: Explain how you will attract and retain clients, including your marketing channels, sales tactics, and pricing strategy.
- Funding Request: If applicable, specify the amount of funding needed to start and expand your operations, detailing how the funds will be used.
- Financial Projections: Provide an estimate of your financial outlook for the next few years, including projected income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
How does a Laboratory Testing business make money?
A laboratory testing business can make money by charging a fee for each test it performs. The fees charged can vary depending on the type of test and the complexity of the test. The laboratory may also offer consulting services or laboratory equipment for an additional fee. Additionally, the laboratory may receive grant funding or other forms of financial support from government agencies or private entities to help cover costs.
Creating a strong brand for your laboratory testing business is crucial as it helps to establish credibility and attract customers. Your brand should communicate your company's values, expertise, and differentiate you from competitors. Follow these steps to develop a compelling laboratory testing brand:
- Identify Your Unique Value Proposition: Determine what sets your lab apart, whether it's specialized services, cutting-edge technology, or exceptional customer service.
- Choose a Memorable Name: Select a name that is relevant to your services, easy to remember, and resonates with your target audience.
- Design a Professional Logo: Your logo should be distinctive and convey your brand's essence. Consider hiring a professional designer to ensure quality.
- Create a Consistent Visual Identity: Use a cohesive color scheme, typography, and imagery across all marketing materials to reinforce your brand identity.
- Develop a Brand Voice: Decide on the tone and language that reflect your brand's personality, whether it's authoritative, friendly, or informative, and use it consistently in all communications.
- Launch a Website: Establish an online presence with a professional website that provides information about your services, qualifications, and how clients can contact you.
- Engage in Marketing: Utilize online and offline marketing strategies to promote your brand and reach your target audience effectively.
How to come up with a name for your Laboratory Testing business?
When coming up with a name for your Laboratory Testing business, it is important to choose one that is memorable and easy to pronounce. Consider incorporating words like “lab”, “testing”, “analytics”, or “solutions” into your business name to indicate the type of services you offer. Additionally, you may want to include words that reflect the values that are important to you, such as “reliable”, “accurate”, or “innovative”. Finally, it’s a good idea to run a search on the internet to make sure the name isn’t already taken.

Starting a laboratory testing business requires not only expertise in the field but also ensuring that the business is legally recognized. Formalizing your business registration is a critical step to establish your lab's legitimacy and to comply with local, state, and federal regulations. Below are the key bullet points to guide you through this process:
- Choose a business structure: Decide whether your lab will be a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation. Each structure has different legal, tax, and financial implications.
- Register your business name: If your business name is different from your own, you'll need to register a 'Doing Business As' (DBA) name.
- Obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN): Apply for an EIN via the IRS website. This number is necessary for tax purposes and to open a business bank account.
- Apply for licenses and permits: You'll need to obtain the necessary licenses and permits specific to laboratory operations, which can vary by location and type of testing.
- Register for state taxes: Depending on your location, register your business with your state's taxation department to handle sales tax, income tax, and other state taxes.
- Comply with OSHA regulations: Ensure your lab meets Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requirements to protect the well-being of your employees.
Resources to help get you started:
Explore vital publications, industry reports, and newsletters providing laboratory testing entrepreneurs with insights on market trends, operational best practices, and strategic business growth advice:
- CLIA Lab Navigator : A comprehensive guide and database for navigating the complexities of the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) certification and lab setup. No direct link provided.
- Lab Manager Magazine : Offers articles, webinars, and product news to help laboratory professionals manage their operations more effectively. Available at: https://www.labmanager.com/
- Dark Daily : An electronic resource featuring breaking news and trends in laboratory and diagnostics, including operational strategies for profitability. Visit: https://www.darkdaily.com/
- The Journal of mHealth : Provides insights into technological advancements, market trends, and regulatory changes affecting the mobile health sector, relevant for labs involved in digital health. Check out: https://www.thejournalofmhealth.com/
- Bioinformatics Review : Offers information on the latest tools and techniques in bioinformatics, crucial for labs engaged in genetic and molecular testing. For more information, go to: https://bioinformaticsreview.com/
- Medical Laboratory Observer : Provides clinical lab professionals with peer-reviewed articles, product news, and industry reports to enhance lab services. Access at: https://www.mlo-online.com/
Starting a laboratory testing business requires adherence to various regulations to ensure safety, quality, and compliance. The process of acquiring necessary licenses and permits can be intricate, depending on your location and the types of tests you'll offer. Here are the steps you should follow to obtain the proper documentation:
- Determine the specific regulations that apply to your type of laboratory by consulting with local, state, and federal health departments.
- Apply for a business license with your city or county clerk's office to legally operate in your area.
- Contact the state's Department of Health or similar regulatory body to apply for a clinical laboratory license if conducting medical or diagnostic testing.
- For specialized testing, such as environmental or food testing, obtain the necessary permits from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- Ensure compliance with the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) by applying for certification if your lab will be processing human specimens for health assessment or diagnosis.
- Consider obtaining accreditation from professional organizations, such as the College of American Pathologists (CAP) or the American Association for Laboratory Accreditation (A2LA), for credibility and quality assurance.
What licenses and permits are needed to run a laboratory testing business?
Licenses and permits required to operate a laboratory testing business may vary depending on the jurisdiction and type of business, but generally include a business license, laboratory permit or certification, occupational safety permits, and any necessary special permits or certifications for specific types of tests. You will also need to become certified or registered with the state and federal agencies that regulate the specific type of testing you will be providing (e.g., water quality testing). Depending on your location and the nature of your business, other permits may also be required.
Establishing a solid financial foundation is crucial for the successful launch of your laboratory testing business. Opening a business bank account will help you manage your finances effectively, while securing funding will enable you to cover startup costs and maintain operations. Follow these steps to navigate this phase of your business setup:
- Research banks that offer business banking services and compare their account options, fees, and perks. Choose a bank that aligns with your business needs and offers beneficial services such as online banking and low transaction fees.
- Prepare the necessary documentation, such as your business license, EIN, ownership agreements, and personal identification, to open a business bank account.
- Consider your funding needs and create a comprehensive business plan that clearly outlines your financial projections and funding requirements.
- Explore different funding options such as small business loans, investors, grants, and crowdfunding platforms to find the best fit for your laboratory testing business.
- Apply for funding with a well-prepared pitch or proposal that highlights the potential profitability and growth of your business within the laboratory testing industry.
- Once funding is secured, manage your finances diligently, keeping business and personal expenses separate, and regularly review your financial statements to ensure you remain on track.
Setting the right prices for your laboratory testing services is crucial to ensure business viability while remaining competitive. Careful consideration of various factors will help you arrive at a pricing strategy that reflects the value of your services and covers operational costs. Follow these guidelines:
- Analyze Costs: Determine all costs involved in performing each test, including equipment, supplies, labor, maintenance, and overhead expenses.
- Market Research: Investigate competitor pricing to understand where your services fit within the current market landscape.
- Value-Based Pricing: Consider the value your services provide to customers, such as faster turnaround times or higher accuracy, and price accordingly.
- Volume Discounts: Offer discounts for high-volume customers to encourage bulk orders and repeat business.
- Dynamic Pricing: Be prepared to adjust prices as market conditions, technology, and cost structures change.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure your pricing complies with any applicable laws or regulations in your region.
- Transparent Billing: Provide clear and itemized billing to maintain trust and avoid confusion with clients.
What does it cost to start a Laboratory Testing business?
Initiating a laboratory testing business can involve substantial financial commitment, the scale of which is significantly influenced by factors such as geographical location, market dynamics, and operational expenses, among others. Nonetheless, our extensive research and hands-on experience have revealed an estimated starting cost of approximately $172000 for launching such an business. Please note, not all of these costs may be necessary to start up your laboratory testing business.
Establishing a laboratory testing business requires careful selection of equipment and supplies to ensure accurate and reliable results. The equipment you purchase should meet industry standards and be suitable for the types of tests you plan to conduct. Here are some important steps to guide you in acquiring the right laboratory testing equipment and supplies:
- Identify the types of tests your laboratory will perform and the equipment required for these tests, such as microscopes, centrifuges, spectrophotometers, and chromatography systems.
- Consider purchasing both new and certified pre-owned equipment to balance cost and quality. Pre-owned equipment can be cost-effective, provided it is from a reputable supplier and comes with a warranty.
- Choose suppliers with good after-sales support and maintenance services to ensure ongoing reliability and accuracy of your equipment.
- Stock up on consumables like reagents, test tubes, pipettes, gloves, and other items that will need regular replenishment.
- Invest in calibration standards and quality control samples to validate your equipment and keep it running accurately.
- Ensure that your laboratory complies with all required safety equipment, including fume hoods, biosafety cabinets, fire extinguishers, and personal protective equipment.
List of Software, Tools and Supplies Needed to Start a Laboratory Testing Business:
- Computers, software and printers
- Testing and measuring equipment
- Laboratory safety equipment
- Equipment maintenance, calibration and testing supplies
- Laboratory consumables and supplies
- Data storage and analysis software
- Laboratory furniture and fixtures
- Quality assurance and control software and systems
- Laboratory software and communications systems
- Laboratory security systems
Securing the right business insurance is a crucial step in protecting your laboratory testing venture against unforeseen risks. It not only safeguards your financial stability but also provides peace of mind as you focus on growing your business. Here are several types of insurance you might consider:
- General Liability Insurance: Covers injuries or property damage caused by your business operations.
- Professional Liability Insurance (Errors and Omissions): Protects against claims of negligence or harm due to professional services or advice.
- Property Insurance: Insures your laboratory equipment and premises against damage from fires, theft, and other disasters.
- Workers' Compensation Insurance: Provides benefits to employees who suffer work-related injuries or illnesses.
- Product Liability Insurance: Covers damages related to products you've tested, should they cause harm post-release.
- Business Interruption Insurance: Compensates for lost income and pays for operating expenses if your business is temporarily halted.
- Data Breach Insurance: Protects against losses resulting from breaches of sensitive data, which is critical for labs handling confidential information.
Consult with an insurance agent who specializes in scientific or medical fields to tailor a policy that fits the unique aspects of your laboratory testing business.
Launching a marketing campaign for your laboratory testing services is crucial for establishing your presence in the market and attracting clients. A well-planned strategy will not only raise awareness of your services but also build trust with potential customers. Below are some key steps to promote your lab effectively:
- Develop a Strong Brand: Create a professional logo and consistent branding materials that reflect the quality and reliability of your services.
- Build a Professional Website: Ensure your website is informative, easy to navigate, and includes clear calls to action for potential clients to get in touch or request services.
- Utilize SEO: Optimize your website for search engines to increase visibility for those looking for laboratory testing services online.
- Engage on Social Media: Use platforms relevant to your target audience to share informative content, news, and updates about your services.
- Network with Industry Professionals: Attend conferences, workshops, and networking events to build relationships with potential clients and referral sources.
- Offer Promotions: Introduce your services with special promotions or discounts to encourage first-time clients to choose your lab.
- Invest in Advertising: Consider paid advertising in industry publications, online platforms, or local media to reach a broader audience.
Expanding your laboratory testing business is crucial for long-term success and sustainability. Whether you're looking to offer new services, reach more clients, or improve efficiency, growth strategies must be thoughtfully planned and executed. Here are some actionable steps to help you scale up your laboratory testing enterprise:
- Diversify Testing Services: Introduce new tests and services to meet emerging market needs and attract a broader client base.
- Invest in Technology: Upgrade to advanced testing equipment and software to increase capacity, improve accuracy, and reduce turnaround times.
- Enhance Marketing Efforts: Boost your online presence, attend industry conferences, and engage in networking to promote your services.
- Build Partnerships: Form strategic alliances with other healthcare providers, research institutions, and businesses to expand your reach.
- Train and Hire Staff: Ensure your team has the expertise to support new services by providing training or hiring additional specialized personnel.
- Seek Accreditation: Obtain certifications from relevant bodies to enhance credibility and meet regulatory requirements.
- Explore Geographic Expansion: Open new locations or offer remote services to access untapped markets.
- Start a Laboratory
- Laboratory Buildout & Design
- Infectious Disease
- Lab Consulting Services
- Pathology Lab Solutions
- Lab Licensing Applications
- Test Menu Design
- Test Validation Services
- Commercialization
- Lab Growth Strategy
- Lab Management Services
- Remote Data Review
- Recruiting & Staffing Services
- Temp/Traveler Lab Staffing
- Pathologist Recruitment
- Job Seeker Services
- Lab Director Services
- Technical Consultant Services
- RCM Solutions
- Payer Strategy Solutions
- Laboratory Billing Audit
- RCM Spotlight
- Instrument Services
- Instrumentation & Supplies
- LCMS Instrument Solutions
- Chemistry & Immunoassay Analyzers
- Lab Instrument Refurbishment
- Quality & Compliance Consulting
- Regulatory Compliance Consulting
- Inspection Preparation
- Alternative Proficiency Testing
- Lab Information System
- CovidNow / SalivaNow
- Direct to Consumer
- News & Press
- Philanthropy
- Strategic Partnership
- LinkedIn Community
- Facebook Community
- Clinical Lab Jobs
- Send Your Resume
- Temp/Traveler Lab Work
- Interview & Resume Tips
- Join Our Team
- Lab Director Opportunities
- Lab Director Jobs
- Lab Regulations By State
- Articles & Industry News
- Webinars & Newsletters
- Ethics & Compliance
- Medical Lab Jobs
- Candidate Services
- Social Media Resources
- Lab Regulations by State
- Lab Personnel FAQs
- Pathology CPT Codes

Industry Insights
by lighthouselab | Apr 25, 2022 | Clinical Laboratory , Consulting Services , Industry Insights , Tips for New Lab Owners | 5 comments

One of the first steps you need to take to transform your ideas for a lab business into a functioning laboratory is to create a business plan. A business plan details your business’s objectives and how it will achieve its goals. Your business plan will help keep executive members focused on what’s good for the company and can help your business attract investments from external interests.
The document provides relevant marketing, financial, and operational information that explains how the business plans to achieve its goals. And just as your business changes and adapts, you will need to periodically revisit and revise your business plan to keep it current. Understand these key components of any successful laboratory business plan:
1. Executive Summary

Your executive summary should include the following:
- The mission statement: a short statement, either a single sentence or short paragraph, that describes the company’s purpose of existence.
- The business opportunity : describe the need or opportunity the market presents and how your business meets the need or opportunity.
- The target market: the customer base you’re targeting. You can define your target market by checking out the competition, analyzing your products and services, and choosing specific demographics to serve.
- The products and services: describe what your business offers and how these products and services appeal to your target market.
- The marketing and sales strategy: briefly outline your plans for marketing your products and services. How will you generate interest in your laboratory and convert that interest into actual sales?
- The competition: What businesses do you compete with? Why will customers choose to use your business rather than your competitors’?
- Financial analysis: summarize the financial plan, including projections for at least the next three years. These projected statements are often called pro-forma financial statements, or simply pro-formas. They include the overall budget, current and projected financing needs, a market analysis, and the company’s marketing strategy.
- Owners and staff : describe the owners, key staff members, and their relevant expertise.
- Implementation plan: outline the steps and schedule for taking your business from the planning stage to a functioning laboratory.
The executive summary provides a lot of information, but remember to keep it short—no more than two pages long. One of the easiest ways to write the summary is to complete sections of your business plan, then write a couple of sentences summarizing each section. When readers have completely read through the executive summary, they should understand what your business does, how it does it, and how it stands above the competition.
2. Products and Services
In this section of your business plan, clearly describe the products and services you offer, including pricing and unique features and benefits. Explain the demand for your products and services. If pertinent, include information about manufacturing processes, your company’s intellectual property, proprietary technology, and details about research and development.
Include a paragraph or two about how your lab will process and fulfill customer orders. Describe specialized equipment your lab needs to create and deliver products. You can also explain future products or services you plan to offer.
3. Market Analysis
Market analysis is a key component of any successful laboratory business plan . That’s because the healthcare landscape changes constantly, and the success of your laboratory depends on how well you understand the market. When writing your market analysis, include information on your target market, your competition, and potential changes in the industry that could impact your business. Describe the expected consumer demand for your lab’s products, as well as how easy or difficult it might be to grab market share.
When determining your target market, consider factors such as age, gender, location, and income level. Understand what needs or problems your target market has that your laboratory can solve.
Your competition includes any other businesses that are offering similar products or services to your target market. Research your competition carefully. Find out what they’re offering, how much they’re charging, and their strengths and weaknesses. Knowing this information can help you differentiate your own products and services and make your business stand out.
Finally, stay aware of any potential changes in the medical industry that could impact your laboratory business. These could include new regulations, technological advances, or changing demographics. Understanding these potential changes can help your business adapt and stay ahead of the competition.
4. Marketing Strategy
In the marketing strategy section of your business plan, you’ll describe how your laboratory will attract and keep customers. Explain your marketing campaign ideas and how you plan to deliver marketing messages.
Once again, it’s important for you to know your target market well so that you can develop a plan to reach them. You can implement your strategy with traditional marketing tactics like print ads, direct mailers, and radio advertising. Or you can use or include more modern marketing methods, like social media marketing and search engine optimization.
Your marketing strategy will contain your business’s value proposition. This proposition introduces your brand to consumers and explains why your company deserves their business. The marketing strategy should address the four Ps of marketing: product, price, place, and promotion.
5. Budget and Financial Planning
The financial plan, the final piece in your business plan, discusses potential costs and how to manage them. This section will include financial planning and future projections. Established businesses often include statements and balance sheets in this section. New businesses discuss financial targets, estimates, and potential investors for the first few years.
Include a pro-forma that projects future income and expenses. The main components of a pro-forma are:
- Revenue: Money you expect to bring in from patients, healthcare providers, and insurance companies. Don’t forget potential revenue sources such as government contracts.
- Expenses: The cost of supplies, equipment, staff salaries, infrastructure, leasehold improvements, and technology.
- Profit: The difference between revenue and expenses.
The pro-forma statement can help you obtain financing from lenders and investors. It can also help you plan for years in the future and anticipate changes as your business grows.
Start Your Business with Lighthouse Lab Services
Starting any business can be tough, but creating a successful laboratory comes with unique challenges. If you’re starting a medical laboratory business , rely on the expertise of Lighthouse Lab Services.
We have built over 150 laboratories across the country. You can work with our team of experts from the initial consultation through the launch of your business. Contact us for a free consultation to get started!
Sharing is caring!
Thank you for this good piece of information and guidance.
Thank you for your comment! Hearing this encourages us to keep writing more helpful articles for the medical laboratory industry.
I need to study the marketing plan for laboratory
A master piece of information. I am interested in opening a geologic laboratory as a private business
Glad you found this guide to be helpful! Good luck with your lab!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Name * First Last
- What are you interested in? * Lab Startup Program Instrument Service I'm a Job Seeker Toxicology Lab Consulting Recruiting or Temp Staffing Services Lab Consulting Services Lab Director Services RCM & Payer Strategy Solutions General Inquiry
- I consent to receive text messages from this business
State Licensing Contact Form
- State Contact Information * Alabama Alaska American Samoa Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware District of Columbia Florida Georgia Guam Hawaii Idaho Illinois Indiana Iowa Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine Maryland Massachusetts Michigan Minnesota Mississippi Missouri Montana Nebraska Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey New Mexico New York North Carolina North Dakota Northern Mariana Islands Ohio Oklahoma Oregon Pennsylvania Puerto Rico Rhode Island South Carolina South Dakota Tennessee Texas Utah U.S. Virgin Islands Vermont Virginia Washington West Virginia Wisconsin Wyoming Armed Forces Americas Armed Forces Europe Armed Forces Pacific Select to receive that state's contact information
- Additional Comments

- 3DConfigure
- Wet Lab Gallery
- Tech Lab Gallery
- Industrial Furniture Gallery
- Products Gallery
- Verticals Gallery
- Design Workbenches
- Submit Custom Request
How to Start a Laboratory Business from Scratch
9/30/2020 | 16 Likes | Verticals & Applications , Casework , Chemical Resistant , Cleanroom , ESD Environments , Healthcare , IT & Computers , Monitoring Applications , Pharmaceuticals , Sample Processing , Tech Lab , Wet Lab ,
What can you do to make your new laboratory startup venture a success? We take a look at the top 10 questions everyone should ask themselves before green-lighting a new laboratory venture.
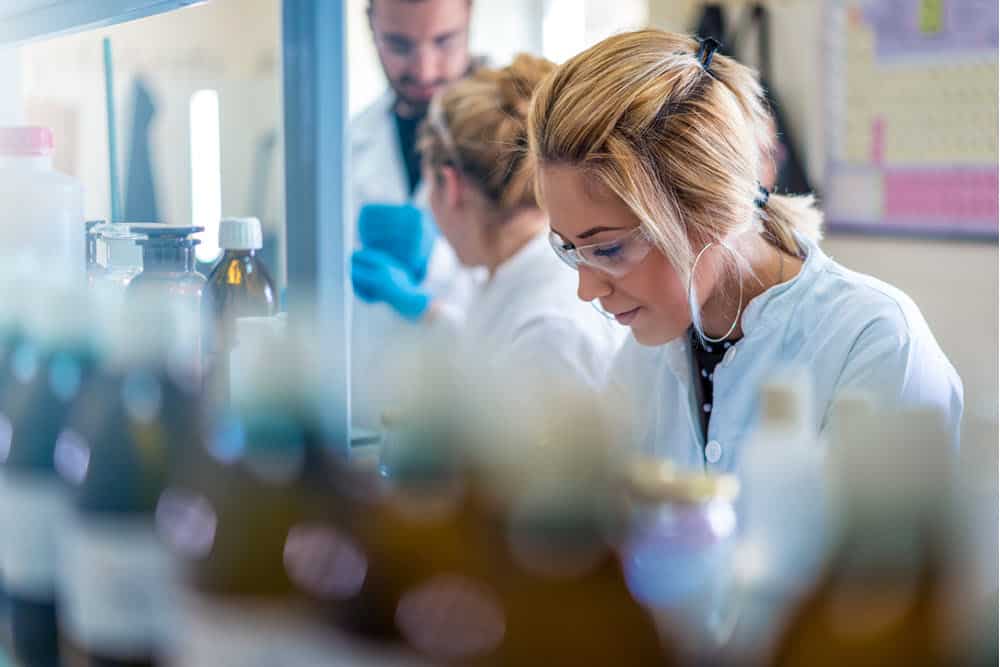

1. What is the Business Case for Your New Laboratory Startup?
Take the time to create a detailed business plan upfront — one that addresses the difficult questions — before expending scarce financial and human resources .
A good place to start is by researching the market demand and identifying the business case for your new venture.
Here are a couple of business case examples – but yours will need to be more detailed, backed up by solid technical and market research.
- To take advantage of new research/testing opportunities, such as those created by the Covid pandemic.
- Use new lab technologies to serve unmet demand in the market by out-competing/displacing other laboratories relying on older technology.
2. Who Needs Your Laboratory Services, e.g. Who is the Customer?
The next step in creating a solid laboratory business plan is to identify “ who is the customer? ”
In reality, there are often multiple answers to this question, so perhaps we should rephrase the question as “ who are the stakeholders? ”
Startup laboratories will need to identify what products and services they are offering to prospective customers in the market place.
But they will also need to treat their investors (e.g. the angel and VC firms making substantial upfront investments) as key stakeholders by delivering on the promises they have made in terms of project milestones and product and service deliveries.

3. What is the Funding Model and Return on Investment (ROI) for Your New Laboratory Project?
In normal times, commercial laboratories with a recurring revenue stream would find answering questions about funding sources and return on investment (ROI) to be fairly straightforward.
However, we don’t live in normal times right now.
The current Covid pandemic has shifted demand across many sectors of the economy, including the lab sector, which makes these economic models and investment calculations more difficult.
For example, demand for clinical healthcare testing (including Covid virus and vaccine trials testing) is up, while demand in other areas (such as petroleum well testing) is down.
This puts additional pressure on lab startups to identify viable funding sources to support the business after the initial funding runs out — by signing long-term customer contracts, obtaining multi-phase government research grants, or pursuing direct sales opportunities, such as direct sales of home testing kits sold to consumers over the internet.
It also puts greater pressure on controlling costs and justifying expenditures.
Fortunately, there are clever, cost-effective solutions available, such as efficient storage and flexible furniture options (such as mobile carts) that can help you get the most use out of your available square footage — while maximizing ROI at the same time.
Some lab startups may also benefit from taking advantage of local startup accelerators, which offer shared workspaces during the early venture stages.
4. Which Regulatory Regimes will Govern Your Laboratory Operations?
Every business is subject to some form of federal, state, or local regulations.
Broadly speaking, most of these regulations have to do with public safety; for example, does your facility meet fire regulations? Is it structurally sound? Are there enough emergency exits? etc.
In contrast, laboratory facilities tend to be highly regulated, often falling under one or more regulatory regimes that are either mandated by government agencies or set forth by industry trade groups that issue “certifications.”
The intended use of your laboratory will determine which sets of regulations or certification guidelines apply.
For example, laboratories designed for pharmaceutical or food manufacturing testing will need to comply with the FDA’s Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations.
Laboratories designed to handle potentially dangerous materials are subject to even more stringent regulations. Facilities handling radioactive materials must comply with the Department of Energy regulations, while labs handling potentially dangerous biological pathogens fall under CDC biosafety regulations, which classify labs according to four biosafety levels, BSL-1 through BSL-4.
(Only a few laboratories around the world qualify for the BSL-4 rating, designated for handling the most dangerous pathogens. These labs must incorporate highly redundant safety systems, including isolated clean room chambers where lab personnel wear special PPE, such as “spacesuit” type protective garments.)
5. What Kind of Lab Facilities Do You Need to Achieve Your Goals?
Now that we’ve identified the business case, the customer, the funding sources, and the regulatory regimes that govern your new laboratory startup, it’s time for the facility project managers to begin working with the architects and designers to develop a list of “architectural programming requirements“ for the new laboratory.
One useful piece of advice: avoid “reinventing the wheel.”
There are many well-documented laboratory designs that can provide inspiration for your projects. Evaluate as many as you can to identify what would work for you and what you’d like to do differently.
Another useful resource is the publication Forensic Science Laboratories: Handbook for Facility Planning, Design, Construction, and Relocation , published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). While (as the title suggests) its focus is forensic science laboratories, it clearly documents a set of best practices for managing laboratory construction projects.
From a design perspective, laboratory facilities generally include one or more of these components:
In the language of laboratory design, wet labs are the areas that handle liquid chemicals. Designers need to pay particular attention to specifying chemically resistant surfaces, a sufficient number of wet sinks (often with their own special waste handling drainage system), as well as fume hoods to protect workers from potential exposure to noxious gases or dangerous particulates.
Dry Labs / Tech Labs
The term “dry lab” traditionally refers to laboratory zones that handle dry chemicals in small amounts.
Thanks to the revolution in scientific computing, however, the role of dry labs has expanded tremendously over the past few decades to incorporate computer systems as well. This has led to the rise of the “ tech lab ,” where lab researchers access and manage computer workstations or provide IT services to the organization. The computer systems can be a major source of heat, so these areas will usually need beefed up HVAC systems. Redundant power systems (such as backup generators or batteries) are also typically required.
Laboratory Clean Rooms
An increasing number of laboratories, such as those supporting the manufacture of printing microelectronics onto silicon wafers, require the use of cleanrooms to prevent microparticles from contaminating surfaces or to protect lab personnel from dangerous pathogens.
Electronics Labs
Microelectronics can be damaged by even small amounts of electricity, such as static shocks. Laboratories engaged in prototyping and testing electronic equipment need to be equipped with anti-electrostatic discharge (ESD) systems to prevent inadvertent damage to electronic equipment.
6. How Will Your Laboratory Needs Change Over the Next 10 Years?
Predicting the future is always difficult, but if we were to make one forecast, it would be that change is inevitable.
Laboratory equipment is changing year-by-year, experimental methods are evolving rapidly, and computer-based scientific discovery methods are becoming one of the dominant forces in laboratory science.
So, given that change is inevitable, what can you do today when designing your laboratory to prevent it from becoming obsolete in 10 years?
The answer is to design in flexibility so that you can make changes over time without having to endure the interruptions caused by extensive renovation projects.
It’s this need for flexibility that is driving many laboratory customers toward specifying modular furniture solutions for their new lab projects. Unlike traditional casework installations, modular laboratories are built out of standardized components (including wet sink installations, fume hoods, workbenches, storage units, etc.) that can be installed on-site using ordinary hand tools.
As your needs change in the future, the task of rearranging the modules to meet your current requirements is greatly simplified. If you need to expand, you simply contact the factory (e.g. Formaspace) to order additional matching components to complete your lab expansion project. And, if you need to move, you can also easily disassemble and move the entire laboratory furniture set up to a new location without losing your initial investment.

7. What’s the Best Approach for Choosing a Lab Location?
The high cost of laboratory real estate, particularly in the so-called science clusters (located in the Boston and New York regions on the East Coast and the San Francisco Bay Area and San Diego on the West Coast), can be a determining factor when deciding where to locate your new lab startup.
In a departure from past practices, many new lab operations are opening in facilities originally designed for other purposes, such as underutilized retail locations, which can be leased at a relative discount compared to facilities that were originally purpose-built for laboratory operations.
If you’re evaluating the potential of converting an existing space into a lab facility, we recommend looking at our patented FabWall system. The modular FabWall system bolts securely into the floor, allowing you to divide open spaces into functional areas quickly and efficiently. Simply attach modular elements (such as wet sinks, workbenches, fume hood, and the like) directly to the FabWall.
The use of mobile lab furniture is another trend that facilitates the quick conversion of open spaces not originally designed for laboratory use.
Entire spaces can be kitted out quickly with workstations mounted on heavy-duty industrial-strength casters. Each workstation can support its own storage systems, shelving, as well as built-in electrical and networking connections.

8. How Can You Assure Laboratory Safety, Security, and Sustainability?
Safety first is the right mantra for laboratory design.
Here, details matter.
Double-check all safety requirements and make sure you are in compliance.
Questions you should ask yourself include: Are the fume hoods sized appropriately to protect lab workers? Are there a sufficient number of eyewash stations and first aid kits available? Is access to PPE well-thought-out – to encourage proper use? Is there adequate storage for potentially dangerous chemicals or fragile scientific equipment? Have you provided easily accessible drying racks for highly breakable glassware?
In many cases, specifying mobile storage carts can help prevent accidents when transporting heavy equipment; these can also make it easier to safely transport equipment in need of maintenance or service away from heavily trafficked areas to a dedicated service bay.
Protecting personnel from the Covid-19 virus is also another important consideration. Are lab workbenches spaced far enough apart to encourage social distancing? Are lab employees protected from one another by the use of transparent shields when they need to work in close quarters? Is the HVAC system designed to provide enhanced ventilation, ideally pulling air up and out of the facility rather than pushing it down toward the floor? Can you offer outdoor work areas for employees to conduct some of their work activities outside as well as provide pleasant outdoor areas for taking breaks and eating meals?
Greater emphasis is also being placed on lab security, especially given recent reports of foreign espionage directed at pharmaceutical research labs developing Coronavirus vaccines. Are your computer system sufficiently isolated and protected? Also, given that more employees will be accessing the outdoors, does the facility’s security perimeter policy take this into account?
Sustainability is another major concern in laboratory design. As we mentioned earlier, modular furniture designs can be reconfigured without difficulty, even moved to new locations if needed. This not only protects your original investment, it can also help you accrue LEED credits when performing future renovations or moving to a new facility.
Laboratory energy use is another important sustainability issue, especially given that most laboratories use energy at a greater rate than comparable office buildings (due to higher airflow requirements from fume hoods or cleanroom installations). Reducing energy use in laboratories remains a challenge, but new designs are showing it is possible, by increasing natural ventilation or redesigning the airflow in cleanroom installations for greater efficiency.

9. Will You be Able to Attract and Retain Lab Expertise/Talent?
The ability to attract and retain talent is a major concern for all companies, and laboratory facilities are no exception.
There’s a simple test you can take: Would you want to work in the new laboratory you’re planning?
Does your design provide enough of the in-demand features that today’s employees are looking for, including open sightlines, plenty of natural light, good noise control to prevent distractions, even some connection to the outside world, such as green plants or other natural elements?
Are you providing enough amenities to retain today’s workers? Keep in mind that wellness on-the-job is important these days, and offering a comfortable, ergonomic workspace is as good for you as it is for your employees. Formaspace can help you specify lab seating that is both easy to clean and maintain in lab conditions but also provides workers with enhanced back support as well as the ability to change positions throughout the day. That’s also a feature that’s available in Formaspace desks, tables, and workstations. Our optional sit-to-stand furniture allows employees to change from working in a seated position to a standing position throughout the day for increased blood circulation and reduced fatigue.

10. Where Can You Find the Right Laboratory Partners?
This brings us to our final question to ask when you are making plans to launch a new laboratory facility.
Where can you find the right laboratory partners who can share their experience?
One approach is to join one or more lab trade associations that represent your industry sector and speak to other members about whom they can recommend as reliable partners to work with.
It’s these kinds of word-of-mouth recommendations that may lead you to Formaspace.
Formaspace stands ready to help make your new lab project venture a success. We build all our lab furniture here in Austin, Texas, at our factory headquarters, using locally produced steel and other American-made raw materials.
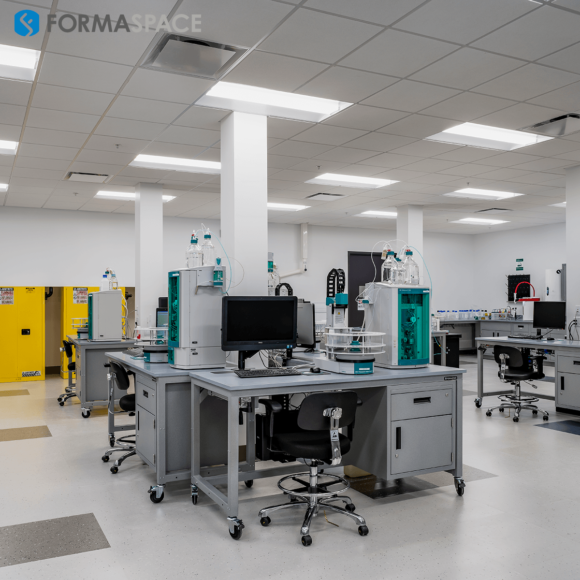

We have built furniture systems for hundreds of laboratories nation-wide; our client list includes Abbot Laboratories, Amgen, Baxter, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson&Johnson, Merck & Co., Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and Quest Diagnostics Inc.
Formaspace is also a great resource to turn to when you have questions about laboratory design. Our Design Consultants are standing by to answer any questions you have. We can also provide full-service assistance in designing your next laboratory project – even it’s your first one.
Will your project be next? We hope so.
Take the next step.
Talk to your Formaspace Design Consultant today and see how we can partner with you to make your next lab project a success.

Food safety testing – All you need to know
Food safety testing is a scientific-based method that evaluates the safety of food based on microbiological, physical, ...
Get your HACCP in 1 hour!

Create Your Food Safety System in 15 Minutes

- Food safety testing is a scientific-based method that evaluates the safety of food based on microbiological, physical, or chemical composition.
- Food safety testing must be accurate, specific, reproducible, established, and cost-effective.
- Proper food safety testing contributes as a solution to the growing demand for safe food and sustainability of supply all over the world.
Risking food safety can cost lives. Every year, countries all over the world suffer from economic losses due to food safety problems. It has been estimated that low to middle-income countries suffers at least $100 billion in losses per year as a result of foodborne illnesses. The importance of having access to a clean, safe, and sustainable food supply is a necessity for humans. To preserve the safety of the food supply, the food industry has established a set of food safety testing procedures.
The fact that no one can survive without proper nutrition shows how important access to safe food is. For everyday consumers, there is no way of telling if a product is safe other than through sensory or physical analysis. So how would they know if the food they are eating is safe? This point is where the role of food businesses in ensuring food safety comes in. As part of the human right to adequate food, every food industry body is mandated to ensure the safety of the public through food safety.
Learn what types of food safety testing do a food product must go through before reaching households in this article and get to know the best way t manage your food safety testing results.
Why is food safety testing important?
When we talk about any foodborne disease , the first factor that comes to mind is contamination by disease-causing microorganisms such as viruses, parasites, bacteria, and molds. In reality, chemical substances, as well as physical articles, can cause foodborne diseases or related injuries.
To detect these hazards respective food safety testing procedures are used. Through these scientific methods, food businesses ensure and verify that their products are free from food hazards that can harm public health. Food safety testing programs are also part of the solution to achieve global harmonization of food safety and security and to address the enormous demand for safe food all over the world. With proper food safety testing and quality assurance, food loss and production of unsafe food are minimized along with the other challenges of foodborne illnesses.
Food safety testing can also be used to evaluate foods that have been altered to withstand drastic conditions. Results from such tests can be used to inform and educate the public about the safety or dangers of such foods.
What is the goal of food safety testing?
The main goal of conducting food safety testing is to analyze food products and determine if they are safe for consumption. Testings support the claim of food businesses regarding their compliance with food safety regulations and laws and that their operations are up to food safety standards. These activities are essential in providing the best and safest consumption experience and ensuring food quality. The requirements for conducting food safety testing highlight the importance of food safety .
Food safety testing procedures are the responsibilities of food handlers and food manufacturers. Every food business is mandated to conduct particular food safety testing and to have a food safety testing lab to achieve the following specific goals:
Safety and prevention of illnesses
As mentioned, food safety testings evaluate food products for their safety. Procedures for detecting whether the correct doneness of the food was achieved can be backed up by further testing. Such testing can be done by acquiring samples or a food ingredient from the processed batch and testing them for the presence of target microorganisms. The results from these evaluations can be used as a basis for whether to release products to market safely. Food safety testings are specific, precise, and reproducible. Therefore, credible food safety testing procedures can be used on an honest basis.
Inform consumers
Perhaps the best example for the function of food safety testing as a form of educating everyday consumers is the case of genetically modified foods (GMO). As an answer to the never-ending concerns of consumers regarding GMOs, the FDA has concluded that all genetically modified food products require special safety testing and food safety testing laboratories. Through proper food safety testing, newly developed consumer products can be evaluated before their release in the market to reduce consumer exposure and preserve their safety. Results from such evaluations are commonly peer-reviewed to ensure accuracy.
Sustainability
Scientific food safety testing methods are part of the answer to sustainability and the growing food demand. By ensuring that the produced foods are safe, losses are reduced and the consistent production of food can keep up with the growing food demand. To achieve a sustainable future, the complementing features of food safety and security must be thoroughly emphasized.
Increased productivity
In relation to sustainability, the lack of foodborne illnesses also ensures that all members of the community can perform their tasks without interruptions. Foodborne illnesses contribute to the major factors that use up medical services and lower service in any industry. Food safety testing provides an accurate basis to ensure the safety of all members of the community.
All of these goals are only achievable if food safety testing is conducted consistently with precision and accuracy. As such, the importance of regularly updating the results as a response to potential changes must be emphasized for all food industry segments. To ensure that the results of your food safety testing are always organized and updated, use digital solutions offered by FoodDocs. We will explain more later in this article.
What are the main types of food safety testing?
Food safety testings normally deal with the chemical composition of food, the presence of pathogens, the physical properties of food, and the potential presence of unwanted and potentially unsafe ingredients or adulterants. Established and respective testing methods are available for each target concern such as traditional agar methods for detecting the presence of unwanted microbial growth. Proper identification of the presence of potential hazards is part of a comprehensive HACCP plan and food safety management system. The correct execution of accurate testing methods is essential to achieve this goal and requires testing experience.
Here are some of the most common food safety testing conducted in food safety labs:
Microbiological testing
A wide variety of pathogenic microorganisms or those that can cause foodborne illnesses are the primary sources of food problems. Some pathogens can manifest signs of spoilage in foods, whereas some can be undetectable unless with a food safety test. Some of the common foodborne illness-causing pathogens include:
- Escherichia coli (causes traveler's diarrhea)
- Staphylococcus aureus
This type of food safety testing takes time but is accurate and is often used as a solid basis for food safety. Each foodborne pathogen has its microbiological testing protocol but all methods involve acquiring a sample of food from each batch and testing for the presence of the target foodborne pathogen. The presence of pathogenic microorganisms can be an indication of inadequate or inappropriate processing, problems with raw materials, damaged packaging, or inappropriate storage temperature for storage.
Alternatively, swab testing is also conducted to test for the level of sanitation on food contact materials and surfaces such as tables, conveyor belts, and plastic crates for storage. More advanced food testing laboratories also offer DNA-based tests which yield instant results when compared with traditional agar-based methods.
Chemical testing
This type of testing is commonly used to detect problems such as the presence of adulterants, excessive cleaning agents, or even indications of processing abuse in the form of chemical by-products. Chemical tests can also be used to establish standard processing operations by determining if unsafe byproducts are produced within certain ranges of parameters. Examples of chemical tests that are common in various food industry segments include:
- Trace element or contamination detection
- Food safety testing kits for the presence of sanitizing agents on food contact materials and surfaces
- Detection of pesticide residues
- Chemical property tests such as proper acidity levels in canned foods
Although not very obvious, food safety testing can also include nutritional analyses of foods. This type of testing involves an approximation of the nutritional composition of a product which includes fat, protein, carbohydrates, caloric value, and other major compositions. This analysis can be considered chemical testing but is more commonly used for labeling requirements.
Physical testing
The presence of filth, sharp objects, and insect parts are all considered physical contaminants and are potential carriers of foodborne illnesses and related injuries. Food safety testing involved in this type of analysis can include the use of machines such as metal detectors or x-rays. More traditional testing methods such as using a sifter with different mesh sizes to detect pieces of any physical hazard during raw material receiving. Additionally, sensory evaluations, mostly aroma and visual observation, are also part of physical food safety testing. This, perhaps, is the most convenient way of food safety testing. Some food contaminants such as microbial growth can produce unwanted odor and can serve as signs of spoilage. Although, consumption of finished products for analysis of safety is not very advisable especially for past due food items.
Depending on the analyzed food safety hazards of a food product and food process operations, food safety testing can significantly vary. Testing procedures are established after the identification of the potential hazards and their significance in processing.
Characteristics of a good food safety testing
There is a lot at stake when conducting an actual test method. A poorly designed food safety testing procedure can result in false-negative results which can release finished products that are potentially contaminated. As such, food safety tests must be standardized and have particular characteristics for application to be considered effective.
Below are some characteristics every test procedure should have to solve food safety challenges:
- Specific. A food safety testing must be able to identify its target contaminant. A broad-range food safety test can sometimes confuse and may lead to incorrect diagnoses. If you are keen on using multi-target food safety testing methods, make sure that your test procedures have specific markers to measure your desired target. Specificity also indicates that the food safety test must not cross-react with other food substances which can indicate a false-positive result.
- Accurate. The results of an analysis for food safety must be able to read beyond the acceptable food safety standards of a parameter for clarity but offer accurate readings. Your testing procedure must be able to give results that are not vague and can be easily distinguished for ease of use. If a testing procedure gives a very wide range of results, then the purpose of the testing is defeated.
- Reproducible. Food safety tests are routine tasks. This means that they have to be repeated to ensure the consistency of food quality and safety of food production. As such, the test must be precise in producing results.
- Established. Regulatory bodies and concerned organizations have also established guidelines for food safety tests and their acceptable results. Any deviation from these established steps must be justified in your food safety management system manual.
- Cost-effective. Some food tests, cost quite a bit, especially the ones with the technology to give instant or rapid results. This fact is because faster results mean the faster release of finished products. Make sure that the benefits agree with your means to sustain continuous use of this test. Although, opting to buy affordable food safety sensing supplies must not mean sacrificing effectiveness.
Food testing procedures are usually established through a series of tests conducted by food industry experts and are commonly designed to be used by food processing plants. As the food industry moves toward globalization and away from traditional methods, more advanced technology and efficient food safety tests become available. The results of these tests can become too much to handle given the frequency of testing for some procedures. Additionally, it may become hard to keep up with them if you have a lot of tests for your food manufacturing practices. Allow our food safety management feature with a built-in HACCP plan builder to help you organize and consistently monitor these tests.

Digital solution to help in food safety testing
A single food establishment can have a variety of food safety testings for its food manufacturing practices. Not to mention, if you are dealing with GMOs, you would have to submit to a stricter approach to food safety as the FDA has concluded that all genetically modified food products require special safety testing. It would be crucial if you miss a scheduled food safety test as this can mean a higher risk of causing an outbreak of foodborne disease. As such, it must be part of your food safety management system and HACCP plan to establish the necessary food safety testing.
At FoodDocs, our food safety experts have developed a digital Food Safety Management System (FSMS) which can help you organize and monitor your food safety testings and make sure that not a single test is missed. Our digital FSMS allows food manufacturers and any food establishment to switch from your traditional manual FSMS to a completely digital system in just 15 minutes. Our digital FSMS provides you with complete monitoring forms, checklists, and food safety testing procedures based on your food business operations.
Let us help you achieve continuous compliance and solve your challenges with food safety regulations and achieve sustainability with our systems. When you join us at FoodDocs, you can also gain the following benefits:
- Our machine-learned system suggests the most important food safety testing and laboratory evaluations related to your food business.
- We automatically set up the standard frequency required for specific tests and the corresponding monitoring form for these food tests that are automatically prefilled for your convenience. Your only remaining task is to verify the logged entries.
- Ensure the quality and safety of your foods by never missing any of your food safety tasks as our system automatically notifies through our mobile app.
- Under our built-in HACCP plan builder, all automatically generated testing procedures and appropriate frequencies are mentioned in your analysis plan section. The general tests that we include depend on your food business but will include water quality, air, and other environmental analyses.
- Monitor your food processes and testings using our real-time dashboard that reflects your everyday progress. This report can be downloaded for documentation.
- As a complementary feature of food safety testing, our FSMS also has a food production traceability feature that will allow you to track down any non-compliant batches based on your tests.
- Keep all information and documents in your cloud storage for easier accessibility and more efficient organization.
Remaining compliant with food safety laws and regulations while fulfilling the goals of food safety testing has never been this easy. Our objective at FoodDocs is to create a safe food supply chain by making digital FSMS more accessible and efficient for all food businesses.
Signing up with us at FoodDocs also means you get 20% more free time on managing food safety tasks. You can use this time to focus on managing your business with very minimal involvement in food safety tasks. Our user-friendly system was built to accommodate every food business owner's needs. You can easily set up your digital FSMS after you sign up for our free 14-day trial .

Similar posts
Fish company egersund seafood: the safety of food products raised 100%.
FoodDocs helped us to systematize all stages of food safety control. The annual audit showed that the safety of our food products is 100%.
The "correct" ways to call HACCP
Our team at FoodDocs has encountered many different “interpretations” of how the most famous food safety program is spelled (and pronounced).
How Coju’s juice bar implemented FoodDocs’ solution in no time, independently
Read, how the implementation of the FoodDocs food safety management system was done in no time and free of any hassle.
(877) 753-6631

877.753.6631

Food Testing, Labeling and Consulting Services
The biggest label change in 25 years.
Our experts will help you every step of the way to get your products ready for the new FDA Label requirements.
We're Here To Help

FDA Compliant Food Label Services
Pet Food Laboratory Testing & Labeling

Food Consulting Services

Restaurant Menus
RL FOOD TESTING LABORATORY, Inc
Food testing, fda nutrition labeling & food consulting services.
Whether you are looking for FDA-approved Nutrition Facts Labels or need food laboratory analysis, we’ve got you covered. We offer a wide variety of services, making us a one-stop shop for all of your food labeling and food testing needs.
FDA Food Labels
Food labeling is required for most prepared foods. If you are planning to sell your product in a retail environment, then you will more than likely be required to comply with FDA labeling regulations.
Food Testing
Many food products being sold in retail will require laboratory testing such as Shelf Life Testing for determining an expiration date, or Allergen Testing to detect any traces of food allergens.
Food Consulting
Often times, food companies — big and small — need expert help. Whether it is a recipe modification or help with a HACCP plan for food safety, it is imperative for the success of your business to get the right advice.
Why RL Food Testing?
Your recipes are safe with us.

Work Accuracy Guarantee
100% accurate and FDA compliant or your money back.*

We have helped thousands of happy clients since 2005

7 Days a Week!
Available 7 days-a-week to answer your questions.

A+ rating with BBB

What our Customers are Saying

"I am a startup online bakery in California. Trying to navigate the nutritional labeling world and requirements was daunting. I did not know the first thing about getting nutritional labels done for my products. I was beyond grateful when I found RL Food Testing Laboratory. I do not know what I would have done without there incredible help, knowledge and professionalism. They were kind and patient with all of my questions and help needed. Something not common in todays market place is an actual phone call. I can speak to anyone if I have questions. They are also very fast in returning emails. The end product looks fantastic and I have peace of mind these were done correctly and their rates are exceptional. They also email important information and changes coming. I appreciate this!! I have had multiple labels done and I would not trust this to anyone else. Thank you all at RL Food Testing Laboratory."
"We started our company with nothing more than a few great recipes, business experience, an optimistic outlook, but we had absolutely NO KNOWLEDGE of the food industry. Many calls were made and R.L. was the only one who returned my call in less than 24 hours. RL not only has made what others in the industry have described to us as a very difficult process simplified and easy, but also something we could afford as well. Their friendly team goes above and beyond what we ask as well as pay for. As our favorite R.L. team member Maria says, "We are here to grow with you!" R.L. is fast, reliable, well priced, always available, and completely dedicated to your companies needs. We are truly grateful for this company and more importantly their team!"
"Working with Maria and the entire team at RL has been a genuine pleasure. We've worked them for a few years now, and have received nothing but the best quality service, professionalism, and results. I've recommended RL to several other small business owners and will continue to do so in the future. Using RL makes us feel like we're using our money wisely, we feel valued as people, and we can't recommend them enough."
"For the past 5 years, Cinnaholic has partnered with RL Food Testing Laboratory to ensure our compliance with the FDA nutrition labeling guidelines. The process is easy and our main point of contact, Maria, is quick to respond and provide assistance as needed. The team at RL Food Testing Laboratory completes requests in a timely manner and proactively assists in managing label requirement updates. These are just a few highlights of why we're thankful for our partnership!"
"We have worked with RL Food Testing Laboratory team on a few client’s nutrition and ingredients labels and the team was very helpful and supportive. We also work with them on our all-natural nutrition and ingredient label which we thought was going to be a nightmare but Maria was very knowledgeable and everything turn out great."
Recent Reviews
Meet THE OWNERS

Co-founder and Senior Nutrition Chemist
Roger is the senior chemist at RL Food Testing Laboratory, one of the premiere food testing lab resources in the US. He graduated from UCLA with background in Biochemistry and Organic Chemistry

Sharon M. Vessels
President & CEO – Co founder
Sharon manages all aspects of RL Food Testing Laboratory as well as ensuring RLFT is up to date on the various USDA and FDA regulations surrounding food labeling and testing.
Our Clients

Information
Call Us 877.753.6631
We’re Here To Help!
Contact Us [email protected]
We’ll Reply Within 24 Hours
- More Information
- Our Services
RL Food Testing Laboratories Food Labeling, Testing and Consulting Services
Restaurant menu nutrition labeling, food label services, canadian nutrition labels, fda food nutrition labels, food testing services, food nutrition analysis, shelf life testing, pet food analysis, food allergen testing, recipe modifications, privacy overview.
- Professional
- Accessibility
- Search website Search Site
- Food Safety
- safefood for business
- How to protect your food hypersensitive customers
- How to implement Natasha’s Law
- The fourteen allergens
- Coeliac and gluten-free guides
- Gluten-free under the law
- Further Resources
- Definitions
Plan properly for microbiological testing
- What to test for? Contamination issues
- Controlling food pests
- Hygiene for small food businesses
- Protect your business from food fraud
- Precautionary Allergen Labelling
- Cooking demos
- Cutting down on food waste
- Product shelf-life testing: All you need to know
- Food safety skills fund
- Join the Knowledge Network
- Managing metabolmics interpretation
- Catering to All
- Joe Dunne: Virtual audit technology
- Martin Danaher: A day in the life
- Joost L.D. Nelis: Smartphones as a food safety tool
- Food intolerance podcast transcript
- Food fraud podcast transcript
- Remote auditing podcast transcript
- Transcript: Lactose-free, milk allergy, milk intolerance, explained
- Impact of Covid on the food industry podcast transcript
- Food packaging podcast transcript
- Allergen control podcast transcript
- Hygiene and cleaning podcast transcript
- Food allergen labelling podcast transcript
- Lab Testing Explained
- Microbiological testing: what food businesses need to know
- Food safety laboratories
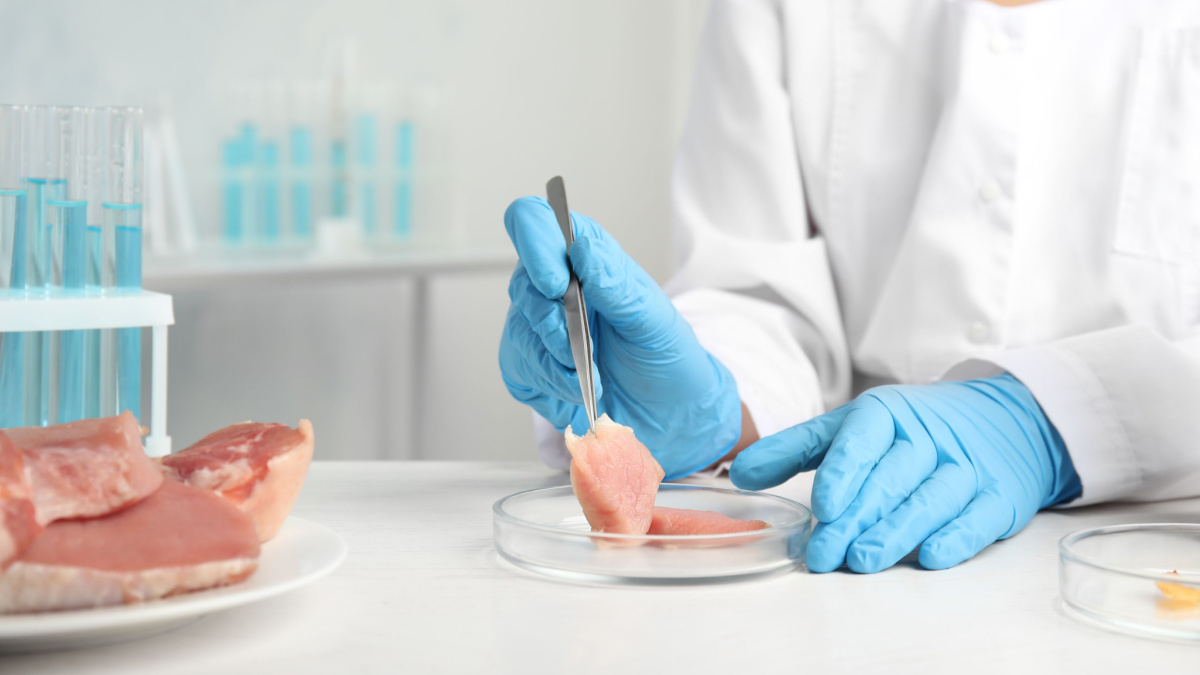

A properly designed microbiological testing plan is vital for small businesses if they are to achieve their objectives and avoid wasting time and money, writes Roy Betts
Food producers frequently need to do microbiological testing. Some producers will have a good knowledge of what to do in these situations, for others it will be challenging journey into the unknown. Here we try to shed some light onto the process of getting foods tested for microorganisms, hopefully making that journey a little less fearful for the uninitiated. The first thing to make clear is that testing will never assure safety. You can never ‘test’ a food safe. Safety is designed and manufactured into foods, and this involves the correct use of risk assessment and risk management procedures. The classic risk management procedure is correct implementation of HACCP and testing plays a role as a HACCP verification activity.
As a testing laboratory we will often get requests from producers to test their products for ‘full micro’. This term has no meaning and would tend to suggest that the requester has no real understanding of what they need, what the significance of the tests are and more importantly, what they will do with the results. On occasion, even producers who have long standing sampling and testing plans may find that they have not revisited their plans for many years and may be doing unnecessary testing, or worse not testing for something that they really need to. So, what are the steps when thinking of undertaking microbiological testing?
1. Define the need
The first requirement is to understand the need: ‘why do I want to test? This may be driven by legislation, or customer specifications, or simply that the producer has identified a requirement to do a particular test. There must be a reason why a test is required, and this must be understood. It may be for safety reasons: testing for a pathogen to verify the HACCP plan is working, or for the presence of a viable microorganism in a sterile food. It may be for quality reasons: testing for a spoilage organism that would reduce shelf life, or it could be to check hygiene in production by looking for ‘hygiene indicators’. Never set out to test a food until you know the objective of why you are testing.
2. Determine the goal
Before you start to test, you must know what you will do with the results. When you get a test result you will have information that you did not have before, and you must know how you will use that information. If you test for a pathogen, never assume that every test will be negative. What will you do when you get a positive pathogen result? What action will you take. You need to determine and document this before you start testing. Similarly, if the test is for a spoilage organism or hygiene indicator organism, you will need to have set ‘accept/reject’ criteria and maybe also an ‘action level’, but the question is what action will you take. Again, this must be determined and documented before you start to test.
3. Establish the criteria
It is usual for companies that undertake microbiological testing to set out their ‘microbiological criteria’. These are important statements that document several key points about the microbiological testing that you do. Some of the items that must be included in any microbiological criterion are listed here:
a) The test item: is this a product at the start of its shelf life; an end of life sample; a work in progress sample; an ingredient; an environmental sample from a particular point in production. Basically, what are you going to test.
b) What are you going to test for: This may be a single organism, or a whole range of organisms and groups. This part of the criterion may be driven by legislation, customer specification, a need for HACCP verification or simply a perceived risk, but the decision must be based around the Step 1 noted above: you must know why you are testing
c) How are you going to test it: what test method do you want to use? It is possible that the test method will be defined in legislation, or in a supplier specification, but it is up to you to decide how the test will be conducted and what method will be used. If you don’t feel that you have the right knowledge and expertise to do this, it may be worth calling in a reputable consultant to help.
d) Sampling: how many samples are you going to test, and how often? This is an important consideration as it can have major cost implications. Again, you may be driven to a particular testing frequency by legislative or customer requirements, but it’s important to understand why you are testing at the frequency you choose and the implications of testing too frequently, or infrequently. Frequent testing may give a greater confidence that HACCP is working well but could be costly. However infrequent testing could be more costly. Take an example of monthly testing for a pathogen, you’ve been getting negative results, then you suddenly obtain a positive- you need to recall. But does this mean you have to recall all production over the month as you have no data to prove the pathogen was absent since the last negative test. If you were testing daily, then your consideration may only be recalling a day’s production. This is only a hypothetical situation but shows how carefully you must consider test frequency when setting a microbiological criterion.
e) ‘Accept/reject’ criteria: You now know what you are going to test, how you are going to test it and how often, but the next question is, what will you do with the results? What does acceptable look like and why? What does unacceptable look like and why? If an unacceptable result occurs, what action are you going to take? Depending on the test you’ve done, actions may range from doing a production line audit and some extra cleaning and testing right through to informing the authorities and doing a full public recall. The action you take will depend on the type of test you’ve done and in some cases the level of organism detected, but you must document your intended actions in the criteria you set.
4. Confident testing
After understanding the need for testing and the treatment of results, you can now start to think about getting testing done. Some food producers will have their own on-site laboratories, others will use contract laboratories to do the work. Whichever you use, you must have confidence that the laboratory will deliver a high-quality service that is consistent with your requirements.
If you have your own on-site laboratory, how do you know that it is using the most appropriate methods or handling the samples in the correct way? Basically, how do you know you have confidence in its results. You can achieve this in several ways: employing previously trained microbiologists with a proven track record; sending your staff on appropriate training courses; ensuring your laboratory takes part in proficiency testing for all the test methods it operates; ultimately and perhaps the target for all testing laboratories would be accreditation. Accreditation offers the best assurance that a laboratory is operating to a high standard of quality, that staff are trained, methods are appropriate, equipment serviced and calibrated and quality assurance systems in place.
If you are going to use a contract testing laboratory, you will be looking for one that is accredited by the national accreditation body within the country that it is sited (e.g., UKAS in the UK and INAB in Ireland), but you must also ensure that the methods it will use on your tests are appropriate. Check that the methods are included within the scope of that laboratory’s accreditation. Do the methods they use fulfil the requirements that you will have detailed in section 3(c).
A good example may be that a laboratory is accredited and has a method for Listeria detection within its accreditation scope, however you are testing to a legal requirement that states the use of one very specific method for Listeria detection. It’s up to you to ensure that the specific method noted in legislation is used, or your test result may well be unacceptable for its intended use.
When using contract laboratories, you also must check how the samples will be transported and delivered to that laboratory. Remember that microorganisms are living, and it is unlikely that they will remain at static numbers in your sample for long periods of time, they will either grow to higher levels or die off. You must ensure that the way the sample is handled from the point it is taken in your factory, to the point the microbiological test is initiated, allows the absolute minimum change in microbial number. This may require chilled storage and rapid transport to the laboratory, and an assurance from the laboratory that they will test the sample immediately on arrival or use chilled storage for the minimum time before testing commences.
Finally, you must also agree how results will be transmitted from contract laboratory to you. You will undoubtably want to have any result that is above your ‘accept/reject’ criteria (3e) reported to you with all haste, as you may have major actions to take.
Final thoughts
Setting out to do microbiological tests on foods may initially sound easy, but it is not. It is not unusual to see food producers waste enormous sums of money on testing approaches that are poorly designed, and give inappropriate, unwanted, or unacceptable results. Spending time on planning a good testing approach, asking ‘why am I doing this?’, ‘what will the results show me?’ and ‘what am I going to do with any out of specification results that I obtain?’, will be time very well spent. Once you have spent that time, then document all those factors and reasons. It will be important in the future to fully understand why you made the decisions that you did, documentation is the only way to do this. You may find that talking to an expert that can help you design the testing regime and the criteria that best fit your needs, will be of benefit to you. Finally keep in close contact with your testing laboratory, they are your partner in doing this work, you will rely on their competency to get correct results.
Remember, testing does not make a food safe, that is the job of a well-constructed and implemented HACCP system, but a properly designed microbiological testing plan will complement this and give confidence that the system is operating as expected.
About Roy Betts
Roy Betts is a Fellow at Campden BRI, an independent international food consultancy and research organisation. His role is to ensure that the industry maintains a full awareness of all microbiological concerns and to help companies respond to and manage microbiological issues relevant to them and their products.
Train your staff for free about food microbiology with our FREE safefood for business training Module 2.

Sign up for our family focused healthy eating and food safety news.
- Mobile search Search Site
The site content is redirecting to the NI version.
Recommended

About us | Advertise with us | Contact us
What makes a great food testing lab partner?
- Odnoklassniki
- Facebook Messenger
- LiveJournal
Posted: 10 September 2020 | Charon Willis | No comments yet
Charon Willis from PAS highlights some key considerations to bear in mind when it comes to ensuring the right level of partnership from contract laboratories.

Selecting an analytical testing service provider can be multifaceted. Just imagine there was a laboratory comparison site, what selection criteria would you input to find that trusted partner and the best choice for you? Here, I outline a few things worth considering…
Technical competence
The basics – a recognised international standard against which a certified audit body and qualified auditor has given them approval.
A laboratory accredited to the international standard for testing laboratories, ISO 17025, will have proven systems. This helps confirm technical competence, choice of suitable test methods, that they committed to the highest standards of quality and accuracy and also are impartial and motivated to demonstrate continuous improvement.
How do they measure their own performance?
Obtaining the correct result is paramount of course, and proficient results should demonstrate that both accuracy and precision are being achieved. In addition, most labs want to maintain a good reputation, and customer service is usually recognised as a key part of that – whether it is account management, quoting, reporting, or availability to talk with the technical teams. This becomes especially important when issues are encountered.
Peer recommendations are ideal to whittle down choice. In our experience, the main reasons given for moving away from an existing testing provider are that the current incumbent takes too much time to respond, suffers from too frequent delays, or does not proactively communicate information, such as increasing prices in a contract without informing you.
Start with the end in mind
Testing usually serves a simple set of purposes; that it is safe, authentic, legal and of high quality, as well as confirmation that the product delivers on brand and meets claims regarding unique selling points.
The tests, however, change throughout the lifetime of the product, for example, inception, product development and refinement, compliance with customer requirements, maintenance and due diligence and issue investigation management. These can impact your choice of partner or tax the desire to select a single provider.
Routine vs specialised testing
Few laboratories can do every test needed, so which choice comes first – the one for routine or the one for specialised testing?
Often, appointing a provider for large quantities of testing require contracts and tenders. So, the question is whether selecting a laboratory based on the larger routine test volume is the most suitable decision for maintenance and due diligence? If so, will that service provider be willing to manage the remaining tests using subcontracting for you? The potential risk here is the communication chain is longer and reduces effectiveness when technical discussion is needed with the specialist. Or is the best option to build a relationship from the beginning with a supplier that covers the tests that are low volume, non-routine, more specialised and use investigation experts that can resolve issues? This could work on the basis that it is easier to subcontract the routine and perhaps involve less complex tests. It also means the specialist is able to build up experience of your products and can quickly call on that knowledge.
The choice is then whether the rest is better managed under your direct control or by the specialised lab on your behalf.
Direct access to an expert can be key
A testing partner should be able to advise on tests, accounting for the unique nature of your products, processes, any claims, and the regulatory requirements. Interpretation of what the results mean can be reasonably expected and choosing a supplier who will offer free advice on whether results comply with, or exceed, legislative limits or guidelines is worth considering.
How much input is needed from your partner?
The expectation of the depth and breadth of knowledge required of an ingredient supplier, a manufacturer, importer, or retailer can be, quite frankly, mind boggling. For this reason, questions such as how to report dioxins or when is it advisable to test for acrylamide, or 2-MCPD, 3-MCPD and glycidyl esters are useful, if only to endorse what you thought. A laboratory team with a broad scope of expertise and in-depth knowledge of food supply chain challenges can react swiftly and from a bespoke array of perspectives. This can support overarching business strategies with a practical solution, perhaps for new product development, assessing risk management, HACCP and other control processes, or investigating foreign body and contamination issues. Selection of a partner that relishes these challenges is advantageous.

If there is limited technical experience available in your business about a particular issue, a laboratory that has an experienced team that can help understand what the problem is, be it an unusual taste, odour, texture, a foreign body, a microbial contamination, is an asset and worth having in your contacts to help through an investigation and the decision-making process of what to do now and in the future.
Supporting important brand values and company strategy
For example, samples might be transported abroad; this can be done quickly, but does it suit your green targets reducing CO2 emissions if air flights are used? Help when the unexpected happens
For the food, feed and supplements sectors, continuity of supply, including an analytical service, can be critical. Businesses will have crisis management and contingency plans when the worst happens.
COVID-19 challenged these plans when social distancing was introduced – this was not something many plans had previously anticipated or accommodated. Implementing the two-metre rule is challenging in a laboratory with specific areas such as fume cupboards or laminar air flow cabinets, and leads to limited numbers of personnel in a lab at any one time. Many overcame the physical and mental challenges needed to protect staff. How did your partner manage things for you? Could they offer essential testing if you needed it?
Information security
Many laboratories can provide certificates, reports and dashboards on customer portals, even linking exports from their system into yours. Processes and policies at the laboratory end are addressed in the accreditation standard, and as recipients you will be provided with your personal log on and expected to maintain confidentiality. With the increasing threat of hacking, choosing a supplier who prioritises data protection is vital.
Future proofing: forming a two-way partnership and sharing information
Mostly, the information flow goes one way; from your testing provider to you, and several examples have been mentioned above on how to receive added-value services and insights. Internationally recognised and published analytical methods are preferable, however, some products (for example with high fibre, colour, sugar, oil, or made with high temperature processes) may require special attention during testing, such as adjustment to homogenisation or extraction or detection to achieve the sensitivity needed and the right results. This also holds true where the end consumer desires novel or unusual ingredients, for example, different sugars, insects, sea moss, or the interesting array of plant and seed extracts that are being employed, or, indeed, processes such as UV treatment or microbial fermentation.
The lab will always appreciate as much information as possible about the product so that they can confirm that the method is still suitable, or to ascertain adjustments to the international method or even the creation of a new method for you. All labs should be happy to sign a non-disclosure agreement to protect both parties.
While many laboratories have their own, or access to, horizon scanning tools, it is important to realise as manufacturers you may have access to information that they do not. For example, the Food Industry Intelligence Network (Fiin) is confidential to food business operators. Therefore, you may be aware of an alert that is not widely known which could impact your own supply chain. With this background information increased tests can be requested.
About the author
Charon Willis has more than 25 years of food industry experience and an MSc in Food Analysis and Composition. Her experience includes hands-on chemistry analysis, as well as providing advice to laboratories around the world on testing foods, feeds and supplements, quality management, and laboratory layout. In her current role as Commercial Manager at PAS , she will endeavour to find customers the best expert to help with food, feed and raw material testing services, or consultant for legal, safety, authenticity, crisis management and issue investigation.
Issue 4 2020
Related topics
Contaminants , Equipment , Food Fraud , Food Safety , Hygiene , Lab techniques , Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) , Mycotoxins , Rapid Detection
Related organisations
Premier Analytical Services (PAS)

UV-Vis analysis of food samples: tips and tricks for QA/QC
By Thermo Fisher Scientific

AI’s potential to enhance food safety practices
By John Simpson

Concerns rise over high PFAS levels in global water supply
By Grace Galler

Researchers share guidelines to help children “build tolerance” to food allergens

Corn plants offer solution to arsenic-contaminated soil challenges
By Leah Hockley
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
© Russell Publishing Limited , 2010-2024. All rights reserved. Terms & Conditions | Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy
Website design and development by e-Motive Media Limited .

Privacy Overview
This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorised as "Necessary" are stored on your browser as they are as essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. For our other types of cookies "Advertising & Targeting", "Analytics" and "Performance", these help us analyse and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these different types of cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may have an effect on your browsing experience. You can adjust the available sliders to 'Enabled' or 'Disabled', then click 'Save and Accept'. View our Cookie Policy page.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Performance cookies are includes cookies that deliver enhanced functionalities of the website, such as caching. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Analytics cookies collect information about your use of the content, and in combination with previously collected information, are used to measure, understand, and report on your usage of this website.
Advertising and targeting cookies help us provide our visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns.
How to write a business plan for a performance testing laboratory?

Putting together a business plan for a performance testing laboratory can be daunting - especially if you're creating a business for the first time - but with this comprehensive guide, you'll have the necessary tools to do it confidently.
We will explore why writing one is so important in both starting up and growing an existing performance testing laboratory, as well as what should go into making an effective plan - from its structure to content - and what tools can be used to streamline the process and avoid errors.
Without further ado, let us begin!
In this guide:
Why write a business plan for a performance testing laboratory?
- What information is needed to create a business plan for a performance testing laboratory?
- How do I build a financial forecast for a performance testing laboratory?
The written part of a performance testing laboratory business plan
- What tool should I use to write my performance testing laboratory business plan?
Having a clear understanding of why you want to write a business plan for your performance testing laboratory will make it simpler for you to grasp the rationale behind its structure and content. So before delving into the plan's actual details, let's take a moment to remind ourselves of the primary reasons why you'd want to create a performance testing laboratory business plan.
To have a clear roadmap to grow the business
Running a small business is tough! Economic cycles bring growth and recessions, while the business landscape is ever-changing with new technologies, regulations, competitors, and consumer behaviours emerging constantly.
In such a dynamic context, operating a business without a clear roadmap is akin to driving blindfolded: it's risky, to say the least. That's why crafting a business plan for your performance testing laboratory is vital to establish a successful and sustainable venture.
To create an effective business plan, you'll need to assess your current position (if you're already in business) and define where you want the business to be in the next three to five years.
Once you have a clear destination for your performance testing laboratory, you'll have to:
- Identify the necessary resources (human, equipment, and capital) needed to reach your goals,
- Determine the pace at which the business needs to progress to meet its objectives as scheduled,
- Recognize and address the potential risks you may encounter along the way.
Engaging in this process regularly proves advantageous for both startups and established companies. It empowers you to make informed decisions about resource allocation, ensuring the long-term success of your business.
To get visibility on future cash flows
If your small performance testing laboratory runs out of cash: it's game over. That's why we often say "cash is king", and it's crucial to have a clear view of your performance testing laboratory's future cash flows.
So, how can you achieve this? It's simple - you need to have an up-to-date financial forecast.
The good news is that your performance testing laboratory business plan already includes a financial forecast (which we'll discuss further in this guide). Your task is to ensure it stays current.
To accomplish this, it's essential to regularly compare your actual financial performance with what was planned in your financial forecast. Based on your business's current trajectory, you can make adjustments to the forecast.
By diligently monitoring your performance testing laboratory's financial health, you'll be able to spot potential financial issues, like unexpected cash shortfalls, early on and take corrective actions. Moreover, this practice will enable you to recognize and capitalize on growth opportunities, such as excess cash flow enabling you to expand to new locations.
To secure financing
Crafting a comprehensive business plan for your performance testing laboratory, whether you're starting up or already established, is paramount when you're seeking financing from banks or investors.
Given how fragile small businesses are, financiers will want to ensure that you have a clear roadmap in place as well as command and control of your future cash flows before entertaining the idea of funding you.
For banks, the information in your business plan will be used to assess your borrowing capacity - which is defined as the maximum amount of debt your business can afford alongside your ability to repay the loan. This evaluation helps them decide whether to extend credit to your business and under what terms (interest rate, duration, repayment options, collateral, etc.).
Similarly, investors will thoroughly review your plan to determine if their investment can yield an attractive return. They'll be looking for evidence that your performance testing laboratory has the potential for healthy growth, profitability, and consistent cash flow generation over time.
Now that you understand the importance of creating a business plan for your performance testing laboratory, let's delve into the necessary information needed to craft an effective plan.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

Information needed to create a business plan for a performance testing laboratory
You need the right data in order to project sales, investments and costs accurately in the financial forecast of your performance testing laboratory business plan.
Below, we'll cover three key pieces of information you should gather before drafting your business plan.
Carrying out market research for a performance testing laboratory
Carrying out market research before writing a business plan for a performance testing laboratory is essential to ensure that the financial projections are accurate and realistic.
Market research helps you gain insight into your target customer base, competitors, pricing strategies and other key factors which can have an impact on the commercial success of your business.
In particular, it is useful in forecasting revenue as it provides valuable data regarding potential customers’ spending habits and preferences.
You may uncover that customers may be looking for a more comprehensive performance testing laboratory, one that offers a range of services beyond just basic performance testing. Additionally, it could be that customers are seeking out a laboratory that is able to deliver rapid turnaround times and cost-effective solutions.
This information can then be used to create more accurate financial projections which will help investors make informed decisions about investing in your performance testing laboratory.
Developing the sales and marketing plan for a performance testing laboratory
Budgeting sales and marketing expenses is essential before creating a performance testing laboratory business plan.
A comprehensive sales and marketing plan should provide an accurate projection of what actions need to be implemented to acquire and retain customers, how many people are needed to carry out these initiatives, and how much needs to be spent on promotions, advertising, and other aspects.
This helps ensure that the right amount of resources is allocated to these activities in order to hit the sales and growth objectives forecasted in your business plan.
The staffing and capital expenditure requirements of a performance testing laboratory
Whether you are starting or expanding a performance testing laboratory, it is important to have a clear plan for recruitment and capital expenditures (investment in equipment and real estate) in order to ensure the success of the business.
Both the recruitment and investment plans need to be coherent with the timing and level of growth planned in your forecast, and require appropriate funding.
The performance testing laboratory might incur staffing costs such as salaries for engineers, testers, and software developers, as well as benefits and other expenses associated with the employees. The laboratory might also incur equipment costs such as purchasing and maintaining test and measurement equipment, servers, and other hardware and software necessary for the laboratory to perform its tests.
In order to create a realistic financial forecast, you will also need to consider the other operating expenses associated with running the business on a day-to-day basis (insurance, bookkeeping, etc.).
Once you have all the necessary information to create a business plan for your performance testing laboratory, it is time to start creating your financial forecast.
What goes into your performance testing laboratory's financial forecast?
The financial forecast of your performance testing laboratory's business plan will enable you to assess the growth, profitability, funding requirements, and cash generation potential of your business in the coming years.
The four key outputs of a financial forecast for a performance testing laboratory are:
- The profit and loss (P&L) statement ,
- The projected balance sheet ,
- The cash flow forecast ,
- And the sources and uses table .
Let's look at each of these in a bit more detail.
The projected P&L statement
The projected P&L statement for a performance testing laboratory shows how much revenue and profits your business is expected to generate in the future.
Ideally, your performance testing laboratory's P&L statement should show:
- Healthy growth - above inflation level
- Improving or stable profit margins
- Positive net profit
Expectations will vary based on the stage of your business. A startup will be expected to grow faster than an established performance testing laboratory. And similarly, an established company should showcase a higher level of profitability than a new venture.
The projected balance sheet of your performance testing laboratory
Your performance testing laboratory's forecasted balance sheet enables the reader of your plan to assess your financial structure, working capital, and investment policy.
It is composed of three types of elements: assets, liabilities and equity:
- Assets: represent what the business owns and uses to produce cash flows. It includes resources such as cash, equipment, and accounts receivable (money owed by clients).
- Liabilities: represent funds advanced to the business by lenders and other creditors. It includes items such as accounts payable (money owed to suppliers), taxes due and loans.
- Equity: is the combination of what has been invested by the business owners and the cumulative profits and losses generated by the business to date (which are called retained earnings). Equity is a proxy for the value of the owner's stake in the business.
Your performance testing laboratory's balance sheet will usually be analyzed in conjunction with the other financial statements included in your forecast.
Two key points of focus will be:
- Your performance testing laboratory's liquidity: does your business have sufficient cash and short-term assets to pay what it owes over the next 12 months?
- And its solvency: does your business have the capacity to repay its debt over the medium-term?
The cash flow forecast
A projected cash flow statement for a performance testing laboratory is used to show how much cash the business is generating or consuming.
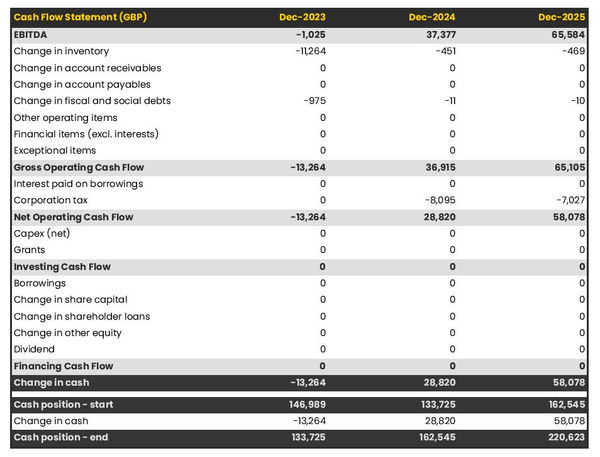
The cash flow forecast is usually organized by nature to show three key metrics:
- The operating cash flow: do the core business activities generate or consume cash?
- The investing cash flow: how much is the business investing in long-term assets (this is usually compared to the level of fixed assets on the balance sheet to assess whether the business is regularly maintaining and renewing its equipment)?
- The financing cash flow: is the business raising new financing or repaying financiers (debt repayment, dividends)?
As we discussed earlier, cash is king and keeping an eye on future cash flows an imperative for running a successful business. Therefore, you can expect the reader of your performance testing laboratory business plan to pay close attention to your cash flow forecast.
Also, note that it is customary to provide both yearly and monthly cash flow forecasts in a business plan - so that the reader can analyze seasonal variation and ensure the performance testing laboratory is appropriately funded.
The initial financing plan
The initial financing plan, also known as a sources and uses table, is a valuable resource to have in your business plan when starting your performance testing laboratory as it reveals the origins of the money needed to establish the business (sources) and how it will be allocated (uses).

Having this table helps show what costs are involved in setting up your performance testing laboratory, how risks are shared between founders, investors and lenders, and what the starting cash position will be. This cash position needs to be sufficient to sustain operations until the business reaches a break-even point.
Now that you have a clear understanding of what goes into the financial forecast of your performance testing laboratory business plan, let's shift our focus to the written part of the plan.
Need inspiration for your business plan?
The Business Plan Shop has dozens of business plan templates that you can use to get a clear idea of what a complete business plan looks like.

The written part of a performance testing laboratory business plan is composed of 7 main sections:
- The executive summary
- The presentation of the company
- The products and services
- The market analysis
- The strategy
- The operations
- The financial plan
Throughout these sections, you will seek to provide the reader with the details and context needed for them to form a view on whether or not your business plan is achievable and your forecast a realistic possibility.
Let's go through the content of each section in more detail!
1. The executive summary
The executive summary, the first section of your performance testing laboratory's business plan, serves as an inviting snapshot of your entire plan, leaving readers eager to know more about your business.
To compose an effective executive summary, start with a concise introduction of your business, covering its name, concept, location, history, and unique aspects. Share insights about the services or products you intend to offer and your target customer base.
Subsequently, provide an overview of your performance testing laboratory's addressable market, highlighting current trends and potential growth opportunities.
Then, present a summary of critical financial figures, such as projected revenues, profits, and cash flows.
You should then include a summary of your key financial figures such as projected revenues, profits, and cash flows.
Lastly, address any funding needs in the "ask" section of your executive summary.
2. The presentation of the company
In your performance testing laboratory business plan, the second section should focus on the structure and ownership, location, and management team of your company.
In the structure and ownership part, you'll provide an overview of the business's legal structure, details about the owners, and their respective investments and ownership shares. This clarity is crucial, especially if you're seeking financing, as it helps the reader understand which legal entity will receive the funds and who controls the business.
Moving on to the location part, you'll offer an overview of the company's premises and their surroundings. Explain why this particular location is of interest, highlighting factors like catchment area, accessibility, and nearby amenities.
When describing the location of your performance testing laboratory, you may want to focus on its ability to easily access a wide variety of resources. You could emphasize the potential for a diverse pool of participants who could be recruited from the surrounding region. Additionally, you may want to highlight the proximity to reliable infrastructure, such as reliable transportation and communications networks that could ensure reliability and efficiency when running tests. You could also highlight the relatively low cost of operation in the area, helping to make the laboratory an attractive investment for a third party financier.
Finally, you should introduce your management team. Describe each member's role, background, and experience.
Don't forget to emphasize any past successes achieved by the management team and how long they've been working together. Demonstrating their track record and teamwork will help potential lenders or investors gain confidence in their leadership and ability to execute the business plan.
3. The products and services section
The products and services section of your business plan should include a detailed description of what your company offers, who are the target customers, and what distribution channels are part of your go-to-market.
For example, your performance testing laboratory might offer customers a range of services such as load testing, performance benchmarking, and reliability testing. Load testing helps customers to identify and address potential performance issues that may arise when a system is under a heavy load. Performance benchmarking allows customers to measure the performance of their systems against the industry standard, which helps them identify and address any areas where their system is underperforming. Reliability testing helps customers to ensure their systems are stable and reliable, so they can deliver the best user experience.
4. The market analysis
When presenting your market analysis in your performance testing laboratory business plan, you should detail the customers' demographics and segmentation, target market, competition, barriers to entry, and any regulations that may apply.
The goal of this section is to help the reader understand how big and attractive your market is, and demonstrate that you have a solid understanding of the industry.
You should start with the demographics and segmentation subsection, which gives an overview of the addressable market for your performance testing laboratory, the main trends in the marketplace, and introduces the different customer segments and their preferences in terms of purchasing habits and budgets.
The target market section should follow and zoom on the customer segments your performance testing laboratory is targeting, and explain how your products and services meet the specific needs of these customers.
For example, your target market might include businesses that develop software and software applications. These businesses need performance testing to ensure their software runs smoothly on different systems. Additionally, businesses that sell or distribute hardware such as computers and printers may also need performance testing to ensure their products meet the needs of their customers.
Then comes the competition subsection, where you should introduce your main competitors and explain what differentiates you from them.
Finally, you should finish your market analysis by giving an overview of the main regulations applicable to your performance testing laboratory.
5. The strategy section
When you write the strategy section of your performance testing laboratory business plan, remember to cover key elements such as your competitive edge, pricing strategy, sales & marketing plan, milestones, and risks and mitigants.
In the competitive edge subsection, elaborate on what makes your company stand out from competitors. This becomes especially important if you're a startup, aiming to carve a place for yourself amidst established players in the marketplace.
The pricing strategy subsection should demonstrate how you plan to maintain profitability while offering competitive prices to attract customers.
Outline your sales & marketing plan, detailing how you'll reach out to new customers and retain existing ones through loyalty programs or special offers.
For the milestones subsection, outline your company's achievements to date and your main objectives for the future, complete with specific dates to set clear expectations for progress.
Lastly, the risks and mitigants subsection should address the main risks that could affect your plan's execution. Explain the measures you've put in place to minimize these risks, assuring potential investors or lenders.
Your performance testing laboratory may face a variety of risks. For example, your testing equipment could malfunction or fail due to a variety of reasons, such as wear and tear, improper use, or technical glitches. This could potentially lead to inaccurate test results, or even worse, a costly delay in the testing process. Additionally, your laboratory could face the risk of data breaches, as sensitive customer information may be collected and stored. If this data is not adequately protected, it could be exposed to unauthorized personnel, leading to potential legal and financial consequences.
6. The operations section
The operations of your performance testing laboratory must be presented in detail in your business plan.
Begin by addressing your staff, specifying the main roles and your recruitment plan to support the anticipated growth. Outline the qualifications and experience needed for each role and discuss your recruitment strategies, which may involve using job boards, referrals, or headhunters.
Next, clearly state your performance testing laboratory's operating hours, allowing the reader to gauge the adequacy of your staffing levels. Additionally, mention any considerations for varying opening times during peak seasons and your approach to handling customer queries outside regular operating hours.
The key assets and intellectual property (IP) required to run your business should also be highlighted. If you rely on licenses, trademarks, physical structures like equipment or property, or lease agreements, ensure they are well-documented in this section.
You may have key assets such as specialized software and hardware to support performance testing. This could include tools such as network analysis software, process monitoring, and stress testing tools. Additionally, you might have intellectual property in the form of methodologies, strategies, and data models that are unique to your laboratory. These could be used to help you develop efficient performance tests and analyze results quickly.
Finally, provide a comprehensive list of suppliers you intend to collaborate with, along with a breakdown of their services and main commercial terms, such as price, payment terms, break clauses and contract duration. Investors often seek insight into the reasons behind your supplier choices, which may include a preference for higher-quality products or established relationships from past ventures.
7. The presentation of the financial plan
The financial plan section is where we will include the financial forecast we talked about earlier in this guide.
Now that you have a clear idea of the content of a performance testing laboratory business plan, let's look at some of the tools you can use to create yours.
What tool should I use to write my performance testing laboratory's business plan?
In this section, we will be reviewing the two main options for writing a performance testing laboratory business plan efficiently:
- Using specialized software,
- Outsourcing the drafting to the business plan writer.
Using an online business plan software for your performance testing laboratory's business plan
Using online business planning software is the most efficient and modern way to write a performance testing laboratory business plan.
There are several advantages to using specialized software:
- You can easily create your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can access a library of dozens of complete business plan samples and templates for inspiration
- You get a professional business plan, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank or investors
- You can easily track your actual financial performance against your financial forecast
- You can create scenarios to stress test your forecast's main assumptions
- You can easily update your forecast as time goes by to maintain visibility on future cash flows
- You have a friendly support team on standby to assist you when you are stuck
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try The Business Plan Shop for free by signing up here .
Need a solid financial forecast?
The Business Plan Shop does the maths for you. Simply enter your revenues, costs and investments. Click save and our online tool builds a three-way forecast for you instantly.
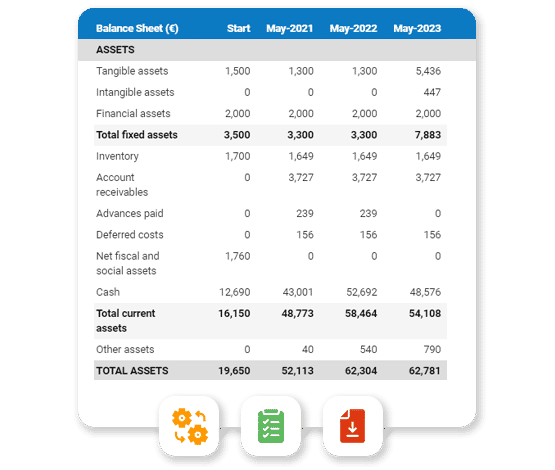
Hiring a business plan writer to write your performance testing laboratory's business plan
Outsourcing your performance testing laboratory business plan to a business plan writer can also be a viable option.
Business plan writers are skilled in creating error-free business plans and accurate financial forecasts. Moreover, hiring a consultant can save you valuable time, allowing you to focus on day-to-day business operations.
However, it's essential to be aware that hiring business plan writers will be expensive, as you're not only paying for their time but also the software they use and their profit margin.
Based on experience, you should budget at least £1.5k ($2.0k) excluding tax for a comprehensive business plan, and more if you require changes after initial discussions with lenders or investors.
Also, exercise caution when seeking investment. Investors prefer their funds to be directed towards business growth rather than spent on consulting fees. Therefore, the amount you spend on business plan writing services and other consulting services should be insignificant compared to the amount raised.
Keep in mind that one drawback is that you usually don't own the business plan itself; you only receive the output, while the actual document is saved in the consultant's business planning software. This can make it challenging to update the document without retaining the consultant's services.
For these reasons, carefully consider outsourcing your performance testing laboratory business plan to a business plan writer, weighing the advantages and disadvantages of seeking outside assistance.
Why not create your performance testing laboratory's business plan using Word or Excel?
Using Microsoft Excel and Word (or their Google, Apple, or open-source equivalents) to write a performance testing laboratory business plan is a terrible idea.
For starters, creating an accurate and error-free financial forecast on Excel (or any spreadsheet) is very technical and requires both a strong grasp of accounting principles and solid skills in financial modelling.
As a result, it is unlikely anyone will trust your numbers unless - like us at The Business Plan Shop - you hold a degree in finance and accounting and have significant financial modelling experience in your past.
The second reason is that it is inefficient. Building forecasts on spreadsheets was the only option in the 1990s and early 2000s, nowadays technology has advanced and software can do it much faster and much more accurately.
And with the rise of AI, software is also becoming smarter at helping us detect mistakes in our forecasts and helping us analyse the numbers to make better decisions.
Also, using software makes it easy to compare actuals vs. forecasts and maintain our forecasts up to date to maintain visibility on future cash flows - as we discussed earlier in this guide - whereas this is a pain to do with a spreadsheet.
That's for the forecast, but what about the written part of my performance testing laboratory business plan?
This part is less error-prone, but here also software brings tremendous gains in productivity:
- Word processors don't include instructions and examples for each part of your business plan
- Word processors don't update your numbers automatically when they change in your forecast
- Word processors don't handle the formatting for you
Overall, while Word or Excel may be viable options for creating a performance testing laboratory business plan for some entrepreneurs, it is by far not the best or most efficient solution.
- Using business plan software is a modern and cost-effective way of writing and maintaining business plans.
- A business plan is not a one-shot exercise as maintaining it current is the only way to keep visibility on your future cash flows.
- A business plan has 2 main parts: a financial forecast outlining the funding requirements of your performance testing laboratory and the expected growth, profits and cash flows for the next 3 to 5 years; and a written part which gives the reader the information needed to decide if they believe the forecast is achievable.
We hope that this in-depth guide met your expectations and that you now have a clear understanding of how to write your performance testing laboratory business plan. Do not hesitate to contact our friendly team if you have questions additional questions we haven't addressed here.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- How to write a business plan to secure a bank loan?
- Key steps to write a business plan?
- Top mistakes to avoid in your business plan
Do you know entrepreneurs interested in starting or growing a performance testing laboratory? Share this article with them!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here
FDA's Lab Accreditation Final Rule: Food Testing Oversight is Finally Here
Fda's final rule on lab accreditation for food testing provides essential directives for quality standards and assurances.

Photo credit : yacobchuk/iStock / Getty Images Plus via Getty Images
Today's food laboratories remain largely free of regulatory oversight. That is about to change with the Food and Drug Administration's (FDA's) issuance of a final rule 1 establishing a program for the testing of food, in certain circumstances, by accredited laboratories. There should be no delay in the implementation of this well-constructed rule.
Not only does this final rule provide specific quality standards and assurances to a segment of food testing, but it also opens the door for all laboratories to adhere to these essential elements. FDA said as much in the final rule: "We expect that creating model laboratory standards based on ISO/IEC [International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission] 17025:2017 accreditation may encourage other laboratories to work toward these standards, including accreditation."
The agency teased the possibility of future rulemaking to expand the scope of oversight. The final rule suggests that FDA may require "additional specific follow-up testing" in accordance with the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act regulations. If an expanded scope were pursued, then FDA would go through another notice-and-comment rulemaking, but it would still use the testing processes established in this final rule.
For all of these reasons, this final rule is a notable achievement for food safety and advocates of quality food laboratory testing. As stated by the Food Laboratory Alliance, a coalition of organizations supporting this mission, "The goal is not—and could not be—to test all food. The goal should be that all testing of food should be reliable and accurate."
Limited Scope
Before examining the details of how this oversight program will proceed, it is important to understand when food testing falls under its jurisdiction. All of the following testing scenarios exist already, but now they will be subject to the final rule requirements for laboratory testing:
- If a food product or environment must be tested to address an identified or suspected food safety problem, then FDA may direct a food laboratory order. Through this order, the FDA will specify what is tested, under what time frame, and the manner and method of testing to be conducted.
- In administrative procedural settings when an identified or suspected food safety problem is presented to the FDA (1) as part of evidence for a hearing prior to the issuance of a mandatory food recall order, (2) as part of a corrective action plan submitted after an order suspending the registration of a food facility, or (3) as part of evidence submitted for an appeal of an administrative detention.
- To support the admission of an article of imported food.
- To support the removal of food from an import alert through successful consecutive testing.
- In response to explicit testing requirements that address an identified or suspected food safety problem with sprouts, shell eggs, and bottled drinking water. For shell eggs, the requirement applies to farms with more than 3,000 laying hens. For bottled drinking water, five samples from the same sampling site must be tested if they originally tested positive for the pathogen Escherichia coli .
Food Testing Infrastructure
Effective February 1, 2022, the final rule establishes a structure to which food laboratories must adhere if they want to conduct testing for FDA-directed purposes. It is a voluntary program, but if laboratories choose to perform the testing, they must adhere to the requirements of the final rule.
In a nutshell, any person with an ownership or consignment interest in a food product or its food testing environment may choose to have its food sample tested for an FDA-specified purpose. If the owner or consignee chooses to have its product or environment tested, then it must use a laboratory that has been accredited through laboratory accreditation for analyses of foods (LAAF) accreditation.
FDA outlines the LAAF program in four tiers. First, the agency will review applications and grant recognition to select accreditation bodies that meet its criteria. With this FDA recognition, the accreditation body may begin assessing laboratories for LAAF accreditation. Second, if a laboratory meets the accreditation requirements, it becomes designated as a LAAF-accredited laboratory. Once this is accomplished, the LAAF-accredited laboratory may conduct food testing as specified by FDA. Finally, in tier four, the food testing results and accompanying information are submitted to FDA for review.
Accreditation Bodies
Accreditation bodies must meet several criteria for FDA to recognize and authorize them to LAAF-accredit laboratories. One requirement is that an accreditation body must demonstrate its compliance with international standard ISO/IEC 17011:2017 and be a full member of the International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperative (ILAC), as well as a signatory to the ILAC Mutual Recognition Arrangement. An eligible accreditation body must also ensure that it does not own, have a financial interest in, manage, or otherwise control any laboratory it LAAF-accredits, among other impartiality provisions. A recognized accreditation body must audit its compliance with these requirements.
Among its responsibilities, a recognized accreditation body must conduct onsite assessments of a laboratory seeking LAAF accreditation to determine if it is capable of conducting each method of food testing. The recognized accreditation body continues to oversee the performance of the laboratory it accredits to LAAF to ensure its continued compliance with quality testing requirements.
Quality Standards for LAAF-Accredited Laboratories
A laboratory that is LAAF-accredited must demonstrate its capability of conducting each stated method of food testing. The baseline requirement for LAAF accreditation is adherence to international standard ISO/IEC 17025:2017. FDA notes that this standard, along with the accreditation body standard ISO/IEC 17011:2017, are "the most appropriate globally recognized and widely used standards."
In addition, laboratories must successfully pass a proficiency test every 12 months for each testing method within its LAAF accreditation scope. Proficiency testing is used to assist laboratories in verifying that their performance of each test is comparable with others performing the same analysis. It is an objective means of assessing analytical performance and documenting quality assurance. The final rule acknowledges "the critical role that proficiency testing plays" in the LAAF program.
If no proficiency testing program is available for the test method, then an approved comparison program may be used. All proficiency testing and comparison program results, regardless of their outcome, must be sent to the recognized accreditation body within 30 calendar days of receipt.
Procedures for monitoring the validity of test results must include the use of reference materials or quality control samples with each batch of samples tested. FDA notes that these tools are "vital to a laboratory's demonstration of capability to conduct a method."
As noted by the Food Laboratory Alliance, "It is essential for all laboratories that test food to follow appropriate standards to ensure accurate and reliable test results, ultimately providing for the betterment of public health and a stronger commerce system."
LAAF-accredited laboratories that conduct analyses of food samples are responsible for submitting all results, reports, studies, and notifications to FDA. The final rule details what information must accompany full analytical reporting. This includes name and street address; all sampling plans and sample collection reports, validation, and verification studies (as required); calculations; identification of software used; certificate of analysis; qualifications of the analysts performing the analysis; and identification of the source and purity of reference standards, among other requirements. If FDA does not receive all required information, then the related food testing may be considered invalid.
With FDA's permission, LAAF-accredited laboratories may submit an abridged analytical report for each major food testing discipline. Disciplines are categorized as biological, chemical, or physical. Permission will be granted if the last five full analytical reports for the discipline contain no administrative errors or shortcomings in validity and if the LAAF-accredited laboratory has successfully implemented any required corrective actions. The LAAF-accredited laboratory must also be clear of suspension or probation.
Even LAAF-accredited laboratories that receive permission to file an abridged analytical report may be required to submit a full analytical report if the matter warrants it. This may refer to an enforcement proceeding, FDA investigation, audit, or for public health purposes.
Before analyzing a sample, an LAAF-accredited laboratory must develop or obtain certain information to accompany the test results. Written documentation of a sampler's applicable qualifications, sampling plan, and a collection report for each sample collected is required.
Testing may be conducted by any LAAF-accredited laboratory, regardless of location. Unless FDA has granted an exception, however, the sampling of an import must occur after its arrival on U.S. soil.
Public Registry
Names and contact details of recognized accreditation bodies and LAAF-accredited laboratories will appear on a public FDA website. This is intended to provide food owners and consignees with easy access to available LAAF resources.
Implementation
While the final rule became effective on February 1, 2022, the implementation will occur in methodical stages. FDA intends to first onboard accreditation bodies and recognize officially those passing the eligibility criteria. Next, those recognized accreditation bodies will begin LAAF-accrediting laboratories. Once a sufficient number of laboratories are LAAF accredited, the FDA will give owners and consignees six months before they are required to use them.
The timeline for accomplishing these steps was not announced; however, implementation should not be delayed. Accuracy and reliability in food testing are too important.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services. "21 CFR Parts 1, 11, 16, and 129: Laboratory Accreditation for Analyses of Foods." Federal Register 86, No. 230 (December 3, 2021). https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2021-12-03/pdf/2021-25716.pdf .
Robin E. Stombler is President of Auburn Health Strategies LLC, a strategic and business development firm representing health and science organizations. She serves as Vice Chair of the Board of Directors for the American Association for Laboratory Accreditation (A2LA), and also established and directed the Food Laboratory Alliance.
Share This Story

Restricted Content
You must have JavaScript enabled to enjoy a limited number of articles over the next 30 days.
Related Articles

FDA Announces Final Rule for Laboratory Accreditation for Analyses of Foods

FDA publishes proposed rule to establish laboratory accreditation program for food testing
Food Lab Accreditation Takes Off With FDA, USDA Support
Get our emagazine delivered directly to your inbox, stay in the know on the latest science-based solutions for food safety..
Copyright ©2024. All Rights Reserved BNP Media.
Design, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing
Chat With Us
Schedule A Call Back
Our Experts are ready to assist you, Let's Connect with Us By submit your enquiry.
Welcome to Corpseed. Please type your query, and we shall provide immediate assistance.
Didn't receive code? Resend OTP
Your Enquiry has been received !!
Our legal advisor will contact you shortly.., how to start a food testing laboratory in india.

- Introduction: Food Testing Laboratory
In recent times, witnessing the massive rise of covid-19 cases has made us realize the significance of testing in our daily lives, especially when it comes to quality checks of food that we consume. Even though the bad quality and processing of food don’t directly affect the transmission of covid, they do contribute to hundreds of other diseases, even the fatal ones. Also, you might have noticed that the food industry of India often comes under the scrutiny of foreign media for its poor quality as compared to global standards. And, this not only damages its reputation but also harms its export figures. All these make prior testing of food by accredited and certified laboratories a must to ensure its safety and hygiene. In this article, we will discuss the roles of a food testing laboratory in a detailed manner, alongside the compliances required to start it in India.
Table of Contents
Food Testing Laboratory in India
Roles of a food testing laboratory in india, significance of food testing laboratory, techniques used in a food testing laboratory , regulations and norms for food testing laboratory in india .
--------------Blog Contact Form-------------
Despite being the last step in the food manufacturing chain, the testing of food products stands as the most crucial step, without which the government authority may not let businesses sell their edible products in the Indian market. Food testing has become necessary to determine the safety of edible products for public consumption as it makes sure they are free of any physical, chemical, or biological contamination.
To get a better understanding of it, you can take examples of potentially dangerous food impurities, such as metals, pathogens, cleaning agents, additives, and pesticides. You may here get shocked if we tell you this is just the tip of the iceberg. Besides this, the food testing laboratory also conducts a scientific analysis of the edible products to find out their properties, including structure, compositions, and physicochemical characteristics.
The presence of food testing laboratory is crucial for the food industry of the country and the reason we are saying this is the roles they play, which includes:
- Testing the quality of a food product
- Inspection and grading of food products.
- Testing to check food’s authenticity
- Testing for any impurities
- Nutritional labeling of food products.
- Analysis of food nutrient contents
- Shelf-life testing
- Sensory assessment
Throughout the country, over six hundred food testing laboratories are present. This figure considers every NABL ( National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories ) certified laboratory, as well as those held by FSSAI, food business operators, central-state governments, private key players, etc.
Besides this, several food testing labs are also operating there, which primarily focus on testing raw materials and finished products. Unlike the ones mentioned above, these are comparatively smaller and help food business operators of the country obtain required test reports for concerned food items. If we think of the benefits of it from a consumer perspective, then it protects them from all the potential diseases that can arise from contaminated food.
And what about manufacturers? Well, a food testing laboratory assures the safety of food products of a manufacturer and helps it get regulatory approval to enter the market. Not just this, it also indirectly contributes to the brand reputation, which can ultimately reap high growth for its business.
- Analytical testing
Also known as material testing or analytical chemistry testing, it is used to identify the chemical characteristics of a particular food product. In simple terms, a food testing laboratory does it for identifying and finding the chemical components that are present in a food product, such as pH, additives, adulterants, minerals, preservatives, etc.
- Microbiological analysis and testing
Microbiological analysis of food products takes into use biochemical practices to detect and identify the presence of microorganisms in a food product. Mainly, it is used for the raw materials applied in food preparation and sometimes for the final products as well. And the significance of it can’t be underestimated at any cost because if any contaminated microorganisms enter the food manufacturing and supplying chain, it can lead to a potential outbreak of food poisoning cases among the general public and disruption in food production, which means loss of substantial revenue and stability.
- Nutritional analysis
A food testing laboratory uses nutritional analysis techniques to determine the nutritional contents of a food product. It is a vital part of material testing that helps food business operators get all the required information on nutritional content to mention on the packaging of their food products and comply with the regulatory frameworks, or we should say, saves them from any legal consequences.
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India leaves no stone unturned when it comes to the proper quality check of food products available in the market for public consumption. It has put several measures in place that every food business operator in the country is obliged to follow. This includes timely mandatory testing from a certified testing laboratory. Here, someone might ask, ‘But what about the regulations and norms for starting a laboratory for food testing?’ Because without them, anyone could start one for himself, which will only compromise their authenticity over time. Considering this, FSSAI has set a certain set of norms for establishing laboratories for food testing in the country, which are as follows:
- As per FSSAI, every food testing laboratory is required to put a Quality Management System (QMS) in place. Besides this, it must also have relevant testing equipment and parameters for quality checks.
- The laboratory is required to operate under the purview of a Government-recognized authority, such as NABL, FSSAI, etc.
- The staff of the laboratory must be trained and well-versed in handling all the testing requirements.
- There must be at least one certified food analyst present in all the laboratories that are indulged in the testing of food products.
- The FSSAI recognizes three types of labs, namely, Level 1, Level 2, and Referral lab, and mandates them to possess all the testing gear and equipment required as per the scope of their recognition levels.
Thinking of starting a food testing laboratory? Well, if yes, then let us tell you it can not only result in a successful business with high margins for you but also contribute to making the food industry of the country safer for the general public. Just make sure you follow all the compliances required for it and you’re good to go. In case you need any help with that, feel free to come in contact with Corpseed ITES, which is India’s best business legal and Company and has been working in this field for years.
FSSAI Basic
If you are into food business with revenue below 12 Lakhs, you must obtain an FSSAI Registration before starting operations. Corpseed can help you to obtain FSSAI registration for your business.
FSSAI State
If you are into food business with revenue above 20 Lakhs, you must obtain an FSSAI License before starting operations. Corpseed can help you to obtain FSSAI state license for your business. Guaranteed satisfaction or your money back.
FSSAI Central
FSSAI Central License PAN India in no time. In case you want to import/export or sell your products on an E-Commerce Website, you must obtain an FSSAI Central License. Team Corpseed will help you to obtain FSSAI central license.
This portion of the site is for informational purposes only. The content is not legal advice. The statements and opinions are the expression of author, not corpseed, and have not been evaluated by corpseed for accuracy, completeness, or changes in the law.
BOOK A FREE CONSULTATION
Get help from an experienced legal adviser. Schedule your consultation at a time that works for you and it's absolutely FREE.

Shamshad Alam
Latest articles.

Thank you for your vote! Would you have any suggestions for improvements?
Thanks so much for sharing your experience with us , we hope to see you again soon. .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Sample Food Testing Lab Business Plan Template 1. Industry Overview. Food testing labs engage in food testing, and food testing is a process used to check whether a food is safe and that it does not contain harmful contaminants, or that it contains only permitted additives at acceptable levels, or that it contains the right levels of key ingredients and its label declarations are correct, or ...
Information needed to create a business plan for a food hygiene testing laboratory. Drafting a food hygiene testing laboratory business plan requires research so that you can project sales, investments and cost accurately in your financial forecast, and convince the reader that there is a viable commercial opportunity to be seized.
CBC (a more complete test that counts platelets in addition to white and red blood cell counts)- $30. Blood sugar (suited for diabetics or people who are trying to determine if they have a blood sugar problem)- $15. Electrolytes (for people on diuretics)- $20. Creatine (tests for heart or kidney difficulties)- $15.
In a Food Hygiene Testing Laboratory business plan, the following financial information should be included: 1. Start-up Costs: This includes the initial expenses required to set up the laboratory, such as lease or purchase of premises, equipment, supplies, licensing fees, legal and consulting fees, and any renovations or improvements needed. ...
Break-even volumes = Total Fixed Costs ÷ (Revenue per unit -VC per unit) Say, for example, Average Revenue/Test in your lab is $65.00. Then, annual break-even volumes = $103,795 ÷ ($65.00 - $21.67) or 2,396 tests. At 2,396 tests, enough Incremental Profit is earned to cover the lab's fixed costs of $103,795.
Starting a food testing lab business can be an exciting and lucrative venture for individuals with a passion for food safety and quality. As concerns about foodborne illnesses and contamination continue to rise, the demand for reliable and efficient food testing services has reached an all-time high.
1. Perform market analysis. Starting a laboratory testing business requires a comprehensive understanding of the market dynamics. It's crucial to assess the demand for testing services, identify potential competitors, and understand customer needs.
3. Market Analysis. Market analysis is a key component of any successful laboratory business plan. That's because the healthcare landscape changes constantly, and the success of your laboratory depends on how well you understand the market. When writing your market analysis, include information on your target market, your competition, and ...
When writing the strategy section of a business plan for your environmental testing laboratory, it is essential to include information about your competitive edge, pricing strategy, sales & marketing plan, milestones, and risks and mitigants. The competitive edge subsection should explain what sets your company apart from its competitors.
A good place to start is by researching the market demand and identifying the business case for your new venture. Here are a couple of business case examples - but yours will need to be more detailed, backed up by solid technical and market research. To take advantage of new research/testing opportunities, such as those created by the Covid ...
Building an effective testing program requires a commitment to many aspects of a company's operation. It means deciding whether, what kind of, and how much in-plant testing is appropriate for your plant. It means deciding what testing and how much testing you should outsource to a contract laboratory. It entails implementing a laboratory ...
The landscape of the food industry is constantly evolving. Your lab partner should be adapting to meet new products and regulatory changes in requirements for testing and labelling. Evaluation of new methods and instruments should be scheduled regularly to ensure the most efficient and effective processing of your samples.
A copy of the testing methods that the laboratory is accredited to perform. A sampling plan - this is a plan or schedule of what testing will be undertaken and when it will be completed. Test Reports - All test reports provided by your selected food testing laboratory should be kept to verify your external testing activities.
Choose the solution that makes most sense for your business. Tip #4: Set a Budget. Just like any operational or capital expense, sampling and testing will have an impact on your company's bottom line. This brings us to Tip #4: Factor costs associated with sampling and laboratory services into your business plan and create a budget.
Jan 7, 2022. Food safety testing is a scientific-based method that evaluates the safety of food based on microbiological, physical, or chemical composition. Food safety testing must be accurate, specific, reproducible, established, and cost-effective. Proper food safety testing contributes as a solution to the growing demand for safe food and ...
RL Foods Laboratory Provides Food Testing Services, FDA Certified Food Nutrition Labels, Food Consulting & Restaurant Menu Disclosures. ... food companies — big and small — need expert help. Whether it is a recipe modification or help with a HACCP plan for food safety, it is imperative for the success of your business to get the right ...
The projected P&L statement for a medical laboratory shows how much revenue and profit your business is expected to make in the future. A healthy medical laboratory's P&L statement should show: Sales growing at (minimum) or above (better) inflation. Stable (minimum) or expanding (better) profit margins.
Similarly, if the test is for a spoilage organism or hygiene indicator organism, you will need to have set 'accept/reject' criteria and maybe also an 'action level', but the question is what action will you take. Again, this must be determined and documented before you start to test. 3. Establish the criteria.
About the author. Charon Willis has more than 25 years of food industry experience and an MSc in Food Analysis and Composition. Her experience includes hands-on chemistry analysis, as well as providing advice to laboratories around the world on testing foods, feeds and supplements, quality management, and laboratory layout.
The written part of a performance testing laboratory business plan. The written part of a performance testing laboratory business plan is composed of 7 main sections: The executive summary; The presentation of the company; The products and services; The market analysis; The strategy; The operations; The financial plan
February 16, 2022. Today's food laboratories remain largely free of regulatory oversight. That is about to change with the Food and Drug Administration's (FDA's) issuance of a final rule 1 establishing a program for the testing of food, in certain circumstances, by accredited laboratories. There should be no delay in the implementation of this ...
food testing laboratories to progressively raise the quality of testing and safety standards of food testing laboratories. 3.0 Setting up a Basic Food Testing and Analysis Laboratory The major components of a laboratory involve: a. Selection, identifying building facilities and construction, if required for various analyses b.
The presence of food testing laboratory is crucial for the food industry of the country and the reason we are saying this is the roles they play, which includes: Testing the quality of a food product. Inspection and grading of food products. Testing to check food's authenticity. Testing for any impurities. Nutritional labeling of food products.