
- Tips & Guides

How To Avoid Using “We,” “You,” And “I” in an Essay
- Posted on October 27, 2022 October 27, 2022
Maintaining a formal voice while writing academic essays and papers is essential to sound objective.
One of the main rules of academic or formal writing is to avoid first-person pronouns like “we,” “you,” and “I.” These words pull focus away from the topic and shift it to the speaker – the opposite of your goal.
While it may seem difficult at first, some tricks can help you avoid personal language and keep a professional tone.
Let’s learn how to avoid using “we” in an essay.
What Is a Personal Pronoun?
Pronouns are words used to refer to a noun indirectly. Examples include “he,” “his,” “her,” and “hers.” Any time you refer to a noun – whether a person, object, or animal – without using its name, you use a pronoun.
Personal pronouns are a type of pronoun. A personal pronoun is a pronoun you use whenever you directly refer to the subject of the sentence.
Take the following short paragraph as an example:
“Mr. Smith told the class yesterday to work on our essays. Mr. Smith also said that Mr. Smith lost Mr. Smith’s laptop in the lunchroom.”
The above sentence contains no pronouns at all. There are three places where you would insert a pronoun, but only two where you would put a personal pronoun. See the revised sentence below:
“Mr. Smith told the class yesterday to work on our essays. He also said that he lost his laptop in the lunchroom.”
“He” is a personal pronoun because we are talking directly about Mr. Smith. “His” is not a personal pronoun (it’s a possessive pronoun) because we are not speaking directly about Mr. Smith. Rather, we are talking about Mr. Smith’s laptop.
If later on you talk about Mr. Smith’s laptop, you may say:
“Mr. Smith found it in his car, not the lunchroom!”
In this case, “it” is a personal pronoun because in this point of view we are making a reference to the laptop directly and not as something owned by Mr. Smith.
Why Avoid Personal Pronouns in Essay Writing
We’re teaching you how to avoid using “I” in writing, but why is this necessary? Academic writing aims to focus on a clear topic, sound objective, and paint the writer as a source of authority. Word choice can significantly impact your success in achieving these goals.
Writing that uses personal pronouns can unintentionally shift the reader’s focus onto the writer, pulling their focus away from the topic at hand.
Personal pronouns may also make your work seem less objective.
One of the most challenging parts of essay writing is learning which words to avoid and how to avoid them. Fortunately, following a few simple tricks, you can master the English Language and write like a pro in no time.
Alternatives To Using Personal Pronouns
How to not use “I” in a paper? What are the alternatives? There are many ways to avoid the use of personal pronouns in academic writing. By shifting your word choice and sentence structure, you can keep the overall meaning of your sentences while re-shaping your tone.
Utilize Passive Voice
In conventional writing, students are taught to avoid the passive voice as much as possible, but it can be an excellent way to avoid first-person pronouns in academic writing.
You can use the passive voice to avoid using pronouns. Take this sentence, for example:
“ We used 150 ml of HCl for the experiment.”
Instead of using “we” and the active voice, you can use a passive voice without a pronoun. The sentence above becomes:
“150 ml of HCl were used for the experiment.”
Using the passive voice removes your team from the experiment and makes your work sound more objective.
Take a Third-Person Perspective
Another answer to “how to avoid using ‘we’ in an essay?” is the use of a third-person perspective. Changing the perspective is a good way to take first-person pronouns out of a sentence. A third-person point of view will not use any first-person pronouns because the information is not given from the speaker’s perspective.
A third-person sentence is spoken entirely about the subject where the speaker is outside of the sentence.
Take a look at the sentence below:
“In this article you will learn about formal writing.”
The perspective in that sentence is second person, and it uses the personal pronoun “you.” You can change this sentence to sound more objective by using third-person pronouns:
“In this article the reader will learn about formal writing.”
The use of a third-person point of view makes the second sentence sound more academic and confident. Second-person pronouns, like those used in the first sentence, sound less formal and objective.
Be Specific With Word Choice
You can avoid first-personal pronouns by choosing your words carefully. Often, you may find that you are inserting unnecessary nouns into your work.
Take the following sentence as an example:
“ My research shows the students did poorly on the test.”
In this case, the first-person pronoun ‘my’ can be entirely cut out from the sentence. It then becomes:
“Research shows the students did poorly on the test.”
The second sentence is more succinct and sounds more authoritative without changing the sentence structure.
You should also make sure to watch out for the improper use of adverbs and nouns. Being careful with your word choice regarding nouns, adverbs, verbs, and adjectives can help mitigate your use of personal pronouns.
“They bravely started the French revolution in 1789.”
While this sentence might be fine in a story about the revolution, an essay or academic piece should only focus on the facts. The world ‘bravely’ is a good indicator that you are inserting unnecessary personal pronouns into your work.
We can revise this sentence into:
“The French revolution started in 1789.”
Avoid adverbs (adjectives that describe verbs), and you will find that you avoid personal pronouns by default.
Closing Thoughts
In academic writing, It is crucial to sound objective and focus on the topic. Using personal pronouns pulls the focus away from the subject and makes writing sound subjective.
Hopefully, this article has helped you learn how to avoid using “we” in an essay.
When working on any formal writing assignment, avoid personal pronouns and informal language as much as possible.
While getting the hang of academic writing, you will likely make some mistakes, so revising is vital. Always double-check for personal pronouns, plagiarism , spelling mistakes, and correctly cited pieces.
You can prevent and correct mistakes using a plagiarism checker at any time, completely for free.
Quetext is a platform that helps you with all those tasks. Check out all resources that are available to you today.
Sign Up for Quetext Today!
Click below to find a pricing plan that fits your needs.
You May Also Like

Mastering Tone in Email Communication: A Guide to Professional Correspondence
- Posted on April 17, 2024

Mastering End-of-Sentence Punctuation: Periods, Question Marks, Exclamation Points, and More
- Posted on April 12, 2024

Mastering the Basics: Understanding the 4 Types of Sentences
- Posted on April 5, 2024

Can You Go to Jail for Plagiarism?
- Posted on March 22, 2024 March 22, 2024

Empowering Educators: How AI Detection Enhances Teachers’ Workload
- Posted on March 14, 2024

The Ethical Dimension | Navigating the Challenges of AI Detection in Education
- Posted on March 8, 2024

How to Write a Thesis Statement & Essay Outline
- Posted on February 29, 2024 February 29, 2024

The Crucial Role of Grammar and Spell Check in Student Assignments
- Posted on February 23, 2024 February 23, 2024
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- Homework Help
- Essay Examples
- Citation Generator
Writing Guides
- Essay Title Generator
- Essay Topic Generator
- Essay Outline Generator
- Flashcard Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Introduction Generator
- Literature Review Generator
- Hypothesis Generator
Writing Guides / How to Write an Expository Essay (Updated for 2021)
How to Write an Expository Essay (Updated for 2021)

Have you been asked to write an expository essay? One of the most common assignments at all levels of education, an expository essay is something almost all students need to learn. Teachers often assign expository essays to assess your learning about any subject.
This article will provide you with the tools and techniques you need to write the best possible expository essays. Whether you are a total beginner to expository essay writing, or an experienced student who just wants to improve your expository essay writing skills, this article will offer you helpful tips, topic ideas, and even a sample outline. Let’s begin.
View 120,000+ High Quality Essay Examples
Learn-by-example to improve your academic writing
What is an Expository Essay? A Clear Definition
An expository essay is a piece of formal academic writing. The term “expository” means to expose, expound, and explain. When you write an expository essay, you are exposing the main ideas of the subject, expounding on a topic in detail, or explaining the meaning of a topic, idea, or phenomenon. You will typically be expected to have an introduction, body, and conclusion, plus a strong thesis statement to keep your ideas focused.
Although you want to have a clear argument in an expository essay, an expository essay is different from a persuasive or argumentative essay. Although an expository essay might involve some research or reference to outside sources, it is also different from a research paper. An expository essay can resemble other types of academic essays, too, such as compare/contrast essays, definition essays, cause and effect essays, or process essays. In fact, many common academic essays can be classified as expository essays.
When you write an expository essay, pretend you are a teacher . Your goal is to inform the reader, such as by providing facts about a subject or explaining the importance of a topic. An expository essay can be about literature, the arts, history, business, or religion.
How to Write an Expository Essay
To write an expository essay, you will begin with a clear idea and then progress through the steps of effective scholarly writing. The first step in writing an expository essay is selecting the topic. If a topic has been selected for you, you’ll need to determine the approach you will be taking. No two expository essays will be alike, because each student will think slightly differently about the subject and will have a special style of exposition. Your teacher is looking for your unique voice when you write, and also for interesting ideas in your expository essay.
After you have decided on the topic you will tackle in the expository essay, you will want to brainstorm your ideas. Methods of brainstorming include a free writing session, in which you quickly jot down some thoughts without censoring yourself. Another type of brainstorming method involves drawing pictures or diagrams such as word maps. You can also brainstorm with other people like your classmates or a writing tutor.
Next, take what you have learned in your brainstorming session and start doing some research to substantiate your main ideas. Now that you have a strong idea about what you want to write about, you can develop an outline, do some research, and write a rough draft. The outline of your expository essay gives you a road map. An indispensible part of writing an expository essay, outlining helps you to stay organized. A good outline will also make the writing process easier.
Once you finish the outline, you can get started on a first draft or rough draft. This first draft might not be perfect, which is why it is always best to re-read your essay or have a writing tutor to review your work. If you want the best possible feedback for your expository essay, polish your rough draft and make sure that you addressed all the issues that you wanted to discuss. Make sure you have no grammatical or spelling errors, and that your arguments are grounded in factual evidence.
Remember always follow the instructions that your instructor or professor gave you. If you have been asked to write a minimum of 500 words, make sure that you write 500 words and no fewer. If you have been asked to compare five different presidents, make sure you do write about all five and not about two or three. Many students get caught up in the act of writing the essay and forget to follow the instructions.
Avoiding Plagiarism
Academic honesty is expected of all students when they write expository essays. When you do research on the topic you selected for the expository essay, you will sometimes be paraphrasing from what you have read. Make sure you properly cite your sources when you paraphrase. Any time you borrow information or a direct quote, you need to cite the source using whatever citation format your instructor asked you to use. The most common citation formats include APA , MLA , and Chicago. If you are ever in doubt, it is better to include a citation than to omit one. You might get accused of plagiarism if you inadvertently took someone else’s idea and incorporated that information into your expository essay.
Is an Expository Essay a Research Paper?
You might need to do research for your expository essay, looking in books or journals for credible information. However, an expository essay is not a research paper. A research paper consists of you collecting, summarizing, and analyzing the data and then presenting the results of your research in a paper. Many research papers are also longer than expository essays. Although expository essays are not research papers, they do often require you to do research. The purpose for doing the research is explain your topic using credible information and facts, rather than just your emotions or opinions.
Not all expository essays will require you to do research. In fact, some expository essays specifically call upon you to not use any outside sources or to rely only on your own ideas. If you are unsure whether your instructor expects you to do research, ask.
Expository Essay Format
Unless you have been explicitly instructed otherwise, an expository should be formatted with an introduction, body, and conclusion . This typical format is used for a reason: students who do not follow this format risk rambling about the subject, veering off-topic, and failing to respond to the essay prompt. Formatting an expository essay in a logical and organized fashion will help you explain your topic and inform your reader. If you want to write a good expository essay, always try to please your reader with straightforward language and strong organization. The expository essay follows a similar format to a traditional five-paragraph essay. This does not necessarily mean that your expository essay must have exactly five paragraphs. Some expository essays will be too long to only include five paragraphs. The five-paragraph essay format that includes an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion is a model or a skeleton. Consider that each body paragraph is actually just a section or a main idea of your expository essay. Notice how the following expository essay outline can be used for an essay of just five paragraphs or a longer essay too.
[related essays]
Expository Essay Outline
I. Introduction
A. Powerful opening statement.
B. Introduce the main points of the essay.
1. Main point.
2. Main point.
3. Main point.
C. Thesis Statement.
II. Body paragraph/Section on first main point
A. Topic sentence.
B. Develop ideas using factual support and examples.
C. Transition to next paragraph/section.
III. Body paragraph/Section on second main point
B. Develop ideas using factual support and examples.
IV. Body paragraph/Section on third main point
A. Topic sentence
B. Develop ideas using factual support and examples
C. Transition to the conclusion.
V. Conclusion
A. Reiterate the thesis statement or main idea.
B. Reflect on the main points and what they mean.
C. Offer some closing insight or wisdom.
Expository Essay Outline Example
A. Opening statement: Diverse workplaces are 35% more likely to outperform their more homogenous counterparts.
B. Main points
1. Workforces are more diversified than ever before due to globalization, but also due to changing social norms.
2. A diverse workforce also has the potential to offer creative and innovative solutions that can help companies gain competitive advantage.
3. Diversification is part of corporate social responsibility, which improves the company’s reputation and brand identity.
C. Thesis: Companies with strong diversity management policies will be equipped to meet the challenges of a globalized workforce.
II. Workforces are more diversified than ever before due to globalization, but also due to changing social norms.
A. Globalization has encouraged companies to establish a presence in multiple countries, creating an international workforce.
B. Even domestic companies are diversifying due to changing demographics in the labor force.
C. Companies are recognizing that a diverse workforce reflects the values and norms of the current generation.
III. A diverse workforce also has the potential to offer creative and innovative solutions that can help companies gain competitive advantage.
A. When a company expands into a new market, it needs to understand the new target market’s values, norms, and beliefs.
B. Likewise, a company entering a new market needs strategic methods of communicating products and services.
C. Companies with diverse workforces will have a competitive advantage over companies that do not.
D. A diverse team will be capable of coming up with more novel ideas than a homogenous team because each member will think differently about each issue or challenge.
IV. Diversification is part of corporate social responsibility, which improves the company’s reputation and brand identity.
A. Corporate social responsibility is a top-down process whereby senior management commits to an ethical approach to human resources practices.
B. Corporate social responsibility boosts a company’s image among consumers and can be incorporated into public relations and media relations strategies.
A. To sum up, a diverse workforce presents a strategic advantage for companies, allowing for more innovative marketing and improved public relations.
B. Diversity is part of corporate social responsibility, which is becoming increasingly important for remaining competitive.
C. Diverse teams bring more to the table, enabling the most creative solutions.
D. Diverse workforces facilitate breaking into new markets.
Example Expository Essay
Diverse workplaces are 35% more likely to outperform their more homogenous counterparts (Hunt, 2015). Therefore, diversity needs to be considered a key factor determining the success of an organization. Diversity strategies in human resources are increasingly important to businesses of all sizes and in all sectors. Diversification not only increases competitive advantage, but also in many cases helps organizations avoid lawsuits. Workforces are more diversified than ever before due to globalization, but also due to changing social norms. A diverse workforce also has the potential to offer creative and innovative solutions that can help companies gain competitive advantage. Diversification is part of corporate social responsibility, which improves the company’s reputation and brand identity. Companies with strong diversity management policies will be equipped to meet the challenges of a globalized workforce.
Workforces are more diversified than ever before due to globalization, but also due to changing social norms. Social norms and the political climate are encouraging workforces to diversify in order to attract top talent and also to respond to the challenges of globalization. Globalization has encouraged companies to establish a presence in multiple countries, creating an international workforce. The workforce is migratory in some cases, but in other situations, the workforce is diverse due to changing demographics. Even domestic companies are diversifying due to changing demographics in the labor force. Companies are recognizing that a diverse workforce reflects the values and norms of the current generation.
A diverse workforce also has the potential to offer creative and innovative solutions that can help companies gain competitive advantage. For example, when a company expands into a new market, it needs to understand the new target market’s values, norms, and beliefs. Not all products and services will appeal to all people. Similarly, a company cannot use the same marketing or communications strategies in every new market because of differences in culture, language, and values. Likewise, a company entering a new market needs strategic methods of communicating products and services with business partners or clients. Because of the way diverse teams improve the way companies develop or market their products and services, companies with diverse workforces will have a competitive advantage over companies that do not. A diverse team will be capable of coming up with more novel ideas than a homogenous team because each member will think differently about each issue or challenge.
Diversification is part of corporate social responsibility, which improves the company’s reputation and brand identity. Corporate social responsibility refers to ethical policies, principles, and strategies that include everything from using fair trade suppliers to creating a healthy work environment. Because it is related to organizational culture, corporate social responsibility is typically a top-down process. In other words, senior management commits to an ethical approach to human resources practices. By practicing corporate social responsibility in the C-suite, the middle managers and all employees have a model they can follow. Corporate social responsibility boosts a company’s image among consumers and can be incorporated into public relations and media relations strategies. For instance, organizations that have diverse workforces can boast about their diversification in the media and attract new clients and the best talent from around the world.
In conclusion, a diverse workforce presents a strategic advantage for companies, allowing for more innovative marketing and improved public relations. Diversity is no longer an option for work forces, even in domestic companies. Companies need diverse work forces to come up with creative solutions to problems or creative approaches to product design and development. Diversity is part of corporate social responsibility, an ethical strategy that is becoming increasingly important for remaining competitive. Diverse teams bring more to the table in their companies, enabling the most effective solutions. Diverse workforces facilitate breaking into new markets. Ultimately, investing in and developing a diverse workforce is a cost-effective strategy for organizational success.
Hunt, V. (2015). Why diversity matters. Retrieved online: https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/organization/our-insights/why-diversity-matters
Expository Essay Topics
Expository essays can be about almost anything. Having trouble coming up with an expository essay topic? Here are some ideas.
Explain the Four Noble Truths of Buddhism.
Discuss the theme of submission in Islam.
What are three general doctrinal differences between Protestantism and Catholicism?
Compare and contrast two different Native American religions.
Discuss the causes and effects of the Protestant Reformation in Europe.
What were the causes of the Civil War?
Describe the spread of Buddhism from India to East Asia.
Explain Jared Diamond’s theory in Guns Germs and Steel.
Explain the rise of global terrorism, and jihadism in particular.
What does it mean to be a learning organization and why is it important?
Describe two different risk management strategies, and explain which one would be more appropriate for your selected company.
Differentiate between different models of leadership, using examples from case studies.
Write an expository essay on the impact of labor laws on the ways businesses operate.
What are three of the most important philosophies of nursing and why?
Explain the importance of evidence-based practice.
What are the most important characteristics or roles of a nurse leader?
Why is it important for a nurse to be a patient advocate?
What are the themes of Flannery O’Connor’s short story “A Good Man is Hard to Find”?
Compare and contrast Hamlet and Oedipus as tragic heroes.
Analyze the character of Rama in the Ramayana.
Discuss the literary devices Walt Whitman uses in Leaves of Grass.
Political Science
Explain the instruments of power used in foreign policy and strategy.
Compare and contrast Machiavelli’s The Prince with Sun Tzu’s Art of War.
What are the similarities and differences between liberalism, neo-liberalism, and realism?
What strategies would you recommend for resolving the crisis in the Middle East?
Choosing two artists, show how each uses chiaroscuro in their paintings.
Offer a formal analysis of any one of DeKooning’s paintings.
Explain some of the defining features of Impressionism.
How and why did cubism and abstraction evolve? In your discussion, explain the social, cultural, historical, and political context of these movements.
Why Are Expository Essays So Important?
If writing expository essays frustrates or frightens you, it might help to realize why they are important. In addition to providing your instructor with evidence that you have mastered the art of scholarly writing, expository essays also show how well you have mastered the subject matter. When you are asked to explain, describe, or analyze something you learned in class, you are writing an expository essay useful for assessing your learning.
Beyond its value for teachers, expository essays also resemble different types of business communications . Therefore, the tools and skills you use for expository essay writing can be transferred easily to your current and future work. If you are new to expository essay writing, developing your skills now will help you perform better in future coursework and in your professional life. Expository essays allow you to improve essential written communications skills.
Expository essays are going to be one of the most common assignments you will have throughout your education. The vast majority of essays you will be asked to prepare are technically expository essays. Compare/contrast essays, cause/effect essays, process essays, analytical essays, and some argumentative essays are all expository essays. When you write an expository essay, you are explaining something, providing as much information as possible.
An expository essay is a work of non-fiction, and is usually written in the third person because you are explaining something to your reader. You might need to write an expository essay in almost any subject, from the arts to the sciences. Therefore, practicing writing expository essays will help you improve your performance. Eventually, you will get better at writing expository essays.
Expository essays generally follow the five-paragraph essay format with an introduction, body, and conclusion. Likewise, expository essays are thesis-driven. Your thesis is the main idea of the essay, or central argument. Before you start writing an expository essay, it is helpful to brainstorm your ideas and write a rough outline to organize your thoughts. If you need help writing your expository essay, ask for help or consult a writing tutor
Take the first step to becoming a better academic writer.
Writing tools.
- How to write a research proposal 2021 guide
- Guide to citing in MLA
- Guide to citing in APA format
- Chicago style citation guide
- Harvard referencing and citing guide
- How to complete an informative essay outline

How to Write a Synthesis Essay: Tips and Techniques

Why Using Chat-GPT for Writing Your College Essays is Not Smart

The Importance of an Outline in Writing a Rhetorical Analysis Essay

A Guide to Choosing the Perfect Compare and Contrast Essay Topic
Expository Essay: 3 Building Blocks to Propose an Idea and Defend It
by Dixie-Ann Belle | 0 comments
Free Book Planning Course! Sign up for our 3-part book planning course and make your book writing easy . It expires soon, though, so don’t wait. Sign up here before the deadline!
If you saw the words “expository essay” on a writing assignment, would your mind draw a blank? Would you immediately feel as if you had stumbled into unexplored territory?
Well there's good news.
This post is written by guest writer Dixie-Ann Belle. You can learn more about Dixie-Anne at the end of this article. Welcome Dixie-Ann!
You might not realize it, but chances are this is not your first encounter with this type of essay. Once you have been writing essays in academic environments, you have probably already worked on expository writing.
In this article, I hope to help you recognize this essay type and understand the expository essay outline. Comprehending the building blocks is instrumental in knowing how to construct an exceptional expository essay.
Lay a Strong Foundation
Over the years, I have taught and tutored college students one on one as they write academic essays, in face to face classrooms and online, and I have noticed a pattern. They often approach essays in one of two ways.
Some consider them with apprehension and are fearful of making mistakes. Others feel confident that they have written many essays before and think they have already mastered expository writing.
Interestingly, it's the latter who often end up the most shaken when they realize that they are not as familiar as they think with this type of writing.
What I hope to instill in my students is that they should not feel intimidated whatever their situation or essay assignment.
I encourage them to make sure they understand the foundations of the expository essay structure. I try to get them to grasp the basic blocks that need to be there, and once they do, they have a good chance of crafting a substantial piece of writing.
What is an Expository Essay?
Students are typically assigned one of at least four types of essays: the persuasive/argumentative essay, the descriptive essay, the technical essay, or the expository essay.
Writing an expository essay is one of the most important and valuable skills for you to master.
According to the Purdue Online Writing Lab:
The expository essay is a genre of essay that requires the student to investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, expound on the idea, and set forth an argument concerning that idea in a clear and concise manner.
Keep in mind that your expository writing centers on giving your reader information about a given topic or process. Your goal is to inform, describe, or define the subject for your readers.
As you work to achieve this, your essay writing must be formal, objective, and concise. No matter what your discipline, it's almost guaranteed that you will be required to write this common type essay one day.
Some expository essay examples could include:
- Define the term ‘democracy'
- Compare and contrast the benefits of cable television vs streaming
- Outline the process that generates an earthquake
- Classify the different types of tourism
- Outline the aspects of a good fitness program
The possibilities are endless with expository writing, and it can cover a wide variety of topics and specialties.
3 Building Blocks of a Great Expository Essay
To make sure you're on the right track with this type of paper, it helps to understand the three building blocks of the expository essay format and how to apply them to the final expository essay structure .
1. Write an introduction
Most students know that an introductory paragraph should grab the interest of the reader. However, they might not realize that it should also provide context for the essay topic.
Ask yourself : What are you talking about in this essay? Why is this topic important? Some background details could help to establish the subject for your reader.
For example:
If you were writing an essay on the impact smartphones have on society, you might want to start with some information on the evolution of smartphones, the number of smartphones in society, the way people use the phones and more.
The introduction should start off with general information.
You then work your way down to the more specific and principal part of your introduction and the crown of your whole essay, the thesis statement.
What is the thesis statement?
Your thesis statement states in concise language what this essay is going to be about. It is one clear sentence which expresses the subject and the focus of this piece of writing. If there is a prompt, the thesis statement should directly answer that prompt.
Our smart phones topic might create a thesis statement like: Smart phones have many positive impacts for adults in the business world.
Right away the reader has some idea of what's ahead.
2. Write your body paragraphs
With your thesis statement clear in your mind and your introduction setting the scene, it is time to write your body paragraphs.
Each body paragraph contains supporting information including factual evidence for your essay topic. Each paragraph should each focus on one idea.
Depending on your word count and the teacher requirements, you can write any number of body paragraphs, but there are usually at least three for a basic five paragraph essay.
Each body paragraph should start with a topic sentence. A topic sentence is one single statement that explains the point of the paragraph. It directly refers to your thesis statement and tells you what the body paragraph is going to be about.
Remember our smart phone thesis statement? You need something that will relate to that thesis sentence and will alert the reader to what is to come.
Here's one possibility:
Smart phones can help increase productivity for professional adults.
This topic sentence not only reminds us that you are talking about positive impacts for adults with smart phones, it now shows us what the following paragraph will cover.
The best body paragraphs will go on to include different types of details, all of which would support your topic sentence. A good abbreviation to encapsulate the different details is spelt TEEES.
The TEEES Body Paragraph Structure
Let's break down this abbreviation and explore the types of details you'll need in your body paragraphs
T: Topic sentence
You'll begin with your topic sentence establishing the purpose of this paragraph. We'll use our example from above:
Smartphones can help increase productivity for professional adults.
E: Explanation
This is where you expand on your topic and include additional supportive information.
If you were talking about smartphones and productivity, maybe you could mention what elements of the smartphone make it optimal for productivity.
E: Evidence
This is the information from reputable sources you researched for your topic. Here's where you can talk about all the information you have discovered from experts who have carefully studied this subject.
For our smartphone essay, perhaps you could mention a quote from a technology reporter who has been following the rise of smartphones for years.
E: Examples
This would be concrete subject matter to support your point.
Maybe here you can list some of the smartphone apps which have proven to increase productivity in the workplace.
S: Significant/Summarizing sentence
This is the last sentence in the body paragraph which summarizes your point and ends this part of your essay. There should be no doubt in the reader's mind that you have finished talking about your topic, and you are moving on to another in the next paragraph. Here's how we could conclude this paragraph on smartphones and productivity:
Smartphones have transformed the productivity of the modern workforce.
3. Write the conclusion
Once you have written your body paragraphs, you're in the home stretch. You have presented all of your points and supported them with the appropriate subject matter. Now you need to conclude.
A lot of students are confused by conclusions. Many of them have heard different rules about what is supposed to be included.
One of the main requirements to keep in mind when ending an expository essay is that you do not add new information.
This is not the time to throw in something you forgot in a previous body paragraph. Your conclusion is supposed to give a succinct recap of the points that came before.
Sometimes college students are instructed to re-state the thesis, and this puzzles them. It doesn't mean re-writing the thesis statement word for word. You should express your thesis statement in a new way.
For example, here's how you could approach the conclusion for our smartphone essay.
You've come up with three points to support your thesis statement, and you've explored these three points in your body paragraphs. After brainstorming, you might decide the benefits of smartphones in the workplace are improved productivity, better communication, and increased mobility.
Your conclusion is the time to remind your reader of these points with concise language. Your reader should be able to read the conclusion alone and still come away with the basic ideas of your essay.
Plan Your Essay Based on an Expository Essay Outline
While writing fiction, it is sometimes okay to “pants” it and just leap into writing your story.
When writing essays in academia, this is rarely a good idea. Planning your essay helps organize your ideas, helps you refine many of your points early on and saves time in the long run.
There are lots of great brainstorming techniques you can use to get your ideas together, but after that, it's time to create a topic to sentence outline.
There are three steps to creating your topic to sentence essay outline.
- Develop a powerful thesis statement. Remember, this is the overarching idea of your entire essay, so you have completed a significant step once you have one done.
- Come up with the ideas you would like to support your thesis statement.
- Based on your points, craft your topic sentences.
Here is an example of a topic to sentence outline:
Having these important foundation details completed is a great way to develop your essay as you build on each part. It is also an effective method to make sure you are on the right track.
Depending on your instructor (or tutor, if you have one), you can show your outline to them to get feedback before you launch into your entire essay.
Even if you don't have anyone to provide a critique, the outline can make it easier to revise how you will approach the rest of your paragraph essay.
You now have some firm foundations to help you as you construct your expository essay.
How do you organize an expository essay? Let us know in the comments .
Take fifteen minutes to practice writing your own expository essay.
First, choose an expository writing assignment topic. If you can't think of one, use one of the expository essay examples below .
- What are the nutritional elements of a healthy breakfast?
- What are some of the most influential types of music?
- Compare and contrast the benefits of electric and gas cars.
- What are the major steps to planning a stress-free vacation?
- How do smartphones affect mental health?
- Define true love.
Craft a thesis statement about your topic. Then, write three topic sentences for your body paragraphs.
With the time you have left, start writing your essay. You might be surprised how much you can write in fifteen minutes when you have a clear outline for your essay!
When your time is up, share your outline and your essay in the Pro Practice Workshop here . After you post, please be sure to give feedback to your fellow writers.
Happy writing!
Dixie-Ann Belle
Since she started scribbling stories in her notebooks as a child, Dixie-Ann Belle has been indulging her love of well crafted content. Whether she is working as a writing teacher and tutor or as a freelance writer, editor and proofreader, she enjoys helping aspiring writers develop their work and access their creativity.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Expository Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is an expository essay?
The expository essay is a genre of essay that requires the student to investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, expound on the idea, and set forth an argument concerning that idea in a clear and concise manner. This can be accomplished through comparison and contrast, definition, example, the analysis of cause and effect, etc.
Please note : This genre is commonly assigned as a tool for classroom evaluation and is often found in various exam formats.
The structure of the expository essay is held together by the following.
- A clear, concise, and defined thesis statement that occurs in the first paragraph of the essay.
It is essential that this thesis statement be appropriately narrowed to follow the guidelines set forth in the assignment. If the student does not master this portion of the essay, it will be quite difficult to compose an effective or persuasive essay.
- Clear and logical transitions between the introduction, body, and conclusion.
Transitions are the mortar that holds the foundation of the essay together. Without logical progression of thought, the reader is unable to follow the essay’s argument, and the structure will collapse.
- Body paragraphs that include evidential support.
Each paragraph should be limited to the exposition of one general idea. This will allow for clarity and direction throughout the essay. What is more, such conciseness creates an ease of readability for one’s audience. It is important to note that each paragraph in the body of the essay must have some logical connection to the thesis statement in the opening paragraph.
- Evidential support (whether factual, logical, statistical, or anecdotal).
Often times, students are required to write expository essays with little or no preparation; therefore, such essays do not typically allow for a great deal of statistical or factual evidence.
- A bit of creativity!
Though creativity and artfulness are not always associated with essay writing, it is an art form nonetheless. Try not to get stuck on the formulaic nature of expository writing at the expense of writing something interesting. Remember, though you may not be crafting the next great novel, you are attempting to leave a lasting impression on the people evaluating your essay.
- A conclusion that does not simply restate the thesis, but readdresses it in light of the evidence provided.
It is at this point of the essay that students will inevitably begin to struggle. This is the portion of the essay that will leave the most immediate impression on the mind of the reader. Therefore, it must be effective and logical. Do not introduce any new information into the conclusion; rather, synthesize and come to a conclusion concerning the information presented in the body of the essay.
A complete argument
Perhaps it is helpful to think of an essay in terms of a conversation or debate with a classmate. If I were to discuss the cause of the Great Depression and its current effect on those who lived through the tumultuous time, there would be a beginning, middle, and end to the conversation. In fact, if I were to end the exposition in the middle of my second point, questions would arise concerning the current effects on those who lived through the Depression. Therefore, the expository essay must be complete, and logically so, leaving no doubt as to its intent or argument.
The five-paragraph Essay
A common method for writing an expository essay is the five-paragraph approach. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays. If it sounds straightforward, that is because it is; in fact, the method consists of:
- an introductory paragraph
- three evidentiary body paragraphs
- a conclusion
How to Write an Expository Essay
#scribendiinc
Does Expository Writing Have You Confused?
Maybe you find yourself on this page because your instructor asked you to write an expository essay, and you aren't exactly sure what's expected of you—if so, you've certainly found the right place. Expository writing, or exposition, is a type of discourse used to describe, explain, define, inform, or clarify. It literally means "to expose." Exposition can be found in writing or oral discourse, but for the sake of this article, we'll stick with expository writing.
You are likely familiar with expository writing already, even if the name sounds unfamiliar. Common examples include newspaper articles, how-to manuals, and assembly instructions. Expository writing is also the most frequent type of academic writing !
Present the facts, and only the facts
If you are asked to write an expository essay, then you are essentially being asked to present the facts; there is no place for bias or opinion in expository writing. In a way, this makes writing simple—it is a matter of gathering and presenting the facts about a certain topic.
Something important to keep in mind when writing exposition is that you should not assume your readers have any knowledge of the topic; don't gloss over basic or important details, even if you think they're common knowledge.
When writing expository essays, it is best to use third person narration, although second person is acceptable in some instances, such as for instructions—or articles on expository writing.
Characteristics of expository writing
There are a few characteristics of expository writing you should remember when crafting an expository essay. The first is to keep a tight focus on the main topic, avoiding lengthy tangents, wordiness, or unrelated asides that aren’t necessary for understanding your topic.
In the same vein, be sure to pick a topic that is narrow, but not so narrow that you have a hard time writing anything about it (for example, writing about ice cream would be too broad, but writing about ice cream sold at your local grocery store between 5:00 and 5:15 pm last Saturday would be too narrow).
You must also be sure to support your topic, providing plenty of facts, details, examples, and explanations, and you must do so in an organized and logical manner. Details that can support your expository writing include:
- Comparisons
- Descriptive details
- Definitions
- Charts and graphs
Formatting an expository essay
The typical format for an expository essay in school is the traditional five-paragraph essay. This includes an introduction and a conclusion, with three paragraphs for the body of the paper. Most often, these three paragraphs are limited to one subtopic each.
This is the basic essay format, but expository writing does not need to be limited to five paragraphs. No matter how long your essay is, be sure your introduction includes your thesis statement and that the paper is based on facts rather than opinions. And, as with all good essay writing , make sure to connect your paragraphs with transitions.
Methods for writing an expository essay
There are a few different methods for writing an expository essay. These include:
- Compare and contrast
- Cause and effect
- Problem and solution
- Extended definition
Generally, you will want to pick one method for each piece of expository writing. However, you may find that you can combine a few methods. The important thing is to stay focused on your topic and stick to the facts.
Now that you have a clearer understanding of expository writing, you're ready to write your essay. One final tip: be sure to give yourself plenty of time for the writing process. After you've completed your first draft, let your paper sit for a few days—this lets you return to it with fresh eyes. If you'd like a second opinion, our essay editors are always available to help.
Image source: picjumbo_com/Pixabay.com
Let’s Make an Impact on Your Reader
Hire one of our expert editors , or get a free sample.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Essay Writing: Traffic Signals for the Reader

Five Habits to Avoid in Your Academic Writing

How to Write a Great Thesis Statement
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Expository Essay
4-minute read
- 29th March 2020
An expository essay explains something. This means investigating an idea, looking at evidence, coming to a conclusion, and explaining your thinking. But how do you write a strong expository essay? Our top tips include:
- Read the essay prompt carefully and using it to guide your research.
- Come up with a thesis statement (i.e., a position that you’ll explain).
- Plan the structure of your essay before you start writing.
- Once you have a first draft, revise and proofread to make sure it is perfect.
For more advice on how this works, check out the guide below.
1. Read Your Essay Prompt
Most expository essay prompts will ask you to do one of the following:
- Define and explain a concept or theory.
- Compare and contrast two ideas.
- Examine a problem and propose a solution.
- Describe a cause and effect relationship.
- Explain a step-by-step process.
- Analyze a broad subject and classify examples into groups.
When you’ve been set an expository assignment, then, check the prompt or question carefully. You can use the phrasing to guide your research. You may also need to select a topic to write about. If so, try to think of something:
- You already know at least something about.
- You find interesting enough to research.
- That fits with the instructions in the essay prompt (e.g., if you’ve been asked to contrast two things, you’ll need a topic that allows for a comparison).
- That is narrow enough to discuss in one essay.
Start by brainstorming topics, then narrow it down to one or two ideas.
2. Come Up with a Thesis Statement
Once you have a topic, you’ll need to do some research and develop a thesis statement. This is the proposition or position that you’ll explain in your essay.
Your thesis statement should be something you can back up with evidence and facts, as well as something that answers the question in your essay prompt. Keep in mind, too, that an expository essay should present a balanced account of the facts available, not personal opinions. For instance, we’ve come up with thesis statements for a few example essay prompts:
When you’ve selected a thesis, make sure you’ve got evidence to back it up! This may mean doing a little more research before you start writing.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
3. Structuring an Expository Essay
The exact length and content of your essay will depend on the topic and prompt. However, most expository essays follow a similar basic structure:
- Introduction – A paragraph where you introduce the essay topic and your thesis statement (i.e., the issue or idea you will explain in the essay).
- Main Body – A series of short paragraphs in which you explain your thesis statement, providing evidence and arguments to support each point.
- Conclusion – A final paragraph where you restate your thesis and how your evidence supports this. Try not to introduce any new information here (if it’s important, it should go in the main body).
- References – If required, include a bibliography of sources you’ve used.
Before you start writing, then, create an essay outline with the structure above in mind and plan what each paragraph will say.
4. Editing and Proofreading
When you have a first draft, take a break and re-read it. Now comes the redrafting ! This is where you go back over your essay and look for areas to improve. Do you provide enough evidence? Is your argument clear? Even a few tweaks may increase your mark, so make sure to redraft at least once!
Finally, make sure to have your essay proofread before you submit it for marking. This will ensure your writing is error free and easy to read, giving you an even better chance of getting the grades you deserve.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
3-minute read
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
How to Write an Expository Essay: Types, Tips, and Topics
by Yen Cabag | 6 comments

Writing essays is an important skill for students of all ages, from third graders to degree-seekers. The more adept you become at writing an essay, the better your chances of getting a higher grade or getting into the best schools.
But even in the workforce, having advanced research and reporting skills can be a significant advantage, since your supervisor may ask you to write up reports or present your research on a given topic.
Different kinds of essays require different kinds of content. To review, the most common types of essays include:
- Descriptive
- Expository
- Argumentative
In this article, we will be taking a close look at expository essays. (To learn about establishing background information in a story, check out our post on narrative exposition .)
What Is an Expository Essay?
An expository essay is a type of essay wherein the writer investigates and expounds on an idea, evaluates evidence, and presents an argument about that idea in a clear and concise manner.
The word expository comes from exposition , the noun form of “expose,” which means to uncover something to let others know what it is.
6 Types of Expository Essays
Expository essays can come in many different forms, depending on the goal of the writer: do you intend to explain something, or to show how one thing is better than another? Are you tasked with explaining how something works or how to make something?
Here are the most common types of expository essays:
Descriptive or Definition Essays
This type of expository essay is meant to describe a place, an experience, or a concept by appealing to the senses. The topic might be anything from a concrete object like an animal, city, or tree, or it can also be an abstract idea, such as relationships, love, or freedom.
This type of essay can include a discussion of the literal definition of the topic, as well as what it connotes or the ideas that the word might bring to a person’s mind.
Procedure or “How-To” Essays
This type of essay explains the process of doing or making something. An effective way of doing this is to include the steps that the reader can take.
This can include the following topics:
- scientific processes, like a laboratory experiment
- life skills, such as cooking, baking, repairing, or creating something
- natural processes, like the metamorphosis of animals and insects
- mechanical or technological processes, like how a piano or a computer works
Comparison Essays
This essay compares and contrasts at least two different things, places, people, or ideas. This includes highlighting their similarities, as well as illustrating their differences.
A good way of writing this type of essay is to pick themes around which to make your comparisons. For example, in comparing two cities for livability, you may want to compare populations, the quality of available schools, accessibility and convenience, or pollution and stress levels, among other factors.
Cause-and-Effect Essays
This essay attempts to uncover the relationship between two objects, with the goal of determining whether one thing causes another.
You may need to provide supporting evidence to demonstrate the cause and effect relationship between the two ideas.
Problem/Solution Essays
This type of essay presents a problem and offers a possible solution.
The best way to write this type of essay is by offering several potential solutions. Then, highlight the pros and cons of each.
Based on those pros and cons, present your personal recommendations for the reader, while still leaving room for the reader to decide for themselves.
Alternatively, a problem/solution essay may also have only one solution, and in this case, the reader does not need to make a choice.
How to Write an Expository Essay
You can write an expository essay using the following steps.
1. Define your thesis statement.
Because an expository essay generally goes in-depth on a given subject, it’s important that you specify your thesis statement from the get-go. State it in a clear and concise manner in the first paragraph of your essay.
If you are given free rein to choose your topic, use this time to brainstorm possible ideas and choose one that you are genuinely interested in. This will make the process of researching and writing more engaging for you.
Defining your thesis statement will also let you decide on the type of expository essay you will write.
2. Research on your topic and take notes.
Remember that your expository essay needs relevant facts and support to get your point across to your audience. Research as much as possible, collecting the relevant details in bullet points that you take while reading.
3. Outline your essay.
From your bullet point notes, organize your findings. Form a logical sequence of headings that you can later expand.
A good outline will include the following:
- Introduction
- Body paragraphs
- Conclusion
The body of your essay can be anywhere from 2-3 paragraphs to several paragraphs long. As you compose your outline, write down the different headings for your paragraphs so you can see exactly how each one transitions into the next.
4. Write your first draft.
Start with an introduction, where you include your thesis statement. Then, write a sentence that transitions logically into your body paragraphs.
Important: For the body of your essay, remember to include evidential support.
Because an expository essay expounds on your thesis statement, it’s crucial that you include evidence to prove your point. Undeniable facts will back up whatever point you’re making in the essay, rather than a flimsy argument that can easily be dismantled. Your evidential support can come in different ways:
- Factual: Actual facts and can help prove your point. Citing academic sources for those facts will help establish your credibility.
- Logical: Arguments based on logic are formed when you deduce something from given information.
- Statistical: Statistical evidence supports your claim based on research conducted by others, or by a survey that you yourself perform.
- Anecdotal: A qualitative real-life story may also help to support your claim.
Include as much evidence as you can to support your thesis statement. But remember to keep your writing clear and well-directed by focusing on one key idea per paragraph.
Finally, state your conclusion, and restate your thesis to remind your readers of your essay’s purpose.

5. Refine your work.
After you write your first draft, carefully review and proofread your work . Check that your points make sense, and ask yourself whether the current layout is the best, most logical way to present your information.
If you find any paragraphs that do not connect well, either rewrite more effective transitional sentences or find a more suitable place for the paragraph.
Writing Expository Essays
Writing expository essays is a great practice in critical thinking. Not only will you learn important research skills, but you will also be able to gather evidence in support of your claims.
For more writing tips, check out our guides on how to write an essay and how to write a research paper to refine your expository and persuasive writing skills.
Did you find post essay helpful? Let us know in the comments below!
If you enjoyed this post, then you might also like:
- How to Write an Essay: 7 Steps for Clear, Effective Writing
- How to Write a Thesis Statement
- How to Write a Hook: 10 Ways to Capture Your Readers’ Attention
- How to Write a Research Paper: The Complete Guide for Students
Yen Cabag is the Blog Writer of TCK Publishing. She is also a homeschooling mom, family coach, and speaker for the Charlotte Mason method, an educational philosophy that places great emphasis on classic literature and the masterpieces in art and music. She has also written several books, both fiction and nonfiction. Her passion is to see the next generation of children become lovers of reading and learning in the midst of short attention spans.
This is good to learn how to outline, therm, main point and Minor points. Thanks very much
You’re very welcome, Nicholas! We’re glad you found the post helpful :)
Thanks it really help me
A comprehensive and useful guide to writing an expository essay. I appreciate what you have posted on the blog. It’s very insightful and helpful.
Thanks Anna, we’re glad you found it helpful! :)
This is very helpful to write an excellent expository essay with your guide.Thankyou for your good work, your highly appreciated.

Learn More About
- Fiction (223)
- Nonfiction (71)
- Blogging (46)
- Book Promotion (29)
- How to Get Reviews (9)
- Audiobooks (17)
- Book Design (11)
- Ebook Publishing (13)
- Hybrid Publishing (8)
- Print Publishing (9)
- Self Publishing (70)
- Traditional Publishing (53)
- How to Find an Editor (11)
- Fitness (4)
- Mindfulness and Meditation (7)
- Miscellaneous (117)
- New Releases (17)
- Career Development (73)
- Online Courses (46)
- Productivity (45)
- Personal Finance (21)
- Podcast (179)
- Poetry Awards Contest (2)
- Publishing News (8)
- Readers Choice Awards (5)
- Reading Tips (145)
- Software (17)
- Technology (16)
- Contests (4)
- Grammar (60)
- Word Choice (64)
- Writing a Book (62)
- Writing Fiction (195)
- Writing Nonfiction (73)
- Words with Friends Cheat
- Wordle Solver
- Word Unscrambler
- Scrabble Dictionary
- Anagram Solver
- Wordscapes Answers
Make Our Dictionary Yours
Sign up for our weekly newsletters and get:
- Grammar and writing tips
- Fun language articles
- #WordOfTheDay and quizzes
By signing in, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy .
We'll see you in your inbox soon.
What Is an Expository Essay? Examples and Guide

- DESCRIPTION woman with yellow shirt working on laptop with expository essay definition
- SOURCE Prostock-Studio / iStock / Getty Images Plus / via Getty created by YourDictionary
- PERMISSION Used under Getty Images license
We all have our different ways of explaining the same things. Ask three people to explain how to eat some corn on the cob, and you’ll get three different explanations. That’s the real beauty of the expository essay, and it means you already have the basic tools to write a great one. So what is an expository essay and how can you refine your approach?
What Is an Expository Essay?
An expository essay is a type of essay that involves explaining an idea or theme within a given subject or topic. That could be an in-depth look at a poem or story, or it could be an explanation of a historical event.
The key word here is exposition , or the act of exposing something. Unlike descriptive or narrative essays, expository essays are about exposing or revealing something deeper in a given subject through research, close reading, and critical thinking. The goal is to explain a subject beyond just a surface level description.
Types of Expository Essays
If that sounds familiar or similar to other essay forms , you wouldn’t be entirely wrong. The expository essay is an umbrella term that contains other, more specific essay types, including:
- Cause and effect essays
- Compare and contrast essays
- Analytical essays
- Dissertations and theses
Even simple book reports can get into the expository essay zone. If you’ve ever written a traditional five-paragraph essay , you’ve probably written an expository essay. Expository essays are generally objective by nature.
General Structure and Format of an Expository Essay
The format of an expository essay is about as basic as it gets. It’s not exactly the most creative or exciting in its format, but that just gives more opportunity for your actual writing to shine.
Your expository essay will probably look like:
- An introduction paragraph that provides a hook, background information, and a thesis statement
- Three body paragraphs that dive into the actual exposition of the essay (whether that’s specific line reads, research-based evidence, or discussion of themes)
- A conclusion that restates the thesis, brings things together, and considers themes within a larger context
With longer expository essays or more in-depth topics, you’ll understandably include more body paragraphs. Otherwise, don’t overthink the structure of your essay too much. Focus more on the actual words and sentences.
Expository Essay Examples
Now you know what an expository essay is, and you have a good idea of what it all entails. With a few more tips for writing an expository essay , you’ll be pumping out some award-winning words in no time.
We can’t write your essay for you. Partly because we don’t know what you’re explaining, partly because you probably have better points and thoughts than we could ever come up with. But we can give you a pretty good example of what your completed expository essay might look like.

- DESCRIPTION full expository essay example with labels
- SOURCE Created by Karina Goto for YourDictionary
- PERMISSION Owned by YourDictionary, Copyright YourDictionary
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Introductions can feel like a bit of a thankless task. Your reader already knows that they’re reading an essay, so why do you need to introduce it? Well, no one wants to start in the middle of a discussion. Providing some context and background helps to ease your reader in, and the intro is a good way to get a little bit of your voice upfront.
While some teenagers have to deal with zits, math tests, and asking a crush to prom, others wear colored bodysuits and perform martial arts against strange, extra-dimensional evil. Premiering in the U.S. in the early 90s, Power Rangers presented a weird, new form of entertainment, introducing children to martial arts and Japanese culture in the trappings of Saturday morning programming and the after-school special. Despite its often fantastical leanings, Power Rangers presented an integral turning point in children’s programming and media at large.
Example of an Expository Essay Body Paragraph
While every part of an essay is important, you should devote most of your time to the body paragraphs. This is where you’ll do most of your analysis, exposition, and all the other good stuff that goes into figuring out your subject and relaying that to your reader.
Although it presented something new and largely unseen by Western audiences, Power Rangers was anything but. All of the action scenes were taken directly from Japan’s Super Sentai series (specifically Kyoryu Sentai Zyuranger ), intercut with scenes of an American cast existing within tranquil Angel Grove. The Super Sentai series stayed within the traditions of the long-running line of programming known as tokusatsu , meaning “special effects” (a reference to the use of practical special effects). Transplanting Japanese cultural media and overlaying it upon an American production and audience posed its own challenges, but the almost immediate success came from its own storytelling. At first blush, winding fantastical adventures and impressive martial arts into the everyday lives of American teens (who dealt with bullying, teamwork, and celebrating birthdays) seems disparate. However, the combination led to instantly relatable stories that resonated with children, imparting ideas of community and selflessness through skills and talents of all forms, physical, mental, and emotional.
Expository Essay Conclusion Example
Much like the intro, the conclusion to an essay can seem ornamental or extraneous. If you think of an essay as a full thought, the conclusion is a space to finish your thoughts. Unlike most of the rest of the essay, it’s an opportunity to show a little emotion and get into some topics that are potentially outside the main bounds of your subject.
In conclusion, Power Rangers presented an amalgam of different cultural ideas to create a new children’s media landscape. The original series has since given rise to ongoing series, along with offshoot books, comics, and other media. For many kids, the show was an introduction to new ideas that were still grounded within the parks, schools, and suburbs of their lives. It was a form of escapism and imagination that stayed within the bounds of a reality that could be cruel, difficult to understand, or full of light. It just took some friends, some martial arts, and the ability to morph into something new.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Expository Writing: Definition and Examples

Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
What is expository writing, what is an expository paragraph, expository writing examples, how prowritingaid can help you with expository composition.
One of the most common types of writing is expository writing. Whether you’re a student taking an English class or a professional trying to communicate to others in your field, you’ll need to use expository writing in your day-to-day work.
So, what exactly does this term mean?
The short answer is that expository writing refers to any writing designed primarily to explain or instruct.
Read on to learn the definition of expository writing as well as some examples of what this type of writing can look like.
Before we look at examples of expository writing, let’s start with a quick definition of what this term actually means.
Expository Writing Definition
The term expository writing refers to any writing that’s designed to explain something. We use the word expository to describe any passage of writing that’s supposed to present information and help you understand it in an objective way.
Some common examples of expository writing include academic essays, textbooks, instructional guides, and news reports. Good expository writing should be factual, objective, and clear.

To better understand what this term means, think about the difference between a scientific article, a short story, and an advertisement.
The scientific article is considered expository writing because its primary purpose is to explain a particular topic in more detail. It presents data, analyzes what that data means, and focuses on the facts.
On the other hand, the short story isn’t considered expository writing, because its core purpose isn’t to explain or inform—instead, it’s probably trying to entertain you or to take you on a journey. Short stories are narrative writing.
Similarly, an advertisement isn’t expository writing because its core purpose isn’t to explain or inform—instead, it’s trying to persuade you to buy what it’s selling. Advertisements are persuasive writing.
Here’s a quick rundown of what expository essays should and shouldn’t do.
An expository essay should:
Teach the reader about a particular topic
Focus on the facts
Follow a clearly organized structure
Present information and details from credible sources
An expository essay should not:
Try to change the reader’s mind about something
Present the author’s personal opinions
Include made-up narratives or stories
Follow experimental or nonlinear structures

An expository paragraph is exactly what it sounds like—a paragraph of expository writing.
A well-written expository paragraph should follow a specific format to make it as clear and easy to read as possible. Most expository paragraphs do the following things:
Start with a topic sentence, which explains what the paragraph will be about
Then, include 3 – 5 body sentences that provide supporting details for the topic sentence
Finally, wrap things up with a closing sentence that summarizes what the paragraph has said
Writing an expository paragraph is a great way to practice expository writing. That’s because the paragraph follows the same structure as a more complex expository essay, just on a smaller scale.
Most expository essays should follow this format:
Start with an introductory paragraph that includes the thesis statement, which tells the reader the core statement of the essay
Then, include 3 – 5 body paragraphs that provide factual evidence to support the thesis statement
Finally, wrap things up with a concluding paragraph that summarizes what the body paragraphs and thesis statement said
You can see the similarities between the two formats. If you can write a fantastic expository paragraph, you’ll be well-prepared to move on to writing a full expository essay.
Example of Expository Paragraph
Here’s an example of an expository paragraph that follows the structure described above.
The leading cause of death in the United States is heart disease, which can be fatal if it leads to heart attack or cardiac arrest. Heart attacks occur when a blockage in the coronary artery prevents oxygenated blood from reaching the heart. Cardiac arrests occur when the heart stops pumping entirely, which prevents the patient from breathing normally. Both of these problems can be deadly, even in seemingly healthy people who don’t have noticeable risk factors. As a result, heart disease is an important problem that many doctors and scientists are researching.

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
There are many ways you can present information in an expository essay. Here are four of the most popular ways, along with examples of each one.
Problem and Solution Essay
A problem and solution essay presents the reader with a problem and then considers possible solutions to that problem.
Here’s an example passage you might find in a problem and solution essay:
Among the many proposed solutions to rising carbon emissions, one promising possibility is carbon trapping. Scientists are figuring out how to pull carbon emissions out of the atmosphere and trap it in less harmful forms, such as by injecting carbon dioxide underground so it will turn to stone.
Compare and Contrast Essay
This type of essay takes two subjects and compares and contrasts them. It focuses on highlighting the differences and similarities between those two things.
Here’s an example passage of this type of expository writing:
Though country music and R&B music have very different sounds, they also share many similarities. For one thing, both types of music embody a specific cultural identity. For another, both genres trace their roots back to the 1920s, when the Victor Talking Machine Company signed singers from the American South.
Classification Essay
In a classification essay, you describe the categories within a certain group of things.
Here’s an example passage you might find in a classification essay:
There are three ways in which artificial intelligence might become stronger than humans in the future: high speed, high collective intelligence, and high quality. A speed AI would be able to perform calculations and experience the world much faster than humans. A collective intelligence, like a hive mind, would be able to break down a complex task into several parts and pursue them simultaneously. Finally, a quality AI would simply be able to solve more complex problems than humans could.
Process Essay
In a process essay, you give the reader the steps for completing a specific process. This is similar to a how-to guide or an instruction manual.
Here’s an example passage you might find in this type of expository writing:
Caramelize the chopped onions in a frying pan. When the onions have caramelized, mix in the bell peppers, mushrooms, and tomatoes and stir for 4 – 6 minutes or until all the ingredients have softened. If you want to add meat, you can add ground beef and cook for another 4 – 6 minutes. Season with salt and pepper to taste.
Good expository writing should be easy to read. After all, the purpose of exposition is to explain things to your readers, and you won’t be able to accomplish that if they have trouble understanding your writing.
That’s why ProWritingAid can help you write an expository essay. The grammar checker can help you ensure your sentences flow well, you’re not missing any necessary punctuation, and all your words are precise and clear.
Good luck, and happy writing!
Hannah is a speculative fiction writer who loves all things strange and surreal. She holds a BA from Yale University and lives in Colorado. When she’s not busy writing, you can find her painting watercolors, playing her ukulele, or hiking in the Rockies. Follow her work on hannahyang.com or on Twitter at @hannahxyang.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.1: Expository Essays
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 4531
Learning Objectives
- Understand the function and use of expository essays
- Identify eight types of expository essays
- Apply expository essay structure
What Is an Expository Essay?
An essay that explains a writer’s ideas by defining, explaining, informing, or elaborating on points to allow the reader to clearly understand the concept.
Many of your future academic workplace writing assignments will be expository–explaining your ideas or the significance of a concept or action. An expository essay allows the writer the opportunity to explain his or her ideas about a topic and to provide clarity for the reader by using:
- Explanations
- Definitions
It may also include the writer outlining steps of a procedure in a way that is straightforward for the reader to follow. It is purely informative and often contains elements of summary.
Imagine you need to verbally explain a concept to your classmates, maybe a behavioural theory. What are the key elements on which you would focus? How would you organize the information? You could explain who came up with the theory, the specific area of study to which it is related, its purpose, and the significant details to explain the theory. Telling these four elements to your classmates would give them a complete, yet summarized, picture of the theory, so they could apply the theory in future discussions.
Although you did this verbally, you were still fulfilling the elements of an expository essay by providing definition, details, explanations, and maybe even facts if you have a really good memory. This is the same process that you would use when you write an expository essay. You may actually be doing this all the time; for example, when you are giving someone directions to a place or explaining how to cook something. In the following sections of the chapter, you will practise doing this more in different expository written forms.
The Structure of an Expository Essay
Sections versus paragraphs.
Before looking at the general structure of an expository essay, you first need to know that in your post-secondary education, you should not consider your essay as writing being constructed with five paragraphs as you might have been used to in high school. You should instead think of your essay in terms of sections (there may be five), and each section may have multiple paragraphs.
To understand further why you need to think beyond the five-paragraph essay, imagine you have been asked to submit a six-page paper (approximately 1,500 words). You already know that each paragraph should be roughly 75 to 200 words long. If you divide the required word count by five paragraphs (1,500 by 5), you end with 300 words per paragraph, way above the number you should have in a paragraph. If your paragraphs are too long, they likely have too many ideas and your reader may become confused. Your paragraphs should be two-third of a page at most, and never longer than a page.
Instead, if you think of your essays being divided into sections (with possibly more than one paragraph per section), your writing will likely be more organized and allow your reader to follow your presentation of ideas without creating too much distance between your paragraph’s supporting points and its topic sentence.
As you will see in Section 4.5, some essay forms may require even more than five paragraphs or sections because of how many points are necessary to address. For the rest of this chapter, the term paragraph will also imply section.
Sections of an Expository Essay
An expository essay, regardless of its purpose, should have at least five sections, which are:
- Introduction
- First body section/paragraph
- Second body section/paragraph
- Third body section/paragraph
- Conclusion.
The introduction should state the topic of your paper: your thesis statement as well as brief signposts of what information the rest of the paper will include. That is, you only want to mention the content of the body paragraphs; you do not want to go in to a lot of detail and repeat what will be in the rest of the essay.
The first body section or paragraph should focus on one of your main points and provide evidence to support that point. There should be two to three supporting points: reasons, facts, statistics, quotations, examples, or a mix of these. Both the second and third body sections should follow the same pattern. Providing three body sections with one point each that supports the thesis should provide the reader with enough detail to be convinced of your argument or fully understand the concept you are explaining. However, remember that some sections will require more explanation, and you may need to separate this information into multiple paragraphs.
You can order your sections in the most logical way to explain your ideas. For example, if you are describing a process, you may use chronological order to show the definite time order in which the steps need to happen. You will learn about the different ways to organize your body paragraphs in the next chapter.
The concluding paragraph , or conclusion, can be a little tricky to compose because you need to make sure you give a concise summary of the body paragraphs, but you must be careful not to simply repeat what you have already written. Look back at the main idea of each section/paragraph, and try to summarize the point using words different from those you have already used. Do not include any new points in your concluding paragraph.
Consider Your Audience: How Much Do They Know?
Later in this chapter, you will work on determining and adapting to your audience when writing, but with an expository essay, since you are defining or informing your audience on a certain topic, you need to evaluate how much your audience knows about that topic (aside from having general common knowledge). You want to make sure you are giving thorough, comprehensive, and clear explanations on the topic. Never assume the reader knows everything about your topic (even if it is covered in the reader’s field of study). For example, even though some of your instructors may teach criminology, they may have specialized in different areas from the one about which you are writing; they most likely have a strong understanding of the concepts but may not recall all the small details on the topic. If your instructor specialized in crime mapping and data analysis for example, he or she may not have a strong recollection of specific criminological theories related to other areas of study. Providing enough background information without being too detailed is a fine balance, but you always want to ensure you have no gaps in the information, so your reader will not have to guess your intention. Again, we will practise this more in Section 4.9.
What Comes Next?
In the next eight sections (4.2 through 4.9), we will look at different expository modes, or rhetorical modes, you will often be assigned. These are:
- Illustration
- Description
- Classification
- Process analysis
- Compare and contrast
- Cause and effect
Rhetorical modes refers simply to the ways to communicate effectively through language. As you read about these modes, keep in mind that the rhetorical mode a writer chooses depends on his or her purpose for writing. Sometimes writers incorporate a variety of modes in any one essay. In this chapter, we also emphasize the rhetorical modes as a set of tools that will allow you greater flexibility and effectiveness in communicating with your audience and expressing your ideas.
In a few weeks, you will need to submit your first essay–an expository sample–and you will be given the choice of topic: one from each of the modes. Think about which types of expository essays are easier and which are more challenging for you. As mentioned, as you progress through your studies, you will be exposed to each of these types. You may want to explore a mode you find more challenging than the others in order to ensure you have a full grasp on developing each type. However, it is up to you. As you work through the sections, think about possible topics you may like to cover in your expository essay and start brainstorming as you work through the self-practice exercises.
After we explore each of the individual modes in the eight sections that follow, we will look at outlining and drafting; it is at this point you will want to fine tune and narrow the topic you will write about, so you can focus on that when doing the exercises.
Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Paper Types / How to Write an Expository Essay
How to Write an Expository Essay
Every student has to write an expository essay at least once in their educational career. These are actually fairly simple essays to write, but they do require some serious research skills. Like most academic essays, the expository essay requires formal writing with an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Guide Overview
- Focus on the thesis
- Listen to the assignment
- Explain, don’t argue
- Revise and edit, revise and edit
- Choosing the right topic
Tips for Writing a Kick-Butt Essay
Want to really impress your professor? Here are a few ways you can turn an ordinary essay into something that will blow their socks off.
Focus on the Thesis
Your thesis is the central point of the entire essay, so if it’s amazing, you’re off to a great start. Begin with this and make sure you decide on something that is impressive to kick off the essay.
Listen to the Assignment
Your professor may give you hints on what they’re looking for. If you just write down the basics of the assignment, you could miss out on some key points. For example, your professor may hint at a preferred topic or give tips that could result in a higher score. Write it all down and then analyze what is wanted before you write.
Long before you actually put pen to paper or fingers to keyboard to write the essay, you need to complete the pre-writing phase. This is where you do research and outline your essay. You’ll be amazed at how much better your writing is when you have these basic elements in place first. If you need help with these basic elements consider using an Expository Essay Template.
Explain, Don’t Argue
If you’re not careful, an expository essay can turn into a persuasive or argumentative essay. Focus on explaining the topic, rather than convincing people of something about it.
Revise and Edit, Revise and Edit
Going over the essay once to edit and polish isn’t really enough. If you’re tight on time, such as when writing an essay for an exam, just once will do. However, if you have time, it’s a good idea to edit immediately, then let the essay sit overnight or even longer. When you come back, you won’t be as close to the writing and can look at it more objectively.
Choosing the Right Topic
Topics for an expository essay vary widely, but ideally, you should select something you’re interested in writing about. Topics can answer a question such as “How can we prevent bullying in school?” or they can describe something like a historical building in your area. Other interesting topics to inspire you include:
- How does technology affect our relationships?
- How to treat a burn
- What are the must-haves for a freshman in college?
- How to handle anxiety attacks naturally
- How to train your dog to stop barking on command
- Research the history of a monument in your area
- Why roller skating is a great exercise
As you can see, there’s no limit to the types of topics you can choose for your essay and it really comes down to what the professor assigns you and what you enjoy writing about. How narrow your topic is will also depend on how much you plan to write. An entire history of the Civil War won’t fit into two page, for example, so you’ll need to narrow it down to a specific battle or element of the Civil War.
Writing an expository essay can actually be a fun experience if you approach it the right way. When you enjoy the topic and are interested in it, your essay will show that and will stand out from those written out of boredom.
Finally, if you’re ever facing writer’s block for your college paper, consider WriteWell Essay Templates to help you get started.
EasyBib Writing Resources
Writing a paper.
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Research Paper
- Thesis Statement
- Writing a Conclusion
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing an Outline
- Writing a Summary
EasyBib Plus Features
- Citation Generator
- Essay Checker
- Expert Check Proofreader
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tools
Plagiarism Checker
- Spell Checker
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

The Admissions Strategist
Expository writing: how to write an incredible expository essay.
Expository essays are frequently assigned in English classes and are evaluated in various standardized exams.
But what exactly is an expository essay, and how do you write a good one?
In this article, we’ll tell you everything you need to know to pen a high-scoring expository paper.
What Is an Expository Essay?
The word expository means “intended to explain or describe something.”
An expository essay requires you to investigate an idea, gather supporting evidence, and present your point of view on a topic.
- You may be wondering how this differs from a persuasive essay.
- While both essay types require you to provide evidence to support a claim, persuasive essays are more argumentative.
A persuasive essay includes a counterargument, which addresses and rebuts an opposing viewpoint.
Expository essays, on the other hand, focus on clearly explaining and supporting your point of view.
Parts of an Expository Essay
A strong expository essay should consist of:
- An introductory paragraph with a clear thesis
- Evidence that supports the thesis (typically in three body paragraphs)
- A conclusion
Below, we’ll look at how to construct the expository essay piece by piece.
For clarity, we’ll focus on a somewhat formulaic process for expository writing.
Once you’ve mastered these basics, you can take risks and sprinkle more creativity throughout your essays.
Introduction
The introduction frames the topic of your essay.
It also provides readers with any necessary background information or context.
A simple format for your introduction is:
- Grabber/Hook – A compelling sentence or two that draws readers into your essay.
- Background Information (as needed) – Any basic information the reader needs to know about the topic to understand your essay.
- Thesis Statement – This is the most important sentence of your entire essay. See below for more information.
Thesis Statement
The thesis statement is the roadmap for your entire essay, so it must be clear and concise. It should state your point of view on the topic.
- The thesis may also briefly mention the supporting evidence you’ll expand on in the body of the essay.
For instance, a thesis statement might say:
Students should read more literature because it improves vocabulary, reading comprehension, and empathy.
The writer’s viewpoint is immediately clear: Students should read more literature.
The writer also indicates that her supporting evidence will mention several benefits of reading literature: improved vocabulary, better reading comprehension, and increased empathy.
- Most likely, each of these points will form one of the writer’s body paragraphs.
If your teacher (or a standardized test) assigns you a topic, here’s another way to think of a thesis statement: The thesis is your answer to the question being asked.
- Let’s say you receive a prompt that says, “Your community is thinking of starting a program encouraging people to limit car usage. Explain how limiting car usage would benefit your community.”
This prompt is essentially asking, “How would limiting car usage benefit your community ?”
- Thus, your thesis could answer the question by saying something like, “Limiting car usage would benefit the community because it would decrease traffic, improve public health, and reduce air pollution.”
This approach ensures that you’re on topic and directly addressing the prompt.
Supporting Evidence
Once you’ve clearly stated your point of view, it’s time to support it. To do this, you’ll need evidence . Sometimes, this will mean doing your own research.
On other occasions, especially exams, you’ll be provided with relevant resources.
These may include newspaper articles, primary sources, photos, or even audio recordings.
- Your job is to sort through these resources and find evidence that supports your thesis. It’s important to note that if you can’t find evidence supporting your thesis, you’ll need to change it.
Strong evidence may include research findings, quotes from experts, and statistics. Make sure that your evidence is from credible sources and clearly supports your thesis statement.
Organizing Evidence
After finding your supporting evidence, you’ll organize it into body paragraphs, typically three of them.
Each body paragraph should focus on one general idea.
In addition, each of these general ideas should be logically connected to your thesis statement.
- Your body paragraphs should start with a topic sentence that introduces the idea that the body paragraph will elaborate upon.
Remember our sample thesis about students reading more literature?
- The topic sentence of the first body paragraph could read, “To start with, reading literature is essential because it expands students’ vocabulary.”
After the topic sentence, the paragraph should introduce 2-3 pieces of evidence supporting this idea.
If a piece of evidence doesn’t clearly relate to the body paragraph’s topic sentence, it needs to be moved or deleted.
Analyzing Evidence
When you introduce a piece of evidence, follow it up with a sentence analyzing the evidence in your own words.
- Explain the connection between the evidence and your thesis statement.
- How does it support your point of view?
- How do you interpret this evidence?
Remember that essays don’t only reflect your writing skills; they also reflect your critical thinking skills.
Instead of merely quoting evidence, you must also explain your thought process.
As a result, an effective body paragraph can follow this formula:
- Topic sentence
- Evidence #1
- Analysis of Evidence #1
- Evidence #2
- Analysis of Evidence #2
- Evidence #3 (Optional)
- Analysis of Evidence #3 (Optional)
- Concluding/transitional sentence
The final sentence of the body paragraph should remind readers of the paragraph’s main point and connect it to the next paragraph.
Transitions are important because they help readers follow your train of thought without confusion.
They smoothly guide readers through your paper.
Transition words and phrases include:
- For example
- For instance
- To illustrate
- Specifically
- On the other hand
- Consequently
- As a result
- Additionally
- Furthermore
Get personalized advice!
Like stories, essays have a beginning, middle, and end.
- The introduction is your beginning, the body paragraphs form the middle, and the conclusion brings the paper to an end.
The conclusion synthesizes the information included in your essay.
As the name suggests, it also draws a conclusion from the information presented.
- Instead of simply restating the thesis, you should revisit the thesis in light of the supporting evidence you’ve provided. Do not introduce any new information in the conclusion.
Remember that the conclusion is your last chance to make an impression on the reader. It should be logical and convincing.
Try to end with a strong and/or memorable final sentence.
In total, an expository essay includes these pieces:
– Introduction
- Hook/grabber
- Background information
– Body paragraphs (usually three)
– conclusion.
- Synthesis of evidence
- Explanation of what this evidence shows (connected to thesis)
- Strong final sentence
If you include each of these pieces, you’ll have a clear, logical, and effective expository essay.
Once you become comfortable following this formula, you may wish to vary it or infuse it with your own style.
Just make sure that all the essential pieces are present in your essay.
The Expository Essay Writing Process
Before you can effectively assemble an expository essay, you’ll need to gather information and plan your approach.
Typically, the writing process includes:
- Carefully reading the prompt (if applicable)
- Brainstorming
- Gathering evidence
- Revising/editing
Let’s take a closer look at each step in the process.
1. Reading the Prompt
If you’re provided with a prompt, understanding it is an essential first step.
Misinterpreting the prompt will result in a low score, even if your essay is well-written.
- Read the prompt at least 2-3 times, underline key words and phrases. If the prompt is complicated, you may want to rewrite it in your own words.
Does the prompt have multiple parts? If so, make sure you understand each part and that your essay clearly addresses all of them.
2. Brainstorming
Once you’ve read the prompt, begin brainstorming how you will approach it.
- If you’ve been provided with relevant resources, this may also include a first read-through or skimming of these texts.
What position will you take? How are you planning to support your viewpoint? Jot down any idea that pops into your head.
- It doesn’t matter if the idea is good—right now, you’re just trying to find inspiration. You’ll change, add, or remove information later.
If you haven’t been provided with a prompt, you’ll need to brainstorm a topic that interests you.
It should also be a topic on which you’re at least somewhat knowledgeable.
3. Gathering Evidence
At this point, you’ll find evidence that supports your point of view.
- It helps to write at least a rough draft of your thesis statement before beginning this step.
- This way, you’ll have a clear idea of what sort of evidence you need to find.
After writing your thesis statement, find credible evidence that supports it.
- This may require you to go to the library or browse scholarly databases on the Internet.
Alternatively, you may have been provided with resources.
In that case, read through the resources carefully, underlining or circling evidence that reinforces your thesis.
4. Planning
Planning ensures that your essay is organized, focused, and cohesive.
It also allows you to catch potential mistakes before they happen.
- For instance, you might realize that some of your evidence doesn’t fit, or that one of your body paragraphs is lacking support.
You can then address these areas of weakness before writing your essay.
- At the top of your planning sheet (or a document on your computer) write your thesis statement.
- Continually reference the thesis to ensure that you’re focused and on topic.
- Next, determine the focus of each body paragraph and the 2-3 pieces of evidence that will support it.
Sometimes, students think that planning is too time-consuming.
However, a plan will save you time in the long run.
With all your quotes and evidence organized in one place, writing your essay is much faster and easier.
Once you have a completed plan, begin writing your essay.
- Remember to analyze each piece of evidence and clearly connect your points with transitions.
Use a formal, academic tone and avoid slang or overly casual language.
Vary your sentence structure, including both short and long sentences. Pay attention to spelling, grammar, and punctuation.
6. Revising
Students often skip the revising and editing step of the writing process.
This is a mistake. Slowly read through your essay at least once before submitting it.
- Look for misspelled words, incorrect verb tenses, and punctuation or grammar mistakes. Does your writing flow well? Does everything make sense?
- Are all of your points clear? Have you used the same word or phrase repetitively? (If you have, try to substitute a synonym.) Did you use transitions connecting your ideas?
Ensure that you submit the best, most polished version of your essay possible. Mistakes and unclear sentences make a poor impression.
Advice From the Experts:
From Dr. Carrie Brown, professor of English and creative writing at Sweet Briar College and novelist :
When I’m working with students on expository writing — on writing in any rhetorical mode, really — I remind them that almost inevitably they have to stumble their way through some lousy sentences before they discover what they actually want to say. (This takes us back to that famous question: How do I know what I mean until I see what I say?) Some messy writing usually precedes orderly, elegant writing, and every writer needs patience during that messy process, because that process is important: out of that process emerges clear thinking, which is the true key to clear writing. Once writers have waded around in the muck for a while, then they can step back and examine those sentences or numbered phrases or bulleted points — whatever method felt most natural to the writer by which to set down emerging thoughts — to discover which are relevant, which are simply repetitions of earlier thoughts, which are superfluous or meaningless, and in what order they ought to proceed. A trick that seems to work for students with a strong tendency toward auditory learning can actually record themselves speaking aloud, trying to address the topic, and then play back that recording, meanwhile transposing ideas — and usually improving and clarifying them — as they go.
From Adam Cole, author and writing expert:
Know your audience – Whatever you are writing, you will get the best results if you are thinking about who is reading it, why they are reading it, and what you should do to make sure the interaction between you and the reader is optimal. While the audience for an expository piece may be obvious, writing directly to that audience is not so obvious. It affords you an opportunity to think clearly and write clearly without having to worry about your identity, ego or success. If you are in school, the audience for expository writing is your professor, and you should be fulfilling the boxes in their rubric to the letter. If they haven’t given you a rubric, ask for one. If they won’t, find one or create one based on conversations with them, their former students, or another professor.
From Tangela Walker-Craft – Simply Necessary, Inc. , Family and Parenting Blogger:
Write in complete sentences. Write in paragraph form. Each paragraph should contain 3 to 5 sentences for short essay questions, and 5 to 10 sentences for long essay questions. Vary sentence length and structure; try not to begin sentences with the same word or words. Use facts and information taken from reading passages to answer questions; refer back to the reading passage to stay focused. Underline important information in reading passages to make it easier to go back to them when answering questions. Proofread. Proofreading sentences backwards makes finding spelling mistakes and punctuation errors easier because it forces test-takers to focus on individual words instead of automatically “seeing” what he or she intended to write.
From Peter Donahue, a writing expert and teacher:
1. Write for clarity, not formality. As a teacher, I see a lot of expository writing where the writer is more concerned with following the conventions of academic jargon than she is with expressing ideas. A good example is the use of “utilize” instead of “use,” because it “sounds more formal,” or the avoidance of the pronoun “I” because it “sounds too informal.” So, rather than trying to appear formal, expository writing should aim to be clear. George Orwell’s 1946 essay, “Politics and the English Language,” says more on this topic, and is a worthwhile read. 2. Think synthetically, write analytically. Synthetic thinking starts with small details, or an open-ended question. As thoughts continue to develop, the main idea is clarified (or discovered) at the end the process. Contrariwise, Analytical thinking starts with a “given:” a major premise or generalization. It then proceeds to break down the main idea into its components and deal with each separately. Expository writing is usually presented most effectively in an analytic format — the main idea first, the support afterwards. On the other hand, literary writing, like a poem or discursive essay, is often presented synthetically. The key is knowing the difference between thought process and written format. We can think something synthetically, and then write it analytically. And in fact, this process can be the key to effective expository writing for many people. Don’t assume that because a thesis appears in the first paragraph, you have to think of it first. You could try drafting it synthetically, to clarify your thinking. Then rewrite it analytically to present it more effectively for your reader.
From Jessica Moody, curriculum expert :
Expository writing is first about structure, second about clarity, and third about content. Depending on the type of expository writing there is a specific structure expected. Even in college essays each sentence on the essay has a purpose and can be labeled as a thesis statement, topic sentence, evidence, or explanation of evidence. If the structure is not there, most of the time there is not much clarity and the content is lacking because it is confusing. This is the same for any type of expository writing. My suggestion for people becoming better at expository writing is to study the structure of the piece, the paragraph structures and the sentence structures. If you understand how to break down the structure then you can learn to replicate any style or form you want.
Final Touches: Expository Essay Writing
Writing an excellent expository essay isn’t as complicated as it seems. Simply follow the steps and include the essential pieces outlined here.
Your essay is sure to showcase both your thinking and writing skills —and earn you a high score!
Learn how we can help you with college and career guidance! Check out our YouTube channel!
Click Here to Schedule a Free Consult!

Calm your anxiety by learning every aspect of the college application process and how to excel at navigating it.

- Ethics & Honesty
- Privacy Policy
- Join Our Team
(732) 339-3835
Expository Essay
Complete Guide to Expository Essays: Writing Help and Topics
11 min read
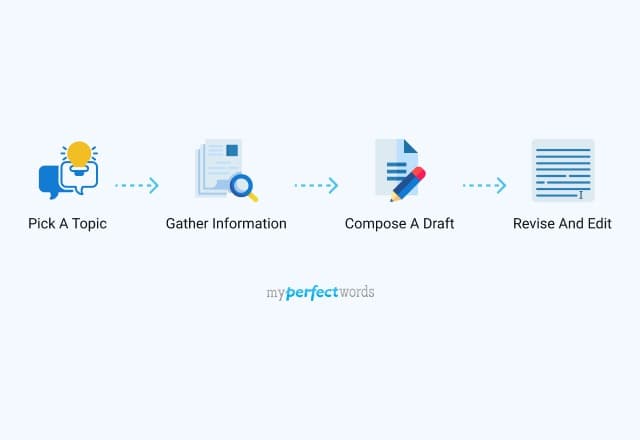
People also read
Interesting Expository Essay Topics For Your Next Paper
How to Write an Expository Essay Outline Like a Pro
Types of Expository Writing - Definition and Examples
Free Expository Essay Examples For Students
Ultimate Guide to Writing an Expository Essay About a Person
Learn to Write an Expository Essay About Yourself
Learn the Basics of Crafting an Expository Essay about a Book
Learn to Write Expository Essay About Mental Health - Examples & Tips
How to Write an Expository Essay about Bullying: A Guide
Expository Essay About Dogs: Steps, Examples & Topics
A Guide to Writing an Expository Essay about Education
Expository Essay About Friendship: A Writing Guide
Discover How to Write Expository Essays About Music – A Step-by-Step Guide
Writing essays can be a real challenge for many students. They often struggle to organize their thoughts and convey them clearly in expository essays.
This struggle leads to essays that lack clarity and fail to captivate the reader’s interest.
But worry not! This guide is your go-to helper. We're going to break down the ins and outs of expository writing using simple steps. Plus, we’ve included some tips and topic ideas, so you can craft essays that are both clear and engaging!
So, keep reading!
- 1. What is an Expository Essay?
- 2. Expository Essay Vs. Argumentative Essay
- 3. Types of Expository Essay
- 4. Structure of an Expository Essay
- 5. How to Write an Expository Essay?
- 6. Expository Essay Example
- 7. Tips for Writing a Good Expository Essay
- 8. Expository Essay Topics
What is an Expository Essay?
An expository essay is a type of essay that seeks to inform, describe, or explain a particular subject or topic.
It's distinct in its approach as it emphasizes presenting facts, analyzing information, and providing a comprehensive understanding without incorporating personal opinions or biases.
Why Write an Expository Essay?
The purpose of writing an expository essay extends beyond academic requirements.
This form of writing nurtures the ability to research deeply, logically organize thoughts, and articulate information coherently.
Developing these skills not only enhances academic performance but also prepares individuals for effectively communicating complex ideas in various real-world scenarios.
Expository Essay Vs. Argumentative Essay
Expository and argumentative essays vary in their purposes and approaches.
Expository essays aim to inform or describe a topic without personal opinions, using a neutral, informative tone.
On the other hand, argumentative essays seek to persuade by presenting a clear viewpoint and supporting it with evidence.
Expository essays follow a simpler structure, providing information, while argumentative essays involve complex structures, presenting and countering arguments. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right essay type for specific writing goals.
Types of Expository Essay
Before we dive into the different types of expository essays, let's check out five common ones:
Descriptive Essays
Descriptive essays aim to create a detailed image or sensory experience in the reader's mind by vividly describing a particular place, object, person, or event.
They use rich language and sensory details to paint a clear picture and evoke emotions, making the reader feel like they're experiencing what's being described.
Process Analysis Essays
In a process analysis essay , the writer breaks down a series of steps needed to achieve a specific task or goal.
They provide a clear, step-by-step guide, making complex tasks easy to understand. For example, they might explain how to bake a cake, fix a bicycle, or perform a scientific experiment.
Compare and Contrast Essays
Compare and contrast essays focus on exploring the similarities and differences between two or more subjects.
They present a balanced view, showing how things are alike and how they're different. Whether it's comparing different cultures, products, historical events, or ideas, these essays aim to offer insights into relationships and contrasts.
Cause and Effect Essays
Cause and effect essays delve into examining the causes that lead to specific effects or the effects that arise from certain causes.
They analyze the relationship between events, explaining why things happen and what outcomes result from those actions or occurrences. They aim to provide a clear understanding of the connections between different elements.
Problem and Solution Essays
Focused on a specific issue, problem and solution essays identify a problem, its causes, and effects, and propose solutions to address and resolve the problem.
They aim to offer practical, effective solutions to real-life issues, providing a roadmap for solving problems or improving situations.
Structure of an Expository Essay
An expository essay typically comprises three main parts: the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Here's what the general structure of an expository essay looks like:
Introduction
The introduction of an expository essay is where the writer presents the topic, provides background information, and ends with a clear thesis statement .
This section aims to grab the reader's attention and set the stage for the discussion that follows.
Body Paragraphs
The body of the essay contains a series of paragraphs that delve deeper into the topic.
Each paragraph should begin with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea or argument.
These paragraphs present evidence, examples, or explanations supporting the thesis statement. Smooth transitions between paragraphs ensure a coherent flow of information.
The conclusion of an expository essay restates the thesis statement using different wording. It summarizes the key points discussed in the body paragraphs.
Finally, it offers a sense of closure, wrapping up the essay's main ideas. It's not just a repetition of earlier information but rather a synthesis of the key points to leave a lasting impression on the reader.
How to Write an Expository Essay?
Writing an expository essay involves a step-by-step process to effectively communicate information. Here's a guide to crafting an expository essay:
Select a Topic
When selecting a topic for an expository essay, it's crucial to choose something that's not only interesting but also suitable for an informative discussion.
Consider the following pointers while choosing an expository essay topic:
- Select a topic that personally interests you.
- Choose a topic that can be explained within the essay's scope
- Choose subjects allowing for an objective, fact-based analysis.
- Consider prevalent issues or areas of curiosity for discussion.
Conduct Research
When researching for your expository essay, explore diverse and credible sources like books, scholarly articles, and reputable websites.
Ensure the information gathered directly relates to your topic and is from reliable sources. Verify the credibility by checking the author's credentials and publication dates.
Consider various perspectives to present a well-rounded view. Organize your findings systematically, keeping detailed notes for citation. This approach helps in crafting a well-informed and supported expository essay.
Create an Outline
Develop a structured outline for your essay. Organize your thoughts, decide on the main points, and arrange them logically.
Here's what the general structure of an expository essay looks like:
This outline template provides a clear structure, allowing for a well-organized and coherent expository essay.
View this in-depth guide on creating an expository essay outline for a structured essay!
Write The Introduction
The introduction of an expository essay plays a pivotal role in engaging the reader and setting the stage for the discussion. Here are the essential components:
- Engaging Hook : Begin your essay with a captivating fact, question, quote, or story related to the topic to captivate the reader's attention and encourage them to continue reading.
- Background Context: Offer essential background information about the topic, providing the necessary context for the reader to understand its relevance and importance.
- Clear Thesis Statement: End the introduction with a clear thesis statement. It should express the main idea or argument of your essay. This statement helps guide the reader, indicating the purpose and direction of your essay.
Compose Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs serve as the essay's core.
Each paragraph starts with a topic sentence introducing the main idea. Back up this idea with evidence or examples to support your point.
Make sure each paragraph smoothly connects to the next for a logical flow of ideas. This structured approach ensures a coherent and well-supported discussion throughout your expository essay.
Write the Conclusion
In the conclusion of your expository essay, recap the main points without introducing new information.
Restate the thesis in different words to reinforce the main argument. Additionally, offer closing thoughts or discuss the broader implications related to the topic. This section serves as a summary, emphasizing the significance of the essay's ideas and their broader relevance.
Revise and Edit
Revision and editing are crucial steps in the essay writing process.
Review the content for coherence and logical flow, ensure the essay structure is smooth and well-organized, and focus on clear, concise language.
Check for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors, verify citations, and seek feedback for improvements. Finally, perform a final proofread to ensure the essay is error-free and polished for submission.
Expository Essay Example
Below is an example illustrating the concept of climate change and its effects, exploring the causes, impacts, and potential solutions.
This essay serves as a basic example of how an expository essay on climate change might be structured, offering insights into its causes, effects, and potential solutions.
Need more examples? Check out these expertly crafted expository essay examples on multiple topics and themes!
Tips for Writing a Good Expository Essay
Here are some tips for writing a good expository essay:
- Ensure the essay has a clear and narrowly defined topic for effective exploration.
- Present facts, statistics, and evidence without incorporating personal opinions or biases.
- Utilize a well-structured format with logical sequencing of ideas and paragraphs.
- Provide detailed and comprehensive explanations to support each point or idea.
- Use diverse and relevant examples to illustrate and reinforce key points.
- Present information in a concise and easily understandable manner, avoiding unnecessary details.
- Use transitional words and phrases for seamless connections between paragraphs and ideas.
- Make sure that all information presented is relevant and sourced from credible, reputable materials.
Expository Essay Topics
Expository essay topics typically revolve around subjects that can be explained, clarified, or described without personal opinions.
They cover a wide array of areas such as science, technology, education, health, social issues, historical events, and more. These topics should allow for in-depth exploration and factual analysis.
Here are some essay topics for students:
Expository Essay Topics for High School Students
- The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers
- Benefits of Exercise and Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Exploring Climate Change: Causes and Effects
- The Importance of Education in Today's Society
- Understanding Cyberbullying and its Impact
- Analyzing a Historical Event: The Civil Rights Movement
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of E-Learning
- Explaining the Process of Photosynthesis
- The Effects of Video Games on Adolescents
- The Role of Leadership in Problem Solving
Expository Essay Topics for University Students
- The Future of Artificial Intelligence and its Ethical Implications
- Analyzing the Impact of Globalization on World Economies
- Climate Change: Policy Interventions and Global Strategies
- The Psychology Behind Procrastination and Ways to Overcome It
- Exploring Renewable Energy Sources and Their Viability
- The Evolution of Social Media and its Societal Impact
- Gender Disparities in the Workplace: Causes and Solutions
- The Effects of Stress on Mental Health in Modern Society
- Analyzing the Influence of Cultural Diversity in Global Business
- Understanding Quantum Mechanics: Principles and Applications
Can’t pick a topic? Have a look at these extensive expository essay topics and get more ideas!
With our steps, tips, and topics, you have all you need to get started on your expository essay.
If you're still encountering challenges in composing your expository essay, our custom essay writing service is here to help.
Our proficient writers specialize in creating well-structured, informative expository essays. With our expert support, you can be sure you’ll receive a top-quality, plagiarism-free essay.
Reach out to our expository essay writing service today to get the help you need. Place your order today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is an Expository Essay and How to Write It

You’ve been asked to write an expository essay on a particular topic. You know that an essay is generally a written composition that is usually limited in length and reflects the author’s perspective. However, the “expository” part is a little less clear. Keep reading, and you’ll get enough information to understand what an expository essay is and how to create an effective expository essay that meets the assignment requirements.
Table of Contents
What is an expository essay, what is the purpose of expository writing, when should you write an expository essay, 5 types of expository essays, how to structure an expository essay, how to write an expository essay, key takeaways, frequently asked questions about expository essays.
The expository essay is the appropriate type of essay to write if you need to inform your audience. If your intent is to critically compare, argue, or persuade, you will want to consider a different essay format. To explain it in more detail:
- An expository essay is a type of academic writing that aims to present a balanced and objective analysis of a specific topic.
- Expository essays often employ various techniques to enhance clarity and understanding. These techniques may include definition, comparison and contrast, cause and effect analysis, problem and solution exploration, or descriptive explanations. The writer should also ensure that the essay maintains a neutral and objective tone, avoiding personal biases or emotional language.
- In an expository essay, the writer typically starts with an introduction that presents the topic and provides an overview of what will be discussed in the essay. The body paragraphs then delve into the details, presenting evidence, examples, and relevant information to support the main points. Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect or subtopic, and the information should be organized logically and coherently.
- Expository essays are commonly assigned in academic settings as they encourage critical thinking, research skills, and the ability to present information in a clear and concise manner.
- The ability to write an expository essay is an essential skill for students and professionals. It promotes critical thinking, objectivity, and clear and concise communication.

The primary goal of expository writing is to explain or clarify a concept, process, or phenomenon using evidence, examples, and logical reasoning. Unlike persuasive or argumentative essays, the purpose of an expository essay is not to convince the reader of a particular viewpoint or opinion, but rather to provide clear and concise information.
The main objectives of expository writing are:
- Informing: Expository writing aims to educate and provide readers with new or valuable information. It seeks to convey facts, details, concepts, or ideas about a topic in a straightforward and concise manner.
- Explaining: Expository writing helps readers grasp complex subjects by breaking them down into simpler terms. It aims to clarify abstract concepts, processes, or phenomena, making them more accessible and understandable.
- Instructing: Expository writing provides step-by-step instructions or guidelines on how to perform a task, accomplish a goal, or understand a process. It offers a clear sequence of actions or explanations to ensure readers can follow and replicate the instructions.
- Presenting an analysis: Expository writing often involves analyzing and evaluating information, data, or evidence related to a particular subject. It may include comparing and contrasting different viewpoints, examining cause-and-effect relationships, or offering an objective evaluation of a situation.
Overall, the purpose of expository writing is to provide readers with accurate, unbiased, and well-organized information about a specific topic. It aims to enhance understanding, broaden knowledge, and facilitate learning by presenting information in a clear, coherent, and logical manner.
An expository essay is a good choice when the goal is to inform, explain, describe, or instruct. You may be assigned an expository essay as part of an in-class exam or coursework assignment. Here are some common situations in which writing an expository essay would be appropriate:
- Academic Assignments: Expository essays are frequently assigned in educational settings. Teachers often use this type of essay to assess students’ understanding of a particular subject or to teach them how to research and present information effectively. They are common in subjects such as English, history, science, social studies, or any discipline that requires a clear explanation or analysis of a topic.
- Instructional or How-to Writing: When you want to provide step-by-step instructions or guidance on how to perform a task, solve a problem, or achieve a specific outcome, an expository essay can be an appropriate format. This type of writing is commonly used in manuals, guidebooks, tutorials, or any instructional material.
- Journalism or News Writing: Expository writing is prevalent in journalism, where the goal is to inform readers about current events, news stories, or investigative reports. Journalists strive to present objective information, provide background details, and explain complex issues clearly to their audience.
- Professional or Technical Writing: In various professional fields, such as business, healthcare, engineering, or law, expository writing is utilized to convey information to colleagues, clients, or the general public. This includes writing reports, memos, manuals, research papers, or any form of communication that requires clear and factual presentation of information.

Expository essays can serve different purposes and present information in various ways. Here are five common types of expository essays:
- Descriptive essay: This type of expository essay focuses on describing a person, place, object, event, or any subject in detail. It aims to create a vivid and sensory-rich portrayal of the topic, using language that appeals to the reader’s senses and emotions.
- Process essay: Also known as a “how-to” essay, a process essay explains a sequence of steps or procedures to accomplish a task or achieve a particular outcome. It provides clear instructions and guidance, breaking down complex processes into manageable and easy-to-follow stages.
- Compare-and-contrast essay: This type of expository essay explores the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. It involves examining various aspects, characteristics, or elements of the subjects and highlighting their similarities, differences, or both.
- Cause-and-effect essay: A cause-and-effect essay explores the reasons (causes) behind an event, situation, or phenomenon, as well as the consequences (effects) that result from it. It aims to analyze and explain the relationship between causes and effects, demonstrating how one factor leads to another.
- Problem-and-solution essay: In this type of expository essay, a specific problem or issue is identified and analyzed, followed by the presentation of potential solutions or strategies to address it. The essay outlines the problem, examines its causes and effects, and proposes practical solutions or recommendations.
It’s important to note that these are not the only types of expository essays, and there can be variations or combinations of these types. Additionally, within each type, the specific approach and structure can vary depending on the requirements of the assignment or the writer’s purpose.
Structuring an expository essay involves organizing your thoughts, ideas, and information in a clear and logical manner. Here is a commonly used structure for an expository essay:
- Begin with an attention-grabbing hook to engage the reader.
- Provide some background information on the topic to set the context.
- Present a clear and concise thesis statement that states the main idea or purpose of the essay.
- Start each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main point of the paragraph.
- Support your topic sentence with evidence, facts, examples, or expert opinions that relate to the main point.
- Provide detailed explanations, analysis, or descriptions to clarify and develop your ideas.
- Use transitional words and phrases to ensure smooth flow and coherence between paragraphs and ideas.
- Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect or subtopic related to the main idea.
- Restate the thesis statement but rephrase it in a way that reinforces the main idea.
- Summarize the main points discussed in the body paragraphs.
- Avoid introducing new information or ideas in the conclusion.
- End with a closing statement that leaves a lasting impression.
Writing an expository essay involves a systematic approach to presenting information in a clear and objective manner. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to write an expository essay:
- Understand the purpose and requirements: Familiarize yourself with the purpose of the essay and any specific guidelines or requirements. Then, determine the topic or subject of your expository essay and gather relevant information and resources.
- Conduct research and gather information: Conduct thorough research on your topic to gather factual information, examples, evidence, or expert opinions.
- Plan and outline: Develop a clear and coherent outline that includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Decide on the main points or subtopics you will cover in each paragraph of your expository essay and arrange your ideas in a logical order that flows well.
- Write the introduction: Be sure to include a clear and concise thesis statement that states the main idea or purpose of your expository essay.
- Write the body paragraphs: Write one paragraph for each main idea, using transitions to ensure a smooth flow throughout.
- Write the conclusion: Restate your thesis statement and summarize the evidence.
- Revise and edit: Review your expository essay for clarity, coherence, and logical flow, and check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. Remember to always maintain an objective tone and focus on presenting information rather than expressing personal opinions.
As you can see, effective expository essays vary widely based on their topic and ultimate purpose. However, they have several important characteristics in common. When you’re writing an expository essay, keep the following tips in mind:
- Use clear, concise, and formal language, avoiding unnecessary jargon or complex terms.
- The thesis statement needs to be clear, concise, and appropriately focused.
- Provide sufficient evidence and examples to support your claims and make your writing more credible.
- Consider the logical flow of your ideas and make sure they are presented in a coherent manner.
- Use appropriate transitions to connect your sentences, paragraphs, and ideas.
- Remember that the specific structure of your expository essay may vary depending on the requirements of your assignment or the complexity of your topic. Adapt the structure as needed while ensuring that your essay is organized and focused on conveying information effectively.
You should consider writing an expository essay when you need to explain, inform, or describe a particular topic or subject to your readers. Expository essays are usually assigned in academic settings, but they can also be used in other contexts, such as writing articles or blog posts. For example, an expository essay would be appropriate for purposes such as explaining the benefits of a healthy lifestyle, describing the process of a scientific experiment, or discussing the impact of technology on society.
Expository essay: The main purpose of an expository essay is to explain, describe, or inform the reader about a particular topic or subject. It should be written in a neutral manner, focusing on presenting facts, explaining concepts, and offering a clear understanding of the topic. Argumentative essay: The primary purpose of an argumentative essay is to present a well-structured argument or position on a specific issue. The writer takes a clear stance on a topic and provides strong arguments, counterarguments, and evidence to support their position. The language used may be more passionate and persuasive to convince the reader.
The length of an expository essay can vary depending on the specific requirements or guidelines provided by your instructor or the purpose of your writing. Expository essays can range from a few hundred words for shorter essays to several thousand words for more in-depth or research-based essays. The number of body paragraphs typically range from three to five, but it can vary based on the complexity of the topic and the amount of information you need to convey.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 10-Point Manuscript Checklist to Ensure High-Quality Journal Submissions
- Confusing Elements of a Research Paper That Trip Up Most Academics
- How to Present Data and Statistics in Your Research Paper: Language Matters
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)
Organization vs. Organisation: Is there a Difference?
Paperpal now supports research paper pdfs: a game-changer for latex users, you may also like, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , how to make translating academic papers less challenging, self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how..., 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures.
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
UMGC Effective Writing Center How to Use Sources in an Expository Essay
Explore more of umgc.
- Writing Resources
Let's take a quick look at a sample essay that uses sources. Our goal is to examine the techniques used by the student author, Jane Doe, to integrate research into her expository essay done in APA style.
APA Level 1 Subheadings
First, note that in APA style, all major sections have a subtitle on top of them. In this five-paragraph essay, the main sections are single paragraphs, so that is where you will see the titles and subtitles. The first paragraph is the introduction paragraph, and you see the repetition of the main title from the title page on top of the intro paragraph—this is standard APA style.
Say Hello to the Intro
Next comes the introduction paragraph itself, which serves several functions.
- provides background context for the topic
- generates reader interest
- introduces the thesis, which should come at or near the end of the paragraph
Let read Jane’s thesis and examine how she led up to it.
Thesis: “The result is that prison overcrowding is a serious financial burden for Americans.”
So, this is the overall concept, the controlling idea that the essay will illustrate, corroborate and, hopefully, present a convincing case for. Let’s return to the beginning of the intro to see how she led up to this thesis. Her introduction begins: “Something needs to be done about prison overcrowding and the lack of rehabilitation programs.” This is Jane’s thought and opinion expressed in her own words.
Example of General Knowledge
Next sentence—“Without proper rehabilitation, prisoners become repeat offenders.” These are also Jane’s words. However, does this idea (the lack of rehabilitation causes repeat offenders) need a citation?
No, it does not. Anyone who has studied this issue, and Jane has, knows the terrible problem of repeat offenders because of the lack of rehabilitation in these human warehouses we’ve created. Jane’s statement is probably an example of General Knowledge , which is something Jane (and most adults in America) probably knew before even beginning the paper. The high rate of repeat offenders is a generally accepted and unfortunate fact.
Example of Common Knowledge
Next sentence: “This means we have to build new facilities just to keep up with the overcrowding.” Again, these are Jane’s words. But this idea is pretty specific and probably not something Jane knew before she began researching the topic. So, does the sentence need a citation?
No. And here’s why: Common Knowledge . Common knowledge is something known by everyone or nearly everyone in a specific field or academic discipline. It usually does not have to be cited because it’s not associated with a single author anymore. In other words, before writing her paper, Jane probably didn’t know that “we have to build new facilities just to keep up with the overcrowding.” But once she began reading about America’s prison system, it became clear that this is common knowledge among researchers and writers in this field. They all share this idea and do not cite it. The knowledge is common to them.
Let’s look at this example from history: You’re writing a paper on the assassination of Abraham Lincoln, and you wish to use the following fact in your research essay:
Abraham Lincoln was shot by John Wilkes Booth . Would you have to cite that? No, it is an example of general knowledge —something known by most everyone without having to do any research.
Next: Abraham Lincoln was shot by John Wilkes Booth in Ford’s Theatre. Would you have to cite that? No. Although you may not have known the name of the theatre before you began your research, as you read about the assassination you saw that “Ford’s Theatre” is an example of common knowledge —something that is known by virtually every historian in the field.
Last: Abraham Lincoln was shot by the actor John Wilkes Booth in Ford’s Theatre while watching the play “Our American Cousin.” Do any of those facts need citing? No. Booth’s profession (actor) and the name of the play are common knowledge . Perhaps you didn’t know that before you began researching, but as you read you saw these facts in virtually every source you consulted.
So, let’s return to Jane’s statement: “This means we have to build new facilities just to keep up with the overcrowding.” Is it general knowledge? No. Jane probably didn’t know it before she began researching. Is it common knowledge? Yes. As Jane did her research, she saw that this idea--the expanding need for new prison facilities--is a concept known and shared by experts in this field. Therefore, no citation is needed.
Back to Jane's Essay
Now this next sentence in her intro: “The current cost to our nation to incarcerate inmates is $75 billion per year, which is expected to quadruple in the next decade (Crawford, 2010).”
This is clearly statistical information associated with a single source, Crawford. It’s not common knowledge, and so must be cited. Notice that Jane chose NOT to quote from Crawford but to put the stats in her own sentence. This is a good choice because quotations should be used only when the original wording is important for some reason. It’s also easy to see a strong justification for the use of this source’s statistics: Jane’s subject is the financial burden of the prison system, so it was important for her to establish right away the numbers that support this notion of “financial burden.”
In her introduction, Jane used a single source in an effective way (summarized instead of quoted) for an important reason—to provide clarification of what she meant by “financial burden.” And this in-text citation (Crawford, 2010) refers to the full reference citation on the References page at the end of the paper.
Beefing Up the Body
Let’s turn now to Jane’s first body paragraph with the APA Level One subheading, Rehabilitation . Note that in this paragraph, Jane uses the classic formula for a body paragraph in an expository essay. That formula is:
- State the main point of the paragraph
- Explain/elaborate on the main point
- Support the main point
- Conclude the paragraph, typically with your own words.
If you put a sentence in a body paragraph, if must fulfill one of those four functions or you should consider whether it belongs or not.
Let’s read the paragraph’s stated main point: “First, prison overcrowding is a financial burden because prisoners are not getting enough rehabilitation to transition back to society.” So, the point is stated in Jane’s own words and becomes the point that the paragraph will have to develop and support to a convincing degree--“lack of rehabilitation.”
In the Explain/Elaborate sentence, Jane writes, “The responsibility of the Bureau of Prisons is to safely confine its prisoner population; however, another mission of the Bureau is to rehabilitate.” Since there is no citation, we assume that Jane found that the twin role of the Bureau of Prisons (confine and rehabilitate) is common knowledge among those who study this issue; in other words, it is stated repeatedly in the sources she consulted.
But then Jane does something smart. She chooses one of the experts who know about the dual role of the Bureau of Prisons to add the voice of authority to her paragraph: She summarizes the opinion of an expert named Pavis in her first support sentence. Jane writes in her own words: “We must provide inmates with skills that will aid them in their ability to readjust after being released” (Pavis, 2012). When we check on the reference page citation, we see that Pavis was writing for an academic journal.
What you see at this point in Jane’s paragraph is another common use of research— to support a point you have just stated in your own words . Doing so shows that what you assert is accepted by experts in this field, and therefore your assertion is given credibility.
Now let’s look at Jane’s next two sentences: “Most inmates come to jail with little or no education at all. Once released, these prisoners are right back where they started from.”
Again, due to her research and thinking on this topic, Jane has formed some specific opinions. These opinions belong to her and are expressed in her own words. But because this is an academic research essay, Jane also knows that she must add the voices of published authorities to support her assertions .
In this case, she chooses an article that Talbot published in 2008. Let’s read this quotation and see if there is justification for using the author’s exact words to take up space in Jane’s paper.
"Talbot (2008) states, 'Many will be drug abusers who received no treatment for their addiction while on the inside, sex offenders who got no counseling, and illiterate high school dropouts who took no classes and acquired no job skills.'"
That was well written by Talbot and paints a bleak picture of people who are doomed to repeat offensives due to the lack of basic help. One other thing to notice is how Jane set up the Talbot quote with her lead-in sentence: “Once released these prisoners are right back where they started from.” And then she lets Talbot tell us exactly who these prisoners are and why their relapse is likely.
The lack of rehabilitation—the subject of this paragraph—is driven home with Jane’s concluding sentence, which should be in her own words unless there is some compelling reason for it not to be: “The more prisoners that are rehabilitated, the quicker they can start to contribute to society once they are released.” After the dark picture she has painted, she provides the solution—the same one she opened with at the top of the paragraph—the need for more rehabilitation.
Quick Review
- Common Knowledge— these are facts and concepts already known by those who regularly write and research in a given area. You will be acquiring common knowledge as you research. As long as you are sure you have seen this information in the majority of sources you consulted, you do not need to cite it.
- Your Own Opinions— as a product of your reading and thinking about the topic, you will synthesize the material to form your own opinions, your own positions and beliefs. These are also yours and don’t need to be cited. However, it is a very, very good idea to add the voice of published experts to back up your opinions, especially in the form of quotations and paraphrases.
- Summarize or Quote? You can do only three things with a source: summarize information from it, paraphrase it in your own phrasing and sentences, or quote from it directly. Before choosing which option to use, be sure to have a good reason for your chosen action.
- Signal Phrase. Finally, it’s always a good idea to introduce any quote you use with a signal phrase. Quotes shouldn’t seem like they just dropped out of the sky and landed in your paper. You should introduce who is speaking and it should be clear how the quote relates to the sentence immediately before it.
Follow those four strategies and you’ll be well on your way to using research effectively in your essays.

How to Use Sources in an APA Research Paper or Essay
Follow along with the UMGC Effective Writing Center as we walk through how to use sources in an APA Research Paper.
Our helpful admissions advisors can help you choose an academic program to fit your career goals, estimate your transfer credits, and develop a plan for your education costs that fits your budget. If you’re a current UMGC student, please visit the Help Center .
Personal Information
Contact information, additional information.
By submitting this form, you acknowledge that you intend to sign this form electronically and that your electronic signature is the equivalent of a handwritten signature, with all the same legal and binding effect. You are giving your express written consent without obligation for UMGC to contact you regarding our educational programs and services using e-mail, phone, or text, including automated technology for calls and/or texts to the mobile number(s) provided. For more details, including how to opt out, read our privacy policy or contact an admissions advisor .
Please wait, your form is being submitted.
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It's worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline. A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Maintaining a formal voice while writing academic essays and papers is essential to sound objective. One of the main rules of academic or formal writing is to avoid first-person pronouns like "we," "you," and "I.". These words pull focus away from the topic and shift it to the speaker - the opposite of your goal.
An expository essay can resemble other types of academic essays, too, such as compare/contrast essays, definition essays, cause and effect essays, or process essays. In fact, many common academic essays can be classified as expository essays. When you write an expository essay, pretend you are a teacher. Your goal is to inform the reader, such ...
Writing an expository essay is one of the most important and valuable skills for you to master. According to the Purdue Online Writing Lab: The expository essay is a genre of essay that requires the student to investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, expound on the idea, and set forth an argument concerning that idea in a clear and concise manner.
The expository essay is a genre of essay that requires the student to investigate an idea, evaluate evidence, expound on the idea, and set forth an argument concerning that idea in a clear and concise manner. This can be accomplished through comparison and contrast, definition, example, the analysis of cause and effect, etc.
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Learning how to write a good expository essay is an academic writing skill that lays the foundation for the type of expository writing that's necessary for numerous professions.
An expository essay asks for a critical explanation of a specific idea, theory, or topic. Our expert tips can help you write a well-structured and informative piece.
Formatting an expository essay. The typical format for an expository essay in school is the traditional five-paragraph essay. This includes an introduction and a conclusion, with three paragraphs for the body of the paper. Most often, these three paragraphs are limited to one subtopic each. This is the basic essay format, but expository writing ...
1. Read Your Essay Prompt. Most expository essay prompts will ask you to do one of the following: Define and explain a concept or theory. Compare and contrast two ideas. Examine a problem and propose a solution. Describe a cause and effect relationship. Explain a step-by-step process.
You can write an expository essay using the following steps. 1. Define your thesis statement. Because an expository essay generally goes in-depth on a given subject, it's important that you specify your thesis statement from the get-go. State it in a clear and concise manner in the first paragraph of your essay.
An expository essay is a type of essay that involves explaining an idea or theme within a given subject or topic. We guide you through writing one with examples.
The term expository writing refers to any writing that's designed to explain something. We use the word expository to describe any passage of writing that's supposed to present information and help you understand it in an objective way. Some common examples of expository writing include academic essays, textbooks, instructional guides, and ...
Although you did this verbally, you were still fulfilling the elements of an expository essay by providing definition, details, explanations, and maybe even facts if you have a really good memory. This is the same process that you would use when you write an expository essay. You may actually be doing this all the time; for example, when you ...
If you're not careful, an expository essay can turn into a persuasive or argumentative essay. Focus on explaining the topic, rather than convincing people of something about it. Revise and Edit, Revise and Edit. Going over the essay once to edit and polish isn't really enough. If you're tight on time, such as when writing an essay for an ...
An expository essay is a type of academic or research essay. An expository essay exposes information. Overview of an expository essay. An expository essay is the traditional academic essay: you give information and analyze what it means. To write an effective expository essay, research needs to be conducted on the topic to find credible sources.
However, a plan will save you time in the long run. With all your quotes and evidence organized in one place, writing your essay is much faster and easier. 5. Writing. Once you have a completed plan, begin writing your essay. Remember to analyze each piece of evidence and clearly connect your points with transitions.
Here are some tips for writing a good expository essay: Ensure the essay has a clear and narrowly defined topic for effective exploration. Present facts, statistics, and evidence without incorporating personal opinions or biases. Utilize a well-structured format with logical sequencing of ideas and paragraphs.
An expository essay is an unbiased, factual piece of writing that provides an in-depth explanation of a topic or set of ideas. It aims to explain a topic from all angles and takes no decisive stance on it. Expository essays make no new arguments on a topic but rather explain preexisting information in a structured format.
Expository essay: The main purpose of an expository essay is to explain, describe, or inform the reader about a particular topic or subject. It should be written in a neutral manner, focusing on presenting facts, explaining concepts, and offering a clear understanding of the topic. Argumentative essay: The primary purpose of an argumentative ...
That formula is: State the main point of the paragraph. Explain/elaborate on the main point. Support the main point. Conclude the paragraph, typically with your own words. If you put a sentence in a body paragraph, if must fulfill one of those four functions or you should consider whether it belongs or not.