

I Have a Dream Speech
Martin luther king, jr., ask litcharts ai: the answer to your questions.
| 1 key example |
King's style in this speech is made up of sentences that are short, dramatic, and meant to resonate with large groups of people. One noticeable feature is King's use of repetition. Near the end of his speech, he begins multiple consecutive sentences with "I have a dream": "I have a dream that one day on the red hills of Georgia [...], I have a dream that one day, even in the state of Mississippi [...], I have a dream that one day my four little children [...]." This pattern gives momentum to the speech, especially when spoken aloud. Each new description of the dream builds upon the previous one, growing in a crescendo to the final conclusion.
While King primarily uses short, clipped sentences in the speech, he also varies the length of his sentences throughout:
I have a dream today that every valley shall be exalted, every hill and every mountain shall be made low, the rough places shall be made plain, and the crooked places shall be made straight and the glory of the Lord will be revealed and all flesh shall see it together. This is our hope. Cite this Quote
The first sentence of the paragraph is long and discursive, evocatively showing King's dream of peace through biblical imagery. But the next sentence is short and simple. This variance in length is pleasing to the ear. In addition, King demonstrates that he can use any number of beautiful images to describe his dream of equality but that, in the end, his hope is quite simple—so simple it can be described in a four-word sentence: "This is our hope." The length of the sentences suggests that, while King's dream is not complicated, the beauty of the goal is immense and worth the struggle.
Lastly, King's short sentences are filled with simple grammatical constructions in the first and second person. King speaks to the audience directly, using the word "you" regularly, and speaks of himself using "I." This makes King's speech feel honest and intimate, as if he is speaking directly to each member of the audience:
I am not unmindful that some of you come here out of excessive trials and tribulation. Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. Some of you have come from areas where your quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality. You have been the veterans of creative suffering. Cite this Quote
Here, King does not say, "Some people have come fresh from narrow jail cells"—he says, "Some of you," bringing the problem directly home to the listener. He places his personal familiarity with Black Americans' suffering at the forefront, building a bond between himself and his audience. King's style throughout the speech thus creates both rhetorical power and emotional intimacy, making his argument land more effectively with his audience.
Tips and ideas for teaching high school ELA
4 Ways to Analyze Rhetorical Devices in MLK’s “I Have a Dream”

Reverend Martin Luther King, Jr. is known for his powerful speeches – in particular, his “I Have a Dream” speech. Ripe for rhetorical devices analysis and inspired by seminal documents such as the Declaration of Independence and the US Constitution, this speech has become a staple in many ELA classrooms.
Observant teachers of American literature courses should note some similarities between King’s “I Have a Dream” speech and another famous speech on the rights of blacks – Frederick Douglass’ “What to the Slave is the Fourth July?”. It is certainly worth noting that the speeches, written almost 100 years apart, address many of the same issues.
With Martin Luther King day just around the corner, and Black History Month following soon after, many teachers are turning to this revered speech for analysis, particularly of MLK’s rhetorical devices. This is the approach I’ve taken in my own classroom in years past (although earlier in the year due to district curriculum maps).
Looking for some structure for your dive into King’s rhetorical devices? Search no further.
rhetorical devices
All good lessons and units begin with ensuring that students are familiar with the vocabulary and terminology (both general and domain-specific) that will be used. At its most basic level, a rhetorical device is “any language that helps an author or speaker achieve a particular purpose”. This purpose is usually persuasion since rhetoric is often referred to as the art of persuasion.
When you hear the words rhetorical devices , many of us automatically picture what I think of as the big three – ethos, pathos, and logos. During my lessons with my students, we start by reviewing the definitions of these terms and several examples of each. We then view several commercials and/or ads and determine which of the devices (also often called appeals) is being used AND how it impacts the commercial and/or ad.
A little deeper
Once your students have mastered the art of these three, then it’s time to move on to some other devices. Some of these devices will be familiar to your students as they are often taught as literary devices while others may be completely foreign. The devices you choose to cover will depend on the focus of your unit and your anchor text(s). Commonly taught devices include:
- alliteration
- anaphora – repetition of a word or expression at the beginning of successive clauses (“… we cannot dedicate – we cannot consecrate – we cannot hallow – this ground.” The Gettysburg Address)
- epistrophe – repetition of a word or expression at the end of successive clauses (“of the people, by the people, for the people” – The Gettsyburg Address)
- hyperbole – extravagant exaggeration
- synecdoche – a figure of speech by which a part is put for the whole ( creature for man )
Merriam-Webster has a list of the 31 most common rhetorical devices that can be found here.
rhetorical devices in MLK's "I have a dream" speech
Once students have a grasp of the different types of rhetorical devices, it’s time to apply that knowledge to King’s speech. First, have the students annotate for the different devices. Depending on your students’ level, you can assign them specific devices to look for or turn them loose and see what they find. I personally like to color-code all of my annotations. Here’s what my master copy looks like:

Devices and their frequency are easily seen with this method.
From here, students can begin to break down and analyze the devices. There are four ways to do this.
Rhetorical Devices Chart
The easiest way to collect and analyze the devices is a simple chart. Students can list the device in one column, the quote from the text in the second, and an explanation of the device’s effect in the third.

Rhetorical pyramid

The second way to analyze King’s use of devices is to create a rhetorical pyramid. For this activity, students simply draw a large triangle in the middle of their page and label each point with a different rhetorical device. I’ve used the tried and true ethos, pathos, and logos, but you can choose any three. Or, let the students choose and have them justify why they chose those three devices. From there, students provide examples of each of the devices. A rhetorical pyramid is especially helpful for visual students by helping them see connections between the devices.
Rhetorical Precis
A rhetorical precis is a type of writing that summarizes a text or speech. It includes not only the summary of the text or speech but also an analysis of its content and delivery. A rhetorical precis has four parts:
- 1st sentence – presents author’s name, title, and genre of work. Uses verbs such as “argue”, “claim”, or “assert”
- 2nd sentence – explains development and evidence of thesis. Done chronologically
- 3rd sentence – state author’s purpose and WHY the author composed the text
- 4th sentence – tell about intended audience
SOAPSTone/SPACE CAT Analysis
The final option is for students to complete a SOAPSTone analysis of the speech. SOAPSTone stands for
Examine the speech in light of these different areas.
An alternate to SOAPSTone would be SPACE CAT, which stands for:
So there you have it. Four ways to analyze “I Have a Dream” rhetorical devices. What’s your go-to rhetorical analysis strategy? Reply below.
Want to incorporate all these activities? Check out my “I Have a Dream” Rhetorical Devices Mini Flipbook.

Looking for more American lit teaching ideas? Check out 7 Units for a Complete American Literature Curriculum.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Copyright l Windows into Literature l All Rights Reserved
- Speech Writing
- Delivery Techniques
- PowerPoint & Visuals
- Speaker Habits
- Speaker Resources
- Speech Critiques
- Book Reviews
- Browse Articles
- ALL Articles
- Learn About Us
- About Six Minutes
- Meet Our Authors
- Write for Us
- Advertise With Us
Speech Analysis: I Have a Dream – Martin Luther King Jr.
“I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King Jr. is one of the most memorable speeches of all time.
It is worthy of lengthy study as we can all learn speechwriting skills from King’s historic masterpiece.
This article is the latest in a series of video speech critiques which help you analyze and learn from excellent speeches.
Speech Video: Martin Luther King Jr. delivers “I Have a Dream”
I encourage you to:
- Watch the video;
- Read the analysis in this speech critique;
- Study the speech text in the complete transcript; and
- Share your thoughts on this presentation.
Speech Critique – I Have a Dream – Martin Luther King Jr.
Much of the greatness of this speech is tied to its historical context, a topic which goes beyond the scope of this article.
Instead, I’ll focus on five key lessons in speechwriting that we can extract from Martin Luther King’s most famous speech.
- Emphasize phrases by repeating at the beginning of sentences
- Repeat key “theme” words throughout your speech
- Utilize appropriate quotations or allusions
- Use specific examples to “ground” your arguments
- Use metaphors to highlight contrasting concepts
Lesson #1: Emphasize Phrases by Repeating at the Beginning of Sentences
Anaphora (repeating words at the beginning of neighbouring clauses) is a commonly used rhetorical device. Repeating the words twice sets the pattern, and further repetitions emphasize the pattern and increase the rhetorical effect.
“ I have a dream ” is repeated in eight successive sentences, and is one of the most often cited examples of anaphora in modern rhetoric. But this is just one of eight occurrences of anaphora in this speech. By order of introduction, here are the key phrases:
- “One hundred years later…” [paragraph 3]
- “Now is the time…” [paragraph 6]
- “We must…” [paragraph 8]
- “We can never (cannot) be satisfied…” [paragraph 13]
- “Go back to…” [paragraph 14]
- “I Have a Dream…” [paragraphs 16 through 24]
- “With this faith, …” [paragraph 26]
- “Let freedom ring (from) …” [paragraphs 27 through 41]
Read those repeated phrases in sequence. Even in the absence of the remainder of the speech, these key phrases tell much of King’s story . Emphasis through repetition makes these phrases more memorable, and, by extension, make King’s story more memorable.
Lesson #2: Repeat Key “Theme” Words Throughout Your Speech
Repetition in forms like anaphora is quite obvious , but there are more subtle ways to use repetition as well. One way is to repeat key “theme” words throughout the body of your speech.
If you count the frequency of words used in King’s “I Have a Dream”, very interesting patterns emerge. The most commonly used noun is freedom , which is used twenty times in the speech. This makes sense, since freedom is one of the primary themes of the speech.
Other key themes? Consider these commonly repeated words:
- freedom (20 times)
- we (30 times), our (17 times), you (8 times)
- nation (10 times), america (5 times), american (4 times)
- justice (8 times) and injustice (3 times)
- dream (11 times)
“I Have a Dream” can be summarized in the view below, which associates the size of the word with its frequency.
Lesson #3: Utilize Appropriate Quotations or Allusions
Evoking historic and literary references is a powerful speechwriting technique which can be executed explicitly (a direct quotation) or implicitly (allusion).
You can improve the credibility of your arguments by referring to the (appropriate) words of credible speakers/writers in your speech. Consider the allusions used by Martin Luther King Jr.:
- “Five score years ago…” [paragraph 2] refers to Lincoln’s famous Gettysburg Address speech which began “ Four score and seven years ago… ” This allusion is particularly poignant given that King was speaking in front of the Lincoln Memorial.
- “ Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness ” [and the rest of paragraph 4] is a reference to the United States Declaration of Independence.
- “ It came as a joyous daybreak to end the long night of their captivity. ” [paragraph 2] alludes to Psalms 30:5 “ For his anger is but for a moment; his favor is for a lifetime. Weeping may linger for the night, but joy comes with the morning. “
- “ Let us not seek to satisfy our thirst for freedom by drinking from the cup of bitterness and hatred. ” [paragraph 8] evokes Jeremiah 2:13 “ for my people have committed two evils: they have forsaken me, the fountain of living water, and dug out cisterns for themselves, cracked cisterns that can hold no water. “
- More biblical allusions from King’s “I Have a Dream” speech can be found here .
Lesson #4: Use specific examples to “ground” your arguments
Your speech is greatly improved when you provide specific examples which illustrate your logical (and perhaps theoretical) arguments.
One way that Martin Luther King Jr. accomplishes this is to make numerous geographic references throughout the speech:
- Mississippi, New York [paragraph 13]
- Mississippi, Alabama, South Carolina, Georgia, Louisiana [14]
- Georgia [18]
- Mississippi [19]
- Alabama [22]
- New Hampshire [32], New York [33], Pennsylvania [34], Colorado [35], California [36], Georgia [37], Tennessee [38], Mississippi [39]
Note that Mississippi is mentioned on four separate occasions. This is not accidental; mentioning Mississippi would evoke some of the strongest emotions and images for his audience.
Additionally, King uses relatively generic geographic references to make his message more inclusive:
- “slums and ghettos of our northern cities” [paragraph 14]
- “the South” [25]
- “From every mountainside” [40]
- “from every village and every hamlet” [41]
Lesson #5: Use Metaphors to Highlight Contrasting Concepts
Metaphors allow you to associate your speech concepts with concrete images and emotions.
To highlight the contrast between two abstract concepts, consider associating them with contrasting concrete metaphors. For example, to contrast segregation with racial justice, King evokes the contrasting metaphors of dark and desolate valley (of segregation) and sunlit path (of racial justice.)
- “joyous daybreak to end the long night of their captivity” [paragraph 2]
- “the Negro lives on a lonely island of poverty in the midst of a vast ocean of material prosperity” [3]
- “rise from the dark and desolate valley of segregation to the sunlit path of racial justice” [6]
- “This sweltering summer of the Negro’s legitimate discontent will not pass until there is an invigorating autumn of freedom and equality.” [7]
- “sweltering with the heat of oppression, will be transformed into an oasis of freedom and justice.” [19]
How can you employ contrasting metaphors in your next speech?
Speech Transcript: I Have a Dream – Martin Luther King Jr.
Note: The formatting has been added by me, not by MLK, to highlight words or phrases which are analyzed above.
[1] I am happy to join with you today in what will go down in history as the greatest demonstration for freedom in the history of our nation.
[2] Five score years ago , a great American, in whose symbolic shadow we stand today, signed the Emancipation Proclamation. This momentous decree came as a great beacon light of hope to millions of Negro slaves who had been seared in the flames of withering injustice. It came as a joyous daybreak to end the long night of their captivity.
[3] But one hundred years later , the Negro still is not free. One hundred years later , the life of the Negro is still sadly crippled by the manacles of segregation and the chains of discrimination. One hundred years later , the Negro lives on a lonely island of poverty in the midst of a vast ocean of material prosperity. One hundred years later , the Negro is still languished in the corners of American society and finds himself an exile in his own land. And so we’ve come here today to dramatize a shameful condition.
[4] In a sense we’ve come to our nation’s capital to cash a check. When the architects of our republic wrote the magnificent words of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence, they were signing a promissory note to which every American was to fall heir. This note was a promise that all men, yes, black men as well as white men, would be guaranteed the “unalienable Rights” of “Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness.” It is obvious today that America has defaulted on this promissory note, insofar as her citizens of color are concerned. Instead of honoring this sacred obligation, America has given the Negro people a bad check, a check which has come back marked “insufficient funds.”
[5] But we refuse to believe that the bank of justice is bankrupt. We refuse to believe that there are insufficient funds in the great vaults of opportunity of this nation. And so, we’ve come to cash this check, a check that will give us upon demand the riches of freedom and the security of justice.
[6] We have also come to this hallowed spot to remind America of the fierce urgency of Now. This is no time to engage in the luxury of cooling off or to take the tranquilizing drug of gradualism. Now is the time to make real the promises of democracy. Now is the time to rise from the dark and desolate valley of segregation to the sunlit path of racial justice. Now is the time to lift our nation from the quicksands of racial injustice to the solid rock of brotherhood. Now is the time to make justice a reality for all of God’s children.
[7] It would be fatal for the nation to overlook the urgency of the moment. This sweltering summer of the Negro’s legitimate discontent will not pass until there is an invigorating autumn of freedom and equality. Nineteen sixty-three is not an end, but a beginning. And those who hope that the Negro needed to blow off steam and will now be content will have a rude awakening if the nation returns to business as usual. And there will be neither rest nor tranquility in America until the Negro is granted his citizenship rights. The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.
[8] But there is something that I must say to my people, who stand on the warm threshold which leads into the palace of justice: In the process of gaining our rightful place, we must not be guilty of wrongful deeds. Let us not seek to satisfy our thirst for freedom by drinking from the cup of bitterness and hatred. We must forever conduct our struggle on the high plane of dignity and discipline. We must not allow our creative protest to degenerate into physical violence. Again and again, we must rise to the majestic heights of meeting physical force with soul force.
[9] The marvelous new militancy which has engulfed the Negro community must not lead us to a distrust of all white people, for many of our white brothers, as evidenced by their presence here today, have come to realize that their destiny is tied up with our destiny. And they have come to realize that their freedom is inextricably bound to our freedom.
[10] We cannot walk alone.
[11] And as we walk, we must make the pledge that we shall always march ahead.
[12] We cannot turn back.
[13] There are those who are asking the devotees of civil rights, “When will you be satisfied?” We can never be satisfied as long as the Negro is the victim of the unspeakable horrors of police brutality. We can never be satisfied as long as our bodies, heavy with the fatigue of travel, cannot gain lodging in the motels of the highways and the hotels of the cities. We cannot be satisfied as long as the negro’s basic mobility is from a smaller ghetto to a larger one. We can never be satisfied as long as our children are stripped of their self-hood and robbed of their dignity by signs stating: “For Whites Only.” We cannot be satisfied as long as a Negro in Mississippi cannot vote and a Negro in New York believes he has nothing for which to vote. No, no, we are not satisfied, and we will not be satisfied until “justice rolls down like waters, and righteousness like a mighty stream.”
[14] I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations. Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. And some of you have come from areas where your quest — quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality. You have been the veterans of creative suffering. Continue to work with the faith that unearned suffering is redemptive. Go back to Mississippi, go back to Alabama, go back to South Carolina, go back to Georgia, go back to Louisiana, go back to the slums and ghettos of our northern cities, knowing that somehow this situation can and will be changed.
[15] Let us not wallow in the valley of despair, I say to you today, my friends.
[16] And so even though we face the difficulties of today and tomorrow, I still have a dream . It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream.
[17] I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: “We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.”
[18] I have a dream that one day on the red hills of Georgia, the sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave owners will be able to sit down together at the table of brotherhood.
[19] I have a dream that one day even the state of Mississippi, a state sweltering with the heat of injustice, sweltering with the heat of oppression, will be transformed into an oasis of freedom and justice.
[20] I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.
[21] I have a dream today!
[22] I have a dream that one day, down in Alabama, with its vicious racists, with its governor having his lips dripping with the words of “interposition” and “nullification” — one day right there in Alabama little black boys and black girls will be able to join hands with little white boys and white girls as sisters and brothers.
[23] I have a dream today!
[24] I have a dream that one day every valley shall be exalted, and every hill and mountain shall be made low, the rough places will be made plain, and the crooked places will be made straight; “and the glory of the Lord shall be revealed and all flesh shall see it together.”
[25] This is our hope, and this is the faith that I go back to the South with.
[26] With this faith , we will be able to hew out of the mountain of despair a stone of hope. With this faith , we will be able to transform the jangling discords of our nation into a beautiful symphony of brotherhood. With this faith , we will be able to work together, to pray together, to struggle together, to go to jail together, to stand up for freedom together, knowing that we will be free one day.
[27] And this will be the day — this will be the day when all of God’s children will be able to sing with new meaning:
[28] My country ’tis of thee, sweet land of liberty, of thee I sing. [29] Land where my fathers died, land of the Pilgrim’s pride, [30] From every mountainside, let freedom ring !
[31] And if America is to be a great nation, this must become true.
[32] And so let freedom ring from the prodigious hilltops of New Hampshire.
[33] Let freedom ring from the mighty mountains of New York.
[34] Let freedom ring from the heightening Alleghenies of Pennsylvania.
[35] Let freedom ring from the snow-capped Rockies of Colorado.
[36] Let freedom ring from the curvaceous slopes of California.
[37] But not only that. Let freedom ring from Stone Mountain of Georgia.
[38] Let freedom ring from Lookout Mountain of Tennessee.
[39] Let freedom ring from every hill and molehill of Mississippi.
[40] From every mountainside, let freedom ring .
[41] And when this happens, when we allow freedom ring, when we let it ring from every village and every hamlet, from every state and every city, we will be able to speed up that day when all of God’s children, black men and white men, Jews and Gentiles, Protestants and Catholics, will be able to join hands and sing in the words of the old Negro spiritual:
[42] Free at last! Free at last!
[43] Thank God Almighty, we are free at last!
Please share this...
This article is one of a series of speech critiques of inspiring speakers featured on Six Minutes . Subscribe to Six Minutes for free to receive future speech critiques.
Add a Comment Cancel reply
E-Mail (hidden)
Subscribe - It's Free!
| Follow Us |
Similar Articles You May Like...
- Speech Analysis: Franklin Roosevelt Pearl Harbor Address
- Speech Analysis: Winston Churchill’s “Iron Curtain”
- Speech Analysis: Gettysburg Address – Abraham Lincoln
- 5 Speechwriting Lessons from Obama’s Inaugural Speech
- Book Review – Lend Me Your Ears: Great Speeches in History (William Safire)
- I Have a Dream: 50th Anniversary
Find More Articles Tagged:
95 comments.
I realize that there are several good reasons that Mr. King had to stay rooted at the lectern with the microphones, yet even if he had a nice stage area with freedom to walk around and still be heard by his audience, I have a hard time imagining his speech being more powerful. It all comes down to the voice, and still more importantly, the content, rhetorical devices and structure.
When a new speaker in my club stays rooted at the podium, and the evaluator encourages him/her to move around as the number 1 critique, I sometimes would disagree. Sure most speeches are more lighthearted than “I have a dream”, and more movement is often called for, yet remaining rooted at the lectern can often give a very good impression of being calm, stable, and anchored. Especially if one is speaking as some form of authority as Mr. King obviously was, these are good qualities.
I just wonder if there has been an unfortunate shift in the way speeches are now perceived (in Toastmasters and everywhere else) that we’ve sometimes lost sight of the fact that at the end of the day, content and substance are the MOST important, and the most memorable elements of a speech. Not whether the speaker moved around or not, not what he or she was wearing, not what he or she did with his hands (and for the record Martin Luther King Jr. did have good usage of his hands in the speech). Those are all just gravy. These classics are a nice reminder of the fact though, so thanks for including it.
One of the greatest speeches of all time and a fantastic anaysis also. Many thanks indeed for the hard work that goes in to producing such valluable insights. Rgds Vince
This was an excellent article. Thank you for posting it here for us, for it really opened my understanding to some things I’d not really seen with the eye of an aspiring, hopeful, future speech writer and speaker, nor even (to my shame), a decent listener!
To explain, I am a new Toastmaster, or Toastmaster Wannabe, I should say, and I need all the tips and help I can get. Public speaking “paralyzes” me. So thanks not only for this particular lesson, but a great big thanks for the entire web site! I have already bookmarked it.
His contribution into equality of races in America that we witness now is tremendous.
And it’s not just my opinion. That’s what famous peers said on Martin Luther King: http://www.tributespaid.com/quotes-on/martin-luther-king
That was a really good video from one of the most hard working men of all time. Without him, I’m sure slavery would be still going on. And it’s sad how right when the freedom started, he was killed, and not able to see his dream. But I’m sure he’s watching from heaven in peace.
this analysis was very helpful and had lots of good note!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Excellent critique on the content of one of the best speeches of all time.
Maybe in a previous post you critiqued the Delivery of Dr. King’s famous speech. If not, it is something you might consider writing about.
He is a master at using all the Verbal Elements of Delivery: Pronunciation and Enunciation, projection, inflectional, cadence, and the pause.
Thanks! Fred
i found this speech very wonderfull and effective because of its words and expressions whiche were very persuasive also the manner whiche marten lother king had delivered the speesh was very amasing because it stems from heart
I have a dream comes up a lot and he wants to get the point through peoples mind and so he uses a lot of sentences because he doesn’t want to live like this or have his family and other families all across the world live the way he had to. what he is saying is I don’t want to put up with this anymore, and we people do not want to be judged by our colour, hair, or the way we look but by the way our personality is.
Metaphor: let the freedom ring. thank you
This was a great analysis. It showed not only what a great speaker Dr. King was but also the depth of his spiritual awareness. I believe that Dr. King was a great man. He along with other brave men and women, transformed American society from a fake democracy into one in which all people can participate and achieve. The miraculous aspect of his great work is that he transformed an openly racist culture into one of tolerance almost overnight and led a spiritual transformation of our nation. I once met Dr. King when I was a teenager. He led a protest/picket campaign against a supermarket chain, in a community where I lived that refused to hire black teenagers as “Bag boys” in its stores. I was one of those teenagers. I met him after a speech he presented at a local movie theater prior to the protest campaign. I got to talk to him one on one. I relive and retell this meeting and conversation in my book, “Talking Penny.” I’ll never forget the words he said to me.
This article is amazing, it really helped me understand King´s speech in a deeper way. Furthermore it is very good structred and short but easy to follow and to understand. Thank you for your help with that article!
Thanks for sharing this resource! I look forward to sharing it with my students.
THIS WAS GREAT HELP. Thank you so much.
i love you right now. biggest help ever on my rhetorical analysis essay for my writing class. biggest life saver. i owe you.
Thanks for your analysis of this powerful speech. I have my HS public speaking students analyze this speech, and you’ve added to what I can help them see.
Great article and website find. I’m subscribed now… How did I miss this before now?? Will promote this too.. Great blog!
It’s not about the words is it? It’s about the delivery/passion? How you deliver it – It’s not about the words?
hello andrew am s fascinated by this analysis infact am gonna peruse through like ten more times. besides am a speaking champion in uganda but still need more of these, am gonna contest for guild presidency this year march 2011 tchao!
Why does he repeat the word justice?
This page was EXTREMELY heplful! Thank you!
Questions: -Some examples of repetition in King’s speech were “we cannot be satisfied” and “now is the time.” This adds to the appeal of the speech because it makes it stronger and more powerful. These terms that King repeats are key words that have to do with ending racism. People remember these words and it wraps the entire speech into a couple of repetitive words. Other examples of repetition in this speech are “we must,” “go back,” and, “I have a dream.” That one repetition example was so important that it became the title of the speech. Something that I noticed about repetition is that it starts at the beginning of the sentence then continue with something different to stress the repeated term.
Wow! This Article really helped me understand this speech at a whole new level. Way to go Andrew!! Thanks so much for your help.
I once never thought that one day the speech will be suitable in my academic study, but it is so important, thank you!
I think martin’ repetition of “I have a dream” ‘s phrase is significant;by stressing on it he wants to assure the audience about his unbreakable optimism viewed as prophesy
Excellent critique. Would like to read similar critiques of his other speeches
The more memorable and more dynamic 2nd 10-minute part of the speech-which starts with the “I Have a Dream” theme-was impropmptu. It was not part of the written speech draft that Dr. King prepared and read on the podium. Essentially, Dr. King was constructing the 2nd part as he spoke.Dr. King achieved this rare feat because of the abundant collection of speech material he has assembled thru the years from prodigious reading and actual speeches delivered in other locations.
Continued…
Invariably, Dr. King was the most dynamic when he is unshackled from the written draft. While the 1st (prepared and written) part of the speech was good, the 2nd impromptu part was much better-more like electrifying.
Dr. King’s rare genius results from his rare ability to seamlessly merge his own eloquence with the eloquence of others (direct quotes, allusions or paraphrases)> The whole eventually appears as if written by him in one coherent whole.
There are those who propound that the more memorable 2nd part was inspired at a higher level. Some use the words “divinely inspired.” Whatever its genuine nature,it is amazing than a speaker could craft an impromptu portion that would be considered a oratorical masterpiece.
How did Dr. King come to deliver the 2nd 10-minute improptu part that starts with the “I Have A Dream” segment? A gospel singer, Mahalia Jackson, sitted at his right, blurted out: “Tell them about the dream, Dr. King.” Dr. King must have heard it, as he began to articulate his “dream.” The rest is history.
it is a very nice speech
great work andrew,i am taking a course in public speaking and i absolutely love your work. i look forward to be like you one day – an excellent public speaker..
This article was very interesting and very helpful in a paper I had to write for school. Thank you for posting this.
Martin luther king jr. uses repetition to get his point across. to stop the segregation between white and african americans. one way he uses repetition is when he says “let freedom ring” four times in a row to give african americans all the rights that a white man has. the most common use of repetition is when he says “i have a dream” to show what he thinks is right, and what should change wich can grab peoples attenion
Thank you for sharing this insightful, detailed, and illuminating analysis. I will be recommending your site to my speech students.
Thank you for this excellent analysis, Andrew. I saw it in the Ragan newsletter and referenced it in my blog. I especially like your focus on repetition in speaking, a subject I harp on quite a bit.
I find this man inspirational and am choosing to wirte about him for an english literature piece. This has really started me off and has really helped. Dr. Luther King was an amazing man and he changed the way that we look at the world. He changed the world and is arguably the worlds most significant person.
this work is absolutely amazing!
I found this feature very helpful with my current linguistics topic of study.
“I have a dream” that you would be my teacher, I understand the speech after looking at your website keep up the good work.
Thank you for sharing this amazing masterpiece. It is well clarified and well presented and organised. I agree that it is one of the high standard and posh speech. Thanks again
that was a very good speach and that martin luther king was still mostly famoum. martin was an insperation and that we should all have a dream that the nation will rise up to meet the standeds of america
thats a very good speach and my grandad would be proud of this website and of the creator
Why did King say “Five score years ago” when he could of said “One hundred years ago” and then later, why did he say “One hundred years later” instead of “Five score years ago”? I’m analyzing his language in this speech and I came across this, so it made me wonder… anyone care to answer?
Here five scores means 20 years ago..
I studied Rev. King’s I Have a Dream speech in a writing class; it is a speech, a piece of writing, that always moves me. The anaphora is so pronounced, so captivating, the listener cannot help but be swept away. I am always in tears by the time I reach the end, and I have read this speech many times. I hope every student is given the opportunity to study these words, to understand them, and to appreciate the sacrifices made since then.
This is an excellent analysis of Dr. King’s speech! I have learned a lot, and will use it as a reference for future speeches I make.
I enjoyed this analysis. I would love to this speech highlighted with different colors like the critique on Churchill’s “iron curtain.”
I thought all five lessons were important, and easy to understand. They broke each part of his speech down in a way I wouldn’t have thought to. However, I particularly liked and took an interest in lesson 1 and 2. The repetition was strategic and purposeful rather than like in high school we were always told to use synonyms and expand our vocabulary. It was making a point, and it is true, when I think of this speech “I have a dream” is the very first thing that comes to mind, and this was a strategy and exactly what he wanted when he wrote this! Excellent!
I have read MLK’S speech several times. It is always fresh and timeless.It is the master of all speeches. The above analysis helped me to appreciate the speech than ever before.
The visual representation and summary of the frequency of word usage in the speech is a great idea. It appears to be similar to concept maps, and would be useful for both writing and analyzing speeches. It could serve as an initial framework to clear up ideas and ensure that a speech is centered around the intended themes. The quotations used, especially those from the Bible, add extra power to the speech. At that time, more Americans were familiar with the contents of the Bible and would be motivated to action at the quotations and allurement to scriptural passages. Religion is a subject that is always taken very seriously and is something people are highly passionate about, so a well-used quotation or reference can do more to persuade people many techniques.
A very good analysis of this famous speech that not only gave good advice on speech writing in general, but also helped me understand the speech on a deeper level.
I thought this analysis was absolutely amazing. I found it very insightful and gave me a look into the details of the speech. I’ve learned about MLK and the “I have a Dream” speech but I’ve never learned this much about it. This gave me a different perspective of what it actually took him to write the speech. I particularly took interest in the theme of freedom, learning what Anaphora is and the impact on the pauses, pronunciation, projection, and of course, the repetition. This was a great analysis and I think many people can learn more about the speech with this critique.
The breakdown of the speech brought things to my attention that I had otherwise over looked. It is clear that much time and consideration was put into the construction of the speech. The metaphors used, added a power to the speech that showed the commitment and passion Dr. King felt. It is also clear that he knew what he was doing. The time he took to connect things together in the speech was evident. While reviewing the video, it seemed that he kept a strong and steady pace from the beginning until almost the end; then toward the end of the speech, when he really wanted to show emphasis, his voice and physical motions showed changed to show his feelings. Something else I viewed as powerful was Dr. King’s use of examples that the audience could relate to. The use of events that had taken place pulled in more audience support, and again showed his commitment and passion.
The best speech of all time. So motivating and important. I like this new look at it too. Helps me see it in a whole new light.
I think the analysis was amazing. I’ve learned about the “I Have a Dream” speech in just about every year of school, but I have never looked this deep into it. I have listened to the speech before, but would have never understood or picked up on anything like I did after reading this. The metaphors used the allusions, and very strong arguments all came together to make a perfect speech. No wonder this is nationally known, he is a genius. His strategy to go around points that were needed to be made was phenomenal. Apart from the speech, the analysis broke it down beyond perfect to show everyone what exactly was going through Dr. King’s head. Everyone can benefit from listening to this well constructed speech and speech analysis.
Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream Speech,” is one of the most memorable speeches of all time. This speech was one of the main reasons for the breaking of the color barrier. Dr. King is very passionate and emotional throughout his speech, which is seen through his vocal variety, the way he emphasizes certain words, and how overall powerful he is while giving this speech. Through the use of repeating specific phrases, “Now is the time, I have a dream, Let freedom ring,” his use of allusions, and the way he uses his metaphors, really make this speech so personal. By repeating the phrases, people throughout America see how passionate he is, and he gets his point across. His use of allusions when quoting Abraham Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address, and quoting multiple biblical verses, really adds a personalized effect to Dr. King’s audience. He is stating that one of America’s former presidents, who gave the Gettysburg Address, signed the Emancipation Proclamation, and when quoting the bible verses, saying that God created man equal. Finally with his use of metaphors, Dr. King uses the phrases of dark and desolate valleys to mean segregation. Its the little things that Dr. King did to make this speech so powerful and ultimately, destroy the color barrier for the United States.
I really enjoyed this analysis of MLK’s speech. It’s really interesting that he repeats things so many times. You always hear how you should come back to a point to get that certain point across, but I never thought about going back to the same point or saying the same thing numerous times. Reading all of the statements he repeated was a huge eye opener. I also never really thought about how he brought all of this other history into his speech like the geography of the states he decribed or the statements from other important documents. This was overall a very good analysis and I actually enjoyed reading about it.
This is an outstanding speech made at a very crucial time. I feel that one of the major points is that many speakers of this time were very focused on retaliatory a acts, and specific incidences for relations to people. Though there are a few geographical references in Dr. Martin Luther Kings speech, what set it apart to me is that he took a collection of many local problems, categorized them into regions, then into speaking about the state of the nation as a whole. By doing this he gives everyone a feeling of unity and purpose, followed by relating this now entire group of people to other major historical events that people can relate to. By referring to Lincoln, this was something that people had heard personal stories and first hand accounts about their own ancestors fighting for justice. Then relating the same group to the trials of the people and perseverance of biblical characters, which are very well known, helps give credibility, a sense of relation, and a foundation to build up and succeed just as others who faced towering obstacles had overcome them. By referencing these groups and making repetitive notations from their trials to those of the current situation makes this a great speech. It not only motivated the intended audience but became, in itself, the next story that future generations could refer to in times of trial.
I thought this analysis was great. In high school we barely talked about the “I Have A Dream Speech” and it was great to finally learn about it and go into detail about the organization of the speech. I never would have noticed some of his strategies without reading this analysis. I think anyone who is attempting to write a powerful speech would benefit from watching Dr. King’s speech and reading this analysis.
I always believed that in order to speech to count it has to change the way of the people and the way that ourselves think today. Martin Luther King’s speech did just that and it was a speech that made history and really saved our society and our nation from what could have been a terrible future up until today for America.He used the term “we” the most which for a speech like this is very important because he’s addressing what he wants all America to be like. Overall, one of the greatest speeches ever to take place in history.
The “I Have a Dream” speech has always been iconic, since the day it was first given and even now. The vividness of Martin Luther King JR.’s descriptions and the strong words he chooses to express his wishes communicate on a deep level with listeners and inspire the wish for change, just as they did then. All of this combined with strong his strong voices and unique delivery style leaves listeners aching to make a change, even years after his voice rang out across the reflecting pool at the Lincoln memorial.
The “I have a Dream Speech” has been a well known speech among people for several years. I have listened to the speech before but I never picked up on certain verbal accents and change in volume throughout the speech. In the speech he kept a very good pace,but would change his volume when he was trying to get his point across. I also paid attention to the words that he choose to use because he was very good at conveying his message and I felt that his word choices were a positive factor. I also noticed that he said “we” a lot which I also liked because he was not just referring to himself, but his entire audience. This speech is a great speech and is a great tool for someone who wants to conduct a speech.
I thought that the critique was very interesing. Everyone knows that the “I Have A Dream” speech is a very memorabe one indeed. We always listened to it at school, but we never really looked into the speech with great detail so the critique really taught me a lot. I learned from this critique that Dr. Msrtin Luther King Jr. used a lot of metaphors througout his speech, and I think that’s one of the reasons the speech was so strong, and his repetition at the beginning of his sentences really caught the attention of everone listening that day, and when people listen to it today.
Andrew– an amazing analysis!!
A very good analysis to help students understand the requirements for speech writing. Students did benefit from it. thank you
This is a great article. Breaks everything down on how great this speech was and how and why it was so great. Martin Luther King used repetition in the perfect way to get his message through. The beginning of the speech had consecutive repetition which actually grabbed the audience attention. This article was extremely helpful in understanding why this speech was so great.
Thanks a lot for this well-structured analysis of the speech. It is a speech that has touched me ever since I first encountered it as a teenager. Now being an English teacher (at a German high school) I finally get to teach young adults (like I once was) about it and your analysis is of great help to me!
This website with the critiques to the Martin Luther King speech was very useful i really enjoyed and liked it!
What a fabulous article you wrote! I will be letting my children read it.
Many many thanks for making this available to the general public.I intend to use this with my students, if I may, and shall report on their reaction.
I have read this speech over twenty times and this analysis has given me a different perspective. This analysis was inspirational and I felt as if I were reading it for the first time. was
The line “We can never be satisfied as long as the Negro is the victim of the unspeakable horrors of police brutality” is still so relevant in 2016.
I feel like this was a great speech. This man was a great man and did great things. I like when he started to talk about how every one should be free, it is true every one should have freedom no matter where your from or who you are. When he said i am free in the last word of his speech i thought that was very powerful, because that was a statement he wanted to be free so he was. I’m glad he was part of are history and that he did what he thought was right, because he has help the world out.
I agree with Andrew Dlugan, on what he believes to be the key factors or most important parts of the “I Have A Dream” speech. He gives different lessons on all parts of the speech, in which he breaks down the different aspects of them. Lesson #2 states the important themes, phrases and words Dr. King used throughout the speech. Andrew believes that this was very important part of the speech because it’s where Dr. King emphasized what he was saying by repeating them over and over indicating the importance of it.
I think that the most important thing in this speech is when he repeats the key “theme” words. That way the people know who/what you’re talking about and whom you’re talking about. Especially with a speech like this spoken among thousands of people.
What makes this speech a great speech is that there is a lot of dedication towards equality.
This speech is great because he wants freedom and justice for all, not just for African American people.
Lesson number four was a very unique importance reflecting the “I have a dream…” speech. I believe your perspective and the way you feel in this case is very important. Especially since MLK gave specific and clarity throughout his speech. Lesson number four is all about providing examples that could give you an logical illustration of what is being said and that is specifically what makes a great speech.
This is a great speech, I liked how he used repetitiveness. It really makes a point on what he’s trying to get through.
This article is a great analysis to the speech. Martin Luther King’s speech is powerful and strongly impacting to whoever has heard or listened to it. In line 41 to me was very powerful that shows that when it would happen we would all be equal that we always were but it would finally be accepted by more. Martin Luther King is an amazing speaker and his voice was powerful and used his voice to speak what he wanted to prove.
This was a wonderful analysis to this speech. Martin Luther king’s was very powerful especially how he spoke it with ,importance and a powerful impact. My favorite line was line (7) Nineteen sixty three is not an end but a beginning. My personal preference on what it means is it is the beginning to start all over with everyone being able to be treated the same and not be judged by the color of their skin. This was a wonderful speech.
What makes “I have a dream” speech great is the fact that Martin Luther King Jr. used his voice to fight against racial segregation and discrimination. “I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.” is my favorite quote from the speech. I believe this quote is so powerful because in this world, there are a lot of judgement on people’s appearances and having Martin Luther King Jr. lecture people on that, I believed it opened a lot of minds.
Mahalo for sharing this lesson … It’s perfect for breaking down King’s message and increasing awareness of figures of speech for students to learn to use in their own writing.
An excellent analysis. I have a question, Why did Martin Luther King use Alabama, Georgia, and Missisipi in his speech? Please enlighten me.
To show emphasis in the deep South,
Iam so impressed. I like the step by step approach with examples.I wish to to learn as an M.ed English student. Also,I wish to start public speaking club with students I teach and my church.I will like you to support me.
Thank you for this article.
There is a good reason why speeches like this are often presented as good examples; something to feel inspired from. It is so full of wonderful elements, like the repeated phrases for instances, which make a huge impact on the overall speech. Public speaking courses can benefit a lot from showing such an example.
” Now is the time…” is actually a form of parallel structure, not repetition.
Actually it is anaphora, and what comes after “Now is the time …” is the parallel structure. I hope it helped you.
Thank you for your inspiring analysis of this historic speech!
This was such a great eye opener to the various mistakes I have been making in most of the speeches I have been giving! Kudos!!!
Thank you so much for this very helpful analysis of language of Luther’s speech. I was preparaing my lesson and ı found this! I ve found lots of useful info for my students. Thank you so much 🙂
The speech analysis of Martin Luther King Jr’s famous ” I Have A Dream Speech”inspired me to teach a fabulous lesson to high school speech-language therapy students of multi-ethnic backgrounds.
Recent Tweets
RT @craigstacey1: GREAT place to watch Dr. King’s speech & apply his lessons to make an impact http://t.co/Rnb9tTRzkY @6minutes #DreamDay — @TuckExecEd Aug 28th, 2013
What a great analysis: I Have a Dream – Martin Luther King Jr. http://t.co/8eY24TNwoe via @6minutes — @marietaillard Aug 28th, 2013
Grade 12s: check out the insightful analysis of the famous “I Have a Dream” speech. It will help your Sales Pitch. http://t.co/Ad2atgo0Jd — @sean_donaghey Oct 18th, 2013
#Speech critics: Why study other speakers? Here a speech analysis about “I have a dream” – Martin Luther King http://t.co/9SP47tJSYd #learn — TheRedCarpetAcademy (@TheRCAcademy) May 6th, 2015
A rhetorical analysis of “I Have a Dream” speech https://t.co/BCVt8m3RgX — @Ms_Krueger_HHS Jan 18th, 2016
Spend some time today with the Martin Luther King, Jr. “I Have a Dream” speech: https://t.co/j1koUpMS7C https://t.co/E05Kl0rMLd — @ValpoLife Jan 18th, 2016
Speech Analysis: I Have a Dream – Martin Luther King Jr. https://t.co/6e37ukhLHs by @6minutes @DrCoffae #eng225 #functionalredundancy — @JoyCamachoMSM Sep 15th, 2016
Speech Analysis: I Have a Dream – Martin Luther King Jr. https://t.co/PEkZMxQdD7 by @6minutes — @JackwoodwardJ Jul 2nd, 2017
Here’s an insightful analysis that I share with my university #ESL classes. It’s definitely worth reading.… https://t.co/bCKCv04513 — Eric H. Roth (@compellingtalks) Jan 20th, 2019
Speech Analysis: I Have a Dream – Martin Luther King Jr. by Andrew Dlugan read it here… https://t.co/hPTqWX1kQM — Sandra Zimmer (@sandrazimmer) Jan 21st, 2019
27 Blog Links
Speech Analysis: I Have a Dream - Martin Luther King Jr. MLK « Gilbert Toastmasters — Jan 19th, 2009
Analysis of MLK’s I Have a Dream Speech - Speaking Freely — Jan 19th, 2009
Jkwadraat weblog » Blog Archive » Leren van Martin Luther King - I have a dream! Speech Analysis — Jan 20th, 2009
Analyzing a Speech: “I have a dream.” « Talk for Change Toastmasters — Jan 24th, 2010
Starting 2011 with a brand new meeting — Jan 17th, 2011
MLK Jr & the the power of speech « KCOBY — Jan 17th, 2011
Speeches that Changed the World — Jan 28th, 2011
McKinnon Language Solutions » Blog Archive » Speech Analysis – I have a Dream – Dr Martin Luther King — Jan 29th, 2011
March 8th + 10th « Ms Kleen's English course's weblog — Mar 8th, 2011
danielstillman.com - What I learned about Sketchnotes — Apr 8th, 2011
Production Assignment 17 « Sanfordb1's Blog — Jan 8th, 2012
Speech as Case Study: Martin Luther King, Jr. « RCM 401: Oral Rhetoric — Jan 16th, 2012
Break it down | simpson speaks — Feb 7th, 2012
“I Have a Dream” Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. (1929-1968) « DARISOANJ — Feb 7th, 2012
Presentation Lessons from Kevin Hart « Alex Rister — Feb 8th, 2012
Corpus Study [Antconc] « Language and Personality of Facebook Users — Apr 30th, 2012
Concordance Exercise « Language and Personality: A Case Study of 5 Respondents based on 'The Big 5 Personality Domain' — May 9th, 2012
Concordance Exercise | SKBP 1023_Lisa Noorazmi — May 11th, 2012
Concordance exercise « Language and Personality: Based on 'The Big 5 Personality Domain' — May 23rd, 2012
Corcodance Exercise « Language and Personality: A Case Study of 5 Respondents based on 'The Big 5 Personality Domain' — May 27th, 2012
AntConc – Concordance | 'Aisyah Zaili A137793 — May 29th, 2012
Martin Luther King’s inspirational speech- I Have A Dream « Language and Personality of Facebook Users — May 29th, 2012
“I HAVE A DREAM” |GROUP WORK|CONCORDANCE|ANTCONC « Language and Personality of Facebook Users — May 30th, 2012
ENGLISH RESOURCES - MLK SPEECH – RHETORIC — Oct 30th, 2012
Martin Luther King Jr I Have A Dream Speech | Public Speaking Singapore — Feb 24th, 2013
Links of the Week: 2013.10 | Creating Communication — Apr 28th, 2013
English for Social Interaction - “Being economical with the truth” — May 16th, 2013
| [ ] | [ ] | [ ] |
| [ ] | [ ] | [ ] |
| [ ] | [ ] | [ ] |
| Follow Six Minutes |
Six Minutes Copyright © 2007-2022 All Rights Reserved.
Read our permissions policy , privacy policy , or disclosure policy .
Comments? Questions? Contact us .
I Have a Dream Speech Rhetorical Analysis
I have a dream speech rhetorical analysis lyrics.
How to Format Lyrics:
- Type out all lyrics, even repeating song parts like the chorus
- Lyrics should be broken down into individual lines
- Use section headers above different song parts like [Verse], [Chorus], etc.
- Use italics ( <i>lyric</i> ) and bold ( <b>lyric</b> ) to distinguish between different vocalists in the same song part
- If you don’t understand a lyric, use [?]
To learn more, check out our transcription guide or visit our transcribers forum

Find answers to frequently asked questions about the song and explore its deeper meaning
Genius is the world’s biggest collection of song lyrics and musical knowledge

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
- My Storyboards
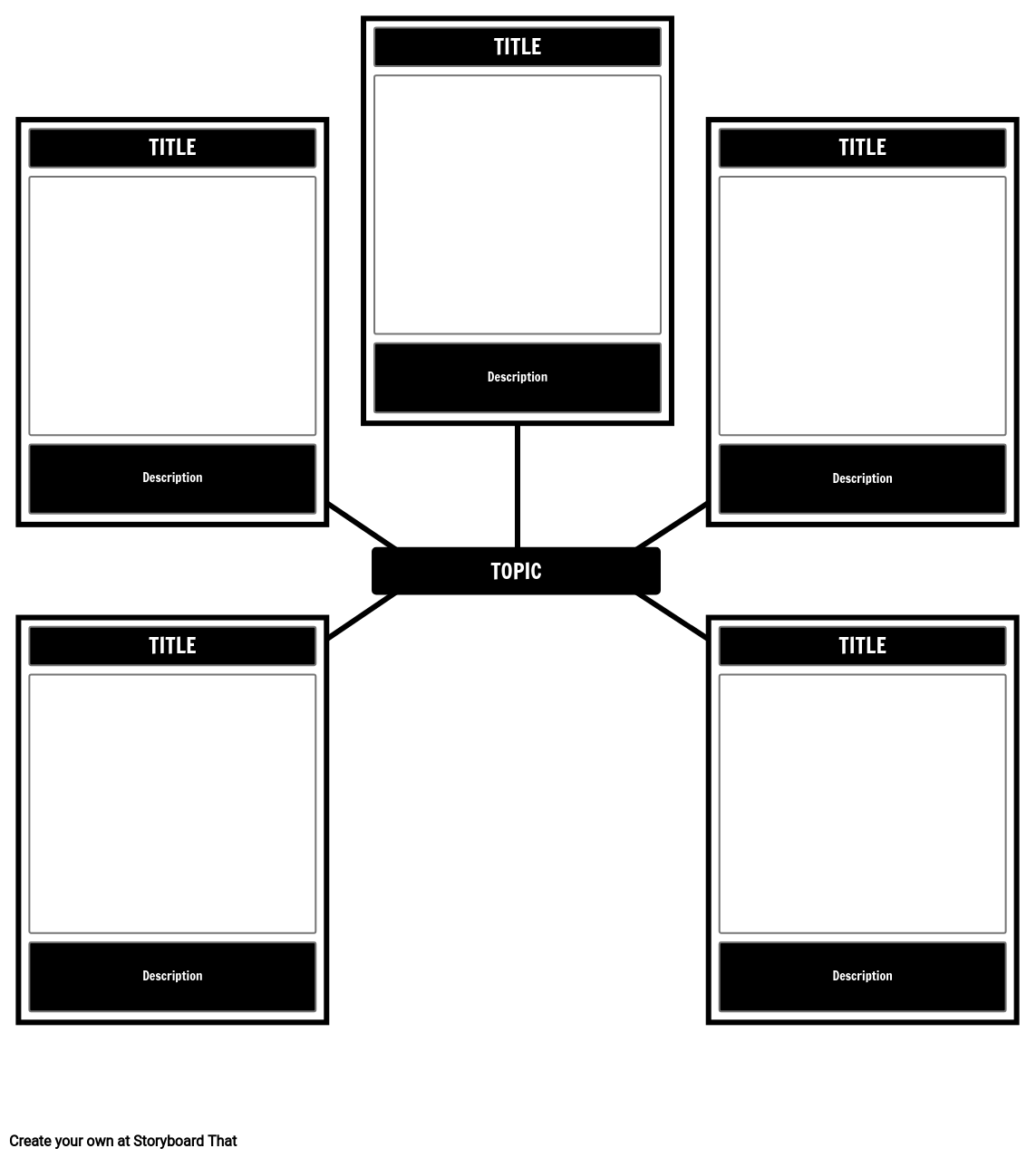
Rhetorical Devices in I Have a Dream
In this activity, activity overview, template and class instructions, more storyboard that activities.
- This Activity is Part of Many Teacher Guides

When teaching speeches and letters, it’s helpful to refresh or introduce students to rhetorical devices that enhance rhetorical strategies. After reading “I Have A Dream”, ask your students to do a scavenger hunt using the Storyboard Creator. Give them the following five rhetorical devices and have them create a storyboard that depicts and explains the use of each device in the speech: repetition, analogy, parallelism, restatement, and antithesis.
(These instructions are completely customizable. After clicking "Copy Activity", update the instructions on the Edit Tab of the assignment.)
Student Instructions
- Click "Start Assignment".
- Write the rhetorical devices in each heading: Antithesis, Repetition, Analogy, Parallelism, and Restatement.
- Find an example of each device in "I Have a Dream", and write the quote in the description boxes.
- Add appropriate scenes, characters, and items to each.
- Save and Exit
Lesson Plan Reference
Grade Level 9-12
Difficulty Level 2 (Reinforcing / Developing)
Type of Assignment Individual
Type of Activity: Spider Maps
How to Incorporate 'I Have a Dream' into the Curriculum for Teaching Rhetorical Devices
Introducing 'i have a dream' and rhetorical devices.
Begin the lesson by setting the historical context of Martin Luther King Jr.’s "I Have a Dream" speech. Discuss its significance in the Civil Rights Movement to provide students with a background understanding. Then, introduce the concept of rhetorical devices. Explain simple devices such as metaphors, similes, repetition, and anaphora, using clear examples from everyday language. This initial step lays the groundwork for deeper analysis and helps students to start identifying these devices in the speech.
Analyzing the Speech for Rhetorical Devices
Guide the students through a reading of select portions of "I Have a Dream". Encourage them to annotate instances of rhetorical devices as they read. This can be done in groups or individually, depending on the class size and student preferences. After the annotation exercise, facilitate a group discussion. In this discussion, have students share the devices they identified and talk about how these devices enhance the impact of the speech. This step not only reinforces their understanding of rhetorical devices but also fosters critical thinking and discussion skills.
Creating Storyboards to Visualize Rhetorical Devices
Introduce the Storyboard Creator tool, or any similar digital tool available, and explain how it can be used to visually represent rhetorical devices. Assign different sections of "I Have a Dream" to groups or individual students for a detailed rhetorical analysis. The task is to create storyboards that illustrate the rhetorical devices they find in their assigned sections. Encourage students to be creative in their depictions, using symbols, colors, and images to convey the meaning and effect of the rhetorical devices.
Presenting and Reflecting on the Findings
Conclude the lesson with presentations. Each group or student presents their storyboard to the class, explaining the rhetorical devices they illustrated. This not only helps reinforce their understanding but also allows for peer learning. Follow up with a reflective writing exercise. Ask students to write about how their understanding of "I Have a Dream" has changed through learning about these rhetorical devices and the impact these devices have on the power of the speech.
Frequently Asked Questions about Rhetorical Devices in I Have a Dream
What are the main rhetorical devices used in "i have a dream".
Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech masterfully employs several rhetorical devices. The main devices include anaphora, evident in the repeated use of the phrase “I have a dream”; metaphor, such as referring to justice as a "bank of justice"; and alliteration, as seen in phrases like “life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness”. The speech also utilizes pathos to evoke emotional responses and ethos to establish King’s credibility.
How does the use of rhetorical devices impact the overall message of the speech?
The impact of these rhetorical devices on the overall message of the speech is profound. They enhance its emotional appeal, making it more persuasive and memorable. The repetitive nature of anaphora, for instance, creates a rhythmic pattern that reinforces the speech's call for equality and freedom. Metaphors and alliterative phrases make complex concepts more relatable and impactful. By appealing to emotions (pathos) and establishing his moral authority (ethos), King effectively connects with his audience, both intellectually and emotionally.
Can the rhetorical strategies in "I Have a Dream" be considered effective in terms of persuasive speech?
In terms of persuasive speech, the rhetorical strategies in "I Have a Dream" are exceptionally effective. They demonstrate King’s oratorical skill in weaving together various techniques to create a speech that is not only persuasive but also inspiring. The use of repetition, powerful imagery, and emotional appeal makes the speech resonate with a wide audience, transcending time and remaining relevant decades later.
How do the rhetorical devices in "I Have a Dream" compare to those used in other famous speeches?
When compared to other famous speeches, the rhetorical devices in "I Have a Dream" stand out for their harmonious integration and the balance between emotional appeal and logical argumentation. While other great speeches also use similar devices, King’s speech is unique in its poetic cadence and its profound impact on the Civil Rights Movement. It’s a testament to King’s ability to use language not just to persuade, but to inspire and mobilize, a quality that many great speeches aspire to achieve.
I Have a Dream

Try 1 Month For
30 Day Money Back Guarantee New Customers Only Full Price After Introductory Offer
Learn more about our Department, School, and District packages

- Thousands of images
- Custom layouts, scenes, characters
- And so much more!!
Create a Storyboard


A Summary and Analysis of Martin Luther King’s ‘I Have a Dream’ Speech
By Dr Oliver Tearle (Loughborough University)
‘I Have a Dream’ is one of the greatest speeches in American history. Delivered by Martin Luther King, Jr. (1929-68) in Washington D.C. in 1963, the speech is a powerful rallying cry for racial equality and for a fairer and equal world in which African Americans will be as free as white Americans.
If you’ve ever stayed up till the small hours working on a presentation you’re due to give the next day, tearing your hair out as you try to find the right words, you can take solace in the fact that as great an orator as Martin Luther King did the same with one of the most memorable speeches ever delivered.
He reportedly stayed up until 4am the night before he was due to give his ‘I Have a Dream’, writing it out in longhand. You can read the speech in full here .
‘I Have a Dream’: background
The occasion for King’s speech was the march on Washington , which saw some 210,000 African American men, women, and children gather at the Washington Monument in August 1963, before marching to the Lincoln Memorial.
They were marching for several reasons, including jobs (many of them were out of work), but the main reason was freedom: King and many other Civil Rights leaders sought to remove segregation of black and white Americans and to ensure black Americans were treated the same as white Americans.
1963 was the centenary of the Emancipation Proclamation , in which then US President Abraham Lincoln (1809-65) had freed the African slaves in the United States in 1863. But a century on from the abolition of slavery, King points out, black Americans still are not free in many respects.
‘I Have a Dream’: summary
King begins his speech by reminding his audience that it’s a century, or ‘five score years’, since that ‘great American’ Abraham Lincoln signed the Emancipation Proclamation. This ensured the freedom of the African slaves, but Black Americans are still not free, King points out, because of racial segregation and discrimination.
America is a wealthy country, and yet many Black Americans live in poverty. It is as if the Black American is an exile in his own land. King likens the gathering in Washington to cashing a cheque: in other words, claiming money that is due to be paid.
Next, King praises the ‘magnificent words’ of the US Constitution and the Declaration of Independence . King compares these documents to a promissory note, because they contain the promise that all men, including Black men, will be guaranteed what the Declaration of Independence calls ‘inalienable rights’: namely, ‘life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness’.
King asserts that America in the 1960s has ‘defaulted’ on this promissory note: in other words, it has refused to pay up. King calls it a ‘sacred obligation’, but America as a nation is like someone who has written someone else a cheque that has bounced and the money owed remains to be paid. But it is not because the money isn’t there: America, being a land of opportunity, has enough ‘funds’ to ensure everyone is prosperous enough.
King urges America to rise out of the ‘valley’ of segregation to the ‘sunlit path of racial justice’. He uses the word ‘brotherhood’ to refer to all Americans, since all men and women are God’s children. He also repeatedly emphasises the urgency of the moment. This is not some brief moment of anger but a necessary new start for America. However, King cautions his audience not to give way to bitterness and hatred, but to fight for justice in the right manner, with dignity and discipline.
Physical violence and militancy are to be avoided. King recognises that many white Americans who are also poor and marginalised feel a kinship with the Civil Rights movement, so all Americans should join together in the cause. Police brutality against Black Americans must be eradicated, as must racial discrimination in hotels and restaurants. States which forbid Black Americans from voting must change their laws.
Martin Luther King then comes to the most famous part of his speech, in which he uses the phrase ‘I have a dream’ to begin successive sentences (a rhetorical device known as anaphora ). King outlines the form that his dream, or ambition or wish for a better America, takes.
His dream, he tells his audience, is ‘deeply rooted’ in the American Dream: that notion that anybody, regardless of their background, can become prosperous and successful in the United States. King once again reminds his listeners of the opening words of the Declaration of Independence: ‘We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.’
In his dream of a better future, King sees the descendants of former Black slaves and the descendants of former slave owners united, sitting and eating together. He has a dream that one day his children will live in a country where they are judged not by the colour of their skin but by the content of their character.
Even in Mississippi and Alabama, states which are riven by racial injustice and hatred, people of all races will live together in harmony. King then broadens his dream out into ‘our hope’: a collective aspiration and endeavour. King then quotes the patriotic American song ‘ My Country, ’Tis of Thee ’, which describes America as a ‘sweet land of liberty’.
King uses anaphora again, repeating the phrase ‘let freedom ring’ several times in succession to suggest how jubilant America will be on the day that such freedoms are ensured. And when this happens, Americans will be able to join together and be closer to the day when they can sing a traditional African-American hymn : ‘Free at last. Free at last. Thank God almighty, we are free at last.’
‘I Have a Dream’: analysis
Although Martin Luther King’s speech has become known by the repeated four-word phrase ‘I Have a Dream’, which emphasises the personal nature of his vision, his speech is actually about a collective dream for a better and more equal America which is not only shared by many Black Americans but by anyone who identifies with their fight against racial injustice, segregation, and discrimination.
Nevertheless, in working from ‘I have a dream’ to a different four-word phrase, ‘this is our hope’. The shift is natural and yet it is a rhetorical masterstroke, since the vision of a better nation which King has set out as a very personal, sincere dream is thus telescoped into a universal and collective struggle for freedom.
What’s more, in moving from ‘dream’ to a different noun, ‘hope’, King suggests that what might be dismissed as an idealistic ambition is actually something that is both possible and achievable. No sooner has the dream gathered momentum than it becomes a more concrete ‘hope’.
In his ‘I Have a Dream’ speech, King was doing more than alluding to Abraham Lincoln’s signing of the Emancipation Proclamation one hundred years earlier. The opening words to his speech, ‘Five score years ago’, allude to a specific speech Lincoln himself had made a century before: the Gettysburg Address .
In that speech, delivered at the Soldiers’ National Cemetery (now known as Gettysburg National Cemetery) in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania in November 1863, Lincoln had urged his listeners to continue in the fight for freedom, envisioning the day when all Americans – including Black slaves – would be free. His speech famously begins with the words: ‘Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.’
‘Four score and seven years’ is eighty-seven years, which takes us back from 1863 to 1776, the year of the signing of the Declaration of Independence. So, Martin Luther King’s allusion to the words of Lincoln’s historic speech do two things: they call back to Lincoln’s speech but also, by extension, to the founding of the United States almost two centuries before. Although Lincoln and the American Civil War represented progress in the cause to make all Americans free regardless of their ethnicity, King makes it clear in ‘I Have a Dream’ that there is still some way to go.
In the last analysis, King’s speech is a rhetorically clever and emotionally powerful call to use non-violent protest to oppose racial injustice, segregation, and discrimination, but also to ensure that all Americans are lifted out of poverty and degradation.
But most of all, King emphasises the collective endeavour that is necessary to bring about the world he wants his children to live in: the togetherness, the linking of hands, which is essential to make the dream a reality.
Discover more from Interesting Literature
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
I Have a Dream Speech Analysis Research Paper
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Searching for I Have a Dream speech analysis? Look no further! This literary analysis focuses on rhetorical devices and persuasive techniques used by Martin Luther King, Jr.
Introduction
- Summary & the Key Messages
- Analysis of the Structure
- Ethos, Logos, & Pathos
“I Have a Dream” is the most famous speech by Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. It is also considered as the best and greatest speech that was proclaimed in the history of the United States. It gathered more than 200,000 Americans of all races at the Lincoln Memorial on August 28, 1963.
The speech is an excellent example of persuasive rhetoric filled with many expressive means and stylistic devices, such as metaphors, repetitions, allusions, epithets and persuasive constructions. The speech has become a symbol of a new era of freedom and symbol of the American civil rights movement.
I Have a Dream: Summary & the Key Messages
“I Have a Dream” is a representation of the “America Dream” about a free and equal society. As Leff & Kauffeld (1989) mention, “Martin Luther King Jr.’s speech won immediate and sustained praise and has become a moral compass in American political culture” (p. 181).
The speech had a great influence on minds and visions of all Americans and “forever “legitimized” civil rights in the minds of most Amricans” (Leff & Kauffeld 1989, p. 181).
Marin Luther King was among the founders of the American civil rights movement. He led an active political life. He attended the Morehouse College in Atlanta, and then studied theology at Crozer Theological Seminary in Pennsylvania and Boston University.
In 1955, he became a president of the Montgomery Improvement Association and gained a public recognition for his activities in the campaign. He also is one of the organizers of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference in 1957. In 1963, the members of the conference led mass demonstrations in Alabama. These demonstrations resulted in the passage in the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
During one of the march demonstrations for Jobs and Freedom, King pronounced his famous speech. (Durgut 2008). The main purpose of the speech is expressed in its name “I Have a Dream”. The dream of the author was to live in a free society and make all people equal regardless race and social position.
Passionately and powerfully, he claimed that reformation of the society is a task of the future. His words became a meaningful expression of the political and cultural situation in the country and “shaped” the idea for which every American should struggle.
Thus, his speech was aimed at inspiring Americans to take actions and improve their lives. The key message of the speech is “We hold these truths to be self evident, that all men are created equal” (King 1963, n. p.). In order to come to this subject, the author divides the speech into three parts: introduction, first part (American reality) and second part (the prospects of the future).
First of all, he outlines the problem, “One hundred years later, the life of the Negro is still sadly crippled by the manacles of segregation and the chains of discrimination” (King 1963, n. p.), then he provides the detailed description of the racial injustice and inequality that face Americans.
He also inspired the listeners to rebel against these injustices claiming that “Now is the time” for changes, “now is the time to make real the promises of democracy” (King 1963, n. p.). Thus, he prepared people for the second part of his speech in which he presented the results of the changes.
King also expresses the dissatisfactions with the policies and laws which discriminated African Americans and their rights. The intended audience was the government representatives.
However, the author was intended to “touch minds” of all people, both black and white from all social layers. Emotionally and with anticipation, he addresses the people of America and, especially Negro people to whom he belongs:
But there is something that I must say to my people, who stand on the warm threshold which leads into the palace of justice: In the process of gaining our rightful place, we must not be guilty of wrongful deeds. Let us not seek to satisfy our thirst for freedom by drinking from the cup of bitterness and hatred (King 1963, n. p.).
He says “we” in order to show his concern and participation. When emphasizing the word “we” he demonstrates that everybody who understands the problem and seeks changes is involved and the “problem” is not a concern of the particular individuals, but it is a common problem and everybody should make his/her contribution to solve it.
The purpose of the author is to inform and inspire people for struggle and prepare them for changes. He builds his speech so that it was meaningful not only for political activists and Negro people, but to everybody. He says:
…the Negro community must not lead us to a distrust of all white people, for many of our white brothers, as evidenced by their presence here today, have come to realize that their destiny is tied up with our destiny (King 1963, n. p.).
Thus, we can see that the speech is addressed to white people as well. Moreover, King says that “all people are brothers” and there is no racial distinction. Next important trait of the speech is that it was written at the time when the question of racial discrimination was urgent.
Black people faced inequality and violence. “King is known as a charismatic orator. His way of persuading people was to use the power of words instead of physical violence” (Durgut 2008, n. p.).
He knew exactly how to use words, and after he delivered the speech “I Have a Dream”, he gained a great appreciation from people and was called “The Man of the Year” by The Times magazine.
Moreover, a year later, he was awarded by the Nobel Peace Prize for his great contribution to the establishment of justice and peace in the world. These facts demonstrate how people assumed about the author and his activities.
During the time when the speech was proclaimed, television transferred the recent events of the raising struggle for civil rights. There were the episodes of the violence in Birmingham and Alabama. The March on Washington became the first step towards equality and justice.
Regardless the fact that by the time when the speech was proclaimed Abraham Lincoln put an end to slavery and signed the Emancipation Proclamation, discrimination and inequality still had a great power and did not decrease at local and even national levels.
This reality inspired King that something should be done in order to “open people’s eyes” and spread the ideas of equality and justice. In his speech, the author makes allusions to the documents that also addressed the same ideas as his speech.
He refers to the Emancipation Proclamation and the Bill of Rights; the author also cites the words from the Declaration of Independence, and addresses the Bible in order to show that God created all people equal and it was the responsibility of every person to preserve that equality. King met a great response from the audience.
The text of the speech was heard by a broad audience due to television and this allowed the author to reach “the hearts” of many people around America.
These days, the text of the speech is widely available for all who wants to read it. It can be found on the Internet at the American Rhetoric and other sites, as well as in many anthologies and books. The audio and video versions of the speech are also available on the Internet.
The main idea the all people should be treated equal is heard in every line of the text. In order to make the speech emotional and persuasive, King made use many stylistic devices, as well as paid a great attention to the content.
“I have a Dream” is a political speech with the elements of a sermon. According to the Aristotelian classification, it is a deliberative speech. The distinctive feature of this type of speech is the purpose of it. It aims at enabling the audience to make a judgment or a decision during the speech.
I Have a Dream: Analysis of the Speech Structure
There are three main parts of the speech: exordium, narration and argumentation and peroratio (introduction, main part and closing) (Black 2008). In every part of the speech, King presents particular information. With regard to the content, structure of the text has a great importance in representation of this content.
Every type of speech should begin with the exordium, “the functions of the exordium are to make the audience attentive, docile and benevolent” (Durgut 2008, n. p.).
Traditionally, the content of the introduction of the speech should present the salutation of the audience, the main idea and some general additional information to attract the listeners’ attention. Martin Luther King managed to include all the points into one sentence, “I am happy to join with you today in what will go down in history as the greatest demonstration for freedom in the history of our nation” (King 1963, n. p.).
Furthermore, the narration presents arguments, evidences and prospects for the future. The main part of Luther’s speech can also be divided into two parts. The first part of the main text provides the audience with the historical background of the “problem”.
The author describes social and political events that had place “Five score years ago” and the results that people could see “one hundred years later” (3 times) (King 1963, n. p.). In the next paragraphs, he calls people for action telling “now is the time” which he uses four times, “Now is the time to make real the promises of democracy.
Now is the time to rise from the dark… Now is the time to lift our nation… Now is the time to make justice a reality…” (King 1963, n. p.). The author also set goals for people who are ready to protect their rights and freedoms, “and as we walk, we must make the pledge that we shall march ahead. We cannot turn back” (King 1963, n. p.).
He claims that people “can never be satisfied” as long as they have to be the victims of unjust policies and racial prejudice. In order to supper his argument, the author uses convincing evidences which he observed in the society.
He also makes allusions to historical documents, such as The Emancipation Proclamation, the United States Constitution and the Declaration of Independence. In addition, he refers to the Bible as to a foundation of the “human law and justice”. The second part of the text is the author’s expectations.
He looks into the future with the words “I Have a Dream”, it is the main theme of the paragraph, as well as the speech as a whole. He begins this part with an emotional introduction, “I say to you today, my friends, that in spite of the difficulties and frustrations of the moment I still have a dream.
It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream” (King 1963, n. p.). He addresses a strong message for Caucasian people about peace and equality, and he expresses his hope that the positive changes will come in the nearest future, “King gave advice how to act and what to change currently, so his vision of the common future for the American society might come true one day” (Durgut 2008, n. p.).
He claims, “let freedom ring from” all over the United States and people will live happy. This idea is voiced in the peroration of the speech, and it provides strong and persuasive ending of the text.
As it has already been mentioned, King was a skillful orator and his speech is an example of high quality rhetoric. His speech presents all types of appeals, such as ethos, pathos and logos. “Pathos refers to how well you can appeal to someone’s emotion” (Black 2008, p. 48).
Ethos, Logos, & Pathos in I Have a Dream
Dr. Martin Luther King’s persuasive “I Have a Dream” speech was fueled by emotional components. He said that “African Americans were living on a lonely island of poverty in the midst of a vast ocean of material prosperity.” (Black 2008 p. 48).
He persuaded to give the black Americans the equal rights, in the passage of his speech he says that “all men – yes, black men as well as Caucasians men – would be guaranteed the unalienable rights of life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness” (King 1963, n. p.).
He uses logos when referring to historical documents and the Bible. Providing that all people are equal and friend, Martin Luther King uses ethos.
Language and style of the speech are bright, expressive and persuasive. He makes use various methods to convince the audience. Thus, he widely uses repetitions of key phrases and “theme words”, make allusions to significant historical events and important documents, provides specific examples to make his arguments significant and use broad metaphors to emphasize important moments and highlight the most important concepts and ideas.
So, the most important phrases that serve to attract the audience’s attention, such as “Now is the time…”, “We can never (cannot) be satisfied…”, “I Have a Dream…”, “Let freedom ring (from) …” are repeated in the successful sentences, or at the beginning of the sentences.
The theme words are repeated extensively through the text, they are “freedom” (20 times), “dream” (11), “we” (30), “our” (17), “justice” (8). Among the most “impressive” metaphors used by King are:
“Joyous daybreak to end the long night of their captivity”;
“The Negro lives on a lonely island of poverty in the midst of a vast ocean of material prosperity”;
“Rise from the dark and desolate valley of segregation to the sunlit path of racial justice”. (King 1963, n. p.).
Thus, we can come to a conclusion that the speech “I Have a Dream” is the most impressive political speeches that had a great influence on the history of the United States, and shaped visions of many Americans.
It is one of the best examples of the rhetorical art and persuasive writing. Thus, as Kenneth Tamarkin & Jeri W. Bayer (2002) say, “Martin Luther’s “I Have a Dream” speech is an eloquent appeal for integration and equality” (p. 399), and the representation of the American dream.
I Have a Dream Analysis: FAQ
- What Am I Have a Dream Speech about? One of the most iconic speeches in US history aims to put an end to racism in America. The key message of I Have a Dream by Martin Luther King, Jr. Is the importance of equal civil and economic rights for all US citizens.
- What Was the Purpose of the I Have a Dream Speech? In I Have a Dream , Martin Luther King, Jr. addressed the issues of racism and segregation in the US. He encouraged using non-violent protests as a weapon to fight inequality.
- When Was the I Have a Dream Speech? The speech was delivered on August 28, 1963, during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Martin Luther King presented his speech from the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., to over 250,000 civil rights supporters.
Reference List
Black, Barry C. (2008). From the hood to the hill: A story of overcoming. New York: Thomas Nelson Inc.
Durgut, Ismail. (2008). “I Have a Dream”: an example of classical rhetoric in a post-modern speech . London: GRIN Verlag.
King, Martin Luther. (1963). I Have a Dream. American Rhetoric . Retrieved from https://americanrhetoric.com/speeches/mlkihaveadream.htm
Leff, Michael C., & Kauffeld, Fred J. (1989). Texts in context: critical dialogues on significant episodes in American political rhetoric . Davis: Routledge.
Tamarkin, Kenneth, & Bayer, Jeri W. (2002). McGraw-Hill’s GED Social Studies . New York: McGraw-Hill Professional.
- Martin Luther King's Speech: A Summary
- "I Have a Dream" Speech by Martin Luther King Jr
- Martin Luther King Jr’s “I Have a Dream” Speech Critique
- Fallacy Summary and Application Paper
- Martin Luther King Junior
- Stephen Colbert's Speech
- Essay on Martin Luther King’s I Have a Dream Speech
- Steve Jobs Commencement Speech Analysis
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, March 25). I Have a Dream Speech Analysis. https://ivypanda.com/essays/martin-luther-kings-i-have-a-dream-speech-analysis/
"I Have a Dream Speech Analysis." IvyPanda , 25 Mar. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/martin-luther-kings-i-have-a-dream-speech-analysis/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'I Have a Dream Speech Analysis'. 25 March.
IvyPanda . 2019. "I Have a Dream Speech Analysis." March 25, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/martin-luther-kings-i-have-a-dream-speech-analysis/.
1. IvyPanda . "I Have a Dream Speech Analysis." March 25, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/martin-luther-kings-i-have-a-dream-speech-analysis/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "I Have a Dream Speech Analysis." March 25, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/martin-luther-kings-i-have-a-dream-speech-analysis/.
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — I Have a Dream — Rhetorical Analysis of Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream” Speech
Rhetorical Analysis of Martin Luther King's "I Have a Dream" Speech
- Categories: I Have a Dream Martin Luther King
About this sample

Words: 667 |
Published: Jun 14, 2024
Words: 667 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Bibliography

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 622 words
3 pages / 1228 words
1 pages / 597 words
1 pages / 601 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on I Have a Dream
On August 28, 1963, Martin Luther King Jr. delivered his iconic "I Have a Dream" speech during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. This powerful address has become one of the most memorable moments in American history, [...]
On August 28, 1963, Martin Luther King Jr. delivered his iconic "I Have a Dream" speech during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. This speech has since become one of the most celebrated and influential speeches in [...]
Have you ever wondered what made Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech so iconic? Why is it still remembered and celebrated today, more than half a century after it was delivered? The purpose of this essay is to [...]
Imagine being in a crowded room, listening to a persuasive speaker who captivates your attention and moves you to tears. You may not realize it, but you have just witnessed the power of rhetoric. Rhetoric, the art of effective [...]
Martin Luther King Junior stamps August the 28, 1963, as a historical landmark of equality for black Americans, ironically in the Lincoln Memorial. Not only does King proclaim equality, but the format in which his speech was [...]
On August 28, 1963 Reverend Martin Luther King Jr. gave the monumental I Have a Dream speech. One hundred years earlier, the Emancipation Proclamation had been issued in 1863 freeing all the slaves. Two years later the Civil War [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Cart – Checkout
Martin luther king and the rule of three.
I’ve been thinking about Martin Luther King as a speaker again recently, because of the holiday, of course, but also because of the release of the movie Selma . And for one other reason: I often use King as an example of a great speaker when I’m working one-on-one with executives and professional speakers.
No surprise there; King is one of the giants of the last century. What is surprising, perhaps, is that while the discussion often centers on his magnificent voice, its passion and authority, and his captivating use of the pause – all of his vocal techniques, in other words, honed in years of preaching – my clients often don’t think about King’s rhetorical expertise until I point it out to them.
King uses two main techniques, (appropriate) repetition and the rule of threes, to convey emotion through his rhetoric. And while everyone has noticed the first one – it’s how the speech is known – few have remarked on the second. But this less-recognized rhetorical technique is the one, I believe, that makes the speech resonate so powerfully with audiences from its first delivery at the Washington Mall on August 23, 1963, to today.
First let’s look at the use of repetition to create passion:
I say to you today, my friends, that in spite of the difficulties and frustrations of the moment I still have a dream. It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream.
I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: “We hold these truths to be self – evident; that all men are created equal.”
I have a dream that one day on the red hills of Georgia the sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave owners will be able to sit down together at the table of brotherhood.
I have a dream that one day even the state of Mississippi, a desert state sweltering in the heat of injustice and oppression, will be transformed into an oasis of freedom and justice.
I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.
I have a dream today.
I have a dream that one day the state of Alabama, whose governor’s lips are presently dripping with the words of interposition and nullification, will be transformed into a situation where little black boys and black girls will be able to join hands with little white boys and white girls and walk together as sisters and brothers.
There’s a real art to repetition. How do you manage it so that it doesn’t sound simple – minded but rather, as in this case, creates a crescendo of emotion that builds with each reaffirmation of the phrase, “I have a dream”?
The key is the phrase that’s repeated. It has to be able to bear the weight, and the words have to be affirmative, simple, and evocative. In King’s case, the words were perfect. But it’s not easy to find the right ones. The political world is full of repetitive phrasing and chanting of key phrases that the speaker begins and the audience takes over, but most of them are quickly forgotten.
And King repeats the phrase in different ways in his sentences, sometimes at the beginning of a longer sentence and sometimes essentially standing on its own, creating further interest and tension.
Then there’s the Rule of Three. The rule of three plays magnificently at the end of the speech, when King invokes a spiritual and brings the audience to its feet:
When we let freedom ring, when we let it ring from every village and every hamlet, from every state and every city, we will be able to speed up that day when all of God’s children, black men and white men, Jews and Gentiles, Protestants and Catholics, will be able to join hands and sing in the words of the old Negro spiritual, “Free at last! Free at last! Thank God Almighty, we are free at last!”
There are actually two sets of threes here: the groupings of black and white, Jews and Gentiles, and Protestants and Catholics, as well as the final triumphant, “Free at last!”
And there are further subtleties. By giving us two groups of two — every village and every hamlet and every state and every city — King creates in us a need to have the completion of a group of three. And of course he balances the two sets of groups perfectly. It’s an amazing performance.
Perhaps you’re thinking, Well, that was easy for Reverend King. He was a great speaker and had time to prepare. But how can I achieve that kind of rhetorical passion in my communications, which are mostly off the cuff?
You may be astonished to find out that the second half of King’s speech, where these quotes come from, was ad-libbed.
What is it about groups of three that heighten emotion and create passion? Why do we respond so powerfully to them? It’s a mystery — something psychological. Some say it has to do with religious symbolism, since there are groups of three in most major religions, but that may be putting the cart before the horse: the religions may have settled on groups of threes for the same psychological reasons that everyone else finds them powerful.
Whatever the reason, we find something complete and satisfying in a group of three, like a three-legged stool that can stand firmly on uneven ground. And so you should use them in your communications – as well as repetition – when you’re striving to convey passion.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
About the author: nick morgan.
Related Posts

Great post!
Good morning Nick
For me no greater example of the power of public speaking than Dr King. All you stated above plus amazing metaphors. I love the analysis done by Nancy Duarte on Dr King’s speech.
A fun memory for our family in relation to this great speech. One Saturday morning early, around 7. am, I was preparing to give a talk about Dr King and this great speech. As is my custom, I lined up the chairs in the kitchen for my imaged audience and would recite my speech aloud. As I was repeating then section of “I have a Dream” a roar came through the ceiling , “Dad I am trying to have A Dream, please be quiet”. We still chuckle about that.
Thank you and I wish you a great weekend.
Kind regards John Keating
[…] it often enough, and the Power of Repetition causes your brain to associate anything “think” with negative feelings: guilt, shame, […]
Leave A Comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Public Speaking Podcast
A podcast launched in a time of great change. Just One Question with Dr Nick Morgan has over 50 episodes featuring some of the worlds most elite and accomplished speakers. More importantly the podcast brings light to our industry as we undergo a public speaking and communication reformation.

© Copyright 2024 | All Rights Reserved Public Words Inc | Legal | Privacy
BLOG PODCAST NEWS SUBSCRIBE
Sign up to our weekly blog for useful articles, tips and podcasts for boosting your public speaking career:
CALL US NOW
© Copyright 2024 | All Rights Reserved Public Words Inc | Legal Policy | Privacy Policy
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Read Martin Luther King Jr.'s 'I Have a Dream' speech in its entirety

Civil rights leader Martin Luther King Jr. addresses the crowd at the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., where he gave his "I Have a Dream" speech on Aug. 28, 1963, as part of the March on Washington. AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Civil rights leader Martin Luther King Jr. addresses the crowd at the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., where he gave his "I Have a Dream" speech on Aug. 28, 1963, as part of the March on Washington.
Monday marks Martin Luther King, Jr. Day. Below is a transcript of his celebrated "I Have a Dream" speech, delivered on Aug. 28, 1963, on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial. NPR's Talk of the Nation aired the speech in 2010 — listen to that broadcast at the audio link above.

Martin Luther King Jr. and other civil rights leaders gather before a rally at the Lincoln Memorial on Aug. 28, 1963, in Washington. National Archives/Hulton Archive via Getty Images hide caption
Rev. Martin Luther King Jr.: Five score years ago, a great American, in whose symbolic shadow we stand today, signed the Emancipation Proclamation. This momentous decree came as a great beacon light of hope to millions of Negro slaves who had been seared in the flames of withering injustice. It came as a joyous daybreak to end the long night of their captivity.
But 100 years later, the Negro still is not free. One hundred years later, the life of the Negro is still sadly crippled by the manacles of segregation and the chains of discrimination. One hundred years later, the Negro lives on a lonely island of poverty in the midst of a vast ocean of material prosperity. One hundred years later the Negro is still languished in the corners of American society and finds himself in exile in his own land. And so we've come here today to dramatize a shameful condition. In a sense we've come to our nation's capital to cash a check.

Code Switch
The power of martin luther king jr.'s anger.
When the architects of our republic wrote the magnificent words of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence, they were signing a promissory note to which every American was to fall heir. This note was a promise that all men — yes, Black men as well as white men — would be guaranteed the unalienable rights of life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness.
It is obvious today that America has defaulted on this promissory note insofar as her citizens of color are concerned. Instead of honoring this sacred obligation, America has given the Negro people a bad check, a check which has come back marked insufficient funds.
But we refuse to believe that the bank of justice is bankrupt.

Martin Luther King is not your mascot
We refuse to believe that there are insufficient funds in the great vaults of opportunity of this nation. And so we've come to cash this check, a check that will give us upon demand the riches of freedom and the security of justice.
We have also come to this hallowed spot to remind America of the fierce urgency of now. This is no time to engage in the luxury of cooling off or to take the tranquilizing drug of gradualism.
Now is the time to make real the promises of democracy. Now is the time to rise from the dark and desolate valley of segregation to the sunlit path of racial justice. Now is the time to lift our nation from the quick sands of racial injustice to the solid rock of brotherhood. Now is the time to make justice a reality for all of God's children.

Civil rights protesters march from the Washington Monument to the Lincoln Memorial for the March on Washington on Aug. 28, 1963. Kurt Severin/Three Lions/Hulton Archive/Getty Images hide caption
It would be fatal for the nation to overlook the urgency of the moment. This sweltering summer of the Negro's legitimate discontent will not pass until there is an invigorating autumn of freedom and equality. 1963 is not an end, but a beginning. Those who hope that the Negro needed to blow off steam and will now be content will have a rude awakening if the nation returns to business as usual.
There will be neither rest nor tranquility in America until the Negro is granted his citizenship rights. The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.
But there is something that I must say to my people who stand on the warm threshold which leads into the palace of justice. In the process of gaining our rightful place, we must not be guilty of wrongful deeds. Let us not seek to satisfy our thirst for freedom by drinking from the cup of bitterness and hatred.

Throughline
Bayard rustin: the man behind the march on washington (2021).
We must forever conduct our struggle on the high plane of dignity and discipline. We must not allow our creative protest to degenerate into physical violence. Again and again, we must rise to the majestic heights of meeting physical force with soul force. The marvelous new militancy which has engulfed the Negro community must not lead us to a distrust of all white people, for many of our white brothers, as evidenced by their presence here today, have come to realize that their destiny is tied up with our destiny.
And they have come to realize that their freedom is inextricably bound to our freedom. We cannot walk alone. And as we walk, we must make the pledge that we shall always march ahead. We cannot turn back.
There are those who are asking the devotees of civil rights, when will you be satisfied? We can never be satisfied as long as the Negro is the victim of the unspeakable horrors of police brutality. We can never be satisfied as long as our bodies, heavy with the fatigue of travel, cannot gain lodging in the motels of the highways and the hotels of the cities.
We cannot be satisfied as long as the Negro's basic mobility is from a smaller ghetto to a larger one. We can never be satisfied as long as our children are stripped of their selfhood and robbed of their dignity by signs stating: for whites only.
We cannot be satisfied as long as a Negro in Mississippi cannot vote and a Negro in New York believes he has nothing for which to vote.
No, no, we are not satisfied, and we will not be satisfied until justice rolls down like waters, and righteousness like a mighty stream.

How The Voting Rights Act Came To Be And How It's Changed
I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations. Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. Some of you have come from areas where your quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality. You have been the veterans of creative suffering. Continue to work with the faith that unearned suffering is redemptive. Go back to Mississippi, go back to Alabama, go back to South Carolina, go back to Georgia, go back to Louisiana, go back to the slums and ghettos of our Northern cities, knowing that somehow this situation can and will be changed.
Let us not wallow in the valley of despair, I say to you today, my friends.
So even though we face the difficulties of today and tomorrow, I still have a dream. It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream. I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.

People clap and sing along to a freedom song between speeches at the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom in 1963. Express Newspapers via Getty Images hide caption
I have a dream that one day on the red hills of Georgia, the sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave owners will be able to sit down together at the table of brotherhood.
I have a dream that one day even the state of Mississippi, a state sweltering with the heat of injustice, sweltering with the heat of oppression will be transformed into an oasis of freedom and justice.
I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character. I have a dream today.
I have a dream that one day down in Alabama with its vicious racists, with its governor having his lips dripping with the words of interposition and nullification, one day right down in Alabama little Black boys and Black girls will be able to join hands with little white boys and white girls as sisters and brothers. I have a dream today.
I have a dream that one day every valley shall be exalted, every hill and mountain shall be made low, the rough places will be made plain, and the crooked places will be made straight, and the glory of the Lord shall be revealed, and all flesh shall see it together.
Nikole Hannah-Jones on the power of collective memory

- LISTEN & FOLLOW
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
- Amazon Music
Your support helps make our show possible and unlocks access to our sponsor-free feed.
This is our hope. This is the faith that I go back to the South with. With this faith, we will be able to hew out of the mountain of despair a stone of hope. With this faith we will be able to transform the jangling discords of our nation into a beautiful symphony of brotherhood. With this faith we will be able to work together, to pray together, to struggle together, to go to jail together, to stand up for freedom together, knowing that we will be free one day.
This will be the day when all of God's children will be able to sing with new meaning: My country, 'tis of thee, sweet land of liberty, of thee I sing. Land where my fathers died, land of the pilgrims' pride, from every mountainside, let freedom ring.
And if America is to be a great nation, this must become true. And so let freedom ring from the prodigious hilltops of New Hampshire. Let freedom ring from the mighty mountains of New York. Let freedom ring from the heightening Alleghenies of Pennsylvania. Let freedom ring from the snowcapped Rockies of Colorado. Let freedom ring from the curvaceous slopes of California. But not only that, let freedom ring from Stone Mountain of Georgia. Let freedom ring from Lookout Mountain of Tennessee. Let freedom ring from every hill and molehill of Mississippi. From every mountainside, let freedom ring.
And when this happens, and when we allow freedom ring, when we let it ring from every village and every hamlet, from every state and every city, we will be able to speed up that day when all of God's children, Black men and white men, Jews and Gentiles, Protestants and Catholics, will be able to join hands and sing in the words of the old Negro spiritual: Free at last. Free at last. Thank God almighty, we are free at last.
Correction Jan. 15, 2024
A previous version of this transcript included the line, "We have also come to his hallowed spot to remind America of the fierce urgency of now." The correct wording is "We have also come to this hallowed spot to remind America of the fierce urgency of now."
Metaphors in American Politics
Your guide to political metaphors used in american media – andrew j. gallagher, ph.d., metaphors of martin luther king’s “i have a dream” speech.
This coming Wednesday will mark the 50 th anniversary of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech from August 28 th , 1963. The speech was the high point of the march on Washington attended by approximately 300,000 people, intended to improve civil rights for blacks and minorities in the United States. Dr. King’s speech and the march spurred the U.S. Congress to pass the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
Now recognized as one of the most powerful speeches of the 20 th century, Dr. King’s speech was a masterpiece of political rhetoric. For the past few days, historians and television pundits have been analyzing the importance of the speech and the march. I would like to add a brief analysis of the metaphors used in the speech. Dr. King was not only academically trained – he earned a Ph.D. in theology from Boston University – he was also a Baptist minister. His education, along with his skills as a preacher, helped him become one of the most gifted orators of modern times. He was also a master of using metaphors to make a point in his speeches. The “I Have a Dream” speech is a “goldmine” of metaphors. I will break down some of his most important metaphors into semantic categories such as banking, food and drink, buildings, music and nature. I will highlight the metaphors with boldface and italic type.
One of the most explicit metaphors he uses to make his point about the lack of civil rights is a banking metaphor. He suggests that the thousands of marchers have come to Washington to cash a check while he claims that the government has given the people of color a check with insufficient funds , or a promissory note that no one has paid.
“It is obvious today that America has defaulted on this promissory note insofar as her citizens of color are concerned. Instead of honoring this sacred obligation, America has given the Negro people a bad check which has come back marked “insufficient funds.” ”
Food and Drink
We are all familiar with the experience of eating and drinking. Dr. King uses metaphors of drinking in several instances to correlate drinking a liquid to drinking attitudes or opinions. Dr. King suggests:
“Let us not seek to satisfy our thirst for freedom by drinking from the cup of bitterness and hatred .”
Later he uses a complex metaphor comparing a liquid to political actions, speaking of George Wallace, the governor of Alabama at the time who was a strong proponent of segregation.
“I have a dream that one day the state of Alabama, whose governor’s lips are presently dripping with the words of interposition and nullification, will be transformed into a situation where little black boys and black girls will be able to join hands with little white boys and white girls and walk together as sisters and brothers.”
The idea of entering a building is used metaphorically to indicate progress being made toward a certain goal. We often speak of having doors of opportunities or crossing a threshold to reach a new goal. Dr. King uses both of these metaphors to describe the work necessary to make progress on civil rights in the United States. Dr. King also makes a comparison of the differences in civil rights to the differences of a normal house compared to a palace.
“Now is the time to open the doors of opportunity to all of God’s children.”
“But there is something that I must say to my people who stand on the warm threshold which leads into the palace of justice.”
By far the most common metaphors used in the speech are those of nature. Dr. King uses metaphors of mountains, valleys, deserts, oases, stones, solid rocks, quicksand, islands, oceans, waters, streams, wind, whirlwinds, and storms.
Dr. King describes an America almost 100 years after the Emancipation Proclamation:
“One hundred years later, the Negro lives on a lonely island of poverty in the midst of a vast ocean of material prosperity.”
He compares the differences in civil rights to the differences in light and shadows between a valley and a mountaintop.
“Now is the time to rise from the dark and desolate valley of segregation to the sunlit path of racial justice.”
“Again and again we must rise to the majestic heights of meeting physical force with soul force.”
“Let us not wallow in the valley of despair .”
In another visually powerful metaphor, he compares injustice to being a desert while justice is an oasis of water.
“I have a dream that one day even the state of Mississippi, a desert state, sweltering with the heat of injustice and oppression, will be transformed into an oasis of freedom and justice.”
He also describes justice as being solid rock while injustice is quicksand .
“Now is the time to lift our nation from the quicksands of racial injustice to the solid rock of brotherhood.”
In a very powerful metaphor, he describes justice as water in a mighty river.
“We can never be satisfied as long as a Negro in Mississippi cannot vote and a Negro in New York believes he has nothing for which to vote. No, no, we are not satisfied, and we will not be satisfied until justice rolls down like waters and righteousness like a mighty stream .”
He offers his support for the thousands of marchers who experienced discrimination first hand in their own lives by comparing this discrimination to strong windstorms.
“Some of you have come from areas where your quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality.”
Dr. King also uses contrasts from nature based on light and dark and different seasons of the year.
“Five score years ago, a great American, in whose symbolic shadow we stand signed the Emancipation Proclamation. This momentous decree came as a great beacon light of hope to millions of Negro slaves who had been seared in the flames of withering injustice. It came as a joyous daybreak to end the long night of captivity.”
“This sweltering summer of the Negro’s legitimate discontent will not pass until there is an invigorating autumn of freedom and equality.”
Music and Sounds
The final set of metaphors that Dr. King uses in the speech is related to music and sounds. After spending most of the speech using visual metaphors, he adds a few based on auditory metaphors of sounds and music.
“With this faith we will be able to hew out of the mountain of despair a stone of hope . With this faith we will be able to transform the jangling discords of our nation into a beautiful symphony of brotherhood.”
More importantly, he finishes the speech with a powerful metaphor of a bell ringing, borrowing a phrase, “let freedom ring” from the national song, “My Country ‘Tis of Thee.” We normally associate the ringing of bells with churches, but they have also been used historically in towns to signal emergencies or celebrations. In the song, and in Dr. King’s speech, the ringing of the bells is meant to signify the echoing of the sounds all across the country. In a rhetorical style common to Baptist preaching, he repeats the phrase many times for effect, in fact, a total of twelve times.
“And when this happens, when we allow freedom to ring , when we let it ring from every village and every hamlet, from every state and every city, we will be able to speed up that day when all of God’s children, black men and white men, Jews and Gentiles, Protestants and Catholics, will be able to join hands and sing in the words of the old Negro spiritual, “Free at last! Free at last! Thank God Almighty, we are free at last!””
You can read the entire text of the speech at http://abcnews.go.com/Politics/martin-luther-kings-speech-dream-full-text/story?id=14358231 or view the speech at http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HRIF4_WzU1w . It is moving to watch the speech after all these years. Watch how the audience reacts to some of his phrases. Note too that he reads from his notes for the first part of the speech but then does the last five minutes from memory as he gets more and more inspired. Pretty amazing!
Comments and questions are welcome!
Update! Update! Update!
I have a second analysis of this famous speech in another post – Martin Luther King’s “Dream” Speech, Part 2 . Please read this post as well to complete your research.
Next time: More on metaphors of sounds
Share this:
19 thoughts on “ metaphors of martin luther king’s “i have a dream” speech ”.
I was really surprised by all the references to nature. I learned last week that at a certain point during the speech he left his text at the prompting of an associate and just started, off the cuff, to speak about his dream. Obviously MLK jr not only wrote speeches using metaphors, he spoke naturally in metaphors also. Does rich rhetoric still live in American political speeches anymore? I’d be interested to know if there is any current politician you know of who transcends the rest with visionary discourse using original or creative metaphors.
Great questions Janice! I think his use of metaphors grew out of his experience as a Baptist preacher. I am no expert on these traditions but I believe Biblical parables, analogies and metaphors are common tools used in Sunday sermons. As for the use of metaphors in contemporary speeches, I think that most metaphor usage is unconscious, i.e., the metaphors are such common parts of everyday speech that they are used without much forethought. However, that being said, I think some politicians (and their speechwriters) use specific metaphors to make points in their speeches. I don’t think anyone today uses metaphors to the extent that MLK did in that speech. However, President Obama uses metaphors in colorful ways in his state-of-the-union addresses as he did in his inaugural addresses. I believe the amount of unusual metaphors increases directly with the importance of the speech. I will post more comments on this if I hear of any more colorful speeches in the news…
I noticed two variations: “”whose governor’s lips are presently ” and ” “with its governor having his lips.” I’ll have to re-listen to the speech. My guess is the latter was spoken, the former an edited version. But that’s a guess. For what it’s worth the first ‘googles’ 361,000, the latter 1,040,000. Excellent article. Thank you. My seventh graders hunting these down and finding tenor, vehicle and ground.
In paragraph 1, King uses a simile to describe the signing of the Emancipation Proclamation as “…a joyous daybreak to end the long night of captivity.” What is the long night of captivity?
Hello Niayza! The long night of captivity that MLK refers to is the hundreds of years of slavery for African-Americans in the United States. The Emancipation Proclamation signed by Abraham Lincoln freed all of the slaves. Dr. King used a contrasting rhetorical style with metaphors comparing night (darkness, evil) with day (light, goodness) to illustrate how the slaves had gone from a horrible situation to one of justice, a common theme in many of his speeches. By the way, technically speaking, describing the change as going from night to day is a metaphor, not a simile, since there is no use of like or as . Thanks for a great question. Let me know if you have any other questions.
i want to know that ,if this can be cited in any research paper, if the answer is yes, what is the method according to MLA style.
Hello Muhammed. Great question! I will provide an answer as a separate blog post coming soon. Let me know if you have any more specific questions.
This is just great. Just great.
Thanks Judy! I am glad you found the blog useful!
Can you do at least some similes please… I really needed them for an assignment thanks for the metaphors…
Hello! Thanks for your request on the blog. Unfortunately, the reason I do not discuss similes in MLK’s “I Have a Dream Speech” is because there is only one. As you may know, similes require the strict syntactic form using the words “like” or “as.” Thus they are always less common than metaphors in most speeches. In the “Dream” speech, the only simile is this: “No, no, we are not satisfied, and we will not be satisfied until justice rolls down like waters and righteousness like a mighty stream.” Please let me know if I can help you understanding the metaphors in the speech.
Wow, it just very great blog. Thankz a lot for write this kind of metaphor analysis. It just unintentionally that I also try to do my assignment dealing with this speech and metaphor. I want to aks several question, what does it mean on the words “Symbolic shadow” and what do I need to do first before analysing the metaphor? Thank you.
Hello Salam! I do not quite understand the phrase “symbolic shadow.” Can you explain the context in which it was written? The term “shadow” generally means something dark or sinister. You can read my blog post on “Metaphors of color: black and white” from March of 2014. You can just do a search for “shadow” among the posts and you can find this and other posts that discuss the use of metaphors for shadows. If you have any further questions, please let me know! Thanks for your interest in the blog.
Yes, Then.. Thank you very much, Andrew.
When King says he has a dream, that dream is a metaphor. It is not something he was sleeping and thought up. It is a vision for the future of his country.
I believe that those conceptual metaphors employed by Martin Luther Kings were informed from his pure patriotism and not from an hypocritical mouth as we have in political speeches of contemporary political leaders , most especially in third world nations
I couldn’t agree more. Martin Luther King, Jr. was not only a great orator but a true patriot. I am not sure about politicians in third world nations, but many of our elected officials seem to represent corporations more than the common people. Thanks for the comment!
When Martin Luther Kings stated ‘I have a dream’, his dream was his passion to help the American electorates as a true democrat .He was focused ,dogged and determined in bringing this to reality by defending the American’s rule of law and making life better for the common man. Such dream eludes most African leaders who are troubled by egocentricism and lust for wealth.
Interesting comment Mr. Aremu. While I agree that Martin Luther King, Jr was indeed a true patriot who tried to make life better for Americans, I am not sure to whom you are referring when you mention “African leaders who are troubled by egocentrism and lust for wealth.” Are you referring to leaders in Africa or African-American leaders in the United States? Can you provide an example?
Comments are closed.
The Daily Show Fan Page

Explore the latest interviews, correspondent coverage, best-of moments and more from The Daily Show.
The Daily Show
S29 E68 • July 8, 2024
Host Jon Stewart returns to his place behind the desk for an unvarnished look at the 2024 election, with expert analysis from the Daily Show news team.
Extended Interviews

The Daily Show Tickets
Attend a Live Taping
Find out how you can see The Daily Show live and in-person as a member of the studio audience.
Best of Jon Stewart

The Weekly Show with Jon Stewart
New Episodes Thursdays
Jon Stewart and special guests tackle complex issues.
Powerful Politicos

The Daily Show Shop
Great Things Are in Store
Become the proud owner of exclusive gear, including clothing, drinkware and must-have accessories.
About The Daily Show

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This pattern gives momentum to the speech, especially when spoken aloud. Each new description of the dream builds upon the previous one, growing in a crescendo to the final conclusion. While King primarily uses short, clipped sentences in the speech, he also varies the length of his sentences throughout:
Martin Luther King, Jr. uses rhetoric in his speech to persuade his listeners during the Civil Rights Movement. There are three rhetorical devices in his ''I Have a Dream'' speech. He uses ...
A rhetorical precis has four parts: 1st sentence - presents author's name, title, and genre of work. Uses verbs such as "argue", "claim", or "assert". 2nd sentence - explains development and evidence of thesis. Done chronologically. 3rd sentence - state author's purpose and WHY the author composed the text. 4th sentence ...
However, his most famous speech, the so-called "I Have A Dream" speech, is dominated by one particular rhetorical device: anaphora. Anaphora is a type of parallelism in which a phrase is repeated ...
It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream. Then King's favorite parallelism grouping — another TETRACOLON, with, again, ANAPHORA: 1. I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: "We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.".
Published: Jan 18th, 2009. "I Have a Dream" by Martin Luther King Jr. is one of the most memorable speeches of all time. It is worthy of lengthy study as we can all learn speechwriting skills from King's historic masterpiece. This article is the latest in a series of video speech critiques which help you analyze and learn from excellent ...
In "I Have a Dream", Martin Luther King Jr. extensively uses repetitions, metaphors, and allusions. Other rhetorical devices that you should note are antithesis, direct address, and enumeration. Rhetorical devices are language tools used to make speakers' arguments both appealing and memorable. Note that there is often an overlap between ...
In "I Have a Dream", Martin Luther King Jr. extensively uses repetitions, metaphors, and allusions. Other rhetorical devices that you should note are antithesis, direct address, and enumeration. Rhetorical devices are language tools used to make speakers' arguments both appealing and memorable. Note that there is often an overlap between ...
I Have a Dream Speech Rhetorical Analysis Lyrics. I am happy to join with you today in what will go down in history as the greatest demonstration for freedom in the history of our nation. Five ...
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos. "I Have a Dream" incorporates Aristotle's three essential rhetorical appeals: logos, ethos, and pathos. King's speech appeals to logos —the structure and ...
Many literary devices are used in Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech. Some of the most prominent ones are alliteration, allusion, hyperbole, and imagery. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr ...
Students can then use these I Have a Dream ethos, pathos, and logos sections to illustrate each example quote with characters, scenes, and emotions. Take logos for example. The logos of the speech are the reasoning and examples that Dr. King uses to back up his argument. These logos quotes can be from famous cases, statistics, or even history.
What are the main rhetorical devices used in "I Have a Dream"? Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech masterfully employs several rhetorical devices. The main devices include anaphora, evident in the repeated use of the phrase "I have a dream"; metaphor, such as referring to justice as a "bank of justice"; and alliteration, as ...
Martin Luther King then comes to the most famous part of his speech, in which he uses the phrase 'I have a dream' to begin successive sentences (a rhetorical device known as anaphora ). King outlines the form that his dream, or ambition or wish for a better America, takes. His dream, he tells his audience, is 'deeply rooted' in the ...
Introduction. "I Have a Dream" is the most famous speech by Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. It is also considered as the best and greatest speech that was proclaimed in the history of the United States. It gathered more than 200,000 Americans of all races at the Lincoln Memorial on August 28, 1963. The speech is an excellent example of ...
Assonance, a literary device involving the repetition of vowel sounds, can be found in several instances throughout King's speech. One notable example is when he states, "I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: 'We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.'"
Anaphora. I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up...I have a dream that one day on the hills of Georgia, sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave owners will be able to sit down together at the table of brotherhood. I have a dream that one day even the state of Mississippi... Anaphora. Go back to Mississippi.
This document provides a 2,281 word analysis of Martin Luther King Jr.'s iconic "I Have a Dream" speech, focusing on its rhetorical devices and techniques. It summarizes the key messages of the speech, which expressed King's dream of a free and equal society for all Americans regardless of race. The analysis then examines the speech's structure, use of ethos, logos and pathos, and influence ...
And while everyone has noticed the first one - it's how the speech is known - few have remarked on the second. But this less-recognized rhetorical technique is the one, I believe, that makes the speech resonate so powerfully with audiences from its first delivery at the Washington Mall on August 23, 1963, to today.
Repetition is a powerful rhetorical device in a speech. It enables the speaker to emphasize key points, and it makes it easier for the audience to remember those key points.
1. Full text to the "I Have A Dream" speech by Dr. Martin Luther King Junior. I am happy to join with you today in what will go down in history as the greatest demonstration for freedom in the history of our nation. Five score years ago, a great American, in whose symbolic shadow we stand today, signed the Emancipation Proclamation.
AFP via Getty Images. Monday marks Martin Luther King, Jr. Day. Below is a transcript of his celebrated "I Have a Dream" speech, delivered on Aug. 28, 1963, on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial ...
This coming Wednesday will mark the 50 th anniversary of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech from August 28 th, 1963. The speech was the high point of the march on Washington attended by approximately 300,000 people, intended to improve civil rights for blacks and minorities in the United States. Dr.
The source for The Daily Show fans, with episodes hosted by Jon Stewart, Ronny Chieng, Jordan Klepper, Dulcé Sloan and more, plus interviews, highlights and The Weekly Show podcast.
RHETORICAL DEVICES- LISTEN CAREFULLY TO THE PERSUASIVE SPEECH. IDENTIFY AND EXPLAIN WHERE YOU HEAR OR SEE THE USE OF THE FOLLOWING RHETORICAL DEVICES: parallelism and restatement in his speech. King uses the phrase "one hundred years later" to repeat and stress the idea that many years have passed and progress has not occurred.