UnboundLocalError: local variable 'fig' referenced before assignment
I am getting the above error while plotting the bar graphs and appending them to results. Is there any solution.
UnboundLocalError: local variable ‘fig’ referenced before assignment Traceback (most recent call last): File “C:\Users\Local\Temp\ipykernel_20424\180331076.py”, line 16, in update_graphs File “C:\Users\Lib\site-packages\plotly\express_chart_types.py”, line 368, in bar return make_figure( File “C:\Users\Lib\site-packages\plotly\express_core.py”, line 2182, in make_figure fig = init_figure( File “C:\Users\Lib\site-packages\plotly\express_core.py”, line 2327, in init_figure for annot in fig.layout.annotations: UnboundLocalError: local variable ‘fig’ referenced before assignment
fig =px.bar(x='country',y='population')
I assume x and y are columns of a DataFrame, but you never specify the DataFrame to use.
could also be a scope issue when fig=px.bar() was declared in a different function or not in the function where result.append() was declared.
@dashapp , is result.append() right below fig = px.bar()?
@adamschroeder I updated it as a new topic
hi @dashapp I don’t think this is a solution yet, but heads up that you have a spelling mistake with ‘var’. You probably meant val.
What is “output.append”? What is output coming from?
@adamschroeder Sorry that was a typo. so when I click a value from the dropdown output should return a bar plot and empty container. Suppose I select two columns output should be two bar graphs and empty container which can take hoverdata and click data. My code is working properly and only error is with fig. Even if I remove fig variable and add the graph in figure variable in dcc.graph, the error persists. It has something to do with plotly. Can you check this.
An UnboundLocalError is raised when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned. In most cases this will occur when trying to modify a local variable before it is actually assigned within the local scope. Python doesn’t have variable declarations, so it has to figure out the scope of variables itself. It does so by a simple rule: If there is an assignment to a variable inside a function, that variable is considered local.
Python has lexical scoping by default, which means that although an enclosed scope can access values in its enclosing scope, it cannot modify them (unless they’re declared global with the global keyword). A closure binds values in the enclosing environment to names in the local environment. The local environment can then use the bound value, and even reassign that name to something else, but it can’t modify the binding in the enclosing environment. UnboundLocalError happend because when python sees an assignment inside a function then it considers that variable as local variable and will not fetch its value from enclosing or global scope when we execute the function. However, to modify a global variable inside a function, you must use the global keyword.
In my case the error is UnboundLocalError: local variable ‘fig’ referenced before assignment
Traceback (most recent call last): File “C:\Users\Local\Temp\ipykernel_20424\180331076.py”, line 16, in update_graphs
File “C:\Users\Lib\site-packages\plotly\express_chart_types.py”, line 368, in bar return make_figure( File “C:\Users\Lib\site-packages\plotly\express_core.py”, line 2182, in make_figure fig = init_figure( File “C:\Users\Lib\site-packages\plotly\express_core.py”, line 2327, in init_figure for annot in fig.layout.annotations:
I haven’t used fig variable at all. Its just related to plotly fig.
I get the error too. But I found my d1 is empty dataframe. when I fix the filt operation, it works

Related Topics
Local variable referenced before assignment in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024 Reading time · 4 min

# Local variable referenced before assignment in Python
The Python "UnboundLocalError: Local variable referenced before assignment" occurs when we reference a local variable before assigning a value to it in a function.
To solve the error, mark the variable as global in the function definition, e.g. global my_var .
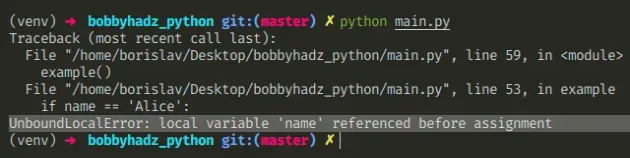
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
We assign a value to the name variable in the function.
# Mark the variable as global to solve the error
To solve the error, mark the variable as global in your function definition.
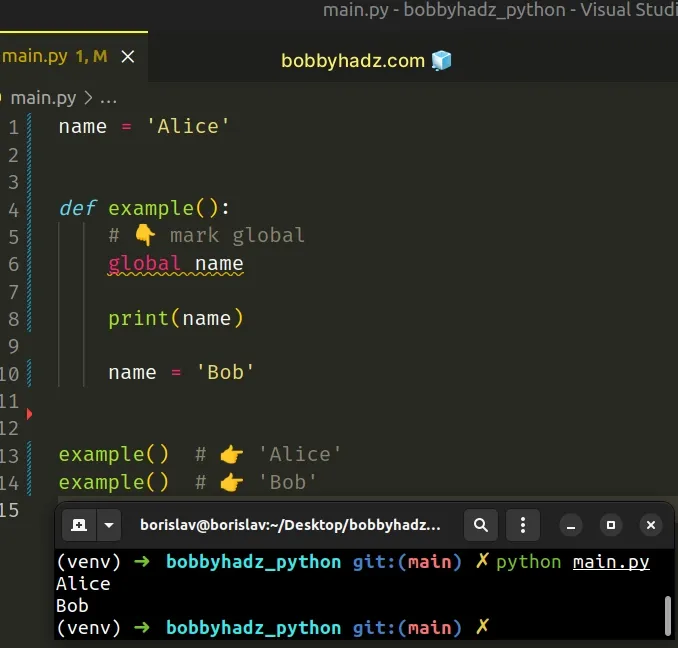
If a variable is assigned a value in a function's body, it is a local variable unless explicitly declared as global .
# Local variables shadow global ones with the same name
You could reference the global name variable from inside the function but if you assign a value to the variable in the function's body, the local variable shadows the global one.
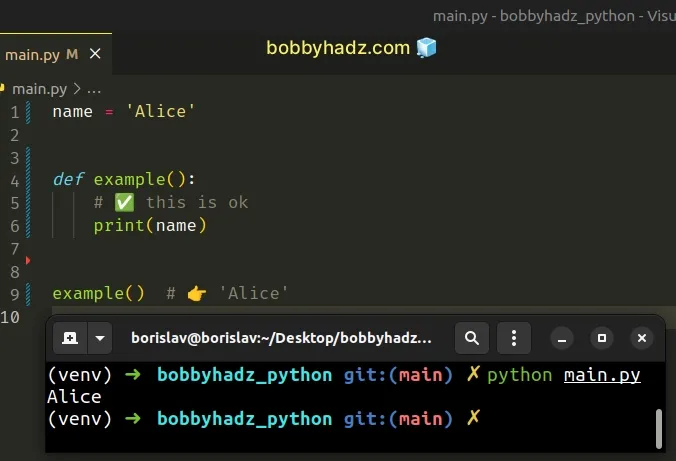
Accessing the name variable in the function is perfectly fine.
On the other hand, variables declared in a function cannot be accessed from the global scope.
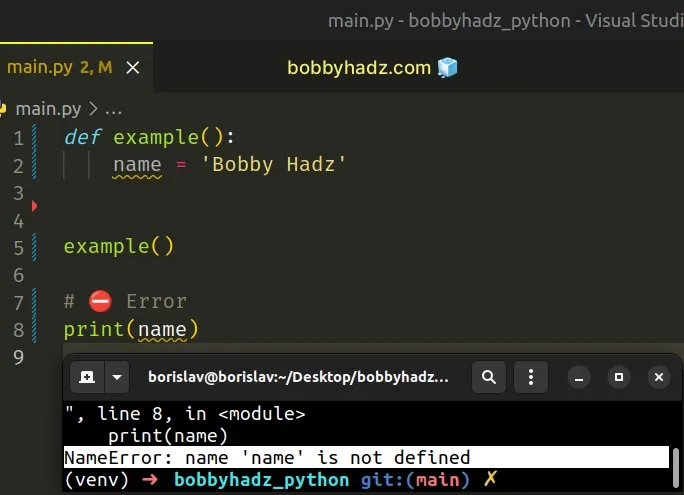
The name variable is declared in the function, so trying to access it from outside causes an error.
Make sure you don't try to access the variable before using the global keyword, otherwise, you'd get the SyntaxError: name 'X' is used prior to global declaration error.
# Returning a value from the function instead
An alternative solution to using the global keyword is to return a value from the function and use the value to reassign the global variable.
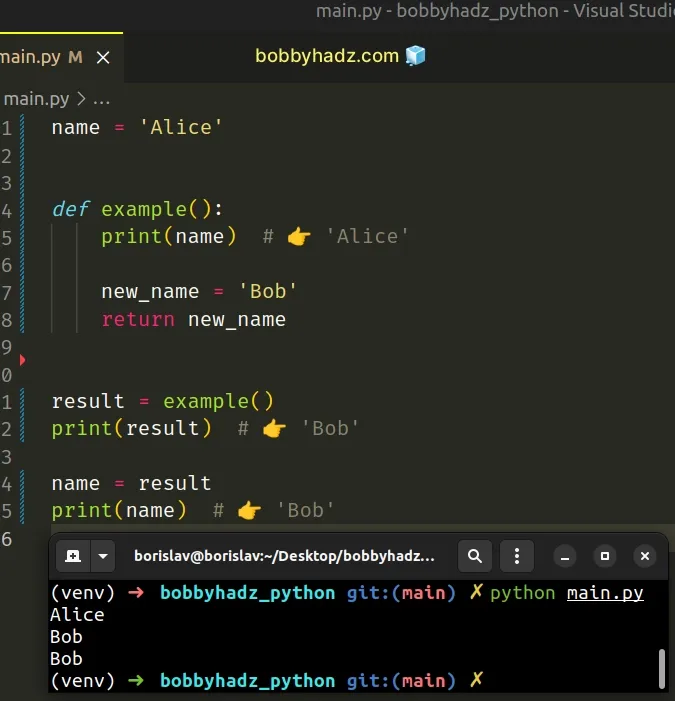
We simply return the value that we eventually use to assign to the name global variable.
# Passing the global variable as an argument to the function
You should also consider passing the global variable as an argument to the function.
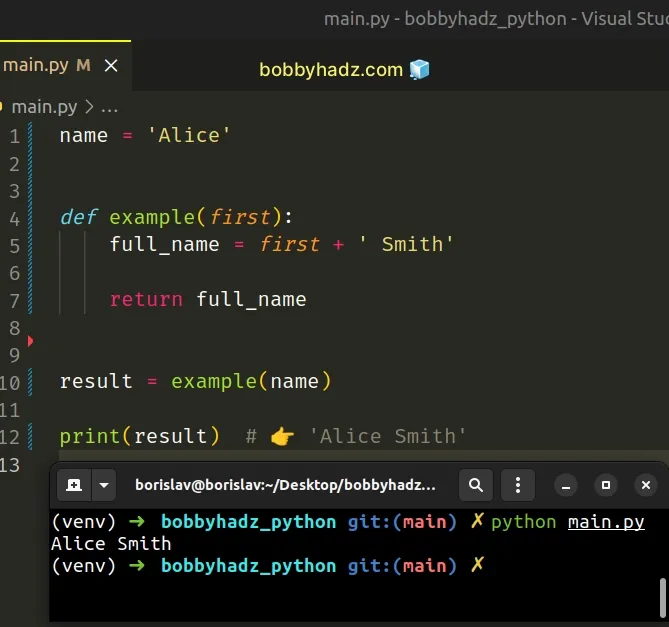
We passed the name global variable as an argument to the function.
If we assign a value to a variable in a function, the variable is assumed to be local unless explicitly declared as global .
# Assigning a value to a local variable from an outer scope
If you have a nested function and are trying to assign a value to the local variables from the outer function, use the nonlocal keyword.
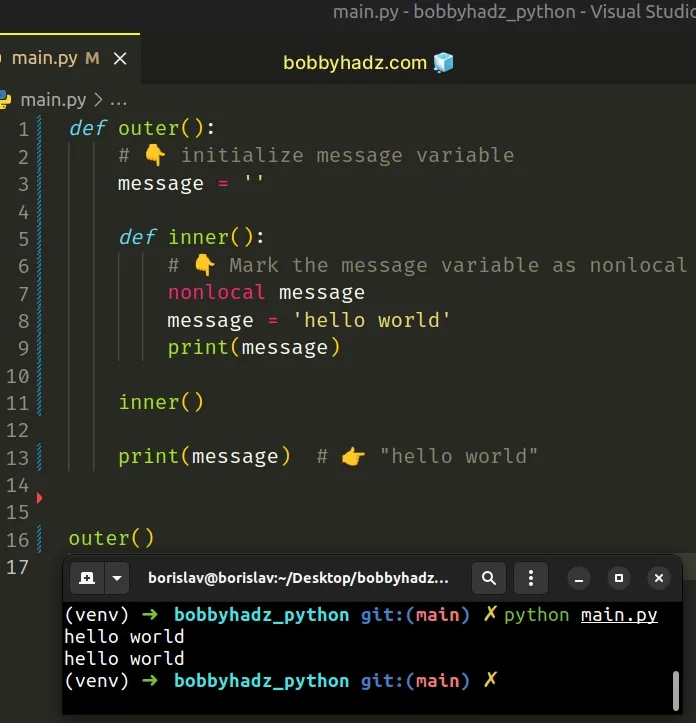
The nonlocal keyword allows us to work with the local variables of enclosing functions.
Had we not used the nonlocal statement, the call to the print() function would have returned an empty string.
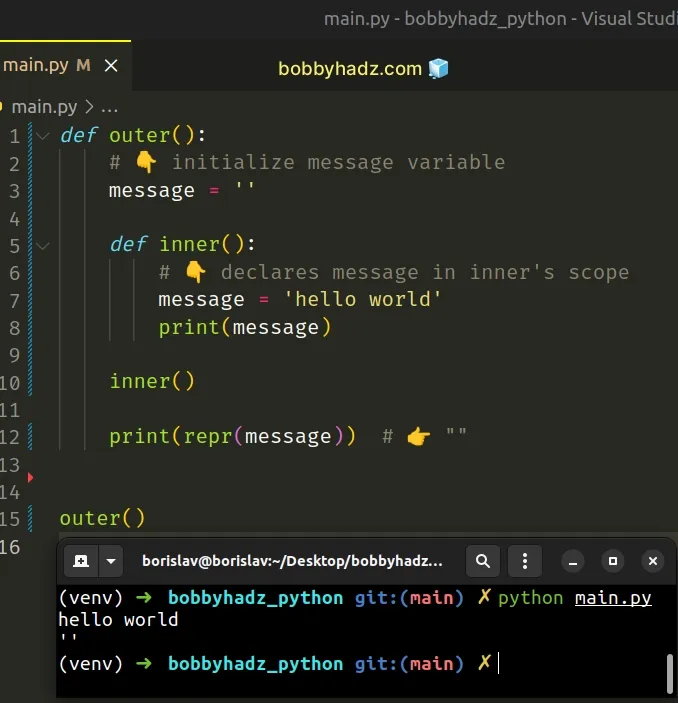
Printing the message variable on the last line of the function shows an empty string because the inner() function has its own scope.
Changing the value of the variable in the inner scope is not possible unless we use the nonlocal keyword.
Instead, the message variable in the inner function simply shadows the variable with the same name from the outer scope.
# Discussion
As shown in this section of the documentation, when you assign a value to a variable inside a function, the variable:
- Becomes local to the scope.
- Shadows any variables from the outer scope that have the same name.
The last line in the example function assigns a value to the name variable, marking it as a local variable and shadowing the name variable from the outer scope.
At the time the print(name) line runs, the name variable is not yet initialized, which causes the error.
The most intuitive way to solve the error is to use the global keyword.
The global keyword is used to indicate to Python that we are actually modifying the value of the name variable from the outer scope.
- If a variable is only referenced inside a function, it is implicitly global.
- If a variable is assigned a value inside a function's body, it is assumed to be local, unless explicitly marked as global .
If you want to read more about why this error occurs, check out [this section] ( this section ) of the docs.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- SyntaxError: name 'X' is used prior to global declaration

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev
How to fix UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment in Python
by Nathan Sebhastian
Posted on May 26, 2023
Reading time: 2 minutes

One error you might encounter when running Python code is:
This error commonly occurs when you reference a variable inside a function without first assigning it a value.
You could also see this error when you forget to pass the variable as an argument to your function.
Let me show you an example that causes this error and how I fix it in practice.
How to reproduce this error
Suppose you have a variable called name declared in your Python code as follows:
Next, you created a function that uses the name variable as shown below:
When you execute the code above, you’ll get this error:
This error occurs because you both assign and reference a variable called name inside the function.
Python thinks you’re trying to assign the local variable name to name , which is not the case here because the original name variable we declared is a global variable.
How to fix this error
To resolve this error, you can change the variable’s name inside the function to something else. For example, name_with_title should work:
As an alternative, you can specify a name parameter in the greet() function to indicate that you require a variable to be passed to the function.
When calling the function, you need to pass a variable as follows:
This code allows Python to know that you intend to use the name variable which is passed as an argument to the function as part of the newly declared name variable.
Still, I would say that you need to use a different name when declaring a variable inside the function. Using the same name might confuse you in the future.
Here’s the best solution to the error:
Now it’s clear that we’re using the name variable given to the function as part of the value assigned to name_with_title . Way to go!
The UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment occurs when you reference a variable inside a function before declaring that variable.
To resolve this error, you need to use a different variable name when referencing the existing variable, or you can also specify a parameter for the function.
I hope this tutorial is useful. See you in other tutorials.
Take your skills to the next level ⚡️
I'm sending out an occasional email with the latest tutorials on programming, web development, and statistics. Drop your email in the box below and I'll send new stuff straight into your inbox!
Hello! This website is dedicated to help you learn tech and data science skills with its step-by-step, beginner-friendly tutorials. Learn statistics, JavaScript and other programming languages using clear examples written for people.
Learn more about this website
Connect with me on Twitter
Or LinkedIn
Type the keyword below and hit enter
Click to see all tutorials tagged with:

Python UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment
by Suf | Programming , Python , Tips
If you try to reference a local variable before assigning a value to it within the body of a function, you will encounter the UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment.
The preferable way to solve this error is to pass parameters to your function, for example:
Alternatively, you can declare the variable as global to access it while inside a function. For example,
This tutorial will go through the error in detail and how to solve it with code examples .
Table of contents
What is scope in python, unboundlocalerror: local variable referenced before assignment, solution #1: passing parameters to the function, solution #2: use global keyword, solution #1: include else statement, solution #2: use global keyword.
Scope refers to a variable being only available inside the region where it was created. A variable created inside a function belongs to the local scope of that function, and we can only use that variable inside that function.
A variable created in the main body of the Python code is a global variable and belongs to the global scope. Global variables are available within any scope, global and local.
UnboundLocalError occurs when we try to modify a variable defined as local before creating it. If we only need to read a variable within a function, we can do so without using the global keyword. Consider the following example that demonstrates a variable var created with global scope and accessed from test_func :
If we try to assign a value to var within test_func , the Python interpreter will raise the UnboundLocalError:
This error occurs because when we make an assignment to a variable in a scope, that variable becomes local to that scope and overrides any variable with the same name in the global or outer scope.
var +=1 is similar to var = var + 1 , therefore the Python interpreter should first read var , perform the addition and assign the value back to var .
var is a variable local to test_func , so the variable is read or referenced before we have assigned it. As a result, the Python interpreter raises the UnboundLocalError.
Example #1: Accessing a Local Variable
Let’s look at an example where we define a global variable number. We will use the increment_func to increase the numerical value of number by 1.
Let’s run the code to see what happens:
The error occurs because we tried to read a local variable before assigning a value to it.
We can solve this error by passing a parameter to increment_func . This solution is the preferred approach. Typically Python developers avoid declaring global variables unless they are necessary. Let’s look at the revised code:
We have assigned a value to number and passed it to the increment_func , which will resolve the UnboundLocalError. Let’s run the code to see the result:
We successfully printed the value to the console.
We also can solve this error by using the global keyword. The global statement tells the Python interpreter that inside increment_func , the variable number is a global variable even if we assign to it in increment_func . Let’s look at the revised code:
Let’s run the code to see the result:
Example #2: Function with if-elif statements
Let’s look at an example where we collect a score from a player of a game to rank their level of expertise. The variable we will use is called score and the calculate_level function takes in score as a parameter and returns a string containing the player’s level .
In the above code, we have a series of if-elif statements for assigning a string to the level variable. Let’s run the code to see what happens:
The error occurs because we input a score equal to 40 . The conditional statements in the function do not account for a value below 55 , therefore when we call the calculate_level function, Python will attempt to return level without any value assigned to it.
We can solve this error by completing the set of conditions with an else statement. The else statement will provide an assignment to level for all scores lower than 55 . Let’s look at the revised code:
In the above code, all scores below 55 are given the beginner level. Let’s run the code to see what happens:
We can also create a global variable level and then use the global keyword inside calculate_level . Using the global keyword will ensure that the variable is available in the local scope of the calculate_level function. Let’s look at the revised code.
In the above code, we put the global statement inside the function and at the beginning. Note that the “default” value of level is beginner and we do not include the else statement in the function. Let’s run the code to see the result:
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial! The UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment occurs when you try to reference a local variable before assigning a value to it. Preferably, you can solve this error by passing parameters to your function. Alternatively, you can use the global keyword.
If you have if-elif statements in your code where you assign a value to a local variable and do not account for all outcomes, you may encounter this error. In which case, you must include an else statement to account for the missing outcome.
For further reading on Python code blocks and structure, go to the article: How to Solve Python IndentationError: unindent does not match any outer indentation level .
Go to the online courses page on Python to learn more about Python for data science and machine learning.
Have fun and happy researching!
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
[SOLVED] Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment

Python treats variables referenced only inside a function as global variables. Any variable assigned to a function’s body is assumed to be a local variable unless explicitly declared as global.
Why Does This Error Occur?
Unboundlocalerror: local variable referenced before assignment occurs when a variable is used before its created. Python does not have the concept of variable declarations. Hence it searches for the variable whenever used. When not found, it throws the error.
Before we hop into the solutions, let’s have a look at what is the global and local variables.

Local Variable Declarations vs. Global Variable Declarations
![unboundlocalerror local variable 'fig' referenced before assignment plotly [Fixed] typeerror can’t compare datetime.datetime to datetime.date](https://www.pythonpool.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/typeerror-cant-compare-datetime.datetime-to-datetime.date_-300x157.webp)
Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment Error with Explanation
Try these examples yourself using our Online Compiler.
Let’s look at the following function:
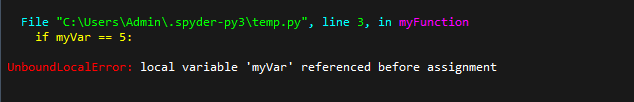
Explanation
The variable myVar has been assigned a value twice. Once before the declaration of myFunction and within myFunction itself.
Using Global Variables
Passing the variable as global allows the function to recognize the variable outside the function.
Create Functions that Take in Parameters
Instead of initializing myVar as a global or local variable, it can be passed to the function as a parameter. This removes the need to create a variable in memory.
UnboundLocalError: local variable ‘DISTRO_NAME’
This error may occur when trying to launch the Anaconda Navigator in Linux Systems.
Upon launching Anaconda Navigator, the opening screen freezes and doesn’t proceed to load.
Try and update your Anaconda Navigator with the following command.
If solution one doesn’t work, you have to edit a file located at
After finding and opening the Python file, make the following changes:
In the function on line 159, simply add the line:
DISTRO_NAME = None
Save the file and re-launch Anaconda Navigator.
DJANGO – Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment [Form]
The program takes information from a form filled out by a user. Accordingly, an email is sent using the information.
Upon running you get the following error:
We have created a class myForm that creates instances of Django forms. It extracts the user’s name, email, and message to be sent.
A function GetContact is created to use the information from the Django form and produce an email. It takes one request parameter. Prior to sending the email, the function verifies the validity of the form. Upon True , .get() function is passed to fetch the name, email, and message. Finally, the email sent via the send_mail function
Why does the error occur?
We are initializing form under the if request.method == “POST” condition statement. Using the GET request, our variable form doesn’t get defined.
Local variable Referenced before assignment but it is global
This is a common error that happens when we don’t provide a value to a variable and reference it. This can happen with local variables. Global variables can’t be assigned.
This error message is raised when a variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value within the local scope of a function, even though it is a global variable.
Here’s an example to help illustrate the problem:
In this example, x is a global variable that is defined outside of the function my_func(). However, when we try to print the value of x inside the function, we get a UnboundLocalError with the message “local variable ‘x’ referenced before assignment”.
This is because the += operator implicitly creates a local variable within the function’s scope, which shadows the global variable of the same name. Since we’re trying to access the value of x before it’s been assigned a value within the local scope, the interpreter raises an error.
To fix this, you can use the global keyword to explicitly refer to the global variable within the function’s scope:
However, in the above example, the global keyword tells Python that we want to modify the value of the global variable x, rather than creating a new local variable. This allows us to access and modify the global variable within the function’s scope, without causing any errors.
Local variable ‘version’ referenced before assignment ubuntu-drivers
This error occurs with Ubuntu version drivers. To solve this error, you can re-specify the version information and give a split as 2 –
Here, p_name means package name.
With the help of the threading module, you can avoid using global variables in multi-threading. Make sure you lock and release your threads correctly to avoid the race condition.
When a variable that is created locally is called before assigning, it results in Unbound Local Error in Python. The interpreter can’t track the variable.
Therefore, we have examined the local variable referenced before the assignment Exception in Python. The differences between a local and global variable declaration have been explained, and multiple solutions regarding the issue have been provided.
Trending Python Articles
![unboundlocalerror local variable 'fig' referenced before assignment plotly [Fixed] nameerror: name Unicode is not defined](https://www.pythonpool.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Fixed-nameerror-name-Unicode-is-not-defined-300x157.webp)
- Free Python 3 Tutorial
- Control Flow
- Exception Handling
- Python Programs
- Python Projects
- Python Interview Questions
- Python Database
- Data Science With Python
- Machine Learning with Python
- Python Program That Prints Out the Decimal Equivalents of 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, . . . ,1/10
- How to Convert PIL Image into pygame surface image?
- Python program to print the binary value of the numbers from 1 to N
- Python Program for Sum the digits of a given number
- Python program to print number of bits to store an integer and also the number in Binary format
- Python program to get all pairwise combinations from a list
- Python program to repeat M characters of a string N times
- How to format a string using a dictionary in Python
- Python program to convert binary to ASCII
- Python program to convert unix timestamp string to readable date
- Python program to print an array of bytes representing an integer
- Python Program to Multiply Two Binary Numbers
- Python Program to Find Sum of First and Last Digit
- Python Program to Sort Words in Alphabetical Order
- Python program to convert integer to roman
- Python - Lambda Function to Check if value is in a List
- Python - Get first element from a List of tuples
- Get Your System Information - Using Python Script
- Python - Get the object with the max attribute value in a list of objects
UnboundLocalError Local variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python
Handling errors is an integral part of writing robust and reliable Python code. One common stumbling block that developers often encounter is the “UnboundLocalError” raised within a try-except block. This error can be perplexing for those unfamiliar with its nuances but fear not – in this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the UnboundLocalError and provide a comprehensive guide on how to effectively use try-except statements to resolve it.
What is UnboundLocalError Local variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python?
The UnboundLocalError occurs when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value within a function or method. This error typically surfaces when utilizing try-except blocks to handle exceptions, creating a puzzle for developers trying to comprehend its origins and find a solution.
Why does UnboundLocalError: Local variable Referenced Before Assignment Occur?
below, are the reasons of occurring “Unboundlocalerror: Try Except Statements” in Python :
Variable Assignment Inside Try Block
Reassigning a global variable inside except block.
- Accessing a Variable Defined Inside an If Block
In the below code, example_function attempts to execute some_operation within a try-except block. If an exception occurs, it prints an error message. However, if no exception occurs, it prints the value of the variable result outside the try block, leading to an UnboundLocalError since result might not be defined if an exception was caught.
In below code , modify_global function attempts to increment the global variable global_var within a try block, but it raises an UnboundLocalError. This error occurs because the function treats global_var as a local variable due to the assignment operation within the try block.
Solution for UnboundLocalError Local variable Referenced Before Assignment
Below, are the approaches to solve “Unboundlocalerror: Try Except Statements”.
Initialize Variables Outside the Try Block
Avoid reassignment of global variables.
In modification to the example_function is correct. Initializing the variable result before the try block ensures that it exists even if an exception occurs within the try block. This helps prevent UnboundLocalError when trying to access result in the print statement outside the try block.
Below, code calculates a new value ( local_var ) based on the global variable and then prints both the local and global variables separately. It demonstrates that the global variable is accessed directly without being reassigned within the function.
In conclusion , To fix “UnboundLocalError” related to try-except statements, ensure that variables used within the try block are initialized before the try block starts. This can be achieved by declaring the variables with default values or assigning them None outside the try block. Additionally, when modifying global variables within a try block, use the `global` keyword to explicitly declare them.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Python Errors
- 10 Ways to Use Slack for Effective Communication
- 10 Ways to Use Google Docs for Collaborative Writing
- NEET MDS 2024 Result: Toppers List, Category-wise Cutoff, and Important Dates
- NDA Admit Card 2024 Live Updates: Download Your Hall Ticket Soon on upsc.gov.in!
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests...
Provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement . We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
UnboundLocalError: local variable 'pdf' referenced before assignment #172
awalker4 commented Aug 1, 2023 • edited
Successfully merging a pull request may close this issue.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
UnboundLocalError: local variable 'fig' referenced before assignment. Traceback (most recent call last): File "C:\Users\Local\Temp\ipykernel_20424\180331076.py", line 16, in update_graphs. File "C:\Users\Lib\site-packages\plotly\express_chart_types.py", line 368, in bar return make_figure
File "weird.py", line 5, in main. print f(3) UnboundLocalError: local variable 'f' referenced before assignment. Python sees the f is used as a local variable in [f for f in [1, 2, 3]], and decides that it is also a local variable in f(3). You could add a global f statement: def f(x): return x. def main():
If a variable is assigned a value in a function's body, it is a local variable unless explicitly declared as global. # Local variables shadow global ones with the same name You could reference the global name variable from inside the function but if you assign a value to the variable in the function's body, the local variable shadows the global one.
The UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment occurs when you reference a variable inside a function before declaring that variable. To resolve this error, you need to use a different variable name when referencing the existing variable, or you can also specify a parameter for the function. I hope this tutorial is useful.
After upgrading from 3.7.1 to 3.8.1 (as installed via pip/PyPI), simple plots break with UnboundLocalError: local variable 'config_dict' referenced before assignment. Minimum working example: import plotly.graph_objs as go go.Figure() Ex...
UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment. Example #1: Accessing a Local Variable. Solution #1: Passing Parameters to the Function. Solution #2: Use Global Keyword. Example #2: Function with if-elif statements. Solution #1: Include else statement. Solution #2: Use global keyword. Summary.
Even with an "if ... else" statement, it should fail. I leave the many ifs even though that is bad practice just to show that it is not about adding an else or not. In a try statement, an except will not change it either, not speaking of finally.What you need is to draw the declaration of a variable before any if block (or before any try block or other cascading code blocks).
Local Variables Global Variables; A local variable is declared primarily within a Python function.: Global variables are in the global scope, outside a function. A local variable is created when the function is called and destroyed when the execution is finished.
Output. Hangup (SIGHUP) Traceback (most recent call last): File "Solution.py", line 7, in <module> example_function() File "Solution.py", line 4, in example_function x += 1 # Trying to modify global variable 'x' without declaring it as global UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment Solution for Local variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python
Conclusion. In conclusion , To fix "UnboundLocalError" related to try-except statements, ensure that variables used within the try block are initialized before the try block starts.
It gives me following error: UnboundLocalError: local variable 'a' referenced before assignment whic... Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
UnboundLocalError: local variable 'fig' referenced before assignment #2. laudv opened this issue Sep 2, 2020 · 0 comments Comments. Copy link laudv commented Sep 2, 2020. ... UnboundLocalError: local variable 'fig' referenced before assignment ...
To make this work, you need to move the assignment to won inside main(): def main(): won = 0 ... If you want to make the value of won available outside main() , I'd suggest returning it from the function like so:
To prevent UnboundLocalError, the secret is in scope declaration. Declare a variable as global within a function if you're modifying a global variable. Alternatively, use nonlocal for variables in nested functions. python Global variable fix def func(): global var Hello, Global! var = 1 Changed it, see? Nested function fix def outer(): var = 0 def inner(): nonlocal var Outer! Lemme borrow this ...
UnboundLocalError: local variable 'fig' referenced before assignment #950. eyildiz-ugoe opened this issue Sep 20, 2018 · 1 comment Comments. Copy link eyildiz-ugoe commented Sep 20, 2018. ... (3,)) UnboundLocalError: local variable 'fig' referenced before assignment ...
Thanks for contributing an answer to Stack Overflow! Please be sure to answer the question.Provide details and share your research! But avoid …. Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers.
If the class definition doesn't exist in the scope where you use it, Python will call it a local variable. So the problem is that somehow that class definition didn't happen. - Andrew McGregor
UnboundLocalError: local variable 'pdf' referenced before assignment #172. Closed awalker4 opened this issue Aug 1, 2023 · 0 comments · Fixed by #199. Closed UnboundLocalError: local variable 'pdf' referenced before assignment #172. awalker4 opened this issue Aug 1, 2023 · 0 comments · Fixed by #199. Comments.