

100 Reported Speech Examples: How To Change Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of communicating what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. For example, if your friend said, “ I am going to the store ,” in reported speech, you might convey this as, “ My friend said he was going to the store. ” Reported speech is common in both spoken and written language, especially in storytelling, news reporting, and everyday conversations.
Reported speech can be quite challenging for English language learners because in order to change direct speech into reported speech, one must change the perspective and tense of what was said by the original speaker or writer. In this guide, we will explain in detail how to change direct speech into indirect speech and provide lots of examples of reported speech to help you understand. Here are the key aspects of converting direct speech into reported speech.
Reported Speech: Changing Pronouns
Pronouns are usually changed to match the perspective of the person reporting the speech. For example, “I” in direct speech may become “he” or “she” in reported speech, depending on the context. Here are some example sentences:
- Direct : “I am going to the park.” Reported : He said he was going to the park .
- Direct : “You should try the new restaurant.” Reported : She said that I should try the new restaurant.
- Direct : “We will win the game.” Reported : They said that they would win the game.
- Direct : “She loves her new job.” Reported : He said that she loves her new job.
- Direct : “He can’t come to the party.” Reported : She said that he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct : “It belongs to me.” Reported : He said that it belonged to him .
- Direct : “They are moving to a new city.” Reported : She said that they were moving to a new city.
- Direct : “You are doing a great job.” Reported : He told me that I was doing a great job.
- Direct : “I don’t like this movie.” Reported : She said that she didn’t like that movie.
- Direct : “We have finished our work.” Reported : They said that they had finished their work.
- Direct : “You will need to sign here.” Reported : He said that I would need to sign there.
- Direct : “She can solve the problem.” Reported : He said that she could solve the problem.
- Direct : “He was not at home yesterday.” Reported : She said that he had not been at home the day before.
- Direct : “It is my responsibility.” Reported : He said that it was his responsibility.
- Direct : “We are planning a surprise.” Reported : They said that they were planning a surprise.
Reported Speech: Reporting Verbs
In reported speech, various reporting verbs are used depending on the nature of the statement or the intention behind the communication. These verbs are essential for conveying the original tone, intent, or action of the speaker. Here are some examples demonstrating the use of different reporting verbs in reported speech:
- Direct: “I will help you,” she promised . Reported: She promised that she would help me.
- Direct: “You should study harder,” he advised . Reported: He advised that I should study harder.
- Direct: “I didn’t take your book,” he denied . Reported: He denied taking my book .
- Direct: “Let’s go to the cinema,” she suggested . Reported: She suggested going to the cinema .
- Direct: “I love this song,” he confessed . Reported: He confessed that he loved that song.
- Direct: “I haven’t seen her today,” she claimed . Reported: She claimed that she hadn’t seen her that day.
- Direct: “I will finish the project,” he assured . Reported: He assured me that he would finish the project.
- Direct: “I’m not feeling well,” she complained . Reported: She complained of not feeling well.
- Direct: “This is how you do it,” he explained . Reported: He explained how to do it.
- Direct: “I saw him yesterday,” she stated . Reported: She stated that she had seen him the day before.
- Direct: “Please open the window,” he requested . Reported: He requested that I open the window.
- Direct: “I can win this race,” he boasted . Reported: He boasted that he could win the race.
- Direct: “I’m moving to London,” she announced . Reported: She announced that she was moving to London.
- Direct: “I didn’t understand the instructions,” he admitted . Reported: He admitted that he didn’t understand the instructions.
- Direct: “I’ll call you tonight,” she promised . Reported: She promised to call me that night.
Reported Speech: Tense Shifts
When converting direct speech into reported speech, the verb tense is often shifted back one step in time. This is known as the “backshift” of tenses. It’s essential to adjust the tense to reflect the time elapsed between the original speech and the reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how different tenses in direct speech are transformed in reported speech:
- Direct: “I am eating.” Reported: He said he was eating.
- Direct: “They will go to the park.” Reported: She mentioned they would go to the park.
- Direct: “We have finished our homework.” Reported: They told me they had finished their homework.
- Direct: “I do my exercises every morning.” Reported: He explained that he did his exercises every morning.
- Direct: “She is going to start a new job.” Reported: He heard she was going to start a new job.
- Direct: “I can solve this problem.” Reported: She said she could solve that problem.
- Direct: “We are visiting Paris next week.” Reported: They said they were visiting Paris the following week.
- Direct: “I will be waiting outside.” Reported: He stated he would be waiting outside.
- Direct: “They have been studying for hours.” Reported: She mentioned they had been studying for hours.
- Direct: “I can’t understand this chapter.” Reported: He complained that he couldn’t understand that chapter.
- Direct: “We were planning a surprise.” Reported: They told me they had been planning a surprise.
- Direct: “She has to complete her assignment.” Reported: He said she had to complete her assignment.
- Direct: “I will have finished the project by Monday.” Reported: She stated she would have finished the project by Monday.
- Direct: “They are going to hold a meeting.” Reported: She heard they were going to hold a meeting.
- Direct: “I must leave.” Reported: He said he had to leave.
Reported Speech: Changing Time and Place References
When converting direct speech into reported speech, references to time and place often need to be adjusted to fit the context of the reported speech. This is because the time and place relative to the speaker may have changed from the original statement to the time of reporting. Here are some examples to illustrate how time and place references change:
- Direct: “I will see you tomorrow .” Reported: He said he would see me the next day .
- Direct: “We went to the park yesterday .” Reported: They said they went to the park the day before .
- Direct: “I have been working here since Monday .” Reported: She mentioned she had been working there since Monday .
- Direct: “Let’s meet here at noon.” Reported: He suggested meeting there at noon.
- Direct: “I bought this last week .” Reported: She said she had bought it the previous week .
- Direct: “I will finish this by tomorrow .” Reported: He stated he would finish it by the next day .
- Direct: “She will move to New York next month .” Reported: He heard she would move to New York the following month .
- Direct: “They were at the festival this morning .” Reported: She said they were at the festival that morning .
- Direct: “I saw him here yesterday.” Reported: She mentioned she saw him there the day before.
- Direct: “We will return in a week .” Reported: They said they would return in a week .
- Direct: “I have an appointment today .” Reported: He said he had an appointment that day .
- Direct: “The event starts next Friday .” Reported: She mentioned the event starts the following Friday .
- Direct: “I lived in Berlin two years ago .” Reported: He stated he had lived in Berlin two years before .
- Direct: “I will call you tonight .” Reported: She said she would call me that night .
- Direct: “I was at the office yesterday .” Reported: He mentioned he was at the office the day before .
Reported Speech: Question Format
When converting questions from direct speech into reported speech, the format changes significantly. Unlike statements, questions require rephrasing into a statement format and often involve the use of introductory verbs like ‘asked’ or ‘inquired’. Here are some examples to demonstrate how questions in direct speech are converted into statements in reported speech:
- Direct: “Are you coming to the party?” Reported: She asked if I was coming to the party.
- Direct: “What time is the meeting?” Reported: He inquired what time the meeting was.
- Direct: “Why did you leave early?” Reported: They wanted to know why I had left early.
- Direct: “Can you help me with this?” Reported: She asked if I could help her with that.
- Direct: “Where did you buy this?” Reported: He wondered where I had bought that.
- Direct: “Who is going to the concert?” Reported: They asked who was going to the concert.
- Direct: “How do you solve this problem?” Reported: She questioned how to solve that problem.
- Direct: “Is this the right way to the station?” Reported: He inquired whether it was the right way to the station.
- Direct: “Do you know her name?” Reported: They asked if I knew her name.
- Direct: “Why are they moving out?” Reported: She wondered why they were moving out.
- Direct: “Have you seen my keys?” Reported: He asked if I had seen his keys.
- Direct: “What were they talking about?” Reported: She wanted to know what they had been talking about.
- Direct: “When will you return?” Reported: He asked when I would return.
- Direct: “Can she drive a manual car?” Reported: They inquired if she could drive a manual car.
- Direct: “How long have you been waiting?” Reported: She asked how long I had been waiting.
Reported Speech: Omitting Quotation Marks
In reported speech, quotation marks are not used, differentiating it from direct speech which requires them to enclose the spoken words. Reported speech summarizes or paraphrases what someone said without the need for exact wording. Here are examples showing how direct speech with quotation marks is transformed into reported speech without them:
- Direct: “I am feeling tired,” she said. Reported: She said she was feeling tired.
- Direct: “We will win the game,” he exclaimed. Reported: He exclaimed that they would win the game.
- Direct: “I don’t like apples,” the boy declared. Reported: The boy declared that he didn’t like apples.
- Direct: “You should visit Paris,” she suggested. Reported: She suggested that I should visit Paris.
- Direct: “I will be late,” he warned. Reported: He warned that he would be late.
- Direct: “I can’t believe you did that,” she expressed in surprise. Reported: She expressed her surprise that I had done that.
- Direct: “I need help with this task,” he admitted. Reported: He admitted that he needed help with the task.
- Direct: “I have never been to Italy,” she confessed. Reported: She confessed that she had never been to Italy.
- Direct: “We saw a movie last night,” they mentioned. Reported: They mentioned that they saw a movie the night before.
- Direct: “I am learning to play the piano,” he revealed. Reported: He revealed that he was learning to play the piano.
- Direct: “You must finish your homework,” she instructed. Reported: She instructed that I must finish my homework.
- Direct: “I will call you tomorrow,” he promised. Reported: He promised that he would call me the next day.
- Direct: “I have finished my assignment,” she announced. Reported: She announced that she had finished her assignment.
- Direct: “I cannot attend the meeting,” he apologized. Reported: He apologized for not being able to attend the meeting.
- Direct: “I don’t remember where I put it,” she confessed. Reported: She confessed that she didn’t remember where she put it.
Reported Speech Quiz
Thanks for reading! I hope you found these reported speech examples useful. Before you go, why not try this Reported Speech Quiz and see if you can change indirect speech into reported speech?
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
Indirect speech: typical errors.
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
acting or speaking together, or at the same time

Alike and analogous (Talking about similarities, Part 1)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Indirect Speech Definition and Examples
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Indirect speech is a report on what someone else said or wrote without using that person's exact words (which is called direct speech). It's also called indirect discourse or reported speech .
Direct vs. Indirect Speech
In direct speech , a person's exact words are placed in quotation marks and set off with a comma and a reporting clause or signal phrase , such as "said" or "asked." In fiction writing, using direct speech can display the emotion of an important scene in vivid detail through the words themselves as well as the description of how something was said. In nonfiction writing or journalism, direct speech can emphasize a particular point, by using a source's exact words.
Indirect speech is paraphrasing what someone said or wrote. In writing, it functions to move a piece along by boiling down points that an interview source made. Unlike direct speech, indirect speech is not usually placed inside quote marks. However, both are attributed to the speaker because they come directly from a source.
How to Convert
In the first example below, the verb in the present tense in the line of direct speech ( is) may change to the past tense ( was ) in indirect speech, though it doesn't necessarily have to with a present-tense verb. If it makes sense in context to keep it present tense, that's fine.
- Direct speech: "Where is your textbook? " the teacher asked me.
- Indirect speech: The teacher asked me where my textbook was.
- Indirect speech: The teacher asked me where my textbook is.
Keeping the present tense in reported speech can give the impression of immediacy, that it's being reported soon after the direct quote,such as:
- Direct speech: Bill said, "I can't come in today, because I'm sick."
- Indirect speech: Bill said (that) he can't come in today because he's sick.
Future Tense
An action in the future (present continuous tense or future) doesn't have to change verb tense, either, as these examples demonstrate.
- Direct speech: Jerry said, "I'm going to buy a new car."
- Indirect speech: Jerry said (that) he's going to buy a new car.
- Direct speech: Jerry said, "I will buy a new car."
- Indirect speech: Jerry said (that) he will buy a new car.
Indirectly reporting an action in the future can change verb tenses when needed. In this next example, changing the am going to was going implies that she has already left for the mall. However, keeping the tense progressive or continuous implies that the action continues, that she's still at the mall and not back yet.
- Direct speech: She said, "I'm going to the mall."
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she was going to the mall.
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she is going to the mall.
Other Changes
With a past-tense verb in the direct quote, the verb changes to past perfect.
- Direct speech: She said, "I went to the mall."
- Indirect speech: She said (that) she had gone to the mall.
Note the change in first person (I) and second person (your) pronouns and word order in the indirect versions. The person has to change because the one reporting the action is not the one actually doing it. Third person (he or she) in direct speech remains in the third person.
Free Indirect Speech
In free indirect speech, which is commonly used in fiction, the reporting clause (or signal phrase) is omitted. Using the technique is a way to follow a character's point of view—in third-person limited omniscient—and show her thoughts intermingled with narration.
Typically in fiction italics show a character's exact thoughts, and quote marks show dialogue. Free indirect speech makes do without the italics and simply combines the internal thoughts of the character with the narration of the story. Writers who have used this technique include James Joyce, Jane Austen, Virginia Woolf, Henry James, Zora Neale Hurston, and D.H. Lawrence.
- Indirect Speech in the English Language
- Direct Speech Definition and Examples
- French Grammar: Direct and Indirect Speech
- How to Teach Reported Speech
- Definition and Examples of Direct Quotations
- How to Use Indirect Quotations in Writing for Complete Clarity
- Backshift (Sequence-of-Tense Rule in Grammar)
- What Is Attribution in Writing?
- Indirect Question: Definition and Examples
- Reported Speech
- Using Reported Speech: ESL Lesson Plan
- Constructed Dialogue in Storytelling and Conversation
- The Subjunctive Present in German
- What Are Reporting Verbs in English Grammar?
- Preterit(e) Verbs
- Dialogue Guide Definition and Examples

- Practical Tips
- Spoken English

Direct To Indirect Speech: Complete Rules With Examples

Direct and indirect speech is often a confusing topic for English learners. The basic idea is this:
- In direct speech, we quote a person’s exact words. For example, Meera said, “I can speak English fluently.”
- In indirect speech, we do not quote the person’s exact words but provide a summary of what was said. For example, Meera said that she could speak English fluently.
The critical difference is that direct speech uses the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech summarizes what was said. While the definition is simple, the challenge for English language learners is using the proper tenses when converting a phrase from direct to indirect and vice versa.
Why Should You Learn Direct To Indirect Speech Rules?
There are several occasions – in your professional and personal – where you might need to describe an action or event to others. For example, you might have to repeat the team leader’s instructions to your teammates at the workplace. In this scenario, you convert your team leader’s direct to indirect speech.
Knowing conversion rules can help you present or describe the event correctly without making any grammatical errors or spoken English blunders.
In this post, we walk you through the rules of converting direct to indirect speech, helping you speak English fluently online and offline.
How To Use Direct Speech?
The rule is simple: Use direct speech when you want to repeat what someone says as it is, and ensure that the spoken text is sandwiched between quotation (speech) marks.
John said, “I want to learn to speak English fluently.”
It’s common to see the direct speech in newspaper articles and books. For example,
The District Collector announced, “The Chief Minister will inaugurate the city centre next week.”
As you can notice, in direct speech, we use the verb say (said in the past tense) to denote what was spoken. You can also use related verbs like ‘asked,’ ‘replied,’ ‘told,’ ‘informed,’ ‘shouted,’ etc.
How To Use Indirect Speech?
Indirect speech is also reported speech, as we use it to inform/repeat what someone else said. Using the two examples above, we can convert it into indirect speech as follows:
John said that he wanted to learn to speak English fluently.
The District Collector announced that the Chief Minister would inaugurate the city centre the week after.
Another example,
Direct Speech: “I feel cold.”
Indirect Speech: She says that she feels cold.
If you notice these examples carefully, you can see that the tense changes when converting from direct to indirect speech. To illustrate this point, in the following example, direct speech is in the present simple tense, while indirect speech is written in the simple past tense.
Direct Speech: “I live in the city centre.”
Indirect Speech: He said he lived in the city centre.
Tense Change Rules: Direct To Indirect Speech
Similarly, other tenses follow similar rules when changing from direct to indirect speech. Use the following table to help you better understand the tense change rules:
Modal Verbs: Direct To Indirect Speech
When converting direct to indirect speech, you must change modal verbs accordingly. Here are a few examples to help you understand better:
Changing Time Expressions: Direct To Indirect Speech
Sometimes it becomes necessary to change the time expressions when converting from direct to indirect speech. A few examples,
- Direct speech: Sheila said, “I am meeting my brother tomorrow.”
- Indirect speech: Sheila said that she was meeting her brother the following day.
Here are a few examples of other typical time expressions and how they change:
Changing Place Expressions: Direct To Indirect Speech
Like time expressions, you might also have to change words representing places when reporting indirect speech. For example,
- Direct speech: “It’s raining here.”
- Indirect speech: She said that it was raining there.
Here are a few examples of other common place expressions and how they change:
However, the place words only change when you report something from a different location.
Over To You
Now that you’ve seen the rules to convert direct to indirect speech, it’s time to put them into practice. The most efficient way to improve English speaking is to practice what you’ve learned. Join online English-speaking practice classes to gain confidence and mastery in your daily conversations.
Recent Posts
Como usar uma calculadora martingale para melhorar suas estratégias de opções binárias, 35 positive words to describe your best female friend, 20 stylish and popular idioms related to success, how can you teach your child to speak english at home, 40 different ways to say happy birthday.
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- August 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
Related Posts

Broadening Your Vocabulary: Unlocking 40 Altern...

Using Instagram To Learn English: Top 10 Accoun...

50 Commonly Used English Abbreviations For Text...

Never Miss a Blog
Enter your Email ID below to get our insightful blogs into your inbox.

My English Grammar
Ultimate English Grammar, Vocabulary, and Names Database
Indirect Speech
Introduction.
Communicating effectively requires us to master a variety of grammatical rules. One such critical element is the appropriate use of ‘Indirect Speech’, also known as reported speech. Indirect speech allows us to convey what another person has said without quoting them directly.
Table of Contents
What is Indirect Speech?
Indirect Speech is a way of expressing the words or utterances of a speaker in a reported manner. In contrast to direct speech, where the original speaker’s words are quoted verbatim, indirect speech is more about reporting the essence or meaning of what the speaker said rather than quoting them exactly.
For example:
Direct Speech: Lisa said, “I am going shopping.”
Indirect Speech: Lisa said that she was going shopping.
Changes in Verb Tenses
Tense shifts.
When you transform sentences from direct to indirect speech, the verb tenses typically shift back a step in time. This phenomenon is often referred to as ‘sequence of tenses’ or ‘backshift’. However, the backshift is not applied if the spoken words still apply at the time of reporting or the words express a universal truth.
Here are the typical conversions:
- Present Simple changes to Past Simple. E.g., “I like pizza” becomes “She said that she liked pizza.”
- Present Continuous changes to Past Continuous. E.g., “I am eating pizza” becomes “She said that she was eating pizza.”
- Will changes to would. E.g., “I will go” becomes “He said that he would go.”
- Past Simple changes to Past Perfect. E.g., “I ate lunch” becomes “She said that she had eaten lunch.”
Exceptions to Tense Shifts
There are exceptions to these rules, such as when the direct speech element is a universal truth or a fact. Consider the below examples:
- John said, “The sun rises in the east” becomes “John said that the sun rises in the east.”
- She said, “Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius” becomes “She said that water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.”
Changes in Pronouns and Time Expressions
Pronoun changes.
When changing from direct to indirect speech, it’s often necessary to modify the pronouns to match the speaker and listener’s point of view. For example:
- “I love you,” he said. (Direct)
- He said he loved me. (Indirect)
Time Expression Changes
Time expressions often undergo necessary modifications when moving from direct to indirect speech. Here are some examples:
- “Today” becomes “That day.”
- “Now” becomes “Then.”
- “Tomorrow” becomes “The next day” or “the following day.”
- “Next week” becomes “The following week.”
Indirect Commands and Requests
We can also convey commands and requests indirectly. For indirect commands, we use “to” + base verb and for indirect requests we use “if” or “whether” + subject + could/would, followed by the base verb.
- Direct: “Close the window!” – Indirect: He told me to close the window.
- Direct: “Can you lend me the book?” – Indirect: She asked if I could lend her the book.
Indirect Questions
When posing indirect questions, we need to ensure that the word order follows the structure of a standard statement, rather than a direct question.
Direct: “Where are you going?” – Indirect: He asked me where I was going.
Mastering indirect speech is essential but can be challenging because of the need to adjust verb tenses, pronouns, and time expressions. However, with practice, it becomes easier, and steadily, you find yourself communicating more effectively and efficiently, especially in formal and written contexts. Keep practicing, and soon converting direct speech to indirect speech will become second nature.
Related Posts:

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- B1-B2 grammar
Reported speech: statements

Do you know how to report what somebody else said? Test what you know with interactive exercises and read the explanation to help you.
Look at these examples to see how we can tell someone what another person said.
direct speech: 'I love the Toy Story films,' she said. indirect speech: She said she loved the Toy Story films. direct speech: 'I worked as a waiter before becoming a chef,' he said. indirect speech: He said he'd worked as a waiter before becoming a chef. direct speech: 'I'll phone you tomorrow,' he said. indirect speech: He said he'd phone me the next day.
Try this exercise to test your grammar.
Grammar B1-B2: Reported speech 1: 1
Read the explanation to learn more.
Grammar explanation
Reported speech is when we tell someone what another person said. To do this, we can use direct speech or indirect speech.
direct speech: 'I work in a bank,' said Daniel. indirect speech: Daniel said that he worked in a bank.
In indirect speech, we often use a tense which is 'further back' in the past (e.g. worked ) than the tense originally used (e.g. work ). This is called 'backshift'. We also may need to change other words that were used, for example pronouns.
Present simple, present continuous and present perfect
When we backshift, present simple changes to past simple, present continuous changes to past continuous and present perfect changes to past perfect.
'I travel a lot in my job.' Jamila said that she travelled a lot in her job. 'The baby's sleeping!' He told me the baby was sleeping. 'I've hurt my leg.' She said she'd hurt her leg.
Past simple and past continuous
When we backshift, past simple usually changes to past perfect simple, and past continuous usually changes to past perfect continuous.
'We lived in China for five years.' She told me they'd lived in China for five years. 'It was raining all day.' He told me it had been raining all day.
Past perfect
The past perfect doesn't change.
'I'd tried everything without success, but this new medicine is great.' He said he'd tried everything without success, but the new medicine was great.
No backshift
If what the speaker has said is still true or relevant, it's not always necessary to change the tense. This might happen when the speaker has used a present tense.
'I go to the gym next to your house.' Jenny told me that she goes to the gym next to my house. I'm thinking about going with her. 'I'm working in Italy for the next six months.' He told me he's working in Italy for the next six months. Maybe I should visit him! 'I've broken my arm!' She said she's broken her arm, so she won't be at work this week.
Pronouns, demonstratives and adverbs of time and place
Pronouns also usually change in indirect speech.
'I enjoy working in my garden,' said Bob. Bob said that he enjoyed working in his garden. 'We played tennis for our school,' said Alina. Alina told me they'd played tennis for their school.
However, if you are the person or one of the people who spoke, then the pronouns don't change.
'I'm working on my thesis,' I said. I told her that I was working on my thesis. 'We want our jobs back!' we said. We said that we wanted our jobs back.
We also change demonstratives and adverbs of time and place if they are no longer accurate.
'This is my house.' He said this was his house. [You are currently in front of the house.] He said that was his house. [You are not currently in front of the house.] 'We like it here.' She told me they like it here. [You are currently in the place they like.] She told me they like it there. [You are not in the place they like.] 'I'm planning to do it today.' She told me she's planning to do it today. [It is currently still the same day.] She told me she was planning to do it that day. [It is not the same day any more.]
In the same way, these changes to those , now changes to then , yesterday changes to the day before , tomorrow changes to the next/following day and ago changes to before .
Do this exercise to test your grammar again.
Grammar B1-B2: Reported speech 1: 2
Language level
Thank you for the information. It states that If what the speaker has said is still true or relevant, it's not always necessary to change the tense. I wonder if it is still correct to change the tense in this example: 'London is in the UK', he said. to He said London was in the UK. Or it has to be the present tense.
- Log in or register to post comments
Hello Wen1996,
Yes, your version of the sentence is also correct. In this case, the past tense refers to the time the speaker made this statement. But this doesn't mean the statement isn't also true now.
Best wishes, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Good evening from Turkey.
Is the following example correct: Question: When did she watch the movie?
She asked me when she had watched the movie. or is it had she watched the movie.
Do Subjects come before the verbs? Thank you.
Hello muratt,
This is a reported question, not an actual question, as you can see from the fact that it has no question mark at the end. Therefore no inversion is needed and the normal subject-verb word order is maintained: ...she had watched... is correct.
You can read more about this here:
https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/grammar/b1-b2-grammar/reported-speech-questions
The LearnEnglish Team
Thank you for your response.
Hello Sir, kindly help with the following sentence-
She said, "When I was a child I wasn't afraid of ghosts."
Please tell me how to write this sentence in reported/ indirect speech.
Hello! I was studying reported speech and I didn't really understand the difference between 'need' and 'need to' when we shift them. Could you please explain a little bit about the semi-modal need? I came across to this while I was studying: Backshift Changes need (no change) ‘You needn’t come till six o’clock,’ he said. He said we needn’t come till six o’clock. AND need to (becomes needed to) She said, 'I need to have a party.' She said she needed to have a party. Why do we change 'need to' but not 'need'? Could you also please give a positive indirect reported speech with the word 'need' and a negative indirect speech with the word 'need to'? Thanks in advance!
Hello Meldo,
'need' can be used -- and is most often used -- as an ordinary verb. In the text you copied above, this is the second entry ('need to'). Since it is an ordinary verb, in indirect speech, it backshifts in the way other ordinary verbs do. An example of a negative form here is 'They told me I didn't need to bring my passport'.
Particularly in British English (only very rarely in American English), 'need' can also be used as a modal verb. In this case, it behaves as a modal verb, i.e. no 's' is added to a third person singular form, infinitives after it are used without 'to' and 'do/does/did' is not used to form questions, negatives or past simple forms. This is also why '-ed' is not added for a backshift.
When 'need' is a modal, it's most commonly used in the negative. It is possible to use it in questions (e.g. 'Need I bring my passport?' or 'I asked if I need bring my passport'), but it's generally not used in the affirmative.
You might find this BBC page and this Cambridge Dictionary explanation helpful if you'd like to read more.
Hope this helps.
Do we change 'had better' in indirect reported speech? I think no, but I just wanted to make sure. Can you also give an example with 'had better' in an indirect speech? Thanks a lot! The best English grammar site ever!
Hello Melis_06,
'had better' is not generally changed in reported speech. Here's an example for you:
- direct: 'You had better be on time!'
- indirect: They told us we had better be on time.
Glad you find our site useful!
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.
Direct and Indirect Speech: Useful Rules and Examples
Are you having trouble understanding the difference between direct and indirect speech? Direct speech is when you quote someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. This can be a tricky concept to grasp, but with a little practice, you’ll be able to use both forms of speech with ease.

Direct and Indirect Speech
When someone speaks, we can report what they said in two ways: direct speech and indirect speech. Direct speech is when we quote the exact words that were spoken, while indirect speech is when we report what was said without using the speaker’s exact words. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I love pizza,” said John. Indirect speech: John said that he loved pizza.
Using direct speech can make your writing more engaging and can help to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion. However, indirect speech can be useful when you want to summarize what someone said or when you don’t have the exact words that were spoken.
To change direct speech to indirect speech, you need to follow some rules. Firstly, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb. Secondly, you need to change the pronouns and adverbs in the reported speech to match the new speaker. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will go to the park,” said Sarah. Indirect speech: Sarah said that she would go to the park.
It’s important to note that when you use indirect speech, you need to use reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked” to indicate who is speaking. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is it?” asked Tom. Indirect speech: Tom asked what time it was.
In summary, understanding direct and indirect speech is crucial for effective communication and writing. Direct speech can be used to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion, while indirect speech can be useful when summarizing what someone said. By following the rules for changing direct speech to indirect speech, you can accurately report what was said while maintaining clarity and readability in your writing.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech
When it comes to reporting speech, there are two ways to go about it: direct and indirect speech. Direct speech is when you report someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. Here are some of the key differences between direct and indirect speech:
Change of Pronouns
In direct speech, the pronouns used are those of the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the pronouns have to be changed to reflect the perspective of the reporter. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John.
- Indirect speech: John said he was going to the store.
In the above example, the pronoun “I” changes to “he” in indirect speech.
Change of Tenses
Another major difference between direct and indirect speech is the change of tenses. In direct speech, the verb tense used is the same as that used by the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the verb tense may change depending on the context. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am studying for my exams,” said Sarah.
- Indirect speech: Sarah said she was studying for her exams.
In the above example, the present continuous tense “am studying” changes to the past continuous tense “was studying” in indirect speech.
Change of Time and Place References
When reporting indirect speech, the time and place references may also change. For example:
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” said Tom.
- Indirect speech: Tom said he would meet you at the park the next day.
In the above example, “tomorrow” changes to “the next day” in indirect speech.
Overall, it is important to understand the differences between direct and indirect speech to report speech accurately and effectively. By following the rules of direct and indirect speech, you can convey the intended message of the original speaker.
Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
When you need to report what someone said in your own words, you can use indirect speech. To convert direct speech into indirect speech, you need to follow a few rules.
Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks
The first step is to remove the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text. This is because indirect speech does not use the exact words of the speaker.
Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker
To indicate that you are reporting what someone said, you need to use a reporting verb such as “said,” “asked,” “told,” or “exclaimed.” You also need to use a linker such as “that” or “whether” to connect the reporting verb to the reported speech.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I love ice cream,” said Mary.
- Indirect speech: Mary said that she loved ice cream.
Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb
When you use indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb.
- Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store.
Step 4: Change the Pronouns
You also need to change the pronouns in the reported speech to match the subject of the reporting verb.
- Direct speech: “Are you busy now?” Tina asked me.
- Indirect speech: Tina asked whether I was busy then.
By following these rules, you can convert direct speech into indirect speech and report what someone said in your own words.
Converting Indirect Speech Into Direct Speech
Converting indirect speech into direct speech involves changing the reported speech to its original form as spoken by the speaker. Here are the steps to follow when converting indirect speech into direct speech:
- Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb used in the indirect speech. This will help you determine the tense of the direct speech.
- Change the pronouns: The next step is to change the pronouns in the indirect speech to match the person speaking in the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “She said that she was going to the store,” the direct speech would be “I am going to the store,” if you are the person speaking.
- Change the tense: Change the tense of the verbs in the indirect speech to match the tense of the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “He said that he would visit tomorrow,” the direct speech would be “He says he will visit tomorrow.”
- Remove the reporting verb and conjunction: In direct speech, there is no need for a reporting verb or conjunction. Simply remove them from the indirect speech to get the direct speech.
Here is an example to illustrate the process:
Indirect Speech: John said that he was tired and wanted to go home.
Direct Speech: “I am tired and want to go home,” John said.
By following these steps, you can easily convert indirect speech into direct speech.
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct and indirect speech are two ways to report what someone has said. Direct speech reports the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech reports the meaning of what was said. Here are some examples of both types of speech:
Direct Speech Examples
Direct speech is used when you want to report the exact words spoken by someone. It is usually enclosed in quotation marks and is often used in dialogue.
- “I am going to the store,” said Sarah.
- “It’s a beautiful day,” exclaimed John.
- “Please turn off the lights,” Mom told me.
- “I will meet you at the library,” said Tom.
- “We are going to the beach tomorrow,” announced Mary.
Indirect Speech Examples
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, is used to report what someone said without using their exact words. It is often used in news reports, academic writing, and in situations where you want to paraphrase what someone said.
Here are some examples of indirect speech:
- Sarah said that she was going to the store.
- John exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
- Mom told me to turn off the lights.
- Tom said that he would meet me at the library.
- Mary announced that they were going to the beach tomorrow.
In indirect speech, the verb tense may change to reflect the time of the reported speech. For example, “I am going to the store” becomes “Sarah said that she was going to the store.” Additionally, the pronouns and possessive adjectives may also change to reflect the speaker and the person being spoken about.
Overall, both direct and indirect speech are important tools for reporting what someone has said. By using these techniques, you can accurately convey the meaning of what was said while also adding your own interpretation and analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech refer to the ways in which we communicate what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, using quotation marks to indicate that you are quoting someone. Indirect speech, on the other hand, involves reporting what someone has said without using their exact words.
How do you convert direct speech to indirect speech?
To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb, such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.” For example, “I love ice cream,” said Mary (direct speech) can be converted to “Mary said that she loved ice cream” (indirect speech).
What is the difference between direct speech and indirect speech?
The main difference between direct speech and indirect speech is that direct speech uses the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. Direct speech is usually enclosed in quotation marks, while indirect speech is not.
What are some examples of direct and indirect speech?
Some examples of direct speech include “I am going to the store,” said John and “I love pizza,” exclaimed Sarah. Some examples of indirect speech include John said that he was going to the store and Sarah exclaimed that she loved pizza .
What are the rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech?
The rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech include changing the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb and use appropriate reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.”
What is a summary of direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech are two ways of reporting what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions and introduce a reporting verb.
You might also like:
- List of Adjectives
- Predicate Adjective
- Superlative Adjectives
Related Posts:

This website is AMNAZING
MY NAAMEE IS KISHU AND I WANTED TO TELL THERE ARE NO EXERCISES AVAILLABLEE BY YOUR WEBSITE PLEASE ADD THEM SSOON FOR OUR STUDENTS CONVIENCE IM A EIGHT GRADER LOVED YOUR EXPLABATIO
sure cries l miss my friend

89 Direct and Indirect Speech Examples

Understand the concept of Direct and Indirect Speech examples with step-by-step guides on how to convert Direct Speech into Indirect Speech and vice versa. Learn how to use the proper tense , pronouns , and modals while converting Direct and Indirect Speech with Examples .
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples are discussed in the following. This will help you to be skilled in Changing Tenses, Pronouns, Time, and Place words from Direct Speech to Indirect Speech with examples in different sentences.
Direct Speech Examples
When a speech is quoted with exact words used by the speaker is called Direct speech or narration .
Direct Speech: Ravi says, “I am tired.”
The speech which is quoted above in actual words (“ I am tired” is called the Reported Speech and the verb (“ says “) that introduces speech is called the Reporting Verb. The above speech is called Direct Speech .
Indirect Speech Examples
On the other hand, when the speech is reported in the form of a narrative, without quoting the speaker’s actual words , it is called Indirect speech or narration.
Indirect Speech: Ravi says that He was tired.
The above speech is reported in the form of a narrative, without quoting the speaker’s actual words , but keeping the meaning the same. So, it is Indirect Speech
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples in sentences
Direct: He said, “You are intelligent.” Indirect: He said that I was intelligent.
Direct: You will say, “I am right.” Indirect: You will say that you are right.
Direct: Rita said, “She is my favourite player.” Indirect: Rita said that she was her favourite player.
Direct: I said to you, ‘I wish to start a business next year.’ Indirect: I told you that I wished to start a business in the following years.
Direct: Mother said to her, “Are you feeling feverish?” Indirect: Mother inquired of her if she was feeling feverish.
Direct: She said to him, ‘Which of the books do you want to buy?’ Indirect: She asked him which of the books he wanted to buy.
Direct: The teacher said, “Boys, go to your classes.” Indirect: The teacher ordered the boys to go to their classes.
Direct: Mother said, ‘May you be happy.’ Indirect: Mother wished that I might be happy.
More Direct & Indirect Speech Resources:
Change of Tenses in Direct and Indirect Speech Examples.
Direct: He says, “You will make a good result.” Indirect: He says that I shall make a good result.
Direct: Mother says, “I made the fish curry.” Indirect: Mother says that She made the fish curry.
Direct: He will say, “I shall be there within an hour.” Indirect: He will say that he will be there for an hour.
Direct: They say, “We won the match.” Indirect: They say that they won the match.
Direct: They said to us, “You make a mistake.” Indirect: They told us that we made a mistake
Direct: The teacher said to us, “Oil floats on water.” Indirect: The teacher told us that oil floats on water
Direct: She said to me, “I am writing a letter now.” Indirect: She told me that she was writing a letter then.
Direct: The doctor said to me, “You have brought the patient in time.” Indirect: The doctor told me that I had brought the patient in time.
Direct: Mother said, “I took tea.” Indirect: Mother said that she had taken tea.
Direct: My friend said to me, “you were doing a good job.” Indirect: My friend told me that I had been doing a good job.
Direct: The man said to me, “I had not seen you before.” Indirect: The man told me that he had not seen me before.
Direct: He said to me, “I shall not do it.” Indirect: He told me that he would not do it.
Direct: He said to me, “My father will visit there.” Indirect: He told me that his father would visit there.
Direct: He said to me, “I can try it.” Indirect: He told me that he could try it.
Direct: He said to me, “You may go .” Indirect: He told me that I might go .
Change of Pronouns Examples from Direct to Indirect Speech
Direct: He said to me, “ I am ill.” Indirect: He told me that he was ill.
Direct: They will say to you, “ We have made it.” Indirect: They will tell you that they have made it.
Direct: You said to him, “ You are not like me.” Indirect: You told him that he was not like you.
Direct: He said to me, “ My name is John.” Indirect: He tells me that his name is John.
Direct: They said to me, “ This is our playground.” Indirect: They told me that that was their playground.
Direct: He says to me, “Elders give us blessings.” Indirect: He tells me that elders give them blessings.
Direct: He said to me, “ You are not smart .” Indirect: He told me that I was not smart.
Direct: She said to him, “ I am not your friend.” Indirect: She told him that she was not his friend.
Direct: He said to us, “ I shall give you money.” Indirect: He told us that he would give us money.
Direct: You said, “ He is right.” Indirect: You said that he was right.
Direct: I said, “ They will be late.” Indirect: I said that they would be late.
Change of Time & Place: Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct: He said to me, “ This is my house.” Indirect: He told me that that was his house.
Direct: She said to him, “ These are golden flowers.” Indirect: She told him that those were golden flowers.
Direct: He said, “I have done it today .” Indirect: He said that he had done it that day.
Direct: She said to him, “I bought the book yesterday .” Indirect: She said that she had the book the previous day.
Direct: They said, ‘We will play now. ‘ Indirect: They said that they would play then .
Direct: You said, ‘ Here lives a lion.’ Indirect: You said that there lived a lion.
Direct: She always says, ‘I like these flowers.’ Indirect: She always says that she likes those flowers.
Direct: He said, ‘I will come here tomorrow. ‘ Indirect: He said that he would go there the next day .
Direct: I said, ‘You will get it today or tomorrow.’ Indirect: I said that you would get it that day or the next day.
Direct: He said to me, ‘ Come here .’ Indirect: He told me to go there.
Direct: He said, ‘I shall go there the day after tomorrow .’ Indirect: He said that he would go there in two day’s time.
Direct: He said to me, ‘I saw your sister two years ago. ‘ Indirect: He told me that he had seen my sister two years before.
Direct: He said to me, “I have no friend here .” Indirect: He told me that he had no friends here.
Direct: I said, ‘We cannot be happy in this world. Indirect: I said that we could not be happy in this world.
Assertive Sentences Examples: Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct: Peter says, “My mother teaches me English.” Indirect: Peter says that his (Peter’s) mother teaches him English.
Direct: Shyam will say, “I have done this work. Indirect: Shyam will say that he has done that work.
Direct: Bappa said to him, “I am ten years old.” Indirect: Bappa told him that he was ten years old.
Direct: Laltu said, “I am watching television now. Indirect: Laltu said that he was watching television then.
Direct: He said to me, “My mother is now sleeping.’ Indirect: He told me that his mother was sleeping then.
Direct: I said, “The teacher has taken me to the task. Indirect: I said that the teacher had taken me to the task.
Direct: Mother said to me, “I have taken the medicine twice today.” Indirect: Mother told me that she had taken the medicine twice that day.
Direct: My sister said to me, “The bird flew away. Indirect: My sister told me that the bird had flown away.
Direct: Namrata said, “They came here yesterday.’ Indirect: Namrata said that they had come there the previous day.
Direct: Jamuna said, “Lalan was listening to my words. Indirect: Jamuna said that Lalan had been listening to her words.
Direct: He said, “I shall take rice.” Indirect: He said that he would take rice.
Direct: They said, “We shall leave for Goa tomorrow.” Indirect: They said that they would leave for Goa the next day.
Direct: Ashisbabu said, “Now we shall start the ceremony.’ Indirect: Ashisbabu said that they should start the ceremony then.
Examples of Universal truth or habitual truth, Historical truth
Direct: Lopa said, “God is almighty.” Indirect: Lopa said that God is almighty.
Direct: Father said, “God is good.” Indirect: Father said that God is good.
Direct: Keats said, “Beauty is truth, truth beauty.” Indirect: Keats said that beauty is truth, truth beauty.
Direct: The teacher said, “The earth moves round the sun.” Indirect: The teacher said that the earth moves round the sun.
Direct: My grandfather said, “Honesty is the best policy.” Indirect: My grandfather said that honesty is the best policy.
Direct: Father said, “The sun rises in the east.” Indirect: Father said that the sun rises in the east.
Direct: Saurav said, “My grandfather recites the Geeta every morning.” Indirect: Saurav said that his grandfather recites the Geeta every morning.
Direct: Arindam’s uncle said, “I walk for half an hour every afternoon.” Indirect: Arindam’s uncle said that he walks for half an hour every afternoon.
Direct: He said, “Man is mortal.” Indirect: He said that man is mortal.
Direct: The old man said, “God is merciful.” Indirect: The old man said that God is merciful.
Direct: The teacher said, “Ashoka was a great emperor.” Indirect: The teacher said that Ashoka was a great emperor.
Direct: The student answered, “Lord Buddha died in his eightieth year.” Indirect: The student answered that Lord Buddha died in his eightieth year.
Direct: He said, “Babar was the first emperor of the Mughal empire.” Indirect: He said that Babar was the first emperor of the Mughal Empire.
Interrogative Sentences Examples: Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct: The boy said to me. “Is the mango sweet?” Indirect: The boy asked me whether(or, if) the mango was sweet.
Direct: Tanmay said to me, “Are you ill?” Indirect: Tanmay asked me whether (or, if) I was ill.
Direct: I said to him, “Do you know him?” Indirect: I asked him whether he knew him.
Direct: Rabin said to me, “Is there any problem?” Indirect: Rabin enquired of me if there was any problem.
Direct: I said to my brother, “Are you going to school?” Indirect: I asked my brother whether he was going to school.
Direct: The teacher said to the student. Did you come to school yesterday?” Indirect: The teacher enquired of the student whether he (the student) had come to school the day before.
Direct: I said to Binay, “Did you see Palash?” Indirect: I asked Binay whether he (Binay) had seen Palash.
Direct: His mother angrily said to him, “Do you know better than your elder brother?” Indirect: His mother asked him angrily whether he supposed that he knew better than his elder brother.
Direct: The judge said to the accused, “Have you anything to say in justification of your action?” Indirect: The judge wanted to know from the accused if he had anything to say in justification of his action.
Direct: Sadhan said to Nabin, “Have you read the letter?” Indirect: Sadhan asked Nabin if he had read the letter.
Direct: Santosh said to Seema, “Can you lend me a pen?” Indirect: Santosh asked Seema if she could lend him (Santosh) a pen.
Direct: The trainer said to Tarun, “Can you swim?” Indirect: The trainer asked Tarun whether he (Tarun) could swim.
Direct: The poet said, “Real happiness is only a dream.” Indirect: The poet said that real happiness is only a dream.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples of “Wh-word”
Direct: He said to me, “What are you doing?” Indirect: He asked me what I was doing.
Direct: I said to him, “What is your name?” Indirect: I asked him what his name was.
Direct: The passerby said to me, “What is the time now by your watch?” Indirect: The passerby asked me what time it was then by my watch.
Direct: I said to Basu, “Where do you live?” Indirect: I asked Basu where he (Basu) lived.
Direct: Dinu said to Manu, “Where are you going?” Indirect: Dinu asked Manu where he (Manu) was going.
Direct: I said to Gopal, “Where is your pencil box?” Indirect: I enquired of Gopal where his (Gopal’s) pencil box was.
Direct: The passenger asked, “When will the train start?” Indirect: The passenger asked (or, wanted to know) when the train would start.
Direct: Ratan said to me, “How are you?” Indirect: Ratan wanted to know from me how I was.
Direct: Suman said to me, “How did you know this? Indirect: Suman enquired (asked) me how I had known that.
Direct: I said to the policeman, “Why did you strike the boy?” Indirect: I wanted to know from the policeman why he had struck the boy.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples of Imperative Sentences
Direct: The teacher said to the students, “Sit down.” Indirect: The teacher told the students to sit down.
Direct: The commander-in-chief said to the soldiers, “March forward.” Indirect: The commander-in-chief ordered the soldiers to march forward.
Direct: The master said to his servant, Polish my shoes,” Indirect: The master ordered his servant to polish his master’s shoes.
Direct: Ratanbabu said to the man, “Leave the house at once,” Indirect: Ratanbaby ordered the man to leave the house at once.
Direct: The teacher said to his pupils, “Go out.” Indirect: The teacher told his pupils to go out.
Direct: Mother said to me, “Go to school at once.” Indirect: Mother ordered/urged me to go to school that very moment.
Direct: He said to Sujay. “Let’s have a cup of tea. Indirect: He invited Sujay to have a cup of tea with him.
Direct: Sunillbabe said to Sistab. Please lend me some money.” Indirect: Sunilbabe requested Sisibaba to lend him (Sababu) some money.
Direct: Father said, “Go on, apply for the job.” Indirect: Father advised/encouraged me to apply for the job.
Direct: The teacher said to the boy, “Don’t spit on the floor. Indirect: The teacher forbade the boy to spit on the floor.
Direct: I said to my brother, “Do not run in the sun.” Indirect: I advised my brother not to run in the sun. Or I forbade my brother to run in the sun.
Direct: The teacher said to me, “Do not waste time.” Indirect: The teacher advised me not to waste time.
Direct: He said to his sons, “Do not quarrel among yourselves.” Indirect: He advised his sons not to quarrel among themselves.
Direct Speech and Indirect Speech Examples with “Let”
Direct: Mukti said, “Let’s go for a walk.” Indirect: Mukti suggested that they should go for a walk.
Direct: The inspector said to the constable, “Let the man go.” Indirect: The inspector ordered the constable to let the man go.
Direct: Rama said, “Let’s arrange a musical party.” Indirect: Rama suggested that they should arrange a musical party.
Direct: The clergyman said, “The nations of the world should forget their differences and work together for peace.” Indirect: The clergyman suggested that the nations of the world should forget their differences and work together for peace.
Direct: Ramen said, “I must not delay any longer.” Indirect: Ramen said that he ought not to delay any longer.
Direct: He said, “I must return before 5 in the evening.” Indirect: He said that he must (or, would have to) return before 5 in the evening.
Direct: Rima said to me, “You ought to be careful when driving.” Indirect: Nima advised me to be careful when driving.
Direct: My father said, “You ought not to trust a man who is a habitual liar.” Indirect: My father warned me against trusting a man who was a habitual liar
Direct: Father said, “You should not be late in reaching school.” Indirect: Father advised me not to be late in reaching school. Or, Father said that I should not be late in reaching school.
Direct: Somen said, “It might rain tonight.” Indirect: Somen said that it might rain that night, Or Somen said that there was the possibility of rainfall that night,
Optative Sentences Examples
Direct: He said, “May God bless you.’ Indirect: He prayed that God might bless him (or, me).
Direct: The priest said to the accused, “May God pardon your sins.” Indirect: The priest prayed to God that He might pardon his sins (or, the sins of the accused).
Direct: We said, “May Mother Teresa’s soul rest in peace.” Indirect: We prayed that Mother Teresa’s soul might rest in peace.
Direct: The retiring teacher said to his pupils, “I bid all of you goodbye.” Indirect: The retiring teacher bade goodbye (or, farewell) to all his pupils.
Direct: They said, “Long live Netaji.” Indirect: They prayed for Netaji’s long life.
Direct: My grandfather said to me, “May you be happy.” Indirect: My grandfather blessed me wishing that I might be happy. Or. My grandfather blessed me by wishing me a happy life. Or, My grandfather wished that I might be happy.
Direct: His father said to him, “May you prosper.” Indirect: His father wished him prosperity. Or. His father wished that he might prosper.
Direct: Ajay said to his brother, “Welcome home.” Indirect: Ajay bade his brother welcome.
Direct: Rahul said to his playmates, “Good morning, I hope you are quite well.” Indirect: Rahul wished his playmates a good morning and expressed his hope that they were quite well.
Exclamatory Sentences
Direct: The students said, “Hurrah! Our school won the match.” Indirect: The students shouted with delight (exclaimed with joy) that their school had won the match.
Direct: He said, “Alas! I am ruined.” Indirect: He lamented that he was ruined.
Direct: He said, “What a fool I am !” Indirect: He reproached (feata lucuíba) himself for being such a big fool.
Direct: The audience said to the actor, “How wonderful is your acting !” Indirect: The audience expressed to the actor their appreciation of his fine acting.
Direct: Returning from the place of the accident, he said, “What a ghastly sight it was!” Indirect: Returning from the place of the accident he expressed his disgust at the ghastliness of the sight.
Direct: Looking at the Tajmahal the tourist said, “What an exquisitely beautiful creation !” Indirect: Looking at the Tajmahal the tourist exclaimed in wonder that it was indeed an extremely beautiful creation.
Direct: The youth said, “Alas! I am undone by the death of my father.” Indirect: The youth lamented that he was undone by his father’s death.
Direct: The coach of the team said to his players, “Bravo! You have played extremely well.” Indirect: The coach of the team cheered the players and said that they had played extremely well indeed.
Direct: Nabinbabu said to Sajal, “What a pity you could not succeed in spite of such great efforts !” Indirect: Nabinbabu expressed his sympathy for Sajal for not being successful in spite of his great efforts.
More than one sentence
Direct: Sanu said to Sushama over the telephone, “I have got the tickets. Meet me at the station at 6.30 p.m.” Indirect: Sanu informed Sushama over the telephone that he had got the tickets and suggested that she meet him at the station at 6.30 p.m.
Direct: The supervisor of the examination said to the candidates, “Do not forget to put your names at the top of the page. Write down also the roll and the number.” Indirect: The supervisor of the examination advised the candidates not to forget to put their names at the top of the page and also reminded them to write down their roll and number therein.
Direct: Surabhi said to Mohan, “Let’s buy some flour. We will prepare bread at home.’ Indirect: Surabhi suggested to Mohan that they buy some flour and make bread themselves at home.
Direct: My assistant said to me, “You look tired. Why don’t you take a rest for a couple of days?” Indirect: My assistant told me that I looked tired, and suggested that I should take a rest for a couple of days.
Direct: My friend said to me, “Why don’t you open a bank account? I have opened one.” Indirect: My friend advised me to open a bank account and he also informed me that he had opened one.
Frequently Asked Questions Direct and Indirect Speech Examples
Q: What are the 10 examples of direct and indirect speech?
- Direct Speech: Rohan said, “She works hard.”
- Indirect Speech: Rohan said that she worked hard
- Direct Speech: Rohan said, “She is singing a song.”
- Indirect Speech: Rohan said that she was singing a song.
- Direct Speech: The guest said shouting, “We have arrived .”
- Indirect Speech: The guest said shouting that they had arrived.
- Direct Speech: My sister said, “It has been raining hard for 3 days”.
- Indirect Speech: My sister said that it had been raining hard for 3 days.
- Direct Speech: Father said, “I visited the Taj yesterday.”
- Indirect Speech: Father said that he had visited the Taj the previous day.
- Direct Speech: Boys said, “They were travelling in the park.”
- Indirect Speech: Boys said that they had been travelling in the park.
- Direct Speech: The reporters commented that the Kohinoor had been lost long ago.
- Indirect Speech: The reporters commented, “The Kohinoor had been lost long ago”.
- D i rect Speech: Jyotsna said, “ She had been doing the work for 3 hours”.
- Indirect Speech: Jyotsna said that she had been doing the work for 3 hours.
- Direct: The boy said to his mother, “ The sun rises in the East”. Indirect: The boy told his mother that the sun rises in the East. [ Universal Truth ]
- Direct: The monk answered, “ Man is mortal”. Indirect: The monk answered that man is mortal. [ Universal Truth ]
Q: What is direct and indirect speech with examples for Class 5?
Ans: When a sentence is quoted with the exact words used by the speaker, it is called a sentence in Direct Speech.
When the sentence is spoken or written in the form of a narrative without quoting the speaker’s actual words but keeping the meaning the same, it is called a sentence in Indirect Speech .
(1) I said to him that I had once seen him before. Ans: I said to him, “ I once saw you ago.”
(2) She said that she had a dream that night. Ans : She said, “I have a dream tonight.”
(3) The boy said. “We were playing.” Ans: The boy said that they had been playing.
(4) He told me that I should obey my parents. Ans: He said to me, “You will obey your parents.”
(5) Amal said to Bimal, “I gave you, my pen.” Ans: Amal told Bimal that he had given him his pen.
Q: What is the example of direct and indirect speech Class 9?
Ans: Direct: You say, ‘I am always busy.’ Indirect: You say that you are always busy.
Direct: The child will say, ‘Mum knows everything.’ Indirect: The child will say that Mum knows everything.
Direct: He said, ‘I need some money.’ Indirect: He said that he needed some money,
Direct: She said, ‘I am waiting for him.’ Indirect: She said that she was waiting for him.
Q: What are the 5 rules of indirect speech?
Ans: The five rules of indirect speech consist of Assertive sentence, Interrogative Sentence, Imperative Sentence, Optative Sentence, and Exclamatory Sentence.
Related posts:

![change to indirect speech examples NARRATION CHANGE [Direct and Indirect]](https://learninginsight.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/NARRATION-CHANGE-Direct-and-Indirect.webp)

NARRATION CHANGE [Direct and Indirect] – 50+ Examples
Table of Contents
Narration change, also known as reported speech or indirect speech, is a linguistic tool that allows us to express someone else’s words or thoughts in our own words. It involves transforming direct speech into indirect speech, a skill that can greatly enhance the clarity and variety of communication.
Before we embark on our journey of understanding narration change, let’s differentiate between direct and indirect speech. Direct speech involves quoting someone’s exact words within quotation marks. In contrast, indirect speech entails paraphrasing or summarizing what someone said without using their exact phrasing.
The Significance of Narration Change
Crafting engaging narratives.
Narration change breathes life into dialogues by adding variety and dynamism to conversations.
Expressing Different Viewpoints
By effectively utilizing narration change, communicators can present multiple perspectives on the same subject, enriching the discourse and making it more comprehensive.
Rules and Guidelines for Narration Change
Manipulating pronouns and verb tenses.
When converting direct speech to indirect speech, alterations to pronouns and verb tenses are often necessary to maintain accuracy and context.
Employing Reporting Verbs
Selecting appropriate reporting verb s, such as “said,” “asked,” “explained,” or “suggested,” is pivotal in conveying the speaker’s intentions and emotions.
The Art of Mastering Narration Change
A step-by-step approach.
- Identify the original direct speech.
- Determine the required changes in tense and pronouns.
- Opt for a suitable reporting verb .
- Rearrange the sentence structure if needed.
Examples of NARRATION CHANGE [Direct and Indirect]
Narration change is a powerful tool that empowers communicators to present information with flair and precision. By skillfully altering perspectives and adapting speech , writers can captivate readers and elevate the overall quality of their content.
Direct and Indirect Speech: The Ultimate Guide
Direct and Indirect Speech are the two ways of reporting what someone said. The use of both direct and indirect speech is crucial in effective communication and writing. Understanding the basics of direct and indirect speech is important, but mastering the advanced techniques of these two forms of speech can take your writing to the next level. In this article, we will explore direct and indirect speech in detail and provide you with a comprehensive guide that covers everything you need to know.
Table of Contents
What is Direct Speech?
Direct speech is a way of reporting what someone said using their exact words. Direct speech is typically enclosed in quotation marks to distinguish it from the writer’s own words. Here are some examples of direct speech:
- “I am going to the store,” said John.
- “I love ice cream,” exclaimed Mary.
- “The weather is beautiful today,” said Sarah.
In direct speech, the exact words spoken by the speaker are used, and the tense and pronouns used in the quote are maintained. Punctuation is also important in direct speech. Commas are used to separate the quote from the reporting verb, and full stops, question marks, or exclamation marks are used at the end of the quote, depending on the tone of the statement.
What is Indirect Speech?
Indirect speech is a way of reporting what someone said using a paraphrased version of their words. In indirect speech, the writer rephrases the speaker’s words and incorporates them into the sentence. Here are some examples of indirect speech:
- John said that he was going to the store.
- Mary exclaimed that she loved ice cream.
- Sarah said that the weather was beautiful that day.
In indirect speech, the tense and pronouns may change, depending on the context of the sentence. Indirect speech is not enclosed in quotation marks, and the use of reporting verbs is important.
Differences Between Direct and Indirect Speech
The structure of direct and indirect speech is different. Direct speech is presented in quotation marks, whereas indirect speech is incorporated into the sentence without quotation marks. The tenses and pronouns used in direct and indirect speech also differ. In direct speech, the tense and pronouns used in the quote are maintained, whereas, in indirect speech, they may change depending on the context of the sentence. Reporting verbs are also used differently in direct and indirect speech. In direct speech, they are used to introduce the quote, while in indirect speech, they are used to report what was said.
How to Convert Direct Speech to Indirect Speech
Converting direct speech to indirect speech involves changing the tense, pronouns, and reporting verb. Here are the steps involved in converting direct speech to indirect speech:
- Remove the quotation marks.
- Use a reporting verb to introduce the indirect speech.
- Change the tense of the verb in the quote if necessary.
- Change the pronouns if necessary.
- Use the appropriate conjunction if necessary.
Here is an example of converting direct speech to indirect speech:
Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John. Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store.
How to Convert Indirect Speech to Direct Speech
Converting indirect speech to direct speech involves using the same tense, pronouns, and reporting verb as the original quote. Here are the steps involved in converting indirect speech to direct speech:
- Remove the reporting verb.
- Use quotation marks to enclose the direct speech.
- Maintain the tense of the verb in the quote.
- Use the same pronouns as the original quote.
Here is an example of converting indirect speech to direct speech:
Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store. Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John.
Advanced Techniques for Using Direct and Indirect Speech
Using direct and indirect speech effectively can add depth and complexity to your writing. Here are some advanced techniques for using direct and indirect speech:
Blending Direct and Indirect Speech
Blending direct and indirect speech involves using both forms of speech in a single sentence or paragraph. This technique can create a more engaging and realistic narrative. Here is an example:
“Sarah said, ‘I can’t believe it’s already winter.’ Her friend replied that she loved the cold weather and was excited about the snowboarding season.”
In this example, direct speech is used to convey Sarah’s words, and indirect speech is used to convey her friend’s response.
Using Reported Questions
Reported questions are a form of indirect speech that convey a question someone asked without using quotation marks. Reported questions often use reporting verbs like “asked” or “wondered.” Here is an example:
“John asked if I had seen the movie last night.”
In this example, the question “Have you seen the movie last night?” is reported indirectly without using quotation marks.
Using Direct Speech to Convey Emotion
Direct speech can be used to convey emotion more effectively than indirect speech. When using direct speech to convey emotion, it’s important to choose the right tone and emphasis. Here is an example:
“She screamed, ‘I hate you!’ as she slammed the door.”
In this example, the use of direct speech and the exclamation mark convey the intense emotion of the moment.
- When should I use direct speech?
- Direct speech should be used when you want to report what someone said using their exact words. Direct speech is appropriate when you want to convey the speaker’s tone, emphasis, and emotion.
- When should I use indirect speech?
- Indirect speech should be used when you want to report what someone said using a paraphrased version of their words. Indirect speech is appropriate when you want to provide information without conveying the speaker’s tone, emphasis, or emotion.
- What are some common reporting verbs?
- Some common reporting verbs include “said,” “asked,” “exclaimed,” “whispered,” “wondered,” and “suggested.”
Direct and indirect speech are important tools for effective communication and writing. Understanding the differences between these two forms of speech and knowing how to use them effectively can take your writing to the next level. By using advanced techniques like blending direct and indirect speech and using direct speech to convey emotion, you can create engaging and realistic narratives that resonate with your readers.
Related Posts
What is WH Question Words? Definition and Examples
Active Passive Voice: Difference, Usage, and Examples
Rules Articles: a, an, the With Examples
Simple Subject and Predicate Examples With Answers
100 Question Tags Examples with Answers
List of Contractions in English With Examples
Add comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Easy Insightful Literature Notes
Transformation of Sentence: Direct & Indirect Speech
A direct speech can be transformed into an indirect speech and vice versa using a suitable reporting verb and a linker depending on the sentence. Let’s have an example first.
- Tina said to me, “Are you busy now?” [direct speech]
- Tina asked me whether I was busy then. [indirect speech]
Direct Speech
Indirect Speech
- Look, if the reporting verb in direct speech (said) is in past tense, the reporting verb in indirect speech (asked) would also be in past tense. ‘Whether’ is the linker added here as it is a ‘yes-no’ type question (Refer to list 1 below).
- ‘Are’ changes to ‘was’. As the reporting verb was in past tense, the verb in the reported speech will also be in past. (Refer to list 2 below)
- ‘Now’ has become ‘then’. Time and place expressions change if the reporting verb is in past tense. (Refer to list 3 below)
- The question mark (?) has changed to a full stop(.).
- Another important thing, the format of question (v + s + o) has changed to the format of a statement (s + v + o). In indirect speech the pattern always comes to subject + verb + object.
List of Reporting verbs and linkers (list 1)
Verbs of Reported speech (if the reporting verb is in past tense) (list 2) Direct speech → Indirect speech Am / is / are → was / were Was / were → had been Has / have → had Had → had had Shall / will → would Can → could May → might Must, should → must, should Verb1 → verb2 Verb2 → had + verb3
Change of time and place expressions in past tense (list 3) now → then ago → before today → that day yesterday → the previous day tomorrow → the next day last night → the previous night here → there this → that these → those
Narration change of Assertive sentence
- Robin said, “I went to Delhi yesterday.” – Robin said that he had gone to Delhi the previous day .
- She said to her husband, “I want to go with you.” – She told her husband that she wanted to go with him.
Narration change of Interrogative sentence
- He said to me, “Do you know English?” – He asked me whether I knew English.
- She said to me, “Did you go there?” – She wanted to know whether I had gone there.
- I said to him, “What are you doing?” – I asked him what he was doing.
- Rahul said to his mother, “How do you do all these things together?” – Rahul asked his mother how she did all those things together.
Narration change of Imperative sentence
- He said to me, “Go there right now.” – He ordered me to go there right then.
- My teacher said to me, “Obey your parents.” – My teacher asked me to obey my parents.
- She said to me, “Please don’t go there.” – She requested me not to go there.
- He said to her, “Let’s go home.” – He suggested her that they should go home.
- His mother said, “Let him eat whatever he likes.” – His mother suggested that he might be allowed to eat whatever he liked.
Narration change of Optative sentence
- He said to the boy, “May god bless you.” – He prayed that God might bless the boy.
- The girl said, “Had I the wings of a dove.” – The girl wished that she had the wings of a dove.
Narration change of Exclamatory sentence
- “How happy we are here!” said the children. – The children exclaimed in joy that they were very happy there.
- The children said, “How happy we were there!” – The children exclaimed in sorrow that they had been very happy there.
- He said to me, “Good bye!” – He bade me good bye.
- She said to me, “Good evening!”—She wished me good evening.
Narration change of Vocatives
- Teacher said, “ Robin , stand up.” – Teacher asked Robin to stand up.
- The Bishop said to the convict, “Always remember, my son , that the poor body is the temple of the living God.” – The Bishop addressed the convict as his son and advised him to always remember that the poor body is the temple of the living God.
Narration change of question tag
- He said to me, “You went to Kolkata, didn’t you?” – He asked me whether I had gone to Kolkata and assumed that I had.
- I said to him, “Tina didn’t tell a lie, did she?” – I asked him if Tina had told a lie and assumed that she had not.
We serve cookies on this site to offer, protect and improve our services. KNOW MORE OK
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Reported Speech /
How to Change Sentences into Indirect Speech
- Updated on
- Dec 19, 2023

Change sentences into indirect speech: Indirect Speech often known as reported speech is a linguistic tool . It helps to quote someone else words that are not the actual words of the speaker. In this blog article, we learn about the meaning of indirect speech , examples of indirect speech, and practice exercises to master the art of changing sentences to indirect speech.
This Blog Includes:
Understanding indirect speech, examples of indirect speech, exercise to change sentences from direct to indirect speech.
MUST READ! Reported Speech: Definition, Rules, Usage with Examples, Tips, Exercises for Students
Indirect Speech includes paraphrasing speakers’ words instead of defining the actual words of the speaker. This linguistic device is used to maintain politeness of tone and social dynamics. It is an important concept that allows a speaker to convey information tactfully while maintaining the meaning of the words spoken by the speaker.
Let us comprehend the few examples of Indirect Speech for the proper understanding of the concept.
Rules for Changing Sentences To Indirect Speech
Here are the key rules for converting sentences from direct speech to indirect speech. These rules include changes in verb tense, pronouns, and other elements to maintain the meaning of the original statement.
Changes in Tenses
Simple Present Changes to Simple Past
For example, He said,” I like chocolates”.
He said that he liked chocolates.
Present Continuous Changes to Past Continuous
For example, He said,” We are studying”.
He said that they were studying.
Present Perfect Changes to Past Perfect
For example, He said,” They have finished”
He said that they had finished.
Present Perfect Continuous Changes to Past Perfect Continuous,
For example, She said, “ They have been living in Canada since 1970.”
She said that they had been living in Canada since 1970.
Simple Past Changes to Past Perfect
For example, He said, “ They played in the garden”.
He said that they had played in the garden.
Past Continuous Changes to Past Perfect Continuous
For example, He said,” They had grown vegetables.”
He said that they had been growing vegetables.
Future Indefinite Changes will and shall and should accordingly
For example, He said,” He will go to the market.”
He said that he would go to the market.
Changes in the Pronouns
Pronouns in the direct speech change according to the perspective of the speaker.
- First-person changes according to subject
- Second-person changes according to the object
- Third-person pronoun there is no change.
- Follows the SON rule that is easy to remember
For Example She said, ” I love her job .” (direct speech)
She said that she loved her job . (indirect speech)
Also Read Tenses Rules: Charts, Examples, Types [PDF Available]
Changes in the Adverbs of Time and Place
Adverbs change according to the context
- Now to then,
- Here to there,
- Today to the same day,
- Yesterday to the last day, etc.
For example: He said,” I will go to school tomorrow .” (Direct Speech)
He said that he would go to the school the next day. (Indirect Speech)
Must Read: Subject-Verb Agreement: Definition, 12 Rules & Examples
Let’s check your understanding of the sentences that have been changed from direct to indirect speech:
- “I can’t believe you did that!” exclaimed Sonali.
- “What time is the meeting?” asked the teacher.
- “I love this song!” shouted Mohit
- “Where did you find that book?” inquired the teacher
- “I’ll be there by 3 PM,” promised Alia
- “Stop right there!” commanded the officer
- “Would you like some coffee?” offered James
- “Let’s go to the beach this weekend,” suggested Rohit
- “I don’t want to go to the dentist,” complained Tina.
- “Congratulations on your promotion!” cheered Mary.
Answers
Match your answers with the solved exercises to analyze the understanding of the concept.
- Sonali exclaimed with surprise that she couldn’t believe he had done that.
- The teacher asked about the time of the meeting.
- Mohit enthusiastically shouted that he loved that song.
- The teacher inquired where the book had been found.
- Alia promised that she would be there by 3 PM.
- The officer commanded me to stop right there.
- James offered coffee.
- Rohit suggested going to the beach that weekend.
- Tina complained that she didn’t want to go to the dentist.
- Mary cheered and congratulated on the promotion.
Must Read: Figures of Speech: Types, Usage & Examples [Download PDF]
Direct speech is the actual words spoken by a person and is written in quotation marks, while indirect speech defines the meaning of the original statement without quoting the actual words of the speaker. Indirect speech involves various changes in verb tense, pronouns, and other elements.
Pronouns change according to the SON Rule where SON stands for: First-person changes according to (S-Subject) Second-person changes according to(O- Object) A third-person there is (N- No Change)
A few reporting verbs used in indirect speech are “said,” “told,” “asked,” “explained,” inquired, commanded, requested, exclaimed with joy, etc.” The choice of reporting verb reflects the tone and meaning of the reported speech.
Direct Speech: It’s been raining since this afternoon. Indirect Speech: He said it’d been raining since that afternoon.
To advance your grammar knowledge and read more informative blogs, check out our Learn English page and don’t forget to follow Leverage Edu .
Amanpreet Kaur
📚✨ From Classroom Chats Entered Into The Wordy World ….. Yes , If you all Remember that teacher who kept you on your toes with pop quizzes and endless homework? YEP! THAT WAS Me ! 🌟 But with the blessings of almighty and the key motivation of my husband who came across the spark of writing in me has insisted me to pave my way away from chalk dust to creative burst!💫 Being in this new world of writing I can compose pun-tastic content, poetry full of emotions and humorous articles that can even make Shakespeare envious of me 📝🎭.Yippee! from teaching young minds to educating worldwide readers it's an epic career switch. From teaching grammar lessons to grammatically flawless copy, I'm todays' wordsmith on a mission! Let me spin literary magic all around and conquer my exact destination of proving myself as The Best Writer in The World.🚀🏆 My promise is to provide you with valuable insights, solutions to your questions, and a momentary escape from the routine. I believe in the power of words to create connections, provoke thought, and foster growth. Woods are lovely dark and deep But I have promises to keep and Miles to go before I sleep ……..🌳✨🌌
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
GrammarSimple.Com
40 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Sentences
Table of Contents
Direct And Indirect Speech Examples
While using English, we use direct and indirect speeches quite often. If a sentence is expressed exactly as it came out of the mouth of the person who said it, it becomes a direct speech. However Indirect Speech (also called reported speech) refers to transmitting a sentence that someone has said. It is often used in daily language.
For example,
- Susan told me she ate pizza yesterday. (Indirect Speech)
Susan said, “I ate pizza yesterday.”. (Direct Speech)
- Mathilda told me she had to go out. (Indirect Speech)
Mathilda said: “I have to go out.”. (Direct Speech)
- Julie asked if the train had left when she arrived at the ticket office. (Indirect Speech)
Julie asked: “Did the train leave?” (Direct Speech)
Related Posts
Causative Have and Get, Causative Verbs Examples and Sentences
Using An, Definition and Example Sentences
Tenses, Active Voice and Passive Voice
About the author.
English Study Here
100 examples of direct and indirect speech.
100 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech in English, 100 Examples of reported speech in english;
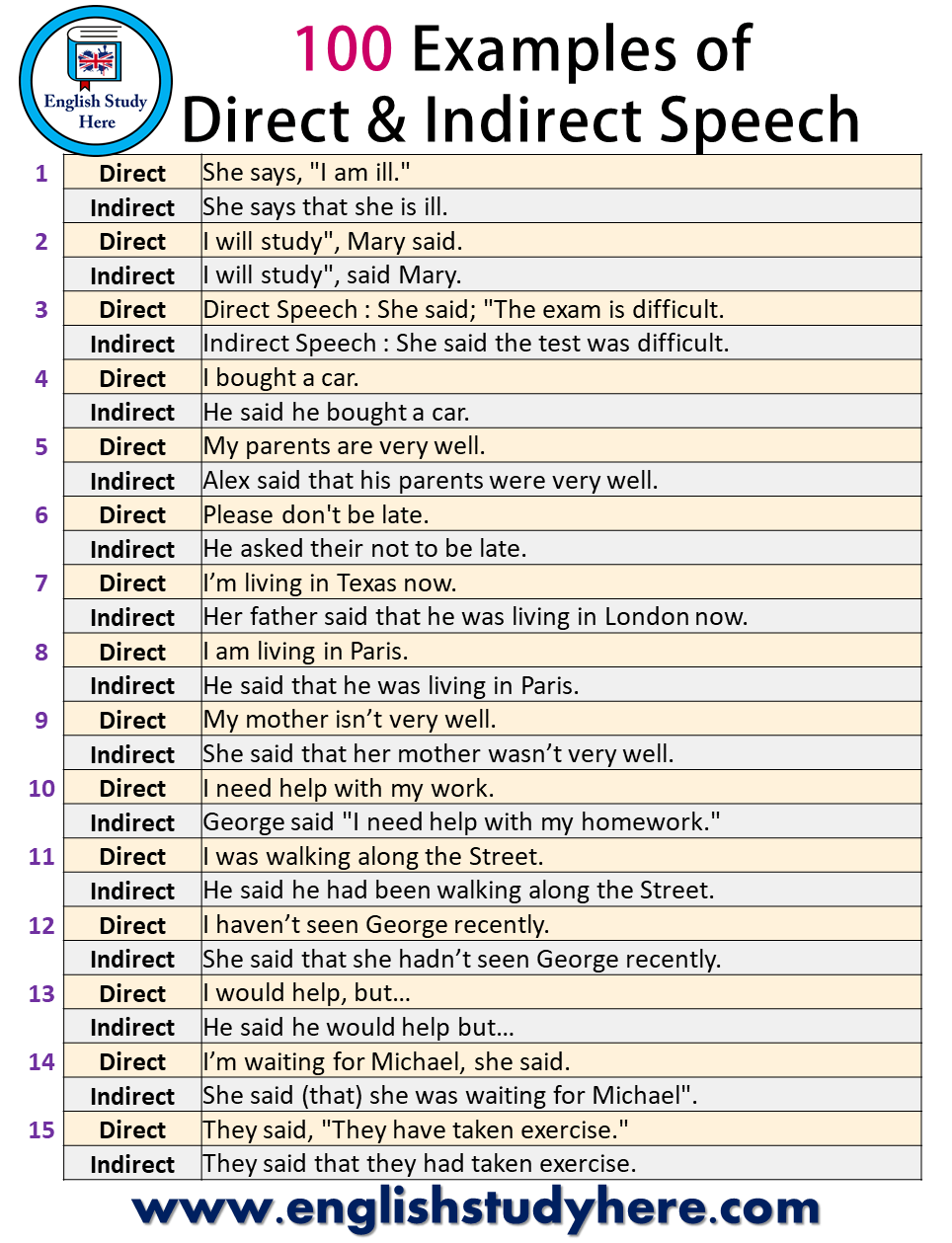
Related Posts

Present Perfect Continuous Tense in English

20 Examples of Prefixes

100 Abstract Nouns in English
About the author.

Direct and Indirect Speech Worksheet, Exercises, Examples, Rules
Understanding the Direct and Indirect Speech examples and rules is crucial for English grammar. Practice all the Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises, worksheet and the rules with examples here.

Table of Contents
Direct and Indirect Speech examples: The concept of indirect and direct speech is one of the fundamental concepts in English Grammar. As language is used to convey our thoughts and feelings to others, the concept of speech becomes even more important from the language perspective. When you use direct speaking, you repeat exactly what someone has stated. To indicate where the speaker’s words begin and end, you use quotation marks. When you report what someone has said without using their exact words, you are utilizing indirect speaking. You do not use quotation marks, and you modify the speaker’s words to fit the grammar and punctuation of the sentence in which they are reported. Here we discussed some direct and indirect speech examples which are very useful for board exams and other one-day exams.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples
Here are some direct and indirect speech examples are given below:
Direct Speech Examples:
- “I am going to the store,” said Sarah.
- “It’s a beautiful day,” exclaimed John.
- “Please turn off the lights,” Mom told me.
- “I will meet you at the library,” said Tom.
- “We are going to the beach tomorrow,” announced Mary.
Indirect Speech Examples:
- Sarah said that she was going to the store.
- John exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
- Mom told me to please turn off the lights.
- Tom said that he would meet me at the library.
- Mary announced that they were going to the beach the next day.
Remember, when converting from direct to indirect speech:
- Change the pronouns to match the subject of the reporting clause.
- Adjust the tense of the reported verb (usually one step back in time).
- Modify time expressions (today -> that day, tomorrow -> the next day, etc.).
- Use reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” “asked,” “exclaimed,” etc.
- If the sentence is a question, change it to a statement and use the appropriate reporting verb.
Indirect speech is used when reporting what someone else said without quoting their exact words. It is essential to pay attention to the changes in pronouns, tenses, and reporting verbs to convey the speaker’s original message accurately.
Direct and Indirect Speech Meaning
Since all sentences are constructed, spoken, and written using either direct or indirect speech, as was previously mentioned, this is significant. When we need to repeat a remark or action of someone via written or verbal communication, we employ both direct and indirect speech. It is employed to provide a direct-indirect description of what someone stated. Before proceeding to the Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and Examples
Direct Speech
Direct speech repeats or quotes what has been expressed or spoken. We may need to quote something spoken by a third person while speaking to another. Direct speech is used when a third party is directly cited. Inverted commas (” “) are used to write sentences in direct speech. The cited statement or sentence is written between the commas.
Indirect Speech
Indirect speech or reported speech is typically used to discuss the past, therefore we modify the tense of the words uttered into. We employ reporting verbs such as ‘tell,”say,’ and ‘ask,’ and the word ‘that’ can be used to introduce the reported in place of (” “) Direct and indirect speech introduces the concepts of’reported speech’ and’reported verb’.

Direct Speech Examples
Direct and Indirect Speech are the two types of speech that are used to explain with examples what other people say (or reported Speech).
Direct Speech: Direct speech is exactly what it sounds like: text that records a person’s exact words as they were spoken at the moment. In order for the reader to realise that the quoted text is the speaker’s own story, it is frequently surrounded by quotation marks.
some examples of direct speech:
- Statement: She said, “I will be there by 5 PM.”
- Question: He asked, “Have you finished the report?”
- Command: The coach shouted, “Run faster!”
- Exclamation: Mary exclaimed, “What a beautiful sunset!”
- Request: Tom said, “Please pass me the salt.”
- Response: John said, “Yes, I can help you with that.”
- Assertion: Sarah declared, “I’m confident that I can do this.”
- Expression of Emotion: Jane cried, “I’m so happy for you!”
- Confirmation: The teacher asked, “Is everyone ready for the test?”
- Offer: Mike said, “Would you like some more coffee?”
Indirect Speech Examples
Indirect Speech: The terms reported speech, indirect narration, and indirect speech are all used to describe indirect communication. Indirect speech is the term used in grammar to describe when you describe someone else’s statement in your own words without changing the statement’s meaning.
some examples of direct speech transformed into indirect speech:
- Indirect Speech: She said that she was going to the store.
- Indirect Speech: He said that he would call me later.
- Indirect Speech: They said that they had finished their project.
- Indirect Speech: She said that it was raining outside.
- Indirect Speech: He exclaimed that he loved that song.
- Indirect Speech: She asked if I could help her with her homework.
- Indirect Speech: They told us that they were going to the party.
- Indirect Speech: He said that he wouldn’t be able to attend the meeting.
- Indirect Speech: She requested me to pass her the salt.
- Indirect Speech: He admitted that he hadn’t seen the movie.
- Indirect Speech: They informed us that the concert started at 7 PM.
- Indirect Speech: She explained that she had been working on that project.
- Indirect Speech: He warned not to touch that.
- Indirect Speech: She promised to meet me at the cafe.
- Indirect Speech: They assured us that they could solve that problem.
Indirect speech is commonly used in writing, conversations, and storytelling to report what someone else has said in a more contextual and flowing manner.
10 Direct and Indirect Speech Examples
- Direct: She said, “I am going to the store.” Indirect: She said that she was going to the store.
- Direct: He asked, “Have you completed your homework?” Indirect: He asked if I had completed my homework.
- Direct: They exclaimed, “We won the match!” Indirect: They exclaimed with joy that they had won the match.
- Direct: The teacher said, “The exam will be on Friday.” Indirect: The teacher announced that the exam would be on Friday.
- Direct: She whispered, “I have a secret.” Indirect: She whispered that she had a secret.
- Direct: He complained, “I haven’t had any coffee today.” Indirect: He complained that he hadn’t had any coffee that day.
- Direct: The child asked, “Can I have some ice cream?” Indirect: The child asked if he could have some ice cream.
- Direct: She said, “I don’t like spinach.” Indirect: She said that she didn’t like spinach.
- Direct: He warned, “Be careful with that glass!” Indirect: He warned me to be careful with that glass.
- Direct: The manager announced, “The meeting is postponed.” Indirect: The manager announced that the meeting was postponed.

Change into Indirect Speech Answer
we can easily change into indirect speech answer examples are given below.
Direct speech – Reporting the message of the Speaker in the exact words as spoken by him.
Direct speech example : Suman said ‘I am busy now’.
Indirect speech : Reporting the message of the Speaker in our own words
Indirect speech example: Suman said that she was busy then.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples Rules
Below we have mentioned some rules for converting direct speech into indirect speech. These rules will help students in mastering this topic.
Rule 1: All present tenses in indirect speech are converted to the matching past tense when the reporting verb in direct speech is in the past tense
For example, Direct: She said , ‘I am sad’.
Indirect: She said that she was happy
Rule 2: The tenses of the direct speech are not changed if the words used are within double quotes (“”) or the reporting verb is in the present or future tense
Direct: He said, ” Humans are social animals”
Indirect: He said that Humans are social animals.
Direct: He says/will say, ‘I am running’
Indirect: He says/will say he is running
Rule 3: Past Tense and Future Tense Conversion
The past tense and future tense will change in the following tense in indirect speech.
- Simple past changes to Past Perfect
- Past Continuous Changes to Past Perfect Continuous
- Simple Future Changes to Present Conditional
- Future Continuous to Conditional Continuous
Rule 4: Interrogative sentences starting with Wh questions do not require a joining clause (conjunction) while converting into indirect speech. They act as a joining clause. Said/Said to changes into demanded, inquired, or asked
Direct: The boy asked, “Where do you live?”
Indirect: The boy inquired where I lived
Rule 5: Interrogative sentences starting with a helping verb or auxiliary verb, while converting them into indirect speech, joining clause “if” or “whether” is used.
Direct: She said, ‘Will you go home?’
Indirect: She asked whether we would go home.
Learn: Rules of Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples: Important for Board Exams
Understanding Direct and Indirect Speech with Examples is the most significant component of English Grammar since direct and indirect speech construct questions in many competitive tests as well as in the board exams.
Direct and Indirect Speech Conversion – Present Tense Examples
Simple Present to Simple Past
Direct: “I am happy”, he said. Indirect: He said that he was happy.
Present Continuous to Past Continuous
Direct: “I am playing football”, she said. Indirect: She said that she was playing football.
Present Perfect to Past Perfect
Direct: He said, “she has completed her work”. Indirect: He said that she had completed her work.
Present Perfect Continuous to Past Perfect Continuous
Direct: “I have been to San Francisco”, She told me. Indirect: She told me that she had been to San Francisco.
CLAT ONLINE LIVE CLASSES 2024
Direct and Indirect speech conversion – Past Tense Examples
Simple Past to Past Perfect
Direct: “I did the work”, he said. Indirect: He said that he had done the work.
Past Continuous to Past Perfect Continuous
Direct: “I was reading a novel”, she said. Indirect: She said that she had been reading a novel.
Direct and Indirect Speech Conversion – Interrogative Sentences Examples
Direct: “Where do you stay?” asked the boy. Indirect: The boy enquired where I stayed.
Note: While changing the interrogative sentence into indirect speech remove the question mark ‘?’.
Direct: She said, “Will you come to the party?” Indirect: She asked whether I would come to the party.
Note: While changing the interrogative sentence reporting verbs (verbs used in the first part) such as ‘said/ said to’ changes to enquired, asked, or demanded.
Direct and Indirect Speech Conversion- Modals Examples
- Can becomes Could
- May changes to Might
- Must change to had to /Would have to
- Will changes would
- Direct: She said, “Her sister can dance.”
- Indirect: She said that her sister could dance.
- Direct: They said, “We may go to the party.”
- Indirect: They said that they might buy a dress.
- Direct: Rahul said, “I must complete the work on time.”
- Indirect: Rahul said that he had to complete the work on time.
Note: Could, Would, Should, Might, and Ought to modal verbs do not change.
Direct and Indirect Speech Conversion- Pronoun Examples
The first person in the direct speech changes as per the subject of the sentence.
Direct: My brother said, “I am in class Twelfth.” Indirect: My brother said that he was in class Twelfth.
The second person of direct speech changes as per the object of reporting speech.
Direct: She says to her students, “You have done your work.” Indirect: She tells them that they have done their work.
The third person of direct speech doesn’t change.
Direct: My friend says, “She dances well.” Indirect: My friend says that she dances well.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises 1: Convert the following sentences from direct speech to indirect speech.
- Direct: She said, “I am going to the park.” Indirect: She said that she was going to the park.
- Direct: “I love ice cream,” he exclaimed. Indirect: He exclaimed that he loved ice cream.
- Direct: “We will visit the museum tomorrow,” they told us. Indirect: They told us that they would visit the museum the next day.
- Direct: “I have completed my homework,” said Jane. Indirect: Jane said that she had completed her homework.
- Direct: “It’s raining outside,” he said. Indirect: He said that it was raining outside.
Direct and Indirect speech Exercises 2: Rewrite the following paragraph in indirect speech.
Direct: “I can’t come to the party,” Lisa said. “I have a doctor’s appointment. Peter won’t be able to make it either. He’s stuck in traffic. But we hope you all have a fantastic time.”
Indirect: Lisa said that she couldn’t come to the party as she had a doctor’s appointment. She also mentioned that Peter wouldn’t be able to make it as he was stuck in traffic. However, they hoped that everyone would have a fantastic time.
Direct and Indirect speech Exercises 3: Convert the following questions from direct speech to indirect speech.
- Direct: She asked, “Are you coming to the meeting?” Indirect: She asked if I was coming to the meeting.
- Direct: “Will they finish the project on time?” he wondered. Indirect: He wondered if they would finish the project on time.
- Direct: “Can you pass me the salt?” she asked her friend. Indirect: She asked her friend if she could pass her the salt.
- Direct: “Have you seen my keys?” he inquired. Indirect: He inquired if I had seen his keys.
- Direct: “Did they enjoy the movie?” he asked. Indirect: He asked if they had enjoyed the movie.
Remember to change the pronouns, tenses, time expressions, and other relevant changes when converting from direct to indirect speech. Practicing these exercises will help you become more proficient in reporting speech accurately.
50 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises
50 examples of direct and indirect speech exercises are given below. Read 50 examples of direct and indirect speech exercises to improve your practice
- Direct : The weather is nice today, said George. Indirect : George said that the weather was nice that day.
- Direct : He asked her, “How often do you play?” Indirect : He asked her how often she played.
- Direct : She said, “I work in a bank.” Indirect : She said that she worked in a bank.
- Direct: My mother said , “ I’m angry with you.” Indirect : My mother said she was angry with me.
- Direct : She said’ “I can help you tomorrow.” Indirect : She said that she could help me tomorrow.
- Direct : My son says, “I will not eat food.” Indirect : My son says that he will not eat food.
- Direct : “Dance with me!” Maria said to me Indirect : Maria told me to dance with her.
- Direct : Must I do the city? Indirect : My sister asked if she had to do the city.
- Direct : Please wash your hands! Indirect : My father told me to wash my hands.
- Direct : She said, “I went to the shopping center.” Indirect : She said that she had gone to the shopping center.
- Direct : I write poems. Indirect : He says that he writes poems.
- Direct : She said: “I would buy new house if I were rich”. Indirect : She said that she would buy new house if she had been rich”.
- Direct : May I go out? Indirect : She wanted to know if she might go out.
- Direct : She is American, she said. Indirect : She said she was American.
- Direct : My son, do the exercise.“ Indirect : Sh told her son to do the exercise.
- Direct : I don’t know what to do. Indirect : Samuel added that he didn’t know what to do.
- Direct : I am reading a book, he explained. Indirect : He explained that he was reading a book.
- Direct : My father said, “I am cooking dinner.” Indirect : My father said he was cooking dinner.
- Direct : My sister said, “I had already eaten.” Indirect : My sister said she had already eaten.
- Direct : My boyfriend asked, “Do you like horror films?” Indirect : Do you like horror films? my boyfriend asked.
- Direct : I never get up late, my mother said. Indirect : My mother said that she never got up late.
- Direct : She said, “I might come early.” Indirect : She said she might come early.
- Direct : I am leaving home now.” Indirect : He said that he left home then.
- Direct : Are you living here? Indirect : He asked me if I was living here.
- Direct : I’m going to come. Indirect : She said that she was going to come.
- Direct : We can communicate smoothly. Indirect : They said that they could communicate smoothly.
- Direct : My mother isn’t very well. Indirect : She said that her mother wasn’t very well.
- Direct : I need help with my work. Indirect : George said “I need help with my homework.”
- Direct : I was walking along the Street. Indirect : He said he had been walking along the Street.
- Direct : I haven’t seen George recently. Indirect : She said that she hadn’t seen George recently.
- Direct : I would help, but… Indirect : He said he would help but…
- Direct : I’m waiting for Michael, she said. Indirect : She said (that) she was waiting for Michael”.
- Direct : They said, “They have taken exercise.” Indirect : They said that they had taken exercise.
- Direct : I can speak perfect Spanish. Indirect : He said he could speak perfect Spanish.
- Direct : I haven’t seen Mary. Indirect : He said he hadn’t seen Mary.
- Direct : What is your name? she asked me. Indirect : She asked me what my name was.
- Direct : I was sleeping when Mary called. Indirect : He said that he had been sleeping when Mary called.
- Direct : Please help me! Indirect : He asked me to help his.
- Direct : “I’ve found a new job,” my mother said. Indirect : My mother said that she had found a new job.
- Direct : Go to bed! mother said to the children. Indirect : The mother told the children to go to bed.
- Direct : Mark arrived on Sunday, he said. Indirect : He said that Mark had arrived on Sunday.
- Direct : I have been to France, she told me. Indirect : She told me that she had been to France.
- Direct : Michael said, “I have finished my lunch.” Indirect : She said that she had finished his lunch.
- Direct : My brother said, “I met Alex yesterday.’ Indirect : My brother said that he had met Alex yesterday.
- Direct : The dentist said, “Your father doesn’t need an operation.” Indirect : The dentist said that my father doesn’t need an operation.
- Direct : He said, “Man is mortal.” Indirect : He said that man is mortal.
- Direct : Sansa said, “I am very busy now”. Indirect : Sansa said that she was very busy then.
- Direct : He said, “I am a football player.” Indirect : He said that he was a football player.
- Direct : Michael said, “I will buy a new car.” Indirect : Michael said that she will buy a new car.
- Direct : Mark said, “Bill needs a pencil.” Indirect : Mark said that Bill needed a pencil.
Reported Speech Examples with Answers
Example 1: Direct Speech: “I am going to the party tonight,” she said. Reported Speech: She said that she was going to the party tonight.
Example 2: Direct Speech: “We have been working on this project for months,” they exclaimed. Reported Speech: They exclaimed that they had been working on that project for months.
Example 3: Direct Speech: “He will come back tomorrow,” he assured us. Reported Speech: He assured us that he would come back the next day.
Example 4: Direct Speech: “I won’t be able to attend the meeting,” she told him. Reported Speech: She told him that she wouldn’t be able to attend the meeting.
Example 5: Direct Speech: “They had already left,” he informed me. Reported Speech: He informed me that they had already left.
Example 6: Direct Speech: “I didn’t see her at the event,” John said. Reported Speech: John said that he hadn’t seen her at the event.
Example 7: Direct Speech: “We’re planning a surprise for you,” they whispered. Reported Speech: They whispered that they were planning a surprise for me.
Example 8: Direct Speech: “It’s raining outside,” she observed. Reported Speech: She observed that it was raining outside.
Example 9: Direct Speech: “I have finished my homework,” he mentioned. Reported Speech: He mentioned that he had finished his homework.
Example 10: Direct Speech: “I am reading a great book,” she told me. Reported Speech: She told me that she was reading a great book.
Remember that in reported speech, the tense may shift back (usually one tense back) from the original direct speech, and some pronoun changes might occur depending on the context. Also, changes in time expressions, adverbs, and demonstratives might be necessary.
Direct and Indirect Speech Worksheet
Direct and indirect speech worksheet is a great way to practice and understand how reported speech works in English. Below, you’ll find a direct and indirect speech worksheet with exercises designed to test knowledge of converting sentences from direct to indirect speech and vice versa.
Instructions: Convert the following sentences from direct speech to indirect speech, and vice versa. Make sure to change the tense, pronouns, and time expressions where necessary.
Part A: Convert from Direct to Indirect Speech
- She said, “I am reading a book.”
- He said, “I will go to the park tomorrow.”
- The teacher said, “The Earth revolves around the Sun.”
- “I have finished my homework,” said John.
- The doctor said, “You need to take this medicine twice a day.”
Part B: Convert from Indirect to Direct Speech
- She said that she had been waiting for the bus since morning.
- He told me that he was going to visit his grandparents the next day.
- They said that they had seen the movie the previous week.
- She mentioned that she could play the piano.
- The boy exclaimed that he had won the race.
- She said that she was reading a book.
- He said that he would go to the park the next day.
- The teacher said that the Earth revolves around the Sun.
- John said that he had finished his homework.
- The doctor said that I needed to take that medicine twice a day.
- “I have been waiting for the bus since morning,” she said.
- “I am going to visit my grandparents tomorrow,” he told me.
- “We saw the movie last week,” they said.
- “I can play the piano,” she mentioned.
- “I have won the race!” the boy exclaimed.
This worksheet covers basic transformations between direct and indirect speech, focusing on the changes in verb tenses, pronouns, and time expressions. Adjustments in complexity can be made to cater to different learning levels.
Sharing is caring!
Q. How do you know if a speech is direct or indirect?
Ans. Direct speech is exactly what it sounds like: text that records a person's exact words as they were spoken at the moment. Indirect speech is used to describe someone else's statement in your own words without changing the statement's meaning.
Q. Why do we use indirect speech?
Ans. Indirect speech is used to report what someone may have said, so it is always used in the past tense.
Q. What are the two parts of direct speech?
Ans. The two parts of direct speech are reporting verb and reported speech.
Q. Why do we learn direct and indirect speech?
Ans. Direct speech reveals the tone and moods of the characters. Indirect speech, if not used properly, creates a distance between the utterance and the reader's perception of it.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Trending Articles
- AP Inter Results 2024 Link
- NEET Syllabus 2024 [Reduced]

CBSE Board Exam 2024
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Previous Year Papers
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Previous Year paper
- CUET Participating College & Universities
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main Syllabus 2024
- JEE Main Exam Analysis 2023
- NEET 2024
- NEET Syllabus 2024
- NEET State wise Cut off
- NEET Rank Predictor
- NEET OMR Sheet
- NEET College Predictor
Recent Posts
Important exams, ncert solutions.
- NCERT Class 12
- NCERT Class 11
- NCERT Class 10
- NCERT Class 9
NCERT Books
School syllabus.
- CBSE Class 12
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Class 9
- JEE Mains 2024
Our Other Websites
- Teachers Adda
- Bankers Adda
- Adda Malayalam
- Adda Punjab
- Current Affairs
- Defence Adda
- Adda Bengali
- Engineers Adda
- Adda Marathi
- Adda School

Get all your queries solved in one single place. We at Adda247 school strive each day to provide you the best material across the online education industry. We consider your struggle as our motivation to work each day.
Download Adda247 App
Follow us on
- Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
English for Students
- Confused Words
- What is NEW?
- Nursery Rhymes
- Beauties of English
- Intermediate Level
- Advanced English
- Plain English
- Your English Teacher
- Business Letters
- Difficult Words
- Social Letters
- Short Stories
- English Poems
- Poem Topics
- TOP 100 Poems
- English Songs
- Famous Quotations
- Business Dictionary
Popular Pages
- Transformation of Sentences
- Direct to Indirect Speech
- Confused and Misused Words, Vocabulary
- Intermediary-level
- Privacy Policy

Rules for Changing Indirect to Direct Speech
Back to: Direct and Indirect Speech (Narration)
Narration change from Indirect to direct speech follows the reverse rules of changing the narration from Direct to Indirect speech. So, if you attentively learn the rules of narration change from Direct to Indirect, it would be easy to change narration from Indirect to Direct speech.
To convert indirect speech to direct speech, we have to add punctuation marks at proper places.
Reported clause of the sentence should be put inside a quotation mark. A comma also have to be added. e.g.
- Indirect: Ritu said that she was eating rice.
- Direct: Ritu said, “I am eating rice.”
In case of changing narration from indirect to direct speech, conjunction such as that, if, whether, should be omitted. e.g.
- Indirect: Mohan asked if I was okay.
- Direct: Mohan said, “Are you okay?”
Here the conjunction ‘if’ is omitted.
While changing indirect to direct speech, the tense of the sentence changes. The tense of the reported clause is restored to the tense in which the original speaker has spoken the words. e.g.
- Indirect : Priya said that she liked reading books.
- Direct: Priya said, “I like reading books.”
In this case, the sentence does not always ends with full stop. While changing indirect to direct speech, the ending punctuation mark depends on the type of sentence. It can be an exclamatory mark in case of exclamatory sentence or a question mark in case of interrogative sentence. e.g.
- Indirect: Bipasha asked Rakesh what he was doing.
- Direct: Bipasha said to Rakesh, “What are you doing?”
- Indirect: She exclaimed with horror that the sight was very horrible.
- Direct: She said, “What a horrible sight!”
Pronouns, time, place also changes accordingly from indirect to direct. e.g.
- Indirect: Father told me to go home then.
- Direct: Father said, “Go home now.”
Here ‘then’ changes to ‘now’.
- Indirect: Rupa said that she read poetry.
- Direct: Rupa said, “I read poetry.”
‘She’ pronoun is replaced by ‘I’.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Direct: "I will help you," she promised. Reported: She promised that she would help me. Direct: "You should study harder," he advised. Reported: He advised that I should study harder. Direct: "I didn't take your book," he denied. Reported: He denied taking my book. Direct: "Let's go to the cinema," she suggested.
However, indirect speech implicitly shares the content of the person's original words. Example: Direct Speech: He said, "I am hungry." Indirect Speech: He said that he was hungry. Notably, an essential component of indirect speech is the change in verb tense. In the direct speech example, the speaker uses the present tense "am."
Change the pronouns accordingly. You should also change the pronoun based on who the speaker, doer, and receiver of the action is. Example: Direct Speech: Wendy says, "Ron, y ou should take care of yourself .". Indirect Speech: Wendy told Ron that he should take care of himself.
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Future Tense. An action in the future (present continuous tense or future) doesn't have to change verb tense, either, as these examples demonstrate. Direct speech: Jerry said, "I'm going to buy a new car." Indirect speech: Jerry said (that) he's going to buy a new car. Direct speech: Jerry said, "I will buy a new car."
Direct speech (exact words): Mary: Oh dear. We've been walking for hours! I'm exhausted. I don't think I can go any further. I really need to stop for a rest. Peter: Don't worry. I'm not surprised you're tired. I'm tired too.
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please. Instead, say request or say. For example: "Please don't interrupt the event," said the host.
Direct speech: Sheila said, "I am meeting my brother tomorrow.". Indirect speech: Sheila said that she was meeting her brother the following day. Here are a few examples of other typical time expressions and how they change: Direct Speech. Indirect Speech. Yesterday. The day before. Now.
Indirect Speech is a way of expressing the words or utterances of a speaker in a reported manner. In contrast to direct speech, where the original speaker's words are quoted verbatim, indirect speech is more about reporting the essence or meaning of what the speaker said rather than quoting them exactly. For example:
Look at these examples to see how we can tell someone what another person said. direct speech: 'I love the Toy Story films,' she said. indirect speech: She said she loved the Toy Story films. direct speech: 'I worked as a waiter before becoming a chef,' he said. indirect speech: He said he'd worked as a waiter before becoming a chef. direct speech: 'I'll phone you tomorrow,' he said.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech. Change of Pronouns. Change of Tenses. Change of Time and Place References. Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech. Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks. Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker. Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb. Step 4: Change the Pronouns.
When introducing indirect speech with a reporting verb, use a comma to separate the reporting verb from the reported speech. Example: She said, "I'll be there on time." Rule 11: Question Mark to Full Stop. If the direct speech is a question, change the question mark to a full stop when converting to indirect speech. Example:
Change of Tenses in Direct and Indirect Speech Examples. Direct: He says, "You will make a good result.". Indirect: He says that I shall make a good result. Direct: Mother says, "I made the fish curry.". Indirect: Mother says that She made the fish curry. Direct: He will say, "I shall be there within an hour.".
Narration change, also known as reported speech or indirect speech, is a linguistic tool that allows us to express someone else's words or thoughts in our own words. It involves transforming direct speech into indirect speech, a skill that can greatly enhance the clarity and variety of communication. Before we embark on our journey of ...
Here are the steps involved in converting direct speech to indirect speech: Remove the quotation marks. Use a reporting verb to introduce the indirect speech. Change the tense of the verb in the quote if necessary. Change the pronouns if necessary. Use the appropriate conjunction if necessary.
A direct speech can be transformed into an indirect speech and vice versa using a suitable reporting verb and a linker depending on the sentence. Let's have an example first. Tina said to me, "Are you busy now?" [direct speech] Tina asked me whether I was busy then. [indirect speech] Direct Speech. Speaker. Reporting verb. Direct speech ...
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
Rules for Changing Sentences To Indirect Speech. Here are the key rules for converting sentences from direct speech to indirect speech. These rules include changes in verb tense, pronouns, and other elements to maintain the meaning of the original statement.
Mathilda told me she had to go out. (Indirect Speech) Mathilda said: "I have to go out.". (Direct Speech) Julie asked if the train had left when she arrived at the ticket office. (Indirect Speech) Julie asked: "Did the train leave?" (Direct Speech) It is too late. I said it was too late.
100 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech in English, 100 Examples of reported speech in english; 1 Direct She says, "I am ill." Indirect She says that she is ill. 2 Direct I will study", Mary said. Indirect I will study", said Mary. 3 Direct She said; "The exam is difficult. Indirect She said the test was difficult. 4 Direct I bought a car. Indirect He said he bought a car. 5 ...
Change into Indirect Speech Answer. we can easily change into indirect speech answer examples are given below. Direct speech - Reporting the message of the Speaker in the exact words as spoken by him. Direct speech example: Suman said 'I am busy now'.. Indirect speech: Reporting the message of the Speaker in our own words. Indirect speech example: Suman said that she was busy then.
These examples are enough for you to understand how to change an Indirect to Direct Speech. Follow all the rules which we learned for changing the Direct to Indirect Speech in reverse for changing Indirect to Direct Speech. Go to the section on 'Transformation-of-Sentences-1' to continue. Go to the 'Intermeduary Index' Page. HOME PAGE
Rule 1. To convert indirect speech to direct speech, we have to add punctuation marks at proper places. Reported clause of the sentence should be put inside a quotation mark. A comma also have to be added. e.g. Indirect: Ritu said that she was eating rice. Direct: Ritu said, "I am eating rice.". Rule 2.