Advertisement

Recycling of construction and demolition waste and its impact on climate change and sustainable development
- Published: 01 April 2021
- Volume 19 , pages 2129–2138, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- M. A. T. Alsheyab ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0487-7718 1 , 2
3981 Accesses
37 Citations
20 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
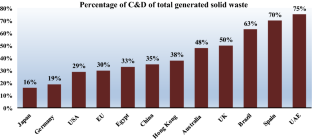
The huge generated amounts of construction and demolition (C&D) waste around the world, which amounts up to more than 25% of the total generated waste, has become a serious environmental challenge that needs to be addressed. This analytical review paper sheds light on the different adverse environmental impacts of the presently used conventional management method of landfilling and proposes waste recycling as an alternative sustainable management option. Analysis showed that C&D waste recycling could be an effective mitigation option to reduce the risk of landslides; reduce the energy consumption; offset the greenhouse emissions where about 39% is attributed to the construction industry; recover added-value materials; create jobs; and protect the earth’s natural resources. The results of analysis highlight the importance of on-site recycling and segregation at source for offsetting the greenhouse gas emissions as well as mitigating the risks of the hazardous portion. The results of this analytical review promote the importance of diverting construction and demolition waste from landfill sites to recycling and help decision makers to adopt the recycling option to achieve sustainable development.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Environmental feasibility of recycling construction and demolition waste

Sustainable Method for Construction and Demolition Waste: A Review
A study on the waste generation rates and recycling potential for the construction and demolition waste in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Adnan E, Bernd K, Ehsan R (2014) An evaluation of environmental impacts of construction projects. Rev Ingen Constr RIC 29(3):234–254
Article Google Scholar
Al-Ansary MS, El-Haggar SM, Taha MA (2004) Sustainable guidelines for managing demolition waste in Egypt, 9–11 November 2004, Barcelona, Spain
Caicedo B, Giraldo E, Yamin L, Soler N (2002) The landslide of Dona Juana Landfill in Bogota. A case study. In: Conference: proceedings of the fourth international congress on environmental geotechnics (4th ICEG), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil At: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
CDRA Report (2017) Benefits of construction and demolition debris recycling in the United States
Cherilyn V, Kyle M-J, Brett C (2014) An energetic life cycle assessment of C&D waste and container glass recycling in Cape Town, South Africa. Resour Conserv Recycl 88:39–49
Christian F, Mads W (2009) EU as a recycling society: present recycling levels of municipal waste and construction and demolition waste in the EU. European Topic Centre on Sustainable Consumption and Production, Copenhagen
Google Scholar
Danfeng Y, Huabo D, Qingbin S, Xiaoyue Li, Hao Z, Hui Z, Yicheng L, Weijun S, Jinben W (2018) Characterizing the environmental impact of metals in construction and demolition waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:13823–13832
Duan H, Hu J, Tan Q, Liu L, WangLi YJ (2015) Systematic characterization of generation and management of e-waste in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1929–1943
Eneh AEO, Oluigbo SN (2012) Mitigating the impact of climate change through waste recycling. Res J Environ Earth Sci 4(8):776–781
CAS Google Scholar
EPA (2016) Recycling Economic Information (REI) Report
EPA (2015) advancing sustainable materials management: fact sheet assessing trends in material generation, recycling, composting, combustion with energy recovery and landfilling in the United States
EPA (2020) Construction and demolition debris management in the United States. 2015 U.S., Office of Resource Conservation and Recovery
EPA's (2016) Recycling Economic Information (REI) Report
Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction (2019). https://www.worldgbc.org/sites/default/files/2019%20Global%20Status%20Report%20for%20Buildings%20and%20Construction.pdf
Guidance on applying the Waste Hierarchy (2011) pb13530-waste-hierarchy-guidance. www.defra.gov.uk
Humam ZF, Faisal ZS (2020) A mini review of construction and demolition waste management in India. Waste Manag Res 38(7):708–716
Kanayochukwu CA, Joel A, Chidozie CN (2015) Spatiality, seasonality and ecological risks of heavy metals in the vicinity of a degenerate municipal central dumpsite in Enugu, Nigeria. J Environ Health Sci Eng 13:1–15
Knut S, Dirk J, Stephanie S, Christian T (2004) Definition of waste recovery and disposal options, final report
Li L, Weber R, Liu JG, Hu JX (2016) Long-term emissions of hexabromocyclododecane as a chemical of concern in products in China. Environ Int 91:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.03.007
Article CAS Google Scholar
Marinkovic S, Radonjanin V, Malesev M, Ignjatovic I (2010) Comparative environmental assessment of natural and recycled aggregate concrete. Waste Manag 30:2255–2264
Mawed M, Al Nuaimi M, Kashawni G (2020) Construction and demolition waste management in the UAE: application and obstacles. Int J Geomate 18(70):235–245
Miguel M, Jorge B, Manuel DP, Miguel B (2013) Construction and demolition waste indicators. Waste Manag Res 31:241–255
Navarro F, Vincenzo T (2019) Waste mismanagement in developing countries: a review of global issues. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:1060
Nunes KRA, Mahler CF (2020) Comparison of construction and demolition waste management between Brazil. Eur Union USA Waste Manag Res 38(4):415–422
Oliver C, Helmut R (2008) Material flow analysis with software STAN. J Environ Eng Manag 18(1):3
Ritzen MJ, Haagen T, Rovers R, Vroon ZAEP, Geurts CPW (2016) Environmental impact evaluation of energy saving and energy generation: case study for two Dutch dwelling types. Build Environ 108:73–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2016.07.020
Sasitharan N, Ismail AR, Ade A, Aftab HM, Imran L (2012) Issues on construction waste: the need for sustainable waste management. In: IEEE colloquium on humanities, science and engineering research (CHUSER 2012), December 3–4, 2012, Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia
Serdar U, Aynur K, Volkan A (2017) Construction and demolition waste recycling plants revisited: management issues. Proc Eng 172:1190–1197
Vivian WYT (2009) Comparing the implementation of concrete recycling in the Australian and Japanese construction industries. J Clean Prod 17:688–702
Weisheng L, Vivian WYT (2013) Construction waste management policies and their effectiveness in Hong Kong: a longitudinal review. Renew Sustain Environ Rev 23:214–223
Wilson D (2015) UNEP; International Solid Waste Association, Global waste management outlook 2015
Zhao W, Ren H, Rotter VS (2011) A system dynamics model for evaluating the alternative of type in construction and demolition waste recycling. Resour Conserv Recycl 55(11):933–944
Download references
Acknowledgements
The author wish to thank all those who assisted in conducting this work.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Ministry of Development Planning and Statistics, Doha, Qatar
M. A. T. Alsheyab
Qatar University, Doha, Qatar
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to M. A. T. Alsheyab .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declare that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Shabani.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Alsheyab, M.A.T. Recycling of construction and demolition waste and its impact on climate change and sustainable development. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19 , 2129–2138 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03217-1
Download citation
Received : 08 December 2020
Revised : 18 January 2021
Accepted : 13 February 2021
Published : 01 April 2021
Issue Date : March 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03217-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Construction and demolition waste
- Sustainable development
- Environmental impact assessment
- And climate change
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

A waste minimisation framework for the procurement of design and build construction projects
- Architecture, Building and Civil Engineering
Publication date
Ethos persistent id, administrator link.
- https://repository.lboro.ac.uk/account/articles/9456404
Usage metrics

- Other built environment and design not elsewhere classified

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

MANAGING AND MINIMIZING WASTAGE OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS: A CASE STUDY ON SELECTED PUBLIC BUILDING PROJECTS IN ADDIS ABABA

2023, MANAGING AND MINIMIZING WASTAGE OF CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS ON SELECTED PUBLIC BUILDING PROJECTS IN ADDIS ABABA
Waste is a significant issue in the building sector, impacting the nation's economy and the environment. This study aims to identify primary waste causes in the Ethiopian construction industry and develop strategies to prevent and eliminate these issues. The research involved 113 questionnaires from construction firms in Ethiopia. The main causes of material waste include manufacturing defects, over ordering, rework, wrong material handling, ambiguities, and material damage. Most construction companies attempt to reduce waste at the source, but recycling is more effective when combined with other waste reduction strategies. The study concluded that considering construction waste increases national income, encourages companies to decrease waste, and keeps the environment clean. The study recommends the establishment of new building waste departments in municipalities and ministries, waste management rules, and efficient approaches to reduce construction waste. Owners should use contractors' prior experience with waste management when awarding contracts, designers should consider material and component dimensions, and contractors should create waste management plans and allocate qualified workers and employees to construction projects.

Related Papers
Turkish Online Journal of Qualitative Inquiry (TOJQI)
Prof. Dr. Subash Thanappan , Galeta Chala
All over the world, the development of construction related industries depend on the natural and artificial resources. The generation of wastes from the construction industries and its management is a big task for the proponents and stake holders of the industry. The quantity of waste generation from the construction industryis highly related to the construction methods, improper management, the onsite sorting and recycling abilities for construction waste, the levels of education and trainingsgiven to workers and the design concepts. The current research focuses to identify the contributory factors that influences the generation of construction material wastage.In addition, the study aims to deeply analyze the impact of construction material waste on cost at building construction project and recommends the strategies to minimize the construction material wastage. Data collection was done through questionnaire survey and interviews among the different stake holders in building construction (Clients, Consultants, Contractors and other Professionals) in Addis Ababa. Stratified Sampling technique was considered as a tool to opt for the Sites with regards to all the civil engineering professionals, stakeholders like contractors, consultants, and clients.The current study focuses in identifying and analyzing the major impacts of the construction material wastage at building construction site in Kolfe Keranio sub city, Addis Ababa. The outcome of the result would bring strong information to clients, consultants and contractors and other stakeholders in minimizing the overall cost due to material wastage.
Asmara Seyoum
ABSTRACT Construction industry is an industry, which is involved in the planning execution and evaluation (monitorin g) of all types of civil works. Physical infrastructures such as buildings, communication & energy related construction works, water supply & sewerage civil works etc. are some of the major projects (program) in the construction industry. Construction industry plays an important role in social, economical & political development of a country. Construction is not only one of the major sectors of an economy but it is also the largest and accounts from 12% to 25% of the GNP of both developed & developing countries. It consumes the higher percentage of the annual budget of a country; specifically in our country Ethiopia, it covers 58% of the annual budget. However, the industry has been experiencing such problems as managing and minimizing wastage of construction n materials due to lack of effective management and planning. One of the very important sections that should specify in the construction project management is managing and minimizing wastage of construction materials at construction projects. The successf ul execution of construction projects within given cost, time and quality, good handling of construction materials on construction site requires systematic planning and controlling of the construction works. This explains also that the management of materials becomes the most pertinent source of construction waste. The type of materials produced to serve the industry range from raw goods such as sand, aggregates, soil and water to manufactured goods such as bricks, cement, plasterboard, metals (steel and iron), timber, concrete, cement, and plaster. Because of a high rate of consumption of these materials, waste is generated in large quantities, which can have significant impact on the environment. Now a day‟s in Ethiopia construction industries are booming due to implementing major infrastructure projects together with many public buildings, commercial building and housing development programmes. Therefore, this research were attempt to assess the current situation of managing and minimizing wastage of construction materials in the Addis Ababa on selected public building construction projects and formulate and give recommendations with respect to handling of construction materials in accordance with the outcome of the paper. The main tools for the collection of data included questionnaires, interviews and site visit were used to identify the various efforts that have been made in the past to evaluate and examine the causes and sources of construction materials waste on building construction project. Simple statistical analysis involving tables and percentages were used in analyze the results from the questionnaire. Secondary sources of data were obtained from relevant literature that covered research, publication on the subject matter. The findings of this research indicate that the level of contribution of the waste sources to the generation of waste saw differences between the perceptions of the respondents (Contractors, consultants and client). The results from analysis ranked from the first to fifth positio n by contractors, consultants and owners that the most significant factors causing construction waste on building construction projects are: - Site supervision factors, Materials handling and storage factors,Design and documentation factors, Site management and practices factors and Operations factors. The results of this study recommended that there is a need to establish a new construction waste department to develop waste management policies and develop the effective strategy to reduce construction waste. The study recommended the owners to take the waste management history of the contractors as a criterion in awarding contracts. The study recommended the consultants to give attention to avoid design and planning errors at the design and planning stages. The study also recommended the contractors to assign qualification staff and workforce in construction projects and to prepare waste management plan. Key words: - Benefits of Waste Minimization, Causes and sources of materials, Construction, Construction m aterials, Construction Materials Management, Waste managing & Waste minimizing.
26th Annual Conference of the International Group for Lean Construction
Tadesse Ayalew
Journal of Engineering Science
Tamene Adugna
Construction sites generate a large amount of material wastes and have become a common problem with associated risks in Ethiopia. However, the sources of such wastes are not well recognised. Therefore, the purpose of this research was to analyse the risk factors that contribute to material wastes in building construction projects. To achieve this goal, the factors that cause construction wastes were identified from literature and construction experts via focus group discussions and personal interviews. Following this, the factors were subjected to a questionnaire survey to identify the most critical factors of construction wastes. The questionnaire was distributed purposively to 85 construction experts representing contractors, consultants, and clients and 70 questionnaires were duly received for analysis. The data were analysed with a mean score and ranked to identify the most critical factors generating material wastes at construction sites. According to the results of the study f...
Muhwezi Lawrence
Nihal A. Osman
The rapid economic growth and urbanization in Ethiopia have led to extensive construction activities in major cities. Construction activities have known to generate large quantities of wastes that pose serious environmental problems. This paper presents the challenges of construction waste management practices in Mekelle city and explores appropriate measures to address the issues in a more sustainable way. Field observation, questionnaire survey, interviewing of public sector officials at different levels was conducted to identify the source and management options of construction waste in the city. The findings showed that the majority of survey participants felt that their firms have taken various measures to manage construction waste. It was revealed that 40% of the respondents exercise illegal dumping as a common method of waste management, which is closely followed by reuse and recycling. It is evident that over 75% of the construction- generated has potential for recycling and...
American Journal of Civil Engineering
Garba Wokjira Fayisa
In the construction industry, construction material is one of the major cost components and it is 50% to 70% of the total construction cost. However, the industry generates 30%-65% of wastage for landfill. Effective use of construction material is profitable in the industry as well as in the economy of any country. However, material wastage management in construction are rarely studied by Ethiopian context. Hence, this research is aimed to investigate cause of construction material wastage and rank highly wasted construction material wastage on public building projects in western Oromia. The Study uses both primary and secondary data by structured questionnaires and case study (interviews and site visits). The research has covered a population of General and Building contractors from level one to three and their supervisor’s that are employed in western Oromia on public buildings. The purposive sampling techniques were used to collect the data and Analyzed and presented by mean scor...
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology (IJERT)
IJERT Journal
https://www.ijert.org/the-perspective-of-tradesmen-on-material-wastage-in-the-construction-industry https://www.ijert.org/research/the-perspective-of-tradesmen-on-material-wastage-in-the-construction-industry-IJERTV9IS080086.pdf Construction material wastage has been identified as a major threat to the environment, cost of delivery, and project duration. This paper sought to identify the significant level of the major sources and factors influencing material wastage from the perspective of tradesmen and to assess the quantities of the various categories of waste on building construction sites in the Upper West Region of Ghana. The study was carried out employing both open and closed-ended questionnaire survey. A total of 150 respondents representing different trades were involved in the study. The findings revealed that frequent design changes and poor design, excessive quantities of materials than required, poor material handling and storage on-site, poor strategy for waste minimization, and poor site management and conditions were the highest-ranking factors that influence construction material waste generation. It was further revealed that wood, sandcrete block, concrete, and metal were the most wasteful construction materials. The study recommended the investment of considerable efforts to ensure due diligence to improve all contractual documents. Contractors should endeavour to employ qualified on-site technical supervising and administrative staff to implement and safeguard effective site management practices to ensure material waste minimizing.
Emmanuel C EZE , Eyong Obenke Patrick , Osusha Loya
Material waste generated by the activities of the construction industry poses serious danger to both the construction projects concerned and the environment at large. Previous researches both at local and international level have neglected construction operatives and craft men who are the majority stakeholder. The study was aim to assess the perception of construction operatives, Tradesmen and Artisans on materials waste generation in the construction industry, with a view to encouraging better performance of construction projects in Nigeria. The study employed questionnaire survey. Tables and figures where used to present the collected data and Mean item score (MIS) and percentage were used to analyze the data collected. Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney U-Test were used to test the hypotheses. It was discovered that formwork from wood/timber, Mortar from Rendering/plastering and Blockwork/ Brickwork are the most wasteful material generated on sites; Design (Frequent design changes and poor design), Poor materials storage system and Theft and vandalism are the most important factors that influence material waste generation during construction; Proper site supervision and management techniques, Adequate storage of material, and Staff training and awareness on waste management are the measures of minimizing construction material waste; and saving cost of disposal and transport, increased profit and save construction time loss are the most important benefits of material waste minimization. It was recommended that site operatives and craft men should be carried along in every management decision regarding waste management plan development as they constitute the major stakeholders on sites.
International journal of engineering research and technology
George Dokyi
Construction material wastage has been identified as a major threat to the environment, cost of delivery, and project duration. This paper sought to identify the significant level of the major sources and factors influencing material wastage from the perspective of tradesmen and to assess the quantities of the various categories of waste on building construction sites in the Upper West Region of Ghana. The study was carried out employing both open and closed-ended questionnaire survey. A total of 150 respondents representing different trades were involved in the study. The findings revealed that frequent design changes and poor design, excessive quantities of materials than required, poor material handling and storage on-site, poor strategy for waste minimization, and poor site management and conditions were the highest-ranking factors that influence construction material waste generation. It was further revealed that wood, sandcrete block, concrete, and metal were the most wasteful...
RELATED PAPERS
Thomas Meade
Ms Glow Whitening
Robert Dohner
KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering
Thủy Nguyễn
European Journal of Cancer
Kathi Apostolidis
Biuletyn Instytutu Hodowli i Aklimatyzacji Roślin
Piotr Ochodzki
Brayan stiven Cano valencia
Proceedings
Remus Hanea
Physica Scripta
Joana Rita Martins Lopes
Economía Agraria y Recursos Naturales
Milagros Estrada
Soo-jong Rey
Studies in health technology and informatics
Nikolaos Kakaletsis
Si Won Song
Applied Petrochemical Research
Physical Review D
Charling Tao
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology
Mylo Wagner
Andualem Tsegaye
Knowledge & Management of Aquatic Ecosystems
Iva Langrová
International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders
Margrethe Halvorsen
Journal of Medicinal Plants Research
Mohammed Abubakar
Physiological Reports
James Bagley
The EMBO Journal
Heinz Saedler
Nuclear Engineering and Design
Andrei Blahoianu
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

- Construction and Demolition Recycling Ordinance
The City has a Construction and Demolition (C&D) Ordinance (05-09) requiring all demolition projects, all commercial projects valued over $200,000, all new commercial projects over 1,000 square feet, all new residential construction projects, and all residential additions and improvements that increase building area, volume, or size to recycle a minimum of 65% of all inert materials and 65% of all other materials.
City of Santa Clarita Franchised Hauler List
Please reference the steps below in order to obtain Environmental Services agency Clearance:
Cdmmp application, deposit payment, agency clearance, cdmmp deposit refunds.
It is your responsibility to ensure all recycling requirements are met throughout the process of your project and all documentation is kept and submitted. All projects must be finalized with Building and Safety before refunds can be processed. Refer to the two options below to obtain your diversion records:
1. Request a diversion report from the franchised waste hauler you hired for your project’s waste services. 2. Complete a self-haul verification form for any material that was self-hauled directly to the landfill or a recycling center. Copies of all weight tickets, scale reports or diversion reports must be provided for all material documented on your completed verification form.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is a cdmmp.
A Construction and Demolition Materials Management Plan (CDMMP) is a form to assist applicants in planning C&D recycling efforts. This form is collected prior to building permit. A PDF of the City of Santa Clarita’s CDMMP can be found here: CDMMP Form 2023_FINAL
DO I HAVE TO COMPLETE A CDMMP?
You must fill out a CDMMP and pay a deposit if your project is one of the following: • A commercial project valuated over $200,000 or new commercial construction or additions over 1,000 sq. ft. • A new residential construction project • A residential addition or improvement that increases the building area, volume or size • All demolition projects
ARE THERE FEES INVOLVED?
There is no fee, however you must supply a deposit for the project. The deposit is calculated at 2% of the highest valuation or $15,000, whichever is less, for a construction project and 10% of the highest valuation or $15,000, whichever is less, for a demolition project. The deposit may be made in the form of cash, check, credit card, or letter of credit. If you choose to submit a letter of credit, please request a letter of credit template to provide to your bank and allow for extra time to process. Both the deposit and the approved CDMMP must be received by the City before a building permit may be issued.
Whoever will pay the deposit will need to complete and submit a W-9 so that we can refund the deposit at the end of the project, as long as requirements are met. If you are using a company card for payment, please be sure to include the company and individual’s name during payment processing. (Proof of 65% recycle or reuse of all project materials). No taxpayer identification number is required since this is a refund and not a payment.
WHAT ARE MY OPTIONS TO DISPOSE OF C&D WASTE?
If you plan to utilize a temporary bin or roll-off service, you must work with one of the City’s franchised haulers. You can also self haul your waste if you have your own trucks and equipment and are licensed to do so. Whichever you choose, please keep in mind that you must keep all waste diversion documentation to prove a 65% recycling or reuse rate has been achieved for your project.
HOW DO I GET MY DEPOSIT BACK?
Once your project is finalized by Building and Safety, you will need to provide proof of diversion. If you worked with a franchised hauler, simply ask them for a diversion report and they will provide one to you. If you chose to self-haul your materials, you must provide verification that at least 65% of your materials were diverted from the landfill by completing a self-haul verification form and providing all weight tickets or scale reports for each load removed from the project site.
Diversion reports may be submitted in person at the Permit Center in City Hall, uploaded to the online eService Portal , via email to [email protected] or mail to the following address:
Environmental Services 23920 Valencia Blvd., Suite 225 Santa Clarita, CA 91355-2196
Please make sure the diversion report includes the correct project address and project name and copies of each wegith ticket. Once those reports have been provided and staff verifies your diversion percentage, you will receive your refund check in the mail within approximately 4-6 weeks.

Join our Mailing List
Sign up for our monthly newsletter for green events, energy saving and recycling tips and local environmental information.
Phone: (661) 286-4098 Email: [email protected]
If you have any questions, comments, or requests please visit our Resident Service Center and select the appropriate topic.

© 2024 Green Santa Clarita All Rights Reserved.
- Recycle Hero
- Residential Recycling
- Residential Organics
- Residential Waste Services
- Bulky Items & Illegal Dumping
- Hazardous Waste
- Reduce and Reuse
- Recycling for Businesses
- Commercial Waste Services
- Hazardous Waste – Commercial
- RMDZ (Recycling Market Development Zones)
- Hauler Transition 2023
- Trash Talks
- Holiday Tree Recycling
- Green Guide
- Energy Efficiency
- Automotive Maintenance and Car Care
- Pool & Fountain Maintenance
- Air Quality
- Kids and Students
- Climate Change
- Santa Clara River Water Quality
- Enhanced Watershed Management Plan
- Pesticide Pollution Prevention
- Septic System Care
- Measure W – Safe, Clean Water Program
- Integrated Regional Water Management Plan Information
- Large Water Volume Discharge
- Water Conservation
- Alternative Fueling Station Finder
- Drainage Benefit Assessment Areas (DBAAs)
- Sustainable Development
- Stormwater Information
- Temporary and Rolloff Bins
- Business Energy Efficiency

- Agency Overview
- Public Works Week
- Public Works History
- Capital Improvements Projects – Five Year Plan
- News and Events
- Federal Policies and Programs
- Emergency Management
- Careers with the Public Works Agency
- County of Ventura Website
- ADA Transition Plan English
- ADA Transition Plan Spanish
- Human Resources
- Space for Lease
- Private Property/Roads Frequently Asked Questions
- Awarded Contracts
- Bids and Subs
- Check Permit Status
- Field Book Index
- Floodplain Permits
- Grading Permits
- Water Availability
- Engineering Services Projects
- Instructions For Using Bonfire
- Projects Out To Bid
- Customer Survey
- Cuestionario
- Active Transportation Plan Website
- Ventura County Road Closures
- Advance Planning
- Design and Construction
- Encroachment Permits
- Transportation Operations and Maintenance
- Public Transportation
- Traffic Engineering
- County, City, and Caltrans Projects
- Report Water Waste
- Pay Bill Online
- Start or Stop Water Service
- Business Hazardous Waste Disposal
- Business Recycling and Disposal
- Construction & Demolition Debris Management
- Electronic Waste
- Household Hazardous Waste
- IWMD – Frequently Asked Questions
- Organic Waste Recycling (SB1383)
- Recycling Market Development Zone
- Residential Recycling Program
- Used Oil Recycling
- Carpet Recycling
- Water Quality
- Engineering and Development
- Public Meetings
- Service Areas
- Schedule of Rates
- Publications and Documents
- Legislation
- Water Conservation
- W&S – Frequently Asked Questions
- CEQA Compliance
- Matilija Dam Ecosystem Restoration Project
- Calleguas Creek
- Cuyama River
- Coastal Creeks
- Flood Zone 4 (South)
- Santa Clara River Levee (SCR-1)
- Operations & Maintenance
- County Stormwater Program
- Groundwater Resources
- Watershed Planning and Permits
- Flood Preparedness
- Sandbag 101
- Hydrology Manual
- Flood Warning System
- Happy Valley Bioswale
- VCFloodInfo.org
- Accela Citizen Access – County Permit System
- Construction Projects
- CountyView – GIS Maps
- Hazardous Waste Dropoff Reservation
- Information on PWA Permits
- Pay My Water Bill
- PWA Interactive Maps
- Report a Concern/Ask a Question
- Start/Stop Water Service
- Storm Data and Flood Warning System
Report a Concern
CONSTRUCTION AND DEMOLITION DEBRIS RECYCLING
Quick links.
- Residential Recycling & Disposal
- Hazardous Wastes
- Waste Collection Codes, Agreements, and Rates
C&D Telephone: (805) 658-4321
C&D Email: [email protected]
Telephone: (805) 658-4321
Fax: (805) 658-4324
General Questions: [email protected]
Hours: 8:00 am to 5:00 pm, Monday through Friday, excluding holidays
Location: 800 South Victoria Ave, Ventura, CA 93009
All new Construction & Demolition Debris Recycling Plans (formerly known as Form B/C) must be submitted online through Citizen Access (see our C&D Guide to Citizen Access for step-by-step instructions).
After a Recycling Plan is submitted to Citizen Access:
- Applicants will receive a Pre-Approval email once their Recycling Plan has been reviewed and approved.
- When the project is finished, applicants must upload recycling receipts to their plan through Citizen Access.
- Applicants will receive a Final Approval email once the receipts are reviewed and approved.
If you have questions about Recycling Plans or getting a Final Agency Clearance signature, please email [email protected] or call (805) 658-4321 and select option 1.
Where to Recycle or Donate Materials
See the C&D Debris Recycling Facilities list.
To comply with Ventura County Ordinance 4590 , project applicants must self-haul to a sorting facility, use an Authorized Solid Waste Collector, salvage usable materials, and/or reuse materials onsite:
Construction & Demolition Debris Sorting Facilities in Ventura County
• Del Norte Regional Recycling and Transfer Station : 111 S. Del Norte Ave, Oxnard, CA 93030
• Gold Coast Recycling and Transfer Station : 5275 Colt St, Ventura, CA 93003
• Simi Valley Landfill and Recycling Center : 2801 Madera Rd, Simi Valley, CA 93065
Recycling receipts must be requested at all sorting facilities.
Customers who do not request a recycling receipt will not receive the correct documentation to show they have properly disposed of their materials.
Authorized Solid Waste Collectors
- American Resource Recovery, Inc. (EJ Harrison & Sons, Inc.) | (805) 247-9155
- Athens Services | (805) 856-0113
- E.J. Harrison & Sons, Inc. | (805) 647-1414
- G.I. Industries, Inc. (Waste Management) | (805) 522-9400
- J&L Hauling & Disposal, Inc. | (805) 565-4634
- MarBorg Industries | (805) 963-1852
- Mountainside Disposal, Inc. | (661) 831-2837
- Newbury Disposal Company | (805) 647-1414
- Peach Hill Soils | (805) 529-6164
- Santa Clara Valley Disposal | (805) 647-1414
Recycling receipts must be requested from Authorized Solid Waste Collectors. It is best to request them while you are initially setting up your service.
Salvage/Donate
- Oxnard ReStore: 1850 Eastman Ave, Oxnard, 93030
- Simi Valley ReStore: 1293A E. Los Angeles Ave, Simi Valley, 93065
- Online options such as Facebook Marketplace, Craigslist, Freecycle, etc.
For ReStore, please ask for a receipt or similar documentation showing you have donated/sold your reusable materials. For other reuses, submit a Statement of Compliance explaining how your materials were salvaged and, if possible, contact information for verification by the recipient.
How to Get Recycling Receipts
Self-Hauling to a C&D Sorting Facility
Self-hauling is only permitted by residents hauling their own material or by contractors using their own equipment as a part of their total construction/demolition service.
When self-hauling to a C&D Sorting Facility, residents/contractors must inform the gate operator they have a C&D Recycling Plan with the County of Ventura and need a recycling receipt. If a recycling receipt is not requested, the facility will give a generic receipt which will not show compliance with recycling requirements.
Renting a Bin from an Authorized Solid Waste Collector
If your site will be renting a bin from an Authorized Solid Waste Collector, notify the collector during the initial service setup that you will need a recycling receipt for a C&D Recycling Plan.
Please note, C&D sorting is often not possible from three-cubic-yard bins (the square bins lifted over the front of a truck). The minimum size for sorting is usually 10 cubic yards and must be a roll-off box (the type of container lifted onto the back of a truck). Ask your Solid Waste Collector about bin size requirements for proper sorting.
Donating/Salvage
Please request a receipt or similar form of documentation showing materials were donated/sold.
Reusing Materials On-site
If materials are being reused on-site, a Statement of Compliance must be submitted.
What is the C&D Debris Recycling Program?
The California Green Building Code (CALGreen) requires 65% of construction and demolition debris to be diverted from landfills.
This means reusing and recycling materials that remain after:
✓ Construction of new buildings
✓ Demolition of buildings
✓ Additions and alterations to non-residential projects
✓ Additions and alterations to residential buildings that increase the structure’s conditioned area, volume, or size
For applicable projects to comply with CALGreen, a C&D Recycling Plan must be submitted to the County through Citizen Access (for contractors working for the County of Ventura, see our FAQ below on submitting a Recycling Plan).
Does my project require a Recycling Plan?
Projects that require a Recycling Plan include:
✓ Construction of new residential and non-residential buildings
✓ Demolition of residential and non-residential buildings
Projects that may be exempt from submitting a Recycling Plan include:
• Projects consisting solely of additions or alterations of existing residential dwellings that do NOT increase the structure’s conditioned area, volume, or size
• Projects consisting solely of the installation of prefabricated structures such as manufactured or modular home, metal barns, patio enclosures and covers
• Projects consisting solely of the installation of prefabricated accessories such as signs or antennas where no foundation or other structural building modifications are required
• Projects consisting solely of the installation, removal, or relocation of solar panels
• Projects consisting solely of an above or in-ground pool and/or spa
• Work for which only a plumbing permit, an electrical permit, and/or a mechanical permit is required
What if I never made a Citizen Access account, but I have an Approved Form B and am ready to turn in my recycling receipts/Form C?
Form C is no longer required for most projects, regardless of when you first submitted your Form B – Recycling Plan.
If you still have a copy of your Approved Form B Recycling Plan, please email it with your recycling receipts to [email protected] when your project is complete. You will receive a follow up email once your application and receipts have been reviewed and approved.
If you cannot find a copy of your Approved Form B Recycling Plan, please email [email protected] with the following:
- Project Manager name, phone number, and email
- Contact name, phone number, and email
- Project description, site address, and Assessor’s Parcel Number
- Recycling receipts
- You will receive a follow up email once your receipts have been reviewed and approved.
What if I salvaged, reused materials onsite, or placed them in a curbside recycling/yard waste cart?
In these situations, a Statement of Compliance must be submitted as a receipt. You may download our Statement Template Word Doc ( en español ) or write your own statement that includes:
- Applicant’s Name or Company
- Property Owner’s Name
- Project Address
- Assessor’s Parcel Number
- Project Description
- Material and Management Method (e.g., reused, curbside recycling)
I’m working on behalf of a County of Ventura project – how do I submit a Recycling Plan?
Projects completed by contractors working for the County of Ventura must follow the C&D Recycling process described in awarded contracts:
• Complete and sign Form B – County Project Recycling Plan and email it to [email protected]. You will receive an email once your plan has been reviewed and approved.
• Once your project is finished, complete and sign Form C – Recycling Report and email it to [email protected]. Please be sure to attach all receipts showing you have recycled your debris. You will receive an email once your report and receipts have been reviewed and approved.
Other Questions?
Please contact us at [email protected] or (805) 658-4321


ARCHIVE: CALGreen Construction Waste Management Requirements
The contents of this page have been removed. You can find information about this program by visiting https://calrecycle.ca.gov/LGCentral/Library/CandDModel/ .
Please update your links and bookmarks, as this redirect page will be deleted on June 14, 2024.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The construction industry generates many environmental pollutants, such as noise, air pollution, solid and liquid waste, water pollution, harmful gases, and dust (Adnan et al. 2014).It is classified as the world's largest consumer of raw materials, the highest energy-consuming sector, reaching up to 36% of the total energy consumption, and one of the highest energy-related CO2 emissions ...
Based on Observations at Swedish Construction Site Master's Thesis in the Master's Programme Design and Construction Project Management MAHLET TESFAYE HAILE ... Appendix 5 Components for Designing Out Waste in Construction Projects ….83 . VI CHALMERS Architecture and Civil Engineering, Master's Thesis BOMX02-17-92
the same equation 3.10 developed in chapter 3. The five counties that are considered separately are: Allegheny County with 16.9%. (180,863 tons) of the total annual quantity (1,070,165.2 tons) disposed in Pennsylvania. in 2009, Montgomery County with 7.9% (85,006 tons) of the total annual quantity.
(1) Background: Globally, numerous development projects are being undertaken to expand and improve urban infrastructure facilities, which result in around 30% to 40% of construction and demolition (C&D) waste in the total waste generation. Due to its detrimental impacts on the environment and human health, several researchers have been striving to find effective methods to manage these large ...
Abstract. Construction waste leads to disasters, and the solution for that consists of 5 steps. For. one, bring an end of being a part of causing waste by prevention. On the other hand, waste can ...
During the construction phase, a negative impact on the. This thesis follows the style of Construction Management and Economics. environment will occur, whether indirect or direct (Yahya and Boussabaine, 2006). Despite the importance of the impact on the environmental that the construction waste.
A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirement of the University of Wolverhampton for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) Toggle navigation. ... Further work is necessary to implement construction waste management and waste management at the industrial level, as well as identifying the actual quantity C&D waste so far, and its ...
Category Sub-categories; 1. Construction and demolition waste stakeholders: 1.1 Lack of perception among construction and demolition stakeholders including clients, architects, contractors, and sub-contractors (Murtagh et al., 2016) 1.2 Emphasis on the role of clients as the main stakeholder in construction and demolition waste management (Arif et al., 2012). 1.3 Client's inappropriate ...
Emirates University (UAEU), and the author of this thesis entitled " Construction Waste Management Practices in Abu Dhabi; Investigation and Evaluation ", hereby, solemnly declare that this thesis is my own original research work that has been done and prepared by me under the supervision of Dr. Amna Shibeika, in the College of
Construction and Demolition (C&D) waste is one of the most voluminous and harmful categories of solid waste worldwide, comprising 40% of the total volume of global waste. Waste minimisation is essential for sustainable waste management for environmental, social and economic benefits. Libya has particularly egregious C&D
Construction Waste (CW) is defined as "building and site improvement materials and other solid wastes resulting from construction, remodelling, and renovation or repair operations". ... REFERENCES [1]. Y. Li, "Developing a sustainable construction waste estimation and management system," PhD Thesis, Hong Kong University of Science and ...
The construction sector is the major resource-consuming and waste-producing sector in our modern society, using - on average - more than 40% of the total raw materials extracted from the earth around the world (Krausmann et al., 2017), and at the same time generating more than one third of the world's solid waste by weight (up to more than 75% when excavated soil is accounted for as well ...
This work provides a basis for future research into the automated estimation of construction waste in BIM which could become a useful tool in waste-prevention policies. Next Article in Journal. The Current State, Challenges, and Opportunities of Recycling Plastics in Western Australia ... Ph.D. Thesis, University of the West of England, Bristol ...
CONSTRUCTION WASTE GENERATION IN MALAYSIAN CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY SASITHARAN NAGAPAN . A thesis submitted in . fulfilment of the requirements for award of the . Doctor of Philosophy . Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering . Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia . DECEMBER 2014 $ +
v ABSTRACT This study assessed the construction waste management approaches in higher educational institutions of Ethiopia by particularly focusing on Bahir Dar University. The study adapted a descriptive and explanatory design and a quantitative and qualitative approach
construction waste sources, management planning and practices: in the case of 40/60 conduminum and real estates housing in addis ababa by: mahlet alem assefa advisor: chalachew getahun (phd) this thesis submitted to department of project management school of graduate student, st, marys university for partial fulfillment of the requirements for ...
Both construction Waste Minimisation (WM) and construction procurement activities play an effective role in attaining sustainability by giving due consideration to the environment, community and social conditions in delivering built assets. The construction industry has a major impact on the environment, both in terms of resource consumption and increasing waste production. Recent figures ...
An extensive amount of construction waste originates as a result of poor design (Chandrakanthi et al., 2002;Al-Hajj and Hamani, 2011; Othman and Abdelrahim, 2020). This foregoing seems to support ...
The results of this study recommended that there is a need to establish a new construction waste department to develop waste management policies and develop the effective strategy to reduce construction waste. The study recommended the owners to take the waste management history of the contractors as a criterion in awarding contracts.
The City has a Construction and Demolition (C&D) Ordinance (05-09) requiring all demolition projects, all commercial projects valued over $200,000, all new commercial projects over 1,000 square feet, all new residential construction projects, and all residential additions and improvements that increase building area, volume, or size to recycle ...
To comply with Ventura County Ordinance 4590, project applicants must self-haul to a sorting facility, use an Authorized Solid Waste Collector, salvage usable materials, and/or reuse materials onsite:. Construction & Demolition Debris Sorting Facilities in Ventura County • Del Norte Regional Recycling and Transfer Station: 111 S. Del Norte Ave, Oxnard, CA 93030
Construction projects like Levi's Stadium are a rarity. The magnitude, the manpower, and the ... Benjamin Riddle wrote a thesis paper called "The Machine in the Arena" in 2019 that includes information on the role of stadiums in their greater communities. Thomas Grant wrote "Green Monsters: Examining the Environmental Impact of Sports ...
Part of CalRecycle's guide to assist jurisdictions in increasing the diversion of construction and demolition (C&D) debris from California landfills, this page describes issues of consideration during the planning and development phases of adopting a C&D ordinance. ... ARCHIVE: CALGreen Construction Waste Management Requirements. The contents ...