- Artificial Intelligence
- Generative AI
- Business Operations
- Cloud Computing
- Data Center
- Data Management
- Emerging Technology
- Enterprise Applications
- IT Leadership
- Digital Transformation
- IT Strategy
- IT Management
- Diversity and Inclusion
- IT Operations
- Project Management
- Software Development
- Vendors and Providers
- Enterprise Buyer’s Guides
- United States
- Middle East
- España (Spain)
- Italia (Italy)
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
- Data Analytics & AI
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- Your California Privacy Rights

Our Network
- Computerworld
- Network World
6 essential elements of a good business plan
Entrepreneurs, executives and venture capitalists discuss how to craft a business plan that will impress investors and be a good road map for your company..

Whether you are just starting out and need startup investment or are looking to expand your business and raise capital, a business plan is a must. Indeed, a business plan is not only essential if you want to get people to invest in your idea, it can help you articulate what it is you hope to accomplish with your business – your mission, goal(s) and values – and plot the company’s growth trajectory.
However, to be successful, a business plan cannot just be a bulleted list of an entrepreneur’s thoughts and musings, hopes and dreams. It needs to be a serious business document with the following six elements.
1. Executive summary
“An executive summary is the ‘elevator pitch’ of your business plan,” explains David Mercer, founder, SME Pals , a blog dedicated to helping entrepreneurs. “More often than not, landing a new investor relies on hooking them with a great elevator pitch. Without grabbing their attention, your business plan, no matter how well researched and presented, may not stand out enough.”
The executive summary should, in brief, describe the “problem you are going to solve, and why that problem needs to be solved right now,” by you, says Peter Arvai, CEO, Prezi presentation software. “If you aren’t able to communicate that deeper purpose to others, you will have a very hard time convincing investors to fund your idea and people to join your team.”
Tip: Write the Executive Summary last, after you’ve done all your research and put everything down on paper.
[ Related: 12 tips for creating a must-read business blog ]
2. Description and bios of your leadership/executive team
“The entrepreneur should clearly demonstrate what they are bringing to this venture – the idea, the technical ability or the passion,” says Hossein Rahnama, founder & CEO, Flybits . “Investors want to understand how you will execute using your personal strength.”
You should also “talk about the leadership team,” says Andrew Witkin, CEO, StickerYou . “If the leadership team has a previous track record of building and delivering businesses, this should be highlighted. Business plans serve multiple purposes, but one of them is to build trust, and the team is as important as the product to potential investors and partners.”
“Investors bet on jockeys, not horses, and knowing about who will execute on an idea is key to an investor making an investment decision,” says Richard J. Foster, president, Foster Management & Holdings. “Very frequently I’ll see multiple companies with the same idea, but the one to invest in is the one with the team who has the experience and the credentials to succeed. Having the best idea with the wrong team is a recipe for failure, but proving that your team is the [right] one to execute [your idea] can make all of the difference.”
3. Description of your product(s) or service(s)
“When developing a business plan, it’s crucial to clearly [explain] the need your product or service is trying to address,” says Elena Filimonova, senior vice president, global marketing and strategy, CGS . “Your business plan should highlight how the product or service will address the need, what is unique about your offering and why it would be difficult to replicate. To do this, you should outline key differentiators, features and why the product or service is something that stands out in the market.”
[ Related: 11 ways to build your online brand ]
4. Market/competitive analysis
“Every business plan should have a section that defines the target sales market – who you are selling to,” says Victor Clarke, owner, Clarke Inc. “This is the part that requires considerable research into areas such as industry sales data related to the service or product you are selling and trends within the industry. You should look at competitors and see who they are targeting, look at your current customer base and create a profile of an ideal customer or client for your product.”
“For a business plan to be effective and attractive to investors and partners, you must be able to provide tangible data and information that supports the notion that your demographic is strong and growing, and that market trends support the continued need for your service or product offering,” says Brock Murray, cofounder & COO, seoplus+ .
[ Related: 7 attributes of a successful CMO in the digital age ]
“Sequoia Capital has a great framework that every business plan should use: separate your Total Addressable Market (everyone who conceivably needs your product category), Serviceable Addressable Market (everyone who needs your specific product or service, limited by factors like where you can do business) and Serviceable Obtainable Market (the portion of the market you can realistically capture),” says Christopher S. Penn, vice president, Marketing Technology, SHIFT Communications . “For example, lots of companies say everyone is a customer, and while that may be a TAM, if the company has only one salesperson, their SOM is significantly smaller. VCs and investors especially want to understand what’s realistically obtainable, and splitting out your addressable markets… shows them you’re not just presenting pipe dreams.”
Also be sure to “include a competitive analysis section,” says Bryan Robertson, founder & chief revenue officer, Mindyra . “Every business has competition, so it’s a good idea to research companies in your industry who are fighting for the same customers. You should include specific details about their strengths and weaknesses. This forces you to become very familiar with your market. It also encourages you to think of ways to differentiate your business [from] the competition.”
5. Financials (how much cash you need and when you’ll pay it back)
“Make sure that the plan goes into exacting detail about how much startup capital will be needed, where it will come from and how it will be paid back,” says Bruce Stetar, executive director, Graduate Business Programs, SNHU . “Equal importance should be given to how you [plan to] pay back capital as how you acquire it. Investors want to know when they will see a return. Failing to plan adequately for capital acquisition and payback is one of the chief reasons that new businesses fail.”
“Whether you’re hoping to receive funding to build a brick-and-mortar shop or a technology venture, you must have your numbers straight,” says Erica Swallow, founder & CEO, Southern Swallow . “For tech entrepreneurs, I’m a big fan of the startup financial model template developed by startup investor David Teten, in collaboration with a couple of colleagues. Based in a nearly fully-automated Excel worksheet, it enables early-stage entrepreneurs to map out their financial plan, without being too overwhelming. It’s the best startup financial model I’ve encountered over the past five years.”
6. Marketing plan
“It is critical to have a plan [for] how you are going to spend your marketing budget,” says Deborah Sweeney, CEO, MyCorporation . “Assess different options (paid search, salespeople, flyers, [social media], etc.) and the associated ROI with each.”
“The plan should cover both sales and advertising strategies and costs,” says Stetar, as well as customer acquisition costs. “Be conservative here since you will look good if your over achieve but it will cost you investor confidence if you under achieve.”
A successful business plan is one is easy to read and follow
You need to make your business plan easy to read and follow. “There’s nothing more daunting than to receive an all-text business plan, 30 pages in length,” says Swallow. “Keep your potential investors engaged by including product and user photos, team headshots, colorful headings, financial graphs, charts, tables, anything to make reading more of a pleasure. Even bullet points help.”
Indeed, “don’t underestimate the importance of visuals,” says Arvai. “Researchers have found that presentations using visual aids are, on average, 43 percent more persuasive than those without.”
Finally, before you go public with your plan, “have trusted mentors and expert peers look over it [and give you] their feedback,” says Sam Lundin, CEO, Vimbly . “Having [someone] review your business plan [before you present it to investors] is crucial.”
Related content
Boomi burnishes api management capabilities, tiaa modernizes the customer journey with ai, 10 it skills where expertise pays the most, what is erp enterprise resource planning systems explained, from our editors straight to your inbox, show me more, colorado ai legislation further complicates compliance equation.

UK government’s Pensions Dashboards Programme delayed

Raj Polanki’s five steps by which CIOs can lead holistically

CIO Leadership Live with Sri Adusumilli, Chief Information Officer, TruckPro LLC

CIO Leadership Live NZ with Tim Partington, Director Digital & Technology, Skills Consulting Group

CIO Leadership Live UK with Charlene Hunter, MBE, CEO & Founder, Coding Black Females

A Fundamental Question: Open or Closed Source?

Sponsored Links
- Everybody's ready for AI except your data. Unlock the power of AI with Informatica
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This is the ultimate guide to creating a comprehensive and effective plan to start a business . In today’s dynamic business landscape, having a well-crafted business plan is an important first step to securing funding, attracting partners, and navigating the challenges of entrepreneurship.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Embarking on the journey of creating a successful business requires a solid foundation, and a well-crafted business plan is the cornerstone. Here is the process of writing a comprehensive business plan and the main parts of a winning business plan . From setting objectives to conducting market research, this guide will have everything you need.
Executive Summary

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Think of it as an elevator pitch in written form: it should be compelling enough to engage potential investors or stakeholders and provide them with a clear understanding of what your business is about, its goals, and why it’s a promising investment.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives

In the Overview and Business Objectives section, outline your business’s core goals and the strategic approaches you plan to use to achieve them. This section should set forth clear, specific objectives that are attainable and time-bound, providing a roadmap for your business’s growth and success.
It’s important to detail how these objectives align with your company’s overall mission and vision. Discuss the milestones you aim to achieve and the timeframe you’ve set for these accomplishments.
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
- Introducing three new products within the first two years of operation.
- Achieving annual revenue growth of 30%.
- Expanding our customer base to over 10,000 clients by the end of the third year.
Company Description

The Company Description section is your opportunity to delve into the details of your business. Provide a comprehensive overview that includes your company’s history, its mission statement, and its vision for the future.
Highlight your unique selling proposition (USP) – what makes your business stand out in the market. Explain the problems your company solves and how it benefits your customers.
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market

Defining Your Target Market is critical for tailoring your business strategy effectively. This section should describe your ideal customer base in detail, including demographic information (such as age, gender, income level, and location) and psychographic data (like interests, values, and lifestyle).
Elucidate on the specific needs or pain points of your target audience and how your product or service addresses these. This information will help you know your target market and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis

The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
This analysis will enable you to spot market opportunities and anticipate potential challenges. Include data and statistics to back up your claims, and use graphs or charts to illustrate market trends.
This section should demonstrate that you have a deep understanding of the market in which you operate and that your business is well-positioned to capitalize on its opportunities.
Example: The market for eco-friendly technology products has experienced significant growth in recent years, with an estimated annual growth rate of 10%. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable solutions continues to rise.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis

A SWOT analysis in your business plan offers a comprehensive examination of your company’s internal and external factors. By assessing Strengths, you showcase what your business does best and where your capabilities lie.
Weaknesses involve an honest introspection of areas where your business may be lacking or could improve. Opportunities can be external factors that your business could capitalize on, such as market gaps or emerging trends.
Threats include external challenges your business may face, like competition or market changes. This analysis is crucial for strategic planning, as it helps in recognizing and leveraging your strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and preparing for potential threats.
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
- Innovative and eco-friendly product offerings.
- Strong commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Skilled and experienced team with expertise in technology and sustainability.
Weaknesses:
- Limited brand recognition compared to established competitors.
- Reliance on third-party manufacturers for product development.
Opportunities:
- Growing consumer interest in sustainable products.
- Partnerships with environmentally-focused organizations and influencers.
- Expansion into international markets.
- Intense competition from established technology companies.
- Regulatory changes could impact the sustainable technology market.
Competitive Analysis

In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
By conducting a thorough competitive analysis, you can gain insights into your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to develop strategies to differentiate your business and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Example: Key competitors include:
GreenTech: A well-known brand offering eco-friendly technology products, but with a narrower focus on energy-saving devices.
EarthSolutions: A direct competitor specializing in sustainable technology, but with a limited product range and higher prices.
By offering a diverse product portfolio, competitive pricing, and continuous innovation, we believe we can capture a significant share of the growing sustainable technology market.
Organization and Management Team

Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Showcasing your team’s background, skills, and accomplishments instills confidence in investors and other stakeholders, proving that your business has the leadership and talent necessary to achieve its objectives and manage growth effectively.
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered

Describe the products or services your business offers, focusing on their unique features and benefits. Explain how your offerings solve customer pain points and why they will choose your products or services over the competition.
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Example: EcoTech offers a range of eco-friendly technology products, including energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers, and smart home devices that optimize energy usage. Our products are designed to help customers reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Marketing and Sales Strategy

In this section, articulate your comprehensive strategy for reaching your target market and driving sales. Detail the specific marketing channels you plan to use, such as social media, email marketing, SEO, or traditional advertising.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
This section is critical to convey to investors and stakeholders that you have a well-thought-out approach to market your business effectively and drive sales growth.
Example: Our marketing strategy includes digital advertising, content marketing, social media promotion, and influencer partnerships. We will also attend trade shows and conferences to showcase our products and connect with potential clients. Our sales strategy involves both direct sales and partnerships with retail stores, as well as online sales through our website and e-commerce platforms.
Logistics and Operations Plan

The Logistics and Operations Plan is a critical component that outlines the inner workings of your business. It encompasses the management of your supply chain, detailing how you acquire raw materials and manage vendor relationships.
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Quality control measures are essential to maintain product standards and customer satisfaction. This plan assures investors and stakeholders of your operational competency and readiness to meet business demands.
Highlighting your commitment to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction underlines your business’s capability to maintain smooth, effective operations even as it scales.
Example: EcoTech partners with reliable third-party manufacturers to produce our eco-friendly technology products. Our operations involve maintaining strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring quality control, and managing inventory.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan

In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Ground these projections in solid assumptions based on your market analysis, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth scenarios. Break down revenue streams and include an analysis of the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and potential investments.
This section should also discuss your break-even analysis, cash flow projections, and any assumptions about external funding requirements.
By presenting a thorough and data-backed financial forecast, you instill confidence in potential investors and lenders, showcasing your business’s potential for profitability and financial stability.
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Example: Over the next three years, we expect to see significant growth in revenue, driven by new product launches and market expansion. Our financial projections include:
- Year 1: $1.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $200,000.
- Year 2: $3 million in revenue, with a net profit of $500,000.
- Year 3: $4.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $1 million.
These projections are based on realistic market analysis, growth rates, and product pricing.
Income Statement

The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing your income statement allows you to monitor the health of your business, evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize profitability and growth.
Example: The income statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
- Revenue: $1,500,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $800,000
- Gross Profit: $700,000
- Operating Expenses: $450,000
- Net Income: $250,000
This statement highlights our company’s profitability and overall financial health during the first year of operation.
Cash Flow Statement

A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
By including a cash flow statement in your business plan, you demonstrate your ability to manage your company’s finances effectively.
Example: The cash flow statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
Operating Activities:
- Depreciation: $10,000
- Changes in Working Capital: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Operating Activities: $210,000
Investing Activities:
- Capital Expenditures: -$100,000
- Net Cash from Investing Activities: -$100,000
Financing Activities:
- Proceeds from Loans: $150,000
- Loan Repayments: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Financing Activities: $100,000
- Net Increase in Cash: $210,000
This statement demonstrates EcoTech’s ability to generate positive cash flow from operations, maintain sufficient liquidity, and invest in growth opportunities.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan

1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively.
2. Conduct thorough research: Before writing your business plan, gather as much information as possible about your industry, competitors, and target market. Use reliable sources and industry reports to inform your analysis and make data-driven decisions.
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
5. Be flexible and adaptable: A business plan is a living document that should evolve as your business grows and changes. Be prepared to update and revise your plan as you gather new information and learn from your experiences.
6. Use visuals to enhance understanding: Include charts, graphs, and other visuals to help convey complex data and ideas. Visuals can make your business plan more engaging and easier to digest, especially for those who prefer visual learning.
7. Seek feedback from trusted sources: Share your business plan with mentors, industry experts, or colleagues and ask for their feedback. Their insights can help you identify areas for improvement and strengthen your plan before presenting it to potential investors or partners.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
The template is divided into the following sections:
- Mission statement
- Business Overview
- Key products or services
- Target market
- Financial highlights
- Company goals
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Measurable, time-bound objectives
- Company History
- Mission and vision
- Unique selling proposition
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Pain points
- Industry trends
- Customer needs
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Competitor products and services
- Market positioning
- Pricing strategies
- Organizational structure
- Key roles and responsibilities
- Management team backgrounds
- Product or service features
- Competitive advantages
- Marketing channels
- Advertising campaigns
- Promotional activities
- Sales strategies
- Supply chain management
- Inventory control
- Production processes
- Quality control measures
- Projected revenue
- Assumptions
- Cash inflows
- Cash outflows
- Net cash flow
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s goals, objectives, and the steps required to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap as you start a business , guiding the company’s direction and growth while identifying potential obstacles and opportunities.
Typically, a business plan covers areas such as market analysis, financial projections, marketing strategies, and organizational structure. It not only helps in securing funding from investors and lenders but also provides clarity and focus to the management team.
A well-crafted business plan is a very important part of your business startup checklist because it fosters informed decision-making and long-term success.

Why You Should Write a Business Plan
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
- Attract Investors and Secure Funding : A well-written business plan demonstrates your venture’s potential and profitability, making it easier to attract investors and secure the necessary funding for growth and development. It provides a detailed overview of your business model, target market, financial projections, and growth strategies, instilling confidence in potential investors and lenders that your company is a worthy investment.
- Clarify Business Objectives and Strategies : Crafting a business plan forces you to think critically about your goals and the strategies you’ll employ to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for success. This process helps you refine your vision and prioritize the most critical objectives, ensuring that your efforts are focused on achieving the desired results.
- Identify Potential Risks and Opportunities : Analyzing the market, competition, and industry trends within your business plan helps identify potential risks and uncover untapped opportunities for growth and expansion. This insight enables you to develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, positioning your business for long-term success.
- Improve Decision-Making : A business plan serves as a reference point so you can make informed decisions that align with your company’s overall objectives and long-term vision. By consistently referring to your plan and adjusting it as needed, you can ensure that your business remains on track and adapts to changes in the market, industry, or internal operations.
- Foster Team Alignment and Communication : A shared business plan helps ensure that all team members are on the same page, promoting clear communication, collaboration, and a unified approach to achieving the company’s goals. By involving your team in the planning process and regularly reviewing the plan together, you can foster a sense of ownership, commitment, and accountability that drives success.
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
- Startup Business Plan: Tailored for new ventures, a startup business plan outlines the company’s mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. It helps entrepreneurs clarify their vision, secure funding from investors, and create a roadmap for their business’s future. Additionally, this plan identifies potential challenges and opportunities, which are crucial for making informed decisions and adapting to changing market conditions.
- Internal Business Plan: This type of plan is intended for internal use, focusing on strategies, milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation. It serves as a management tool for guiding the company’s growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. The internal business plan also helps identify areas of improvement, fosters collaboration among team members, and provides a reference point for measuring performance.
- Strategic Business Plan: A strategic business plan outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for the company’s direction. It typically includes a SWOT analysis, market research, and competitive analysis. This plan allows businesses to align their resources with their objectives, anticipate changes in the market, and develop contingency plans. By focusing on the big picture, a strategic business plan fosters long-term success and stability.
- Feasibility Business Plan: This plan is designed to assess the viability of a business idea, examining factors such as market demand, competition, and financial projections. It is often used to decide whether or not to pursue a particular venture. By conducting a thorough feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs can avoid investing time and resources into an unviable business concept. This plan also helps refine the business idea, identify potential obstacles, and determine the necessary resources for success.
- Growth Business Plan: Also known as an expansion plan, a growth business plan focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. It includes market analysis, new product or service offerings, and financial projections to support expansion plans. This type of plan is essential for businesses looking to enter new markets, increase their customer base, or launch new products or services. By outlining clear growth strategies, the plan helps ensure that expansion efforts are well-coordinated and sustainable.
- Operational Business Plan: This type of plan outlines the company’s day-to-day operations, detailing the processes, procedures, and organizational structure. It is an essential tool for managing resources, streamlining workflows, and ensuring smooth operations. The operational business plan also helps identify inefficiencies, implement best practices, and establish a strong foundation for future growth. By providing a clear understanding of daily operations, this plan enables businesses to optimize their resources and enhance productivity.
- Lean Business Plan: A lean business plan is a simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements such as value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structure. It is perfect for startups looking for a flexible, adaptable planning approach. The lean business plan allows for rapid iteration and continuous improvement, enabling businesses to pivot and adapt to changing market conditions. This streamlined approach is particularly beneficial for businesses in fast-paced or uncertain industries.
- One-Page Business Plan: As the name suggests, a one-page business plan is a concise summary of your company’s key objectives, strategies, and milestones. It serves as a quick reference guide and is ideal for pitching to potential investors or partners. This plan helps keep teams focused on essential goals and priorities, fosters clear communication, and provides a snapshot of the company’s progress. While not as comprehensive as other plans, a one-page business plan is an effective tool for maintaining clarity and direction.
- Nonprofit Business Plan: Specifically designed for nonprofit organizations, this plan outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation. It helps secure grants and donations while ensuring the organization stays on track with its objectives. The nonprofit business plan also helps attract volunteers, board members, and community support. By demonstrating the organization’s impact and plans for the future, this plan is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability within the nonprofit sector.
- Franchise Business Plan: For entrepreneurs seeking to open a franchise, this type of plan focuses on the franchisor’s requirements, as well as the franchisee’s goals, strategies, and financial projections. It is crucial for securing a franchise agreement and ensuring the business’s success within the franchise system. This plan outlines the franchisee’s commitment to brand standards, marketing efforts, and operational procedures, while also addressing local market conditions and opportunities. By creating a solid franchise business plan, entrepreneurs can demonstrate their ability to effectively manage and grow their franchise, increasing the likelihood of a successful partnership with the franchisor.
Using Business Plan Software

Creating a comprehensive business plan can be intimidating, but business plan software can streamline the process and help you produce a professional document. These tools offer a number of benefits, including guided step-by-step instructions, financial projections, and industry-specific templates. Here are the top 5 business plan software options available to help you craft a great business plan.
1. LivePlan
LivePlan is a popular choice for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features. It offers over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, and the ability to track your progress against key performance indicators. With LivePlan, you can create visually appealing, professional business plans that will impress investors and stakeholders.
2. Upmetrics
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
Bizplan is designed to simplify the business planning process with a drag-and-drop builder and modular sections. It offers financial forecasting tools, progress tracking, and a visually appealing interface. With Bizplan, you can create a business plan that is both easy to understand and visually engaging.
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
5. Tarkenton GoSmallBiz
Developed by NFL Hall of Famer Fran Tarkenton, GoSmallBiz is tailored for small businesses and startups. It features a guided business plan builder, customizable templates, and financial projection tools. GoSmallBiz also offers additional resources, such as CRM tools and legal document templates, to support your business beyond the planning stage.
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are to guide the company’s strategy, attract investment, and evaluate performance against objectives. Here’s a closer look at each of these:
- It outlines the company’s purpose and core values to ensure that all activities align with its mission and vision.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of the market, including trends, customer needs, and competition, helping the company tailor its products and services to meet market demands.
- It defines the company’s marketing and sales strategies, guiding how the company will attract and retain customers.
- It describes the company’s organizational structure and management team, outlining roles and responsibilities to ensure effective operation and leadership.
- It sets measurable, time-bound objectives, allowing the company to plan its activities effectively and make strategic decisions to achieve these goals.
- It provides a comprehensive overview of the company and its business model, demonstrating its uniqueness and potential for success.
- It presents the company’s financial projections, showing its potential for profitability and return on investment.
- It demonstrates the company’s understanding of the market, including its target customers and competition, convincing investors that the company is capable of gaining a significant market share.
- It showcases the management team’s expertise and experience, instilling confidence in investors that the team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
- It establishes clear, measurable objectives that serve as performance benchmarks.
- It provides a basis for regular performance reviews, allowing the company to monitor its progress and identify areas for improvement.
- It enables the company to assess the effectiveness of its strategies and make adjustments as needed to achieve its objectives.
- It helps the company identify potential risks and challenges, enabling it to develop contingency plans and manage risks effectively.
- It provides a mechanism for evaluating the company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow.
Can I write a business plan by myself?
Yes, you can write a business plan by yourself, but it can be helpful to consult with mentors, colleagues, or industry experts to gather feedback and insights. There are also many creative business plan templates and business plan examples available online, including those above.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
A typical business plan ranges from 20 to 50 pages, but the length may vary depending on the complexity and needs of the business.
What is a business plan outline?
A business plan outline is a structured framework that organizes the content of a business plan into sections, such as the executive summary, company description, market analysis, and financial projections.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
The five most common business plan mistakes include inadequate research, unrealistic financial projections, lack of focus on the unique selling proposition, poor organization and structure, and failure to update the plan as circumstances change.
What questions should be asked in a business plan?
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan focuses on the overall vision, goals, and tactics of a company, while a strategic plan outlines the specific strategies, action steps, and performance measures necessary to achieve the company’s objectives.
How is business planning for a nonprofit different?
Nonprofit business planning focuses on the organization’s mission, social impact, and resource management, rather than profit generation. The financial section typically includes funding sources, expenses, and projected budgets for programs and operations.
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.

11 Key Components of a Business Plan
3 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024
Somebody asked me what the key components of a good business plan were, and I’m glad they did—it’s one of my favorite topics.
It gives me a chance to review and revise another of the lists that I’ve done off and on for years (such as the one from yesterday on common business plan mistakes ).
- 1. Measure a business plan by the decisions it causes
I’ve written about this one in several places. Like everything else in business, business plans have business objectives.
Does the plan accomplish its objective ? Whether it is better management, accountability, setting stepping stones to the future, convincing somebody to invest, or something else?
Realistically, it doesn’t matter whether your business plan is well-written, complete, well-formatted, creative, or intelligent. It only matters that it does the job it’s supposed to do. It’s a bad plan if it doesn’t.
- 2. Concrete specifics
Dates, deadlines, major milestones, task responsibilities, sales forecasts, spending budgets, and cash flow projections.
Ask yourself how executable it is. Ask yourself how you’ll know, on a regular basis, how much progress you’ve made and whether or not you’re on track.
- 3. Cash flow
Cash flow is the single most important concept in business. A business plan without cash flow is a marketing plan, strategic plan, summary, or something else—and those can be useful, but get your vocabulary right.
A business model, lean canvas, pitch deck, and so on can be useful in some contexts, like raising investment. But those aren’t business plans.
- 4. Realistic
While it is true that all business plans are wrong , assumptions, drivers, deadlines, milestones, and other such details should be realistic, not crazy.
The plan is to be executed. Impossible goals and crazy forecasts make the whole thing a waste of time.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- 5. Short, sweet, easy-to-read summaries of strategy and tactics
Not all business plans need a lot of text.
The text and explanations are for outsiders, such as investors and bankers; however, many companies ought to use business planning to improve their business operations. If you don’t need the extra information, leave it out.
Define strategy and tactics in short bullet point lists. Tactics, by the way, are related to the marketing plan, product plan, financial plan, and so on. Strategy without tactics is just fluff.
- 6. Alignment of strategy and tactics
It’s surprising how often they don’t match.
Strategy is focus, key target markets , key product/service features, important differentiators, and so forth. Tactics are things like pricing, social media, channels, and financials, and the two should match.
A gourmet restaurant (strategy) should not have a drive-through option (tactics.)
- 7. Covers the event-specific, objective-specific bases
A lot of components of a business plan depend on the usage.
Internal plans have no need for descriptions of company teams. Market analysis hits one level for an internal plan but often has to be proof of market or validation for a plan associated with investment. Investment plans need to know something about exits; internal plans don’t.
- 8. Easy in, easy out
Don’t make anybody work to find what information is where in the plan. Keep it simple.
Use bullets as much as possible, and be careful with naked bullets for people who don’t really know the background. Don’t show off.
- 9. As lean as possible
Just big enough to do the job . It has to be reviewed and revised regularly to be useful. Nothing should be included that isn’t going to be used.
- 10. Geared for change
A good business plan is the opposite of written in stone. It’s going to change in a few weeks.
List assumptions because reviewing assumptions is the best way to determine when to change the plan and when to stick with it.
- 11. The right level of aggregation and summary
It’s not accounting. It’s planning.
Projections look like accounting statements, but they aren’t. They are summarized. They aren’t built on elaborate financial models. They are just detailed enough to generate good information.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

10 Min. Read
Use This Simple Business Plan Outline to Organize Your Plan

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes

7 Min. Read
5 Consequences of Skipping a Business Plan

When Should You Write a Business Plan?
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

From template to plan in 30 minutes
- Step-by-step guidance
- Crystal clear financials
- Expert advice at your fingertips
- Funding & lender ready formats
- PLUS all the tools to manage & grow

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.


5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.

7 Key Components of a Precise Business Plan (2024)
Learn the art of entrepreneurship with a business plan. Dive into executive summaries, discover templates, and understand what to include for a strategic edge.

Hadar Peretz
7 minute read

Short answer
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document outlining a company's vision, objectives, market analysis, marketing and sales strategies, organizational structure, and financial projections to guide its growth.
Innovation in Planning: The Untold Ingredient to Business Success
In the turbulent landscape of entrepreneurship, where over 20% of small ventures falter in their early days , this blog post sheds light on the importance of a well-structured business plan.
It delves into the specifics of an executive summary, steps, what to include, and innovation in business planning , guiding businesses to thrive rather than become failure statistics.
3 Main Purposes of a Business Plan
Embarking on the entrepreneurial journey without a business plan is like sailing in turbulent waters without a map.
A business plan serves three pivotal roles that steer the helm of a startup toward the shores of success.
1) Navigation Tool: Direction for Your Business
A business plan is your business’s North Star, providing direction and ensuring you stay on course amidst the storm of uncertainties.
Let’s take the example of “Bean There Coffee Shop,” a start-up that envisioned being a community hub. Their business plan outlined their mission, target market, competition analysis, and financial forecasts.
This helped them navigate the competition and establish a loyal customer base by providing a cozy ambiance that encouraged customer interaction.
2) Attraction for Investments: Encouraging Potential Investors
Your business plan is your passport to the realm of investors. Bean There Coffee Shop required a modern interior to reflect its brand's personality.
The detailed business plan showcased their unique selling proposition to investors, who were enticed by the predicted ROI and agreed to fund the renovations.
3) Measurement of Success: Evaluating Progress and Growth
A business plan sets a baseline to measure progress. Bean There Coffee Shop sets quarterly targets for customer retention and revenue in its business plan.
By comparing actual performance with the plan, they gauged their success and identified areas for improvement.
6 Key Elements of a Business Plan
Drafting a business plan might seem daunting initially, but breaking it down into core components makes it manageable and effective.
It’s about telling your business’s story in a compelling way to garner support and guide your actions.
1) Executive Summary
The executive summary is your business narrative condensed into a snapshot. For instance, the executive summary of Bean There Coffee Shop encapsulated its vision, mission, the experience it aimed to provide, and financial aspirations succinctly, giving readers an essence of what to expect in the subsequent sections.
For more information on executive summary design, delve into the design aspects of an executive summary. To glean insights on crafting a compelling and visually appealing executive summary for your startup venture.
2) Company Description
Delve into the what and why of your business. Bean There Coffee Shop described its longing to foster community interactions, reflecting its ethos in its service and interior design , resonating with the locals and creating a clientele.
3) Market Analysis
Understanding your market landscape is crucial. Analyze your competitors, the preferences of your target audience, and market trends.
For Bean There Coffee Shop, studying coffee consumption trends and identifying a locale lacking a community-centric cafe was a game-changer.
4) Organization and Management
Outline your business structure and team. Investors want to know who steers the ship.
At Bean There Coffee Shop, the experienced baristas and a seasoned manager showcased a competent team, instilling confidence in potential investors.
5) Product Line
Describe your offerings. Bean There Coffee Shop highlighted its organic coffee and locally sourced pastries, striking a chord with environmentally conscious consumers.
6) Marketing and Sales
How you plan to lure customers and keep them coming back is vital. Bean There Coffee Shop’s loyalty programs and community events were a hit, creating a buzz and building a loyal customer base.
What is a Business Plan in Entrepreneurship?
In the realm of entrepreneurship, a business plan goes beyond being just a document—it is a vibrant testament to your business vision and the roadmap illustrating how you aim to overcome challenges and achieve your objectives.
It's like the script of your entrepreneurial saga waiting to unfold.
A Framework for Strategy
A business plan embodies the strategy and operations of your entrepreneurial endeavor. Here's a simplified breakdown of what it may encompass:
Market Analysis: A thorough exploration of the market including size, demographics, and consumer behaviors.
Competitor Analysis: A detailed examination of competitors, their strengths, weaknesses, and market position.
Marketing Strategy: Tactics and channels you plan to use to promote your business.
Financial Projections: Anticipated income, expenses, and profitability over a certain period.
Risk Management
Venturing into entrepreneurship is akin to navigating turbulent waters, where risks are inevitable. A business plan aids in:
Identifying Potential Risks: Whether it's market fluctuation or operational challenges, a business plan helps in foreseeing possible hurdles.
Devising Contingency Plans: Strategies to mitigate identified risks, ensuring the business stays on the right track.
For instance, a cafe's business plan might highlight the risk of decreased foot traffic during winter months and propose hosting indoor events or offering seasonal promotions to maintain revenue.
Communication with Stakeholders
A business plan serves as a conduit between entrepreneurs and stakeholders, articulating the business vision, goals, and strategies.
When seeking investments for expansion, a well-drafted business plan can effectively communicate the growth potential and return on investment to investors, facilitating the funding process.
7 Steps of a Business Plan
Creating a business plan is a blend of art and science, distilled into seven systematic steps to ensure your entrepreneurial venture is on a trajectory toward success.
1) Research, Research, and Research
Before you set pen to paper, immerse yourself in thorough research about your industry, market, and competition. This step lays the groundwork for informed decision-making as you progress through subsequent stages of business planning.
Industry Insights: Delve into current industry trends, challenges, and opportunities to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Market Dynamics: Explore market demographics, customer preferences, and purchasing behaviors to tailor your business approach.
Competitor Analysis: Assess the strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning of competitors to identify your business’s unique selling proposition.
2) Defining Your Business Objectives
Having clear objectives is crucial. Whether it's capturing market share, hitting revenue targets, or achieving expansion goals, defining these objectives paves the way for a focused strategy.
Establishing well-defined objectives also serves as a yardstick for measuring your business’s performance over time.
3) Company Description
Articulate the ethos, offerings, and unique value proposition of your business.
Providing a compelling company description helps stakeholders, including potential investors and employees, to grasp your business's mission and the problems it aims to solve
4) Market Analysis
Delve into market trends, customer behavior, and competition analysis to tailor your strategies.
A robust market analysis provides the data necessary to target your audience effectively and position your business for success in a competitive landscape.
5) Organization and Management
Detail your organizational structure, key team members, and their expertise.
Illustrating a solid organizational structure demonstrates your business’s capacity to execute its strategies and achieve its objectives.
6) Service or Product Line
Describe your products or services, highlighting the benefits to customers. Detailing the attributes and advantages of your offerings allows stakeholders to understand the value your business brings to the market.
7. Marketing and Sales
Illustrate your marketing and sales strategy to attract and retain customers.
Outlining clear strategies for marketing and sales is crucial for driving business growth and achieving your financial objectives.
Market Positioning: Define how your products or services will be positioned in the market and how you intend to differentiate your offerings from competitors.
Promotional Strategies: Outline the various promotional tactics you will employ, such as social media marketing, search engine optimization, and paid advertising.
Sales Process: Describe the steps of your sales process from lead generation to closing sales, and identify the metrics you will use to measure sales effectiveness.
Customer Retention: Highlight the strategies for customer retention such as loyalty programs, excellent customer service, and regular engagement to keep customers coming back.
Pricing Strategy: Determine the pricing strategy that will be most effective for your market, considering factors like cost, competition, and perceived value.
Time to Master Your Business Pitch
Now that you have a robust business plan, it’s time to translate it into a compelling business pitch.
The mastery of your pitch lies in knowing your audience, presenting data compellingly, and choosing the right format for resonance.
Understanding Audience Expectations
Understanding your audience is pivotal. Tailoring your pitch to meet the expectations of investors, potential partners, or customers enhances its effectiveness significantly.
Here’s our CEO, Itai Amoza, discussing the key elements that make a presentation engaging:

Emphasizing Data Visualization for a Better Appeal
Visual presentation of data, through graphs or charts, can make complex information easily digestible.
Using the right data visualization tools can effectively narrate the story of your venture compellingly.
PDF (conservative) vs. Interactive
Choosing between a traditional PDF or interactive presentations like those on Storydoc or PowerPoint can significantly impact the engagement level of your audience.
Interactive formats allow for dynamic presentations with embedded videos and other multimedia elements making your pitch more engaging and memorable.

Consider Business Plan One-pager
Creating a one-page business plan rather than a multi-page business plan involves summarizing your business's essential aspects concisely.
This includes your value proposition, company overview, market analysis, the problem and solution, marketing strategy, financial projections, and a call to action for potential investors or partners.
Ready to Narrate Your Story? Begin with This Business Plan Template
Ah, the exhilarating journey of a startup. It's like crafting a story, with characters, plots, and a dash of suspense on what the next chapter brings.
Now, before you get swept away in this narrative, remember, that every good story needs a structured outline, and in the startup world, that outline is your business plan.
Pick a business plan one-pager template:
Create story from scratch

I am a Marketing Specialist at Storydoc, I research, analyze and write on our core topics of business presentations, sales, and fundraising. I love talking to clients about their successes and failures so I can get a rounded understanding of their world.

Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live.
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.
Create your best presentation to date
Try Storydoc interactive presentation maker for 14 days free (keep any presentation you make forever!)
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools
10 Essential Components of a Business Plan and How to Write Them

Business Plan Template
Ayush Jalan
- January 4, 2024
12 Min Read
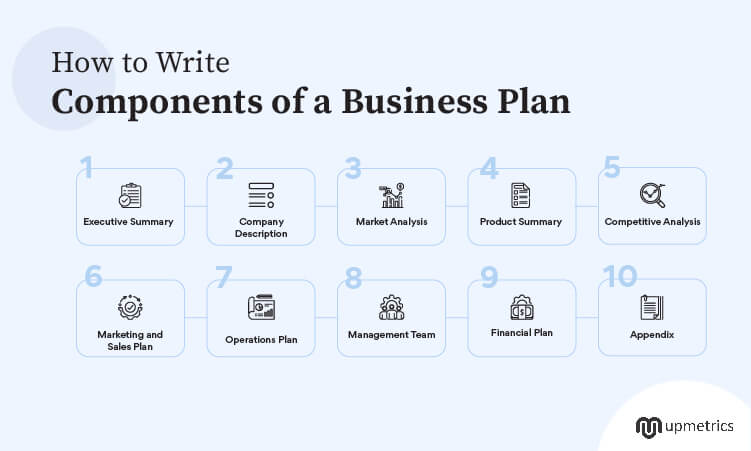
A business plan is an essential document for any business, whether it’s a startup or an established enterprise. It’s the first thing any interested investor will ask for if they like your business idea and want to partner with you.
That’s why it’s important to pay attention when writing your business plan and the components inside it. An incomplete business plan can give the impression that you’re unqualified—discouraging investors and lenders.
A good business plan reduces ambiguity and communicates all essential details such as your financials, market analysis, competitive analysis, and a timeline for implementation of the plan. In this article, we’ll discuss the 10 important business plan components.
10 Important Business Plan Components
A comprehensive and well-thought-out business plan acts as a roadmap that guides you in making sound decisions and taking the right actions at the right times. Here are its key components and what to include in them.
1. Executive summary
The executive summary is one of the most important parts of a business plan. It’s the first thing potential investors will read and should therefore provide a clear overview of your business and its goals.
In other words, it helps the reader get a better idea of what to expect from your company. So, when writing an executive summary of your business, don’t forget to mention your mission and vision statement.
Mission statement
A mission statement is a brief statement that outlines your objectives and what you want to achieve. It acts as a guiding principle that informs decisions and provides a clear direction for the organization to follow.
For instance, Google’s mission is to “organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” It’s short, inspiring, and immediately communicates what the company does.
A mission statement should be realistic, and hint towards a goal that is achievable in a reasonable amount of time with the resources you currently have or are going to acquire in the near future.
Vision statement
While a mission statement is more actionable and has an immediate effect on the daily activities of the company, a vision statement is more aspirational and has a much broader scope.
In other words, it highlights where the company aims to go in the future and the positive change it hopes to make in the world within its lifetime.
2. Company description
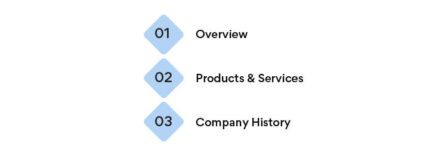
The second component of your business plan is the company description. Here, you provide a brief overview of your company, its products or services, and its history. You can also add any notable achievements if they are significant enough for an investor to know.
A company overview offers a quick bird’s-eye view of things such as your business model , operational capabilities, financials, business philosophy, size of the team, code of conduct, and short-term and long-term objectives.
Products and services
The products and services part of your company description explains what your business offers to its customers, how it’s delivered, and the costs involved in acquiring new customers and executing a sale.
Company History
Company history is the timeline of events that took place in your business from its origin to the present day. It includes a brief profile of the founder(s) and their background, the date the company was founded, any notable achievements and milestones, and other similar facts and details.
If you’re a startup, you’ll probably not have much of a history to write about. In that case, you can share stories of the challenges your startup faced during its inception and how your team overcame them.
3. Market analysis

The market analysis section of your business plan provides an in-depth analysis of the industry, target market, and competition. It should underline the risks and opportunities associated with your industry, and also comment on the attributes of your target customer.
Demographics and segmentation
Understanding the demographics of your customers plays a big role in how well you’re able to identify their traits and serve them.
By dividing your target audience into smaller and more manageable groups, you can tailor your services and products to better meet their needs.
You can use demographics such as age, gender, income, location, ethnicity, and education level to better understand the preferences and behaviors of each segment, and use that data to create more effective marketing strategies.
Target market and size
Understanding your target market lies at the core of all your marketing endeavors. After all, if you don’t have a clear idea of who you’re serving, you won’t be able to serve well no matter how big your budget is.
For instance, Starbucks’ primary target market includes working professionals and office workers. The company has positioned itself such that many of its customers start their day with its coffee.
Estimating the market size helps you know how much scope there is to scale your business in the future. In other words, you’re trying to determine how much potential revenue exists in this market and if it’s worth the investment.
Market need
The next step is to figure out the market need, i.e., the prevalent pain points that people in that market experience. The easiest way to find these pain points is to read the negative reviews people leave on Amazon for products that are similar to yours.
The better your product solves those pain points, the better your chances of capturing that market. In addition, since your product is solving a problem that your rivals can’t, you can also charge a premium price.
To better identify the needs of your target customers, it helps to take into account things such as local cultural values, industry trends, buying habits, tastes and preferences, price elasticity, and more.
4. Product Summary
The product summary section of your business plan goes into detail about the features and benefits that your products and services offer, and how they differ from your competitors. It also outlines the manufacturing process, pricing, cost of production, inventory, packaging, and capital requirements.
5. Competitive analysis
Unless you’ve discovered an untapped market, you’re probably going to face serious competition and it’s only going to increase as you scale your business later down the line.
This is where the competitive analysis section helps; it gives an overview of the competitive landscape, introduces your immediate rivals, and highlights the current dominant companies and their market share.
In such an environment, it helps to have certain competitive advantages against your rivals so you can stand out in the market. Simply put, a competitive advantage is the additional value you can provide to your customers that your rivals can’t—perhaps via unique product features, excellent customer service, or more.

Want to Perform Competitive Analysis for Your Business?
Discover your competition’s secrets effortlessly with our user-friendly and Free Competitor Analysis Generator!
6. Marketing and sales plan

The marketing and sales plan is one of the most important business plan components. It explains how you plan to penetrate the market, position your brand in the minds of the buyers, build brand loyalty, increase sales, and remain competitive in an ever-changing business environment.
Unique selling proposition
A unique selling proposition (USP) conveys how your products and services differ from those of your competitors, and the added value those differences provide.
A strong USP will stand out in a competitive market and make potential customers more likely to switch to your brand—essentially capturing the market share of your rivals.
Marketing Plan
Your product might be unique, but if people don’t even know that it exists, it won’t sell. That’s where marketing comes in.
A marketing plan outlines strategies for reaching your target market and achieving sales goals. It also outlines the budget required for advertising and promotion.
You may also include data on the target market, target demographics, objectives, strategies, a timeline, budget, and the metrics considered for evaluating success.
Sales and distribution plan
Once people are made aware of your product, the next step is to ensure it reaches them. This means having a competent sales and distribution plan and a strong supply chain.
Lay out strategies for reaching potential customers, such as online marketing, lead generation, retail distribution channels, or direct sales.
Your goal here is to minimize sales costs and address the risks involved with the distribution of your product. If you’re selling ice cream, for example, you would have to account for the costs of refrigeration and cold storage.
Pricing strategy
Pricing is a very sensitive yet important part of any business. When creating a pricing strategy , you need to consider factors such as market demand, cost of production, competitor prices, disposable income of target customers, and profitability goals.
Some businesses have a small profit margin but sell large volumes of their product, while others sell fewer units but with a massive markup. You will have to decide for yourself which approach you want to follow.
Before setting your marketing plans into action, you need a budget for them. This means writing down how much money you’ll need, how it will be used, and the potential return you are estimating on this investment.
A budget should be flexible, meaning that it should be open to changes as the market shifts and customer behavior evolves. The goal here is to make sure that the company is making the best use of its resources by minimizing the wastage of funds.
7. Operations plan
The operations plan section of your business plan provides an overview of how the business is run and its day-to-day operations. This section is especially important for manufacturing businesses.
It includes a description of your business structure, the roles and responsibilities of each team member, the resources needed, and the procedures you will use to ensure the smooth functioning of your business. The goal here is to maximize output whilst minimizing the wastage of raw material or human labor.
8. Management team
At the core of any successful business lies a dedicated, qualified, and experienced management team overlooking key business activities.
This section provides an overview of the key members of your management team including their credentials, professional background, role and responsibilities, experience, and qualifications.
A lot of investors give special attention to this section as it helps them ascertain the competence and work ethic of the members involved.
Organizational structure
An organizational structure defines the roles, responsibilities, decision-making processes, and authority of each individual or department in an organization.
Having a clear organizational structure improves communication, increases efficiency, promotes collaboration, and makes it easier to delegate tasks. Startups usually have a flatter organizational hierarchy whereas established businesses have a more traditional structure of power and authority.
9. Financial Plan
Financials are usually the least fun thing to talk about, but they are important nonetheless as they provide an overview of your current financial position, capital requirements, projections, and plans for repayment of any loans.
Your financial plan should also include an analysis of your startup costs, operating costs, administration costs, and sources of revenue.
Funding requirements
Once an investor has read through your business plan, it’s time to request funding. Investors will want to see an accurate and detailed breakdown of the funds required and an explanation of why the requested funds are necessary for the operation and expansion of your business.
10. Appendix
The appendix is the last section of your business plan and it includes additional supporting documents such as resumes of key team members, market research documents, financial statements, and legal documents.
In other words, anything important or relevant that couldn’t fit in any of the former sections of your business plan goes in the appendix.
Write a Business Plan Worth Reading
Starting a business is never easy, but it’s a little less overwhelming if you have a well-made business plan. It helps you better navigate the industry, reduce risk, stay competitive, and make the best use of your time and money.
Remember, since every business is unique, every business plan is unique too, and must be regularly updated to keep up with changing industry trends. Also, it’s very likely that interested investors will give you feedback, so make sure to implement their recommendations as well.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
About the Author

Ayush is a writer with an academic background in business and marketing. Being a tech-enthusiast, he likes to keep a sharp eye on the latest tech gadgets and innovations. When he's not working, you can find him writing poetry, gaming, playing the ukulele, catching up with friends, and indulging in creative philosophies.
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates
- Setting up in the UK
- Start-up business
- A growing business
- Maturing company considering exit strategy
- An individual
- Bookkeeping & accounting
- Choosing the right structure
- Corporate finance
- Forensic accounting & litigation
- Mergers, acquisitions & disposals
- Profit & cashflow forecasting
- Raising finance
- Share schemes
- Strategic planning
- Corporate tax planning
- Estate planning
- Personal tax planning
- R&D tax credits
- Self assessment
- The patent box
- Trust & executorships
- VAT planning and compliance
- Agriculture
- Contracting
- Estate & letting agents
- Family enterprise
- Hospitality
- Legal practices
- Pension schemes
- Property & construction
- Our Approach
- There are no suggestions because the search field is empty.
What should a business plan include?
1. the executive summary, 2. a description of the business, 3. the market(s) the business will operate in, 4. a swot analysis.
5. Management team and personnel
6. The products or services offered
7. marketing.
8. A financial plan
The contents of a business plan
This is placed as number one on our list of components of a business plan , but it can easily be the final stage. That's because sometimes it's easiest to write your summary after you've covered all the other details.
A great summary is one of the key features of a business plan. It serves as an overview of your entire business and the elements surrounding it.
Be sure to outline succinctly the 5 "W"s (Who, What, Why, When, Where) as well as the mission statement . Think about why you started the business along with where you would like it to be in the future, how will you get there? Your mission statement is the start of creating a culture that people in your organisation will live and work by.
This section should contain details of things such as your goals and the customers you will service. What are the products and services you will offer to your customers? You'll need to provide an overview of them and how they will address customers' needs and wants?
You've come up with this great business idea , but how will it do in the market? Or, more importantly, what is the market for it? How well do you know the market? What does a typical buyer look like, what is their income level? Does the business have the hallmarks of disruptive innovation ?
This is the time to research and determine who your target market is and ask specific questions that relate to your product or service. Put you idea to the test. What have others done before you and what can you do differently and better? Analyse what information you've uncovered and outline it's potential impact in your plan.
Create a detailed list of your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. This needs to be done with an open and honest approach, keep emotions out of it, focus on being objective when analysing your business and those of your competitors.
Any strengths you uncover will represent internal, positive factors in your business that are within your control. Weaknesses are also internal, but are negative factors that need to be improved.
Both opportunities and threats are external factors. While opportunities will potentially positively impact on your business, threats represent negative factors beyond your control. For example, are there high barriers to entering the market? Does a competitor have the market cornered due to brand loyal customers? These could harm your enterprise, so you need to strategise for it in your plan.
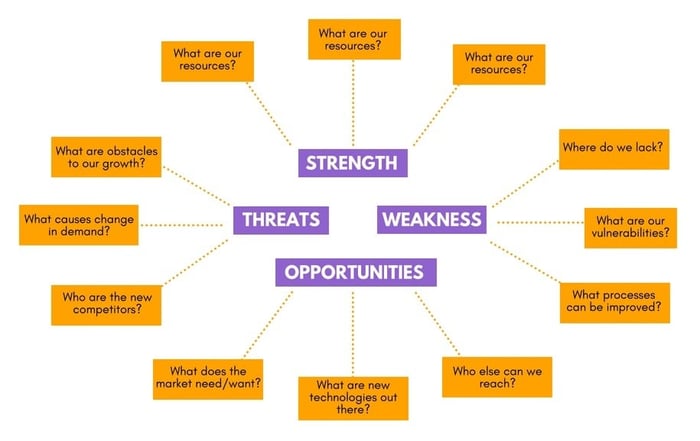
5. The management team and personnel
Who will run the business, who are the directors in the business? What are the skills of the management team and how do their different responsibilities make maximum use of their abilities. What is the chain of command in terms of decision making?
Also use this section to identify how the management team, and taking on employees will help maximise strengths, while addressing identified weaknesses to help improve the business.
Finally, which of the UK's business structures will you choose to operate through?
- Limited company
- Partnership
- Limited liability partnership
In this section you need to detail what will be produced and how it will be sold. You should explain how your product or service will meet a particular need in the marketplace, and how you'll get customers returning to make repeat purchases. Repeat custom is after all the lifeblood of many a good business.
Who will you rely on, in terms of suppliers, to help you assemble your products? What intellectual property, patents or copyright do you own, or might you be at risk of potentially infringing?
What is the branding to your business? What are the key messages you want to communicate with your target market and how will you go about reaching them? How will you achieve market share and at what cost in terms of your budget?
8. Let's talk money: A financial plan
Ideas are great, but how will you make them a reality and sustain a viable business. Creating a financial plan will give you the opportunity to address your financial concerns and talk money, think about start-up costs, financial projections , funding and investor pitches.
You'll need to list how much your start-up will cost, everything from stationary to leases should be outlined and balanced against your financial projections.
Don't fear change, your business plan isn't written in stone
It’s important to remember that your business plan isn’t written in stone. This is a document that you and your staff can improve and update as the business grows and changes. Your plan should be reviewed regularly.
Consider implementing a monthly review to track progress or make adjustments to your strategy. Accountability and motivation are key in making sure your goals are met, think about the people involved and what can you do to keep them inspired.
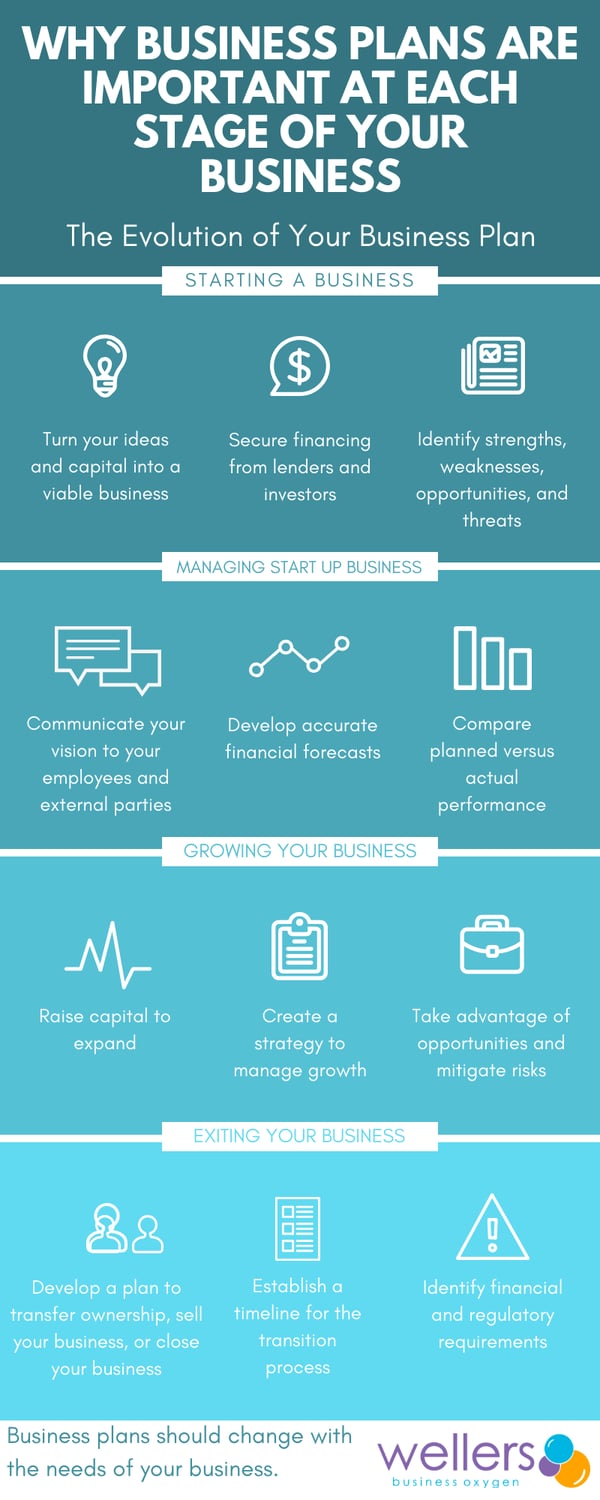
This post was created on 26/06/2018 and updated on 18/02/2022.
Please be aware that information provided by this blog is subject to regular legal and regulatory change. We recommend that you do not take any information held within our website or guides (eBooks) as a definitive guide to the law on the relevant matter being discussed. We suggest your course of action should be to seek legal or professional advice where necessary rather than relying on the content supplied by the author(s) of this blog.

Related posts -
Leave a comment -, subscribe to email updates, popular posts, posts by topic.
- Business insight (78)
- Personal Tax (48)
- Hospitality (44)
- Tax developments (42)
Click below for office location details
Wellers London
Wellers Oxford
Wellers Thame
Wellers Banbury
- Business Services
- Specialist Sectors
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
subscribe to newsletter
Connect with us.
Your Article Library
9 basic features of a good plan – explained.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Nine Basic Features of a Good Management Plan are: 1. It should define objectives, 2.It should be simple, 3. It should be clear, 4. It should be comprehensive, 5. It should be flexible, 6. It should be economical, 7. It should establish standards, 8. It should be balanced, 9. It should be practicable!
1. It should define objectives:
Objectives are the ultimate goals towards which all activities are directed.
A statement which lays down objectives should be clear and definite and everyone in the organisation should understand it in the same sense.
2. It should be simple:
If a plan is expressed in a language which is not understandable by the personnel of the concern or it is complicated, it may create problems for those who are to actually put it into action.
3. It should be clear:
A good plan must not contain anything that is ambiguous or indefinite.
4. It should be comprehensive:
A good plan should contain all that is necessary for the attainment of the objectives of the enterprise. If a master plan is prepared for the whole organisation it will be more useful as it can be seen that nothing is left from it.
5. It should be flexible:
A flexible plan adjusts the changes in the plans without any delay. Hence a plan must not be rigid. A plan should be broad enough to meet the future challenges and uncertainties.
6. It should be economical:
A plan should be made keeping in mind the resources available with the concern and making optimum utilisation of the available resources. In other words, a plan must recover its cost and should result in the least operating cost.
7. It should establish standards:
A plan must lay down the standards to be achieved. The actual performance is compared with these standards and deviations if any are noted.
8. It should be balanced:
It is necessary ensure that there is a proper coordination between different types of plans such as short-term and long term plans, “plans of different departments etc. A business enterprise usually has a number of department’s viz., production, marketing, finance etc. Each department frames its own plans. It is for the management to see that all these plans are well balanced.
9. It should be practicable:
A plan is worth only if it is practically workable and realistic. It should be formulated keeping in view the limitations of planning. If a plan is good in theory but bad in practice, it is of no use. Similarly, if the desired results are not achieved by a plan, it leads to frustration at all levels in the organisation.
Related Articles:
- How to make your Business Plan Tremendously Effective? (9 Principles)
- Formulating the Financial Plan of a Firm: 6 Basic Considerations
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Salesforce is closed for new business in your area.
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- May 10, 2024 • 27:42 Stormy Daniels Takes the Stand
- May 9, 2024 • 34:42 One Strongman, One Billion Voters, and the Future of India
- May 8, 2024 • 28:28 A Plan to Remake the Middle East
- May 7, 2024 • 27:43 How Changing Ocean Temperatures Could Upend Life on Earth
- May 6, 2024 • 29:23 R.F.K. Jr.’s Battle to Get on the Ballot
- May 3, 2024 • 25:33 The Protesters and the President
- May 2, 2024 • 29:13 Biden Loosens Up on Weed
- May 1, 2024 • 35:16 The New Abortion Fight Before the Supreme Court
- April 30, 2024 • 27:40 The Secret Push That Could Ban TikTok
- April 29, 2024 • 47:53 Trump 2.0: What a Second Trump Presidency Would Bring
- April 26, 2024 • 21:50 Harvey Weinstein Conviction Thrown Out
- April 25, 2024 • 40:33 The Crackdown on Student Protesters
Stormy Daniels Takes the Stand
The porn star testified for eight hours at donald trump’s hush-money trial. this is how it went..
Hosted by Michael Barbaro
Featuring Jonah E. Bromwich
Produced by Olivia Natt and Michael Simon Johnson
Edited by Lexie Diao
With Paige Cowett
Original music by Will Reid and Marion Lozano
Engineered by Alyssa Moxley
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music | YouTube
This episode contains descriptions of an alleged sexual liaison.
What happened when Stormy Daniels took the stand for eight hours in the first criminal trial of former President Donald J. Trump?
Jonah Bromwich, one of the lead reporters covering the trial for The Times, was in the room.
On today’s episode

Jonah E. Bromwich , who covers criminal justice in New York for The New York Times.

Background reading
In a second day of cross-examination, Stormy Daniels resisted the implication she had tried to shake down Donald J. Trump by selling her story of a sexual liaison.
Here are six takeaways from Ms. Daniels’s earlier testimony.
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Jonah E. Bromwich covers criminal justice in New York, with a focus on the Manhattan district attorney’s office and state criminal courts in Manhattan. More about Jonah E. Bromwich
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business plan is an effective way of communicating with potential investors, and the level of expertise and time used in preparing a business plan also gives professional credibility to entrepreneurs. It analyzes and predicts the chances of success for the investor and helps to raise capital. Features of a Good Business Plan 1. Executive Summary
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
It needs to be a serious business document with the following six elements. 1. Executive summary. "An executive summary is the 'elevator pitch' of your business plan," explains David ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
Make a plan for increasing revenue - but in increments that make sense and are achievable. You don't need an unrealistic plan. Company leaders and employees will only grow frustrated and discouraged if they're unable to hit any target goals laid out in the plan. 9. Clearly identifies assumptions.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
Nothing should be included that isn't going to be used. 10. Geared for change. A good business plan is the opposite of written in stone. It's going to change in a few weeks. List assumptions because reviewing assumptions is the best way to determine when to change the plan and when to stick with it. 11.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
For a thorough explanation of how to write a business plan, refer to Shopify's guide. 12 components of a business plan. Business plans vary depending on the product or service. Some entrepreneurs choose to use diagrams and charts, while others rely on text alone. Regardless of how you go about it, good business plans tend to include the ...
Above all, the numbers should help answer why your business can do it better. 4. Competitive Analysis. A good business plan will present a clear comparison of your business vs your direct and indirect competitors. This is where you prove your knowledge of the industry by breaking down their strengths and weaknesses.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
Innovation in Planning: The Untold Ingredient to Business Success. In the turbulent landscape of entrepreneurship, where over 20% of small ventures falter in their early days, this blog post sheds light on the importance of a well-structured business plan.. It delves into the specifics of an executive summary, steps, what to include, and innovation in business planning, guiding businesses to ...
Here are its key components and what to include in them. 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is one of the most important parts of a business plan. It's the first thing potential investors will read and should therefore provide a clear overview of your business and its goals.
6. Strategy and implementation plans. When it comes to starting a business, having a solid plan of attack is essential. That's why the strategy and implementation plan section of your business ...
Although the exact structure of business plans vary, my personal requirements for plans that I create and plans that I review for potential investments include the following 10 components: Summary ...
Key components of a successful business plan. 1. Executive summary. If you ask us about one business plan component that is the most important, we would say it is the executive summary. The executive summary is the first component that is included in your plan. It is important as it tells your readers (aka investors) what your business is, in a ...
1. The executive summary. This is placed as number one on our list of components of a business plan, but it can easily be the final stage. That's because sometimes it's easiest to write your summary after you've covered all the other details. A great summary is one of the key features of a business plan. It serves as an overview of your entire ...
4. Ongoing Evaluation and Adaptation: The fourth essential characteristic of an effective plan is ongoing evaluation and adaptation. Planning is not a one-time event, but rather an ongoing process. It is important to regularly assess the progress of your plan, measure the outcomes against your goals and objectives, and make necessary adjustments to stay on track.
ADVERTISEMENTS: Nine Basic Features of a Good Management Plan are: 1. It should define objectives, 2.It should be simple, 3. It should be clear, 4. It should be comprehensive, 5. It should be flexible, 6. It should be economical, 7. It should establish standards, 8. It should be balanced, 9.
Unlimited. $ 330. user/month. Einstein 1 Service. $ 500. user/month. Case Management. Manage the entire case lifecycle from a single system. Automatically create cases from web or email, send auto-responses, and route work to the right queue or agent for faster, more accurate case resolution.
On today's episode. Jonah E. Bromwich, who covers criminal justice in New York for The New York Times. Stormy Daniels leaving court on Thursday, after a second day of cross-examination in the ...