Accessibility Links
- Skip to content
- Skip to search IOPscience
- Skip to Journals list
- Accessibility help
- Accessibility Help
Click here to close this panel.
Purpose-led Publishing is a coalition of three not-for-profit publishers in the field of physical sciences: AIP Publishing, the American Physical Society and IOP Publishing.
Together, as publishers that will always put purpose above profit, we have defined a set of industry standards that underpin high-quality, ethical scholarly communications.
We are proudly declaring that science is our only shareholder.

The Impact of Time Management on Students' Academic Achievement
S N A M Razali 1 , M S Rusiman 1 , W S Gan 1 and N Arbin 2
Published under licence by IOP Publishing Ltd Journal of Physics: Conference Series , Volume 995 , International Seminar on Mathematics and Physics in Sciences and Technology 2017 (ISMAP 2017) 28–29 October 2017, Hotel Katerina, Malaysia Citation S N A M Razali et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 995 012042 DOI 10.1088/1742-6596/995/1/012042
Article metrics
115210 Total downloads
Share this article
Author affiliations.
1 Department of Mathematics and Statistic, Faculty of Applied Science and Technology University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Batu Pahat, Johor, Malaysia.
2 Department of Mathematic, Faculty of Science and Mathematics, Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris, 35900 Perak, Malaysia.
Buy this article in print
Time management is very important and it may actually affect individual's overall performance and achievements. Students nowadays always commented that they do not have enough time to complete all the tasks assigned to them. In addition, a university environment's flexibility and freedom can derail students who have not mastered time management skills. Therefore, the aim of this study is to determine the relationship between the time management and academic achievement of the students. The factor analysis result showed three main factors associated with time management which can be classified as time planning, time attitudes and time wasting. The result also indicated that gender and races of students show no significant differences in time management behaviours. While year of study and faculty of students reveal the significant differences in the time management behaviours. Meanwhile, all the time management behaviours are significantly positively related to academic achievement of students although the relationship is weak. Time planning is the most significant correlated predictor.
Export citation and abstract BibTeX RIS
Content from this work may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 licence . Any further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the title of the work, journal citation and DOI.
College Students’ Time Management: a Self-Regulated Learning Perspective
- Review Article
- Published: 27 October 2020
- Volume 33 , pages 1319–1351, ( 2021 )
Cite this article

- Christopher A. Wolters ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8406-038X 1 &
- Anna C. Brady 1
27k Accesses
67 Citations
10 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Despite its recognized importance for academic success, much of the research investigating time management has proceeded without regard to a comprehensive theoretical model for understanding its connections to students’ engagement, learning, or achievement. Our central argument is that self-regulated learning provides the rich conceptual framework necessary for understanding college students’ time management and for guiding research examining its relationship to their academic success. We advance this larger purpose through four major sections. We begin by describing work supporting the significance of time management within post-secondary contexts. Next, we review the limited empirical findings linking time management and the motivational and strategic processes viewed as central to self-regulated learning. We then evaluate conceptual ties between time management and processes critical to the forethought, performance, and post-performance phases of self-regulated learning. Finally, we discuss commonalities in the antecedents and contextual determinants of self-regulated learning and time management. Throughout these sections, we identify avenues of research that would contribute to a greater understanding of time management and its fit within the framework of self-regulated learning. Together, these efforts demonstrate that time management is a significant self-regulatory process through which students actively manage when and for how long they engage in the activities deemed necessary for reaching their academic goals.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Examining the relations of time management and procrastination within a model of self-regulated learning
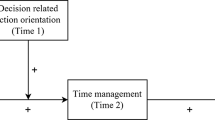
Willing, able, and engaged: roles of action-state orientation, intrinsic academic motivation, and time management on academic engagement
Are Mastery-Oriented College Students Better Time Managers?
Adams, G. A., & Jex, S. M. (1999). Relationships between time management, control, work family conflict, and strain. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 4 (1), 72–77.
Google Scholar
Aeon, B., & Aguinis, H. (2017). It’s about time: new perspectives and insights on time management. Academy of Management Perspectives, 31 , 309–330.
Ames, C. (1992). Classrooms: goals, structures, and student motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 84 , 261–271.
Asikainen, H., & Gijbels, D. (2017). Do students develop towards more deep approaches to learning during studies? A systematic review on the development of students’ deep and surface approaches to learning in higher education. Educational Psychology Review, 29 , 205–234.
Balduf, M. (2009). Underachievement among college students. Journal of Advanced Academics, 20 , 274–294.
Banahan, L., & Mullendore, R. (2014). Navigating the first college year. A guide for parents and families . Columbia: University of South Carolina, National Resource Center for The First-Year Experience and Students in Transition.
Bandura, A. (1986). The explanatory and predictive scope of self-efficacy theory. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 4 , 359–373.
Bartels, J. M., Magun-Jackson, S., & Ryan, J. J. (2010). Dispositional approach-avoidance achievement motivation and cognitive self-regulated learning: the mediation of achievement goals. Individual Differences Research, 8 , 97–110.
Basila, C. (2014). Good time management and motivation level predict student academic success in college on-line courses. International Journal of Cyber Behavior, Psychology and Learning, 4 , 45–52.
Bembenutty, H. (2009). Academic delay of gratification, self-regulation of learning, gender differences, and expectancy-value. Personality and Individual Differences, 46 , 347–352.
Beuhler, R., Griffin, D., & Peetz, J. (2010). The planning fallacy: cognitive, motivational, and social origins. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 43 , 1–62.
Bidjerano, T., & Dai, D. Y. (2007). The relationship between the big-five model of personality and self-regulated learning strategies. Learning and Individual Differences, 17 , 69–81.
Boekaerts, M. (1996). Self-regulated learning at the junction of cognition and motivation. European Psychologist, 1 , 100–112.
Boekaerts, M., & Corno, L. (2005). Self-regulation in the classroom: a perspective on assessment and intervention. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 54 , 199–231.
Bond, M. J., & Feather, N. T. (1988). Some correlates of structure and purpose in the use of time. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55 , 321–329.
Britton, B. K., & Glynn, S. M. (1989). Mental management and creativity: a cognitive model of time management for intellectual productivity. In J. Glover, R. Ronning, & C. Reynolds (Eds.), Handbook of creativity (pp. 429–440). New York: Plenum.
Britton, B. K., & Tesser, A. (1991). Effects of time-management practices on college grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 83 , 405–410.
Buehler, R., & Griffin, D. (2015). When plans lead to optimistic forecasts. In M. D. Mumford & M. Frese (Eds.), The psychology in planning in organizations: research and applications (pp. 31–57). New York: Routledge.
Burlison, J. D., Murphy, C. S., & Dwyer, W. O. (2009). Evaluation of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire for predicting academic performance in college students of varying scholastic aptitude. College Student Journal, 43 , 1313–1323.
Burnette, J., O’Boyle, E., VanEpps, E., Pollack, J., & Finkel, E. (2013). Mind-sets matter: a meta-analytic review of implicit theories and self-regulation. Psychological Bulletin, 139 (3), 655–701.
Burt, C. D., Weststrate, A., Brown, C., & Champion, F. (2010). Development of the time management environment (TiME) scale. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 25 , 649–668.
Butler, D., & Winne, P. (1995). Feedback and self-regulated learning: a theoretical synthesis. Review of Educational Research, 65 , 245–281.
Cano, F. (2006). An in-depth analysis of the Learning and Study Strategies Inventory (LASSI). Educational and Psychological Measurement, 66 , 1023–1038.
Capdeferro, N., Romero, M., & Barberà, E. (2014). Polychronicity: review of the literature and a new configuration for the study of this hidden dimension of online learning. Distance Education, 35 , 294–310.
Cassidy, S. (2011). Self-regulated learning in higher education: identifying key component processes. Studies in Higher Education, 36 , 989–1000.
Chang, A., & Nguyen, L. T. (2011). The mediating effects of time structure on the relationships between time management behaviour, job satisfaction, and psychological well-being. Australian Journal of Psychology, 63 , 187–197.
Choi, B. (2016). How people learn in an asynchronous online learning environment: the relationships between graduate students’ learning strategies and learning satisfaction. Canadian Journal of Learning and Technology, 42 , 1–15.
Chuderski, A. (2016). Time pressure prevents relational learning. Learning and Individual Differences, 49 , 361–365.
Claessens, B. J. C., van Eerde, W., Rutte, C. G., & Roe, R. A. (2007). A review of the time management literature. Personnel Review, 36 , 255–276.
Conti, R. (2001). Time flies: investigating the connection between intrinsic motivation and the experience of time. Journal of Personality, 69 (1), 1–26.
Corno, L., Cronbach, L. J., Kupermintz, H., Lohman, D. F., Mandinach, E. B., Porteus, A. W., & Talbert, J. E. (2002). Remaking the concept of aptitude: extending the legacy of Richard E Snow . Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Crede, M., & Kuncel, N. R. (2008). Study habits, skills, and attitudes: the third pillar supporting collegiate academic performance. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 3 (6), 425–453.
Crede, M., & Phillips, L. A. (2011). A meta-analytic review of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire. Learning and Individual Differences, 21 , 337–346.
Crede, M., Roch, S. G., & Kieszczynka, U. M. (2010). Class attendance in college: a meta-analytic review of the relationship of class attendance with grades and student characteristics. Review of Educational Research, 80 , 272–295.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1996). Creativity: flow and the psychology of discovery and invention . New York: HarperCollins Publishers.
Dembo, M. H., & Eaton, M. J. (2000). Self-regulation of academic learning in middle-level schools. The Elementary School Journal, 100 , 473–490.
Dent, A., & Koenka, A. (2016). The relation between self-regulated learning and academic achievement across childhood and adolescence: a meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 28 , 425–474.
Díaz-Morales, J. F., Ferrari, J. R., & Cohen, J. R. (2008). Indecision and avoidant procrastination: the role of morningness—eveningness and time perspective in chronic delay lifestyles. The Journal of General Psychology, 135 (3), 228–240.
Donker, A., de Boer, H., Kostons, D., Dignath van Ewijk, C., & van der Werf, M. (2014). Effectiveness of learning strategy instruction on academic performance: a meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 11 , 1–26.
Douglas, H. E., Bore, M., & Munro, D. (2016). Coping with university education: the relationships of time management behaviour and work engagement with the five factor model aspects. Learning and Individual Differences, 45 , 268–274.
Doumen, S., Broeckmans, J., & Masui, C. (2014). The role of self-study time in freshmen’s achievement. Educational Psychology, 34 , 385–402.
Duncan, T. G., & McKeachie, W. J. (2005). The making of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire. Educational Psychologist, 40 , 117–128.
Duncheon, J. C., & Tierney, W. G. (2013). Changing conceptions of time: implications for educational research and practice. Review of Educational Research, 83 , 236–272.
Dunlosky, J., & Ariel, R. (2011). Self-regulated learning and the allocation of study time. In B. Ross (Ed.), Psychology of learning and motivation (Vol. 54, pp. 103–140). San Diego: Academic Press.
Dunning, D., Heath, C., & Suls, J. (2004). Flawed self-assessments. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 5 (3), 69–106.
Efklides, A. (2011). Interactions of metacognition with motivation and affect in self-regulated learning: the MASRL model. Educational Psychologist, 46 , 6–25.
Eilam, B., & Aharon, I. (2003). Students’ planning in the process of self-regulated learning. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 28 , 304–334.
Ferrari, J. R., & Díaz-Morales, J. F. (2007). Procrastination: different time orientations reflect different motives. Journal of Research in Personality, 41 , 707–714.
Flake, J. K., Barron, K. E., Hulleman, C., McCoach, B. D., & Welsh, M. E. (2015). Measuring cost: the forgotten component of expectancy-value theory. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 41 , 232–244.
Flanigan, A. E., & Kiewra, K. A. (2018). What college instructors can do about student cyber-slacking. Educational Psychology Review, 30 , 585–597.
Francis-Smythe, J. A., & Robertson, I. T. (1999a). On the relationship between time management and time estimation. British Journal of Psychology, 90 , 333–347.
Francis-Smythe, J. A., & Robertson, I. T. (1999b). Time-related individual differences. Time & Society, 8 , 273–292.
Fromme, K., Corbin, W., & Kruse, M. (2008). Behavioral risks during the transition from high school to college. Developmental Psychology, 44 (5), 1497–1504.
Gable, P. A., & Poole, B. D. (2012). Time flies when you’re having approach-motivated fun: effects of motivational intensity on time perception. Psychological Science, 23 (8), 879–886.
Gevers, J. M., Rutte, C. G., & Van Eerde, W. (2006). Meeting deadlines in work groups: implicit and explicit mechanisms. Applied Psychology, 55 , 52–72.
Green, P., & Skinner, D. (2005). Does time management training work? An evaluation. International Journal of Training and Development, 9 , 124–139.
Gulec, M., Selvi, Y., Boysan, M., Aydin, A., Oral, E., & Aydin, E. F. (2013). Chronotype effects on general well-being and psychopathology levels in healthy young adults. Biological Rhythm Research, 44 , 457–468.
Guzman, G., Goldberg, T., & Swanson, H. (2018). A meta-analysis of self-monitoring on reading performance of K-12 students. School Psychology Quarterly, 33 (1), 160–168.
Hadwin, A., & Oshige, M. (2011). Self-regulation, coregulation, and socially shared regulation: exploring perspectives of social in self-regulated learning theory. Teachers College Record, 113 , 240–264.
Hafner, A., Stock, A., Pinneker, L., & Strohle, S. (2014). Stress prevention through a time management training intervention: an experimental study. Educational Psychology, 34 , 403–416.
Hahn, C., Cowell, J. M., Wiprzycka, U. J., Goldstein, D., Ralph, M., Hasher, L., & Zelazo, P. D. (2012). Circadian rhythms in executive function during the transition to adolescence: the effect of synchrony between chronotype and time of day. Developmental Science, 15 (3), 408–416.
Harkin, B., Webb, T. L., Chang, B. P. I., Prestwich, A., Conner, M., Kellar, I., et al. (2016). Does monitoring goal progress promote goal attainment? A meta-analysis of the experimental evidence. Psychological Bulletin, 142 (2), 198–229.
Hattie, J., Biggs, J., & Purdie, N. (1996). Effects of learning skills interventions on student learning: a meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 66 , 99–136.
Haynes, N., Comer, J., & Hamilton-Lee, M. (1988). Gender and achievement status differences on learning factors among Black high school students. Journal of Educational Research, 81 , 233–237.
Hensley, L. C., Wolters, C. A., Won, S., & Brady, A. C. (2018). Academic probation, time management, and time use in a college success course. Journal of College Reading and Learning, 48 , 105–123.
Hicks, T., & Heastie, S. (2008). High school to college transition: a profile of the stressors, physical and psychological health issues that affect the first-year on-campus college students. Journal of Cultural Diversity, 15 (3), 143–147.
Hilbrecht, M., Zuzanek, J., & Mannell, R. C. (2008). Time use, time pressure and gendered behavior in early and late adolescence. Sex Roles, 58 , 342–357.
Hofer, B. K., Yu, S. L., & Pintrich, P. R. (1998). Teaching college students to be self-regulated learners. In D. H. Schunk & B. J. Zimmerman (Eds.), Self-regulated learning: from teaching to self-reflective practice (pp. 57–85). New York: Guilford Press.
Horstmanshof, L., & Zimitat, C. (2007). Future time orientation predicts academic engagement among first-year university students. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 77 (Pt 3), 703–718.
Huie, F. C., Winsler, A., & Kitsantas, A. (2014). Employment and first-year college achievement: the role of self-regulation and motivation. Journal of Education and Work, 27 , 110–135.
Husman, J., & Lens, W. (1999). The role of the future in student motivation. Educational Psychologist, 34 , 113–125.
Kanfer, R., Frese, M., & Johnson, R. (2017). Motivation related to work: a century of progress. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102 (3), 338–355.
Kantrowitz, T. M., Grelle, D. M., Beaty, J. C., & Wolf, M. B. (2012). Time is money: polychronicity as a predictor of performance across job levels. Human Performance, 25 , 114–137.
Kauderer, S., & Randler, C. (2013). Differences in time use among chronotypes in adolescents. Biological Rhythm Research, 44 , 601–608.
Kaufman-Scarborough, C., & Lindquist, J. D. (1999). Time management and polychronicity: comparisons, contrasts, and insights for the workplace. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 14 , 288–312.
Keating, D. P. (2012). Cognitive and brain development in adolescence. Enfance, 64 , 267–279.
Kesici, Ş., Baloğlu, M., & Deniz, M. E. (2011). Self-regulated learning strategies in relation with statistics anxiety. Learning and Individual Differences, 21 , 472–477.
Kim, K. R., & Seo, E. H. (2015). The relationship between procrastination and academic performance: a meta-analysis. Personality and Individual Differences, 82 , 26–33.
Kitsantas, A., Winsler, A., & Huie, F. (2008). Self-regulation and ability predictors of academic success during college: a predictive validity study. Journal of Advanced Academics, 20 , 42–68.
Koch, C. J., & Kleinmann, M. (2002). A stitch in time saves nine: behavioural decision-making explanations for time management problem. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 11 , 199–217.
Komarraju, M., Karau, S. J., & Schmeck, R. R. (2009). Role of the Big Five personality traits in predicting college students’ academic motivation and achievement. Learning and Individual Differences, 19 , 47–52.
Konig, C. J., & Waller, M. J. (2010). Time for reflection: a critical examination of polychronicity. Human Performance, 23 , 173–190.
Kooij, D. T. A. M., Kanfer, R., Betts, M., & Rudolph, C. W. (2018). Future time perspective: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 103 (8), 867–893.
Krumrei-Mancuso, E. J., Newton, F. B., Kim, E., & Wilcox, D. (2013). Psychosocial factors predicting first-year college student success. Journal of College Student Development, 54 , 247–266.
Landrum, R. E., Turrisi, R., & Brandel, J. M. (2006). College students’ study time: course level, time of semester, and grade earned. Psychological Reports, 98 (3), 675–682.
Liborius, P., Bellhauser, H., & Schmitz, B. (2017). What makes a good study day? An intraindividual study on university students’ time investment by means of time-series analyses. Learning and Instruction.
Linnenbrink-Garcia, L., & Patall, E. (2016). Motivation. In L. Corno & E. Anderman (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (3rd ed., pp. 91–1030). New York: Routledge.
Liu, O. L., Rijmen, F., MacCann, C., & Roberts, R. (2009). The assessment of time management in middle-school students. Personality and Individual Differences, 47 , 174–179.
Locke, E., & Latham, G. (2019). The development of goal setting theory: a half-century retrospective. Motivation Science, 5 , 93–105.
Loureiro, F., & Garcia-Marques, T. (2015). Morning or evening person? Which type are you? Self-assessment of chronotype. Personality and Individual Differences, 86 , 168–171.
Lynch, D. J. (2010). Application of online discussion and cooperative learning strategies to online and blended college courses. College Student Journal, 44 , 920–927.
Macan, T. H. (1994). Time management: test of a process model. Journal of Applied Psychology, 79 , 381–391.
Macan, T. H., Shahani, C., Dipboye, R. L., & Phillips, A. P. (1990). College students’ time management: correlations with academic performance and stress. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82 , 760–768.
MacCann, C., & Roberts, R. D. (2010). Do time management, grit, and self-control relate to academic achievement independently of conscientiousness? In R. E. Hicks (Ed.), Personality and individual differences: current directions (pp. 79–90). Bowen Hills: Australian Academic Press.
MacCann, C., Fogarty, G. J., & Roberts, R. D. (2012). Strategies for success in education: time management is more important for part-time than full-time community college students. Learning and Individual Differences, 22 , 618–623.
McCrae, R., & Lockenhoff, C. (2010). Self-regulation and the five-factor model of personality traits. In R. Hoyle (Ed.), Handbook of personality and self-regulation (pp. 143–168). New York: Wiley.
McInerney, D., & King, R. (2018). Culture and self-regulation in educational contexts. In D. Schunk & J. Greene (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (2nd ed., pp. 485–502). New York: Routledge.
Meeuwisse, M., Born, M. P., & Severiens, S. E. (2013). Academic performance differences among ethnic groups: do the daily use and management of time offer explanations? Social Psychology of Education, 16 , 599–615.
Melancon, J. G. (2002). Reliability, structure, and correlates of Learning and Study Strategies Inventory scores. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 62 , 1020–1027.
Miele, D. B., & Scholer, A. A. (2018). The role of metamotivational monitoring in motivation regulation. Educational Psychologist, 53 , 1–21.
Miller, R. B., & Brickman, S. J. (2004). A model of future-oriented motivation and self-regulation. Educational Psychology Review, 16 , 9–33.
Muis, K. R. (2007). The role of epistemic beliefs in self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 42 , 173–190.
Nelson, T., & Narens, L. (1990). Metamemory: a theoretical framework and some new findings. In G. H. Bower (Ed.), The psychology of learning and motivation (pp. 125–173). New York: Academic Press.
Nonis, S., Teng, J., & Ford, C. (2005). A cross-cultural investigation of time management practices and job outcomes. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 29 , 409–428.
Nonis, S. A., Philhours, M. J., & Hudson, G. I. (2006). Where does the time go? A diary approach to business and marketing students’ time use. Journal of Marketing Education, 28 , 121–134.
Olaussen, B. S., & Bråten, I. (1998). Identifying latent variables measured by the Learning and Study Strategies Inventory (LASSI) in Norwegian college students. The Journal of Experimental Education, 67 , 82–96.
Olejnik, S., & Nist, S. L. (1992). Identifying latent variables measured by the Learning and Study Strategies Inventory (LASSI). The Journal of Experimental Education, 60 , 151–159.
Panadero, E. (2017). A review of self-regulated learning: six models and four directions for research. Frontiers in Psychology, 8 , 1–28.
Panadero, E., Brown, G., & Strijbos, J. (2016). The future of student self-assessment: a review of known and unknowns and potential directions. Educational Psychology Review, 28 (803), 830.
Panek, E. (2014). Left to their own devices: college students’ “guilty pleasure” media use and time management. Communication Research, 41 , 561–577.
Pekrun, R., Goetz, T., Titz, W., & Perry, R. P. (2002). Academic emotions in students’ self-regulated learning and achievement: a program of qualitative and quantitative research. Educational Psychologist, 37 , 91–105.
Pintrich, P. R. (2000). The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 451–502). San Diego: Academic.
Pintrich, P. R. (2004). A conceptual framework for assessing motivation and self-regulated learning in college students. Educational Psychology Review, 16 , 385–407.
Pintrich, P. R., & Zusho, A. (2007). Student motivation and self-regulated learning in the college classroom. In R. P. Perry & J. C. Smart (Eds.), The scholarship of teaching and learning in higher education: an evidence based perspective (pp. 731–810). New York: Springer.
Pintrich, P. R., Smith, D. A., Garcia, T., & McKeachie, W. J. (1993). Reliability and predictive validity of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 53 , 801–813.
Pintrich, P. R., Wolters, C. A., & Baxter, G. P. (2000). Assessing metacognition and self-regulated learning. In G. Schraw & J. Impara (Eds.), Issues in the measurement of metacognition (pp. 43–97). Lincoln: Buros Institute of Mental Measurement.
Plant, E. A., Ericsson, K. A., Hill, L., & Asberg, K. (2005). Why study time does not predict grade point average across college students: implications of deliberate practice for academic performance. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 30 , 96–116.
Prevatt, F., Petscher, Y., Proctor, B. E., Hurst, A., & Adams, K. (2006). The revised Learning and Study Strategies Inventory: an evaluation of competing models. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 66 (3), 448–458.
Pychyl, T. A., Morin, R. W., & Salmon, B. R. (2000). Procrastination and the planning fallacy: an examination of the study habits of university students. Journal of Social Behavior and Personality, 15 , 135–150.
Ranellucci, J., Hall, N. C., & Goetz, T. (2015). Achievement goals, emotions, learning, and performance: a process model. Motivation Science, 1 , 98–120.
Rhodes, M., & Tauber, S. (2011). The influence of delaying judgments of learning on metacognitive accuracy: a meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 137 (1), 131–148.
Richards, J. H. (1987). Time management—a review. Work & Stress, 1 , 73–78.
Rickert, N. P., Meras, I. L., & Witkow, M. R. (2014). Theories of intelligence and students’ daily self-handicapping behaviors. Learning and Individual Differences, 36 , 1–8.
Roskes, M., Elliot, A. J., Nijstad, B. A., & De Dreu, C. K. (2013). Time pressure undermines performance more under avoidance than approach motivation. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 39 , 803–813.
Rytkonen, H., Parpala, A., Lindblom-Ylanne, S., Virtanen, V., & Postareff, L. (2012). Factors affecting bioscience students’ academic achievement. Instructional Science, 40 , 241–256.
Sanders, L., Reedy, D., & Frizell, M. (Eds.). (2018). Learning centers in the 21 st century: a modern guide for learning assistance professionals in higher education . Bentonville: AR. Iona Press.
Sansgiry, S. S., Bhosle, M., & Sail, K. (2006). Factors that affect academic performance among pharmacy students. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 70 , 1–9.
Schell, K. L., & Conte, J. M. (2008). Associations among polychronicity, goal orientation, and error orientation. Personality and Individual Differences, 44 , 288–298.
Schraw, G. (2006). Knowledge: structures and processes. In P. Alexander & P. Winne (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (2nd ed., pp. 245–263). Mahwah: Erlbaum Associates.
Schunk, D. H., & Zimmerman, B. J. (1997). Social origins of self-regulatory competence. Educational Psychologist, 32 , 195–208.
Schunk, D. H., & Zimmerman, B. J. (Eds.). (1998). Self-regulated learning: from teaching to self-reflective practice . New York: Guilford Press.
Sen, S., & Yilmaz, A. (2016). Devising a structural equation model of relationships between preservice teachers’ time and study environment management, effort regulation, self-efficacy, control of learning beliefs, and metacognitive self-regulation. Science Education International, 27 , 301–316.
Shaunessy-Dedrick, E., Suldo, S. M., Roth, R. A., & Fefer, S. A. (2015). Students’ perceptions of factors that contribute to risk and success in accelerated high school courses. The High School Journal, 98 , 109–137.
Shell, D. F., & Husman, J. (2001). The multivariate dimensionality of personal control and future time perspective beliefs in achievement and self-regulation. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 26 (4), 481–506.
Simons, J., Vansteenkiste, M., Lens, W., & Lacante, M. (2004). Placing motivation and future time perspective theory in a temporal perspective. Educational Psychology Review, 16 , 121–139.
Sinatra, G., Kienhues, D., & Hofer, B. (2014). Addressing challenges to public understanding of science: epistemic cognition, motivated reasoning, and conceptual change. Educational Psychologist, 49 , 123–138.
Sirois, F. M. (2014). Procrastination and stress: exploring the role of self-compassion. Self and Identity, 13 , 128–145.
Sitzmann, T., & Ely, K. (2011). A meta-analysis of self-regulated learning in work-related training and educational attainment: what we know and where we need to go. Psychological Bulletin, 137 (3), 421–442.
Sitzmann, T., Ely, K., Brown, K., & Bauer, K. (2010). Self-assessment of knowledge: a cognitive learning or affective measure? Academy of Management Learning & Education, 9 , 169–191.
Snow, R. (1989). Cognitive-conative aptitude interactions in learning. In R. Kanfer, P. Ackerman, & R. Cudeck (Eds.), Abilities, motivation, and methodology: the Minnesota symposium on learning and individual differences (pp. 435–474). Hillsdale: Erlbaum Associates.
Snow, R. E., Corno, L., & Jackson III, D. (1996). Individual differences in affective and conative functions. In D. C. Berliner & R. C. Calfee (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (pp. 243–310). New York: Macmillan Library Reference.
Soderstrom, N. C., & Bjork, R. A. (2014). Testing facilitates the regulation of subsequent study time. Journal of Memory and Language, 73 , 99–115.
Steel, P. (2007). The nature of procrastination: a meta-analytic and theoretical review of quintessential self-regulatory failure. Psychological Bulletin, 133 (1), 65–94.
Stevens, T., & Tallent-Runnels, M. K. (2004). The learning and study strategies inventory-high school version: issues of factorial invariance across gender and ethnicity. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 64 , 332–346.
Strunk, K. K., Cho, Y., Steele, M. R., & Bridges, S. L. (2013). Development and validation of a 2× 2 model of time-related academic behavior: procrastination and timely engagement. Learning and Individual Differences, 25 , 35–44.
Tanner, J. R., Stewart, G., Maples, G. M., & Totaro, M. W. (2009). How business students spend their time—do they really know? Research in Higher Education Journal, 3 , 1–9.
Terenzini, P., Rendon, L., Upcraft, M. L., Millar, S., Allison, K., Gregg, P., & Jalomo, R. (1994). The transition to college: diverse students, diverse stories. Research in Higher Education, 35 , 57–73.
Trueman, M., & Hartley, J. (1996). A comparison between the time-management skills and academic performance of mature and traditional-entry university students. Higher Education, 32 , 199–215.
Truschel, J., & Reedy, D. L. (2009). National survey—what is a learning center in the 21st century? Learning Assistance Review, 14 , 9–22.
Tsai, H. C., & Liu, S. H. (2015). Relationships between time-management skills, Facebook interpersonal skills and academic achievement among junior high school students. Social Psychology of Education, 18 , 503–516.
U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, What Works Clearinghouse (2016). Studies of interventions for students in developmental education intervention report: first year experience courses for students in developmental education . Retrieved from http://whatworks.ed.gov . Accessed 20 Jan 2020.
Urdan, T., & Schoenfelder, E. (2006). Classroom effects on student motivation: goal structures, social relationships, and competence beliefs. Journal of School Psychology, 44 , 331–349.
Usher, E. L., & Pajares, F. (2008). Sources of self-efficacy in school: critical review of the literature and future directions. Review of Educational Research, 78 , 751–796.
van Den Hurk, M. (2006). The relation between self-regulated strategies and individual study time, prepared participation and achievement in a problem-based curriculum. Active Learning in Higher Education, 7 , 155–169.
van der Meer, J., Jansen, E., & Torenbeek, M. (2010). ‘It’s almost a mindset that teachers need to change’: first-year students’ need to be inducted into time management. Studies in Higher Education, 35 , 777–791.
van Eerde, W. (2015). Time management and procrastination. In M. D. Mumford & M. Frese (Eds.), The psychology of planning in organizations: research and applications (pp. 312–333). New York: Routledge.
Wagner, P., Schober, B., & Spiel, C. (2008). Time students spend working at home for school. Learning and Instruction, 18 , 309–320.
Weiner, B. (2005). Motivation from an attribution perspective and the social psychology of perceived competence. In A. Elliot & C. Dweck (Eds.), Handbook of competence and motivation (pp. 73–84). New York: Guildford.
Weinstein, C. E., Palmer, D. R., & Acee, T. W. (2016). LASSI user’s manual (3th ed.). Clearwater: H & H Pub.
Winne, P. H. (1995). Inherent details in self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 30 , 173–187.
Winne, P. H., & Baker, R. (2013). The potentials of educational data mining for researching metacognition, motivation, and self-regulated learning. Journal of Educational Data Mining, 5 , 1–8.
Winne, P., & Hadwin, A. (1998). Studying as self-regulated learning. In D. Hacker, J. Dunlosky, & A. Graesser (Eds.), Metacognition in educational theory and practice (pp. 277–304). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Winne, P. H., & Hadwin, A. F. (2008). The weave of motivation and self-regulated learning. Motivation and self-regulated learning: theory, research, and applications (pp. 297–314). New York: Taylor & Francis.
Winne, P., & Perry, N. (2000). Measuring self-regulated learning. In M. Boekaerts, P. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 531–566). San Diego: Academic Press.
Witkow, M. R. (2009). Academic achievement and adolescents’ daily time use in the social and academic domains. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 19 , 151–172.
Wolters, C. A. (2003). Regulation of motivation: evaluating an underemphasized aspect of self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 38 , 189–205.
Wolters, C. A. (2011). Regulation of motivation: contextual and social aspects. Teachers College Record, 113 , 265–283.
Wolters, C. A., & Gonzalez, A. L. (2008). Classroom climate and motivation: a step toward integration. Advances in Motivation and Achievement: Social Psychological Influences, 15 , 493–519.
Wolters, C. A., & Hoops, L. D. (2015). Self-regulated learning interventions for motivationally disengaged college students. In T. L. Cleary (Ed.), Self-regulated learning interventions with at-risk youth: Enhancing adaptability, performance, and well-being (pp. 67–88). Washington: American Psychological Association.
Wolters, C., & Taylor, D. (2012). A self-regulated learning perspective on student engagement. In S. L. Christenson, A. Reschly, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of research on student engagement (pp. 635–651). New York: Springer.
Wolters, C. A., & Won, S. (2018). Validity and the use of self-report questionnaires to assess self-regulated learning. In D. H. Schunk & J. A. Greene (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (pp. 307–322). New York: Routledge.
Wolters, C. A., Won, S., & Hussain, M. (2017). Examining the relations of time management and procrastination within a model of self-regulated learning. Metacognition and Learning, 12 , 381–399.
Won, S., & Yu, S. L. (2018). Relations of perceived parental autonomy support and control with adolescents’ academic time management and procrastination. Learning and Individual Differences, 61 , 205–215.
Woolfolk, A. E., & Woolfolk, R. L. (1986). Time management: an experimental investigation. Journal of School Psychology, 24 , 267–275.
Xie, K., Heddy, B. C., & Greene, B. A. (2019). Affordances of using mobile technology to support experience-sampling method in examining college students’ engagement. Computers & Education, 128 , 183–198.
Xu, J. (2008). Models of secondary school students’ interest in homework: a multilevel analysis. American Educational Research Journal, 45 , 1180–1205.
Xu, J. (2010). Predicting homework time management at the secondary school level: a multilevel analysis. Learning and Individual Differences, 20 , 34–39.
Xu, J., Du, J., & Fan, X. (2013). “Finding our time”: predicting students’ time management in online collaborative groupwork. Computers & Education, 69 , 139–147.
Xu, J., Yuan, R., Xu, B., & Xu, M. (2014). Modeling students’ time management in math homework. Learning and Individual Differences, 34 , 33–42.
Yamada, M., Goda, Y., Matsuda, T., Saito, Y., Kato, H., & Miyagawa, H. (2016). How does self-regulated learning relate to active procrastination and other learning behaviors? Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 28 , 326–343.
Young, D. G., & Hopp, J. M. (2014). 2012-2013 national survey of first-year seminars: exploring high-impact practices in the first college year (Research report No. 4) . Columbia: University of South Carolina.
Zimbardo, P., & Boyd, J. (1999). Putting time in perspective: a valid, reliable individual-differences metric. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 77 , 1271–1288.
Zimmerman, B. J. (1989). A social cognitive view of self-regulated academic learning. Journal of Educational Psychology, 81 , 329–339.
Zimmerman, B. J. (2000). Attaining self-regulation: a social cognitive perspective. In M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation: theory, research, and applications (pp. 13–29). San Diego: Academic Press.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Risemberg, R. (1997). Becoming a self-regulated writer: a social cognitive perspective. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 22 , 73–101.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Schunk, D. (2012). Motivation: an essential dimension of self-regulated learning. In D. Schunk & B. Zimmerman (Eds.), Motivation and self-regulated learning: theory, research and applications (pp. 1–30). New York: Routledge.
Zimmerman, B. J., Greenberg, D., & Weinstein, C. E. (1994). Self-regulating academic study time: a strategy approach. In D. H. Schunk & B. J. Zimmerman (Eds.), Self-regulation of learning and performance: issues and educational applications (pp. 181–199). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Zusho, A. (2017). Toward an integrated model of student learning in the college classroom. Educational Psychology Review, 29 , 301–324.
Zusho, A., & Pintrich, P. (2003). Skill and will: the role of motivation and cognition in the learning of college chemistry. International Journal of Science Education, 25 , 1081–1094.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Dennis Learning Center, The Ohio State University, 250B Younkin Success Building, 1640 Neil Ave., Columbus, OH, 43201, USA
Christopher A. Wolters & Anna C. Brady
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Christopher A. Wolters .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Wolters, C.A., Brady, A.C. College Students’ Time Management: a Self-Regulated Learning Perspective. Educ Psychol Rev 33 , 1319–1351 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09519-z
Download citation
Published : 27 October 2020
Issue Date : December 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09519-z

Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Self-regulated learning
- Time management
- Postsecondary students
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Time management for STEMM students during the continuing pandemic
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Cell Biology, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15261, USA.
- 2 Department of Biological Sciences, Winston-Salem State University, Winston-Salem, NC 27110, USA.
- 3 Department of Biochemistry, Cancer Biology, Neuroscience and Pharmacology, Meharry Medical College, Nashville, TN 37208, USA.
- 4 Teachers College, Columbia University, New York, NY 10027, USA. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 5 Department of Molecular Physiology and Biophysics, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN 37232, USA; Hinton and Garza Lopez Family Consulting Company, Iowa City, IA 52246, USA. Electronic address: [email protected].
- PMID: 35027254
- PMCID: PMC9392870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.12.010
One of the biggest obstacles to success is a lack of practical time management skills. Here, we provide suggestions on how to optimize time management.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
PubMed Disclaimer
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figure 1.. Task priority matrix (A) and…
Figure 1.. Task priority matrix (A) and calendar (B) as time management tools.
Similar articles
- The impact of COVID-19 on medical students' practical skills and hygiene behavior regarding venipuncture: a case control study. Meyer A, Stosch C, Klatt AR, Streichert T. Meyer A, et al. BMC Med Educ. 2022 Jul 19;22(1):558. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03601-6. BMC Med Educ. 2022. PMID: 35850715 Free PMC article.
- Virtual Skills Teaching of Nursing Students during COVID-19: A Problem-Solving Approach. Hajira B, Rana A, Naeem F, Qammer Y. Hajira B, et al. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2022 Apr;32(4):548-549. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2022.04.548. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2022. PMID: 35330537 Review.
- Teaching clinical practical and communication skills of the clinical skills lab of the University of Veterinary Medicine Hannover, Foundation, Germany during the COVID-19 pandemic. Brombacher-Steiert S, Ehrich R, Schneider C, Müller LR, Tipold A, Wissing S. Brombacher-Steiert S, et al. GMS J Med Educ. 2021 Jun 15;38(5):Doc86. doi: 10.3205/zma001482. eCollection 2021. GMS J Med Educ. 2021. PMID: 34286066 Free PMC article.
- The Science of Effective Mentorship in STEMM. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Policy and Global Affairs; Board on Higher Education and Workforce; Committee on Effective Mentoring in STEMM; Dahlberg ML, Byars-Winston A, editors. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Policy and Global Affairs; Board on Higher Education and Workforce; Committee on Effective Mentoring in STEMM, et al. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2019 Oct 30. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2019 Oct 30. PMID: 31958221 Free Books & Documents. Review.
- Developing students' time management skills in clinical settings: practical considerations for busy nursing staff. Cleary M, Horsfall J. Cleary M, et al. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2011 Jun;42(6):248-9. doi: 10.3928/00220124-20110523-04. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2011. PMID: 21627057
- Climbing the mountain of adversity and removing barriers along the path. Hinton A Jr, Shuler HD, Murray SA, Davis J, Damo S. Hinton A Jr, et al. iScience. 2023 Dec 19;27(1):108510. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108510. eCollection 2024 Jan 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38299027 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
- Project Strengthen: An STEMM-focused career development workshop to prepare underrepresented minority students for graduate school. Barongan T, Neikirk K, Shao B, Vue N, Spencer EC, Kabugi K, Conley Z, Vang L, Vue M, Vang N, Garza-Lopez E, Crabtree A, Alexander S, Dal A, Beasley HK, Marshall AG, Killion M, Stephens DC, Martinez D, Palavicino-Maggio CB, Jenkins F, Davis J, Damo SM, Morra CN, Murray SA, Vang C, Morton DJ, Vue Z, Shuler H, Hinton A Jr. Barongan T, et al. iScience. 2023 Aug 29;26(10):107766. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107766. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37736045 Free PMC article.
- Strategies for change: thriving as an individual with a disabilty in STEMM. Crabtree A, Neikirk K, Marshall A, Barongan T, Beasley HK, Lopez EG, Stephens D, Murray S, Spencer EC, Martinez D, Vang C, Jenkins F, Damo S, Vue Z. Crabtree A, et al. Pathog Dis. 2023 Jan 17;81:ftac045. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftac045. Pathog Dis. 2023. PMID: 36449689 Free PMC article.
- Intentional and unintentional benefits of minority writing accountability groups. Spencer EC, Neikirk K, Campbell SL, Powell-Roach KL, Morton D, Shuler H, Murray SA, Hinton A Jr. Spencer EC, et al. Trends Microbiol. 2022 Nov;30(11):1015-1018. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2022.08.005. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Trends Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36030147 Free PMC article.
- Evaluating diversity, equity, and inclusion consultation requests. Fernandez AI, Starbird C, Davis-Reyes B, Termini CM, Hinton A Jr, McCall T. Fernandez AI, et al. Trends Mol Med. 2022 Sep;28(9):707-709. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2022.06.006. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Trends Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35868960 Free PMC article.
- Adams RV and Blair E (2019) Impact of time management behaviors on undergraduate engineering students’ performance. SAGE Open 9 215824401882450
- Parke MR et al. (2018) When daily planning improves employee performance: the importance of planning type, engagement, and interruptions. J. Appl. Psychol 103, 300–312 - PubMed
- Stemmle D (2019) Time Management Secrets for College Students: The Underground Playbook for Managing School, Work, and Fun!, College Success Academy Press
- Cullman R (2013) Mastering Time Management and Creating Success and Abundance by Giving to Others, CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform
- Tool S (2019) The Eisenhower Matrix: Task Management Through Notebook, Distinguish Between Urgent & important Tasks, Make Real Progress in Your Life, Eisenhower … Your Own Professional Development Plan, independently published.
Publication types
- Search in MeSH
Related information
Grants and funding.
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R25 HL106365/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM133353/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full text sources.
- Elsevier Science
- Europe PubMed Central
- PubMed Central
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.

Time Management: It’s Effects on the Academic Performance of the Students
― paper details ―.
- Dr. Fhrizz S. De Jesus and Merlina C. Garcia
- Educational Development
- Paper ID: MIJRDV2I40007
- Pages: 49-61
- ISSN: 2583-0406
- Publication Year: 2023
Abstract ―
The importance of time management skills for students cannot be overstated. It is crucial for them to prioritize and organize their time based on what is most important to them. This can be achieved by creating a schedule or a to-do list that outlines their daily tasks and priorities. Additionally, students must prepare for exams in advance by reviewing their notes or lectures, allowing them to use their time more effectively and achieve better grades. After completing their academic responsibilities and household chores, it is essential for students to take some time to relax and have fun. It is also essential for students to understand how to manage their time when participating in academic activities to avoid rushing through tasks and compromising their quality. Implementing an enhancement and sustainability plan for NEUST Off-Campus Program San Leonardo students is highly recommended as it will help them improve their time management skills.
Keywords ―
time management, academic performance, students, skill.
Cite this Publication ―
Dr. Fhrizz S. De Jesus and Merlina C. Garcia (2023), Time Management: It’s Effects on the Academic Performance of the Students. Multidisciplinary International Journal of Research and Development (MIJRD), Volume: 02 Issue: 04, Pages: 49-61. https://www.mijrd.com/papers/v2/i4/MIJRDV2I40007.pdf
Related Papers ―
Workforce diversity and work adjustment towards productivity, performance, and resiliency of public elementary school teacher, learning and development engagement in improving the teaching competencies of public elementary school teachers, the importance of holistic approaches from various perspective practices in strategic planning within education, strategic plan implementation in public secondary schools: a comprehensive literature review, strategic planning for baguio city’s private schools amid educational transformation, exploring the evolving paradigm of strategic planning in education: a comprehensive literature review.
109 Time Management Topics & Essay Examples
Learn about the effects of poor time management, timetables, and organizational skill! Explore this list of 106 topics about time , compiled by our experts .
⌚ How to Write a Time Management Essay: Do’s and Don’ts
🏆 best research titles about time management, 📌 most interesting time management topics to write about, 👍 good research topics about time: management & organization, ❓ time management essay questions.
When writing a Time Management Essay, it may be easy to revert to merely enumerating and explaining how to achieve perfection through various approaches. While this is an essential part of such essays, you should not forget about other aspects of it. Here are some examples of what you should do in your paper:
- Explain the intent of your essay. Are you teaching stress management tactics to save people the time they spend worrying or discipline? Your readers should be aware of your subject.
- When mentioning a tactic, explain its purpose. People will be more intent to listen to you when they understand the intent behind the ideas that you are presenting. Compare these statements: “Keeping a bullet journal helps manage time better” and “A bullet journal’s purpose is helping people get subconsciously ready for today’s tasks.” Which one attempts to clarify the process?
- Describe the mechanisms behind the outlined techniques. Doing so helps people adjust any goal-setting process to their own needs rather than blindly following it.
- Use credible sources to back up your claims. For example, when writing about mind mapping, you can reference some of the studies conducted on this method.
- If you can, give precedents of the successful implementation of the idea that you are describing. Mention people or even companies that have benefited from applying these methods to their daily working process.
All this advice should be used together with standard essay-writing rules. Outlining and brainstorming may save you, the writer, time that you would have spent on rewriting faulty paragraphs. You should do your research beforehand and structure your work so that the topics within it do not overlap.
Additionally, reference credible book and journal titles since your audience will believe factual, source-supported evidence more willingly.
Finally, when it comes to thinking about time management essay titles, choose one that is reflective of your subject and approach it. Each structural choice should help you further your thesis statement, linking to it and helping your readers follow your train of thought.
There are other things you should avoid doing when covering your topic. All of them center on the idea that time management essay topics should be respectful of the reader. Do not:
- Write about your audience as if they are incompetent. Advice that seems condescending place is often unappreciated and neglected.
- Name-drop inventors and techniques with no explanation. Doing so will only confuse your readers needlessly and make you seem unaware of your subject yourself.
- Plagiarize from anywhere, including time management essay samples. Gaining inspiration is one thing, while purposefully copying and not referencing stolen content is an academic crime.
- Leave your paragraphs inconclusive. Apart from academically referenced facts, you should also voice your own resolutions that your used sources support.
- Promise your readers a solution to all of their problems. You are merely demonstrating sample means to better anyone’s time-management. Using these methods is an entirely different thing.
Other evident don’ts are those that your instructor should outline. Do not ignore the rules of essay writing that have been stated to you explicitly, such as the maximum word count. Your essay’s structure is reflective of your discipline and time-management.
Therefore, a careless outline or a disregard for the rules demonstrates that your work has had no positive effect on you and may have the same outcome on your readers.
Want to know more paper samples? Find more at IvyPanda!
- Time Management Theories and Models Report In using the time management grid, I developed a grid and filled it with the tasks that I was supposed to accomplish.
- Time Management and Its Effect in Reducing Stress among Students One of the causes of stress among high school students and college students is the difficulty in interacting with a completely new set of students and an even larger social group within the body of […]
- Reflection on Time Management Skills While there is enough time available to improve my planning skills, I still have a long way to go to master the art of time-management.
- The Importance of Time Management Time is one of the most important resources within the operations and execution of tasks and or activities of organizations and individuals.
- Time Management at the Workplace Traditionally, time management is associated with one’s ability to accomplish more assignment and duties within a certain period of time, but often the first task for a time manages is to eliminate some of the […]
- Procrastination and Time Management In case the available time is not properly allocated to all activities to be achieved within a given period, then the available time will not be allocated to the correct event.
- Time Management in Tertiary Studies The essay endeavours to examine the importance of time management and the role of lectures in relation to tertiary studies. To start with, the essay will explore the importance of time management in the lives […]
- Time and Stress Management for Better Productivity Procrastination is the forwarding of events that have to be done at a specific time to another time in the future.
- School Principal: Successful Time Management As the key administrator of the school, the principal is expected to set the tone for a society of learners-teachers who unreservedly exchange information, thoughts and ideas.
- Tools of Time Management for Students Students can write down all of the projects they need to complete and the deadlines for those. It is also crucial for individuals to study at what time of the day they can be the […]
- Time Management in Everyday Life Time and tide wait for none and this is a very old saying but at the very same time it is extremely important to realize and absorb the essence of the same.
- Time Management for Nurses It is important for healthcare professionals to find time for patients because of identifying their needs and to know what can be done to improve the situation.
- Time Management of a Nurse Graduate This essay discusses why time management is a critical skill for a nurse graduate and what strategies can be employed to alleviate the impact of transition from a student to a healthcare worker.
- Poor Time Management and Addressing Strategies I knew that I should not do it but the first time I broke the rule I did it unconsciously. In fact, because of these phone checks, I paid more attention to the phone rather […]
- Value of Time Management First, when speaking about time management and the basic skills, it is crucial to mind the most important activities that should be performed and goals that should be achieved to guarantee the development of a […]
- “Just in Time” – Philosophy of Management All the benefits of this system tend to be woven in the quality, efficiency and effectiveness of the processes that are involved.
- Time Management: An Essential Skill for Top Performers According to Cornell’s system, the top column of a paper should have a cue column and a note-taking column. In this method, individuals should draw a circle in the middle of the paper and then […]
- Time Management Among Essential Student Skills It is important to realize that the learning environment is often challenging and may require the application and development of specific skills and competencies in order to experience success.
- Budget Plan: Time Management Aspects The application will not be able to diagnose this, but it will be able to warn the patient and recommend possibly going to the doctor.
- Plan-Do-Study-Act for Time Management at Home I will have to stick to a sleep schedule to change my current sleep habit, resulting in the recommended seven to eight hours every night.
- Time Management Tools in the Workplace Thus, one can intelligently distribute the available time on the number of tasks and assess productivity at the end of the day. The Medical Assisting Pocket is a tool that enables them to improve and […]
- Completion of Time Management At the same time, there is a growing feeling of helplessness in front of an avalanche of problems urgently requiring the intervention and the belief that lack of time like lack of air leads to […]
- Three Easy Ways to Improve Your Time Management For effective time management to be achieved, the level of disorganization has to be kept at the lowest level in both workplace and learning environments. As a result, there is no time wastage in moving […]
- Concise Time Management and Personal Development Suppose that creativity can be encouraged by exploring some of the qualities and characteristics of creative thinkers and the activities/steps that can be undertaken to improve the processes involved.
- Time Management Theory and Study Skills It is during this time that a right balance between work and leisure would be the decisive factor in shaping ones future course of life.
- Time Management Skills and Techniques Because of the lack of experience in the arrangement of activities, the experience of managing time is likely to be rather deplorable.
- Time Management Issues Among Managers The authors concluded that managers should get control over the time and content of their roles to ensure the management of their time effectively.
- Why the Poor Stewardship of Time? When asked by my teacher why I was a notorious timekeeper I used to answerer, “my home is the furthest and I could not make it early as my colleagues”.
- Time Management: How to Beat Your Procrastination? In order to manage time effectively the following solutions can be applied: The most popular solution is to make a schedule to keep track of important facts and ideas that can be of any use […]
- Quality and Time Management Improvement Techniques Because of the lack of consistency in the types of information retrieved, the firm needs to adopt the approach that allows for arranging the existing data within the shortest amount of time.
- Time Management: Getting Things Done At any time, the individual knows the task to complete and the manner in which it is to be completed. The GTD system can easily lead to a disconnect between the tasks to be completed, […]
- The Just-in-Time Management Concept The concept of Just-in-Time is a comparatively recent addition to the array of manufacturing strategies that are supposed to help reduce the waste levels in the organization, at the same time improving the product quality […]
- Time Management for a Post-Graduate Student The various articles in these encyclopedias will help to form a basis for the research and will also act as a guide in conducting further research in other publications.
- Students’ Time Management Strategies Students should keep track of the time they have to meet their responsibilities. The third strategy involves keeping reminders to keep students focused on their assignments and their deadlines.
- Time Management and Building Team The strength of the article is that it takes more time in explaining what a team is and what many think a team to be.
- Time Management: Lesson Pacing To begin with lesson pacing can be described as a given rate or speed at which a teacher tends to present a task to pupils in a class.
- Achieving Objectives Through Time Management
- Developing Good Time Management Skills
- Adulthood: Time Management and Transition
- Apply Time Management Technique to a Project
- Conflict Resolution and Time Management
- Time Management and Its Suitable Strategies for Adult Learners
- Unpreparedness and Time Management in the US Army
- Problems Associated with Poor Time Management for Students
- Analyzing Better Time Management Skills
- The Personality Assessment and the Time Management Section
- The Strengths and Weaknesses of Time Management and Their Relationship with Stress in the Workplace
- Becoming a Better Learner Through Time Management
- Time Management Is a Crucial Component of the Art of Nursing
- Importance of Planning and Time Management Techniques
- The Impact of Time Management and Causes of Stress in the Workplace
- Punctuality: Time Management and Cardinal Virtue
- Business and Effective Time Management Uses
- The Challenge of Time Management and Its Effects on Adult Learning
- The Interference Caused by Time Management, the Internet, and Sports on Education
- Expectations for Time Management and Involvement
- The Relationships Between Scope Definition and Time Management
- Effective Time Management: Identifying and Correcting Time Wasters
- The Importance of Time Management: Priorities, Being Organizing and Setting Goals
- Time Management Is an Important Ingredient for Success
- The Reality of the Effectiveness of Time Management from the Perspective of the Employees of the Beauty Clinic of Dentistry
- Problems with Time Management, Distractions, and Procrastination
- Effective Communication and Time Management for a Patient
- The Importance of Spoken Communication, Written Communication, and Time Management
- Effective Management Versus Effective Time Management
- Influence of Work Motivation, Leadership Effectiveness, and Time Management on Employees
- The Effects of Technology on Poor Time Management and Sleep Deprivation Among Students
- The Key Aspect of Time Management and Productivity
- The Different Techniques for Effective Time Management
- The Process of Improving Time Management
- Comparison of Time Management Perception of Students Studying at the Department of Physical Education and Sports Teaching and Program in Primary School Education
- Importance of Time Management and Deadlines to the Work of Public Relations
- The Importance of Effective Time Management
- The Relation Between Time Management and Academic Performance Among University Students
- The Importance and Challenges of Time Management for Today’s Student Leaders
- Good Study Skills and Time Management Dissertation or Thesis Complete
- How to Solve Time Management Problems?
- How Have Sports Taught Me Time Management?
- Is Procrastination a Problem of Time Management?
- What Does Time Management Mean?
- Why Is Time Management Important?
- What Time Management for Adult Students?
- How Can Technology Improve One’s Time Management Skills?
- How Can Time Management Skills Effect Educational Achievement?
- How Better Time Management Aids?
- How Can Students Improve Their Self-Discipline and Time Management Skills?
- Can Poor Time Management Make a Student-Athlete Fail?
- Why Student-Athletes Struggle with Time Management?
- What Are Important Aspects of Time Management?
- What Connection Between Time Management and Unpreparedness in the Army?
- How Does Time Management Work?
- What Does Time Management Mean to Me?
- Why College Students Use Their Time Management and Study Skills?
- What Can Time Management Bring to Your Personal Growth?
- What Are the First Two Key Steps of Controlling Time Management?
- How Can Expectations Influence Time Management?
- What Is the Biggest Academic Challenge of Time Management?
- Who’s Got the Monkey: Concept of Time Management
- What Is the Relationship Between Time Management and Stress Management?
- How Does Social Media Effect Time Management?
- Why Time Management Is a Leader, Success Is All About Growing
- How to Prioritize and Manage Time?
- How to Use Effectively Time Management Within Education?
- How to Enhance Academic Performance with Time Management
- How Can Hospitality Organizations Successfully Apply the Skills and Principles of Time Management?
- Lifespan Development Essay Titles
- Professional Development Research Ideas
- Cognitive Development Essay Ideas
- Organization Development Research Ideas
- Motivation Research Ideas
- Process Management Questions
- Success Ideas
- Management Styles Essay Titles
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 1). 109 Time Management Topics & Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/time-management-essay-examples/
"109 Time Management Topics & Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 1 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/time-management-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '109 Time Management Topics & Essay Examples'. 1 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "109 Time Management Topics & Essay Examples." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/time-management-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "109 Time Management Topics & Essay Examples." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/time-management-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "109 Time Management Topics & Essay Examples." March 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/time-management-essay-examples/.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Time management scores o f the student's show the wa y to score of academic achievement as. concluded that students who scored poor in academic achieve ment gained significantly lower in time ...
Time management can be defined as clusters of behavioral skills that are important in the organization of study and course load (Lay & Schouwenburg, 1993).Empirical evidence suggests that effective time management is associated with greater academic achievement (McKenzie & Gow, 2004; Trueman & Hartley, 1996) as students learn coping strategies that allow them to negotiate competing demands.
The Impact of Time Management on Students' Academic Achievement. S N A M Razali 1, M S Rusiman 1, W S Gan 1 and N Arbin 2. Published under licence by IOP Publishing Ltd Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Volume 995, International Seminar on Mathematics and Physics in Sciences and Technology 2017 (ISMAP 2017) 28-29 October 2017, Hotel Katerina, Malaysia Citation S N A M Razali et al 2018 ...
individual characteristics and others influence in time management research (Claessens et al, 2007). This is also in line with related empirical findings. For example, high achieving students were found to exhibit more self-regulated learning ... The effectiveness of Time Management Strategies Instruction on students' academic time management ...
Despite its recognized importance for academic success, much of the research investigating time management has proceeded without regard to a comprehensive theoretical model for understanding its connections to students' engagement, learning, or achievement. Our central argument is that self-regulated learning provides the rich conceptual framework necessary for understanding college students ...
To facilitate the process of learning and managing personal res ponsibilities of. students, this paper aims to teach practical methods of study a nd time management, supported from an empir ical ...
This research entitled ''The Role of Time Management on Distance Learning among DTTE Students during the Pandemic" is quantitative. The research instruments of this study are based on the ...
fellow students, time management, control over time, the pace of learning, motivation, and expectations of efficiency or effectiveness stand out as the most significant (Govindasamy, 2002; Fresen & Lesley, 2006; Goyal et al., 2010). Whatore, it is m even now, common digital competence frameworks already begin to exist, in which, at the
Self-Regulated Learning and Time Management. In contrast to the models with a narrower focus on time management (e.g., Macan 1994), SRL represents a more comprehensive framework that has successfully and repeatedly been used to understand post-secondary students academic engagement, learning, and achievement. '.
Time Management. A number of studies have identified the positive impact of time management. Time management skills have been shown to have a positive impact on student learning and student out-comes (Kearns & Gardiner, 2007; Kelly, 2002; McKenzie & Gow, 2004) and Krause and Coates (2008) report that the capacity to successfully manage their ...
Keywords: time management, academic stress, stressors, time organization. 1. Introduction. Higher education is a stressful period in the lives of students due to various reasons such as living away from families, a heavy curriculum or ineffectiveness in higher education programs (Bhujade, 2017). From the moment an individual enters college, he ...
This chapter seeks to explore the current state of affairs regarding time management; identifies the impact on student lives as well as misperceptions and offers strategies for students, faculty and administrators. Given that the lack of time management skills has been associated with lower academic performance, anyone involved in post-secondary education is encouraged to make time to read ...
important. Owing to the importance of time management this study deals with investigating the relationship of student‟s time management and academic achievement in the higher educational institutes of Islamabad. The paper is organized as follows; section 2 reviews the relevant literature. Data and methodology are presented in section 3.
For STEMM students to enter, thrive, and be innovative in their future careers, they must possess excellent time management skills. We provide methods, resources, and strategies to help students better manage their time, which requires clear goal setting and proper time allocation to complete tasks. We begin by discussing goal setting followed ...
Keywords— time management, academic performance, students, skill. INTRODUCTION According to Aduke (2015), time management provides individuals the ways for structuring and controlling their activities. Time management is the ability to organize, plan, arrange, and account for one's time in order to increase the performance of the students.
One of the biggest obstacles to success is a lack of practical time management skills. Here, we provide suggestions on how to optimize time management. ... Time management for STEMM students during the continuing pandemic Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Apr;47(4):279-283. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.12.010. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Authors Sandra A Murray ...
Time management is of great significance to the learning of college students. As a personality trait, time management has huge differences among individuals.
Abstract ― . The importance of time management skills for students cannot be overstated. It is crucial for them to prioritize and organize their time based on what is most important to them. This can be achieved by creating a schedule or a to-do list that outlines their daily tasks and priorities. Additionally, students must prepare for exams ...
Student-athletes have a dual role as both students and athletes and have. certain responsibilities to both roles. Student-athletes must find a way to. successfully budget their time in both of these roles. Large portions of college. campuses are comprised of student-athletes. These teams can create revenue for the.
An overview of common issues with student time management and interventions which have proved effective in practice: developed through taking an action research approach to our work as student-facing learning developers at the University of Reading. Full write-up available here (PDF). Using student feedback to develop resources for time ...
The study on the relationship between time management skills and academic performance of students was conducted at Mariano Peralta National High School's Open High School Program.
The authors concluded that managers should get control over the time and content of their roles to ensure the management of their time effectively. Time Management in Tertiary Studies. The essay endeavours to examine the importance of time management and the role of lectures in relation to tertiary studies.
time management qualitative research - Free download as Word Doc (.doc), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document discusses a study on senior high school students' perceptions of the effects of time management on their academic performance. The study aims to understand how students view time management and how it ...