Save £500 when you enrol by 30th September!
- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.

General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument. Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.
A guide to writing history essays
This guide has been prepared for students at all undergraduate university levels. Some points are specifically aimed at 100-level students, and may seem basic to those in upper levels. Similarly, some of the advice is aimed at upper-level students, and new arrivals should not be put off by it.
The key point is that learning to write good essays is a long process. We hope that students will refer to this guide frequently, whatever their level of study.
Why do history students write essays?
Essays are an essential educational tool in disciplines like history because they help you to develop your research skills, critical thinking, and writing abilities. The best essays are based on strong research, in-depth analysis, and are logically structured and well written.
An essay should answer a question with a clear, persuasive argument. In a history essay, this will inevitably involve a degree of narrative (storytelling), but this should be kept to the minimum necessary to support the argument – do your best to avoid the trap of substituting narrative for analytical argument. Instead, focus on the key elements of your argument, making sure they are well supported by evidence. As a historian, this evidence will come from your sources, whether primary and secondary.
The following guide is designed to help you research and write your essays, and you will almost certainly earn better grades if you can follow this advice. You should also look at the essay-marking criteria set out in your course guide, as this will give you a more specific idea of what the person marking your work is looking for.
Where to start
First, take time to understand the question. Underline the key words and consider very carefully what you need to do to provide a persuasive answer. For example, if the question asks you to compare and contrast two or more things, you need to do more than define these things – what are the similarities and differences between them? If a question asks you to 'assess' or 'explore', it is calling for you to weigh up an issue by considering the evidence put forward by scholars, then present your argument on the matter in hand.
A history essay must be based on research. If the topic is covered by lectures, you might begin with lecture and tutorial notes and readings. However, the lecturer does not want you simply to echo or reproduce the lecture content or point of view, nor use their lectures as sources in your footnotes. They want you to develop your own argument. To do this you will need to look closely at secondary sources, such as academic books and journal articles, to find out what other scholars have written about the topic. Often your lecturer will have suggested some key texts, and these are usually listed near the essay questions in your course guide. But you should not rely solely on these suggestions.
Tip : Start the research with more general works to get an overview of your topic, then move on to look at more specialised work.
Crafting a strong essay
Before you begin writing, make an essay plan. Identify the two-to-four key points you want to make. Organize your ideas into an argument which flows logically and coherently. Work out which examples you will use to make the strongest case. You may need to use an initial paragraph (or two) to bring in some context or to define key terms and events, or provide brief identifying detail about key people – but avoid simply telling the story.
An essay is really a series of paragraphs that advance an argument and build towards your conclusion. Each paragraph should focus on one central idea. Introduce this idea at the start of the paragraph with a 'topic sentence', then expand on it with evidence or examples from your research. Some paragraphs should finish with a concluding sentence that reiterates a main point or links your argument back to the essay question.
A good length for a paragraph is 150-200 words. When you want to move to a new idea or angle, start a new paragraph. While each paragraph deals with its own idea, paragraphs should flow logically, and work together as a greater whole. Try using linking phrases at the start of your paragraphs, such as 'An additional factor that explains', 'Further', or 'Similarly'.
We discourage using subheadings for a history essay (unless they are over 5000 words in length). Instead, throughout your essay use 'signposts'. This means clearly explaining what your essay will cover, how an example demonstrates your point, or reiterating what a particular section has added to your overall argument.
Remember that a history essay isn't necessarily about getting the 'right' answer – it's about putting forward a strong case that is well supported by evidence from academic sources. You don't have to cover everything – focus on your key points.
In your introduction or opening paragraph you could indicate that while there are a number of other explanations or factors that apply to your topic, you have chosen to focus on the selected ones (and say why). This demonstrates to your marker that while your argument will focus on selected elements, you do understand the bigger picture.
The classic sections of an essay
Introduction.
- Establishes what your argument will be, and outlines how the essay will develop it
- A good formula to follow is to lay out about 3 key reasons that support the answer you plan to give (these points will provide a road-map for your essay and will become the ideas behind each paragraph)
- If you are focusing on selected aspects of a topic or particular sources and case studies, you should state that in your introduction
- Define any key terms that are essential to your argument
- Keep your introduction relatively concise – aim for about 10% of the word count
- Consists of a series of paragraphs that systematically develop the argument outlined in your introduction
- Each paragraph should focus on one central idea, building towards your conclusion
- Paragraphs should flow logically. Tie them together with 'bridge' sentences – e.g. you might use a word or words from the end of the previous paragraph and build it into the opening sentence of the next, to form a bridge
- Also be sure to link each paragraph to the question/topic/argument in some way (e.g. use a key word from the question or your introductory points) so the reader does not lose the thread of your argument
- Ties up the main points of your discussion
- Should link back to the essay question, and clearly summarise your answer to that question
- May draw out or reflect on any greater themes or observations, but you should avoid introducing new material
- If you have suggested several explanations, evaluate which one is strongest
Using scholarly sources: books, journal articles, chapters from edited volumes
Try to read critically: do not take what you read as the only truth, and try to weigh up the arguments presented by scholars. Read several books, chapters, or articles, so that you understand the historical debates about your topic before deciding which viewpoint you support. The best sources for your history essays are those written by experts, and may include books, journal articles, and chapters in edited volumes. The marking criteria in your course guide may state a minimum number of academic sources you should consult when writing your essay. A good essay considers a range of evidence, so aim to use more than this minimum number of sources.
Tip : Pick one of the books or journal articles suggested in your course guide and look at the author's first few footnotes – these will direct you to other prominent sources on this topic.
Don't overlook journal articles as a source. They contain the most in-depth research on a particular topic. Often the first pages will summarise the prior research into this topic, so articles can be a good way to familiarise yourself with what else has 'been done'.
Edited volumes can also be a useful source. These are books on a particular theme, topic or question, with each chapter written by a different expert.
One way to assess the reliability of a source is to check the footnotes or endnotes. When the author makes a claim, is this supported by primary or secondary sources? If there are very few footnotes, then this may not be a credible scholarly source. Also check the date of publication, and prioritise more recent scholarship. Aim to use a variety of sources, but focus most of your attention on academic books and journal articles.
Paraphrasing and quotations
A good essay is about your ability to interpret and analyse sources, and to establish your own informed opinion with a persuasive argument that uses sources as supporting evidence. You should express most of your ideas and arguments in your own words. Cutting and pasting together the words of other scholars, or simply changing a few words in quotations taken from the work of others, will prevent you from getting a good grade, and may be regarded as academic dishonesty (see more below).
Direct quotations can be useful tools if they provide authority and colour. For maximum effect though, use direct quotations sparingly – where possible, paraphrase most material into your own words. Save direct quotations for phrases that are interesting, contentious, or especially well-phrased.
A good writing practice is to introduce and follow up every direct quotation you use with one or two sentences of your own words, clearly explaining the relevance of the quote, and putting it in context with the rest of your paragraph. Tell the reader who you are quoting, why this quote is here, and what it demonstrates. Avoid simply plonking a quotation into the middle of your own prose. This can be quite off-putting for a reader.
- Only include punctuation in your quote if it was in the original text. Otherwise, punctuation should come after the quotation marks. If you cut out words from a quotation, put in three dots (an ellipsis [ . . .]) to indicate where material has been cut
- If your quote is longer than 50 words, it should be indented and does not need quotation marks. This is called a block quote (use these sparingly: remember you have a limited word count and it is your analysis that is most significant)
- Quotations should not be italicised
Referencing, plagiarism and Turnitin
When writing essays or assignments, it is very important to acknowledge the sources you have used. You risk the charge of academic dishonesty (or plagiarism) if you copy or paraphrase words written by another person without providing a proper acknowledgment (a 'reference'). In your essay, whenever you refer to ideas from elsewhere, statistics, direct quotations, or information from primary source material, you must give details of where this information has come from in footnotes and a bibliography.
Your assignment may be checked through Turnitin, a type of plagiarism-detecting software which checks assignments for evidence of copied material. If you have used a wide variety of primary and secondary sources, you may receive a high Turnitin percentage score. This is nothing to be alarmed about if you have referenced those sources. Any matches with other written material that are not referenced may be interpreted as plagiarism – for which there are penalties. You can find full information about all of this in the History Programme's Quick Guide Referencing Guide contained in all course booklets.
Final suggestions
Remember that the easier it is to read your essay, the more likely you are to get full credit for your ideas and work. If the person marking your work has difficulty reading it, either because of poor writing or poor presentation, they will find it harder to grasp your points. Try reading your work aloud, or to a friend/flatmate. This should expose any issues with flow or structure, which you can then rectify.
Make sure that major and controversial points in your argument are clearly stated and well- supported by evidence and footnotes. Aspire to understand – rather than judge – the past. A historian's job is to think about people, patterns, and events in the context of the time, though you can also reflect on changing perceptions of these over time.
Things to remember
- Write history essays in the past tense
- Generally, avoid sub-headings in your essays
- Avoid using the word 'bias' or 'biased' too freely when discussing your research materials. Almost any text could be said to be 'biased'. Your task is to attempt to explain why an author might argue or interpret the past as they do, and what the potential limitations of their conclusions might be
- Use the passive voice judiciously. Active sentences are better!
- Be cautious about using websites as sources of information. The internet has its uses, particularly for primary sources, but the best sources are academic books and articles. You may use websites maintained by legitimate academic and government authorities, such as those with domain suffixes like .gov .govt .ac or .edu
- Keep an eye on word count – aim to be within 10% of the required length. If your essay is substantially over the limit, revisit your argument and overall structure, and see if you are trying to fit in too much information. If it falls considerably short, look into adding another paragraph or two
- Leave time for a final edit and spell-check, go through your footnotes and bibliography to check that your references are correctly formatted, and don't forget to back up your work as you go!
Other useful strategies and sources
- Student Learning Development , which offers peer support and one-on-one writing advice (located near the central library)
- Harvard College's guide to writing history essays (PDF)
- Harvard College's advice on essay structure
- Victoria University's comprehensive essay writing guide (PDF)

Writing a history essay

An essay is a piece of sustained writing in response to a question, topic or issue. Essays are commonly used for assessing and evaluating student progress in history. History essays test a range of skills including historical understanding, interpretation and analysis, planning, research and writing.
To write an effective essay, students should examine the question, understand its focus and requirements, acquire information and evidence through research, then construct a clear and well-organised response. Writing a good history essay should be rigorous and challenging, even for stronger students. As with other skills, essay writing develops and improves over time. Each essay you complete helps you become more competent and confident in exercising these skills.
Study the question
This is an obvious tip but one sadly neglected by some students. The first step to writing a good essay, whatever the subject or topic, is to give plenty of thought to the question.
An essay question will set some kind of task or challenge. It might ask you to explain the causes and/or effects of a particular event or situation. It might ask if you agree or disagree with a statement. It might ask you to describe and analyse the causes and/or effects of a particular action or event. Or it might ask you to evaluate the relative significance of a person, group or event.
You should begin by reading the essay question several times. Underline, highlight or annotate keywords or terms in the text of the question. Think about what it requires you to do. Who or what does it want you to concentrate on? Does it state or imply a particular timeframe? What problem or issue does it want you to address?
Begin with a plan
Every essay should begin with a written plan. Start constructing a plan as soon as you have received your essay question and given it some thought.
Prepare for research by brainstorming and jotting down your thoughts and ideas. What are your initial responses or thoughts about the question? What topics, events, people or issues are connected with the question? Do any additional questions or issues flow from the question? What topics or events do you need to learn more about? What historians or sources might be useful?
If you encounter a mental ‘brick wall’ or are uncertain about how to approach the question, don’t hesitate to discuss it with someone else. Consult your teacher, a capable classmate or someone you trust. Bear in mind too that once you start researching, your plan may change as you locate new information.
Start researching
After studying the question and developing an initial plan, start to gather information and evidence.
Most will start by reading an overview of the topic or issue, usually in some reliable secondary sources. This will refresh or build your existing understanding of the topic and provide a basis for further questions or investigation.
Your research should take shape from here, guided by the essay question and your own planning. Identify terms or concepts you do not know and find out what they mean. As you locate information, ask yourself if it is relevant or useful for addressing the question. Be creative with your research, looking in a variety of places.
If you have difficulty locating information, seek advice from your teacher or someone you trust.
Develop a contention
All good history essays have a clear and strong contention. A contention is the main idea or argument of your essay. It serves both as an answer to the question and the focal point of your writing.
Ideally, you should be able to express your contention as a single sentence. For example, the following contention might form the basis of an essay question on the rise of the Nazis:
Q. Why did the Nazi Party win 37 per cent of the vote in July 1932? A. The Nazi Party’s electoral success of 1932 was a result of economic suffering caused by the Great Depression, public dissatisfaction with the Weimar Republic’s democratic political system and mainstream parties, and Nazi propaganda that promised a return to traditional social, political and economic values.
An essay using this contention would then go on to explain and justify these statements in greater detail. It will also support the contention with argument and evidence.
At some point in your research, you should begin thinking about a contention for your essay. Remember, you should be able to express it briefly as if addressing the essay question in a single sentence, or summing up in a debate.
Try to frame your contention so that is strong, authoritative and convincing. It should sound like the voice of someone well informed about the subject and confident about their answer.
Plan an essay structure

Once most of your research is complete and you have a strong contention, start jotting down a possible essay structure. This need not be complicated, a few lines or dot points is ample.
Every essay must have an introduction, a body of several paragraphs and a conclusion. Your paragraphs should be well organised and follow a logical sequence.
You can organise paragraphs in two ways: chronologically (covering events or topics in the order they occurred) or thematically (covering events or topics based on their relevance or significance). Every paragraph should be clearly signposted in the topic sentence.
Once you have finalised a plan for your essay, commence your draft.
Write a compelling introduction
Many consider the introduction to be the most important part of an essay. It is important for several reasons. It is the reader’s first experience of your essay. It is where you first address the question and express your contention. It is also where you lay out or ‘signpost’ the direction your essay will take.
Aim for an introduction that is clear, confident and punchy. Get straight to the point – do not waste time with a rambling or storytelling introduction.
Start by providing a little context, then address the question, articulate your contention and indicate what direction your essay will take.
Write fully formed paragraphs
Many history students fall into the trap of writing short paragraphs, sometimes containing as little as one or two sentences. A good history essay contains paragraphs that are themselves ‘mini-essays’, usually between 100-200 words each.
A paragraph should focus on one topic or issue only – but it should contain a thorough exploration of that topic or issue.
A good paragraph will begin with an effective opening sentence, sometimes called a topic sentence or signposting sentence. This sentence introduces the paragraph topic and briefly explains its significance to the question and your contention. Good paragraphs also contain thorough explanations, some analysis and evidence, and perhaps a quotation or two.
Finish with an effective conclusion
The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay. A good conclusion should do two things. First, it should reiterate or restate the contention of your essay. Second, it should close off your essay, ideally with a polished ending that is not abrupt or awkward.
One effective way to do this is with a brief summary of ‘what happened next’. For example, an essay discussing Hitler’s rise to power in 1933 might close with a couple of sentences about how he consolidated and strengthened his power in 1934-35.
Your conclusion need not be as long or as developed as your body paragraphs. You should avoid introducing new information or evidence in the conclusion.
Reference and cite your sources
A history essay is only likely to succeed if it is appropriately referenced. Your essay should support its information, ideas and arguments with citations or references to reliable sources.
Referencing not only acknowledges the work of others, but it also gives authority to your writing and provides the teacher or assessor with an insight into your research. More information on referencing a piece of history writing can be found here .
Proofread, edit and seek feedback
Every essay should be proofread, edited and, if necessary, re-drafted before being submitted for assessment. Essays should ideally be completed well before their due date then put aside for a day or two before proofreading.
When proofreading, look first for spelling and grammatical errors, typographical mistakes, incorrect dates or other errors of fact.
Think then about how you can improve the clarity, tone and structure of your essay. Does your essay follow a logical structure or sequence? Is the signposting in your essay clear and effective? Are some sentences too long or ‘rambling’? Do you repeat yourself? Do paragraphs need to be expanded, fine-tuned or strengthened with more evidence?
Read your essay aloud, either to yourself or another person. Seek feedback and advice from a good writer or someone you trust (they need not have expertise in history, only in effective writing).
Some general tips on writing
- Always write in the third person . Never refer to yourself personally, using phrases like “I think…” or “It is my contention…”. Good history essays should adopt the perspective of an informed and objective third party. They should sound rational and factual – not like an individual expressing their opinion.
- Always write in the past tense . An obvious tip for a history essay is to write in the past tense. Always be careful about your use of tense. Watch out for mixed tenses when proofreading your work. One exception to the rule about past tense is when writing about the work of modern historians (for example, “Kershaw writes…” sounds better than “Kershaw wrote…” or “Kershaw has written…”).
- Avoid generalisations . Generalisation is a problem in all essays but it is particularly common in history essays. Generalisation occurs when you form general conclusions from one or more specific examples. In history, this most commonly occurs when students study the experiences of a particular group, then assume their experiences applied to a much larger group – for example, “All the peasants were outraged”, “Women rallied to oppose conscription” or “Germans supported the Nazi Party”. Both history and human society, however, are never this clear cut or simple. Always try to avoid generalisation and be on the lookout for generalised statements when proofreading.
- Write short, sharp and punchy . Good writers vary their sentence length but as a rule of thumb, most of your sentences should be short and punchy. The longer a sentence becomes, the greater the risk of it becoming long-winded or confusing. Long sentences can easily become disjointed, confused or rambling. Try not to overuse long sentences and pay close attention to sentence length when proofreading.
- Write in an active voice . In history writing, the active voice is preferable to the passive voice. In the active voice, the subject completes the action (e.g. “Hitler [the subject] initiated the Beer Hall putsch [the action] to seize control of the Bavarian government”). In the passive voice, the action is completed by the subject (“The Beer Hall putsch [the action] was initiated by Hitler [the subject] to seize control of the Bavarian government”). The active voice also helps prevent sentences from becoming long, wordy and unclear.
You may also find our page on writing for history useful.
Citation information Title : ‘Writing a history essay’ Authors : Jennifer Llewellyn, Steve Thompson Publisher : Alpha History URL : https://alphahistory.com/writing-a-history-essay/ Date published : April 13, 2020 Date updated : December 20, 2022 Date accessed : Today’s date Copyright : The content on this page may not be republished without our express permission. For more information on usage, please refer to our Terms of Use.

Subscription Offers
Give a Gift

How To Write a Good History Essay
The former editor of History Review Robert Pearce gives his personal view.
First of all we ought to ask, What constitutes a good history essay? Probably no two people will completely agree, if only for the very good reason that quality is in the eye – and reflects the intellectual state – of the reader. What follows, therefore, skips philosophical issues and instead offers practical advice on how to write an essay that will get top marks.
Witnesses in court promise to tell the truth, the whole truth and nothing but the truth. All history students should swear a similar oath: to answer the question, the whole question and nothing but the question. This is the number one rule. You can write brilliantly and argue a case with a wealth of convincing evidence, but if you are not being relevant then you might as well be tinkling a cymbal. In other words, you have to think very carefully about the question you are asked to answer. Be certain to avoid the besetting sin of those weaker students who, fatally, answer the question the examiners should have set – but unfortunately didn’t. Take your time, look carefully at the wording of the question, and be certain in your own mind that you have thoroughly understood all its terms.
If, for instance, you are asked why Hitler came to power, you must define what this process of coming to power consisted of. Is there any specific event that marks his achievement of power? If you immediately seize on his appointment as Chancellor, think carefully and ask yourself what actual powers this position conferred on him. Was the passing of the Enabling Act more important? And when did the rise to power actually start? Will you need to mention Hitler’s birth and childhood or the hyperinflation of the early 1920s? If you can establish which years are relevant – and consequently which are irrelevant – you will have made a very good start. Then you can decide on the different factors that explain his rise.
Or if you are asked to explain the successes of a particular individual, again avoid writing the first thing that comes into your head. Think about possible successes. In so doing, you will automatically be presented with the problem of defining ‘success’. What does it really mean? Is it the achievement of one’s aims? Is it objective (a matter of fact) or subjective (a matter of opinion)? Do we have to consider short-term and long-term successes? If the person benefits from extraordinary good luck, is that still a success? This grappling with the problem of definition will help you compile an annotated list of successes, and you can then proceed to explain them, tracing their origins and pinpointing how and why they occurred. Is there a key common factor in the successes? If so, this could constitute the central thrust of your answer.
Save 35% with a student subscription to History Today
The key word in the above paragraphs is think . This should be distinguished from remembering, daydreaming and idly speculating. Thinking is rarely a pleasant undertaking, and most of us contrive to avoid it most of the time. But unfortunately there’s no substitute if you want to get the top grade. So think as hard as you can about the meaning of the question, about the issues it raises and the ways you can answer it. You have to think and think hard – and then you should think again, trying to find loopholes in your reasoning. Eventually you will almost certainly become confused. Don’t worry: confusion is often a necessary stage in the achievement of clarity. If you get totally confused, take a break. When you return to the question, it may be that the problems have resolved themselves. If not, give yourself more time. You may well find that decent ideas simply pop into your conscious mind at unexpected times.
You need to think for yourself and come up with a ‘bright idea’ to write a good history essay. You can of course follow the herd and repeat the interpretation given in your textbook. But there are problems here. First, what is to distinguish your work from that of everybody else? Second, it’s very unlikely that your school text has grappled with the precise question you have been set.
The advice above is relevant to coursework essays. It’s different in exams, where time is limited. But even here, you should take time out to do some thinking. Examiners look for quality rather than quantity, and brevity makes relevance doubly important. If you get into the habit of thinking about the key issues in your course, rather than just absorbing whatever you are told or read, you will probably find you’ve already considered whatever issues examiners pinpoint in exams.
The Vital First Paragraph
Every part of an essay is important, but the first paragraph is vital. This is the first chance you have to impress – or depress – an examiner, and first impressions are often decisive. You might therefore try to write an eye-catching first sentence. (‘Start with an earthquake and work up to a climax,’ counselled the film-maker Cecil B. De Mille.) More important is that you demonstrate your understanding of the question set. Here you give your carefully thought out definitions of the key terms, and here you establish the relevant time-frame and issues – in other words, the parameters of the question. Also, you divide the overall question into more manageable sub-divisions, or smaller questions, on each of which you will subsequently write a paragraph. You formulate an argument, or perhaps voice alternative lines of argument, that you will substantiate later in the essay. Hence the first paragraph – or perhaps you might spread this opening section over two paragraphs – is the key to a good essay.
On reading a good first paragraph, examiners will be profoundly reassured that its author is on the right lines, being relevant, analytical and rigorous. They will probably breathe a sign of relief that here is one student at least who is avoiding the two common pitfalls. The first is to ignore the question altogether. The second is to write a narrative of events – often beginning with the birth of an individual – with a half-hearted attempt at answering the question in the final paragraph.
Middle Paragraphs
Philip Larkin once said that the modern novel consists of a beginning, a muddle and an end. The same is, alas, all too true of many history essays. But if you’ve written a good opening section, in which you’ve divided the overall question into separate and manageable areas, your essay will not be muddled; it will be coherent.
It should be obvious, from your middle paragraphs, what question you are answering. Indeed it’s a good test of an essay that the reader should be able to guess the question even if the title is covered up. So consider starting each middle paragraph will a generalisation relevant to the question. Then you can develop this idea and substantiate it with evidence. You must give a judicious selection of evidence (i.e. facts and quotations) to support the argument you are making. You only have a limited amount of space or time, so think about how much detail to give. Relatively unimportant background issues can be summarised with a broad brush; your most important areas need greater embellishment. (Do not be one of those misguided candidates who, unaccountably, ‘go to town’ on peripheral areas and gloss over crucial ones.)
The regulations often specify that, in the A2 year, students should be familiar with the main interpretations of historians. Do not ignore this advice. On the other hand, do not take historiography to extremes, so that the past itself is virtually ignored. In particular, never fall into the trap of thinking that all you need are sets of historians’ opinions. Quite often in essays students give a generalisation and back it up with the opinion of an historian – and since they have formulated the generalisation from the opinion, the argument is entirely circular, and therefore meaningless and unconvincing. It also fatuously presupposes that historians are infallible and omniscient gods. Unless you give real evidence to back up your view – as historians do – a generalisation is simply an assertion. Middle paragraphs are the place for the real substance of an essay, and you neglect this at your peril.
Final Paragraph
If you’ve been arguing a case in the body of an essay, you should hammer home that case in the final paragraph. If you’ve been examining several alternative propositions, now is the time to say which one is correct. In the middle paragraph you are akin to a barrister arguing a case. Now, in the final paragraph, you are the judge summing up and pronouncing the verdict.
It’s as well to keep in mind what you should not be doing. Do not introduce lots of fresh evidence at this stage, though you can certainly introduce the odd extra fact that clinches your case. Nor should you go on to the ‘next’ issue. If your question is about Hitler coming to power, you should not end by giving a summary of what he did once in power. Such an irrelevant ending will fail to win marks. Remember the point about answering ‘nothing but the question’? On the other hand, it may be that some of the things Hitler did after coming to power shed valuable light on why he came to power in the first place. If you can argue this convincingly, all well and good; but don’t expect the examiner to puzzle out relevance. Examiners are not expected to think; you must make your material explicitly relevant.
Final Thoughts
A good essay, especially one that seems to have been effortlessly composed, has often been revised several times; and the best students are those who are most selfcritical. Get into the habit of criticising your own first drafts, and never be satisfied with second-best efforts. Also, take account of the feedback you get from teachers. Don’t just look at the mark your essay gets; read the comments carefully. If teachers don’t advise how to do even better next time, they are not doing their job properly.
Relevance is vital in a good essay, and so is evidence marshalled in such a way that it produces a convincing argument. But nothing else really matters. The paragraph structure recommended above is just a guide, nothing more, and you can write a fine essay using a very different arrangement of material. Similarly, though it would be excellent if you wrote in expressive, witty and sparklingly provocative prose, you can still get top marks even if your essay is serious, ponderous and even downright dull.
There are an infinite number of ways to write an essay because any form of writing is a means of self-expression. Your essay will be unique because you are unique: it’s up to you to ensure that it’s uniquely good, not uniquely mediocre.
Robert Pearce is the editor of History Review .
Popular articles

Reassessing William the Conqueror

How to Rescue the Reputation of the Nasty Normans

- Essay Writing Guides
How To Write A History Essay
Essay writing is one of the most effortful student assignments. Not everybody can skillfully enunciate their views and ideas, especially when it comes to an essay that requires the presentation of arguments and counterarguments. Simultaneously, it is one of the best tools to improve your critical thinking and research skills.
A history essay is a particular type of creative work that requires brilliant research potential and the ability to analyze and track the consistent picture of historical events. To craft a successful history essay, students should go beyond the regular history classes and demonstrate their significant knowledge in political science, sociology, and even psychology.
If you were lucky to get a creative assignment in history, get ready to experience not the easiest time in your life. To make the overall process more efficient and straightforward, use this history essay writing guide for assistance.
What is a History Essay?
To elaborate an impeccable history paper, it is crucial to answer the ‘what is history essay’ question. The history essay’s essence lies in the successful introduction and confirmation of statements related to some historical events or personalities. To make your work sound professional, you need to:
- elucidate the factors that have led to such consequences;
- build a logical bridge between the past and the present by describing the importance of the phenomenon you are dealing with.
A top-notch history paper never focuses on the past mainly. It rather comes up with the impact the past events have on the present. An ability to fully reveal the given influence is the most significant proof that the author has a good understanding of the topic and can easily share their perspective professionally and to the point.
Having the instructions and practical tips on how to write a history essay is the first key to a successful paper. Many students just start rewriting the historical events in their own words at this stage. Instead, your essay should provide clear answers to three central questions: what, why, and how. These questions may become good starting points for your history essay and help you stay coherent.
Before You Start: Preparing to Write

Having three questions in mind when preparing to write a history essay is already half a work done. Carry out a little brainstorm session and formulate several sub-questions using the mentioned interrogative adverbs. They will contribute much to the creation of an effective structure in your history essay. Here’s a breakdown of the main questions addressed.
- Who are the main characters of the given events?
- Who is against the given events?
- Who won from the given events? Who lost?
- Who is currently in the winning position thanks to the mentioned events?
- What circumstances caused the given events?
- What changes did the given events cause?
- What kind of effect did the events have on the present?
- What conclusions have been made after these events?
- Why did the given events take place?
- Why were they supported/not supported by people?
You may also come up with your suggestions regarding the specific topic to make your essay even more professional.
Nonetheless, it is not enough only to write down the questions. You have to analyze and evaluate them profoundly. You may be very accurate about the described shreds of evidence, proofs, and arguments. However, if your essay doesn’t provide precise answers to the fundamental questions, it is unlikely to be highly scored. To stay coherent and to the point, use an explanation/interpretation scheme that implies the reasons why something has happened, followed by the profound analysis of the events.
When the above-mentioned work is done and questions have been answered, you are ready to form your paper’s thesis statement. If we talk about the history essay, its thesis statement should be strong enough to prove the significance and value of your work. Besides, convincing arguments help create a solid bone to structure your essay around.
Your paper’s thesis statement should accurately elucidate the essay’s essence and be supported with the concise arguments that would become its paragraphs. All you need to do is specify them and then elaborate in more detail.
You can change the arguments throughout the essay, but the thesis statement should remain the same and be rational enough to stay relevant till the end.
Research Stage
Nominally, the sources you will be using for your history essay can be divided into primary and secondary ones. Primary sources refer directly to the description of the events or personalities you base your paper on. Secondary sources represent the works of experienced historians, sociologists, and politicians that contain the profound analysis of the events described within your topic.
The professional history essay cannot exist without trustful primary sources. It can be challenging to find and identify them. Fortunately, the XXIst century provides a decent range of opportunities to complete thorough research work. You can have access to the best scholars’ papers, databases of the world libraries, and blogs of famous experts. Crowd-sourced websites can also be of good service. However, they should be used very selectively after you make sure they are credible.
Secondary sources are as important as the primary ones. You need to be sure of their credibility and choose exclusively scholarly works. Check whether the author of the paper you are going to use in your essay is a professional historian and can be trusted. To make the right choice, ask yourself several questions before referring to any source:
- What do you know about the author?
- Does the author have an academic degree and enough experience to be trusted?
- What can you say about the publishing house? Is it academic? If it is a website, check its nature and audience. The idea to use materials published on Government online platforms in your paper sounds just perfect.
History Essay Outline
Coming to the outline stage means that you have done all the preparatory work and are ready to move forward. The outline is frequently skipped by students, which makes them regret it later. The outline is a so-called roadmap to indicate the direction you need to move in and mark the proper placing of arguments and ideas.
Like all other types of essays, a history paper consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
Introduction
Are you wondering how to start a history essay? With the catching introduction, of course. Introduction to your history essay should serve as a so-called hook to immediately grab the readers’ attention. To make it as catching as possible, you may use a few simple yet trusting methods:
- Include some facts or impressive statistics. This will help easily win people’s trust and make your paper more relevant;
- Rhetorical questions always help define the sense of your creative work. Use them in the introduction to indicate the main points your work will be based on;
- Quotations may also be of good service in case you want to make people intrigued.
Provided the hook has worked, don’t hesitate to introduce your paper’s theme: mention the key events or persons your essay is about. Usually, a good introduction ends with a strong thesis statement. Make it short and up to the point. Besides, make sure it provides a smooth transition to the body section of your history essay.
Divide your critical ideas described in the essay and between the paragraphs: one paragraph = one idea. Each idea needs to be supported by concise arguments. There is no standard scheme to build your body paragraphs on. However, you may take the following algorithm for the basis:
- A sentence related to the thesis statement and elucidating the idea;
- Context of your history essay;
- Facts in the form of quotation or rewritten
- Analysis and your point of view
- Description of the controversial points
- Smooth transition to the next paragraph
It is highly recommended to place the arguments of your body section in correct order. Start with the weakest ones and leave the strongest ones for a dessert.
You should put your best effort into making this paragraph as impressive and convincing as possible. The final part of your paper should focus on the main points of the essay and again prove the theory mentioned in the thesis statement. Don’t make the conclusion too complicated – it needs to be simple and straightforward. The conclusion is not a part of the paper where you may introduce some new facts and ideas. Its main goal is in summarizing the critical points previously specified in the essay. If you want to make a conclusion sound professional, don’t forget to mention the historical events’ relevance to today’s reality.
How to Choose a Topic for a History Essay?
In case you were lucky to choose the topic for your history essay by yourself, don’t skip this part. Selecting from a pile of history essay topics may be challenging as you need to know your educational level, interests, and ability to elaborate on the theme. An adequately chosen history essay topic is a basis for a good paper. It affects the overall writing process and the level of your engagement in the subject. Use these tips to choose the best topic for your history paper:
- Focus on the theme that sounds interesting to you. If history is not your cup of tea, try to pick the theme that seems more interesting than others. History is tightly connected with all aspects of human life. So, there should be something that makes your heart beat faster.
- Don’t be guided by interest only when choosing a topic for the history essay. You should know at least something about the given theme. Even the most exciting issues can turn out to be a nightmare to deal with if you know absolutely nothing about them.
- Analyze the broadness of the topic. If it is too broad, you won’t be able to elaborate the theme decently. For example, the topic “Ancient Egypt” is unclear. You won’t be able to elucidate all its aspects and perspectives properly. However, dealing with “Attitudes Towards Women in Ancient Egypt” narrows your research scope and lets you stay clear and precise.
- Make sure the topic you are going to choose has been analyzed before, and you can find a lot of credible materials to base your research on. Even narrow themes can be challenging if they are unexplored.
- If you have a chance to use the theme you have already been dealing with before, don’t hesitate to do it. There is no need to rewrite your old paper – you have an excellent opportunity to analyze things from another perspective. Reusing the topic is hugely advantageous, as you have all the research work done already and may concentrate on your personal opinion.
- In case sitting on the fence while choosing the topic for your history essay becomes unbearable, you can always ask your tutor for a piece of advice. In such a way, you will demonstrate your respect and trust.
- Avoid offbeat themes. They may be interesting, however, totally new. If you are not afraid of being stuck at the research stage – go ahead!
- Make a little brainstorm session before choosing any topic. Provided you can come up with at least five strong arguments related to the theme, don’t hesitate to pick it.
History Essay Examples
Nothing can be more helpful than a brilliant history essay example you can use for your future work. You may take a look at the essay’s purpose, analyze the structure, get an idea about transitions and vocabulary used. Check on these top-notch examples of history paper to get inspired and motivated:
- https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/us-history-slavery-essay/5916771
- https://www.markedbyteachers.com/international-baccalaureate/history/compare-and-contrast-the-causes-of-the-first-world-war-and-the-second-world-war.html
- https://www.markedbyteachers.com/international-baccalaureate/history/how-far-do-trotsky-fa-a-tm-s-own-misjudgments-account-for-his-failure-in-the-power-struggle-which-followed-lenin-fa-a-tm-s-death.html
- https://www.markedbyteachers.com/international-baccalaureate/history/compare-and-contrast-the-policies-of-alexander-ii-and-alexander-iii.html
Writing Tips for a History Essay
Interpretation of the past may be pretty controversial. So are the rules on how to write a perfect history essay. Nevertheless, there are some standard conventions and guidelines for elaborating professional history papers without any special effort from your side. Just follow the below tips to get the highest grade under the toughest history essay rubric.
Use the past tense
The present tense is just inappropriate when dealing with the history essay. Moreover, it can undermine confidence in the qualifications and expertise of the author. The present tense is acceptable only when you draw parallels between past events and the current time.
Avoid generalizations
Specificity and accuracy are the best friends of a highly professional history essay. If you talk about some specific period, introduce exact dates or centuries. In case you mention some personalities, provide their full names. History paper is senseless without these critical details.
Exclude anachronisms
When dealing with some historical events from today’s perspective, it is easy to get lost in chronological order. Such a jumble can confuse the readers and make your work less credible. Mind the vocabulary you use when talking about a specific epoch.
Try not to judge the epoch from a modern perspective
Every generation has its advantages and drawbacks. Your main task as an author is to analyze both and convey them clearly to a reader. Don’t be judgmental.
Paraphrasing is always better than quoting
Stuffing your history essay with the quotes can be more of a hindrance than help. Don’t be afraid to showcase your analytical skills and dive deep into the profound analysis of past events. If paraphrasing is impossible, use the quote indicating its source.
Be responsible for the context
As an author, you assume full responsibility for your personal opinion and ideas. At the same time, you should be sure of the sources you use in your paper. History essays don’t stand uncertainty and double standards.
Choose the proper citation style
As a rule, history papers require Chicago citation style. A poorly arranged citation page can question your reputation as a history expert.
Stick to the proper voice
A formal academic voice is the most appropriate one when we talk about the history essay. Also, avoid passive voice phrases, redundant constructions, and generalizations.
Take care of thorough proofreading
You have made it: your history essay is ready and waits to be polished. The editing stage is crucial as even the brightest ideas can get lost in a sea of mistakes, impurities, and vague phrases. How to proofread your history essay to make it shine? Check the below instructions to learn how to do it:
- Read your history essay aloud several times to make sure it is clear and sounds smooth. Avoid long sentences and inaccurate phrases with unclear meaning.
- Proper style is important when we talk about the academic history essay. Make sure it is formal but readable. Readers should easily percept your message and clearly understand the goal of your research.
- Proofreading may be challenging in case you have spent a lot of time elaborating on the content. If you can ask someone to look at your history paper with a fresh pair of eyes, it would be perfect. Independent readers can identify the weak places in your work faster, and you will get a valuable second opinion on your piece of writing.
Write My History Essay for Me, Please!
History paper is one of the most complicated types of writing. Students dealing with history topics should know more than just a material of a regular history syllabus. Moreover, this paper requires a lot of time and effort to do research, analyze, and establish logical connections and predictions. You have to deal with the vast amount of dates, personalities, and theories that may not always be true. No wonder a lot of students choose to ask someone to write their history assignment for them. This decision appears to be justified as our essay writing service offers help provided by the actual history scholars who, by the way, are excellent in writing.
All you need to do is formulate the task specifying the detailed instructions to your assignment and indicate the deadline. In case you want some specific sources to be used when elaborating on your history paper, you should mention them in your reference list.
In case your history essay is ready and you just need to make it shine, our essay service is always ready to help you with editing and proofreading. In such a way, you pay only for a specific service, not for the whole writing package.
A brilliantly elaborated history essay can serve as a good base for all your future works. You may get a clear idea about the content, research process, vocabulary, structure, and citation style. Just place the order, and our highly professional expert will be there to help you with your history paper.

- Academic Writing Guides

- Research Paper Writing Guides
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a History Essay
Last Updated: December 27, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA . Emily Listmann is a Private Tutor and Life Coach in Santa Cruz, California. In 2018, she founded Mindful & Well, a natural healing and wellness coaching service. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. Emily also received her Wellness Coach Certificate from Cornell University and completed the Mindfulness Training by Mindful Schools. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 246,077 times.
Writing a history essay requires you to include a lot of details and historical information within a given number of words or required pages. It's important to provide all the needed information, but also to present it in a cohesive, intelligent way. Know how to write a history essay that demonstrates your writing skills and your understanding of the material.
Preparing to Write Your Essay

- The key words will often need to be defined at the start of your essay, and will serve as its boundaries. [2] X Research source
- For example, if the question was "To what extent was the First World War a Total War?", the key terms are "First World War", and "Total War".
- Do this before you begin conducting your research to ensure that your reading is closely focussed to the question and you don't waste time.

- Explain: provide an explanation of why something happened or didn't happen.
- Interpret: analyse information within a larger framework to contextualise it.
- Evaluate: present and support a value-judgement.
- Argue: take a clear position on a debate and justify it. [3] X Research source

- Your thesis statement should clearly address the essay prompt and provide supporting arguments. These supporting arguments will become body paragraphs in your essay, where you’ll elaborate and provide concrete evidence. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Your argument may change or become more nuanced as your write your essay, but having a clear thesis statement which you can refer back to is very helpful.
- For example, your summary could be something like "The First World War was a 'total war' because civilian populations were mobilized both in the battlefield and on the home front".

- Pick out some key quotes that make your argument precisely and persuasively. [5] X Research source
- When writing your plan, you should already be thinking about how your essay will flow, and how each point will connect together.
Doing Your Research

- Primary source material refers to any texts, films, pictures, or any other kind of evidence that was produced in the historical period, or by someone who participated in the events of the period, that you are writing about.
- Secondary material is the work by historians or other writers analysing events in the past. The body of historical work on a period or event is known as the historiography.
- It is not unusual to write a literature review or historiographical essay which does not directly draw on primary material.
- Typically a research essay would need significant primary material.

- Start with the core texts in your reading list or course bibliography. Your teacher will have carefully selected these so you should start there.
- Look in footnotes and bibliographies. When you are reading be sure to pay attention to the footnotes and bibliographies which can guide you to further sources a give you a clear picture of the important texts.
- Use the library. If you have access to a library at your school or college, be sure to make the most of it. Search online catalogues and speak to librarians.
- Access online journal databases. If you are in college it is likely that you will have access to academic journals online. These are an excellent and easy to navigate resources.
- Use online sources with discretion. Try using free scholarly databases, like Google Scholar, which offer quality academic sources, but avoid using the non-trustworthy websites that come up when you simply search your topic online.
- Avoid using crowd-sourced sites like Wikipedia as sources. However, you can look at the sources cited on a Wikipedia page and use them instead, if they seem credible.

- Who is the author? Is it written by an academic with a position at a University? Search for the author online.
- Who is the publisher? Is the book published by an established academic press? Look in the cover to check the publisher, if it is published by a University Press that is a good sign.
- If it's an article, where is published? If you are using an article check that it has been published in an academic journal. [8] X Research source
- If the article is online, what is the URL? Government sources with .gov addresses are good sources, as are .edu sites.

- Ask yourself why the author is making this argument. Evaluate the text by placing it into a broader intellectual context. Is it part of a certain tradition in historiography? Is it a response to a particular idea?
- Consider where there are weaknesses and limitations to the argument. Always keep a critical mindset and try to identify areas where you think the argument is overly stretched or the evidence doesn't match the author's claims. [9] X Research source

- Label all your notes with the page numbers and precise bibliographic information on the source.
- If you have a quote but can't remember where you found it, imagine trying to skip back through everything you have read to find that one line.
- If you use something and don't reference it fully you risk plagiarism. [10] X Research source

Writing the Introduction

- For example you could start by saying "In the First World War new technologies and the mass mobilization of populations meant that the war was not fought solely by standing armies".
- This first sentences introduces the topic of your essay in a broad way which you can start focus to in on more.

- This will lead to an outline of the structure of your essay and your argument.
- Here you will explain the particular approach you have taken to the essay.
- For example, if you are using case studies you should explain this and give a brief overview of which case studies you will be using and why.

Writing the Essay

- Try to include a sentence that concludes each paragraph and links it to the next paragraph.
- When you are organising your essay think of each paragraph as addressing one element of the essay question.
- Keeping a close focus like this will also help you avoid drifting away from the topic of the essay and will encourage you to write in precise and concise prose.
- Don't forget to write in the past tense when referring to something that has already happened.

- Don't drop a quote from a primary source into your prose without introducing it and discussing it, and try to avoid long quotations. Use only the quotes that best illustrate your point.
- If you are referring to a secondary source, you can usually summarise in your own words rather than quoting directly.
- Be sure to fully cite anything you refer to, including if you do not quote it directly.

- Think about the first and last sentence in every paragraph and how they connect to the previous and next paragraph.
- Try to avoid beginning paragraphs with simple phrases that make your essay appear more like a list. For example, limit your use of words like: "Additionally", "Moreover", "Furthermore".
- Give an indication of where your essay is going and how you are building on what you have already said. [15] X Research source

- Briefly outline the implications of your argument and it's significance in relation to the historiography, but avoid grand sweeping statements. [16] X Research source
- A conclusion also provides the opportunity to point to areas beyond the scope of your essay where the research could be developed in the future.
Proofreading and Evaluating Your Essay

- Try to cut down any overly long sentences or run-on sentences. Instead, try to write clear and accurate prose and avoid unnecessary words.
- Concentrate on developing a clear, simple and highly readable prose style first before you think about developing your writing further. [17] X Research source
- Reading your essay out load can help you get a clearer picture of awkward phrasing and overly long sentences. [18] X Research source

- When you read through your essay look at each paragraph and ask yourself, "what point this paragraph is making".
- You might have produced a nice piece of narrative writing, but if you are not directly answering the question it is not going to help your grade.

- A bibliography will typically have primary sources first, followed by secondary sources. [19] X Research source
- Double and triple check that you have included all the necessary references in the text. If you forgot to include a reference you risk being reported for plagiarism.
Sample Essay

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.historytoday.com/robert-pearce/how-write-good-history-essay
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/writing-a-good-history-paper
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/thesis_statement_tips.html
- ↑ http://history.rutgers.edu/component/content/article?id=106:writing-historical-essays-a-guide-for-undergraduates
- ↑ https://guides.lib.uw.edu/c.php?g=344285&p=2580599
- ↑ http://www.hamilton.edu/documents/writing-center/WritingGoodHistoryPaper.pdf
- ↑ http://www.bowdoin.edu/writing-guides/
- ↑ https://www.wgtn.ac.nz/hppi/publications/Writing-History-Essays.pdf
About This Article

To write a history essay, read the essay question carefully and use source materials to research the topic, taking thorough notes as you go. Next, formulate a thesis statement that summarizes your key argument in 1-2 concise sentences and create a structured outline to help you stay on topic. Open with a strong introduction that introduces your thesis, present your argument, and back it up with sourced material. Then, end with a succinct conclusion that restates and summarizes your position! For more tips on creating a thesis statement, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lea Fernandez
Nov 23, 2017
Did this article help you?

Matthew Sayers
Mar 31, 2019
Millie Jenkerinx
Nov 11, 2017
Oct 18, 2019
Shannon Harper
Mar 9, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

- Written Essays
How to write source-based history essays

The biggest assessment task you will be required to complete is a written research essay which develops an argument and uses a range of sources.
All types of assessment tasks will need you to use essay-writing skills in some form, but their fundamental structure and purpose remains the same.
Therefore, learning how to write essays well is central to achieving high marks in History.
What is an 'essay'?
A History essay is a structured argument that provides historical evidence to substantiate its points.
To achieve the correct structure for your argument, it is crucial to understand the separate parts that make up a written essay.
If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece.
Most essays will require you to write:
- 1 Introduction Paragraph
- 3 Body Paragraphs
- 1 Concluding Paragraph
Explanations for how to structure and write each of these paragraphs can be found below, along with examples of each:
Essay paragraph writing advice

How to write an Introductory Paragraph
This page explains the purpose of an introduction, how to structure one and provides examples for you to read.

How to write Body Paragraphs
This page explains the purpose of body paragraphs, how to structure them and provides examples for you to read.

How to write a Conclusion
This page explains the purpose of conclusions, how to structure them and provides examples for you to read.
More essay resources
What do you need help with, download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
How to Write a Good History Essay. A Sequence of Actions and Useful Tips
/rating_on.png)
Before you start writing your history essay, there is quite a lot of work that has to be done in order to gain success.
You may ask: what is history essay? What is the difference between it and other kinds of essays? Well, the main goal of a history essay is to measure your progress in learning history and test your range of skills (such as analysis, logic, planning, research, and writing), it is necessary to prepare yourself very well.
Your plan of action may look like this. First of all, you will have to explore the topic. If you are going to write about a certain historical event, think of its causes and premises, and analyze what its impact on history was. In case you are writing about a person, find out why and how he or she came to power and how they influenced society and historical situations.
The next step is to make research and collect all the available information about the person or event, and also find evidence.
Finally, you will have to compose a well-organized response.
During the research, make notes and excerpts of the most notable data, write out the important dates and personalities. And of course, write down all your thoughts and findings.
It all may seem complicated at first sight, but in fact, it is not so scary! To complete this task successfully and compose a good history essay, simply follow several easy steps provided below.
Detailed Writing Instruction for Students to Follow
If you want to successfully complete your essay, it would be better to organize the writing process. You will complete the assignment faster and more efficient if you divide the whole work into several sections or steps.
- Introduction
Writing a good and strong introduction part is important because this is the first thing your reader will see. It gives the first impression of your essay and induces people to reading (or not reading) it.
To make the introduction catchy and interesting, express the contention and address the main question of the essay. Be confident and clear as this is the moment when you define the direction your whole essay will take. And remember that introduction is not the right place for rambling! The best of all is, to begin with, a brief context summary, then go to addressing the question and express the content. Finally, mark the direction your essay about history will take.
Its quality depends on how clear you divided the whole essay into sections in the previous part. As long as you have provided a readable and understandable scheme, your readers will know exactly what to expect.
The body of your essay must give a clear vision of what question you are considering. In this section, you can develop your idea and support it with the evidence you have found. Use certain facts and quotations for that. When being judicial and analytical, they will help you to easily support your point of view and argument.
As long as your essay has a limited size, don’t be too precise. It is allowed to summarize the most essential background information, for example, instead of giving a precise list of all the issues that matter.
It is also good to keep in mind that each paragraph of your essay’s body must tell about only one issue. Don’t make a mess out of your paper!
It is not only essential to start your essay well. How you will end it also matters. A properly-written conclusion is the one that restates the whole paper’s content and gives a logical completion of the issue or question discussed above. Your conclusion must leave to chance for further discussion or arguments on the case. It’s time, to sum up, give a verdict.
That is why it is strongly forbidden to provide any new evidence or information here, as well as start a new discussion, etc.
After you finish writing, give yourself some time and put the paper away for a while. When you turn back to it will be easier to take a fresh look at it and find any mistakes or things to improve. Of course, remember to proofread your writing and check it for any grammar, spelling and punctuation errors. All these tips will help you to learn how to write a history essay.


Tips from my first year - essay writing
This is the third of a three part series giving advice on the essay writing process, focusing in this case on essay writing.
Daniel is a first year BA History and Politics student at Magdalen College . He is a disabled student and the first in his immediate family to go to university. Daniel is also a Trustee of Potential Plus UK , a Founding Ambassador and Expert Panel Member for Zero Gravity , and a History Faculty Ambassador. Before coming to university, Daniel studied at a non-selective state school, and was a participant on the UNIQ , Sutton Trust , and Social Mobility Foundation APP Reach programmes, as well as being part of the inaugural Opportunity Oxford cohort. Daniel is passionate about outreach and social mobility and ensuring all students have the best opportunity to succeed.

History and its related disciplines mainly rely on essay writing with most term-time work centring on this, so it’s a good idea to be prepared. The blessing of the Oxford system though is you get plenty of opportunity to practice, and your tutors usually provide lots of feedback (both through comments on essays and in tutorials) to help you improve. Here are my tips from my first year as an Oxford Undergraduate:
- Plan for success – a good plan really sets your essay in a positive direction, so try to collect your thoughts if you can. I find a great way to start my planning process is to go outside for a walk as it helps to clear my head of the detail, it allows me to focus on the key themes, and it allows me to explore ideas without having to commit anything to paper. Do keep in mind your question throughout the reading and notetaking process, though equally look to the wider themes covered so that when you get to planning you are in the right frame of mind.
- Use what works for you – if you try to use a method you aren’t happy with, it won’t work. That doesn’t mean you shouldn’t experiment; to the contrary I highly encourage it as it can be good to change up methods and see what really helps you deliver a strong essay. However, don’t feel pressured into using one set method, as long as it is time-efficient and it gets you ready for the next stage of the essay process it is fine!
- Focus on the general ideas – summarise in a sentence what each author argues, see what links there are between authors and subject areas, and possibly group your ideas into core themes or paragraph headers. Choose the single piece of evidence you believe supports each point best.
- Make something revision-ready – try to make something which you can come back to in a few months’ time which makes sense and will really get your head back to when you were preparing for your essay.
- Consider what is most important – no doubt if you spoke about everything covered on the reading list you would have far more words than the average essay word count (which is usually advised around 1,500-2,000 words - it does depend on your tutor.) You have a limited amount of time, focus, and words, so choose what stands out to you as the most important issues for discussion. Focus on the important issues well rather than covering several points in a less-focused manner.
- Make it your voice – your tutors want to hear from you about what you think and what your argument is, not lots of quotes of what others have said. Therefore, when planning and writing consider what your opinion is and make sure to state it. Use authors to support your viewpoint, or to challenge it, but make sure you are doing the talking and driving the analysis. At the same time, avoid slang, and ensure the language you use is easy to digest.
- Make sure you can understand it - don’t feel you have to use big fancy words you don’t understand unless they happen to be relevant subject-specific terminology, and don’t swallow the Thesaurus. If you use a technical term, make sure to provide a definition. You most probably won’t have time to go into it fully, but if it is an important concept hint at the wider historical debate. State where you stand and why briefly you believe what you are stating before focusing on your main points. You need to treat the reader as both an alien from another planet, and a very intelligent person at the same time – make sure your sentences make sense, but equally make sure to pitch it right. As you can possibly tell, it is a fine balancing act so my advice is to read through your essay and ask yourself ‘why’ about every statement or argument you make. If you haven’t answered why, you likely require a little more explanation. Simple writing doesn’t mean a boring or basic argument, it just means every point you make lands and has impact on the reader, supporting them every step of the way.
- Keep introductions and conclusions short – there is no need for massive amounts of setting the scene in the introduction, or an exact repeat of every single thing you have said in the essay appearing in the conclusion. Instead, in the first sentence of your introduction provide a direct answer to the question. If the question is suitable, it is perfectly fine to say yes, no, or it is a little more complicated. Whatever the answer is, it should be simple enough to fit in one reasonable length sentence. The next three sentences should state what each of your three main body paragraphs are going to argue, and then dive straight into it. With your conclusion, pick up what you said about the key points. Suggest how they possibly link, maybe do some comparison between factors and see if you can leave us with a lasting thought which links to the question in your final sentence.
- Say what you are going to say, say it, say it again – this is a general essay structure; an introduction which clearly states your argument; a main body which explains why you believe that argument; and a conclusion which summarises the key points to be drawn from your essay. Keep your messaging clear as it is so important the reader can grasp everything you are trying to say to have maximum impact. This applies in paragraphs as well – each paragraph should in one sentence outline what is to be said, it should then be said, and in the final sentence summarise what you have just argued. Somebody should be able to quickly glance over your essay using the first and last sentences and be able to put together the core points.
- Make sure your main body paragraphs are focused – if you have come across PEE (Point, Evidence, Explain – in my case the acronym I could not avoid at secondary school!) before, then nothing has changed. Make your point in around a sentence, clearly stating your argument. Then use the best single piece of evidence available to support your point, trying to keep that to a sentence or two if you can. The vast majority of your words should be explaining why this is important, and how it supports your argument, or how it links to something else. You don’t need to ‘stack’ examples where you provide multiple instances of the same thing – if you have used one piece of evidence that is enough, you can move on and make a new point. Try to keep everything as short as possible while communicating your core messages, directly responding to the question. You also don’t need to cover every article or book you read, rather pick out the most convincing examples.
- It works, it doesn’t work, it is a little more complicated – this is a structure I developed for writing main body paragraphs, though it is worth noting it may not work for every question. It works; start your paragraph with a piece of evidence that supports your argument fully. It doesn’t work; see if there is an example which seems to contradict your argument, but suggest why you still believe your argument is correct. Then, and only if you can, see if there is an example which possibly doesn’t quite work fully with your argument, and suggest why possibly your argument cannot wholly explain this point or why your argument is incomplete but still has the most explanatory power. See each paragraph as a mini-debate, and ensure different viewpoints have an opportunity to be heard.
- Take your opponents at their best – essays are a form of rational dialogue, interacting with writing on this topic from the past, so if you are going to ‘win’ (or more likely just make a convincing argument as you don’t need to demolish all opposition in sight) then you need to treat your opponents fairly by choosing challenging examples, and by fairly characterising their arguments. It should not be a slinging match of personal insults or using incredibly weak examples, as this will undermine your argument. While I have never attacked historians personally (though you may find in a few readings they do attack each other!), I have sometimes chosen the easier arguments to try to tackle, and it is definitely better to try to include some arguments which are themselves convincing and contradictory to your view.
- Don’t stress about referencing – yes referencing is important, but it shouldn’t take too long. Unless your tutor specifies a method, choose a method which you find simple to use as well as being an efficient method. For example, when referencing books I usually only include the author, book title, and year of publication – the test I always use for referencing is to ask myself if I have enough information to buy the book from a retailer. While this wouldn’t suffice if you were writing for a journal, you aren’t writing for a journal so focus on your argument instead and ensure you are really developing your writing skills.
- Don’t be afraid of the first person – in my Sixth Form I was told not to use ‘I’ as it weakened my argument, however that isn’t the advice I have received at Oxford; in fact I have been encouraged to use it as it forces me to take a side. So if you struggle with making your argument clear, use phrases like ‘I believe’ and ‘I argue’.
I hope this will help as a toolkit to get you started, but my last piece of advice is don’t worry! As you get so much practice at Oxford you get plenty of opportunity to perfect your essay writing skills, so don’t think you need to be amazing at everything straight away. Take your first term to try new methods out and see what works for you – don’t put too much pressure on yourself. Good luck!

How to Write a History Essay?
04 August, 2020
10 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
There are so many types of essays. It can be hard to know where to start. History papers aren’t just limited to history classes. These tasks can be assigned to examine any important historical event or a person. While they’re more common in history classes, you can find this type of assignment in sociology or political science course syllabus, or just get a history essay task for your scholarship. This is Handmadewriting History Essay Guide - let's start!

Purpose of a History Essay
Wondering how to write a history essay? First of all, it helps to understand its purpose. Secondly, this essay aims to examine the influences that lead to a historical event. Thirdly, it can explore the importance of an individual’s impact on history.
However, the goal isn’t to stay in the past. Specifically, a well-written history essay should discuss the relevance of the event or person to the “now”. After finishing this essay, a reader should have a fuller understanding of the lasting impact of an event or individual.
Need basic essay guidance? Find out what is an essay with this 101 essay guide: What is an Essay?
Elements for Success
Indeed, understanding how to write a history essay is crucial in creating a successful paper. Notably, these essays should never only outline successful historic events or list an individual’s achievements. Instead, they should focus on examining questions beginning with what , how , and why . Here’s a pro tip in how to write a history essay: brainstorm questions. Once you’ve got questions, you have an excellent starting point.
Preparing to Write

Evidently, a typical history essay format requires the writer to provide background on the event or person, examine major influences, and discuss the importance of the forces both then and now. In addition, when preparing to write, it’s helpful to organize the information you need to research into questions. For example:
- Who were the major contributors to this event?
- Who opposed or fought against this event?
- Who gained or lost from this event?
- Who benefits from this event today?
- What factors led up to this event?
- What changes occurred because of this event?
- What lasting impacts occurred locally, nationally, globally due to this event?
- What lessons (if any) were learned?
- Why did this event occur?
- Why did certain populations support it?
- Why did certain populations oppose it?
These questions exist as samples. Therefore, generate questions specific to your topic. Once you have a list of questions, it’s time to evaluate them.
Evaluating the Question

Seasoned writers approach writing history by examining the historic event or individual. Specifically, the goal is to assess the impact then and now. Accordingly, the writer needs to evaluate the importance of the main essay guiding the paper. For example, if the essay’s topic is the rise of American prohibition, a proper question may be “How did societal factors influence the rise of American prohibition during the 1920s? ”
This question is open-ended since it allows for insightful analysis, and limits the research to societal factors. Additionally, work to identify key terms in the question. In the example, key terms would be “societal factors” and “prohibition”.
Summarizing the Argument
The argument should answer the question. Use the thesis statement to clarify the argument and outline how you plan to make your case. In other words. the thesis should be sharp, clear, and multi-faceted. Consider the following tips when summarizing the case:
- The thesis should be a single sentence
- It should include a concise argument and a roadmap
- It’s always okay to revise the thesis as the paper develops
- Conduct a bit of research to ensure you have enough support for the ideas within the paper
Outlining a History Essay Plan

Once you’ve refined your argument, it’s time to outline. Notably, many skip this step to regret it then. Nonetheless, the outline is a map that shows where you need to arrive historically and when. Specifically, taking the time to plan, placing the strongest argument last, and identifying your sources of research is a good use of time. When you’re ready to outline, do the following:
- Consider the necessary background the reader should know in the introduction paragraph
- Define any important terms and vocabulary
- Determine which ideas will need the cited support
- Identify how each idea supports the main argument
- Brainstorm key points to review in the conclusion
Gathering Sources
As a rule, history essays require both primary and secondary sources . Primary resources are those that were created during the historical period being analyzed. Secondary resources are those created by historians and scholars about the topic. It’s a good idea to know if the professor requires a specific number of sources, and what kind he or she prefers. Specifically, most tutors prefer primary over secondary sources.
Where to find sources? Great question! Check out bibliographies included in required class readings. In addition, ask a campus Librarian. Peruse online journal databases; In addition, most colleges provide students with free access. When in doubt, make an appointment and ask the professor for guidance.
Writing the Essay
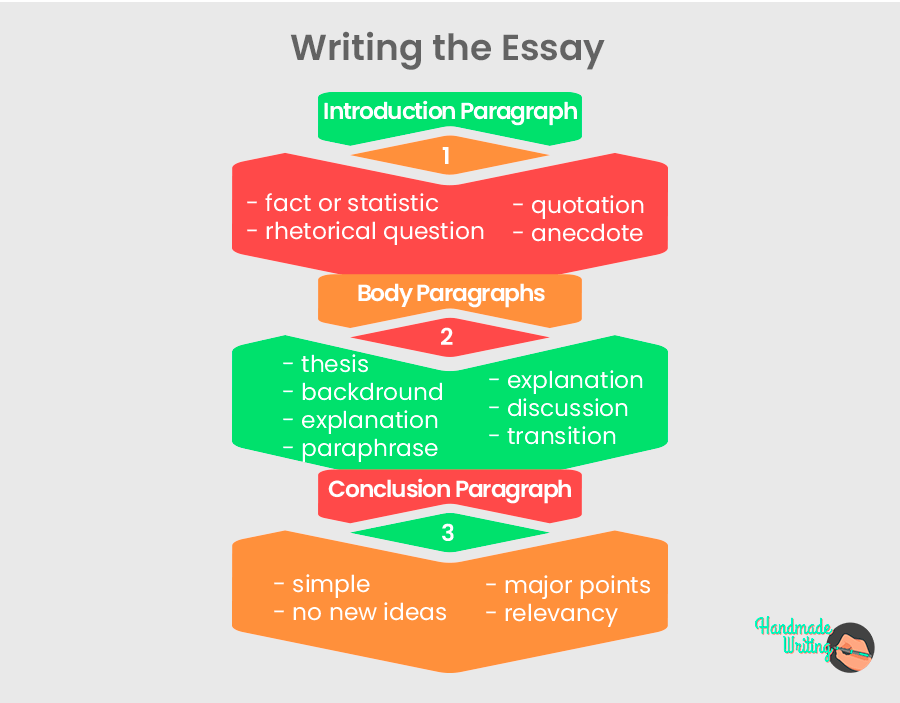
Now that you have prepared your questions, ideas, and arguments; composed the outline ; and gathered sources – it’s time to write your first draft. In particular, each section of your history essay must serve its purpose. Here is what you should include in essay paragraphs.
Introduction Paragraph
Unsure of how to start a history essay? Well, like most essays, the introduction should include an attention-getter (or hook):
- Relevant fact or statistic
- Rhetorical Question
- Interesting quotation
- Application anecdote if appropriate
Once you’ve captured the reader’s interest, introduce the topic. Similarly, present critical historic context. Namely, it is necessary to introduce any key individuals or events that will be discussed later in the essay. At last, end with a strong thesis which acts as a transition to the first argument.
Body Paragraphs
Indeed, each body paragraph should offer a single idea to support the argument. Then, after writing a strong topic sentence, the topic should be supported with correctly cited research. Consequently, a typical body paragraph is arranged as follows:
- Topic sentence linking to the thesis
- Background of the topic
- Research quotation or paraphrase #1
- Explanation and analysis of research
- Research quotation or paraphrase #2
- Transition to the next paragraph
Equally, the point of body paragraphs is to build the argument. Hence, present the weakest support first and end with the strongest. Admittedly, doing so leaves the reader with the best possible evidence.
Conclusion Paragraph
You’re almost there! Eventually, conclusion paragraphs should review the most important points in the paper. In them, you should prove that you’ve supported the argument proposed in the thesis. When writing a conclusion paragraph keep these tips in mind:
- Keep it simple
- Avoid introducing new information
- Review major points
- Discuss the relevance to today
Problems with writing Your History essay ? Try our Essay Writer Service!

Proofreading Your Essay
Once the draft is ready and polished, it’s time to proceed to final editing. What does this process imply? Specifically, it’s about removing impurities and making the essay look just perfect. Here’s what you need to do to improve the quality of your paper:
- Double check the content. In the first place, it’s recommended to get rid of long sentences, correct vague words. Also, make sure that all your paragrahps contain accurate sentences with transparent meaning.
- Pay attention to style. To make the process of digesting your essay easier, focus on crafting a paper with readable style, the one that is known to readers. Above all, the main mission here is to facilitate the perception of your essay. So, don’t forget about style accuracy.
- Practice reading the essay. Of course, the best practice before passing the paper is to read it out loud. Hence, this exercise will help you notice fragments that require rewriting or a complete removal.
History Essay Example
Did you want a history essay example? Take a look at one of our history essay papers.
Make it Shine
An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it’s achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine:
- Write a substantial introduction. Particularly, it’s the first impression the professor will have of the paper.
- State a clear thesis. A strong thesis is easier to support.
- Incorporate evidence critically. If while researching you find opposing arguments, include them and discuss their flaws.
- Cite all the research. Whether direct quotations or paraphrases, citing evidence is crucial to avoiding plagiarism, which can have serious academic consequences.
- Include primary and secondary resources. While primary resources may be harder to find, the professor will expect them—this is, after all, a history essay.
History Essay Sample
Ready to tackle the history essay format? Great! Check out this history essay sample from an upper-level history class. While the essay isn’t perfect, the professor points out its many strengths.
Remember: start early and revise, revise, revise . We can’t revise history, but you can revise your ideas until they’re perfect.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
History Essay Examples

Top History Essay Examples To Get Inspired By
Published on: May 4, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
History essays are a crucial component of many academic programs, helping students to develop their critical thinking, research, and writing skills.
However, writing a great history essay is not always easy, especially when you are struggling to find the right approach. This is where history essay examples come in handy.
By reading and examining samples of successful history essays, you can gain inspiration, learn new ways to approach your topic. Moreover, you can develop a better understanding of what makes a great history essay.
In this blog, you will find a range of history essay examples that showcase the best practices in history essay writing.
Read on to find useful examples.
On This Page On This Page -->
Sample History Essays
Explore our collection of excellent history paper examples about various topics. Download the pdf examples for free and read to get inspiration for your own essay.
History Essay Samples for Middle School
The Impact of Ancient Civilizations on Modern Society
The Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire
The Causes and Consequences of the American Revolution
History Writing Samples for High School Students
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on Society
Grade 10 History Essay Example: World War 1 Causes and Effects
Grade 12 History Essay Example: The Impact of Technology on World War II
Ancient History Essay Examples
The Societal and Political Structures of the Maya Civilization
The Role of Phoenicians in the Development of Ancient Mediterranean World
The Contributions of the Indus Civilization
Medieval History Essay Examples
The Crusades Motivations and Consequences
The Beginning of Islamic Golden Age
The Black Death
Modern History Essay Examples
The Suez Crisis and the End of British Dominance
The Rise of China as an Economic Powerhouse
World History Essay Examples
The Role of the Silk Road in Shaping Global Trade and Culture
The Rise and Fall of the Ottoman Empire
The Legacy of Ancient Greek Philosophy and Thought

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
American History Essay Examples
The Civil Rights Movement and its Impact on American Society
The American Civil War and its Aftermath
The Role of Women in American Society Throughout History
African History Essay Examples
The Impact of Colonialism on African Societies
The Rise and Fall of the Mali Empire
European History Essay Examples
The Protestant Reformation and the Rise of Protestantism in Europe
The French Revolution and its Impact on European Politics and Society
The Cold War and the Division of Europe
Argumentative History Essay Examples
Was the US Civil War Primarily About Slavery or States
The Effects of British Colonization on Colonies
Art History Essay Examples
The Influence of Greek and Roman Art on Neoclassicism
The Depiction of Women in Art Throughout History
The Role of Art in the Propaganda of Fascist Regimes
How to Use History Essay Examples
History essay examples are a valuable tool for students looking for inspiration and guidance on how to approach their own essays.
By analyzing successful essays, you can learn effective writing techniques that can be expected in a high-quality history essay.
Here are some tips that will help you take full advantage of the samples above.
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples
- Analyze the Structure:
Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument.
- Study the Thesis Statement:
The thesis statement is the backbone of any successful history essay. Analyze how the author crafted their thesis statement, and consider how you can apply this to your own writing.
- Take Note of the Evidence:
Effective history essays rely on using strong evidence to support their arguments. Take note of the sources and types of evidence used in the essay. Consider how you can apply similar evidence to support your own arguments.
- Pay Attention to the Formatting and Other Academic Formalities:
The sample essays also demonstrate how you can incorporate academic formalities and standards while keeping the essay engaging. See how these essays fulfill academic standards and try to follow them in your own writing.
- Practice Writing:
While analyzing history essay examples can be helpful, it is important to also practice writing your own essays. Use the examples as inspiration, but try to craft your own unique approach to your topic.
History essays are an essential aspect of learning and understanding the past. By using history essay examples, students can gain inspiration on how to develop their history essays effectively.
Furthermore, following the tips outlined in this blog, students can effectively analyze these essay samples and learn from them.
However, writing a history essay can still be challenging.
Looking for an online essay writing service that specializes in history essays? Look no further!
Our history essay writing service is your go-to source for well-researched and expertly crafted papers.
And for an extra edge in your academic journey, explore our AI essay writing tool . Make history with your grades by choosing our online essay writing service and harnessing the potential of our AI essay writing tool.
Get started today!
Cathy A. (Law, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- Why Is Your CV Getting Rejected and How to Avoid It
- Where to Find Images for Presentations
- What Is an Internship? Everything You Should Know
How Long Should a Thesis Statement Be?
- How to Write a Character Analysis Essay
- Best Colours for Your PowerPoint Presentation: Top Colour Combinations
- How to Write a Nursing Essay – With Examples
- Top 5 Essential Skills You Should Build As An International Student
- How Professional Editing Services Can Take Your Writing to the Next Level
- How to Write an Effective Essay Outline: Template & Structure Guide
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips
17 academic words and phrases to use in your essay
(Last updated: 20 October 2022)
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
For the vast majority of students, essay writing doesn't always come easily. Writing at academic level is an acquired skill that can literally take years to master – indeed, many students find they only start to feel really confident writing essays just as their undergraduate course comes to an end!
If this is you, and you've come here looking for words and phrases to use in your essay, you're in the right place. We’ve pulled together a list of essential academic words you can use in the introduction, body, and conclusion of your essays .
Whilst your ideas and arguments should always be your own, borrowing some of the words and phrases listed below is a great way to articulate your ideas more effectively, and ensure that you keep your reader’s attention from start to finish.
It goes without saying (but we'll say it anyway) that there's a certain formality that comes with academic writing. Casual and conversational phrases have no place. Obviously, there are no LOLs, LMFAOs, and OMGs. But formal academic writing can be much more subtle than this, and as we've mentioned above, requires great skill.
So, to get you started on polishing your own essay writing ability, try using the words in this list as an inspirational starting point.
Words to use in your introduction
The trickiest part of academic writing often comes right at the start, with your introduction. Of course, once you’ve done your plan and have your arguments laid out, you need to actually put pen to paper (or fingers to keyboard) and begin your essay.
You need to consider that your reader doesn’t have a clue about your topic or arguments, so your first sentence must summarise these. Explain what your essay is going to talk about as though you were explaining it to a five year old – without losing the formality of your academic writing, of course! To do this, use any of the below words or phrases to help keep you on track.
1. Firstly, secondly, thirdly
Even though it sounds obvious, your argument will be clearer if you deliver the ideas in the right order. These words can help you to offer clarity and structure to the way you expose your ideas. This is an extremely effective method of presenting the facts clearly. Don’t be too rigid and feel you have to number each point, but using this system can be a good way to get an argument off the ground, and link arguments together.
2. In view of; in light of; considering
These essay phrases are useful to begin your essay. They help you pose your argument based on what other authors have said or a general concern about your research. They can also both be used when a piece of evidence sheds new light on an argument. Here’s an example: The result of the American invasion has severely impaired American interests in the Middle East, exponentially increasing popular hostility to the United States throughout the region, a factor which has proved to be a powerful recruitment tool for extremist terrorist groups (Isakhan, 2015). Considering [or In light of / In view of] the perceived resulting threat to American interests, it could be argued that the Bush administration failed to fully consider the impact of their actions before pushing forward with the war.
3. According to X; X stated that; referring to the views of X
Introducing the views of an author who has a comprehensive knowledge of your particular area of study is a crucial part of essay writing. Including a quote that fits naturally into your work can be a bit of a struggle, but these academic phrases provide a great way in.
Even though it’s fine to reference a quote in your introduction, we don’t recommend you start your essay with a direct quote. Use your own words to sum up the views you’re mentioning, for example:
As Einstein often reiterated, experiments can prove theories, but experiments don’t give birth to theories.
Rather than:
“A theory can be proved by experiment, but no path leads from experiment to the birth of a theory.” {Albert Einstein, 1954, Einstein: A Biography}.
See the difference?
And be sure to reference correctly too, when using quotes or paraphrasing someone else's words.
Adding information and flow
The flow of your essay is extremely important. You don’t want your reader to be confused by the rhythm of your writing and get distracted away from your argument, do you? No! So, we recommend using some of the following ‘flow’ words, which are guaranteed to help you articulate your ideas and arguments in a chronological and structured order.
4. Moreover; furthermore; in addition; what’s more
These types of academic phrases are perfect for expanding or adding to a point you’ve already made without interrupting the flow altogether. “Moreover”, “furthermore” and “in addition” are also great linking phrases to begin a new paragraph.
Here are some examples: The dissociation of tau protein from microtubules destabilises the latter resulting in changes to cell structure, and neuronal transport. Moreover, mitochondrial dysfunction leads to further oxidative stress causing increased levels of nitrous oxide, hydrogen peroxide and lipid peroxidases.
On the data of this trial, no treatment recommendations should be made. The patients are suspected, but not confirmed, to suffer from pneumonia. Furthermore, five days is too short a follow up time to confirm clinical cure.
5. In order to; to that end; to this end
These are helpful academic phrases to introduce an explanation or state your aim. Oftentimes your essay will have to prove how you intend to achieve your goals. By using these sentences you can easily expand on points that will add clarity to the reader.
For example: My research entailed hours of listening and recording the sound of whales in order to understand how they communicate.
Dutch tech companies offer support in the fight against the virus. To this end, an online meeting took place on Wednesday...
Even though we recommend the use of these phrases, DO NOT use them too often. You may think you sound like a real academic but it can be a sign of overwriting!
6. In other words; to put it another way; that is; to put it more simply
Complement complex ideas with simple descriptions by using these sentences. These are excellent academic phrases to improve the continuity of your essay writing. They should be used to explain a point you’ve already made in a slightly different way. Don’t use them to repeat yourself, but rather to elaborate on a certain point that needs further explanation. Or, to succinctly round up what just came before.
For example: A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between phenomena. In other words, there is no treatment effect.
Nothing could come to be in this pre-world time, “because no part of such a time possesses, as compared with any other, a distinguishing condition of existence rather than non-existence.” That is, nothing exists in this pre-world time, and so there can be nothing that causes the world to come into existence.
7. Similarly; likewise; another key fact to remember; as well as; an equally significant aspect of
These essay words are a good choice to add a piece of information that agrees with an argument or fact you just mentioned. In academic writing, it is very relevant to include points of view that concur with your opinion. This will help you to situate your research within a research context.
Also , academic words and phrases like the above are also especially useful so as not to repeat the word ‘also’ too many times. (We did that on purpose to prove our point!) Your reader will be put off by the repetitive use of simple conjunctions. The quality of your essay will drastically improve just by using academic phrases and words such as ‘similarly’, ‘as well as’, etc. Here, let us show you what we mean:
In 1996, then-transport minister Steve Norris enthused about quadrupling cycling trips by 2012. Similarly, former prime minister David Cameron promised a “cycling revolution” in 2013…
Or Renewable Energy Initiative (AREI) aims to bridge the gap of access to electricity across the continent (...). Another key fact to remember is that it must expand cost-efficient access to electricity to nearly 1 billion people.
The wording “not only… but also” is a useful way to elaborate on a similarity in your arguments but in a more striking way.
Comparing and contrasting information
Academic essays often include opposite opinions or information in order to prove a point. It is important to show all the aspects that are relevant to your research. Include facts and researchers’ views that disagree with a point of your essay to show your knowledge of your particular field of study. Below are a few words and ways of introducing alternative arguments.
8. Conversely; however; alternatively; on the contrary; on the other hand; whereas
Finding a seamless method to present an alternative perspective or theory can be hard work, but these terms and phrases can help you introduce the other side of the argument. Let's look at some examples:
89% of respondents living in joint families reported feeling financially secure. Conversely, only 64% of those who lived in nuclear families said they felt financially secure.
The first protagonist has a social role to fill in being a father to those around him, whereas the second protagonist relies on the security and knowledge offered to him by Chaplin.
“On the other hand” can also be used to make comparisons when worded together with “on the one hand.”
9. By contrast; in comparison; then again; that said; yet
These essay phrases show contrast, compare facts, and present uncertainty regarding a point in your research. “That said” and “yet” in particular will demonstrate your expertise on a topic by showing the conditions or limitations of your research area. For example:
All the tests were positive. That said, we must also consider the fact that some of them had inconclusive results.
10. Despite this; provided that; nonetheless
Use these phrases and essay words to demonstrate a positive aspect of your subject-matter regardless of lack of evidence, logic, coherence, or criticism. Again, this kind of information adds clarity and expertise to your academic writing.
A good example is:
Despite the criticism received by X, the popularity of X remains undiminished.
11. Importantly; significantly; notably; another key point
Another way to add contrast is by highlighting the relevance of a fact or opinion in the context of your research. These academic words help to introduce a sentence or paragraph that contains a very meaningful point in your essay.
Giving examples
A good piece of academic writing will always include examples. Illustrating your essay with examples will make your arguments stronger. Most of the time, examples are a way to clarify an explanation; they usually offer an image that the reader can recognise. The most common way to introduce an illustration is “for example.” However, in order not to repeat yourself here are a few other options.
12. For instance; to give an illustration of; to exemplify; to demonstrate; as evidence; to elucidate
The academic essays that are receiving top marks are the ones that back up every single point made. These academic phrases are a useful way to introduce an example. If you have a lot of examples, avoid repeating the same phrase to facilitate the readability of your essay.
Here’s an example:
‘High involvement shopping’, an experiential process described by Wu et al. (2015, p. 299) relies upon the development of an identity-based alliance between the customer and the brand. Celebrity status at Prada, for example, has created an alliance between the brand and a new generation of millennial customers.
Concluding your essay
Concluding words for essays are necessary to wrap up your argument. Your conclusion must include a brief summary of the ideas that you just exposed without being redundant. The way these ideas are expressed should lead to the final statement and core point you have arrived at in your present research.
13. In conclusion; to conclude; to summarise; in sum; in the final analysis; on close analysis
These are phrases for essays that will introduce your concluding paragraph. You can use them at the beginning of a sentence. They will show the reader that your essay is coming to an end:
On close analysis and appraisal, we see that the study by Cortis lacks essential features of the highest quality quantitative research.
14. Persuasive; compelling
Essay words like these ones can help you emphasize the most relevant arguments of your paper. Both are used in the same way: “the most persuasive/compelling argument is…”.
15. Therefore; this suggests that; it can be seen that; the consequence is
When you’re explaining the significance of the results of a piece of research, these phrases provide the perfect lead up to your explanation.
16. Above all; chiefly; especially; most significantly; it should be noted
Your summary should include the most relevant information or research factor that guided you to your conclusion. Contrary to words such as “persuasive” or “compelling”, these essay words are helpful to draw attention to an important point. For example:
The feasibility and effectiveness of my research has been proven chiefly in the last round of laboratory tests.
Film noir is, and will continue to be, highly debatable, controversial, and unmarketable – but above all, for audience members past, present and to come, extremely enjoyable as a form of screen media entertainment.
17. All things considered
This essay phrase is meant to articulate how you give reasons to your conclusions. It means that after you considered all the aspects related to your study, you have arrived to the conclusion you are demonstrating.
After mastering the use of these academic words and phrases, we guarantee you will see an immediate change in the quality of your essays. The structure will be easier to follow, and the reader’s experience will improve. You’ll also feel more confident articulating your ideas and using facts and examples. So jot them all down, and watch your essays go from ‘good’ to ‘great’!
Essay exams: how to answer ‘To what extent…’
How to write a master’s essay.
- academic writing
- writing a good essay
- writing essays
- writing tips
Writing Services
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Editing Service Examples
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.
The Ivy Coach Daily
- College Admissions
- College Essays
- Early Decision / Early Action
- Extracurricular Activities
- Standardized Testing
- The Rankings
September 6, 2024
Common App Word Count Limit: How Long Should My Essay Be?

You should always use all the real estate they give you when writing your application essays. This means going to the maximum word limit , or as close as possible to it, on every written prompt. Just like the employee who shows up to the office late and leaves early appears lazy and uninterested in their job, the applicant who doesn’t take advantage of every last word seems to have better things to do than write their college application essays. And if you’re an academically ambitious high schooler intent on attending a highly selective college, you quite literally don’t have anything better to do than give your application your all. Your future is counting on it!
You might think those 100-character prompts often found in college supplements don’t apply to this rule, but think again. You want to max the word or character count wherever you see a blank space waiting for you to fill with words — with one notable exception.
What Is the Common App Essay Word Count Limit?
The Common Application’s Personal Statement has a word limit of 650; you should go up to that limit or risk coming across as noncommittal. But is that all there is to this story? Not quite.
How to Use the Common App Additional Information Section
There is an age-old expression in elite college admissions that many students in 2024 are blissfully unaware of: “The thicker the file, the thicker the student.” Are we at Ivy Coach contradicting ourselves? No. We’re referring to the Additional Information section of The Common App. We often get prospective clients who come to us for a PostMortem after rejection from their top school. They have no idea what they could have possibly done wrong, and yet when one of our former elite college admissions officers takes a look at their application, the Additional Information section is filled with redundancies and superfluous information!
The Additional Information section should only include courses taken outside of school (along with corresponding grades) or list genuinely impressive activities that didn’t make it onto the activities list but complement your singular admissions hook . It’s also okay to include a published abstract in this section (unless the school has a section for abstracts, like Columbia University . Don’t make admissions officers read the same thing twice — their time is valuable!). Each time you apply, The Common App. will save the current incarnation of your application. So, be sure to check for redundancies before each submission (e.g., delete the abstract in Additional Information for Columbia if you’re including it under the Abstract section).
In most cases, the Additional Information section should be left blank. Fill out those essays (including the optional ones!). Go up to the maximum word count wherever possible. But don’t include a link to a video of your violin performance if your singular hook is computer science. Don’t include a poem if your hook is environmental advocacy. Your singular hook should be the focus of your application, and the Additional Information section should only include information that supports or enhances this hook.
Respect the Time of Admissions Officers
Don’t waste admissions officers’ time — applicant pools to elite schools have swelled to the tens of thousands in recent years. They’ll probably only give your application a total of 8 minutes of consideration. This, of course, is more than enough time. The 8-minute rule is a guideline that suggests admissions officers spend about 8 minutes on each application, given the large number of applications they have to review. You don’t want to thrust them into a situation where they spend most of those precious 8 minutes deciphering some extraneous information that makes you a less competitive applicant.
If navigating these confusing and seemingly contradictory rules about applying to highly selective schools makes your head spin, take out the guesswork by relying on Ivy Coach ’s team of former elite college admissions officers to help your child earn admission to the school of their dreams. We will ensure their application communicates their singular hook as efficiently and effectively as possible.
If you’re interested in optimizing your child’s case for admission to a highly selective college, fill out our complimentary consultation form , and we’ll be in touch.
You are permitted to use www.ivycoach.com (including the content of the Blog) for your personal, non-commercial use only. You must not copy, download, print, or otherwise distribute the content on our site without the prior written consent of Ivy Coach, Inc.
Related Articles

Common App vs. Coalition App: Which Should You Choose?
May 28, 2024

What Is Common Application Account Rollover?
May 23, 2024

The Rhodes Scholarship: 2024 Rhodes Scholars
May 18, 2024

The Pros and Cons of Applying Through The Common Application
September 28, 2023

When Are College Applications Due?
September 18, 2023

Ethnic Background Subcategories on The Common Application
April 20, 2023
TOWARD THE CONQUEST OF ADMISSION
If you’re interested in Ivy Coach’s college counseling, fill out our complimentary consultation form and we’ll be in touch.
Fill out our short form for a 15-minute consultation to learn about Ivy Coach’s services.

COMMENTS
40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays
History words ... History words
How to write an introduction for a history essay
A Brief Guide to Writing the History Paper - Harvard University
Essays are an essential educational tool in disciplines like history because they help you to develop your research skills, critical thinking, and writing abilities. The best essays are based on strong research, in-depth analysis, and are logically structured and well written. An essay should answer a question with a clear, persuasive argument.
Writing Historical Essays - Department of History
How to Write a History Essay
Writing a history paper requires much more than just sitting down at a computer. It involves a lot of early planning, detailed research, critical thinking, skilled organization, and careful writing and rewriting. The first rule of essay writing is to start early so that you have plenty of time to follow these steps.
Writing a history essay
How To Write a Good History Essay
reading and taking notes, writing an outline, composing a draft, and revising your draft into a. polished essay. These stages often overlap. This guide addresses some of the most common questions related to researching, writing, and formatting a history research paper. It provides visual examples for the main stages of the.
Write in the past tense when discussing history. If a historical event took place in the past, write about it in the past. Be precise. Focus on your thesis and only provide information that is needed to support or develop your argument. Be formal. Try not to use casual language, and avoid using phrases like "I think.".
led instruction.• write in a formal, academic voice. Avoid using the first or second person (e.g., "i" and "you"), and shy away from passive sentence constructions. phrases such as "i think" or. in my opinion" are redundant in. xpository writing.• Proof. for fUrTHer reading. f writing history s.
Also, avoid passive voice phrases, redundant constructions, and generalizations. Take care of thorough proofreading. You have made it: your history essay is ready and waits to be polished. The editing stage is crucial as even the brightest ideas can get lost in a sea of mistakes, impurities, and vague phrases.
Download Article. 1. Have a clear structure. When you come to write the body of the essay it is important that you have a clear structure to your argument and to your prose. If your essay drifts, loses focus, or becomes a narrative of events then you will find your grade dropping.
If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece. Most essays will require you to write: 1 Introduction Paragraph. 3 Body Paragraphs. 1 Concluding Paragraph.
Writing a history essay requires a lot of work and experience. A student needs to show a high level of knowledge and understanding of historical events, as well analytical and research skills. No wonder many students find it challenging to compose a well-written essay! To achieve success, use the following tips to level-up your writing abilities
Tips from my first year - essay writing | Faculty of History
Make it Shine. An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it's achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine: Write a substantial introduction.
30+ History Essay Examples to Help You Get Started
Don'ts: Don't plagiarize: Plagiarism is a serious offense and can result in a failing grade. Always make sure to give credit to the sources you have used in your essay. Don't use too much ...
17 academic words and phrases to use in your essay
You should always use all the real estate they give you when writing your application essays. This means going to the maximum word limit, or as close as possible to it, on every written prompt. Just like the employee who shows up to the office late and leaves early appears lazy and uninterested in their job, the applicant who doesn't take advantage of every last word seems to have better ...