- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by

Taking On the Ph.D. Later in Life

By Mark Miller
- April 15, 2016
ROBERT HEVEY was fascinated by gardening as a child, but then he grew up and took a 30-year career detour. Mr. Hevey earned a master’s in business and became a certified public accountant, working for accounting firms and businesses ranging from manufacturing to enterprise software and corporate restructuring.
“I went to college and made the mistake of getting an M.B.A. and a C.P.A.,” he recalled with a laugh.
Now 61, Mr. Hevey is making up for lost time. He’s a second-year Ph.D. student in a plant biology and conservation program offered jointly by Northwestern University and the Chicago Botanic Garden. Mr. Hevey, whose work focuses on invasive species, started on his master’s at age 53, and he expects to finish his doctorate around five years from now, when he will be 66.
“When I walk into a classroom of 20-year-olds, I do raise the average age a bit,” he says.
While the overall age of Ph.D. candidates has dropped in the last decade, about 14 percent of all doctoral recipients are over age 40, according to the National Science Foundation. Relatively few students work on Ph.D.s at Mr. Hevey’s age, but educators are seeing increasing enrollment in doctoral programs by students in their 40s and 50s. Many candidates hope doctorates will help them advance careers in business, government and nonprofit organizations; some, like Mr. Hevey, are headed for academic research or teaching positions.
At Cornell University, the trend is driven by women. The number of new female doctoral students age 36 or older was 44 percent higher last year than in 2009, according to Barbara Knuth, senior vice provost and dean of the graduate school.
“One of the shifts nationally is more emphasis on career paths that call for a Ph.D.,” Dr. Knuth said. “Part of it is that we have much more fluidity in career paths. It’s unusual for people to hold the same job for many years.”
“The people we see coming back have a variety of reasons,” she added. “It could be a personal interest or for career advancement. But they are very pragmatic and resilient: strong thinkers, willing to ask questions and take a risk in their lives.”
Many older doctoral candidates are motivated by a search for meaning, said Katrina Rogers, president of Fielding Graduate University in Santa Barbara, Calif., which offers programs exclusively for adult learners in psychology, human and organizational development and education.
“Students are asking what they can do with the rest of their lives, and how they can have an impact,” she said. “They are approaching graduate school as a learning process for challenging themselves intellectually, but also along cognitive and emotional lines.”
Making a home for older students also makes business sense for universities and colleges, said Barbara Vacarr, director of the higher education initiative at Encore.org, a nonprofit organization focused on midlife career change. “The convergence of an aging population and an undersupply of qualified traditional college students are both a call to action and an opportunity for higher education.”
Some schools are serving older students in midcareer with pragmatic doctoral programs that can be completed more quickly than the seven or eight years traditionally required to earn a Ph.D. Moreover, many of those do not require candidates to spend much time on campus or even leave their full-time jobs.
That flexibility can help with the cost of obtaining a doctorate. In traditional programs, costs can range from $20,000 a year to $50,000 or more — although for some, tuition expenses are offset by fellowships. The shorter programs are less costly. The total cost at Fielding, for example, is $60,000.
Susan Noyes, an occupational therapist in Portland, Me., with 20 years’ experience under her belt, returned to school at age 40 for a master’s degree in adult education at the University of Southern Maine, then pursued her Ph.D. at Lesley University in Cambridge, Mass. During that time, she continued to work full time and raise three children. She finished the master’s at 44 — a confidence-builder that persuaded her to work toward a Ph.D. in adult learning, which she earned at age 49.
Dr. Noyes, 53, made two visits annually to Lesley’s campus during her doctoral studies, usually for a week to 10 days. She now works as an assistant professor of occupational therapy at the University of Southern Maine.
At the outset of her graduate education, Dr. Noyes wasn’t looking for a career change. Instead, she wanted to update her skills and knowledge in the occupational therapy field. But she soon found herself excited by the chance to broaden her intellectual horizons. “I’ve often said I accidentally got my Ph.D.,” she said.
Lisa Goff took the traditional Ph.D. path, spending eight years getting her doctorate in history. An accomplished business journalist, she decided to pursue a master’s degree in history at the University of Virginia in 2001 while working on a book project. Later, she decided to keep going for her doctorate, which she earned in 2010, the year she turned 50. Her research is focused on cultural history, with a special interest in landscapes.
Dr. Goff had planned to use the degree to land a job in a museum, but at the time, museum budgets were being cut in the struggling economy. Instead, a university mentor persuaded her to give teaching a try. She started as an adjunct professor in the American studies department at the University of Virginia, which quickly led to a full-time nontenure-track position. This year, her fourth full year teaching, her position was converted to a tenure-track job.
“I thought an academic job would be grueling — not what I wanted at all,” she recalls. “But I love being in the classroom, finding ways to get students to contribute and build rapport with them.”
As a graduate student, she never found the age gap to be a challenge. “Professors never treated me as anything but another student, and the other students were great to me,” Dr. Goff said. The toughest part of the transition, she says, was the intellectual shock of returning to a rigorous academic environment. “I was surprised to see just how creaky my classroom muscles were,” she recalled. “I really struggled in that first class just to keep up.”
Mr. Hevey agrees, saying he has experienced more stress in his academic life than in the business world. “I’m using my brain in such a different way now. I’m learning something new every day.”
His advice to anyone considering a similar move? “Really ask yourself if this is something you want to do. If you think it would just be nice to be a student again, that’s wrong. It’s not a life of ease: You’ll be working all the time, perhaps for seven or eight years.”
Mr. Hevey does not expect to teach, but he does hope to work in a laboratory or do research. “I’m certainly not going to start a new career at 66 or 67,” he said. “But I’m not going to go home and sit on the couch, either.”
Make the most of your money. Every Monday get articles about retirement, saving for college, investing, new online financial services and much more. Sign up for the Your Money newsletter here .
Let Us Help You Plan for Retirement
The good news is that we’re living longer. the bad news is you need to save for all those future retirement years. we’re here to help..
For a growing number of older Americans, signing up for a mortgage that is most likely to outlive them makes good economic sense. But there are risks to consider .
If you’re on Medicare, you could save money on prescription drugs this year — in many cases, by thousands of dollars. Here’s why .
Entering your 40s can throw you into an emotional tailspin — one that may lead you to spend more and jeopardize your nest egg. Here is how to avoid that .
It’s difficult to know when to get help managing finances after you retire . Communicating with loved ones, even when you don’t want to, is the first step.
These days, many Americans thinking about retiring feel the stakes are higher than ever. We sought the advice of financial planners on some of the most pressing questions.
Retirement plan administrators are noting an uptick in 401(k) hardship withdrawals . But taking that money out can harm your future financial security.
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
Average age of a phd student: when is it too late, published by steve tippins on june 16, 2022 june 16, 2022.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 02:36 am
In 2020, the average age of a graduate from a PhD program in the United States was 33. However, 6% of the graduates were over 45.
When people ask what the average age of a PhD student is, many times they’re really asking, “Am I too old to get a PhD?” The answer is almost always no. Let’s explore some different scenarios.
When Is It Too Late to Get a PhD?
As an academic career coach, I’ve been asked by more than a few people if it’s too late for them to get a PhD. Some of these people were even in their twenties, worried that working for two years after their undergraduate degree had inexorably barred them from the halls of academia.
Others were past middle age, looking for a career change. In either case, the answer is ultimately no, it’s not too late to get a PhD . However, there are some important things to keep in mind if this is something you’re considering.
Getting a PhD for Your Career

Let’s say you want to get a PhD to pursue a career in academia or elsewhere. You enter a PhD program at 25 or even 30, the average PhD duration takes six to eight years. That means you will finish when you are around 30 to 37. The normal retirement age to get Social Security in the United States is 67, so that’s at least 30 years ahead of you – lots of time for your career. If you look around academia, there’s a lot of people older than 67.
You have a chance for a very long career, even if you’re 42 and finish your PhD at 50. That’s still over 15 years before retirement age. These days, very few people stay at a job for 15 years. Rest assured that you have ample opportunity to have a meaningful career.
Over 50% of doctoral candidates don’t finish their dissertations.
Student Loan Debt Considerations
If you’re 61 and taking loans out, it will be a while before you pay those off. Debt is something to think about before getting a PhD. If you can get into a PhD program that pays your tuition or even provides you a stipend, you may be able to graduate with a much smaller student loan debt. That assistance could allow you to consider a PhD later in life.
What Is the Minimum Age for Getting a PhD?

To get a PhD, you have to have graduated from undergraduate school. From there, some people can go right into a PhD program. If you graduate at the traditional age of 22, you’d be getting your PhD somewhere around age 25 at a minimum.
There are stories about people who graduate from high school at 12 and college at 16. They could theoretically get their PhD at 19 or 20. However, people like this are quite rare.
Can You Get a PhD by Age 25?
It is possible to get a PhD by age 25, particularly if you graduate from college at 21 or 22. If it takes three or four years to get a PhD, you could graduate by 25.
What Is The Best Age to Get a PhD?
The best age to get a PhD is three years ago. The second best time is now. In reality, the best age to get a PhD is whenever you are able to complete it. The earlier you finish your PhD, the more of a life and career you’ll have with it , but there is no optimal age.
Does Having a Master’s Shorten the Time it Takes to Get a PhD?

Having a Master’s can shorten the time it takes to get a PhD , depending on your discipline. If PhD programs in your discipline are structured such that they assume you have a Master’s before you enter, then yes, you’re going to finish a PhD faster.
If you enter without a Master’s, you may have to get the Master’s first to be allowed in the PhD program. Otherwise, you may have to take some remedial coursework. If your discipline is not set up in that manner, having a Master’s may not allow you to move faster.
Final Thoughts
As society ages and with employers having problems finding eligible workers, the problem of ageism will become less severe. Getting a PhD at any age is going to be a viable option. If you are interested in a PhD and it’s something you have a burning desire to do, don’t let age stop you.

Are you considering getting your PhD? We’re here to help. Check out our Dissertation Coaching and Academic Career Coaching services.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
Phd by publication.
PhD by publication, also known as “PhD by portfolio” or “PhD by published works,” is a relatively new route to completing your dissertation requirements for your doctoral degree. In the traditional dissertation route, you have Read more…

What Does Ph.D. Stand For?
“What does Ph.D. stand for?” This is a question that can be answered several different ways. First of all, typically Ph.D. stands for doctor or doctorate in philosophy. I know that can be a little Read more…

A Professor’s Top 3 Pieces of Advice for Ph.D. Students
When it comes to getting a Ph.D., there is no one-size-fits-all approach to ensuring success in graduate school. Every student must find their own path to navigating the most rigorous academic experience that most people Read more…
Subscribe to Updates
Get the latest creative news from FooBar about art, design and business.
By signing up, you agree to the our terms and our Privacy Policy agreement.
10 Time Management Tips for Older PhD Students Who Want to Balance Work and Studies
Breaking barriers: empowering black women over 40 to excel in information systems phd programs. , the top 8 must-know tips for phd preparation: how to get started.

You’ve Decided to Pursue a PhD in Your 40s – Now, What?
First, I want to say congratulations on deciding to pursue a PhD in your 40s. Now that the big decision is made, let’s move to some less daunting activities that’ll get you sitting in your first classroom in a few months. ( Please note that the steps in this post are mainly directed toward pursuing a traditional Ph.D. However, these steps should also apply to DBA and Executive PhDs. ).
I classify these as early activities and application activities.
Early Decisions to Pursue a PhD
The early activities involve some early decisions you must make. These decisions include; the location of the PhD program, the PhD concentration, and what to study. Once you have answers to these questions, the rest of the application process becomes a little more straightforward.
#1 Location:
The general location where you desire to do your pursue a PhD should be decided. For the most part, if you’re pursuing a PhD in your 40s, there’s a chance you have settled in a particular location. This means that you prefer to do a PhD near or around that location. On the other hand, you may be looking for a fresh start in life and have the flexibility to choose where you want to do it. In that case, you have many more location options: North, South, West, or East.
#2 Schools:
After you’ve decided on the general location, it’s time to hone in on the school or schools. If possible, try not to make that decision blindly. In other words, try and find someone who might tell you one or two things about the schools, the culture especially. Given that pursue a PhD education is more than just schooling, it’s important that you understand the culture of the people you’ll be working very closely with for 4 years. Some PhD programs are collegial. Others are not and could be stressful. If you’re in your 40s and 50s and seeking your pursue a PhD, you probably want to avoid PhD programs with non-collegial cultures.
#3 PhD Concentration:
There are many PhD concentrations in business schools. The one you select should complement your current skills or experiences. For example, if you are a technologist, you might consider pursue a PhD concentration in information systems. You might consider management science or operations research if you are a math or statistics professional. See our post on concentrations.
Application Activities for a PhD in your 40s’
Now Let’s look at some of the requirements for gaining admission to a Ph.D. program. PhD program requirements include taking a GRE/GMAT, identifying and sending your transcripts (bachelors and masters), writing your personal statement, securing some good recommendation letters, etc. Figure 1 is a visual of those steps. Steps 1 to 5 can take about 6 months to 1 year. We address GRE/GMAT and transcripts in this post.

#1 GRE/GMAT
If you’ve taken a GRE/GMAT within the last 5 years, then you can skip this step. If you have not, you should start studying for the GMAT or GRE exam. Most universities in the US accept either of these. However, if you have a clearer idea of the schools you’ll like to apply to, you should find out their preference. Usually, this information is posted on their Ph.D. information website.
#2 Get ready to send your transcripts:
If you’re a domestic student, the process of sending your transcripts to your schools of interest usually takes a few simple steps. Most universities have an automated process that allows former students to log in and order and sends their transcripts to schools for a small fee.
The process is a lot more involved if you’re an international student. International transcripts sometimes need to be evaluated and translated. There are college credential evaluation services that could evaluate your transcripts for a fee. This process can take a longer time to complete than you initially anticipated. So, plan accordingly. You could also call the graduate office of your schools of interest and ask if they could recommend an evaluation service or if they do the transcript evaluation themselves. Some schools do. So, it’s worth a try.
See more on writing your personal statement and securing some good recommendation letters .
Related Posts
7 tangible strategies for coping with burnout while pursuing your phd after 40, a 2023 resolution to start a phd in information systems – make a bold move, 7 career options: what you can do with a phd in information systems or technology, is it worth it to get a phd in information systems.
Comments are closed.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

Getting a PhD in Your 50s and 60s: The Ultimate Guide
There’s a significant rise in the number of mature students returning to university to complete postgraduate degrees. You plan to be one of them. But you find yourself asking if it is feasible to start getting a PhD in your 50s and 60s.
It’s never too late getting a PhD in your 50s and 60s because there’s no age limit in the pursuit of higher education. To give you a head start on this exciting new endeavor, we present to you the ultimate guide to getting a PhD in your prime years.
It is critical to know what to expect, such as the challenges and benefits of reviving an academic existence as a mid- or late-career student, so you can plan for the years ahead. Read on to find out how.
Why You Should Pursue a PhD at a Later Stage in Life
Why would anyone in their right mind regurgitate a period of woe and misery in their golden years when they should already be relaxing? Well, many people, not just nerds, love studying.
There’s an entire population dedicated to life-long learning. They form the bulk of those going back to school to complete degrees that were halted mid-life due to the untimely arrival of kids, financial downfall, death in the family, or other unfortunate circumstances. These mature students don’t need a reason to return to school. Their passion drives them.
For others, the purpose is economical. Those in the middle of their career embark on a PhD to change its direction, improve their prospects, upgrade their qualification set, or to accrue further knowledge. In fields like teaching and research, a doctorate is a veritable advantage.
Nina Grunfeld , founder of Life Clubs , a network that helps people achieve life changes, explains that many, particularly women, want to return to study because they’re disgruntled or have a desire to improve themselves, revive their career, or discover new passions.
“A milestone age is often a trigger,” Grunfeld adds.
“At the Open University , favored by many part-time learners, numbers of postgraduate students over the age of 45 have been increasing steadily for the past three years, with the greatest rise (32%) in students over 65.”
Others undertake a PhD to crown a significant achievement or just to prove they can do it. This writer’s friend did it to slap her diploma in the face of her wealthy future sister-in-law, who denigrated her economic status. Education, after all, is one of the world’s greatest equalizers.
Most crave a PhD for the prestige the three letters can add to their names. If, however, you have a natural yearning for knowledge and in-depth study of a subject you’re passionate about, the heck with your age. Go for it!

Reasons Not to Get a PhD
Thoroughly assess your reasons for pursuing a PhD, because although it’s fulfilling academically, it’s also a huge financial commitment. If you’re dissatisfied with your current job, or you think it would just be fun to be a student again, neither will give you the strength to withstand the rigors of extreme study.
On the other hand, if you’re sure that gaining this qualification will fit in with your life goals, then forge ahead!
The Benefits of Pursuing a PhD
Do you want a research doctorate, or do you want to teach? Both are the standard reasons for undertaking PhD studies. Once completed, a PhD will make you an expert in your chosen field, possibly even beyond borders!
Apart from aspects previously mentioned, especially beneficial for older people is the fact that learning builds new neural connections that improve cognitive ability, memory function, and problem-solving ability. Education is also good for boosting one’s spirit. Classroom or online learning is a social endeavor that breaks isolation and fosters social connections.
According to the American Council on Education , social connection with teachers and peers is one of the reasons mature students over 50 pursue higher learning.
There are retirement communities (some located on campus) that partner with colleges and universities to offer residents post-secondary courses. Most of these are on the East Coast, but there are a couple in California and Florida.
Political scientist Chris Blattman explains how a PhD intangibly molds an individual: “A PhD program doesn’t just teach you, it socializes you. It gradually changes what you think is interesting and important, the peer group you compare yourself to, the value you place on leisure and family over career, and the kind of life you will value when you emerge.”
How Long Does It Take to Complete a PhD Program?
Most full-time students can complete theirs in five to six years. Part-timers can take as long as eight to 10 years. Students with a master’s degree complete their PhD in four or five years.
Some programs, like the MACRM (Master of Arts in Public Policy with Certificate in Research Methods) at the University of Chicago’s Harris Public Policy , offer a combination of methods. This master’s program provides intense and applied research training plus the option of a PhD at the end.
Study Methods
Studying for a PhD here is different compared to Europe. Our students are usually in direct contact with their professors. They’re expected to do a lot of teaching and marking, which encroaches on their free time off-campus. The earlier you accept this, the better you’ll cope and adopt solutions.
According to the World Economic Forum , the USA had the most doctoral graduates in 2017: 71,000. Germany and the UK followed, with 28,000 each.
In 2016, about 14% of all doctoral recipients were over age 40, per the National Science Foundation . Educators see increasing enrollment in doctoral programs by students in their 40s and 50s.
At Cornell University , women drive the trend . “The number of new female doctoral students age 36 or older was 44% higher in 2015 than in 2009,” says Barbara Knuth , senior vice provost and dean of the graduate school.
What Are the Requirements?
Generally, a PhD applicant should have completed a relevant undergraduate degree. Ideally, he should have also secured a master’s degree (with substantial research) in a related subject. Thankfully, this is optional here. Most PhD programs in the US, unlike in the UK, don’t require a master’s degree for admission. Students can move straight to doing a PhD with an undergraduate degree.
Here’s a sample of PhD requirements from the University of California, Berkeley , a public research university regarded as one of our most prestigious. This is a list of their graduate programs and application deadlines. We chose Berkeley as an example, because it had the highest number of top-ranked doctoral programs nationwide, according to a National Research Council report .
Required documentation includes, but isn’t limited to official transcripts, course descriptions from previous institutions attended, proof of language proficiency, references, and cover letters.
How to Apply
For admission to your chosen institution, visit its website. Check its rankings, course listings, faculty, and requirements specific to your field of study. Talk to other students and professors, learn about your desired department, and uncover the social scene.
Deadlines for applications to PhD programs are usually between December and February. You’ll get an answer by April. Most institutions recommend that you apply way in advance to give both parties plenty of time for arrangements. They require international students to have a TOEFL score of around 90, but this varies depending on the institution.
In Europe, students choose their PhD subject area before they apply. Here, potential PhD students can take up to a year or two deciding on their research subject while attending classes at a graduate level. Students normally apply to more than one institution—and separately because there’s no central organization that processes applications.
Students in Europe are expected to apply with existing knowledge of the subject via a master’s degree. They begin PhD studies right away. Here, universities accept that students don’t have an in-depth understanding of their subject and permit them to decide later.
Tips to Get a (Slight) Advantage
Get the best quality general research pre-training possible. Apply to as many top schools as you can. Visit all the institutions that accepted you. Narrow down your choices according to fit and quality.
Applying to many places is crucial because the admissions process is competitive and random. Whittling 100 promising candidates down to 30 is subjective. Even outstanding candidates might not be admitted.
Institutions are more likely to admit you if you demonstrate a good fit with their faculty. That’s why you have to research the faculty and their work, and explain how you fit in. Mention in your cover letter the staff members you see as complementary to your research. Note that deciding committees in politics programs take cover letters more seriously than their counterparts in economics.
Strive to gain entry into one of the top 10 schools in your field because it gives you a better chance at an academic job. This is true in economics, the most hierarchical field in social science.
Which University Should You Attend?

Rankings shouldn’t be the main deciding factor, but they’re an excellent indicator of educational expertise. To choose the best from the 4,000 nationwide, see this list of our best universities in 2020 and how they feature in worldwide rankings. The top five are Stanford University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, California Institute of Technology, Harvard University, and Princeton.
How to Choose the Right Institution
Consider these factors.
Your field of study, their programs, specialties, facilities, and faculty rating. Your choice depends on your preferred career and the course credit you’ve accumulated.
If you’re certain about your field of interest and feel confident it will sustain you for the entire program, you’ll have a greater chance of getting accepted.
Researching their specialties will tell you if they’re appropriate for your area of study. See what areas they’ve worked in, their study focus, what they’ve published, and how well their work has been received. Also, investigate the quality of their student-faculty, as a postgrad study is collaborative and intense. You need to have the right people in your group.
What is the university best known for? Choose one renowned in the field you’re interested in to ensure you have the appropriate experts on hand to help you. Evaluate the kinds of research projects done in the university.
Choosing a venue depends on your circumstances. Staying near your home allows you to work part-time while studying. Most PhDs require only occasional visits to the university, so you may opt to take the course far from home, then travel when necessary. Alternatively, you could move closer to your university for greater immersion into the social scene and a closer connection to the student community.
If you choose to study away from home, contact your chosen university’s accommodation office first. Many university towns have student accommodation in place, but spots tend to go quickly, so apply early. Next, research on- and off-campus accommodation. Check online local listings and bulletin boards for private rentals.
Social Life
Check out student life on social media. What organizations do they have? Are they the sort you would want to join?
Staff/Student Ratio
The more staff available to each student, the better.
Choose From These Categories of Institutions
- Public Universities (aka state colleges)—open to anyone who qualifies. They’re funded by state governments. Being larger, they can accommodate many students and offer a wide variety of degree programs. Some offer scholarships.
- Private Non-Profit Colleges —their tuition is much higher than that of state universities or community colleges, but they don’t profit from it. As they’re smaller, they offer specific courses and specialized degrees. They receive funds only from tuition fees and donations.
- Private For-Profit Colleges —similar to non-profits in course study and general cost, but they’re set up as a business. This affects the type of degree programs offered.
- Liberal Arts Colleges —offer one expansive area of study rather than specific degree tracks. As they’re smaller, instructors give you more attention. Though most focus on undergraduate education, some offer good postgraduate degree programs too. Campus culture is quite different from that of a traditional university.
- Online Postgraduate Colleges —perfect for those juggling jobs and family as it offers flexibility in assignment completion. Most coursework and classroom discussions are held online, but you may have to go to a physical classroom part of the time, especially as you get closer to graduation. An online degree is as valuable as one you physically attend.
Ask Your Intended University These Questions
- What are my chances of finding a job after graduation? See the career prospects below.
- How flexible is your program? This depends on the subject area. The Humanities and the Arts offer a greater degree of flexibility than science-oriented ones. North American institutions offer slightly less flexibility than their European counterparts. See whether you can pick and choose components, or if the whole program is indelibly fixed from beginning to end.
- What research resources are available? Decent computer networks and an equipped library are not enough. Serious research requires office-based administration support, reprographic services, and essentials of a proper business center. Disregard any institution that lacks support.
- How versatile is your department? Some departments prefer one research method. Others favor newer ones, non-traditional teaching styles, or a radical approach. Extensive departments offer a wider spectrum of methods and potential areas of study. You may thrive better with a broader tradition of research methodologies or value the security of knowing what is expected of you.
- What are your non-academic amenities? Also, check out other facilities, like leisure programs, for maintaining a work/life balance. Small universities in remote towns offer lesser cultural or social options.
How to Get Into a Top Institution
Entry into the top 10 or 15 schools is extremely competitive. Focus on getting exceptional recommendations, experience, grades, and GRE scores. Most departments appoint a small committee of four to six faculty members for admissions. The committee changes every year, so results are hard to predict.
Work on research projects with professors. Try before you commit. Become a research assistant (RA) in your department or secure RA jobs with professors in top departments in your area. This will help with references and your statement.
How to Fund Your Studies

The cost of traditional programs can vary between $20,000 to $60,000 per year. Shorter programs are cheaper. If a PhD is going to drown you in debt, think twice. Attend an institution with full funding if you can. This is often a barter deal: free tuition in exchange for research and teaching.
Another reason for applying in advance is to give plenty of time to arrange funding. Deadlines for application for funding can be as early as December for studies beginning in the fall. Many students can get part or full funding through scholarships, fellowships, bursaries, loans, and government assistance. Help is also available for parents, such as childcare subsidies, single-parent grants, bursaries, and free school meals for children.
Some PhD students will receive a university stipend with an assistantship position, but this varies between institutions and between departments within institutions. This is an example from Cornell University . Many government schemes like The Fulbright Program offer scholarships.
You can also obtain bursaries from abroad. An example is the Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries in the UK, open to all nationalities. In Canada, senior citizens can have their tuition waived for one undergraduate and graduate degree.
What to Do After Admission
Once you’ve secured funding and accommodation, these are the next steps:
Find a Supervisor
Write your research proposal if you’re self-proposing your PhD. Then find an institution and a supervising academic to support you during your research. Choose those with whom you’ll work well. To achieve this, you must network and meet people in your field of research.
Apply for an Assistantship
Doctorate assistantships are advertised on university websites and wherever academic jobs are advertised. Applications for these are very competitive, so apply for several.
Clarify Duties in Your Department
While researching and writing, many PhD students take on additional responsibilities, such as helping professors and lecturers with their classes or marking and evaluating undergraduate work. These extra tasks may be paid or not.
Prepare for Your Dissertation Early
A dissertation is a means to contribute new knowledge, theories, or practices to your field. Introduce an entirely new concept, develop it, and defend its worth. Your dissertation should be around 70,000 to 100,000 words.
Your subject area will determine if you have to write your dissertation while attending classes or do so after research completion. Regardless, preps always help at crunch time.
You are expected to defend your dissertation with a public presentation. Afterward, you will have a private session with the dissertation committee to evaluate if you’ve earned your doctorate. This is why it’s important to have a positive relationship with faculty, peers, and supervisors.
Career Prospects
What type of job can you expect after graduation?
Traditionally, graduate school hones students to become future scholars and live an intellectual life, produce innovative research, and become professors at four-year institutions. Fulfilling research careers are plentiful, but there are other ways PhD recipients can use their degrees to benefit society. For instance, they can pursue alternative academic careers in K-12 administration or the nonprofit sector.
The top 10 to 20 schools staff the top 100 to 200 universities. So PhDs outside the top 30 schools are unlikely to lead to careers in research universities, though this varies by discipline. Graduates of lower-ranked programs can work for the government or at teaching universities, international institutions, and think tanks. Job satisfaction rates are usually high.
If you aim to teach in a business department in a community college or a four-year school, an MBA may be enough. You need a doctorate, however, for a full-time job at a four-year teaching-focused school. Community colleges may hire you full-time with just a master’s, but you’ll be competing against those with doctorates.
Jobs should properly compensate you for the time spent completing your PhD. Ask your targeted institutions what the employment rate is for their graduates and their links to prospective employers. Institutions with strong ties to private companies offer more chances of future employment.
Ultimately, it boils down to your chosen subject matter. Some PhD courses like law will definitely enhance your career. Non-vocational fields like Greek mythology, however, are less likely to improve your future earning capacity or alter your career trajectory. Intellectually, of course, the reward is priceless.
Advantages of Being an Older Student
The obvious one is that your decision to return to university is likely the result of planning over several years, not a rushed, uneducated hack at the dartboard. This gives you ample time to choose your field of study.
Your work experience, professionalism, people skills, and ability to manage multiple commitments will prove invaluable throughout your studies. Course tutors also treat older students differently than their younger, undergraduate counterparts—in a good way.
Keeping Up With the Young Ones
Despite there being no age barriers in a PhD entry, age makes a difference somewhat on campus. The gap in the life experience of a young adult and a mature student is vast. The ramifications for the latter have to do with social life, interactions during class discussions and group projects, and how older students are treated by professors and non-academic staff.
For an Equal Footing…
Join organizations, societies, and sports clubs. These aren’t exclusive to undergraduate students. Not all activities are drunken, drug-crazed meet-ups. Being a part of a campus association could benefit your career development in the way of learning a unique skill or developing a new interest.
Maintaining a Balance
Many mature students return to school juggling study with family and work commitments. This makes prioritizing studies challenging. Some, especially working moms, feel guilty about not giving everyone equal attention. So they study part-time or employ creative means to manage their time.
Avenues of Support
As a mature student, you may wonder how you’ll cope with the demands of scholastic life as you’ve been out of academia for many years and can’t remember the last time you wrote an essay.
Fear not. Most universities run workshops on topics like researching, essay writing, referencing, and library use—usually at the start of the academic year. Approach your university for help with matters off-limits to family and friends. Ask your tutor for advice. Your cohort group is also a source of support and shared experiences.
The Value of Networking
Although a PhD elevates academic achievement, it doesn’t guarantee employment in your field. Networking adds value to your career and provides growth opportunities. Relationships ease career transitions needed to pursue better opportunities. Give back by sharing your connections and expertise.
Ageism and Sexism in Academia
US universities may not be perfect, but education-related discrimination is minimal compared to many countries. Be thankful for this, and take advantage of the privilege. To illustrate what women PhD applicants have to deal with in other countries, in China , you cannot apply for a PhD after age 40.
In the Philippines, admissions departments ask invasive questions and request antiquated requirements, such as copies of marriage certificates. These are requested from both foreign and local applicants but ONLY WOMEN. You may think this requirement is from a patriarchal provincial college, but it’s an item from actual requirement lists from two of the country’s Ivy League universities, which are supposed to be progressive.
The pursuit of a PhD is a life-changer. We trust the pathways we presented will help you make the right choice based on your needs and preferred course of study. Good luck with your aspirations in higher education, which will hopefully lead to your dream career. The fulfillment will surely be unparalleled.
A Scottish student in her 50s encapsulates the postgraduate sentiment impeccably: “There is value to being an older PhD student, and there is value to universities having us. There just needs to be more of us.”
- PhD Studies: Three Reasons Why It’s Never Too Late to Get a PhD
- The New York Times: Taking On the PhD Later in Life
- The Independent: Real late starter—age is no obstacle if you’re motivated
- World Economic Forum: Which countries have the most doctoral graduates?
- The World University Rankings: Best Universities in the United States 2020
- The World University Rankings: World University Rankings 2020
- Berkeley Graduate Division: Graduate Programs & Deadlines to Apply
- Berkeley News: National Research Council ranks UC Berkeley’s PhD programs among nation’s best
- Thesis Rush: Can You Get A PhD Without Masters? Let’s Find Out!
- Senior Living Blog: University-Based Retirement Communities
- Inside Higher Ed: Receiving Your Doctorate to Work at a Community College?
- Quora: What is the lowest accepted GPA for Harvard admission?
- How to apply for a Postgrad Solutions Study Bursary
- Save the Student: 10 ways American unis are different from UK unis
- Postgrad: PhD in UK
- Postgrad: PhD in USA
- Postgrad: Graduate School USA
- Postgrad: How To Get A PhD
- Postgrad: Studying for a PhD—the basics
- Postgrad: 5 Steps to Getting Ready for Postgrad Study in the USA
- Postgrad: Common PhD Myths
- Postgrad: What? Where? Why? When? How? Is A Phd Right For Me?
- Postgrad: 5 Things To Ask When Looking For A Phd
- Postgrad: What Are the Different Types of Postgraduate University in the US?
- Postgrad: PhD Studentships
Hey there, my name is Anja, I’ve seen and supported my mom’s incredible transformation in her fifties. Seeing how my mom “awakened” and took full control over her life really impressed me. I got inspired and started dreaming about how we could inspire more people, especially women, to open up and create a second life for themselves. That’s how the idea of aginggreatly.com came to life…
Recent Posts
Retire in France or Spain
Most people choose to retire in specific countries because they wish to reduce their cost of living and, at the same time, maintain a high quality of life. Spain and France are favored mostly for...
Best Places To Retire in the Caribbean
The Caribbean is one of the most exotic and affordable travel destinations globally. It consists of endless seas and beaches that make it an excellent place for a vacation. While most people view the...

Older PhDs student experiences – should you pursue a PhD later in life?
In today’s world, it’s not uncommon for individuals to change careers or pursue higher education later on in life.
For those considering a PhD program at an older age, there may be some hesitations and concerns about the experience.
- Will it be worth it?
- How difficult is it to balance academic responsibilities with other commitments such as family and work?
- What are the experiences of older PhD candidates?
- And many more questions…
In this article, we will explore the unique challenges and rewards of pursuing a PhD later in life, and share the insights and experiences of older PhD candidates.
Whether you’re considering a career change or simply seeking personal growth, read on to discover if pursuing a PhD is right for you.
Two specific case studies:
This case study explores the experiences of two mature PhD students, who despite their age, successfully navigated through their doctoral programs.
These students come from diverse backgrounds, having pursued their PhDs in Marketing and Computer Engineering. Their stories highlight the importance of determination, support systems, and practical experiences in achieving their academic goals.
Case 1: Marketing PhD Student at 48
Background:.
This student began their PhD journey at the age of 43, having accumulated 15 years of corporate experience, 5 years of teaching, and some consulting work. They decided to pursue a PhD after talking with their advisor during their master’s program.
Challenges:
One of the main challenges faced by this student was knowing when to stop working and take breaks. Managing workload and maintaining mental health were essential aspects of their PhD journey.
Key Factors for Success:
The student emphasized the importance of having a good advisor and a support network. Their prior experience in the corporate world helped them form interesting and relevant research questions. This also made them more relatable to students when teaching.
The student is now in the final stages of their PhD and has been offered a tenure-track assistant professor position at a university in New York.
Case 2: Computer Engineering PhD Student at 32
This student completed their PhD at the age of 32, having taken five years off after their master’s to work in the aerospace industry. They had always planned on getting a PhD and built significant experience in their field during their time off.
Working full-time while pursuing a PhD consumed most of their time, making it difficult to balance work, studies, and personal life. They acknowledged that having children would have added another layer of complexity to their situation.
The student’s success can be attributed to a fantastic advisor, a passionate research topic, and the ability to work from home. Their company’s financial support for their PhD program played a significant role in their decision to continue working full-time.
Having completed their PhD in three years, the student now plans to continue climbing the technical ladder within their company and aims to achieve a Technical Fellowship.
The experiences of these mature PhD students demonstrate the importance of determination, support systems, and real-world experience in successfully completing a doctoral program. Both students managed to overcome challenges and leverage their unique backgrounds to achieve their academic and professional goals.
If you want to know more about how to do a PhD at an older age you can check out my other articles:
- What is the PhD student average age? Too late for your doctorate?
- What is the average masters students age? Should you return to graduate school?
- Typical Graduate Student Age [Data for Average Age]
- Balancing PhD and family life – tips for balancing a busy life
Life Experience Helps with a doctoral degree
Life experience can be a valuable asset when pursuing a PhD. The journey towards obtaining a doctoral degree can often be challenging and demanding, requiring dedication, hard work, and resilience.
Other benefits can include:
Iindividuals with life experience may have an advantage as they already possess a certain level of maturity, self-discipline, and time-management skills.
Life experience can bring a unique perspective and insight to research, as individuals may draw from their personal experiences to inform their research questions and design.
Moreover, being part of a cohort with diverse backgrounds and experiences can also enrich the doctoral experience, leading to greater learning and growth as a researcher.
You’re never too old to become a PhD student
Age is just a number, and this is especially true when it comes to academic pursuits. It is never too late to do a PhD, as academia welcomes learners of all ages. Long gone are the days when PhD candidates had to be in their early 20s to pursue this degree.
Nowadays, more and more people in their 30s or 40s are pursuing doctoral degrees, and many have even found great success after graduation.
Here are some potential advantages and drawbacks of doing a PhD later in life:
Advantages:
- Greater maturity: You have a better understanding of what you want to do and can focus on your goals.
- Real-world experience: You have a better understanding of real-world problems and can work on more relevant research.
- Stronger mental health: Having other commitments in your life can help you maintain a better work-life balance and prevent you from dwelling on research-related stress.
- Financial resources: You may have more financial resources at your disposal, which can be helpful during your PhD journey.
- Less need for validation: You’re likely pursuing the degree for genuine reasons rather than seeking status or validation.
- Better relationships with professors: You may find it easier to connect with your professors as peers and friends.
- Research relevance: Your research may be more relevant to managers because you’ve experienced management roles.
- Time constraints: You may not have as much time to enjoy the benefits of your PhD, especially if you plan to retire in your 60s.
- Additional life commitments: You may have more personal responsibilities, such as children, a spouse, or aging parents, which can make it more challenging to balance your PhD work.
- Potential need for relocation: You may have to move around for job opportunities, which could be difficult if you have a family or other commitments.
- Opportunity cost: Pursuing a PhD at this stage in life may come at the expense of other career opportunities or financial gains.
- Difficulty in obtaining tenure: You may not obtain tenure until your late 50s, which may be a drawback for some individuals.
- Not a financially sound decision: If you’re pursuing a PhD to make more money, the return on investment may not be as high as you expect.
Older PhD candidates often have a wealth of experience and knowledge that can only enhance their research and academic contributions.
So if you are considering pursuing a postgraduate degree, don’t let your age hold you back. It’s never too old to follow your academic dreams!
If you want to know more about how doing a PhD later in life you can check out my other articles:
Who is the oldest person to do a PhD?
The oldest person to earn a PhD was a 95-year-old woman named Ingeborg Rapoport.
She was a Jewish-German physician who began her PhD studies in the 1930s but was unable to complete them due to the Nazi regime.
After a successful medical career, she decided to resume her studies in 2008 at the age of 94 at the University of Hamburg in Germany.
Her doctoral thesis focused on diphtheria and included research conducted in the 1930s, making her research especially significant.
In 2015, Rapoport successfully defended her thesis and earned her doctorate, becoming the oldest person in history to do so.
Her achievement received widespread recognition and admiration, and she demonstrated that age is just a number when it comes to academic achievement.
Wrapping up – doing a PhD later in life
In this article, we explore the unique challenges and rewards of pursuing a PhD later in life, drawing from the experiences of older PhD candidates.
Two case studies showcase the importance of determination, support systems, and practical experiences in successfully completing a doctoral program.
Life experience offers numerous benefits for older PhD students, such as a broader perspective, problem-solving skills, transferable skills, time management, an established professional network, emotional resilience, enhanced credibility, motivation and purpose, adaptability, and mentorship opportunities.
Age should not be a barrier to pursuing a PhD, as older candidates often bring valuable real-world experience and knowledge to their research.
Key advantages of pursuing a PhD in your 40s include greater maturity, real-world experience, stronger mental health, financial resources, less need for validation, better relationships with professors, and research relevance.
Drawbacks may include time constraints, additional life commitments, potential need for relocation, opportunity cost, difficulty in obtaining tenure, and lower return on investment.
The oldest person to earn a PhD was 95-year-old Ingeborg Rapoport, exemplifying that it’s never too late to follow your academic dreams.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

Ecologist and environmental social scientist
- Funders and Collaborators

Five tips for starting (and continuing) a PhD
On 4th September 2020
In Advice for other students
Lots of the specific stuff you learn as a PhD student, as well as general approaches to your work, begins with informal advice rather than formal training. I’ve received lots of advice from others during my PhD, since the very early stages of my project. This has helped me both build a PhD project that I’m happy with, and actually enjoy my life while I do my PhD (the two, of course, being closely but not entirely linked!). As it’s the start of the academic year I want to share a few of my own tips along those lines, to help get your PhD off to a good start, and keep it on a trajectory you’re happy with:
1. Keep notes on everything you read
My PhD, like many, kicked off with lots of reading of textbooks and academic papers. My reading has ebbed and flowed, but not really stopped, since then. Reading is a big thing during your PhD. It’s useful to keep track of what you’ve been reading because you won’t remember all of it, but you will want to come back to a lot of it.
My system for keeping notes on my reading is highly unsophisticated, but it works: I have (currently) three Word Documents, called Reading_[insert year here] stored on Dropbox so I can access them anywhere. I’ve got a separate one for each year of my PhD because 1) each document is a bit more manageable than one scary enormous one, and 2) I find it surprisingly easy to remember when-ish I was reading different stuff because my reading has gone through some quite distinct phases (e.g. more stuff relevant to study design early on, more stuff about analysis later) so it seemed like a reasonable and simple way to organise my notes.
The notes I make on what I read vary a lot: at my laziest, I just copy and paste the paper title, first author and abstract into the doc, and I’m done. If I’m feeling enthusiastic, I make more extensive notes on the paper and my thoughts on it, or copy specific sections that are especially interesting or relevant to my work. I make sure that each paper title or reference is formatted as a heading so that I can scan through the document easily, and create a contents page for each document. Now, if I want to find a specific paper or read publications on a particular theme, I can Ctrl+F to find key words in my Reading documents.
2. Read a couple of theses
I’m going to disagree with tip #2 in Five Tips for Starting Your PhD Out Right and say you don’t need to read them cover to cover – I don’t think this is necessary in the early stages in your project, unless you really want to do so, or if you feel that every chapter is highly relevant to your own PhD. But I do think it’s helpful to flick through and see different thesis structures (trends in how to structure a thesis evolve over time, and also vary by subject area, so look at recent graduates in your field for ideas of what’s likely to be appropriate for you).
Theses might also contain some specific content that you didn’t realise you’ll need to add to your own thesis (such as more detailed methodology than you usually see in a published paper) or useful references if the PhD is closely related to your own work. I think it works well to look through the theses of recent graduates in your research group, your supervisor, or others working on similar stuff to you. But you can also search for theses online, for example by using EThOS .
3. Start a Word document called “Thesis”
You can use other people’s theses (see previous tip) as a guide to add appropriate headings and subheadings to this document which will act as your own thesis structure / outline. Okay, I did this in third year, not first year, but I reckon it would have been helpful to start this earlier. Since I started this document, I’ve made good progress on actually organising my thoughts and even writing a few things down. And if you’ve got this document ready from early on in your project, you can populate it with notes and ideas whenever they occur to you at any point during your PhD.
Recently, I’ve been going through my Reading documents (remember tip #1) page by page and copying across notes from papers that I have read (and often forgotten about) into the appropriate sections of my Thesis document. It’s surprising how quickly my rough structure has been populated with ideas and material for literature review and synthesis, and how this has helped me link different ideas together i.e. stuff I read in first year and forgot about, with stuff I’ve been reading recently, with stuff that’s coming out of my own analysis. Actually, now that it’s getting quite full, I’ve split my Thesis doc up so that I’m just working with one document per empirical chapter. In first year, a simple thesis structure in a single document is a good place to start.
4. Think about how to make the flexibility of your PhD (and your control over it) work best for you
This one’s quite big-picture, and I’m kind of cheating the list-of-five by squeezing several tips into one. But I think that the general principle of this tip is important, and can be interpreted in different ways to suit different people: PhDs are often inherently flexible, in how you set your daily, weekly and monthly schedule, and I think that you should make the most of that.
The nature of your PhD flexibility and your control over it depend on the details of your project, how you’re going to be working with your supervisors and institution. But there are usually opportunities for flexibility, even if you have to be in the lab most days. PhD-life-flexibility can be exploited for your professional or personal development, to maximise your productivity, to create opportunities that are fun or useful now, or allow you to flex creative muscles you haven’t had the opportunity to flex before.
Below I list the kinds of things you can think about to best use the flexibility of your PhD. These are all things that can work alongside the core research / write / defend thesis requirements of your PhD, and while you definitely don’t have to make any firm plans on day one, I think that it’s really valuable to think about ideas like this (and any more you have) early in your project. It’s all about what you want to get out of your time whilst doing your PhD , including but not limited to the PhD itself, and how you want to structure that time:
- How do you want to set your daily schedule, where do you want to work? What’s going to be most pleasant and productive for you, and fit in with your home life?
- What things do you want to do outside of your PhD (sports, reading non-PhD-related books, joining local clubs and groups, always protecting weekends off) to actively maintain a healthy work-life balance (which is better for both your wellbeing, and the state of your thesis)?
- Are there times when you’re going to be working extra hard (like fieldwork)? How do you want to balance that with rest and recuperation afterwards (an extended post-fieldwork holiday…?)?
- Do you want to take an interruption from your PhD for an internship or job?
- Do you want to practise writing by starting a blog or try a bit of science journalism ?
- Do you want to get involved with science outreach?
- Do you want to build a professional profile and network by making a website or getting on social media?
- Do you want to teach undergraduates or Masters students?
- What training courses would you like to do (and where do you find out about them)?
- Do you want to try turning one or more of your chapters into academic papers?
5. Talk to people, lots, in both general and specific ways
Starting a PhD can be overwhelming, and knowing where to start, or where to go next, can be really tough. Having conversations with other PhD students about what they are working on, how they are finding their PhD, what kind of training they have received, might point you to interesting new research topics, training opportunities, or just give you a bit of a general feel for what it’s going to be like doing a PhD in your new department. These general conversations are important because they can provide you with nuggets of wisdom you didn’t know you needed and, crucially, help you feel connected to and supported by your colleagues and peers.
Asking your supervisor or others specific questions like are there any academics whose work you recommend I look into? / do you recommend any textbooks on [planning a research project], [planning fieldwork], [fundamentals of landscape ecology], [fundamentals of development research] [insert another topic you’re not sure about yet but want to learn about]? / are there any conferences I should look out for? can give you some useful starting points for directing your own learning in the early stages of your project. So, think specifically about what you need at the start of your PhD, and ask for help with it.
…And one bonus tip: read advice from other (ex-) PhD students
There are similar posts to this one with advice on starting your PhD here , and I particularly like the twenty top tips from Lucy Taylor here . There are actual full guides to PhD life like The A-Z of the PhD Trajectory and The Unwritten Rules of Ph.D. Research which can be very helpful to read through at any stage of your PhD (though I guess you maximise your use of them if you read them early!) and to use as reference books as and when you need them. There are lots of people blogging about their past and present PhD experiences, which can offer great advice and comfort at every stage in your PhD. Personally, I love the Thesis Whisperer and like to check in with it semi-regularly. Reading TW feels a bit like my tip #5: it’s about seeking out help and advice, sometimes when you didn’t even know you needed it.


Practical tips on how to be an interdisciplinary individual
It all depends.
Add Comment →
- Doing an internship during your PhD – Ellie Wood
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

HTML Text Five tips for starting (and continuing) a PhD / Ellie Wood by blogadmin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution CC BY 3.0
Plain text Five tips for starting (and continuing) a PhD by blogadmin @ is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution CC BY 3.0
Powered by WordPress & Theme by Anders Norén
Report this page
To report inappropriate content on this page, please use the form below. Upon receiving your report, we will be in touch as per the Take Down Policy of the service.
Please note that personal data collected through this form is used and stored for the purposes of processing this report and communication with you.
If you are unable to report a concern about content via this form please contact the Service Owner .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER COLUMN
- 06 November 2018
Twenty things I wish I’d known when I started my PhD
- Lucy A. Taylor 0
Lucy A. Taylor earned her zoology PhD from the University of Oxford, UK. She is now a postdoctoral researcher at Save the Elephants in Nairobi, Kenya, and a visiting researcher in the Department of Zoology at Oxford.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Starting a PhD can be tough. Looking back, there are many things I wish I’d known at the beginning. Here, I have curated a list of advice from current PhD students and postdoctoral researchers from the Department of Zoology at my institution, the University of Oxford, UK, to aid new graduate students.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-018-07332-x
This is an article from the Nature Careers Community, a place for Nature readers to share their professional experiences and advice. Guest posts are encouraged. You can get in touch with the editor at [email protected].
Related Articles

What makes a good PhD student?
Make the most of PhDs

‘I saw that discrimination wasn’t hearsay or rumours — it really did exist’
Career Q&A 05 JUN 24
Need a policy for using ChatGPT in the classroom? Try asking students
Career Column 05 JUN 24

Why China has been a growing study destination for African students
Nature Index 05 JUN 24

I was denied tenure — how do I cope?
Career Feature 06 JUN 24

Racing across the Atlantic: how we pulled together for ocean science
Career Feature 03 JUN 24

How I run a virtual lab group that’s collaborative, inclusive and productive
Career Column 31 MAY 24

Brazil’s plummeting graduate enrolments hint at declining interest in academic science careers
Career News 21 MAY 24
Postdoctoral Associate- Cancer Epidemiology
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Head of Climate Science and Impacts Team (f/m/d)
You will play a pivotal role in shaping the scientific outputs and supporting the organisation's mission and culture. Your department has 20+ staff.
Ritterstraße 3, 10969 Berlin
Climate Analytics gGmbH
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Warmly Welcomes Talents Abroad
Qiushi Chair Professor; Qiushi Distinguished Scholar; ZJU 100 Young Researcher; Distinguished researcher
No. 3, Qingchun East Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang (CN)
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital Affiliated with Zhejiang University School of Medicine
Proteomics expert (postdoc or staff scientist)
We are looking for a (senior) postdoc or postdoc-level staff scientist from all areas of proteomics to become part of our Proteomics Center.
Frankfurt am Main, Hessen (DE)
Goethe University (GU) Frankfurt am Main - Institute of Molecular Systems Medicine
Tenured Position in Huzhou University School of Medicine (Professor/Associate Professor/Lecturer)
※Tenured Professor/Associate Professor/Lecturer Position in Huzhou University School of Medicine
Huzhou, Zhejiang (CN)
Huzhou University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Our Culture
- Open and FAIR Data
- Research projects
- Publications
- Cellular Genomics
- Decoding Biodiversity
- Delivering Sustainable Wheat
- Earlham Biofoundry
- Transformative Genomics
- Scientific Groups Our groups work at the forefront of life science, technology development, and innovation.
- High-Performance Sequencing Dedicated and efficient high-throughput genomics led by experts in sequencing and bioinformatics.
- Single-cell and Spatial Analysis Platforms to support single- or multi-cell analysis, from cell isolation, to library preparation, sequencing and analysis.
- Earlham Biofoundry Providing expertise in synthetic biology approaches and access to laboratory automation
- Tools and resources Explore our software and datasets which enable the bioscience community to do better science.
- Cloud Computing Infrastructure for Data-intensive Bioscience
- Web Hosting for Sites, Tools and Web Services
- Earlham Enterprises Ltd
- Events Calendar Browse through our upcoming and past events.
- About our training High-quality, specialist training and development for the research community.
- Year in industry Supporting undergraduate students to develop skills and experience for future career development.
- Internships and opportunities Opportunities for the next generation of scientists to develop their skills and knowledge in the life sciences.
- Immersive visitors A bespoke, structured training programme, engaging with the faculty, expertise and facilities at the Earlham Institute.
- News Catch up on our latest news and browse the press archive.
- Articles Explore our science and impact around the world through engaging stories.
- Impact Stories Find out how we are contributing to the major challenges of our time.
- Impact Through Policy Advocacy Engaging across the political spectrum to exchange knowledge and inform public policy.
- Public engagement and outreach Communicating our research to inspire and engage learning.
- Communications at EI We work across digital, multimedia, creative design and public relations to communicate our research.
- Our Vision and Mission
- Inclusivity, diversity, equality and accessibility
- Scientific Advisory Board
- Our Management Team
- Operations Division
- Careers overview
- Postgraduate Studies
- Group leaders
- Fellowships
- Life at Earlham Institute
- Living in Norfolk

10 things you need to know before starting a PhD degree
So you want to do a PhD degree, huh? Here we've got everything you need to know about getting started.
So you want to do a PhD degree, huh? Are you sure about that? It’s not going to be an easy decision, so I’ve put together a list of 10 things you need to know before starting a PhD degree. Oh, and don’t panic!
I have recently graduated from the University of Manchester with a PhD in Plant Sciences after four difficult, but enjoyable, years. During those four years, I often felt slightly lost – and there was more than one occasion on which I didn’t even want to imagine writing up my thesis in fear of delving into fits of panic.
On reflection, I realise that – to quote a colleague – commencing my PhD was like “jumping in the deep end with your eyes closed.” If only I’d known to take a deep breath.
1. Are you sure you want to do a PhD degree?
Let’s be under no false impressions, completing a PhD isn’t easy. There will be times when you feel like Wile E Coyote chasing after the Roadrunner – a little bit out of your depth a lot of the time. It’s four years of your life, so make sure it is what you really want to do.
If you want to pursue a career in science, a PhD isn’t always necessary.
It is possible to make great inroads into industry without a doctoral degree. That said, a PhD can also be a very useful qualification with many transferable skills to add to your CV.
By the time you’ll have finished, you can include essentials such as time management, organisational skills, prioritising workloads, attention to detail, writing skills, presenting to an audience – and most importantly – resilience, to name but a few.
2. Choose your project, and supervisor, wisely.
This is very important.
Time after time, our experienced scientists at EI, including Erik Van-Den-Bergh (and I agree) say, “ make sure you’re extremely passionate about exactly that subject. ” When I saw the PhD opening that I eventually was offered, I remember being demonstrably ecstatic about the project before I’d even started it.
I was always interested in calcium signalling and organised a meeting with my potential supervisor immediately, which (to quote Billy Connolly) I leapt into in a mood of gay abandon.
Not only does this help you to keep engaged with your project even through the painstakingly slow times, it also greatly enhances your ability to sell yourself in an interview. If you can show passion and enthusiasm about the project and the science then you’ll be that one step ahead of other candidates – which is all the more important now that many studentships are competitive.
You have to be the best out of many, often exceptional candidates.
However, as important as it is to be passionate about your project, make sure that the person who will be supervising you is worthy.
Does your potential supervisor have a prolific track record of publishing work? What is the community of scientists like in the lab you may be working in? Are there experienced post-doctoral scientists working in the lab? Who will your advisor be? Is your supervisor an expert in the field you are interested in? Is the work you will be doing ground-breaking and novel, or is it quite niche?
There is nothing more frustrating – and I know many PhD degree students with this problem – than having a supervisor who is rarely there to talk to, shows little interest in your work, and cannot help when you are struggling in the third year of your project and some guidance would be much appreciated.
Personally, and I was very lucky to have this, I think it’s incredibly useful to have two supervisors. My PhD degree was split between the University of Manchester and the Marine Biological Association in Plymouth. Between my supervisors, I had two people with expertise in different fields, who could give me some fantastic advice from different perspectives. This also meant that I had two people to check through my thesis chapters and provide useful comments on my drafts.

Make sure you are passionate about your subject before taking it to PhD level. And by passionate I mean really passionate.
For a start, you will most likely have to write a literature review in your first three months, which if done well will form the main bulk of your thesis introduction and will save you a lot of stress and strain when it comes to writing up.
At the end of your first year, you will have to write a continuation report, which is your proof that you deserve to carry on to the end of your three or four years. This doesn’t leave much time for lab work, which means time management is incredibly important. If you think you’ll be able to swan in at 11 and leave at 3, think again.
Fundamentally, never, ever rest on your laurels! As tempting as it may be to slack-off slightly in the second year of your four year PhD, don’t.
4. Be organised.
This is a no-brainer but still, it’s worth a mention. Take an hour on a Monday morning to come up with a list of short-term and long-term goals. You’ll probably have to present your work at regular lab meetings, so it’s always worth knowing what has to be done (lest you look a pillock in front of the lab when there’s nothing to show for your last two weeks.)
It’s always good to have a timeline of what will be done when. If you have a PCR, maybe you can squeeze in another experiment, read a few papers, start writing the introduction to your thesis, or even start collecting the data you already have into figures.
The more good use you make of your time, the easier it’ll be to finish your PhD in the long run. Plus, it’s lovely to sit back and look at actual graphs, rather than worry about having enough to put into a paper. Once you’ve typed up your data, you’ll realise you’ve done far more than you had anticipated and the next step forward will be entirely more apparent.
5. Embrace change – don’t get bogged down in the details.
Felix Shaw – one of our bioinformatics researchers at EI – put it best when he said, “ it felt like I was running into brick walls all the way through [my PhD]… you’d run into a brick wall, surmount it, only to run straight into another. ”
You’ll find that, often, experiments don’t work. What might seem like a great idea could turn out to be as bad as choosing to bat first on a fresh wicket on the first day of the third Ashes test at Edgbaston. (Yeah, we don't know what that means either - Ed).
Resilience is key while completing your PhD. Be open to change and embrace the chance to experiment in different ways. You might even end up with a thesis chapter including all of your failures, which at the very least is something interesting to discuss during your viva voce .
6. Learn how to build, and use, your network.
As a PhD student, you are a complete novice in the world of science and most things in the lab will be – if not new to you – not exquisitely familiar. This matters not, if you take advantage of the people around you.
Firstly, there are lab technicians and research assistants, who have probably been using the technique you are learning for years and years. They are incredibly experienced at a number of techniques and are often very happy to help show you how things are done.
There are postdocs and other PhD students, too. Not only can they help you with day-to-day experiments, they can offer a unique perspective on how something is done and will probably have a handy back-catalogue of fancy new techniques to try.
There are also a bunch of PIs, not limited to your own, who are great to talk to. These people run labs of their own, have different ideas, and might even give you a job once you’ve completed your PhD.
Don’t limit yourself to the labs directly around you, however. There are a massive number of science conferences going on all around the world. Some of them, such as the Society of Biology Conference, take place every year at a similar time in different locations, attracting many of the leaders in their respective fields.
If you are terrified by the prospect of speaking at a full-blown science conference and having your work questioned by genuine skeptics, there are also many student-led conferences which will help you dangle your fresh toes in the murky waters of presenting your work.
One such conference, the Second Student Bioinformatics Symposium, which took place at Earlham Institute in October 2016, was a great place for candidates to share their projects with peers, who are often much more friendly than veteran researchers with 30 year careers to their name when it comes to the questions at the end of your talk.
Another great reason to attend conferences, of course, is the social-side too – make the most of this. You never know who you might meet and connect with over a few drinks once the talks are over and the party commences.
7. Keep your options open.
You should be aware that for every 200 PhD students, only 7 will get a permanent academic post , so it’s incredibly unlikely that you’ll become a Professor – and even if you make PI, it probably won’t be until your mid-forties.
You may also, despite having commenced along the academic path, decide that actually, working in a lab environment isn’t for you. Most PhD graduates, eventually, will not pursue an academic career, but move on to a wide range of other vocations.
It might be that Science Communication is more up your street. This was certainly the case for me – and I made sure that I took part in as many public engagement events as possible while completing my PhD. Most Universities have an active public engagement profile, while organisations such as STEM can provide you with ample opportunities to interact with schools and the general public.
You might also consider entrepreneurship as a route away from academia, which might still allow you to use your expert scientific knowledge. There are a variety of competitions and workshops available to those with a business mind, a strong example being Biotechnology YES.
I, for example, took part in the Thought for Food Challenge, through which I have been able to attend events around the world and meet a vast array of like-minded individuals. Many of the participants from the challenge have gone on to set up successful businesses and have even found jobs as a result of the competition.

8. Balance.
Remember that you still have a life outside of your PhD degree – and that this can be one of the greatest opportunities to make amazing friends from around the world.
A science institute is usually home to the brightest students from a variety of countries and can provide a chance to experience a delightful range of different people and cultures. Don’t just stick to the people in your lab, go to events for postgraduate students and meet people from all over campus.
There are usually academic happy hours happening on Fridays after work where you can buy cheap beer, or some lucky institutions even have their own bar. At Norwich Research Park, we not only have the Rec Centre, along with bar, swimming pool, calcetto, samba classes, archery, and a range of other activities, but there are also biweekly “Postdoc pub clubs” which are very fun to join on a Tuesday evening.
Maintain your hobbies and keep up with friends outside of your PhD and you’ll probably find it’s not that gruelling a process after all.
Plus, the people you meet and become friends with might be able to help you out – or at least be able to offer a sympathetic shoulder.

9. Practical advice.
If, after reading all of this, you’re still going to march forth and claim your doctorhood, then this section should be rather useful.
Firstly, make sure your data is backed up. It’s amazing how many people don’t do this and you’d be bonkers not to. Keep your work saved on a shared drive, so that if your computer decides to spontaneously combust upon pressing the return key, you won’t have lost all of your precious work – or have to go through every one of your lab books and type it all up again.
Secondly, don’t leave your bag in the pub with your half-written thesis in it. I did this, the bag was fine, I was in a state of terror for at least half an hour before the kind person at Weatherspoons located said bag.
Thirdly, read. Read broadly, read anything and everything that’s closely related to your project – or completely unrelated. It’s sometimes amazing where you might find a stroke of inspiration, a new technique you hadn’t thought of … or even in idea of where you might like to go next.
Finally, ask questions – all of the time. No matter how stupid it might sound in your head, everyone’s probably been asked it before, and if you don’t ask, you don’t get.
You’ll probably look far less stupid if you just ask the person standing next to you how the gradient PCR function works on your thermal cycler rather than standing there randomly prodding buttons and looking flustered, anyway.
10. Savour the positives.
At the end of all of this, it has to be said that doing a PhD is absolutely brilliant. There’s no other time in your life that you’ll be this free to pursue your very own project and work almost completely independently. By the time you come to the end of your PhD, you will be the leading expert in the world on something. A real expert! Until the next PhD student comes along …
Related reading.

A PhD, is it worth it? Just ask our students

The realities of doing a PhD

My advice for PhD students? See what bites

COVID and my PhD: to lockdown and back

How does a PhD work and how to find the right one

Building the confidence to take on a PhD
PhD life, 10 things we learned in our first six months

What’s the third year of a PhD like? Tips for navigating your PhD

PhD by experience
- Scientific Groups
- High-Performance Sequencing
- Single-cell and Spatial Analysis
- Tools and resources
- Events Calendar
- About our training
- Year in industry
- Internships and opportunities
- Immersive visitors
- Impact Stories
- Impact Through Policy Advocacy
- Public engagement and outreach
- Communications at EI

Community Blog
Keep up-to-date on postgraduate related issues with our quick reads written by students, postdocs, professors and industry leaders.
What Is The Age Limit for A PhD?

- By Dr Harry Hothi
- August 17, 2020

Introduction
I have seen and personally worked with PhD candidates of all ages, some older than me, some younger. In all my time within academia, I haven’t come across any university that places a limit on the age of an individual that wants to apply for and pursue a full time doctoral degree; indeed the practice of doing so would be rightly considered a form of discrimination at most academic institutions and even against the law in some countries.
However, a quick search on Google is enough to see that the question about age limits for doing a PhD is something that is asked quite often. This leads me to believe that there are many very capable potential doctoral candidates in the world that haven’t pursued their dreams of academic research almost entirely because they believe that they’re too old to do so.
There is No Age Limit for Doing a PhD
Simply put there is no age limit for someone considering doing a PhD. Indeed, on the opposite end of the scale, even the definition of a minimum’ age at which someone can start a PhD is not really well defined.
One of the youngest PhD graduates in recent times is thought to be Kim Ung-Yong who is a South Korean professor who purportedly earned a PhD in civil engineering at the age of 15 [1]. For the vast majority however, the practical considerations of progressing through the different stages of education (i.e. high school, undergraduate degree, a Master’s degree, etc.) mean that most won’t start their PhD projects until they’re at least in their early to mid 20’s; in the UK, for example, the average age for a PhD graduate is between 26 and 27 years old [2].
Meanwhile, the oldest person to be awarded a PhD degree in the United Kingdom is thought to be 95 year old Charles Betty, who gained his doctorate from the University of Northampton in 2018 after completing his 48,000 word thesis on why elderly expats living in Spain decide to return to the UK’ [3].
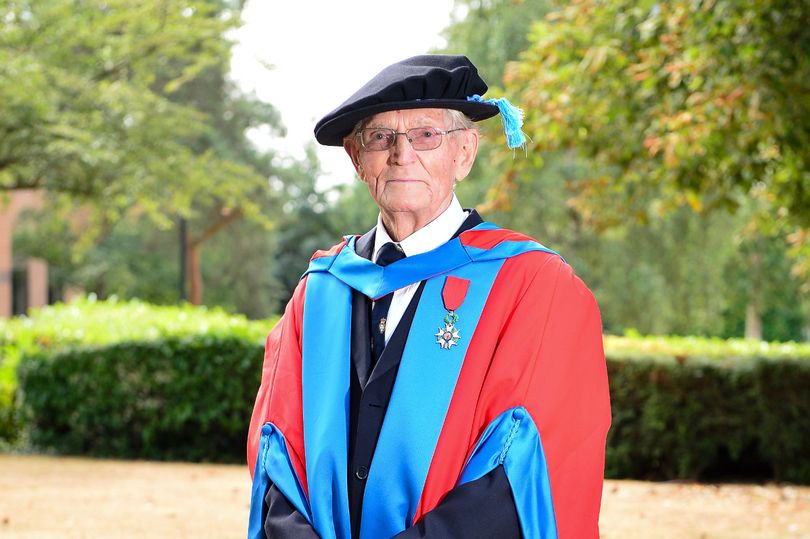

What does the data say?
According to data published by the National Science Foundation (NSF), a total of 54,904 people earned PhDs at universities in the United States of America in 2016; 46% of all new doctorates were women and 31% were international candidates [4].
Looking at the age distributions available for 51,621 of these new PhD graduates in 2016, 44% (n=22,863) were aged 30 or below, 43% (n=22,038) were aged between 31 and 40 and 13% (n=6,720) were over the age of 40 when they were awarded their doctoral degree. In this same year, over 50% of PhD students in subjects related to physical sciences, earth sciences, life sciences, mathematics, computer sciences and engineering were below the age of 31, whilst less than 10% of these STEM graduates were older than 41.
Conversely, 61% of PhDs in humanities and arts and 52% in other non-engineering and science disciplines gained their doctorates between 31 and 40 years of age. Interestingly, the analysis by the NSF found that 94% of doctoral candidates aged below 31 supported their research financially through research or teaching assistantships, grants or fellowships. Only 36% of PhDs aged over 41 at graduation reported receiving similar types of financial support; approximately 50% of this age group were found to have self-funded their studies.
The reasons for fewer doctoral candidates aged over 41 receiving external funding to support their time as research students is not clear. On the face of it, the data may appear to suggest a bias towards funding younger students which unfortunately may be the case in some instances. In Germany, for example, the German Federal Training Assistance Act (BAfG) provides funding support for higher education but places a limit of 30 years for undergraduate degrees and 35 years for postgraduate students at graduate school. However, another explanation, at least in some cases, may be that non-STEM related subjects are less likely to be associated with specific project funding and NSF analysis suggests PhDs in these subjects are more often undertaken by older doctoral candidates.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages?
No one should be discouraged from pursuing a PhD program or entering into higher education based on how old they are and indeed there are several (albeit subjective) benefits and disadvantages of doing a PhD in your younger’ or older’ years.
A perceived advantage may be that gaining a PhD in your 20’s can potentially give you more time to develop your career. Younger doctoral students could earn their PhD and enter into academic jobs before starting a family (although many people successfully carry out doctoral research whilst also looking after young children). You could even afford yourself the time and flexibility to implement a career change further down the line if you so wanted.
Conversely, entering a graduate school and becoming a PhD student in later years means that you’ll be doing so having gained a lot more life experience and for some STEM research projects in particular, having work experience in industry can be invaluable. As an older PhD candidate you’re likely to be better equipped to work independently and the relationships / connections you’ll have built over time may be a useful factor in helping you progress faster. I’ve met several older students at university who had the opportunity to undertake PhD research years ago but have no regrets in having waited and started the adventure in later years.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
It’s inevitable that the question of age limits for pursing a PhD is going to invite some controversial opinions from some people; this unfortunately may always be the case when talking about differing social and demographic factors.
There’s no doubt however that PhD programs can help career advancement or a career change regardless of age however there’s also nothing to stop you from becoming a graduate student just for the academic pursuit!
The answer here is very simple: there is no age limit for doing a PhD.
[1] http://scienceandnaturea.blogspot.com
[2] https://www.eui.eu/
[3] https://www.telegraph.co.uk/
[4] https://ncses.nsf.gov/

The answer is simple: there is no age limit for doing a PhD; in fact, the oldest known person to have gained a PhD in the UK was 95 years old.

Scientific misconduct can be described as a deviation from the accepted standards of scientific research, study and publication ethics.

The unit of analysis refers to the main parameter that you’re investigating in your research project or study.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Browse PhDs Now

In the UK, a dissertation, usually around 20,000 words is written by undergraduate and Master’s students, whilst a thesis, around 80,000 words, is written as part of a PhD.

Fieldwork can be essential for your PhD project. Use these tips to help maximise site productivity and reduce your research time by a few weeks.

Prof Cotton gained her DPhil in the school of education at Oxford University. She is now the Director of Academic Practice and Professor of Higher Education at Plymouth Marjon University.

Raluca is a final year PhD student at Queen Mary University of London. Her research is on exploring the algorithms of rolling horizon evolutionary algorithms for general video game playing.
Join Thousands of Students
Something went wrong. Wait a moment and try again.

Academia & mental health
Doing a PhD in your 30s
Over time, I’ve seen quite a few tweets from people asking whether one should do a PhD in their 30s and what it is like. I personally am of the opinion that it is never too late for education, including a PhD, and when it came to me making a decision to do one at the age of 29 it did not even occur to me that I might be ‘too old’. However, at that time I was single and without children, so the decision seemed a lot simpler. Nevertheless, there are a few things I learned along the way about doing a PhD from the age of 29 until 35 (yes it took me 6 years to finish) that I’d like to share with you.
Let’s start with the positives!
The major benefit of starting a PhD at 29 was that I was more mature – it’s a fairly obvious one I know, but in hindsight it was important. It meant that I (mostly) knew what I wanted and why I was doing a PhD. I had already tried other careers and was quite certain that a career in academia would be a good long-term fit for me and I was not wrong.
Also, because I had had a career before starting this degree, I had work experience which helped me not only with the PhD itself but also in the work I was doing alongside the PhD. I was self-funded which meant that I had to work part-time, and in my first year I worked as supply teacher in secondary schools; a job I was able to get thanks to my previous teaching qualifications. Later when I started working as a teaching assistant in my Department, the teaching qualification and experience also came in very handy. My previous work experience helped me build a profile for myself as a reliable and effective employee, which in turn helped me find employment after the PhD. This is, of course, not to say that if you don’t have work experience you won’t be a reliable employee, but rather that in my case I noticed it as a benefit.
I was more confident too as a lot of the insecurities about my looks and persona that I had in my teens and early 20s were mostly gone by 29. I felt right in my own skin, if that makes sense. Previous work experience in a job that I loved also enabled me to find out what I was good at and what were my potential weaknesses, which helped me in my PhD when it came to e.g., picking a topic or deciding on the methodology. Knowing who I was and being overall quite confident was also important in the fight against the imposter syndrome, which like with most people kicked in for me too. At those times it was useful to be able to remind myself that there were other things I was good at and that no matter what happened with the PhD that wouldn’t change.
Although when you start your academic career later in life it means that some of your colleagues who are younger or the same age as you might be further along in their careers, don’t let that bother you. I personally find my own Department to be rather diverse in terms of staff ages and when people made a start in academia and that’s great. I found it rather refreshing that I was given the choice to completely change my career and start a PhD at 29 and that has never been an issue for me in terms of age or being ‘a late starter’.
Nevertheless, there were some negatives too which are worth sharing and considering.
Overall, I think my previous career was a big help during the PhD but having had a job/career before also meant that it was fairly difficult to adjust to the PhD way of life/work as it is a lot less structured and with a lot less accountability to other people. I really missed having co-workers and meaningful deadlines, and it took me quite a while to figure out what routine worked best for me. Finding a routine also meant getting back into being a student again and all that this entails, like reading and writing academic papers, improving my concentration and sitting long hours at a desk. It had been a while since I did all that for my BA and MA, but eventually I got the hand of it.
Another important consideration are finances. I personally went from having a decent and steady salary to spending my savings on my PhD and working multiple part-time jobs. This is a bit different if you are funded, but even then the stipends are usually not large enough to allow for comfortable living. I would say that in most cases, the PhD years will mean living on a tighter budget. Especially, if you are coming from a well-paid and steady job, you may find this change in your financial circumstances a bit tough.
I guess a fairly important consideration when starting a PhD later in life is family, whether you already have one or you are planning for one. I personally left family planning until after I finished my PhD and found a job, as I found it too much to be thinking about both at the same time. However, I know of many PhD colleagues who have had a baby during the PhD or started the PhD with children.
What I want to say at the end of this post is that regardless of at what age you start your PhD, it will come with its unique challenges. However, none of these challenges are unsurmountable, especially if you are reasonably prepared for them and know what to expect. As I said at the start, I don’t believe that one is ever too old to do a PhD so if that’s what you really want to do, go for it!
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
How the PhD Program Works
Program Overview
Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending your doctoral dissertation.
Admission to candidacy.
You begin by taking courses required for your program of study. All programs requires a preliminary exam, which may be either oral or written.
Some programs may have further requirements, such as an additional exam or research paper. If you enter with a master’s degree or other transfer credit, you may satisfy the formal course requirements more quickly.
Beginning the Wharton PhD Curriculum How the first two years of the Wharton program helped students discover their interests, learn the tools of the profession, and fuel their passion for teaching.
The Doctoral Dissertation
Upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, you are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies.
Your doctoral dissertation should contain original research that meets standards for published scholarship in your field. You are expected to be an expert in the topic you choose to research.
You are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, but you can start thinking about and working on research of relevance at any time.
The dissertation process culminates with a “defense,” in which you defend the proposal orally before your dissertation committee.
While working on your dissertation, you interact extensively with Wharton faculty. Together with interested faculty, you create your own research community that includes your dissertation advisor and dissertation committee.
Policies and Procedures
Get more detailed explanation of course requirements, academic standards, the Teacher Development Program, time limits, and dissertation procedures and requirements.
Sample Program Sequence
Years 1 & 2.
Coursework Examination Research Papers Research Activities Field-Specific Requirements
Directed Reading & Research Admission to Candidacy Formulation of Research Topic
Years 4 & 5
Continued Research Oral Examination Dissertation
Hear From Our Doctoral Community
The diverse skill set you need to become a professor, uniting great minds, wharton’s stat bridge ma program takes flight, why i chose academic research instead of consulting.
Andrea Contigiani

- Soch with Coach
- Straight Up
FIVE points you absolutely MUST KNOW before starting your PhD journey

Keep your checklists ready! Here are some of the things that one should not miss before applying for PhD
1. Background check of supervisor and research group. How to do it?
.png?w=640&auto=format%2Ccompress)
To ensure that your interest aligns with the potential supervisors you have shortlisted, look into their previous works and other contributions to the field. Look into the lab/group they are heading and their current projects. Ensure that you are working in a productive and supportive environment.
2. Gained admission into a reputed institution but forgot to look into your supervisor? This might not be a wise move
.png?w=640&auto=format%2Ccompress)
Well, relying solely on your institution's reputation would lead you nowhere. Examine your supervisor's Google Scholar profile, research articles and their publications. Understand the relevance of their project with yours and their ability to provide fruitful guidance.
3. Do not forget to ask for help. But how does one go about seeking help from former and current PhD students?
.png?w=640&auto=format%2Ccompress)
To make a more informed decision, do not hesitate to pose questions to alumni and current students about the lab facilities, the work culture, and the collective approach towards the research projects. Gain a deeper insight into their journey so far and make notes to give your journey a headstart.
4. You think finances don't matter while pursuing PhD? You are wrong.
.png?w=640&auto=format%2Ccompress)
Ensuring financial stability throughout your time is crucial as you will be dedicating a duration of your time solely to research. Look for fellowships available before starting your PhD, and other TA (training assistant) programmes offered by your institution. If your PhD programme exceeds five years, inquire about the additional support available.
5. Why hesitate while choosing the best for yourself?
.png?w=640&auto=format%2Ccompress)
Landed at a good university? Great. Helpful supervisor? Even better. What about other facilities aiding your research such as advanced equipment, the best library facilities and other adequate resources? Look out for them. Check if your institute has collaborations with other universities, and if there are opportunities for you to present at international conferences, and publish in prestigious journals.
For more information look into a recent post by The All-India Research Scholars Association ( AIRSA ) here
Before joining any institute for a PhD program, it's crucial to remember several points many students overlook. @AIRSAIndia advises prospective @PMOIndia @dpradhanbjp @DrJitendraSingh @AjaySoodIISc @PrinSciAdvGoI @TimesNow @timesofindia @the_hindu @TheLallantop @ThePrintIndia … pic.twitter.com/L3n9YjCEtg — All India Research Scholars Association (@AIRSAIndia) May 30, 2024


How to write a PhD thesis: a step-by-step guide
A draft isn’t a perfect, finished product; it is your opportunity to start getting words down on paper, writes Kelly Louise Preece
Kelly Louise Preece

Created in partnership with

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} How to develop a researcher mindset as a PhD student
Formative, summative or diagnostic assessment a guide, emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, how to assess and enhance students’ ai literacy, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Congratulations; you’ve finished your research! Time to write your PhD thesis. This resource will take you through an eight-step plan for drafting your chapters and your thesis as a whole.

Organise your material
Before you start, it’s important to get organised. Take a step back and look at the data you have, then reorganise your research. Which parts of it are central to your thesis and which bits need putting to one side? Label and organise everything using logical folders – make it easy for yourself! Academic and blogger Pat Thomson calls this “Clean up to get clearer” . Thomson suggests these questions to ask yourself before you start writing:
- What data do you have? You might find it useful to write out a list of types of data (your supervisor will find this list useful too.) This list is also an audit document that can go in your thesis. Do you have any for the “cutting room floor”? Take a deep breath and put it in a separate non-thesis file. You can easily retrieve it if it turns out you need it.
- What do you have already written? What chunks of material have you written so far that could form the basis of pieces of the thesis text? They will most likely need to be revised but they are useful starting points. Do you have any holding text? That is material you already know has to be rewritten but contains information that will be the basis of a new piece of text.
- What have you read and what do you still need to read? Are there new texts that you need to consult now after your analysis? What readings can you now put to one side, knowing that they aren’t useful for this thesis – although they might be useful at another time?
- What goes with what? Can you create chunks or themes of materials that are going to form the basis of some chunks of your text, perhaps even chapters?
Once you have assessed and sorted what you have collected and generated you will be in much better shape to approach the big task of composing the dissertation.
Decide on a key message
A key message is a summary of new information communicated in your thesis. You should have started to map this out already in the section on argument and contribution – an overarching argument with building blocks that you will flesh out in individual chapters.
You have already mapped your argument visually, now you need to begin writing it in prose. Following another of Pat Thomson’s exercises, write a “tiny text” thesis abstract. This doesn’t have to be elegant, or indeed the finished product, but it will help you articulate the argument you want your thesis to make. You create a tiny text using a five-paragraph structure:
- The first sentence addresses the broad context. This locates the study in a policy, practice or research field.
- The second sentence establishes a problem related to the broad context you have set out. It often starts with “But”, “Yet” or “However”.
- The third sentence says what specific research has been done. This often starts with “This research” or “I report…”
- The fourth sentence reports the results. Don’t try to be too tricky here, just start with something like: “This study shows,” or “Analysis of the data suggests that…”
- The fifth and final sentence addresses the “So What?” question and makes clear the claim to contribution.
Here’s an example that Thomson provides:
Secondary school arts are in trouble, as the fall in enrolments in arts subjects dramatically attests. However, there is patchy evidence about the benefits of studying arts subjects at school and this makes it hard to argue why the drop in arts enrolments matters. This thesis reports on research which attempts to provide some answers to this problem – a longitudinal study which followed two groups of senior secondary students, one group enrolled in arts subjects and the other not, for three years. The results of the study demonstrate the benefits of young people’s engagement in arts activities, both in and out of school, as well as the connections between the two. The study not only adds to what is known about the benefits of both formal and informal arts education but also provides robust evidence for policymakers and practitioners arguing for the benefits of the arts. You can find out more about tiny texts and thesis abstracts on Thomson’s blog.
- Writing tips for higher education professionals
- Resource collection on academic writing
- What is your academic writing temperament?
Write a plan
You might not be a planner when it comes to writing. You might prefer to sit, type and think through ideas as you go. That’s OK. Everybody works differently. But one of the benefits of planning your writing is that your plan can help you when you get stuck. It can help with writer’s block (more on this shortly!) but also maintain clarity of intention and purpose in your writing.
You can do this by creating a thesis skeleton or storyboard , planning the order of your chapters, thinking of potential titles (which may change at a later stage), noting down what each chapter/section will cover and considering how many words you will dedicate to each chapter (make sure the total doesn’t exceed the maximum word limit allowed).
Use your plan to help prompt your writing when you get stuck and to develop clarity in your writing.
Some starting points include:
- This chapter will argue that…
- This section illustrates that…
- This paragraph provides evidence that…
Of course, we wish it werethat easy. But you need to approach your first draft as exactly that: a draft. It isn’t a perfect, finished product; it is your opportunity to start getting words down on paper. Start with whichever chapter you feel you want to write first; you don’t necessarily have to write the introduction first. Depending on your research, you may find it easier to begin with your empirical/data chapters.
Vitae advocates for the “three draft approach” to help with this and to stop you from focusing on finding exactly the right word or transition as part of your first draft.

This resource originally appeared on Researcher Development .
Kelly Louse Preece is head of educator development at the University of Exeter.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
How to develop a researcher mindset as a PhD student
A diy guide to starting your own journal, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, what does a university faculty senate do, hybrid learning through podcasts: a practical approach, how exactly does research get funded.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
At the New York Fed, our mission is to make the U.S. economy stronger and the financial system more stable for all segments of society. We do this by executing monetary policy, providing financial services, supervising banks and conducting research and providing expertise on issues that impact the nation and communities we serve.

Introducing the New York Innovation Center: Delivering a central bank innovation execution

Do you have a request for information and records? Learn how to submit it.

Learn about the history of the New York Fed and central banking in the United States through articles, speeches, photos and video.
Markets & Policy Implementation
- Effective Federal Funds Rate
- Overnight Bank Funding Rate
- Secured Overnight Financing Rate
- SOFR Averages & Index
- Broad General Collateral Rate
- Tri-Party General Collateral Rate
- Treasury Securities
- Agency Mortgage-Backed Securities
- Repos & Reverse Repos
- Securities Lending
- Central Bank Liquidity Swaps
- System Open Market Account Holdings
- Primary Dealer Statistics
- Historical Transaction Data
- Agency Commercial Mortgage-Backed Securities
- Agency Debt Securities
- Discount Window
- Treasury Debt Auctions & Buybacks as Fiscal Agent
- Foreign Exchange
- Foreign Reserves Management
- Central Bank Swap Arrangements
- ACROSS MARKETS
- Statements & Operating Policies
- Survey of Primary Dealers
- Survey of Market Participants
- Annual Reports
- Primary Dealers
- Standing Repo Facility Counterparties
- Reverse Repo Counterparties
- Foreign Exchange Counterparties
- Foreign Reserves Management Counterparties
- Operational Readiness
- Central Bank & International Account Services
- Programs Archive
As part of our core mission, we supervise and regulate financial institutions in the Second District. Our primary objective is to maintain a safe and competitive U.S. and global banking system.

The Governance & Culture Reform hub is designed to foster discussion about corporate governance and the reform of culture and behavior in the financial services industry.

Need to file a report with the New York Fed? Here are all of the forms, instructions and other information related to regulatory and statistical reporting in one spot.

The New York Fed works to protect consumers as well as provides information and resources on how to avoid and report specific scams.
The Federal Reserve Bank of New York works to promote sound and well-functioning financial systems and markets through its provision of industry and payment services, advancement of infrastructure reform in key markets and training and educational support to international institutions.

The New York Fed provides a wide range of payment services for financial institutions and the U.S. government.

The New York Fed offers several specialized courses designed for central bankers and financial supervisors.

The New York Fed has been working with tri-party repo market participants to make changes to improve the resiliency of the market to financial stress.
- High School Fed Challenge
- College Fed Challenge
- Teacher Professional Development
- Classroom Visits
- Museum & Learning Center Visits
- Educational Comic Books
- Lesson Plans and Resources
- Economic Education Calendar

We are connecting emerging solutions with funding in three areas—health, household financial stability, and climate—to improve life for underserved communities. Learn more by reading our strategy.

The Economic Inequality & Equitable Growth hub is a collection of research, analysis and convenings to help better understand economic inequality.

This Economist Spotlight Series is created for middle school and high school students to spark curiosity and interest in economics as an area of study and a future career.

« Taking Stock: Dollar Assets, Gold, and Official Foreign Exchange Reserves | Main | Can Discount Window Stigma Be Cured? »
Thinking of Pursuing a PhD in Economics? Info on Graduate School and Beyond
Kasey Chatterji-Len and Anna Kovner

Becoming a PhD economist can provide a fulfilling and financially secure career path. However, getting started in the field can be daunting if you don’t know much about the preparation you’ll need and the available job opportunities. If you’re wondering what it means to be an economics researcher or how to become one, please read on. We’ll review how to prepare for a career in economics research, what an economics PhD program entails, and what types of opportunities it might bring. Economic education is a core component of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s mission to serve the community. To empower would-be economists, this post provides information for students who seek a career in economics research. We hope this information will be helpful to students interested in economics, regardless of their background and economic situation. This information is most applicable to students applying to programs in the United States.
The Breadth of Economics Research
Academic disciplines conduct research in different ways, so it’s important to have a basic understanding of the types of questions economists ask and how they approach answering them. There are many definitions of economics, but a broadly useful one is the study of how people, organizations, and governments make decisions under different constraints, and how those decisions may affect their outcomes.
When answering these questions, economists seek to ground their analyses in models and to be quantitatively precise about the effects they assign to any given cause. The range of topics economists can study is wide, but the accepted approaches to answering questions are stricter. Some examples of what economists might ask:
- How do different public housing programs affect the children who live there?
- Does a certain type of law encourage businesses to innovate?
- How will a change in the interest rate affect inflation and unemployment rates?
- How much does affordable health insurance improve people’s health?
- How can poor countries eradicate poverty?
There are many different subfields within economics, including, but not limited to behavioral, econometrics, energy/environmental, development, financial, international, monetary, public, and urban economics. You can familiarize yourself with the latest work in economics by subscribing to working paper series, such as NBER’s New This Week or the New York Fed’s Staff Reports . To get an idea of the breadth of questions economists can answer, you could listen to Stephen Dubner’s “ Freakonomics Radio ” podcast. You may also want to explore the Journal of Economic Perspectives , the New York Fed’s Liberty Street Economics blog, VoxDev , or VoxEU .
What Is a PhD Program Like?
Economics PhD programs typically last five to seven years. Unlike masters programs, they are often fully funded with a stipend, though most require students to complete teaching assistant and/or research assistant (RA) work as part of their funding package. In the first two years, students take classes, many of which are mathematically demanding. The rest of the program can include additional classes but is primarily devoted to original research with the aim of producing publishable papers that will constitute the dissertation.
Faculty advisors are a central part of PhD programs, as students look to them for guidance during the research process. Economics PhD programs are offered within university economics departments, but there are similar programs in public policy and business schools. You can look at their websites to understand any differences in coursework and subsequent job placements.
What Can You Do with an Economics PhD?
Upon graduation, students can obtain jobs in a variety of industries. Many PhD students hope to become university professors. Governments and public policy-related institutions such as the Federal Reserve System, the U.S. federal government, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) also hire economists to work on policy, lead programs, and conduct research. Finally, economics PhD graduates can also find employment at a variety of private sector companies, including banks, economic consulting firms, and big tech companies. The pay for these different positions can vary. According to the American Economics Association (AEA), the average starting salary for economics assistant professors in 2022-23 was approximately $140,000 at PhD granting institutions and $98,000 at BA granting institutions.
Programs often publish the placements of their PhD graduates, so you can look online to see specific employment outcomes. See, for example, the University of Maryland’s placements . Ultimately, economists are highly regarded as authorities on a variety of topics. Governments, nonprofits, philanthropic foundations, financial institutions, and non-financial businesses all look to economists to answer important questions about how to best achieve their goals. Thus, earning an economics Ph.D. can potentially help you to influence issues that are important to you.
Preparing for an Economics PhD Program
There are several components to an economics PhD program application: college transcripts, GRE scores, letters of recommendation, and personal statements. Please download the Appendix linked below to learn more about transcripts and letters of recommendation. The Appendix details ways in which you can select coursework, obtain research experience, and develop relationships to position yourself for success as a PhD applicant.
If you feel that you are too far along in your academic career to take enough of the classes described in the Appendix, this does not necessarily preclude you from pursuing an economics PhD. For example, it’s possible to take some of these classes through a master’s program, or through a pre-doctoral RA job. Some pre-doctoral RA jobs, such as the one here at the New York Fed , may enable you to take classes in preparation for graduate school. If you are concerned about your transcript, reach out to an economist at your university for advice; program standards for coursework and grades vary, and it’s a good idea to get more personalized advice.
Research Experience
If you’re interested in becoming an economics researcher and applying to PhD programs, it’s best to get research experience as soon as possible. Working as an RA is a great way to learn how to conduct research and get a better idea of whether it’s the right career path for you. Additionally, it can help you obtain a letter of recommendation for graduate school applications and improve your qualifications.
All types of academic research can be enriching, but it’s beneficial to gain experience working directly with an economist. To find a position, you can reach out to professors whose work you find interesting or find an RA program at your school. Typical RA tasks may involve data collection and cleaning, as well as running analyses and creating charts to represent results. This is where coding skills become crucial; having taken math, statistics, and econometrics courses will also enable you to take on more responsibilities.
You may also have the opportunity to conduct your own research, possibly under the supervision of a professor at your university. This research could be self-initiated or part of a course such as a thesis workshop. Self-directed research is a great opportunity to learn about all stages of the research process. It’s also an excellent opportunity to create a writing sample for graduate school applications. Ultimately, though, your motivation for conducting your own research project should be that you want to answer a question. One thing economists have in common is a love of answering questions using data and theory.
Research experience is also often obtained after completing an undergraduate or master’s degree. Taking on a full-time RA position before applying to PhD programs is very common and can make you a more competitive applicant. You may either get an RA job working for a professor or participate in a pre-doctoral RA program.
Research assistant programs are more structured than positions with individual professors or projects, which could be helpful. Universities, parts of the government, think tanks, research organizations, and the Federal Reserve System are all good places to look for research assistant programs. To help you decide which opportunities are most desirable, you may want to ask potential employers : Where do people in this program tend to go afterward? Will I be working directly with an economist? How much of my time will be spent on academic research work? Will I be able to take classes as part of this program? Considering whether an economist will be able to evaluate your performance is an important factor for recommendation letters. The ability to take classes, either through tuition reimbursement or waivers, can also be an important benefit.
The Research Analyst program here at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York is one example of these programs and you should check it out here . The Federal Reserve Board of Governors also has a large program, and many other regional Federal Reserve Banks have similar programs. In addition, the PREDOC website and the NBER post listings of RA opportunities. J-PAL and IPA also tend to recruit RAs for economic development projects. Another source of RA opportunities is the @econ_ra account on X.
Who Should Get a PhD in Economics?
A PhD may not be for everyone, but it is for anyone—people of all genders, religions, ethnicities, races, and national origins have PhDs in economics. Many economists majored in economics, but others majored in math, physics, or chemistry. Because economics is such an integral part of policymaking, it is important that economists come from a wide range of backgrounds so policy can be stronger and more effective. The inclusion of differing perspectives helps ensure that the contribution of economists to work in public policy, academia, and beyond effectively serves the broadest range of society.
- Coursework Appendix

Kasey Chatterji-Len is a research analyst in the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Research and Statistics Group.

Anna Kovner is the director of Financial Stability Policy Research in the Bank’s Research and Statistics Group.
How to cite this post: Kasey Chatterji-Len and Anna Kovner, “Thinking of Pursuing a PhD in Economics? Info on Graduate School and Beyond,” Federal Reserve Bank of New York Liberty Street Economics , May 31, 2024, https://libertystreeteconomics.newyorkfed.org/2024/05/thinking-of-pursuing-a-phd-in-economics-info-on-graduate-school-and-beyond/.
You may also be interested in: AEA: Resources for Students
PREDOC: Guidance for Undergraduates
RA Positions-Not at the NBER
Disclaimer The views expressed in this post are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the position of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York or the Federal Reserve System. Any errors or omissions are the responsibility of the author(s).
Share this:
Post a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
(Name is required. Email address will not be displayed with the comment.)

Liberty Street Economics features insight and analysis from New York Fed economists working at the intersection of research and policy. Launched in 2011, the blog takes its name from the Bank’s headquarters at 33 Liberty Street in Manhattan’s Financial District.
The editors are Michael Fleming, Andrew Haughwout, Thomas Klitgaard, and Asani Sarkar, all economists in the Bank’s Research Group.
Liberty Street Economics does not publish new posts during the blackout periods surrounding Federal Open Market Committee meetings.
The views expressed are those of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect the position of the New York Fed or the Federal Reserve System.
Economic Inequality
Most Read this Year
- Credit Card Delinquencies Continue to Rise—Who Is Missing Payments?
- The Post-Pandemic r*
- Spending Down Pandemic Savings Is an “Only-in-the-U.S.” Phenomenon
- The Evolution of Short-Run r* after the Pandemic
- Auto Loan Delinquency Revs Up as Car Prices Stress Budgets
- Economic Indicators Calendar
- FRED (Federal Reserve Economic Data)
- Economic Roundtable
- OECD Insights
- World Bank/All about Finance
We encourage your comments and queries on our posts and will publish them (below the post) subject to the following guidelines:
Please be brief : Comments are limited to 1,500 characters.
Please be aware: Comments submitted shortly before or during the FOMC blackout may not be published until after the blackout.
Please be relevant: Comments are moderated and will not appear until they have been reviewed to ensure that they are substantive and clearly related to the topic of the post.
Please be respectful: We reserve the right not to post any comment, and will not post comments that are abusive, harassing, obscene, or commercial in nature. No notice will be given regarding whether a submission will or will not be posted.
Comments with links: Please do not include any links in your comment, even if you feel the links will contribute to the discussion. Comments with links will not be posted.
Send Us Feedback
The LSE editors ask authors submitting a post to the blog to confirm that they have no conflicts of interest as defined by the American Economic Association in its Disclosure Policy. If an author has sources of financial support or other interests that could be perceived as influencing the research presented in the post, we disclose that fact in a statement prepared by the author and appended to the author information at the end of the post. If the author has no such interests to disclose, no statement is provided. Note, however, that we do indicate in all cases if a data vendor or other party has a right to review a post.
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- Request a Speaker
- International, Seminars & Training
- Governance & Culture Reform
- Data Visualization
- Economic Research Tracker
- Markets Data APIs
- Terms of Use

When the PhD path leads to career struggles

A doctoral degree is a major commitment. Think carefully.
I appreciated reading Kara Miller’s The Big Idea column “PhD: Pretty heavily disappointed” (Business, May 22), about people with doctoral degrees struggling to build careers in academia. It made me think back to a conversation I had when I was about to graduate from high school.
I happened to run into a former track coach of mine, and as we were reminiscing he asked me what I planned as a major in college. “History,” I responded. He said, “Why don’t you take some computer classes also? It never hurts to be able to do something useful.”
I did not reflect on his motivation at the time, but my track coach was a young guy, and he was probably giving me advice straight from his own life, as a parent trying to raise his own young children. I did take computer classes in college and ultimately received a PhD in chemical engineering. I always remember that conversation as being a kind of turning point.
Earning a doctoral degree is a life commitment of great proportion. It can take, as Miller notes, between four and seven years. If we think of working life as roughly between the ages of 22 and 65, then a PhD requires more than 10 percent of a person’s working life. People need to think carefully about that investment.
Advertisement
Two powerful arguments in favor of the path of science, technology, engineering, and math are that there tend to be more STEM jobs for PhDs, and many universities’ STEM departments are generous in covering their PhD students’ tuition and cost of studies, including a stipend toward food, rent, and other expenses.
Stuart Gallant
Not much has changed in 30 years
As I prepared to graduate in 1995 with a doctor of education degree from the Harvard Graduate School of Education, my mother memorably said to me, “Of my four children, you are the one with the most education and the smallest salary.” Apparently not much has changed in 30 years.
I must congratulate these students, however, on following their passion rather than following the money. I can’t help but think that their lives, though stressful, may contain greater happiness.
Peggy Clark
Lawyers & electricians & philosophers, oh my!
Kara Miller’s column on the career challenges for people with doctoral degrees generated more than 260 comments on Boston.Globe.com. The following is an edited sample of readers’ reactions:
Lots of law school grads are underemployed as well. (PL)
So true, PL. The market in Massachusetts is flooded with talented lawyers seeking work. (Roforma)
Supply and demand, the market at work. (guk)
Investing in education and research in all fields is the hallmark of a society with staying power. Disinvesting from these endeavors signals decline and decay. (Massachusetts citizen)
Electricians, plumbers, mechanics, and other skilled technical professions have no problems getting $100k jobs with great benefits. (ramsen)
Not enough turnover from tenured professors, leaving little space for new faculty. Although the tenured, well-established professors are needed, it’s the junior faculty who are hungry and with new ideas that help build new programs. The whole graduate program model is a bad model. I worked two jobs, had my tuition and some type of minimal student health insurance and could barely cover the rent with my stipend, and the second job paid for everything else. Though I was working on many faculty projects, it was the faculty who said this would be good for me. Never did they say it was also good for them. (TravelerofNJ2)
I just retired from a tenured faculty position in science. I’m in my early 70s. I have colleagues who are still doing what they do well into their 70s, a couple approaching 80. There is no active incentive from the university to move the older faculty on, to make way for a new generation. (Lola-lola)
The next step is for adjuncts to go on strike across the nation and hold colleges and universities accountable. The current system is completely absurd. (Wordsmith2358)
Universities should be required to release disclosure data about the fate of their PhD graduates. (davidman820)
I knew an attorney who managed a Cheesecake Factory. She had worked in food services through school. As an attorney, she really did not make that much money and was not doing the field of law of her choice. How many real estate closings can you do without dying of boredom? She went into management in the food industry and makes the same salary. (Antietem)
It was always a question and puzzling to me why people study philosophy. (Blazer27)

Globe Opinion
- Getting Results.
- Newsletters
Jury ends second day of deliberations without reaching verdict in fraud trial roiled by bag of cash
Steve Karnowski
Associated Press
This photo supplied by the U.S. Attorney's Office for Minnesota shows cash from a bag that was left at the home of a juror in a massive fraud case, June 2, 2024, outside Minneapolis, Minn. Authorities have confiscated cellphones and taken all seven defendants into custody as investigators try to determine who attempted to bribe the juror to acquit them on charges of stealing more than $40 million from a program meant to feed children during the pandemic. (U.S. Attorney's Office for Minnesota via AP)
MINNEAPOLIS – A jury ended a second day of deliberations Wednesday without reaching a verdict in the trial of seven Minnesotans accused in a scheme to steal more than $40 million from a program meant to feed children during the coronavirus pandemic, while FBI agents try to establish who left a bag with $120,000 in cash for a juror.
Federal authorities confiscated the defendants' cellphones to search for clues and took all seven into custody on Monday before deliberations began. The trial judge also sequestered the jury after dismissing the juror who turned over the gift bag, along with another juror who reported hearing about the bribe attempt.
Recommended Videos
FBI agents searched the home of one of the defendants Wednesday, according to a neighbor who witnessed the search and spoke to The Associated Press on condition of anonymity because of safety concerns. News of the FBI raid was first reported by KARE-TV. The home searched is identified in court records as the home of Abdiaziz Shafii Farah, who prosecutors have described as a ringleader of the seven.
The neighbor described seeing several FBI agents armed with assault weapons standing outside the home. The agents used a megaphone to instruct the home's residents, who came outside and stood in the driveway, the neighbor said.
Minneapolis FBI spokesperson Diana Freedman said in emails to the AP that “The FBI was present in Savage, MN conducting court authorized law enforcement activity,” but that “I cannot provide or confirm any additional information.”
Farah’s attorney, Andrew Birrell, would not comment when reached by the AP.
According to an FBI agent’s affidavit, a woman rang the doorbell at the home of “Juror #52” in the Minneapolis suburb of Spring Lake Park late Sunday, the night before the case went to the jury. The juror wasn't home, so the woman handed her relative a gift bag with a curly ribbon and images of flowers and butterflies, saying it was a “present” for the juror.
“The woman told the relative to tell Juror #52 to say not guilty tomorrow and there would be more of that present tomorrow,” the agent wrote. “After the woman left, the relative looked in the gift bag and saw it contained a substantial amount of cash.”
The juror called police right after she got home and gave them the bag, which held stacks of $100, $50 and $20 bills totaling around $120,000.
U.S. District Judge Nancy Brasel and attorneys for both sides learned about the attempted bribe Monday morning, before the last closing arguments.
Freedman said the investigation is ongoing, and no further information is public. No arrests have been announced.
Anyone involved in the attempted bribe could face federal charges of bribery of a juror and influencing a juror, with a maximum potential penalty of 15 years in prison.
The seven defendants are the first of 70 to stand trial in what federal prosecutors have called one of the nation's largest COVID-19-related fraud cases, an extensive scheme to exploit rules that were kept lax so that the economy wouldn't crash during the pandemic.
Prosecutors say the seven collectively stole more than $40 million from a program designed to feed children in Minnesota, and that the overall conspiracy diverted $250 million in federal funds.
At its center was a nonprofit called Feeding Our Future. Prosecutors say just a fraction of the money went to feed low-income kids, with the rest spent on luxury cars, jewelry, travel and property. Federal authorities say they have recovered about $50 million.
Eighteen other defendants have pleaded guilty. Those awaiting trial include Aimee Bock, the founder of Feeding our Future. She has maintained her innocence, saying she never stole and saw no evidence of fraud among her subcontractors.
These seven defendants are: Abdiaziz Shafii Farah, Mohamed Jama Ismail, Abdimajid Mohamed Nur, Said Shafii Farah, Abdiwahab Maalim Aftin, Mukhtar Mohamed Shariff and Hayat Mohamed Nur. All were charged with wire fraud conspiracy and money laundering, and some faced additional charges in the 43-count indictment. Each had their own lawyers.
The common thread in their defense is that investigators failed to dig deep enough to see they served real meals to real kids.
The food aid came from the U.S. Department of Agriculture and was administered by the state, which funneled the meal money through nonprofit organizations and other partners. As rules were eased to speed support to the needy, the defendants allegedly produced invoices for meals never served, ran shell companies, laundered money, indulged in passport fraud and accepted kickbacks.
An Associated Press analysis published last June documented how thieves across the country plundered billions in federal COVID-19 relief dollars. Fraudsters potentially stole more than $280 billion, while another $123 billion was wasted or misspent. Combined, the loss represented 10% of the $4.3 trillion the government disbursed by last fall. Nearly 3,200 defendants have been charged and about $1.4 billion in stolen pandemic aid has been seized, according to the U.S. Justice Department.
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Let's starts with negative points: You're 40 years old right now. So realistically you will finish your PhD at the age of 45 or even more if you're doing it in countries like the US or Canada. So ...
It sounds like you are thinking about a PhD in Philosophy with a hope of an academic job. We can imagine you getting the PhD in 6 years (so 34), and then maybe needing to be a postdoc for a few years (let's be optimistic and say 4), and so we're talking about you starting a TT job at the age of 38 if it works out well.
While the overall age of Ph.D. candidates has dropped in the last decade, about 14 percent of all doctoral recipients are over age 40, according to the National Science Foundation. Relatively few ...
In 2020, the average age of a graduate from a PhD program in the United States was 33. However, 6% of the graduates were over 45. When people ask what the average age of a PhD student is, many times they're really asking, "Am I too old to get a PhD?". The answer is almost always no.
Application Activities for a PhD in your 40s'. Now Let's look at some of the requirements for gaining admission to a Ph.D. program. PhD program requirements include taking a GRE/GMAT, identifying and sending your transcripts (bachelors and masters), writing your personal statement, securing some good recommendation letters, etc. Figure 1 is ...
Educators see increasing enrollment in doctoral programs by students in their 40s and 50s. At Cornell University, women drive the trend. "The number of new female doctoral students age 36 or older was 44% higher in 2015 than in 2009," says Barbara Knuth, senior vice provost and dean of the graduate school.
Here are some potential advantages and drawbacks of doing a PhD later in life: Advantages: Greater maturity: You have a better understanding of what you want to do and can focus on your goals. Real-world experience: You have a better understanding of real-world problems and can work on more relevant research.
March 20, 2022. A Ph.D. After 40. Lauren Easterling offers advice for successful job searches after obtaining your doctorate or completing a postdoc in midlife. By Lauren Easterling. wbritten/istock/getty images plus. When I started by Ph.D. program, I was 31 years old. I was a little bit older than some of the other students in my cohort but ...
Even if you disagree with your supervisors or advisors, do your best to always remain respectful in those disagreements. Remember: 90 percent of your happiness during a PhD will be based on your relationships with your committee, so do your best to be a great student. You will feel really uncomfortable.
So, it's important to do whatever you need to do to get over impostor syndrome. Have a good cheerleader—such as your partner, a friend, or a family member—to remind you that you're smart, motivated, and hard-working. Accept the compliment because it is true. And remind yourself that everyone is "faking it until they make it."
The first part of a PhD can be very important. This guide explains how to prepare for your PhD, settle into your department and start planning your project. ... Upon starting your PhD, you will usually go through some form of induction. This will be carried out by your university, a specific department, and / or your supervisor.
As it's the start of the academic year I want to share a few of my own tips along those lines, to help get your PhD off to a good start, and keep it on a trajectory you're happy with: 1. Keep notes on everything you read. My PhD, like many, kicked off with lots of reading of textbooks and academic papers. My reading has ebbed and flowed ...
20. Enjoy your PhD! It can be tough, and there will be days when you wish you had a 'normal' job, but PhDs are full of wonderful experiences and give you the opportunity to work on something ...
Starting a Ph.D. program can be a daunting experience, whether one is starting straight out of an undergraduate program, after a Master's program, or even later in life. As a current third year Ph.D. student, I can remember feeling overwhelmed when I first started graduate school and wishing I had more resources to prepare me for what was to ...
5. Embrace change - don't get bogged down in the details. Felix Shaw - one of our bioinformatics researchers at EI - put it best when he said, " it felt like I was running into brick walls all the way through [my PhD]… you'd run into a brick wall, surmount it, only to run straight into another. It's true.
2,270 21 24. 2. I completely agree with this post. There was a 6x year old PhD candidate in my old group that worked 4 days of the week for a company, while 1 day in the week he would be working on his research. He needed a bit longer than more 'traditional' PhD candidates but still finished his PhD successfully.
Looking at the age distributions available for 51,621 of these new PhD graduates in 2016, 44% (n=22,863) were aged 30 or below, 43% (n=22,038) were aged between 31 and 40 and 13% (n=6,720) were over the age of 40 when they were awarded their doctoral degree. In this same year, over 50% of PhD students in subjects related to physical sciences ...
And your life experience helps I treated my PhD like a 9-to-5 40 hour week job and swept through. Most of the younger ones around me struggled with work-life balance through lack of practice. And once you have it, most academics will assume you got it in your 20's and have a lifetime's research in your field.
We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us.
2. Identify the problems before setting to solve them. This may sound simple, but trust me, finding a problem is sometimes way harder than coming up with a solution to an existing problem. I ...
I'm 40 and started my PhD in October. Granted, that's about where our similarities end. I did opt for a career and money, but it was because I hated uni (dropped out) and it turns out that for most actors, money comes from temping jobs. However, I graduated zoology two years ago, and after a bit of relevant work, started a PhD in environmental ...
The major benefit of starting a PhD at 29 was that I was more mature - it's a fairly obvious one I know, but in hindsight it was important. It meant that I (mostly) knew what I wanted and why I was doing a PhD. I had already tried other careers and was quite certain that a career in academia would be a good long-term fit for me and I was ...
How the PhD Program Works. Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending ...
Gain a deeper insight into their journey so far and make notes to give your journey a headstart. 4. You think finances don't matter while pursuing PhD? You are wrong. Ensuring financial stability throughout your time is crucial as you will be dedicating a duration of your time solely to research.
It often starts with "But", "Yet" or "However". The third sentence says what specific research has been done. This often starts with "This research" or "I report…". The fourth sentence reports the results. Don't try to be too tricky here, just start with something like: "This study shows," or "Analysis of the data ...
2.0 PhD PROGRAM OVERVIEW. The PhD program is comprised of core courses and research experiences, which build a student's "toolbox". The remainder of credits are designed to build research domain expertise. The three-year and four-plus year plans of study outline the recommended sequence of courses and dissertation credits.
Over the last few years, graduate psychology degree programs, both at the master's and doctoral levels, have shifted their admission criteria from an emphasis on standardized testing to components that reflect applicants' experiences. According to the most recent edition of Graduate Study in Psychology, 1 for 2022-23 applications ...
What Can You Do with an Economics PhD? Upon graduation, students can obtain jobs in a variety of industries. Many PhD students hope to become university professors. ... (AEA), the average starting salary for economics assistant professors in 2022-23 was approximately $140,000 at PhD granting institutions and $98,000 at BA granting institutions.
It can take, as Miller notes, between four and seven years. If we think of working life as roughly between the ages of 22 and 65, then a PhD requires more than 10 percent of a person's working life.
This photo supplied by the U.S. Attorney's Office for Minnesota shows cash from a bag that was left at the home of a juror in a massive fraud case, June 2, 2024, outside Minneapolis, Minn ...