- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore

Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Advanced Admit Card
- JEE Advanced Admit Card 2024
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- KCET Result
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Admit Card
- TS ICET 2024 Hall Ticket
- CMAT Result 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- NEET Rank Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Admit Card 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top NLUs Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Top NIFT Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Cut Off 2024
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- CUET 2024 Exam Live
- CUET Answer Key 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Diversity In India Essay
Diversity in India is a remarkable phenomenon, one that has been celebrated since ancient times. It is a country where different cultures, religions, languages, and traditions coexist in harmony, reflecting its traditional adage of ‘unity in diversity’. India is home to a plethora of different ethnicities, languages, religions and cultures, each with its own unique set of customs and beliefs. Here are a few sample essays on the topic ‘Diversity In India’.
100 Words Essay On Diversity In India
200 words essay on diversity in india, 500 words essay on diversity in india.

India is a country with a rich and diverse cultural heritage, and it is no surprise that it is also home to a variety of people from different religions, ethnicities and backgrounds. Diversity in India is a reflection of the many different groups and cultures that coexist in the country. India’s diversity is not only celebrated but embraced and admired.
When it comes to diversity in India, there are several types. The most common are religious, linguistic, regional, and ethnic diversity. India is one of the most religiously diverse countries in the world, with Hindus, Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains and many other belief systems calling the country home. Additionally, India is home to several languages including Hindi, Sanskrit, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, Punjabi, Gujarati, and Bengali.
India’s ethnic diversity is also quite remarkable. The population is divided into numerous ethnic groups including the Scheduled Tribes, Scheduled Castes, Other Backward Classes, and many more. Each of these ethnic groups has their own distinct culture, language, and customs, making them unique and inspiring. There are also many dialects of each language and they are spoken throughout the country's states and regions.
Benefits | The many different types of diversity in India are beneficial in several ways. Firstly, it leads to a more harmonious and peaceful environment, as people from different backgrounds are able to share their unique perspectives and experiences, leading to mutual understanding and respect. Secondly, diversity allows for a variety of talents and skills to be cultivated, leading to a more vibrant and successful economy. Lastly, diversity leads to an increased appreciation and understanding of different cultures and beliefs, which is beneficial for the country’s progress and development.
Unity In Diversity | The concept of ‘unity in diversity’ is an integral part of India’s culture and identity. This concept is evident in everything from the country’s festivals and celebrations, to its freedom of expression and equal rights for all. It is this idea of diverse people coming together to form one unified nation that makes India stand out among other countries in the world.
India is a land of unique and diverse cultures, religions, languages, and customs. The concept of ‘unity in diversity’ is a cornerstone of India’s culture and identity, and is something that should be celebrated and embraced. The different patterns of culture, religion, language, and customs make India one of the most interesting countries in the world.
Geographical Diversity | India's diversity is also visible in its geographical landscape. India is a land of mountains, valleys, plains, deserts, and seas. It has the highest mountain range, the Himalayas. It also has the largest desert, the Thar Desert, and the longest river, the Ganges.
Social, Economical And Cultural Advantages Of Diversity
India’s diversity is beneficial both economically and socially, allowing the country to prosper and grow.
The diversities in India have been beneficial for its people. One of the most significant benefits is that it has enabled India to be a culturally, socially, politically and economically united nation. The diversity in India has also helped to promote a sense of understanding and tolerance among its people. It is this sense of understanding and tolerance that has enabled India to become a strong and unified nation.
India's unique diversity has enabled the country to be a leader in the field of science, technology, and innovation. India is home to a number of leading technology companies and has been a major player in the global economy.
India's diversity has also been beneficial in terms of promoting cultural exchange and understanding. India has given the world a number of great cultural traditions such as yoga, Ayurveda, and music. This has enabled people from different cultures and religions to come together and exchange ideas and experiences.
Impact of Diversity In India
The diversity in India has had a major positive impact on the country, both in terms of its economy and its culture. The diverse population has enabled India to become a multicultural hub, with people from all walks of life interacting with each other, exchanging ideas, and bringing different perspectives to the table. This has enabled the country to become a melting pot of different cultures, thereby increasing its economic power. The presence of different religions has also resulted in the development of a more tolerant and inclusive society.
The diversity of India has also enabled it to preserve its traditions and practices. By embracing different cultures, India has been able to protect its own culture and customs. This has enabled the country to benefit from its traditional values and practices, while also benefiting from the knowledge and innovation brought in by its diverse population.
India’s diversity is a source of strength and a major source of pride for the country. It has enabled the country to become a major player in the global economy, while preserving its traditional values and customs. The presence of different religions, languages, and cultures has enabled the country to become a more tolerant and inclusive society. It is this unique diversity that has enabled India to become the vibrant, dynamic and economically powerful nation that it is today.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)
Register FREE for ALLEN Digital Scholarship Admission Test (ADSAT)

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PW JEE Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for JEE coaching

PW NEET Coaching
Enrol in PW Vidyapeeth center for NEET coaching

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Diversity in India: A Tapestry of Cultural and Traditions

- Updated on
- Apr 23, 2024

Essay on Diversity in India: “Unity in diversity is India’s strength. There is simplicity in every Indian. There is unity in every corner of India.” As India celebrates 77 years of independence, it’s crucial to explore the vast diversity that defines this nation. Despite the colonial past, which attempted to diminish the rich tapestry of Indian culture, the country today is a vibrant mosaic of languages, religions, and traditions.
Table of Contents
- 0.1 Cultural Diversity
- 0.2 Social Diversity
- 0.3 Religious Diversity
- 0.4 Linguistic Diversity
- 0.5 Geographical Diversity
- 0.6 Conclusion
Cultural Diversity
India’s cultural landscape is as varied as its geography. Each region boasts its unique festivals, arts, and culinary traditions. For instance, classical dance forms like Kathak in the north and Bharatanatyam in the south highlight regional narratives and myths. The popularity of Western dance forms has not overshadowed these traditional dances, reflecting a resurgence in interest in and pride in indigenous arts. Similarly, festivals like Diwali and Eid are celebrated with fervor across the country, showcasing unity in diversity.
India is the home of numerous different religious traditions. Hindus (82.41%), Muslims (11.6%), Christians (2.32%), Sikhs (1.99%), Buddhists (0.77%), Jains (0.41%), and tribal cultures (many of whom still engage in animism and magic) comprise the population of India.
Quick Read: Essay on the Role of Youth in Nation-Building
Social Diversity
India’s social fabric is woven with threads from numerous ethnic groups and castes. This diversity is a double-edged sword, presenting challenges in terms of social equality while also enriching the societal structure with a variety of perspectives and practices. Urban areas, in particular, display a melting pot of cultures, with people from various backgrounds living and working together, which promotes a broader understanding and acceptance of diverse social norms.
Religious Diversity
Home to major religions such as Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, and Jainism, India’s religious diversity is a testament to its pluralistic society. This multiplicity of belief systems coexisting is one of India’s greatest strengths, fostering a culture of mutual respect and tolerance. The peaceful cohabitation of diverse religious communities, however, is occasionally challenged by conflicts, underscoring the need for continuous dialogue and reconciliation.
Linguistic Diversity
With over 1,600 languages and dialects spoken, the linguistic diversity in India is staggering. Hindi and English are widely used, but state-specific languages such as Tamil, Telugu, Marathi, and Bengali hold equal importance. The Indian constitution’s recognition of 22 official languages is a clear indicator of the country’s commitment to embracing its linguistic heritage. This diversity is also evident in literature, with works ranging from the ancient epics of Ramayana and Mahabharata to modern writings in various vernaculars.
Every language embodies the history and customs of its people and reflects a unique legacy. The Indian Constitution, which affirms India’s commitment to inclusivity and cultural preservation, recognises and defends this diversity by defending the rights of linguistic minorities and fighting for the preservation of endangered languages.
Geographical Diversity
From the snowy peaks of the Himalayas in the north to the tropical beaches of the south, India’s geographical diversity influences its climate, agriculture, and lifestyle. This diversity not only dictates the economic activities of different regions but also shapes the cultural identities of the people, from the attire they wear to the food they eat.
India has breathtaking geographical diversity, with the sun-kissed beaches of the south and the towering Himalayas of the north, as well as the lush forests of Kerala and Rajasthan. In addition to influencing regional traditions and means of subsistence, this geographic diversity has given India an unmatched biodiversity. India is a large country with a diverse range of natural environments, including deserts, evergreen forests, steep mountains, perennial and non-perennial river systems, long coastlines, and fertile plains. Its total land area is 3.28 million square kilometres.
Quick Read: Importance of Mental Health Essay
While significant achievements have marked India’s journey since independence, the shadow of colonial influence still lingers, impacting perceptions and values. Yet, the resurgence of pride in one’s heritage and the continuous celebration of its diversity are signs of a maturing nation that values its past while forging a new identity. India’s diversity is not just a fact of life but the very fabric that makes it unique on the global stage. As India moves forward, it is the recognition and preservation of this diversity that will empower it to overcome its colonial hangovers and redefine what it means to be modern and Indian on its terms. The path ahead lies in embracing the richness of its diverse heritage, thus truly fulfilling the dreams that fueled its struggle for freedom 77 years ago.
Ans: India is a multicultural nation home to all of the world’s main religions. The number of languages spoken in India is over 1600. India’s terrain is diverse, with mountains, plains, plateaus, deserts, and islands among its features. Aside from this, migration from all over the world has given rise to a variety of ethnic groups in India.
Ans: The acceptance of a range of individual characteristics within a society or group is referred to as diversity. Aspects including color, ethnicity, gender, age, financial situation, sexual orientation, religious views, abilities, and more can all be considered in these differences.
Ans: India is referred to as the “land of diversity” for a variety of reasons, including its diverse culinary options, language usage, holiday celebrations, and religious and cultural practices.
Check out our Popular Essay Topics for Students
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Aayushi Vardhan
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out

Essay on Diversity in India
Students are often asked to write an essay on Diversity in India in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Diversity in India
Introduction.
India is a vast country known for its diverse culture, religion, and languages. This diversity is what makes India unique and special.
Cultural Diversity
India is home to various cultures. Each culture has its own set of traditions, festivals, and rituals, contributing to the rich tapestry of Indian society.
Religious Diversity
India is a secular country where people of different religions live together. These religions include Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, and Jainism.
Linguistic Diversity
India is a linguistically diverse country with more than 1600 spoken languages. Each state has its own regional language, adding to the country’s multiculturalism.
In conclusion, diversity in India is a symbol of unity in diversity. It is a country where diverse cultures, religions, and languages coexist peacefully.
250 Words Essay on Diversity in India
India, often referred to as a ‘sub-continent’, is renowned for its rich diversity. The country’s vast landscape is a mosaic of various cultures, languages, religions, and traditions, making it a vibrant and colorful nation.
India’s cultural diversity is one of its most striking features. With over 2,000 distinct ethnic groups and more than 1,600 spoken languages, the country is a melting pot of cultures. Every state in India has its unique dance forms, music, cuisine, and art, contributing to a cultural kaleidoscope that is as diverse as it is vibrant.
Religion is another facet of India’s diversity. The country is the birthplace of several religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. Additionally, it embraces Islam, Christianity, and other faiths, fostering a spirit of religious coexistence and tolerance.
The linguistic diversity in India is unparalleled. Each state has its language, and there are several dialects within each language. The constitution of India recognizes 22 official languages, reflecting the linguistic pluralism of the country.
The diversity in India is a testament to the country’s inherent capacity to absorb, integrate, and embrace differences. It is a living example of unity in diversity, where diverse cultural, religious, and linguistic elements coexist and enrich the social fabric. This diversity is not just the country’s identity but also its strength, fostering mutual respect, understanding, and harmony among its people.
500 Words Essay on Diversity in India
Introduction: the melting pot of cultures.
India, often referred to as the “land of diversity”, is a unique amalgamation of various cultures, religions, languages, and traditions. This diversity, deeply embedded in the country’s historical roots and societal fabric, is what makes India a vibrant and dynamic nation.
Cultural diversity is one of the most striking features of India. The country is home to numerous ethnic groups, each with its distinct customs, traditions, and languages. The coexistence of these diverse cultures under one political and geographical entity is a testament to India’s pluralistic society. From the folk dances of Punjab to the martial arts of Kerala, from the sand art of Odisha to the bamboo dance of Mizoram, each region contributes to the cultural mosaic of the country.
India is the birthplace of four major world religions: Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. It also embraces other religions such as Islam, Christianity, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, and Baha’i, demonstrating the nation’s religious tolerance and acceptance. This religious diversity is reflected in the myriad of festivals celebrated throughout the year, such as Diwali, Eid, Christmas, and Paryushan, each marking a unique blend of customs, traditions, and rituals.
Linguistic diversity is another defining characteristic of India. With over 2,000 distinct languages spoken across the country, India stands as one of the most linguistically diverse nations globally. Each language, with its unique script and literature, adds to the rich tapestry of Indian culture.
Geographical Diversity
From the snow-capped peaks of the Himalayas to the serene backwaters of Kerala, from the deserts of Rajasthan to the dense forests of the Northeast, India’s geographical diversity is unparalleled. This geographical variance has given rise to diverse ecosystems and biodiversity, making India one of the 17 mega-diverse countries in the world.
Diversity in Indian Cuisine
Indian cuisine is a gastronomic reflection of the country’s diversity. Each region has its unique culinary tradition, influenced by local produce, culture, and history. The rich and spicy curries of Rajasthan, the seafood-centric cuisine of Bengal, the coconut-infused dishes of Kerala, and the simple yet flavorful food of Gujarat are just a few examples of India’s diverse culinary landscape.
Conclusion: Unity in Diversity
Despite the immense diversity, there exists a unique sense of unity among Indians, often encapsulated in the phrase “Unity in Diversity”. This unity is evident in the mutual respect and harmony with which people of different cultures, religions, and languages coexist in India. The diversity of India is not merely a demographic fact but a living, influential force that shapes the nation’s worldview and its approach to global relations. It is a testament to India’s resilience, adaptability, and inclusivity. The diversity of India thus stands as a beacon of pluralism and multiculturalism in an increasingly globalized world.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Status of Women in India
- Essay on Indian Freedom Struggle
- Essay on India Is Incredible Travel And Explore
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
Diversity of India
Last updated on April 30, 2024 by ClearIAS Team

Despite numerous foreign invasions, a vast synthesis of the cultures, faiths, and languages of the people from all castes and communities has maintained its cohesion and unity.
Even if stark economic and social disparities have prevented the formation of egalitarian social relations, national unity and integrity have been preserved.
This fusion has transformed India into a singular mosque of cultures. India thus presents a situation that appears to be multicultural within the context of a single, cohesive cultural whole.
Also read: Minorities in India
Table of Contents
What does diversity mean?
The word “diversity” places more emphasis on differences than on unfairness. It refers to group disparities, or distinctions separating one group of individuals from another.
- These differences could be biological, religious, linguistic, or anything else. Diversity refers to the variety of races, religions, languages, castes, and cultures.
- Integrity refers to unity. It is a state of social psychology. It suggests a sense of unity and togetherness. It represents the ties that keep a society’s members together.
- Essentially, “unity in diversity” means “diversity without fragmentation” and “unity without uniformity.” It is predicated on the idea that diversity enhances interpersonal communication.
- When we refer to India as a country with rich cultural diversity, we are referring to the wide variety of social groupings and cultures that call India home. These groups identify primarily through cultural traits like language, religion, sect, race, or caste.
Also read: Environmental Racism

The different forms of India’s diversity include the following.
Religious diversity
- India is a country that is home to many different religions.
- The Indian population is made up of Hindus (82.41%), Muslims (11.6%), Christians (2.32%), Sikhs (1.99%), Buddhists (0.77%), and Jains (0.41%), in addition to the tribal societies, many of which continue to practice animism and magic.
- Hindus are divided into several sects, including Vaishnavas, Shaivites, Shaktas, and Smartas. Similarly, there are various Muslim sects, including Shi’ites, Sunnis, Ahmadis, etc.
Language diversity
- The major language families among the languages spoken in India are the Dravidian languages, which are spoken by 20% of Indians, and the Indo-Aryan languages, which are spoken by 75% of Indians.
- The Austroasiatic, Sino-Tibetan, Tai-Kadai, and a few other minor language families and isolates are home to other languages.
- After Papua New Guinea, India has the second-highest number of languages in the world. India’s ethnic variety was divided into the following groups according to the 1931 census: Negrito, Proto-Australoid, Mongoloid, Mediterranean, Western Brachycephals, and Nordic.
Also Read: Endangered Languages of India
The Caste Diversity
- The Caste Diversity includes members of all three major world races, namely Caucasoid, Mongoloid, and Negroid: India is a nation with Both varna and jati have been referred to as “caste” in the past.
- According to functional differentiation, society is divided into four groups called Varna. Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, Shudras, and an outcaste.
- While the term “Jati” designates a hereditary endogamous status group engaged in a certain traditional profession. There are more than 3000 jatis, and there isn’t a single system for classifying and ranking them across all of India.
- The jati system is dynamic and allows for movement, which has allowed jatis to vary their location throughout time. M. N. Srinivas referred to this method of upward mobility as “Sanskritization.”
Ethnic diversity
- Ethnic diversity Regional differences are reflected in cultural patterns.
- Due to demographic diversity , Indian culture is extremely diverse and is a fusion of many other cultures.
- Every region, caste, and religion has its unique traditions and culture. As a result, there are variations in music, dance, theatre, and architecture.
Geographic diversity
- With a total land area of 3.28 million square kilometres, India is a big nation with a wide variety of natural landscapes , including deserts, evergreen forests, steep mountains, perennial and non-perennial river systems, lengthy coasts, and fertile plains.
- In addition to the major forms of variety already mentioned, India also has diversity in many other areas, such as tribal, rural, and urban patterns of habitation, patterns of marriage and kinship along religious and regional lines, and more.
Also read: Salient features of Indian Society
Factors Promoting Unity in Diversity of India
- Constitutional identity : A single person is elected to lead the entire nation. Even Nevertheless, the majority of states adhere to a standard 3-tier structure of government, bringing
- Furthermore, regardless of their age, gender, class, caste, or religion, all citizens are guaranteed certain fundamental rights under the Constitution.
- Religion tolerance is the distinctive characteristic of faiths in India, and as a result, many different religions coexist there. The Constitution itself guarantees the freedom of religion and practice. Additionally, the state accords equal preference to all religions and has no official state religion.
- Interstate movement : Article 19 (1) (d) of the Constitution ensures freedom of movement throughout India’s territory, fostering a sense of brotherhood and solidarity among the people.
- Other elements that contribute to consistency in the criminal justice system and policy implementation include the uniformity of the law, penal code, and administrative tasks (such as All India Services).
- Economic integration : The Goods and Service Tax (GST) has paved the way for “one country, one tax, one national market,” thereby facilitating unity among different regions. The Indian Constitution also guarantees the freedom of trade, commerce, and intercourse within the territory of India under Article.
- Institution of pilgrimage and religious practices: Spirituality and religion are very important in India. Religious sites and sacred rivers can be found all over the length and breadth of the country, from Badrinath and Kedarnath in the north to Rameshwaram in the south, Jagannath Puri in the east, and Dwaraka in the west. They are closely tied to the long-standing tradition of pilgrimage, which has always drawn people to different regions of the nation and given them a feeling of geo-cultural identity.
- Fairs and festivals : These serve as integrating factors as well because people from all across the nation participate in them. Hindus around the nation celebrate Diwali, just as Muslims and Christians celebrate Id and Christmas, respectively. In India, interreligious celebrations are also observed.
- Weather integration via the monsoon : The monsoon season affects the entire Indian subcontinent’s flora and fauna, agricultural activities, and way of life, including holidays. Sports and cinema are widely popular throughout the nation, serving as unifying forces. Factors that undermine India’s unity include:
- Regionalism : Regionalism favours the interests of a certain region or region over those of the nation. It may also hurt national integration. Regional demands and the resulting law and order situation
- Polarising politics : Politicians would occasionally invoke ascriptive identities like caste, religion, etc. to gain support. Violence, feelings of mistrust, and suspicion among minorities can emerge from this kind of polarising politics.
- Unbalanced development Backwardness of a region can be brought on by uneven socioeconomic growth, poor economic policies, and the resulting economic inequities. As a result, this may spark acts of violence, ignite migrant waves, or even fuel separatist demands. For instance, numerous examples of secessionist demands and tendencies have emerged as a result of the North East’s economic underdevelopment.
- Ethnic diversity and nativism: Ethnic diversity has frequently resulted in conflicts between various ethnic groups, particularly as a result of reasons like employment competition, a lack of resources, and threats to identity For instance, Bodos and Muslims who speak Bengali frequently fight in Assam. The son of the soil idea, which links people to their place of birth and bestows upon them certain advantages, privileges, duties, and obligations that may not apply to others, has served to emphasize this.
- Geographic isolation: Isolation can also result in separatist thinking and identity problems. Geographically, the North-East is separated from the rest of the nation by a small passageway called the Siliguri corridor, sometimes known as the “Chicken’s Neck.”The area is less developed economically than the rest of the nation and has poor infrastructure. As a result, it has seen several incidents of separatist and cross-border terrorism.
- Inter-religious disputes : Inter-religious disputes not only deteriorate relations between two communities by sowing distrust and fear, but they also damage the nation’s secular fabric.
- Conflicts between states : This may cause feelings of regionalism to grow. Additionally, it may have an impact on interstate commerce and communication. For instance, the Karnataka-Tamil Cauvery River dispute
- External influences : External influences, such as foreign organizations, terrorist organizations, and extremist groups, can occasionally inspire violence and foster feelings of secession. g. Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) is alleged to have supported and trained mujahideen to fight in Jammu and Kashmir and incite separatist sentiment among local groupings.
Despite the difficulties diversity might provide, there is no denying the vital role sociocultural diversity has played in maintaining and advancing Indian culture.
The handling of diversity in Indian society, not diversity itself, is the issue. Because the benefits of growth haven’t been divided fairly or certain groups’ cultures haven’t received the acknowledgement they deserve, problems like regionalism, communalism, and ethnic conflicts have emerged.
Therefore, the Constitution and its ideas must serve as the foundation of our society. Any culture that has attempted to homogenize itself has experienced eventual stagnation and decline.
The most notable instance in this situation is Pakistan’s attempt to force its culture on East Pakistan, ultimately leading to Bangladesh’s establishment.

Article Written By: Atheena Fathima Riyas

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
April 16, 2024 at 8:41 pm
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
Take ClearIAS Mock Exams: Analyse Your Progress
Analyse Your Performance and Track Your All-India Ranking
Ias/ips/ifs online coaching: target cse 2025.

Are you struggling to finish the UPSC CSE syllabus without proper guidance?

“A Kaleidoscope of Cultures: Exploring the Rich Tapestry of Cultural Diversity in India”

Written By Avinash Sharan
Uncategorized, 0 comment(s), 15th september 2023, cultural diversity in india: celebrating unity in diversity, introduction.
Cultural Diversity in India is a much talkked topic specially in Social Science. This is due to the fact that India is a country filled with paradoxes and contains a treasure trove of diverse cultures that are both inspirational and humbling. It has a wide array of cultures and societies, which is referred to as its cultural diversity. It reveals the social characteristics, beliefs, ideas, and practises of individuals. In India, there are numerous distinct communities that are very different from one another. The languages, customs, dress codes, and eating habits of Indians differ from one another most noticeably on a cultural level.
Indian culture is influenced by numerous religions, and the country’s blend of different cultures and customs is obvious. Indian history has had a significant impact on Indian culture. In terms of morality and manners, societies differ in how they appear and organize themselves. It refers to the way that people actually live. From the snow-capped Himalayas in the north to the tropical beaches in the south, and from the deserts of the west to the lush greenery of the east, India’s geography is as diverse as its culture. In this article, we embark on a journey to unravel the mosaic of cultural diversity that defines India.
1. A Linguistic Odyssey
Firstly, India is a linguistic kaleidoscope. With over 19,500 languages and dialects spoken across the country, it’s a linguist’s dream. Hindi, Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, and Tamil are just a few of the major languages. Each linguistic region has its own unique script, traditions, and cultural nuances. The linguistic diversity is a testament to India’s multiculturalism.
Linguistic Paradise:
Today, India is a linguistic paradise that sets off on an enthralling voyage via languages and dialects. India is frequently praised as a place of diversity and contrasts. It is a linguistic giant, exhibiting an unparalleled linguistic tapestry on Earth with more than 19,500 languages and dialects spoken there. India’s diverse regional dialects and rich cultural heritage are reflected in the country’s astoundingly diverse linguistic landscape. The diversity of languages in India is at the center of its linguistic odyssey. Hindi is the most extensively spoken language in the country and is one of the numerous languages that are spoken. But in addition to Hindi, India is home to many other languages, each with its own distinctive grammar and vocabulary. Tamil, Telugu, Marathi, Bengali, Urdu etc.
Linguistic Diversity:
India’s multiculturalism, which has been shaped by centuries of migrations, invasions, and exchanges, is reflected in this linguistic diversity. Each linguistic area has a unique cultural identity that is frequently entwined with its language. India’s languages serve as archives for its rich cultural legacy, preserving everything from the lyrical poems of Tamil Nadu to the melodious poetry of Bengal to the ancient Sanskrit scriptures to the poetic devotion of Punjabi. The continual evidence to India’s linguistic traditions’ tenacity is also shown by the country’s linguistic odyssey.
Lastly, Despite the difficulties that globalization and urbanization are posing for many languages, India continues to cherish and protect its linguistic diversity. India guarantees that its linguistic odyssey endures and is a crucial component of its national identity through government initiatives, educational programs, and cultural events, allowing everyone to explore
2. A Tapestry of Religions
To begin with, India is the birthplace of major religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. It’s also home to substantial Muslim, Christian, Zoroastrian, and Jewish communities. The religious landscape is a testament to the nation’s religious tolerance, and places of worship from different faiths coexist harmoniously.
Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism
India is more than simply a country; it is a profoundly spiritual trip that is tied together by a complex web of different religions and faiths. It serves as a symbol of religious plurality and tolerance because it attests to the coexistence of various religious traditions. India’s religious environment is a lively kaleidoscope where devotion and spirituality take on innumerable manifestations. Hinduism, one of the oldest religions in the world, is at the centre of India’s religious mosaic. The vivid holidays like Diwali and Holi, as well as its rich mythology and traditions, are profoundly ingrained in the country’s cultural fabric. Here, Siddhartha Gautama gave birth to Buddhism, another ancient religion of India. Buddhists all around the world place a great deal of importance on locations like Bodh Gaya and Sarnath.
Islam, Christianity, Zoroastrian, and Jewish
On the other hand, a sizable Muslim population lives in India, and the country’s Islamic legacy may be seen in the magnificent Mughal architecture, deft calligraphy, and the Hajj pilgrimage. With old cathedrals like the St. Thomas Cathedral attesting to the faith’s origins, Christianity has found a place in India. The Golden Temple in Amritsar serves as an example of the virtues of equality and service to humanity that Sikhism, which originated in Punjab, upholds. Last but not the least, the religious diversity of India is also influenced by Jainism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, and many indigenous tribal religions. Beyond its borders, the nation’s religious plurality fosters the traditions of those who have been persecuted, including the Parsis who fled Persia.
Religious Harmony:
The peaceful coexistence of many religions is what makes India’s religious tapestry so fascinating. Beyond its borders, the nation’s religious plurality fosters the traditions of those who have been persecuted, including the Parsis who fled Persia. The peaceful coexistence of many religions is what makes India’s religious tapestry so fascinating. The freedom to practise one’s religion is protected by the Indian Constitution, creating a setting free from intimidation or bias. Indians recognise the complex interplay of faiths that has defined the nation’s cultural ethos and respect one other’s festivals, rituals, and celebrations, proving that this variety is not a source of separation but rather a source of unity. India offers the world a priceless lesson in tolerance, acceptance, and the persistent capacity of spirituality to transcend boundaries and promote harmony in this complex tapestry of religions.
3. Festivals Galore
India is synonymous with festivals. Diwali, Holi, Eid, Christmas, Durga Puja, and many more punctuate the Indian calendar. Each festival is celebrated with fervor and joy, reflecting the religious and cultural diversity of the country. The vibrant colors, music, and rituals vary from region to region, making each celebration a unique experience.
The Festival of Lights, or Diwali, is a beloved Hindu holiday that exudes happiness and harmony. It represents how good has triumphed over evil and light over darkness. Oil lamps, colourful candles, and pyrotechnics are used by families to illuminate their houses. People gather to worship and rejoice with large feasts as well as to share presents and sweets. Diwali highlights the vibrant cultural diversity of India while highlighting the victory of inner light, optimism, and thankfulness.
Holi, also known as the Festival of Colours, is a riotous and colourful Hindu holiday that is enthusiastically observed. To celebrate the triumph of love and joy over hate and winter, people of all ages get together to jokingly hurl vibrantly coloured powders and water at one another. To celebrate the triumph of good over evil, bonfires are lighted and traditional treats like gujiya are enjoyed. Holi is a holiday that is treasured and enjoyed all over the world because it crosses socioeconomic and religious boundaries and fosters unity and fraternity.
Ramadan, a month of fasting and introspection, comes to a conclusion on Eid-ul-Fitr, one of the most important Islamic holidays. At mosques, families assemble for special prayers, which are followed by feasts with classic fare like biryani and sheer kurma. Eid emphasises the virtues of generosity, thankfulness, and community among Muslims all over the world. It is also a time for giving and receiving gifts as well as charitable deeds.
Christians all around India celebrate Christmas to remember the birth of Jesus. The celebrations involve going to midnight Mass, putting up Christmas lights and trees, exchanging gifts, and indulging in a lavish meal. A festive atmosphere is produced by carolers and the use of colourful decorations to light up the streets. People of all religions celebrate Christmas as a season of peace, community, and sharing joy and love across all religious barriers.
A major Hindu festival known as Durga Puja commemorates the goddess Durga’s triumph over the buffalo monster Mahishasura. It is mostly observed in West Bengal. Beautiful artistic and cultural exhibitions are shown in elaborate pandals, which are temporary temples. Visitors to these pandals offer prayers, immerse finely constructed Durga statues in water features, and pay homage. The event features vivacious processions, age-old dances, and ethnic performances that foster a sense of community and respect for the goddess’s power and goodness. A cultural spectacle known as Durga Puja unites the spirit of art, spirituality, and celebration.
4. Gastronomic Delights
Indian cuisine is as diverse as its culture. From spicy curries in the south to hearty kebabs in the north, and from vegetarian delights in Gujarat to seafood feasts in Kerala, Indian food is a gastronomic adventure. Each region has its own culinary traditions, ingredients, and flavors, offering a sensory delight for food enthusiasts.
Indian cuisine’s:
The stunning culinary environment of India entices the palate with tales of long-standing customs, distinctive regional flavours, and a rich cultural past. Indian food is made up of a wide variety of spices, ingredients, and preparation methods that differ greatly from place to region. Every region of the nation provides a distinctive culinary experience that is a reflection of its geography, climate, culture, and history. Without delving into India’s many flavours, one cannot begin to discover its culinary treasures. Indian cuisine’s creative use of spices and herbs, which results in a symphony of flavours that span from hot and pungent to aromatic and delicate, is the essence of the cuisine. Among the spices used in cooking include cumin, coriander, turmeric, cardamom, and chilli. The art of blending these spices, known as masala, is an ancient craft passed down through generations.
Varieties From Different Corners Of India
Punjab, for example, is known throughout Northern India for its rich and substantial cuisine. In this region, basic foods like tandoori chicken, butter chicken, and naan bread are bursting with smoky, creamy, and spicy flavours. Similarly, as we move to the South, a feast of dosas, idlis, and sambar is in store. So, these dishes highlight the subtle flavour balancing and liberal use of coconut, tamarind, and curry leaves.
Similarly, seafood delicacies like fish curry and prawn masala, which are flavoured with the aromatic sweetness of coconut and spices, are abundant in coastal regions like Kerala. Gujarat tempts Westerners with its vegetarian thalis, which include a variety of foods including dhokla, thepla, and kadhi. Eastern India offers its own unique repertoire, with dishes like roshogolla and mishti doi in Bengal, and the iconic rasgulla.
Varied street food & culinary wonders:
One must also enjoy India’s varied street food if they want to fully appreciate its culinary wonders. The streets come alive with a dizzying blend of fragrances and flavours, from the hot chaats of Delhi’s Chandni Chowk to Mumbai’s renowned vada pav vendors and Kolkata’s cherished kathi rolls.
Similarly, a strong sense of tradition and community lies at the core of Indian cuisine. Food is a way to celebrate, create art, and connect with others. It crosses linguistic, religious, and social barriers to bring people together through the joy of eating. Finally, India is a gourmet paradise where each meal is a trip into the heart and soul of a country because of its strong passion for food.
5. Traditional Attire
The clothing of India is as diverse as its people. From the colorful sarees of the women in the south to the vibrant turbans worn by men in Rajasthan, traditional attire reflects the regional and cultural identity of the wearers. Moreover, the textiles, embroidery, and designs vary dramatically, adding to the rich tapestry of Indian culture.
An Elegant and Diverse Kaleidoscope of Indian Clothes
Indian clothing is a fascinating representation of the nation’s diverse and historically rooted cultural tapestry. A fashion connoisseur’s paradise, India’s dress customs are as varied as its landscapes, languages, and traditions. India’s traditional clothing differs widely from state to state, each of which boasts its own distinctive designs and inspirations.
The Saree Is A Classic Icon
Perhaps the most recognisable of all Indian clothing is the saree, a symbol of elegance and femininity. It spans decades and geographical boundaries and is draped in numerous ways all throughout the nation. However, each variety of saree in India, from the beautiful Kanjivaram sarees of the South to the vivid and complex Banarasi silk sarees of the North, tells a tale of workmanship and talent.
The Multipurpose Salwar Kameez
Another preferred option is the comfy but fashionable salwar kameez. It is made up of a long tunic (kameez), baggy pants (salwar) and a duppatta (matching scarf or stole). However, women appreciate this outfit for its adaptability and frequently choose it for both everyday wear and special occasions.
Elegant Men’s Clothing
Depending on the occasion and area, Indian men can display their own sense of style by dressing in the kurta-pajama or the dhoti-kurta. At weddings and other ceremonial occasions, men wear the long coat-like sherwani, which exudes regal majesty.
Relevance to Culture and Adaptation
Indian clothing has great cultural and religious importance in addition to being purely fashionable. One’s style of dress frequently reflects their culture, customs, and social standing. Indian fashion has adapted to and embraced fusion trends, fusing traditional elegance with modern aesthetics, thanks to the effect of modernization and globalization.
Finally, Indian clothing is a colorful representation of the nation’s artistic talent and cultural variety. It reflects India’s history, customs, and the persistent attractiveness of its clothing designs, representing not just fashion but also the rich tapestry of India’s legacy. Whether wearing a saree, a sherwani, or a chic fusion ensemble, Indian clothing continues to wow the globe with its enduring allure.
6. The Arts and Crafts
India has a rich tradition of art and craftsmanship. From intricate Rajasthani miniatures to the vibrant Madhubani paintings of Bihar, and from the silk sarees of Varanasi to the delicate craftsmanship of Kashmiri shawls, the country boasts a stunning array of artistic expressions.
Distinctive Cultural Legacy:
The complex tapestry of creativity and cultural expression seen in Indian arts and crafts spans millennia. Indian workmanship features an astounding variety of styles, materials, and techniques and is deeply rooted in the rich traditions of this multicultural and ancient nation. Each area of India is proud of its own distinctive cultural legacy, from the beautiful zari embroidery of Varanasi to the fine ceramics of Khurja. The creative legacy of the nation is intricately woven into its history, religion, and social structure, creating a kaleidoscope of styles, from the vibrant Madhubani paintings of Bihar, which represent legendary tales, to the delicate filigree jewellery of Orissa.
craftsmen of India
The skilled craftsmen of India continue to create beautiful fabrics, jewellery, woodwork, and metals, sometimes using only their hands and little tools. India’s arts and crafts are far more than simply beautiful; they also support innumerable people by providing a means of subsistence. The arts and crafts of India are a monument to the continuing force of human ingenuity and the significance of safeguarding cultural heritage in a society that is increasingly dominated by mass manufacturing.
7. Dance and Music
Dance and music are integral to Indian culture. Classical dance forms like Bharatanatyam , Kathak, and Odissi have deep roots, while traditional music includes Hindustani and Carnatic styles. Bollywood, India’s film industry, is a global phenomenon that blends traditional and contemporary elements.
Classical Dances:
The compelling cultural variety, spirituality, and history of India are all reflected in its dance and music traditions. This enormous country is home to an astounding array of classical and folk dance styles, each with its own distinctive style and story. The traditional dance styles of Bharatanatyam, Kathak, Odissi, and Kathakali feature elaborate movements and narrative that frequently reference classical literature and mythology . These dances, which have their origins in Hindu and Buddhist rites, are not only aesthetic presentations but also spiritual manifestations.
Folk Dances:
India’s folk dances, in addition to its classical dance, reflect the nation’s regional variety. Every state and community has its own dance, from the vivacious Bhangra of Punjab to the elegant Garba of Gujarat and the colourful Bihu of Assam. These folk dances are marked by colorful costumes, lively music, and community participation, making them a vibrant reflection of India’s cultural tapestry.
Hindustani and Carnatic music:
Hindustani and Carnatic music, two of India’s classical traditions, are known for their complicated melodies, rhythms, and improvisational approaches. Moreover, these genres heavily include traditional instruments including the sitar, tabla, veena, and flute. Bollywood music, which has received prominence on a global scale, is the consequence of the combination of traditional and modern components in India’s popular music. Similarly, India’s dance and music, in essence, serve as a live example of the nation’s capacity to embrace its cultural variety and weave it into a dynamic tapestry of artistic expression, enriching the globe with its entrancing rhythms and motions.
8. Unity in Diversity
Despite the incredible diversity, India’s strength lies in its unity. The Constitution of India recognizes the importance of diversity and promotes cultural and religious tolerance. Indians take pride in their multicultural identity and often say, “Unity in Diversity.”
The term “Unity in Diversity” perfectly captures the social fabric of India. India is a very diverse country, with many different languages, religions, cultures, and customs. The Indian culture has always emphasised the togetherness that transcends these apparent disparities notwithstanding these contrasts. The values of tolerance, cohabitation, and respect for one another’s views are at the foundation of this oneness. India has consistently shown a remarkable capacity for integrating this variety, knitting it into the very fabric of its character.
Indian Constitution – Promoting Secularism
This dedication is demonstrated by the Indian Constitution, which defends secularism and ensures the freedom of religion and culture. Likewise, people from all backgrounds come together to enthusiastically celebrate holidays like Diwali, Eid, Christmas, and Holi , which strengthens the sense of community. The richness of this oneness is enhanced by the many foods, fashions, musical styles, and artistic expressions from other cultures. Therefore, India’s “Unity in Diversity” is an example of the ability of diversity to produce a peaceful and inclusive society, and it serves as a source of strength and resiliency.
To conclude, Cultural diversity in India is not just a statistic; it’s a way of life. It’s the essence of India, the heartbeat of the nation. As we explore this vast tapestry of cultures, we are reminded of the beauty that arises when different traditions, languages, and beliefs come together to create a harmonious whole. Therefore, India’s cultural diversity is not just a source of pride; it’s a source of inspiration for the world, showing how unity can thrive amidst diversity.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)

Unity in Diversity: The Essence of India’s Composite Culture | Essay Writing for UPSC by Vikash Ranjan Sir | Triumph ias
Table of Contents
India’s Mosaic: A Celebration of Unity in Diversity
(relevant for essay writing for upsc civil services examination).

India’s vibrant landscape is dotted with myriad cultures, traditions, and histories. Dive into the mesmerizing mosaic of India’s composite culture and discover how it epitomizes unity in diversity.

The Threads of Time
From the ancient Indus Valley Civilization to modern-day India, the country has imbibed, evolved, and celebrated a myriad of influences, giving birth to its unique identity.
A Symphony of Cultures
Whether it’s the resonating chants from temples, the melodic calls for prayer from mosques, or the harmonious carols from churches, India embraces them all with open arms. Languages, festivals, art – every facet of Indian life reflects its harmonious blend.
Conclusion: A Lesson for the World
In times of global divisiveness, India’s composite culture stands tall as a testament to the strength and beauty of unity in diversity.
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus , aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching . These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques
India, Composite Culture, Unity in Diversity, Religions, Languages, Festivals, Art, Architecture, Historical Evolution.

Sociology Optional Syllabus Course Commencement Information
- Enrolment is limited to a maximum of 250 Seats.
- Course Timings: Evening Batch
- Course Duration: 4.5 Months
- Class Schedule: Monday to Saturday
- Batch Starts from: Admission open for online batch
Book Your Seat Fast Book Your Seat Fast
We would like to hear from you. Please send us a message by filling out the form below and we will get back with you shortly.
Instructional Format:
- Each class session is scheduled for a duration of two hours.
- At the conclusion of each lecture, an assignment will be distributed by Vikash Ranjan Sir for Paper-I & Paper-II coverage.
Study Material:
- A set of printed booklets will be provided for each topic. These materials are succinct, thoroughly updated, and tailored for examination preparation.
- A compilation of previous years’ question papers (spanning the last 27 years) will be supplied for answer writing practice.
- Access to PDF versions of toppers’ answer booklets will be available on our website.
- Post-course, you will receive two practice workbooks containing a total of 10 sets of mock test papers based on the UPSC format for self-assessment.
Additional Provisions:
- In the event of missed classes, video lectures will be temporarily available on the online portal for reference.
- Daily one-on-one doubt resolution sessions with Vikash Ranjan Sir will be organized post-class.
Syllabus of Sociology Optional
FUNDAMENTALS OF SOCIOLOGY
- Modernity and social changes in Europe and emergence of sociology.
- Scope of the subject and comparison with other social sciences.
- Sociology and common sense.
- Science, scientific method and critique.
- Major theoretical strands of research methodology.
- Positivism and its critique.
- Fact value and objectivity.
- Non- positivist methodologies.
- Qualitative and quantitative methods.
- Techniques of data collection.
- Variables, sampling, hypothesis, reliability and validity.
- Karl Marx- Historical materialism, mode of production, alienation, class struggle.
- Emile Durkheim- Division of labour, social fact, suicide, religion and society.
- Max Weber- Social action, ideal types, authority, bureaucracy, protestant ethic and the spirit of capitalism.
- Talcott Parsons- Social system, pattern variables.
- Robert K. Merton- Latent and manifest functions, conformity and deviance, reference groups.
- Mead – Self and identity.
- Concepts- equality, inequality, hierarchy, exclusion, poverty and deprivation.
- Theories of social stratification- Structural functionalist theory, Marxist theory, Weberian theory.
- Dimensions – Social stratification of class, status groups, gender, ethnicity and race.
- Social mobility- open and closed systems, types of mobility, sources and causes of mobility.
- Social organization of work in different types of society- slave society, feudal society, industrial /capitalist society
- Formal and informal organization of work.
- Labour and society.
- Sociological theories of power.
- Power elite, bureaucracy, pressure groups, and political parties.
- Nation, state, citizenship, democracy, civil society, ideology.
- Protest, agitation, social movements, collective action, revolution.
- Sociological theories of religion.
- Types of religious practices: animism, monism, pluralism, sects, cults.
- Religion in modern society: religion and science, secularization, religious revivalism, fundamentalism.
- Family, household, marriage.
- Types and forms of family.
- Lineage and descent.
- Patriarchy and sexual division of labour.
- Contemporary trends.
- Sociological theories of social change.
- Development and dependency.
- Agents of social change.
- Education and social change.
- Science, technology and social change.
INDIAN SOCIETY: STRUCTURE AND CHANGE
Introducing indian society.
- Indology (GS. Ghurye).
- Structural functionalism (M N Srinivas).
- Marxist sociology (A R Desai).
- Social background of Indian nationalism.
- Modernization of Indian tradition.
- Protests and movements during the colonial period.
- Social reforms.
SOCIAL STRUCTURE
- The idea of Indian village and village studies.
- Agrarian social structure – evolution of land tenure system, land reforms.
- Perspectives on the study of caste systems: GS Ghurye, M N Srinivas, Louis Dumont, Andre Beteille.
- Features of caste system.
- Untouchability – forms and perspectives.
- Definitional problems.
- Geographical spread.
- Colonial policies and tribes.
- Issues of integration and autonomy.
- Social Classes in India:
- Agrarian class structure.
- Industrial class structure.
- Middle classes in India.
- Lineage and descent in India.
- Types of kinship systems.
- Family and marriage in India.
- Household dimensions of the family.
- Patriarchy, entitlements and sexual division of labour
- Religious communities in India.
- Problems of religious minorities.
SOCIAL CHANGES IN INDIA
- Idea of development planning and mixed economy
- Constitution, law and social change.
- Programmes of rural development, Community Development Programme, cooperatives,poverty alleviation schemes
- Green revolution and social change.
- Changing modes of production in Indian agriculture.
- Problems of rural labour, bondage, migration.
3. Industrialization and Urbanisation in India:
- Evolution of modern industry in India.
- Growth of urban settlements in India.
- Working class: structure, growth, class mobilization.
- Informal sector, child labour
- Slums and deprivation in urban areas.
4. Politics and Society:
- Nation, democracy and citizenship.
- Political parties, pressure groups , social and political elite
- Regionalism and decentralization of power.
- Secularization
5. Social Movements in Modern India:
- Peasants and farmers movements.
- Women’s movement.
- Backward classes & Dalit movement.
- Environmental movements.
- Ethnicity and Identity movements.
6. Population Dynamics:
- Population size, growth, composition and distribution
- Components of population growth: birth, death, migration.
- Population policy and family planning.
- Emerging issues: ageing, sex ratios, child and infant mortality, reproductive health.
7. Challenges of Social Transformation:
- Crisis of development: displacement, environmental problems and sustainability
- Poverty, deprivation and inequalities.
- Violence against women.
- Caste conflicts.
- Ethnic conflicts, communalism, religious revivalism.
- Illiteracy and disparities in education.

Mr. Vikash Ranjan, arguably the Best Sociology Optional Teacher , has emerged as a versatile genius in teaching and writing books on Sociology & General Studies. His approach to the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus is remarkable, and his Sociological Themes and Perspectives are excellent. His teaching aptitude is Simple, Easy and Exam Focused. He is often chosen as the Best Sociology Teacher for Sociology Optional UPSC aspirants.
About Triumph IAS
Innovating Knowledge, Inspiring Success We, at Triumph IAS , pride ourselves on being the best sociology optional coaching platform. We believe that each Individual Aspirant is unique and requires Individual Guidance and Care, hence the need for the Best Sociology Teacher . We prepare students keeping in mind his or her strength and weakness, paying particular attention to the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus , which forms a significant part of our Sociology Foundation Course .
Course Features
Every day, the Best Sociology Optional Teacher spends 2 hours with the students, covering each aspect of the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus and the Sociology Course . Students are given assignments related to the Topic based on Previous Year Question to ensure they’re ready for the Sociology Optional UPSC examination.
Regular one-on-one interaction & individual counseling for stress management and refinement of strategy for Exam by Vikash Ranjan Sir , the Best Sociology Teacher , is part of the package. We specialize in sociology optional coaching and are hence fully equipped to guide you to your dream space in the civil service final list.
Specialist Guidance of Vikash Ranjan Sir

The Best Sociology Teacher helps students to get a complete conceptual understanding of each and every topic of the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus , enabling them to attempt any of the questions, be direct or applied, ensuring 300+ Marks in Sociology Optional .
Classrooms Interaction & Participatory Discussion
The Best Sociology Teacher, Vikash Sir , ensures that there’s explanation & DISCUSSION on every topic of the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus in the class. The emphasis is not just on teaching but also on understanding, which is why we are known as the Best Sociology Optional Coaching institution.
Preparatory-Study Support

Online Support System (Oss)
Get access to an online forum for value addition study material, journals, and articles relevant to Sociology on www.triumphias.com . Ask preparation related queries directly to the Best Sociology Teacher , Vikash Sir, via mail or WhatsApp.
Strategic Classroom Preparation

Comprehensive Study Material
We provide printed booklets of concise, well-researched, exam-ready study material for every unit of the Sociology Optional Syllabus / Sociology Syllabus , making us the Best Sociology Optional Coaching platform.
Why Vikash Ranjan’s Classes for Sociology?
Proper guidance and assistance are required to learn the skill of interlinking current happenings with the conventional topics. VIKASH RANJAN SIR at TRIUMPH IAS guides students according to the Recent Trends of UPSC, making him the Best Sociology Teacher for Sociology Optional UPSC.
At Triumph IAS, the Best Sociology Optional Coaching platform, we not only provide the best study material and applied classes for Sociology for IAS but also conduct regular assignments and class tests to assess candidates’ writing skills and understanding of the subject.
Choose T he Best Sociology Optional Teacher for IAS Preparation?
At the beginning of the journey for Civil Services Examination preparation, many students face a pivotal decision – selecting their optional subject. Questions such as “ which optional subject is the best? ” and “ which optional subject is the most scoring? ” frequently come to mind. Choosing the right optional subject, like choosing the best sociology optional teacher , is a subjective yet vital step that requires a thoughtful decision based on facts. A misstep in this crucial decision can indeed prove disastrous.
Ever since the exam pattern was revamped in 2013, the UPSC has eliminated the need for a second optional subject. Now, candidates have to choose only one optional subject for the UPSC Mains , which has two papers of 250 marks each. One of the compelling choices for many has been the sociology optional. However, it’s strongly advised to decide on your optional subject for mains well ahead of time to get sufficient time to complete the syllabus. After all, most students score similarly in General Studies Papers; it’s the score in the optional subject & essay that contributes significantly to the final selection.
“ A sound strategy does not rely solely on the popular Opinion of toppers or famous YouTubers cum teachers. ”
It requires understanding one’s ability, interest, and the relevance of the subject, not just for the exam but also for life in general. Hence, when selecting the best sociology teacher, one must consider the usefulness of sociology optional coaching in General Studies, Essay, and Personality Test.
The choice of the optional subject should be based on objective criteria, such as the nature, scope, and size of the syllabus, uniformity and stability in the question pattern, relevance of the syllabic content in daily life in society, and the availability of study material and guidance. For example, choosing the best sociology optional coaching can ensure access to top-quality study materials and experienced teachers. Always remember, the approach of the UPSC optional subject differs from your academic studies of subjects. Therefore, before settling for sociology optional , you need to analyze the syllabus, previous years’ pattern, subject requirements (be it ideal, visionary, numerical, conceptual theoretical), and your comfort level with the subject.
This decision marks a critical point in your UPSC – CSE journey , potentially determining your success in a career in IAS/Civil Services. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose wisely, whether it’s the optional subject or the best sociology optional teacher . Always base your decision on accurate facts, and never let your emotional biases guide your choices. After all, the search for the best sociology optional coaching is about finding the perfect fit for your unique academic needs and aspirations.
To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus , aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching . These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques. Sociology, Social theory, Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Sociology Optional Syllabus. Best Sociology Optional Teacher, Sociology Syllabus, Sociology Optional, Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Optional Coaching, Best Sociology Teacher, Sociology Course, Sociology Teacher, Sociology Foundation, Sociology Foundation Course, Sociology Optional UPSC, Sociology for IAS,
Follow us :
🔎 https://www.instagram.com/triumphias
🔎 www.triumphias.com
🔎https://www.youtube.com/c/TriumphIAS
https://t.me/VikashRanjanSociology
Find More Blogs
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Art & Culture
- Offbeat Travel
- Volunteering
- Nostalgiphilia
- Culture Directory
- Collaborate
Indian Cultural diversity: The True Essence and Beauty of India
- Indian Culture
- Indian Heritage
Table of contents
India the land of diversity, diversity in architecture , diversity in indian clothing, diversity in indian food, diversity in religion, diversity in indian customs and tradition, diversity of indian languages, diversity in indian art forms, diversity in indian festivals, diversity in indian music, diversity in indian cinema, diversity in indian litrature, diversity in indian celebration.

Indian culture is one of the most ancient cultures present in the world. The country is quite diverse and is home to several communities, each of whom has their own culture and traditions. It is this combination of various splendid cultures that make India one of a kind. The Indian cultural diversity is what makes India unique and beautiful.

Situated in the continent of Asia and enclosed by the Arabian sea, the Indian Ocean, and the Bay of Bengal, the nation, is divided into twenty-nine states and seven union territories. Pakistan, China, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Bhutan , and Nepal form the neighbouring countries of India.

India is a land of diversity each state in the country is home to several communities who live in harmony with each other while preserving and upholding their own distinct culture and traditions. From Delhi , the capital of India, to Tamil Nadu , the southernmost state of India, the land, is blessed with amazing scenic beauty. The country is also home to several historical monuments which add to the varied heritage of India.
Recommended Read – Understanding the Culture of Indian States [Infographic]

India is a country that is incredibly diversified and that of Indian architecture . India’s architecture spans from ancient caves to contemporary skyscrapers. As India grows, India’s architecture continues to diversify through continuously reverting to its roots while maintaining current trends.
India is also classified by the Dravidian and the Nagara architectural styles as the focal focus of Hindu architecture. In the empires, in the South of India, the Dravidian style prospered, whilst in the North of India, the Nagara style predominately appeared. India’s history, culture and religion are ingrained in its architecture.

India’s vast and boundless array of traditional dress is full of aesthetic beauty. Made from many states of the country are fabrics, weaving processes, embellishments, styles and accessories of multiple sorts. A compelling epic about craftsmanship, culture or legacy tells a story in each piece. The land is a centre of heritage mode. Its diversity was a muse for a number of notable connoisseurs of fashion. In addition to the western clothing, Indians have their own ethnic attire like dhoti, kurta, sari, sherwani, turban etc. Dhoti is a piece of cloth draped around the waist by men. Dhoti is sometimes called Laacha or Dhuti. Kurta is one of India’s famous men’s ethnic clothing. It is usually worn on holidays today by folks. Likewise, the saree is the favourite choice for Indian women. A saree is a long robe, gracefully drawn by women around their bodies. Saree is Indian women’s most trendy clothing worldwide. Indian women are mostly seen in lovely sarees during religious and cultural events. However, due to their convenience, the sarees are substituted by salwar suits for the preferred daily wear.

Indian food is one of the world’s most tasteful and nuanced. There is no flavour homogeneity between North and South or East and West but rather an incredible richness of tastes. One of India’s assets is its culinary diversity.
Indian food contains so much that one ought to discuss more than just “Indian cuisines.” Each region offers a number of traditional meals and its own culinary features.
Each area is specialised in cuisine, not solely at regional, but also at the provincial level. The diversity in cuisine stem from diverse local cultures, geography (whether the region is near the sea, desert or mountains), and the economy. Indigenous kitchen likewise relies heavily on fresh local products and is seasonal.
Indian cuisine tends generally to seek a balance between spices and herbs that offers delicious dishes with surprising therapeutic and medicinal benefits.

Indian religions have influenced and shaped the Indian culture

The vast differences in the customs, traditional beliefs and rituals can be witnessed if one analyses the differences in the culture prevalent in the northern and southern part of India. The festivals, the art forms, and to an extent, even the dressing style of the people are quite different in Northern India when compared to those in Southern India . While most of the Indian women wear the saree, the style of draping the saree varies in different parts of India. This difference can be seen, not only among different states but also among the various communities within the same state.

Though Hindi is the most commonly used language in India, there exist many other languages too. As diverse the country is, each state has its distinct language, such as Kannada, (which, is spoken in Karnataka), Malayalam, (which, is spoken in Kerala), Tamil , is spoken in Tamil Nadu, etc. Apart from the fact that each state has its own language, it is also worth mentioning that some states in India have more than one and sometimes more than three prevalent languages. Due to this, it would not come as a surprise that most Indians are bilingual (or sometimes Multilingual), and can effortlessly handle more than one or two languages.

The family has always been an integral part of Indian society. In an Indian family, all the members share a close-knit connection. Joint families are also common in the country. In joint families, all the members of the family live under the same roof. However, in present times, nuclear families are becoming more common. In India, arranged marriages are relatively more common. The concept of an arranged marriage might seem a bit confusing to people from the western part of the world. However, in India, arranged marriages are more encouraged and are still very much prevalent in the country.

The unique and splendid art forms of India have a significant position in the culture of India. Each state is blessed with its unique art form and differs considerably from that of its neighbour. Though, it is worthwhile to note that many art forms of India are in some ways the amalgamation of other art forms borrowed from the neighbouring states. From the elegant Mohiniyattam , which focuses on the elegant and graceful movements of the dancer to the Ghoomar , a folk dance in Rajasthan, the art forms vary from each other but are equally beautiful and magical.

The festivals of India , too, are worth mentioning. As said earlier, each state has its own festivals, from the fragrant Onam, the festival of Kerala , which is characterized by the making of a floral carpet to the Pôhela Boishakh, (the onset New Year according to the Bengali calendar), the festivals are both colourful and equally incredible.

Music plays a significant role in the culture of any country, and India, too, is not an exception. Carnatic music , Hindustani music are the most popular in India. These are usually accompanied by the tune of the traditional musical instruments such as the tabla and the veena. Indian music is quite soothing and pleasing to the ear.

The movies produced in India, too, reflect the culture of the society. Each state in India has its own movie industry, though Bollywood is the most popular among them. The movie industries in India are known by different terms such as Mollywood (Malayalam movie industry), Tollywood, etc. Owing to the number of movies produced each year in different languages across India, adding to the fact that Indians love movies, India has now become one of the greatest producers of films.

India has also been blessed with many intellectuals and legendary writers and poets who are renowned worldwide for their contributions to humanity. Prominent among them is Rabindranath Tagore , the first Asian and Indian to win the Nobel Prize . His work Gitanjali continues to spread its message and inspires all those who read it. Other prominent writers of India include Sarojini Naidu, Aurobindo Ghosh, among others. Artists such as Raja Ravi Varma, Rabindranath Tagore, and M F Hussain have helped in changing the face of Indian art.

Festivals and celebrations are a common occurrence in India as they occur almost every other day; however, the grandeur and pomp of these festivals are quite impressive. The country is also home to many heritage sites and monuments , including the Taj Mahal. It is all these facts combined that makes the Indian culture unique and distinct from others.

The seventh-largest country in the world, India has set itself a unique and distinct place among the other countries of the world. The host of a culture that has been prevalent for a long time, India is perhaps one of the most diverse countries in the world. From the attire worn by the people belonging to different communities to the languages spoken and even in the food habits, the country both reflects its diversity and varied heritage.
Cover Photo by Tom Chen on Unsplash
Image credits: The copyright for the images used in this article belong to their respective owners. Best known credits are given under the image. For changing the image credit or to get the image removed from Caleidoscope, please contact us.
very good knowledge
Very good guys
It’s very helpful for my science homework theme page: celebrating cultural diversity
Thanks Aarradhya, all the best for your class project!
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
INSPIRING READS
Sonepur cattle fair: a celebration of tradition and trade, temples of orissa – illustrious architectural wonders of india, sita kund: the heartbeat of bihar’s cultural legacy, traditional indian summer dishes to beat the heat and be healthy, the celebration of indian new year in various cultures of india, usher in a new ugadi festival by saving water , trending topics.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
Affiliate disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, we may earn commissions from qualifying purchases from Amazon. Learn more
© caleidoscope - 2024.

Diversity of India, Types, Constitutional Provisions, Associated Challenges
Diversity of India gives India a title of land of diversity. Know all forms of Diversity of India like Cultural, Religion, Society, Geography & Ethnic diversity for UPSC Exam preparation.

Table of Contents
About Diversity of India
In India, diversity means that people vary from one another in terms of their physical characteristics as well as their regional, cultural, and religious beliefs. Language and ritual variations are just a few examples of the differences. The lives of Indians are enriched by this variety. This article will assist students in comprehending diversity and its forms in India. The UPSC Syllabus includes Diversity of India as a significant topic Indian Society for UPSC Exam. The UPSC Mock Test can help candidates prepare for the exam with more precision.
We’re now on WhatsApp . Click to Join
What is Diversity of India?
The term “diversity” emphasizes differences more than injustice. It alludes to differences between groups of people or inequalities within those groups. These distinctions could be linguistic, philosophical, biological, or in any other way. Diversity is the wide range of racial groups, religions, dialects, castes, and cultural traditions.
Integrity means harmony. It is a societal psychological condition. It implies a feeling of cohesion and harmony. It stands for the bonds that bind members of a community together. “Unity in diversity” essentially refers to “diversity without fragmentation” and “unity without uniformity.” The foundation of it is the notion that diversity improves interpersonal dialogue.
When we say that India is a nation with a rich cultural diversity, we mean the many different social and cultural subgroups that call India home. These groups distinguish themselves mainly by cultural characteristics such as language, faith, sect, race, or caste.
Also Read: Caste System in India
Types of Diversity in India
Cultural d iversity of india.
India’s cultural diversity is a rich tapestry woven from a myriad of traditions, languages, religions, and customs. This vibrant mosaic has been shaped by centuries of interaction between diverse cultures, both within India and beyond its borders. The result is a country that is as diverse as it is vast, with each region offering its own unique blend of customs, traditions, and beliefs.
Religious Diversity of India
Due to the rich diversity of India is called the ‘land of diversity’. India is a nation where many various religions are practised. Hindus make up the majority of the people in India (82.41%), followed by Muslims (11.6%), Christians (2.32%), Sikhs (1.9%), Buddhists (0.77%), and Jains (0.41%), as well as the tribal groups, many of which still engage in animism and magic. There are numerous groups within the Hindu religion, including the Vaishnavas, Shaivites, Shaktas, and Smartas. There are numerous Muslim groups as well, such as Shi’ites, Sunnis, Ahmadis, etc.
Language Diversity of India
The Dravidian languages, spoken by 20% of Indians, and the Indo-Aryan languages, spoken by 75% of Indians, are the two main language groups among the languages spoken in India. Other languages can be found in the Austroasiatic, Sino-Tibetan, Tai-Kadai, and a few other minor language groups and isolates. India has the second-highest number of languages in the globe, right behind Papua New Guinea. According to the 1931 census, the ethnic diversity of India was split into the following groups: Western Brachycephalians, Negritos, Proto-Australoids, Mongoloid, Mediterranean, and Nordic.
Caste Diversity in India
Members of the three main global races—Caucasoid, Mongoloid, and Negroid—are included in the caste diversity: India is a country that Both varna and jati have previously been referred to as “caste.” The four Varna categories that functional differentiation divides society into are described as such. a Shudra, a Vaishya, a Kshatriya, and a Brahmin.
While “Jati” refers to a hereditary endogamous status group practising a particular customary trade. There isn’t a single method in place in all of India for categorizing and ranking the more than 3000 jatis. The dynamic and mobile nature of the Jati system has enabled Jatis to change its location over time. This process of ascent was referred to as “Sanskritization” by M. N. Srinivas.
Ethnic Diversity of India
Ethnic diversity Cultural trends reveal regional variations. Indian culture is very varied and a fusion of many other cultures as a result of the country’s diverse population. Every country, caste, and faith has its distinctive customs and cultures. There are consequently differences in music, dance, theatre, and architecture.
Geographic Diversity in India
India is a large country with a total land area of 3.28 million square kilometres and a diverse range of natural environments, including deserts, evergreen woods, steep mountains, perennial and non-perennial river systems, long coastlines, and fertile plains. India has diversity in many other areas besides the main ones already mentioned, including tribal, rural, and urban patterns of habitation, patterns of marriage and kinship along religious and regional lines, and more.
Diversity of India and Constitutional Provisions
A single person with a constitutional identity is chosen to lead the complete country. Furthermore, regardless of their age, gender, class, caste, or religion, all citizens are guaranteed certain basic rights under the Constitution, even though the majority of states adhere to a standard three-tier structure of government.
Religion India is known for its tolerance, which makes it possible for a wide variety of beliefs to coexist there. The freedom of faith and practice is guaranteed by the Constitution itself. The state has no official state religion and gives all religions similar priority. The freedom of mobility guaranteed by Article 19 (1) (d) of the Indian Constitution promotes a spirit of brotherhood and unity among the populace.
The uniformity of the law, penal code, and administrative duties are additional factors that contribute to consistency in the criminal justice system and policy execution (such as All India Services). By enabling “one country, one tax, one national market,” the Goods and Service Tax (GST) has cleared the way for regional cohesion. Additionally, Article 21 of the Indian Constitution promises freedom of commerce, trade, and intercourse relations within Indian Territory.
Diversity of India From North to South and East to West
- In India, spirituality and faith are very significant. From Badrinath and Kedarnath in the north to Rameshwaram in the south, Jagannath Puri in the east, and Dwaraka in the west, religious sites and sacred rivers can be found all over the length and width of the nation.
- They have a strong connection to the age-old practice of pilgrimage, which has always attracted people to various parts of the country and given them a sense of geo-cultural identification.
- Because people from all over the country attend fairs and festivals, they also function as integrating factors. Similar to how Muslims and Christians celebrate Id and Christmas, so do Hindus across the country on Diwali. Interreligious holidays are also celebrated in India.
- The entire Indian subcontinent’s flora and fauna, agricultural pursuits, and way of life, including vacations, are impacted by weather integration through the monsoon season. The country as a whole enjoys sports and movies, which act as unifying factors.
Diversity of India and Associated Threats and Challenges
Diversity of India faces certain threats and the social fabric of the society gets disrupted by the following means and modes are mentioned below:
Regionalism
In contrast to national interests, regionalism frequently emphasizes the interests of a specific area or region. It may also harm national unity. Regional demands and the resulting unrest have a negative impact on law and order.
Divisive Politics
Politicians will occasionally invoke ascriptive identities like caste, faith, etc. to win support. Violence, feelings of distrust, and suspicion among minorities can result from this kind of polarizing politics.
Development Imbalance
The backwardness of a region can be brought on by uneven socioeconomic growth, poor economic policies, and the resulting economic disparities. As a result, this may spark acts of violence, ignite migration surges, or even fuel separatist demands. For instance, the North East area has experienced a rise in secessionist demands and tendencies due to the region’s economic disadvantage.
Ethnic Differentiation
Conflicts between various ethnic groups have frequently resulted from ethnic differences, particularly as a result of issues like employment competition, a lack of resources, identity threats, etc. For instance, Bodos and Muslims who understand Bengali frequently fight in Assam. The Son of the Land doctrine, which links people to their place of birth and bestows upon them certain advantages, rights, roles, and obligations that may not apply to others, has served to emphasize this.
Geographical Isolation
Geographic isolation can also result in identity problems and calls for secession. Because the Siliguri corridor, which connects the North-East to the rest of the nation, is so narrow, the region is physically isolated from the rest of the nation. The area is relatively more backward than the rest of the nation and has poor infrastructure. This has led to several incidents of secession and cross-border terrorism, among other things.
Inter-Religious Conflicts
Interreligious conflicts damage the secular fabric of the nation as well as relations between two communities by sowing distrust and dread.
Inter-State Conflicts
This may cause feelings of regionalism to develop. Additionally, it may have an impact on interstate commerce and contact. Consider the conflict over the Cauvery River between Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. External forces like terrorist organizations or extremist groups can occasionally instigate violence and sow feelings of secession. Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI), for instance, has been charged with aiding and training mujahideen to engage in combat in Jammu and Kashmir and fostering separatist sentiment among local organizations.
Diversity of India UPSC
The problem, not diversity itself, is how it is handled in Indian culture. Problems like regionalism, communalism, and ethnic conflicts have arisen as a result of an unfair distribution of the benefits of growth or an undervaluation of some groups’ cultures. As a result, the Constitution and its principles must be the cornerstone of our community. Any society that has tried to become homogeneous has eventually experienced stagnation and decline. Students can read all the details related to UPSC by visiting the official website of StudyIQ UPSC Online Coaching.
Sharing is caring!
Diversity of India FAQs
Why india is called diversity.
India is called the 'land of diversity' because India have various types of food, speak different languages, celebrate different festivals, and practice different religions and traditions.
How many parts of diversity are there in India?
Modern India stands as one of the most diverse countries in the world, a subcontinent that is home to over 100 languages, over 700 different tribes.
What is diversity definition?
It means collective differences, that is, differences which mark off one group of people from another.
What is the main cause of diversity in India?
There are various reasons but the following are considered as the major reasons for diversity in India: geography of India, which includes the plains, the plateaus, the deserts, the mountains, etc.
What is the concept of diversity?
Diversity means having a range of people with various racial, ethnic, socioeconomic, and cultural backgrounds and various lifestyles, experience, and interests.
- indian society

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Exam 2024
- UPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Mains Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPSC Age Limit 2024
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Full Form

Recent Posts
- UPPSC Exam 2024
- UPPSC Calendar
- UPPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPPSC Application Form 2024
- UPPSC Eligibility Criteria 2024
- UPPSC Admit card 2024
- UPPSC Salary And Posts
- UPPSC Cut Off
- UPPSC Previous Year Paper
BPSC Exam 2024
- BPSC 70th Notification
- BPSC 69th Exam Analysis
- BPSC Admit Card
- BPSC Syllabus
- BPSC Exam Pattern
- BPSC Cut Off
- BPSC Question Papers
IB ACIO Exam
- IB ACIO Salary
- IB ACIO Syllabus
CSIR SO ASO Exam
- CSIR SO ASO Exam 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Result 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date
- CSIR SO ASO Question Paper
- CSIR SO ASO Answer key 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Syllabus 2024
Study Material Categories
- Daily The Hindu Analysis
- Daily Practice Quiz for Prelims
- Daily Answer Writing
- Daily Current Affairs
- Indian Polity
- Environment and Ecology
- Art and Culture
- General Knowledge
- Biographies
IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy
General Studies
All Programmes
Study Material
Diversity in India
Quest for upsc cse panels.

Sub-Categories:
GS-I: Social Issues
What is Diversity?
What are the various manifestations of diversity in india, what are the elements of unity in india, what does india gain through its unity and diversity, what are the factors that threaten india’s diversity, what are the existing mechanisms to promote unity and diversity in india, how to strike a balance between unity and diversity in india.
Mains: Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.

From the perspective of society, diversity refers to the presence of a wide range of differences among people within a given community, organization, or group. These differences can include but are not limited to race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, age, physical abilities, religious beliefs, political beliefs , and more.
India's diversity stems from historical influences, including waves of invasions , the emergence of religions , and Western colonialism . Geographically, the country's rugged terrain, river systems, coastline, and climate have also shaped distinct cultures, traditions, and languages across regions.
Geographical Diversity and Biodiversity:
India's geography is diverse, featuring towering mountain ranges such as the Himalayas and the Western Ghats , as well as vast plains like the Indo-Gangetic along with the Deccan Plateau.
- The country also boasts a variety of climates and ecosystems, from the wettest areas of the northeast to the arid deserts of the west .
- India is one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries , home to around 8% of all recorded species. India has over 45,000 plants and 91,000 animal species, and various ecosystems .
Religious Diversity :
India is characterized by diverse religious beliefs and practices.
- India is the birthplace of four of the world’s major religions, i.e. Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism.
- India is also home to people of many religions of the world, including a huge population of Muslims( 3rd largest in the world) and Christians, along with Jews , Parsis , etc.
Caste Diversity :
Caste plays a significant role in shaping the diverse fabric of Indian society . There are more than 3,000 Jatis in India. These are hierarchically graded in different ways in different regions.
- It may also be noted that the practice of the caste system is not confined to Hindus alone. Castes among Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, and other communities also exist in India.
Linguistic Diversity :
More than 19,500 languages or dialects are spoken in India as mother tongue.
- 121 languages are spoken by 10,000 or more people in India.
- Austric family - Santhal, Munda, Ho, etc.
- Dravidian family -Telugu, Tamil, Kannada, Malayalam, etc.
- Sino-Tibetan family - Sikkimese, Sikkimese, Bodo, etc.
- Indo-European family - Hindi, Punjabi, Sindhi, Marathi, etc.
Racial Diversity :
India is a country of great racial diversity, with a wide variety of different ethnic and linguistic groups.
- The population is primarily an admixture of the following races: Indo-Aryans, Dravidians, and Mongoloids.
- The country is also home to several tribal groups, each with distinct cultures and traditions.
Diversity in Social Life :
Indian society is greatly heterogeneous along various regions and sub-regions differing from one another. Diversity can be seen in -
- Family Structure , Marriage Types and Rituals
- Festivals, Cuisine and food habits, Clothing, settlement patterns
- Literature, Epics, Drama, Cinema, and Theatre.
Despite all the diversities, India remained united with a unitary spirit. The thread which binds all Indians together is known as " Unity among diversity" . This unity can be seen across various spheres
Geographical unity
The Indian Subcontinent constitutes a distinctive geographic entity, and the Himalayas provide a formidable physical barrier to the North , while seas are across the East, South, and West.
- The geology of the Indian subcontinent is unique due to its location on a separate tectonic plate, the Indian Plate , which collided with the Eurasian Plate to create the Himalayan mountain range, resulting in distinctive geological features and land formations.
Historical unity
From the very beginning, the entire geographical part was known as Bharat Varsha , and this name is present in the Vedas and Puranas .
- Most of the geographical territory of India came under the rule of great emperors like Ashoka and Akbar .
- British rule and the subsequent Nationalistic Movement led to further territorial integration.
Cultural unity
Despite having different cultural groups, there is a lot of unity in terms of ideas, philosophy, literature, etc.
- Being the country of festivals, it is observed that people from all cultural backgrounds come together and celebrate all the festivals like Diwali, Holi, Eid, Christmas, Gurupurab, Durga Puja, Onam, Baisakhi , etc reflecting the cultural diversity and unity of India.
- The manner of performance of social ceremonies is usually the same in all parts of the country.
- Despite its vast cultural diversity, India shares a sense of unity in its customs, practices, and social life , such as respect for elders, hospitality, joint family systems, etc.
Religious unity
Religious unity is still evident as almost all major religions practiced in India provide a similar teaching of values of tolerance and solidarity.
- Despite the diversity, there is also a sense of unity and tolerance towards different religions, with people of different faiths living and working together in harmony.
- This unity is reflected in the country's secular constitution, and most people in India have historically lived in peace with their neighbours regardless of their religious beliefs.
- National Integration - Unity in diversity can inject the feeling of harmony and brotherhood, despite having cultural, regional, or social differences among them.
- Global recognition - A country that is highly diverse but remains united not only builds a strong platform of growth but also attains recognition at the global level. It becomes an example for the world to follow.
- Peaceful co-existence - The peaceful co-existence can only be maintained through unity in a diverse country.
- Economic growth: Diversity can bring economic advantages as well, as different regions of the country have their own strengths and resources, leading to a more diversified economy.
- Tolerance and social cohesion: India's diversity can promote greater tolerance and understanding among different groups, leading to a more cohesive society.
- Innovation : Diversity in perspective and background can lead to more creative thinking and spur innovation and progress. The diverse range of languages and cultures also enables more effective communication with different parts of the world.
- Religious and ethnic conflicts : India has a history of religious and ethnic conflicts, which can lead to violence and loss of life. These conflicts can threaten the unity and diversity of the country.
- Discrimination and marginalization: Certain groups, such as Dalits and tribes, have faced discrimination and marginalization based on their caste and ethnicity. This can lead to social and economic disparities and threaten the diversity of the country.
- Forced assimilation and cultural homogenization: With the rise of globalization, there is a risk of cultural homogenization and the loss of traditional customs and practices. This can lead to the erosion of diversity in India.
- Political polarization: Political polarization in India based on religious, caste, and linguistic lines can also threaten diversity as it can fuel tension and conflicts between different groups.
- Climate change and environmental degradation: Climate change and environmental degradation can also threaten the diversity in India, as it can lead to the loss of biodiversity and the displacement of communities that rely on natural resources.
Constitutional mechanisms:
- Provisions for Geographical Unity: The spirit of the Constitution is that India is an " indestructible Union of the Destructible states” . Promoting ‘unity and integrity of the nation’ is one of the objectives stated in the preamble.
- Provisions for ethnic and Cultural Unity : Article 29 of the constitution mandates the state to protect the distinguished culture and traditions of various ethnic groups.
- Provision for religious Unity : The constitution of India defines it as a secular country. As per Article 25 of the constitution, the people are allowed to preach and propagate any religion. Further, under Article 15 , the state is directed to ensure that there shall be no discrimination on the ground of religion with any person.
- Provision for unity in diverse languages : The constitution of India doesn't impose any single language as a national language. Schedule 8 of the constitution recognizes 22 languages of our country.
Policy mechanisms:
- ‘Ek Bharat, Shreshtha Bharat’ - Programme aims to enhance interaction & promote mutual understanding between people of different states/UTs
- New Education Policy 2020 - Has ‘3 Language formula’ in School Education.
- One Nation-One Ration Card - To promote inter-state mobility among the workforce.
- Establishment of bodies like National Integration Council , Inter-state Council.
To strike a balance between unity and diversity in India, it is essential to acknowledge and appreciate the differences among various groups while promoting a sense of togetherness, trust, and solidarity .
- It is crucial to refrain from attempting to assimilate or be assimilated into other cultures, but instead, show respect for the unique identities of each group.
- The process of balancing diversity with unity is an ongoing one, and it is essential to cultivate multiple identities.
- Regardless of one's racial, ethnic, linguistic, or religious identity, every citizen of India should prioritize their Indian identity .
- Ultimately, the key to achieving this balance is to recognize and embrace the differences while simultaneously promoting a sense of unity and common purpose.
Previous Year Questions
Q) Describe any four cultural elements of diversity in India and rate their relative significance in building a national identity. (2015)
Q) Has the formation of linguistic States strengthened the cause of Indian Unity? ( 2016 )
Q) In the context of diversity of India, can it be said that the regions form cultural units rather than the States? Give reasons with examples for your viewpoint. ( 2017 )
Q) The spirit of tolerance and love is not only an interesting feature of Indian society from very early times, but it is also playing an important part at the present. Elaborate. ( 2017 )
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q) what is meant by melting pot and salad bowl theory in the context of society.
The melting pot theory refers to the idea that different cultural groups will come together and mix, creating a homogenous society where everyone shares the same culture.
The salad bowl theory, on the other hand, suggests that different cultural groups will retain their distinctiveness and coexist harmoniously, creating a diverse society where different cultures coexist and maintain their individuality.
Q) What is meant by the phrase ‘vasudhaiva kutumbakam ’?
" Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam" is a phrase in Sanskrit, meaning "the world is one family." It expresses the idea that all people are interconnected and that every human being is a member of a larger global community. It is a core principle of Indian culture and philosophy, which emphasizes the interconnectedness and unity of all life. The phrase is often invoked to promote universal brotherhood and a sense of belonging to a global community.
© 2024 Vajiram & Ravi. All rights reserved
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Religion in India: Tolerance and Segregation
Indians say it is important to respect all religions, but major religious groups see little in common and want to live separately, table of contents.
- The dimensions of Hindu nationalism in India
- India’s Muslims express pride in being Indian while identifying communal tensions, desiring segregation
- Muslims, Hindus diverge over legacy of Partition
- Religious conversion in India
- Religion very important across India’s religious groups
- Near-universal belief in God, but wide variation in how God is perceived
- Across India’s religious groups, widespread sharing of beliefs, practices, values
- Religious identity in India: Hindus divided on whether belief in God is required to be a Hindu, but most say eating beef is disqualifying
- Sikhs are proud to be Punjabi and Indian
- 1. Religious freedom, discrimination and communal relations
- 2. Diversity and pluralism
- 3. Religious segregation
- 4. Attitudes about caste
- 5. Religious identity
- 6. Nationalism and politics
- 7. Religious practices
- 8. Religion, family and children
- 9. Religious clothing and personal appearance
- 10. Religion and food
- 11. Religious beliefs
- 12. Beliefs about God
- Acknowledgments
- Appendix A: Methodology
- Appendix B: Index of religious segregation

This study is Pew Research Center’s most comprehensive, in-depth exploration of India to date. For this report, we surveyed 29,999 Indian adults (including 22,975 who identify as Hindu, 3,336 who identify as Muslim, 1,782 who identify as Sikh, 1,011 who identify as Christian, 719 who identify as Buddhist, 109 who identify as Jain and 67 who identify as belonging to another religion or as religiously unaffiliated). Interviews for this nationally representative survey were conducted face-to-face under the direction of RTI International from Nov. 17, 2019, to March 23, 2020.
To improve respondent comprehension of survey questions and to ensure all questions were culturally appropriate, Pew Research Center followed a multi-phase questionnaire development process that included expert review, focus groups, cognitive interviews, a pretest and a regional pilot survey before the national survey. The questionnaire was developed in English and translated into 16 languages, independently verified by professional linguists with native proficiency in regional dialects.
Respondents were selected using a probability-based sample design that would allow for robust analysis of all major religious groups in India – Hindus, Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists and Jains – as well as all major regional zones. Data was weighted to account for the different probabilities of selection among respondents and to align with demographic benchmarks for the Indian adult population from the 2011 census. The survey is calculated to have covered 98% of Indians ages 18 and older and had an 86% national response rate.
For more information, see the Methodology for this report. The questions used in this analysis can be found here .
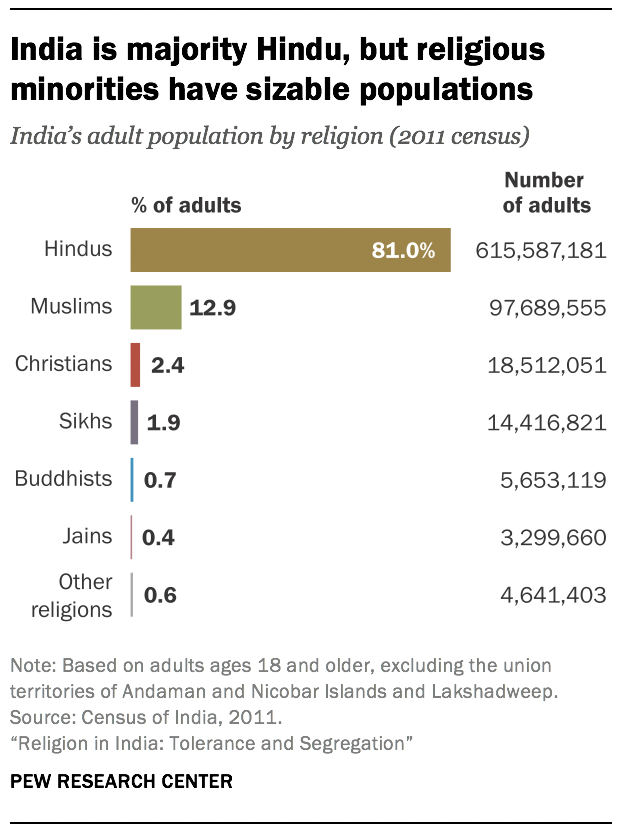
More than 70 years after India became free from colonial rule, Indians generally feel their country has lived up to one of its post-independence ideals: a society where followers of many religions can live and practice freely.
India’s massive population is diverse as well as devout. Not only do most of the world’s Hindus, Jains and Sikhs live in India, but it also is home to one of the world’s largest Muslim populations and to millions of Christians and Buddhists.
A major new Pew Research Center survey of religion across India, based on nearly 30,000 face-to-face interviews of adults conducted in 17 languages between late 2019 and early 2020 (before the COVID-19 pandemic ), finds that Indians of all these religious backgrounds overwhelmingly say they are very free to practice their faiths.
Related India research
This is one in a series of Pew Research Center reports on India based on a survey of 29,999 Indian adults conducted Nov. 17, 2019, to March 23, 2020, as well as demographic data from the Indian Census and other government sources. Other reports can be found here:
- How Indians View Gender Roles in Families and Society
- Religious Composition of India
- India’s Sex Ratio at Birth Begins To Normalize
Indians see religious tolerance as a central part of who they are as a nation. Across the major religious groups, most people say it is very important to respect all religions to be “truly Indian.” And tolerance is a religious as well as civic value: Indians are united in the view that respecting other religions is a very important part of what it means to be a member of their own religious community.
These shared values are accompanied by a number of beliefs that cross religious lines. Not only do a majority of Hindus in India (77%) believe in karma, but an identical percentage of Muslims do, too. A third of Christians in India (32%) – together with 81% of Hindus – say they believe in the purifying power of the Ganges River, a central belief in Hinduism. In Northern India, 12% of Hindus and 10% of Sikhs, along with 37% of Muslims, identity with Sufism, a mystical tradition most closely associated with Islam. And the vast majority of Indians of all major religious backgrounds say that respecting elders is very important to their faith.
Yet, despite sharing certain values and religious beliefs – as well as living in the same country, under the same constitution – members of India’s major religious communities often don’t feel they have much in common with one another. The majority of Hindus see themselves as very different from Muslims (66%), and most Muslims return the sentiment, saying they are very different from Hindus (64%). There are a few exceptions: Two-thirds of Jains and about half of Sikhs say they have a lot in common with Hindus. But generally, people in India’s major religious communities tend to see themselves as very different from others.
This perception of difference is reflected in traditions and habits that maintain the separation of India’s religious groups. For example, marriages across religious lines – and, relatedly, religious conversions – are exceedingly rare (see Chapter 3 ). Many Indians, across a range of religious groups, say it is very important to stop people in their community from marrying into other religious groups. Roughly two-thirds of Hindus in India want to prevent interreligious marriages of Hindu women (67%) or Hindu men (65%). Even larger shares of Muslims feel similarly: 80% say it is very important to stop Muslim women from marrying outside their religion, and 76% say it is very important to stop Muslim men from doing so.
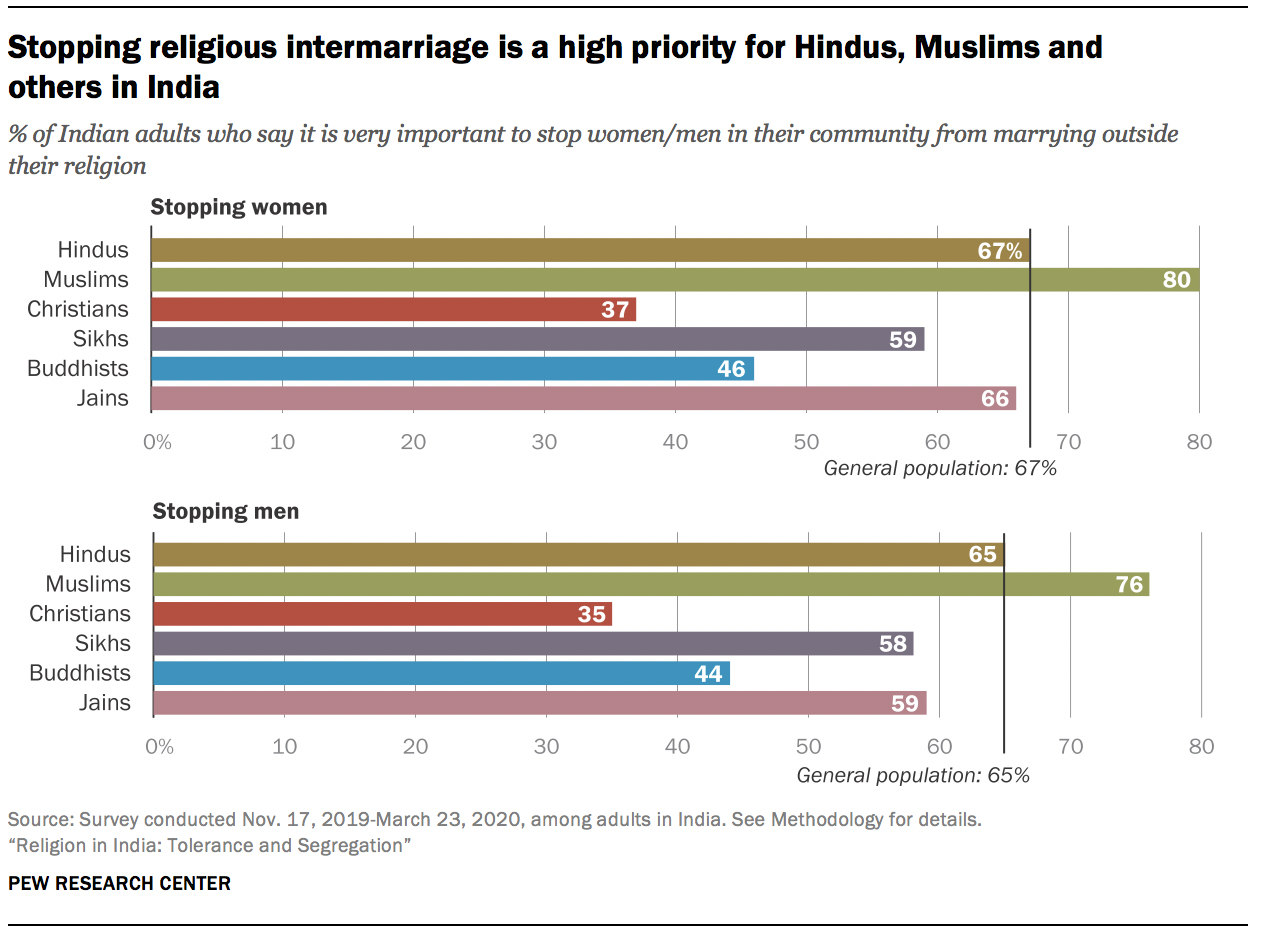
Moreover, Indians generally stick to their own religious group when it comes to their friends. Hindus overwhelmingly say that most or all of their close friends are also Hindu. Of course, Hindus make up the majority of the population, and as a result of sheer numbers, may be more likely to interact with fellow Hindus than with people of other religions. But even among Sikhs and Jains, who each form a sliver of the national population, a large majority say their friends come mainly or entirely from their small religious community.
Fewer Indians go so far as to say that their neighborhoods should consist only of people from their own religious group. Still, many would prefer to keep people of certain religions out of their residential areas or villages. For example, many Hindus (45%) say they are fine with having neighbors of all other religions – be they Muslim, Christian, Sikh, Buddhist or Jain – but an identical share (45%) say they would not be willing to accept followers of at least one of these groups, including more than one-in-three Hindus (36%) who do not want a Muslim as a neighbor. Among Jains, a majority (61%) say they are unwilling to have neighbors from at least one of these groups, including 54% who would not accept a Muslim neighbor, although nearly all Jains (92%) say they would be willing to accept a Hindu neighbor.
Indians, then, simultaneously express enthusiasm for religious tolerance and a consistent preference for keeping their religious communities in segregated spheres – they live together separately . These two sentiments may seem paradoxical, but for many Indians they are not.
Indeed, many take both positions, saying it is important to be tolerant of others and expressing a desire to limit personal connections across religious lines. Indians who favor a religiously segregated society also overwhelmingly emphasize religious tolerance as a core value. For example, among Hindus who say it is very important to stop the interreligious marriage of Hindu women, 82% also say that respecting other religions is very important to what it means to be Hindu. This figure is nearly identical to the 85% who strongly value religious tolerance among those who are not at all concerned with stopping interreligious marriage.
In other words, Indians’ concept of religious tolerance does not necessarily involve the mixing of religious communities. While people in some countries may aspire to create a “melting pot” of different religious identities, many Indians seem to prefer a country more like a patchwork fabric, with clear lines between groups.
One of these religious fault lines – the relationship between India’s Hindu majority and the country’s smaller religious communities – has particular relevance in public life, especially in recent years under the ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP). Led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, the BJP is often described as promoting a Hindu nationalist ideology .
The survey finds that Hindus tend to see their religious identity and Indian national identity as closely intertwined: Nearly two-thirds of Hindus (64%) say it is very important to be Hindu to be “truly” Indian.
Most Hindus (59%) also link Indian identity with being able to speak Hindi – one of dozens of languages that are widely spoken in India. And these two dimensions of national identity – being able to speak Hindi and being a Hindu – are closely connected. Among Hindus who say it is very important to be Hindu to be truly Indian, fully 80% also say it is very important to speak Hindi to be truly Indian.
The BJP’s appeal is greater among Hindus who closely associate their religious identity and the Hindi language with being “truly Indian.” In the 2019 national elections, 60% of Hindu voters who think it is very important to be Hindu and to speak Hindi to be truly Indian cast their vote for the BJP, compared with only a third among Hindu voters who feel less strongly about both these aspects of national identity.
Overall, among those who voted in the 2019 elections, three-in-ten Hindus take all three positions: saying it is very important to be Hindu to be truly Indian; saying the same about speaking Hindi; and casting their ballot for the BJP.
These views are considerably more common among Hindus in the largely Hindi-speaking Northern and Central regions of the country, where roughly half of all Hindu voters fall into this category, compared with just 5% in the South.
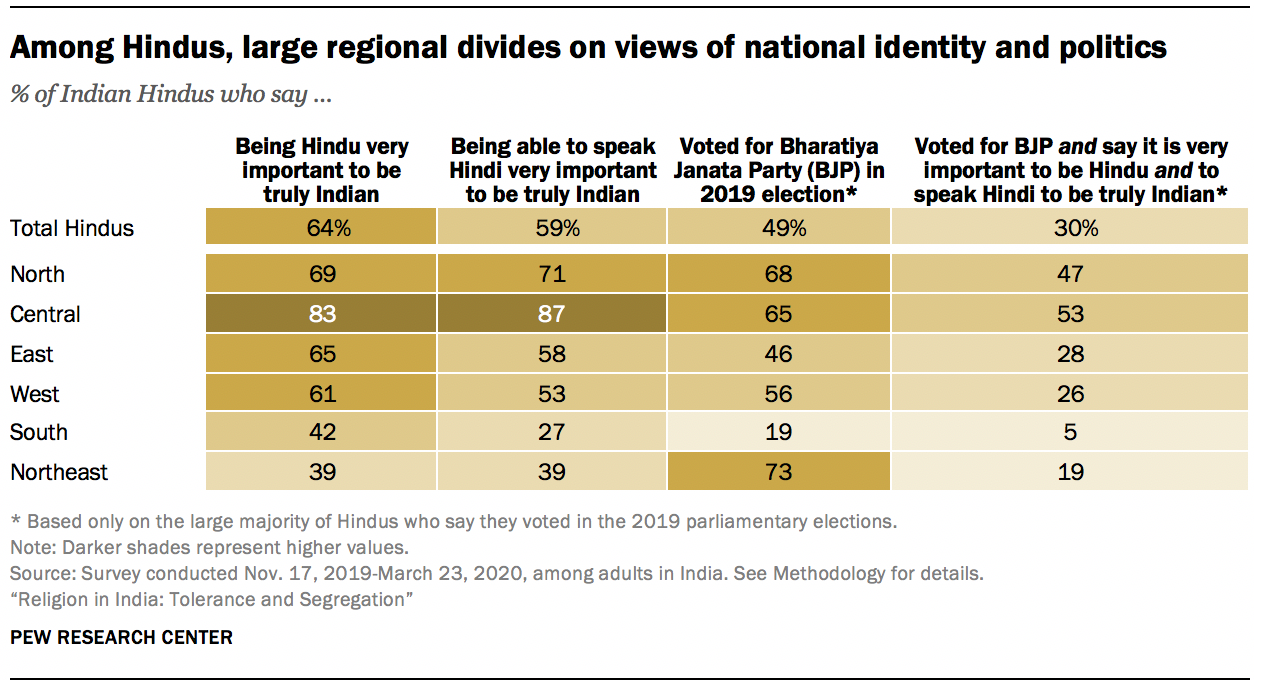
Whether Hindus who meet all three of these criteria qualify as “Hindu nationalists” may be debated, but they do express a heightened desire for maintaining clear lines between Hindus and other religious groups when it comes to whom they marry, who their friends are and whom they live among. For example, among Hindu BJP voters who link national identity with both religion and language, 83% say it is very important to stop Hindu women from marrying into another religion, compared with 61% among other Hindu voters.
This group also tends to be more religiously observant: 95% say religion is very important in their lives, and roughly three-quarters say they pray daily (73%). By comparison, among other Hindu voters, a smaller majority (80%) say religion is very important in their lives, and about half (53%) pray daily.
Even though Hindu BJP voters who link national identity with religion and language are more inclined to support a religiously segregated India, they also are more likely than other Hindu voters to express positive opinions about India’s religious diversity. Nearly two-thirds (65%) of this group – Hindus who say that being a Hindu and being able to speak Hindi are very important to be truly Indian and who voted for the BJP in 2019 – say religious diversity benefits India, compared with about half (47%) of other Hindu voters.
This finding suggests that for many Hindus, there is no contradiction between valuing religious diversity (at least in principle) and feeling that Hindus are somehow more authentically Indian than fellow citizens who follow other religions.
Among Indians overall, there is no overwhelming consensus on the benefits of religious diversity. On balance, more Indians see diversity as a benefit than view it as a liability for their country: Roughly half (53%) of Indian adults say India’s religious diversity benefits the country, while about a quarter (24%) see diversity as harmful, with similar figures among both Hindus and Muslims. But 24% of Indians do not take a clear position either way – they say diversity neither benefits nor harms the country, or they decline to answer the question. (See Chapter 2 for a discussion of attitudes toward diversity.)
India’s Muslim community, the second-largest religious group in the country, historically has had a complicated relationship with the Hindu majority. The two communities generally have lived peacefully side by side for centuries, but their shared history also is checkered by civil unrest and violence. Most recently, while the survey was being conducted, demonstrations broke out in parts of New Delhi and elsewhere over the government’s new citizenship law , which creates an expedited path to citizenship for immigrants from some neighboring countries – but not Muslims.
Today, India’s Muslims almost unanimously say they are very proud to be Indian (95%), and they express great enthusiasm for Indian culture: 85% agree with the statement that “Indian people are not perfect, but Indian culture is superior to others.”
Relatively few Muslims say their community faces “a lot” of discrimination in India (24%). In fact, the share of Muslims who see widespread discrimination against their community is similar to the share of Hindus who say Hindus face widespread religious discrimination in India (21%). (See Chapter 1 for a discussion of attitudes on religious discrimination.)
But personal experiences with discrimination among Muslims vary quite a bit regionally. Among Muslims in the North, 40% say they personally have faced religious discrimination in the last 12 months – much higher levels than reported in most other regions.
In addition, most Muslims across the country (65%), along with an identical share of Hindus (65%), see communal violence as a very big national problem. (See Chapter 1 for a discussion of Indians’ attitudes toward national problems.)
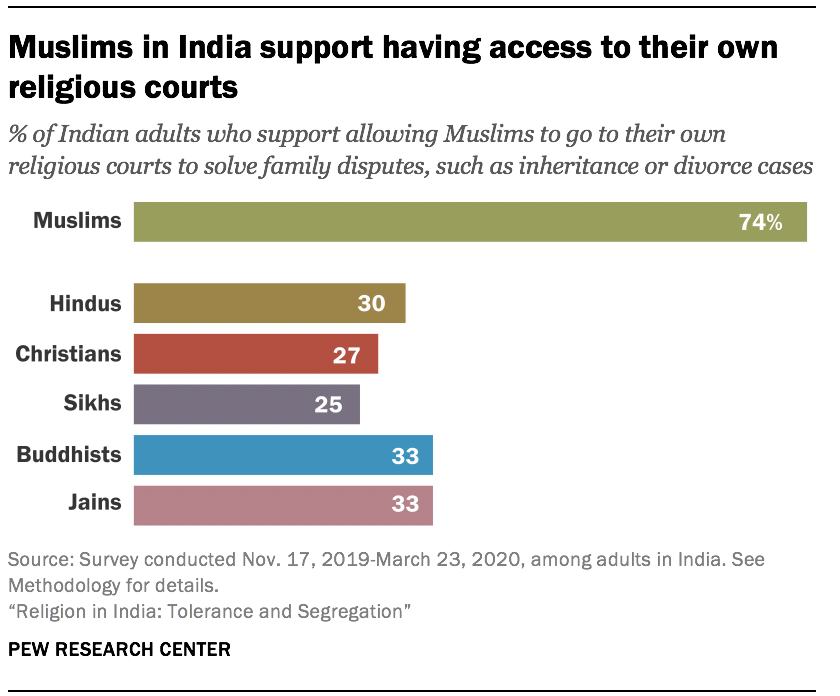
Like Hindus, Muslims prefer to live religiously segregated lives – not just when it comes to marriage and friendships, but also in some elements of public life. In particular, three-quarters of Muslims in India (74%) support having access to the existing system of Islamic courts, which handle family disputes (such as inheritance or divorce cases), in addition to the secular court system.
Muslims’ desire for religious segregation does not preclude tolerance of other groups – again similar to the pattern seen among Hindus. Indeed, a majority of Muslims who favor separate religious courts for their community say religious diversity benefits India (59%), compared with somewhat fewer of those who oppose religious courts for Muslims (50%).
Sidebar: Islamic courts in India
Since 1937, India’s Muslims have had the option of resolving family and inheritance-related cases in officially recognized Islamic courts, known as dar-ul-qaza. These courts are overseen by religious magistrates known as qazi and operate under Shariah principles . For example, while the rules of inheritance for most Indians are governed by the Indian Succession Act of 1925 and the Hindu Succession Act of 1956 (amended in 2005), Islamic inheritance practices differ in some ways, including who can be considered an heir and how much of the deceased person’s property they can inherit. India’s inheritance laws also take into account the differing traditions of other religious communities, such as Hindus and Christians, but their cases are handled in secular courts. Only the Muslim community has the option of having cases tried by a separate system of family courts. The decisions of the religious courts, however, are not legally binding , and the parties involved have the option of taking their case to secular courts if they are not satisfied with the decision of the religious court.
As of 2021, there are roughly 70 dar-ul-qaza in India. Most are in the states of Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh. Goa is the only state that does not recognize rulings by these courts, enforcing its own uniform civil code instead. Dar-ul-qaza are overseen by the All India Muslim Personal Law Board .
While these courts can grant divorces among Muslims, they are prohibited from approving divorces initiated through the practice known as triple talaq, in which a Muslim man instantly divorces his wife by saying the Arabic/Urdu word “talaq” (meaning “divorce”) three times. This practice was deemed unconstitutional by the Indian Supreme Court in 2017 and formally outlawed by the Lok Sabha, the lower house of India’s Parliament, in 2019. 1
Recent debates have emerged around Islamic courts. Some Indians have expressed concern that the rise of dar-ul-qaza could undermine the Indian judiciary, because a subset of the population is not bound to the same laws as everyone else. Others have argued that the rulings of Islamic courts are particularly unfair to women, although the prohibition of triple talaq may temper some of these criticisms. In its 2019 political manifesto , the BJP proclaimed a desire to create a national Uniform Civil Code, saying it would increase gender equality.
Some Indian commentators have voiced opposition to Islamic courts along with more broadly negative sentiments against Muslims, describing the rising numbers of dar-ul-qaza as the “Talibanization” of India , for example.
On the other hand, Muslim scholars have defended the dar-ul-qaza, saying they expedite justice because family disputes that would otherwise clog India’s courts can be handled separately, allowing the secular courts to focus their attention on other concerns.
Since 2018, the Hindu nationalist party Hindu Mahasabha (which does not hold any seats in Parliament) has tried to set up Hindu religious courts , known as Hindutva courts, aiming to play a role similar to dar-ul-qaza, only for the majority Hindu community. None of these courts have been recognized by the Indian government, and their rulings are not considered legally binding.
The seminal event in the modern history of Hindu-Muslim relations in the region was the partition of the subcontinent into Hindu-majority India and Muslim-majority Pakistan at the end of the British colonial period in 1947. Partition remains one of the largest movements of people across borders in recorded history, and in both countries the carving of new borders was accompanied by violence, rioting and looting .
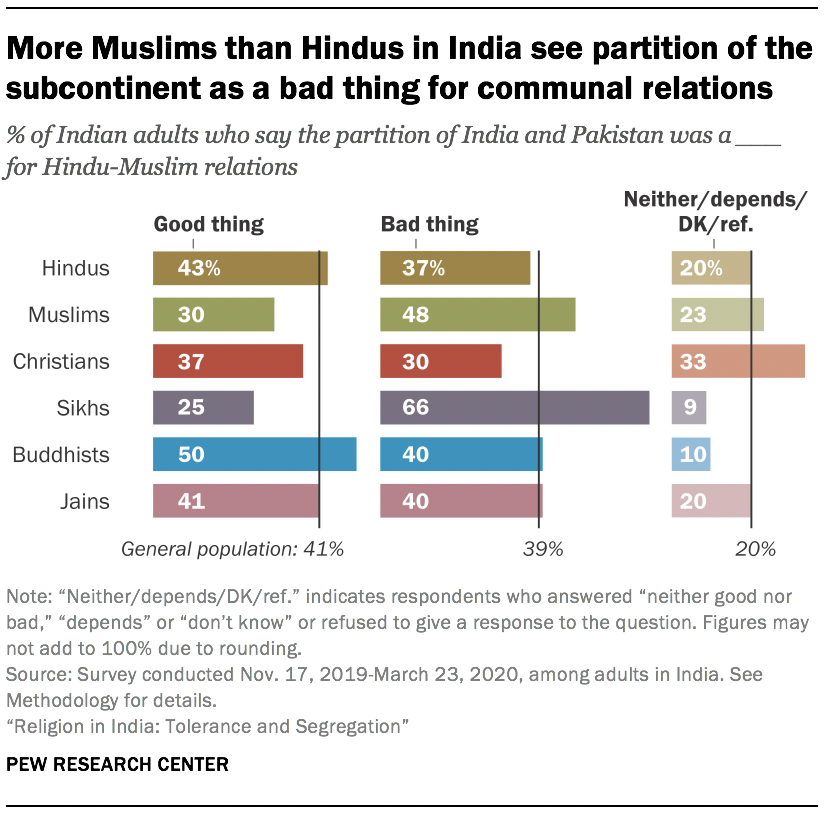
More than seven decades later, the predominant view among Indian Muslims is that the partition of the subcontinent was “a bad thing” for Hindu-Muslim relations. Nearly half of Muslims say Partition hurt communal relations with Hindus (48%), while fewer say it was a good thing for Hindu-Muslim relations (30%). Among Muslims who prefer more religious segregation – that is, who say they would not accept a person of a different faith as a neighbor – an even higher share (60%) say Partition was a bad thing for Hindu-Muslim relations.
Sikhs, whose homeland of Punjab was split by Partition, are even more likely than Muslims to say Partition was a bad thing for Hindu-Muslim relations: Two-thirds of Sikhs (66%) take this position. And Sikhs ages 60 and older, whose parents most likely lived through Partition, are more inclined than younger Sikhs to say the partition of the country was bad for communal relations (74% vs. 64%).
While Sikhs and Muslims are more likely to say Partition was a bad thing than a good thing, Hindus lean in the opposite direction: 43% of Hindus say Partition was beneficial for Hindu-Muslim relations, while 37% see it as a bad thing.
Context for the survey
Interviews were conducted after the conclusion of the 2019 national parliamentary elections and after the revocation of Jammu and Kashmir’s special status under the Indian Constitution. In December 2019, protests against the country’s new citizenship law broke out in several regions.
Fieldwork could not be conducted in the Kashmir Valley and a few districts elsewhere due to security concerns. These locations include some heavily Muslim areas, which is part of the reason why Muslims make up 11% of the survey’s total sample, while India’s adult population is roughly 13% Muslim, according to the most recent census data that is publicly available, from 2011. In addition, it is possible that in some other parts of the country, interreligious tensions over the new citizenship law may have slightly depressed participation in the survey by potential Muslim respondents.
Nevertheless, the survey’s estimates of religious beliefs, behaviors and attitudes can be reported with a high degree of confidence for India’s total population, because the number of people living in the excluded areas (Manipur, Sikkim, the Kashmir Valley and a few other districts) is not large enough to affect the overall results at the national level. About 98% of India’s total population had a chance of being selected for this survey.
Greater caution is warranted when looking at India’s Muslims separately, as a distinct population. The survey cannot speak to the experiences and views of Kashmiri Muslims. Still, the survey does represent the beliefs, behaviors and attitudes of around 95% of India’s overall Muslim population.
These are among the key findings of a Pew Research Center survey conducted face-to-face nationally among 29,999 Indian adults. Local interviewers administered the survey between Nov. 17, 2019, and March 23, 2020, in 17 languages. The survey covered all states and union territories of India, with the exceptions of Manipur and Sikkim, where the rapidly developing COVID-19 situation prevented fieldwork from starting in the spring of 2020, and the remote territories of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep; these areas are home to about a quarter of 1% of the Indian population. The union territory of Jammu and Kashmir was covered by the survey, though no fieldwork was conducted in the Kashmir region itself due to security concerns.
This study, funded by The Pew Charitable Trusts and the John Templeton Foundation, is part of a larger effort by Pew Research Center to understand religious change and its impact on societies around the world. The Center previously has conducted religion-focused surveys across sub-Saharan Africa ; the Middle East-North Africa region and many other countries with large Muslim populations ; Latin America ; Israel ; Central and Eastern Europe ; Western Europe ; and the United States .
The rest of this Overview covers attitudes on five broad topics: caste and discrimination; religious conversion; religious observances and beliefs; how people define their religious identity, including what kind of behavior is considered acceptable to be a Hindu or a Muslim; and the connection between economic development and religious observance.
Caste is another dividing line in Indian society, and not just among Hindus
Religion is not the only fault line in Indian society. In some regions of the country, significant shares of people perceive widespread, caste-based discrimination.
The caste system is an ancient social hierarchy based on occupation and economic status. People are born into a particular caste and tend to keep many aspects of their social life within its boundaries, including whom they marry. Even though the system’s origins are in historical Hindu writings , today Indians nearly universally identify with a caste, regardless of whether they are Hindu, Muslim, Christian, Sikh, Buddhist or Jain.
Overall, the majority of Indian adults say they are a member of a Scheduled Caste (SC) – often referred to as Dalits (25%) – Scheduled Tribe (ST) (9%) or Other Backward Class (OBC) (35%). 2
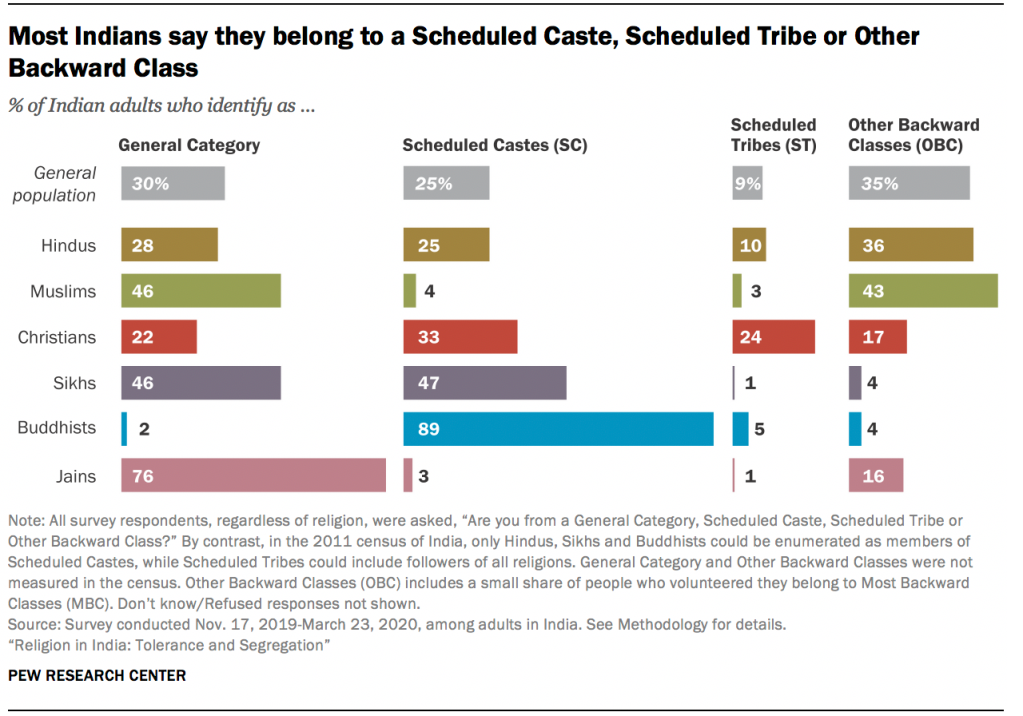
Buddhists in India nearly universally identify themselves in these categories, including 89% who are Dalits (sometimes referred to by the pejorative term “untouchables”).
Members of SC/ST/OBC groups traditionally formed the lower social and economic rungs of Indian society, and historically they have faced discrimination and unequal economic opportunities . The practice of untouchability in India ostracizes members of many of these communities, especially Dalits, although the Indian Constitution prohibits caste-based discrimination, including untouchability, and in recent decades the government has enacted economic advancement policies like reserved seats in universities and government jobs for Dalits, Scheduled Tribes and OBC communities.
Roughly 30% of Indians do not belong to these protected groups and are classified as “General Category.” This includes higher castes such as Brahmins (4%), traditionally the priestly caste. Indeed, each broad category includes several sub-castes – sometimes hundreds – with their own social and economic hierarchies.
Three-quarters of Jains (76%) identify with General Category castes, as do 46% of both Muslims and Sikhs.
Caste-based discrimination, as well as the government’s efforts to compensate for past discrimination, are politically charged topics in India . But the survey finds that most Indians do not perceive widespread caste-based discrimination. Just one-in-five Indians say there is a lot of discrimination against members of SCs, while 19% say there is a lot of discrimination against STs and somewhat fewer (16%) see high levels of discrimination against OBCs. Members of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes are slightly more likely than others to perceive widespread discrimination against their two groups. Still, large majorities of people in these categories do not think they face a lot of discrimination.
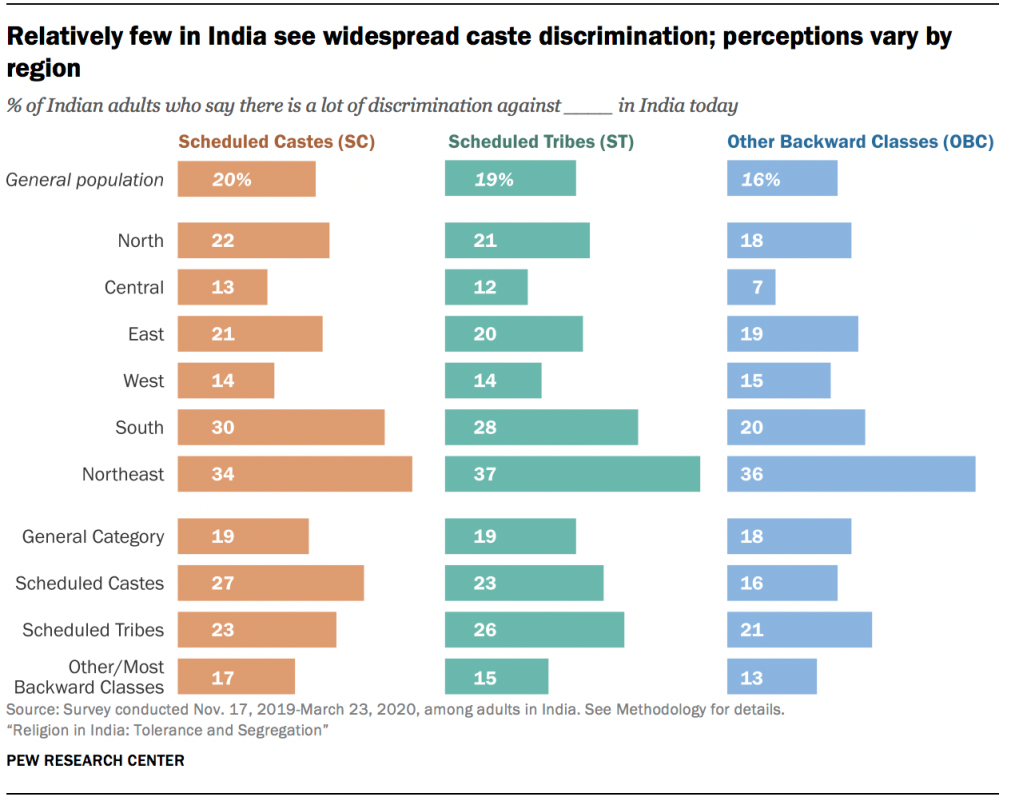
These attitudes vary by region, however. Among Southern Indians, for example, 30% see widespread discrimination against Dalits, compared with 13% in the Central part of the country. And among the Dalit community in the South, even more (43%) say their community faces a lot of discrimination, compared with 27% among Southern Indians in the General Category who say the Dalit community faces widespread discrimination in India.
A higher share of Dalits in the South and Northeast than elsewhere in the country say they, personally, have faced discrimination in the last 12 months because of their caste: 30% of Dalits in the South say this, as do 38% in the Northeast.
Although caste discrimination may not be perceived as widespread nationally, caste remains a potent factor in Indian society. Most Indians from other castes say they would be willing to have someone belonging to a Scheduled Caste as a neighbor (72%). But a similarly large majority of Indians overall (70%) say that most or all of their close friends share their caste. And Indians tend to object to marriages across caste lines, much as they object to interreligious marriages. 3
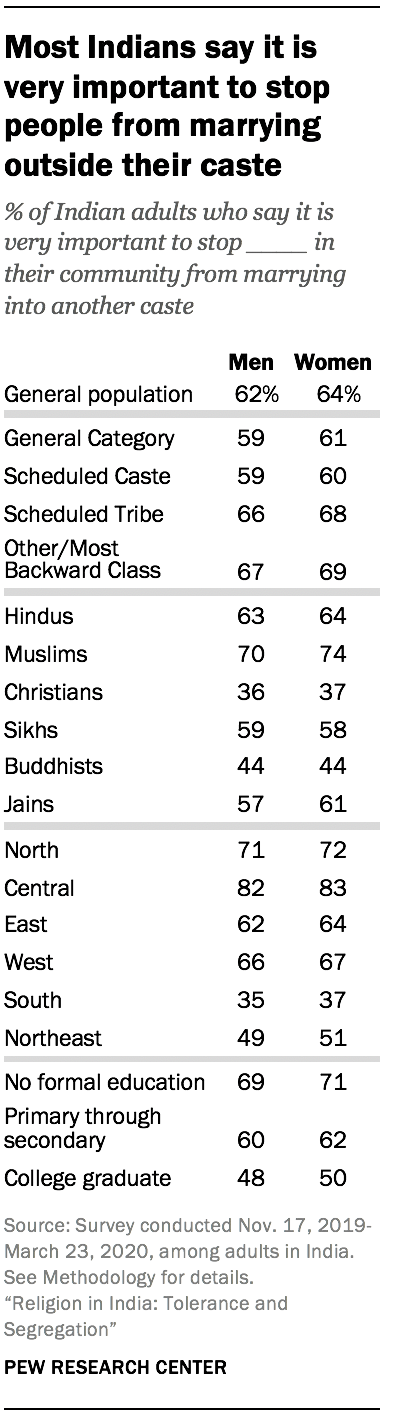
Overall, 64% of Indians say it is very important to stop women in their community from marrying into other castes, and about the same share (62%) say it is very important to stop men in their community from marrying into other castes. These figures vary only modestly across members of different castes. For example, nearly identical shares of Dalits and members of General Category castes say stopping inter-caste marriages is very important.
Majorities of Hindus, Muslims, Sikhs and Jains consider stopping inter-caste marriage of both men and women a high priority. By comparison, fewer Buddhists and Christians say it is very important to stop such marriages – although for majorities of both groups, stopping people from marrying outside their caste is at least “somewhat” important.
People surveyed in India’s South and Northeast see greater caste discrimination in their communities, and they also raise fewer objections to inter-caste marriages than do Indians overall. Meanwhile, college-educated Indians are less likely than those with less education to say stopping inter-caste marriages is a high priority. But, even within the most highly educated group, roughly half say preventing such marriages is very important. (See Chapter 4 for more analysis of Indians’ views on caste.)
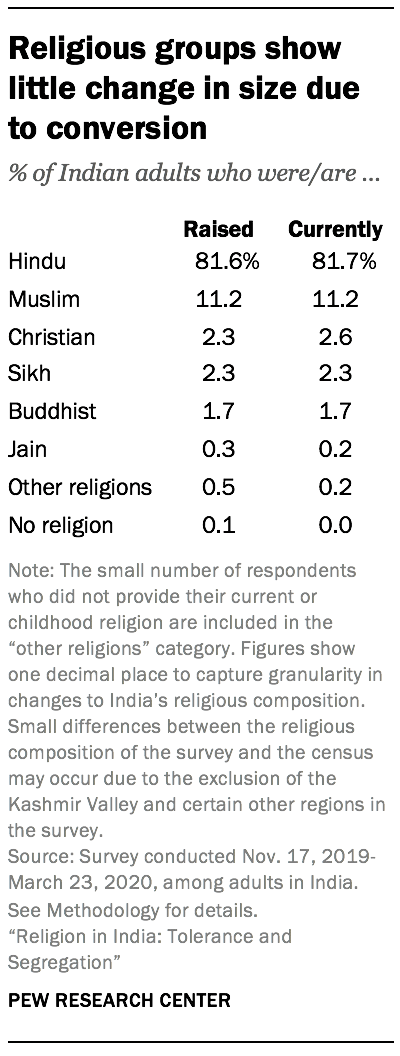
In recent years, conversion of people belonging to lower castes (including Dalits) away from Hinduism – a traditionally non-proselytizing religion – to proselytizing religions, especially Christianity, has been a contentious political issue in India. As of early 2021, nine states have enacted laws against proselytism , and some previous surveys have shown that half of Indians support legal bans on religious conversions. 4
This survey, though, finds that religious switching, or conversion, has a minimal impact on the overall size of India’s religious groups. For example, according to the survey, 82% of Indians say they were raised Hindu, and a nearly identical share say they are currently Hindu, showing no net losses for the group through conversion to other religions. Other groups display similar levels of stability.
Changes in India’s religious landscape over time are largely a result of differences in fertility rates among religious groups, not conversion.
Respondents were asked two separate questions to measure religious switching: “What is your present religion, if any?” and, later in the survey, “In what religion were you raised, if any?” Overall, 98% of respondents give the same answer to both these questions.
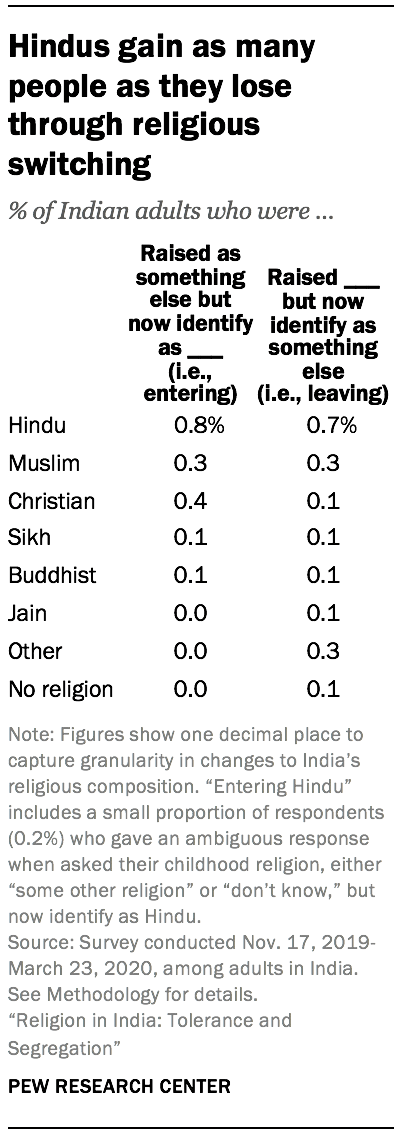
An overall pattern of stability in the share of religious groups is accompanied by little net gain from movement into, or out of, most religious groups. Among Hindus, for instance, any conversion out of the group is matched by conversion into the group: 0.7% of respondents say they were raised Hindu but now identify as something else, and although Hindu texts and traditions do not agree on any formal process for conversion into the religion, roughly the same share (0.8%) say they were not raised Hindu but now identify as Hindu. 5 Most of these new followers of Hinduism are married to Hindus.
Similarly, 0.3% of respondents have left Islam since childhood, matched by an identical share who say they were raised in other religions (or had no childhood religion) and have since become Muslim.
For Christians, however, there are some net gains from conversion: 0.4% of survey respondents are former Hindus who now identify as Christian, while 0.1% are former Christians.
Three-quarters of India’s Hindu converts to Christianity (74%) are concentrated in the Southern part of the country – the region with the largest Christian population. As a result, the Christian population of the South shows a slight increase within the lifetime of survey respondents: 6% of Southern Indians say they were raised Christian, while 7% say they are currently Christian.
Some Christian converts (16%) reside in the East as well (the states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal); about two-thirds of all Christians in the East (64%) belong to Scheduled Tribes.
Nationally, the vast majority of former Hindus who are now Christian belong to Scheduled Castes (48%), Scheduled Tribes (14%) or Other Backward Classes (26%). And former Hindus are much more likely than the Indian population overall to say there is a lot of discrimination against lower castes in India. For example, nearly half of converts to Christianity (47%) say there is a lot of discrimination against Scheduled Castes in India, compared with 20% of the overall population who perceive this level of discrimination against Scheduled Castes. Still, relatively few converts say they, personally, have faced discrimination due to their caste in the last 12 months (12%).
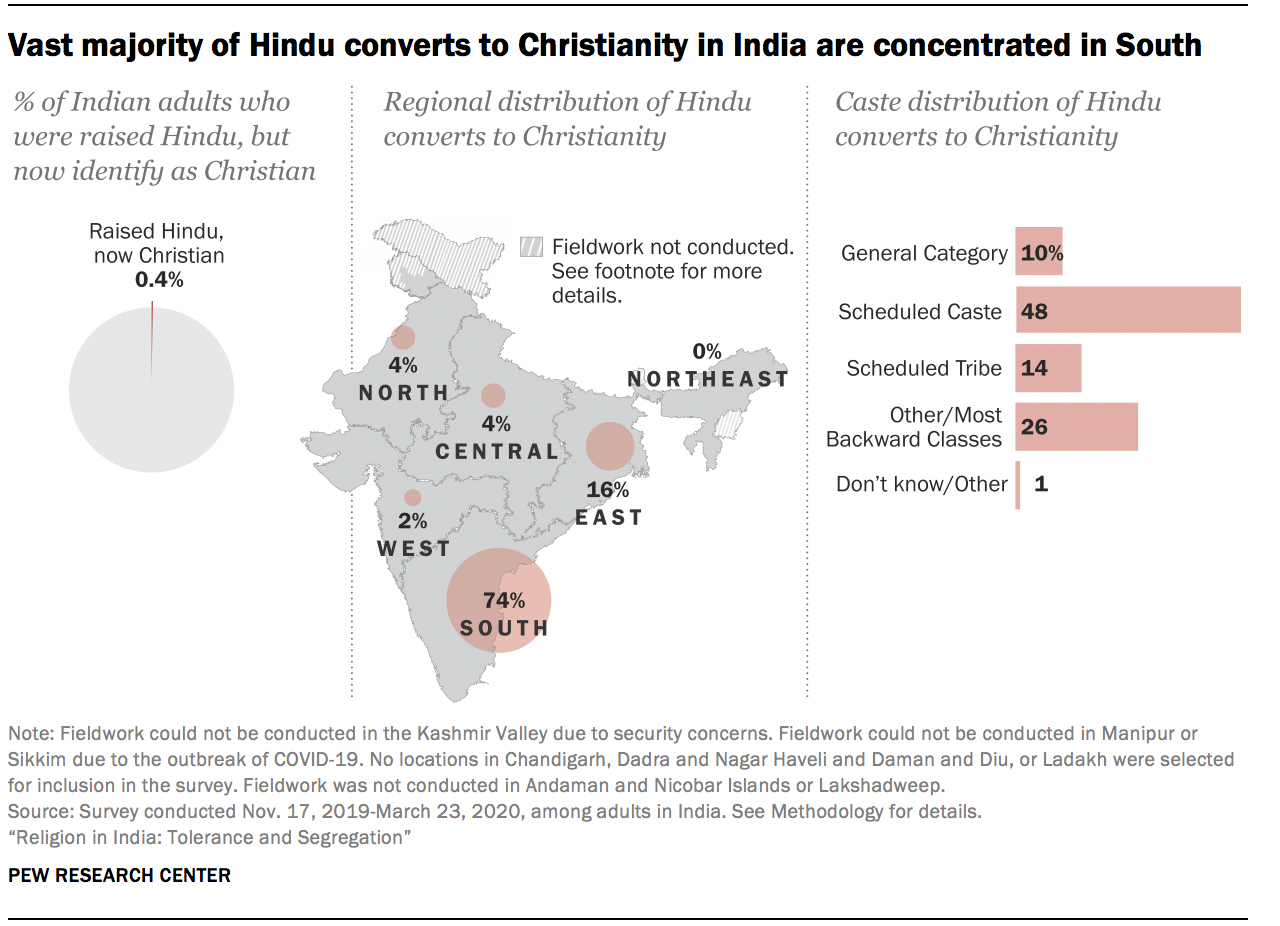
Though their specific practices and beliefs may vary, all of India’s major religious communities are highly observant by standard measures. For instance, the vast majority of Indians, across all major faiths, say that religion is very important in their lives. And at least three-quarters of each major religion’s followers say they know a great deal about their own religion and its practices. For example, 81% of Indian Buddhists claim a great deal of knowledge about the Buddhist religion and its practices.
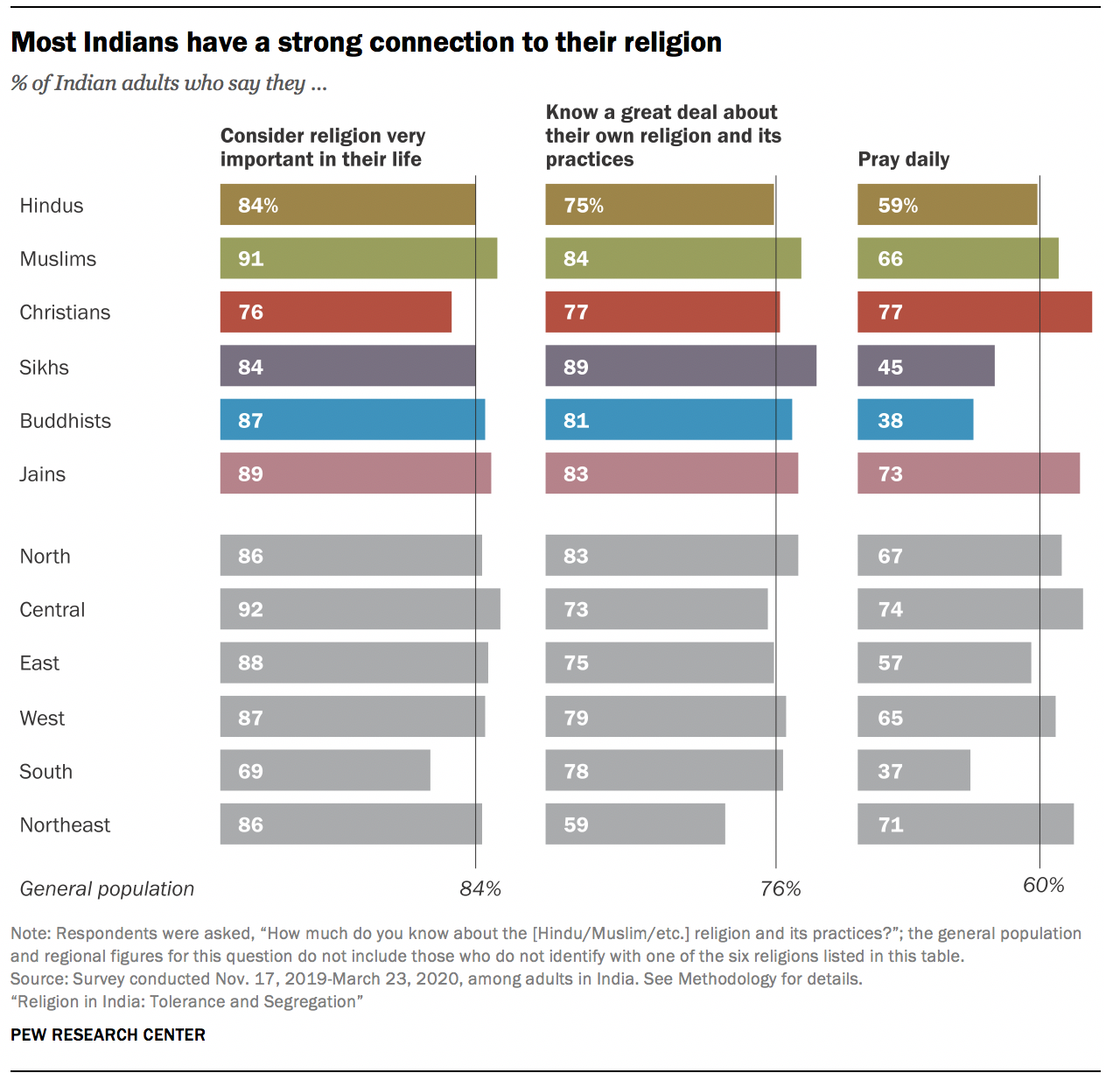
Indian Muslims are slightly more likely than Hindus to consider religion very important in their lives (91% vs. 84%). Muslims also are modestly more likely than Hindus to say they know a great deal about their own religion (84% vs. 75%).
Significant portions of each religious group also pray daily, with Christians among the most likely to do so (77%) – even though Christians are the least likely of the six groups to say religion is very important in their lives (76%). Most Hindus and Jains also pray daily (59% and 73%, respectively) and say they perform puja daily (57% and 81%), either at home or at a temple. 6
Generally, younger and older Indians, those with different educational backgrounds, and men and women are similar in their levels of religious observance. South Indians are the least likely to say religion is very important in their lives (69%), and the South is the only region where fewer than half of people report praying daily (37%). While Hindus, Muslims and Christians in the South are all less likely than their counterparts elsewhere in India to say religion is very important to them, the lower rate of prayer in the South is driven mainly by Hindus: Three-in-ten Southern Hindus report that they pray daily (30%), compared with roughly two-thirds (68%) of Hindus in the rest of the country (see “ People in the South differ from rest of the country in their views of religion, national identity ” below for further discussion of religious differences in Southern India).
The survey also asked about three rites of passage: religious ceremonies for birth (or infancy), marriage and death. Members of all of India’s major religious communities tend to see these rites as highly important. For example, the vast majority of Muslims (92%), Christians (86%) and Hindus (85%) say it is very important to have a religious burial or cremation for their loved ones.
The survey also asked about practices specific to particular religions, such as whether people have received purification by bathing in holy bodies of water, like the Ganges River, a rite closely associated with Hinduism. About two-thirds of Hindus have done this (65%). Most Hindus also have holy basil (the tulsi plant) in their homes, as do most Jains (72% and 62%, respectively). And about three-quarters of Sikhs follow the Sikh practice of keeping their hair long (76%).
For more on religious practices across India’s religious groups, see Chapter 7 .
Nearly all Indians say they believe in God (97%), and roughly 80% of people in most religious groups say they are absolutely certain that God exists. The main exception is Buddhists, one-third of whom say they do not believe in God. Still, among Buddhists who do think there is a God, most say they are absolutely certain in this belief.
While belief in God is close to universal in India, the survey finds a wide range of views about the type of deity or deities that Indians believe in. The prevailing view is that there is one God “with many manifestations” (54%). But about one-third of the public says simply: “There is only one God” (35%). Far fewer say there are many gods (6%).
Even though Hinduism is sometimes referred to as a polytheistic religion , very few Hindus (7%) take the position that there are multiple gods. Instead, the most common position among Hindus (as well as among Jains) is that there is “only one God with many manifestations” (61% among Hindus and 54% among Jains).
Among Hindus, those who say religion is very important in their lives are more likely than other Hindus to believe in one God with many manifestations (63% vs. 50%) and less likely to say there are many gods (6% vs. 12%).
By contrast, majorities of Muslims, Christians and Sikhs say there is only one God. And among Buddhists, the most common response is also a belief in one God. Among all these groups, however, about one-in-five or more say God has many manifestations, a position closer to their Hindu compatriots’ concept of God.
Most Hindus feel close to multiple gods, but Shiva, Hanuman and Ganesha are most popular
Traditionally, many Hindus have a “personal god,” or ishta devata: A particular god or goddess with whom they feel a personal connection. The survey asked all Indian Hindus who say they believe in God which god they feel closest to – showing them 15 images of gods on a card as possible options – and the vast majority of Hindus selected more than one god or indicated that they have many personal gods (84%). 7 This is true not only among Hindus who say they believe in many gods (90%) or in one God with many manifestations (87%), but also among those who say there is only one God (82%).
The god that Hindus most commonly feel close to is Shiva (44%). In addition, about one-third of Hindus feel close to Hanuman or Ganesha (35% and 32%, respectively).
There is great regional variation in how close India’s Hindus feel to some gods. For example, 46% of Hindus in India’s West feel close to Ganesha, but only 15% feel this way in the Northeast. And 46% of Hindus in the Northeast feel close to Krishna, while just 14% in the South say the same.
Feelings of closeness for Lord Ram are especially strong in the Central region (27%), which includes what Hindus claim is his ancient birthplace , Ayodhya. The location in Ayodhya where many Hindus believe Ram was born has been a source of controversy: Hindu mobs demolished a mosque on the site in 1992, claiming that a Hindu temple originally existed there. In 2019, the Indian Supreme Court ruled that the demolished mosque had been built on top of a preexisting non-Islamic structure and that the land should be given to Hindus to build a temple, with another location in the area given to the Muslim community to build a new mosque. (For additional findings on belief in God, see Chapter 12 .)
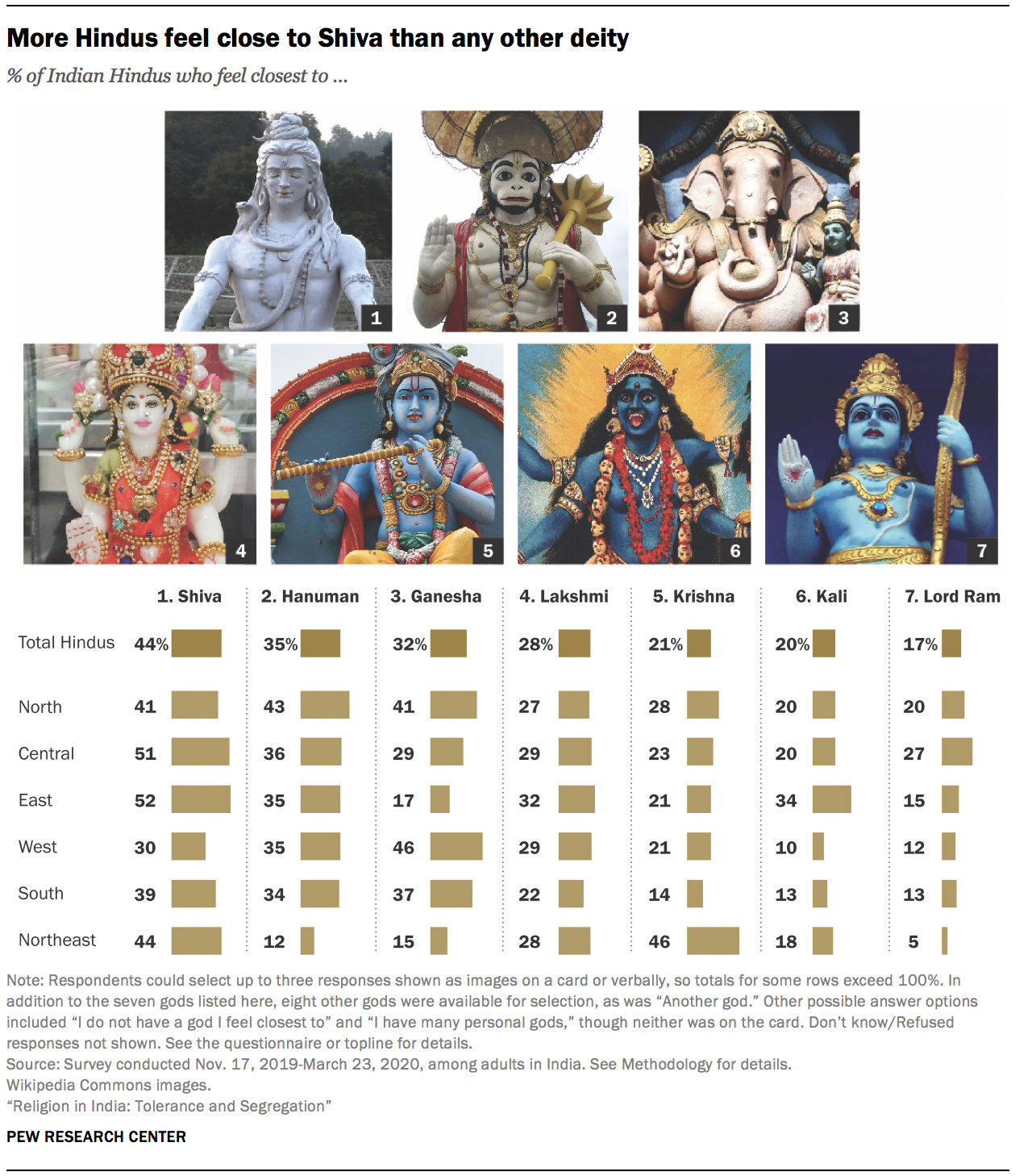
Sidebar: Despite economic advancement, few signs that importance of religion is declining
A prominent theory in the social sciences hypothesizes that as countries advance economically, their populations tend to become less religious, often leading to wider social change. Known as “secularization theory,” it particularly reflects the experience of Western European countries from the end of World War II to the present.
Despite rapid economic growth, India’s population so far shows few, if any, signs of losing its religion. For instance, both the Indian census and the new survey find virtually no growth in the minuscule share of people who claim no religious identity. And religion is prominent in the lives of Indians regardless of their socioeconomic status. Generally, across the country, there is little difference in personal religious observance between urban and rural residents or between those who are college educated versus those who are not. Overwhelming shares among all these groups say that religion is very important in their lives, that they pray regularly and that they believe in God.
Nearly all religious groups show the same patterns. The biggest exception is Christians, among whom those with higher education and those who reside in urban areas show somewhat lower levels of observance. For example, among Christians who have a college degree, 59% say religion is very important in their life, compared with 78% among those who have less education.
The survey does show a slight decline in the perceived importance of religion during the lifetime of respondents, though the vast majority of Indians indicate that religion remains central to their lives, and this is true among both younger and older adults.
Nearly nine-in-ten Indian adults say religion was very important to their family when they were growing up (88%), while a slightly lower share say religion is very important to them now (84%). The pattern is identical when looking only at India’s majority Hindu population. Among Muslims in India, the same shares say religion was very important to their family growing up and is very important to them now (91% each).
The states of Southern India (Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu and Telangana) show the biggest downward trend in the perceived importance of religion over respondents’ lifetimes: 76% of Indians who live in the South say religion was very important to their family growing up, compared with 69% who say religion is personally very important to them now. Slight declines in the importance of religion, by this measure, also are seen in the Western part of the country (Goa, Gujarat and Maharashtra) and in the North, although large majorities in all regions of the country say religion is very important in their lives today.
Despite a strong desire for religious segregation, India’s religious groups share patriotic feelings, cultural values and some religious beliefs. For instance, overwhelming shares across India’s religious communities say they are very proud to be Indian, and most agree that Indian culture is superior to others.
Similarly, Indians of different religious backgrounds hold elders in high respect. For instance, nine-in-ten or more Hindus, Muslims, Buddhists and Jains say that respecting elders is very important to what being a member of their religious group means to them (e.g., for Hindus, it’s a very important part of their Hindu identity). Christians and Sikhs also overwhelmingly share this sentiment. And among all people surveyed in all six groups, three-quarters or more say that respecting elders is very important to being truly Indian.
Within all six religious groups, eight-in-ten or more also say that helping the poor and needy is a crucial part of their religious identity.
Beyond cultural parallels, many people mix traditions from multiple religions into their practices: As a result of living side by side for generations, India’s minority groups often engage in practices that are more closely associated with Hindu traditions than their own. For instance, many Muslim, Sikh and Christian women in India say they wear a bindi (a forehead marking, often worn by married women), even though putting on a bindi has Hindu origins.
Similarly, many people embrace beliefs not traditionally associated with their faith: Muslims in India are just as likely as Hindus to say they believe in karma (77% each), and 54% of Indian Christians share this view. 8 Nearly three-in-ten Muslims and Christians say they believe in reincarnation (27% and 29%, respectively). While these may seem like theological contradictions, for many Indians, calling oneself a Muslim or a Christian does not preclude believing in karma or reincarnation – beliefs that do not have a traditional, doctrinal basis in Islam or Christianity.
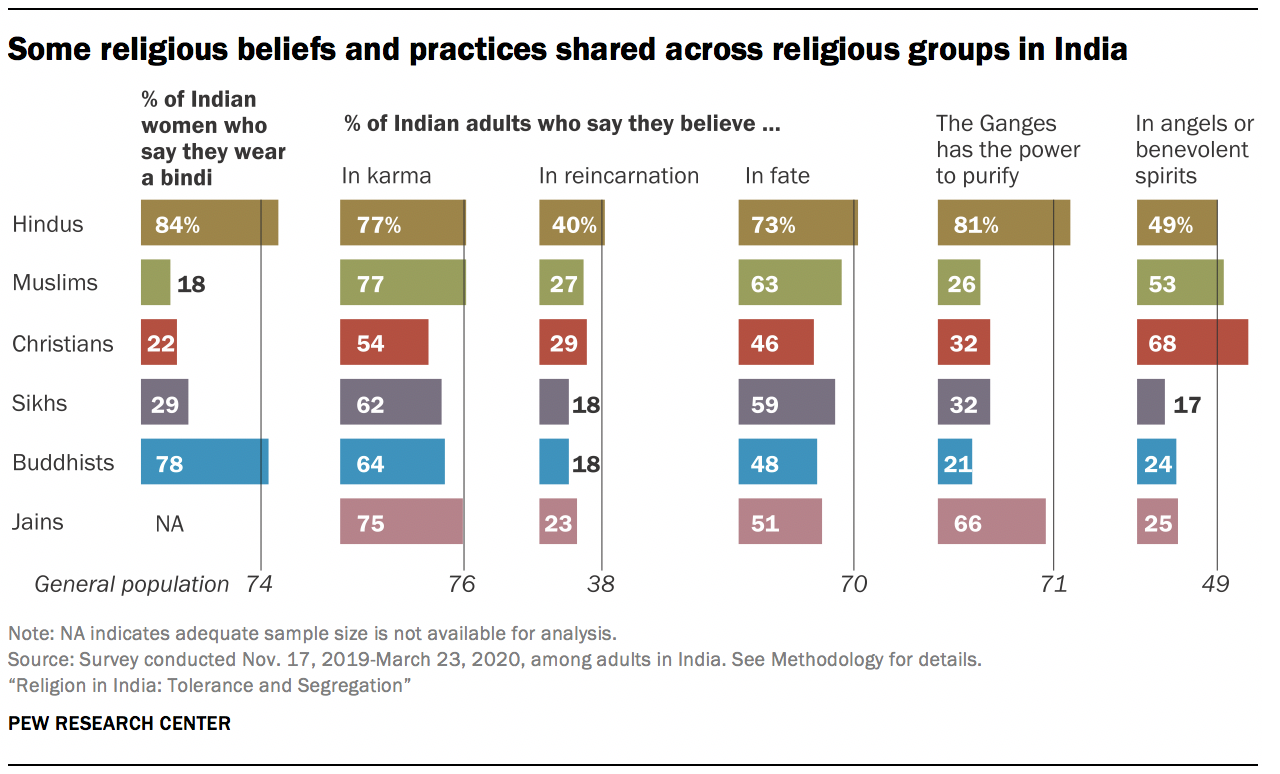
Most Muslims and Christians say they don’t participate in celebrations of Diwali, the Indian festival of lights that is traditionally celebrated by Hindus, Sikhs, Jains and Buddhists. But substantial minorities of Christians (31%) and Muslims (20%) report that they do celebrate Diwali. Celebrating Diwali is especially common among Muslims in the West, where 39% say they participate in the festival, and in the South (33%).
Not only do some followers of all these religions participate in a celebration (Diwali) that consumes most of the country once a year, but some members of the majority Hindu community celebrate Muslim and Christian festivals, too: 7% of Indian Hindus say they celebrate the Muslim festival of Eid, and 17% celebrate Christmas.
While there is some mixing of religious celebrations and traditions within India’s diverse population, many Hindus do not approve of this. In fact, while 17% of the nation’s Hindus say they participate in Christmas celebrations, about half of Hindus (52%) say that doing so disqualifies a person from being Hindu (compared with 35% who say a person can be Hindu if they celebrate Christmas). An even greater share of Hindus (63%) say a person cannot be Hindu if they celebrate the Islamic festival of Eid – a view that is more widely held in Northern, Central, Eastern and Northeastern India than the South or West.
Hindus are divided on whether beliefs and practices such as believing in God, praying and going to the temple are necessary to be a Hindu. But one behavior that a clear majority of Indian Hindus feel is incompatible with Hinduism is eating beef: 72% of Hindus in India say a person who eats beef cannot be a Hindu. That is even higher than the percentages of Hindus who say a person cannot be Hindu if they reject belief in God (49%), never go to a temple (48%) or never perform prayers (48%).
Attitudes toward beef appear to be part of a regional and cultural divide among Hindus: Southern Indian Hindus are considerably less likely than others to disqualify beef eaters from being Hindu (50% vs. 83% in the Northern and Central parts of the country). And, at least in part, Hindus’ views on beef and Hindu identity are linked with a preference for religious segregation and elements of Hindu nationalism. For example, Hindus who take a strong position against eating beef are more likely than others to say they would not accept followers of other religions as their neighbors (49% vs. 30%) and to say it is very important to be Hindu to be truly Indian (68% vs. 51%).
Relatedly, 44% of Hindus say they are vegetarians, and an additional 33% say they abstain from eating certain meats. Hindus traditionally view cows as sacred, and laws pertaining to cow slaughter have been a recent flashpoint in India . At the same time, Hindus are not alone in linking beef consumption with religious identity: 82% of Sikhs and 85% of Jains surveyed say that a person who eats beef cannot be a member of their religious groups, either. A majority of Sikhs (59%) and fully 92% of Jains say they are vegetarians, including 67% of Jains who do not eat root vegetables . 9 (For more data on religion and dietary habits, see Chapter 10 .)
Sidebar: People in the South differ from rest of the country in their views of religion, national identity
The survey consistently finds that people in the South (the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana, and the union territory of Puducherry) differ from Indians elsewhere in the country in their views on religion, politics and identity.
For example, by a variety of measures, people in the South are somewhat less religious than those in other regions – 69% say religion is very important in their lives, versus 92% in the Central part of the country. And 37% say they pray every day, compared with more than half of Indians in other regions. People in the South also are less segregated by religion or caste – whether that involves their friendship circles, the kind of neighbors they prefer or how they feel about intermarriage. (See Chapter 3 .)
Hindu nationalist sentiments also appear to have less of a foothold in the South. Among Hindus, those in the South (42%) are far less likely than those in Central states (83%) or the North (69%) to say being Hindu is very important to be truly Indian. And in the 2019 parliamentary elections, the BJP’s lowest vote share came in the South. In the survey, just 19% of Hindus in the region say they voted for the BJP, compared with roughly two-thirds in the Northern (68%) and Central (65%) parts of the country who say they voted for the ruling party.
Culturally and politically, people in the South have pushed back against the BJP’s restrictions on cow slaughter and efforts to nationalize the Hindi language . These factors may contribute to the BJP’s lower popularity in the South, where more people prefer regional parties or the Indian National Congress party.
These differences in attitudes and practices exist in a wider context of economic disparities between the South and other regions of the country. Over time, Southern states have seen stronger economic growth than the Northern and Central parts of the country. And women and people belonging to lower castes in the South have fared better economically than their counterparts elsewhere in the country. Even though three-in-ten people in the South say there is widespread caste discrimination in India, the region also has a history of anti-caste movements . Indeed, one author has attributed the economic growth of the South largely to the flattening of caste hierarchies.
Muslim identity in India
Most Muslims in India say a person cannot be Muslim if they never pray or attend a mosque. Similarly, about six-in-ten say that celebrating Diwali or Christmas is incompatible with being a member of the Muslim community. At the same time, a substantial minority express a degree of open-mindedness on who can be a Muslim, with fully one-third (34%) saying a person can be Muslim even if they don’t believe in God. (The survey finds that 6% of self-described Muslims in India say they do not believe in God; see “ Near-universal belief in God, but wide variation in how God is perceived ” above.)
Like Hindus, Muslims have dietary restrictions that resonate as powerful markers of identity. Three-quarters of Indian Muslims (77%) say that a person cannot be Muslim if they eat pork, which is even higher than the share who say a person cannot be Muslim if they do not believe in God (60%) or never attend mosque (61%).
Indian Muslims also report high levels of religious commitment by a host of conventional measures: 91% say religion is very important in their lives, two-thirds (66%) say they pray at least once a day, and seven-in-ten say they attend mosque at least once a week – with even higher attendance among Muslim men (93%).
By all these measures, Indian Muslims are broadly comparable to Muslims in the neighboring Muslim-majority countries of Pakistan and Bangladesh, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in those countries in late 2011 and early 2012. In Pakistan, for example, 94% of Muslims said religion is very important in their lives , while 81% of Bangladeshi Muslims said the same. Muslims in India are somewhat more likely than those elsewhere in South Asia to say they regularly worship at a mosque (70% in India vs. 59% in Pakistan and 53% in Bangladesh), with the difference mainly driven by the share of women who attend.
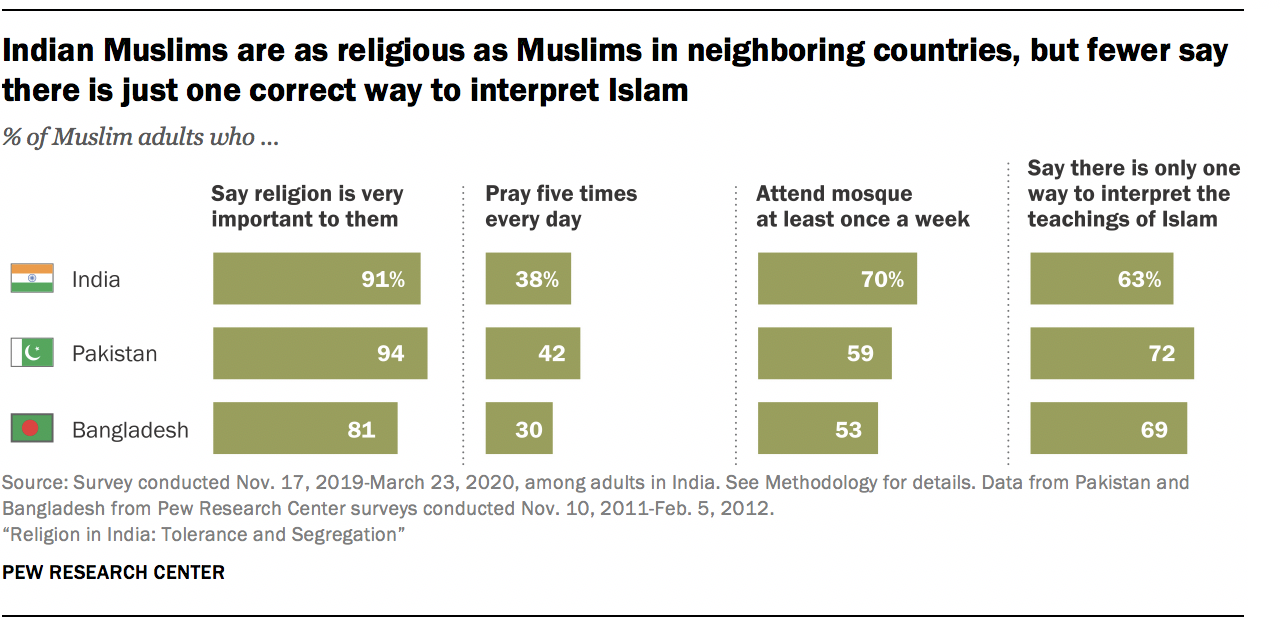
At the same time, Muslims in India are slightly less likely to say there is “only one true” interpretation of Islam (72% in Pakistan, 69% in Bangladesh, 63% in India), as opposed to multiple interpretations.
When it comes to their religious beliefs, Indian Muslims in some ways resemble Indian Hindus more than they resemble Muslims in neighboring countries. For example, Muslims in Pakistan and Bangladesh almost universally say they believe in heaven and angels, but Indian Muslims seem more skeptical: 58% say they believe in heaven and 53% express belief in angels. Among Indian Hindus, similarly, 56% believe in heaven and 49% believe in angels.
Majority of Muslim women in India oppose ‘triple talaq’ (Islamic divorce)
Many Indian Muslims historically have followed the Hanafi school of thought, which for centuries allowed men to divorce their wives by saying “talaq” (which translates as “divorce” in Arabic and Urdu) three times. Traditionally, there was supposed to be a waiting period and attempts at reconciliation in between each use of the word, and it was deeply frowned upon (though technically permissible) for a man to pronounce “talaq” three times quickly in a row. India’s Supreme Court ruled triple talaq unconstitutional in 2017, and it was banned by legislation in 2019 .
Most Indian Muslims (56%) say Muslim men should not be allowed to divorce this way. Still, 37% of Indian Muslims say they support triple talaq, with Muslim men (42%) more likely than Muslim women (32%) to take this position. A majority of Muslim women (61%) oppose triple talaq.
Highly religious Muslims – i.e., those who say religion is very important in their lives – also are more likely than other Muslims to say Muslim men should be able to divorce their wives simply by saying “talaq” three times (39% vs. 26%).
Triple talaq seems to have the most support among Muslims in the Southern and Northeastern regions of India, where half or more of Muslims say it should be legal (58% and 50%, respectively), although 12% of Muslims in the South and 16% in the Northeast do not take a position on the issue either way.
Sikhism is one of four major religions – along with Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism – that originated on the Indian subcontinent. The Sikh religion emerged in Punjab in the 15th century, when Guru Nanak, who is revered as the founder of Sikhism, became the first in a succession of 10 gurus (teachers) in the religion.
Today, India’s Sikhs remain concentrated in the state of Punjab. One feature of the Sikh religion is a distinctive sense of community, also known as “Khalsa” (which translates as “ones who are pure”). Observant Sikhs differentiate themselves from others in several ways, including keeping their hair uncut. Today, about three-quarters of Sikh men and women in India say they keep their hair long (76%), and two-thirds say it is very important to them that children in their families also keep their hair long (67%). (For more analysis of Sikhs’ views on passing religious traditions on to their children, see Chapter 8 .)
Sikhs are more likely than Indian adults overall to say they attend religious services every day – 40% of Sikhs say they go to the gurdwara (Sikh house of worship) daily. By comparison, 14% of Hindus say they go to a Hindu temple every day. Moreover, the vast majority of Sikhs (94%) regard their holy book, the Guru Granth Sahib, as the word of God, and many (37%) say they read it, or listen to recitations of it, every day.
Sikhs in India also incorporate other religious traditions into their practice. Some Sikhs (9%) say they follow Sufi orders, which are linked with Islam, and about half (52%) say they have a lot in common with Hindus. Roughly one-in-five Indian Sikhs say they have prayed, meditated or performed a ritual at a Hindu temple.
Sikh-Hindu relations were marked by violence in the 1970s and 1980s, when demands for a separate Sikh state covering the Punjab regions in both India and Pakistan (also known as the Khalistan movement) reached their apex. In 1984, Prime Minister Indira Gandhi was assassinated by her Sikh bodyguards as revenge for Indian paramilitary forces storming the Sikh Golden Temple in pursuit of Sikh militants. Anti-Sikh riots ensued in Northern India, especially in the state of Punjab.

According to the Indian census, the vast majority of Sikhs in India (77%) still live in Punjab, where Sikhs make up 58% of the adult population. And 93% of Punjabi Sikhs say they are very proud to live in the state.
Sikhs also are overwhelmingly proud of their Indian identity. A near-universal share of Sikhs say they are very proud to be Indian (95%), and the vast majority (70%) say a person who disrespects India cannot be a Sikh. And like India’s other religious groups, most Sikhs do not see evidence of widespread discrimination against their community – just 14% say Sikhs face a lot of discrimination in India, and 18% say they personally have faced religious discrimination in the last year.
At the same time, Sikhs are more likely than other religious communities to see communal violence as a very big problem in the country. Nearly eight-in-ten Sikhs (78%) rate communal violence as a major issue, compared with 65% of Hindus and Muslims.
The BJP has attempted to financially compensate Sikhs for some of the violence that occurred in 1984 after Indira Gandhi’s assassination, but relatively few Sikh voters (19%) report having voted for the BJP in the 2019 parliamentary elections. The survey finds that 33% of Sikhs preferred the Indian National Congress Party – Gandhi’s party.
- Ahmed, Hilal. 2019. “ Siyasi Muslims: A story of political Islams in India .” ↩
- All survey respondents, regardless of religion, were asked, “Are you from a General Category, Scheduled Caste, Scheduled Tribe or Other Backward Class?” By contrast, in the 2011 census of India, only Hindus, Sikhs and Buddhists could be enumerated as members of Scheduled Castes, while Scheduled Tribes could include followers of all religions. General Category and Other Backward Classes were not measured in the census. A detailed analysis of differences between 2011 census data on caste and survey data can be found here . ↩
- According to the 2004 and 2009 National Election Studies by the Centre for the Study of Developing Societies (CSDS), roughly half of Indians or more said that marriages of boys and girls from different castes should be banned . In 2004, a majority also said this about people from different religions. ↩
- In both the 2004 and 2009 National Election Studies (organized by CSDS), roughly half of Indians said that “There should be a legal ban on religious conversions.” ↩
- This includes 0.2% of all Indian adults who now identify as Hindu but give an ambiguous response on how they were raised – either saying “some other religion” or saying they don’t know their childhood religion. ↩
- Puja is a specific worship ritual that involves prayer along with rites like offering flowers and food, using vermillion, singing and chanting. ↩
- Fifteen named deities were available for selection, though no answer options were read aloud. Respondents could select up to three of those 15 deities by naming them or selecting the corresponding image shown on a card. The answer option “another god” was available on the card or if any other deity name was volunteered by the respondent. Other possible answer options included “I do not have a god I feel closest to” and “I have many personal gods,” though neither was on the card. See the questionnaire or topline for the full list of gods offered. ↩
- The religious origins of karma are debated by scholars, but the concept has deep roots in Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Jainism. ↩
- For an analysis of Jain theology on the concept of jiva (soul) see Chapple, Christopher K. 2014. “Life All Around: Soul in Jainism.” In Biernacki, Loriliai and Philip Clayton, eds. “ Panentheism Across the World’s Traditions .” ↩
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Beliefs & Practices
- Christianity
- International Political Values
- International Religious Freedom & Restrictions
- Interreligious Relations
- Other Religions
- Pew-Templeton Global Religious Futures Project
- Religious Characteristics of Demographic Groups
- Religious Identity & Affiliation
- Religiously Unaffiliated
- Size & Demographic Characteristics of Religious Groups
How common is religious fasting in the United States?
8 facts about atheists, spirituality among americans, how people in south and southeast asia view religious diversity and pluralism, religion among asian americans, most popular, report materials.
- Questionnaire
- இந்தியாவில் மதம்: சகிப்புத்தன்மையும், தனிமைப்படுத்துதலும்
- भारत में धर्म: सहिष्णुता और अलगाव
- ভারতে ধর্ম: সহনশীলতা এবং পৃথকীকরণ
- भारतातील धर्म : सहिष्णुता आणि विलग्नता
- Related: Religious Composition of India
- How Pew Research Center Conducted Its India Survey
- Questionnaire: Show Cards
- India Survey Dataset
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center

Essay on Diversity in India for Students and Children in 1000 Words
On this page, we have published an Essay on Diversity in India for Students and Childrens in 1000 Words. We have explained its characteristics, unity in various fields, and 10 lines.
Start reading the Essay on Diversity in India…
Table of Contents
India is a unique nation. There are great contrasts in topographical conditions, occupants, and their societies in its different parts. A few locales are hot and dry like African deserts, while some are cold like Dhruv areas.
Someplace there is an overabundance of a downpour, at that point someplace there is an absence of it. Seeing the residents of Tamil Nadu, Punjab, and Assam together, one cannot consider them as one race or part of one culture.
The occupants of the nation have various religions, fluctuated nourishment and attire, as much as their dialects or lingos.
Read: Essay on Unity in Diversity in India
Solidarity in Diversity
Regardless of the decent variety of this class, the entire of India is established in the string of solidarity.
There are many methods of this principle, whose roots have grown to all corners of the country. Varieties and varieties outside are physical, yet the ceaseless stream of solidarity streaming in the act of Indians is passionate and neurotic.
It is the mainstay of Indian culture of the solidarity of India.the culture of India is very different from others that exists from old-time and continues to evolve with its specialties.
There are some extraordinary highlights of this, which have additionally fortified the underlying foundations of the recipe of Indian solidarity.
Characteristics of Diversity in India
Some of the features of Diversity in India topic is mentioned below:
- The stream of Indian culture has remained uninterrupted.
- It has been the main religion, philosophy, and thought. The meaning of faith here is neither ‘religion’ nor ‘religion.’ This religion of Indian culture is inclusive, liberal, and the essence of the truth of life.
- One of the supernatural elements of Indian culture is tolerance. The general meaning of tolerance here is not tolerance, but a glorious peace, a vast emotion, which is self-judgmental and macroeconomic.
- It is not rooted or fixed but conscious and dynamic. It has not changed its body (not soul) as per time but has made it very receptive.
- It is not all-round, all-round. All its aspects are mature, advanced, developed, and complete. There is neither vacancy nor narrowness in it.
These characteristics of Indian culture have tied this country into a reliable and complete emotional unity.
Political Unity
There was always political unity in India. Nation and Emperor, titles like Maharajadhiraja, Digvijay, and Ashwamedh and Rajasuya Yajna have been a symbol of the awakened political integration of India.
The whole of India was a powerful governmental entity, even during the historical period, the Mauryan period, the Gupta period, and then the Mughal period.
It is the reason that even after small disputes, big wars, and widespread upheaval within the country, the thread of political unity was not broken.
Communalism, linguism, regionalism, and other such elements emerged during those days. Further, the international powers tried to break the national federation of the country. However, even with their help, they never succeeded.
Even when there was a storm of war, anarchy, and instability within the country, the subtle but strong imagination of political unity could not disappear for a single moment from the minds and minds of the people. History testifies that foreign powers have never been able to run a free reign on a country of political unity. The history of India is a revival of this.
Read: Essay on Unity is Strength
Unity In Indian Culture
A powerful aspect of Indian culture is its religious unity. There may be external variations in all religions and communities of India, but the source of all their souls is the same.
Moksha, Nirvana, or Kaivalya are different names of the same destination. There may be a variety of rituals in Indian religions, but there is a complete resemblance in their original spirit.
Religious Unity
This religious unity and vivid imagination of religion gave a comprehensive view of the country, which has an infinite power to cover and connect the practice of the people. All appreciate Nanak , Tulsi, Buddha, Mahavira .
All are bowed before the country’s temples, mosques, and gurudwaras; The faith of the people towards the pilgrimage and the four dharmas are the essential elements of this cultural unity.
Its culture is the strongest pillar of India’s unity. The element of cultural harmony is visible behind the variety of living, food, clothing, and festivals. The same pattern of rites (birth, marriage, last rites at the time of death, etc.) exists everywhere.
Human life Diversity in India
The consistent uniformity of conduct, behavior, etiquette, morality, and philosophy of life for men, women, and boys and girls is a strong basis of the cultural unity of the country.
The interrelations and exchanges between languages, the essential elements of literature, the permanent values and the original creative inspirations of the fine arts are all proof of the fundamental unity of our cultural unity. The profound and essential integration of India is less to be seen and more to be experienced. The country is beloved by all.
It cannot be imagined how much the people, rivers, mountains, lush green fields, folk songs, folklore and philosophy of life, how much love, affection, and emotional affection are attached to the people. No exception will be tolerated about these Indians because they are all their own.
10 Lines on Diversity in India
- India is a very old and ancient country that has lots of Diversity and unity. People living in various religions like Hindu, Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Parsis, etc. reside here.
- There is a multiplicity of languages in India, but in reality, they are all cast in the same mold.
- In the field of stone art, sculpture, painting, dance, music, cinema, etc., we find an all India likeness.
- There are impressive contrasts inland conditions, occupants, and their societies in its different parts.
- Indian culture is very ancient and continues to evolve with its peculiarities.
- A powerful aspect of Indian culture is its religious unity.
- India is Famous all over the world because the character of “unity in diversity” is seen here.
- People use about 1650 languages and dialects according to their religion and desire.
- Despite being different from culture, tradition, religion, and language, people still respect each other here.
- India has a reputation for its rich and old cultural heritage, which is due to people of different religions.
Despite such variations in India, a very durable and robust stream of unity is flowing in this regard, after the experience and realization of all Indians, no external evidence or certificate is required.
But even then, it would not be irrelevant to cite the statement of a well-known historian like BA Smith. He said that in India. I hope, you liked this Essay on Diversity in India for students and children.
Leave a comment Cancel reply

Essay on India
Here we have shared the Essay on India in detail so you can use it in your exam or assignment of 150, 250, 400, 500, or 1000 words.
You can use this Essay on India in any assignment or project whether you are in school (class 10th or 12th), college, or preparing for answer writing in competitive exams.
Topics covered in this article.
Essay on India in 150 words
Essay on india in 200-300 words, essay on india in 500-1000 words.
India, a diverse and culturally rich country located in South Asia, is renowned for its vibrant festivals, ancient heritage sites, and diverse landscapes. With a population of over 1.3 billion people, India is a melting pot of religions, languages, and ethnicities. It is a secular nation that upholds democracy and freedom. India has made significant contributions to art, literature, science, and philosophy. Despite challenges, it has achieved progress in various fields, including technology and economic growth. As the world’s largest democracy, India’s cultural richness, traditions, and hospitality attract tourists from around the world. With a young and dynamic workforce, India is emerging as a global player in innovation and entrepreneurship. India’s resilience, cultural heritage, and growing influence continue to captivate the world, making it an important player on the global stage.
India, known as the land of diversity, is a country of rich culture, history, and traditions. It is located in South Asia and is the seventh-largest country by land area. India is renowned for its vibrant festivals, ancient heritage sites, and diverse landscapes, ranging from the majestic Himalayas to the serene backwaters of Kerala.
With a population of over 1.3 billion people, India is a melting pot of different religions, languages, and ethnicities. It is a secular country that upholds the principles of democracy and freedom. India has made significant contributions to art, literature, science, and philosophy throughout history.
Despite its challenges, India has achieved notable progress in various fields, including technology, space exploration, and economic growth. It is the world’s largest democracy and has a parliamentary system of government. India’s cultural richness, traditions, and hospitality attract millions of tourists from around the world each year.
In recent years, India has emerged as a global player, contributing to the world economy, science, and technology. It is home to a young and dynamic workforce that is driving innovation and entrepreneurship.
In conclusion, India is a country that embraces diversity, celebrates its rich cultural heritage, and strives for progress. With its vast landscapes, ancient history, and vibrant culture, India continues to captivate the world. The resilience and spirit of its people, coupled with its growing influence, make India a significant player on the global stage.
Title: India – A Tapestry of Diversity, Heritage, and Progress
Introduction :
India, a nation located in South Asia, is a land of rich cultural heritage, diverse traditions, and breathtaking landscapes. With a population of over 1.3 billion people, India is known for its vibrant festivals, ancient history, and varied cuisines. This essay explores the multifaceted aspects of India, including its rich cultural tapestry, historical significance, economic growth, and contributions to the world. From the majestic Himalayas in the north to the serene backwaters of Kerala in the south, India’s beauty and diversity captivate the hearts of millions. Let us embark on a journey through the vibrant and enchanting land of India.
Cultural Heritage
India’s cultural heritage is as vast and diverse as its geographical expanse. It is a melting pot of religions, languages, and customs. The country is home to numerous religions, including Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, and Jainism. Each religion has its own unique rituals, traditions, and festivals, contributing to the colorful tapestry of Indian culture. Festivals like Diwali, Eid, Holi, Christmas, and Durga Puja are celebrated with great enthusiasm and are a reflection of India’s religious diversity.
Historical Significance
India boasts a rich history that spans thousands of years. It has been the birthplace of several ancient civilizations, including the Indus Valley Civilization and the Maurya and Gupta Empires. The country has been the center of learning and trade for centuries, attracting scholars, explorers, and traders from around the world. The Mughal Empire, known for its architectural marvels like the Taj Mahal, left a lasting legacy on India’s history. The British colonial rule in India and the subsequent struggle for independence led by Mahatma Gandhi shaped the modern history of the nation.
Economic Growth
India has experienced significant economic growth in recent years. It is one of the world’s fastest-growing major economies and has become a prominent player on the global stage. The country has embraced economic liberalization, attracting foreign investments and fostering entrepreneurship. India’s information technology industry, pharmaceutical sector, and service industries have flourished, contributing to its economic prosperity. However, challenges such as poverty, income inequality, and unemployment persist, highlighting the need for inclusive growth and sustainable development.
Contributions to the World
India has made remarkable contributions to various fields, including science, literature, arts, and spirituality. Ancient Indian scholars made significant advancements in mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. Indian literature, such as the Vedas, Ramayana, and Mahabharata, continues to inspire and influence people worldwide. Indian art forms like classical music, dance, and cinema have gained international recognition for their richness and beauty. Spiritual traditions like yoga and meditation have transcended borders, offering tools for holistic well-being.
Unity in Diversity
India’s strength lies in its unity amidst diversity. Despite its linguistic, religious, and cultural differences, the people of India have come together as a nation. The Constitution of India, adopted in 1950, upholds the principles of democracy, secularism, and unity. The diverse fabric of Indian society is reflected in its official languages, Hindi and English, and the recognition of regional languages. India’s unity in diversity is celebrated through cultural exchange, interfaith dialogue, and the promotion of national integration.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
India faces a range of challenges, including poverty, environmental degradation, healthcare disparities, and social inequality. Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts in education, healthcare, sustainable development, and social welfare. However, India also presents immense opportunities for progress. With a young and dynamic workforce, a vibrant entrepreneurial spirit, and a growing middle class, India has the potential to achieve inclusive growth, technological advancements, and social transformation.
Conclusion :
India, with its diverse cultures, historical significance, economic growth, and contributions to the world, stands as a shining example of unity in diversity. The nation’s cultural heritage, ancient history, and rapid development reflect its resilience and potential. As India continues its journey toward progress and prosperity, it must embrace sustainable development, address societal challenges, and build an inclusive and equitable society. India’s beauty, traditions, and people leave an indelible mark on the hearts and minds of those who explore its captivating tapestry.
Related Posts

Essential Elements of Valid Contract (Explained With Examples)

What is World Population? Main Causes, Effects, Top 20 Countries
Unity in Diversity Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on unity in diversity.
Unity in Diversity is a concept that signifies unity among individuals who have certain differences among them. These differences can be on the basis of culture, language, ideology, religion , sect, class, ethnicity, etc. Furthermore, the existence of this concept has been since time immemorial. Since then, it has been used by a variety of political and social organizations to symbolize unity among various persons or communities. People from many cultures, religious beliefs, and social statuses coexisting in peace and love is a prime illustration of “Unity in Diversity.” People have consistently shown this praiseworthy behaviour almost everywhere on Earth . The concept has certainly resulted in the ethical and moral evolution of humanity.

Unity in Diversity
The phrase “Unity in Diversity” refers to harmony and peace. It is employed among various groups to ensure that tolerance is uniform. Caste, creed, race, and nationality are all examples of diversity. Physical, cultural, linguistic, and political differences are also included in unity in diversity.
It educates all humans and living beings to unify and find methods to bond with one another despite their differences. This will create an environment in which individuals can coexist harmoniously. “Unity in Diversity” is a long-standing concept that may be traced back to Western and Eastern traditions.
Unity in Diversity in India
The existence of oneness despite numerous distinctions is the meaning of unity in variety. India is one of the excellent examples one can learn to understand the concept of Unity in diversity. We can clearly observe that people of all religions, creeds, castes, dialects, cultures, lifestyles, dressing sense, faith in God, rituals of worship, and so on coexist peacefully under one roof, i.e. in one country of India. We can never forget the liberation movements led by Indians of all faiths, religions and castes to establish India as an independent country. In India, the struggle for freedom is a magnificent example of unity in diversity.
India is the world’s largest and most populous country, home to people of various religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, Sikhism, Jainism, Christianity, and Parsees, all of which believe in the same Dharma and Karma doctrine. The Indian society is god-fearing by nature, believing in soul purification, reincarnation, salvation, heaven’s luxury, and hell’s punishments. People here celebrate their religious holidays (Holi, Diwali, Eid, Christmas, Good Friday, Mahavir Jayanti, Buddha Jayanti, Ganesh Chaturthi and so on) in a very peaceful manner, without causing harm to other religious people.
In India, Hindi is the mother tongue, but many other dialects and languages are spoken by people of various religions and regions (such as English, Urdu, Sanskrit, Bhojpuri, Bihari, Punjabi, Marathi, Bengali, Odiya, Gujarati, Malayali, Kashmiri, and so on); however, everyone is proud to be a citizen of great India.
The story of India’s unity amid variety is remarkable because it conveys a clear message that the country is more powerful than any religion or community in particular. Around 1.3 billion people live in harmony and contentment. With the world’s second-largest population of numerous ethnic and religious groupings, India is now the most important secular country, with a distinct character of unity in diversity.
Advantages of Unity in Diversity
First of all, following Unity in Diversity implies an interaction between many types of individuals. These individuals will probably have certain differences among them. This would occur also in workplaces, schools, public places, etc. Most noteworthy, working with diverse people provides an opportunity for exposure. Furthermore, this interaction would build up a tolerance in people. Hence, people would respect the opinion of others.
Unity in Diversity certainly enhances the quality of teamwork. This is because of the development of trust and bonding among people. As such the coordination and cooperation becomes very efficient. Consequently, the rate of completion of projects significantly increases.
In the world of business, a new principle is being followed. This principle is to think global and act locally. The reason for using this principle by companies is different social and cultural traditions. This principle is certainly a victory for the concept of Unity in Diversity. Also, more and more companies are doing business in different regions of the World.
The concept of Unity in Diversity is effective in solving various social problems . This is possible as diverse people tend to know each other. Consequently, this increases mutual respect among the people.
Unity in Diversity is very useful for a diverse country. Above all, the concept allows people of different religions, cultures, castes, to live together peacefully. The belief in Unity in Diversity certainly reduces the chances of riots and disturbances.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Unity in Diversity in Politics
The phrase Unity in Diversity has become a symbol of Canadian multiculturalism. Adélard Godbout, Premier of Quebec, first used this phrase in Canada. Canada certainly is an excellent example of Unity in Diversity. Above all, there is very low racism in Canada. Furthermore, the people of Canada are warm and friendly. They are very welcoming of foreigners in Canada. There are almost no incidents of hate speech and discrimination against foreigners in Canada.
The European Union, in 2000, adopted Unity in Diversity as its official motto. Above all, this was in reference to many diverse Nations of the European Union. This diversity of European Union member states was due to differences in culture. Furthermore, the adoption of Unity in Diversity as a motto shows unity. It shows Europeans have come together irrespective of differences.
India is another brilliant example of Unity in Diversity . In India, people of diverse religions, cultures, castes, sects, etc. have been living together. Furthermore, they have been living together for many centuries. This certainly shows the intense tolerance and unity of the Indian people. Hence, India is a country that perfectly demonstrates Unity in Diversity.
In conclusion, Unity in Diversity is an integral part of ethics and morality. The concept is certainly essential for the future progress of human society. People must display faith in this concept. Above all, they must keep aside feelings of racism , discrimination, and oppression. Without Unity in Diversity, the demise of humanity will certainly happen.
FAQs on Unity in Diversity Essay
Q1 How Unity in Diversity enhances the quality of teamwork?
A1 Unity in Diversity certainly enhances the quality of teamwork. This is because Unity in Diversity causes the development of trust and bonding among people. This ultimately results in significantly increasing the rate of completion of projects.
Q2 Why India is a brilliant example of Unity in Diversity?
A2 India is certainly a brilliant example of Unity in Diversity. This is because India has people of diverse religions, cultures, castes, sects, etc. Above all, these people have been living together peacefully for many centuries. Within a kilometer, you can discover mosques, temples, churches, and other religious buildings.
Q3. How can one sustain unity in the presence of diversity?
A3 . To keep unity in the variety by accepting other people’s choices, letting others express their opinions, and continually interacting with others without questioning their religion, caste, or financial strength. Unity in diversity can also be preserved by raising knowledge about the value of unity in diversity and incorporating the notion into primary education. Also, through instilling tolerance in all people, regardless of their culture, traditions, or values.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


COMMENTS
500 Words Essay On Diversity In India. India is a land of unique and diverse cultures, religions, languages, and customs. The concept of 'unity in diversity' is a cornerstone of India's culture and identity, and is something that should be celebrated and embraced. The different patterns of culture, religion, language, and customs make ...
India's diversity is its strength, making it a vibrant and fascinating country. It teaches us the value of unity amidst differences. 250 Words Essay on India the Land of Diversity Introduction. India, often referred to as the "Land of Diversity," is a unique amalgamation of various cultures, religions, languages, and traditions.
India - A Land Of Diversity Essay. India is a kaleidoscope of cultures that includes umpteen variations in food, clothing, language, music and religious beliefs. This colourful spread has been shaped by the long history and unique geography of this land. Though cut off from the world by three oceans and the highest chain of mountains, this ...
500 Words Essay on Cultural Diversity in India Introduction to Cultural Diversity in India. India, often hailed as the epitome of cultural diversity, is a country where myriad cultures, religions, languages, and traditions coexist in harmony. This cultural diversity is the cornerstone of India's pluralistic society and has shaped its history ...
Essay on Diversity in India: "Unity in diversity is India's strength. There is simplicity in every Indian. There is unity in every corner of India.". As India celebrates 77 years of independence, it's crucial to explore the vast diversity that defines this nation. Despite the colonial past, which attempted to diminish the rich tapestry ...
In conclusion, diversity in India is a symbol of unity in diversity. It is a country where diverse cultures, religions, and languages coexist peacefully. 250 Words Essay on Diversity in India Introduction. India, often referred to as a 'sub-continent', is renowned for its rich diversity.
In addition to the major forms of variety already mentioned, India also has diversity in many other areas, such as tribal, rural, and urban patterns of habitation, patterns of marriage and kinship along religious and regional lines, and more. Also read: Salient features of Indian Society. Factors Promoting Unity in Diversity of India
2. Diversity and pluralism. Indians are much more likely to view their country's religious diversity as an asset than as a liability. About half of Indians (53%) say religious diversity benefits the country, while 24% say it is harmful. The remainder (24%) don't take a position either way.
Therefore, India's "Unity in Diversity" is an example of the ability of diversity to produce a peaceful and inclusive society, and it serves as a source of strength and resiliency. Cultural Diversity in India: Celebrating Unity in Diversity Conclusion. To conclude, Cultural diversity in India is not just a statistic; it's a way of life.
India's least populous territory, the southern archipelago of Lakshadweep, had about 60,000 people in 2011. That was on par with Greenland and Bermuda, and equaled roughly a tenth of Wyoming's residents at that time. Hindus were a majority in 28 of India's 35 states in 2011. Around 94% of the world's Hindus (966 million) lived in India ...
India's Mosaic: A Celebration of Unity in Diversity (Relevant for Essay Writing for UPSC Civil Services Examination) India's Mosaic: A Celebration of Unity in Diversity. India's vibrant landscape is dotted with myriad cultures, traditions, and histories. Dive into the mesmerizing mosaic of India's composite culture and discover how it ...
In India, religious beliefs and practices are distinguished by diversity. Secularism in India means the equality of treatment by the State for all religions. By the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act in 1976, India is a secular state. The Indian subcontinent gave rise to four significant religions worldwide, namely Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism ...
Due to the rich diversity of India is called the 'land of diversity'. India is a nation where many various religions are practised. Hindus make up the majority of the people in India (82.41%), followed by Muslims (11.6%), Christians (2.32%), Sikhs (1.9%), Buddhists (0.77%), and Jains (0.41%), as well as the tribal groups, many of which ...
India is characterized by diverse religious beliefs and practices. India is the birthplace of four of the world's major religions, i.e. Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. Caste Diversity: Caste plays a significant role in shaping the diverse fabric of Indian society. There are more than 3,000 Jatis in India.
India's diversity has inspired many writers to describe their perceptions of the country's culture. These writings paint a complex and often conflicting picture of the culture of India. India is one of the most ethnically and religiously diverse countries in the world. The concept of "Indian culture" is a very complex and complicated matter.
This study is Pew Research Center's most comprehensive, in-depth exploration of India to date. For this report, we surveyed 29,999 Indian adults (including 22,975 who identify as Hindu, 3,336 who identify as Muslim, 1,782 who identify as Sikh, 1,011 who identify as Christian, 719 who identify as Buddhist, 109 who identify as Jain and 67 who identify as belonging to another religion or as ...
In conclusion, the cultural diversity of India is not a mere assortment of traditions; it is a living, breathing testament to the unity that can arise from embracing differences. From the languages spoken to the food savored, from the houses inhabited to the games played, and from the arts cherished to the monuments revered, India's cultural ...
500+ Words Essay on Incredible India. India represents "Unity in Diversity" . Our country is a mixture of cultures, regions, traditions, diversity in food, languages, etc. Our people of India are so polite, understanding and helping in nature. The national bird of India is Peacock and is very beautiful.
Factors Leading to Unity amidst Diversity in India: Constitutional identity: The entire country is governed by one single Even, most of the states follow a generalised scheme of 3-tier government structure, thus imparting uniformity in national governance framework.Further, the Constitution guarantees certain fundamental rights to all citizens regardless of their age, gender, class, caste ...
10 Lines on Diversity in India. India is a very old and ancient country that has lots of Diversity and unity. People living in various religions like Hindu, Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Parsis, etc. reside here. There is a multiplicity of languages in India, but in reality, they are all cast in the same mold.
Essay on India in 150 words. India, a diverse and culturally rich country located in South Asia, is renowned for its vibrant festivals, ancient heritage sites, and diverse landscapes. With a population of over 1.3 billion people, India is a melting pot of religions, languages, and ethnicities.
500+ Words Essay on Unity in Diversity. Unity in Diversity is a concept that signifies unity among individuals who have certain differences among them. These differences can be on the basis of culture, language, ideology, religion, sect, class, ethnicity, etc. Furthermore, the existence of this concept has been since time immemorial.