- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers

How to Write a Medical Research Paper
Last Updated: February 5, 2024 Approved
This article was co-authored by Chris M. Matsko, MD . Dr. Chris M. Matsko is a retired physician based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. With over 25 years of medical research experience, Dr. Matsko was awarded the Pittsburgh Cornell University Leadership Award for Excellence. He holds a BS in Nutritional Science from Cornell University and an MD from the Temple University School of Medicine in 2007. Dr. Matsko earned a Research Writing Certification from the American Medical Writers Association (AMWA) in 2016 and a Medical Writing & Editing Certification from the University of Chicago in 2017. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 89% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 202,819 times.
Writing a medical research paper is similar to writing other research papers in that you want to use reliable sources, write in a clear and organized style, and offer a strong argument for all conclusions you present. In some cases the research you discuss will be data you have actually collected to answer your research questions. Understanding proper formatting, citations, and style will help you write and informative and respected paper.
Researching Your Paper

- Pick something that really interests you to make the research more fun.
- Choose a topic that has unanswered questions and propose solutions.

- Quantitative studies consist of original research performed by the writer. These research papers will need to include sections like Hypothesis (or Research Question), Previous Findings, Method, Limitations, Results, Discussion, and Application.
- Synthesis papers review the research already published and analyze it. They find weaknesses and strengths in the research, apply it to a specific situation, and then indicate a direction for future research.

- Keep track of your sources. Write down all publication information necessary for citation: author, title of article, title of book or journal, publisher, edition, date published, volume number, issue number, page number, and anything else pertaining to your source. A program like Endnote can help you keep track of your sources.
- Take detailed notes as you read. Paraphrase information in your own words or if you copy directly from the article or book, indicate that these are direct quotes by using quotation marks to prevent plagiarism.
- Be sure to keep all of your notes with the correct source.
- Your professor and librarians can also help you find good resources.

- Keep all of your notes in a physical folder or in a digitized form on the computer.
- Start to form the basic outline of your paper using the notes you have collected.
Writing Your Paper

- Start with bullet points and then add in notes you've taken from references that support your ideas. [1] X Trustworthy Source PubMed Central Journal archive from the U.S. National Institutes of Health Go to source
- A common way to format research papers is to follow the IMRAD format. This dictates the structure of your paper in the following order: I ntroduction, M ethods, R esults, a nd D iscussion. [2] X Research source
- The outline is just the basic structure of your paper. Don't worry if you have to rearrange a few times to get it right.
- Ask others to look over your outline and get feedback on the organization.
- Know the audience you are writing for and adjust your style accordingly. [3] X Research source

- Use a standard font type and size, such as Times New Roman 12 point font.
- Double-space your paper.
- If necessary, create a cover page. Most schools require a cover page of some sort. Include your main title, running title (often a shortened version of your main title), author's name, course name, and semester.

- Break up information into sections and subsections and address one main point per section.
- Include any figures or data tables that support your main ideas.
- For a quantitative study, state the methods used to obtain results.

- Clearly state and summarize the main points of your research paper.
- Discuss how this research contributes to the field and why it is important. [4] X Research source
- Highlight potential applications of the theory if appropriate.
- Propose future directions that build upon the research you have presented. [5] X Research source
- Keep the introduction and discussion short, and spend more time explaining the methods and results.

- State why the problem is important to address.
- Discuss what is currently known and what is lacking in the field.
- State the objective of your paper.
- Keep the introduction short.

- Highlight the purpose of the paper and the main conclusions.
- State why your conclusions are important.
- Be concise in your summary of the paper.
- Show that you have a solid study design and a high-quality data set.
- Abstracts are usually one paragraph and between 250 – 500 words.

- Unless otherwise directed, use the American Medical Association (AMA) style guide to properly format citations.
- Add citations at end of a sentence to indicate that you are using someone else's idea. Use these throughout your research paper as needed. They include the author's last name, year of publication, and page number.
- Compile your reference list and add it to the end of your paper.
- Use a citation program if you have access to one to simplify the process.

- Continually revise your paper to make sure it is structured in a logical way.
- Proofread your paper for spelling and grammatical errors.
- Make sure you are following the proper formatting guidelines provided for the paper.
- Have others read your paper to proofread and check for clarity. Revise as needed.
Expert Q&A

- Ask your professor for help if you are stuck or confused about any part of your research paper. They are familiar with the style and structure of papers and can provide you with more resources. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Refer to your professor's specific guidelines. Some instructors modify parts of a research paper to better fit their assignment. Others may request supplementary details, such as a synopsis for your research project . Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Set aside blocks of time specifically for writing each day. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Do not plagiarize. Plagiarism is using someone else's work, words, or ideas and presenting them as your own. It is important to cite all sources in your research paper, both through internal citations and on your reference page. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 2
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3178846/
- ↑ http://owl.excelsior.edu/research-and-citations/outlining/outlining-imrad/
- ↑ http://china.elsevier.com/ElsevierDNN/Portals/7/How%20to%20write%20a%20world-class%20paper.pdf
- ↑ http://intqhc.oxfordjournals.org/content/16/3/191
- ↑ http://www.ruf.rice.edu/~bioslabs/tools/report/reportform.html#form
About This Article

To write a medical research paper, research your topic thoroughly and compile your data. Next, organize your notes and create a strong outline that breaks up the information into sections and subsections, addressing one main point per section. Write the results and discussion sections first to go over your findings, then write the introduction to state your objective and provide background information. Finally, write the abstract, which concisely summarizes the article by highlighting the main points. For tips on formatting and using citations, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Joshua Benibo
Jun 5, 2018
Did this article help you?
Dominic Cipriano
Aug 16, 2016
Obiajulu Echedom
Apr 2, 2017
Noura Ammar Alhossiny
Feb 14, 2017
Dawn Daniel
Apr 20, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to start your research paper [step-by-step guide]
1. Choose your topic
2. find information on your topic, 3. create a thesis statement, 4. create a research paper outline, 5. organize your notes, 6. write your introduction, 7. write your first draft of the body, 9. write your conclusion, 10. revise again, edit, and proofread, frequently asked questions about starting your research paper, related articles.
Research papers can be short or in-depth, but no matter what type of research paper, they all follow pretty much the same pattern and have the same structure .
A research paper is a paper that makes an argument about a topic based on research and analysis.
There will be some basic differences, but if you can write one type of research paper, you can write another. Below is a step-by-step guide to starting and completing your research paper.
Choose a topic that interests you. Writing your research paper will be so much more pleasant with a topic that you actually want to know more about. Your interest will show in the way you write and effort you put into the paper. Consider these issues when coming up with a topic:
- make sure your topic is not too broad
- narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general
Academic search engines are a great source to find background information on your topic. Your institution's library will most likely provide access to plenty of online research databases. Take a look at our guide on how to efficiently search online databases for academic research to learn how to gather all the information needed on your topic.
Tip: If you’re struggling with finding research, consider meeting with an academic librarian to help you come up with more balanced keywords.
If you’re struggling to find a topic for your thesis, take a look at our guide on how to come up with a thesis topic .
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing. It can be defined as a very brief statement of what the main point or central message of your paper is. Our thesis statement guide will help you write an excellent thesis statement.
In the next step, you need to create your research paper outline . The outline is the skeleton of your research paper. Simply start by writing down your thesis and the main ideas you wish to present. This will likely change as your research progresses; therefore, do not worry about being too specific in the early stages of writing your outline.
Then, fill out your outline with the following components:
- the main ideas that you want to cover in the paper
- the types of evidence that you will use to support your argument
- quotes from secondary sources that you may want to use
Organizing all the information you have gathered according to your outline will help you later on in the writing process. Analyze your notes, check for accuracy, verify the information, and make sure you understand all the information you have gathered in a way that you can communicate your findings effectively.
Start with the introduction. It will set the direction of your paper and help you a lot as you write. Waiting to write it at the end can leave you with a poorly written setup to an otherwise well-written paper.
The body of your paper argues, explains or describes your topic. Start with the first topic from your outline. Ideally, you have organized your notes in a way that you can work through your research paper outline and have all the notes ready.
After your first draft, take some time to check the paper for content errors. Rearrange ideas, make changes and check if the order of your paragraphs makes sense. At this point, it is helpful to re-read the research paper guidelines and make sure you have followed the format requirements. You can also use free grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .
Tip: Consider reading your paper from back to front when you undertake your initial revision. This will help you ensure that your argument and organization are sound.
Write your conclusion last and avoid including any new information that has not already been presented in the body of the paper. Your conclusion should wrap up your paper and show that your research question has been answered.
Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit, and proofread your paper.
Tip: Take a break from your paper before you start your final revisions. Then, you’ll be able to approach your paper with fresh eyes.
As part of your final revision, be sure to check that you’ve cited everything correctly and that you have a full bibliography. Use a reference manager like Paperpile to organize your research and to create accurate citations.
The first step to start writing a research paper is to choose a topic. Make sure your topic is not too broad; narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general.
The format of your research paper will vary depending on the journal you submit to. Make sure to check first which citation style does the journal follow, in order to format your paper accordingly. Check Getting started with your research paper outline to have an idea of what a research paper looks like.
The last step of your research paper should be proofreading. Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit and proofread your paper.
There are plenty of software you can use to write a research paper. We recommend our own citation software, Paperpile , as well as grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.25(3); 2014 Oct

How to Write a Scientific Paper: Practical Guidelines
Edgard delvin.
1 Centre de recherche, CHU Sainte-Justine
2 Département de Biochimie, Université de Montréal, Montréal, Canada
Tahir S. Pillay
3 Department of Chemical Pathology, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Pretoria
4 Division of Chemical Pathology, University of Cape Town
5 National Health Laboratory Service, CTshwane Academic Division, Pretoria, South Africa
Anthony Newman
6 Life Sciences Department, Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Precise, accurate and clear writing is essential for communicating in health sciences, as publication is an important component in the university criteria for academic promotion and in obtaining funding to support research. In spite of this, the development of writing skills is a subject infrequently included in the curricula of faculties of medicine and allied health sciences. Therefore clinical investigators require tools to fill this gap. The present paper presents a brief historical background to medical publication and practical guidelines for writing scientific papers for acceptance in good journals.
INTRODUCTION
A scientific paper is the formal lasting record of a research process. It is meant to document research protocols, methods, results and conclusions derived from an initial working hypothesis. The first medical accounts date back to antiquity. Imhotep, Pharaoh of the 3 rd Dynasty, could be considered the founder of ancient Egyptian medicine as he has been credited with being the original author of what is now known as the Edwin Smith Papyrus ( Figure 1 ). The Papyrus, by giving some details on cures and anatomical observations, sets the basis of the examination, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of numerous diseases. Closer to the Common Era, in 460 BCE, Hippocrates wrote 70 books on medicine. In 1020, the Golden age of the Muslim Culture, Ibn Sina, known as Avicenna ( Figure 2a ), recorded the Canon of medicine that was to become the most used medical text in Europe and Middle East for almost half a millennium. This was followed in the beginning of the 12 th Century bytheextensivetreatiseofMaimonides( Figure 2b ) (Moses ben Maimon) on Greek and Middle Eastern medicine. Of interest, by the end of the 11 th Century Trotula di Ruggiero, a woman physician, wrote several influential books on women’s ailment. A number of other hallmark treatises also became more accessible, thanks to the introduction of the printing press that allowed standardization of the texts. One example is the De Humani Corporis Fabrica by Vesalius which contains hundreds of illustrations of human dissection. Thomas A Lang provides an excellent concise history of scientific publications [ 1 ]. These were the days when writing and publishing scientific or philosophical works were the privilege of the few and hence there was no or little competition and no recorded peer reviewing system. Times have however changed, and contemporary scientists have to compose with an increasingly harsh competition in attracting editors and publishers attention. As an example, the number of reports and reviews on obesity and diabetes has increased from 400 to close to 4000/year and 50 to 600/year respectively over a period of 20 years ( Figure 3 ). The present article, essentially based on TA Lang’s guide for writing a scientific paper [ 1 ], will summarize the steps involved in the process of writing a scientific report and in increasing the likelihood of its acceptance.

The Edwin Smith Papyrus (≈3000 BCE)

Avicenna and Maimonides

Annual publication load in the field of obesity and diabetes over 20 years.
Reasons for publishing are varied. One may write to achieve a post-graduate degree, to obtain funding for pursuing research or for academic promotion. While all 3 reasons are perfectly legitimate, one must ask whether they are sufficient to be considered by editors, publishers and reviewers. Why then should the scientist write? The main reason is to provide to the scientific community data based on hypotheses that are innovative and thus to advance the understanding in a specific domain. One word of caution however, is that if a set of experiments has not been done or reported, it does not mean that it should be. It may simply reflect a lack of interest in it.
DECIDING ON PUBLISHING AND TARGETING THE JOURNAL
In order to assist with the decision process, pres-ent your work orally first to colleagues in your field who may be more experienced in publishing. This step will help you in gauging whether your work is publishable and in shaping the paper.
Targeting the journal, in which you want to present your data, is also a critical step and should be done before starting to write. One hint is to look for journals that have published similar work to yours, and that aims readers most likely to be interested in your research. This will allow your article to be well read and cited. These journals are also those that you are most likely to read on a regular basis and to cite abundantly. The next step is to decide whether you submit your manuscript to a top-ranking impact factor journal or to a journal of lower prestige. Although it is tempting to test the waters, or to obtain reviewers comments, be realistic about the contribution your work provides and submit to a journal with an appropriate rank.
Do not forget that each rejection delays publication and that the basin of reviewers within your specialty is shallow. Thus repeated submission to different journals could likely result in having your work submitted for review to the same re-viewer.
DECIDING ON THE TYPE OF MANUSCRIPT
There are several types of scientific reports: observational, experimental, methodological, theoretical and review. Observational studies include 1) single-case report, 2) collective case reports on a series of patients having for example common signs and symptoms or being followed-up with similar protocols, 3) cross-sectional, 4) cohort studies, and 5) case-control studies. The latter 3 could be perceived as epidemiological studies as they may help establishing the prevalence of a condition, and identify a defined population with and without a particular condition (disease, injury, surgical complication). Experimental reports deal with research that tests a research hypothesis through an established protocol, and, in the case of health sciences, formulate plausible explanations for changes in biological systems. Methodological reports address for example advances in analytical technology, statistical methods and diagnostic approach. Theoretical reports suggest new working hypotheses and principles that have to be supported or disproved through experimental protocols. The review category can be sub-classified as narrative, systematic and meta-analytic. Narrative reviews are often broad overviews that could be biased as they are based on the personal experience of an expert relying on articles of his or her own choice. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses are based on reproducible procedures and on high quality data. Researchers systematically identify and analyze all data collected in articles that test the same working hypothesis, avoiding selection bias, and report the data in a systematic fashion. They are particularly helpful in asking important questions in the field of healthcare and are often the initial step for innovative research. Rules or guidelines in writing such report must be followed if a quality systematic review is to be published.
For clinical research trials and systematic reviews or meta-analyses, use the Consort Statement (Consolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials) and the PRISMA Statement (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) respectively [ 2 , 3 ]. This assures the editors and the reviewers that essential elements of the trials and of the reviews were tackled. It also speeds the peer review process. There are several other Statements that apply to epidemiological studies [ 4 ], non-randomized clinical trials [ 5 ], diagnostic test development ( 6 ) and genetic association studies ( 7 ). The Consortium of Laboratory Medicine Journal Editors has also published guidelines for reporting industry-sponsored laboratory research ( 8 ).
INITIAL STEPS IN THE PROCESS OF WRITING A SCIENTIFIC DOCUMENT
Literature review is the initial and essential step before starting your study and writing the scientific report based on it. In this process use multiple databases, multiple keyword combinations. It will allow you to track the latest development in your field and thus avoid you to find out that someone else has performed the study before you, and hence decrease the originality of your study. Do not forget that high-ranking research journals publish results of enough importance and interest to merit their publication.
Determining the authorship and the order of authorship, an ethical issue, is the second essential step, and is unfortunately often neglected. This step may avoid later conflicts as, despite existing guidelines, it remains a sensitive issue owing to personal biases and the internal politics of institutions. The International Committee of Medical Editors has adopted the following guidelines for the biomedical sciences ( 9 ).
“Authorship credit should be based only on: 1) Substantial contributions to the conception and design, or acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; 2) Drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; and 3) Final approval of the version to be published. Conditions 1, 2 and 3 must be all met. Acquisition of funding, the collections of data, or general supervision of the research group, by themselves, do not justify authorship.” ( 9 , 10 )
The order of authorship should reflect the individual contribution to the research and to the publication, from most to least ( 11 ). The first author usually carries out the lead for the project reported. However the last author is often mistakenly perceived as the senior author. This is perpetuated from the European tradition and is discouraged. As there are divergent conventions among journals, the order of authorship order may or may not reflect the individual contributions; with the exception that the first author should be the one most responsible for the work.
WRITING EFFECTIVELY
Effective writing requires that the text helps the readers 1) understand the content and the context, 2) remember what the salient points are, 3) find the information rapidly and, 4) use or apply the information given. These cardinal qualities should be adorned with the precise usage of the language, clarity of the text, inclu-siveness of the information, and conciseness. Effective writing also means that you have to focus on the potential readers’ needs. Readers in science are informed individuals who are not passive, and who will formulate their own opinion of your writing whether or not the meaning is clear. Therefore you need to know who your audience is. The following 4 questions should help you writing a reader-based text, meaning written to meet the information needs of readers [ 12 ].
What do you assume your readers already know? In other words, which terms and concepts can you use without explanation, and which do you have to define?
What do they want to know? Readers in science will read only if they think they will learn something of value.
What do they need to know? Your text must contain all the information necessary for the reader to understand it, even if you think this information id obvious to them.
What do they think they know that is not so? Correcting misconceptions can be an important function of communication, and persuading readers to change their minds can be a challenging task.
WRITING THE SCIENTIFIC PAPER
Babbs and Tacker ’ s advice to write as much of the paper before performing the research project or experimental protocol may, at first sight, seem unexpected and counterintuitive [ 13 ], but in fact it is exactly what is being done when writing a research grant application. It will allow you to define the authorship alluded to before. The following section will briefly review the structure of the different sections of a manuscript and describe their purpose.
Reading the instructions to authors of the Journal you have decided to submit your manuscript is the first important step. They provide you with the specific requirements such as the way of listing the authors, type of abstract, word, figure or table limits and citation style. The Mulford Library of University of Toledo website contains instructions to authors for over 3000 journals ( http://mulford.meduoiho.edu/instr/ ).
The general organization of an article follows the IMRAD format (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion). These may however vary. For instance, in clinical research or epidemiology studies, the methods section will include details on the subjects included, and there will be a statement of the limitation of the study. Although conclusions may not always be part of the structure, we believe that it should, even in methodological reports.
The tile page provides essential information so that the editor, reviewers, and readers will identify the manuscript and the authors at a glance as well as enabling them to classify the field to which the article pertains.
The title page must contain the following:
- The tile of the article – it is an important part of the manuscript as it is the most often read and will induce the interested readers to pursue further. Therefore the title should be precise, accurate, specific and truthful;
- Each author’s given name (it may be the full name or initials) and family name;
- Each author’s affiliation;
- Some journals ask for highest academic degree;
- A running title that is usually limited to a number of characters. It must relate to the full title;
- Key words that will serve for indexing;
- For clinical studies, the trial’s registration number;
- The name of the corresponding author with full contact information.
The abstract is also an important section of your manuscript. Importantly, the abstract is the part of the article that your peers will see when consulting publication databases such as PubMed. It is the advertisement to your work and will strongly influence the editor deciding whether it will be submitted to reviewers or not. It will also help the readers decide to read the full article. Hence it has to be comprehensible on its own. Writing an abstract is challenging. You have to carefully select the content and, while being concise, assure to deliver the essence of your manuscript.
Without going into details, there are 3 types of abstracts: descriptive, informative and structured. The descriptive abstract is particularly used for theoretical, methodological or review articles. It usually consists of a single paragraph of 150 words or less. The informative abstract, the most common one, contains specific information given in the article and, are organized with an introduction (background, objectives), methods, results and discussion with or without conclusion. They usually are 150 to 250 words in length. The structured abstract is in essence an informative abstract with sections labeled with headings. They may also be longer and are limited to 250 to 300 words. Recent technology also allows for graphical or even video abstracts. The latter are interesting in the context of cell biology as they enable the investigator to illustrate ex vivo experiment results (phagocytosis process for example).
Qualities of abstracts:
- Understood without reading the full paper. Shoul dcontain no abbreviations.lf abbreviations are used, they must be defined. This however removes space for more important information;
- Contains information consistent with the full report. Conclusions in the abstract must match those given in the full report;
- Is attractive and contains information needed to decide whether to read the full report.
Introduction
The introduction has 3 main goals: to establish the need and importance of your research, to indicate how you have filled the knowledge gap in your field and to give your readers a hint of what they will learn when reading your paper. To fulfil these goals, a four-part introduction consisting of a background statement, a problem statement, an activity statement and a forecasting statement, is best suited. Poorly defined background information and problem setting are the 2 most common weaknesses encountered in introductions. They stem from the false perception that peer readers know what the issue is and why the study to solve it is necessary. Although not a strict rule, the introduction in clinical science journals should target only references needed to establish the rationale for the study and the research protocol. This differ from more basic science or cell biology journals, for which a longer and elaborate introduction may be justified because the research at hand consists of several approaches each requiring background and justification.
The 4-part introduction consists of:
- A background statement that provides the context and the approach of the research;
- A problem statement that describes the nature, scope and importance of the problem or the knowledge gap;
- An activity statement, that details the research question, sets the hypothesis and actions undertaken for the investigation;
- A forecasting statement telling the readers whattheywillfìndwhen readingyourarticle [ 14 ].
Methods section
This section may be named “Materials and Methods”, “Experimental section” or “Patients and Methods” depending upon the type of journal. Its purpose to allow your readers to provide enough information on the methods used for your research and to judge on their adequacy. Although clinical and “basic” research protocols differ, the principles involved in describing the methods share similar features. Hence, the breadth of what is being studied and how the study can be performed is common to both. What differ are the specific settings. For example, when a study is conducted on humans, you must provide, up front, assurance that it has received the approval of you Institution Ethics Review Board (IRB) and that participants have provided full and informed consent. Similarly when the study involves animals, you must affirm that you have the agreement from your Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). These are too often forgotten, and Journals (most of them) abiding to the rules of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) and World Association of Medical Editors (WAME) will require such statement. Although journals publishing research reports in more fundamental science may not require such assurance, they do however also follow to strict ethics rules related to scientific misconduct or fraud such as data fabrication, data falsification. For clinical research papers, you have to provide information on how the participants were selected, identify the possible sources of bias and confounding factors and how they were diminished.
In terms of the measurements, you have to clearly identify the materials used as well as the suppliers with their location. You should also be unambiguous when describing the analytical method. If the method has already been published, give a brief account and refer to the original publication (not a review in which the method is mentioned without a description). If you have modified it, you have to provide a detailed account of the modifications and you have to validate its accuracy, precision and repeatability. Mention the units in which results are reported and, if necessary, include the conversion factors [mass units versus “système international” (S.I.)]. In clinical research, surrogate end-points are often used as biomarkers. Under those circumstances, you must show their validity or refer to a study that has already shown that are valid.
In cases of clinical trials, the Methods section should include the study design, the patient selection mode, interventions, type of outcomes.
Statistics are important in assuring the quality of the research project. Hence, you should consult a biostatistician at the time of devising the research protocol and not after having performed the experiments or the clinical trial.
The components of the section on statistics should include:
- The way the data will be reported (mean, median, centiles for continuous data);
- Details on participant assignments to the different groups (random allocation, consecutive entry);
- Statistical comparison tools (parametric or non parametric statistics, paired or unpaired t-tests for normally distributed data and so on);
- The statistical power calculation when determining the sample size to obtain valid and significant comparisons together with the a level;
- The statistical software package used in the analysis.
Results section
The main purpose of the results section is to report the data that were collected and their relationship. It should also provide information on the modifications that have taken place because of unforeseen events leading to a modification of the initial protocol (loss of participants, reagent substitution, loss of data).
- Report results as tables and figures whenever possible, avoid duplication in the text. The text should summarize the findings;
- Report the data with the appropriate descriptive statistics;
- Report any unanticipated events that could affect the results;
- Report a complete account of observations and explanations for missing data (patient lost).
The discussion should set your research in context, reinforce its importance and show how your results have contributed to the further understanding of the problem posed. This should appear in the concluding remarks. The following organization could be helpful.
- Briefly summarize the main results of your study in one or two paragraphs, and how they support your working hypothesis;
- Provide an interpretation of your results and show how they logically fit in an overall scheme (biological or clinical);
- Describe how your results compare with those of other investigators, explain the differences observed;
- Discuss how your results may lead to a new hypothesis and further experimentation, or how they could enhance the diagnostic procedures.
- Provide the limitations of your study and steps taken to reduce them. This could be placed in the concluding remarks.
Acknowledgements
The acknowledgements are important as they identify and thank the contributors to the study, who do not meet the criteria as co-authors. They also include the recognition of the granting agency. In this case the grant award number and source is usually included.
Declaration of competing interests
Competing interests arise when the author has more than one role that may lead to a situation where there is a conflict of interest. This is observed when the investigator has a simultaneous industrial consulting and academic position. In that case the results may not be agreeable to the industrial sponsor, who may impose a veto on publication or strongly suggest modifications to the conclusions. The investigator must clear this issue before starting the contracted research. In addition, the investigator may own shares or stock in the company whose product forms the basis of the study. Such conflicts of interest must be declared so that they are apparent to the readers.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Thomas A Lang, for his advice in the preparation of this manuscript.

Introduction
Subjects and methods, acknowledgment, how to write a research paper.
- Split-Screen
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
- Peer Review
- Open the PDF for in another window
- Get Permissions
- Cite Icon Cite
- Search Site
Andrei V. Alexandrov; How to Write a Research Paper. Cerebrovasc Dis 1 August 2004; 18 (2): 135–138. https://doi.org/10.1159/000079266
Download citation file:
- Ris (Zotero)
- Reference Manager
Background: Busy strokologists often find little time for scientific writing. They sometimes develop a mental condition equivalent to that known by neurologists as writer’s cramp. It may result in permanent damage to academic career. This paper provides advice how to prevent or treat this condition. Methods: Prepare your manuscript following the IMRaD principle (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion), with every part supporting the key message. When writing, be concise. Clearly state your methods here, while data belong to Results. Successful submissions combine quality new data or new thinking with lucid presentation. Results: Provide data that answer the research question. Describe here most important numeric data and statistics, keeping in mind that the shorter you can present them, the better. The scientific community screens abstracts to decide which full text papers to read. Make your point with data, not arguments. Conclusions: Conclusions have to be based on the present study findings. The time of lengthy and unfounded speculations is over. A simple message in a clearly written manuscript will get noticed and may advance our understanding of stroke.
By now you probably wrote an abstract and submitted it to a stroke conference. Your mentor reminds you several times to start drafting a paper, and you have no idea where to start. As a simple trick, copy and paste your abstract so that Background becomes your introduction. For the rest, follow the IMRaD principle: Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion [ 1, 2, 3 ]. Think what ‘take home message’ you’d like to deliver and to whom. The title sells the paper.
‘Busy strokologists often find little time ... to treat this condition’: this introduction concisely describes the study hypothesis, rationale, purpose, and objectives. A three-paragraph introduction is plenty for most topics. Expand with facts from papers previously published by others, among whom you may occasionally find your mentor. Do a thorough literature search for earlier sources dealing with your subject [ 4, 5, 6 ]. Tell here what is known in the field. You do not need to refer to every paper ever written on this topic. Select key references and remember that for publishing purposes, less is better than more. Consult your mentor as often as possible – he is the senior author after all.
The third paragraph should state the research question [ 7 ]. You may take an original paper already published in Cerebrovascular Diseases to use as a template. Formulate the research question clearly since data presentation should provide equally clear answers.
The first author drafts the manuscript and determines co-authors [ 8 ]. Although general guidelines are available [ 8 ], the reality often demands seeking advice from your mentor. Inappropriate inclusion of authors will decrease the likelihood of manuscript acceptance.
Describe subject selection criteria and data collection tools. Make this description detailed enough so that if someone wants to repeat the study, it will be possible. If new imaging technology was used, tell how and by whom these tests were validated. Avoid presenting actual data in this section: ‘Study subjects were recruited from 1,215 patients admitted to our stroke unit from August 1999 through August 2002’. Instead say: ‘Study subjects were recruited from consecutive patients admitted to our stroke unit. Inclusion criteria were ...’. Methods may disclose power calculations, estimated sample size, and stopping rules.
Provide additional evidence that would increase confidence in the reliability of your methods. Control for biases, validation of research tools, ‘blinding’ of observers – all of these facts, if established before the study initiation, will strengthen the manuscript. Describe in detail the outcome models or dependent variables. For clinical outcomes or surrogate markers, reference a pivotal trial or study that established their relevance.
Documentation of protection of research subjects is essential. Clearly state if a local ethics committee approved your study. This ensures patients or animal rights protection, particularly if experiments were performed. The author also needs to disclose funding sources and potential for commercial bias such as connections with the pharmaceutical industry. Data safety monitoring, independent data acquisition and analysis during clinical trials and appropriate overseeing committees should be mentioned if applicable.
Major scientific journals currently accept less than 25% of submitted manuscripts. If rejected, it does not necessarily mean your manuscript is poor. Rejection means that reviewers did not give it a high enough priority. You should not be too disappointed because, after all, you got very good advice how to improve your manuscript. Follow reviewers’ suggestions and you increase the likelihood that another esteemed journal will accept it. The most important factors for publication are the quality, novelty, reliability and scientific or clinical importance of your work. A manuscript should disclose new information or a new way of thinking about old information. If not, it will not be published – regardless of how well it is written. Avoid redundant or duplicate publications since these should not be published. Scientific publishing is extremely competitive, and chances are that by the time you conceived the project, 10 other groups were already doing it and 5 others have already published it. Stay on top of current literature and know the limitations of research done by others.
The last paragraph of this section should describe tools of statistical analysis appropriate to study design. Consult a statistician before embarking on a project, work with a statistician to analyze and interpret the data, and have a statistician reviewing the whole manuscript for clarity of statistical analysis and data presentation.
Your results are the most important part of the manuscript. Present them clearly by avoiding long and confusing sentences. The shorter you can present your data in tables and figures, the better. Remain focused and disciplined. The flurry of numbers and ‘p’ values should follow simple logics. Start by describing your study subjects, use actual numbers for study demographics. Avoid opening sentences like: ‘Table 1 summarizes our findings in sub-group C’. This makes reviewers frustrated since they have to flip back and forth through pages to understand what was done to study subjects.
Make data presentation so clear and simple that a tired person riding late on an airplane can take your manuscript and get the message at first reading. Very few people can write a perfect manuscript on the first draft. Return to the draft, read it, change cumbersome parts, read other papers and change the draft again, and again, and again. I still do it before I give the manuscript to my co-authors. But do not hold it for too long. Remember, ‘10 other groups ...’.
Present results to colleagues since they would likely ask for more data or analyses. Most likely the reviewers of any esteemed journal would do the same, so include data in the first draft of your manuscript. The internal review is helpful to determine sufficient data to answer the research question.
Most importantly, provide data relevant to the research question. Observations beyond the primary research question can be included in the manuscript, if they strengthen your case. Remember to stay in focus. If you get lost from the aim of the study, so will be reviewers. Prestigious journals have a strict word limit for papers they accept. You need all this space to deliver the key message, so do not mess around but concentrate on the essential. Packing manuscript with data is better than splitting the paper into separate small ones.
Mention a statistical test that generated specific ‘p’ values or coefficients. Show absolute numbers as well as percentages so that reviewers can judge the significance of your observations. Remember that statistical difference does not necessarily translate into clinical significance.
Make your point with data, not arguments.
This section should start with: ‘Our study showed ...’ to lucidly summarize your study findings. Discussion is often the weakest part of the manuscript. Do not repeat the introduction. Do not present any new data that were not shown in the results section and avoid repeating data presentation. There is no reason to underline how terrific your results are – let them speak for themselves.
The second paragraph may describe the novelty of your findings or if they parallel previous research. Remember, only the beginners try to refer to all published papers in the field. No esteemed journal can afford the space needed for this. A skillful selection of the most pertinent references demonstrates a command of the relevant literature. Confirmatory research makes passing the review process more difficult. Arbitrarily, the ratio of abstracts to original papers in curriculum vitae should be less than 3 to 1. If there are too many abstracts, you either have writer’s cramp or the quality of your research is insufficient for publication.
The third paragraph may describe how your study contradicts previous research or established dogmas. If there was disagreement about study interpretation by co-authors, mention different conclusions drawn from your results or other studies [ 9, 10 ]. Avoid general statements that are not founded in data. Do not provide your opinion how to solve a problem that was not directly evaluated in your study. Do not write a review of all possible mechanisms that you have not accounted for in your study. You can write a short but to-the-point Discussion.
The fourth paragraph should describe study limitations. If you do not discuss study weaknesses, the reviewers will. Study limitations may be contrasted with study strengths. This part may also mention unresolved questions and direction of future research.
The concluding paragraph can summarize the potential significance of your findings and what changes to research or clinical practice your data may support. This is a critical part since it is easy to overestimate the significance of your research. Avoid broad claims and strong statements. Remember that even pioneer break-through studies require independent confirmation. Publication in a peer-reviewed journal means completion of your project and dissemination of research results [ 11, 12 ].
Clinicians need to develop skills in scientific writing. If you make a significant observation, a proper and fast scientific communication is required [ 12 ]. Improving your scientific writing is a life-long process. If and when your papers are rejected, remember that most manuscripts face the same fate. Avoid choosing an inappropriate journal for your manuscript submission. Common reasons for rejection include inappropriate or incomplete statistics; over-interpretation of results; inappropriate or sub-optimal instrumentation; a sample too small or biased; difficult-to-follow writing; insufficient problem statement; inaccuracy or inconsistency of the data reported; incomplete, inaccurate, or outdated review of the literature; insufficient data presented, and defective tables or figures [ 13, 14, 15 ]. When reading criticism, learn from your mistakes or the advice given to you. While wrestling with reviewers, you will become a better scientific writer but also a better, more critical scientist. In the long run this will make a major difference to your academic career, and probably will also improve your patient care. Most likely, your way of writing will become more evidence based.
An anonymous and probably frustrated academician once said: ‘Publish or perish!’. This brutally honest statement should motivate you to learn yet another set of useful skills. Good luck!
The author is not a native English speaker. I am indebted to John Norris, MD, FRCP, for – among many things during fellowship training – his patience with my ‘a’s and ‘the’s, and the first lessons in study design, analysis, and presentation. The infamous ‘Norris Rules’ that he taught his fellows are partly reflected in this paper.
Email alerts
Citing articles via, related articles.
- Online ISSN 1421-9786
- Print ISSN 1015-9770
INFORMATION
- Contact & Support
- Information & Downloads
- Rights & Permissions
- Terms & Conditions
- Catalogue & Pricing
- Policies & Information
- People & Organization
- Stay Up-to-Date
- Regional Offices
- Community Voice
SERVICES FOR
- Researchers
- Healthcare Professionals
- Patients & Supporters
- Health Sciences Industry
- Medical Societies
- Agents & Booksellers
Karger International
- S. Karger AG
- P.O Box, CH-4009 Basel (Switzerland)
- Allschwilerstrasse 10, CH-4055 Basel
- Tel: +41 61 306 11 11
- Fax: +41 61 306 12 34
- Contact: Front Office
- Experience Blog
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
- Page Content
- Sidebar Content
- Main Navigation
- Quick links
- All TIP Sheets
- Choosing and Using a Dictionary
- How to Use a Thesaurus
How to Start (and Complete) a Research Paper
- Using the Butte College Library
- Evaluating Websites
TIP Sheet HOW TO START (AND COMPLETE) A RESEARCH PAPER
You are a re-entry student and it's been fourteen years since you've written a paper. You coasted through high school on your charm and good looks and never actually wrote a research paper. You have written research papers, but every time is like the first time, and the first time was like a root canal. How do you start? Here is a step-by-step approach to starting and completing a research paper.
- Choose a topic.
- Read and keep records.
- Form a thesis.
- Create a mind map or outline.
- Read again.
- Rethink your thesis.
- Draft the body.
- Add the beginning and end.
- Proofread and edit.
You may read this TIP Sheet from start to finish before you begin your paper, or skip to the steps that are causing you the most grief.
1. Choosing a topic: Interest, information, and focus Your job will be more pleasant, and you will be more apt to retain information if you choose a topic that holds your interest. Even if a general topic is assigned ("Write about impacts of GMO crops on world food supply"), as much as possible find an approach that suits your interests. Your topic should be one on which you can find adequate information; you might need to do some preliminary research to determine this. Go to the Reader's Guide to Periodical Literature in the reference section of the library, or to an electronic database such as Proquest or Wilson Web, and search for your topic. The Butte College Library Reference Librarians are more than happy to assist you at this (or any) stage of your research. Scan the results to see how much information has been published. Then, narrow your topic to manageable size:
Once you have decided on a topic and determined that enough information is available, you are ready to proceed. At this point, however, if you are having difficulty finding adequate quality information, stop wasting your time; find another topic.
2. Preliminary reading & recordkeeping Gather some index cards or a small notebook and keep them with you as you read. First read a general article on your topic, for example from an encyclopedia. On an index card or in the notebook, record the author, article and/or book title, and all publication information in the correct format (MLA or APA, for example) specified by your instructor. (If you need to know what publication information is needed for the various types of sources, see a writing guide such as S F Writer .) On the index cards or in your notebook, write down information you want to use from each identified source, including page numbers. Use quotation marks on anything you copy exactly, so you can distinguish later between exact quotes and paraphrasing. (You will still attribute information you have quoted or paraphrased.)
Some students use a particular index card method throughout the process of researching and writing that allows them great flexibility in organizing and re-organizing as well as in keeping track of sources; others color-code or otherwise identify groups of facts. Use any method that works for you in later drafting your paper, but always start with good recordkeeping.
3. Organizing: Mind map or outline Based on your preliminary reading, draw up a working mind map or outline. Include any important, interesting, or provocative points, including your own ideas about the topic. A mind map is less linear and may even include questions you want to find answers to. Use the method that works best for you. The object is simply to group ideas in logically related groups. You may revise this mind map or outline at any time; it is much easier to reorganize a paper by crossing out or adding sections to a mind map or outline than it is to laboriously start over with the writing itself.
4. Formulating a thesis: Focus and craftsmanship Write a well defined, focused, three- to five-point thesis statement, but be prepared to revise it later if necessary. Take your time crafting this statement into one or two sentences, for it will control the direction and development of your entire paper.
For more on developing thesis statements, see the TIP Sheets "Developing a Thesis and Supporting Arguments" and "How to Structure an Essay."
5. Researching: Facts and examples Now begin your heavy-duty research. Try the internet, electronic databases, reference books, newspaper articles, and books for a balance of sources. For each source, write down on an index card (or on a separate page of your notebook) the publication information you will need for your works cited (MLA) or bibliography (APA) page. Write important points, details, and examples, always distinguishing between direct quotes and paraphrasing. As you read, remember that an expert opinion is more valid than a general opinion, and for some topics (in science and history, for example), more recent research may be more valuable than older research. Avoid relying too heavily on internet sources, which vary widely in quality and authority and sometimes even disappear before you can complete your paper.
Never copy-and-paste from internet sources directly into any actual draft of your paper. For more information on plagiarism, obtain from the Butte College Student Services office a copy of the college's policy on plagiarism, or attend the Critical Skills Plagiarism Workshop given each semester.
6. Rethinking: Matching mind map and thesis After you have read deeply and gathered plenty of information, expand or revise your working mind map or outline by adding information, explanations, and examples. Aim for balance in developing each of your main points (they should be spelled out in your thesis statement). Return to the library for additional information if it is needed to evenly develop these points, or revise your thesis statement to better reflect what you have learned or the direction your paper seems to have taken.
7. Drafting: Beginning in the middle Write the body of the paper, starting with the thesis statement and omitting for now the introduction (unless you already know exactly how to begin, but few writers do). Use supporting detail to logically and systematically validate your thesis statement. For now, omit the conclusion also.
For more on systematically developing a thesis statement, see TIP sheets "Developing a Thesis and Supporting Arguments" and "How to Structure an Essay."
8. Revising: Organization and attribution Read, revise, and make sure that your ideas are clearly organized and that they support your thesis statement. Every single paragraph should have a single topic that is derived from the thesis statement. If any paragraph does not, take it out, or revise your thesis if you think it is warranted. Check that you have quoted and paraphrased accurately, and that you have acknowledged your sources even for your paraphrasing. Every single idea that did not come to you as a personal epiphany or as a result of your own methodical reasoning should be attributed to its owner.
For more on writing papers that stay on-topic, see the TIP Sheets "Developing a Thesis and Supporting Arguments" and "How to Structure an Essay." For more on avoiding plagiarism, see the Butte College Student Services brochure, "Academic Honesty at Butte College," or attend the Critical Skills Plagiarism Workshop given each semester.
9. Writing: Intro, conclusion, and citations Write the final draft. Add a one-paragraph introduction and a one-paragraph conclusion. Usually the thesis statement appears as the last sentence or two of the first, introductory paragraph. Make sure all citations appear in the correct format for the style (MLA, APA) you are using. The conclusion should not simply restate your thesis, but should refer to it. (For more on writing conclusions, see the TIP Sheet "How to Structure an Essay.") Add a Works Cited (for MLA) or Bibliography (for APA) page.
10. Proofreading: Time and objectivity Time permitting, allow a few days to elapse between the time you finish writing your last draft and the time you begin to make final corrections. This "time out" will make you more perceptive, more objective, and more critical. On your final read, check for grammar, punctuation, correct word choice, adequate and smooth transitions, sentence structure, and sentence variety. For further proofreading strategies, see the TIP Sheet "Revising, Editing, and Proofreading."
Home | Calendars | Library | Bookstore | Directory | Apply Now | Search for Classes | Register | Online Classes | MyBC Portal MyBC -->
Butte College | 3536 Butte Campus Drive, Oroville CA 95965 | General Information (530) 895-2511
Researching a Disorder
- More Information |
When a disorder is first diagnosed, the doctor or other health care professional often gives a handout that summarizes key points of information. (See also Introduction to Making the Most of Health Care .)
If people want to learn more about their disorder, many other sources of information are available. In the United States, people typically turn to the internet, either searching on a term in a search engine (such as Google), or asking their contacts on social media. However, although the internet provides a huge volume of information, the accuracy of that information varies widely. It can be hard to judge the credibility of online sources. Other ways of finding information include asking doctors, nurses, or other practitioners to tell them about the disorder or to recommend reliable sources of information. Some local, university, or hospital libraries have useful resources, including a research librarian.
Generally, governmental medical sources are authoritative and reliable. On the internet, reliable resources that provide a large amount of useful and accurate information to the public include the
National Institutes of Health ( NIH )
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality ( AHRQ )
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC )
These sites also provide links to other helpful and reliable sites. Some major and regional health systems also maintain reliable, online disease and treatment resources for patients and physicians. Many disease-specific, patient-oriented sites (such as the National Multiple Sclerosis Society or the Alzheimer's Association) provide information for people with a particular disorder. In contrast, sites designed to sell specific products or a specific service may be less reliable. Their information may be biased or inaccurate.
Support groups may provide helpful information, as well as psychologic support. Such groups can be found through local newspapers, hospitals, offices of doctors or other health care practitioners, and the internet. Most cities in the United States have support groups, sometimes for specific disorders. For example, Gilda’s Club, which is located in several cities, offers support for people living with cancer. Other people who have the same disorder or who care for someone with the same disorder may have many practical and useful suggestions for day-to-day living, such as where to find pieces of specialized equipment, what equipment works best, and how to interact with or care for someone with a disorder.
Another resource is chat rooms on the internet. Such sites enable people to communicate with one another about specific disorders and to share possible resources; however, on these sites in particular, the scientific validity of the information should not be assumed. One person's individual illness experience or suggestions may not be appropriate for another person with the same disorder.
More Information
The following English-language resources may be useful. Please note that THE MANUALS is not responsible for the content of any but the last resource.
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ): This organization produces evidence to improve the quality of health care by making it safer, as well as more accessible, equitable, and affordable.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC is part of the US Department of Health and Human Services and provides science-based, data-driven, health information.
National Institutes of Health (NIH): This site provides access to health information, updates on clinical research trials, and science education resources for students and educators.
STANDS—Commentary : This commentary succinctly explains what health care consumers should look for when scouring the internet for reliable health information.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.

Epidemiology Research Essay: A Guide with Steps, Insights, & Tips

As a nursing student, one of the best pieces of advice you will get is to learn how to write an epidemiology essay. Although not so challenging, an epidemiology class can easily fall within challenging nursing school classes . We are here to change that narrative. Epidemiology is the scientific study of the distribution and determinants of disease and health-related events in a specific population. While these essays or research papers seem challenging at first, you will be on your way to getting a top grade on your paper once you get the hang of it. The following guide will exhaustively explore all the steps you need to write a high-quality paper.
Steps for Writing an Epidemiology Essay
In nursing or med school, you will be assigned to write an essay about a specific disease either of your choice or one that your professor or instructor specifies. Instead of panicking, we’ve compiled this step-by-step guide to writing an epidemiology research essay to help you write a paper that meets the rubric requirements. Our epidemiology essay writers find the entire process thrilling and rewarding, albeit tiresome. Having gone through the process endless times, we have mastered all it takes to write a perfect epidemiology research essay, and here are the steps:
1. Pick a Topic (Disease)
Sometimes professors will ask students to choose a topic for their epidemiology paper. While this is exciting, it can become challenging because there are tons of epidemiology topics available, and you may need help to pick the right one. To make things easier, you must be clear about the topic.
First, you need to understand what epidemiology entails. Consider any topic that covers health risks for people due to genetics and environmental conditions. Make sure you pick an interesting topic that can lead to powerful results.
Related Reading:
- Steps for Choosing the best nursing dissertation topic .
- Hot research topics on nursing to consider for your next paper.
2. Conduct the Research
You must have all the suitable material to write a compelling epidemiology essay. If your instructor still needs to give you materials for your research, start by doing the work yourself. The best places to start include organizations such as the CDC , WHO , PubMed , NIH , NHS , etc. You need to gather as much information as possible so that all the information flows well when you start writing.
3. Come Up with an Outline for Your Essay
To write a well-structured essay, you need to have a relevant outline. An outline will help organize your thoughts, which helps in creating a well-balanced paper. An example of an outline for an epidemiology essay would be like this:
Introduction
- Disease Description
- Social Determinants of Health
- Epidemiologic Triangle
- Community Health Nurse
- National Agency or Organization Helping Out
- Global Implication
Related Reading: Get over the embarrassment when you repeat a class .
This section introduces your topic, background data, and research details. If you are writing a paper about a disease like HIV/AIDS, share how it has affected people worldwide and briefly state how it is spread. Then show the aim of your essay. For instance, you can say: “ The following paper will provide a compelling overview of what HIV/AIDS is, including the social determinants leading to its progression.
Simultaneously, the essay will provide the epidemiological triangle showing how the disease is spread, the actions taken by the community health nurse, and the contribution made by the different government agencies…etc.â€
Describe the Chosen Disease
Now that you have decided which disease to write about, it is time to describe it. The definition of the disease should be as straightforward as possible. Also, please provide what you think are the possible causes, common symptoms, how it is transmitted, complications, and treatment.
Moreover, include a demographic of interest (incidence, prevalence, morbidity, and mortality). Incidence refers to the measure of disease that makes it possible to determine the probability of a person being diagnosed with a particular disease in a given period. For instance, if five women are diagnosed with HIV from a group of 200 women (HIV-free) for a year, then the incidence of HIV will be 0.025.
Prevalence is the measure of a disease that makes it easy to determine a person's likelihood of getting a disease. In other words, prevalence is the total number of disease cases in a given population.
Morbidity is simply another name for a disease. A patient can have several morbidities. These can range from heart disease to cancer and so much more. Mortality is also referred to as death. The mortality rate is the number of deaths caused by a disease.
Still, in this section, say whether the disease is reportable. If it is, provide details such as when it is reported and to whom.
Write Down the Social Determinants of the Disease
Social determinants are non-medical causes that influence the outcome of a disease. These conditions influence health outcomes, including stigma, poverty, lack of education, access to quality healthcare, etc. As you list them, show how they lead to the development of a disease.
This section is crucial, as it will help understand where the disease is coming from and those likely to be impacted. For instance, if you are writing about infectious diseases like HIV/AIDS, you can say that poor people or those with proper education are the most likely to get the disease. Some can be lured to engage in sexual activities with promises of money, food, and shelter.
Discuss the Epidemiology Triangle Related to the Disease
As an epidemiologist, it is imperative to understand the process by which a disease spreads is essential. They use a tool to help them understand how this process occurs. This tool is referred to as an epidemiology triangle . In other words, an epidemiology triangle is a simple tool for explaining the organisms that cause disease and the conditions that allow this to happen.
You should be aware that diseases such as HIV/AIDS spread from one person to another. An epidemiology triangle can guide people to understand how disease spreads from one person in a given situation.
This triangle consists of the following:
- Causative Agent
- Environment
In the same example of HIV/AIDS, the causal agent is HIV. The host is the organism carrying the virus and transmitting it to another person. The environment is the social and economic factors that influence the rate at which the disease spreads.
You should also note whether any considerations are given to schools, communities, or the public. If so, please list them down. Also, mention if these regions are responsible for the spread of the disease through inappropriate behavior or practices. Show how all these people can benefit from measures that will keep them safe. These measures could be things like education, posters, and pamphlets.
Discuss the Role of Community Health Nurses
A community health nurse is responsible for encouraging healthy living, preventing diseases, and providing medical treatment. Research their role in case finding, reporting, data collection, data analysis, and follow-ups, and include them in your essay.
Additionally, say why the demographic data is essential. Demographic data encompasses all aspects of a population. This data helps in providing greater accountability and treatment measures. When done correctly, this data can help treat people of different ethnic backgrounds, gender, and age difference. These people can be treated with the correct data by considering specific demographic factors.
Point Out the Organization that Organization Helping Out
If an organization (s) addresses the disease you are discussing, please mention it. Also, mention the measures they have in place to resolve or combat the impact of the disease.
For instance, say how governments are actively involved in helping to find solutions to a particular disease. Include measures put in place by governments to support these organizations and society in general. You can list government-funded institutions that conduct studies to solve health problems.
What are the Global Implications?
List down the implications for the disease in question. What is the mortality rate? Have there been any economic damages or social or psychological impacts? How do different countries address these impacts? Has it affected different cultures? Is the particular disease endemic? All these questions are essential and must be addressed in the paper. For instance, if you are writing epidemiology of HIV, you can say the implications are;
HIV affects people in every country, thus resulting in governments and healthcare institutions prioritizing it. Researchers in every country have been engaged internationally to study and find ideas to help manage the disease.
In this section, write down the summary of your paper. Say what the epidemiology has discovered about the disease in question. Also, add what government agencies and international communities should do to solve the health problem.
Remember that this is a concluding paragraph and should be a summary of what you have written. Refrain from introducing any new points or ideas.
This section provides detailed information about all the materials you used in your epidemiology paper. Write this section in a separate paper and ensure you follow the same formatting style.
Related Reads:
- Overcoming burnout in nursing/med school.
- Challenges in nursing school and their respective solutions.
How to Format Your Epidemiology Paper
When writing your epidemiology essay, your paper should have the following sections: title page, introduction, body, conclusion, and references when writing in APA format
- Title of 10-12 words reflecting the content of your essay, formatted in APA, AMA, or Harvard referencing styles.
- Write and double-space the title, your name, and the name of the college
- Create a page header and include the running head, which should be in capital letters.
- The topic of the essay.
The purpose of an introduction paragraph is to provide the reader with a clear picture of what the body will be about.
A good introduction should summarize, incorporate and evaluate the collected data in a way that will set the stage for the body of the essay. It should also have the thesis statement of your paper, which is the main idea or argument in your entire paper.
If you want the readers drawn to reading your epidemiology paper, ensure that you have a catchy or thought-provoking hook statement or attention grabber.
Ensure there is also a logical flow of ideas to avoid confusing your readers. You can also signpost ideas so that the readers have a clear roadmap of the paper right from the start.
Related: Tips for writing an outstanding nursing class essay.
This is the longest and most important part of your essay. It contains all the main ideas and points you are trying to convey. This is where you guide the reader through all ideas, arguments, and points supporting your research topics. You must explain all of them in detail.
Related: How to formulate a PICOT Question or statement .
Use the insert page breaker feature in Microsoft Word to begin a new page when setting up your reference paper. Remember that the header and margins are similar to that of the body, and the pagination will continue from the body of your essay. The header and page number will also appear correctly in the reference section if the paper is set correctly.
To format your entries, include the following:
- Author(s) name
- The year and date(where applicable)
- The source's full title
- If it is a book, write the city where it was published.
- If it is articles or essays, write down the name of the books where they appear.
- Write the volume, issue number, and the page where you sourced the article.
- Write the URL of the source if it is from the Web.
Other rules to keep in mind for APA format:
- Your assignment must be printed on 8½-by-11-inch
- Leave a 1-inch margin on each side
- Make sure there are page numbers
Related Readings:
- How to critically appraise an epidemiology-nursing article.
- Do nursing school grades matter?
- Steps for writing an annotated bibliography.
- Writing a reflective nursing essay.
- Debatable or argumentative nursing topics.
Tips for Writing a Compelling Epidemiology Essay
Nursing epidemiology essays, just like other academic writing, must meet specific criteria to be A+ level. Follow these tips to avoid mistakes that could cost you a higher grade.
- Avoid using Colloquialisms; this is an academic paper and needs to be written with some level of professionalism.
- Make sure you revise the essay. Revising entails paying attention to the little things you missed while writing the essay. It involves checking the word choice to ensure clarity. Try to avoid the use of passive voice and use active voice instead. In addition, use online tools to edit your work.
- This is the final polishing technique after revisions. It involves checking formatting issues, misspellings, punctuation, and any other mistakes you might have missed.
- Read your work aloud to pick out any errors you might have missed. Remove all unnecessary words and repetition.
- Make sure your work is precise and to the point. Consider checking that every sentence, word, or phrase makes sense.
- Even when grammatically correct, long sentences can muddle the intended meaning, so avoid them.
- If you are asked to make a concept map for your epidemiology paper, ensure that you develop a well-labeled, refined, and illustrative nursing concept map .
Writing an epidemiology essay as a nursing student can be challenging at first. However, once you have all the correct information and steps with you, it will be a smooth ride. Ensure you understand the topic and have all the right data before writing. With this in place, you can follow the above steps to perfect your paper. Also, revise and proofread your work to meet the required standards.
Related Reading: The cost of getting your paper done at NurseMyGrade .
Are you stuck with an epidemiology essay or paper? Do you need someone to pay to do your epidemiology essay? We can help. Our established nursing and medical writers at NurseMyGrade have a wealth of knowledge in writing epidemiology papers. It does not matter whether it is tough or challenging; they always get it right. The good thing, they use scholarly peer-reviewed nursing journals that are country specific. So, if you are an Australian nursing or med student, they will only use relevant Australian-based peer-reviewed journals. The same applies to our clients from Canada, the USA, or the UK.
We write 100% original, non-AI generated, and well-polished papers that can serve as excellent references for inspiration when writing your future nursing or med school papers. Trust us today and get top-quality papers. We also handle online classes for nursing students at an affordable fee. Just tell us, “ do my online nursing class ,†and we will reach out to you and figure out a personalized approach for mutual benefit.
Struggling with
Related Articles

Persuasive Speech Topics and Ideas About Healthcare

Best Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) Nursing Research Topics and Ideas


Nursing Report Writing Guide for Nursing Students
NurseMyGrades is being relied upon by thousands of students worldwide to ace their nursing studies. We offer high quality sample papers that help students in their revision as well as helping them remain abreast of what is expected of them.
Disease Research Paper

View sample disease research paper. Browse research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a health research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.
Disease is a phenomenon that appears to have struck people globally at all times. However, the conceptions of what disease is have varied with time and place. This research paper gives an overview over various conceptions of disease and highlights what is at stake in the debates on the concept of disease. The core questions for the article are: what is disease and what are the ethical issues entangled in this question?
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code, introduction.
Disease is a phenomenon experienced by most people during their lifetime, and it is something most people fear. Disease is a core concept in the health sciences, in philosophy, and in bioethics, but it is difficult to define. Broadly speaking there are three types of definitions of disease: descriptivist, normativity, and hybrid definitions of disease, claiming that disease is given by phenomena described in nature, by human norms, or both nature and human norms, respectively.
The concept of disease is ethically important as it sets standards and limits, e.g., to what a health-care system is supposed to do and who deserves access to certain goods. It also influences people’s self-conception, their relations to others, their social roles, and their social status. Disease also raises a series of ethical issues, especially related to overdiagnosis and underdiagnosis, undertreatment and overtreatment, medicalization, and just distribution of healthcare resources. This makes disease an important concept with far-reaching implications for individuals, health professionals, health insurers, health policy makers, bioethicists, and politicians.
History And Development
From the interest of understanding and helping people, a wide range of theories and conceptions of disease have emerged. Such theories have altered with time and place. Table 1 gives a brief outline of some theories of disease.
This eagerness to understand disease can make us wonder, why is it so important to understand what disease is? Why is the concept of disease needed? There appear to be many reasons why the concept of disease is important:
- Disease implies a right to attention and care, as disease is related to suffering.
- Disease (in many countries) implies a right to treatment and is thus of great importance to individuals, health professionals, health-care institutions, health insurers, and health policy makers.
- Disease (in many countries) implies exemptions from duties, such as the duty to work or to take care of others (e.g., relatives or friends).
- Disease (in many countries) implies a right to economic compensation (e.g., during sick leave) and therefore is important to individuals, employers, insurers, and health policy makers.
- Disease may exempt from accountability and moral responsibility (in cases of crime).
- Disease is important for individuals to understand their own situation: “I cannot do or be as I would like, because I am diseased.”
- Disease is important for individuals to explain situation to themselves and others.
- Disease has been important to delimit the tasks of health care from other social tasks and topics.
- Disease has been important to classify and organize the tasks of health care, e.g., in taxonomies and hospital departments.
- Disease has been important to delineate the subject matter of health-related sciences.
Table 1 . Brief overview of some influential theories of disease throughout the history of medicine
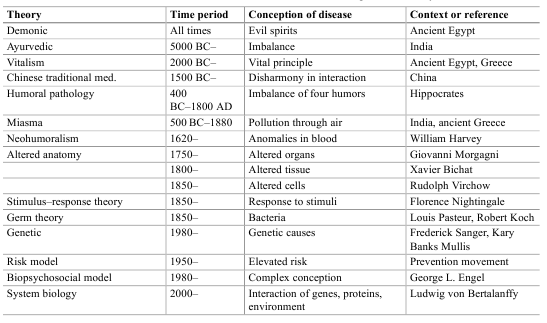
Hence, disease is an important concept with far-reaching implications for individuals, health professionals, health insurers, health policy makers, bioethicists, and politicians. It sets standards, e.g., for how health professionals are educated and how health insurance is regulated, and it sets limits, e.g., who deserves access to certain goods. It also influences people’s self-conception, their relations to others, their social roles, and their social status (see below).
Conceptual Clarification/Definition
There have been many definitions of disease, all trying to highlight or clarify the various important aspects of disease given in the list above (Reznek 1987; Humber and Almeder 1997; Caplan et al. 1981; Cooper 2002; Murphy 2008; Ereshefsky 2009). At present, there is little agreement on how to define disease. The various definitions can be classified in descriptivist, normativist, and hybrid definitions.
Descriptivist positions define disease in terms of biological or mental phenomena which can be described in nature (Davies 2003). Hence, such definitions are often also called naturalist definitions. According to the most referred descriptivist definition, disease is an internal condition disturbing natural functioning. Hence, if a bodily or mental function is reduced below what is statistically normal, then there is disease. This definition is oftentimes called “the biostatistical theory of disease,” and it takes into account differences due to gender, age, and species, so that functional differences in such factors do not become diseases (Boorse 1975). That is, a person is not diseased although the person’s heart has reduced functioning at the age of 100 years old compared to the total population. Diseases are kinds that occur in nature, i.e., natural kinds, and they can be classified on the basis of characteristics that can be described in nature.
According to normativist definitions, disease is a social convention. Disease is the judgment that someone is harmed in a way that (is decided that) can be explained in terms of bodily or mental conditions or processes. Hence, human norms of harm decide what disease is and not biological or mental phenomena, therefore the name normativist. Accordingly, diseases are not natural kinds, although they may be classified according to phenomena which are considered to occur in nature. The reason is that the phenomena that is studied and classified in nature are so classified because they serve human interests, e.g., helping people. The electrical signals in the heart (measured by ECG) are of relevance for medicine because professionals think that they relate to something harmful that can be avoided. When the troponin level in the blood appears to be better in order to characterize, treat, or prevent disease, e.g., myocardial infarction, professionals (and subsequently laypersons) will pay attention to troponin. Correspondingly, it is because blood pressure is related to something harmful that hypertension is of interest in medicine. According to a normativist conception of disease, the phenomena that are measured and manipulated in medicine are relevant to medicine due to human interests (to understand and to help).
Table 2 . Three levels apparent in reflections on disease
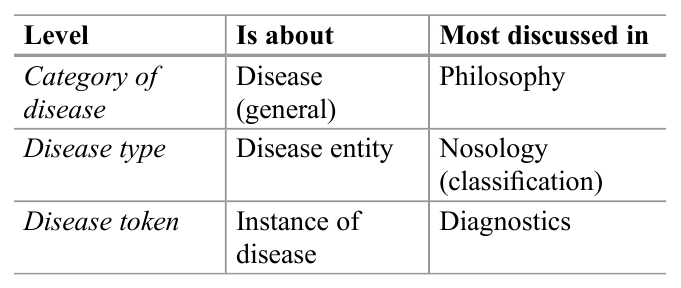
Hybrid definitions of disease can be placed between descriptivist and normativist definitions of disease, as they combine elements from both. For example, disease has been defined as harmful dysfunction, where dysfunction is a description of phenomena in nature, while the issue whether it is harmful is a value judgment. Only those deviations from normal functioning that are harmful can be termed disease (Wakefield 1992).
The debates on the concept of disease are sometimes complex and confusing. One reason for this can be that it is not always clear what is discussed, e.g., because the three levels described in Table 2 are confused.
There are also a wide range of terms related to disease, which sometimes are used synonymously, such as malady, illness, sickness, injury, wound, lesion, defect, deformity, disorder, disability, impairment, deficit, etc. (Culver and Gert 1982). This research paper will not address all these terms but will try to clarify the relationship between some of them below, i.e., disease, illness, and sickness.
The Ethical Dimension Of Disease
Inherent in the debates on the concept of disease, there are a series of ethical issues, such as disease’s inherent imperative to help, over diagnosis, overtreatment, medicalization, and justice. These will be briefly discussed in the following.
The Imperative To Help
The most obvious ethical aspect of disease is the imperative to help persons who suffer from disease. The term disease indicates that there is something that may be eased. Hence, disease calls us to help persons who are diseased in the best possible manner, either from duty (deontology), in order to maximize the total well-being (consequentialism); from the character of the professional (virtue ethics); or from the calling in the sufferer’s face (proximity ethics).
Who Decides What Disease Is?
In clinical practice as well in public debates, there are controversies on whether specific conditions count as disease. Previously, drapetomania (slaves running away), homosexuality, and dissidence have been counted as disease. Today it is discussed whether obesity, sorrow, baldness, freckles, and caffeine-induced insomnia count as disease. Specific interest groups may argue that something is a disease, while professionals may be hesitant, or conversely professionals may measure certain biological conditions that are not experienced by persons at all (and may be never will). Correspondingly, society may consider something to be a disease, while persons and professionals disagree. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may be but one example. Hence, who decides? This is a moral question that relates to the debate between descriptivists and normativists.
Descriptivists tend to claim that nature decides. It is given by nature whether something is a disease or not, i.e., by abnormal functioning of some organ or process. But where to set the limits between normal and pathological? Does nature tell us the limit of glycated hemoglobin (A1C) in the blood for having diabetes type 1? Although hard core descriptivists claim that nature does, critiques argue that such limits are defined from human interests of trying to help people in the best possible manner. If they are right, there are normative aspects at the core of the descriptivists’ conception of disease. Normativists on the other hand are clear that disease is based on human interests and values. However, it is not clear how values and interests are to be balanced. Is it the patients’, the professionals’, relatives, or society’s values and interests that will decide what disease is?
In order to try to clarify some of the conceptual and normative issues, it has been suggested to differentiate between various perspectives of disease, as indicated in Table 3.
Table 3 . Characteristics of three perspectives of human ailment: disease, illness, and sickness
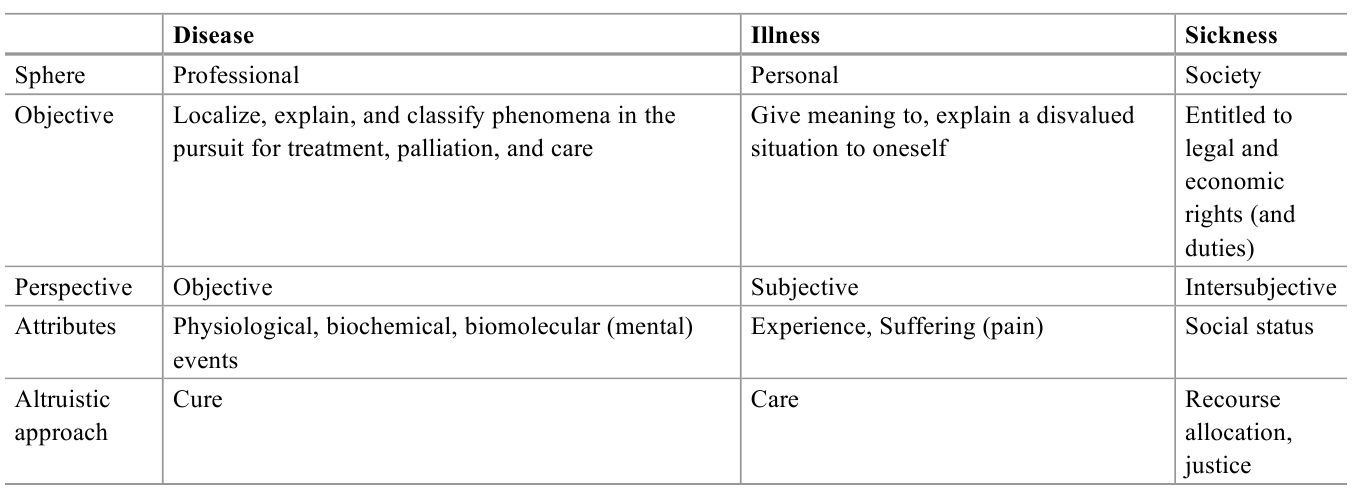
The three perspectives can explain some of the conceptual controversies, as it may be difficult to cover all perspectives of human ailment by one concept. Moreover, the perspectives may also clarify some of the normative issues in terms of conflict of interest between persons, professionals, and society (Hofmann 2002). Impotence (at the age of 70) may not be considered to be a disease from a medical perspective or a sickness from a social perspective, but it definitely may be perceived to be an illness, i.e., it is illness, but not disease and sickness. If all perspectives cohere, there is little controversy. If the perspectives diverge, there may be conceptual and ethical challenges.
Figure 1 indicates the relationship between the concepts of illness, sickness, and disease. Other perspectives, such as existential and risk-related perspectives, may be added.
Figure 1 . The relationship between the concepts of illness, sickness, and disease
As can be seen from vast and vivid debates on specific diseases, such as obesity, ADHD, and myalgic encephalomyelitis, there is no general agreement on whose perspective is prevailing. While descriptivist definitions of disease will favor the professional perspective, normativist definitions will have a higher affinity to social perspectives. Several positions in bioethics will favor the personal perspective on human ailment, i.e., illness (Toombs 1990; Carel 2008).
Underdiagnosis And Overdiagnosis, Undertreatment And Overtreatment
The concept of disease delimits diseased from non-diseased, and where this limit is set is of ethical significance. If the limit is set so that suffering persons who could have been helped are excluded, this is morally wrong. They are underdiagnosed, may be undertreated, and may experience unnecessary uncertainty, anxiety, pain, and death. Conversely, if the limits are too low, it is morally wrong as well. Then healthy persons are diagnosed as having a disease. They may become anxious from being diagnosed and they may be treated unnecessarily and have side effects from unnecessary treatment. While underdiagnosed persons oftentimes gain attention in the media (“could have been saved”), over diagnosed persons get little attention. They do not know that they are over diagnosed but are actually happy that “they found something and saved my life.” Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) may be one example, as it can result in invasive breast cancers, but it does not always do so. When found, DCIS are oftentimes treated as breast cancer, although one does not know whether they would actually have caused symptoms, suffering, or death.
Making Risk A Disease
Another ethical issue related to the concept of disease is the predictive aspirations in modern medicine. A wide range of tests are able to predict diseases. The ethical drive for this is to detect disease before it becomes noticeable and, by prevention or early treatment, to avoid disease or diminish its consequences. However, very few tests are perfect. The outcomes of tests are uncertain and so are the outcomes of subsequent treatment. Hence, the test provides a risk, or a range of risks, for a certain disease. For example, 55–65 % of women who inherit a BRCA1 mutation will develop breast cancer by age 70 years, while about 12 % of women in the general population will develop breast cancer sometime during their lives. Hence, testing positive for the BRCA1 mutation significantly increases the risk of breast cancer but does not mean that the person will have breast cancer. It is a risk estimate. Such risk estimates do not only give people important opportunities to save their lives and reduce suffering; it also gives them difficult choices, as it is uncertain whether they will become diseased, e.g., should a woman prophylactically remove her breasts? Hence, handling risk factors as disease poses ethical challenges to health policy makers, health professionals, and, last but not least, to individual persons. This also connects to ethical challenges with the right to know and the right not to know. The issue of making risk a disease relates to another ethical issue in modern medicine: medicalization.
Medicalization
It has been widely argued that the conception of disease has become too wide and inclusive, e.g., that it has come to include conditions that are considered to be part of ordinary life, such as sorrow (Horwitz and Wakefield 2007), stress, unhappiness, and various kinds of social behavior. It may be ethically challenging when the conceptions of disease make ordinary life conditions or behaviors subject to medical attention. Hence, the critique of medicalization is closely connected to the (unreflective) expansion of the concept of disease.
Disease As An Existential Threat
As disease traditionally has been life threatening and because most people die from a disease, disease is an existential issue. Hence, getting the message of having a disease may be disturbing and challenging, meriting attention and care, beyond handling the disease. Moreover, some diseases have symbolic attributes. Cancer has been considered to be a death sentence and has been a stigma. While the existential aspects of disease have been were at the core in the hospital tradition and still are in many parts of the world, they have gained less attention in modern Western medicine.
Social Prestige And Stigma
Disease is normally considered to be something negative. However, it may also have some positive aspects, such as increased attention, right to treatment, economic compensation, and freedom from duties (work), as pointed out before. Specific disease labels may give identity and strong relations between persons with the same disease. Conversely, not being labeled diseased may make people feel deserted, in despair, and guilty. Hence, disease labeling may influence people’s self-conception and self-esteem.
Moreover, professionals appear to have a relatively stable prestige hierarchy for disease entities (Album and Westin 2008). Organ specific diseases have higher prestige than vague diseases. Diseases related to organs placed in the upper part of the body, such as brain and heart, have higher prestige than those related to organs in lower body parts. Acute diseases prevail over chronic diseases. Hi-tech diseases trump low-tech or no-tech diseases. Such prestige hierarchies of disease tend also to be present in laypeople and patients as well. When disease hierarchies influence how patients are handled or how resources are allocated or prioritized, it becomes ethically challenging.
Conceptions of disease also raise ethical concerns beyond prestige hierarchies. The 90–10 gap is ethically relevant, as 90 % of research resources go to diseases relevant for 10 % of the global population. Correspondingly, it may also be argued that the disease concepts used in the economically richer part of the world is of little relevance to the poorer part of the world. It appears to be ethically important to increase the attention to disease entities that prevail in poorer populations, as well as avoiding a general disease concept that is biased toward affluent populations.
Disease is a phenomenon experienced by most people during life. It is something most people fear, and it is a core concept in the health sciences, in philosophy, and in bioethics. Descriptivists tend to define disease as the malfunctioning of some organ or process and argue that diseases are natural kinds. Normativists, on the other hand, argue that disease is not discovered in nature but is the judgment that someone is harmed in a way that can be explained in terms of bodily or mental conditions or processes. Hybrid conceptions of disease claim that disease is both descriptive and normative, e.g., as harmful dysfunction.
The concept of disease sets standards and limits, e.g., to what a health-care system is supposed to do and who deserves access to certain goods. It also influences people’s self-conception, their relations to others, their social roles, and their social status. Hence, disease is an important concept with far-reaching implications for individuals, health professionals, health insurers, health policy makers, bioethicists, and politicians. It also raises a series of ethical issues, especially related to over diagnosis and underdiagnoses, under treatment and overtreatment, medicalization, and just distribution of health-care resources.
Bibliography :
- Album, D., & Westin, S. (2008). Do diseases have a prestige hierarchy? A survey among physicians and medical students. Social Science and Medicine, 66(1), 182–188.
- Boorse, C. (1975). On the distinction between disease and illness. Philosophy and Public Affairs, 5, 49–68.
- Caplan, A., Englehardt, H., Jr., & McCartney, J. (Eds.). (1981). Concepts of health and disease: Interdisciplinary perspectives. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
- Carel, H. (2008). Illness: The cry of the flesh. Dublin: Acumen.
- Cooper, R. (2002). Disease. Studies in the History and Philosophy of Biology & the Biomedical Sciences, 33, 263–282.
- Culver, C. M., & Gert, B. (1982). Philosophy in medicine. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Davies, P. S. (2003). Norms of nature. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Ereshefsky, M. (2009). Defining ‘health’ and ‘disease’. Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and Biomedical Sciences, 40(3), 221–227.
- Hofmann, B. (2002). On the triad disease, illness and sickness. Journal of Medicine and Philosophy, 27(6), 651–674.
- Horwitz, A. V., & Wakefield, J. C. (2007). The loss of sadness. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Humber, J. M., & Almeder, R. F. (Eds.). (1997). What is disease? Totowa, NJ: Humana Press.
- Murphy, D. (2008). Health and disease. In A. Plutynski & S. Sarkar (Eds.), The blackwell companion to the philosophy of biology (pp. 287–298). Oxford: Blackwell Publishing.
- Reznek, L. (1987). The nature of disease. New York: Routledge.
- Toombs, K. (1990). The meaning of illness: A phenomenological account of the different perspectives of physician and patient. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
- Wakefield, J. (1992). The concept of mental disorder: On the boundary between biological facts and social values. American Psychologist, 47, 373–388.
- Mukherjee, S. (2011). The emperor of all maladies. A biography of cancer. New York: Scribner.
- Sigerist, H. A. (1961). History of Medicine. Vol. II: Early Greek, Hindu, and Persian Medicine. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Sontag, S. (1978). Illness as metaphor. New York: Farrar. Strays and Giroux.
- Taylor, F. K. (1979). The concepts of illness, disease and morbus. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

An Easy Way to Write Essays on Diseases

On the one hand, writing essays on diseases seems to be not that tricky. You have an opportunity to be original and even creative. Can you imagine the number of diseases that you can highlight in your disease essay? What is more, there is a lot of material available almost about every disease.
On the other hand, this great variety of ideas may confuse you. What particular disease should you choose to present in the disease essay (unless specified, of course)?
Well, there is just one thing we can advise you. Think of the disease that you are interested in most of all. Does someone you know suffer from Alzheimer’s disease? Do you have a neighbor who suffers from some kind of exotic disease? Choose whatever you want to learn more about.
Fine, you will pick a good idea for your essay on disease. What is next? Next, you need to think of how to disclose your topic. We can offer a simple plan that will help you create an informative essay on diseases.
Start with a brief overview of the chosen disease. Explain why you have selected this particular disease.
Tell about the causes of the disease, people who are more likely to have it, the main disease carriers, etc.
Describe the main symptoms of the disease in your essay. Here you can also tell about the major effects that the disease has on the human organism.
Finally, describe in your essay on disease the ways of preventing and treating it. Certainly, if you want to amaze your tutor with the essay on disease, this part of the paper should be based on the most up-to-date facts.
If you need more ideas for your essay on disease, make use of the following links: essays on alcoholism and an essay on HIV/AIDS .
A Research Paper on Alzheimer’s Disease
This research paper will delve into Alzheimer’s Disease, covering its causes, symptoms, progression, and current treatments. It will also explore ongoing research in finding a cure and ways to manage this debilitating condition. On PapersOwl, there’s also a selection of free essay templates associated with Alzheimers Disease.
How it works
In this paper, Alzheimer’s disease will be delved into, investigated and dissected. This will include all that is known about the disease as much of it is unknown still, despite increasing efforts from the medical community to uncover its origin. The disease’s causes, symptoms and stages will be discussed and illuminated. The effects on other body systems, its signs and symptoms and any other complications will be highlighted as well. Additionally, advancements in treating this disease are carefully examined.
In this paper, I will be giving an overview of Alzheimer’s disease. This will include its history, prognosis and treatment available and recent advancements made towards finding a cure. Alzheimer’s disease is a somewhat recently discovered phenomenon. It is a specific type of dementia, a disease that impairs a person’s cognitive functioning and behavioral abilities to the point that it interferes with that person’s daily life. The disease was discovered in 1906 by Dr. Alois Alzheimer who noted shrinkage around nerve cells in his patient’s brain who had also reported,” symptoms of memory loss, paranoia and psychological changes.”, according to the National Institute of Aging. After the patient passed, Dr. Alzheimer dissected her brain, finding strange clumps which we now know are amyloid plaques as well as tangled fibers now called neurofibrillary. Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by the symptoms of the aforementioned patient’s, however the disease is a very slowly progressing one, so most afflicted don’t know until the symptoms become obvious to those around them. “Alzheimer’s disease is the most frequent cause of irreversible dementia in adults. The intellectual impairment progresses gradually from forgetfulness to total impairment.” (Mace, Rabins 15) Symptoms usually appear in a person’s mid-60’s, however there are rare cases of early on-set Alzheimer’s where symptoms are exhibited in a person’s 30’s and 40’s. The disease usually progresses to the point that a person afflicted is unable to take care of themselves due to severe memory loss and loss of motor skills, requiring full time assistance. They may also experience forms of delusion such as hallucinations or paranoia that cause them to act impulsively in the moderate stage of dementia, according to the National Institute of Aging. Most diagnosed with this disease will reach this point sadly, as they usually have an average of eight years left to live after the diagnosis as there is no cure, only treatments. The difficulty in treating Alzheimer’s is highlighted by the fact that the first FDA approved drug to treat it wasn’t available until 1993, almost a full century after its discovery. As of today, there are a total of five FDA approved drugs for treating Alzheimer’s disease, none of which truly treat the disease but only prolong the symptoms that will eventually surface. “If we had a drug or other intervention that made people with Alzheimer’s disease even a little better, nevermind curing the disease, I’d sing its praises to the rooftops.[…] But there is not.” (Dedsen 4)
Alzheimer’s disease affects every body system in humans due to the fact that it destroys the brain. It atrophizes, or shrinks, the brain’s neurons and their networks die off, resulting in shrinking of various brain regions. There is no cure as of yet because there is no known way to reverse deterioration of these precious cells. Warning signs of the disease include symptoms of memory loss, severe enough that it affects job performance, difficulty with familiar tasks, issues with language, difficulty with keeping track of time or place, decreased judgment skills, severe mood changes and inability to recognize loved ones, especially in the late stages of the disease, according to the Alzheimer’s Association. Even a change of a person’s sense of humor can be a warning sign. Most individuals who reach the late stages of this disease will require full time assistance such as live in nurses.
On the bright side, specialists typically accurately diagnose Alzheimer’s at a rate of 95%. The only true way to confirm Alzheimer’s disease is through autopsy, however there are a multitude of tests specialists utilize to differentiate Alzheimer’s from other forms of dementia. These include genetic testing, magnetic resonance imaging, urinalysis, blood tests, electroencephalogram, spinal tap, computed tomography scan, chest X-ray and a mental status test, according to the Alzheimer’s Association. In contrast, the prognosis with treatment for those affected is currently bleak. There are few medications available to those with Alzheimer’s and none prevent or cure the disease. Average life expectancy is eight years after diagnosis, but it can range from one to twenty years for some, all according to the Alzheimer’s Association.
Currently, there are hundreds of studies being conducted on treating and preventing Alzheimer’s disease. Most medications being proposed are modifying therapies, meaning that they could alter how the disease progresses. others include cognitive enhancers for improving memory or attentiveness and lastly symptomatic agents which may lessen symptoms such as hallucinations. The focus areas of research currently being conducted are clinical and laboratory research. Clinical research at the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging focus on normal aging, mild cognitive impairment and dementia disorders. This process is used in the hopes of discovering patterns or signs that may help specialists discover risk of Alzheimer’s even sooner than previously possible. Laboratory research includes studying amyloid and tau proteins. Both of these proteins have strong associations with those at risk for Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia. Amyloid proteins are being studied with both human and mouse models to determine any genetic factors that might predispose people to this disease. Additionally, tau proteins are being studied to ascertain the possibility of preventing the build up of this protein that causes neurons to malfunction and die, according to the Alzheimer’s Association. Currently, there is no prevention of the disease itself, only medication that may slow down the progress of the disease in certain individuals. There are tests available to help determine if you or a loved one may be at risk, but no prevention. Alzheimer’s is a devastating disease due to the fact that it’s largely out of our control. Later generations may see improvements in treating it or preventing it or ideally finding a cure. However, the fact that it’s been known for over a century and there has yet to be substantial slowing of the progress of the disease through medication, no available prevention and no cure whatsoever is depressing to say the least. It is “the only one of the nation’s leading 10 causes of death for which there is no effective treatment.” (Dedsen 4) However, having said this, there has been a greater push and call for urgency in discovering a cure for the disease. President Obama signed The National Plan to Address Alzheimer’s Disease into effect in January of 2011. This initiative gave greater funding for new research projects, better tools for clinicians, easier access to information to help caregivers and created an awareness campaign, according to the National Institute of Aging. There has even been news about its awareness efforts in pop culture thanks to Seth Rogen and his wife Lauren MIller Rogen, who’s mother passed away due to complications from being diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, creating the program, “Hilarity for Charity”. This program is described as being,” a non-profit movement dedicated to raising awareness, inspiring change and accelerating progress in Alzheimer’s care, research and support through the engagement of millenials.” For six years in a row now, the Rogens have put on a stand-up special grouping together various comedians to help raise funds for Alzheimer’s research, the most recent of which can be streamed on netflix. While there is no cure, seeing such a push for progress in understanding and fighting this disease can only give one hope that major advancements will be made in the future.
- About Hilarity for Charity. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://hilarityforcharity.org/about/
- Alzheimer’s Disease Fact Sheet. (2016, August). Retrieved from https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-disease-fact-sheet
- Bredesen, D. (2017) The End of Alzheimer’s: The First Program to Prevent and Reverse Cognitive Decline. New York, NY: Penguin Random House.
- R. C. (n.d.). Research and Prognosis on Alzheimer’s Disease. Retrieved from https://www.gulfbend.org/poc/view_doc.php?type=doc&id=3249&cn=231
- Mace, N. L., & Rabins, P. V. (2017). The 36-hour day: A family guide to caring for people who have Alzheimer disease, related dementias and memory loss. New York: Grand Central.
- Obama administration presents national plan to fight Alzheimer’s disease. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.nia.nih.gov/news/obama-administration-presents-national-plan-fight-alzheimers-disease
- What Is Alzheimer’s? (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers
Cite this page
A Research Paper on Alzheimer's Disease. (2019, Aug 31). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/a-research-paper-on-alzheimers-disease/
"A Research Paper on Alzheimer's Disease." PapersOwl.com , 31 Aug 2019, https://papersowl.com/examples/a-research-paper-on-alzheimers-disease/
PapersOwl.com. (2019). A Research Paper on Alzheimer's Disease . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/a-research-paper-on-alzheimers-disease/ [Accessed: 26 May. 2024]
"A Research Paper on Alzheimer's Disease." PapersOwl.com, Aug 31, 2019. Accessed May 26, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/a-research-paper-on-alzheimers-disease/
"A Research Paper on Alzheimer's Disease," PapersOwl.com , 31-Aug-2019. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/a-research-paper-on-alzheimers-disease/. [Accessed: 26-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2019). A Research Paper on Alzheimer's Disease . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/a-research-paper-on-alzheimers-disease/ [Accessed: 26-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 13 May 2024
Long-term weight loss effects of semaglutide in obesity without diabetes in the SELECT trial
- Donna H. Ryan 1 ,
- Ildiko Lingvay ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7006-7401 2 ,
- John Deanfield 3 ,
- Steven E. Kahn 4 ,
- Eric Barros ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6613-4181 5 ,
- Bartolome Burguera 6 ,
- Helen M. Colhoun ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8345-3288 7 ,
- Cintia Cercato ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6181-4951 8 ,
- Dror Dicker 9 ,
- Deborah B. Horn 10 ,
- G. Kees Hovingh 5 ,
- Ole Kleist Jeppesen 5 ,
- Alexander Kokkinos 11 ,
- A. Michael Lincoff ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8175-2121 12 ,
- Sebastian M. Meyhöfer 13 ,
- Tugce Kalayci Oral 5 ,
- Jorge Plutzky ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7194-9876 14 ,
- André P. van Beek ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0335-8177 15 ,
- John P. H. Wilding ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2839-8404 16 &
- Robert F. Kushner 17
Nature Medicine ( 2024 ) Cite this article
41k Accesses
3 Citations
2411 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Health care
- Medical research
In the SELECT cardiovascular outcomes trial, semaglutide showed a 20% reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events in 17,604 adults with preexisting cardiovascular disease, overweight or obesity, without diabetes. Here in this prespecified analysis, we examined effects of semaglutide on weight and anthropometric outcomes, safety and tolerability by baseline body mass index (BMI). In patients treated with semaglutide, weight loss continued over 65 weeks and was sustained for up to 4 years. At 208 weeks, semaglutide was associated with mean reduction in weight (−10.2%), waist circumference (−7.7 cm) and waist-to-height ratio (−6.9%) versus placebo (−1.5%, −1.3 cm and −1.0%, respectively; P < 0.0001 for all comparisons versus placebo). Clinically meaningful weight loss occurred in both sexes and all races, body sizes and regions. Semaglutide was associated with fewer serious adverse events. For each BMI category (<30, 30 to <35, 35 to <40 and ≥40 kg m − 2 ) there were lower rates (events per 100 years of observation) of serious adverse events with semaglutide (43.23, 43.54, 51.07 and 47.06 for semaglutide and 50.48, 49.66, 52.73 and 60.85 for placebo). Semaglutide was associated with increased rates of trial product discontinuation. Discontinuations increased as BMI class decreased. In SELECT, at 208 weeks, semaglutide produced clinically significant weight loss and improvements in anthropometric measurements versus placebo. Weight loss was sustained over 4 years. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03574597 .
Similar content being viewed by others
Effects of a personalized nutrition program on cardiometabolic health: a randomized controlled trial

Two-year effects of semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: the STEP 5 trial

What is the pipeline for future medications for obesity?
The worldwide obesity prevalence, defined by body mass index (BMI) ≥30 kg m − 2 , has nearly tripled since 1975 (ref. 1 ). BMI is a good surveillance measure for population changes over time, given its strong correlation with body fat amount on a population level, but it may not accurately indicate the amount or location of body fat at the individual level 2 . In fact, the World Health Organization defines clinical obesity as ‘abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that may impair health’ 1 . Excess abnormal body fat, especially visceral adiposity and ectopic fat, is a driver of cardiovascular (CV) disease (CVD) 3 , 4 , 5 , and contributes to the global chronic disease burden of diabetes, chronic kidney disease, cancer and other chronic conditions 6 , 7 .
Remediating the adverse health effects of excess abnormal body fat through weight loss is a priority in addressing the global chronic disease burden. Improvements in CV risk factors, glycemia and quality-of-life measures including personal well-being and physical functioning generally begin with modest weight loss of 5%, whereas greater weight loss is associated with more improvement in these measures 8 , 9 , 10 . Producing and sustaining durable and clinically significant weight loss with lifestyle intervention alone has been challenging 11 . However, weight-management medications that modify appetite can make attaining and sustaining clinically meaningful weight loss of ≥10% more likely 12 . Recently, weight-management medications, particularly those comprising glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, that help people achieve greater and more sustainable weight loss have been developed 13 . Once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, is approved for chronic weight management 14 , 15 , 16 and at doses of up to 2.0 mg is approved for type 2 diabetes treatment 17 , 18 , 19 . In patients with type 2 diabetes and high CV risk, semaglutide at doses of 0.5 mg and 1.0 mg has been shown to significantly lower the risk of CV events 20 . The SELECT trial (Semaglutide Effects on Heart Disease and Stroke in Patients with Overweight or Obesity) studied patients with established CVD and overweight or obesity but without diabetes. In SELECT, semaglutide was associated with a 20% reduction in major adverse CV events (hazard ratio 0.80, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.72 to 0.90; P < 0.001) 21 . Data derived from the SELECT trial offer the opportunity to evaluate the weight loss efficacy, in a geographically and racially diverse population, of semaglutide compared with placebo over 208 weeks when both are given in addition to standard-of-care recommendations for secondary CVD prevention (but without a focus on targeting weight loss). Furthermore, the data allow examination of changes in anthropometric measures such as BMI, waist circumference (WC) and waist-to-height ratio (WHtR) as surrogates for body fat amount and location 22 , 23 . The diverse population can also be evaluated for changes in sex- and race-specific ‘cutoff points’ for BMI and WC, which have been identified as anthropometric measures that predict cardiometabolic risk 8 , 22 , 23 .
This prespecified analysis of the SELECT trial investigated weight loss and changes in anthropometric indices in patients with established CVD and overweight or obesity without diabetes, who met inclusion and exclusion criteria, within a range of baseline categories for glycemia, renal function and body anthropometric measures.
Study population
The SELECT study enrolled 17,604 patients (72.3% male) from 41 countries between October 2018 and March 2021, with a mean (s.d.) age of 61.6 (8.9) years and BMI of 33.3 (5.0) kg m − 2 (ref. 21 ). The baseline characteristics of the population have been reported 24 . Supplementary Table 1 outlines SELECT patients according to baseline BMI categories. Of note, in the lower BMI categories (<30 kg m − 2 (overweight) and 30 to <35 kg m − 2 (class I obesity)), the proportion of Asian individuals was higher (14.5% and 7.4%, respectively) compared with the proportion of Asian individuals in the higher BMI categories (BMI 35 to <40 kg m − 2 (class II obesity; 3.8%) and ≥40 kg m − 2 (class III obesity; 2.2%), respectively). As the BMI categories increased, the proportion of women was higher: in the class III BMI category, 45.5% were female, compared with 20.8%, 25.7% and 33.0% in the overweight, class I and class II categories, respectively. Lower BMI categories were associated with a higher proportion of patients with normoglycemia and glycated hemoglobin <5.7%. Although the proportions of patients with high cholesterol and history of smoking were similar across BMI categories, the proportion of patients with high-sensitivity C-reactive protein ≥2.0 mg dl −1 increased as the BMI category increased. A high-sensitivity C-reactive protein >2.0 mg dl −1 was present in 36.4% of patients in the overweight BMI category, with a progressive increase to 43.3%, 57.3% and 72.0% for patients in the class I, II and III obesity categories, respectively.
Weight and anthropometric outcomes
Percentage weight loss.
The average percentage weight-loss trajectories with semaglutide and placebo over 4 years of observation are shown in Fig. 1a (ref. 21 ). For those in the semaglutide group, the weight-loss trajectory continued to week 65 and then was sustained for the study period through week 208 (−10.2% for the semaglutide group, −1.5% for the placebo group; treatment difference −8.7%; 95% CI −9.42 to −7.88; P < 0.0001). To estimate the treatment effect while on medication, we performed a first on-treatment analysis (observation period until the first time being off treatment for >35 days). At week 208, mean weight loss in the semaglutide group analyzed as first on-treatment was −11.7% compared with −1.5% for the placebo group (Fig. 1b ; treatment difference −10.2%; 95% CI −11.0 to −9.42; P < 0.0001).
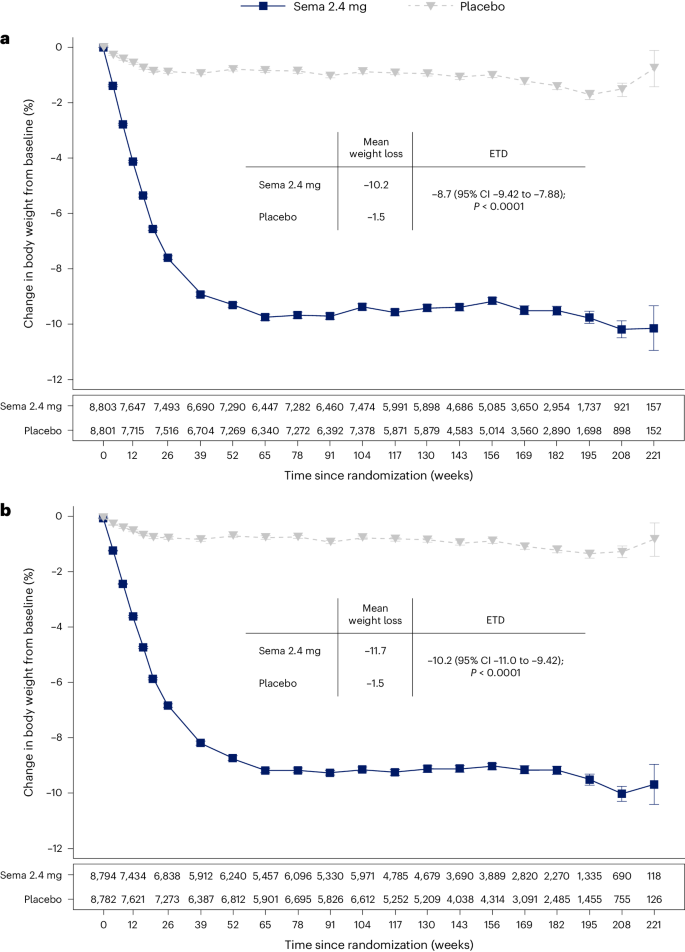
a , b , Observed data from the in-trial period ( a ) and first on-treatment ( b ). The symbols are the observed means, and error bars are ±s.e.m. Numbers shown below each panel represent the number of patients contributing to the means. Analysis of covariance with treatment and baseline values was used to estimate the treatment difference. Exact P values are 1.323762 × 10 −94 and 9.80035 × 10 −100 for a and b , respectively. P values are two-sided and are not adjusted for multiplicity. ETD, estimated treatment difference; sema, semaglutide.
Categorical weight loss and individual body weight change
Among in-trial (intention-to-treat principle) patients at week 104, weight loss of ≥5%, ≥10%, ≥15%, ≥20% and ≥25% was achieved by 67.8%, 44.2%, 22.9%, 11.0% and 4.9%, respectively, of those treated with semaglutide compared with 21.3%, 6.9%, 1.7%, 0.6% and 0.1% of those receiving placebo (Fig. 2a ). Individual weight changes at 104 weeks for the in-trial populations for semaglutide and placebo are depicted in Fig. 2b and Fig. 2c , respectively. These waterfall plots show the variation in weight-loss response that occurs with semaglutide and placebo and show that weight loss is more prominent with semaglutide than placebo.
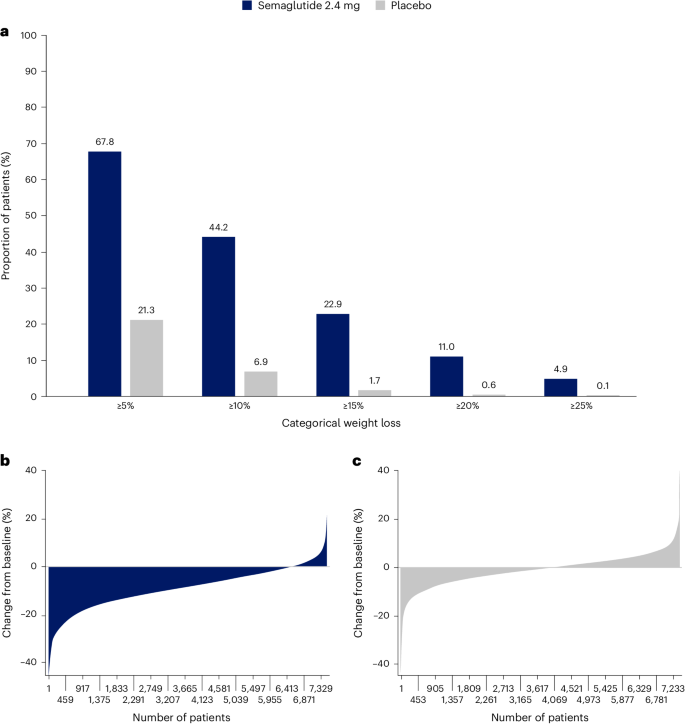
a , Categorical weight loss from baseline at week 104 for semaglutide and placebo. Data from the in-trial period. Bars depict the proportion (%) of patients receiving semaglutide or placebo who achieved ≥5%, ≥10%, ≥15%, ≥20% and ≥25% weight loss. b , c , Percentage change in body weight for individual patients from baseline to week 104 for semaglutide ( b ) and placebo ( c ). Each patient’s percentage change in body weight is plotted as a single bar.
Change in WC
WC change from baseline to 104 weeks has been reported previously in the primary outcome paper 21 . The trajectory of WC change mirrored that of the change in body weight. At week 208, average reduction in WC was −7.7 cm with semaglutide versus −1.3 cm with placebo, with a treatment difference of −6.4 cm (95% CI −7.18 to −5.61; P < 0.0001) 21 .
WC cutoff points
We analyzed achievement of sex- and race-specific cutoff points for WC by BMI <35 kg m − 2 or ≥35 kg m − 2 , because for BMI >35 kg m − 2 , WC is more difficult technically and, thus, less accurate as a risk predictor 4 , 25 , 26 . Within the SELECT population with BMI <35 kg m − 2 at baseline, 15.0% and 14.3% of the semaglutide and placebo groups, respectively, were below the sex- and race-specific WC cutoff points. At week 104, 41.2% fell below the sex- and race-specific cutoff points for the semaglutide group, compared with only 18.0% for the placebo group (Fig. 3 ).
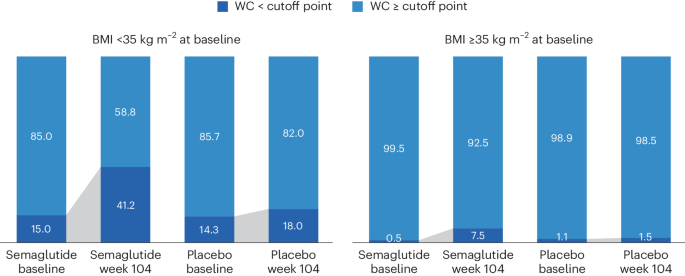
WC cutoff points; Asian women <80 cm, non-Asian women <88 cm, Asian men <88 cm, non-Asian men <102 cm.
Waist-to-height ratio
At baseline, mean WHtR was 0.66 for the study population. The lowest tertile of the SELECT population at baseline had a mean WHtR <0.62, which is higher than the cutoff point of 0.5 used to indicate increased cardiometabolic risk 27 , suggesting that the trial population had high WCs. At week 208, in the group randomized to semaglutide, there was a relative reduction of 6.9% in WHtR compared with 1.0% in placebo (treatment difference −5.87% points; 95% CI −6.56 to −5.17; P < 0.0001).
BMI category change
At week 104, 52.4% of patients treated with semaglutide achieved improvement in BMI category compared with 15.7% of those receiving placebo. Proportions of patients in the BMI categories at baseline and week 104 are shown in Fig. 4 , which depicts in-trial patients receiving semaglutide and placebo. The BMI category change reflects the superior weight loss with semaglutide, which resulted in fewer patients being in the higher BMI categories after 104 weeks. In the semaglutide group, 12.0% of patients achieved a BMI <25 kg m − 2 , which is considered the healthy BMI category, compared with 1.2% for placebo; per study inclusion criteria, no patients were in this category at baseline. The proportion of patients with obesity (BMI ≥30 kg m − 2 ) fell from 71.0% to 43.3% in the semaglutide group versus 71.9% to 67.9% in the placebo group.
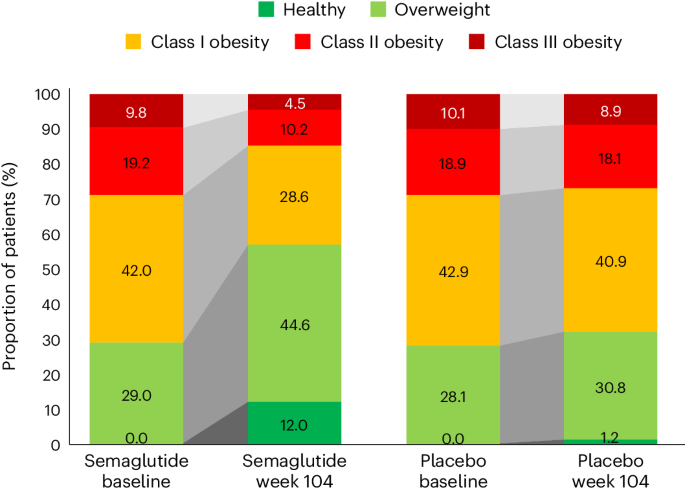
In the semaglutide group, 12.0% of patients achieved normal weight status at week 104 (from 0% at baseline), compared with 1.2% (from 0% at baseline) for placebo. BMI classes: healthy (BMI <25 kg m − 2 ), overweight (25 to <30 kg m − 2 ), class I obesity (30 to <35 kg m − 2 ), class II obesity (35 to <40 kg m − 2 ) and class III obesity (BMI ≥40 kg m − 2 ).
Weight and anthropometric outcomes by subgroups
The forest plot illustrated in Fig. 5 displays mean body weight percentage change from baseline to week 104 for semaglutide relative to placebo in prespecified subgroups. Similar relationships are depicted for WC changes in prespecified subgroups shown in Extended Data Fig. 1 . The effect of semaglutide (versus placebo) on mean percentage body weight loss as well as reduction in WC was found to be heterogeneous across several population subgroups. Women had a greater difference in mean weight loss with semaglutide versus placebo (−11.1% (95% CI −11.56 to −10.66) versus −7.5% in men (95% CI −7.78 to −7.23); P < 0.0001). There was a linear relationship between age category and degree of mean weight loss, with younger age being associated with progressively greater mean weight loss, but the actual mean difference by age group is small. Similarly, BMI category had small, although statistically significant, associations. Those with WHtR less than the median experienced slightly lower mean body weight change than those above the median, with estimated treatment differences −8.04% (95% CI −8.37 to −7.70) and −8.99% (95% CI −9.33 to −8.65), respectively ( P < 0.0001). Patients from Asia and of Asian race experienced slightly lower mean weight loss (estimated treatment difference with semaglutide for Asian race −7.27% (95% CI −8.09 to −6.46; P = 0.0147) and for Asia −7.30 (95% CI −7.97 to −6.62; P = 0.0016)). There was no difference in weight loss with semaglutide associated with ethnicity (estimated treatment difference for Hispanic −8.53% (95% CI −9.28 to −7.76) or non-Hispanic −8.52% (95% CI −8.77 to 8.26); P = 0.9769), glycemic status (estimated treatment difference for prediabetes −8.53% (95% CI −8.83 to −8.24) or normoglycemia −8.48% (95% CI −8.88 to −8.07; P = 0.8188) or renal function (estimated treatment difference for estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <60 or ≥60 ml min −1 1.73 m − 2 being −8.50% (95% CI −9.23 to −7.76) and −8.52% (95% CI −8.77 to −8.26), respectively ( P = 0.9519)).
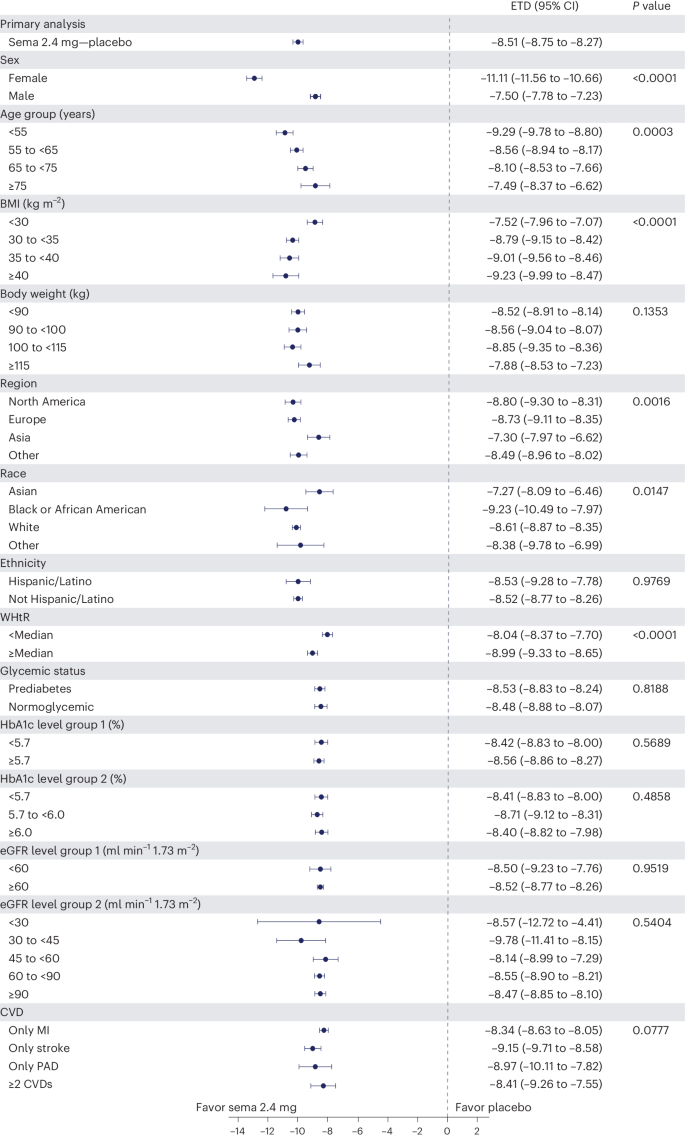
Data from the in-trial period. N = 17,604. P values represent test of no interaction effect. P values are two-sided and are not adjusted for multiplicity. The dots show estimated treatment differences, and the error bars show 95% CIs. Details of the statistical models are available in Methods . ETD, estimated treatment difference; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; MI, myocardial infarction; PAD, peripheral artery disease; sema, semaglutide.
Safety and tolerability according to baseline BMI category
We reported in the primary outcome of the SELECT trial that adverse events (AEs) leading to permanent discontinuation of the trial product occurred in 1,461 patients (16.6%) in the semaglutide group and 718 patients (8.2%) in the placebo group ( P < 0.001) 21 . For this analysis, we evaluated the cumulative incidence of AEs leading to trial product discontinuation by treatment assignment and by BMI category (Fig. 6 ). For this analysis, with death modeled as a competing risk, we tracked the proportion of in-trial patients for whom drug was withdrawn or interrupted for the first time (Fig. 6 , left) or cumulative discontinuations (Fig. 6 , right). Both panels of Fig. 6 depict a graded increase in the proportion discontinuing semaglutide, but not placebo. For lower BMI classes, discontinuation rates are higher in the semaglutide group but not the placebo group.
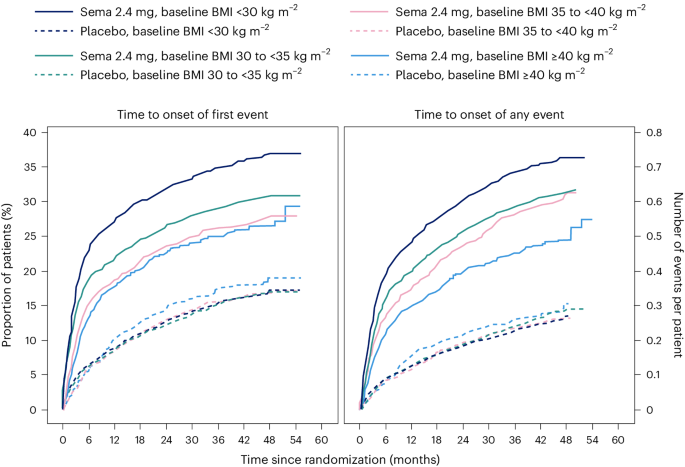
Data are in-trial from the full analysis set. sema, semaglutide.
We reported in the primary SELECT analysis that serious adverse events (SAEs) were reported by 2,941 patients (33.4%) in the semaglutide arm and by 3,204 patients (36.4%) in the placebo arm ( P < 0.001) 21 . For this study, we analyzed SAE rates by person-years of treatment exposure for BMI classes (<30 kg m − 2 , 30 to <35 kg m − 2 , 35 to <40 kg m − 2 , and ≥40 kg m − 2 ) and provide these data in Supplementary Table 2 . We also provide an analysis of the most common categories of SAEs. Semaglutide was associated with lower SAEs, primarily driven by CV event and infections. Within each obesity class (<30 kg m − 2 , 30 to <35 kg m − 2 , 35 to <40 kg m − 2 , and ≥40 kg m − 2 ), there were fewer SAEs in the group receiving semaglutide compared with placebo. Rates (events per 100 years of observation) of SAEs were 43.23, 43.54, 51.07 and 47.06 for semaglutide and 50.48, 49.66, 52.73 and 60.85 for placebo, with no evidence of heterogeneity. There was no detectable difference in hepatobiliary or gastrointestinal SAEs comparing semaglutide with placebo in any of the four BMI classes we evaluated.
The analyses of weight effects of the SELECT study presented here reveal that patients assigned to once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg lost significantly more weight than those receiving placebo. The weight-loss trajectory with semaglutide occurred over 65 weeks and was sustained up to 4 years. Likewise, there were similar improvements in the semaglutide group for anthropometrics (WC and WHtR). The weight loss was associated with a greater proportion of patients receiving semaglutide achieving improvement in BMI category, healthy BMI (<25 kg m − 2 ) and falling below the WC cutoff point above which increased cardiometabolic risk for the sex and race is greater 22 , 23 . Furthermore, both sexes, all races, all body sizes and those from all geographic regions were able to achieve clinically meaningful weight loss. There was no evidence of increased SAEs based on BMI categories, although lower BMI category was associated with increased rates of trial product discontinuation, probably reflecting exposure to a higher level of drug in lower BMI categories. These data, representing the longest clinical trial of the effects of semaglutide versus placebo on weight, establish the safety and durability of semaglutide effects on weight loss and maintenance in a geographically and racially diverse population of adult men and women with overweight and obesity but not diabetes. The implications of weight loss of this degree in such a diverse population suggests that it may be possible to impact the public health burden of the multiple morbidities associated with obesity. Although our trial focused on CV events, many chronic diseases would benefit from effective weight management 28 .
There were variations in the weight-loss response. Individual changes in body weight with semaglutide and placebo were striking; still, 67.8% achieved 5% or more weight loss and 44.2% achieved 10% weight loss with semaglutide at 2 years, compared with 21.3% and 6.9%, respectively, for those receiving placebo. Our first on-treatment analysis demonstrated that those on-drug lost more weight than those in-trial, confirming the effect of drug exposure. With semaglutide, lower BMI was associated with less percentage weight loss, and women lost more weight on average than men (−11.1% versus −7.5% treatment difference from placebo); however, in all cases, clinically meaningful mean weight loss was achieved. Although Asian patients lost less weight on average than patients of other races (−7.3% more than placebo), Asian patients were more likely to be in the lowest BMI category (<30 kg m − 2 ), which is known to be associated with less weight loss, as discussed below. Clinically meaningful weight loss was evident in the semaglutide group within a broad range of baseline categories for glycemia and body anthropometrics. Interestingly, at 2 years, a significant proportion of the semaglutide-treated group fell below the sex- and race-specific WC cutoff points, especially in those with BMI <35 kg m − 2 , and a notable proportion (12.0%) fell below the BMI cutoff point of 25 kg m − 2 , which is deemed a healthy BMI in those without unintentional weight loss. As more robust weight loss is possible with newer medications, achieving and maintaining these cutoff point targets may become important benchmarks for tracking responses.
The overall safety profile did not reveal any new signals from prior studies, and there were no BMI category-related associations with AE reporting. The analysis did reveal that tolerability may differ among specific BMI classes, since more discontinuations occurred with semaglutide among lower BMI classes. Potential contributors may include a possibility of higher drug exposure in lower BMI classes, although other explanations, including differences in motivation and cultural mores regarding body size, cannot be excluded.
Is the weight loss in SELECT less than expected based on prior studies with the drug? In STEP 1, a large phase 3 study of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg in individuals without diabetes but with BMI >30 kg m − 2 or 27 kg m − 2 with at least one obesity-related comorbidity, the mean weight loss was −14.9% at week 68, compared with −2.4% with placebo 14 . Several reasons may explain the observation that the mean treatment difference was −12.5% in STEP 1 and −8.7% in SELECT. First, SELECT was designed as a CV outcomes trial and not a weight-loss trial, and weight loss was only a supportive secondary endpoint in the trial design. Patients in STEP 1 were desirous of weight loss as a reason for study participation and received structured lifestyle intervention (which included a −500 kcal per day diet with 150 min per week of physical activity). In the SELECT trial, patients did not enroll for the specific purpose of weight loss and received standard of care covering management of CV risk factors, including medical treatment and healthy lifestyle counseling, but without a specific focus on weight loss. Second, the respective study populations were quite different, with STEP 1 including a younger, healthier population with more women (73.1% of the semaglutide arm in STEP 1 versus 27.7% in SELECT) and higher mean BMI (37.8 kg m − 2 versus 33.3 kg m − 2 , respectively) 14 , 21 . Third, major differences existed between the respective trial protocols. Patients in the semaglutide treatment arm of STEP 1 were more likely to be exposed to the medication at the full dose of 2.4 mg than those in SELECT. In SELECT, investigators were allowed to slow, decrease or pause treatment. By 104 weeks, approximately 77% of SELECT patients on dose were receiving the target semaglutide 2.4 mg weekly dose, which is lower than the corresponding proportion of patients in STEP 1 (89.6% were receiving the target dose at week 68) 14 , 21 . Indeed, in our first on-treatment analysis at week 208, weight loss was greater (−11.7% for semaglutide) compared with the in-trial analysis (−10.2% for semaglutide). Taken together, all these issues make less weight loss an expected finding in SELECT, compared with STEP 1.
The SELECT study has some limitations. First, SELECT was not a primary prevention trial, and the data should not be extrapolated to all individuals with overweight and obesity to prevent major adverse CV events. Although the data set is rich in numbers and diversity, it does not have the numbers of individuals in racial subgroups that may have revealed potential differential effects. SELECT also did not include individuals who have excess abnormal body fat but a BMI <27 kg m − 2 . Not all individuals with increased CV risk have BMI ≥27 kg m − 2 . Thus, the study did not include Asian patients who qualify for treatment with obesity medications at lower BMI and WC cutoff points according to guidelines in their countries 29 . We observed that Asian patients were less likely to be in the higher BMI categories of SELECT and that the population of those with BMI <30 kg m − 2 had a higher percentage of Asian race. Asian individuals would probably benefit from weight loss and medication approaches undertaken at lower BMI levels in the secondary prevention of CVD. Future studies should evaluate CV risk reduction in Asian individuals with high CV risk and BMI <27 kg m − 2 . Another limitation is the lack of information on body composition, beyond the anthropometric measures we used. It would be meaningful to have quantitation of fat mass, lean mass and muscle mass, especially given the wide range of body size in the SELECT population.
An interesting observation from this SELECT weight loss data is that when BMI is ≤30 kg m − 2 , weight loss on a percentage basis is less than that observed across higher classes of BMI severity. Furthermore, as BMI exceeds 30 kg m − 2 , weight loss amounts are more similar for class I, II and III obesity. This was also observed in Look AHEAD, a lifestyle intervention study for weight loss 30 . The proportion (percentage) of weight loss seems to be less, on average, in the BMI <30 kg m − 2 category relative to higher BMI categories, despite their receiving of the same treatment and even potentially higher exposure to the drug for weight loss 30 . Weight loss cannot continue indefinitely. There is a plateau of weight that occurs after weight loss with all treatments for weight management. This plateau has been termed the ‘set point’ or ‘settling point’, a body weight that is in harmony with the genetic and environmental determinants of body weight and adiposity 31 . Perhaps persons with BMI <30 kg m − 2 are closer to their settling point and have less weight to lose to reach it. Furthermore, the cardiometabolic benefits of weight loss are driven by reduction in the abnormal ectopic and visceral depots of fat, not by reduction of subcutaneous fat stores in the hips and thighs. The phenotype of cardiometabolic disease but lower BMI (<30 kg m − 2 ) may be one where reduction of excess abnormal and dysfunctional body fat does not require as much body mass reduction to achieve health improvement. We suspect this may be the case and suggest further studies to explore this aspect of weight-loss physiology.
In conclusion, this analysis of the SELECT study supports the broad use of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg as an aid to CV event reduction in individuals with overweight or obesity without diabetes but with preexisting CVD. Semaglutide 2.4 mg safely and effectively produced clinically significant weight loss in all subgroups based on age, sex, race, glycemia, renal function and anthropometric categories. Furthermore, the weight loss was sustained over 4 years during the trial.
Trial design and participants
The current work complies with all relevant ethical regulations and reports a prespecified analysis of the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled SELECT trial ( NCT03574597 ), details of which have been reported in papers describing study design and rationale 32 , baseline characteristics 24 and the primary outcome 21 . SELECT evaluated once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg versus placebo to reduce the risk of major adverse cardiac events (a composite endpoint comprising CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction or nonfatal stroke) in individuals with established CVD and overweight or obesity, without diabetes. The protocol for SELECT was approved by national and institutional regulatory and ethical authorities in each participating country. All patients provided written informed consent before beginning any trial-specific activity. Eligible patients were aged ≥45 years, with a BMI of ≥27 kg m − 2 and established CVD defined as at least one of the following: prior myocardial infarction, prior ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, or symptomatic peripheral artery disease. Additional inclusion and exclusion criteria can be found elsewhere 32 .
Human participants research
The trial protocol was designed by the trial sponsor, Novo Nordisk, and the academic Steering Committee. A global expert panel of physician leaders in participating countries advised on regional operational issues. National and institutional regulatory and ethical authorities approved the protocol, and all patients provided written informed consent.
Study intervention and patient management
Patients were randomly assigned in a double-blind manner and 1:1 ratio to receive once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg or placebo. The starting dose was 0.24 mg once weekly, with dose increases every 4 weeks (to doses of 0.5, 1.0, 1.7 and 2.4 mg per week) until the target dose of 2.4 mg was reached after 16 weeks. Patients who were unable to tolerate dose escalation due to AEs could be managed by extension of dose-escalation intervals, treatment pauses or maintenance at doses below the 2.4 mg per week target dose. Investigators were allowed to reduce the dose of study product if tolerability issues arose. Investigators were provided with guidelines for, and encouraged to follow, evidence-based recommendations for medical treatment and lifestyle counseling to optimize management of underlying CVD as part of the standard of care. The lifestyle counseling was not targeted at weight loss. Additional intervention descriptions are available 32 .
Sex, race, body weight, height and WC measurements
Sex and race were self-reported. Body weight was measured without shoes and only wearing light clothing; it was measured on a digital scale and recorded in kilograms or pounds (one decimal with a precision of 0.1 kg or lb), with preference for using the same scale throughout the trial. The scale was calibrated yearly as a minimum unless the manufacturer certified that calibration of the weight scales was valid for the lifetime of the scale. Height was measured without shoes in centimeters or inches (one decimal with a precision of 0.1 cm or inches). At screening, BMI was calculated by the electronic case report form. WC was defined as the abdominal circumference located midway between the lower rib margin and the iliac crest. Measures were obtained in a standing position with a nonstretchable measuring tape and to the nearest centimeter or inch. The patient was asked to breathe normally. The tape touched the skin but did not compress soft tissue, and twists in the tape were avoided.
The following endpoints relevant to this paper were assessed at randomization (week 0) to years 2, 3 and 4: change in body weight (%); proportion achieving weight loss ≥5%, ≥10%, ≥15% and ≥20%; change in WC (cm); and percentage change in WHtR (cm cm −1 ). Improvement in BMI category (defined as being in a lower BMI class) was assessed at week 104 compared with baseline according to BMI classes: healthy (BMI <25 kg m − 2 ), overweight (25 to <30 kg m − 2 ), class I obesity (30 to <35 kg m − 2 ), class II obesity (35 to <40 kg m − 2 ) and class III obesity (≥40 kg m − 2 ). The proportions of individuals with BMI <35 or ≥35 kg m − 2 who achieved sex- and race-specific cutoff points for WC (indicating increased metabolic risk) were evaluated at week 104. The WC cutoff points were as follows: Asian women <80 cm, non-Asian women <88 cm, Asian men <88 cm and non-Asian men <102 cm.
Overall, 97.1% of the semaglutide group and 96.8% of the placebo group completed the trial. During the study, 30.6% of those assigned to semaglutide did not complete drug treatment, compared with 27.0% for placebo.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analyses for the in-trial period were based on the intention-to-treat principle and included all randomized patients irrespective of adherence to semaglutide or placebo or changes to background medications. Continuous endpoints were analyzed using an analysis of covariance model with treatment as a fixed factor and baseline value of the endpoint as a covariate. Missing data at the landmark visit, for example, week 104, were imputed using a multiple imputation model and done separately for each treatment arm and included baseline value as a covariate and fit to patients having an observed data point (irrespective of adherence to randomized treatment) at week 104. The fit model is used to impute values for all patients with missing data at week 104 to create 500 complete data sets. Rubin’s rules were used to combine the results. Estimated means are provided with s.e.m., and estimated treatment differences are provided with 95% CI. Binary endpoints were analyzed using logistic regression with treatment and baseline value as a covariate, where missing data were imputed by first using multiple imputation as described above and then categorizing the imputed data according to the endpoint, for example, body weight percentage change at week 104 of <0%. Subgroup analyses for continuous and binary endpoints also included the subgroup and interaction between treatment and subgroup as fixed factors. Because some patients in both arms continued to be followed but were off treatment, we also analyzed weight loss by first on-treatment group (observation period until first time being off treatment for >35 days) to assess a more realistic picture of weight loss in those adhering to treatment. CIs were not adjusted for multiplicity and should therefore not be used to infer definitive treatment effects. All statistical analyses were performed with SAS software, version 9.4 TS1M5 (SAS Institute).
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
Data will be shared with bona fide researchers who submit a research proposal approved by the independent review board. Individual patient data will be shared in data sets in a deidentified and anonymized format. Information about data access request proposals can be found at https://www.novonordisk-trials.com/ .
Obesity and overweight. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (2021).
Cornier, M. A. et al. Assessing adiposity: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 124 , 1996–2019 (2011).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Afshin, A. et al. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N. Engl. J. Med. 377 , 13–27 (2017).
Jensen, M. D. et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 63 , 2985–3023 (2014).
Poirier, P. et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss: an update of the 1997 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on Obesity and Heart Disease from the Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation 113 , 898–918 (2006).
Dai, H. et al. The global burden of disease attributable to high body mass index in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study. PLoS Med. 17 , e1003198 (2020).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ndumele, C. E. et al. Cardiovascular–kidney–metabolic health: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 148 , 1606–1635 (2023).
Garvey, W. T. et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology comprehensive clinical practice guidelines for medical care of patients with obesity. Endocr. Pr. 22 , 1–203 (2016).
Article Google Scholar
Ryan, D. H. & Yockey, S. R. Weight loss and improvement in comorbidity: differences at 5%, 10%, 15%, and over. Curr. Obes. Rep. 6 , 187–194 (2017).
Wing, R. R. et al. Benefits of modest weight loss in improving cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 34 , 1481–1486 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wadden, T. A., Tronieri, J. S. & Butryn, M. L. Lifestyle modification approaches for the treatment of obesity in adults. Am. Psychol. 75 , 235–251 (2020).
Tchang, B. G. et al. Pharmacologic treatment of overweight and obesity in adults. in (eds. Feingold, K. R. et al.) Endotext https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279038/ (MDText.com, 2000).
Müller, T. D., Blüher, M., Tschöp, M. H. & DiMarchi, R. D. Anti-obesity drug discovery: advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 21 , 201–223 (2022).
Wilding, J. P. H. et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 384 , 989–1002 (2021).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wegovy (semaglutide) summary of product characteristics. European Medicines Agency https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/wegovy-epar-product-information_en.pdf (2023).
WEGOVY (semaglutide) prescribing information. Food and Drug Administration https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/215256s007lbl.pdf (2023).
Sorli, C. et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide monotherapy versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 1): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multinational, multicentre phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 5 , 251–260 (2017).
Ozempic (semaglutide) summary of product characteristics. European Medicines Agency https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/ozempic-epar-product-information_en.pdf (2023).
OZEMPIC (semaglutide) prescribing information. Food and Drug Administration https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/209637lbl.pdf (2017).
Marso, S. P. et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 375 , 1834–1844 (2016).
Lincoff, A. M. et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in obesity without diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 389 , 2221–2232 (2023).
Ross, R. et al. Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: a consensus statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 16 , 177–189 (2020).
Snijder, M. B., van Dam, R. M., Visser, M. & Seidell, J. C. What aspects of body fat are particularly hazardous and how do we measure them? Int. J. Epidemiol. 35 , 83–92 (2006).
Lingvay, I. et al. Semaglutide for cardiovascular event reduction in people with overweight or obesity: SELECT study baseline characteristics. Obesity 31 , 111–122 (2023).
Basset, J. The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. International Diabetes Institute, World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific, International Association for the Study of Obesity & International Obesity Task Force https://www.vepachedu.org/TSJ/BMI-Guidelines.pdf (2000).
Hu, F. in Obesity Epidemiology (ed. Hu, F.) 53–83 (Oxford University Press, 2008).
Browning, L. M., Hsieh, S. D. & Ashwell, M. A systematic review of waist-to-height ratio as a screening tool for the prediction of cardiovascular disease and diabetes: 0·5 could be a suitable global boundary value. Nutr. Res. Rev. 23 , 247–269 (2010).
Sattar, N. et al. Treating chronic diseases without tackling excess adiposity promotes multimorbidity. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 11 , 58–62 (2023).
Obesity classification. World Obesity https://www.worldobesity.org/about/about-obesity/obesity-classification (2022).
Unick, J. L. et al. Effectiveness of lifestyle interventions for individuals with severe obesity and type 2 diabetes: results from the Look AHEAD trial. Diabetes Care 34 , 2152–2157 (2011).
Speakman, J. R. et al. Set points, settling points and some alternative models: theoretical options to understand how genes and environments combine to regulate body adiposity. Dis. Model. Mech. 4 , 733–745 (2011).
Ryan, D. H. et al. Semaglutide effects on cardiovascular outcomes in people with overweight or obesity (SELECT) rationale and design. Am. Heart J. 229 , 61–69 (2020).
Download references
Acknowledgements
Editorial support was provided by Richard Ogilvy-Stewart of Apollo, OPEN Health Communications, and funded by Novo Nordisk A/S, in accordance with Good Publication Practice guidelines ( www.ismpp.org/gpp-2022 ).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, LA, USA
Donna H. Ryan
Department of Internal Medicine/Endocrinology and Peter O’ Donnell Jr. School of Public Health, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA
Ildiko Lingvay
Institute of Cardiovascular Science, University College London, London, UK
John Deanfield
VA Puget Sound Health Care System and University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA
Steven E. Kahn
Novo Nordisk A/S, Søborg, Denmark
Eric Barros, G. Kees Hovingh, Ole Kleist Jeppesen & Tugce Kalayci Oral
Endocrinology and Metabolism Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA
Bartolome Burguera
Institute of Genetics and Cancer, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Helen M. Colhoun
Obesity Unit, Department of Endocrinology, Hospital das Clínicas, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
Cintia Cercato
Internal Medicine Department D, Hasharon Hospital-Rabin Medical Center, Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
Dror Dicker
Center for Obesity Medicine and Metabolic Performance, Department of Surgery, University of Texas McGovern Medical School, Houston, TX, USA
Deborah B. Horn
First Department of Propaedeutic Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece
Alexander Kokkinos
Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Cleveland Clinic, and Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, USA
A. Michael Lincoff
Institute of Endocrinology & Diabetes, University of Lübeck, Lübeck, Germany
Sebastian M. Meyhöfer
Cardiovascular Division, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
Jorge Plutzky
University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Department of Endocrinology, Groningen, the Netherlands
André P. van Beek
Department of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Medicine, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK
John P. H. Wilding
Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL, USA
Robert F. Kushner
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
D.H.R., I.L. and S.E.K. contributed to the study design. D.B.H., I.L., D.D., A.K., S.M.M., A.P.v.B., C.C. and J.P.H.W. were study investigators. D.B.H., I.L., D.D., A.K., S.M.M., A.P.v.B., C.C. and J.P.H.W. enrolled patients. D.H.R. was responsible for data analysis and manuscript preparation. All authors contributed to data interpretation, review, revisions and final approval of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Donna H. Ryan .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
D.H.R. declares having received consulting honoraria from Altimmune, Amgen, Biohaven, Boehringer Ingelheim, Calibrate, Carmot Therapeutics, CinRx, Eli Lilly, Epitomee, Gila Therapeutics, IFA Celtics, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm, Scientific Intake, Wondr Health and Zealand Pharma; she declares she received stock options from Calibrate, Epitomee, Scientific Intake and Xeno Bioscience. I.L. declares having received research funding (paid to institution) from Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Mylan and Boehringer Ingelheim. I.L. received advisory/consulting fees and/or other support from Altimmune, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Biomea, Boehringer Ingelheim, Carmot Therapeutics, Cytoki Pharma, Eli Lilly, Intercept, Janssen/Johnson & Johnson, Mannkind, Mediflix, Merck, Metsera, Novo Nordisk, Pharmaventures, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Shionogi, Structure Therapeutics, Target RWE, Terns Pharmaceuticals, The Comm Group, Valeritas, WebMD and Zealand Pharma. J.D. declares having received consulting honoraria from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Pfizer, Aegerion, Novartis, Sanofi, Takeda, Novo Nordisk and Bayer, and research grants from British Heart Foundation, MRC (UK), NIHR, PHE, MSD, Pfizer, Aegerion, Colgate and Roche. S.E.K. declares having received consulting honoraria from ANI Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novo Nordisk and Oramed, and stock options from AltPep. B.B. declares having received honoraria related to participation on this trial and has no financial conflicts related to this publication. H.M.C. declares being a stockholder and serving on an advisory panel for Bayer; receiving research grants from Chief Scientist Office, Diabetes UK, European Commission, IQVIA, Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation and Medical Research Council; serving on an advisory board and speaker’s bureau for Novo Nordisk; and holding stock in Roche Pharmaceuticals. C.C. declares having received consulting honoraria from Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Merck, Brace Pharma and Eurofarma. D.D. declares having received consulting honoraria from Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim and AstraZeneca, and received research grants through his affiliation from Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim and Rhythm. D.B.H. declares having received research grants through her academic affiliation from Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly, and advisory/consulting honoraria from Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly and Gelesis. A.K. declares having received research grants through his affiliation from Novo Nordisk and Pharmaserve Lilly, and consulting honoraria from Pharmaserve Lilly, Sanofi-Aventis, Novo Nordisk, MSD, AstraZeneca, ELPEN Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Galenica Pharma, Epsilon Health and WinMedica. A.M.L. declares having received honoraria from Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Akebia Therapeutics, Ardelyx, Becton Dickinson, Endologix, FibroGen, GSK, Medtronic, Neovasc, Provention Bio, ReCor, BrainStorm Cell Therapeutics, Alnylam and Intarcia for consulting activities, and research funding to his institution from AbbVie, Esperion, AstraZeneca, CSL Behring, Novartis and Eli Lilly. S.M.M. declares having received consulting honoraria from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daichii-Sankyo, esanum, Gilead, Ipsen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Sandoz and Sanofi; he declares he received research grants from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk. J.P. declares having received consulting honoraria from Altimmune, Amgen, Esperion, Merck, MJH Life Sciences, Novartis and Novo Nordisk; he has received a grant, paid to his institution, from Boehringer Ingelheim and holds the position of Director, Preventive Cardiology, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. A.P.v.B. is contracted via the University of Groningen (no personal payment) to undertake consultancy for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly and Boehringer Ingelheim. J.P.H.W. is contracted via the University of Liverpool (no personal payment) to undertake consultancy for Altimmune, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cytoki, Eli Lilly, Napp, Novo Nordisk, Menarini, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Saniona, Tern Pharmaceuticals, Shionogi and Ysopia. J.P.H.W. also declares personal honoraria/lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medscape, Napp, Menarini, Novo Nordisk and Rhythm. R.F.K. declares having received consulting honoraria from Novo Nordisk, Weight Watchers, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Structure and Altimmune. E.B., G.K.H., O.K.J. and T.K.O. are employees of Novo Nordisk A/S.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Medicine thanks Christiana Kartsonaki, Peter Rossing, Naveed Sattar and Vikas Sridhar for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary Handling Editor: Sonia Muliyil, in collaboration with the Nature Medicine team.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data
Extended data fig. 1 effect of semaglutide treatment or placebo on waist circumference from baseline to week 104 by subgroups..
Data from the in-trial period. N = 17,604. P values represent test of no interaction effect. P values are two-sided and not adjusted for multiplicity. The dots show estimated treatment differences and the error bars show 95% confidence intervals. Details of the statistical models are available in Methods . BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; CV, cardiovascular; CVD, cardiovascular disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; ETD, estimated treatment difference; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; MI, myocardial infarction; PAD, peripheral artery disease; sema, semaglutide.
Supplementary information
Reporting summary, supplementary tables 1 and 2.
Supplementary Table 1. Baseline characteristics by BMI class. Data are represented as number and percentage of patients. Renal function categories were based on the eGFR as per Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration. Albuminuria categories were based on UACR. Smoking was defined as smoking at least one cigarette or equivalent daily. The category ‘Other’ for CV inclusion criteria includes patients where it is unknown if the patient fulfilled only one or several criteria and patients who were randomized in error and did not fulfill any criteria. Supplementary Table 2. SAEs according to baseline BMI category. P value: two-sided P value from Fisher’s exact test for test of no difference.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ryan, D.H., Lingvay, I., Deanfield, J. et al. Long-term weight loss effects of semaglutide in obesity without diabetes in the SELECT trial. Nat Med (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-02996-7
Download citation
Received : 01 March 2024
Accepted : 12 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-02996-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
New method to reveal what drives brain diseases
The brain is often referred to as a "black box" -- one that's difficult to peer inside and determine what's happening at any given moment. This is part of the reason why it's difficult to understand the complex interplay of molecules, cells and genes that underly neurological disorders. But a new CRISPR screen method developed at Scripps Research has the potential to uncover new therapeutic targets and treatments for these conditions.
The method, outlined in a study published in Cell on May 20, 2024, provides a way to rapidly examine the brain cell types linked to key developmental genes at a scale never done before -- helping unravel the genetic and cellular drivers of different neurological diseases.
"We know that certain genetic variations in our genome can make us vulnerable or resilient towards different diseases, but which specific cell types are behind a disease? Which brain regions are susceptible to the genome mutations in those cells? These are the kinds of questions we're trying to answer," says senior author Xin Jin, PhD, an assistant professor in the Department of Neuroscience at Scripps Research. "With this new technology, we want to build a more dynamic picture across brain region, across cell type, across the timing of disease development, and really start understanding how the disease happened -- and how to design interventions."
Thanks to over a decade's efforts in human genetics, scientists have had access to long lists of genetic changes that contribute to a range of human illnesses, but knowing how a gene causes a disease is very different than knowing how to treat the illness itself. Every risk gene may impact one or several different cell types. Comprehending how those cell types -- and even individual cells -- impact a gene and affect disease progression is key to understanding how to ultimately treat that disease.
This is why Jin, along with the study's first author, Xinhe Zheng, a PhD candidate and the Frank J. Dixon Graduate Fellow at Scripps Research, co-invented the new technique, named in vivo Perturb-seq. This method leverages CRISPR-Cas9 technology and a readout, single-cell transcriptomic analysis, to measure its impact on a cell: one cell at a time. Using CRISPR-Cas9, scientists can make precise changes to the genome during brain development, and then closely study how those changes affect individual cells using single-cell transcriptomic analysis -- for tens of thousands of cells in parallel.
"Our new system can measure individual cells' response after genetic perturbations, meaning that we can paint a picture of whether certain cell types are more susceptible than others and react differently when a particular mutation happens," Jin says.
Previously, the method for introducing the genetic perturbations into the brain tissue was very slow, often taking days or even weeks, which created suboptimal conditions for studying gene functions related to neurodevelopment. But Jin's new screening method allows for rapid expression of perturbation agents in living cells within 48 hours -- meaning scientists can quickly see how specific genes function in different types of cells in a very short amount of time.
The method also enables a level of scalability that was previously impossible -- the research team was able to profile more than 30,000 cells in just one experiment, 10-20 times accelerated from the traditional approaches. In many of the brain regions they examined, such as the cerebellum, they were able to collect tens of thousands of cells that previous labeling methods could not reach.
In a pilot study using this new technology, Jin and her team's interest was piqued when they saw a genetic perturbation elicit different effects when perturbed in different cell types. This is important because those impacted cell types are the sites of action for particular diseases or genetic variants. "Despite their smaller population representations, some low-abundant cell types may have a stronger impact than others by the genetic perturbation, and when we systematically look at other cell types across multiple genes, we see patterns. That's why single-cell resolution -- being able to study every cell and how each one behaves -- can offer us a systematic view," Jin says.
With her new technology in hand, Jin plans to apply it to better understand neuropsychiatric conditions and how certain cell types correspond with various brain regions. Moving forward, Jin says she's excited to see this type of technology applied to additional cell types in other organs in the body to better understand a wide range of diseases in terms of tissue, development and aging.
- Brain Tumor
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Nervous System
- Brain Injury
- Neuroscience
- Disorders and Syndromes
- Brain-Computer Interfaces
- Brain damage
- Sleep disorder
- Endocrinology
- Gene therapy
- Adult stem cell
Story Source:
Materials provided by Scripps Research Institute . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Xinhe Zheng, Boli Wu, Yuejia Liu, Sean K. Simmons, Kwanho Kim, Grace S. Clarke, Abdullah Ashiq, Joshua Park, Jiwen Li, Zhilin Wang, Liqi Tong, Qizhao Wang, Keerthi T. Rajamani, Rodrigo Muñoz-Castañeda, Shang Mu, Tianbo Qi, Yunxiao Zhang, Zi Chao Ngiam, Naoto Ohte, Carina Hanashima, Zhuhao Wu, Xiangmin Xu, Joshua Z. Levin, Xin Jin. Massively parallel in vivo Perturb-seq reveals cell-type-specific transcriptional networks in cortical development . Cell , 2024; DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.04.050
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Charge Your Laptop in a Minute?
- Caterpillars Detect Predators by Electricity
- 'Electronic Spider Silk' Printed On Human Skin
- Engineered Surfaces Made to Shed Heat
- Innovative Material for Sustainable Building
- Human Brain: New Gene Transcripts
- Epstein-Barr Virus and Resulting Diseases
- Origins of the Proton's Spin
- Symbiotic Bacteria Communicate With Plants
- Birdsong and Human Voice: Same Genetic Blueprint
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
Diet Review: MIND Diet

Finding yourself confused by the seemingly endless promotion of weight-loss strategies and diet plans? In this series , we take a look at some popular diets—and review the research behind them.
What Is It?
The Mediterranean-DASH Diet Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay, or MIND diet, targets the health of the aging brain. Dementia is the sixth leading cause of death in the United States, driving many people to search for ways to prevent cognitive decline. In 2015, Dr. Martha Clare Morris and colleagues at Rush University Medical Center and the Harvard Chan School of Public Health published two papers introducing the MIND diet. [1,2] Both the Mediterranean and DASH diets had already been associated with preservation of cognitive function, presumably through their protective effects against cardiovascular disease, which in turn preserved brain health.
The research team followed a group of older adults for up to 10 years from the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP), a study of residents free of dementia at the time of enrollment. They were recruited from more than 40 retirement communities and senior public housing units in the Chicago area. More than 1,000 participants filled out annual dietary questionnaires for nine years and had two cognitive assessments. A MIND diet score was developed to identify foods and nutrients, along with daily serving sizes, related to protection against dementia and cognitive decline. The results of the study produced fifteen dietary components that were classified as either “brain healthy” or as unhealthy. Participants with the highest MIND diet scores had a significantly slower rate of cognitive decline compared with those with the lowest scores. [1] The effects of the MIND diet on cognition showed greater effects than either the Mediterranean or the DASH diet alone.
How It Works
The purpose of the research was to see if the MIND diet, partially based on the Mediterranean and DASH diets, could directly prevent the onset or slow the progression of dementia. All three diets highlight plant-based foods and limit the intake of animal and high saturated fat foods. The MIND diet recommends specific “brain healthy” foods to include, and five unhealthy food items to limit. [1]
The healthy items the MIND diet guidelines* suggest include:
- 3+ servings a day of whole grains
- 1+ servings a day of vegetables (other than green leafy)
- 6+ servings a week of green leafy vegetables
- 5+ servings a week of nuts
- 4+ meals a week of beans
- 2+ servings a week of berries
- 2+ meals a week of poultry
- 1+ meals a week of fish
- Mainly olive oil if added fat is used
The unhealthy items, which are higher in saturated and trans fat , include:
- Less than 5 servings a week of pastries and sweets
- Less than 4 servings a week of red meat (including beef, pork, lamb, and products made from these meats)
- Less than one serving a week of cheese and fried foods
- Less than 1 tablespoon a day of butter/stick margarine
*Note: modest variations in amounts of these foods have been used in subsequent studies. [9,10]
This sample meal plan is roughly 2000 calories, the recommended intake for an average person. If you have higher calorie needs, you may add an additional snack or two; if you have lower calorie needs, you may remove a snack. If you have more specific nutritional needs or would like assistance in creating additional meal plans, consult with a registered dietitian.
Breakfast: 1 cup cooked steel-cut oats mixed with 2 tablespoons slivered almonds, ¾ cup fresh or frozen blueberries, sprinkle of cinnamon
Snack: 1 medium orange
- Beans and rice – In medium pot, heat 1 tbsp olive oil. Add and sauté ½ chopped onion, 1 tsp cumin, and 1 tsp garlic powder until onion is softened. Mix in 1 cup canned beans, drained and rinsed. Serve bean mixture over 1 cup cooked brown rice.
- 2 cups salad (e.g., mixed greens, cucumbers, bell peppers) with dressing (mix together 2 tbsp olive oil, 1 tbsp lemon juice or vinegar, ½ teaspoon Dijon mustard, ½ teaspoon garlic powder, ¼ tsp black pepper)
Snack: ¼ cup unsalted mixed nuts
- 3 ounces baked salmon brushed with same salad dressing used at lunch
- 1 cup chopped steamed cauliflower
- 1 whole grain roll dipped in 1 tbsp olive oil
Is alcohol part of the MIND diet?
Wine was included as one of the 15 original dietary components in the MIND diet score, in which a moderate amount was found to be associated with cognitive health. [1] However, in subsequent MIND trials it was omitted for “safety” reasons. The effect of alcohol on an individual is complex, so that blanket recommendations about alcohol are not possible. Based on one’s unique personal and family history, alcohol offers each person a different spectrum of benefits and risks. Whether or not to include alcohol is a personal decision that should be discussed with your healthcare provider. For more information, read Alcohol: Balancing Risks and Benefits .
The Research So Far
The MIND diet contains foods rich in certain vitamins, carotenoids, and flavonoids that are believed to protect the brain by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Although the aim of the MIND diet is on brain health, it may also benefit heart health, diabetes, and certain cancers because it includes components of the Mediterranean and DASH diets, which have been shown to lower the risk of these diseases.
Cohort studies
Researchers found a 53% lower rate of Alzheimer’s disease for those with the highest MIND diet scores (indicating a higher intake of foods on the MIND diet). Even those participants who had moderate MIND diet scores showed a 35% lower rate compared with those with the lowest MIND scores. [2] The results didn’t change after adjusting for factors associated with dementia including healthy lifestyle behaviors, cardiovascular-related conditions (e.g., high blood pressure, stroke, diabetes), depression, and obesity, supporting the conclusion that the MIND diet was associated with the preservation of cognitive function.
Several other large cohort studies have shown that participants with higher MIND diet scores, compared with those with the lowest scores, had better cognitive functioning, larger total brain volume, higher memory scores, lower risk of dementia, and slower cognitive decline, even when including participants with Alzheimer’s disease and history of stroke. [3-8]
Clinical trials
A 2023 randomized controlled trial followed 604 adults aged 65 and older who at baseline were overweight (BMI greater than 25), ate a suboptimal diet, and did not have cognitive impairment but had a first-degree relative with dementia. [9] The intervention group was taught to follow a MIND diet, and the control group continued to consume their usual diet. Both groups were guided throughout the study by registered dietitians to follow their assigned diet and reduce their intake by 250 calories a day. The authors found that participants in both the MIND and control groups showed improved cognitive performance. Both groups also lost about 11 pounds, but the MIND diet group showed greater improvements in diet quality score. The authors examined changes in the brain using magnetic resonance imaging, but findings did not differ between groups. [10] Nutrition experts commenting on this study noted that both groups lost a similar amount of weight, as intended, but the control group likely improved their diet quality as well (they had been coached to eat their usual foods but were taught goal setting, calorie tracking, and mindful eating techniques), which could have prevented significant changes from being seen between groups. Furthermore, the duration of the study–3 years–may have been too short to show significant improvement in cognitive function.
The results of this study showed that the MIND diet does not slow cognitive aging over a 3-year treatment period. Whether the MIND diet or other diets can slow cognitive aging over longer time periods remains a topic of intense interest.
Other factors
Research has found that greater poverty and less education are strongly associated with lower MIND diet scores and lower cognitive function. [11]
Potential Pitfalls
- The MIND diet is flexible in that it does not include rigid meal plans. However, this also means that people will need to create their own meal plans and recipes based on the foods recommended on the MIND diet. This may be challenging for those who do not cook. Those who eat out frequently may need to spend time reviewing restaurant menus.
- Although the diet plan specifies daily and weekly amounts of foods to include and not include, it does not restrict the diet to eating only these foods. It also does not provide meal plans or emphasize portion sizes or exercise .
Bottom Line
The MIND diet can be a healthful eating plan that incorporates dietary patterns from the Mediterranean and DASH , both of which have suggested benefits in preventing and improving cardiovascular disease and diabetes , and supporting healthy aging. When used in conjunction with a balanced plate guide , the diet may also promote healthy weight loss if desired. Whether or not following the MIND diet can slow cognitive aging over longer time periods remains an area of interest, and more research needs to be done to extend the MIND studies in other populations.
- Healthy Weight
- The Best Diet: Quality Counts
- Healthy Dietary Styles
- Other Diet Reviews
- Morris MC, Tangney CC, Wang Y, Sacks FM, Barnes LL, Bennett DA, Aggarwal NT. MIND diet slows cognitive decline with aging. Alzheimer’s & dementia . 2015 Sep 1;11(9):1015-22.
- Morris MC, Tangney CC, Wang Y, Sacks FM, Bennett DA, Aggarwal NT. MIND diet associated with reduced incidence of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia . 2015 Sep 1;11(9):1007-14.
- Dhana K, James BD, Agarwal P, Aggarwal NT, Cherian LJ, Leurgans SE, Barnes LL, Bennett DA, Schneider JA. MIND diet, common brain pathologies, and cognition in community-dwelling older adults. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease . 2021 Jan 1;83(2):683-92.
- Cherian L, Wang Y, Fakuda K, Leurgans S, Aggarwal N, Morris M. Mediterranean-Dash Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) diet slows cognitive decline after stroke. The journal of prevention of Alzheimer’s disease . 2019 Oct;6(4):267-73.
- Hosking DE, Eramudugolla R, Cherbuin N, Anstey KJ. MIND not Mediterranean diet related to 12-year incidence of cognitive impairment in an Australian longitudinal cohort study. Alzheimer’s & Dementia . 2019 Apr 1;15(4):581-9.
- Melo van Lent D, O’Donnell A, Beiser AS, Vasan RS, DeCarli CS, Scarmeas N, Wagner M, Jacques PF, Seshadri S, Himali JJ, Pase MP. Mind diet adherence and cognitive performance in the Framingham heart study. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease . 2021 Jan 1;82(2):827-39.
- Berendsen AM, Kang JH, Feskens EJ, de Groot CP, Grodstein F, van de Rest O. Association of long-term adherence to the mind diet with cognitive function and cognitive decline in American women. The journal of nutrition, health & aging . 2018 Feb;22(2):222-9. Disclosure: Grodstein reports grants from International Nut Council, other from California Walnut Council, outside the submitted work.
- Chen H, Dhana K, Huang Y, Huang L, Tao Y, Liu X, van Lent DM, Zheng Y, Ascherio A, Willett W, Yuan C. Association of the Mediterranean Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) Diet With the Risk of Dementia. JAMA psychiatry . 2023 May 3.
- Liu X, Morris MC, Dhana K, Ventrelle J, Johnson K, Bishop L, Hollings CS, Boulin A, Laranjo N, Stubbs BJ, Reilly X. Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) study: rationale, design and baseline characteristics of a randomized control trial of the MIND diet on cognitive decline. Contemporary clinical trials . 2021 Mar 1;102:106270. Disclosure: several corporations generously donated mixed nuts (International Tree Nut Council Nutrition Research and Education Foundation), peanut butter (The Peanut Institute), extra virgin olive oil (Innoliva-ADM Capital Europe LLP), and blueberries (U.S. Highbush Blueberry Council). These items will be distributed to those participants who are randomized to the MIND diet arm.
- Barnes LL, Dhana K, Liu X, Carey VJ, Ventrelle J, Johnson K, Hollings CS, Bishop L, Laranjo N, Stubbs BJ, Reilly X. Trial of the MIND Diet for Prevention of Cognitive Decline in Older Persons. New England Journal of Medicine . 2023 Jul 18.
- Boumenna T, Scott TM, Lee JS, Zhang X, Kriebel D, Tucker KL, Palacios N. MIND diet and cognitive function in Puerto Rican older adults. The Journals of Gerontology: Series A . 2022 Mar;77(3):605-13.
Last reviewed August 2023
Terms of Use
The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products.
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- About Adverse Childhood Experiences
- Risk and Protective Factors
- Program: Essentials for Childhood: Preventing Adverse Childhood Experiences through Data to Action
- Adverse childhood experiences can have long-term impacts on health, opportunity and well-being.
- Adverse childhood experiences are common and some groups experience them more than others.

What are adverse childhood experiences?
Adverse childhood experiences, or ACEs, are potentially traumatic events that occur in childhood (0-17 years). Examples include: 1
- Experiencing violence, abuse, or neglect.
- Witnessing violence in the home or community.
- Having a family member attempt or die by suicide.
Also included are aspects of the child’s environment that can undermine their sense of safety, stability, and bonding. Examples can include growing up in a household with: 1
- Substance use problems.
- Mental health problems.
- Instability due to parental separation.
- Instability due to household members being in jail or prison.
The examples above are not a complete list of adverse experiences. Many other traumatic experiences could impact health and well-being. This can include not having enough food to eat, experiencing homelessness or unstable housing, or experiencing discrimination. 2 3 4 5 6
Quick facts and stats
ACEs are common. About 64% of adults in the United States reported they had experienced at least one type of ACE before age 18. Nearly one in six (17.3%) adults reported they had experienced four or more types of ACEs. 7
Preventing ACEs could potentially reduce many health conditions. Estimates show up to 1.9 million heart disease cases and 21 million depression cases potentially could have been avoided by preventing ACEs. 1
Some people are at greater risk of experiencing one or more ACEs than others. While all children are at risk of ACEs, numerous studies show inequities in such experiences. These inequalities are linked to the historical, social, and economic environments in which some families live. 5 6 ACEs were highest among females, non-Hispanic American Indian or Alaska Native adults, and adults who are unemployed or unable to work. 7
ACEs are costly. ACEs-related health consequences cost an estimated economic burden of $748 billion annually in Bermuda, Canada, and the United States. 8
ACEs can have lasting effects on health and well-being in childhood and life opportunities well into adulthood. 9 Life opportunities include things like education and job potential. These experiences can increase the risks of injury, sexually transmitted infections, and involvement in sex trafficking. They can also increase risks for maternal and child health problems including teen pregnancy, pregnancy complications, and fetal death. Also included are a range of chronic diseases and leading causes of death, such as cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and suicide. 1 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
ACEs and associated social determinants of health, such as living in under-resourced or racially segregated neighborhoods, can cause toxic stress. Toxic stress, or extended or prolonged stress, from ACEs can negatively affect children’s brain development, immune systems, and stress-response systems. These changes can affect children’s attention, decision-making, and learning. 18
Children growing up with toxic stress may have difficulty forming healthy and stable relationships. They may also have unstable work histories as adults and struggle with finances, jobs, and depression throughout life. 18 These effects can also be passed on to their own children. 19 20 21 Some children may face further exposure to toxic stress from historical and ongoing traumas. These historical and ongoing traumas refer to experiences of racial discrimination or the impacts of poverty resulting from limited educational and economic opportunities. 1 6
Adverse childhood experiences can be prevented. Certain factors may increase or decrease the risk of experiencing adverse childhood experiences.
Preventing adverse childhood experiences requires understanding and addressing the factors that put people at risk for or protect them from violence.
Creating safe, stable, nurturing relationships and environments for all children can prevent ACEs and help all children reach their full potential. We all have a role to play.
- Merrick MT, Ford DC, Ports KA, et al. Vital Signs: Estimated Proportion of Adult Health Problems Attributable to Adverse Childhood Experiences and Implications for Prevention — 25 States, 2015–2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019;68:999-1005. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6844e1 .
- Cain KS, Meyer SC, Cummer E, Patel KK, Casacchia NJ, Montez K, Palakshappa D, Brown CL. Association of Food Insecurity with Mental Health Outcomes in Parents and Children. Science Direct. 2022; 22:7; 1105-1114. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2022.04.010 .
- Smith-Grant J, Kilmer G, Brener N, Robin L, Underwood M. Risk Behaviors and Experiences Among Youth Experiencing Homelessness—Youth Risk Behavior Survey, 23 U.S. States and 11 Local School Districts. Journal of Community Health. 2022; 47: 324-333.
- Experiencing discrimination: Early Childhood Adversity, Toxic Stress, and the Impacts of Racism on the Foundations of Health | Annual Review of Public Health https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-publhealth-090419-101940 .
- Sedlak A, Mettenburg J, Basena M, et al. Fourth national incidence study of child abuse and neglect (NIS-4): Report to Congress. Executive Summary. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health an Human Services, Administration for Children and Families.; 2010.
- Font S, Maguire-Jack K. Pathways from childhood abuse and other adversities to adult health risks: The role of adult socioeconomic conditions. Child Abuse Negl. 2016;51:390-399.
- Swedo EA, Aslam MV, Dahlberg LL, et al. Prevalence of Adverse Childhood Experiences Among U.S. Adults — Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2011–2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2023;72:707–715. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7226a2 .
- Bellis, MA, et al. Life Course Health Consequences and Associated Annual Costs of Adverse Childhood Experiences Across Europe and North America: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Public Health 2019.
- Adverse Childhood Experiences During the COVID-19 Pandemic and Associations with Poor Mental Health and Suicidal Behaviors Among High School Students — Adolescent Behaviors and Experiences Survey, United States, January–June 2021 | MMWR
- Hillis SD, Anda RF, Dube SR, Felitti VJ, Marchbanks PA, Marks JS. The association between adverse childhood experiences and adolescent pregnancy, long-term psychosocial consequences, and fetal death. Pediatrics. 2004 Feb;113(2):320-7.
- Miller ES, Fleming O, Ekpe EE, Grobman WA, Heard-Garris N. Association Between Adverse Childhood Experiences and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes. Obstetrics & Gynecology . 2021;138(5):770-776. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000004570 .
- Sulaiman S, Premji SS, Tavangar F, et al. Total Adverse Childhood Experiences and Preterm Birth: A Systematic Review. Matern Child Health J . 2021;25(10):1581-1594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-021-03176-6 .
- Ciciolla L, Shreffler KM, Tiemeyer S. Maternal Childhood Adversity as a Risk for Perinatal Complications and NICU Hospitalization. Journal of Pediatric Psychology . 2021;46(7):801-813. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpepsy/jsab027 .
- Mersky JP, Lee CP. Adverse childhood experiences and poor birth outcomes in a diverse, low-income sample. BMC pregnancy and childbirth. 2019;19(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-019-2560-8 .
- Reid JA, Baglivio MT, Piquero AR, Greenwald MA, Epps N. No youth left behind to human trafficking: Exploring profiles of risk. American journal of orthopsychiatry. 2019;89(6):704.
- Diamond-Welch B, Kosloski AE. Adverse childhood experiences and propensity to participate in the commercialized sex market. Child Abuse & Neglect. 2020 Jun 1;104:104468.
- Shonkoff, J. P., Garner, A. S., Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health, Committee on Early Childhood, Adoption, and Dependent Care, & Section on Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics (2012). The lifelong effects of early childhood adversity and toxic stress. Pediatrics, 129(1), e232–e246. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-2663
- Narayan AJ, Kalstabakken AW, Labella MH, Nerenberg LS, Monn AR, Masten AS. Intergenerational continuity of adverse childhood experiences in homeless families: unpacking exposure to maltreatment versus family dysfunction. Am J Orthopsych. 2017;87(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1037/ort0000133 .
- Schofield TJ, Donnellan MB, Merrick MT, Ports KA, Klevens J, Leeb R. Intergenerational continuity in adverse childhood experiences and rural community environments. Am J Public Health. 2018;108(9):1148-1152. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2018.304598 .
- Schofield TJ, Lee RD, Merrick MT. Safe, stable, nurturing relationships as a moderator of intergenerational continuity of child maltreatment: a meta-analysis. J Adolesc Health. 2013;53(4 Suppl):S32-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2013.05.004 .
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
ACEs can have a tremendous impact on lifelong health and opportunity. CDC works to understand ACEs and prevent them.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Include your main title, running title (often a shortened version of your main title), author's name, course name, and semester. 3. Compile your results. Divide the paper into logical sections determined by the type of paper you are writing.
Preventing Chronic Disease (PCD) is a peer-reviewed electronic journal established by the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. PCD provides an open exchange of information and knowledge among researchers, practitioners, policy makers, and others who strive to improve the health of the public through chronic disease prevention.
After you get enough feedback and decide on the journal you will submit to, the process of real writing begins. Copy your outline into a separate file and expand on each of the points, adding data and elaborating on the details. When you create the first draft, do not succumb to the temptation of editing.
Step 2: Develop a structure and outline. With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it's time to move on to planning your actual research paper. It might sound obvious, but it's really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper.
The aim of your study as stated in the article is the same as the aim formulated in your study protocol (don't forget - every research project should have a written protocol before starting!). It is helpful to choose one formulation for your objective, and use the same one throughout the whole paper, i.e. in the introduction, the results ...
Example: BODY PARAGRAPH 1. First point. Sub-point. Sub-point of sub-point 1. Essentially the same as the alphanumeric outline, but with the text written in full sentences rather than short points. Example: First body paragraph of the research paper. First point of evidence to support the main argument.
2. ]. In this issue, after an introductory paper by Kotz et al, Kotz and Cals publish the first of a series of monthly compact one-page papers, each highlighting an essential step in preparing and writing a research paper. This series, containing a total of 12 one-pagers, originates from a PhD student course organized at Maastricht University ...
1. Choose your topic. Choose a topic that interests you. Writing your research paper will be so much more pleasant with a topic that you actually want to know more about. Your interest will show in the way you write and effort you put into the paper. Consider these issues when coming up with a topic:
The present article, essentially based on TA Lang's guide for writing a scientific paper [ 1 ], will summarize the steps involved in the process of writing a scientific report and in increasing the likelihood of its acceptance. Figure 1. The Edwin Smith Papyrus (≈3000 BCE) Figure 2.
This paper provides advice how to prevent or treat this condition. Methods: Prepare your manuscript following the IMRaD principle (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion), with every part supporting the key message. When writing, be concise. Clearly state your methods here, while data belong to Results.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
This section presents an extensive array of disease research paper topics, divided into ten categories to guide your selection process. 1. Infectious Diseases. The impact of COVID-19 on global health systems. The role of vaccination in the eradication of polio.
You may read this TIP Sheet from start to finish before you begin your paper, or skip to the steps that are causing you the most grief. 1. Choosing a topic: Interest, information, and focus. Your job will be more pleasant, and you will be more apt to retain information if you choose a topic that holds your interest.
Researching a Disorder. By. , MD, California Association of Long Term Care Medicine. When a disorder is first diagnosed, the doctor or other health care professional often gives a handout that summarizes key points of information. (See also Introduction to Making the Most of Health Care .) If people want to learn more about their disorder, many ...
Follow these points to create an outline of the research: Identify the main points: These are the arguments or topics that are crucial to your research. List them in the order you plan to address them. Keep solid sub-points and supporting evidence: For each main point, jot down sub-points or examples that support it.
Title of 10-12 words reflecting the content of your essay, formatted in APA, AMA, or Harvard referencing styles. Write and double-space the title, your name, and the name of the college. Create a page header and include the running head, which should be in capital letters. The topic of the essay.
Research Proposal. The research proposal has much in common with the research paper. The proposal asks a question or poses a hypothesis that can be tested experimentally. There is no standard format for proposals, but it is important to conform to the guidelines laid down by the funding agency or organization.
Write down all the ideas you want to include or discuss. 3. Gather information. Gather notes, resources and references that you will need to support your content. Also, complete any necessary research or investigations. Each main idea should have two or more supporting topics.
Disease is a phenomenon that appears to have struck people globally at all times. However, the conceptions of what disease is have varied with time and place. This research paper gives an overview over various conceptions of disease and highlights what is at stake in the debates on the concept of disease.
Point 4. Finally, describe in your essay on disease the ways of preventing and treating it. Certainly, if you want to amaze your tutor with the essay on disease, this part of the paper should be based on the most up-to-date facts. If you need more ideas for your essay on disease, make use of the following links: essays on alcoholism and an ...
In this paper, Alzheimer's disease will be delved into, investigated and dissected. This will include all that is known about the disease as much of it is unknown still, despite increasing efforts from the medical community to uncover its origin. The disease's causes, symptoms and stages will be discussed and illuminated.
The risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, including myocardial infarction and stroke, is up to twice as high among persons with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection as in the ...
The global burden of disease attributable to high body mass index in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study. PLoS Med. 17 , e1003198 (2020).
As there is currently no cure for Alzheimer's disease, previous research shows early diagnosis of the condition can help with treating symptoms and slowing disease progression.. The researchers ...
New method to reveal what drives brain diseases. Scripps Research scientists develop CRISPR screen technology to determine disease mechanism from tissues with accelerated speed. May 20, 2024. LA JOLLA, CA — The brain is often referred to as a "black box"—one that's difficult to peer inside and determine what's happening at any given ...
New method to reveal what drives brain diseases Date: May 20, 2024 Source: Scripps Research Institute Summary: The brain is often referred to as a 'black box'-- one that's difficult to peer inside ...
Dementia is the sixth leading cause of death in the United States, driving many people to search for ways to prevent cognitive decline. In 2015, Dr. Martha Clare Morris and colleagues at Rush University Medical Center and the Harvard Chan School of Public Health published two papers introducing the MIND diet.
When you write a thesis, dissertation, or research paper, you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to: Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context; Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
Estimates show up to 1.9 million heart disease cases and 21 million depression cases potentially could have been avoided by preventing ACEs. 1. Some people are at greater risk of experiencing one or more ACEs than others. While all children are at risk of ACEs, numerous studies show inequities in such experiences. ...