Press ESC to close

A Comprehensive Guide to Writing a Research Proposal in English Literature
- backlinkworks
- Writing Articles & Reviews
- September 18, 2023

A Comprehensive Guide to writing a Research Proposal in English Literature
Introduction.
A research proposal is an important step in the process of conducting research in any field, including English literature. IT serves as a roadmap for your study, outlining the objectives, methods, and potential outcomes of your research. In this guide, we will take you through the steps involved in writing a research proposal specifically for English literature.
1. Choose a Topic
Before you can begin writing a research proposal, you need to choose a topic that interests you and aligns with your research interests. Consider the broad areas of English literature that intrigue you and start narrowing down your focus. IT ‘s essential to select a topic that is feasible within the scope of your study and has enough existing literature to support your research.
2. Conduct a Literature Review
Once you have chosen a topic, conduct a thorough literature review to gain an understanding of the existing research in your chosen area. This will help you identify any gaps in the literature that your research can fill. Look for scholarly articles, books, and other relevant sources that provide insights and theories related to your topic.
3. Define the Research Questions or Objectives
Based on your literature review, define the research questions or objectives that your study aims to address. These questions should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Clearly state the purpose of your research and how IT intends to contribute to the existing body of knowledge in English literature.
4. Develop a Methodology
Outline the methodology you will use to carry out your research. This includes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques. Depending on the nature of your study, you may choose qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods approaches. Justify your choice of methodology and explain how IT aligns with your research questions and objectives.
5. Create a Research Timeline
A research proposal should include a timeline or schedule that outlines the various stages of your research and the estimated completion time for each. This will help you manage your time effectively and stay on track throughout the research process. Be realistic when setting deadlines and allow for some flexibility in case unexpected issues arise.
6. Consider Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are essential in any research study. Consider whether your research may involve human subjects and whether you need to obtain approval from an ethics committee. Ensure that your research complies with ethical guidelines and respect the privacy and confidentiality of your participants, if applicable.
7. Write the Proposal
Now that you have gathered all the necessary information, IT ‘s time to write your research proposal. The structure of a research proposal generally includes an introduction, literature review, research questions or objectives, methodology, timeline, and references. Ensure that your proposal is well-organized, concise, and coherent. Use clear and academic language to convey your ideas effectively.
writing a research proposal in English literature requires a systematic approach and careful consideration of the various elements involved. By choosing an interesting topic, conducting a thorough literature review, defining your research questions, developing a methodology, creating a research timeline, and considering ethical considerations, you can create a comprehensive research proposal that lays the foundation for your study.
1. What is the purpose of a research proposal?
A research proposal outlines the objectives, methods, and potential outcomes of a research study. IT serves as a roadmap for the research process and helps in obtaining approval for the study.
2. How long should a research proposal be?
The length of a research proposal may vary, but IT is generally recommended to be around 1500-2000 words. However, IT is essential to check the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency you are submitting your proposal to.
3. Can I change my research topic after writing the proposal?
While IT is possible to change your research topic after writing the proposal, IT is advisable to consult with your supervisor or mentor before making any significant changes. Changing the topic may require substantial modifications to the proposal.
4. Do I need to include a literature review in my research proposal?
Yes, a research proposal should include a literature review as IT demonstrates your familiarity with the existing research in your chosen area and helps justify the need for your study.
5. How should I format my research proposal?
The formatting requirements for research proposals may vary depending on the institution or funding agency. However, IT is generally recommended to follow a standardized format, include proper citations, and use clear and academic language.
Adobe Dimension: Revolutionizing 3D Design and Visual Storytelling
Exploring the features and benefits of the tokoo theme for e-commerce websites.

Recent Posts
- Driving Organic Growth: How a Digital SEO Agency Can Drive Traffic to Your Website
- Mastering Local SEO for Web Agencies: Reaching Your Target Market
- The Ultimate Guide to Unlocking Powerful Backlinks for Your Website
- SEO vs. Paid Advertising: Finding the Right Balance for Your Web Marketing Strategy
- Discover the Secret Weapon for Local SEO Success: Local Link Building Services
Popular Posts

Shocking Secret Revealed: How Article PHP ID Can Transform Your Website!

Unlocking the Secrets to Boosting Your Alexa Rank, Google Pagerank, and Domain Age – See How You Can Dominate the Web!

Uncovering the Top Secret Tricks for Mastering SPIP PHP – You Won’t Believe What You’re Missing Out On!

The Ultimate Collection of Free Themes for Google Sites

Discover the Shocking Truth About Your Website’s Ranking – You Won’t Believe What This Checker Reveals!
Explore topics.
- Backlinks (2,425)
- Blog (2,744)
- Computers (5,318)
- Digital Marketing (7,741)
- Internet (6,340)
- Website (4,705)
- Wordpress (4,705)
- Writing Articles & Reviews (4,208)
English and Comparative Literary Studies
Sample dissertation proposal.
Below is an example of a successful MA dissertation proposal. Note particularly the robust referencing, and the way in which the author has already done preparatory work in the field so that clear areas of critical enquiry have already been formulated.
Modernist Poetics and the Acquisition of the Other Tongue
I will reconsider the role that multilingualism plays in modernist poetry, and particularly Ezra Pound’s, by moving away from a text-based model – in which the poem is understood primarily as translation, appropriation or montage of another language’s representative texts – and towards a more author-centric one, in which the poem documents the lived experience of knowing multiple languages, each of which transcends the finite set of words and texts that its author knows. I hope that my work will extend Robert Stark’s recent assertion that Pound acquired poetic style as if it were a foreign language, but by paying attention to the more literal encounters with foreign languages that make this simile possible. However, in contrast to Stark’s model of ‘apprenticeship’, Steven Yao has argued that modernism marked the point at which mastering the source language stopped being a prerequisite for a literary translator: thus, the different ways in which Pound translated or incorporated Chinese texts into English works over the course of his career, or used original ‘handy language’ in Italian alongside quotations, may represent different heuristic approaches to a code that still remained somehow impenetrable. ‘Barbarism and onomatopoeia’, rather than forming the comfortable pair of terms sometimes used by Stark, might define a driving tension in Pound’s verse practice, between seeing another language as pure sound and as the product of another culture incompletely understood.
Mutlu Konuk Blasing’s Lyric Poetry will be an important source: although she focuses almost exclusively on the role of the mother tongue, and uses it to justify lyric’s untranslatability, many of the phenomena which she associates with first language acquisition, such as the delay in recognising phonemes, are also relevant to second language acquisition. I also hope to move beyond Blasing’s cognitive and psychoanalytic approaches, to position Pound within a broader cultural history of language acquisition theory: texts to investigate may include the prose treatises by Dante that he admired, and contemporary reflections on language-learning by Leo Spitzer. I expect to offer a reading of Cantos LXXII and LXXIII (perhaps alongside T S Eliot’s early French poems) in light of this investigation, as possible oversights in Blasing’s argument.
Both Blasing’s and Stark’s monographs are bound up in questions of genre definition which deserve further consideration. I intend to develop the arguments of those critics, such as Simon Jarvis, who have questioned whether Blasing’s arguments define lyric poetry alone. How might language acquisition also be important for a definition of epic, especially in light of its traditional association with nation-building and Wai Chee Dimock’s recent vision of the genre as a carrier of foreign lexis? If, for Blasing, lyric ‘dramatises’ the struggle to enter a language-speaking community, is it more fully dramatised in a text such as Pound’s Elektra, where traumatic experience is manifested in a conflation of American vernacular and untranslated Greek?
Here, it may be fruitful to compare Pound’s choral dramas to Eliot’s: Murder in the Cathedral, for example, updates English vernacular drama, but by incorporating a ‘babbling’ chorus who imitate classical tragedy. While I expect the changes in Pound’s practice over the course of his career to provide the structure for my final project, I look forward to paying attention to points of comparison with other, less canonical modernists. These could include Hope Mirrlees’s use of montage to search for a ‘holophrase’ in Paris; Basil Bunting’s insistence on a regional vernacular, but against a backdrop of international cultural references; and the artificial languages of Futurist and Dada sound art, which work both to reject subjectivity and forge international communities.
Critical Bibliography
Arrowsmith, Richard Rupert, Modernism and the Museum: Asian, African and Pacific Art and the London Avant-Garde (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010).
(ed.) Bates, Catherine, The Cambridge Companion to the Epic (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010) [essays by Freccero, Whittier-Ferguson and Merchant].
Blasing, Mutlu Konuk, Lyric Poetry: The Pleasure and the Pain of Words (Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press, 2007).
Dimock, Wai Chee, Through Other Continents: American Literature Across Deep Time (Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press, 2006).
Ellis, Rod, Second Language Acquisition (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997).
Hart, Matthew, Nations of Nothing but Poetry: Modernism, Transnationalism and Synthetic Vernacular Writing (Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, 2010).
Jarvis, Simon, ‘The melodics of long poems’, Textual Practice 24.4 (2010).
Kenner, Hugh, The Pound Era (Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press, 1971).
Moody, A David, Ezra Pound: Poet, I: The Young Genius, 1885-1920 (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007).
North, Michael, The Dialect of Modernism: Race, Language and Twentieth-Century Literature (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998).
Patterson, Ian, ‘Time, Free Verse, and the Gods of Modernism’ in Tradition, Translation, Trauma: The Classic and the Modern, eds. Jan Parker and Timothy Mathews (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2011) [and other essays in this volume].
Scott, Clive, Literary Translation and the Rediscovery of Reading (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012) [and earlier works by Scott].
Spitzer, Leo, ‘Learning Turkish’, tr. Tülay Atak, PMLA 126.3 (2011).
Stark, Robert, Ezra Pound’s Early Verse and Lyric Tradition: A Jongleur’s Apprenticeship (Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2012).
- Postgraduate
Research degrees
- Examples of Research proposals
- Apply for 2024
- Find a course
- Accessibility
Examples of research proposals
How to write your research proposal, with examples of good proposals.
Research proposals
Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use.
We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
In your proposal, please tell us if you have an interest in the work of a specific academic at York St John. You can get in touch with this academic to discuss your proposal. You can also speak to one of our Research Leads. There is a list of our Research Leads on the Apply page.
When you write your proposal you need to:
- Highlight how it is original or significant
- Explain how it will develop or challenge current knowledge of your subject
- Identify the importance of your research
- Show why you are the right person to do this research
- Research Proposal Example 1 (DOC, 49kB)
- Research Proposal Example 2 (DOC, 0.9MB)
- Research Proposal Example 3 (DOC, 55.5kB)
- Research Proposal Example 4 (DOC, 49.5kB)
Subject specific guidance
- Writing a Humanities PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- Writing a Creative Writing PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- About the University
- Our culture and values
- Academic schools
- Academic dates
- Press office
Our wider work
- Business support
- Work in the community
- Donate or support
Connect with us
York St John University
Lord Mayor’s Walk
01904 624 624
York St John London Campus
6th Floor Export Building
1 Clove Crescent
01904 876 944
- Policies and documents
- Module documents
- Programme specifications
- Quality gateway
- Admissions documents
- Access and Participation Plan
- Freedom of information
- Accessibility statement
- Modern slavery and human trafficking statement
© York St John University 2024
Colour Picker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Dui id ornare arcu odio.
Felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis ipsum. Et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Faucibus pulvinar elementum integer enim neque volutpat ac. Hac habitasse platea dictumst vestibulum rhoncus.
Nec ullamcorper sit amet risus nullam eget felis eget. Eget felis eget nunc lobortis mattis aliquam faucibus purus.

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Student blogs and videos
- Why Cambridge
- Qualifications directory
- How to apply
- Fees and funding
- Frequently asked questions
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Visiting the University
- Term dates and calendars
- Video and audio
- Find an expert
- Publications
- International Cambridge
- Public engagement
- Giving to Cambridge
- For current students
- For business
- Colleges & departments
- Libraries & facilities
- Museums & collections
- Email & phone search
Faculty of English
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Visiting Scholars
- Academic Staff
- Research Staff
- Postgraduate Students
- Emeritus, Visiting and Honorary Fellows
- Administrative Staff
- Faculty Research
- Research Map
- English Handwriting Online
- Scriptorium
- The Tennysons Archive
- Transkills for English
- Troilus & Criseyde: Translation & Commentary
- Directors of Studies
- Teaching Officers & Research Fellows
- Faculty Computing
- BBC Short Story
- Postgraduate Admissions
Research Proposals
- the research topic briefly outline the area and topic of your research.
- the research context relate your proposed research to other work in its field or related fields, and indicate in what ways your research will differ; you might mention monographs on the subject, as well as important theoretical models or methodological exemplars. This is a chance to show your understanding of the background against which your research will be defined.
- the contribution you will make this is your chance to show how you have arrived at your position and recognised the need for your research, and what it is that makes it both new and important; you should indicate what areas and debates it will have an impact on, what methodological example it sets (if appropriate) – in short how it contributes to knowledge and to the practice of our subject. Give examples of the sort of evidence you might consider, and of the questions it might help you to raise. Show that you are already thinking about the area in detail and not only in outline.
- your methods in some cases there will be little to say here, but if there is something striking about your methodology, you should explain it.
- the sources and resources you will use you should delimit your field of enquiry, showing where the project begins and ends; in certain cases, Cambridge will have unique collections and resources of central relevance to your project, and you should mention these.
- how the project will develop you might indicate some of the possible ways in which the project could develop, perhaps by giving a broader or narrower version depending on what materials and issues you uncover
You should ask yourself how your work might change the present state of scholarship in your field, and whether the topic is well suited to the resources provided at Cambridge. Even for MPhil courses we generally aim to admit not just those who propose a sensible topic, but those who have the potential to modify the present paradigms of research in their field. Most students, though, refine their research topics after they arrive in the light of what they discover or of advice from their supervisor, so you need not feel that you are inscribing your future in tablets of stone as you compose your proposal.
You may find it helpful to look at the following examples of successful research proposals.
It is vital that you show that your research is necessary. It is not enough that it happens to interest you. You should make clear that it will be of use and interest to others working in your field, or on a particular author, or indeed in neighbouring fields. You should show how your work will make a contribution to knowledge and to the practice of our subject.
Related Links
- MPhil in Anglo-Saxon, Norse, and Celtic
- MPhil in Digital Humanities
- Part-time PhD
- MSt in Creative Writing
- MSt in Writing for Performance
- MSt in Crime and Thriller Writing
- Funding for home students
- Funding for overseas students
- Research proposals
- Equality, Diversity, and Inclusivity

© 2016 University of Cambridge
- University A-Z
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Terms and conditions
- Spotlight on...
- About research at Cambridge

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Academic Proposals

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This resource introduces the genre of academic proposals and provides strategies for developing effective graduate-level proposals across multiple contexts.
Introduction
An important part of the work completed in academia is sharing our scholarship with others. Such communication takes place when we present at scholarly conferences, publish in peer-reviewed journals, and publish in books. This OWL resource addresses the steps in writing for a variety of academic proposals.
For samples of academic proposals, click here .
Important considerations for the writing process
First and foremost, you need to consider your future audience carefully in order to determine both how specific your topic can be and how much background information you need to provide in your proposal. While some conferences and journals may be subject-specific, most will require you to address an audience that does not conduct research on the same topics as you. Conference proposal reviewers are often drawn from professional organization members or other attendees, while journal proposals are typically reviewed by the editorial staff, so you need to ensure that your proposal is geared toward the knowledge base and expectations of whichever audience will read your work.
Along those lines, you might want to check whether you are basing your research on specific prior research and terminology that requires further explanation. As a rule, always phrase your proposal clearly and specifically, avoid over-the-top phrasing and jargon, but do not negate your own personal writing style in the process.
If you would like to add a quotation to your proposal, you are not required to provide a citation or footnote of the source, although it is generally preferred to mention the author’s name. Always put quotes in quotation marks and take care to limit yourself to at most one or two quotations in the entire proposal text. Furthermore, you should always proofread your proposal carefully and check whether you have integrated details, such as author’s name, the correct number of words, year of publication, etc. correctly.
Methodology is often a key factor in the evaluation of proposals for any academic genre — but most proposals have such a small word limit that writers find it difficult to adequately include methods while also discussing their argument, background for the study, results, and contributions to knowledge. It's important to make sure that you include some information about the methods used in your study, even if it's just a line or two; if your proposal isn't experimental in nature, this space should instead describe the theory, lens, or approach you are taking to arrive at your conclusions.
Reasons proposals fail/common pitfalls
There are common pitfalls that you might need to improve on for future proposals.
The proposal does not reflect your enthusiasm and persuasiveness, which usually goes hand in hand with hastily written, simply worded proposals. Generally, the better your research has been, the more familiar you are with the subject and the more smoothly your proposal will come together.
Similarly, proposing a topic that is too broad can harm your chances of being accepted to a conference. Be sure to have a clear focus in your proposal. Usually, this can be avoided by more advanced research to determine what has already been done, especially if the proposal is judged by an important scholar in the field. Check the names of keynote speakers and other attendees of note to avoid repeating known information or not focusing your proposal.
Your paper might simply have lacked the clear language that proposals should contain. On this linguistic level, your proposal might have sounded repetitious, have had boring wording, or simply displayed carelessness and a lack of proofreading, all of which can be remedied by more revisions. One key tactic for ensuring you have clear language in your proposal is signposting — you can pick up key phrases from the CFP, as well as use language that indicates different sections in academic work (as in IMRAD sections from the organization and structure page in this resource). This way, reviewers can easily follow your proposal and identify its relatedness to work in the field and the CFP.
Conference proposals
Conference proposals are a common genre in graduate school that invite several considerations for writing depending on the conference and requirements of the call for papers.
Beginning the process
Make sure you read the call for papers carefully to consider the deadline and orient your topic of presentation around the buzzwords and themes listed in the document. You should take special note of the deadline and submit prior to that date, as most conferences use online submission systems that will close on a deadline and will not accept further submissions.
If you have previously spoken on or submitted a proposal on the same topic, you should carefully adjust it specifically for this conference or even completely rewrite the proposal based on your changing and evolving research.
The topic you are proposing should be one that you can cover easily within a time frame of approximately fifteen to twenty minutes. You should stick to the required word limit of the conference call. The organizers have to read a large number of proposals, especially in the case of an international or interdisciplinary conference, and will appreciate your brevity.
Structure and components
Conference proposals differ widely across fields and even among individual conferences in a field. Some just request an abstract, which is written similarly to any other abstract you'd write for a journal article or other publication. Some may request abstracts or full papers that fit into pre-existing sessions created by conference organizers. Some request both an abstract and a further description or proposal, usually in cases where the abstract will be published in the conference program and the proposal helps organizers decide which papers they will accept.
If the conference you are submitting to requires a proposal or description, there are some common elements you'll usually need to include. These are a statement of the problem or topic, a discussion of your approach to the problem/topic, a discussion of findings or expected findings, and a discussion of key takeaways or relevance to audience members. These elements are typically given in this order and loosely follow the IMRAD structure discussed in the organization and structure page in this resource.
The proportional size of each of these elements in relation to one another tends to vary by the stage of your research and the relationship of your topic to the field of the conference. If your research is very early on, you may spend almost no time on findings, because you don't have them yet. Similarly, if your topic is a regular feature at conferences in your field, you may not need to spend as much time introducing it or explaining its relevance to the field; however, if you are working on a newer topic or bringing in a topic or problem from another discipline, you may need to spend slightly more space explaining it to reviewers. These decisions should usually be based on an analysis of your audience — what information can reviewers be reasonably expected to know, and what will you have to tell them?
Journal Proposals
Most of the time, when you submit an article to a journal for publication, you'll submit a finished manuscript which contains an abstract, the text of the article, the bibliography, any appendices, and author bios. These can be on any topic that relates to the journal's scope of interest, and they are accepted year-round.
Special issues , however, are planned issues of a journal that center around a specific theme, usually a "hot topic" in the field. The editor or guest editors for the special issue will often solicit proposals with a call for papers (CFP) first, accept a certain number of proposals for further development into article manuscripts, and then accept the final articles for the special issue from that smaller pool. Special issues are typically the only time when you will need to submit a proposal to write a journal article, rather than submitting a completed manuscript.
Journal proposals share many qualities with conference proposals: you need to write for your audience, convey the significance of your work, and condense the various sections of a full study into a small word or page limit. In general, the necessary components of a proposal include:
- Problem or topic statement that defines the subject of your work (often includes research questions)
- Background information (think literature review) that indicates the topic's importance in your field as well as indicates that your research adds something to the scholarship on this topic
- Methodology and methods used in the study (and an indication of why these methods are the correct ones for your research questions)
- Results or findings (which can be tentative or preliminary, if the study has not yet been completed)
- Significance and implications of the study (what will readers learn? why should they care?)
This order is a common one because it loosely follows the IMRAD (introduction, methods, results and discussion) structure often used in academic writing; however, it is not the only possible structure or even always the best structure. You may need to move these elements around depending on the expectations in your field, the word or page limit, or the instructions given in the CFP.
Some of the unique considerations of journal proposals are:
- The CFP may ask you for an abstract, a proposal, or both. If you need to write an abstract, look for more information on the abstract page. If you need to write both an abstract and a proposal, make sure to clarify for yourself what the difference is. Usually the proposal needs to include more information about the significance, methods, and/or background of the study than will fit in the abstract, but often the CFP itself will give you some instructions as to what information the editors are wanting in each piece of writing.
- Journal special issue CFPs, like conference CFPs, often include a list of topics or questions that describe the scope of the special issue. These questions or topics are a good starting place for generating a proposal or tying in your research; ensuring that your work is a good fit for the special issue and articulating why that is in the proposal increases your chances of being accepted.
- Special issues are not less valuable or important than regularly scheduled issues; therefore, your proposal needs to show that your work fits and could readily be accepted in any other issue of the journal. This means following some of the same practices you would if you were preparing to submit a manuscript to a journal: reading the journal's author submission guidelines; reading the last several years of the journal to understand the usual topics, organization, and methods; citing pieces from this journal and other closely related journals in your research.

Book Proposals
While the requirements are very similar to those of conference proposals, proposals for a book ought to address a few other issues.
General considerations
Since these proposals are of greater length, the publisher will require you to delve into greater detail as well—for instance, regarding the organization of the proposed book or article.
Publishers generally require a clear outline of the chapters you are proposing and an explication of their content, which can be several pages long in its entirety.
You will need to incorporate knowledge of relevant literature, use headings and sub-headings that you should not use in conference proposals. Be sure to know who wrote what about your topic and area of interest, even if you are proposing a less scholarly project.
Publishers prefer depth rather than width when it comes to your topic, so you should be as focused as possible and further outline your intended audience.
You should always include information regarding your proposed deadlines for the project and how you will execute this plan, especially in the sciences. Potential investors or publishers need to know that you have a clear and efficient plan to accomplish your proposed goals. Depending on the subject area, this information can also include a proposed budget, materials or machines required to execute this project, and information about its industrial application.
Pre-writing strategies
As John Boswell (cited in: Larsen, Michael. How to Write a Book Proposal. Writers Digest Books , 2004. p. 1) explains, “today fully 90 percent of all nonfiction books sold to trade publishers are acquired on the basis of a proposal alone.” Therefore, editors and agents generally do not accept completed manuscripts for publication, as these “cannot (be) put into the usual channels for making a sale”, since they “lack answers to questions of marketing, competition, and production.” (Lyon, Elizabeth. Nonfiction Book Proposals Anybody Can Write . Perigee Trade, 2002. pp. 6-7.)
In contrast to conference or, to a lesser degree, chapter proposals, a book proposal introduces your qualifications for writing it and compares your work to what others have done or failed to address in the past.
As a result, you should test the idea with your networks and, if possible, acquire other people’s proposals that discuss similar issues or have a similar format before submitting your proposal. Prior to your submission, it is recommended that you write at least part of the manuscript in addition to checking the competition and reading all about the topic.
The following is a list of questions to ask yourself before committing to a book project, but should in no way deter you from taking on a challenging project (adapted from Lyon 27). Depending on your field of study, some of these might be more relevant to you than others, but nonetheless useful to reiterate and pose to yourself.
- Do you have sufficient enthusiasm for a project that may span years?
- Will publication of your book satisfy your long-term career goals?
- Do you have enough material for such a long project and do you have the background knowledge and qualifications required for it?
- Is your book idea better than or different from other books on the subject? Does the idea spark enthusiasm not just in yourself but others in your field, friends, or prospective readers?
- Are you willing to acquire any lacking skills, such as, writing style, specific terminology and knowledge on that field for this project? Will it fit into your career and life at the time or will you not have the time to engage in such extensive research?
Essential elements of a book proposal
Your book proposal should include the following elements:
- Your proposal requires the consideration of the timing and potential for sale as well as its potential for subsidiary rights.
- It needs to include an outline of approximately one paragraph to one page of prose (Larsen 6) as well as one sample chapter to showcase the style and quality of your writing.
- You should also include the resources you need for the completion of the book and a biographical statement (“About the Author”).
- Your proposal must contain your credentials and expertise, preferably from previous publications on similar issues.
- A book proposal also provides you with the opportunity to include information such as a mission statement, a foreword by another authority, or special features—for instance, humor, anecdotes, illustrations, sidebars, etc.
- You must assess your ability to promote the book and know the market that you target in all its statistics.
The following proposal structure, as outlined by Peter E. Dunn for thesis and fellowship proposals, provides a useful guide to composing such a long proposal (Dunn, Peter E. “Proposal Writing.” Center for Instructional Excellence, Purdue University, 2007):
- Literature Review
- Identification of Problem
- Statement of Objectives
- Rationale and Significance
- Methods and Timeline
- Literature Cited
Most proposals for manuscripts range from thirty to fifty pages and, apart from the subject hook, book information (length, title, selling handle), markets for your book, and the section about the author, all the other sections are optional. Always anticipate and answer as many questions by editors as possible, however.
Finally, include the best chapter possible to represent your book's focus and style. Until an agent or editor advises you to do otherwise, follow your book proposal exactly without including something that you might not want to be part of the book or improvise on possible expected recommendations.
Publishers expect to acquire the book's primary rights, so that they can sell it in an adapted or condensed form as well. Mentioning any subsidiary rights, such as translation opportunities, performance and merchandising rights, or first-serial rights, will add to the editor's interest in buying your book. It is enticing to publishers to mention your manuscript's potential to turn into a series of books, although they might still hesitate to buy it right away—at least until the first one has been a successful endeavor.
The sample chapter
Since editors generally expect to see about one-tenth of a book, your sample chapter's length should reflect that in these building blocks of your book. The chapter should reflect your excitement and the freshness of the idea as well as surprise editors, but do not submit part of one or more chapters. Always send a chapter unless your credentials are impeccable due to prior publications on the subject. Do not repeat information in the sample chapter that will be covered by preceding or following ones, as the outline should be designed in such a way as to enable editors to understand the context already.
How to make your proposal stand out
Depending on the subject of your book, it is advisable to include illustrations that exemplify your vision of the book and can be included in the sample chapter. While these can make the book more expensive, it also increases the salability of the project. Further, you might consider including outstanding samples of your published work, such as clips from periodicals, if they are well-respected in the field. Thirdly, cover art can give your potential publisher a feel for your book and its marketability, especially if your topic is creative or related to the arts.
In addition, professionally formatting your materials will give you an edge over sloppy proposals. Proofread the materials carefully, use consistent and carefully organized fonts, spacing, etc., and submit your proposal without staples; rather, submit it in a neat portfolio that allows easy access and reassembling. However, check the submission guidelines first, as most proposals are submitted digitally. Finally, you should try to surprise editors and attract their attention. Your hook, however, should be imaginative but inexpensive (you do not want to bribe them, after all). Make sure your hook draws the editors to your book proposal immediately (Adapted from Larsen 154-60).

- Future Students
- Parents and Families
Department of English
College of arts and sciences, ph.d. dissertation proposal guidelines.
The following has been adapted for the English Department from the Graduate School’s “Statement on Thesis/Dissertation Proposals.” Guidelines adapted for the Creative Dissertation Proposal Guidelines can be found here .
I. Introduction
A thesis proposal states a problem to be investigated and describes how the research will be performed and reported. Approval signifies that it meets the standards of the University of Rhode Island for the degree desired. Therefore, the preparation and writing of the thesis proposal are of utmost importance. Although the student is expected to seek guidance in the choice of topic and the method of solving the problem involved, responsibility for the proposal lies with the student who will, as far as possible, work independently and demonstrate the ability to plan and outline an acceptable research project. Adherence to the guidelines given below should assure the student that all information necessary for the satisfactory evaluation of the plans for master’s or doctoral research will be included in the proposal.
The thesis proposal should present the required information as concisely and clearly as possible. The ability to describe concisely a research problem and methodology is one of the skills that the proposal process is designed to develop. Therefore, all thesis/dissertation proposals are limited in length to the signature cover-sheet plus 15 or fewer double-spaced, numbered pages in a font size no smaller than 12 point . Proposals longer than this will not be accepted, however, appendices and references are not included in the 15-page limit . Proposals will also be returned for revision if they do not contain the appropriate sections described in the Contents section of this Statement on Thesis/Dissertation Proposals. Sufficient copies of the proposal must be provided to permit distribution to the Graduate School, Institutional Review Board or Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee if required (see Sec. III), department, major professor, thesis or doctoral committee, and the student.
III. Submission
Thesis proposals should be submitted before substantial research has been completed. Typically, it should be submitted before or during the first semester in which the student registers for research credits. In all cases, however, the proposal must be submitted at least one semester before the semester in which the thesis/dissertation itself is to be submitted and defended.
In the English Department, the Dissertation Proposal is submitted for review by the student’s entire dissertation committee once the written and oral comprehensive exams are completed. The student meets with the committee for the purpose of discussing the proposal and the first stages of the dissertation. Then , all copies of the thesis proposal must be signed by the members of the student’s doctoral committee, who thereby approve the proposal for forwarding by the student’s major professor via the Director of Graduate Studies to the Vice Provost for Graduate Studies, Research, and Outreach. The Vice Provost is charged with responsibility for review and approval or rejection of all proposals. Proposals that do not meet the standard of the Graduate School will be returned to the student for revision and resubmission. Approved proposals are returned to the department for distribution, with one copy retained in the student’s file at the Graduate School.
(Sections on “Research Involving Human Subjects” and “Research involving Vertebrate Animals” excluded here, but you may read them by going to the Grad School Webpage and consulting their Statement on the Ph.D. proposal.)
IV. Contents
Thesis Proposals shall contain the following sections, presented in the order shown:
A. Title of the Study
This is the title as the student conceives it at the time the proposal is submitted. It should be no more than 100 characters in length. As the research develops, various rephrasings of the title may prove better suited to the work. In such cases, the most satisfactory one will be used for the dissertation, the final formal report of the investigation. Please note that at that time a title abstract of 40 characters or less must be submitted.
B. Statement of the Problem
This section should be relatively short and sweet — a succinct introduction to your topic, thesis, and the questions that drive your project.
Limit the statement, if possible, to two or three sentences, and note in precise language exactly what is to be investigated. Here is where you introduce your object(s) of study and the principal question or questions you are bringing to it or them. To amplify the Statement of the Problem, it is usually desirable to list:
- The scope or limitations of the problem: e.g., what material will it include and why? Give some thought to the criteria by which you will limit the project, for instance, to a specific time period, geographical locale, genre of literature or film, a particular author or group of authors, a social group, or movement, or school of thought, etc.
- Either one or more hypotheses the research seeks to test or the objectives you expect to attain as a result of the study.
- The major assumptions that underlie both the study as a whole and the methodology you will be following. Note: you will be expanding on this in section D; just give a succinct introduction of the methodology here.
C. The justification for and Significance of the Study
Now you start to get into the substance of your proposal. You may run to a few pages in this section, and amplify on what you introduced in Section B.
This section of the proposal includes:
- A brief statement of the reasons for the selection of the problem: Is there, for instance, a gap in the existing scholarship on this problem? Alternatively, even if this is a topic that has been much discussed, will you be shedding new light on it by examining it in a new context, or bringing to bear a different theoretical framework, or juxtaposing it with other objects with which it has never been considered?
- The relation of the principal literature to the proposal: In the English Department, by “principal literature” we mean both the primary texts or object you plan to treat, as well as the secondary texts that have come to inform your approach to those primary texts. Why these texts? Why now? What is at stake? And what have you got to contribute to our understanding of them?
- An explanation of the study’s importance to the advancement of knowledge and its significance to the student: To show the importance of your study to the advancement of knowledge, you will need to show where that knowledge is now, and how you plan to extend, question, complement, challenge, or revolutionize it (etc).
- The problem selected should be substantial enough to constitute a good example of a report of a scholarly investigation. Completion of a project or several unrelated projects does not satisfy this requirement. At the Ph.D. level, the work should constitute a significant increase in the pool of knowledge.
D. Methodology or Procedures
Again–this is a substantive section of the Proposal. Another few pages.
This section describes the activities necessary to achieve the objectives. Methods should flow naturally from the problems and objectives.
The Graduate School defines methodology in terms of the study population; sampling design and procedures; tools, instruments, and timetables for data collection and testing; definition of terms and concepts. In the English Department, too, you will be expected to present a methodological plan for how your investigation will be carried out, which will necessarily involve a concise statement of the theoretical or critical frameworks most important to your project. Rather than a list of theorists’ or critics’ names, provide specific concepts or well-defined terms from these theorists, and explain how they inform the way you are approaching your problem. Even better, explain how you are intervening in the status quo already established by these existing critics or theorists. You should also give a sense of the kinds of critical activity you plan to carry out: will you do close readings of primary texts? If so, what kind? Will one or more chapters be devoted to a survey of existing scholarship? Will you be conducting archival research, and if so, where, and for what purpose? Does one section of your dissertation rely on your having completed another section first? Is there an interdisciplinary aspect to your project that requires a special methodological approach all its own? A brief, provisional chapter outline is appropriate in this section since it indicates the logic behind how you envision the organization of your material.
E. Resources Required
The last part of the thesis proposal is a statement of the resources needed for the successful completion of the study and an indication of their accessibility to the student proposing to use them. This may be a very brief section, where you summarize the primary and secondary texts necessary to your investigation, with the understanding that the full bibliography will be saved for an appendix. This is also the place to mention travel to archives or to visit any individuals who may be key to your project.
F. Literature Cited in the Proposal
Take note of the following concern of the Graduate School, a concern shared by the English Department:
The most persistent difficulty with thesis proposals is lack of evidence that a search of the literature took place in framing the problem to be studied. The absence of evidence that the scholarly literature in the field has been consulted might be due to one or more of the following reasons:
- That it was omitted because the student was not aware that it was required.
- That the student was unfamiliar with the library as a resource in developing the research proposal.
- That, having searched the literature of the field, the student found that the problem was unique, and therefore, could not be documented. If so, it is important to note where the literature stops and the proposed research starts, itself an intriguing scholarly problem.
- That the thesis problem has been provided “ready-made” as a spin-off from a larger study so that no literature search appeared to be needed. One might question the wisdom of thus isolating the student from the scholarly literature, however valid and important the research topic. (This seems to be directed more at faculty than at students.)
- Since you are limited to only 15 pages for the dissertation proposal, we recommend that you write “See Appendix A” for this section of the proposal, and place your Works Cited in that Appendix. That way you leave more room for the substance of the Proposal. In your “Works Cited,” we recommend that you make sub-divisions where appropriate. For instance, you may want to have a “primary” and a “secondary” list; or a list of “literature,” “film,” and the criticism pertaining to each; or if more than one historical period is covered, you may want to divide your bibliography by period, etc. Make your Works Cited as reflective of the logic of your project as possible.
G. Revised Proposals (not a section of your proposal)
If, as the research proceeds, a significant change in subject or methodology becomes necessary, a revised proposal should be submitted. Sometimes an abbreviated format can be used for such changes. The student or major professor should contact the Graduate School for assistance in such cases.
Literature Review Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Literature Review Template
If you’re working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a strong literature review chapter , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through an A-grade literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction . We start off by discussing the five core sections of a literature review chapter by unpacking our free literature review template . This includes:
- The literature review opening/ introduction section
- The theoretical framework (or foundation of theory)
- The empirical research
- The research gap
- The closing section
We then progress to the sample literature review (from an A-grade Master’s-level dissertation) to show how these concepts are applied in the literature review chapter. You can access the free resources mentioned in this video below.
PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Literature Review Example
Literature review example: frequently asked questions, is the sample literature review real.
Yes. The literature review example is an extract from a Master’s-level dissertation for an MBA program. It has not been edited in any way.
Can I replicate this literature review for my dissertation?
As we discuss in the video, every literature review will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your literature review to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a literature review here .
Where can I find more examples of literature reviews?
The best place to find more examples of literature review chapters would be within dissertation/thesis databases. These databases include dissertations, theses and research projects that have successfully passed the assessment criteria for the respective university, meaning that you have at least some sort of quality assurance.
The Open Access Thesis Database (OATD) is a good starting point.
How do I get the literature review template?
You can access our free literature review chapter template here .
Is the template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the template and you are free to use it as you wish.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

What will it take for you to guide me in my Ph.D research work?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
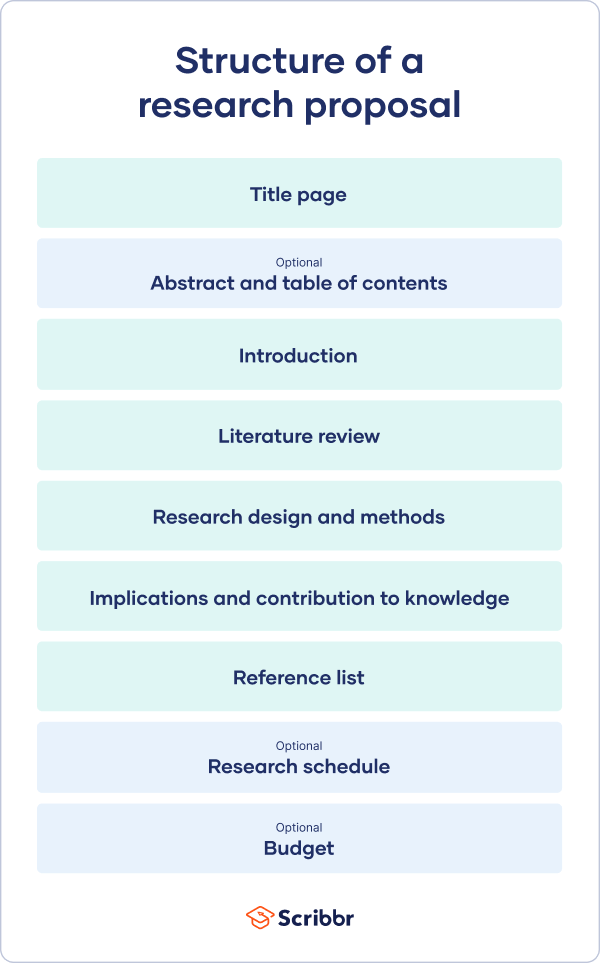
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
Thesis Proposal Sample Archive
Thesis proposals.
Examples of thesis proposals are included here in PDF format. Copies of theses completed in the M.A. in English & Writing Studies program can be accessed through the Pfau Library's CSUSB ScholarWorks database.
Because the Public & Professional Writing concentration is so new, we do not have a sample proposal for it at this time. Please work closely with your readers who can guide you in its construction.
17 Research Proposal Examples

A research proposal systematically and transparently outlines a proposed research project.
The purpose of a research proposal is to demonstrate a project’s viability and the researcher’s preparedness to conduct an academic study. It serves as a roadmap for the researcher.
The process holds value both externally (for accountability purposes and often as a requirement for a grant application) and intrinsic value (for helping the researcher to clarify the mechanics, purpose, and potential signficance of the study).
Key sections of a research proposal include: the title, abstract, introduction, literature review, research design and methods, timeline, budget, outcomes and implications, references, and appendix. Each is briefly explained below.
Watch my Guide: How to Write a Research Proposal
Get your Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
Research Proposal Sample Structure
Title: The title should present a concise and descriptive statement that clearly conveys the core idea of the research projects. Make it as specific as possible. The reader should immediately be able to grasp the core idea of the intended research project. Often, the title is left too vague and does not help give an understanding of what exactly the study looks at.
Abstract: Abstracts are usually around 250-300 words and provide an overview of what is to follow – including the research problem , objectives, methods, expected outcomes, and significance of the study. Use it as a roadmap and ensure that, if the abstract is the only thing someone reads, they’ll get a good fly-by of what will be discussed in the peice.
Introduction: Introductions are all about contextualization. They often set the background information with a statement of the problem. At the end of the introduction, the reader should understand what the rationale for the study truly is. I like to see the research questions or hypotheses included in the introduction and I like to get a good understanding of what the significance of the research will be. It’s often easiest to write the introduction last
Literature Review: The literature review dives deep into the existing literature on the topic, demosntrating your thorough understanding of the existing literature including themes, strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in the literature. It serves both to demonstrate your knowledge of the field and, to demonstrate how the proposed study will fit alongside the literature on the topic. A good literature review concludes by clearly demonstrating how your research will contribute something new and innovative to the conversation in the literature.
Research Design and Methods: This section needs to clearly demonstrate how the data will be gathered and analyzed in a systematic and academically sound manner. Here, you need to demonstrate that the conclusions of your research will be both valid and reliable. Common points discussed in the research design and methods section include highlighting the research paradigm, methodologies, intended population or sample to be studied, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures . Toward the end of this section, you are encouraged to also address ethical considerations and limitations of the research process , but also to explain why you chose your research design and how you are mitigating the identified risks and limitations.
Timeline: Provide an outline of the anticipated timeline for the study. Break it down into its various stages (including data collection, data analysis, and report writing). The goal of this section is firstly to establish a reasonable breakdown of steps for you to follow and secondly to demonstrate to the assessors that your project is practicable and feasible.
Budget: Estimate the costs associated with the research project and include evidence for your estimations. Typical costs include staffing costs, equipment, travel, and data collection tools. When applying for a scholarship, the budget should demonstrate that you are being responsible with your expensive and that your funding application is reasonable.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: A discussion of the anticipated findings or results of the research, as well as the potential contributions to the existing knowledge, theory, or practice in the field. This section should also address the potential impact of the research on relevant stakeholders and any broader implications for policy or practice.
References: A complete list of all the sources cited in the research proposal, formatted according to the required citation style. This demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the relevant literature and ensures proper attribution of ideas and information.
Appendices (if applicable): Any additional materials, such as questionnaires, interview guides, or consent forms, that provide further information or support for the research proposal. These materials should be included as appendices at the end of the document.
Research Proposal Examples
Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section.
1. Education Studies Research Proposals
See some real sample pieces:
- Assessment of the perceptions of teachers towards a new grading system
- Does ICT use in secondary classrooms help or hinder student learning?
- Digital technologies in focus project
- Urban Middle School Teachers’ Experiences of the Implementation of
- Restorative Justice Practices
- Experiences of students of color in service learning
Consider this hypothetical education research proposal:
The Impact of Game-Based Learning on Student Engagement and Academic Performance in Middle School Mathematics
Abstract: The proposed study will explore multiplayer game-based learning techniques in middle school mathematics curricula and their effects on student engagement. The study aims to contribute to the current literature on game-based learning by examining the effects of multiplayer gaming in learning.
Introduction: Digital game-based learning has long been shunned within mathematics education for fears that it may distract students or lower the academic integrity of the classrooms. However, there is emerging evidence that digital games in math have emerging benefits not only for engagement but also academic skill development. Contributing to this discourse, this study seeks to explore the potential benefits of multiplayer digital game-based learning by examining its impact on middle school students’ engagement and academic performance in a mathematics class.
Literature Review: The literature review has identified gaps in the current knowledge, namely, while game-based learning has been extensively explored, the role of multiplayer games in supporting learning has not been studied.
Research Design and Methods: This study will employ a mixed-methods research design based upon action research in the classroom. A quasi-experimental pre-test/post-test control group design will first be used to compare the academic performance and engagement of middle school students exposed to game-based learning techniques with those in a control group receiving instruction without the aid of technology. Students will also be observed and interviewed in regard to the effect of communication and collaboration during gameplay on their learning.
Timeline: The study will take place across the second term of the school year with a pre-test taking place on the first day of the term and the post-test taking place on Wednesday in Week 10.
Budget: The key budgetary requirements will be the technologies required, including the subscription cost for the identified games and computers.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: It is expected that the findings will contribute to the current literature on game-based learning and inform educational practices, providing educators and policymakers with insights into how to better support student achievement in mathematics.
2. Psychology Research Proposals
See some real examples:
- A situational analysis of shared leadership in a self-managing team
- The effect of musical preference on running performance
- Relationship between self-esteem and disordered eating amongst adolescent females
Consider this hypothetical psychology research proposal:
The Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Stress Reduction in College Students
Abstract: This research proposal examines the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction among college students, using a pre-test/post-test experimental design with both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods .
Introduction: College students face heightened stress levels during exam weeks. This can affect both mental health and test performance. This study explores the potential benefits of mindfulness-based interventions such as meditation as a way to mediate stress levels in the weeks leading up to exam time.
Literature Review: Existing research on mindfulness-based meditation has shown the ability for mindfulness to increase metacognition, decrease anxiety levels, and decrease stress. Existing literature has looked at workplace, high school and general college-level applications. This study will contribute to the corpus of literature by exploring the effects of mindfulness directly in the context of exam weeks.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n= 234 ) will be randomly assigned to either an experimental group, receiving 5 days per week of 10-minute mindfulness-based interventions, or a control group, receiving no intervention. Data will be collected through self-report questionnaires, measuring stress levels, semi-structured interviews exploring participants’ experiences, and students’ test scores.
Timeline: The study will begin three weeks before the students’ exam week and conclude after each student’s final exam. Data collection will occur at the beginning (pre-test of self-reported stress levels) and end (post-test) of the three weeks.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: The study aims to provide evidence supporting the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing stress among college students in the lead up to exams, with potential implications for mental health support and stress management programs on college campuses.
3. Sociology Research Proposals
- Understanding emerging social movements: A case study of ‘Jersey in Transition’
- The interaction of health, education and employment in Western China
- Can we preserve lower-income affordable neighbourhoods in the face of rising costs?
Consider this hypothetical sociology research proposal:
The Impact of Social Media Usage on Interpersonal Relationships among Young Adults
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effects of social media usage on interpersonal relationships among young adults, using a longitudinal mixed-methods approach with ongoing semi-structured interviews to collect qualitative data.
Introduction: Social media platforms have become a key medium for the development of interpersonal relationships, particularly for young adults. This study examines the potential positive and negative effects of social media usage on young adults’ relationships and development over time.
Literature Review: A preliminary review of relevant literature has demonstrated that social media usage is central to development of a personal identity and relationships with others with similar subcultural interests. However, it has also been accompanied by data on mental health deline and deteriorating off-screen relationships. The literature is to-date lacking important longitudinal data on these topics.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n = 454 ) will be young adults aged 18-24. Ongoing self-report surveys will assess participants’ social media usage, relationship satisfaction, and communication patterns. A subset of participants will be selected for longitudinal in-depth interviews starting at age 18 and continuing for 5 years.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of five years, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide insights into the complex relationship between social media usage and interpersonal relationships among young adults, potentially informing social policies and mental health support related to social media use.
4. Nursing Research Proposals
- Does Orthopaedic Pre-assessment clinic prepare the patient for admission to hospital?
- Nurses’ perceptions and experiences of providing psychological care to burns patients
- Registered psychiatric nurse’s practice with mentally ill parents and their children
Consider this hypothetical nursing research proposal:
The Influence of Nurse-Patient Communication on Patient Satisfaction and Health Outcomes following Emergency Cesarians
Abstract: This research will examines the impact of effective nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction and health outcomes for women following c-sections, utilizing a mixed-methods approach with patient surveys and semi-structured interviews.
Introduction: It has long been known that effective communication between nurses and patients is crucial for quality care. However, additional complications arise following emergency c-sections due to the interaction between new mother’s changing roles and recovery from surgery.
Literature Review: A review of the literature demonstrates the importance of nurse-patient communication, its impact on patient satisfaction, and potential links to health outcomes. However, communication between nurses and new mothers is less examined, and the specific experiences of those who have given birth via emergency c-section are to date unexamined.
Research Design and Methods: Participants will be patients in a hospital setting who have recently had an emergency c-section. A self-report survey will assess their satisfaction with nurse-patient communication and perceived health outcomes. A subset of participants will be selected for in-depth interviews to explore their experiences and perceptions of the communication with their nurses.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including rolling recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing within the hospital.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the significance of nurse-patient communication in supporting new mothers who have had an emergency c-section. Recommendations will be presented for supporting nurses and midwives in improving outcomes for new mothers who had complications during birth.
5. Social Work Research Proposals
- Experiences of negotiating employment and caring responsibilities of fathers post-divorce
- Exploring kinship care in the north region of British Columbia
Consider this hypothetical social work research proposal:
The Role of a Family-Centered Intervention in Preventing Homelessness Among At-Risk Youthin a working-class town in Northern England
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effectiveness of a family-centered intervention provided by a local council area in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth. This case study will use a mixed-methods approach with program evaluation data and semi-structured interviews to collect quantitative and qualitative data .
Introduction: Homelessness among youth remains a significant social issue. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in addressing this problem and identify factors that contribute to successful prevention strategies.
Literature Review: A review of the literature has demonstrated several key factors contributing to youth homelessness including lack of parental support, lack of social support, and low levels of family involvement. It also demonstrates the important role of family-centered interventions in addressing this issue. Drawing on current evidence, this study explores the effectiveness of one such intervention in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth in a working-class town in Northern England.
Research Design and Methods: The study will evaluate a new family-centered intervention program targeting at-risk youth and their families. Quantitative data on program outcomes, including housing stability and family functioning, will be collected through program records and evaluation reports. Semi-structured interviews with program staff, participants, and relevant stakeholders will provide qualitative insights into the factors contributing to program success or failure.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Budget: Expenses include access to program evaluation data, interview materials, data analysis software, and any related travel costs for in-person interviews.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in preventing youth homelessness, potentially informing the expansion of or necessary changes to social work practices in Northern England.
Research Proposal Template
Get your Detailed Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
This is a template for a 2500-word research proposal. You may find it difficult to squeeze everything into this wordcount, but it’s a common wordcount for Honors and MA-level dissertations.
Your research proposal is where you really get going with your study. I’d strongly recommend working closely with your teacher in developing a research proposal that’s consistent with the requirements and culture of your institution, as in my experience it varies considerably. The above template is from my own courses that walk students through research proposals in a British School of Education.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
8 thoughts on “17 Research Proposal Examples”
Very excellent research proposals
very helpful
Very helpful
Dear Sir, I need some help to write an educational research proposal. Thank you.

Hi Levi, use the site search bar to ask a question and I’ll likely have a guide already written for your specific question. Thanks for reading!
very good research proposal
Thank you so much sir! ❤️
Very helpful 👌
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research Proposal for a PhD thesis in English Literature. perception that spans from Ezra Pound to John Ashbery. More recent criticism has similarly. undervalued women poets' contribution to the scope of the visual in contemporary poetry. Ian. between 'eye' and 'I', and the gendered implications of observing and being observed.
Take your time in composing your research proposal, carefully considering the requirements outlined below. Your proposal should not be more than 2,000 words. PhD degrees are awarded on the basis of a thesis of up to 100,000 words. The 'Summary of roles and responsibilities' in the University's Code of Practice for Supervisors and Research ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
Sample Research Proposal. Last semester, I took an English class with Professor Bethany Schneider entitled "American. Girl," where our syllabus included Louisa May Alcott's Little Women and Laura Ingalls Wilder's. Little House on the Prairie. My experience with both books was fascinating because I was reading.
Advice on Preparing a Research Proposal for a PhD Thesis in English. To be taken on as a PhD student, it is usually assumed that you will already have completed an MA in a relevant subject. This means that you will already have experience of writing a dissertation of between 10,000 and 20,000 words. The possession of an MA indicates (a) that ...
for the PhD or MPhil degrees are the sample of written work and the research proposal. You will probably choose your sample of written work from an already-completed undergraduate or masters-level dissertation or term-paper. Your research proposal will be something new. It will describe the project that you want to complete for the award of the
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
writing a research proposal in English literature requires a systematic approach and careful consideration of the various elements involved. By choosing an interesting topic, conducting a thorough literature review, defining your research questions, developing a methodology, creating a research timeline, and considering ethical considerations ...
Sample dissertation proposal. Below is an example of a successful MA dissertation proposal. Note particularly the robust referencing, and the way in which the author has already done preparatory work in the field so that clear areas of critical enquiry have already been formulated. Modernist Poetics and the Acquisition of the Other Tongue.
The 1,500 word research proposal is an important element of your application to doctoral study, whether full-time or part-time. It offers you the opportunity to outline the research you intend to conduct, including how you plan to go about it, and how your research might make a contribution to a theoretical or empirical evidence base.
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
Research proposals. Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use. We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
An MPhil research proposal should be 500 words long, while a PhD proposal should be 800 words long. It needs to give those assessing your application an impression of the strength and originality of your proposed research, and its potential to make a contribution to knowledge. It should be written in clear, jargon-free prose.
An important part of the work completed in academia is sharing our scholarship with others. Such communication takes place when we present at scholarly conferences, publish in peer-reviewed journals, and publish in books. This OWL resource addresses the steps in writing for a variety of academic proposals. For samples of academic proposals ...
The following has been adapted for the English Department from the Graduate School's "Statement on Thesis/Dissertation Proposals." Guidelines adapted for the Creative Dissertation Proposal Guidelines can be found here. I. Introduction A thesis proposal states a problem to be investigated and describes how the research will be performed and reported. Approval signifies that it meets the […]
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
We then progress to the sample literature review (from an A-grade Master's-level dissertation) to show how these concepts are applied in the literature review chapter. You can access the free resources mentioned in this video below. ... Research Proposal Example/Sample: Full Walkthrough; Research Methodology Example: Full Walkthrough; Process ...
In any research writeup/proposal, you would be required to write a literature review. A literature review is a succinct survey of the literature related to the topic you are researching.
A quality example of a research proposal shows one's above-average analytical skills, including the ability to coherently synthesize ideas and integrate lateral and vertical thinking. Communication skills. The proposal also demonstrates your proficiency to communicate your thoughts in concise and precise language.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
Thesis Proposals. Examples of thesis proposals are included here in PDF format. Copies of theses completed in the M.A. in English & Writing Studies program can be accessed through the Pfau Library's CSUSB ScholarWorks database. Because the Public & Professional Writing concentration is so new, we do not have a sample proposal for it at this time.
17 Research Proposal Examples. By Chris Drew (PhD) / January 12, 2024. A research proposal systematically and transparently outlines a proposed research project. The purpose of a research proposal is to demonstrate a project's viability and the researcher's preparedness to conduct an academic study. It serves as a roadmap for the researcher.
4. Do Your Research. A winning project proposal includes thorough research and knowing the ins and outs, backwards and forwards. Be sure you can back up your problem - and solution - with reputable sources via outlets such as case studies, customer testimonials, user analytics, statistics or charts. 5. Utilize the Smart Method When Setting Goals