- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Daily Times
Your right to know Sunday, June 02, 2024
Commentary / Insight

The misuse and abuse of freedom of speech
With rights come responsibilities - and in this particular context, one's responsibility involves not invoking chaos, mayhem and discord

June 23, 2018
Freedom of speech is under threat and censorship is on the rise. This has been a repetitive narrative for centuries. But today’s threat is not only being instigated by dictators and monarchs, as was the case in the past. Instead, it is being stoked up by the very people who are supposed to protect this principle: democratically elected politicians, cartoonists and writers.
Article 19 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights states that “everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression”. However, this right is surely not unconditional because of the inherent elements of language.
Words, sentences and paragraphs emit effects.They incite emotions in listeners and readers. Language is never neutral. “Language is never innocent,” wrote Roland Barthes, the prominent late literary theorist and philosopher.
But far too often it is the case that commentators and politicians give rise to ill-conceived social views through their platforms. In the case of Europe, public figures like Marine Le Pen and Tommy Robinson proliferate racism, Islamophobia and Xenophobia. They tweet and share posts to turn the tide of public opinion against foreigners.
Sadly, these extreme views are not just confined to the edges of society. Instead, they are part and parcel of the politics in the mainstreams. For instance, Baroness Warsi, a member of the upper house of the British Parliament, recently claimed that “Islamophobia is a problem in the Conservative Party”. A place for Islamophobia in mainstream political parties suggests that the right to freedom of speech is being used for counter-productive, negative and harmful objectives.
These harmful objectives amplified in Britain in the direct aftermath of its Brexit referendum. An anti-immigrant and anti-Muslim atmosphere was created which led to a direct increase in hate crimes targeting minorities. In fact, hate incidents went up by 89 percent in schools and by 23 percent all over the country.
While the intention of banning people from making an offensive statement is good, it nonetheless represents a slippery slope because it would hand too much control to governments in deciding what is or isn’t offensive
This was undoubtedly a blatant misuse of one’s right to freedom of speech and freedom of expression.
Closer to home, the situation is very similar to that in Europe.
In Pakistan, some religious and political figures are deliberately expressing extremist views to stoke up tension, division and extremism among an already polarised population.
These figures express extreme views – both on and offline – which directly target ethnic and religious minorities in the country.
Due to the reckless use of our right to freedom of speech, the mandate to curtail freedom of opinion and expression is, unfortunately, becoming stronger. According to the Pew Research Centre, in the USA, for example, 40 percent of millennials believe that governments “should be able to prevent” people from uttering “statements that are offensive to minority groups”.
Similarly, 70 percent of the German population agrees that people should be stopped from making offensive statements towards minority groups.
Besides these staggering percentages, the even more shocking phenomenon is that both of them are steadfast democratic countries.
It is a profoundly depressing fact that public opinion suggests that the situation is so bad that they want their governments to resort to banning such speeches and thereby introduce measures of censorship.
While the intention of banning people from making an offensive statement is good, it nonetheless represents a slippery slope because it would hand too much control to governments in deciding what is or isn’t offensive to minority groups.
With rights come responsibilities – and in this particular context, one’s responsibility involves not invoking chaos, mayhem and discord. It is therefore understandable why people would want to support government-driven censorship against the exploitation of freedom of speech.
Only by using language for the right purpose can we protect the unequivocal right to freedom of speech. However, this isn’t a one-way street. Public figures, therefore, shouldn’t use freedom of speech in a manner that makes it indefensible.
To protect the rights bestowed in Article 19 involves enacting Voltaire’s famous quote: “I disapprove of what you say, but I will defend to the death your right to say it”.
The writer isthe authorof Diary of a Foreigner: Thoughts on Brexit, and tweets @MuhammedRaza786
Published in Daily Times, June 23 rd 2018.
Submit a Comment
Home Lead Stories Latest News Editor’s Picks
Culture Life & Style Featured Videos
Editorials OP-EDS Commentary Advertise
Cartoons Letters Blogs Privacy Policy
Contact Company’s Financials Investor Information Terms & Conditions

Watch CBS News
How free speech is under attack in the U.S.
February 20, 2022 / 9:12 AM EST / CBS News
When someone says something we disagree with, should we shut them up? In 1927, Supreme Court Justice Louis Brandeis had an answer: "The remedy to be applied is more speech, not enforced silence."
Well, in that case, the internet should have solved everything, notes correspondent David Pogue – it's nothing but more speech. And yet lately, the news is full of stories about people trying to limit other people's expression:
- Florida lawmakers are advancing a pair of bills that would bar school districts from encouraging classroom discussions about sexual orientation or gender identity – what critics are calling "Don't Say Gay" bills.
- Nearly a dozen states have introduced bills that would direct what students can and cannot be taught about the role of slavery in American history and the ongoing effects of racism in the U.S. today .
- A Tennessee school board removed "Maus," a Pulitzer Prize-winning graphic novel about the Holocaust, from its curriculum.
- Spotify faced growing controversy over episodes of Joe Rogan's podcast containing racial slurs and COVID-19 misinformation .
- An incoming Georgetown Law administrator was assailed by a student group for posting a "racist, sexist, and misogynistic" tweet that criticized President Joe Biden's announcement that he would nominate a Black woman for the Supreme Court.
"I would argue that the culture of free speech is under attack in the U.S.," said Jacob Mchangama, the author of "Free Speech," a new book that documents the history of free expression. "And without a robust culture of free speech based on tolerance, the laws and constitutional protection will ultimately erode.

"People both on the left and the right are sort of coming at free speech from different angles with different grievances, that point to a general loss of faith in the First Amendment."
The free-speech erosion is even happening in schools. Since January last year, according to PEN America, Republican lawmakers have introduced more than 150 state laws that would restrict how teachers can discuss race, sexual orientation, and gender identity in the classroom.
Jennifer Given, who teaches high-school history in Hollis, New Hampshire, said of the laws, "It's about making up false narratives to further a political goal of your own.
"It's a really scary time to be a teacher," she told Pogue. "We're self-censoring, We are absolutely avoiding certain things and ideas in an effort to stay within the lines as best we understand them."
In New Hampshire, a new law limits what teachers can say about racism and sexism – and a conservative group is offering a $500 bounty to anyone who turns in a teacher who violates it.
Given said, "The ghost of Senator McCarthy is alive and well in some of our state house hallways."
Pogue asked, "What would happen to you if you did step afoul of this law?"
"That can result in the loss of your license," she replied. "And so, I would not only be unemployable at my school, but I would be unemployable anywhere."
"But what I don't understand is, this is New Hampshire, whose motto is, 'Live Free or Die'!"
"Yeah, yeah," Given laughed. "There's a lot of emphasis on the 'or die' part of late!"

UC Berkeley professor John Powell, an expert on civil liberties and democracy, said of the classroom prohibitions, "That's a very serious freedom of speech issue. To me, that is so far off the rail."
He's especially alarmed at the record number of books that are being banned in schools all over the country. Conservatives object to books about sex, gender issues, and racial injustice (such as Toni Morrison's "Beloved," Alex Gino's "George," and "The 1619 Project"), and liberals object to books containing outdated racial depictions (including John Steinbeck's "Of Mice and Men," Mark Twain's "The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn," and Harper Lee's "To Kill a Mockingbird").
- 10 Most Challenged Books Lists (American Library Association)
- Virginia school board officials suggest burning books banned from schools ("Red & Blue")
"You can't make the Holocaust a nice thing – it wasn't a nice thing!" Powell laughed. "You can't make slavery a nice thing. 'That makes people uncomfortable.' It should make people uncomfortable! The goal of education is not comfort. So, if someone really wants to challenge the Holocaust, let 'em challenge it. But don't ban a discussion on it."
In the mid-1800s, English philosopher John Stuart Mill proposed that governments limit free speech only when it would cause harm to others.
Powell said, "He wrote a book called 'On Liberty,' [about] freedom. And he was very concerned about the government silencing people, that citizens had to have the right to express themselves."
Our laws have generally followed that guideline. In the U.S., public speech can't include obscenity, defamation, death threats, incitement to violence – harms.
But Powell said that the recent restrictions have more to do with culture wars than with preventing harm: " I want to regulate that 'cause I don't like it. To me, that's wrong. That's problematic."
"So, there's a difference between saying something that makes you uncomfortable, and saying something that damages society or incites to riot?" asked Pogue.
"Right, and discomfort is not the same as an injury."
But these days, there are entire new categories of speech that can lead to harm. "Now, there's a concept of disinformation, where you deliberately engage in lies, in fact to cause harm, to cause injury, to exclude some people," said Powell. "But what it really means is our understanding of the First Amendment and our understanding of free speech is evolving. It has to evolve."
- A dozen anti-vaccine accounts are responsible for 65% of disinformation shared online, new report finds
It's probably no coincidence that the new censorship culture arose simultaneously with social networks like Facebook and Twitter.
"The First Amendment was conceived as a protection of citizens from restriction of expression by the government, and not by private companies or other entities," said Jillian York, the director for international freedom of expression at the Electronic Frontier Foundation, and author of "Silicon Values."
Pogue asked, "So for example, Donald Trump getting kicked off Twitter and Facebook ? Is that censorship? Is that bad censorship? Is that good censorship?"
"I think Trump getting kicked off of Facebook and Twitter is kind of complicated," York said. "But the thing that really concerns me the most is that someone like Mark Zuckerberg, whom none of us elected, has the power to remove an elected official. I think that should really worry us, even if we do feel that Trump should be silenced."
York said that the big tech companies censor our speech every day, sometimes by mistake, but always without supervision or transparency. "We saw protest content around Black Lives Matter removed on Facebook's platform, wrongfully," she said. "LGBTQ content has been removed. as well as things like art and satire."
- Faceoff against Facebook: Stopping the flow of misinformation ("Sunday Morning")
- Texas governor signs law prohibiting social media platforms from banning users
- Lawmakers vow stricter regulations on social media platforms to combat misinformation
According to Jacob Mchangama, social networks censor us in another way, too, by making us afraid to speak at all: "There was actually this survey from 2020 by the Cato Institute which showed that 62% of Americans self-censor, who are afraid to sort of express their political views on specific topics.
"It shows this paradox: Americans enjoy the strongest legal constitutional protection of free speech probably in world history. But they still fear the consequences of being fired for speaking out on certain political views. And that's not a healthy sign."
But it's not just America. Since 2019, at least 37 countries have passed laws that increase censorship (of individuals or the media), including in Europe, where Jillian York lives. "There's a lot of debate right now in Germany, for example, over a fairly recent law that restricts hate speech online," York said, "but also creates penalties for things like the country's insult law . So, you know, insulting someone online could be penalized financially."
Overall, it would be easy to get depressed by these attacks on free speech. Especially if you're a teacher, like Jennifer Given.
Pogue asked, "What's the end point for you, if this keeps going this way in New Hampshire?"
"I don't know," she laughed. "There is a point where you start going, 'Maybe I've had it.'"
But if it cheers you up any, Jacob Mchangama points out that we still enjoy more freedom of speech than most countries: "If we were having this discussion in Russia or Turkey, you know, someone would pick me up when I go down on the street, and you might not hear from me for a long time."
He said we should fight to maintain our freedom of civil discussion – and never take it for granted.
"I'm not saying that free speech is just great, and doesn't entail any consequences; it does," he said. "You know, we should think about, how do we mitigate misinformation? How can we ensure that we counter hate speech without compromising free speech?
"And, you know, it's an experiment. But I would argue that it's been a very beneficial experiment. And one which is very much worth continuing."
For more info:
- "Free Speech: A History from Socrates to Social Media" by Jacob Mchangama (Basic Books), in Hardcover, eBook and Audio formats, available via Amazon and Indiebound
- Follow Jacob Mchangama on Twitter
- John A. Powell, professor, University of California, Berkeley School of Law
- "Silicon Values: The Future of Free Speech Under Surveillance Capitalism" by Jillian C. York (Verso), in Hardcover, eBook and Audio formats, available via Amazon and Indiebound
- jilliancyork.com
- Electronic Frontier Foundation
- Jillian York photo: Nadine Barišić
Story produced by Mark Hudspeth. Editor: Mike Levine.
See also
- Censorship on social media? It's not what you think (CBS Reports)
- The psychology behind "cancel culture": Is it justice or censorship?
More from CBS News

This week on "Sunday Morning" (June 2)

Book excerpt: "Eruption" by Michael Crichton and James Patterson

Trump lawyer eager to move forward with appeal of New York conviction

Fact checking Trump's remarks after historic conviction in "hush money" trial

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Freedom of Speech
[ Editor’s Note: The following new entry by Jeffrey W. Howard replaces the former entry on this topic by the previous author. ]
Human beings have significant interests in communicating what they think to others, and in listening to what others have to say. These interests make it difficult to justify coercive restrictions on people’s communications, plausibly grounding a moral right to speak (and listen) to others that is properly protected by law. That there ought to be such legal protections for speech is uncontroversial among political and legal philosophers. But disagreement arises when we turn to the details. What are the interests or values that justify this presumption against restricting speech? And what, if anything, counts as an adequate justification for overcoming the presumption? This entry is chiefly concerned with exploring the philosophical literature on these questions.
The entry begins by distinguishing different ideas to which the term “freedom of speech” can refer. It then reviews the variety of concerns taken to justify freedom of speech. Next, the entry considers the proper limits of freedom of speech, cataloging different views on when and why restrictions on communication can be morally justified, and what considerations are relevant when evaluating restrictions. Finally, it considers the role of speech intermediaries in a philosophical analysis of freedom of speech, with special attention to internet platforms.
1. What is Freedom of Speech?
2.1 listener theories, 2.2 speaker theories, 2.3 democracy theories, 2.4 thinker theories, 2.5 toleration theories, 2.6 instrumental theories: political abuse and slippery slopes, 2.7 free speech skepticism, 3.1 absoluteness, coverage, and protection, 3.2 the limits of free speech: external constraints, 3.3 the limits of free speech: internal constraints, 3.4 proportionality: chilling effects and political abuse, 3.5 necessity: the counter-speech alternative, 4. the future of free speech theory: platform ethics, other internet resources, related entries.
In the philosophical literature, the terms “freedom of speech”, “free speech”, “freedom of expression”, and “freedom of communication” are mostly used equivalently. This entry will follow that convention, notwithstanding the fact that these formulations evoke subtly different phenomena. For example, it is widely understood that artistic expressions, such as dancing and painting, fall within the ambit of this freedom, even though they don’t straightforwardly seem to qualify as speech , which intuitively connotes some kind of linguistic utterance (see Tushnet, Chen, & Blocher 2017 for discussion). Still, they plainly qualify as communicative activity, conveying some kind of message, however vague or open to interpretation it may be.
Yet the extension of “free speech” is not fruitfully specified through conceptual analysis alone. The quest to distinguish speech from conduct, for the purpose of excluding the latter from protection, is notoriously thorny (Fish 1994: 106), despite some notable attempts (such as Greenawalt 1989: 58ff). As John Hart Ely writes concerning Vietnam War protesters who incinerated their draft cards, such activity is “100% action and 100% expression” (1975: 1495). It is only once we understand why we should care about free speech in the first place—the values it instantiates or serves—that we can evaluate whether a law banning the burning of draft cards (or whatever else) violates free speech. It is the task of a normative conception of free speech to offer an account of the values at stake, which in turn can illuminate the kinds of activities wherein those values are realized, and the kinds of restrictions that manifest hostility to those values. For example, if free speech is justified by the value of respecting citizens’ prerogative to hear many points of view and to make up their own minds, then banning the burning of draft cards to limit the views to which citizens will be exposed is manifestly incompatible with that purpose. If, in contrast, such activity is banned as part of a generally applied ordinance restricting fires in public, it would likely raise no free-speech concerns. (For a recent analysis of this issue, see Kramer 2021: 25ff).
Accordingly, the next section discusses different conceptions of free speech that arise in the philosophical literature, each oriented to some underlying moral or political value. Before turning to the discussion of those conceptions, some further preliminary distinctions will be useful.
First, we can distinguish between the morality of free speech and the law of free speech. In political philosophy, one standard approach is to theorize free speech as a requirement of morality, tracing the implications of such a theory for law and policy. Note that while this is the order of justification, it need not be the order of investigation; it is perfectly sensible to begin by studying an existing legal protection for speech (such as the First Amendment in the U.S.) and then asking what could justify such a protection (or something like it).
But of course morality and law can diverge. The most obvious way they can diverge is when the law is unjust. Existing legal protections for speech, embodied in the positive law of particular jurisdictions, may be misguided in various ways. In other words, a justified legal right to free speech, and the actual legal right to free speech in the positive law of a particular jurisdiction, can come apart. In some cases, positive legal rights might protect too little speech. For example, some jurisdictions’ speech laws make exceptions for blasphemy, such that criminalizing blasphemy does not breach the legal right to free speech within that legal system. But clearly one could argue that a justified legal right to free speech would not include any such exception. In other cases, positive legal rights might perhaps protect too much speech. Consider the fact that, as a matter of U.S. constitutional precedent, the First Amendment broadly protects speech that expresses or incites racial or religious hatred. Plainly we could agree that this is so as a matter of positive law while disagreeing about whether it ought to be so. (This is most straightforwardly true if we are legal positivists. These distinctions are muddied by moralistic theories of constitutional interpretation, which enjoin us to interpret positive legal rights in a constitutional text partly through the prism of our favorite normative political theory; see Dworkin 1996.)
Second, we can distinguish rights-based theories of free speech from non-rights-based theories. For many liberals, the legal right to free speech is justified by appealing to an underlying moral right to free speech, understood as a natural right held by all persons. (Some use the term human right equivalently—e.g., Alexander 2005—though the appropriate usage of that term is contested.) The operative notion of a moral right here is that of a claim-right (to invoke the influential analysis of Hohfeld 1917); it thereby correlates to moral duties held by others (paradigmatically, the state) to respect or protect the right. Such a right is natural in that it exerts normative force independently of whether anyone thinks it does, and regardless of whether it is codified into the law. A tyrannical state that imprisons dissidents acts unjustly, violating moral rights, even if there is no legal right to freedom of expression in its legal system.
For others, the underlying moral justification for free speech law need not come in the form of a natural moral right. For example, consequentialists might favor a legal right to free speech (on, e.g., welfare-maximizing grounds) without thinking that it tracks any underlying natural right. Or consider democratic theorists who have defended legal protections for free speech as central to democracy. Such theorists may think there is an underlying natural moral right to free speech, but they need not (especially if they hold an instrumental justification for democracy). Or consider deontologists who have argued that free speech functions as a kind of side-constraint on legitimate state action, requiring that the state always justify its decisions in a manner that respects citizens’ autonomy (Scanlon 1972). This theory does not cast free speech as a right, but rather as a principle that forbids the creation of laws that restrict speech on certain grounds. In the Hohfeldian analysis (Hohfeld 1917), such a principle may be understood as an immunity rather than a claim-right (Scanlon 2013: 402). Finally, some “minimalists” (to use a designation in Cohen 1993) favor legal protection for speech principally in response to government malice, corruption, and incompetence (see Schauer 1982; Epstein 1992; Leiter 2016). Such theorists need not recognize any fundamental moral right, either.
Third, among those who do ground free speech in a natural moral right, there is scope for disagreement about how tightly the law should mirror that right (as with any right; see Buchanan 2013). It is an open question what the precise legal codification of the moral right to free speech should involve. A justified legal right to freedom of speech may not mirror the precise contours of the natural moral right to freedom of speech. A raft of instrumental concerns enters the downstream analysis of what any justified legal right should look like; hence a defensible legal right to free speech may protect more speech (or indeed less speech) than the underlying moral right that justifies it. For example, even if the moral right to free speech does not protect so-called hate speech, such speech may still merit legal protection in the final analysis (say, because it would be too risky to entrust states with the power to limit those communications).
2. Justifying Free Speech
I will now examine several of the morally significant considerations taken to justify freedom of expression. Note that while many theorists have built whole conceptions of free speech out of a single interest or value alone, pluralism in this domain remains an option. It may well be that a plurality of interests serves to justify freedom of expression, properly understood (see, influentially, Emerson 1970 and Cohen 1993).
Suppose a state bans certain books on the grounds that it does not want us to hear the messages or arguments contained within them. Such censorship seems to involve some kind of insult or disrespect to citizens—treating us like children instead of adults who have a right to make up our own minds. This insight is fundamental in the free speech tradition. On this view, the state wrongs citizens by arrogating to itself the authority to decide what messages they ought to hear. That is so even if the state thinks that the speech will cause harm. As one author puts it,
the government may not suppress speech on the ground that the speech is likely to persuade people to do something that the government considers harmful. (Strauss 1991: 335)
Why are restrictions on persuasive speech objectionable? For some scholars, the relevant wrong here is a form of disrespect for citizens’ basic capacities (Dworkin 1996: 200; Nagel 2002: 44). For others, the wrong here inheres in a violation of the kind of relationship the state should have with its people: namely, that it should always act from a view of them as autonomous, and so entitled to make up their own minds (Scanlon 1972). It would simply be incompatible with a view of ourselves as autonomous—as authors of our own lives and choices—to grant the state the authority to pre-screen which opinions, arguments, and perspectives we should be allowed to think through, allowing us access only to those of which it approves.
This position is especially well-suited to justify some central doctrines of First Amendment jurisprudence. First, it justifies the claim that freedom of expression especially implicates the purposes with which the state acts. There are all sorts of legitimate reasons why the state might restrict speech (so-called “time, place, and manner” restrictions)—for example, noise curfews in residential neighborhoods, which do not raise serious free speech concerns. Yet when the state restricts speech with the purpose of manipulating the communicative environment and controlling the views to which citizens are exposed, free speech is directly affronted (Rubenfeld 2001; Alexander 2005; Kramer 2021). To be sure, purposes are not all that matter for free speech theory. For example, the chilling effects of otherwise justified speech regulations (discussed below) are seldom intended. But they undoubtedly matter.
Second, this view justifies the related doctrines of content neutrality and viewpoint neutrality (see G. Stone 1983 and 1987) . Content neutrality is violated when the state bans discussion of certain topics (“no discussion of abortion”), whereas viewpoint neutrality is violated when the state bans advocacy of certain views (“no pro-choice views may be expressed”). Both affront free speech, though viewpoint-discrimination is especially egregious and so even harder to justify. While listener autonomy theories are not the only theories that can ground these commitments, they are in a strong position to account for their plausibility. Note that while these doctrines are central to the American approach to free speech, they are less central to other states’ jurisprudence (see A. Stone 2017).
Third, this approach helps us see that free speech is potentially implicated whenever the state seeks to control our thoughts and the processes through which we form beliefs. Consider an attempt to ban Marx’s Capital . As Marx is deceased, he is probably not wronged through such censorship. But even if one held idiosyncratic views about posthumous rights, such that Marx were wronged, it would be curious to think this was the central objection to such censorship. Those with the gravest complaint would be the living adults who have the prerogative to read the book and make up their own minds about it. Indeed free speech may even be implicated if the state banned watching sunsets or playing video games on the grounds that is disapproved of the thoughts to which such experiences might give rise (Alexander 2005: 8–9; Kramer 2021: 22).
These arguments emphasize the noninstrumental imperative of respecting listener autonomy. But there is an instrumental version of the view. Our autonomy interests are not merely respected by free speech; they are promoted by an environment in which we learn what others have to say. Our interests in access to information is served by exposure to a wide range of viewpoints about both empirical and normative issues (Cohen 1993: 229), which help us reflect on what goals to choose and how best to pursue them. These informational interests are monumental. As Raz suggests, if we had to choose whether to express our own views on some question, or listen to the rest of humanity’s views on that question, we would choose the latter; it is our interest as listeners in the public good of a vibrant public discourse that, he thinks, centrally justifies free speech (1991).
Such an interest in acquiring justified beliefs, or in accessing truth, can be defended as part of a fully consequentialist political philosophy. J.S. Mill famously defends free speech instrumentally, appealing to its epistemic benefits in On Liberty . Mill believes that, given our fallibility, we should routinely keep an open mind as to whether a seemingly false view may actually be true, or at least contain some valuable grain of truth. And even where a proposition is manifestly false, there is value in allowing its expression so that we can better apprehend why we take it to be false (1859: chapter 2), enabled through discursive conflict (cf. Simpson 2021). Mill’s argument focuses especially on the benefits to audiences:
It is is not on the impassioned partisan, it is on the calmer and more disinterested bystander, that this collision of opinions works its salutary effect. (1859: chapter 2, p. 94)
These views are sometimes associated with the idea of a “marketplace of ideas”, whereby the open clash of views inevitably leads to the correct ones winning out in debate. Few in the contemporary literature holds such a strong teleological thesis about the consequences of unrestricted debate (e.g., see Brietzke 1997; cf. Volokh 2011). Much evidence from behavioral economics and social psychology, as well as insights about epistemic injustice from feminist epistemology, strongly suggest that human beings’ rational powers are seriously limited. Smug confidence in the marketplace of ideas belies this. Yet it is doubtful that Mill held such a strong teleological thesis (Gordon 1997). Mill’s point was not that unrestricted discussion necessarily leads people to acquire the truth. Rather, it is simply the best mechanism available for ascertaining the truth, relative to alternatives in which some arbiter declares what he sees as true and suppresses what he sees as false (see also Leiter 2016).
Note that Mill’s views on free speech in chapter 2 in On Liberty are not simply the application of the general liberty principle defended in chapter 1 of that work; his view is not that speech is anodyne and therefore seldom runs afoul of the harm principle. The reason a separate argument is necessary in chapter 2 is precisely that he is carving out a partial qualification of the harm principle for speech (on this issue see Jacobson 2000, Schauer 2011b, and Turner 2014). On Mill’s view, plenty of harmful speech should still be allowed. Imminently dangerous speech, where there is no time for discussion before harm eventuates, may be restricted; but where there is time for discussion, it must be allowed. Hence Mill’s famous example that vociferous criticism of corn dealers as
starvers of the poor…ought to be unmolested when simply circulated through the press, but may justly incur punishment when delivered orally to an excited mob assembled before the house of a corn dealer. (1859: chapter 3, p. 100)
The point is not that such speech is harmless; it’s that the instrumental benefits of permitting its expressions—and exposing its falsehood through public argument—justify the (remaining) costs.
Many authors have unsurprisingly argued that free speech is justified by our interests as speakers . This family of arguments emphasizes the role of speech in the development and exercise of our personal autonomy—our capacity to be the reflective authors of our own lives (Baker 1989; Redish 1982; Rawls 2005). Here an emphasis on freedom of expression is apt; we have an “expressive interest” (Cohen 1993: 224) in declaring our views—about the good life, about justice, about our identity, and about other aspects of the truth as we see it.
Our interests in self-expression may not always depend on the availability of a willing audience; we may have interests simply in shouting from the rooftops to declare who we are and what we believe, regardless of who else hears us. Hence communications to oneself—for example, in a diary or journal—are plausibly protected from interference (Redish 1992: 30–1; Shiffrin 2014: 83, 93; Kramer 2021: 23).
Yet we also have distinctive interests in sharing what we think with others. Part of how we develop our conceptions of the good life, forming judgments about how to live, is precisely through talking through the matter with others. This “deliberative interest” in directly served through opportunities to tell others what we think, so that we can learn from their feedback (Cohen 1993). Such encounters also offer opportunities to persuade others to adopt our views, and indeed to learn through such discussions who else already shares our views (Raz 1991).
Speech also seems like a central way in which we develop our capacities. This, too, is central to J.S. Mill’s defense of free speech, enabling people to explore different perspectives and points of view (1859). Hence it seems that when children engage in speech, to figure out what they think and to use their imagination to try out different ways of being in the world, they are directly engaging this interest. That explains the intuition that children, and not just adults, merit at least some protection under a principle of freedom of speech.
Note that while it is common to refer to speaker autonomy , we could simply refer to speakers’ capacities. Some political liberals hold that an emphasis on autonomy is objectionably Kantian or otherwise perfectionist, valorizing autonomy as a comprehensive moral ideal in a manner that is inappropriate for a liberal state (Cohen 1993: 229; Quong 2011). For such theorists, an undue emphasis on autonomy is incompatible with ideals of liberal neutrality toward different comprehensive conceptions of the good life (though cf. Shiffrin 2014: 81).
If free speech is justified by the importance of our interests in expressing ourselves, this justifies negative duties to refrain from interfering with speakers without adequate justification. Just as with listener theories, a strong presumption against content-based restrictions, and especially against viewpoint discrimination, is a clear requirement of the view. For the state to restrict citizens’ speech on the grounds that it disfavors what they have to say would affront the equal freedom of citizens. Imagine the state were to disallow the expression of Muslim or Jewish views, but allow the expression of Christian views. This would plainly transgress the right to freedom of expression, by valuing certain speakers’ interests in expressing themselves over others.
Many arguments for the right to free speech center on its special significance for democracy (Cohen 1993; Heinze 2016: Heyman 2009; Sunstein 1993; Weinstein 2011; Post 1991, 2009, 2011). It is possible to defend free speech on the noninstrumental ground that it is necessary to respect agents as democratic citizens. To restrict citizens’ speech is to disrespect their status as free and equal moral agents, who have a moral right to debate and decide the law for themselves (Rawls 2005).
Alternatively (or additionally), one can defend free speech on the instrumental ground that free speech promotes democracy, or whatever values democracy is meant to serve. So, for example, suppose the purpose of democracy is the republican one of establishing a state of non-domination between relationally egalitarian citizens; free speech can be defended as promoting that relation (Whitten 2022; Bonotti & Seglow 2022). Or suppose that democracy is valuable because of its role in promoting just outcomes (Arneson 2009) or tending to track those outcomes in a manner than is publicly justifiable (Estlund 2008) or is otherwise epistemically valuable (Landemore 2013).
Perhaps free speech doesn’t merely respect or promote democracy; another framing is that it is constitutive of it (Meiklejohn 1948, 1960; Heinze 2016). As Rawls says: “to restrict or suppress free political speech…always implies at least a partial suspension of democracy” (2005: 254). On this view, to be committed to democracy just is , in part, to be committed to free speech. Deliberative democrats famously contend that voting merely punctuates a larger process defined by a commitment to open deliberation among free and equal citizens (Gutmann & Thompson 2008). Such an unrestricted discussion is marked not by considerations of instrumental rationality and market forces, but rather, as Habermas puts it, “the unforced force of the better argument” (1992 [1996: 37]). One crucial way in which free speech might be constitutive of democracy is if it serves as a legitimation condition . On this view, without a process of open public discourse, the outcomes of the democratic decision-making process lack legitimacy (Dworkin 2009, Brettschneider 2012: 75–78, Cohen 1997, and Heinze 2016).
Those who justify free speech on democratic grounds may view this as a special application of a more general insight. For example, Scanlon’s listener theory (discussed above) contends that the state must always respect its citizens as capable of making up their own minds (1972)—a position with clear democratic implications. Likewise, Baker is adamant that both free speech and democracy are justified by the same underlying value of autonomy (2009). And while Rawls sees the democratic role of free speech as worthy of emphasis, he is clear that free speech is one of several basic liberties that enable the development and exercise of our moral powers: our capacities for a sense of justice and for the rational pursuit a lifeplan (2005). In this way, many theorists see the continuity between free speech and our broader interests as moral agents as a virtue, not a drawback (e.g., Kendrick 2017).
Even so, some democracy theorists hold that democracy has a special role in a theory of free speech, such that political speech in particular merits special protection (for an overview, see Barendt 2005: 154ff). One consequence of such views is that contributions to public discourse on political questions merit greater protection under the law (Sunstein 1993; cf. Cohen 1993: 227; Alexander 2005: 137–8). For some scholars, this may reflect instrumental anxieties about the special danger that the state will restrict the political speech of opponents and dissenters. But for others, an emphasis on political speech seems to reflect a normative claim that such speech is genuinely of greater significance, meriting greater protection, than other kinds of speech.
While conventional in the free speech literature, it is artificial to separate out our interests as speakers, listeners, and democratic citizens. Communication, and the thinking that feeds into it and that it enables, invariably engages our interests and activities across all these capacities. This insight is central to Seana Shiffrin’s groundbreaking thinker-based theory of freedom of speech, which seeks to unify the range of considerations that have informed the traditional theories (2014). Like other theories (e.g., Scanlon 1978, Cohen 1993), Shiffrin’s theory is pluralist in the range of interests it appeals to. But it offers a unifying framework that explains why this range of interests merits protection together.
On Shiffrin’s view, freedom of speech is best understood as encompassing both freedom of communication and freedom of thought, which while logically distinct are mutually reinforcing and interdependent (Shiffrin 2014: 79). Shiffrin’s account involves several profound claims about the relation between communication and thought. A central contention is that “free speech is essential to the development, functioning, and operation of thinkers” (2014: 91). This is, in part, because we must often externalize our ideas to articulate them precisely and hold them at a distance where we can evaluate them (p. 89). It is also because we work out what we think largely by talking it through with others. Such communicative processes may be monological, but they are typically dialogical; speaker and listener interests are thereby mutually engaged in an ongoing manner that cannot be neatly disentangled, as ideas are ping-ponged back and forth. Moreover, such discussions may concern democratic politics—engaging our interests as democratic citizens—but of course they need not. Aesthetics, music, local sports, the existence of God—these all are encompassed (2014: 92–93). Pace prevailing democratic theories,
One’s thoughts about political affairs are intrinsically and ex ante no more and no less central to the human self than thoughts about one’s mortality or one’s friends. (Shiffrin 2014: 93)
The other central aspect of Shiffrin’s view appeals to the necessity of communication for successfully exercising our moral agency. Sincere communication enables us
to share needs, emotions, intentions, convictions, ambitions, desires, fantasies, disappointments, and judgments. Thereby, we are enabled to form and execute complex cooperative plans, to understand one another, to appreciate and negotiate around our differences. (2014: 1)
Without clear and precise communication of the sort that only speech can provide, we cannot cooperate to discharge our collective obligations. Nor can we exercise our normative powers (such as consenting, waiving, or promising). Our moral agency thus depends upon protected channels through which we can relay our sincere thoughts to one another. The central role of free speech is to protect those channels, by ensuring agents are free to share what they are thinking without fear of sanction.
The thinker-based view has wide-ranging normative implications. For example, by emphasizing the continuity of speech and thought (a connection also noted in Macklem 2006 and Gilmore 2011), Shiffrin’s view powerfully explains the First Amendment doctrine that compelled speech also constitutes a violation of freedom of expression. Traditional listener- and speaker-focused theories seemingly cannot explain what is fundamentally objectionable with forcing someone to declare a commitment to something, as with children compelled to pledge allegiance to the American flag ( West Virginia State Board of Education v. Barnette 1943). “What seems most troubling about the compelled pledge”, Shiffrin writes,
is that the motive behind the regulation, and its possible effect, is to interfere with the autonomous thought processes of the compelled speaker. (2014: 94)
Further, Shiffrin’s view explains why a concern for free speech does not merely correlate to negative duties not to interfere with expression; it also supports positive responsibilities on the part of the state to educate citizens, encouraging and supporting their development and exercise as thinking beings (2014: 107).
Consider briefly one final family of free speech theories, which appeal to the role of toleration or self-restraint. On one argument, freedom of speech is important because it develops our character as liberal citizens, helping us tame our illiberal impulses. The underlying idea of Lee Bollinger’s view is that liberalism is difficult; we recurrently face temptation to punish those who hold contrary views. Freedom of speech helps us to practice the general ethos of toleration in a manner than fortifies our liberal convictions (1986). Deeply offensive speech, like pro-Nazi speech, is protected precisely because toleration in these enormously difficult cases promotes “a general social ethic” of toleration more generally (1986: 248), thereby restraining unjust exercises of state power overall. This consequentialist argument treats the protection of offensive speech not as a tricky borderline case, but as “integral to the central functions of the principle of free speech” (1986: 133). It is precisely because tolerating evil speech involves “extraordinary self-restraint” (1986: 10) that it works its salutary effects on society generally.
The idea of self-restraint arises, too, in Matthew Kramer’s recent defense of free speech. Like listener theories, Kramer’s strongly deontological theory condemns censorship aimed at protecting audiences from exposure to misguided views. At the core of his theory is the thesis that the state’s paramount moral responsibility is to furnish the social conditions that serve the development and maintenance of citizens’ self-respect and respect for others. The achievement of such an ethically resilient citizenry, on Kramer’s view, has the effect of neutering the harmfulness of countless harmful communications. “Securely in a position of ethical strength”, the state “can treat the wares of pornographers and the maunderings of bigots as execrable chirps that are to be endured with contempt” (Kramer 2021: 147). In contrast, in a society where the state has failed to do its duty of inculcating a robust liberal-egalitarian ethos, the communication of illiberal creeds may well pose a substantial threat. Yet for the state then to react by banning such speech is
overweening because with them the system’s officials take control of communications that should have been defused (through the system’s fulfillment of its moral obligations) without prohibitory or preventative impositions. (2021: 147)
(One might agree with Kramer that this is so, but diverge by arguing that the state—having failed in its initial duty—ought to take measures to prevent the harms that flow from that failure.)
These theories are striking in that they assume that a chief task of free speech theory is to explain why harmful speech ought to be protected. This is in contrast to those who think that the chief task of free speech theory is to explain our interests in communicating with others, treating the further issue of whether (wrongfully) harmful communications should be protected as an open question, with different reasonable answers available (Kendrick 2017). In this way, toleration theories—alongside a lot of philosophical work on free speech—seem designed to vindicate the demanding American legal position on free speech, one unshared by virtually all other liberal democracies.
One final family of arguments for free speech appeals to the danger of granting the state powers it may abuse. On this view, we protect free speech chiefly because if we didn’t, it would be far easier for the state to silence its political opponents and enact unjust policies. On this view, a state with censorial powers is likely to abuse them. As Richard Epstein notes, focusing on the American case,
the entire structure of federalism, divided government, and the system of checks and balances at the federal level shows that the theme of distrust has worked itself into the warp and woof of our constitutional structure.
“The protection of speech”, he writes, “…should be read in light of these political concerns” (Epstein 1992: 49).
This view is not merely a restatement of the democracy theory; it does not affirm free speech as an element of valuable self-governance. Nor does it reduce to the uncontroversial thought that citizens need freedom of speech to check the behavior of fallible government agents (Blasi 1977). One need not imagine human beings to be particularly sinister to insist (as democracy theorists do) that the decisions of those entrusted with great power be subject to public discussion and scrutiny. The argument under consideration here is more pessimistic about human nature. It is an argument about the slippery slope that we create even when enacting (otherwise justified) speech restrictions; we set an unacceptable precedent for future conduct by the state (see Schauer 1985). While this argument is theoretical, there is clearly historical evidence for it, as in the manifold cases in which bans on dangerous sedition were used to suppress legitimate war protest. (For a sweeping canonical study of the uses and abuses of speech regulations during wartime, with a focus on U.S. history, see G. Stone 2004.)
These instrumental concerns could potentially justify the legal protection for free speech. But they do not to attempt to justify why we should care about free speech as a positive moral ideal (Shiffrin 2014: 83n); they are, in Cohen’s helpful terminology, “minimalist” rather than “maximalist” (Cohen 1993: 210). Accordingly, they cannot explain why free speech is something that even the most trustworthy, morally competent administrations, with little risk of corruption or degeneration, ought to respect. Of course, minimalists will deny that accounting for speech’s positive value is a requirement of a theory of free speech, and that critiquing them for this omission begs the question.
Pluralists may see instrumental concerns as valuably supplementing or qualifying noninstrumental views. For example, instrumental concerns may play a role in justifying deviations between the moral right to free communication, on the one hand, and a properly specified legal right to free communication, on the other. Suppose that there is no moral right to engage in certain forms of harmful expression (such as hate speech), and that there is in fact a moral duty to refrain from such expression. Even so, it does not follow automatically that such a right ought to be legally enforced. Concerns about the dangers of granting the state such power plausibly militate against the enforcement of at least some of our communicative duties—at least in those jurisdictions that lack robust and competently administered liberal-democratic safeguards.
This entry has canvassed a range of views about what justifies freedom of expression, with particular attention to theories that conceive free speech as a natural moral right. Clearly, the proponents of such views believe that they succeed in this justificatory effort. But others dissent, doubting that the case for a bona fide moral right to free speech comes through. Let us briefly note the nature of this challenge from free speech skeptics , exploring a prominent line of reply.
The challenge from skeptics is generally understood as that of showing that free speech is a special right . As Leslie Kendrick notes,
the term “special right” generally requires that a special right be entirely distinct from other rights and activities and that it receive a very high degree of protection. (2017: 90)
(Note that this usage is not to be confused from the alternative usage of “special right”, referring to conditional rights arising out of particular relationships; see Hart 1955.)
Take each aspect in turn. First, to vindicate free speech as a special right, it must serve some distinctive value or interest (Schauer 2015). Suppose free speech were just an implication of a general principle not to interfere in people’s liberty without justification. As Joel Feinberg puts it, “Liberty should be the norm; coercion always needs some special justification” (1984: 9). In such a case, then while there still might be contingent, historical reasons to single speech out in law as worthy of protection (Alexander 2005: 186), such reasons would not track anything especially distinctive about speech as an underlying moral matter. Second, to count as a special right, free speech must be robust in what it protects, such that only a compelling justification can override it (Dworkin 2013: 131). This captures the conviction, prominent among American constitutional theorists, that “any robust free speech principle must protect at least some harmful speech despite the harm it may cause” (Schauer 2011b: 81; see also Schauer 1982).
If the task of justifying a moral right to free speech requires surmounting both hurdles, it is a tall order. Skeptics about a special right to free speech doubt that the order can be met, and so deny that a natural moral right to freedom of expression can be justified (Schauer 2015; Alexander & Horton 1983; Alexander 2005; Husak 1985). But these theorists may be demanding too much (Kendrick 2017). Start with the claim that free speech must be distinctive. We can accept that free speech be more than simply one implication of a general presumption of liberty. But need it be wholly distinctive? Consider the thesis that free speech is justified by our autonomy interests—interests that justify other rights such as freedom of religion and association. Is it a problem if free speech is justified by interests that are continuous with, or overlap with, interests that justify other rights? Pace the free speech skeptics, maybe not. So long as such claims deserve special recognition, and are worth distinguishing by name, this may be enough (Kendrick 2017: 101). Many of the views canvassed above share normative bases with other important rights. For example, Rawls is clear that he thinks all the basic liberties constitute
essential social conditions for the adequate development and full exercise of the two powers of moral personality over a complete life. (Rawls 2005: 293)
The debate, then, is whether such a shared basis is a theoretical virtue (or at least theoretically unproblematic) or whether it is a theoretical vice, as the skeptics avow.
As for the claim that free speech must be robust, protecting harmful speech, “it is not necessary for a free speech right to protect harmful speech in order for it to be called a free speech right” (Kendrick 2017: 102). We do not tend to think that religious liberty must protect harmful religious activities for it to count as a special right. So it would be strange to insist that the right to free speech must meet this burden to count as a special right. Most of the theorists mentioned above take themselves to be offering views that protect quite a lot of harmful speech. Yet we can question whether this feature is a necessary component of their views, or whether we could imagine variations without this result.
3. Justifying Speech Restrictions
When, and why, can restrictions on speech be justified? It is common in public debate on free speech to hear the provocative claim that free speech is absolute . But the plausibility of such a claim depends on what is exactly meant by it. If understood to mean that no communications between humans can ever be restricted, such a view is held by no one in the philosophical debate. When I threaten to kill you unless you hand me your money; when I offer to bribe the security guard to let me access the bank vault; when I disclose insider information that the company in which you’re heavily invested is about to go bust; when I defame you by falsely posting online that you’re a child abuser; when I endanger you by labeling a drug as safe despite its potentially fatal side-effects; when I reveal your whereabouts to assist a murderer intent on killing you—across all these cases, communications may be uncontroversially restricted. But there are different views as to why.
To help organize such views, consider a set of distinctions influentially defended by Schauer (from 1982 onward). The first category involves uncovered speech : speech that does not even presumptively fall within the scope of a principle of free expression. Many of the speech-acts just canvassed, such as the speech involved in making a threat or insider training, plausibly count as uncovered speech. As the U.S. Supreme Court has said of fighting words (e.g., insults calculated to provoke a street fight),
such utterances are no essential part of any exposition of ideas, and are of such slight social value as a step to truth that any benefit that may be derived from them is clearly outweighed by the social interest in order and morality. ( Chaplinsky v. New Hampshire 1942)
The general idea here is that some speech simply has negligible—and often no —value as free speech, in light of its utter disconnection from the values that justify free speech in the first place. (For discussion of so-called “low-value speech” in the U.S. context, see Sunstein 1989 and Lakier 2015.) Accordingly, when such low-value speech is harmful, it is particularly easy to justify its curtailment. Hence the Court’s view that “the prevention and punishment of [this speech] have never been thought to raise any Constitutional problem”. For legislation restricting such speech, the U.S. Supreme Court applies a “rational basis” test, which is very easy to meet, as it simply asks whether the law is rationally related to a legitimate state interest. (Note that it is widely held that it would still be impermissible to selectively ban low-value speech on a viewpoint-discriminatory basis—e.g., if a state only banned fighting words from left-wing activists while allowing them from right-wing activists.)
Schauer’s next category concerns speech that is covered but unprotected . This is speech that engages the values that underpin free speech; yet the countervailing harm of the speech justifies its restriction. In such cases, while there is real value in such expression as free speech, that value is outweighed by competing normative concerns (or even, as we will see below, on behalf of the very values that underpin free speech). In U.S. constitutional jurisprudence, this category encompasses those extremely rare cases in which restrictions on political speech pass the “strict scrutiny” test, whereby narrow restrictions on high-value speech can be justified due to the compelling state interests thereby served. Consider Holder v. Humanitarian Law Project 2010, in which the Court held that an NGO’s legal advice to a terrorist organization on how to pursue peaceful legal channels were legitimately criminalized under a counter-terrorism statute. While such speech had value as free speech (at least on one interpretation of this contested ruling), the imperative of counter-terrorism justified its restriction. (Arguably, commercial speech, while sometimes called low-value speech by scholars, falls into the covered but unprotected category. Under U.S. law, legislation restricting it receives “intermediate scrutiny” by courts—requiring restrictions to be narrowly drawn to advance a substantial government interest. Such a test suggests that commercial speech has bona fide free-speech value, making it harder to justify regulations on it than regulations on genuinely low-value speech like fighting words. It simply doesn’t have as much free-speech value as categories like political speech, religious speech, or press speech, all of which trigger the strict scrutiny test when restricted.)
As a philosophical matter, we can reasonably disagree about what speech qualifies as covered but unprotected (and need not treat the verdicts of the U.S. Supreme Court as philosophically decisive). For example, consider politically-inflected hate speech, which advances repugnant ideas about the inferior status of certain groups. One could concur that there is substantial free-speech value in such expression, just because it involves the sincere expression of views about central questions of politics and justice (however misguided the views doubtlessly are). Yet one could nevertheless hold that such speech should not be protected in virtue of the substantial harms to which it can lead. In such cases, the free-speech value is outweighed. Many scholars who defend the permissibility of legal restrictions on hate speech hold such a view (e.g., Parekh 2012; Waldron 2012). (More radically, one could hold that such speech’s value is corrupted by its evil, such that it qualifies as genuinely low-value; Howard 2019a.)
The final category of speech encompasses expression that is covered and protected . To declare that speech is protected just is to conclude that it is immune from restriction. A preponderance of human communications fall into this category. This does not mean that such speech can never be regulated ; content-neutral time, place, and manner regulations (e.g., prohibiting loud nighttime protests) can certainly be justified (G. Stone 1987). But such regulations must not be viewpoint discriminatory; they must apply even-handedly across all forms of protected speech.
Schauer’s taxonomy offers a useful organizing framework for how we should think about different forms of speech. Where does it leave the claim that free speech is absolute? The possibility of speech that is covered but unprotected suggests that free speech should sometimes be restricted on account of rival normative concerns. Of course, one could contend that such a category, while logically possible, is substantively an empty set; such a position would involve some kind of absoluteness about free speech (holding that where free-speech values are engaged by expression, no countervailing values can ever be weighty enough to override them). Such a position would be absolutist in a certain sense while granting the permissibility of restrictions on speech that do not engage the free-speech values. (For a recent critique of Schauer’s framework, arguing that governmental designation of some speech as low-value is incompatible with the very ideal of free speech, see Kramer 2021: 31.)
In what follows, this entry will focus on Schauer’s second category: speech that is covered by a free speech principle, but is nevertheless unprotected because of the harms it causes. How do we determine what speech falls into this category? How, in other words, do we determine the limits of free speech? Unsurprisingly, this is where most of the controversy lies.
Most legal systems that protect free speech recognize that the right has limits. Consider, for example, international human rights law, which emphatically protects the freedom of speech as a fundamental human right while also affirming specific restrictions on certain seriously harmful speech. Article 19 of the International Covenant of Civil and Political Rights declares that “[e]veryone shall have the right to freedom of expression; this right shall include freedom to seek, receive and impart information and ideas of all kinds”—but then immediately notes that this right “carries with it special duties and responsibilities”. The subsequent ICCPR article proceeds to endorse legal restrictions on “advocacy of national, racial or religious hatred that constitutes incitement to discrimination, hostility or violence”, as well as speech constituting “propaganda for war” (ICCPR). While such restrictions would plainly be struck down as unconstitutional affronts to free speech in the U.S., this more restrictive approach prevails in most liberal democracies’ treatment of harmful speech.
Set aside the legal issue for now. How should we think about how to determine the limits of the moral right free speech? Those seeking to justify limits on speech tend to appeal to one of two strategies (Howard and Simpson forthcoming). The first strategy appeals to the importance of balancing free speech against other moral values when they come into conflict. This strategy involves external limits on free speech. (The next strategy, discussed below, invokes free speech itself, or the values that justify it, as limit-setting rationales; it thus involves internal limits on free speech.)
A balancing approach recognizes a moral conflict between unfettered communication and external values. Consider again the case of hate speech, understood as expression that attacks members of socially vulnerable groups as inferior or dangerous. On all of the theories canvassed above, there are grounds for thinking that restrictions on hate speech are prima facie in violation of the moral right to free speech. Banning hate speech to prevent people from hearing ideas that might incline them to bigotry plainly seems to disrespect listener autonomy. Further, even when speakers are expressing prejudiced views, they are still engaging their autonomous faculties. Certainly, they are expressing views on questions of public political concern, even false ones. And as thinkers they are engaged in the communication of sincere testimony to others. On many of the leading theories, the values underpinning free speech seem to be militate against bans on hate speech.
Even so, other values matter. Consider, for example, the value of upholding the equal dignity of all citizens. A central insight of critical race theory is that public expressions of white supremacy, for example, attack and undermine that equal dignity (Matsuda, Lawrence, Delgado, & Crenshaw 1993). On Jeremy Waldron’s view (2012), hate speech is best understood as a form of group defamation, launching spurious attacks on others’ reputations and thereby undermining their standing as respected equals in their own community (relatedly, see Beauharnais v. Illinois 1952).
Countries that ban hate speech, accordingly, are plausibly understood not as opposed to free speech, but as recognizing the importance that it be balanced when conflicting with other values. Such balancing can be understood in different ways. In European human rights law, for example, the relevant idea is that the right to free speech is balanced against other rights ; the relevant task, accordingly, is to specify what counts as a proportionate balance between these rights (see Alexy 2003; J. Greene 2021).
For others, the very idea of balancing rights undermines their deontic character. This alternative framing holds that the balancing occurs before we specify what rights are; on this view, we balance interests against each other, and only once we’ve undertaken that balancing do we proceed to define what our rights protect. As Scanlon puts it,
The only balancing is balancing of interests. Rights are not balanced, but are defined, or redefined, in the light of the balance of interests and of empirical facts about how these interests can best be protected. (2008: 78)
This balancing need not come in the form of some crude consequentialism; otherwise it would be acceptable to limit the rights of the few to secure trivial benefits for the many. On a contractualist moral theory such as Scanlon’s, the test is to assess the strength of any given individual’s reason to engage in (or access) the speech, against the strength of any given individual’s reason to oppose it.
Note that those who engage in balancing need not give up on the idea of viewpoint neutrality; they can accept that, as a general principle, the state should not restrict speech on the grounds that it disapproves of its message and dislikes that others will hear it. The point, instead, is that this commitment is defeasible; it is possible to be overridden.
One final comment is apt. Those who are keen to balance free speech against other values tend to be motivated by the concern that speech can cause harm, either directly or indirectly (on this distinction, see Schauer 1993). But to justify restrictions on speech, it is not sufficient (and perhaps not even necessary) to show that such speech imposes or risks imposing harm. The crucial point is that the speech is wrongful (or, perhaps, wrongfully harmful or risky) , breaching a moral duty that speakers owe to others. Yet very few in the free speech literature think that the mere offensiveness of speech is sufficient to justify restrictions on it. Even Joel Feinberg, who thinks offensiveness can sometimes be grounds for restricting conduct, makes a sweeping exception for
[e]xpressions of opinion, especially about matters of public policy, but also about matters of empirical fact, and about historical, scientific, theological, philosophical, political, and moral questions. (1985: 44)
And in many cases, offensive speech may be actively salutary, as when racists are offended by defenses of racial equality (Waldron 1987). Accordingly, despite how large it looms in public debate, discussion of offensive speech will not play a major role in the discussion here.
We saw that one way to justify limits on free speech is to balance it against other values. On that approach, free speech is externally constrained. A second approach, in contrast, is internally constrained. On this approach, the very values that justify free speech themselves determine its own limits. This is a revisionist approach to free speech since, unlike orthodox thinking, it contends that a commitment to free speech values can counterintuitively support the restriction of speech—a surprising inversion of traditional thinking on the topic (see Howard and Simpson forthcoming). This move—justifying restrictions on speech by appealing to the values that underpin free speech—is now prevalent in the philosophical literature (for an overview, see Barendt 2005: 1ff).
Consider, for example, the claim that free speech is justified by concerns of listener autonomy. On such a view, as we saw above, autonomous citizens have interests in exposure to a wide range of viewpoints, so that they can decide for themselves what to believe. But many have pointed out that this is not autonomous citizens’ only interest; they also have interests in not getting murdered by those incited by incendiary speakers (Amdur 1980). Likewise, insofar as being targeted by hate speech undermines the exercise of one’s autonomous capacities, appeal to the underlying value of autonomy could well support restrictions on such speech (Brison 1998; see also Brink 2001). What’s more, if our interests as listeners in acquiring accurate information is undermined by fraudulent information, then restrictions on such information could well be compatible with our status as autonomous; this was one of the insights that led Scanlon to complicate his theory of free speech (1978).
Or consider the theory that free speech is justified because of its role in enabling autonomous speakers to express themselves. But as Japa Pallikkathayil has argued, some speech can intimidate its audiences into staying silent (as with some hate speech), out of fear for what will happen if they speak up (Pallikkathayil 2020). In principle, then, restrictions on hate speech may serve to support the value of speaker expression, rather than undermine it (see also Langton 2018; Maitra 2009; Maitra & McGowan 2007; and Matsuda 1989: 2337). Indeed, among the most prominent claims in feminist critiques of pornography is precisely that it silences women—not merely through its (perlocutionary) effects in inspiring rape, but more insidiously through its (illocutionary) effects in altering the force of the word “no” (see MacKinnon 1984; Langton 1993; and West 204 [2022]; McGowan 2003 and 2019; cf. Kramer 2021, pp. 160ff).
Now consider democracy theories. On the one hand, democracy theorists are adamant that citizens should be free to discuss any proposals, even the destruction of democracy itself (e.g., Meiklejohn 1948: 65–66). On the other hand, it isn’t obvious why citizens’ duties as democratic citizens could not set a limit to their democratic speech rights (Howard 2019a). The Nazi propagandist Goebbels is said to have remarked:
This will always remain one of the best jokes of democracy, that it gave its deadly enemies the means by which it was destroyed. (as quoted in Fox & Nolte 1995: 1)
But it is not clear why this is necessarily so. Why should we insist on a conception of democracy that contains a self-destruct mechanism? Merely stipulating that democracy requires this is not enough (see A. Greene and Simpson 2017).
Finally, consider Shiffrin’s thinker-based theory. Shiffrin’s view is especially well-placed to explain why varieties of harmful communications are protected speech; what the theory values is the sincere transmission of veridical testimony, whereby speakers disclose what they genuinely believe to others, even if what they believe is wrongheaded and dangerous. Yet because the sincere testimony of thinkers is what qualifies some communication for protection, Shiffrin is adamant that lying falls outside the protective ambit of freedom of expression (2014) This, then, sets an internal limit on her own theory (even if she herself disfavors all lies’ outright prohibition for reasons of tolerance). The claim that lying falls outside the protective ambit of free speech is itself a recurrent suggestion in the literature (Strauss 1991: 355; Brown 2023). In an era of rampant disinformation, this internal limit is of substantial practical significance.
Suppose the moral right (or principle) of free speech is limited, as most think, such that not all communications fall within its protective ambit (either for external reasons, internal reasons, or both). Even so, it does not follow that laws banning such unprotected speech can be justified all-things-considered. Further moral tests must be passed before any particular policy restricting speech can be justified. This sub-section focuses on the requirement that speech restrictions be proportionate .
The idea that laws implicating fundamental rights must be proportionate is central in many jurisdictions’ constitutional law, as well as in the international law of human rights. As a representative example, consider the specification of proportionality offered by the Supreme Court of Canada:
First, the measures adopted must be carefully designed to achieve the objective in question. They must not be arbitrary, unfair, or based on irrational considerations. In short, they must be rationally connected to the objective. Second, the means, even if rationally connected to the objective in this first sense, should impair “as little as possible” the right or freedom in question[…] Third, there must be a proportionality between the effects of the measures which are responsible for limiting the Charter right or freedom, and the objective which has been identified as of “sufficient importance” ( R v. Oakes 1986).
It is this third element (often called “proportionality stricto sensu ”) on which we will concentrate here; this is the focused sense of proportionality that roughly tracks how the term is used in the philosophical literatures on defensive harm and war, as well as (with some relevant differences) criminal punishment. (The strict scrutiny and intermediate scrutiny tests of U.S. constitutional law are arguably variations of the proportionality test; but set aside this complication for now as it distracts from the core philosophical issues. For relevant legal discussion, see Tsesis 2020.)
Proportionality, in the strict sense, concerns the relation between the costs or harms imposed by some measure and the benefits that the measure is designed to secure. The organizing distinction in recent philosophical literature (albeit largely missing in the literature on free speech) is one between narrow proportionality and wide proportionality . While there are different ways to cut up the terrain between these terms, let us stipulatively define them as follows. An interference is narrowly proportionate just in case the intended target of the interference is liable to bear the costs of that interference. An interference is widely proportionate just in case the collateral costs that the interference unintentionally imposes on others can be justified. (This distinction largely follows the literature in just war theory and the ethics of defensive force; see McMahan 2009.) While the distinction is historically absent from free speech theory, it has powerful payoffs in helping to structure this chaotic debate (as argued in Howard 2019a).
So start with the idea that restrictions on communication must be narrowly proportionate . For a restriction to be narrowly proportionate, those whose communications are restricted must be liable to bear their costs, such that they are not wronged by their imposition. One standard way to be liable to bear certain costs is to have a moral duty to bear them (Tadros 2012). So, for example, if speakers have a moral duty to refrain from libel, hate speech, or some other form of harmful speech, they are liable to bear at least some costs involved in the enforcement of that duty. Those costs cannot be unlimited; a policy of executing hate speakers could not plausibly be justified. Typically, in both defensive and punitive contexts, wrongdoers’ liability is determined by their culpability, the severity of their wrong, or some combination of the two. While it is difficult to say in the abstract what the precise maximal cost ceiling is for any given restriction, as it depends hugely on the details, the point is simply that there is some ceiling above which a speech restriction (like any restriction) imposes unacceptably high costs, even on wrongdoers.
Second, for a speech restriction to be justified, we must also show that it would be widely proportionate . Suppose a speaker is liable to bear the costs of some policy restricting her communication, such that she is not wronged by its imposition. It may be that the collateral costs of such a policy would render it unacceptable. One set of costs is chilling effects , the “overdeterrence of benign conduct that occurs incidentally to a law’s legitimate purpose or scope” (Kendrick 2013: 1649). The core idea is that laws targeting unprotected, legitimately proscribed expression may nevertheless end up having a deleterious impact on protected expression. This is because laws are often vague, overbroad, and in any case are likely to be misapplied by fallible officials (Schauer 1978: 699).
Note that if a speech restriction produces chilling effects, it does not follow that the restriction should not exist at all. Rather, concern about chilling effects instead suggests that speech restrictions should be under-inclusive—restricting less speech than is actually harmful—in order to create “breathing space”, or “a buffer zone of strategic protection” (Schauer 1978: 710) for legitimate expression and so reduce unwanted self-censorship. For example, some have argued that even though speech can cause harm recklessly or negligently, we should insist on specific intent as the mens rea of speech crimes in order to reduce any chilling effects that could follow (Alexander 1995: 21–128; Schauer 1978: 707; cf. Kendrick 2013).
But chilling effects are not the only sort of collateral effects to which speech restrictions could lead. Earlier we noted the risk that states might abuse their censorial powers. This, too, could militate in favor of underinclusive speech restrictions. Or the implication could be more radical. Consider the problem that it is difficult to author restrictions on hate speech in a tightly specified way; the language involved is open-ended in a manner that enables states to exercise considerable judgment in deciding what speech-acts, in fact, count as violations (see Strossen 2018). Given the danger that the state will misuse or abuse these laws to punish legitimate speech, some might think this renders their enactment widely disproportionate. Indeed, even if the law were well-crafted and would be judiciously applied by current officials, the point is that those in the future may not be so trustworthy.
Those inclined to accept such a position might simply draw the conclusion that legislatures ought to refrain from enacting laws against hate speech. A more radical conclusion is that the legal right to free speech ought to be specified so that hate speech is constitutionally protected. In other words, we ought to give speakers a legal right to violate their moral duties, since enforcing those moral duties through law is simply too risky. By appealing to this logic, it is conceivable that the First Amendment position on hate speech could be justified all-things-considered—not because the underlying moral right to free speech protects hate speech, but because hate speech must be protected for instrumental reasons of preventing future abuses of power (Howard 2019a).
Suppose certain restrictions on harmful speech can be justified as proportionate, in both the narrow and wide senses. This is still not sufficient to justify them all-things-considered. Additionally, they must be justified as necessary . (Note that some conceptions of proportionality in human rights law encompass the necessity requirement, but this entry follows the prevailing philosophical convention by treating them as distinct.)
Why might restrictions on harmful speech be unnecessary? One of the standard claims in the free speech literature is that we should respond to harmful speech not by banning it, but by arguing back against it. Counter-speech—not censorship—is the appropriate solution. This line of reasoning is old. As John Milton put it in 1644: “Let [Truth] and Falsehood grapple; who ever knew Truth put to the worse in a free and open encounter?” The insistence on counter-speech as the remedy for harmful speech is similarly found, as noted above, throughout chapter 2 of Mill’s On Liberty .
For many scholars, this line of reply is justified by the fact that they think the harmful speech in question is protected by the moral right to free speech. For such scholars, counter-speech is the right response because censorship is morally off the table. For other scholars, the recourse to counter-speech has a plausible distinct rationale (although it is seldom articulated): its possibility renders legal restrictions unnecessary. And because it is objectionable to use gratuitous coercion, legal restrictions are therefore impermissible (Howard 2019a). Such a view could plausibly justify Mill’s aforementioned analysis in the corn dealer example, whereby censorship is permissible but only when there’s no time for counter-speech—a view that is also endorsed by the U.S. Supreme Court in Brandenburg v. Ohio 395 U.S. 444 (1969).
Whether this argument succeeds depends upon a wide range of further assumptions—about the comparable effectiveness of counter-speech relative to law; about the burdens that counter-speech imposes on prospective counter-speakers. Supposing that the argument succeeds, it invites a range of further normative questions about the ethics of counter-speech. For example, it is important who has the duty to engage in counter-speech, who its intended audience is, and what specific forms the counter-speech ought to take—especially in order to maximize its persuasive effectiveness (Brettschneider 2012; Cepollaro, Lepoutre, & Simpson 2023; Howard 2021b; Lepoutre 2021; Badano & Nuti 2017). It is also important to ask questions about the moral limits of counter-speech. For example, insofar as publicly shaming wrongful speakers has become a prominent form of counter-speech, it is crucial to interrogate its permissibility (e.g., Billingham and Parr 2020).
This final section canvasses the young philosophical debate concerning freedom of speech on the internet. With some important exceptions (e.g., Barendt 2005: 451ff), this issue has only recently accelerated (for an excellent edited collection, see Brison & Gelber 2019). There are many normative questions to be asked about the moral rights and obligations of internet platforms. Here are three. First, do internet platforms have moral duties to respect the free speech of their users? Second, do internet platforms have moral duties to restrict (or at least refrain from amplifying) harmful speech posted by their users? And finally, if platforms do indeed have moral duties to restrict harmful speech, should those duties be legally enforced?
The reference to internet platforms , is a deliberate focus on large-scale social media platforms, through which people can discover and publicly share user-generated content. We set aside other entities such as search engines (Whitney & Simpson 2019), important though they are. That is simply because the central political controversies, on which philosophical input is most urgent, concern the large social-media platforms.
Consider the question of whether internet platforms have moral duties to respect the free speech of their users. One dominant view in the public discourse holds that the answer is no . On this view, platforms are private entities, and as such enjoy the prerogative to host whatever speech they like. This would arguably be a function of them having free speech rights themselves. Just as the free speech rights of the New York Times give it the authority to publish whatever op-eds it sees fit, the free speech rights of platforms give them the authority to exercise editorial or curatorial judgment about what speech to allow. On this view, if Facebook were to decide to become a Buddhist forum, amplifying the speech of Buddhist users and promoting Buddhist perspectives and ideas, and banning speech promoting other religions, it would be entirely within its moral (and thus proper legal) rights to do so. So, too, if it were to decide to become an atheist forum.
A radical alternative view holds that internet platforms constitute a public forum , a term of art from U.S. free speech jurisprudence used to designate spaces “designed for and dedicated to expressive activities” ( Southeastern Promotions Ltd., v. Conrad 1975). As Kramer has argued:
social-media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter and YouTube have become public fora. Although the companies that create and run those platforms are not morally obligated to sustain them in existence at all, the role of controlling a public forum morally obligates each such company to comply with the principle of freedom of expression while performing that role. No constraints that deviate from the kinds of neutrality required under that principle are morally legitimate. (Kramer 2021: 58–59)
On this demanding view, platforms’ duties to respect speech are (roughly) identical to the duties of states. Accordingly, if efforts by the state to restrict hate speech, pornography, and public health misinformation (for example) are objectionable affronts to free speech, so too are platforms’ content moderation rules for such content. A more moderate view does not hold that platforms are public forums as such, but holds that government channels or pages qualify as public forums (the claim at issue in Knight First Amendment Institute v. Trump (2019).)
Even if we deny that platforms constitute public forums, it is plausible that they engage in a governance function of some kind (Klonick 2018). As Jack Balkin has argued, the traditional model of free speech, which sees it as a relation between speakers and the state, is today plausibly supplanted by a triadic model, involving a more complex relation between speakers, governments, and intermediaries (2004, 2009, 2018, 2021). If platforms do indeed have some kind of governance function, it may well trigger responsibilities for transparency and accountability (as with new legislation such as the EU’s Digital Services Act and the UK’s Online Safety Act).
Second, consider the question of whether platforms have a duty to remove harmful content posted by users. Even those who regard them as public forums could agree that platforms may have a moral responsibility to remove illegal unprotected speech. Yet a dominant view in the public debate has historically defended platforms’ place as mere conduits for others’ speech. This is the current position under U.S. law (as with 47 U.S. Code §230), which broadly exempts platforms from liability for much illegal speech, such as defamation. On this view, we should view platforms as akin to bulletin boards: blame whoever posts wrongful content, but don’t hold the owner of the board responsible.
This view is under strain. Even under current U.S. law, platforms are liable for removing some content, such as child sexual abuse material and copyright infringements, suggesting that it is appropriate to demand some accountability for the wrongful content posted by others. An increasing body of philosophical work explores the idea that platforms are indeed morally responsible for removing extreme content. For example, some have argued that platforms have a special responsibility to prevent the radicalization that occurs on their networks, given the ways in which extreme content is amplified to susceptible users (Barnes 2022). Without engaging in moderation (i.e., removal) of harmful content, platforms are plausibly complicit with the wrongful harms perpetrated by users (Howard forthcoming).
Yet it remains an open question what a responsible content moderation policy ought to involve. Many are tempted by a juridical model, whereby platforms remove speech in accordance with clearly announced rules, with user appeals mechanisms in place for individual speech decisions to ensure they are correctly made (critiqued in Douek 2022b). Yet platforms have billions of users and remove millions of pieces of content per week. Accordingly, perfection is not possible. Moving quickly to remove harmful content during a crisis—e.g., Covid misinformation—will inevitably increase the number of false positives (i.e., legitimate speech taken down as collateral damage). It is plausible that the individualistic model of speech decisions adopted by courts is decidedly implausible to help us govern online content moderation; as noted in Douek 2021 and 2022a, what is needed is analysis of how the overall system should operate at scale, with a focus on achieving proportionality between benefits and costs. Alternatively, one might double down and insist that the juridical model is appropriate, given the normative significance of speech. And if it is infeasible for social-media companies to meet its demands given their size, then all the worse for social-media companies. On this view, it is they who must bend to meet the moral demands of free speech theory, not the other way around.
Substantial philosophical work needs to be done to deliver on this goal. The work is complicated by the fact that artificial intelligence (AI) is central to the processes of content moderation; human moderators, themselves subjected to terrible working conditions at long hours, work in conjunction with machine learning tools to identify and remove content that platforms have restricted. Yet AI systems notoriously are as biased as their training data. Further, their “black box” decisions are cryptic and cannot be easily understood. Given that countless speech decisions will necessarily be made without human involvement, it is right to ask whether it is reasonable to expect users to accept the deliverances of machines (e.g., see Vredenburgh 2022; Lazar forthcoming a). Note that machine intelligence is used not merely for content moderation, narrowly understood as the enforcement of rules about what speech is allowed. It is also deployed for the broader practice of content curation, determining what speech gets amplified — raising the question of what normative principles should govern such amplification; see Lazar forthcoming b).
Finally, there is the question of legal enforcement. Showing that platforms have the moral responsibility to engage in content moderation is necessary to justifying its codification into a legal responsibility. Yet it is not sufficient; one could accept that platforms have moral duties to moderate (some) harmful speech while also denying that those moral duties ought to be legally enforced. A strong, noninstrumental version of such a view would hold that while speakers have moral duties to refrain from wrongful speech, and platforms have duties not to platform or amplify it, the coercive enforcement of such duties would violate the moral right to freedom of expression. A more contingent, instrumental version of the view would hold that legal enforcement is not in principle impermissible; but in practice, it is simply too risky to grant the state the authority to enforce platforms’ and speakers’ moral duties, given the potential for abuse and overreach.
Liberals who champion the orthodox interpretation of the First Amendment, yet insist on robust content moderation, likely hold one or both of these views. Yet globally such views seem to be in the minority. Serious legislation is imminent that will subject social-media companies to burdensome regulation, in the form of such laws as the Digital Services Act in the European Union and the Online Safety Bill in the UK. Normatively evaluating such legislation is a pressing task. So, too, is the task of designing normative theories to guide the design of content moderation systems, and the wider governance of the digital public sphere. On both fronts, political philosophers should get back to work.
- Alexander, Larry [Lawrence], 1995, “Free Speech and Speaker’s Intent”, Constitutional Commentary , 12(1): 21–28.
- –––, 2005, Is There a Right of Freedom of Expression? , (Cambridge Studies in Philosophy and Law), Cambridge/New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Alexander, Lawrence and Paul Horton, 1983, “The Impossibility of a Free Speech Principle Review Essay”, Northwestern University Law Review , 78(5): 1319–1358.
- Alexy, Robert, 2003, “Constitutional Rights, Balancing, and Rationality”, Ratio Juris , 16(2): 131–140. doi:10.1111/1467-9337.00228
- Amdur, Robert, 1980, “Scanlon on Freedom of Expression”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 9(3): 287–300.
- Arneson, Richard, 2009, “Democracy is Not Intrinsically Just”, in Justice and Democracy , Keith Dowding, Robert E. Goodin, and Carole Pateman (eds.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 40–58.
- Baker, C. Edwin, 1989, Human Liberty and Freedom of Speech , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2009, “Autonomy and Hate Speech”, in Hare and Weinstein 2009: 139–157 (ch. 8). doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199548781.003.0009
- Balkin, Jack M., 2004, “Digital Speech and Democratic Culture: A Theory of Freedom of Expression for the Information Society”, New York University Law Review , 79(1): 1–55.
- –––, 2009, “The Future of Free Expression in a Digital Age Free Speech and Press in the Digital Age”, Pepperdine Law Review , 36(2): 427–444.
- –––, 2018, “Free Speech Is a Triangle Essays”, Columbia Law Review , 118(7): 2011–2056.
- –––, 2021, “How to Regulate (and Not Regulate) Social Media”, Journal of Free Speech Law , 1(1): 71–96. [ Balkin 2021 available online (pdf) ]
- Barendt, Eric M., 2005, Freedom of Speech , second edition, Oxford/New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199225811.001.0001
- Barnes, Michael Randall, 2022, “Online Extremism, AI, and (Human) Content Moderation”, Feminist Philosophy Quarterly , 8(3/4): article 6. [ Barnes 2022 available online ]
- Beauharnais v. Illinois 343 U.S. 250 (1952).
- Billingham, Paul and Tom Parr, 2020, “Enforcing Social Norms: The Morality of Public Shaming”, European Journal of Philosophy , 28(4): 997–1016. doi:10.1111/ejop.12543
- Blasi, Vincent, 1977, “The Checking Value in First Amendment Theory”, American Bar Foundation Research Journal 3: 521–649.
- –––, 2004, “Holmes and the Marketplace of Ideas”, The Supreme Court Review , 2004: 1–46.
- Brettschneider, Corey Lang, 2012, When the State Speaks, What Should It Say? How Democracies Can Protect Expression and Promote Equality , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Brietzke, Paul H., 1997, “How and Why the Marketplace of Ideas Fails”, Valparaiso University Law Review , 31(3): 951–970.
- Bollinger, Lee C., 1986, The Tolerant Society: Free Speech and Extremist Speech in America , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Bonotti, Matteo and Jonathan Seglow, 2022, “Freedom of Speech: A Relational Defence”, Philosophy & Social Criticism , 48(4): 515–529.
- Brandenburg v. Ohio 395 U.S. 444 (1969).
- Brink, David O., 2001, “Millian Principles, Freedom of Expression, and Hate Speech”, Legal Theory , 7(2): 119–157. doi:10.1017/S1352325201072019
- Brison, Susan J., 1998, “The Autonomy Defense of Free Speech”, Ethics , 108(2): 312–339. doi:10.1086/233807
- Brison, Susan J. and Katharine Gelber (eds), 2019, Free Speech in the Digital Age , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oso/9780190883591.001.0001
- Brown, Étienne, 2023, “Free Speech and the Legal Prohibition of Fake News”, Social Theory and Practice , 49(1): 29–55. doi:10.5840/soctheorpract202333179
- Buchanan, Allen E., 2013, The Heart of Human Rights , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199325382.001.0001
- Cepollaro, Bianca, Maxime Lepoutre, and Robert Mark Simpson, 2023, “Counterspeech”, Philosophy Compass , 18(1): e12890. doi:10.1111/phc3.12890
- Chaplinsky v. New Hampshire 315 U.S. 568 (1942).
- Cohen, Joshua, 1993, “Freedom of Expression”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 22(3): 207–263.
- –––, 1997, “Deliberation and Democratic Legitimacy”, in Deliberative Democracy: Essays on Reason and Politics , James Bohman and William Rehg (eds), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 67–92.
- Dworkin, Ronald, 1981, “Is There a Right to Pornography?”, Oxford Journal of Legal Studies , 1(2): 177–212. doi:10.1093/ojls/1.2.177
- –––, 1996, Freedom’s Law: The Moral Reading of the American Constitution , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- –––, 2006, “A New Map of Censorship”, Index on Censorship , 35(1): 130–133. doi:10.1080/03064220500532412
- –––, 2009, “Forward.” In Extreme Speech and Democracy , ed. J. Weinstein and I. Hare, pp. v-ix. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2013, Religion without God , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Douek, Evelyn, 2021, “Governing Online Speech: From ‘Posts-as-Trumps’ to Proportionality and Probability”, Columbia Law Review , 121(3): 759–834.
- –––, 2022a, “Content Moderation as Systems Thinking”, Harvard Law Review , 136(2): 526–607.
- –––, 2022b, “The Siren Call of Content Moderation Formalism”, in Social Media, Freedom of Speech, and the Future of Our Democracy , Lee C. Bollinger and Geoffrey R. Stone (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press, 139–156 (ch. 9). doi:10.1093/oso/9780197621080.003.0009
- Ely, John Hart, 1975, “Flag Desecration: A Case Study in the Roles of Categorization and Balancing in First Amendment Analysis”, Harvard Law Review , 88: 1482–1508.
- Emerson, Thomas I., 1970, The System of Freedom of Expression , New York: Random House.
- Epstein, Richard A., 1992, “Property, Speech, and the Politics of Distrust”, University of Chicago Law Review , 59(1): 41–90.
- Estlund, David, 2008, Democratic Authority: A Philosophical Framework , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Feinberg, Joel, 1984, The Moral Limits of the Criminal Law Volume 1: Harm to Others , New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/0195046641.001.0001
- –––, 1985, The Moral Limits of the Criminal Law: Volume 2: Offense to Others , New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/0195052153.001.0001
- Fish, Stanley Eugene, 1994, There’s No Such Thing as Free Speech, and It’s a Good Thing, Too , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Fox, Gregory H. and Georg Nolte, 1995, “Intolerant Democracies”, Harvard International Law Journal , 36(1): 1–70.
- Gelber, Katharine, 2010, “Freedom of Political Speech, Hate Speech and the Argument from Democracy: The Transformative Contribution of Capabilities Theory”, Contemporary Political Theory , 9(3): 304–324. doi:10.1057/cpt.2009.8
- Gilmore, Jonathan, 2011, “Expression as Realization: Speakers’ Interests in Freedom of Speech”, Law and Philosophy , 30(5): 517–539. doi:10.1007/s10982-011-9096-z
- Gordon, Jill, 1997, “John Stuart Mill and the ‘Marketplace of Ideas’:”, Social Theory and Practice , 23(2): 235–249. doi:10.5840/soctheorpract199723210
- Greenawalt, Kent, 1989, Speech, Crime, and the Uses of Language , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Greene, Amanda R. and Robert Mark Simpson, 2017, “Tolerating Hate in the Name of Democracy”, The Modern Law Review , 80(4): 746–765. doi:10.1111/1468-2230.12283
- Greene, Jamal, 2021, How Rights Went Wrong: Why Our Obsession with Rights Is Tearing America Apart , Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
- Gutmann, Amy and Dennis Thompson, 2008, Why Deliberative Democracy? Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Habermas, Jürgen, 1992 [1996], Faktizität und Geltung: Beiträge zur Diskurstheorie des Rechts und des demokratischen Rechtsstaats , Frankfurt am Main: Suhrkamp. Translated as Between Facts and Norms: Contributions to a Discourse Theory of Law and Democracy , William Rehg (trans.), (Studies in Contemporary German Social Thought), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1996.
- Hare, Ivan and James Weinstein (eds), 2009, Extreme Speech and Democracy , Oxford/New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199548781.001.0001
- Hart, H. L. A., 1955, “Are There Any Natural Rights?”, The Philosophical Review , 64(2): 175–191. doi:10.2307/2182586
- Heinze, Eric, 2016, Hate Speech and Democratic Citizenship , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198759027.001.0001
- Heyman, Steven J., 2009, “Hate Speech, Public Discourse, and the First Amendment”, in Hare and Weinstein 2009: 158–181 (ch. 9). doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199548781.003.0010
- Hohfeld, Wesley, 1917, “Fundamental Legal Conceptions as Applied in Judicial Reasoning,” Yale Law Journal 26(8): 710–770.
- Holder v. Humanitarian Law Project 561 U.S. 1 (2010).
- Hornsby, Jennifer, 1995, “Disempowered Speech”, Philosophical Topics , 23(2): 127–147. doi:10.5840/philtopics199523211
- Howard, Jeffrey W., 2019a, “Dangerous Speech”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 47(2): 208–254. doi:10.1111/papa.12145
- –––, 2019b, “Free Speech and Hate Speech”, Annual Review of Political Science , 22: 93–109. doi:10.1146/annurev-polisci-051517-012343
- –––, 2021, “Terror, Hate and the Demands of Counter-Speech”, British Journal of Political Science , 51(3): 924–939. doi:10.1017/S000712341900053X
- –––, forthcoming a, “The Ethics of Social Media: Why Content Moderation is a Moral Duty”, Journal of Practical Ethics .
- Howard, Jeffrey W. and Robert Simpson, forthcoming b, “Freedom of Speech”, in Issues in Political Theory , fifth edition, Catriona McKinnon, Patrick Tomlin, and Robert Jubb (eds), Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Husak, Douglas N., 1985, “What Is so Special about [Free] Speech?”, Law and Philosophy , 4(1): 1–15. doi:10.1007/BF00208258
- Jacobson, Daniel, 2000, “Mill on Liberty, Speech, and the Free Society”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 29(3): 276–309. doi:10.1111/j.1088-4963.2000.00276.x
- Kendrick, Leslie, 2013, “Speech, Intent, and the Chilling Effect”, William & Mary Law Review , 54(5): 1633–1692.
- –––, 2017, “Free Speech as a Special Right”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 45(2): 87–117. doi:10.1111/papa.12087
- Klonick, Kate, 2018, “The New Governors”, Harvard Law Review 131: 1589–1670.
- Knight First Amendment Institute v. Trump 928 F.3d 226 (2019).
- Kramer, Matthew H., 2021, Freedom of Expression as Self-Restraint , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Lakier, Genevieve, 2015, “The Invention of Low-Value Speech”, Harvard Law Review , 128(8): 2166–2233.
- Landemore, Hélène, 2013, Democratic Reason: Politics, Collective Intelligence, and the Rule of the Many , Princeton/Oxford: Princeton University Press.
- Langton, Rae, 1993, “Speech Acts and Unspeakable Acts”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 22(4): 293–330.
- –––, 2018, “The Authority of Hate Speech”, in Oxford Studies in Philosophy of Law (Volume 3), John Gardner, Leslie Green, and Brian Leiter (eds.), Oxford: Oxford University Press: ch. 4. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198828174.003.0004
- Lazar, Seth, forthcoming, “Legitimacy, Authority, and the Public Value of Explanations”, in Oxford Studies in Political Philosophy (Volume 10), Steven Wall (ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, forthcoming, Connected by Code: Algorithmic Intermediaries and Political Philosophy, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Leiter, Brian, 2016, “The Case against Free Speech”, Sydney Law Review , 38(4): 407–439.
- Lepoutre, Maxime, 2021, Democratic Speech in Divided Times , Oxford/New York: Oxford University Press.
- MacKinnon, Catharine A., 1984 [1987], “Not a Moral Issue”, Yale Law & Policy Review , 2(2): 321–345. Reprinted in her Feminism Unmodified: Discourses on Life and Law , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1987, 146–162 (ch. 13).
- Macklem, Timothy, 2006, Independence of Mind , Oxford/New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199535446.001.0001
- Maitra, Ishani, 2009, “Silencing Speech”, Canadian Journal of Philosophy , 39(2): 309–338. doi:10.1353/cjp.0.0050
- Maitra, Ishani and Mary Kate McGowan, 2007, “The Limits of Free Speech: Pornography and the Question of Coverage”, Legal Theory , 13(1): 41–68. doi:10.1017/S1352325207070024
- Matsuda, Mari J., 1989, “Public Response to Racist Speech: Considering the Victim’s Story Legal Storytelling”, Michigan Law Review , 87(8): 2320–2381.
- Matsuda, Mari J., Charles R. Lawrence, Richard Delgado, and Kimberlè Williams Crenshaw, 1993, Words That Wound: Critical Race Theory, Assaultive Speech, and the First Amendment (New Perspectives on Law, Culture, and Society), Boulder, CO: Westview Press. Reprinted 2018, Abingdon: Routledge. doi:10.4324/9780429502941
- McGowan, Mary Kate, 2003, “Conversational Exercitives and the Force of Pornography”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 31(2): 155–189. doi:10.1111/j.1088-4963.2003.00155.x
- –––, 2019, Just Words: On Speech and Hidden Harm , Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198829706.001.0001
- McMahan, Jeff, 2009, Killing in War , (Uehiro Series in Practical Ethics), Oxford: Clarendon Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199548668.001.0001
- Milton, John, 1644, “Areopagitica”, London. [ Milton 1644 available online ]
- Meiklejohn, Alexander, 1948, Free Speech and Its Relation to Self-Government , New York: Harper.
- –––, 1960, Political Freedom: The Constitutional Powers of the People , New York: Harper.
- Mill, John Stuart, 1859, On Liberty , London: John W. Parker and Son. [ Mill 1859 available online ]
- Nagel, Thomas, 2002, Concealment and Exposure , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Pallikkathayil, Japa, 2020, “Free Speech and the Embodied Self”, in Oxford Studies in Political Philosophy (Volume 6), David Sobel, Peter Vallentyne, and Steven Wall (eds.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 61–84 (ch. 3). doi:10.1093/oso/9780198852636.003.0003
- Parekh, Bhikhu, 2012, “Is There a Case for Banning Hate Speech?”, in The Content and Context of Hate Speech: Rethinking Regulation and Responses , Michael Herz and Peter Molnar (eds.), Cambridge/New York: Cambridge University Press, 37–56. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139042871.006
- Post, Robert C., 1991, “Racist Speech, Democracy, and the First Amendment Free Speech and Religious, Racial, and Sexual Harassment”, William and Mary Law Review , 32(2): 267–328.
- –––, 2000, “Reconciling Theory and Doctrine in First Amendment Jurisprudence Symposium of the Law in the Twentieth Century”, California Law Review , 88(6): 2353–2374.
- –––, 2009, “Hate Speech”, in Hare and Weinstein 2009: 123–138 (ch. 7). doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199548781.003.0008
- –––, 2011, “Participatory Democracy as a Theory of Free Speech: A Reply Replies”, Virginia Law Review , 97(3): 617–632.
- Quong, Jonathan, 2011, Liberalism without Perfection , Oxford/New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199594870.001.0001
- R v. Oakes , 1 SCR 103 (1986).
- Rawls, John, 2005, Political Liberalism , expanded edition, (Columbia Classics in Philosophy), New York: Columbia University Press.
- Raz, Joseph, 1991 [1994], “Free Expression and Personal Identification”, Oxford Journal of Legal Studies , 11(3): 303–324. Collected in his Ethics in the Public Domain: Essays in the Morality of Law and Politics , Oxford: Clarendon Press, 146–169 (ch. 7).
- Redish, Martin H., 1982, “Value of Free Speech”, University of Pennsylvania Law Review , 130(3): 591–645.
- Rubenfeld, Jed, 2001, “The First Amendment’s Purpose”, Stanford Law Review , 53(4): 767–832.
- Scanlon, Thomas, 1972, “A Theory of Freedom of Expression”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 1(2): 204–226.
- –––, 1978, “Freedom of Expression and Categories of Expression ”, University of Pittsburgh Law Review , 40(4): 519–550.
- –––, 2008, “Rights and Interests”, in Arguments for a Better World: Essays in Honor of Amartya Sen , Kaushik Basu and Ravi Kanbur (eds), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 68–79 (ch. 5). doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199239115.003.0006
- –––, 2013, “Reply to Wenar”, Journal of Moral Philosophy 10: 400–406
- Schauer, Frederick, 1978, “Fear, Risk and the First Amendment: Unraveling the Chilling Effect”, Boston University Law Review , 58(5): 685–732.
- –––, 1982, Free Speech: A Philosophical Enquiry , Cambridge/New York: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 1985, “Slippery Slopes”, Harvard Law Review , 99(2): 361–383.
- –––, 1993, “The Phenomenology of Speech and Harm”, Ethics , 103(4): 635–653. doi:10.1086/293546
- –––, 2004, “The Boundaries of the First Amendment: A Preliminary Exploration of Constitutional Salience”, Harvard Law Review , 117(6): 1765–1809.
- –––, 2009, “Is It Better to Be Safe than Sorry: Free Speech and the Precautionary Principle Free Speech in an Era of Terrorism”, Pepperdine Law Review , 36(2): 301–316.
- –––, 2010, “Facts and the First Amendment”, UCLA Law Review , 57(4): 897–920.
- –––, 2011a, “On the Relation between Chapters One and Two of John Stuart Mill’s On Liberty ”, Capital University Law Review , 39(3): 571–592.
- –––, 2011b, “Harm(s) and the First Amendment”, The Supreme Court Review , 2011: 81–111. doi:10.1086/665583
- –––, 2015, “Free Speech on Tuesdays”, Law and Philosophy , 34(2): 119–140. doi:10.1007/s10982-014-9220-y
- Shiffrin, Seana Valentine, 2014, Speech Matters: On Lying, Morality, and the Law (Carl G. Hempel Lecture Series), Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Simpson, Robert Mark, 2016, “Defining ‘Speech’: Subtraction, Addition, and Division”, Canadian Journal of Law & Jurisprudence , 29(2): 457–494. doi:10.1017/cjlj.2016.20
- –––, 2021, “‘Lost, Enfeebled, and Deprived of Its Vital Effect’: Mill’s Exaggerated View of the Relation Between Conflict and Vitality”, Aristotelian Society Supplementary Volume , 95: 97–114. doi:10.1093/arisup/akab006
- Southeastern Promotions Ltd., v. Conrad , 420 U.S. 546 (1975).
- Sparrow, Robert and Robert E. Goodin, 2001, “The Competition of Ideas: Market or Garden?”, Critical Review of International Social and Political Philosophy , 4(2): 45–58. doi:10.1080/13698230108403349
- Stone, Adrienne, 2017, “Viewpoint Discrimination, Hate Speech Laws, and the Double-Sided Nature of Freedom of Speech”, Constitutional Commentary , 32(3): 687–696.
- Stone, Geoffrey R., 1983, “Content Regulation and the First Amendment”, William and Mary Law Review , 25(2): 189–252.
- –––, 1987, “Content-Neutral Restrictions”, University of Chicago Law Review , 54(1): 46–118.
- –––, 2004, Perilous Times: Free Speech in Wartime from the Sedition Act of 1798 to the War on Terrorism , New York: W.W. Norton & Company.
- Strauss, David A., 1991, “Persuasion, Autonomy, and Freedom of Expression”, Columbia Law Review , 91(2): 334–371.
- Strossen, Nadine, 2018, Hate: Why We Should Resist It With Free Speech, Not Censorship , New York: Oxford University Press
- Sunstein, Cass R., 1986, “Pornography and the First Amendment”, Duke Law Journal , 1986(4): 589–627.
- –––, 1989, “Low Value Speech Revisited Commentaries”, Northwestern University Law Review , 83(3): 555–561.
- –––, 1993, Democracy and the Problem of Free Speech , New York: The Free Press.
- –––, 2017, #Republic: Divided Democracy in the Age of Social Media , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Tadros, Victor, 2012, “Duty and Liability”, Utilitas , 24(2): 259–277.
- Turner, Piers Norris, 2014, “‘Harm’ and Mill’s Harm Principle”, Ethics , 124(2): 299–326. doi:10.1086/673436
- Tushnet, Mark, Alan Chen, and Joseph Blocher, 2017, Free Speech beyond Words: The Surprising Reach of the First Amendment , New York: New York University Press.
- Volokh, Eugene, 2011, “In Defense of the Marketplace of Ideas/Search for Truth as a Theory of Free Speech Protection Responses”, Virginia Law Review , 97(3): 595–602.
- Vredenburgh, Kate, 2022, “The Right to Explanation”, Journal of Political Philosophy , 30(2): 209–229. doi:10.1111/jopp.12262
- Waldron, Jeremy, 1987, “Mill and the Value of Moral Distress”, Political Studies , 35(3): 410–423. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9248.1987.tb00197.x
- –––, 2012, The Harm in Hate Speech (The Oliver Wendell Holmes Lectures, 2009), Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Weinstein, James, 2011, “Participatory Democracy as the Central Value of American Free Speech Doctrine”, Virginia Law Review , 97(3): 491–514.
- West Virginia State Board of Education v. Barnette 319 U.S. 624 (1943).
- Whitten, Suzanne, 2022, A Republican Theory of Free Speech: Critical Civility , Cham: Palgrave Macmillan. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-78631-1
- Whitney, Heather M. and Robert Mark Simpson, 2019, “Search Engines and Free Speech Coverage”, in Free Speech in the Digital Age , Susan J. Brison and Katharine Gelber (eds), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 33–51 (ch. 2). doi:10.1093/oso/9780190883591.003.0003
- West, Caroline, 2004 [2022], “Pornography and Censorship”, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2022 edition), Edward N. Zalta and Uri Nodelman (eds.), URL = < https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2022/entries/pornography-censorship/ >.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) , adopted: 16 December 1966; Entry into force: 23 March 1976.
- Free Speech Debate
- Knight First Amendment Institute at Columbia University
- van Mill, David, “Freedom of Speech”, Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 2023 Edition), Edward N. Zalta & Uri Nodelman (eds.), URL = < https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/win2023/entries/freedom-speech/ >. [This was the previous entry on this topic in the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy – see the version history .]
ethics: search engines and | hate speech | legal rights | liberalism | Mill, John Stuart | Mill, John Stuart: moral and political philosophy | pornography: and censorship | rights | social networking and ethics | toleration
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to the editors and anonymous referees of this Encyclopedia for helpful feedback. I am greatly indebted to Robert Mark Simpson for many incisive suggestions, which substantially improved the entry. This entry was written while on a fellowship funded by UK Research & Innovation (grant reference MR/V025600/1); I am thankful to UKRI for the support.
Copyright © 2024 by Jeffrey W. Howard < jeffrey . howard @ ucl . ac . uk >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2024 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Freedom of Speech
By: History.com Editors
Updated: July 27, 2023 | Original: December 4, 2017

Freedom of speech—the right to express opinions without government restraint—is a democratic ideal that dates back to ancient Greece. In the United States, the First Amendment guarantees free speech, though the United States, like all modern democracies, places limits on this freedom. In a series of landmark cases, the U.S. Supreme Court over the years has helped to define what types of speech are—and aren’t—protected under U.S. law.
The ancient Greeks pioneered free speech as a democratic principle. The ancient Greek word “parrhesia” means “free speech,” or “to speak candidly.” The term first appeared in Greek literature around the end of the fifth century B.C.
During the classical period, parrhesia became a fundamental part of the democracy of Athens. Leaders, philosophers, playwrights and everyday Athenians were free to openly discuss politics and religion and to criticize the government in some settings.
First Amendment
In the United States, the First Amendment protects freedom of speech.
The First Amendment was adopted on December 15, 1791 as part of the Bill of Rights—the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution . The Bill of Rights provides constitutional protection for certain individual liberties, including freedoms of speech, assembly and worship.
The First Amendment doesn’t specify what exactly is meant by freedom of speech. Defining what types of speech should and shouldn’t be protected by law has fallen largely to the courts.
In general, the First Amendment guarantees the right to express ideas and information. On a basic level, it means that people can express an opinion (even an unpopular or unsavory one) without fear of government censorship.
It protects all forms of communication, from speeches to art and other media.
Flag Burning
While freedom of speech pertains mostly to the spoken or written word, it also protects some forms of symbolic speech. Symbolic speech is an action that expresses an idea.
Flag burning is an example of symbolic speech that is protected under the First Amendment. Gregory Lee Johnson, a youth communist, burned a flag during the 1984 Republican National Convention in Dallas, Texas to protest the Reagan administration.
The U.S. Supreme Court , in 1990, reversed a Texas court’s conviction that Johnson broke the law by desecrating the flag. Texas v. Johnson invalidated statutes in Texas and 47 other states prohibiting flag burning.
When Isn’t Speech Protected?
Not all speech is protected under the First Amendment.
Forms of speech that aren’t protected include:
- Obscene material such as child pornography
- Plagiarism of copyrighted material
- Defamation (libel and slander)
- True threats
Speech inciting illegal actions or soliciting others to commit crimes aren’t protected under the First Amendment, either.
The Supreme Court decided a series of cases in 1919 that helped to define the limitations of free speech. Congress passed the Espionage Act of 1917, shortly after the United States entered into World War I . The law prohibited interference in military operations or recruitment.
Socialist Party activist Charles Schenck was arrested under the Espionage Act after he distributed fliers urging young men to dodge the draft. The Supreme Court upheld his conviction by creating the “clear and present danger” standard, explaining when the government is allowed to limit free speech. In this case, they viewed draft resistant as dangerous to national security.
American labor leader and Socialist Party activist Eugene Debs also was arrested under the Espionage Act after giving a speech in 1918 encouraging others not to join the military. Debs argued that he was exercising his right to free speech and that the Espionage Act of 1917 was unconstitutional. In Debs v. United States the U.S. Supreme Court upheld the constitutionality of the Espionage Act.
Freedom of Expression
The Supreme Court has interpreted artistic freedom broadly as a form of free speech.
In most cases, freedom of expression may be restricted only if it will cause direct and imminent harm. Shouting “fire!” in a crowded theater and causing a stampede would be an example of direct and imminent harm.
In deciding cases involving artistic freedom of expression the Supreme Court leans on a principle called “content neutrality.” Content neutrality means the government can’t censor or restrict expression just because some segment of the population finds the content offensive.
Free Speech in Schools
In 1965, students at a public high school in Des Moines, Iowa , organized a silent protest against the Vietnam War by wearing black armbands to protest the fighting. The students were suspended from school. The principal argued that the armbands were a distraction and could possibly lead to danger for the students.
The Supreme Court didn’t bite—they ruled in favor of the students’ right to wear the armbands as a form of free speech in Tinker v. Des Moines Independent School District . The case set the standard for free speech in schools. However, First Amendment rights typically don’t apply in private schools.
What does free speech mean?; United States Courts . Tinker v. Des Moines; United States Courts . Freedom of expression in the arts and entertainment; ACLU .

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

Search the United Nations
- What is hate speech?
- Hate speech vs freedom of speech
- Hate speech and real harm
- Why tackle hate speech?
- A pandemic of hate
- The many challenges of tracking hate
- Targets of hate
- The preventive role of education
- UN Strategy and Plan of Action
- The role of the United Nations
- International human rights law
- Further UN initiatives
- Teach and learn
- Test yourself
- International Day
- Key human rights instruments
- Thematic publications
- Fact sheets [PDF]
- UN offices, bodies, agencies, programmes

Understanding hate speech
Hate speech versus freedom of speech
The need to preserve freedom of expression from censorship by States or private corporations’ is often invoked to counter efforts to regulate hateful expression, in particular online.
Freedom of opinion and expression are, indeed, cornerstones of human rights and pillars of free and democratic societies. These freedoms support other fundamental rights, such as to peaceful assembly, to participate in public affairs, and to freedom of religion. It is undeniable that digital media, including social media, have bolstered the right to seek, receive and impart information and ideas. Therefore, legislative efforts to regulate free expression unsurprisingly raise concerns that attempts to curb hate speech may silence dissent and opposition.
To counter hate speech, the United Nations supports more positive speech and upholds respect for freedom of expression as the norm. Therefore, any restrictions must be an exception and seek to prevent harm and ensure equality or the public participation of all. Alongside the relevant international human rights law provisions, the UN Rabat Plan of Action provides key guidance to States on the difference between freedom of expression and “incitement” (to discrimination, hostility and violence), which is prohibited under criminal law. Determining when the potential of harm is high enough to justify prohibiting speech is still the subject of much debate. But States can also use alternative tools – such as education and promoting counter-messages – to address the whole spectrum of hateful expression, both on and offline.
“Addressing hate speech does not mean limiting or prohibiting freedom of speech. It means keeping hate speech from escalating into something more dangerous, particularly incitement to discrimination, hostility and violence, which is prohibited under international law.”
— United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres, May 2019

Interfaith Diversity Network of West Africa

The Misuse of freedom of speech – A Nation’s tragedy
“Everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression; this right includes freedom to hold opinions without interference and to seek, receive and impart information and ideas through any media and regardless of frontiers.”
― United Nations, Universal Declaration of Human Rights
There is no doubt that the Freedom of Speech is one of the greatest human rights any person can have and yet it is also one of the greatest to be trampled on in the world today.
One of the biggest misconceptions nowadays is that our freedom of speech not only can be exercised but should be exercised at any cost. The problem with the world today is that everyone believes they have the right to express their opinion AND have others listen to it no matter what that might do to the feelings of others. Freedom of speech in 2020 has been abused and misused mainly by the media.
The most attentive and influential use of freedom of speech is through the elements of the media. This spans from public speaking to news reports, to social media. In the world today, these mediums have become discriminative, unpleasant and in many cases, just downright barbarous.
We have seen the social media space fill up with malicious content, trolling and cyber bullying. It seems that the anonymity that social media can provide leads to many users to believe they can say whatever they want while hiding behind their online profile. But even the print media is adorned with writeups and commentaries that contest people’s fundamental human rights.
In Ghana or Nigeria, we see the majority use media as a tool for driving injustice and infringing on constitutional human rights. When it comes to expressing opinions, people do not have a problem doing so either by phone, email, social media or even in person. However, the global nature of online media means the abuse is immediate and far reaching.
The ease of accessibility to social media means that anyone can express their opinions to the downfallof another person simply because they do not like the person or what the person may represent.
Some 3.5 billion people in the world today connect via social media. That is 45% of the world population. Social media can bring people closer together, form links across social and economic divide; bring minority groups togetherfor positive reinforcement; but too often it is used to judge others, to belittle minorities, groups and individuals. Social media is becoming a forum where judging others is the norm and there is an increase in people crossing the boundaries of constitutional rights.
Freedom of speech is scaling new heights everyday but with disregard of the consequences of misusing it; consequences that include suicide and social suicide. People become so engulfed in their virtual lives that that they often fail to realise that the quest for social media relevance may be tied to another’s downfall.
Celebrities, politicians, authors, and the general public, are exposed to cruel and perverted individuals who believe that they can say whatever they want, whenever they want to say it no matter what the consequences may be. Various mainstream issues such as gay rights, feminism, equal pay or gender equality are being fuelled by people who are ignorant to culture, because they feel the need to express what they believe despite being politically incorrect.
Yes, freedom of speech dies give us the right to express how we feel, but it does not give us the right to degrade, humiliate, curse or abuse people.
Social media has changed the way we live our lives. From the way we get our news to the way we interact with our loved ones. Social media is everywhere. It’s unavoidable, it’s powerful, and it’s here to stay, but this form of freedom of speech should not be misused, abused, and thrown around, like trash.
People, we need to think before speaking; before typing. We need to show empathy, see past what we disagree with and not hide behind our online profile.
Freedom of speech is a beautiful thing; a great human right, but it is also dangerous and we need to use it with responsibility.
Davis Mac-Iyalla
Executive Director Interfaith Diversity Network of West Africa
Fellow, Outright International Advocacy UN Religious Program 2020
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
number 59 • Spring 2024
- Subscribe or Renew

The Insoluble Problem of Free Speech
Michael p. zuckert.
The problem of free speech is once again upon us. On college campuses across America in recent years, there have been countless lectures, symposia, and impassioned demonstrations on the subject. Yet this fervor over free speech is nothing new. From time to time throughout American history, challenges to free speech have sparked heated and prolonged debate, with no obvious resolution. Indeed, the nature of speech itself may make it impossible to truly put such debates to rest.
In considering these debates, it must be noted that the norms guiding speech in America have not emerged solely from our Constitution or laws, but have developed in different ways in different institutional settings. Even constitutionally permissible violations of those norms can yield serious and damaging consequences. It is therefore worthwhile to carefully examine what the rules on speech in America consist of, and the potential ramifications of breaking those rules.
To provide some context to this discussion, we should look at another historical moment in which free speech came under scrutiny. Provoked by our national experiences in World War II and the Cold War, many people throughout the 1950s and '60s began to reconsider the nature and effects of free speech. Inspired in large part by a desire to emphasize the differences between us — a free regime — and the totalitarian Nazis and communists, there were significant developments in thinking about free speech, mostly in a libertarian direction.
Prominent liberals during that time, including Supreme Court justice Hugo Black and philosopher Sidney Hook, pushed for an expansive free-speech regime. Black often argued, for example, that the First Amendment supplies absolute protection for speech. As he wrote in his concurrence in Smith v. California , "That Amendment provides, in simple words, that 'Congress shall make no law...abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press.' I read 'no law...abridging' to mean no law abridging ." The Supreme Court and much of the intellectual left broadly opposed many restrictions of speech that had long been taken for granted as valid.
As a student and young professor during those years, I witnessed the virtual abandonment of the regulation of obscenity and pornography, the rejection of laws attempting to monitor or check communist speech and organization, and the landmark 1964 Court ruling against libel laws in New York Times Co. v. Sullivan . Back then, it was conservatives who pushed back against unfettered speech. There are certain conditions that must inhere in a decent society, they argued, which would be undermined by, for example, the free distribution of pornography. They also insisted that it made no sense to simply tolerate propaganda and organizational efforts by groups that had sworn to destroy the American regime — particularly groups allied with America's most formidable international enemy. In short, conservatives took a conservative position, and resisted what appeared to be a reckless expansion of liberty. Liberals, on the other hand, were champions of liberty, and thus stalwart defenders of the First Amendment and freedom of speech.
For those of us who lived through this free-speech free-for-all, the current moment is especially striking because of the reversals we are witnessing. It is now liberals who are often dubious of the general claims of free speech. They frequently sponsor speech codes, support shutting down speakers with whom they disagree, and discourage individual students from espousing a variety of views. In an equally strange development, conservatives are now inclined to defend the First Amendment, support robust free-speech protections, and promote open debate and the uninhibited exchange of ideas.
This shift, though undeniably interesting, is unrelated to broader and more central questions about free speech, particularly why it periodically becomes the focus of national debate. Indeed, neither conservative arguments in favor of free speech nor liberal arguments in favor of curtailing speech adequately address the conflict that is inherent to this contested right.
To begin properly "solving" the problem of free speech, we will need to identify what that problem is and why it keeps surfacing. This will entail studying the hybrid nature of speech. As we will see, speech's dual character may render any "solution" seriously imperfect. Further, different institutional settings call forth different aspects of speech's hybridity, with the result being that there is no perfect free-speech regime.
THE HYBRID CHARACTER OF SPEECH
Speech is a hybrid in that it partakes of both thought and action. Thought is inward, silent, and concealed. So long as it remains purely inward, it has minimal effects on the world. Speech is the expression of thought, whether vocally or via the written word or other forms of communication. Messages in a bottle, on a t-shirt, or in a gesture are all forms of speech.
Understood this way, speech is thought made flesh — made actual in the world, either visibly or audibly. Speech becomes a presence in the social world, and can directly affect those in it. Speech as thought made flesh is also a form of action.
The norms that govern these two elements of the hybrid are quite different. Thought is silent and concealed, but unrestrained. Since at least the Reformation, freedom of thought has been widely and deeply prized by any number of philosophers and political actors — including Benedict Spinoza, John Locke, and Thomas Jefferson — who have argued that thought should not be coerced because, strictly speaking, it cannot be coerced. The norm of untrammeled freedom of thought is also based on the belief that the proper end of thought is truth, and that freedom of thought is a necessary precondition for the pursuit and acquisition of truth. To seek truth implies that we do not possess it, or at least not all of it. We cannot know in advance which paths may or may not lead to truth. Our partial truths may not hold up when we encounter a more complete truth, and so we cannot settle on our current conceptions as fixed points, never to be questioned.
Speech as action is altogether different. When speech takes the form of an action, it affects others. A classic example is Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes's observation that yelling "fire" in a crowded theater could lead to panic and serious harm, even death. Libelous speech can damage the reputations and prospects of those being libeled. The speech involved in hiring a hit man to kill one's rival is surely a kind of action that cannot lay claim to the absolute freedom we claim for thought.
Thus, the norms that are applied to action are quite different from those that are applied to thought. Put simply, action, specifically harmful action, is subject to restriction and control. Presumably, the thinking goes, we can differentiate between harmful and non-harmful actions.
Here is where the problem of free speech arises, however. We have established that speech is composed of both thought, which ought to be free, and action, which ought to be suppressible when harmful. But there is deep uncertainty over which set of norms should govern expression — the action of speech — and to what extent. Attempts to address this problem frequently fail to take account of the hybrid character of speech.
Consider, for example, the absolutist position associated with Justice Black. He rested much of his case for complete freedom of speech on the text of the Constitution. But did the founders actually intend the sort of absolutism Black attributed to them? It has been argued, for example, that the "freedom of speech" referred to in the First Amendment was a term of art that did not apply to all forms of expression, such as libel, pornography, or blasphemy. And if the founders had, in fact, intended for the First Amendment to be understood as Black read it, we would still be free or even duty-bound to ask whether that is a sound standard. When speech is properly understood as a combination of thought and action, the absolutist position attributed by Black to the founders fails; it abstracts away the action side of speech, treating it as if it were pure thought and thus deserving of pure freedom.
In addition to his constitutional arguments, Justice Black and his allies also propounded claims about free speech that are more philosophical. On the whole, these resemble the claims of John Stuart Mill in On Liberty . That book's long opening chapter, "Of the Liberty of Thought and Discussion," discusses the correct scope of liberty in thought and speech. It is followed by chapters that discuss which principles ought to guide governmental and social responses to actions . That is, On Liberty presents a clear division between liberty of thought and speech on the one hand and liberty of action on the other.
Mill combined discussion and thought, distinguishing both from action. He treated speech as if it were entirely homologous with thought, and thus gave no weight to the hybrid quality of speech as sharing in both thought and action. This is significant because Mill assigned quite different norms to these two spheres. As he wrote in his opening chapter, "[T]here ought to exist the fullest liberty of professing and discussing, as a matter of ethical conviction, any doctrine." He later asserted that it is " imperative that human beings should be free to form opinions, and to express their opinions without reserve."
Mill then examined "whether the same reasons do not require that men should be free to act upon their opinions...without hindrance, either physical or moral, from their fellow-men." Mill, who was a sane and mostly sensible fellow, did not promote quite the same absolutist norm for action that he advocated for speech. Although he is known to have favored broad liberty of action, he granted two significant exceptions. First, his well-known "harm principle" established that actions that are harmful to the interests or "rights" of others are illegitimate, and may be punished by the state (though his conception of harm appears not to have extended to potential harms wrought by various forms of speech). Second, his "fairness principle" consisted of "each person's bearing his share...of the labors and sacrifices incurred for defending the society or its members from injury." This doctrine provides a basis on which a state may rightly tax its citizens or demand that they serve in the military.
In short, Black's absolutist, philosophical position on free speech appears to be drawn from Mill, yet the latter failed to adequately account for the hybrid character of speech. He viewed speech as entirely equivalent with thought and thus worthy of complete freedom — for example, by insisting that men should be free to express themselves "without reserve" — and dismissed the component of speech that is correctly understood as action.
Let us look now to the other side of the problem regarding free speech — instances where speech is treated wholly, or almost wholly, as action. In such cases, freedom of speech is not recognized or accepted. Recent examples include totalitarian or authoritarian regimes in which power is exercised on the principle that protecting the ruling person or party is paramount. In such a system, any speech that could threaten the rulers is considered to be a harmful act and can therefore be suppressed.
In addition, leaders of totalitarian regimes frequently intend to implement some kind of large, socially transformative project — the creation of the egalitarian, classless society; the production of the master race; the bringing forth of a holy state — which might be threatened by free thought and speech. In such cases, an abstract commitment to free speech would be unthinkable for two reasons. First, the rulers of such systems proclaim a particular set of ideas as the truth, and shun the notion that further pursuit of the truth is needed. Second, any kind of speech or expression that is contrary to the official ideology could threaten the state's project.
Dictatorial governments are not alone in suppressing speech. Other types of regimes that are not strictly authoritarian or totalitarian may nonetheless be hostile to freedom of speech. In many traditional societies, free speech is rejected — or not even thought of — for quite different reasons. Take the case of Socrates. He was accused of two crimes that turned out to be very similar: corrupting the young, and either believing in gods other than those of Athens or not believing in any gods at all. Since the charge of corrupting the young consisted of bringing them to doubt the authoritative or prevailing opinions about justice and other crucial matters within the city, it amounted to provoking disobedience and thus impiety toward the city fathers. The charge regarding religious belief operated on a similar principle; the only gods that were deemed to count were the city's gods, and thus believing in anything else, or in nothing at all, was a treasonous form of disobedience or impiety. To challenge the great authorities who stood behind the dominant opinions of the city was to challenge the city itself.
Thus, there is not even a conceptual space for freedom of speech in such traditional societies; speech that does not accord with the authoritative opinions and associated institutions is ipso facto destructive. Neither is there room for a conception of freedom of thought, for the necessary truths are already known and incorporated in the authoritative opinions. Free speech necessarily constitutes a type of harmful action.
RECONCILING THOUGHT AND ACTION
Any meaningful solution to the problem of free speech — that it consists of both thought that should be free and action that should arguably be constrained in some cases — must take account of both the thought and action that inhere in speech. A proper orientation toward free speech must embody and be borne from reflection on the hybrid character of speech and the complex normative orders that derive from that hybrid.
There have been attempts to formulate doctrines or guidelines that govern speech while accounting for its dual nature. For example, some have suggested that regulating speech on the basis of time, manner, and place is legitimate, but regulating on the basis of a speech's content is not. This approach partially recognizes that speech is action, and focuses precisely on the act of speaking in a particular context as a behavior subject to control. But it treats the content of speech much as the absolutists do in that it fails to acknowledge that speech, precisely in its content, is a kind of action, and thus can at least potentially be subject to regulation.
Another approach that is somewhat responsive to the hybrid character of speech employs the well-known "clear and present danger" test. This test recognizes that speech can be or can produce action, and focuses on the exact moment when speech is about to become action. When the action is of a kind that authorities have a right to prevent or punish, they may step in the instant speech presents a "clear and present danger" of producing that action. While this approach is in many ways more promising than that which dismisses the content of speech as action, it too fails to note that speech, as opposed to thought, is already action and not merely a potential cause of action.
Moreover, measuring the imminence of a dangerous act is a clumsy and imprecise way to respond to the "action element" of speech. The harmful effects of speech may simply not appear in the world in the form of an immediate threat. Indeed, the dangers may be long term and subtle.
Nevertheless, the "clear and present danger" test sets us on the path we must follow if we are to sort out the complexities of free speech. In a liberal society like America, there is a presumption in favor of liberty of action as well as of thought. Naturally, only harmful action is of concern when formulating norms or guides for speech. The difficulty arises, as explained earlier, in determining what constitutes a harm resulting from speech.
Some harms are easy to identify, such as physical damage (e.g., hiring a hit man). But other claimed harms resulting from speech, many of which have featured prominently in debates on campuses, are more subtle and hence much more controversial. The ubiquitous example is offense. Many people object to certain exercises of speech because the comments in question are found to be offensive, either to individuals or to groups. However, many others refuse to recognize offense as a legitimate harm or to accord it any weight in discussions of free speech.
The institutional setting in which speech takes place can also affect the normative regime appropriate to it. Some speech — the sort we are most interested in these days — occurs on campuses, in the institutional setting of colleges or universities. Other speech takes place in the context of corporations or other organizations that have their own special aims, such as making a profit or curing an illness. Still other speech occurs in the family or in the larger public sphere we call the political society.
Each setting evokes a different aspect of the hybrid character of speech and in different ways. Accordingly, different norms for speech govern these different spheres. Speech that is perfectly acceptable in a family setting may be deemed inappropriate in a corporate environment. Because of this, it would seem that standards governing speech are highly circumstantial, making it very difficult to endorse any of the standard speech doctrines as universally valid.
To make at least some progress on the question of what norms should govern speech, then, it will be helpful to look more closely at the concrete problems that have emerged in various spheres of society. To begin, let us consider the issue of most concern today — speech on campuses.
SPEECH AND THE UNIVERSITY
For simplicity's sake, and because rather different considerations come into play when a school is state-supported, we shall consider only private educational institutions. To understand the free-speech regime that is appropriate to the campus, let us return to the thought aspect of speech. By its nature, thought is turned toward truth. As discussed above, none of us directly possesses the truth about the whole, though we may have opinions about the whole. But when confronted with opposing ideas, we may come to see that we do not have good reasons for holding certain opinions. In this way, thought is set on a quest for truth, a goal sought for both practical and theoretical reasons. The character of Western civilization has been distinguished in part by our self-conscious awareness of this quest.
From the time of Plato until now, with intermittent gaps, there have existed institutions specially dedicated to the search for and dissemination of truth. This is reflected in any number of college and university mottos, where the term veritas , truth, appears more often than any other. Harvard's motto, for example, consists simply of the word veritas , while Yale's motto, lux et veritas , light and truth, is shared by many other colleges and universities.
This orientation toward seeking truth through thought provides guidance for the proper campus policy on speech: an almost irrebuttable presumption in favor of free expression. Thus a thinker like Charles Murray, to take a not exactly random example, has a prima facie right to speak. But of course, the fact that speech in a university setting leans more toward the thought than the action side of things does not mean that speech in this context has no action dimension, nor that it can do no harm.
The institutional setting of the campus has been formed to favor freedom of speech, to the point where this freedom overrides many other considerations. This has meant that speech is primarily valued for and understood in relation to its thought dimension, while its action dimension has not been granted much weight. But the potentially harmful character of speech as action remains a reality even within the university. The harms related to speech ought to be addressed, though not, as has too often been the case recently, through blunt suppression of speech.
If there is a substantive risk of violence at a protest against a particular speaker, for instance, school authorities should provide adequate security rather than cancel the event. This solution is in keeping with the institutional setting of the campus. Of course, that is not to say it is perfect: There will always be a chance that things may get out of hand despite security measures, and adding security is expensive. Schools may also be subject to other forms of harm as a result of spending more on security — facing displeased donors, having less money on hand for other purposes, and so on. Prudent administrators may mitigate such costs, but the underlying challenges — the expense of security and the risk of violence — will remain. In other words, there is no simple fix for the problem of free speech on campus.
There are still other harms that the prevailing norms at universities may lead us to ignore or to address in some indirect way. The harm of offense, though dismissed by many, is often characterized by feelings of exclusion, alienation, or devaluation — all of which can genuinely harm individuals and undermine the university's role as a truth-seeking enterprise. Concerns regarding this harm have led many campuses to adopt speech codes or similar measures directed toward reducing offense, even though the normative standards governing speech on campus do not countenance shutting down speech.
A serious discussion exploring the morality of same-sex marriage should not be prohibited, for example, but neither should its potentially harmful effects be mocked. It is not merely "snowflakes" who may feel hurt, or even profoundly attacked or rejected, by a conversation that touches on matters of fundamental identity. Just as suppressing truth-seeking speech violates the university's norms, so does rending the spirit of community and friendship that provides the best foundation for a common inquiry into truth. In other words, while suppressing speech on campus is wrong, striving to mitigate the harms that speech can inflict is morally appropriate. Various practices that free-speech advocates today readily dismiss, such as "trigger warnings," "safe spaces," or the "right of response," are not self-evidently illegitimate responses to these harms.
The role of authorities on campus should not be to "fix" the particular problem of free speech in the university — and there is no decisive resolution. Instead, by encouraging tact, consideration, and tolerance, schools can help to regulate behavior and facilitate discussions among people who strongly disagree. In this way, they might even enhance the university's pursuit of veritas .
FAMILIES, CORPORATIONS, AND COMMUNITIES
Of course, college campuses are just one type of institution in which speech takes place. In colleges and universities, the thought dimension of speech is predominant, and the norm of freedom of speech reigns supreme. The action dimension of speech remains almost an afterthought.
But what about other institutional settings, such as the family? While robust discussions of abortion and other sensitive topics are appropriate within the university, the family is not an institution in which the thought dimension of speech is pre-eminent. Families are charged with raising and mentoring a new generation, and not in the impersonal way of, say, a junior high. The family's role in caring for children is complex, in part because of the hybrid character of speech, but even more so because of the dual imperatives of parenting.
A family is a place for the formation of children, a means by which to help them become mature adults and thriving members of society. This formation requires a kind of direction and guidance, including the development of rational faculties and moral capacity. It depends as much or more on assertions of authority — "because I said so" — than on rational debate, especially when children are young. Parents also love their children and are thus concerned with their emotional well-being. Psychic harms that children may suffer are of much greater concern to the family than to the university, and the governing norms of these institutions differ accordingly.
The normative spirit of the family, then, is composed of parental authority combined with parental love and affirmation. This combination is necessary for children to grow into self-confident, functional adults. Expressiveness in the family tends toward the action side of speech hybridity, toward the effects of speech rather than the truth-seeking character of thought. For example, the caring and responsible parents of a gay teenager would not be likely to engage in the same sort of robust debate over gay marriage that might be welcomed on a college campus. But these norms are imperfect, too, because they may lead to affirmations that are more or less independent of the truth.
Recently, the institutional setting of the private corporation has also had to contend with fallout in relation to free speech, and it has employed yet another approach. In one example, the National Football League sought to suppress the public protest of a number of its players who had adopted the practice of kneeling while the national anthem played at the start of games. In a separate case, an offensive tweet posted by the actress Roseanne Barr caused an uproar that led the ABC network to cancel her eponymous television show. Some believe that one or both of these cases constitute an illegitimate suppression of speech, while others — myself included — argue that they demonstrate the appropriate normative standard for the institution of the corporation.
It is undeniable that both the players and Roseanne engaged in the action of speech. If they had engaged in the same type of speech on a college campus, it would likely be protected as "thought-like" and therefore free. The corporation, however, invokes a different set of norms.
The norms guiding corporations do not have an inherent direction regarding speech. Rather, their standards are almost entirely instrumental, rooted in whether speech enhances or detracts from their goals, which usually include profit-making. If customers or audiences take offense at speech that is associated with a particular organization, corporations are free — or even encouraged — to respond to that offense in ways that colleges are not. The action component of speech is dominant within the institution, and thus speech is evaluated in terms of its concrete effects.
A final example of an institutional setting in which speech is of concern is the broader political community, where the action side of speech predominates, though less completely than in the family or corporation. The norms of civic life clearly discourage, for instance, the famous Holmesian scenario in which someone cries "fire" in a crowded theater. And up until the late-18th century, it was generally thought that freedom of speech did not protect "seditious libel," which had been a crime in Britain. Criticism of the king — the fount of all political authority and the symbol of law and order in the kingdom — was considered to be harmful to the political community and therefore worthy of punishment.
The doctrine that condemned seditious libel recognized that speech is action, and potentially very harmful action. As such, it was considered legitimate to regulate or suppress it. Thus the normative regime in England in past centuries was more or less at the opposite end of the "speech spectrum" from regimes that embrace freedom of thought and prioritize the thought component of speech.
The United States, as an heir to British legal and political norms, has a history of restricting certain types of speech. In 1798, the federal government passed the first national sedition law, aimed at protecting federal authorities from the criticism they had been receiving from the Democratic-Republican Party (led by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison). The law provided that "if any person shall write, print, utter, or publish...any false, scandalous and malicious writing or writings against the government of the United States, or either house of the Congress of the United States, or the President of the United States, with intent to defame the said government...or to bring them...into contempt or disrepute...then such person...shall be punished by a fine...and by imprisonment." This was quite similar to British sedition laws and was widely thought to be constitutional despite the First Amendment. Like British laws, it treated speech critical of the government entirely as action, and harmful action at that. Such speech therefore had no legitimate claim to freedom.
The strongest argument against this law was put forth by Madison. It consisted of two parts, and led to the idea that speech in the institutional sphere of politics has a claim to freedom, though not quite as strong a claim as that which belongs to thought or even to the sort of thought-dominant speech that prevails on campuses.
The first part of Madison's argument acknowledged one premise of the sedition law, that speech is a type of action. But he challenged the notion that speech that is critical of government constitutes harmful action. Free play of speech is necessary in a republic, he argued, in order for the people to select their leaders wisely. The ability to criticize those in power is essential to democratic politics. Well over 200 years later, this argument still makes good sense to us.
At the same time, Madison pointed to the fact that speech is not solely action. It partakes in thought's quest for truth. The point of free and robust political exchange is to discover truths about matters relevant to governance. Even more so than in the institutional setting of the university, then, the inflicting of obvious harms through speech in the political sphere — such as damage wrought to the reputations or livelihoods of political opponents — is overlooked. This is not to say that the realm of politics can quite tolerate Justice Black's version of absolutism, but it is clear that freedom of speech is the dominant normative regime for political speech. Madison's rationale shows how this broad liberty for speech is specifically tailored to political speech, and does not necessarily apply to other types of speech.
To recapitulate, the family and the corporation each emphasize the action side of speech, with very different results. Parents may conceal certain "harsh truths" from their children, or provide them with not-quite-accurate affirmations, in order to help them succeed in fairly concrete and measurable ways. In other words, they contend with the effects of their speech on others. The corporation's concern with such effects often extends mainly to their bottom line: If speech displeases their audiences or consumers, they will attempt to arrive at some solution that will maintain their profits.
The political community, in Madison's ideal sense, strives to access truths, but does so in a rougher and messier and more damaging way than the university. Politics clearly emphasizes both thought and action. Political speech has obvious consequences, but can also bring us closer to the truth.
Recognizing the hybridity of speech and its role in various institutional settings can grant us insights into the complex normative orders that derive from that hybrid. But speech's hybridity also constitutes a perennial problem. The normative orders at play in each of the above-mentioned institutions will always be imperfect. The university, family, corporation, and political spheres each offer only partial solutions to the potential harms of speech, and cannot perfectly reconcile its action and thought components. At best, these partial solutions produce general rules for behavior that do not account for every nuance of speech.
Such rules can be invaluable, and often steer us well. But free speech will always pose some type of risk — of hurting people, leading individuals to embrace false ideas, or any number of other harms. In other words, there is no single agreed-upon ideal regarding speech, and no perfect order with which to guide it. Strictly speaking, there is no solution to the problem of free speech.
Michael P. Zuckert is the Nancy Reeves Dreux Professor of Political Science at the University of Notre Dame. His next book will be entitled A Nation So Conceived: Abraham Lincoln and the Problem of Democratic Sovereignty .

The Disappearing Conservative Professor
Jon a. shields.
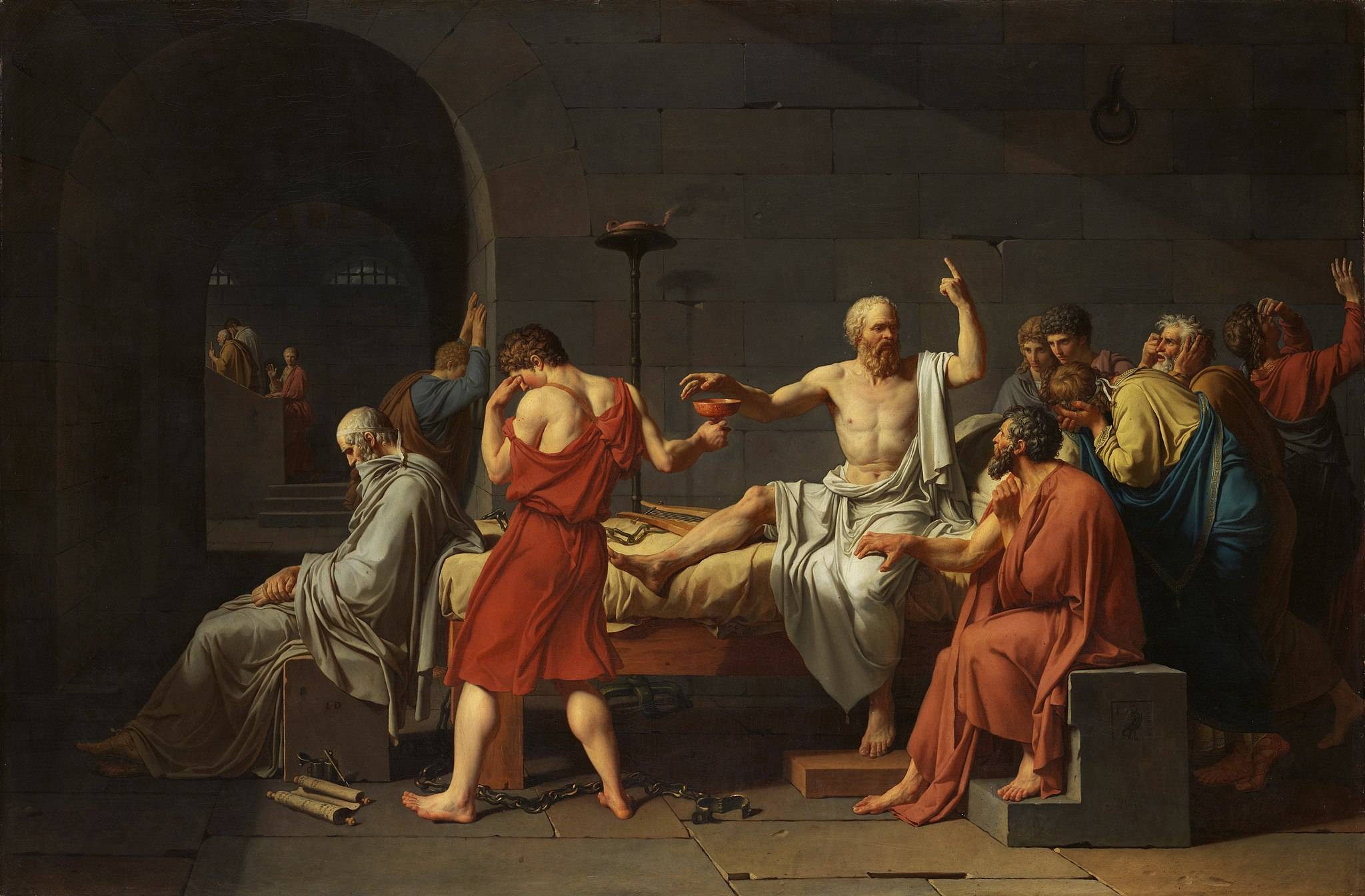

The Value of Free Speech
Harvey c. mansfield, a weekly newsletter with free essays from past issues of national affairs and the public interest that shed light on the week's pressing issues..
advertisement
Sign-in to your National Affairs subscriber account.
Forgot password? | MANAGE MY ACCOUNT
Already a subscriber? Activate your account.
Unlimited access to intelligent essays on the nation’s affairs..

Explore the Constitution
The constitution.
- Read the Full Text

Dive Deeper
Constitution 101 course.
- The Drafting Table
- Supreme Court Cases Library
- Founders' Library
- Constitutional Rights: Origins & Travels

Start your constitutional learning journey
- News & Debate Overview
- Constitution Daily Blog
- America's Town Hall Programs
- Special Projects
- Media Library

America’s Town Hall
Watch videos of recent programs.
- Education Overview
Constitution 101 Curriculum
- Classroom Resources by Topic
- Classroom Resources Library
- Live Online Events
- Professional Learning Opportunities
- Constitution Day Resources

Explore our new 15-unit high school curriculum.
- Explore the Museum
- Plan Your Visit
- Exhibits & Programs
- Field Trips & Group Visits
- Host Your Event
- Buy Tickets

New exhibit
The first amendment, interpretation & debate, freedom of speech and the press, matters of debate, common interpretation, fixing free speech, frontiers for free speech.

by Geoffrey R. Stone
Edward H. Levi Distinguished Service Professor of Law at the University of Chicago Law School

by Eugene Volokh
Gary T. Schwartz Distinguished Professor of Law; Founder and Co-Author of "The Volokh Conspiracy" at Reason Magazine
“Congress shall make no law . . . abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press.” What does this mean today? Generally speaking, it means that the government may not jail, fine, or impose civil liability on people or organizations based on what they say or write, except in exceptional circumstances.
Although the First Amendment says “Congress,” the Supreme Court has held that speakers are protected against all government agencies and officials: federal, state, and local, and legislative, executive, or judicial. The First Amendment does not protect speakers, however, against private individuals or organizations, such as private employers, private colleges, or private landowners. The First Amendment restrains only the government.
The Supreme Court has interpreted “speech” and “press” broadly as covering not only talking, writing, and printing, but also broadcasting, using the Internet, and other forms of expression. The freedom of speech also applies to symbolic expression, such as displaying flags, burning flags, wearing armbands, burning crosses, and the like.
The Supreme Court has held that restrictions on speech because of its content —that is, when the government targets the speaker’s message—generally violate the First Amendment. Laws that prohibit people from criticizing a war, opposing abortion, or advocating high taxes are examples of unconstitutional content-based restrictions. Such laws are thought to be especially problematic because they distort public debate and contradict a basic principle of self-governance: that the government cannot be trusted to decide what ideas or information “the people” should be allowed to hear.
There are generally three situations in which the government can constitutionally restrict speech under a less demanding standard.
1. In some circumstances, the Supreme Court has held that certain types of speech are of only “low” First Amendment value, such as:
a. Defamation: False statements that damage a person’s reputations can lead to civil liability (and even to criminal punishment), especially when the speaker deliberately lied or said things they knew were likely false. New York Times v. Sullivan (1964).
b. True threats: Threats to commit a crime (for example, “I’ll kill you if you don’t give me your money”) can be punished. Watts v. United States (1969).
c. “Fighting words”: Face-to-face personal insults that are likely to lead to an immediate fight are punishable. Chaplinsky v. New Hampshire (1942). But this does not include political statements that offend others and provoke them to violence. For example, civil rights or anti-abortion protesters cannot be silenced merely because passersby respond violently to their speech. Cox v. Louisiana (1965).
d. Obscenity: Hard-core, highly sexually explicit pornography is not protected by the First Amendment. Miller v. California (1973). In practice, however, the government rarely prosecutes online distributors of such material.
e. Child pornography: Photographs or videos involving actual children engaging in sexual conduct are punishable, because allowing such materials would create an incentive to sexually abuse children in order to produce such material. New York v. Ferber (1982).
f. Commercial advertising: Speech advertising a product or service is constitutionally protected, but not as much as other speech. For instance, the government may ban misleading commercial advertising, but it generally can’t ban misleading political speech. Virginia Pharmacy v. Virginia Citizens Council (1976).
Outside these narrow categories of “low” value speech, most other content-based restrictions on speech are presumptively unconstitutional. Even entertainment, vulgarity, “hate speech” (bigoted speech about particular races, religions, sexual orientations, and the like), blasphemy (speech that offends people’s religious sensibilities), and violent video games are protected by the First Amendment. The Supreme Court has generally been very reluctant to expand the list of “low” value categories of speech.
2. The government can restrict speech under a less demanding standard when the speaker is in a special relationship to the government. For example, the speech of government employees and of students in public schools can be restricted, even based on content, when their speech is incompatible with their status as public officials or students. A teacher in a public school, for example, can be punished for encouraging students to experiment with illegal drugs, and a government employee who has access to classified information generally can be prohibited from disclosing that information. Pickering v. Board of Education (1968).
3. The government can also restrict speech under a less demanding standard when it does so without regard to the content or message of the speech. Content-neutral restrictions, such as restrictions on noise, blocking traffic, and large signs (which can distract drivers and clutter the landscape), are generally constitutional as long as they are “reasonable.” Because such laws apply neutrally to all speakers without regard to their message, they are less threatening to the core First Amendment concern that government should not be permitted to favor some ideas over others. Turner Broadcasting System, Inc. v. FCC (1994). But not all content-neutral restrictions are viewed as reasonable; for example, a law prohibiting all demonstrations in public parks or all leafleting on public streets would violate the First Amendment. Schneider v. State (1939).
Courts have not always been this protective of free expression. In the nineteenth century, for example, courts allowed punishment of blasphemy, and during and shortly after World War I the Supreme Court held that speech tending to promote crime—such as speech condemning the military draft or praising anarchism—could be punished. Schenck v. United States (1919). Moreover, it was not until 1925 that the Supreme Court held that the First Amendment limited state and local governments, as well as the federal government. Gitlow v. New York (1925).
But starting in the 1920s, the Supreme Court began to read the First Amendment more broadly, and this trend accelerated in the 1960s. Today, the legal protection offered by the First Amendment is stronger than ever before in our history.
Three issues involving the freedom of speech are most pressing for the future.
Money, Politics, and the First Amendment
The first pressing issue concerns the regulation of money in the political process. Put simply, the question is this: To what extent, and in what circumstances, can the government constitutionally restrict political expenditures and contributions in order to “improve” the democratic process?
In its initial encounters with this question, the Supreme Court held that political expenditures and contributions are “speech” within the meaning of the First Amendment because they are intended to facilitate political expression by political candidates and others. The Court also recognized, however, that political expenditures and contributions could be regulated consistent with the First Amendment if the government could demonstrate a sufficiently important justification. In Buckley v. Valeo (1976), for example, the Court held that the government could constitutionally limit the amount that individuals could contribute to political candidates in order to reduce the risk of undue influence, and in McConnell v. Federal Election Commission (2003), the Court held that the government could constitutionally limit the amount that corporations could spend in the political process in order to influence electoral outcomes.
In more recent cases, though, in a series of five-to-four decisions, the Supreme Court has overruled McConnell and held unconstitutional most governmental efforts to regulate political expenditures and contributions. Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission (2010); McCutcheon v. Federal Election Commission (2014). As a result of these more recent decisions, almost all government efforts to limit the impact of money in the political process have been held unconstitutional, with the consequence that corporations and wealthy individuals now have an enormous impact on American politics.
Those who object to these decisions maintain that regulations of political expenditures and contributions are content-neutral restrictions of speech that should be upheld as long as the government has a sufficiently important justification. They argue that the need to prevent what they see as the corruption and distortion of American politics caused by the excessive influence of a handful of very wealthy individuals and corporations is a sufficiently important government interest to justify limits on the amount that those individuals and corporations should be permitted to spend in the electoral process.
Because these recent cases have all been five-to-four decisions, it remains to be seen whether a differently constituted set of justices in the future will adhere to the current approach, or whether they will ultimately overrule or at least narrowly construe those decisions. In many ways, this is the most fundamental First Amendment question that will confront the Supreme Court and the nation in the years to come.
The Meaning of “Low” Value Speech
The second pressing free speech issue concerns the scope of “low” value speech. In recent years, the Supreme Court has taken a narrow view of the low value concept, suggesting that, in order for a category of speech to fall within that concept, there has to have been a long history of government regulation of the category in question. This is true, for example, of such low value categories as defamation, obscenity, and threats. An important question for the future is whether the Court will adhere to this approach.
The primary justification for the Court’s insistence on a history of regulation is that this limits the discretion of the justices to pick-and-choose which categories of expression should be deemed to have only low First Amendment value. A secondary justification for the Court’s approach is that a history of regulation of a category of expression provides some basis in experience for evaluating the possible effects – and dangers – of declaring a new category of speech to have only low First Amendment value.
Why does this doctrine matter? To cite one illustration, under the Court’s current approach, so-called “hate speech” – speech that expressly denigrates individuals on the basis of such characteristics as race, religion, gender, national origin, and sexual orientation – does not constitute low value speech because it has not historically been subject to regulation. As a result, except in truly extraordinary circumstances, such expression cannot be regulated consistent with the First Amendment. Almost every other nation allows such expression to be regulated and, indeed, prohibited, on the theory that it does not further the values of free expression and is incompatible with other fundamental values of society.
Similarly, under the Court’s approach to low value speech it is unclear whether civil or criminal actions for “invasion of privacy” can be reconciled with the First Amendment. For example, can an individual be punished for distributing on the Internet “private” information about other persons without their consent? Suppose, for example, an individual posts naked photos of a former lover on the Internet. Is that speech protected by the First Amendment, or can it be restricted as a form of “low” value speech? This remains an unresolved question.
Leaks of Classified Information
The Supreme Court has held that the government cannot constitutionally prohibit the publication of classified information unless it can demonstrate that the publication or distribution of that information will cause a clear and present danger of grave harm to the national security. New York Times v. United States (The “Pentagon Papers” case) (1971). At the same time, though, the Court has held that government employees who gain access to such classified information can be restricted in their unauthorized disclosure of that information. Snepp v. United States (1980). It remains an open question, however, whether a government employee who leaks information that discloses an unconstitutional, unlawful, or unwise classified program can be punished for doing so. This issue has been raised by a number of recent incidents, including the case of Edward Snowden. At some point in the future, the Court will have to decide whether and to what extent the actions of government leakers like Edward Snowden are protected by the First Amendment.
I like Professor Stone’s list of important issues. I think speech about elections, including speech that costs money, must remain protected, whether it’s published by individuals, nonprofit corporations, labor unions, media corporations, or nonmedia business corporations. (Direct contributions to candidates, as opposed to independent speech about them, can be restricted, as the Court has held.) And I think restrictions on “hate speech” should remain unconstitutional. But I agree these are likely to be heavily debated issues in the coming years. I’d like to add three more issues as well.
Professional-Client Speech
Many professionals serve their clients by speaking. Psychotherapists try to help their patients by talking with them. Doctors make diagnoses, offer predictions, and recommend treatments. Lawyers give legal advice; financial planners, financial advice. Some of these professionals also do things (such as prescribe drugs, perform surgeries, or file court documents that have legal effect). But much of what they do is speak.
Yet the law heavily regulates such speakers. It bars people from giving any legal, medical, psychiatric, or similar advice unless they first get licenses (which can take years and hundreds of thousands of dollars’ worth of education to get)—though the government couldn’t require a license for people to become journalists or authors. The law lets clients sue professionals for malpractice, arguing that the professionals’ opinions or predictions proved to be “unreasonable” and harmful, though similar lawsuits against newspapers or broadcasters would be unconstitutional.
And the law sometimes forbids or compels particular speech by these professionals. Some states ban psychiatrists from offering counseling aimed at changing young patients’ sexual orientation. Florida has restricted doctors’ questioning their patients about whether the patients own guns. Many states, hoping to persuade women not to get abortions, require doctors to say certain things or show certain things to women who are seeking abortions. The federal government has tried to punish doctors who recommend that their patients use medical marijuana (which is illegal under federal law, but which can be gotten in many states with the doctor’s recommendation).
When are these laws constitutional? Moreover, if there is a First Amendment exception that allows such regulations of professional-client speech, which professions does it cover? What about, for instance, tour guides, fortunetellers, veterinarians, or diet advisors? Courts are only beginning to confront the First Amendment implications of these sorts of restrictions, and the degree to which the government’s interest in protecting clients—and in preventing behavior that the government sees as harmful—can justify restricting professional-client speech.
Crime-Facilitating Speech
Some speech contains information that helps people commit crimes, or get away with committing crimes. Sometimes this is general information, for instance about how bombs are made, how locks can be picked, how deadly viruses can be created, how technological protections for copyrighted works can be easily evaded, or how a contract killer can get away with his crime.
Sometimes this is specific information, such as the names of crime witnesses that criminals might want to silence, the location of police officers whom criminals might want to avoid, or the names of undercover officers or CIA agents. Indeed, sometimes this can be as familiar as people flashing lights to alert drivers that a police officer is watching; people are occasionally prosecuted for this, because they are helping others get away with speeding.
Sometimes this speech is said specifically with the purpose of promoting crime—but sometimes it is said for other purposes: consider chemistry books that talk about explosives; newspaper articles that mention people’s names so the readers don’t feel anything is being concealed; or novels that accurately describe crimes just for entertainment. And sometimes it is said for political purposes, for instance when someone describes how easy it is to evade copyright law or proposed laws prohibiting 3-D printing of guns, in trying to explain why those laws need to be rejected.
Surprisingly, the Supreme Court has never explained when such speech can be restricted. The narrow incitement exception, which deals with speech that aims to persuade people to commit imminent crimes, is not a good fit for speech that, deliberately or not, informs people about how to commit crimes at some point in the future. This too is a field that the Supreme Court will likely have to address in coming decades.
“Hostile Environment Harassment” Rules
Finally, some government agencies, courts, and universities have reasoned that the government may restrict speech that sufficiently offends employees, students, or business patrons based on race, religion, sex, sexual orientation, and the like. Here’s how the theory goes: Laws ban discrimination based on such identity traits in employment, education, and public accommodations. And when speech is “severe or pervasive” enough to create a “hostile or offensive environment” based on those traits, such speech becomes a form of discrimination. Therefore, the argument goes, a wide range of speech—such as display of Confederate flags, unwanted religious proselytizing, speech sharply criticizing veterans, speech suggesting that Muslims are disloyal, display of sexually suggestive materials, sexually-themed humor, sex-based job titles (such as “foreman” or “draftsman”), and more—can lead to lawsuits.
Private employers are paying attention, and restricting such speech by their employees. Universities are enacting speech codes restricting such speech. Even speech in restaurants and other public places, whether put up by the business owner or said by patrons, can lead to liability for the owner. And this isn’t limited to offensive speech said to a particular person who doesn’t want to hear it. Even speech posted on the wall or overheard in the lunchroom can lead to liability, and would thus be suppressed by “hostile environment” law.
To be sure, private employers and business owners aren’t bound by the First Amendment, and are thus generally free to restrict such speech on their property. And even government employers and enterprises generally have broad latitude to control what is said on their property (setting aside public universities, which generally have much less such latitude). But here the government is pressuring all employers, universities, and businesses to impose speech codes, by threatening liability on those who don’t impose such codes. And that government pressure is subject to First Amendment scrutiny.
Some courts have rejected some applications of this “hostile environment” theory on First Amendment grounds; others have upheld other applications. This too is something the Supreme Court will have to consider.
Modal title
Modal body text goes here.
Share with Students
123 Freedom of Speech Topics & Essay Examples
Looking for exciting freedom of speech topics to write about? This issue is definitely worth studying!
🔝 Top 10 Freedom of Speech Essay Topics
⁉️ freedom of speech essay: how to write, 🏆 best freedom of speech essay examples & topic ideas, 🔍 simple & easy freedom of speech essay titles, 💡 most interesting freedom of speech topics to write about, ❓ research questions about freedom of speech.
In your freedom of speech essay, you might want to focus on the historical perspective, elaborate on the negative effects of censorship, or even share your personal experience. Whether you will choose to write an argumentative, persuasive, or narrative essay, our article will help! We’ve gathered a list of excellent topics, ideas, and questions, together with A+ freedom of speech essay examples.
- Freedom of speech as an individual and a collective right
- Freedom of speech and its limitations
- Negative effects of censorship
- The origins of freedom of speech
- Freedom of speech as a negative right
- Democracy and freedom of speech
- Freedom of information in the era of Internet
- Freedom of speech and academic freedom
- Liberalism and freedom of speech
- Freedom of speech in the US
Freedom of speech is an important topic because every person has a fundamental right to express their opinions freely. Our ability to express our thoughts allows society to change and develop.
Essays on freedom of speech can raise awareness of the significance of this issue. That is why it is vital to create powerful and well-developed papers on this cause.
You can discuss various topics in your freedom of speech essay. You can search for them online or consult your professor. Here are our suggestions on freedom of speech essay analysis questions:
- The advantages and disadvantages of free speech policies
- The struggle schools face from the perspective of free speech
- The appropriate use of free speech
- The link between the freedom of speech and yellow journalism
- Speech as a personality trait: What the freedom of speech can reveal about people
- Freedom of speech: Pros and cons
- Freedom of speech in the United States (or other countries)
Once you have selected one of the titles for your essay, it is time to start working on the paper. Here are some do’s of writing the essay:
- Select topics that you are most interested in, as your dedication can help you to keep the reader engaged too. You can select one from the freedom of speech essay titles presented above.
- Develop a well-organized freedom of speech essay outline. Think of the main points you want to discuss and decide how you can present them in the paper. For example, you can include one introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and one concluding paragraphs.
- Define your freedom of speech essay thesis clearly. You should state it at the end of the introduction. The reader should understand the main point of your paper.
- While working on a persuasive essay, do not forget to include a section with an alternative perspective on the problem you are discussing.
- Remember that a concluding paragraph is vital because it includes a summary of all arguments presented in the paper. Rephrase the main points of the essay and add recommendations, if necessary.
- Check out essay examples online to see how you can structure your paper and organize the information.
Remember that you should avoid certain things while writing your essay. Here are some important don’ts to consider:
- Do not focus on your personal opinion solely while writing your paper. Support your claims with evidence from the literature or credible online sources.
- Do not ignore your professor’s requirements. Stick within the word limit and make sure that your essay meets all the criteria from the grading rubric, if there is one.
- Avoid using personal blogs or Wikipedia as the primary sources of information, unless your professor states it in the instructions. Ask your instructor about the literature you can use for the essay.
- When checking other students’ essays online, avoid copying their ideas. Remember that your paper should be plagiarism-free.
- Make sure that your paper is mistake-free. Grammatical mistakes may make the reader think that your opinion is not credible. It is better to check the essay several times before sending it to your professor.
Don’t hesitate to explore our free samples that can help you to write an outstanding essay!
- Freedom of Speech in Social Media Essay Gelber tries to say that the history of the freedom of speech in Australia consists of the periods of the increasing public debates on the issue of human rights and their protection.
- Freedom of Speech on Campus The primary issue identified by the case study is the extent to which free speech can be used and is protected regarding sensitive social aspects and discussions.
- The Internet and Freedom of Speech: Ethics and Restrictions Because of a lack of security technology, across the board prohibition is justified under the law, a concept that is in itself considered unlawful by a strict definition of the First Amendment of the Constitution […]
- Freedom of Speech in China and Political Reform Although the constitution of China has the provision of the freedom of speech, association, press and even demonstration, the freedom is not there in reality since the constitution forbids the undertaking of anything that is […]
- Balancing Freedom of Speech and Responsibility in Online Commenting The article made me perceive the position of absolute freedom of speech in the Internet media from a dual perspective. This desire for quick attention is the creation of information noise, distracting from the user […]
- Freedom of Speech as a Basic Human Right Restricting or penalizing freedom of expression is thus a negative issue because it confines the population of truth, as well as rationality, questioning, and the ability of people to think independently and express their thoughts.
- Freedom of Speech and Propaganda in School Setting One of the practical solutions to the problem is the development and implementation of a comprehensive policy for balanced free speech in the classroom.
- Twitter and Violations of Freedom of Speech and Censorship The sort of organization that examines restrictions and the opportunities and challenges it encounters in doing so is the center of a widely acknowledged way of thinking about whether it is acceptable to restrict speech.
- Freedom of Speech in Social Networks The recent case of blocking the accounts of former US President Donald Trump on Twitter and Facebook is explained by the violation of the rules and conditions of social platforms.
- Teachers’ Freedom of Speech in Learning Institutions The judiciary system has not clearly defined the limits of the First Amendment in learning institutions, and it’s a public concern, especially from the teachers.
- Freedom of Speech in Shouting Fire: Stories From the Edge of Free Speech Even though the First Amendment explicitly prohibits any laws regarding the freedom of speech, Congress continues to make exceptions from it.
- Freedom of Speech as the Most Appreciated Liberty In the present-day world, the progress of society largely depends on the possibility for people to exercise their fundamental rights. From this perspective, freedom of speech is the key to everyone’s well-being, and, in my […]
- Why Defamation Laws Must Prioritize Freedom of Speech The body of the essay will involve providing information on the nature of defamation laws in the USA and the UK, the implementation of such laws in the two countries, and the reason why the […]
- Protesting as a Way of Exercising Freedoms of Speech and Expression However, this department will be very careful in monitoring the behavior of the protestors and engaging in dialogue to solve issues that may lead to conflicts.
- Freedom of Speech: Is Censorship Necessary? One of the greatest achievements of the contemporary democratic society is the freedom of speech. However, it is necessary to realize in what cases the government has the right to abridge the freedom of self-expression.
- Supreme Court Decision: Corporations and Freedom of Speech The Constitution is the framework for the Government of the United States that protects and guarantees the basic rights of the people.
- Value of Copyright Protection in Relation to Freedom of Speech The phrase, freedom of expression is often used to mean the acts of seeking, getting, and transfer of information and ideas in addition to verbal speech regardless of the model used. It is therefore important […]
- Freedom of Speech and the Internet On the one hand, the freedom of expression on the internet allowed the general public to be informed about the true nature of the certain events, regardless of geographical locations and restrictions.
- Newt Gingrich Against Freedom of Speech According to the constitution, the First Amendment is part of the United States Bill of rights that was put in place due to the advocation of the anti-federalists who wanted the powers of the federal […]
- The Freedom of Speech: Communication Law in US By focusing on the on goings in Guatemala, the NYT may have, no doubt earned the ire of the Bush administration, but it is also necessary that the American people are made aware of the […]
- Freedom of Speech and Expression in Music Musicians are responsible and accountable for fans and their actions because in the modern world music and lyrics become a tool of propaganda that has a great impact on the circulation of ideas and social […]
- Freedom of Speech and International Relations The freedom of speech or the freedom of expression is a civil right legally protected by many constitutions, including that of the United States, in the First Amendment.
- The Importance of Freedom of Speech In a bid to nurture the freedom of speech, the United States provides safety to the ethical considerations of free conversations.
- Canada’s Freedom of Speech and Its Ineffectiveness In the developed societies of the modern world, it is one of the major premises that freedom of expression is the pivotal character of liberal democracy.
- American Student Rights and Freedom of Speech As the speech was rather vulgar for the educational setting, the court decided that the rights of adults in public places cannot be identic to those the students have in school.
- Freedom of Speech in Modern Media At the same time, the bigoted approach to the principles of freedom of speech in the context of the real world, such as killing or silencing journalists, makes the process of promoting the same values […]
- Freedom of Speech: Julian Assange and ‘WikiLeaks’ Case Another significant issue is that the precedent of WikiLeaks questions the power of traditional journalism to articulate the needs of the society and to monitor the governments.
- Advertising and Freedom of Speech According to Liodice, the marketer should provide the best information to the targeted consumer. The duty of the marketer is to educate and inform the consumer about the unique features of his or her product.
- Freedom of Speech and Expression This implies that autonomy is the epitome of the freedom of expression in many ways. Perhaps, this is the point of diversion between autonomy and restriction of the freedom of expression.
- Freedom of speech in the Balkans Freedom of speech in Montenegro In Montenegro, the practice of the freedom of speech and press were restricted to some issues by the law.
- “The Weight of the Word” by Chris Berg From this analysis therefore, we see that, state interference in the wiki leaks saga was unwarranted, and it amounted to a breach of the freedom of the press.
- Controversies Over Freedom of Speech and Internet Postings It must be noted though that despite the Freedom of Speech being a first Amendment right, subsequent amendments to the constitution as well as various historical acts such as the Sedition Act of 1798 and […]
- Government’s control versus Freedom of Speech and Thoughts One of the most effective measures that oppressive regimes use the world over is the limitation of the freedom of speech and thoughts.
- Freedom of Speech: Exploring Proper Limits In this respect, Downs mentions the philosophy of educational establishments, where “the function of the University is to seek and to transmit knowledge and to train student in the process whereby truth is to be […]
- Freedom of Speech, Religion and Religious Tolerance As stipulated in Article 19 of the Universal Human Rights Declaration, the pastor has the right to share ideas and information of all kinds regardless of the periphery involved and in this case, he should […]
- Why Free Speech Is An Important Freedom Freedom of speech is an important aspect of social life in a civilized and democratic society. Although there has been debate on the justification of freedom of speech, it is important to realize that society […]
- Human Nature and the Freedom of Speech in Different Countries The paper will look at the human nature that necessitates speech and expression, freedom of speech as applied in different countries and limitations that freedom of speech faces.
- The Freedom Of Speech, Press, And Petition
- How The First Amendment Protects Freedom Of Speech
- The Freedom Of Speech, And Gun Ownership Rights
- The Misconception of Hate Speech and Its Connection with the Freedom of Speech in Our First Amendment
- Limitations On Constitutional Rights On Freedom Of Speech
- Teachers’ and Students’ Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression
- Internet Censorship Means No Freedom of Speech
- Freedom of Speech Part of America’s Constitution
- An Examination of the Disadvantage of Freedom of Speech in Slack Activism
- A Description of Freedom of Speech as One of the Most Important Freedoms
- How Censorship In The Media Is Taking AWay Our Freedom Of Speech
- An Analysis of Freedom of Speech and Its Punishments
- The Effects Of Technology On The Right Of Freedom Of Speech
- Freedom of Speech: Missouri Knights of the Ku Klux Klan v. Kansas City
- Problems with Limiting Freedom of Speech
- How The Freedom Of Speech And Its Interpretation Affects
- Giving Up Freedom Of Speech – Censorship On Hate Sites
- Freedom Of Speech, Religion, And The American Dream
- The Freedom Of Speech Across The World Wide Web
- Freedom of Speech: Should There be Restrictions on Speech in the U.S. Democracy
- An Argument in Favor of the Freedom of Speech and Freedom of the Press in Schools
- Freedom Of Speech And Violent Video Games
- The Importance of Freedom of Speech to the Progress of Society
- The Amendment Is Not Protected Under The Freedom Of Speech
- Should There Be Restrictions to Freedom of Speech
- Why Should Myanmar Have Similar Freedom of Speech Protections to United States
- An Analysis of the Freedom of Speech and the Internet in United States of America
- Freedom of Speech and the First Amendment
- Free Speech : The Benefits Of Freedom Of Speech
- Comparison of Freedom of Speech: Malaysia vs China
- The Fine Line between Freedom of Speech or Hate Speech
- Freedom Of Speech : One Of The Core Principles Of A Democracy
- Prevent Internet Censorship, Save Freedom of Speech
- The Importance of the First Amendment in Providing Freedom of Speech in America
- How the Freedom of Speech Is Possible Through the Internet in China
- The Importance of Freedom of Speech in Higher Education
- Hate Mail and the Misuse of the Freedom of Speech on the Internet
- A Comparison of Freedom of Speech and Private Property
- Importance Of Freedom Of Speech In Colleges
- Freedom Of Speech and Its Legal Limits
- Freedom Of Speech As An International And Regional Human Right
- The Importance of Protecting and Preserving the Right to Freedom of Speech
- An Overview of the Importance of the Freedom of Speech in the United States
- The Communication Decency Act: The Fight for Freedom of Speech on the Internet
- Freedom Of Speech On Students’s Rights In School
- How Far Should the Right to Freedom of Speech Extend
- Journalism and Freedom of Speech
- The Constitution and Freedom of Speech on the Internet in U.S
- ‘Freedom of Speech Means the Freedom to Offend.’
- Does the Law Relating to Obscenity Restict Freedom of Speech?
- Does New Zealand Have Freedom of Speech?
- How Far Should the Right to Freedom of Speech Extend?
- Does South Korea Have Freedom of Speech?
- How the First Amendment Protects Freedom of Speech?
- Does Freedom of Speech Mean You Can Say Anything?
- How Do You Violate Freedom of Speech?
- What Are Mill’s Four Main Arguments in Defence of Freedom of Speech?
- What Violates the Freedom of Speech?
- What Are the Disadvantages of Freedom of Speech?
- Does Freedom of Speech Have Limits?
- Why Does Australia Not Have Freedom of Speech?
- What Are the Three Restrictions to Freedom of Speech?
- How Is Freedom of Speech Abused?
- Who Benefits and Loses from Freedom of Speech?
- Is There Freedom of Speech in Media?
- What Are the Limits of Freedom of Speech in Social Media?
- Does Social Media Allow Freedom of Speech?
- How Is Freedom of Speech Negative?
- Where Is Freedom of Speech Not Allowed?
- Is USA the Only Country with Freedom of Speech?
- Does India Have Freedom of Speech?
- Who Made the Freedom of Speech?
- Why Was Freedom of Speech Created?
- Who Fought for Freedom of Speech?
- Women’s Rights Titles
- Censorship Essay Ideas
- Humanism Research Ideas
- Social Justice Essay Ideas
- Cultural Competence Research Topics
- Personal Values Ideas
- Social Democracy Essay Titles
- Constitution Research Ideas
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 24). 123 Freedom of Speech Topics & Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/freedom-of-speech-essay-examples/
"123 Freedom of Speech Topics & Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 24 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/freedom-of-speech-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '123 Freedom of Speech Topics & Essay Examples'. 24 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "123 Freedom of Speech Topics & Essay Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/freedom-of-speech-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "123 Freedom of Speech Topics & Essay Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/freedom-of-speech-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "123 Freedom of Speech Topics & Essay Examples." February 24, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/freedom-of-speech-essay-examples/.
Free Samples and Examples of Essays, Homeworks and any Papers
- Absolutely free
- Perfect homeworks
- Fast relevant search
- No registration and Anonymous
The misuse of freedom of speech
Filed Under: Essays
Freedom of speech is one of the fundamental rights enshrined in the constitutions of all the democratic countries of the world. It is considered the most important article and right in the modern state, as it lies down the foundation of free, vibrant and democratic society. However, in the recent events this precious right has been violated by both the media and the general public, they can do whatever they want. In other words, media and general public misuse and misinterpret freedom of speech; therefore, there should be some limitations on freedom of speech.
For me, the right to Freedom of speech is about more than citizens utilizing the right to speak freely to their fullest potential; it is about utilizing our rights responsibly. The media on the other hand missus’s freedom of speech the most, some people, mostly politicians use the media to voice their opinions. There have been times when politicians had given hateful speech about the president without anything being censored. There was a Facebook page made by someone, I’m not sure if it still exist, but it was about how much someone hates Pres.
Obama and that who so ever feels the same can join and state their opinion. That alone tells you how misuse the freedom of speech is. Regardless of Pres. Obama being the president of the nation, he’s a human being with feelings, he has love ones who would be hurt to read or hear such things about him. The freedom of expression doesn’t mean that we can and should say what ever we want wherever we want; we should put some limits to free speech if it threatens to harm other individuals and groups of people.
The Term Paper on First Amendment Free Speech Freedom
... court has heard various cases pertaining to the freedom of speech, freedom of the press, issues of libel and slander, ... Carney, John Jr. , 'Theoretical Value in Teaching Freedom of Speech.' Speech Association of the Eastern States. New York, 10 March ... of information available through a diverse representation of media: television, radio, films, newspapers, telephones, computers, magazines, books, ...
In other countries around the world In conclusion, freedom of speech must be curbed if media and general public misuse it. There are many causes of misuse of freedom of speech by media and public. However, if the above-mentioned suggestions are taken into consideration, the situation will improve. Freedom of speech is precious right. Many countries do not have this valuable right. therefore; media and general public should use it responsibly
Similar Papers
The impact of new media on public relation.
... hinder traditional public relations roles like public information dissemination, media relations, reputation ... have the characteristics of a ‘general purpose technology’ (Commonwealth of ... education courses and how people do their banking. Advertising ...
Role of Media on Public
... between the government and the the general public but it also provides us with ... around them. I guess a country where people don’t know the happenings around them ... media some questions arise that – how much freedom should be given to media. ...
The media has far too much power over people’s opinion
... do with politics. The public seems to be driven or even guided during election period and the people tend to use quotes ... the facts. To sum up, the media have obtained so much power over the years that people cannot live without watching TV, ...
First Amendment Free Speech Freedom
... country would grow to be fair and free. Works Cited Carney, John Jr. , 'Theoretical Value in Teaching Freedom of Speech.' Speech ... in public or private meetings. Many consider the First Amendment to be our most precious constitutional freedom. These ...
Neo Nazis And Free Speech
... longer entitled to free speech. When people are given true freedom of speech, it should be ... the correct one. Although other democratic countries have historically censored Neo-Nazi ... this point, stopping the open public expression of Neo-Nazi ideas ...
Speech Social Media
... sites like Twitter & Facebook are free. Social media offer you a wide range of people from different nations, backgrounds, and Culture to ...
The New York Times
Advertisement
The Opinion Pages
Freedom of speech, not freedom from consequences.

Yousef Munayyer is a Palestinian-American writer and analyst.
January 10, 2015
Freedom of speech does not mean freedom from its consequences. The ideal of freedom of speech is one well worth defending but it can only be guaranteed in a perfect world and sadly, as we have seen throughout 2014 and in the early days of 2015, our world is far from perfect.
Writers and artists should be able to express themselves provocatively, but what they will provoke is impossible to know.
The heinous attacks and murders in Paris are the responsibility of the killers alone. Freedom of speech, however, is upheld by certain rules and laws in our society and governments and there is always going to be a minority who refuse to play by the rules. This reality means that merely having a public profile and expressing views on contentious issues can put one at risk.
Should writers and artists be able to express themselves in any way they choose even if it is provocative and offensive? Sure, but they should also expect that provocative expressions will provoke and what exactly it provokes is impossible to know.
Each writer, artist and publisher must decide for themselves which risks they are willing to take. Those who died in Paris knowingly took a risk and died. Did they expect that? I don’t know. Did they deserve that? Certainly not! Could they have avoided such provocations? Yes. But should they have?
My writing often focuses on Palestinian rights and you might be able to imagine the hate mail I get. Every unfamiliar letter, package or knock at the door I receive raises a troubling question in my mind; what if this is one I shouldn't open? I live with that question as do countless people every day who write publicly on emotional issues. The hope is that the contentious convictions you espouse are ones that are truly worth taking on risks for.
For me, freedom and equality for Palestinians is worth taking on risks to espouse. Gratuitous insults at venerated religious figures and others employing sometimes racist and disparaging images is not, simply because it adds nothing of any value to the public discourse. I am well aware that the staff of Charlie Hebdo believed otherwise, and paid the ultimate price for it.
It must also be noted that there is a hypocritical tension around free expression in France, where Islamophobic speech is protected and yet Muslims cannot dress freely in certain public spaces.
I respect the right of Charlie Hebdo to express what they want while simultaneously having no respect for most of the distasteful content they produced. If only more people could see that these two views are not mutually exclusive we would be in a better place. Unfortunately, we are not there yet.
Join Opinion on Facebook and follow updates on twitter.com/roomfordebate .
Topics: Terrorism , free speech , satire

Terror Has Already Led to Self-Restraint

In an Unequal World, Mocking All Serves the Powerful
When satire cuts both ways, to fear offense or reprisals is to give up our values.

Related Discussions
Recent Discussions

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Essay on Freedom of Speech in English Free PDF download

Download Important English Essay on the Topic - Freedom of Speech Free PDF from Vedantu
One of the fundamental rights of the citizens of India is ‘Freedom of Speech’. This is allowed to the citizens by a lot of countries to empower the citizens to share their own thoughts and views. This freedom of speech essay is for students of class 5 and above. The language used in this essay is plain and simple for a better understanding of the students. This freedom of speech essay example will help the students write a paragraph on freedom of speech in their own words easily.
Long Essay on Freedom of Speech
The phrase “Freedom of Speech” has been misinterpreted by some individuals who either do not actually understand the meaning of the phrase completely or have a totally different agenda in mind altogether. Every democratic country gives its citizens this freedom. The same is guaranteed by the Constitution of India too. Irrespective of your gender, religion, caste, or creed, you are guaranteed that freedom as an Indian. The values of democracy in a country are defined by this guaranteed fundamental freedom. The freedom to practice any religion, the freedom to express opinions and disagreeing viewpoints without hurting the sentiments or causing violence is what India is essentially made up of.
Indians stand out for their secularism and for spreading democratic values across the world. Thus, to save and celebrate democracy, enforcing freedom of speech in India becomes a necessity. Freedom of speech is not only about the fundamental rights, it’s also a fundamental duty to be done by every citizen rightfully so as to save the essence of democracy.
In developed democracies like the US, UK, Germany or France, we see a “freedom of speech” that is different from what we see in authoritarian countries like China, Malaysia or Syria and failed democratic countries like Pakistan or Rwanda. These governance systems failed because they lacked freedom of speech. Freedom of press gives us a yardstick to gauge the freedom of speech in a country. A healthy, liberal and strong democracy is reflected by a strong media presence in a country, since they are supposed to be the voice of the common people. A democracy that has a stomach for criticisms and disagreements is taken in a positive way.
Some governments get very hostile when faced with any form of criticism and so they try to oppress any voices that might stand against them. This becomes a dangerous model of governance for any country. For example, India has more than hundred and thirty crores of population now and we can be sure that every individual will not have the same thought process and same views and opinions about one thing. A true democracy is made by the difference of opinions and the respect people have for each other in the team that is responsible for making the policies.
Before making a choice, all aspects and angles of the topic should be taken into consideration. A good democracy will involve all the people - supporters and critics alike, before formulating a policy, but a bad one will sideline its critics, and force authoritarian and unilateral policies upon all of the citizens.
Sedition law, a British-era law, was a weapon that was used in India to stifle criticism and curb freedom of speech during the pre-independence era. Through section 124A of Indian Penal Code, the law states that if a person with his words, written or spoken, brings hatred, contempt or excites tension towards a government or an individual can be fined or jailed or fined and jailed both. This law was used by the Britishers to stifle the freedom fighters. Today it is being used by the political parties to silence criticism and as a result is harming the democratic values of the nation.
Many laws in India also protect the people in rightfully exercising their freedom of expression but the implementation of these laws is proving to be a challenge. Freedom of speech cannot be absolute. In the name of freedom of speech, hatred, tensions, bigotry and violence too cannot be caused in the society. It will then become ironically wrong to allow freedom of speech in the first place. Freedom of speech and expression should not become the reason for chaos and anarchy in a nation. Freedom of speech was stifled when article 370 got revoked in Kashmir. Not that the government was trying to go against the democratic values, but they had to prevent the spread of fake news, terrorism or any type of communal tensions in those areas.
Short Essay on Freedom of Speech
Freedom of speech allows the people of our country to express themselves, and share their ideas, views and opinions openly. As a result, the public and the media can comment on any political activity and also express their dissent towards anything they think is not appropriate.
Various other countries too provide freedom of speech to their citizens but they have certain limitations. Different countries have different restrictions on their freedom of speech. Some countries also do not allow this fundamental right at all and the best example being North Korea. There, the media or the public are not allowed to speak against the government. It becomes a punishable offence to criticize the government or the ministers or the political parties.
Key Highlights of the Essay - Freedom of Speech
Every democratic country gives its citizens the Freedom of Speech so as to enable the citizens to freely express their individual views, ideas and concerns. The freedom to be able to practice any religion, to be able to express individual secularism and for spreading democratic values across the world. In order to be able to save and to celebrate democracy, enforcing freedom of speech in India Is essential. Freedom of speech about fundamental rights is also a fundamental duty of citizens in order to save the essence of democracy. In a country, a healthy, liberal and strong democracy is always reflected and can be seen through a strong media presence, as the media are the voice of the common people. When faced with any form of criticism, we see some governments get very hostile, and they try to oppress and stop any kind of voices that might go against them. This is not favorable for any country.
A good democracy involves all the people - all their various supporters and critics alike, before they begin formulating any policies. India had the Sedition law, a British-era law that is used to stifle criticism and curb freedom of speech during the pre-independence era. The section 124A of Indian Penal Code, this law of sedition stated that if a person with his words, written or spoken, brings hatred, contempt or excites tension towards a government or an individual, then he can be fined or jailed or both. Using freedom of speech, people spread hatred, unnecessary tensions, bigotry and some amount of violence too in the society. Ironically in such cases, it will be wrong to allow freedom of speech. The reasons for chaos and anarchy in a nation should not be due to Freedom of speech and expression. This law was stifled when article 370 got revoked in Kashmir, in order to prevent the spread of fake news, terrorism or any type of communal tensions in those areas.
Freedom of speech gives people of our country, the freedom to express themselves, to be able to share their ideas, views and opinions openly, where the public and the media can express and comment on any political activities and can also be able to express their dissent towards anything they think is not appropriate. Different countries have different restrictions on their freedom of speech. And it is not proper to comment on that .In Fact, there are some countries which does not allow this fundamental right , for example, North Korea where neither the media nor the public have any right to speak against or even for the government and it is a punishable offense to openly criticize the government or the or anyone in particular.
While freedom of speech lets the society grow it could have certain negative outcomes. It should not be used to disrespect or instigate others. The media too should not misuse it. We, the people of this nation, should act responsibly towards utilizing its freedom of speech and expression. Lucky we are to be citizens of India. It’s a nation that respects all its citizens and gives them the rights needed for their development and growth.
A fundamental right of every citizen of India, the ‘Freedom of Speech’ allows citizens to share their individual thoughts and views.

FAQs on Essay on Freedom of Speech in English Free PDF download
1. Mention five lines for Freedom of Speech Essay?
i) A fundamental right that is guaranteed to citizens of a country to be able to express their opinions and points of view without any kind of censorship.
ii) A democracy’s health depends on the extent of freedom of expression of all its citizens.
iii) Freedom of speech is never absolute in nature.
iv) New Zealand, USA or UK rank high in terms of freedom of speech by its citizens.
v) A fundamental right in the Indian constitution is the Freedom of Speech and Expression.
2. Explain Freedom of Speech?
A fundamental right of every citizen of India, Freedom Of Speech allows every citizen the freedom and the right to express all their views, concerns, ideas and issues relating to anything about their country. Freedom of Speech is never actual in nature and has its limits too. It cannot be used for any kind of illegal purposes.The health of a democracy depends on the extent of freedom of expression of its citizens.
3. What happens when there is no Freedom of Speech?
A country will become a police and military state with no democratic and humanitarian values in it if there is no freedom of speech. Freedom of Speech is a fundamental right for all citizens, and a failure to not being able to express one’s ideas, beliefs, and thoughts will result in a non authoritarian and non democratic country. Failure to have freedom of speech in a country would mean that the rulers or the governments of those countries have no respect for its citizens.
4. Where can we get study material related to essay writing ?
It is important to practice some of the important questions in order to do well. Vedantu.com offers these important questions along with answers that have been formulated in a well structured, well researched, and easy to understand manner. Various essay writing topics, letter writing samples, comprehension passages are all available at the online portals today. Practicing and studying with the help of these enable the students to measure their level of proficiency, and also allows them to understand the difficult questions with ease.
You can avail all the well-researched and good quality chapters, sample papers, syllabus on various topics from the website of Vedantu and its mobile application available on the play store.
5. Why should students choose Vedantu for an essay on the topic 'Freedom of Speech’?
Essay writing is important for students as it helps them increase their brain and vocabulary power. Today it is important to be able to practice some important topics, samples and questions to be able to score well in the exams. Vedantu.com offers these important questions along with answers that have been formulated in a well structured, well researched, and easy to understand manner. The NCERT and other study material along with their explanations are very easily accessible from Vedantu.com and can be downloaded too. Practicing with the help of these questions along with the solutions enables the students to measure their level of proficiency, and also allows them to understand the difficult questions with ease.
6. What is Freedom of Speech?
Freedom of speech is the ability to express our opinions without any fear.
7. Which country allows the highest level of Freedom of Speech to its citizens?
The USA is at the highest with a score of 5.73.
8. Is Freedom of Speech absolute?
No, freedom of speech cannot be absolute. It has limitations.
Assessing the Classification of the Dominican Republic as a Third World Country
This essay is about evaluating whether the Dominican Republic can be classified as a Third World country. It examines the country’s significant economic growth, driven by tourism and manufacturing, alongside persistent challenges like poverty, income inequality, and limited access to quality healthcare and education. The essay discusses the country’s relative political stability and infrastructure development, noting disparities between urban and rural areas. It argues that the term “Third World country” is outdated and that the Dominican Republic is better described as an emerging market. This classification reflects its progress and ongoing challenges, providing a more nuanced understanding of its development status.
How it works
The term “Third World country” frequently denotes territories with diminished economic advancement, inferior standards of livelihood, and amplified degrees of destitution and political volatility relative to more industrialized realms. Originally formulated during the Cold War to delineate countries not allied with NATO or the Communist Bloc, the phrase has since transformed, often carrying a derogatory undertone. When scrutinizing whether the Dominican Republic conforms to this categorization, it is imperative to scrutinize diverse socio-economic benchmarks and the country’s developmental trajectory.
The Dominican Republic, situated in the Caribbean, shares the isle of Hispaniola with Haiti.
It has encountered notable economic expansion in recent epochs, propelled chiefly by tourism, manufacturing, and amenities. The nation’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rate has stood amongst the highest in the Latin American and Caribbean sector, recurrently surpassing 5% annually prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. This economic progression has precipitated enhancements in infrastructure, healthcare, and education, augmenting the quality of existence for myriad Dominicans.
Notwithstanding these advancements, the Dominican Republic still grapples with substantial quandaries that align with attributes frequently correlated with “Tertiary Globe” nations. Destitution persists as a formidable predicament, with a considerable segment of the populace residing beneath the poverty threshold. Income disparity is conspicuous, and there exists a palpable dichotomy between opulent localities, such as Punta Cana and Santo Domingo, and the impoverished rural hinterlands. This incongruity constitutes a pivotal element in evaluating the country’s overarching developmental status.
Healthcare and education, albeit ameliorated, harbor potential for augmentation. The healthcare framework has made strides, yet access to superior care can be circumscribed, particularly in rural precincts. Educational reforms have been instituted, notwithstanding, educational outcomes lag behind those of more developed nations, influencing the country’s human capital advancement. These spheres are pivotal in delineating a nation’s advancement, and the Dominican Republic’s divergent outcomes in these realms intimate that it is still traversing the trajectory to surmount these hurdles.
Political constancy stands as another pivotal facet. The Dominican Republic has relished relative political steadiness vis-a-vis myriad of its regional counterparts. Nevertheless, corruption and inefficacy within the administration persist as issues impeding further progression. Endeavors to counter corruption and foster transparency are underway, yet these endeavors necessitate fortification to ascertain sustainable advancement and equitable resource apportionment.
Infrastructure expansion in the Dominican Republic has been conspicuous, notably in tourism-laden locales. Modernized aerodromes, thoroughfares, and harbors have been erected, buttressing economic undertakings and elevating tourism. Notwithstanding, rural precincts frequently lack rudimentary infrastructure such as dependable electricity, potable water, and sanitation amenities. Remedying these disparages is imperative for comprehensive expansion and ameliorating the overall standard of existence for all Dominicans.
The notion of being a “Third World country” is progressively perceived as antiquated and overly simplistic, falling short of encapsulating the intricacies of advancement in a globalized milieu. The Dominican Republic’s economic strides and extant challenges epitomize this complexity. While the country has realized substantial headway, predominantly in economic expansion and infrastructure construction, it still grapples with predicaments typical of burgeoning nations, such as destitution, inequality, and restricted access to superior healthcare and education.
To proffer a more nuanced comprehension, it is pragmatic to allude to contemporary classifications like “developing nation” or “emerging marketplace.” These terms more aptly delineate the dynamic nature of the Dominican Republic’s advancement. As an emerging marketplace, the Dominican Republic is typified by swift economic expansion and substantial investment prospects, yet by predicaments that necessitate resolution to attain high-income status.
In conclusion, pigeonholing the Dominican Republic strictly as a “Third World country” overlooks the significant strides it has undertaken and the complexities of its extant status. While it shares attributes with developing nations, such as destitution and inequality, its robust economic progression, ameliorating infrastructure, and relative political steadiness augur well for a nation on the ascent. A more precise classification would acknowledge it as an emerging marketplace with noteworthy potential, yet with lingering challenges necessitating continuous attention to guarantee comprehensive and sustainable advancement. This equitable perspective permits a superior appreciation of the advancements the Dominican Republic has made and the exertions still mandated to secure a prosperous future for all its denizens.
Cite this page
Assessing the Classification of the Dominican Republic as a Third World Country. (2024, Jun 01). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/assessing-the-classification-of-the-dominican-republic-as-a-third-world-country/
"Assessing the Classification of the Dominican Republic as a Third World Country." PapersOwl.com , 1 Jun 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/assessing-the-classification-of-the-dominican-republic-as-a-third-world-country/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Assessing the Classification of the Dominican Republic as a Third World Country . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/assessing-the-classification-of-the-dominican-republic-as-a-third-world-country/ [Accessed: 1 Jun. 2024]
"Assessing the Classification of the Dominican Republic as a Third World Country." PapersOwl.com, Jun 01, 2024. Accessed June 1, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/assessing-the-classification-of-the-dominican-republic-as-a-third-world-country/
"Assessing the Classification of the Dominican Republic as a Third World Country," PapersOwl.com , 01-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/assessing-the-classification-of-the-dominican-republic-as-a-third-world-country/. [Accessed: 1-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Assessing the Classification of the Dominican Republic as a Third World Country . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/assessing-the-classification-of-the-dominican-republic-as-a-third-world-country/ [Accessed: 1-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Freedom of speech is under threat and censorship is on the rise. This has been a repetitive narrative for centuries. But today's threat is not only being instigated by dictators and monarchs, as ...
"I would argue that the culture of free speech is under attack in the U.S.," said Jacob Mchangama, the author of "Free Speech," a new book that documents the history of free expression.
Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people ...
"There's a crisis around the freedom of speech now because many people don't understand it, they weren't taught what it means and why it matters," said Suzanne Nossel, the chief ...
At least 83 governments worldwide have used the Covid-19 pandemic to justify violating the exercise of free speech and peaceful assembly, Human Rights Watch said today. Authorities have attacked ...
Libel, incitement of violence and child pornography are all forms of speech. Yet we censor all of them, and no one calls it the death knell of the Enlightenment. Free speech is a bedrock value in ...
First and foremost, freedom of speech is being generally mishandled. Speakers, young or old, local or foreign, student or not, must learn how to properly exercise their right to expression. It doesn't matter what limitations or trigger warnings a college places on its campus. Nowadays our first amendment right is mainly used with the intent ...
Freedom of speech, even that which is hateful and repugnant, is the price we pay for democracy, writes Ana Mari Cauce, and as educators we can and should protect it. Over the past year or two, issues surrounding the exercise of free speech and expression have come to the forefront at colleges around the country.
For many liberals, the legal right to free speech is justified by appealing to an underlying moral right to free speech, understood as a natural right held by all persons. (Some use the term human right equivalently—e.g., Alexander 2005—though the appropriate usage of that term is contested.)
Freedom of speech—the right to express opinions without government restraint—is a democratic ideal that dates back to ancient Greece. In the United States, the First Amendment guarantees free ...
Thus, freedom of speech and press were not, for Madison, merely God-given rights. They were preconditions for self-government. Conversely, Madison believed that those who sought to restrict speech ...
To counter hate speech, the United Nations supports more positive speech and upholds respect for freedom of expression as the norm. Therefore, any restrictions must be an exception and seek to ...
Freedom of speech in 2020 has been abused and misused mainly by the media. The most attentive and influential use of freedom of speech is through the elements of the media. This spans from public speaking to news reports, to social media. In the world today, these mediums have become discriminative, unpleasant and in many cases, just downright ...
THE HYBRID CHARACTER OF SPEECH. Speech is a hybrid in that it partakes of both thought and action. Thought is inward, silent, and concealed. So long as it remains purely inward, it has minimal effects on the world. Speech is the expression of thought, whether vocally or via the written word or other forms of communication. Messages in a bottle ...
The freedom of speech also applies to symbolic expression, such as displaying flags, burning flags, wearing armbands, burning crosses, and the like. The Supreme Court has held that restrictions on speech because of its content—that is, when the government targets the speaker's message—generally violate the First Amendment. Laws that ...
Argumentative Essay On Freedom Of Speech. Freedom of speech is the freedom all people have, to express what they consider and express any opinions. It is an ability to express our opinions freely without being punished or censored. All people throughout the world are entitled and must have right to freedom of speech.
Develop a well-organized freedom of speech essay outline. Think of the main points you want to discuss and decide how you can present them in the paper. For example, you can include one introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and one concluding paragraphs. Define your freedom of speech essay thesis clearly.
The misuse of freedom of speech. Freedom of speech is one of the fundamental rights enshrined in the constitutions of all the democratic countries of the world. It is considered the most important article and right in the modern state, as it lies down the foundation of free, vibrant and democratic society. However, in the recent events this ...
The misuse of freedom of speech. Filed Under: Essays. 1 page, 359 words. Freedom of speech is one of the fundamental rights enshrined in the constitutions of all the democratic countries of the world. It is considered the most important article and right in the modern state, as it lies down the foundation of free, vibrant and democratic society.
January 10, 2015. Freedom of speech does not mean freedom from its consequences. The ideal of freedom of speech is one well worth defending but it can only be guaranteed in a perfect world and ...
Argumentative Essay On Freedom Of Speech 817 Words | 4 Pages. Freedom of Speech Freedom of speech is the freedom all people have, to express what they consider and express any opinions. It is an ability to express our opinions freely without being punished or censored. All people throughout the world are entitled and must have right to freedom ...
The misuse of freedom of speech. Freedom of speech is one of the fundamental rights enshrined in the constitutions of all the democratic countries of the world. It is considered the most important article and right in the modern state, as it lies down the foundation of free, vibrant and democratic society. However, in the recent events this ...
Freedom of speech cannot be absolute. In the name of freedom of speech, hatred, tensions, bigotry and violence too cannot be caused in the society. It will then become ironically wrong to allow freedom of speech in the first place. Freedom of speech and expression should not become the reason for chaos and anarchy in a nation.
Although students in public colleges have the right to exercise their First Amendment rights, the Supreme Court has identified several categories of expression as unprotected speech that it deems ...
This essay is about evaluating whether the Dominican Republic can be classified as a Third World country. It examines the country's significant economic growth, driven by tourism and manufacturing, alongside persistent challenges like poverty, income inequality, and limited access to quality healthcare and education.