How to Find Primary Research Articles on Google Scholar

How to Find Primary Research Articles on Google Scholar can be a daunting task. But with the right tips and tricks, you can quickly locate relevant sources to inform your work or study. By leveraging advanced search features like My Library, you’ll be able to stay organized while exploring topics of interest in no time. Let’s dive into how best to find primary research articles on Google Scholar so that you can get started uncovering valuable insights today.
Table of Contents

What is Google Scholar?
Searching for primary research articles on google scholar, tips for effective searches on google scholar, utilizing advanced search features, keeping track of your research with my library on google scholar, additional resources for finding primary research articles on google scholar, faqs in relation to how to find primary research articles on google scholar, how do i search for only primary articles in google scholar, how do i find primary research articles, how do i find research articles on google scholar, how do you tell if an article is a primary or secondary source.
Google Scholar is an online search engine that allows users to find primary research articles. Google Scholar, established in 2004, is a powerful search engine that gives access to scholarly documents including theses, preprints, and books. By using advanced algorithms and natural language processing techniques it offers a more comprehensive view of academic publications than traditional databases or search engines like Google.
How to Find Primary Research Articles on Google Scholar has numerous advantages; it provides a convenient way for researchers to quickly find applicable sources needed for their research without having to browse through many web pages or databases. Secondly, its sophisticated algorithms allow researchers to refine their searches based on relevance and date published to easily narrow down results for specific topics or time periods. Finally, because it indexes content from across the web – including open-access repositories such as PubMed Central – users have access to full-text versions of articles that may not be available elsewhere.
Accessing Google Scholar is easy; simply go to scholar.google.com and start searching with keywords related to your topic area or use the Advanced Search feature if you want more control over your results (e.g., restricting by author name). You can also sign up for an account which will enable you to save searches, create alerts when new content is added that matches your criteria, and organize references into collections known as ‘My Library’ – making tracking progress on a project much more efficient.
Google Scholar is an invaluable resource for researchers looking to access primary research articles. With the right search techniques, you can easily find full-text articles on Google Scholar and maximize your research potential. Next, we’ll explore how to use the search interface and refine results in order to locate these resources more effectively.
“Easily find primary research articles for your #R&D project with Google Scholar. Advanced algorithms and natural language processing make it easier to narrow down results quickly.” #Cypris Click to Tweet
To make the process easier, it is important to understand the search interface and refine your results with filters and preferences.
The first step in searching for primary research articles on Google Scholar is understanding the search interface. This includes learning how to use keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), quotation marks (” “) for exact phrases, and wildcards (*). These search parameters can be employed to refine the results, making them pertinent to your inquiry.
Utilizing filters and personal preferences to narrow down search results can expedite the discovery of what is needed. With advanced features like citation tracking, “My Library” which allows users to save their searches, and “Similar Articles” for discovering related topics within a field of study, the research process is made easier. Additionally, keywords such as Boolean operators (AND, OR NOT), quotation marks (” “) for exact phrases, and wildcards (*) can be used to narrow down results in order to make them more relevant.
Finally, finding full-text articles is key when researching primary research papers on Google Scholar. The platform offers access to free versions of some publications through its “Find Full Text @ Your Library” feature but many require a subscription or purchase fee before viewing them in full detail online or downloading them as PDFs.
Exploring Google Scholar for primary research articles can be laborious, yet with some useful tips and tricks you can enhance your search results. Now that we have an understanding of the search interface, let’s explore how to refine our results and find full-text articles using advanced features such as filters and preferences.
Unlock the power of Google Scholar for primary research papers with advanced features like citation tracking, My Library, and Similar Articles. Use Boolean operators & wildcards to refine your search results. #GoogleScholar #ResearchPapers Click to Tweet
Google Scholar is an invaluable tool for researchers, scientists, and engineers looking to stay up-to-date on the latest research in their field. With its advanced search features, it can help you quickly find primary research articles that are relevant to your project or interests. Here are some suggestions to optimize your utilization of Google Scholar when seeking out primary research papers.
Google Scholar has several advanced search options that allow you to refine your searches and find more specific results. For example, you can limit your search by date range, language, author name, or journal title. Boolean operators, like “AND” and “OR”, can be utilized to form a single query by combining various keywords.

To refine your search even further, you can utilize the filters and preferences available on Google Scholar to narrow down results according to peer-reviewed papers from journals with high-impact factors or exclude certain authors or topics. For instance, if you want only peer-reviewed papers from journals with high-impact factors then simply select those filters before conducting your search. Additionally, if there are certain authors or topics that you would like excluded from your results then this too can be done via the preferences menu within Google Scholar.
Once you have located some applicable articles through basic keyword searches, delving into associated citations and related content can help to expand your understanding of the topic. This is especially helpful if there is not much information available on a particular subject yet, but still offers potential avenues of exploration worth pursuing further down the line. By exploring related articles and citations associated with each article one will often uncover new ideas which could potentially lead them toward interesting discoveries.
By making use of the sophisticated search capabilities, filters, and preferences provided by Google Scholar, one can easily identify primary research material related to their requirements. My Library on Google Scholar is an excellent tool for organizing and tracking your research; let’s explore how it works.
Key Takeaway Google Scholar provides advanced search features, filters and preferences to help researchers quickly locate primary research articles relevant to their project or interests. By making use of these tools and exploring related articlescitations associated with each article one can uncover new ideas that could lead them towards interesting discoveries. Google Scholar is a great aid in locating pertinent research articles.
My Library on Google Scholar is a great asset for scientists and innovators to monitor their research progress. My Library enables users to construct a personalized repository of scholarly works, which they can organize into categories, export as bibliographies, or share with others.
Setting up a personal library in My Library is easy. To create a personal library, simply click the “My Library” link at the top right corner of any page on Google Scholar and select “Create new library” from the drop-down menu. Once your library has been created, you can start adding articles by clicking the “Save” button next to each article title in your search results list.
Organizing your library is also simple; simply drag and drop articles into different folders within My Library for easy access later on. You can also create collections of related topics or research themes which are great for organizing large amounts of data quickly and easily. Moreover, you can label articles with descriptors to make them easier to locate when needed.
By utilizing My Library on Google Scholar, researchers can easily keep track of their research and stay organized. Additionally, by exploring other databases in conjunction with Google Scholar as well as open-access journals and interlibrary loan services, they can find even more primary research articles to further their studies.
Key Takeaway My Library on Google Scholar is a great resource for researchers and innovators to stay organized with their research. Creating a library is straightforward – just hit the ‘Create new library’ button in the top right of any page on Google Scholar, and then drag & drop articles into collections or folders to keep them ordered. Moreover, you can assign labels or tags to make it simpler to locate the material when necessary.
It can provide access to a wide variety of sources, including journal articles, books, and conference papers. Nevertheless, in order to broaden one’s search range, other databases and sources can be used alongside Google Scholar.
Using Other Databases in Conjunction with Google Scholar: Many academic institutions have their own subscription-based library databases that can be accessed through the institution’s website or portal. These databases may include full-text versions of some journals not available on Google Scholar as well as more comprehensive indexing than what is available on Google Scholar. Moreover, numerous universities offer access to specialized databases such as Web of Science or Scopus that enable users to search across multiple areas and sources simultaneously.
Open-access journals, which receive funding from sources such as the NIH and Wellcome Trusts, provide free online content under Creative Commons licenses for readers to share or reuse without permission. Open-access journals typically make all content freely available online and often use Creative Commons licenses so readers are free to share and reuse material without permission from the publisher or author(s). While these publications tend to focus more heavily on scientific topics rather than humanities topics they still contain valuable information worth exploring when searching for primary research articles related specifically to science fields such as biology or medicine.
If a desired article cannot be located elsewhere, interlibrary loan services may provide an avenue to acquire it through either physical or digital means. Through this service, users can request copies of materials held by another library either physically (through mail) or electronically (via email). This allows researchers who do not have immediate access to certain materials due to geographical restrictions the ability to acquire them nonetheless, thus greatly expanding their research capabilities beyond what would otherwise be possible with just local resources alone.
Key Takeaway Google Scholar is a great tool for finding primary research articles, however there are other databases and resources that can be used in conjunction with it to maximize search capabilities. Additionally, open access journals may provide valuable content related to scientific fields while interlibrary loan services can also help researchers acquire materials from libraries located elsewhere.
To search for primary articles in Google Scholar, first, go to the main page and select ‘Advanced Search’. In the Advanced Search window, check off the box that says ‘Only show results from content I can access’ and then select ‘Include Patents’. Finally, click on ‘Search’. This will filter out all secondary sources such as reviews or books, leaving only primary research articles relevant to your query.
Primary research materials can be obtained through multiple avenues, such as searching online repositories, utilizing sophisticated search strategies, and consulting specialists in the discipline. Utilizing PubMed and other online databases, researchers can access an abundance of primary research articles covering a broad range of topics. Advanced search techniques involve combining keywords with Boolean operators (AND/OR) to refine searches for specific results. Consulting experts in the field is also an effective way to locate relevant primary research articles as they have specialized knowledge about certain areas that may not be available from other sources.
Begin your hunt for research articles on Google Scholar by inputting a keyword or phrase in the search field. You can refine your search results by applying filters such as date of publication, author name, and topic area. To further narrow down your search results you can use advanced search features like exact phrases and multiple keywords. Additionally, you may access scholarly literature through library databases that are connected to Google Scholar. Finally, save time by setting up email alerts for newly published papers related to topics of interest.
A primary source is an original document or record that provides first-hand information about a particular topic. Examples of primary sources can include interviews, diaries, letters, articles from when an event occurred, and photos and videos taken during the occurrence. Secondary sources are documents or records created after the fact by someone who did not experience the events firsthand. These may include books, journal articles, and reviews that analyze or discuss research already published by others.
How to find primary research articles on Google Scholar is an essential skill for researchers and innovators. With its advanced search capabilities, My Library feature, and additional resources available online, it can be an invaluable asset in the quest to discover new insights into any given topic. Whether you are looking for one article or hundreds of them on a specific subject matter – Google Scholar is here to help. Use these tips as your guide when searching for primary research articles on Google Scholar so that you can get the most out of this platform’s features.
Discover the power of Cypris to quickly find primary research articles on Google Scholar and unlock insights faster for your R&D and innovation teams. Unlock time-saving solutions with our comprehensive platform that centralizes data sources into one easy-to-use interface.
Similar insights you might enjoy

Gallium Nitride Innovation Pulse

Carbon Capture & Storage Innovation Pulse

Sodium-Ion Batteries Innovation Pulse
Faculty and researchers : We want to hear from you! We are launching a survey to learn more about your library collection needs for teaching, learning, and research. If you would like to participate, please complete the survey by May 17, 2024. Thank you for your participation!

- University of Massachusetts Lowell
- University Libraries
Google Scholar Search Strategies
- About Google Scholar
- Manage Settings
- Enable My Library
- Google Scholar Library
- Cite from Google Scholar
- Tracking Citations
- Add Articles Manually
- Refine your Profile Settings

Using Google Scholar for Research
Google Scholar is a powerful tool for researchers and students alike to access peer-reviewed papers. With Scholar, you are able to not only search for an article, author or journal of interest, you can also save and organize these articles, create email alerts, export citations and more. Below you will find some basic search tips that will prove useful.
This page also includes information on Google Scholar Library - a resource that allows you to save, organize and manage citations - as well as information on citing a paper on Google Scholar.
Search Tips
- Locate Full Text
- Sort by Date
- Related Articles
- Court Opinions
- Email Alerts
- Advanced Search
Abstracts are freely available for most of the articles and UMass Lowell holds many subscriptions to journals and online resources. The first step is make sure you are affiliated with the UML Library on and off campus by Managing your Settings, under Library Links.
When searching in Google Scholar here are a few things to try to get full text:
- click a library link, e.g., "Full-text @ UML Library", to the right of the search result;
- click a link labeled [PDF] to the right of the search result;
- click "All versions" under the search result and check out the alternative sources;
- click "More" under the search result to see if there's an option for full-text;
- click "Related articles" or "Cited by" under the search result to explore similar articles.

Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar:

- click "Sort by date" to show just the new additions, sorted by date; If you use this feature a lot, you may also find it useful to setup email alerts to have new results automatically sent to you.
- click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
Note: On smaller screens that don't show the sidebar, these options are available in the dropdown menu labeled "Any time" right below the search button .
The Related Articles option under the search result can be a useful tool when performing research on a specific topic.
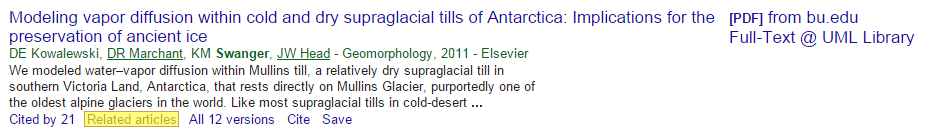
After clicking you will see articles from the same authors and with the same keywords.

You can select the jurisdiction from either the search results page or the home page as well; simply click "select courts". You can also refine your search by state courts or federal courts.
To quickly search a frequently used selection of courts, bookmark a search results page with the desired selection.
How do I sign up for email alerts?
Do a search for the topic of interest, e.g., "M Theory"; click the envelope icon in the sidebar of the search results page; enter your email address, and click " Create alert ". Google will periodically email you newly published papers that match your search criteria. You can use any email address for this; it does not need to be a Google Account.
If you want to get alerts from new articles published in a specific journal; type in the name of this journal in the search bar and create an alert like you would a keyword.
How do I get notified of new papers published by my colleagues, advisors or professors?

First, do a search for your their name, and see if they have a Citations profile. If they do, click on it, and click the "Follow new articles" link in the right sidebar under the search box.
If they don't have a profile, do a search by author, e.g., [author:s-hawking], and click on the mighty envelope in the left sidebar of the search results page. If you find that several different people share the same name, you may need to add co-author names or topical keywords to limit results to the author you wish to follow.
How do I change my alerts?
If you created alerts using a Google account, you can manage them all on the "Alerts" page .

From here you can create, edit or delete alerts. Select cancel under the actions column to unsubscribe from an alert.

This will pop-open the advanced search menu

Here you can search specific words/phrases as well as for author, title and journal. You can also limit your search results by date.
- << Previous: Enable My Library
- Next: Google Scholar Library >>
- Last Updated: Feb 14, 2024 2:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uml.edu/googlescholar
18 Google Scholar tips all students should know
Dec 13, 2022
[[read-time]] min read
Think of this guide as your personal research assistant.

“It’s hard to pick your favorite kid,” Anurag Acharya says when I ask him to talk about a favorite Google Scholar feature he’s worked on. “I work on product, engineering, operations, partnerships,” he says. He’s been doing it for 18 years, which as of this month, happens to be how long Google Scholar has been around.
Google Scholar is also one of Google’s longest-running services. The comprehensive database of research papers, legal cases and other scholarly publications was the fourth Search service Google launched, Anurag says. In honor of this very important tool’s 18th anniversary, I asked Anurag to share 18 things you can do in Google Scholar that you might have missed.
1. Copy article citations in the style of your choice.
With a simple click of the cite button (which sits below an article entry), Google Scholar will give you a ready-to-use citation for the article in five styles, including APA, MLA and Chicago. You can select and copy the one you prefer.
2. Dig deeper with related searches.
Google Scholar’s related searches can help you pinpoint your research; you’ll see them show up on a page in between article results. Anurag describes it like this: You start with a big topic — like “cancer” — and follow up with a related search like “lung cancer” or “colon cancer” to explore specific kinds of cancer.

Related searches can help you find what you’re looking for.
3. And don’t miss the related articles.
This is another great way to find more papers similar to one you found helpful — you can find this link right below an entry.
4. Read the papers you find.
Scholarly articles have long been available only by subscription. To keep you from having to log in every time you see a paper you’re interested in, Scholar works with libraries and publishers worldwide to integrate their subscriptions directly into its search results. Look for a link marked [PDF] or [HTML]. This also includes preprints and other free-to-read versions of papers.
5. Access Google Scholar tools from anywhere on the web with the Scholar Button browser extension.
The Scholar Button browser extension is sort of like a mini version of Scholar that can move around the web with you. If you’re searching for something, hitting the extension icon will show you studies about that topic, and if you’re reading a study, you can hit that same button to find a version you read, create a citation or to save it to your Scholar library.

Install the Scholar Button Chrome browser extension to access Google Scholar from anywhere on the web.
6. Learn more about authors through Scholar profiles.
There are many times when you’ll want to know more about the researchers behind the ideas you’re looking into. You can do this by clicking on an author’s name when it’s hyperlinked in a search result. You’ll find all of their work as well as co-authors, articles they’re cited in and so on. You can also follow authors from their Scholar profile to get email updates about their work, or about when and where their work is cited.
7. Easily find topic experts.
One last thing about author profiles: If there are topics listed below an author’s name on their profile, you can click on these areas of expertise and you’ll see a page of more authors who are researching and publishing on these topics, too.
8. Search for court opinions with the “Case law” button.
Scholar is the largest free database of U.S. court opinions. When you search for something using Google Scholar, you can select the “Case law” button below the search box to see legal cases your keywords are referenced in. You can read the opinions and a summary of what they established.
9. See how those court opinions have been cited.
If you want to better understand the impact of a particular piece of case law, you can select “How Cited,” which is below an entry, to see how and where the document has been cited. For example, here is the How Cited page for Marbury v. Madison , a landmark U.S. Supreme Court ruling that established that courts can strike down unconstitutional laws or statutes.
10. Understand how a legal opinion depends on another.
When you’re looking at how case laws are cited within Google Scholar, click on “Cited by” and check out the horizontal bars next to the different results. They indicate how relevant the cited opinion is in the court decision it’s cited within. You will see zero, one, two or three bars before each result. Those bars indicate the extent to which the new opinion depends on and refers to the cited case.

In the Cited by page for New York Times Company v. Sullivan, court cases with three bars next to their name heavily reference the original case. One bar indicates less reliance.
11. Sign up for Google Scholar alerts.
Want to stay up to date on a specific topic? Create an alert for a Google Scholar search for your topics and you’ll get email updates similar to Google Search alerts. Another way to keep up with research in your area is to follow new articles by leading researchers. Go to their profiles and click “Follow.” If you’re a junior grad student, you may consider following articles related to your advisor’s research topics, for instance.
12. Save interesting articles to your library.
It’s easy to go down fascinating rabbit hole after rabbit hole in Google Scholar. Don’t lose track of your research and use the save option that pops up under search results so articles will be in your library for later reading.
13. Keep your library organized with labels.
Labels aren’t only for Gmail! You can create labels within your Google Scholar library so you can keep your research organized. Click on “My library,” and then the “Manage labels…” option to create a new label.
14. If you’re a researcher, share your research with all your colleagues.
Many research funding agencies around the world now mandate that funded articles should become publicly free to read within a year of publication — or sooner. Scholar profiles list such articles to help researchers keep track of them and open up access to ones that are still locked down. That means you can immediately see what is currently available from researchers you’re interested in and how many of their papers will soon be publicly free to read.
15. Look through Scholar’s annual top publications and papers.
Every year, Google Scholar releases the top publications based on the most-cited papers. That list (available in 11 languages) will also take you to each publication’s top papers — this takes into account the “h index,” which measures how much impact an article has had. It’s an excellent place to start a research journey as well as get an idea about the ideas and discoveries researchers are currently focused on.
16. Get even more specific with Advanced Search.
Click on the hamburger icon on the upper left-hand corner and select Advanced Search to fine-tune your queries. For example, articles with exact words or a particular phrase in the title or articles from a particular journal and so on.
17. Find extra help on Google Scholar’s help page.
It might sound obvious, but there’s a wealth of useful information to be found here — like how often the database is updated, tips on formatting searches and how you can use your library subscriptions when you’re off-campus (looking at you, college students!). Oh, and you’ll even learn the origin of that quote on Google Scholar’s home page.

18. Keep up with Google Scholar news.
Don’t forget to check out the Google Scholar blog for updates on new features and tips for using this tool even better.
Related stories
Ai overviews: about last week.
Here’s what happened with AI Overviews, the feedback we've received, and the steps we’ve taken.

Doodle for Google’s top 55 artists share their wishes for the future

Generative AI in Search: Let Google do the searching for you

A new Mother's Day gift experience on Google Search

Celebrate spring with floral illustrations on Google Books

Find more sustainable ways to get around, with new Maps and Search updates
Let’s stay in touch. Get the latest news from Google in your inbox.

Research Basics: Find Articles Using Google Scholar
- Understanding the Assignment
- Choosing a Research Topic
- Refining a Research Topic
- Developing a Research Question
- Deciding What Types of Sources You Will Need
- Types of Sources
- Search Techniques
- Find Books & eBooks This link opens in a new window
- Choose a Database / Find Articles
- Find Articles Using the EBSCO Articles tab
- Find Journals
- Find Websites using Google
- Find Articles Using Google Scholar
- Find Government Documents This link opens in a new window
- Find Statistics This link opens in a new window
- Interlibrary Loan This link opens in a new window
- How to evaluate your sources This link opens in a new window
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources This link opens in a new window
- Popular vs. Scholary This link opens in a new window
- Wheel of Sources
- Incorporate Sources into Your Research Paper
- Paraphrasing
- Voice Markers
- Using Source Material to Develop/Support an Argument
- Reasons to Cite Your Sources
- Citation & Style Guides This link opens in a new window
- Learning Checks
- Open Access Educational Resources
- Research Help
Ask a Librarian
Chat with a Librarian
Lisle: (630) 829-6057 Mesa: (480) 878-7514 Toll Free: (877) 575-6050 Email: [email protected]
Book a Research Consultation Library Hours

Connect Google Scholar to the BenU Library's Collection
1. starting in google scholar, choose settings..

2. Choose Library Links. Search “Benedictine” and check the boxes. Search "Worldcat" and check the box. Click Save.

You're done! Now when you search in Google Scholar, your results page will include BenU Library links along the right.

Search Google Scholar
Google Scholar promotes itself as a resource that provides one-stop shopping for scholarly literature. It searches across many disciplines and covers a wide variety of resources, including journal articles, theses, books, abstracts, and more. Although Google Scholar is aimed at the academic community, it uses a very broad definition of "scholarly literature."
It is important to realize that not everything in Google Scholar is peer reviewed.
Try a search:

Tutorial: Using Google Scholar
Remember to evaluate websites for reliability and accuracy before you use them in your research assignments.
- << Previous: Find Websites using Google
- Next: Find Government Documents >>
- Last Updated: Feb 2, 2024 11:54 AM
- URL: https://researchguides.ben.edu/research-basics
Kindlon Hall 5700 College Rd. Lisle, IL 60532 (630) 829-6050
Gillett Hall 225 E. Main St. Mesa, AZ 85201 (480) 878-7514

Find Journal Articles: Google Scholar
- Finding Journal Articles
- Good Places to Start - Interdisciplinary Databases
Google Scholar
- Google Scholar This link opens in a new window Google Scholar is a web search engine that finds scholarly literature, including papers, theses, books, and reports. By searching Google Scholar from the library’s webpage, you will have free linked access to the library’s subscription holdings. Other links from Google Scholar may prompt you to pay for articles, but DO NOT PAY for articles. We will help you get the articles you need.
- How to set up Google Scholar

- << Previous: Good Places to Start - Interdisciplinary Databases
- Next: Need Help >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 10:23 AM
- URL: https://researchguides.wcu.edu/FindArticles
HUNTER LIBRARY
176 Central Drive Cullowhee, NC 28723 Administration: 828-227-7485 Reference: 828-227-7465 Circulation: 828-227-7485

QUICK LINKS
Ask-A-Librarian Reserve a Study Room My Account Library Catalog Article Databases Interlibrary Loan
Reference management. Clean and simple.
The top list of academic search engines
1. Google Scholar
4. science.gov, 5. semantic scholar, 6. baidu scholar, get the most out of academic search engines, frequently asked questions about academic search engines, related articles.
Academic search engines have become the number one resource to turn to in order to find research papers and other scholarly sources. While classic academic databases like Web of Science and Scopus are locked behind paywalls, Google Scholar and others can be accessed free of charge. In order to help you get your research done fast, we have compiled the top list of free academic search engines.
Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles
- Abstracts: only a snippet of the abstract is available
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✔
- Links to full text: ✔
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, Vancouver, RIS, BibTeX
BASE is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany. That is also where its name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles (contains duplicates)
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✘
- References: ✘
- Cited by: ✘
- Export formats: RIS, BibTeX

CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open-access research papers. For each search result, a link to the full-text PDF or full-text web page is provided.
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles
- Links to full text: ✔ (all articles in CORE are open access)
- Export formats: BibTeX
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need anymore to query all those resources separately!
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles and reports
- Links to full text: ✔ (available for some databases)
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX (available for some databases)
Semantic Scholar is the new kid on the block. Its mission is to provide more relevant and impactful search results using AI-powered algorithms that find hidden connections and links between research topics.
- Coverage: approx. 40 million articles
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, BibTeX

Although Baidu Scholar's interface is in Chinese, its index contains research papers in English as well as Chinese.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 100 million articles
- Abstracts: only snippets of the abstract are available
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX

RefSeek searches more than one billion documents from academic and organizational websites. Its clean interface makes it especially easy to use for students and new researchers.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 1 billion documents
- Abstracts: only snippets of the article are available
- Export formats: not available
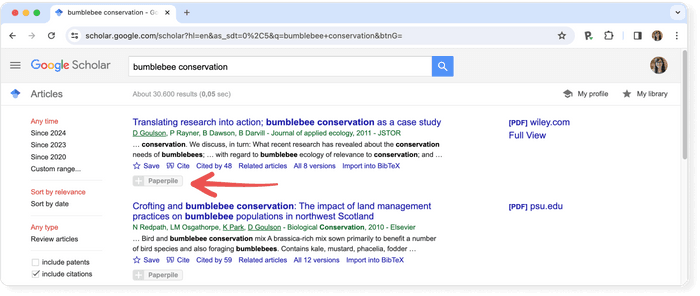
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to save, organize, and cite your references. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons:
Google Scholar is an academic search engine, and it is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only let's you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free, but also often provides links to full text PDF file.
Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature developed at the Allen Institute for AI. Sematic Scholar was publicly released in 2015 and uses advances in natural language processing to provide summaries for scholarly papers.
BASE , as its name suggest is an academic search engine. It is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany and that's where it name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open access research papers. For each search result a link to the full text PDF or full text web page is provided.
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need any more to query all those resources separately!
Finding Scholarly Articles: Home

What's a Scholarly Article?
Your professor has specified that you are to use scholarly (or primary research or peer-reviewed or refereed or academic) articles only in your paper. What does that mean?
Scholarly or primary research articles are peer-reviewed , which means that they have gone through the process of being read by reviewers or referees before being accepted for publication. When a scholar submits an article to a scholarly journal, the manuscript is sent to experts in that field to read and decide if the research is valid and the article should be published. Typically the reviewers indicate to the journal editors whether they think the article should be accepted, sent back for revisions, or rejected.
To decide whether an article is a primary research article, look for the following:
- The author’s (or authors') credentials and academic affiliation(s) should be given;
- There should be an abstract summarizing the research;
- The methods and materials used should be given, often in a separate section;
- There are citations within the text or footnotes referencing sources used;
- Results of the research are given;
- There should be discussion and conclusion ;
- With a bibliography or list of references at the end.
Caution: even though a journal may be peer-reviewed, not all the items in it will be. For instance, there might be editorials, book reviews, news reports, etc. Check for the parts of the article to be sure.
You can limit your search results to primary research, peer-reviewed or refereed articles in many databases. To search for scholarly articles in HOLLIS , type your keywords in the box at the top, and select Catalog&Articles from the choices that appear next. On the search results screen, look for the Show Only section on the right and click on Peer-reviewed articles . (Make sure to login in with your HarvardKey to get full-text of the articles that Harvard has purchased.)
Many of the databases that Harvard offers have similar features to limit to peer-reviewed or scholarly articles. For example in Academic Search Premier , click on the box for Scholarly (Peer Reviewed) Journals on the search screen.
Review articles are another great way to find scholarly primary research articles. Review articles are not considered "primary research", but they pull together primary research articles on a topic, summarize and analyze them. In Google Scholar , click on Review Articles at the left of the search results screen. Ask your professor whether review articles can be cited for an assignment.
A note about Google searching. A regular Google search turns up a broad variety of results, which can include scholarly articles but Google results also contain commercial and popular sources which may be misleading, outdated, etc. Use Google Scholar through the Harvard Library instead.
About Wikipedia . W ikipedia is not considered scholarly, and should not be cited, but it frequently includes references to scholarly articles. Before using those references for an assignment, double check by finding them in Hollis or a more specific subject database .
Still not sure about a source? Consult the course syllabus for guidance, contact your professor or teaching fellow, or use the Ask A Librarian service.
- Last Updated: Oct 3, 2023 3:37 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/FindingScholarlyArticles
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
How to Find Free Articles on Google Scholar
There are tons of resources for students to find articles online, and Google Scholar is a top pick. Here's how to use it.
Are you working on a research project or simply looking for credible information? Google Scholar can help you find free and credible research articles.
Instead of searching for scholarly articles in a standard Google search, you can use a simpler method to find articles. Google Scholar is a division of Google that focuses on scholarly literature, that way you can easily find articles that you need for your research.
Find Free Articles on Google Scholar
You might enjoy reading insanely weird articles on Wikipedia . However, maybe it's time that you read information from the academics that the world has to offer.
It can be frustrating searching the internet for articles, without finding anything that doesn't require payment. Google Scholar offers a wide variety of research articles, many of which are available for free.
Here's how to find free articles on Google Scholar:
- Head to Google Scholar .
- Type out a keyword search in the search bar.
- When the results are displayed, only check for articles with a PDF text link.
- Click on the link for your desired article.
- Check if the article has a free downloadable link, or if you can read it for free online.
- Once you have found a free article, save the PDF document onto your device or read it online.
Typically, free articles on Google Scholar have a visible PDF text link next to the article title. If you are unlucky, the link will lead you to the publisher's website, where you would have to purchase the article.
However, when the article is free, you can save the document or read it online.
Finding Recently Published Articles
Google Scholar allows you to filter your search to a specific time frame. This way, you can find articles that were recently published, or that were published over 5 to 10 years ago.
To find an article according to the year it was published, click Since Year on Google Scholar's left sidebar. This allows you to find article papers that were published from the specified year. You can also choose whether you want the results page on Google Chrome to sort articles by date or relevance.
Click Sort by date to show just the new additions. If you are not too concerned about when the articles were published, you may click on Any time , which you will find in the left sidebar.
If you are looking for a less academic platform to gather information, you can use LinkedIn as a research tool instead.
Improve Your Research Skills
Knowing how to research effectively is not an easy skill to have. Luckily, the internet makes life easier in so many ways. One of those ways is helping you research better.
If you are a research student, you might want to find out how to make the most of your search browser. That way you can get the best results from your research.

How To: Find Sources
- Starting Points and Tips
- Finding Books & eBooks
- Searching Databases & Journals
- Reference Sources
- Statistical Sources
- News Sources
- Biographical Resources
- Using Google Scholar
- Searching the Web
- Finding Videos
- Finding Images
Quick Links
- Academic Coaching
- Databases A-Z
- Library Home
- Locations & Hours
- Password Reset
- Research Guides
- Reserve a Room or Testing Seat
- Wifi Access
- WNC OER Project
- WNC Homepage
Google Scholar
If you can't find information on your topic using the library databases, try this more scholarly version of google that limits the search results primarily to journal articles.

Articles in Google Scholar
Google Scholar returns articles from a wide variety of databases; two of the major ones that are included are JSTOR and Taylor & Francis.
JSTOR is a subscription based database, but allows individuals access to up to 100 articles, per month, with a free account.
Taylor & Francis is a subscription based database that has both open-access (free) and subscription-access articles; in order to find out which one a particular article is, scroll down to the access options to view the various options.

You can also click on the related articles link to see other articles with similar subject matter or on the cited by link to see works that have cited the article in question. While not an exact science, articles that have been cited many times generally indicates that it is an important piece of research.

Tutorials: Google Scholar
The following tutorial from Niche Academy and Utah State University provides a general demonstration of using the Google Scholar database.
This tutorial from Niche Academy and Utah State University provides an overview of how to use Google Scholar, including locating materials, accessing full-text articles, and how to properly cite the sources you find.
Expand or Narrow Your Search
While all search engines and databases have their own search abilities and guidelines, we have compiled some of the more common ways to customize your search results in Google Scholar.
Site Specification
To return results from a specific type of site, you can tell the search engine what kind of domain suffix you are interested in finding information through, such as .gov (government sites), .edu (educational sites), or .com (commercial sites), etc. To do this, type site:gov, site:edu, or site:com after your search terms.
Boolean Operators
Exact Words or Phrases
Put exact words and/or phrases you want in quotes. Example: Searching for "biological anthropology" will return results that specifically use that phrase, whereas searching for biological anthropology will return results containing either or both of those terms and those containing the exact phrase.
Using OR, AND, NOT and/or parentheses to combine or exclude keywords in your search
OR Use OR if there is more than one term that may be applicable and you want results for either of them Example: "biological anthropology" OR "physical anthropology" will return results that contain either of these phrases
AND Use AND to combine terms that you want to search; the results will include items with both terms Example: "biological anthropology" AND forensics will return results that contain both biological anthropology and forensics; it will exclude any that do not mention both
NOT (or -) Using NOT or a minus sign before the word(s) you don't want will tell the search function to look for results with the first word but will exclude any that contain the second one. Example: "biological anthropology" NOT forensics will return results for biological anthropology and will exclude any that mention forensics
Parentheses () Use parentheses to separate search term strings; similarly to how math problems are done, everything within the parentheses is separated from the rest of the terms. Example: ("biological anthropology" OR "physical anthropology") AND forensics will search for biological anthropology and forensics as well as physical anthropology and forensics
Number or Date Ranges
Ranges (..) Number and date ranges can also be specified by putting two periods (..) between the numbers (including their unit of measure, if relevant), such as $150.00..$300.00 to return results showing those dollar ranges or 2001..2021 for results spanning those years.
Wildcard/Truncation Symbol
If you are looking for information about a keyword that may have alternate or multiple suffixes (for example: act, active, activate, activation), you can search for all of the options by adding what is called a wildcard symbol (? or *). If you search for act? or act*, it will return results for act, act ive , act ivate , act ivation , etc. If one option doesn't work, try the other; Google recognizes both, but not all search engines do. This technique can definitely be helpful, but be aware it may produce too many results.
- << Previous: Biographical Resources
- Next: Searching the Web >>
- Last Updated: Aug 28, 2023 9:56 AM
- URL: https://library.wnc.edu/find_sources
Contact the Library at WNC
Carson Campus Library 2201 W. College Parkway Carson City, Nevada 89703 (775) 445-3229
Fallon Campus Library 160 Campus Way Fallon, Nevada 89406 (775) 445-3392
Report a problem Print Page Login to LibApps (Staff Only)
©2021 Western Nevada College | Privacy Policy | Title IX | WNC en Español
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Find Scholarly Articles Online
Last Updated: April 7, 2024 Approved
This article was co-authored by Kim Gillingham, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Kim Gillingham is a retired library and information specialist with over 30 years of experience. She has a Master's in Library Science from Kutztown University in Pennsylvania, and she managed the audiovisual department of the district library center in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, for 12 years. She continues to do volunteer work for various libraries and lending library projects in her local community. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 86% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 269,819 times.
When you have a research project – whether for work, school, or some other purpose – you want the most reliable and up-to-date information. Scholarly articles are some of the best resources for a research project. With a little bit of work, you can find plenty of scholarly articles online for free, as well as other reliable resources, such as government publications. Especially if you find references online, make sure you examine the material critically to evaluate its quality. [1] X Research source
Searching for Free Articles Online

- Use advanced search options to get the best results. You likely won't have the same success if you use key words or plain language searches like you would on any other internet search engine.
- Your results will be a list of citations in order of relevance. Be sure to check the dates, since3 they won't be ordered chronologically. Click a result to get publication information. If it's available, you can view the full text free of charge.

- All of the articles on the DOAJ are completely open access, meaning you can read or print the full text of the articles free of charge.

- For example, if you're doing a science research project, you might look for articles on SciSeek or SciCentral.
- You can search for these websites online, or ask a college professor or research librarian for some recommendations.

- Most professors have a list of all of their publications. Depending on the policy of the publisher, they also may have PDF or online copies of the article available on their own website for you to read or download.

- Many governmental departments also publish scholarly, peer-reviewed articles. For example, the National Institutes of Health in the United States hosts PubMed, which provides abstracts and full text of scholarly articles, many of them free of charge.
- Governmental commissions and committees also may have reliable documents used in drafting and amending legislation, such as position papers and statistical analysis. In addition to using these as sources themselves, you can dig through the citations in those documents to find scholarly articles that may be relevant to your project.

- Before you use a paper written for a non-governmental or nonprofit organization, make sure you understand the mission, purpose, and agenda of the organization itself. While many of these papers will be well-referenced and reliable, some may be slanted towards a particular viewpoint or position.
Using Library Databases

- Check colleges and universities near you as well. That way it won't be inconvenient if you end up having to go to the library to look at articles you've found online.
- Even universities that don't have open access to their databases may still have open access to the general public if you use a computer in the library itself.

- Look for a tab that says "research," "online resources," or something similar. Even if the library allows the general public to access the databases, you may have to create a user account.
Kim Gillingham, MA
Did You Know? Librarians, whether at a public library or a research institution, are trained in information sciences, which means they're experts at tracking down information and finding sources. Don't hesitate to ask a librarian for help!

- If you've never used this particular database, familiarize yourself with the search terms. While they'll generally be the same, there may be some differences from one library system to another.
- Typically you'll also have the option of limiting your results. For example, you may be able to check a box if you want your search to return only peer-reviewed articles.

- In an open-access library, you can click on the title of an article to read the full text of the article. In other libraries, clicking on the title may lead you only to an abstract. If you think the article would be helpful for your project based on the abstract, you typically can access the full text by going to the library.
Evaluating Article Quality

- Sometimes a journal can look and feel scholarly and impressive, but actually be a hastily put together affair with no real standing.
- Do an online search for the name of the publication or the name of the publisher. Look for more information about their reputation in the field.

- You also want to review the author's background for possible bias. If the author is someone who openly advocates for a particular policy or position, their scholarly work may not be objective.

- For example, if you have an article that has been cited 50 times in the past year, that article has made a big impact. However, further review indicates that the article was criticized or dismissed in nearly all of those citations. It would likely be a mistake to rely on that article given all that criticism.

- Research librarians also may be able to point you to other resources that you didn't know about or hadn't considered.
- Some universities allow you to ask the research librarians questions online, without ever going to the library. Don't leave online questions to the last minute, since you may have to wait for a response.
Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/558/01/
- ↑ https://scholar.google.com/intl/en/scholar/about.html
- ↑ https://www.afternic.com/forsale/onlineuniversities.com?utm_source=TDFS_DASLNC&utm_medium=DASLNC&utm_campaign=TDFS_DASLNC&traffic_type=TDFS_DASLNC&traffic_id=daslnc&
- ↑ https://unu.edu/about/unu
- ↑ https://www.prattlibrary.org/research/tools/index.aspx?cat=90&id=5527
- ↑ https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/finding-databases-and-articles
- ↑ https://researchguides.uic.edu/c.php?g=252299&p=1683205
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Shalonda Walker
Apr 10, 2017
Is this article up to date?
Jo Craglesteen
Mar 7, 2017
Jul 10, 2017
Feb 16, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
- Library Home
- Library Guides
How do I find articles?
- Article Search Strategies
- Getting Started
Plan Your Search
Review database descriptions, setting search parameters.
- Finding an Article from a Citation
- EBSCO Databases
- ProQuest Databases
- Find an Article Using a DOI or PMID
Database Search Techniques
Use boolean operators.
The Boolean operators AND, OR, and NOT can help you combine concepts, as well as helping you to expand or narrow your search.
- AND Narrows Your Searc h Joining search terms with AND looks for results which must include all of your keywords: alcoholism AND schizophrenia
- OR Broadens Your Search Joining search terms with OR broadens your search and can be used with synonyms: Latino OR Hispanic
- NOT Limits Your Search Joining search terms with NOT excludes keywords from your search : pets NOT cats
Use Truncation and Wildcards When Applicable
Truncation and wildcards help you search variations of words that may be important for your search.
- wom?n finds woman or women
- philosoph* finds philosopher, philosophers, philosophy...
These symbols can vary from database to database, so check the "Help" or "Search Tips" options in the database you are searching to find the best one for your needs.
Think about your topic for your project and ask yourself the following questions.
- What subject area(s) might your topic fall under? Is your topic interdisciplinary?
- What keywords can you use to describe your topic? Consider synonyms or variant spellings.
Then consider the types of sources that you need for your research:
- Do you need primary or secondary sources ? Popular or scholarly publications?
- Do you need "up-to-the-minute" information or are you looking for materials that cover a specific time period ?
- Are you looking for materials covering a specific geographic area or that were published in a certain place?
- What languages do you need material in?
The answers to these questions will provide valuable information that will help you select the best databases for your topic and develop your search strategy.
Selecting the best database for your needs can make a difference between search success and failure. When you select a database, be sure to review the database descriptions and consider the following:
- What subject areas are covered in the database? Does the database focus on the physical sciences, humanities, business?
- What years does the database cover? Does the database have embargoes on specific years for the journal you are searching?
- What kinds of sources does the database include? Articles, book chapters, dissertations, newspapers?
Use Advanced Search
The advanced or guided search option allows you to select specific fields to search, such as author or title,
Use Subjects Terms or Descriptors
If you find an article on the topic you are interested in, look at the subject terms or descriptors that are listed in the record for the item. These terms are standard within the database, and often can help you locate more articles on that topic. Some databases, such as APAPsycNet or Medline, will have a thesaurus feature built in the database, which will point you to the best subject terms. Take advantage of these features when they are available.
Most databases provide an option to limit your search. These limits can include language, type of resource, publication date, and full text only. If you find yourself getting too many hits, or would like to eliminate certain types of records, set your limits and try again
Ask a Librarian
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Finding an Article from a Citation >>
- Updated: Mar 26, 2024 12:13 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uchicago.edu/articles
- Report a problem
- Login to LibApps
Open sourcetools
Where to find peer reviewed articles for research
This is our ultimate guide to helping you get familiar with your research field and find peer reviewed articles in the Web of Science™. It forms part of our Research Smarter series.
Finding relevant research and journal articles in your field is critical to a successful research project. Unfortunately, it can be one of the hardest, most time-consuming challenges for academics.
This blog outlines how you can leverage the Web of Science citation network to complete an in-depth, comprehensive search for literature. We share insights about how you can find a research paper and quickly assess its impact. We also explain how to create alerts to keep track of new papers in your field – whether you’re new to the topic or about to embark on a literature review.
- Choosing research databases for your search
- Where to find peer reviewed articles? Master the keyword search
- Filter your results and analyze for trends
- Explore the citation network
- Save your searches and set up alerts for new journal articles
1. Choosing research databases for your search
The myriad search engines, research databases and data repositories all differ in reliability, relevancy and organization of data. This can make it tricky to navigate and assess what’s best for your research at hand.
The Web of Science stands out the most powerful and trusted citation database. It helps you connect ideas and advance scientific research across all fields and disciplines. This is made possible with best-in-class publication and citation data for confident discovery and assessment of journal articles. The Web of Science is also publisher-neutral, carefully-curated by a team of expert editors and consists of 19 different research databases.
The Web of Science Core Collection™ is the single most authoritative source for how to find research articles, discover top authors , and relevant journals . It only includes journals that have met rigorous quality and impact criteria, and it captures billions of cited references from globally significant journals, books and proceedings ( check out its coverage ). Researchers and organizations use this research database regularly to track ideas across disciplines and time.
Explore the Web of Science Core Collection
We recommend spending time exploring the Core Collection specifically because its advanced citation network features are unparalleled. If you are looking to do an exhaustive search of a specific field, you might want to switch to one of the field-specific databases like MEDLINE and INSPEC. You can also select “All databases” from the drop-down box on the main search page. This will cover all research databases your institution subscribes to. IF you are still unsure about where to find scholarly journal articles, you can learn more in our Quick Reference Guide, here, or try it out today.
“We recommend spending time exploring the Core Collection specifically because its advanced citation network features are unparalleled.”
2. Where to find peer reviewed articles? Master the keyword search
A great deal of care and consideration is needed to find peer review articles for research. It starts with your keyword search.
Your chosen keywords or search phrases cannot be too inclusive or limiting. They also require constant iteration as you become more familiar with your research field. Watch this video on search tips to learn more:

It’s worth noting that a repeated keyword search in the same Web of Science database will retrieve almost identical results every time, save for newly-indexed research. Not all research databases do this. If you are conducting a literature review and require a reproducible keyword search, it is best to steer clear of certain databases. For example, a research database that lacks overall transparency or frequently changes its search algorithm may be detrimental to your research.
3. Filter your search results and analyze trends
Group, rank and analyze the research articles in your search results to optimize the relevancy and efficiency of your efforts. In the Web of Science, researchers can cut through the data in a number of creative ways. This will help you when you’re stuck wondering where to find peer reviewed articles, journals and authors. The filter and refine tools , as well as the Analyze Results feature, are all at your disposal for this.
“Group, rank and analyze the research papers in your search results to optimize the relevancy and efficiency of your efforts.”
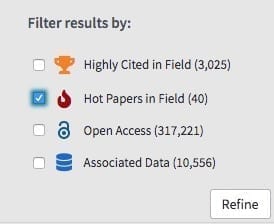
Filter and Refine tools in the Web of Science
You can opt for basic filter and refine tools in the Web of Science. These include subject category, publication date and open access within your search results. You can also filter by highly-cited research and hot research papers. A hot paper is a journal article that has accumulated rapid and significant numbers of citations over a short period of time.
The Analyze Results tool does much of this and more. It provides an interactive visualization of your results by the most prolific author, institution and funding agency, for example. This, combined, will help you understand trends across your field.
4. Explore the citation network
Keyword searches are essentially an a priori view of the literature. Citation-based searching, on the other hand, leads to “systematic serendipity”. This term was used by Eugene Garfield, the founder of Web of Science. New scientific developments are linked to the global sphere of human knowledge through the citation network. The constantly evolving connections link ideas and lead to systematic serendipity, allowing for all sorts of surprising discoveries.
Exploring the citation network helps you to:
- Identify a seminal research paper in any field. Pay attention to the number of times a journal article is cited to achieve this.
- Track the advancement of research as it progresses over time by analyzing the research papers that cite the original source. This will also help you catch retractions and corrections to research.
- Track the evolution of a research paper backward in time by tracking the work that a particular journal article cites.
- View related references. A research paper may share citations with another piece of work (calculated from bibliographic coupling). That means it’s likely discussing a similar topic.

Visualizing the history discoveries in the citation network
The Web of Science Core Collection indexes every piece of content cover-to-cover. This creates a complete and certain view of more than 115 years of the highest-quality journal articles. The depth of coverage enables you to uncover the historical trail of a research paper in your field. By doing so, it helps you visualize how discoveries unfold through time. You can also learn where they might branch off into new areas of research. Achieve this in your search by ordering your result set by date of publication.
As PhD student Rachel Ragnhild Carlson (Stanford University) recently wrote in a column for Nature: [1]
”As a PhD student, I’ve learnt to rely not just on my Web of Science research but on numerous conversations with seasoned experts. And I make sure that my reading includes literature from previous decades, which often doesn’t rise to the top of a web search. This practice is reinforced by mentors in my lab, who often find research gems by filtering explicitly for studies greater than ten years old.”
5. Save your search and set up alerts for new journal articles
Save time and keep abreast of new journal articles in your field by saving your searches and setting up email alerts . This means you can return to your search at any time. You can also stay up-to-date about a new research paper included in your search result. This will help you find an article more easily in the future. Head over to Web of Science to try it out today.
“Everyone should set up email alerts with keywords for PubMed, Web of Science, etc. Those keyword lists will evolve and be fine-tuned over time. However, it really helps to get an idea of recent publications.” Thorbjörn Sievert , PhD student, University of Jyväskylä
[1] Ragnhild Carlson, R. 2020 ‘How Trump’s embattled environment agency prepared me for a PhD’, Nature 579, 458
Related posts
Journal citation reports 2024 preview: unified rankings for more inclusive journal assessment.

Introducing the Clarivate Academic AI Platform

Reimagining research impact: Introducing Web of Science Research Intelligence


13 Tips for Choosing the Perfect Domain Name
Published: May 27, 2024
Choosing the right domain name for your company is so important — ultimately, it’s how your audience will find and remember you.

The best domain is a custom domain that works for you. Sometimes, the best domain name for you might break some best practice rules. I’ve got websites built on domains that follow best practices, including those with keyword-rich domains, and other domains break the best practice rules big time; they’re even hard to spell.
With over 700 million domain names registered , it can be hard to find one that’s unique and functional. But, in this article, I’ll help you find a custom domain that will help your website stand out from the crowd and possibly even boost your SEO. I’ll help you choose and buy a domain while sharing the insights and tips I’ve learned along the way.

Table of Contents
What Makes A Good Domain Name?
How to choose a domain name for your business, how to choose a domain name for your blog, domain name generator, establish brand identity by picking the perfect domain name.
The best domain names balance memorability, longevity, and sometimes SEO. There’s a lot to think about when choosing the right domain name, but before I get into all those steps, let’s first identify what makes a good domain.
Ideally, you’ll pick one domain name you’ll stick with forever. This might seem scary, and it’s okay to change your domain later, but it’s better if you don’t — so don’t take this decision lightly.
The reason why longevity matters is because you want a domain name that’s stable to avoid confusing your audience.
There’s another lesser-known reason, and it’s related to SEO: a domain name builds authority. Basically, an older domain with high-quality content becomes trusted by Google and is theoretically easier to rank. The longer you spend with a domain and the more you build it up, the bigger the potential loss if you change it.
Again, you can change your domain, and there are lots of things you can do to protect that built authority, but the absolute best practice is to choose a domain that you can stick with.
SEO Considerations
As well as authority, your domain name can help bolster your SEO efforts. Domains including a keyword can help websites rank.
You want to balance the benefits of using the keyword in the URL against using a brand keyword. I’ll discuss the nuances of choosing keyword-rich domains later including when I think it’s appropriate and when to stay with the brand name.
Memorability
Your domain name is how your audience will find and remember you. The best domain names are memorable to your audience so they can easily find you again.
If you are ready to establish a presence online for your business, you’ll want to choose a domain name that matches your brand. This way, customers can easily find and trust your site. There are a few steps you can keep in mind when choosing your domain name.

Free Website Design Inspiration Guide
77 Brilliant Examples of Homepages, Blogs & Landing Pages to Inspire You
- Agency Pages
- Ecommerce Pages
- Tech Company Pages
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
4. Stay unique, specific, and on-brand.
With all of these things to keep in mind, it can be hard to brainstorm a domain name that is clear and concise while also remaining unique and true to your business.
But it’s certainly doable. Keep your business name and what you sell at the forefront of your mind, and dig into your niche to ensure that your domain name attracts the online audience you want.
I always find it hard to come up with domains. I usually have to go through a few versions of ideas and get knocked back a lot by the time I’ve searched its availability to find it’s taken.
Nowadays, I use ChatGPT to help me brainstorm domain name ideas. Using a fake scenario, here’s an example of what I’d ask ChatGPT.
I asked ChatGPT, “Can you help me come up with the best domain name for a new blog? I want to share my budget travel adventures.”
ChatGPT came up with some great starting points.
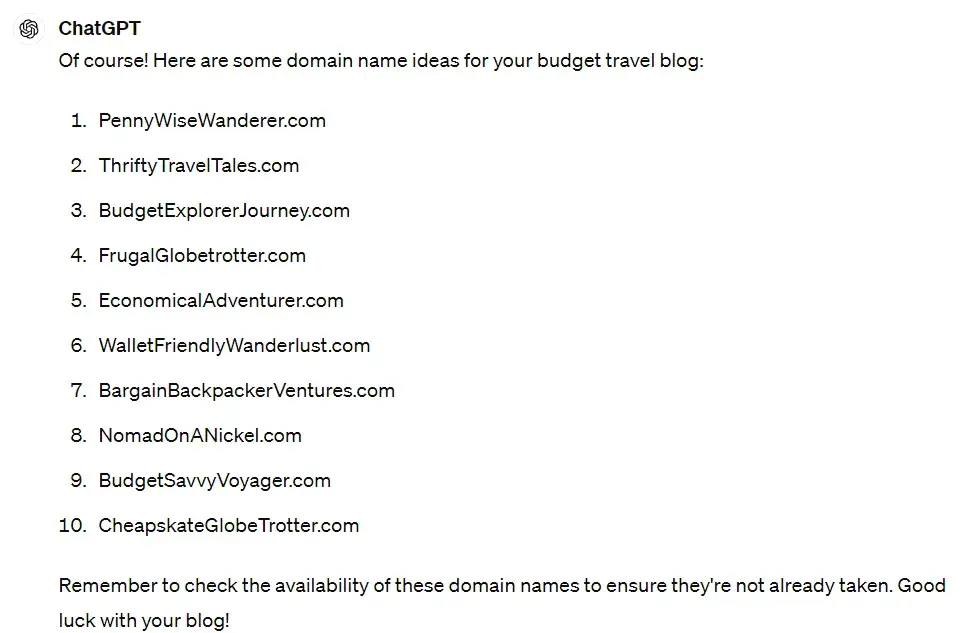
Domain names are hot commodities, but they are also pretty affordable. As long as your idea isn’t trademarked or already in use, grab it before it’s gone! You can always change it later if you decide it just isn’t working.
I understand that this is a lot to digest. But just as there are generators to help you find excellent hashtags and keywords, there are also tools to help you find domain names (in addition to using ChatGPT).
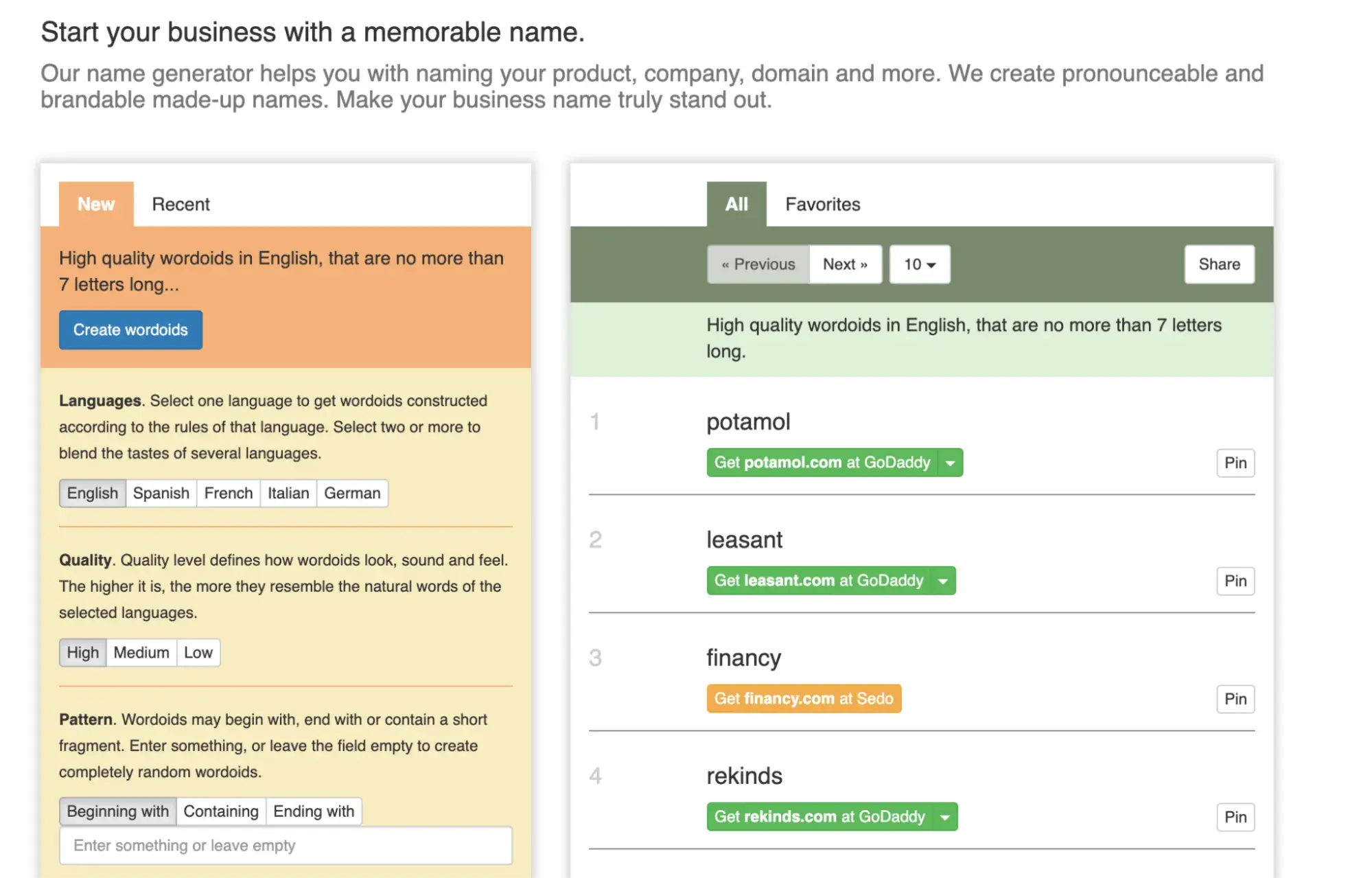
You can take some of the keywords and brand-related words you’ve brainstormed through the above tips and add them to a domain name generator, which will use those words and related words to create lists of available domain names.
Even if you don’t pick a domain name exactly from the generator, it can help inspire your team to find a domain name that is perfect for your business or blog. Here are some of the top domain name generators to try.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

The Best Web Hosting for Small Business Sites in 2024: 12 Favorites

Best Video Hosting Sites: The Top 11 Sites in 2023

Domains and Domain Names: What They Are and 10+ Examples

Everything You Need to Know about Custom Domains

The 13 Best Blog Hosting Sites to Launch a Winning Blog in 2024

14 Best Domain Registrars to Consider This Year

Serverless Functions: Your Website's New Best Friend

The Ultimate Guide to Web Hosting

What Is a CDN? Understanding Content Delivery Networks
10 Best Windows Web Hosting Platforms for 2024
Launch your WordPress website with the help of this free guide and checklist.
CMS Hub is flexible for marketers, powerful for developers, and gives customers a personalized, secure experience
TechRepublic

8 Best Data Science Tools and Software
Apache Spark and Hadoop, Microsoft Power BI, Jupyter Notebook and Alteryx are among the top data science tools for finding business insights. Compare their features, pros and cons.

EU’s AI Act: Europe’s New Rules for Artificial Intelligence
Europe's AI legislation, adopted March 13, attempts to strike a tricky balance between promoting innovation and protecting citizens' rights.

10 Best Predictive Analytics Tools and Software for 2024
Tableau, TIBCO Data Science, IBM and Sisense are among the best software for predictive analytics. Explore their features, pricing, pros and cons to find the best option for your organization.

Tableau Review: Features, Pricing, Pros and Cons
Tableau has three pricing tiers that cater to all kinds of data teams, with capabilities like accelerators and real-time analytics. And if Tableau doesn’t meet your needs, it has a few alternatives worth noting.

Top 6 Enterprise Data Storage Solutions for 2024
Amazon, IDrive, IBM, Google, NetApp and Wasabi offer some of the top enterprise data storage solutions. Explore their features and benefits, and find the right solution for your organization's needs.
Latest Articles

What is the EU’s AI Office? New Body Formed to Oversee the Rollout of General Purpose Models and AI Act
The AI Office will be responsible for enforcing the rules of the AI Act, ensuring its implementation across Member States, funding AI and robotics innovation and more.

Top Tech Conferences & Events to Add to Your Calendar in 2024
A great way to stay current with the latest technology trends and innovations is by attending conferences. Read and bookmark our 2024 tech events guide.

What is Data Science? Benefits, Techniques and Use Cases
Data science involves extracting valuable insights from complex datasets. While this process can be technically challenging and time-consuming, it can lead to better business decision-making.

Gartner’s 7 Predictions for the Future of Australian & Global Cloud Computing
An explosion in AI computing, a big shift in workloads to the cloud, and difficulties in gaining value from hybrid cloud strategies are among the trends Australian cloud professionals will see to 2028.

OpenAI Adds PwC as Its First Resale Partner for the ChatGPT Enterprise Tier
PwC employees have 100,000 ChatGPT Enterprise seats. Plus, OpenAI forms a new safety and security committee in their quest for more powerful AI, and seals media deals.

What Is Contact Management? Importance, Benefits and Tools
Contact management ensures accurate, organized and accessible information for effective communication and relationship building.

How to Use Tableau: A Step-by-Step Tutorial for Beginners
Learn how to use Tableau with this guide. From creating visualizations to analyzing data, this guide will help you master the essentials of Tableau.

HubSpot CRM vs. Mailchimp (2024): Which Tool Is Right for You?
HubSpot and Mailchimp can do a lot of the same things. In most cases, though, one will likely be a better choice than the other for a given use case.

Top 5 Cloud Trends U.K. Businesses Should Watch in 2024
TechRepublic identified the top five emerging cloud technology trends that businesses in the U.K. should be aware of this year.

Pipedrive vs. monday.com (2024): CRM Comparison
Find out which CRM platform is best for your business by comparing Pipedrive and Monday.com. Learn about their features, pricing and more.

Celoxis: Project Management Software Is Changing Due to Complexity and New Ways of Working
More remote work and a focus on resource planning are two trends driving changes in project management software in APAC and around the globe. Celoxis’ Ratnakar Gore explains how PM vendors are responding to fast-paced change.

SAP vs. Oracle (2024): Which ERP Solution Is Best for You?
Explore the key differences between SAP and Oracle with this in-depth comparison to determine which one is the right choice for your business needs.

How to Create Effective CRM Strategy in 8 Steps
Learn how to create an effective CRM strategy that will help you build stronger customer relationships, improve sales and increase customer satisfaction.

CISOs in Australia Urged to Take a Closer Look at Data Breach Risks
A leading cyber expert in Australia has warned CISOs and other IT leaders their organisations and careers could be at stake if they do not understand data risk and data governance practices.

Snowflake Arctic, a New AI LLM for Enterprise Tasks, is Coming to APAC
Data cloud company Snowflake’s Arctic is promising to provide APAC businesses with a true open source large language model they can use to train their own custom enterprise LLMs and inference more economically.
Create a TechRepublic Account
Get the web's best business technology news, tutorials, reviews, trends, and analysis—in your inbox. Let's start with the basics.
* - indicates required fields
Sign in to TechRepublic
Lost your password? Request a new password
Reset Password
Please enter your email adress. You will receive an email message with instructions on how to reset your password.
Check your email for a password reset link. If you didn't receive an email don't forgot to check your spam folder, otherwise contact support .
Welcome. Tell us a little bit about you.
This will help us provide you with customized content.
Want to receive more TechRepublic news?
You're all set.
Thanks for signing up! Keep an eye out for a confirmation email from our team. To ensure any newsletters you subscribed to hit your inbox, make sure to add [email protected] to your contacts list.
MIT Technology Review
- Newsletters
OpenAI and Google are launching supercharged AI assistants. Here’s how you can try them out.
They promise to be leaps ahead of tools like Siri or Alexa.
- James O'Donnell archive page

This week, Google and OpenAI both announced they’ve built supercharged AI assistants: tools that can converse with you in real time and recover when you interrupt them, analyze your surroundings via live video, and translate conversations on the fly.
OpenAI struck first on Monday, when it debuted its new flagship model GPT-4o. The live demonstration showed it reading bedtime stories and helping to solve math problems, all in a voice that sounded eerily like Joaquin Phoenix’s AI girlfriend in the movie Her (a trait not lost on CEO Sam Altman).
On Tuesday, Google announced its own new tools, including a conversational assistant called Gemini Live, which can do many of the same things. It also revealed that it’s building a sort of “do-everything” AI agent, which is currently in development but will not be released until later this year.
Soon you’ll be able to explore for yourself to gauge whether you’ll turn to these tools in your daily routine as much as their makers hope, or whether they’re more like a sci-fi party trick that eventually loses its charm. Here’s what you should know about how to access these new tools, what you might use them for, and how much it will cost.
OpenAI’s GPT-4o
What it’s capable of: The model can talk with you in real time, with a response delay of about 320 milliseconds, which OpenAI says is on par with natural human conversation. You can ask the model to interpret anything you point your smartphone camera at, and it can provide assistance with tasks like coding or translating text. It can also summarize information, and generate images, fonts, and 3D renderings.
How to access it: OpenAI says it will start rolling out GPT-4o’s text and vision features in the web interface as well as the GPT app, but has not set a date. The company says it will add the voice functions in the coming weeks, although it’s yet to set an exact date for this either. Developers can access the text and vision features in the API now, but voice mode will launch only to a “small group” of developers initially.
How much it costs: Use of GPT-4o will be free, but OpenAI will set caps on how much you can use the model before you need to upgrade to a paid plan. Those who join one of OpenAI’s paid plans, which start at $20 per month, will have five times more capacity on GPT-4o.
Google’s Gemini Live
What is Gemini Live? This is the Google product most comparable to GPT-4o—a version of the company’s AI model that you can speak with in real time. Google says that you’ll also be able to use the tool to communicate via live video “later this year.” The company promises it will be a useful conversational assistant for things like preparing for a job interview or rehearsing a speech.
How to access it: Gemini Live launches in “the coming months” via Google’s premium AI plan, Gemini Advanced.
How much it costs: Gemini Advanced offers a two-month free trial period and costs $20 per month thereafter.
But wait, what’s Project Astra? Astra is a project to build a do-everything AI agent, which was demoed at Google’s I/O conference but will not be released until later this year.
People will be able to use Astra through their smartphones and possibly desktop computers, but the company is exploring other options too, such as embedding it into smart glasses or other devices, Oriol Vinyals, vice president of research at Google DeepMind, told MIT Technology Review .
Which is better?
It’s hard to tell without having hands on the full versions of these models ourselves. Google showed off Project Astra through a polished video, whereas OpenAI opted to debut GPT-4o via a seemingly more authentic live demonstration, but in both cases, the models were asked to do things the designers likely already practiced. The real test will come when they’re debuted to millions of users with unique demands.
That said, if you compare OpenAI’s published videos with Google’s, the two leading tools look very similar, at least in their ease of use. To generalize, GPT-4o seems to be slightly ahead on audio, demonstrating realistic voices, conversational flow, and even singing, whereas Project Astra shows off more advanced visual capabilities, like being able to “remember” where you left your glasses. OpenAI’s decision to roll out the new features more quickly might mean its product will get more use at first than Google’s, which won’t be fully available until later this year. It’s too soon to tell which model "hallucinates" false information less often or creates more useful responses.
Are they safe?
Both OpenAI and Google say their models are well tested: OpenAI says GPT-4o was evaluated by more than 70 experts in fields like misinformation and social psychology, and Google has said that Gemini "has the most comprehensive safety evaluations of any Google AI model to date, including for bias and toxicity.”
But these companies are building a future where AI models search, vet, and evaluate the world’s information for us to serve up a concise answer to our questions. Even more so than with simpler chatbots, it’s wise to remain skeptical about what they tell you.
Artificial intelligence
Sam altman says helpful agents are poised to become ai’s killer function.
Open AI’s CEO says we won’t need new hardware or lots more training data to get there.
An AI startup made a hyperrealistic deepfake of me that’s so good it’s scary
Synthesia's new technology is impressive but raises big questions about a world where we increasingly can’t tell what’s real.
- Melissa Heikkilä archive page
Taking AI to the next level in manufacturing
Reducing data, talent, and organizational barriers to achieve scale.
- MIT Technology Review Insights archive page
Is robotics about to have its own ChatGPT moment?
Researchers are using generative AI and other techniques to teach robots new skills—including tasks they could perform in homes.
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.
Public Access
Google Scholar Profiles
Google Scholar Profiles provide a simple way for authors to showcase their academic publications. You can check who is citing your articles, graph citations over time, and compute several citation metrics. You can also make your profile public, so that it may appear in Google Scholar results when people search for your name, e.g., richard feynman .
Best of all, it's quick to set up and simple to maintain - even if you have written hundreds of articles, and even if your name is shared by several different scholars. You can add groups of related articles, not just one article at a time; and your citation metrics are computed and updated automatically as Google Scholar finds new citations to your work on the web. You can choose to have your list of articles updated automatically or review the updates yourself, or to manually update your articles at any time.
Set up your Google Scholar Profile
Setting up your profile
Start here. It's quick and free.
- First, sign in to your Google account, or create one if you don't yet have one. We recommend that you use a personal account, not an account at your institution, so that you can keep your profile for as long as you wish.
- Once you've signed in to your Google account, open the Scholar profile sign up form , confirm the spelling of your name, enter your affiliation, interests, etc. We recommend that you also enter your university email address; this would make your profile eligible for inclusion in Google Scholar search results.
- On the next page, you'll see groups of articles written by people with names similar to yours. Add all articles that you have written; keep in mind your articles may be in several different groups, and some groups may occasionally include articles by several different authors. If you publish under several different names, you may need to do several searches to add all your articles.
- Once you're done with adding articles, it will ask you what to do when the article data changes in Google Scholar. You can either have the updates applied to your profile automatically, or you can choose to review them beforehand. In either case, you can always go to your profile and make changes by hand.
- Finally, you will see your profile. This is a good time to add a few finishing touches - upload your professional looking photo, visit your university email inbox and click on the verification link, double check the list of articles, and, once you're completely satisfied, make your profile public. Voila - it's now eligible to appear in Google Scholar when someone searches for your name!
Select the "Add articles" option from the menu. Search for your articles using titles, keywords, or your name. Your citation metrics will update immediately to account for the articles you added.
If your search doesn't find the right article, click "Add article manually". Then, type in the title, the authors, etc., and click "Save". Keep in mind that citations to manually added articles may not appear in your profile for a few days.
To add a group of related articles, click "Add article groups". If you have written articles under different names, with multiple groups of colleagues, or in different journals, you may need to select multiple groups. Your citation metrics will update immediately to account for the groups you added.
If the menu doesn't appear, sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile.
Alas, we have no way of knowing which articles are really yours . Author names are often abbreviated and different people sometimes share similar names. We use a statistical model to try to tell different authors apart but such automatic processes are not always accurate. The best way to fix this is to look through the articles in your profile and remove the ones that were written by others.
Select the articles you would like to remove and then click the "Delete" button.
If the article checkboxes don't appear, sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile.
Deleted articles are moved to the Trash. To view articles in the Trash, select the "View trash" option from the menu. To restore an article from the Trash, select the article and click the "Restore" button.
Click the title of the article and then click the "Edit" button. When you finish your changes, click the "Save" button.
If the "Edit" button doesn't appear, sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile.
If you've made substantial changes to the article, please keep the following in mind.
- The list of "Scholar articles" at the bottom of the page may no longer match the article you've edited. We recommend that you review this list and "unmerge" the Scholar articles that no longer correspond to your article. Scholar articles affect the computation of your "Cited by" counts and citation metrics.
- As with manual additions of articles, it may take several days for all citations to the edited article to be collected in your profile. You can speed up the process by adding the appropriate article from Google Scholar and then merging it with your version; then, your citation metrics will update right away.
- It's possible that the article you've edited was already in your profile as a separate record. We recommend that you merge duplicate records - click the "Title" column header to sort your articles by title, select the checkboxes next to the duplicate entries, which should now be adjacent, and then click the "Merge" button.
Select both versions of the article and click the "Merge" button. You will then see both citations for the article listed. Select the best citation to the article (you can edit it later if you wish) and click "Merge". This will merge the two versions. Your citation metrics will automatically update to count the versions you've merged as a single article, not two different articles.
Nope, the "Cited by" count after the merge is the number of papers that cite the merged article. One of these probably cites both versions that you've merged; the 27+4=31 formula counts this citation twice. But if the count has dropped below 27... ugh, please do let us know.
The ∗ indicates that the "Cited by" count includes citations that might not match this article. It is an estimate made automatically by a computer program. You can check these citations by clicking on the article's title and looking for "Scholar articles" with a ∗ next to their title.
Making your profile public
Your profile is private and visible only to you until and unless you make your profile public.
Click the "Edit" button next to your name, check the "Make my profile public" box, and click "Save".
You can share the URL displayed by the browser. It looks like this: https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=ID&hl=en …where ID identifies your Google Scholar profile. You can link to it from your homepage, email it to colleagues, or share it on social media. The link only works if the profile is public, and only lets other people see the profile but not make changes to it.
Click the "Edit" button next to your name, uncheck the "Make my profile public" box, and click "Save".
You also need to add a verified email address at your university or institution.
To be eligible for inclusion in Google Scholar search results, your profile needs to be public and needs to have a verified email address at your university (non-institutional email addresses, such as gmail.com, hotmail.com, aol.com, yahoo.com, qq.com, etc., are not suitable for this purpose). To add a verified email to your profile, click the "Edit" button next to your name, add your email address at your institution and click "Save". We will send you an email message with a verification link. Once you click on this link, the email address will be marked verified. Your profile will now be eligible for inclusion in Google Scholar search results.
Rest assured, we will not display your email address on your public profile. Nor will we sell it, trade it, or use it to send you email unrelated to Google Scholar.
Exploring citations to your articles
Click the "Cited by" number for the article.
Click the title of the article.
Click the "Follow" button next to your name, check the "New citations to my articles" box, and click "Done". We'll then email you when newly published articles cite any of the works in your profile.
Click the "Cited by" number for your article and then click the envelope icon in the left sidebar. Then we'll email you when newly published articles cite yours.
Google Scholar considers this article the same as another article in your profile. We display the "Cited by" count next to both of the duplicates, but we only count them once in your citation metrics.
We recommend that you merge the duplicates - select both articles and click the "Merge" button.
Probably not. We compute two versions, All and Recent, of three metrics - h-index, i10-index and the total number of citations. While there's no shortage of other reasonable metrics, the incremental usefulness of adding each number generally goes down, while the user confusion generally goes up.
Your "Cited by" counts come from the Google Scholar index. You can change the articles in your profile, but citations to them are computed and updated automatically as we update Google Scholar.
To change the "Cited by" counts in your profile, you would need to have them updated in Google Scholar. Google Scholar generally reflects the state of the web as it is currently visible to our search robots and to the majority of users. If some of the citations to your article are not included, chances are that the citing articles are not accessible to our search robots or are formatted in ways that make it difficult for our indexing algorithms to identify their bibliographic data or references.
To fix this, you'll need to identify the specific citing articles with indexing problems and work with the publisher of these articles to make the necessary changes (see our inclusion guidelines for details). For most publishers, it usually takes 6-9 months for the changes to be reflected in Google Scholar; for very large publishers, it can take much longer.
Many research funding agencies promote broad access to funded research by mandating that articles describing the research should be publicly available. The Public Access section of a Google Scholar profile contains the articles that are expected to be publicly available based on funding agency mandates. For each article, you can view the applicable mandates and see if it is publicly available. If the article has a publicly available version, a link marked [PDF] or [HTML] appears on the right hand side.
An article can be publicly available from several sources including its publisher, an institutional repository, a research area specific repository and others. The Google Scholar indexing system tries to include all publicly accessible versions that follow our inclusion guidelines . For your own profile, you can update the list of articles and make corrections. You can also make an article publicly available by uploading a PDF of the article to your own Google Drive.
The Public Access Mandates table presents summary statistics about public access mandates for different funding agencies. For each funding agency, you can view the level of public availability of mandated articles overall and over several recent years.
The Google Scholar indexing system automatically extracts funding information from the acknowledgement sections of articles. You can see the funding acknowledgement for an article by clicking on its title on the public access page.
Public access mandates usually specify that funded articles should be publicly available within a given period of time (referred to as the "embargo") after publication. You can see the embargo period for an article by clicking on its title on the public access page.
Your profile should only include articles that you wrote. To remove an article that you didn't write, click "REVIEW", then "MAKE A CORRECTION", select "I'm not an author of this article" from the list of options and click "DONE". The article will be removed from your public access page. It will also be deleted from your profile. If you don't see "MAKE A CORRECTION", sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile.
Click "REVIEW", then "MAKE A CORRECTION", select "This article wasn't funded by any of these agencies" from the list of options and click "DONE". The article will be removed from your public access page. If you don't see "MAKE A CORRECTION", sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile.
Click "REVIEW", then "MAKE A CORRECTION", select "This article's publication date is incorrect" from the list of options, enter the correct date and click "DONE". If the new publication date is outside the scope of the mandate, the article will be removed from your public access page. This will also update the publication date in your profile. If you don't see "MAKE A CORRECTION", sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile.
The simplest thing would be to ask your coauthor to make the article publicly available. Once the publicly available version is included in the Google Scholar index, your public access page will be automatically updated.
You can also indicate this on your public access page. To do this, click "REVIEW", then "MAKE A CORRECTION", select "I'm not the responsible author" from the list of options, select the authors that are responsible for making the article publicly available and then click "DONE". The article will then be listed in the "Recused" section on your public access page. If you don't see "MAKE A CORRECTION", sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile. Once the article is publicly available from another source, it will automatically move to the "Available" section.
The star indicates that one or more of your mandated articles is not yet publicly available and that you have recused yourself from making them available.
The Public Access section is only available for public profiles. If your profile is currently private, click the "Edit" button next to your name, check the "Make my profile public" box, and click "SAVE". If the "Edit" button doesn't appear, sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile.
If your profile is already public and you still don't see the Public Access section, the Google Scholar indexing system has not yet identified any articles with public access mandates in your profile.
The Google Scholar indexing system tries to include all publicly accessible versions that follow our inclusion guidelines . Please contact your publisher and ask them to make sure that the publicly available version is accessible to our search robots.
You can also make the article publicly available by uploading a PDF of the article to your own Google Drive. To do that, click the "UPLOAD PDF" button next to the article on your public access page. If you don't see the "UPLOAD PDF" button, sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile. Please upload only articles that you've written and have the rights to share.
The Google Scholar indexing system tries to include all publicly accessible versions that follow our inclusion guidelines . Please contact the repository administrators and ask them to make sure that the article is accessible to our search robots.
You can also make the article publicly available by uploading a PDF of the article to your own Google Drive . To do that, click the "UPLOAD PDF" button next to the article on your public access page. If you don't see the "UPLOAD PDF" button, sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile. Please upload only articles that you've written and have the rights to share.
Yes, the uploaded article will be linked from your profile. It will also be eligible for inclusion in the Google Scholar index.
Click on the title of the article, and then click "UPDATE PDF". Follow the prompts to upload a PDF file from your computer. The link in your profile will be updated immediately. If the original version was indexed in Google Scholar, it will be replaced in a few days.
Note, the original uploaded article will still be in the "Public research articles" folder in your Google Drive . If you wish, you can delete it from there as well. If you don't see the original article or the 'Public research articles' folder in your Google Drive, sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile.
Go to the "Public research articles" folder in your Google Drive , and delete the article from there. The link to the article will disappear from your profile and the Google Scholar index in a few days.
If you don't see the "Public research articles" folder or the article in question in your Google Drive, sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile.
This error message means that your domain's administrators have disabled public sharing through Google Drive possibly as a part of organizational policy. Please contact your domain's administrators for assistance and clarification.
Public Access Reports for Agencies
In addition to reviewing public access for all your articles, you can also view and export public access reports for individual funding agencies. You can view an agency-specific report by clicking the agency’s name on the left-hand side of the Public Access page on desktops, or by selecting the agency in the dropdown list on the top-left side of the page on mobile phones.
Funding agencies can require articles to be available at a particular repository (e.g., PubMed Central), at a group of repositories (any subject or institutional repository), or anywhere on the web. Agency-specific reports take these requirements into account. When an article is available at a suitable location, it will be linked on the right. If you don’t see the link for an available article, you can provide the link to us. For agencies that specify a particular repository, there is also a link to submit your article to that repository. You can also fix errors - remove articles, correct publication dates, or update funding information.
Updates to your profile
You don't need to do anything! Your citation metrics and citation graph will be automatically updated whenever Google Scholar is updated.
Select "Configure article updates" from the menu. Choose the automatic updates setting and click "Update settings". Your profile will be automatically updated when Google Scholar is updated.
This setting only controls the updates to your list of articles. It does not control the updates to your "Cited by" counts and citation metrics - those are always updated to reflect the current state of the web.
To add a missing article to your profile, select "Add articles" from the menu and search for it. If you can't find your article in Google Scholar, select "Add article manually" to enter its bibliographic record by hand.
Select "Configure article updates" from the menu. Choose the confirmation email setting and click "Update settings". When we identify suitable updates for your profile, we'll send you an email message so that you can review and apply the updates.
You don't need to do anything. Automated updates will not make changes to an article that you have edited.
Reviewing updates to your profile
This happens when the Google Scholar search index changes, and it now considers this entry a duplicate of some other article in your profile. This could happen, e.g., if the publisher re-formats their papers or fixes a typo. We recommend that you accept this suggestion. You can, of course, choose to keep duplicate entries in your profile, but only one of them will be counted towards your citation metrics.
This happens when the Google Scholar search index has changed, and we have been unable to match an article in your profile with the new index. Most of the time, this is because it was considered to be a duplicate of some other article in your profile, but we weren't able to determine which one. Occasionally, the article may have been removed from Google Scholar entirely, e.g., because it's no longer available on the web, or because articles that reference it have become unavailable to our search robots.
To check if the article is a duplicate, go to your profile, click the "Title" column header to sort by title, and look for the article in question. If the same article is indeed listed multiple times, you can safely accept the suggestion to delete the unmatched entry. However, if it isn't a duplicate entry, you can choose to keep it in your profile. Though, since it is not matched in Google Scholar, its "Cited by" count will be zero.
Note that your decision to keep an unmatched entry in your profile will not reinstate the entry in Google Scholar. See the inclusion guidelines for help on including your articles in Google Scholar.
General questions
It's under " My profile " on top of the page or in the side drawer. If this link shows a profile creation form, sign in to the Google account that you used to create your profile and try again.
Select the articles you'd like to export - or check the box next to the "Title" column header to select all articles in your profile - and click the "Export" button. Follow the prompts to download a BibTeX, EndNote, RefMan, or CSV file.
Click the column header labeled "Year".
Click the "Edit" button next to your name, paste the URL into the "Homepage" field, and click "Save".
If the profile is yours, sign in to the Google account that you used to create it, and follow the instructions in the Setup section to make corrections. You can add, delete, edit, and merge articles in your own profile.
If the profile is someone else's, it's best to contact its author and ask them to make a correction.
Note that profile owners can't change their "Cited-by" counts, and that updating an article in a profile does not change it in the Google Scholar search results. To make those kinds of corrections, you usually need to talk to the article's publisher; please refer to the inclusion guidelines .
- Privacy & Terms
Advertisement
Supported by
Google Rolls Back A.I. Search Feature After Flubs and Flaws
Google appears to have turned off its new A.I. Overviews for a number of searches as it works to minimize errors.
- Share full article

By Nico Grant
Reporting from San Francisco
When Sundar Pichai, Google’s chief executive, introduced a generative artificial intelligence feature for the company’s search engine last month, he and his colleagues demonstrated the new capability with six text-based queries that the public could try out.
The questions included “how do you clean a fabric sofa” and “what should I use to get a coffee stain out of my carpet.” These were intended to highlight how Google’s new feature, A.I. Overviews , could generate full and useful information summaries above traditional search results.
But by Friday, only one of the six queries still yielded an A.I. Overview, according to tests by The New York Times. Instead, the feature was noticeably less prevalent. The search for “what should I use to get a coffee stain out of my carpet” now resulted in a snippet of text from a website, JDog Carpet Cleaning & Floor Care, while “how do you clean a fabric sofa” was replaced by a link to HGTV’s website with the answer. (The results of the searches may vary depending on the user and location.)
The disappearance of A.I. Overviews for some of the searches appeared to be part of a broader rollback after the new technology produced a litany of untruths and errors — including recommending glue as part of a pizza recipe and suggesting that people ingest rocks for nutrients. Users loudly complained on social media about the mistakes, in many cases outright making fun of Google.
Liz Reid, who was recently promoted to Google’s head of search, wrote in a blog post on Thursday that the company had pared back A.I. Overviews in certain ways, launching “additional triggering refinements” to offer more careful responses about health, disabling misleading advice and limiting the inclusion of satire and user responses from forums like Reddit.
“We’ll keep improving when and how we show AI Overviews and strengthening our protections,” she wrote, adding that Google was working on updates to improve broad sets of search results.
Ashley Thompson, a Google spokeswoman, said in a statement on Friday that the company had made more than a dozen technical updates to its systems.
“A.I. Overviews are helping people on a large number of queries on Search today, serving as a jumping-off point to content across the web.” The company added that while it was making adjustments to improve A.I. Overviews, it was not pulling back from the feature for the long term.
The backtracking was a blow to Google’s efforts to keep up with its rivals Microsoft and OpenAI, the maker of the ChatGPT chatbot, in the frenzied race to lead A.I. It also underscored the difficult strategic choice that Google faces over whether to embrace A.I. technology that may not be dependable, or keep its highly popular search engine the same — and risk falling behind its peers.
Google had chosen to go slower than Microsoft, which placed more conversational A.I. into its Bing search engine early last year. Google, which has significantly more users than Bing, tested A.I. features for its search engine a year before introducing A.I. Overviews. The company said the new feature would be rolled out to users in the United States immediately and to more than a billion people by the end of the year.
But ultimately, Google ”should have rolled this out more slowly,” said Patrick Hall, an assistant professor of decision sciences at the George Washington University School of Business. “Once something like this happens, you really have to retreat. And if nothing else, there’s reputational harm” to the company.
Google, which has led internet search for more than two decades, has scrambled since OpenAI released ChatGPT in 2022. Some tech industry insiders considered the chatbot’s ability to generate answers to be a serious threat to Google’s search engine, which has been the most popular way to get information online.
Since then, Google has aggressively worked to regain its advantage in A.I., releasing a family of technology named Gemini, including new A.I. models for developers. The company also infused the technology into YouTube, Gmail and Docs, helping users create videos, emails and drafts with less effort.
Last month, Ms. Reid said at Google’s developer conference that the search engine would do more of the googling for users with A.I. Overviews. She highlighted increasingly complex requests that Google could answer with the feature, but those capabilities have not yet been launched for users.
Onstage, simpler questions like “how do I get the smell of a campfire out of my clothes” yielded A.I. answers including air it out, add baking soda and spray with lemon juice.
But when users got their hands on the new service, they found that A.I. Overviews sometimes generated wrong — or downright dangerous — answers, including recommending putting nontoxic glue on pizza to make the cheese stick. It also misunderstood some websites it was quoting and got presidential history wrong.
Of the six questions that Google launched for the public, the only one that consistently triggered an A.I. Overview on Friday was “what are interesting science projects I can do with my son who is 12 years old.”
The answer? Growing crystals, extracting DNA from saliva and writing a message with invisible ink.
Nico Grant is a technology reporter covering Google from San Francisco. Previously, he spent five years at Bloomberg News, where he focused on Google and cloud computing. More about Nico Grant
Explore Our Coverage of Artificial Intelligence
News and Analysis
OpenAI said that it has begun training a new flagship A.I. model that would succeed the GPT-4 technology that drives its popular online chatbot, ChatGPT.
Elon Musk’s A.I. company, xAI, said that it had raised $6 billion , helping to close the funding gap with OpenAI, Anthropic and other rivals.
Google’s A.I. capabilities that answer people’s questions have generated a litany of untruths and errors — including recommending glue as part of a pizza recipe and the ingesting of rocks for nutrients — causing a furor online.
The Age of A.I.
After some trying years during which Mark Zuckerberg could do little right, many developers and technologists have embraced the Meta chief as their champion of “open-source” A.I.
D’Youville University in Buffalo had an A.I. robot speak at its commencement . Not everyone was happy about it.
A new program, backed by Cornell Tech, M.I.T. and U.C.L.A., helps prepare lower-income, Latina and Black female computing majors for A.I. careers.
Publishers have long worried that A.I.-generated answers on Google would drive readers away from their sites. They’re about to find out if those fears are warranted, our tech columnist writes .
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How Marketers Can Adapt to LLM-Powered Search
- Stefano Puntoni,
- Mike Ensing,
- Jarvis Bowers
With the addition of AI-generated overviews, Google, Perplexity, OpenAI and other search engines are changing how consumers find information.
Large language models (LLMs) provide a search experience that’s dramatically different from the web-browser experience. The biggest difference is this: LLMs promise to answer queries not with links, as web browsers do, but with answers . Increasingly, using apps such as ChatGPT or Perplexity, or search portals such as Google’s Search Generative Experience (now AI Overviews) or Bing’s Copilot, customers will learn about products and brands through natural-language outputs. And that process, which will be highly consultative and conversational, will create a new information pipeline that marketers need to monitor to ensure their brands are presented for relevant prompts and described accurately. The authors present three ways for marketers to rise to this challenge.
For millions of consumers around the world, Google is the access point to the internet — and as a result, the company today enjoys a 91% market share in the $50 billion market for search ads. However, thanks to the advent of large language models (LLMs), a shakeup now seems possible for the first time in two decades.
- SP Stefano Puntoni is a professor of marketing at the Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania, and the co-author of Decision-Driven Analytics: Leveraging Human Intelligence to Unlock the Power of Data (Wharton Press).
- ME Mike Ensing is the CEO and co-founder of Revere. He is an entrepreneur, advisor, and tech-industry executive focused on generative AI and its applications for enterprises and brands and has held senior and advisory positions with leading companies such as RealNetworks, Microsoft, and McKinsey.
- JB Jarvis Bowers is the COO and co-founder of Revere, an emerging marketing-technology company focused on elevating brands with LLMs and generative AI. Jarvis is an experienced marketing leader focused on the use of consumer and creative insights, customer data, and emerging platforms to deliver unique brand experiences.
Partner Center
Argentine President Milei to Meet Apple, Google, Meta CEOs in US

Argentina's President Javier Milei waves to supporters outside the Cabildo during the commemoration of the 214th anniversary of the May Revolution, in Cordoba, Argentina May 25, 2024. REUTERS/Leandro Bustamante Gomez
(Reuters) - Argentina's President Javier Milei is set to meet with top-level executives from Google, Meta and Apple during a trip to the United States this week, his spokesman Manuel Adorni said on Monday.
Libertarian Milei is set to travel to San Francisco late on Monday and stay through Friday, during which time he is set to meet Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg, Google CEO Sundar Pichai, Apple CEO Timothy Cook and Open AI CEO Sam Altman.
He will also speak at the Bay Area Council's Pacific Summit and Stanford University's Hoover Institution, a think tank which promotes limited government, and meet with the university's chancellor and the think tank's director, Condoleezza Rice.
Rice served as U.S. Secretary of State and National Security Advisor in the administration of former U.S. President George W. Bush.
Milei is also scheduled to meet with economists from the think tank as well as investors and entrepreneurs linked to artificial intelligence (AI).
The president is set to fly back on Friday evening, after a stopover in El Salvador where he will attend the inauguration of the second term of President Nayib Bukele, who won a landslide re-election in February.
Milei met Tesla CEO Elon Musk in Texas in April, when they discussed a variety of topics, from the need to boost declining birthrates worldwide to pursuing technological development and defending "liberty."
(Reporting by Peter Frontini; Writing by Sarah Morland; Editing by Gabriel Araujo and Brendan O'Boyle)
Copyright 2024 Thomson Reuters .
Join the Conversation
Tags: Argentina , United States , South America
America 2024

Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 worst presidents.
U.S. News Staff Feb. 23, 2024

Cartoons on President Donald Trump
Feb. 1, 2017, at 1:24 p.m.

Photos: Obama Behind the Scenes
April 8, 2022

Photos: Who Supports Joe Biden?
March 11, 2020

NYC’s Verdict on Trump: Not One of Us
Lincoln Mitchell June 1, 2024

Will Trump’s Guilty Verdict Help Biden?
Susan Milligan May 31, 2024

Texas Court Punts Abortion Ban Challenge
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 31, 2024

Key Reactions to Trump’s Guilty Verdict
Lauren Camera and Laura Mannweiler May 31, 2024

5 Key Questions About Trump Verdict
Cecelia Smith-Schoenwalder May 31, 2024

His Own Worst Enemy?
Lauren Camera May 31, 2024


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions. Advanced search. Find articles. with all of the words. with the exact phrase. with at least one of the words. without the ...
Search Help. Get the most out of Google Scholar with some helpful tips on searches, email alerts, citation export, and more. Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar: click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
Google Scholar searches are not case sensitive. 2. Use keywords instead of full sentences. 3. Use quotes to search for an exact match. 3. Add the year to the search phrase to get articles published in a particular year. 4. Use the side bar controls to adjust your search result.
To search for primary articles in Google Scholar, first, go to the main page and select 'Advanced Search'. In the Advanced Search window, check off the box that says 'Only show results from content I can access' and then select 'Include Patents'. Finally, click on 'Search'. This will filter out all secondary sources such as ...
The first step is make sure you are affiliated with the UML Library on and off campus by Managing your Settings, under Library Links. When searching in Google Scholar here are a few things to try to get full text: click a library link, e.g., "Full-text @ UML Library", to the right of the search result; click a link labeled [PDF] to the right of ...
Save interesting articles to your library. It's easy to go down fascinating rabbit hole after rabbit hole in Google Scholar. Don't lose track of your research and use the save option that pops up under search results so articles will be in your library for later reading. 13. Keep your library organized with labels.
Features of Google Scholar. Search all scholarly literature from one convenient place. Explore related works, citations, authors, and publications. Locate the complete document through your library or on the web. Keep up with recent developments in any area of research. Check who's citing your publications, create a public author profile ...
Google Scholar is a special version of Google specially designed for searching scholarly literature. It covers peer-reviewed papers, theses, books, preprints, abstracts and technical reports from all broad areas of research. A Harvard ID and PIN are required for Google Scholar in order to access the full text of books, journal articles, etc. provided by licensed resources to which Harvard ...
Google Scholar promotes itself as a resource that provides one-stop shopping for scholarly literature. It searches across many disciplines and covers a wide variety of resources, including journal articles, theses, books, abstracts, and more.
Google Scholar. Google Scholar is a web search engine that finds scholarly literature, including papers, theses, books, and reports. By searching Google Scholar from the library's webpage, you will have free linked access to the library's subscription holdings. Other links from Google Scholar may prompt you to pay for articles, but DO NOT ...
Go back to find the fundamental research. When we use Google Search, we are interested in the latest. In Google Scholar, we can go back in time with the date filters (or use a custom date range ...
Get 30 days free. 1. Google Scholar. Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
Review articles are another great way to find scholarly primary research articles. Review articles are not considered "primary research", but they pull together primary research articles on a topic, summarize and analyze them. In Google Scholar, click on Review Articles at the left of the search results screen. Ask your professor whether review ...
Head to Google Scholar . Type out a keyword search in the search bar. When the results are displayed, only check for articles with a PDF text link. Click on the link for your desired article. Check if the article has a free downloadable link, or if you can read it for free online. Once you have found a free article, save the PDF document onto ...
Research databases. You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar. These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources. If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author's name. Alternatively, if you're just ...
Google Scholar returns articles from a wide variety of databases; two of the major ones that are included are JSTOR and Taylor & Francis. JSTOR is a subscription based database, but allows individuals access to up to 100 articles, per month, with a free account. Taylor & Francis is a subscription based database that has both open-access (free ...
Do an online search for the name of the publication or the name of the publisher. Look for more information about their reputation in the field. 2. Research the background of the author. Unless the author is someone known to you to be a leader in the field, you need to find out how much authority they have.
With 160+ million publication pages, 25+ million researchers and 1+ million questions, this is where everyone can access science. You can use AND, OR, NOT, "" and () to specify your search ...
Setting Search Parameters. Use Advanced Search. The advanced or guided search option allows you to select specific fields to search, such as author or title, Use Subjects Terms or Descriptors. If you find an article on the topic you are interested in, look at the subject terms or descriptors that are listed in the record for the item. These ...
3. Filter your search results and analyze trends. Group, rank and analyze the research articles in your search results to optimize the relevancy and efficiency of your efforts. In the Web of Science, researchers can cut through the data in a number of creative ways. This will help you when you're stuck wondering where to find peer reviewed ...
Those are generally the free, full-text versions you want. If Google Scholar doesn't have full-text of the article you want, you might still be able to find it elsewhere. Copy a key part of the article's title onto your clipboard and go over to regular Google. Type in filetype:pdf then paste your title snippet.
Google Scholar Metrics. Google Scholar Metrics provide an easy way for authors to quickly gauge the visibility and influence of recent articles in scholarly publications. Scholar Metrics summarize recent citations to many publications, to help authors as they consider where to publish their new research. To get started, you can browse the top ...
The documents reveal how Google Search is using, or has used, clicks, links, content, entities, Chrome data and more for ranking. A trove of leaked Google documents has given us an unprecedented ...
Here are some steps to help you find the right domain name for you. 1. Consider domain extensions. As stated above, .com is the top domain extension for you to consider. For a blog, you might want to get creative with some of the newer, creative options, but your content will be easiest to find if you stick with a classic, common domain extension.
Apache Spark and Hadoop, Microsoft Power BI, Jupyter Notebook and Alteryx are among the top data science tools for finding business insights. Compare their features, pros and cons. By Aminu ...
Google says that you'll also be able to use the tool to communicate via live video "later this year." The company promises it will be a useful conversational assistant for things like ...
Questions. Google Scholar Profiles. Google Scholar Profiles provide a simple way for authors to showcase their academic publications. You can check who is citing your articles, graph citations over time, and compute several citation metrics. You can also make your profile public, so that it may appear in Google Scholar results when people ...
June 1, 2024, 5:04 a.m. ET. When Sundar Pichai, Google's chief executive, introduced a generative artificial intelligence feature for the company's search engine last month, he and his ...
For millions of consumers around the world, Google is the access point to the internet — and as a result, the company today enjoys a 91% market share in the $50 billion market for search ads ...
REUTERS/Leandro Bustamante Gomez. (Reuters) - Argentina's President Javier Milei is set to meet with top-level executives from Google, Meta and Apple during a trip to the United States this week ...