Accessibility Links
- Skip to content
- Skip to search IOPscience
- Skip to Journals list
- Accessibility help
- Accessibility Help
Click here to close this panel.
Purpose-led Publishing is a coalition of three not-for-profit publishers in the field of physical sciences: AIP Publishing, the American Physical Society and IOP Publishing.
Together, as publishers that will always put purpose above profit, we have defined a set of industry standards that underpin high-quality, ethical scholarly communications.
We are proudly declaring that science is our only shareholder.

Embracing the K-12 Curriculum: Accounts of Philippine Teachers and Students
Naci John C. Trance 1 and Lowe Ana Marie L. Trance 1
Published under licence by IOP Publishing Ltd Journal of Physics: Conference Series , Volume 1254 , 1st UPY International Conference on Applied Science and Education 2018 24–26 October 2018, Yogyakarta, Indonesia Citation Naci John C. Trance and Lowe Ana Marie L. Trance 2019 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1254 012031 DOI 10.1088/1742-6596/1254/1/012031
Article metrics
15120 Total downloads
Share this article
Author e-mails.
Author affiliations
1 Iloilo Science and Technology University, Iloilo City, Philippines
Buy this article in print
The Department of Education of the Philippines has implemented the K-12 Curriculum to both elementary and high school levels of Basic Education starting the school year 2012-2013. Thus, we can infer that the current curriculum is still in its infancy stage. Along with this stage is the dynamic change in the perceptions, reactions, and realizations of different stakeholders towards the new curriculum. In this facet, the study has examined various accounts of in-service and pre-service teachers and students to gain an understanding of how they approach the modern educational system.
Export citation and abstract BibTeX RIS
Content from this work may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 licence . Any further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the title of the work, journal citation and DOI.
Overview of Education in the Philippines
- Later version available View entry history
- First Online: 24 December 2021
Cite this chapter

- Lorraine Pe Symaco 3 &
- Marie Therese A. P. Bustos 4
Part of the book series: Springer International Handbooks of Education ((SIHE))
248 Accesses
The Philippines has embarked on significant education reforms for the past three decades to raise the quality of education at all levels and address inclusion and equity issues. The country’s AmBisyon Natin 2040 or the national vision for a prosperous and healthy society by 2040 is premised on education’s role in developing human capital through quality lifelong learning opportunities. Education governance is handled by three government agencies overseeing the broad education sector of the country. At the same time, regional initiatives relating to ASEAN commitments are also witnessed in the sector. However, despite the mentioned education reforms and initiatives, the education system remains beset by challenges. This chapter will give readers an overview of the education system of the Philippines through an account of its historical context and its main providers and programs. Key reforms and issues within the sector are also discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Batalla EVC, Thompson MR (2018) Introduction. In: Thompson MR, Batalla EVC (eds) Routledge handbook of the contemporary Philippines. Routledge, New York, pp 1–13
Google Scholar
Bautista MB, Bernardo AB, Ocampo D (2008) When reforms don’t transform: reflections on institutional reforms in the Department of Education. Available at: https://pssc.org.ph/wp-content/pssc-archives/Works/Maria%20Cynthia%20Rose%20Bautista/When_Reforms_Don_t_Transform.pdf . Accessed 29 Jan 2021
Behlert B, Diekjobst R, Felgentreff C, Manandhar T, Mucke P, Pries L, et al (2019) World Risk Report 2020. Available at: https://reliefweb.int/sites/reliefweb.int/files/resources/WorldRiskReport-2020.pdf . Accessed 29 Jan 2021
Bustos MT (2019) Special educational needs and disabilities in Secondary Education (Philippines). Bloomsbury Education and Childhood Studies. https://doi.org/10.5040/9781350995932.0023
CHED (2005) CHED memorandum order 1: revised policies and guidelines on voluntary accreditation in aid of quality and excellence in higher education. CHED, Pasig
CHED (2008) Manual of regulations for private higher education. CHED, Pasig
CHED (2013) CHED Memoradum Order 20: General Education Curriculum: Holistic Understandings, Intellectual and Civic Cometencies. CHED, Pasig
CHED (2019a) AQRF referencing report of the Philippines 2019. CHED, Quezon City
CHED (2019b) CHED Memorandum Order 3 Extension of the Validity Period of Designated Centres of Excellence (COEs) and Centres of Developments (CODs) for Various Disciplines
CHED (2019c) Professional regulation commission national passing average 2014–2018. Retrieved from https://ched.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2004_2018-PRC-natl-pass-rate-from-2393-heis-as-of-18June2019.pdf
CHED (n.d.-a). Statistics. Available at: https://ched.gov.ph/statistics/ . Accessed 30 Jan 2021
CHED (n.d.-b) About CHED. Available at: http://ched.gov.ph . Accessed 10 Aug 2020
CHED (n.d.-c) Expanded Tertiary Education Equivalency and Accreditation (ETEEAP). Available at: https://ched.gov.ph/expanded-tertiary-education-equivalency-accreditationeteeap/ . Accessed 11 Sept 2020
CHED (n.d.-d) Higher education data and indicators: AY 2009–10 to AY 2019–20. Available at: https://ched.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/Higher-Education-Data-and-Indicators-AY-2009-10-to-AY-2019-20.pdf . Accessed 29 Jan 2021
CHED (n.d.-e) CHED K to 12 transition program. Retrieved from https://ched.gov.ph/k-12-project-management-unit/ . Accessed 1 Mar 2021
Cohen C, Werker E (2008) The political economy of “natural” disasters. J Confl Resolut 52(6):795–819
Article Google Scholar
Department of Budget (DBM) (2020) PRRD signs the P4.506 Trillion National Budget for FY 2021. Available at: https://www.dbm.gov.ph/index.php/secretary-s-corner/press-releases/list-of-press-releases/1778-prrd-signs-the-p4-506-trillion-national-budget-for-fy-2021#:~:text=President%20Rodrigo%20Roa%20Duterte%20today,to%20the%20COVID%2D19%20pandemic . Accessed 11 Feb 2021
Department of Interior and Local Government (DILG) (2020) Regional summary number of Provinces, Cities, Municipalities and Barangays, by region as of September 30, 2020. Retrieved from https://www.dilg.gov.ph/PDF_File/factsfigures/dilg-facts-figures-2020124_c3876744b4.pdf . Accessed 1 Mar 2021
DepEd (2005) Basic Education Sector Reform Agenda (2006–2010). Available at: http://www.fnf.org.ph/downloadables/Basic%20Education%20Sector%20Reform%20Agenda.pdf . Accessed 29 Jan 2021
DepEd (2010) Implementation of the basic Education Madrasah Programs for Muslim Out-of School Youth and Adults, Department Order 57, s. 2010
DepEd (2012) Adoption of the unique learner reference number, Department Order 22, S. 2012
DepEd (2017) Policy guidelines on Madrasah Education in the K to 12 Basic Education Program, Department Order 41, s. 2017
DepEd (2019) Policy guidelines on the K to 12 Basic Education Program, Department Order 21, s. 2019
DepEd (2020) Major projects, programs & activities status of implementation. Available at: https://www.deped.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/List-of-Programs-and-Project-Implementation-Status.Final_.TS_.pdf . Accessed 29 Jan 2021
Department of Education (DepEd) (n.d.-a) Historical perspective of the Philippines Educational System. Available at: https://www.deped.gov.ph/about-deped/history/ . Accessed 11 Sept 2020
DepEd (n.d.-b) Entollment Statistics. DepEd, Pasig.
Early Childhood Care and Development (ECCD) (n.d.) The National Child Development Centre. Available at: https://eccdcouncil.gov.ph/ncdc.html . Accessed 9 Jan 2021
ECCD Council (n.d.) Early Childhood Care 2018 Annual Report. Pasig, ECCD Council, Metro Manila
ECCD Council/UNICEF (n.d.) The National Early Learning Framework of the Philippines . Available at: https://eccdcouncil.gov.ph/downloadables/NELF.pdf . Accessed 28 June 2020
GoP (1990) Barangay-Level Total Development and Protection of Children Act. Republic Act 6972
GoP (1994a) Higher Education Act. Republic Act 7722
GoP (1994b) TESDA Act. Republic Act 7796
GoP (1998) Expanded Government Assistance to Students and Teachers in Private Education Act, Republic Act 8545
GoP (2000) Institutionalizing the System of National Coordination, Assessment, Planning and Monitoring of the Entire Educational System, Executive Order 273, s. 2000
GoP (2001) Governance of Basic Education Act of 2001, Republic Act 9155. Available at: https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/2001/08/11/republic-act-no-9155/ . Accessed 29 Jan 2021
GoP (2002) Early Childhood Care and Development Act. Republic Act 8980
GoP (2007) Amending Executive Order No. 273 (Series of 2000) and Mandating a Presidential Assistant to Assess, Plan and Monitor the Entire Educational System, Executive Order 632, S. 2007
GoP (2013) Enhanced Basic Education Act. Republic Act 10533
GoP (2014) Ladderized Education Act. Republic Act 10647
GoP (2016) Executive Order No. 5, s. 2016. Approving and Adopting the Twenty-five-year long term vision entitled Ambisyon Natin 2040 as guide for development planning
GoP (2018a) PQF Act. Republic Act 10986
GoP (2018b) Organic Law for the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao Act. Republic Act 11054
GoP (2018c) Safe Spaces Act. Republic Act 11313
GoP (2019a) Transnational Higher Education Act. Republic Act 11448
GoP (2019b) Executive Order No. 100, s. 2019. Institutionalising the Diversity and Inclusion Program, Creating an Inter-Agency Committee on Diversity and Inclusion, and for Other Purposes
GoP (2020) Alternative Learning Systems Act . Republic Act 11510
Government of the Philippines (1987) 1987 Constitution of the Republic of the Philippines
GOVPH (n.d.) About the Philippines. Available at: https://www.gov.ph/about-the-philippines . Accessed 29 Jan 2021
Malipot (2019) DepEd in 2019: the quest for quality education continues. Available at: https://mb.com.ph/2019/12/29/year-end-report-deped-in-2019-the-quest-for-quality-education-continues/ (Manila Bulletin). Accessed 9 Jan 2021
Mendoza DJ, Thompson MR (2018) Congress: separate but not equal. In: Thompson MR, Batalla EVC (eds) Routledge handbook of the contemporary Philippines. Routledge, New York, pp 107–117
Chapter Google Scholar
National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) (2017) Philippine Development Plan 2017–2022. Available at: http://pdp.neda.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/PDP-2017-2022-10-03-2017.pdf . Accessed 29 Jan 2021
OECD (2019) Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) Result from PISA 2018 (Philippines). Available at: https://www.oecd.org/pisa/publications/PISA2018_CN_PHL.pdf . Accessed 11 Sept 2020
Paqueo V, Orbeta A Jr (2019) Gender equity in education: helping the boys catch up. Philippine Institute for Development Studies, Quezon City
Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA) (2020) SGD watch Philippines. Available at: https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/phdsd/PH_SDGWatch_Goal04.pdf . Accessed 9 Jan 2021
Philippines Qualifications Framework (PQF) (n.d.-a) The Philippine Education and Training System. Available at: https://pqf.gov.ph/Home/Details/16 . Accessed 9 Jan 2021
PQF (n.d.-b) Philippine Qualifications Framework. Available at: https://pqf.gov.ph/Home/Details/7 . Accessed 9 Jan 2021
Professional Regulations Commission (PRC) (2019) March 2019 LET teachers board exam list of passers. Available at: https://www.prcboardnews.com/2019/04/official-results-march-2019-let-teachers-board-exam-list-of-passers.html . Accessed 11 Sept 2020
PSA (2019a) 2019 Philippines statistical yearbook. PSA, Quezon City
PSA (2019b) Proportion of Poor Filipinos in ARMM registered at 63.0 percent in the First Semester of 2018. Available at: http://rssoarmm.psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/001%20Proportion%20of%20Poor%20Filipinos%20in%20ARMM%20registered%20at%2063.0%20percent%20in%20the%20First%20Semester%20of%202018.pdf . Accessed 11 Sept 2020
PSA (n.d.) List of Institutions with Ladderized Program under EO 358, July 2006 – December 31, 2007. Available at: https://psa.gov.ph/classification/psced/downloads/ladderizedprograms.pdf . Accessed 29 Jan 2021
Schwab K (2019) The global competitiveness report 2020. Available at: http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TheGlobalCompetitivenessReport2019.pdf . Accessed 29 Jan 2021
Senate of the Philippines (SoP) (2007) Senate P.S. Resolution No.96 Resolution directing the committee on education, arts and culture and committee on constitutional amendments, revisions of codes and laws to conduct a joint inquiry, in aid of legislation, into the implementation of executive order no. 632 abolishing the national coordinating council for education (NCCE) and mandating a presidential assistant to exercise its functions
Syjuco A (n.d.) The Philippine Technical Vocational Education and Training (TVET) System . Available at: https://www.tesda.gov.ph/uploads/file/Phil%20TVET%20system%20-%20syjuco.pdf . Accessed 11 Sept 2020
Symaco LP (2013) Geographies of social exclusion: education access in the Philippines. Comp Educ 49(3):361–373. https://doi.org/10.1080/03050068.2013.803784
Symaco, TLP (2019) Special educational needs and disabilities in primary education (Philippines). Bloomsbury Education and Childhood Studies. https://doi.org/10.5040/9781474209472.0025
Technical Education and Skills Development Authority (TESDA) (2007) TESDA circular 2007. Available at: https://tesda.gov.ph/uploads/file/issuances/omnibus_guide_2007.pdf . Accessed 10 Aug 2020
TESDA (2012) Philippines qualification framework. Available at: http://www.tesda.gov.ph/uploads/File/policybrief2013/PB%20Philippine%20Qualification%20Framework.pdf . Accessed 11 Sept 2020
TESDA (2020a) Philippine TVET statistics 2017–2019 report. Available at: https://www.tesda.gov.ph/Uploads/File/Planning2020/TVETStats/20.12.03_BLUE_TVET-Statistics_2017-2019_Final-min.pdf . Accessed 29 Jan 2021
TESDA (2020b) TVET statistics 2020 4th quarter report. TESDA, Taguig
TESDA (2020c) 2020 TVET statistics annual report. TESDA, Taguig
TESDA (n.d.-a) TVET programmes. Available at: https://www.tesda.gov.ph/About/TESDA/24 . Accessed 9 Jan 2021
TESDA (n.d.-b) National Technical Education and Skills Development Plan 2018–2022. Available at: https://www.tesda.gov.ph/About/TESDA/47 . Accessed 9 Jan 2021
TESDA (n.d.-c) Competency standards development. Available at: https://www.tesda.gov.ph/About/TESDA/85 . Accessed 9 Jan 2021
TESDA (n.d.-d) Assessment and certification. Available at: https://www.tesda.gov.ph/About/TESDA/25 . Accessed 9 Jan 2021
Timberman G (2018) Persistent poverty and elite-dominated policymaking. In: Thompson MR, Batalla EVC (eds) Routledge handbook of the contemporary Philippines. Routledge, New York, pp 293–306
TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center (n.d.) TIMSS 2019 international results in Mathematics and Science. Available at: https://timss2019.org/reports/ . Accessed 9 Jan 2021
UNESCO Institute of Statistics (2020) COVID-19 A global crisis for teaching and learning. Available at: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000373233 . Accessed 11 Sept 2020
UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UNESCO UIS) (2021) Philippines education and literacy. http://uis.unesco.org/en/country/ph?theme=education-and-literacy . Accessed 18 Feb 2021
Valencia C (2019) Companies still hesitant to hire K12 graduates. Available at: https://www.philstar.com/business/business-as-usual/2019/09/30/1955967/companies-still-hesitant-hire-k-12-graduates . Accessed 28 June 2020
Worldometer (n.d.) Philippines demographics. https://www.worldometers.info/demographics/philippines-demographics/ . Accessed 27 Sept 2021
Useful Websites
Ambisyon Natin 2040 . http://2040.neda.gov.ph/
Commission on Higher Education (CHED) https://ched.gov.ph/
Department of Education (DepED). https://www.deped.gov.ph/
ECCD Council of the Philippines (ECCD Council). https://eccdcouncil.gov.ph/
National Council on Disability Affairs (NCDA). https://www.ncda.gov.ph/
Technical Education and Skills Development Authority (TESDA) https://www.tesda.gov.ph/
UNESCO Institute for Statistics Philippines profile. http://uis.unesco.org/en/country/ph?theme=education-and-literacy
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Education, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Lorraine Pe Symaco
College of Education, University of the Philippines, Quezon City, Philippines
Marie Therese A. P. Bustos
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lorraine Pe Symaco .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of education, Southern Cross University, Lismore, NSW, Australia
Martin Hayden
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Symaco, L.P., Bustos, M.T.A.P. (2022). Overview of Education in the Philippines. In: Symaco, L.P., Hayden, M. (eds) International Handbook on Education in South East Asia. Springer International Handbooks of Education. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8136-3_1-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8136-3_1-1
Received : 02 November 2021
Accepted : 02 November 2021
Published : 24 December 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-16-8135-6
Online ISBN : 978-981-16-8136-3
eBook Packages : Education Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Education
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
Chapter history
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8136-3_1-3
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8136-3_1-2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8136-3_1-1
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Corpus ID: 153740227
A CRITIQUE OF K-12 PHILIPPINE EDUCATION SYSTEM
- Maria Teresa F. Calderon
- Published 6 March 2015
- Education, Philosophy
16 Citations
English curriculum reform in the philippines: issues and challenges from a 21st century learning perspective, story of tin: narrative inquiry into experiences of first philippine k-12 graduate, behind the science literacy of filipino students at pisa 2018: a case study in the philippines’ educational system, teachers' perceptions on senior high school readiness of higher education institutions in the philippines., a perception-based curricular review on the k to 12 humss strand curriculum.
- Highly Influenced
Does Teacher Licensure Matter? Basic Education Reform in the Philippine Education System
Moving forward in stem education, challenges and innovations in senior high school in the philippines: the case of northern iloilo polytechnic state college, neo-fascism as the apparatus of neoliberalism’s assault on philippine higher education: towards an anti-fascist pedagogy, analysis of potency and supporting capacity: (implementation of 12 years compulsory education policy in pasuruan district east java indonesia), of multidisciplinary: applied business and education research, 20 references, philosophy of education, reading and math scores of freshmen college students of arellano universityv, reading skills for success: a guide to academic texts, reading in a second language: process, product and practice, investing in our children: what we know and don't know about the costs and benefits of early childhood interventions, the importance of reading, public secondary schools: an inquiry on the instructional readiness and management of grade 7 mathematics curriculum, vocabulary and reading comprehension skills among graduate school students at arellano university, manila school year 2008-2009, the effectivity of the english intervention program of arellano university, educational philosophies., related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers

Story of Tin: Narrative Inquiry Into Experiences of First Philippine K-12 Graduate
IOER International Multidisciplinary Research Journal, Volume 2, Issue 1, March 2020
9 Pages Posted: 6 May 2020
Mc Arthur Maravilla
Palawan State University, Puerto Princesa City, Palawan, Philippines
Date Written: March 2020
The implementation of the K-12 Basic Education Program in the Philippines brought significant programs and projects to expand and improve the delivery of basic education in the country. It added two more years of senior high school in the basic education, broadening the goals of basic education to higher education preparation, middle level skills development, entrepreneurship, and employment. The present study used narrative inquiry to narrate the past experiences of Tin as one of the first graduates of this 7-year old educational reform. It examined Tin’s journey from junior high school to senior high school to gain a better understanding of being a K-12 student in the Philippines and a deeper and richer insight on the implementation of the K-12 curriculum. A qualitative analysis of an in-depth interview with Tin highlighted her struggles, both in her junior and senior high schools. In particular, her struggles included some personal conflicts such as being academically competitive amidst being introvert and financially poor, adjustment to a new environment as she transferred from a rural school to an urban school, rigidity of her senior high school academic subjects, and her trouble with her teachers’ teaching styles. The story of Tin provided specific insights as to how similar conditions as hers may be avoided and how the teaching-learning process may be improved, particularly in the light of the K-12 curriculum implementation in the Philippines.
Keywords: Narrative inquiry, Philippine K-12 Basic Education Program, student experiences, Junior High School, Senior High School
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Mc Arthur Maravilla (Contact Author)
Palawan state university, puerto princesa city, palawan, philippines ( email ).
Philippines
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics, related ejournals, pedagogy ejournal.
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

K12 Educational System in the Philippines - A Policy Paper

This is a Final Requirement in PA 241 (Public Policy and Program Administration), a group output required in the degree Master of Public Administration under Prof. Rodrigo Giducos.
Related Papers
Michi Ferreol
In the wake of the passage of the Enhanced Basic Education Act into Philippine law, schools throughout the Philippines were forced to adopt two additional years of high school into their institutional structure, as well as to enforce a variety of curriculum and instructional changes. The policy effectively transitioned the nation from a 10-year basic education structure to a K-12 system, promising a more globalized curriculum and greater employment opportunities for graduates. This change, however, placed tremendous pressure on teachers and administrators—dubbed by Michael Lipsky (1980) as the “street-level bureaucrats” who execute policies on the ground level—as they were expected to comply with the demands of the law within a limited time period. Thus, in an effort to better understand the ground-level experiences of educators in the aftermath of this policy, I conducted semi-structured interviews with 71 teachers and administrators across four Philippine private schools and five public schools in the National Capital Region. Questions ranged from participants’ day-to-day experiences of the implementation process to their attitudes towards the policy itself. These interviews aimed to broadly answer the question: what factors affect the ground-level execution of a newly instituted education policy? Findings revealed that teachers’ attitudes, beliefs, and strategies were heavily shaped not only by the immediate needs of their classrooms, but also by a confluence of macro-, meso-, and micro-level structures. This, in turn, affected how they executed their discretion and met their obligations as street-level bureaucrats.
Christopher Cocal
The implementation of K+12 means larger budget for the Department of Education and more expenditure for the families who will be sending their children to school. K+12 is not only an issue of economics, is more importantly an issue of personal and professional growth and development that will serve as catapult of economic development. This study determined the anticipatory resource management employed by the principals in the different schools of Pangasinan to ensure greater and successful implementation of the K+12 program. The respondents of the study were the 230 out of 539 principals of the different public elementary schools of the six schools divisions of Pangasinan. Results of the study show that the existing physical plant and facilities and instructional resources of the different public elementary schools in Pangasinan do not met the standard requirements set by the Department of Education. There is a great need for the schools to improve their physical facilities and instructional resources to effectively and efficiently implement the K+12 Program. Financial resource is the major problem of the schools with regards to the implementation of the K+12 Program.
Philippines. The paper presents the fears and loopholes of the K-12 system and its implementation in the context of the Philippines. Drawing on the current discourse, studies and loud views, the author concludes that if the goal is to improve the nation's student achievement then the real solution is improving the quality of teachers because " Students don't fail, teachers do. " Keywords: K-12 education system. Philippines education reform. Curriculum
David Michael San Juan
GEO Academic Journal
Andy N Cubalit
The research looked into the significance of K12 Program as implemented in the Philippines and in Thailand. The scope of this research is delimited to the organizational structure, vision and mission, school system, curriculum and grading systems. The descriptive – comparative method was utilized because the purpose of the study was to find differences and similarities on the implementation of the program in the Philippines and Thailand. The researcher found out that there are similarities and differences with the terms used governance, and, implementation of the K12 Program. Cubalit, Andy Noces (2013) A Descriptive Comparison of K to 12 Program as Implemented in the Philippines and in Thailand. University of the Cordilleras, Baguio City
Yuchengco Center
Cecilia L . Calub
Every education system for K-12 will strive to perform their best, however, very few are able to go far and progress. These types of programs aim to offer extensive knowledge to children, at the same time, offer the parents “peace of mind” in knowing that their children receive the best education possible. Most countries like Finland, United Kingdom, New Zealand, Japan, Singapore, Korea, China, and Israel which are among those with the top rated education systems around the world invested much for their education. The Philippines has just recently implemented the K-12 curriculum. Within a country’s educational system, the relevant institutions and policies include the ways in which a society finances and manages its schools, how a society assesses student performance, and who is empowered to make basic educational decisions, such as which curricula to follow, which teachers to hire, what textbooks to purchase, how many classroom or school buildings have to be constructed. In terms of policy, one might speculate that if a nation assesses the performance of students with some sort of national exam and uses this information to monitor teachers, teachers will put aside their other interests and focus mainly on raising student achievement. With this task the teachers have to accomplish, it is just reasonable to provide them more incentives. Moreover, strong school administrators should also know how to go about their jobs systematically for a successful implementation of the curricular program in the country. In the Philippines, the proposed K-12 curriculum has raised brows of many Filipinos in the beginning. Gradually, the acceptance to the new curriculum has paved the way to its total implementation. There are good effects of the K12 implementation but these effects outweigh the negative ones. Change is not just easy to accept, but if this change would benefit the majority in the end, then there is no other way except go for it and cooperate.
Allen Ibale
In 2012 the Philippines launched its " K to 12 " Program, a comprehensive reform of its basic education. Through this reform, the Philippines is catching up with global standards in secondary education and is attaching a high value to kindergarten. The structure, curricula, and philosophy of the education system are undergoing reform and improvement. The key points of the new policy are " preparation " for higher education, " eligibility " for entering domestic and overseas higher educational institutions, and immediate " employability " on graduating, all leading toward a " holistically developed Filipino ". This policy appears admirable and timely, but it faces some pedagogical and socioeconomic problems. The author wants to point out in particular that the policy needs to address gender problems and should be combined with demand-side approaches in order to promote poverty alleviation and human development in the Philippines.
SSRN Electronic Journal
Ronald Mendoza
Kristel Ann Hermosa
In the Philippines, change has shaken the whole country when K-12 curriculum had its full implementation where Kindergarten was mandatory and an additional two (2) years in Senior High School (SHS) were added to the formerly 10-year basic education. “The K to 12 Program was mandated by Republic Act 10533, otherwise known as ‘Basic Education Act of 2013.’ DepEd began the new learning program in its efforts to make a change towards a better Philippines as early as 2011.” What, therefore, made the researchers conduct this study was to find out how was the implementation of the K-12 curriculum in selected Senior High Schools in Masbate City Division, namely: Masbate National Comprehensive High School (MNCHS), the biggest and premiere secondary school in the city; Bolo National High School (BNHS), a secondary school in coastal part of the city; and lastly, Nursery High School (NHS) utilizing SHS teachers’ perspectives. They have sought to identify the challenges and concerns raised by the SHS schools in Masbate City and to offer plausible solutions for the benefit of many.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Bradernantz Geronag
Ijaems Journal
Pauline Gidget Estella
Discussion …
Francis Quimba
Jose Ramon Albert
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to footer
Products and Services
Live stream splunk's user conference for free.
Global broadcast | June 11–12, 2024

Making AI work for you
Cisco AI is where the AI hype ends and meaningful help begins.
Certifications
Cisco Validated
Announced at Cisco Live
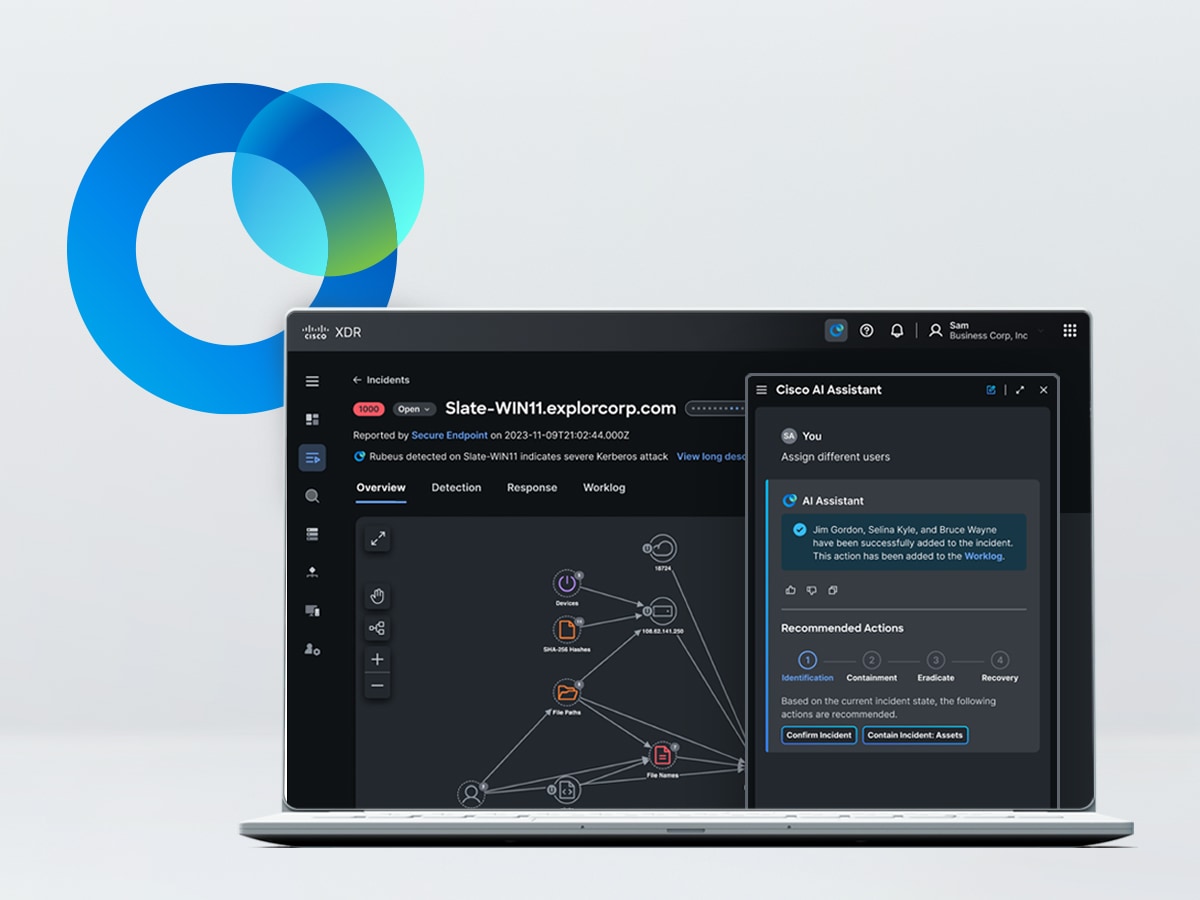
Cisco XDR with AI Assistant
Remediate the highest-priority incidents with an AI-first XDR solution.

Cisco Networking Cloud
One platform experience. Assured, secured, and simplified.
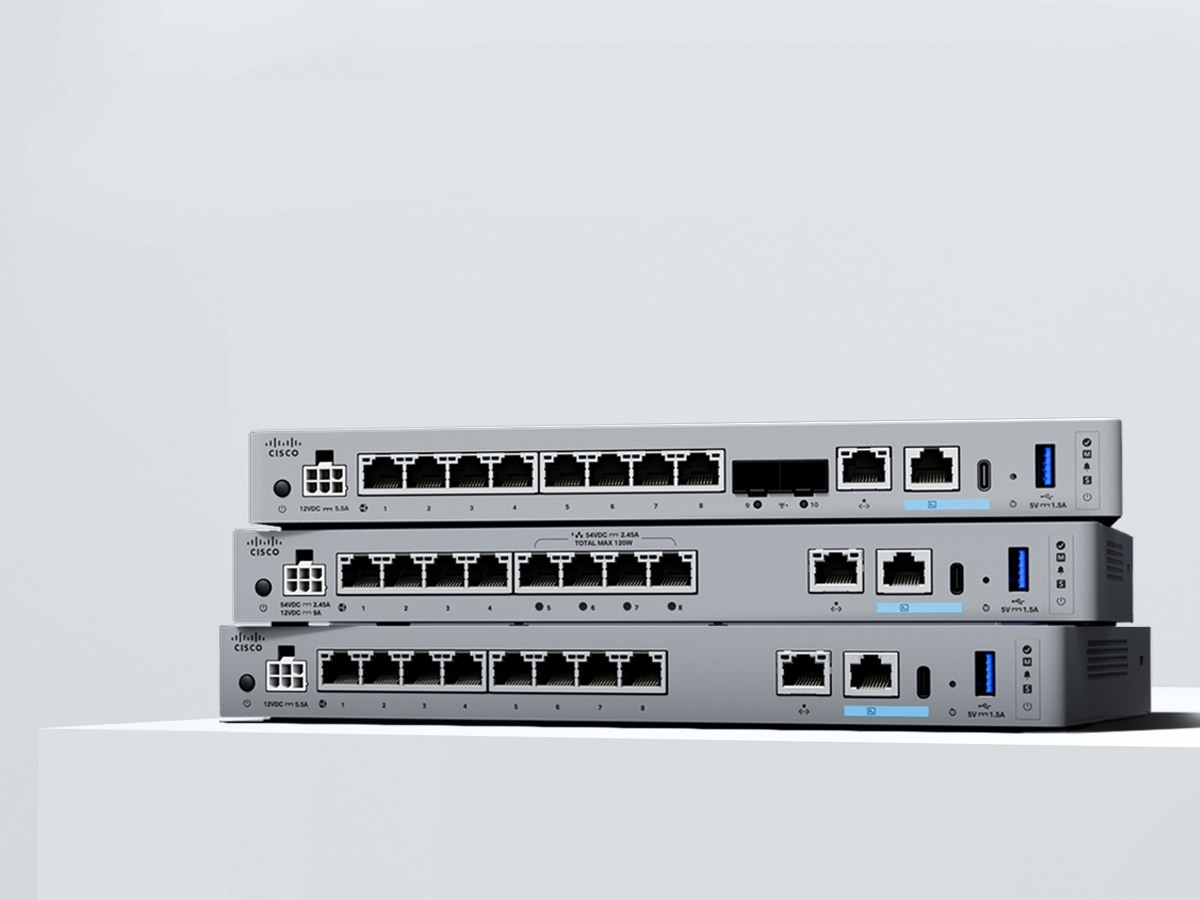

Secure Firewall 1200 Series
Compact, all-in-one SD-WAN firewall for your distributed enterprise branch.
Catch up on what you missed
Keynote: Vision for the Future
CEO Chuck Robbins addresses how to connect and protect your business in the AI era.
Keynote: Go Beyond
Learn about Cisco, Splunk, and reaping the benefits of the AI revolution.
Deep dive sessions
See tech announcements and strategic direction from Cisco's senior tech leaders.
View keynotes and tech sessions in the on-demand library.
Press release
Cisco Live puts AI center stage and more.
Cisco launches $1B global AI investment fund.

Validate your AI skills with certifications
Join all Cisco U. Theater sessions live and direct from Cisco Live or replay them, access learning promos, and more. It's time to Go Beyond the basics and level up your learning.
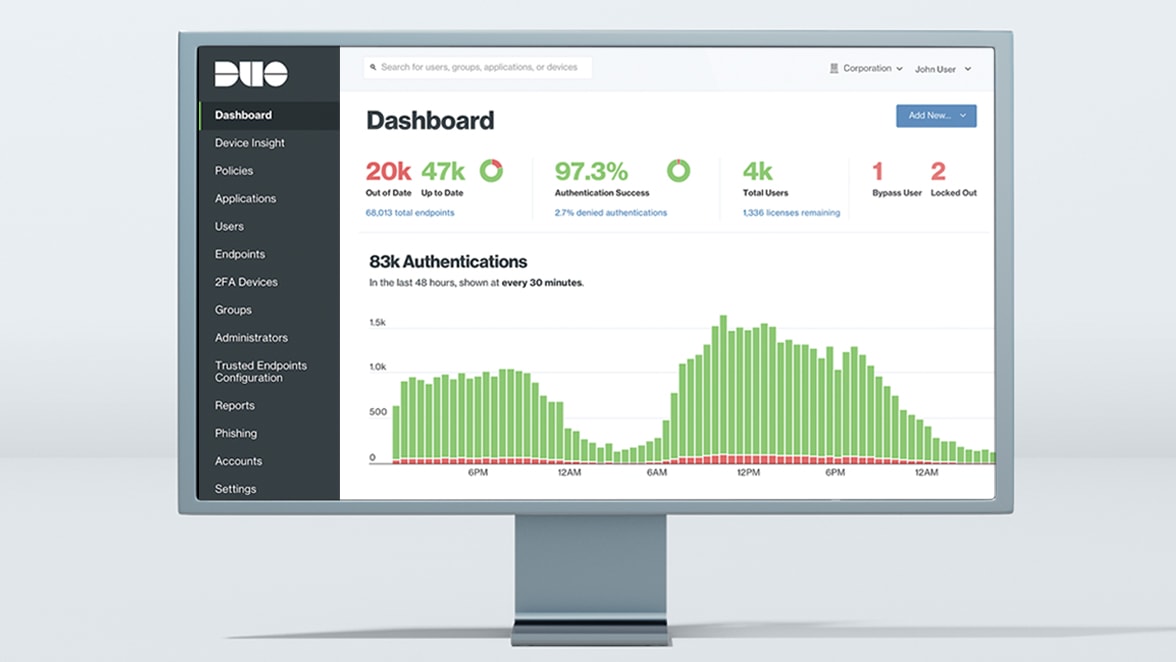
Identity is the new perimeter
Stop identity-based attacks while providing a seamless authentication experience with Cisco Duo's new Continuous Identity Security.
Inside Cisco
- More events
Cisco reveals Nexus HyperFabric
Cisco Nexus HyperFabric makes it easy for customers to deploy, manage, and monitor generative AI models and inference applications without deep IT knowledge and skills.
Cisco and Splunk launch integrated Full-Stack Observability experience
Using Cisco and Splunk observability solutions, customers can build an observability practice that meets their IT environment needs for on-premises, hybrid, and multicloud.
ThousandEyes Digital Experience Assurance shifts IT operations
New Cisco ThousandEyes capabilities and AI-native workflows in Cisco Networking Cloud will deliver Digital Experience Assurance, transforming IT operations.

COMMENTS
With such outcomes, it is necessary to determine the status of the K-12 educational system in the Philippines. This paper attempts to shed light on such concerns by evaluating the performance of ...
16 ABSTRACT. In response to the long-standing crisis faced by its education system, the Philippines has embarked on a major and comprehensive education reform known as K to 12 (K-12). School leaders closest to the ground are in a very good position to lead "bottom-up" initiatives which can make the K-12 Reform work.
The Philippines is the last country in Asia and one of the three nations that has a ten year pre university education program before the implementation of the K-12 system. K-12 program indicates a good quality of education especially for the standard of education system worldwide, qualification tp work abroad, and
the Philippines has stopped temporarily from participating and transformed its basic education program instead. In 2012, the Philippines implemented the compulsory Kindergarten (RA 10157, 2012). Then in 2013, the Department of Education (DepEd), the Commission of Higher Education (CHED), and the Technical Education and Skills
This study critically examines the K-12 curriculum reform in the Philippines and suggests ways on how it can move forward. Specifically, three recent curriculum guides (i.e., science, mathematics, and English) were analysed to determine how they fit with the Education 4.0 milieu.
By investing more time and resources to education, national growth and development can truly be achieved. II. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY This research paper would like to know the perspectives of teachers, parents and students on the implementation of K to 12 programs in the country. This research used a systematic procedure to analyze the data.
Abstract. The Department of Education of the Philippines has implemented the K-12 Curriculum to both elementary and high school levels of Basic Education starting the school year 2012-2013. Thus, we can infer that the current curriculum is still in its infancy stage.
In the school year 2012-2013, the K12 curriculum has been implemented. The curricular change in education resulted in congestion in the basic education curriculum. Thus, the government implemented the Republic Act 10533, also known as the K12 program for public and private institutions for the enactment of the spiral curriculum.
This Paper was presented on the 2nd Annual Conference of the Society for the Philosophical Study of Education-Philippines, March 1, 2014, held at Paulino Cayco Hall, Arellano University, Philippines. The paper presents the fears and loopholes of the K-12 system and its implementation in the context of the Philippines.
Abstract. The Philippines has embarked on significant education reforms for the past three decades to raise the quality of education at all levels and address inclusion and equity issues. The country's AmBisyon Natin 2040 or the national vision for a prosperous and healthy society by 2040 is premised on education's role in developing human ...
This Paper was presented on the 2nd Annual Conference of the Society for the Philosophical Study of Education-Philippines, March 1, 2014, held at Paulino Cayco Hall, Arellano University, Philippines. The paper presents the fears and loopholes of the K-12 system and its implementation in the context of the Philippines. Drawing on the current discourse, studies and loud views, the author ...
The K - 12 Education vision from the Department of Education (DepEd, 2010) every graduate of the Enhanced K - 12 Basic Education Program is an empowered individual who has learned through a program that is rooted on sound principles and geared towards excellence (Mohammad, 2016).
The implementation of the K-12 Basic Education Program in the Philippines brought significant programs and projects to expand and improve the delivery of basic education in the country. It added two more years of senior high school in the basic education, broadening the goals of basic education to higher education preparation, middle level ...
RITO, KARLA. MAGALONA, BEATRISHA. ALAMIL, CHRISTIAN This research approach will measure the overall effectiveness of the implication of the implementation of the K-12 Curriculum to the Grade 10 students of Divine Word College of Legazpi. It covers how the implementation of K-12 curriculum affects the Grade 10 students of DWCL.
Research Paper About k12 Education in the Philippines - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. research paper about k12 education in the philippines
Allen Ibale. In 2012 the Philippines launched its " K to 12 " Program, a comprehensive reform of its basic education. Through this reform, the Philippines is catching up with global standards in secondary education and is attaching a high value to kindergarten. The structure, curricula, and philosophy of the education system are undergoing ...
New Cisco ThousandEyes capabilities and AI-native workflows in Cisco Networking Cloud will deliver Digital Experience Assurance, transforming IT operations. Read press release. Cisco is a worldwide technology leader. Our purpose is to power an inclusive future for all through software, networking, security, computing, and more solutions.
From critical thinking and creative problem solving to communication and collaboration, Adobe Creative Cloud helps students build the skills they need to succeed in K-12, higher education, and the modern workforce. Adobe Creative Cloud for education provides educational institutions with industry-leading creative tools and centralized ...