Case Studies
This guide examines case studies, a form of qualitative descriptive research that is used to look at individuals, a small group of participants, or a group as a whole. Researchers collect data about participants using participant and direct observations, interviews, protocols, tests, examinations of records, and collections of writing samples. Starting with a definition of the case study, the guide moves to a brief history of this research method. Using several well documented case studies, the guide then looks at applications and methods including data collection and analysis. A discussion of ways to handle validity, reliability, and generalizability follows, with special attention to case studies as they are applied to composition studies. Finally, this guide examines the strengths and weaknesses of case studies.

Definition and Overview
Case study refers to the collection and presentation of detailed information about a particular participant or small group, frequently including the accounts of subjects themselves. A form of qualitative descriptive research, the case study looks intensely at an individual or small participant pool, drawing conclusions only about that participant or group and only in that specific context. Researchers do not focus on the discovery of a universal, generalizable truth, nor do they typically look for cause-effect relationships; instead, emphasis is placed on exploration and description.
Case studies typically examine the interplay of all variables in order to provide as complete an understanding of an event or situation as possible. This type of comprehensive understanding is arrived at through a process known as thick description, which involves an in-depth description of the entity being evaluated, the circumstances under which it is used, the characteristics of the people involved in it, and the nature of the community in which it is located. Thick description also involves interpreting the meaning of demographic and descriptive data such as cultural norms and mores, community values, ingrained attitudes, and motives.
Unlike quantitative methods of research, like the survey, which focus on the questions of who, what, where, how much, and how many, and archival analysis, which often situates the participant in some form of historical context, case studies are the preferred strategy when how or why questions are asked. Likewise, they are the preferred method when the researcher has little control over the events, and when there is a contemporary focus within a real life context. In addition, unlike more specifically directed experiments, case studies require a problem that seeks a holistic understanding of the event or situation in question using inductive logic--reasoning from specific to more general terms.
In scholarly circles, case studies are frequently discussed within the context of qualitative research and naturalistic inquiry. Case studies are often referred to interchangeably with ethnography, field study, and participant observation. The underlying philosophical assumptions in the case are similar to these types of qualitative research because each takes place in a natural setting (such as a classroom, neighborhood, or private home), and strives for a more holistic interpretation of the event or situation under study.
Unlike more statistically-based studies which search for quantifiable data, the goal of a case study is to offer new variables and questions for further research. F.H. Giddings, a sociologist in the early part of the century, compares statistical methods to the case study on the basis that the former are concerned with the distribution of a particular trait, or a small number of traits, in a population, whereas the case study is concerned with the whole variety of traits to be found in a particular instance" (Hammersley 95).
Case studies are not a new form of research; naturalistic inquiry was the primary research tool until the development of the scientific method. The fields of sociology and anthropology are credited with the primary shaping of the concept as we know it today. However, case study research has drawn from a number of other areas as well: the clinical methods of doctors; the casework technique being developed by social workers; the methods of historians and anthropologists, plus the qualitative descriptions provided by quantitative researchers like LePlay; and, in the case of Robert Park, the techniques of newspaper reporters and novelists.
Park was an ex-newspaper reporter and editor who became very influential in developing sociological case studies at the University of Chicago in the 1920s. As a newspaper professional he coined the term "scientific" or "depth" reporting: the description of local events in a way that pointed to major social trends. Park viewed the sociologist as "merely a more accurate, responsible, and scientific reporter." Park stressed the variety and value of human experience. He believed that sociology sought to arrive at natural, but fluid, laws and generalizations in regard to human nature and society. These laws weren't static laws of the kind sought by many positivists and natural law theorists, but rather, they were laws of becoming--with a constant possibility of change. Park encouraged students to get out of the library, to quit looking at papers and books, and to view the constant experiment of human experience. He writes, "Go and sit in the lounges of the luxury hotels and on the doorsteps of the flophouses; sit on the Gold Coast settees and on the slum shakedowns; sit in the Orchestra Hall and in the Star and Garter Burlesque. In short, gentlemen [sic], go get the seats of your pants dirty in real research."
But over the years, case studies have drawn their share of criticism. In fact, the method had its detractors from the start. In the 1920s, the debate between pro-qualitative and pro-quantitative became quite heated. Case studies, when compared to statistics, were considered by many to be unscientific. From the 1930's on, the rise of positivism had a growing influence on quantitative methods in sociology. People wanted static, generalizable laws in science. The sociological positivists were looking for stable laws of social phenomena. They criticized case study research because it failed to provide evidence of inter subjective agreement. Also, they condemned it because of the few number of cases studied and that the under-standardized character of their descriptions made generalization impossible. By the 1950s, quantitative methods, in the form of survey research, had become the dominant sociological approach and case study had become a minority practice.
Educational Applications
The 1950's marked the dawning of a new era in case study research, namely that of the utilization of the case study as a teaching method. "Instituted at Harvard Business School in the 1950s as a primary method of teaching, cases have since been used in classrooms and lecture halls alike, either as part of a course of study or as the main focus of the course to which other teaching material is added" (Armisted 1984). The basic purpose of instituting the case method as a teaching strategy was "to transfer much of the responsibility for learning from the teacher on to the student, whose role, as a result, shifts away from passive absorption toward active construction" (Boehrer 1990). Through careful examination and discussion of various cases, "students learn to identify actual problems, to recognize key players and their agendas, and to become aware of those aspects of the situation that contribute to the problem" (Merseth 1991). In addition, students are encouraged to "generate their own analysis of the problems under consideration, to develop their own solutions, and to practically apply their own knowledge of theory to these problems" (Boyce 1993). Along the way, students also develop "the power to analyze and to master a tangled circumstance by identifying and delineating important factors; the ability to utilize ideas, to test them against facts, and to throw them into fresh combinations" (Merseth 1991).
In addition to the practical application and testing of scholarly knowledge, case discussions can also help students prepare for real-world problems, situations and crises by providing an approximation of various professional environments (i.e. classroom, board room, courtroom, or hospital). Thus, through the examination of specific cases, students are given the opportunity to work out their own professional issues through the trials, tribulations, experiences, and research findings of others. An obvious advantage to this mode of instruction is that it allows students the exposure to settings and contexts that they might not otherwise experience. For example, a student interested in studying the effects of poverty on minority secondary student's grade point averages and S.A.T. scores could access and analyze information from schools as geographically diverse as Los Angeles, New York City, Miami, and New Mexico without ever having to leave the classroom.
The case study method also incorporates the idea that students can learn from one another "by engaging with each other and with each other's ideas, by asserting something and then having it questioned, challenged and thrown back at them so that they can reflect on what they hear, and then refine what they say" (Boehrer 1990). In summary, students can direct their own learning by formulating questions and taking responsibility for the study.
Types and Design Concerns
Researchers use multiple methods and approaches to conduct case studies.
Types of Case Studies
Under the more generalized category of case study exist several subdivisions, each of which is custom selected for use depending upon the goals and/or objectives of the investigator. These types of case study include the following:
Illustrative Case Studies These are primarily descriptive studies. They typically utilize one or two instances of an event to show what a situation is like. Illustrative case studies serve primarily to make the unfamiliar familiar and to give readers a common language about the topic in question.
Exploratory (or pilot) Case Studies These are condensed case studies performed before implementing a large scale investigation. Their basic function is to help identify questions and select types of measurement prior to the main investigation. The primary pitfall of this type of study is that initial findings may seem convincing enough to be released prematurely as conclusions.
Cumulative Case Studies These serve to aggregate information from several sites collected at different times. The idea behind these studies is the collection of past studies will allow for greater generalization without additional cost or time being expended on new, possibly repetitive studies.
Critical Instance Case Studies These examine one or more sites for either the purpose of examining a situation of unique interest with little to no interest in generalizability, or to call into question or challenge a highly generalized or universal assertion. This method is useful for answering cause and effect questions.
Identifying a Theoretical Perspective
Much of the case study's design is inherently determined for researchers, depending on the field from which they are working. In composition studies, researchers are typically working from a qualitative, descriptive standpoint. In contrast, physicists will approach their research from a more quantitative perspective. Still, in designing the study, researchers need to make explicit the questions to be explored and the theoretical perspective from which they will approach the case. The three most commonly adopted theories are listed below:
Individual Theories These focus primarily on the individual development, cognitive behavior, personality, learning and disability, and interpersonal interactions of a particular subject.
Organizational Theories These focus on bureaucracies, institutions, organizational structure and functions, or excellence in organizational performance.
Social Theories These focus on urban development, group behavior, cultural institutions, or marketplace functions.
Two examples of case studies are used consistently throughout this chapter. The first, a study produced by Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988), looks at a first year graduate student's initiation into an academic writing program. The study uses participant-observer and linguistic data collecting techniques to assess the student's knowledge of appropriate discourse conventions. Using the pseudonym Nate to refer to the subject, the study sought to illuminate the particular experience rather than to generalize about the experience of fledgling academic writers collectively.
For example, in Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman's (1988) study we are told that the researchers are interested in disciplinary communities. In the first paragraph, they ask what constitutes membership in a disciplinary community and how achieving membership might affect a writer's understanding and production of texts. In the third paragraph they state that researchers must negotiate their claims "within the context of his sub specialty's accepted knowledge and methodology." In the next paragraph they ask, "How is literacy acquired? What is the process through which novices gain community membership? And what factors either aid or hinder students learning the requisite linguistic behaviors?" This introductory section ends with a paragraph in which the study's authors claim that during the course of the study, the subject, Nate, successfully makes the transition from "skilled novice" to become an initiated member of the academic discourse community and that his texts exhibit linguistic changes which indicate this transition. In the next section the authors make explicit the sociolinguistic theoretical and methodological assumptions on which the study is based (1988). Thus the reader has a good understanding of the authors' theoretical background and purpose in conducting the study even before it is explicitly stated on the fourth page of the study. "Our purpose was to examine the effects of the educational context on one graduate student's production of texts as he wrote in different courses and for different faculty members over the academic year 1984-85." The goal of the study then, was to explore the idea that writers must be initiated into a writing community, and that this initiation will change the way one writes.
The second example is Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of a group of twelfth graders. In this study, Emig seeks to answer the question of what happens to the self as a result educational stimuli in terms of academic writing. The case study used methods such as protocol analysis, tape-recorded interviews, and discourse analysis.
In the case of Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of eight twelfth graders, four specific hypotheses were made:
- Twelfth grade writers engage in two modes of composing: reflexive and extensive.
- These differences can be ascertained and characterized through having the writers compose aloud their composition process.
- A set of implied stylistic principles governs the writing process.
- For twelfth grade writers, extensive writing occurs chiefly as a school-sponsored activity, or reflexive, as a self-sponsored activity.
In this study, the chief distinction is between the two dominant modes of composing among older, secondary school students. The distinctions are:
- The reflexive mode, which focuses on the writer's thoughts and feelings.
- The extensive mode, which focuses on conveying a message.
Emig also outlines the specific questions which guided the research in the opening pages of her Review of Literature , preceding the report.
Designing a Case Study
After considering the different sub categories of case study and identifying a theoretical perspective, researchers can begin to design their study. Research design is the string of logic that ultimately links the data to be collected and the conclusions to be drawn to the initial questions of the study. Typically, research designs deal with at least four problems:
- What questions to study
- What data are relevant
- What data to collect
- How to analyze that data
In other words, a research design is basically a blueprint for getting from the beginning to the end of a study. The beginning is an initial set of questions to be answered, and the end is some set of conclusions about those questions.
Because case studies are conducted on topics as diverse as Anglo-Saxon Literature (Thrane 1986) and AIDS prevention (Van Vugt 1994), it is virtually impossible to outline any strict or universal method or design for conducting the case study. However, Robert K. Yin (1993) does offer five basic components of a research design:
- A study's questions.
- A study's propositions (if any).
- A study's units of analysis.
- The logic that links the data to the propositions.
- The criteria for interpreting the findings.
In addition to these five basic components, Yin also stresses the importance of clearly articulating one's theoretical perspective, determining the goals of the study, selecting one's subject(s), selecting the appropriate method(s) of collecting data, and providing some considerations to the composition of the final report.
Conducting Case Studies
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of approaches and methods. These approaches, methods, and related issues are discussed in depth in this section.
Method: Single or Multi-modal?
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of methods. Some common methods include interviews , protocol analyses, field studies, and participant-observations. Emig (1971) chose to use several methods of data collection. Her sources included conversations with the students, protocol analysis, discrete observations of actual composition, writing samples from each student, and school records (Lauer and Asher 1988).
Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) collected data by observing classrooms, conducting faculty and student interviews, collecting self reports from the subject, and by looking at the subject's written work.
A study that was criticized for using a single method model was done by Flower and Hayes (1984). In this study that explores the ways in which writers use different forms of knowing to create space, the authors used only protocol analysis to gather data. The study came under heavy fire because of their decision to use only one method.
Participant Selection
Case studies can use one participant, or a small group of participants. However, it is important that the participant pool remain relatively small. The participants can represent a diverse cross section of society, but this isn't necessary.
For example, the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study looked at just one participant, Nate. By contrast, in Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composition process of twelfth graders, eight participants were selected representing a diverse cross section of the community, with volunteers from an all-white upper-middle-class suburban school, an all-black inner-city school, a racially mixed lower-middle-class school, an economically and racially mixed school, and a university school.
Often, a brief "case history" is done on the participants of the study in order to provide researchers with a clearer understanding of their participants, as well as some insight as to how their own personal histories might affect the outcome of the study. For instance, in Emig's study, the investigator had access to the school records of five of the participants, and to standardized test scores for the remaining three. Also made available to the researcher was the information that three of the eight students were selected as NCTE Achievement Award winners. These personal histories can be useful in later stages of the study when data are being analyzed and conclusions drawn.
Data Collection
There are six types of data collected in case studies:
- Archival records.
- Interviews.
- Direct observation.
- Participant observation.
In the field of composition research, these six sources might be:
- A writer's drafts.
- School records of student writers.
- Transcripts of interviews with a writer.
- Transcripts of conversations between writers (and protocols).
- Videotapes and notes from direct field observations.
- Hard copies of a writer's work on computer.
Depending on whether researchers have chosen to use a single or multi-modal approach for the case study, they may choose to collect data from one or any combination of these sources.
Protocols, that is, transcriptions of participants talking aloud about what they are doing as they do it, have been particularly common in composition case studies. For example, in Emig's (1971) study, the students were asked, in four different sessions, to give oral autobiographies of their writing experiences and to compose aloud three themes in the presence of a tape recorder and the investigator.
In some studies, only one method of data collection is conducted. For example, the Flower and Hayes (1981) report on the cognitive process theory of writing depends on protocol analysis alone. However, using multiple sources of evidence to increase the reliability and validity of the data can be advantageous.
Case studies are likely to be much more convincing and accurate if they are based on several different sources of information, following a corroborating mode. This conclusion is echoed among many composition researchers. For example, in her study of predrafting processes of high and low-apprehensive writers, Cynthia Selfe (1985) argues that because "methods of indirect observation provide only an incomplete reflection of the complex set of processes involved in composing, a combination of several such methods should be used to gather data in any one study." Thus, in this study, Selfe collected her data from protocols, observations of students role playing their writing processes, audio taped interviews with the students, and videotaped observations of the students in the process of composing.
It can be said then, that cross checking data from multiple sources can help provide a multidimensional profile of composing activities in a particular setting. Sharan Merriam (1985) suggests "checking, verifying, testing, probing, and confirming collected data as you go, arguing that this process will follow in a funnel-like design resulting in less data gathering in later phases of the study along with a congruent increase in analysis checking, verifying, and confirming."
It is important to note that in case studies, as in any qualitative descriptive research, while researchers begin their studies with one or several questions driving the inquiry (which influence the key factors the researcher will be looking for during data collection), a researcher may find new key factors emerging during data collection. These might be unexpected patterns or linguistic features which become evident only during the course of the research. While not bearing directly on the researcher's guiding questions, these variables may become the basis for new questions asked at the end of the report, thus linking to the possibility of further research.
Data Analysis
As the information is collected, researchers strive to make sense of their data. Generally, researchers interpret their data in one of two ways: holistically or through coding. Holistic analysis does not attempt to break the evidence into parts, but rather to draw conclusions based on the text as a whole. Flower and Hayes (1981), for example, make inferences from entire sections of their students' protocols, rather than searching through the transcripts to look for isolatable characteristics.
However, composition researchers commonly interpret their data by coding, that is by systematically searching data to identify and/or categorize specific observable actions or characteristics. These observable actions then become the key variables in the study. Sharan Merriam (1988) suggests seven analytic frameworks for the organization and presentation of data:
- The role of participants.
- The network analysis of formal and informal exchanges among groups.
- Historical.
- Thematical.
- Ritual and symbolism.
- Critical incidents that challenge or reinforce fundamental beliefs, practices, and values.
There are two purposes of these frameworks: to look for patterns among the data and to look for patterns that give meaning to the case study.
As stated above, while most researchers begin their case studies expecting to look for particular observable characteristics, it is not unusual for key variables to emerge during data collection. Typical variables coded in case studies of writers include pauses writers make in the production of a text, the use of specific linguistic units (such as nouns or verbs), and writing processes (planning, drafting, revising, and editing). In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, researchers coded the participant's texts for use of connectives, discourse demonstratives, average sentence length, off-register words, use of the first person pronoun, and the ratio of definite articles to indefinite articles.
Since coding is inherently subjective, more than one coder is usually employed. In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, three rhetoricians were employed to code the participant's texts for off-register phrases. The researchers established the agreement among the coders before concluding that the participant used fewer off-register words as the graduate program progressed.
Composing the Case Study Report
In the many forms it can take, "a case study is generically a story; it presents the concrete narrative detail of actual, or at least realistic events, it has a plot, exposition, characters, and sometimes even dialogue" (Boehrer 1990). Generally, case study reports are extensively descriptive, with "the most problematic issue often referred to as being the determination of the right combination of description and analysis" (1990). Typically, authors address each step of the research process, and attempt to give the reader as much context as possible for the decisions made in the research design and for the conclusions drawn.
This contextualization usually includes a detailed explanation of the researchers' theoretical positions, of how those theories drove the inquiry or led to the guiding research questions, of the participants' backgrounds, of the processes of data collection, of the training and limitations of the coders, along with a strong attempt to make connections between the data and the conclusions evident.
Although the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study does not, case study reports often include the reactions of the participants to the study or to the researchers' conclusions. Because case studies tend to be exploratory, most end with implications for further study. Here researchers may identify significant variables that emerged during the research and suggest studies related to these, or the authors may suggest further general questions that their case study generated.
For example, Emig's (1971) study concludes with a section dedicated solely to the topic of implications for further research, in which she suggests several means by which this particular study could have been improved, as well as questions and ideas raised by this study which other researchers might like to address, such as: is there a correlation between a certain personality and a certain composing process profile (e.g. is there a positive correlation between ego strength and persistence in revising)?
Also included in Emig's study is a section dedicated to implications for teaching, which outlines the pedagogical ramifications of the study's findings for teachers currently involved in high school writing programs.
Sharan Merriam (1985) also offers several suggestions for alternative presentations of data:
- Prepare specialized condensations for appropriate groups.
- Replace narrative sections with a series of answers to open-ended questions.
- Present "skimmer's" summaries at beginning of each section.
- Incorporate headlines that encapsulate information from text.
- Prepare analytic summaries with supporting data appendixes.
- Present data in colorful and/or unique graphic representations.
Issues of Validity and Reliability
Once key variables have been identified, they can be analyzed. Reliability becomes a key concern at this stage, and many case study researchers go to great lengths to ensure that their interpretations of the data will be both reliable and valid. Because issues of validity and reliability are an important part of any study in the social sciences, it is important to identify some ways of dealing with results.
Multi-modal case study researchers often balance the results of their coding with data from interviews or writer's reflections upon their own work. Consequently, the researchers' conclusions become highly contextualized. For example, in a case study which looked at the time spent in different stages of the writing process, Berkenkotter concluded that her participant, Donald Murray, spent more time planning his essays than in other writing stages. The report of this case study is followed by Murray's reply, wherein he agrees with some of Berkenkotter's conclusions and disagrees with others.
As is the case with other research methodologies, issues of external validity, construct validity, and reliability need to be carefully considered.
Commentary on Case Studies
Researchers often debate the relative merits of particular methods, among them case study. In this section, we comment on two key issues. To read the commentaries, choose any of the items below:
Strengths and Weaknesses of Case Studies
Most case study advocates point out that case studies produce much more detailed information than what is available through a statistical analysis. Advocates will also hold that while statistical methods might be able to deal with situations where behavior is homogeneous and routine, case studies are needed to deal with creativity, innovation, and context. Detractors argue that case studies are difficult to generalize because of inherent subjectivity and because they are based on qualitative subjective data, generalizable only to a particular context.
Flexibility
The case study approach is a comparatively flexible method of scientific research. Because its project designs seem to emphasize exploration rather than prescription or prediction, researchers are comparatively freer to discover and address issues as they arise in their experiments. In addition, the looser format of case studies allows researchers to begin with broad questions and narrow their focus as their experiment progresses rather than attempt to predict every possible outcome before the experiment is conducted.
Emphasis on Context
By seeking to understand as much as possible about a single subject or small group of subjects, case studies specialize in "deep data," or "thick description"--information based on particular contexts that can give research results a more human face. This emphasis can help bridge the gap between abstract research and concrete practice by allowing researchers to compare their firsthand observations with the quantitative results obtained through other methods of research.
Inherent Subjectivity
"The case study has long been stereotyped as the weak sibling among social science methods," and is often criticized as being too subjective and even pseudo-scientific. Likewise, "investigators who do case studies are often regarded as having deviated from their academic disciplines, and their investigations as having insufficient precision (that is, quantification), objectivity and rigor" (Yin 1989). Opponents cite opportunities for subjectivity in the implementation, presentation, and evaluation of case study research. The approach relies on personal interpretation of data and inferences. Results may not be generalizable, are difficult to test for validity, and rarely offer a problem-solving prescription. Simply put, relying on one or a few subjects as a basis for cognitive extrapolations runs the risk of inferring too much from what might be circumstance.
High Investment
Case studies can involve learning more about the subjects being tested than most researchers would care to know--their educational background, emotional background, perceptions of themselves and their surroundings, their likes, dislikes, and so on. Because of its emphasis on "deep data," the case study is out of reach for many large-scale research projects which look at a subject pool in the tens of thousands. A budget request of $10,000 to examine 200 subjects sounds more efficient than a similar request to examine four subjects.
Ethical Considerations
Researchers conducting case studies should consider certain ethical issues. For example, many educational case studies are often financed by people who have, either directly or indirectly, power over both those being studied and those conducting the investigation (1985). This conflict of interests can hinder the credibility of the study.
The personal integrity, sensitivity, and possible prejudices and/or biases of the investigators need to be taken into consideration as well. Personal biases can creep into how the research is conducted, alternative research methods used, and the preparation of surveys and questionnaires.
A common complaint in case study research is that investigators change direction during the course of the study unaware that their original research design was inadequate for the revised investigation. Thus, the researchers leave unknown gaps and biases in the study. To avoid this, researchers should report preliminary findings so that the likelihood of bias will be reduced.
Concerns about Reliability, Validity, and Generalizability
Merriam (1985) offers several suggestions for how case study researchers might actively combat the popular attacks on the validity, reliability, and generalizability of case studies:
- Prolong the Processes of Data Gathering on Site: This will help to insure the accuracy of the findings by providing the researcher with more concrete information upon which to formulate interpretations.
- Employ the Process of "Triangulation": Use a variety of data sources as opposed to relying solely upon one avenue of observation. One example of such a data check would be what McClintock, Brannon, and Maynard (1985) refer to as a "case cluster method," that is, when a single unit within a larger case is randomly sampled, and that data treated quantitatively." For instance, in Emig's (1971) study, the case cluster method was employed, singling out the productivity of a single student named Lynn. This cluster profile included an advanced case history of the subject, specific examination and analysis of individual compositions and protocols, and extensive interview sessions. The seven remaining students were then compared with the case of Lynn, to ascertain if there are any shared, or unique dimensions to the composing process engaged in by these eight students.
- Conduct Member Checks: Initiate and maintain an active corroboration on the interpretation of data between the researcher and those who provided the data. In other words, talk to your subjects.
- Collect Referential Materials: Complement the file of materials from the actual site with additional document support. For example, Emig (1971) supports her initial propositions with historical accounts by writers such as T.S. Eliot, James Joyce, and D.H. Lawrence. Emig also cites examples of theoretical research done with regards to the creative process, as well as examples of empirical research dealing with the writing of adolescents. Specific attention is then given to the four stages description of the composing process delineated by Helmoltz, Wallas, and Cowley, as it serves as the focal point in this study.
- Engage in Peer Consultation: Prior to composing the final draft of the report, researchers should consult with colleagues in order to establish validity through pooled judgment.
Although little can be done to combat challenges concerning the generalizability of case studies, "most writers suggest that qualitative research should be judged as credible and confirmable as opposed to valid and reliable" (Merriam 1985). Likewise, it has been argued that "rather than transplanting statistical, quantitative notions of generalizability and thus finding qualitative research inadequate, it makes more sense to develop an understanding of generalization that is congruent with the basic characteristics of qualitative inquiry" (1985). After all, criticizing the case study method for being ungeneralizable is comparable to criticizing a washing machine for not being able to tell the correct time. In other words, it is unjust to criticize a method for not being able to do something which it was never originally designed to do in the first place.
Annotated Bibliography
Armisted, C. (1984). How Useful are Case Studies. Training and Development Journal, 38 (2), 75-77.
This article looks at eight types of case studies, offers pros and cons of using case studies in the classroom, and gives suggestions for successfully writing and using case studies.
Bardovi-Harlig, K. (1997). Beyond Methods: Components of Second Language Teacher Education . New York: McGraw-Hill.
A compilation of various research essays which address issues of language teacher education. Essays included are: "Non-native reading research and theory" by Lee, "The case for Psycholinguistics" by VanPatten, and "Assessment and Second Language Teaching" by Gradman and Reed.
Bartlett, L. (1989). A Question of Good Judgment; Interpretation Theory and Qualitative Enquiry Address. 70th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. San Francisco.
Bartlett selected "quasi-historical" methodology, which focuses on the "truth" found in case records, as one that will provide "good judgments" in educational inquiry. He argues that although the method is not comprehensive, it can try to connect theory with practice.
Baydere, S. et. al. (1993). Multimedia conferencing as a tool for collaborative writing: a case study in Computer Supported Collaborative Writing. New York: Springer-Verlag.
The case study by Baydere et. al. is just one of the many essays in this book found in the series "Computer Supported Cooperative Work." Denley, Witefield and May explore similar issues in their essay, "A case study in task analysis for the design of a collaborative document production system."
Berkenkotter, C., Huckin, T., N., & Ackerman J. (1988). Conventions, Conversations, and the Writer: Case Study of a Student in a Rhetoric Ph.D. Program. Research in the Teaching of English, 22, 9-44.
The authors focused on how the writing of their subject, Nate or Ackerman, changed as he became more acquainted or familiar with his field's discourse community.
Berninger, V., W., and Gans, B., M. (1986). Language Profiles in Nonspeaking Individuals of Normal Intelligence with Severe Cerebral Palsy. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 2, 45-50.
Argues that generalizations about language abilities in patients with severe cerebral palsy (CP) should be avoided. Standardized tests of different levels of processing oral language, of processing written language, and of producing written language were administered to 3 male participants (aged 9, 16, and 40 yrs).
Bockman, J., R., and Couture, B. (1984). The Case Method in Technical Communication: Theory and Models. Texas: Association of Teachers of Technical Writing.
Examines the study and teaching of technical writing, communication of technical information, and the case method in terms of those applications.
Boehrer, J. (1990). Teaching With Cases: Learning to Question. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 42 41-57.
This article discusses the origins of the case method, looks at the question of what is a case, gives ideas about learning in case teaching, the purposes it can serve in the classroom, the ground rules for the case discussion, including the role of the question, and new directions for case teaching.
Bowman, W. R. (1993). Evaluating JTPA Programs for Economically Disadvantaged Adults: A Case Study of Utah and General Findings . Washington: National Commission for Employment Policy.
"To encourage state-level evaluations of JTPA, the Commission and the State of Utah co-sponsored this report on the effectiveness of JTPA Title II programs for adults in Utah. The technique used is non-experimental and the comparison group was selected from registrants with Utah's Employment Security. In a step-by-step approach, the report documents how non-experimental techniques can be applied and several specific technical issues can be addressed."
Boyce, A. (1993) The Case Study Approach for Pedagogists. Annual Meeting of the American Alliance for Health, Physical Education, Recreation and Dance. (Address). Washington DC.
This paper addresses how case studies 1) bridge the gap between teaching theory and application, 2) enable students to analyze problems and develop solutions for situations that will be encountered in the real world of teaching, and 3) helps students to evaluate the feasibility of alternatives and to understand the ramifications of a particular course of action.
Carson, J. (1993) The Case Study: Ideal Home of WAC Quantitative and Qualitative Data. Annual Meeting of the Conference on College Composition and Communication. (Address). San Diego.
"Increasingly, one of the most pressing questions for WAC advocates is how to keep [WAC] programs going in the face of numerous difficulties. Case histories offer the best chance for fashioning rhetorical arguments to keep WAC programs going because they offer the opportunity to provide a coherent narrative that contextualizes all documents and data, including what is generally considered scientific data. A case study of the WAC program, . . . at Robert Morris College in Pittsburgh demonstrates the advantages of this research method. Such studies are ideal homes for both naturalistic and positivistic data as well as both quantitative and qualitative information."
---. (1991). A Cognitive Process Theory of Writing. College Composition and Communication. 32. 365-87.
No abstract available.
Cromer, R. (1994) A Case Study of Dissociations Between Language and Cognition. Constraints on Language Acquisition: Studies of Atypical Children . Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 141-153.
Crossley, M. (1983) Case Study in Comparative and International Education: An Approach to Bridging the Theory-Practice Gap. Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the Australian Comparative and International Education Society. Hamilton, NZ.
Case study research, as presented here, helps bridge the theory-practice gap in comparative and international research studies of education because it focuses on the practical, day-to-day context rather than on the national arena. The paper asserts that the case study method can be valuable at all levels of research, formation, and verification of theories in education.
Daillak, R., H., and Alkin, M., C. (1982). Qualitative Studies in Context: Reflections on the CSE Studies of Evaluation Use . California: EDRS
The report shows how the Center of the Study of Evaluation (CSE) applied qualitative techniques to a study of evaluation information use in local, Los Angeles schools. It critiques the effectiveness and the limitations of using case study, evaluation, field study, and user interview survey methodologies.
Davey, L. (1991). The Application of Case Study Evaluations. ERIC/TM Digest.
This article examines six types of case studies, the type of evaluation questions that can be answered, the functions served, some design features, and some pitfalls of the method.
Deutch, C. E. (1996). A course in research ethics for graduate students. College Teaching, 44, 2, 56-60.
This article describes a one-credit discussion course in research ethics for graduate students in biology. Case studies are focused on within the four parts of the course: 1) major issues, 2 )practical issues in scholarly work, 3) ownership of research results, and 4) training and personal decisions.
DeVoss, G. (1981). Ethics in Fieldwork Research. RIE 27p. (ERIC)
This article examines four of the ethical problems that can happen when conducting case study research: acquiring permission to do research, knowing when to stop digging, the pitfalls of doing collaborative research, and preserving the integrity of the participants.
Driscoll, A. (1985). Case Study of a Research Intervention: the University of Utah’s Collaborative Approach . San Francisco: Far West Library for Educational Research Development.
Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Colleges of Teacher Education, Denver, CO, March 1985. Offers information of in-service training, specifically case studies application.
Ellram, L. M. (1996). The Use of the Case Study Method in Logistics Research. Journal of Business Logistics, 17, 2, 93.
This article discusses the increased use of case study in business research, and the lack of understanding of when and how to use case study methodology in business.
Emig, J. (1971) The Composing Processes of Twelfth Graders . Urbana: NTCE.
This case study uses observation, tape recordings, writing samples, and school records to show that writing in reflexive and extensive situations caused different lengths of discourse and different clusterings of the components of the writing process.
Feagin, J. R. (1991). A Case For the Case Study . Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina Press.
This book discusses the nature, characteristics, and basic methodological issues of the case study as a research method.
Feldman, H., Holland, A., & Keefe, K. (1989) Language Abilities after Left Hemisphere Brain Injury: A Case Study of Twins. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 9, 32-47.
"Describes the language abilities of 2 twin pairs in which 1 twin (the experimental) suffered brain injury to the left cerebral hemisphere around the time of birth and1 twin (the control) did not. One pair of twins was initially assessed at age 23 mo. and the other at about 30 mo.; they were subsequently evaluated in their homes 3 times at about 6-mo intervals."
Fidel, R. (1984). The Case Study Method: A Case Study. Library and Information Science Research, 6.
The article describes the use of case study methodology to systematically develop a model of online searching behavior in which study design is flexible, subject manner determines data gathering and analyses, and procedures adapt to the study's progressive change.
Flower, L., & Hayes, J. R. (1984). Images, Plans and Prose: The Representation of Meaning in Writing. Written Communication, 1, 120-160.
Explores the ways in which writers actually use different forms of knowing to create prose.
Frey, L. R. (1992). Interpreting Communication Research: A Case Study Approach Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall.
The book discusses research methodologies in the Communication field. It focuses on how case studies bridge the gap between communication research, theory, and practice.
Gilbert, V. K. (1981). The Case Study as a Research Methodology: Difficulties and Advantages of Integrating the Positivistic, Phenomenological and Grounded Theory Approaches . The Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for the Study of Educational Administration. (Address) Halifax, NS, Can.
This study on an innovative secondary school in England shows how a "low-profile" participant-observer case study was crucial to the initial observation, the testing of hypotheses, the interpretive approach, and the grounded theory.
Gilgun, J. F. (1994). A Case for Case Studies in Social Work Research. Social Work, 39, 4, 371-381.
This article defines case study research, presents guidelines for evaluation of case studies, and shows the relevance of case studies to social work research. It also looks at issues such as evaluation and interpretations of case studies.
Glennan, S. L., Sharp-Bittner, M. A. & Tullos, D. C. (1991). Augmentative and Alternative Communication Training with a Nonspeaking Adult: Lessons from MH. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 7, 240-7.
"A response-guided case study documented changes in a nonspeaking 36-yr-old man's ability to communicate using 3 trained augmentative communication modes. . . . Data were collected in videotaped interaction sessions between the nonspeaking adult and a series of adult speaking."
Graves, D. (1981). An Examination of the Writing Processes of Seven Year Old Children. Research in the Teaching of English, 15, 113-134.
Hamel, J. (1993). Case Study Methods . Newbury Park: Sage. .
"In a most economical fashion, Hamel provides a practical guide for producing theoretically sharp and empirically sound sociological case studies. A central idea put forth by Hamel is that case studies must "locate the global in the local" thus making the careful selection of the research site the most critical decision in the analytic process."
Karthigesu, R. (1986, July). Television as a Tool for Nation-Building in the Third World: A Post-Colonial Pattern, Using Malaysia as a Case-Study. International Television Studies Conference. (Address). London, 10-12.
"The extent to which Television Malaysia, as a national mass media organization, has been able to play a role in nation building in the post-colonial period is . . . studied in two parts: how the choice of a model of nation building determines the character of the organization; and how the character of the organization influences the output of the organization."
Kenny, R. (1984). Making the Case for the Case Study. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 16, (1), 37-51.
The article looks at how and why the case study is justified as a viable and valuable approach to educational research and program evaluation.
Knirk, F. (1991). Case Materials: Research and Practice. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 4 (1 ), 73-81.
The article addresses the effectiveness of case studies, subject areas where case studies are commonly used, recent examples of their use, and case study design considerations.
Klos, D. (1976). Students as Case Writers. Teaching of Psychology, 3.2, 63-66.
This article reviews a course in which students gather data for an original case study of another person. The task requires the students to design the study, collect the data, write the narrative, and interpret the findings.
Leftwich, A. (1981). The Politics of Case Study: Problems of Innovation in University Education. Higher Education Review, 13.2, 38-64.
The article discusses the use of case studies as a teaching method. Emphasis is on the instructional materials, interdisciplinarity, and the complex relationships within the university that help or hinder the method.
Mabrito, M. (1991, Oct.). Electronic Mail as a Vehicle for Peer Response: Conversations of High and Low Apprehensive Writers. Written Communication, 509-32.
McCarthy, S., J. (1955). The Influence of Classroom Discourse on Student Texts: The Case of Ella . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
A look at how students of color become marginalized within traditional classroom discourse. The essay follows the struggles of one black student: Ella.
Matsuhashi, A., ed. (1987). Writing in Real Time: Modeling Production Processes Norwood, NJ: Ablex Publishing Corporation.
Investigates how writers plan to produce discourse for different purposes to report, to generalize, and to persuade, as well as how writers plan for sentence level units of language. To learn about planning, an observational measure of pause time was used" (ERIC).
Merriam, S. B. (1985). The Case Study in Educational Research: A Review of Selected Literature. Journal of Educational Thought, 19.3, 204-17.
The article examines the characteristics of, philosophical assumptions underlying the case study, the mechanics of conducting a case study, and the concerns about the reliability, validity, and generalizability of the method.
---. (1988). Case Study Research in Education: A Qualitative Approach San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Merry, S. E., & Milner, N. eds. (1993). The Possibility of Popular Justice: A Case Study of Community Mediation in the United States . Ann Arbor: U of Michigan.
". . . this volume presents a case study of one experiment in popular justice, the San Francisco Community Boards. This program has made an explicit claim to create an alternative justice, or new justice, in the midst of a society ordered by state law. The contributors to this volume explore the history and experience of the program and compare it to other versions of popular justice in the United States, Europe, and the Third World."
Merseth, K. K. (1991). The Case for Cases in Teacher Education. RIE. 42p. (ERIC).
This monograph argues that the case method of instruction offers unique potential for revitalizing the field of teacher education.
Michaels, S. (1987). Text and Context: A New Approach to the Study of Classroom Writing. Discourse Processes, 10, 321-346.
"This paper argues for and illustrates an approach to the study of writing that integrates ethnographic analysis of classroom interaction with linguistic analysis of written texts and teacher/student conversational exchanges. The approach is illustrated through a case study of writing in a single sixth grade classroom during a single writing assignment."
Milburn, G. (1995). Deciphering a Code or Unraveling a Riddle: A Case Study in the Application of a Humanistic Metaphor to the Reporting of Social Studies Teaching. Theory and Research in Education, 13.
This citation serves as an example of how case studies document learning procedures in a senior-level economics course.
Milley, J. E. (1979). An Investigation of Case Study as an Approach to Program Evaluation. 19th Annual Forum of the Association for Institutional Research. (Address). San Diego.
The case study method merged a narrative report focusing on the evaluator as participant-observer with document review, interview, content analysis, attitude questionnaire survey, and sociogram analysis. Milley argues that case study program evaluation has great potential for widespread use.
Minnis, J. R. (1985, Sept.). Ethnography, Case Study, Grounded Theory, and Distance Education Research. Distance Education, 6.2.
This article describes and defines the strengths and weaknesses of ethnography, case study, and grounded theory.
Nunan, D. (1992). Collaborative language learning and teaching . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Included in this series of essays is Peter Sturman’s "Team Teaching: a case study from Japan" and David Nunan’s own "Toward a collaborative approach to curriculum development: a case study."
Nystrand, M., ed. (1982). What Writers Know: The Language, Process, and Structure of Written Discourse . New York: Academic Press.
Owenby, P. H. (1992). Making Case Studies Come Alive. Training, 29, (1), 43-46. (ERIC)
This article provides tips for writing more effective case studies.
---. (1981). Pausing and Planning: The Tempo of Writer Discourse Production. Research in the Teaching of English, 15 (2),113-34.
Perl, S. (1979). The Composing Processes of Unskilled College Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 13, 317-336.
"Summarizes a study of five unskilled college writers, focusing especially on one of the five, and discusses the findings in light of current pedagogical practice and research design."
Pilcher J. and A. Coffey. eds. (1996). Gender and Qualitative Research . Brookfield: Aldershot, Hants, England.
This book provides a series of essays which look at gender identity research, qualitative research and applications of case study to questions of gendered pedagogy.
Pirie, B. S. (1993). The Case of Morty: A Four Year Study. Gifted Education International, 9 (2), 105-109.
This case study describes a boy from kindergarten through third grade with above average intelligence but difficulty in learning to read, write, and spell.
Popkewitz, T. (1993). Changing Patterns of Power: Social Regulation and Teacher Education Reform. Albany: SUNY Press.
Popkewitz edits this series of essays that address case studies on educational change and the training of teachers. The essays vary in terms of discipline and scope. Also, several authors include case studies of educational practices in countries other than the United States.
---. (1984). The Predrafting Processes of Four High- and Four Low Apprehensive Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 18, (1), 45-64.
Rasmussen, P. (1985, March) A Case Study on the Evaluation of Research at the Technical University of Denmark. International Journal of Institutional Management in Higher Education, 9 (1).
This is an example of a case study methodology used to evaluate the chemistry and chemical engineering departments at the University of Denmark.
Roth, K. J. (1986). Curriculum Materials, Teacher Talk, and Student Learning: Case Studies in Fifth-Grade Science Teaching . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
Roth offers case studies on elementary teachers, elementary school teaching, science studies and teaching, and verbal learning.
Selfe, C. L. (1985). An Apprehensive Writer Composes. When a Writer Can't Write: Studies in Writer's Block and Other Composing-Process Problems . (pp. 83-95). Ed. Mike Rose. NMY: Guilford.
Smith-Lewis, M., R. and Ford, A. (1987). A User's Perspective on Augmentative Communication. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 3, 12-7.
"During a series of in-depth interviews, a 25-yr-old woman with cerebral palsy who utilized augmentative communication reflected on the effectiveness of the devices designed for her during her school career."
St. Pierre, R., G. (1980, April). Follow Through: A Case Study in Metaevaluation Research . 64th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. (Address).
The three approaches to metaevaluation are evaluation of primary evaluations, integrative meta-analysis with combined primary evaluation results, and re-analysis of the raw data from a primary evaluation.
Stahler, T., M. (1996, Feb.) Early Field Experiences: A Model That Worked. ERIC.
"This case study of a field and theory class examines a model designed to provide meaningful field experiences for preservice teachers while remaining consistent with the instructor's beliefs about the role of teacher education in preparing teachers for the classroom."
Stake, R. E. (1995). The Art of Case Study Research. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
This book examines case study research in education and case study methodology.
Stiegelbauer, S. (1984) Community, Context, and Co-curriculum: Situational Factors Influencing School Improvements in a Study of High Schools. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA.
Discussion of several case studies: one looking at high school environments, another examining educational innovations.
Stolovitch, H. (1990). Case Study Method. Performance And Instruction, 29, (9), 35-37.
This article describes the case study method as a form of simulation and presents guidelines for their use in professional training situations.
Thaller, E. (1994). Bibliography for the Case Method: Using Case Studies in Teacher Education. RIE. 37 p.
This bibliography presents approximately 450 citations on the use of case studies in teacher education from 1921-1993.
Thrane, T. (1986). On Delimiting the Senses of Near-Synonyms in Historical Semantics: A Case Study of Adjectives of 'Moral Sufficiency' in the Old English Andreas. Linguistics Across Historical and Geographical Boundaries: In Honor of Jacek Fisiak on the Occasion of his Fiftieth Birthday . Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
United Nations. (1975). Food and Agriculture Organization. Report on the FAO/UNFPA Seminar on Methodology, Research and Country: Case Studies on Population, Employment and Productivity . Rome: United Nations.
This example case study shows how the methodology can be used in a demographic and psychographic evaluation. At the same time, it discusses the formation and instigation of the case study methodology itself.
Van Vugt, J. P., ed. (1994). Aids Prevention and Services: Community Based Research . Westport: Bergin and Garvey.
"This volume has been five years in the making. In the process, some of the policy applications called for have met with limited success, such as free needle exchange programs in a limited number of American cities, providing condoms to prison inmates, and advertisements that depict same-sex couples. Rather than dating our chapters that deal with such subjects, such policy applications are verifications of the type of research demonstrated here. Furthermore, they indicate the critical need to continue community based research in the various communities threatened by acquired immuno-deficiency syndrome (AIDS) . . . "
Welch, W., ed. (1981, May). Case Study Methodology in Educational Evaluation. Proceedings of the Minnesota Evaluation Conference. Minnesota. (Address).
The four papers in these proceedings provide a comprehensive picture of the rationale, methodology, strengths, and limitations of case studies.
Williams, G. (1987). The Case Method: An Approach to Teaching and Learning in Educational Administration. RIE, 31p.
This paper examines the viability of the case method as a teaching and learning strategy in instructional systems geared toward the training of personnel of the administration of various aspects of educational systems.
Yin, R. K. (1993). Advancing Rigorous Methodologies: A Review of 'Towards Rigor in Reviews of Multivocal Literatures.' Review of Educational Research, 61, (3).
"R. T. Ogawa and B. Malen's article does not meet its own recommended standards for rigorous testing and presentation of its own conclusions. Use of the exploratory case study to analyze multivocal literatures is not supported, and the claim of grounded theory to analyze multivocal literatures may be stronger."
---. (1989). Case Study Research: Design and Methods. London: Sage Publications Inc.
This book discusses in great detail, the entire design process of the case study, including entire chapters on collecting evidence, analyzing evidence, composing the case study report, and designing single and multiple case studies.
Related Links
Consider the following list of related Web sites for more information on the topic of case study research. Note: although many of the links cover the general category of qualitative research, all have sections that address issues of case studies.
- Sage Publications on Qualitative Methodology: Search here for a comprehensive list of new books being published about "Qualitative Methodology" http://www.sagepub.co.uk/
- The International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education: An on-line journal "to enhance the theory and practice of qualitative research in education." On-line submissions are welcome. http://www.tandf.co.uk/journals/tf/09518398.html
- Qualitative Research Resources on the Internet: From syllabi to home pages to bibliographies. All links relate somehow to qualitative research. http://www.nova.edu/ssss/QR/qualres.html
Citation Information
Bronwyn Becker, Patrick Dawson, Karen Devine, Carla Hannum, Steve Hill, Jon Leydens, Debbie Matuskevich, Carol Traver, and Mike Palmquist. (1994-2024). Case Studies. The WAC Clearinghouse. Colorado State University. Available at https://wac.colostate.edu/repository/writing/guides/.
Copyright Information
Copyright © 1994-2024 Colorado State University and/or this site's authors, developers, and contributors . Some material displayed on this site is used with permission.
Advertisement
A Case for the Case Study: How and Why They Matter
- Original Paper
- Published: 06 June 2017
- Volume 45 , pages 189–200, ( 2017 )
Cite this article

- Jeffrey Longhofer 1 ,
- Jerry Floersch 1 &
- Eric Hartmann 2
3931 Accesses
13 Citations
3 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
In this special issue we have asked the contributors to make a case for the case study. The guest editors, Jeffrey Longhofer, Jerry Floersch and Eric Hartmann, intergrate ideas from across the disciplines to explore the complexties of case study methods and theory. In education, Gary Thomas explores the importance of ethnographic case studies in understanding the relationships among schools, teachers, and students. Lance Dodes and Josh Dodes use the case study to articulate a psychoanalytic approach to addiction. In policy and generalist practice, Nancy Cartwright and Jeremy Hardie elaborate a model for a case-by-case approach to prediction and the swampy ground prediction serves up to practitioners. Christian Salas and Oliver Turnbull persuasively write about the role of the case study in neuro-psychoanalysis and illustrate it with a case vignette. In political science, Sanford Schram argues for a bottom up and ethnographic approach to studying policy implementation by describing a case of a home ownership program in Philadelphia. Eric Hartman queers the case study by articulating its role in deconstructing normative explanations of sexuality. In applied psychology, Daniel Fishman describes a comprehensive applied psychology perspective on the paradigmatic case study. Richard Miller and Miriam Jaffe offer us important ways of thinking about writing the case study and the use of multi-media. Each contributor brings a unique perspective to the use of the case study in their field, yet they share practical and philosophical assumptions.
Similar content being viewed by others

Qualitative Research: Ethical Considerations

Different uses of Bronfenbrenner’s ecological theory in public mental health research: what is their value for guiding public mental health policy and practice?

Labeling Theory
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
We have invited scholars from education, political science, social work, applied psychology, addictions, psychoanalysis, queer studies, policy, and neuro-psychoanalysis to reflect on how the case study has been used across diverse fields of practice, in the production and dissemination of new knowledge and in creative pedagogy. Case study research and writing teaches us, again and again, that there are no universally effective therapeutic interventions; there is practice, and the practice of theorizing about practice. As self-reflective practitioners, case studies help us focus on a problem, question, or paradox that has arisen in the treatment of our clients. In using and teaching the case study method we learn that there is not one essential story of therapeutic success or organizational outcome, where each practitioner uses the same method to lead clients to inevitably better places. In place of a uniform method, theory, or single narrative arc, there are many and sometimes competing methods and theories (Willemsen et al. 2015 ) and a range of outcomes—some clear successes, to be sure, but most ending in a more ambiguous place: the client still very much in the process of learning how to contend with life’s full array of challenges and difficulties. Moreover, we realize with the case study the necessary role humility plays in caregiving, since, absent a single, totalizing theory or methodology that can account for all human behavior, cognition, and emotion, caregivers are left with the inescapable fact that expertise doesn’t mean always being right; it means always being open to the possibility that during any given client intervention, some important detail can go unnoticed, some vital question can go unasked, some significant shaping force can go undetected. We are fallible. The reflective practitioner doesn’t seek to conceal the possibility of fallibility, but rather assumes that fallibility is foundational in an interpretive practice (and open systems) that is as much an art as it is science. Thus, case studies are not one story retold, but many stories. Not one outcome in many different contexts, but many different outcomes, emerging from detailed accounts of practitioners establishing therapeutic and other kinds of relations with clients. Neither does the case study necessarily reflect one perspective, or even multiple perspectives, but instead a commitment to multiperspectivalism, thus our rationale for inviting scholars from various disciplines to contribute to this special issue on the case study. As you will read, knowledge produced by case studies contributes to the professions by providing richly detailed, complex accounts of individual instances of suffering, flourishing, and recovery. And the case study, across the disciplines, serves many purposes: explanatory, interpretive, understanding.
As you read case studies across the disciplines, you will find that patterns emerge in the framing and production of cases. The paradigmatic approach in social work and psychology connects a specific clinical theory—e.g., psychodynamic, family systems, cognitive-behavioral—to specific client contexts or outcomes. The humanistic approach offers first-person practitioner accounts of encounters with foundational practice realities—e.g., a practitioner explores the lead up to and the consequences of client illness experience, transformation, self-disclosure, and transference. And third, the ethnographic approach stays close to first-person practice to produce rich descriptions of field-based practice, situating and resituating the therapeutic and other relationships in cultural contexts and everyday realities.
There is by no means a consensus within or among the disciplines on how the case study is to be used or about the role of the case study in the production of knowledge. Can it be explanatory? Or is it merely a descriptive precursor to more rigorous methods? Is a single case sufficient? Is the knowledge produced by the case study generalizable? Indeed, in this special collection of essays you’ll find a wide variety of opinion and alignment on these and other questions. As you read we hope you’ll find your own answers to some of the questions. It is our hope that clinical social workers, and others, will find in these essays new ways of thinking about case study research, and that this will contribute to and inspire transdisciplinary dialogue (Damousi et al. 2015 ; Foucault 1994 ).
Some argue for a robust combination of methods, using the case study in combination with quantitative methods (Luyten et al. 2006 ; Marchal et al. 2013 ). For others, like the critical realist sociologist George Steinmetz ( 2004 ), the case is to be used not just as a means of richly describing human experience; for Steinmetz, the case study is crucial to the production of meaningful and new knowledge. In psychoanalysis, where the case has figured as the single most important method for the generation and dissemination of knowledge, there is today contentious debate and disagreement (Luyten et al. 2006 ; Colombo and Michels 2007 ; Edelson 1985 ; Forrester 1996 ; Hoffman 2009 ; Safran 2009 ; Wolpert and Fonagy 2009 ; Willemsen et al. 2017 ) over its explanatory power and significance; and tragically, psychoanalysts have altogether failed to explore the broader literature and debates on the case study; indeed, much of what has exercised their imaginations and caused much anguish has been widely discussed, debated, and resolved in other disciplines. Here, again, with this special issue it is our hope that researchers and practitioners can begin a more meaningful dialogue about the case study.
Many argue, as you will see, that a single case has significant explanatory power (Desmet et al. 2012 ); here, Newton’s theorization of gravity is the definitive example. His account of gravity did not require a sample of cases, or a number larger than one, or a random control trial, or a larger database of cases. He needed only an imagination and robust theory to account for the single observation. Others contend that the strength of explanation is increased with multiple cases. For some its explanatory power is to be found in the comparison of cases (Bergene 2007 ). What is not in doubt, however, is the continuing and widespread use of the case in research, practice, and teaching: criminology (Desmet et al. 2012 ; Feagin et al. 1991 ); psychology, psychiatry, and psychoanalysis (Gottdiener and Suh 2012 ; McLeod and Balamoutsou 1996 , 2010 , 2015 ; Morgan 2012 ; Kächele et al. 2011 ); organizational studies, management and marketing (Easton 2010 ; Perry 1998 ); information sciences (Mingers 2004 ; Tsang 2014 ); operations management (Ketokivi and Choi 2014 ); development (Woolcock 2013 ); environmental science and sustainability (Barth and Thomas 2012 ); telecommunications and policy (Sutherland 2016 ); in medicine and nursing (Payne et al. 2007 ; Hurwitz 2011 ; Van Haselen 2015 ); social work and the narrativized method (Brandell and Varkas 2010 ; Gilgun 1994 ; Mishna 2004 ); political science and international relations (Bennett and Elman 2006 , 2007 ; Gerring 2004 , 2007a , b ; George and Bennett 2004 ; Levy 2008 ; Mahoney et al. 2009 ; Mearsheimer and Walt 2013 ; Yang 2006 ); sociology (Abbott 1992 ; Steinmetz 2004 ; Campbell 1975 ; Thacher 2006 ); migration studies (Iosifides 2012 ); bioethics (Bunch and Dvonch 2000 ); and business (Gerring 2007a , b ). Evaluation researchers have used the case study as a means to explore and deepen our understanding of causality in program outcomes (Koenig 2009 ). In law, medicine, and business, the case method is used not only for teaching about complexity; it is used for sorting through alternative and competing theoretical accounts (Forrester 1996 ). For the sociologist Michael Burawoy ( 1998 ) the extended case study “applies reflexive science to ethnography in order to extract the general from the unique, to move from the “micro” to the “macro,” and to connect the present to the past in anticipation of the future, all by building on preexisting theory” (p. 5). Others, many others, have explored in detail the epistemological status of the case study (see, in particular, Barbara Held’s essay, 2009 ).
In recent years, there have been two efforts to develop psychotherapy case study archives, not unlike the archive of business case studies at Harvard (see, https://cb.hbsp.harvard.edu/cbmp/pages/content/cases ). One, in England and Belgium, the singlecasearchive.com is described as:
The Single Case Archive compiles clinical and empirical single case studies in the field of psychotherapy. Currently these are psychoanalytically oriented cases published in ISI-ranked journals, but the archive is intended to include single case studies from all different psychotherapeutic orientations. These case studies were screened by an international group of researchers for basic information on type of study, patient, therapist and therapy. The objective of this online archive is to facilitate the study of case studies for research, clinical and teaching purposes. With an easy to use search engine, the archive allows the quick identification of relatively homogenous sets of cases in function of specific clinical or research questions.
Second, the Pragmatic Case Studies in Psychotherapy, an online journal and database, is described by its editor Daniel Fishman (see his contribution to this special issue):
In recent years, there has been a vigorous, renewed interest by applied psychology researchers and scholars in case studies of therapy—and other psychosocial interventions—whose process and outcome are systematically described with “thick” qualitative detail (see sample list of references below). These authors have been drawn to the case study from a variety of theoretical and applied perspectives, such as cognitive-behaviorism, psychoanalysis, phenomenology, hermeneutics, humanistic psychology, life-history, personology, and program evaluation. In spite of this diversity, these authors have offered converging rationales for restoring the case study to its former prominence as a vehicle for systematically reporting clinical observations, exploring theory, and documenting advances in professional effectiveness. ( http://pcsp.libraries.rutgers.edu/index.php/pcsp/about/pcspAbout )
In 2007, Lauren Berlant organized a special issue of Critical Inquiry, “making the case.” For Berlant
The case represents a problem-event that has animated some kind of judgment. Any enigma could do—a symptom, a crime, a causal variable, a situation, a stranger, or any irritating obstacle to clarity. What matters is the idiom of the judgment. This varies tremendously across disciplines, professions, and ordinary life scenes: law, medicine, universities, sports bars, chat shows, blogs, each domain with its vernacular and rule-based conventions for folding the singular into the general. Psychoanalysis mobilized the case-study genre to worry at questions of obscured causality, intention, and consent. Biopower uses the case study as a primary instrument in its machinery for making individuals into normative social units. It took aesthetic form in documentary and ficto-narrative genres (the detective story, the fictional autobiography, the medical mystery, the still life) and then in interpretive scholarship. It became available as an ordinary mode of life explanation, especially after the development of mass cultural norms of inducing identification. It took shape in the social sciences and business as a way of rationalizing and debating about how to manage singularity and generalization in research design. Those would be some of the different histories articulated in the concept of the case. As genre, the case hovers about the singular, the general, and the normative. It organizes publics, however fleeting. It expresses a relation of expertise to a desire for shared knowledge. It could be casual expertise, deliberately cultivated, licensed by training—no matter; deciding what defines the surplus to singularity is now the province of the expert, the expert who makes the case (pp. 663–664).
Bent Flyvbjerg ( 2006 ), perhaps the most well known scholar using the case study and also writing about the method, argues that there are five common myths or misunderstandings: (1) general, theoretical knowledge is more valuable than concrete case knowledge; (2) one cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development; (3) the case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process; while other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building; (4) the case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions; (5) it is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of a specific case. In several books and numerous essays, Flyvbjerg ( 2001 ) and colleagues set out to dispel these common myths; and while many of the essays in this special collection do not use or embrace Flyvbjerg’s work, they to varying degrees implicate one or another of the common misunderstandings. Ruddin ( 2006 ) along with Barth and Thomas ( 2012 ) have creatively struggled with the second misunderstanding, generalizability, and offer provocative new understandings. And while we more or less agree with Flyvbjerg’s ideas, we have turned mostly to more recent and far more compelling work done by critical realists.
Across the disciplines, scholars have recently turned to critical realism, a philosophy of social science that works against the grain of both positivism and social constructivism, for insights into how the case study can offer robust explanatory, causal accounts (Dobson 2001 ; Easton 2010 ; Koenig 2009 ; McKeown 2015 ; Wynn and Williams 2012 ; Aastrup and Halldórsson 2008 ; Steinmetz 2004 ; Sutherland 2016 ; Tsang 2014 ; Welch et al. 2011 ). These scholars (from bioethics, information sciences, sociology, political science) argue that with critical realism (CR) case study research can be grounded in fundamentally different ontological (i.e., what we know and take to be real and knowable) and epistemological (i.e., how we know what it is we take to be real and knowable) assumptions. For critical realists, accounting for the constant conjunctions of events or regular (i.e., statistical regularity) relationships occurring among events, behaviors, and mental states, cannot offer explanations of those events. The explanatory account must look at the causal mechanisms underlying statistical regularities, or the constant conjunction of events. At best, positivist methods (i.e., quantitative, statistical methods) can offer accounts not of why things occur but that they occur in regular association: we can count the number of times poverty is associated with poor health outcomes, social mobility, and educational outcomes. But these associations do not offer adequate accounts of the causal mechanisms responsible for those associations; how, for example, do certain dominant class relations or ideologies act as causal mechanisms, producing the regularities found among empirical events? Note here that we do not argue that quantitative or statistical methods are always in the service of positivism; they can also be used by critical realists and by those using the case study method (see Longhofer and Floersch 2012 article for elaboration of this position). Geoff Easton ( 2010 ), using critical realism and the case study in marketing research, concludes the following:
Ironically the requirement for a causal sequence of events provides a reason for accepting the argument that one case is enough. Logic demands if there is a causal sequence it must occur in every case. If it doesn’t this is tantamount to saying that other variables are involved which have not been measured and causality, even in the limited terms required in positivism, is absent. So a single case can disprove but not prove positivist regularity. “...once a theory is disproved by the discovery of a single refuting instance, it should be eliminated from the body of science (Leong 1985 , p. 24). On the other hand it might strengthen the argument for the existence of a regularity if the case chosen is an extreme one where it might be expected that the regularity would break down (Easton 2010 , p. 5).
And some scholars, using complexity theory, have turned to the case study, arguing that it is a useful way of thinking about learning and language. Haggis ( 2008 ), a complexity researcher, argues in defense of the case study in educational research: “Although qualitative case study researchers are usually careful to make it clear that they cannot generalize, this caveat itself indicates how such research is still firmly located within particular ontological and epistemological assumptions which privilege the capacity for a particular kind of generalization” (p. 153).
There is no doubt that the case has been used by scientists to engage the popular imagination in communicating the complexities of living in open systems: social, psychological and biological (Miller 2009 ). In Google Scholar, the tip of the iceberg, Freud’s Case of Dora, a thorough report of a negative outcome, appears more than 19,000 times and continues to engage the imagination, across the disciplines, and remains to this day one of the most widely discussed and debated cases (Ahbel-Rappe 2009 ; Boyce 2015 ; Hare-Mustin 1983 ; Romano 2015 ). The late Oliver Sacks, a neurologist, turned the case into a creative, non-fiction genre: a brain-damaged Hare Krishna who imagined he’d achieved enlightenment; a family man who, following brain surgery, spurned his wife and child but loved strangers; psychiatric patients who appeared to wake from the dead; a man who developed hypersexuality after brain surgery; and a woman haunted by dragons. In The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat ( 1970 ), Sacks considered the case of a man with visual agnosia (a condition resulting in the inability to recognize objects or people, or both). It could be argued that The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat revived the case study as a literary form. And with this case Sacks sought to see the world from the perspectives of sufferers and from those caring for her. One wonders how important his long psychoanalysis with Leonard Shengold was in helping him to explore his cases with such care and detail (see interview, http://www.webofstories.com/play/oliver.sacks/196;jsessionid=0B3E60CFA202B93201963F172675C3B7 ). With Awakenings , a bestseller, along with numerous of his case studies, filmmakers and playwrights began to explore the complexities of his cases: the Oscar-nominated film, Awakenings; and, a chamber opera by Michael Nyman. The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat led to a play by Peter Brook, The Valley of Astonishment . A British mini-series, Discovery , was based on his case studies. And with the play, A Kind of Alaska , Harold Pinter acknowledged for the first time in his long playwriting career, the source of the play: Awakenings (Pinter 1982 ). In his 1973 book, Awakenings , Sacks looks closely at the life histories of patients from the 1920s encephalitis lethargica epidemic. Easton (quoted above) would no doubt concur with the following lines from his last book and memoir, where Sacks writes of the n of 1, the uniqueness of individual brains, minds, selves, and identities as they develop in dynamic open systems. Oliver Sacks writes of this singularity and particularity:
Individuality is deeply imbued in us from the very start, at the neuronal level. Even at a motor level, researchers have shown, an infant does not follow a set pattern of learning to walk or how to reach for something. Each baby experiments with different ways of reaching for objects and over the course of several months discovers or selects his own motor solutions. When we try to envisage the neural basis of such individual learning, we might imagine a “population” of movements (and their neural correlates) being strengthened or pruned away by experience. Similar considerations arise with regard to recovery and rehabilitation after strokes and other injuries. There are no rules; there is no prescribed path of recovery; every patient must discover or create his own motor and perceptual patterns, his own solutions to the challenges that face him; and it is the function of a sensitive therapist to help him in this (Sacks 2015 , p. 368).
Social work exists in a tension between the complex and open worlds of the everyday, experience-near practice and suffering, and the more distant worlds of research, positivism, and closed systems (achieved only under conditions of experimental closure); and between the individual as a site for understanding, action, and change and the surrounding social worlds as constraining and enabling (Longhofer et al. 2013 ; Smith 2011 ). It is also a tension between understanding habitual forms of action, thought, and emotion, and reflexivity: for clients, practitioners, and researchers (Archer 2010 ; Longhofer and Floersch 2012 , 2013; Probst 2015 , Sayer 2011 ; Taylor and White 2001 , 2006 ). It is ultimately a tension between the assumed homogeneity of research subjects and the reality of their singularity (Lahire 2011 ). Lahire writes of the mistaken notion of homogeneity in social research and the reduction of the individual to uniform categories, types, or habitus (e.g., father, mother, child, adolescent, student, social worker): “quite naturally, the abstraction ends up taking bodily form, supported by the evidence of the body’s biological unity. Socially, however, the same body passes through different states and is the irrevocable bearer of heterogeneous and even contradictory schemes of action and habits” (p. 16).
In practice, the singularity of suffering is felt, described, and understood. In what Bourdieu calls the illusio of positivist science and research, singularity is altogether erased. In fact, it could be argued that the sense of the game in much of positivist social work research requires the erasure of singularity. In practice, singularity is taken up by the case study (Easton 2010 ; Ferguson 2016 ; Flyvbjerg 2001 , 2006 ; Flyvbjerg et al. 2012 ), even when practitioners (and researchers) are unaware of its implicit, everyday use and significance in the production and conveyance of expert knowledge and practice (Benner 2000a , b , 2004 ; Dreyfus 2008 ). The “suspension of the objectives of ordinary existence, in favour of new stakes, posited and produced by the game itself” (Bourdieu 2000 , p. 101) is nicely described by George Steinmetz ( 2004 ) in his reflection on the fate of the case study and the study of singularity in positivist sociology and political science:
This does not mean that case studies are “idiographic” raw data waiting to be processed by “nomothetic” theory machines. In the more positivistically dominated social science fields such as sociology and political science, however, the case study has been demoted to subaltern status, with less scientific capital than comparative or large-sample quantitative studies. A revealing sign of this is the continuing use of the term idiographic, a theoretically incoherent survival from the 19th-century German Methodenstreit, which nowadays is used exclusively to assign low scientific capital to case studies (p. 382).
In social work research, sociology, and political science, and increasingly in psychoanalysis (Luyten et al. 2006 ; Bornstein 2007 ), the sense of the game consigns the case study to the idiographic and the individual to the homogeneous.
John Forrester ( 2007 ), whose life’s work in philosophy was dedicated to understanding the use of the case in psychoanalytic theory, writes of singularity: “There is a family of disciplines that works with cases. They are suitably obvious, displaying the sort of obviousness which hovers between the banal and the crucially overlooked: medicine, law, social work, management science, and the sort of psychology in which there are clients or patients. There are a number of different ways of linking them together to give them suitable ties of kinship. One might note that these disciplines have a professional and sometimes a legal obligation to treat their objects as persons…” (p. 810). In a similar way, Berlant ( 2007 ) argues that
To decide to publish something is to confirm that it has made a case for its worthiness as knowledge. To decide not to is not evidence of anything. At the same time, the phrase “knowledge object” obscures how often debates about whether a topic or object is an object or is worthy of becoming an absorbing and potentially transformative case-event are really about whether one can bear to have transference with the low and the hot; professional life is generally so stable and so cool . This is why the topic of the case matters: the conventions of the case, of the fate of singularity in exemplifying narratives and expert commentary, are honed by debates about consensus sensibility. Any time is a good time for some reflection on that, the emergence as a topic of case norms and their relation to the kinds of judgment that reshape events in all (professional) life (pp. 671–672).
And it seems no small coincidence that the most complex aspect of our being human, the most open of human systems, the brain (Freeman 2000 ), always leads us back to the particulars of a case. Perhaps that’s because our brains are not mere data points with blood volumes, but particular brains with particular minds, with particular selves and identities (see Longhofer and Floersch 2012 , for elaboration of a critical realist conception of personhood in a stratified reality). Phineas Gage is without question among neuroscience’s most famous cases. Scores of books and thousands of articles explore the particulars of his case (Fleischman 2002 ; Haas 2001 ; Macmillan 2000 ; Wilgus and Wilgus 2009 ). In a Google Scholar search for Phineas Gage you’ll find more than 7500 hits. In 1848, Gage, a railwayman, was using a 43 inch-long tamping iron to force explosive powder into a hole; it exploded, ripped a hole in his left cheek, penetrated his prefrontal cortex, and left him blind in one eye; and according to those who knew him and John Martyn Harlow, the doctor who treated and studied his case, he seemed no longer familiar. His personality had changed: the link between brain trauma and personality change was established: with one single case. Oliver Sacks wrote of the case:
The weight of consciousness and conscience and conscientiousness itself, the weight of duty, obligation, responsibility, can press on us sometimes with unbearable force, so that we long for a release from its crushing inhibitions, from sanity and sobriety, we long for a holiday from our frontal lobes, a Dionysiac fiesta of sense and impulse. That this is a need of our constrained, civilized, hyperfrontal nature has been recognized in every time and culture. All of us need to take little holidays from our frontal lobes—the tragedy is when, through grave illness or injury, there is no return from the holiday, as with Phineas Gage (Sacks 1995 , p. 64).
It may be only Freud’s case of Dora that has inspired this kind and depth of conversation. Freud wrote five lengthy case studies: (Dora 1905; Rat Man 1909; Little Hans 1909; Paul Schreber 1911; Wolf Man 1918). “Unlike hospital case files, these studies emphasized the interaction of patient and analyst, dramatizing the transference implicated in the clinical encounter, thereby providing examples of how” to engage in practice (Anderson 2013 , pp. 534–535). It is because the psychoanalytic case study takes up the more complex and open system dynamics (Longhofer and Floersch 2012 ) between the practitioner and the patient that it has always been the subject of controversy, scrutiny, and scorn; and at the same time it becomes for the psychoanalyst the source of innovation and creativity in the production and dissemination of knowledge. Legal, medical, and business case studies, on the other hand, do not describe or address these dynamic complexities of interactive kinds (Hacking 1999 ) and only recently have others in the social sciences carefully examined the mutual influence of the researcher and the researched (Hollan and Throop 2008 ).
How do single cases produce this kind of output and reach across the disciplines? And why do we think case studies should matter in social work? First, because we believe clinical social workers and others in the helping professions have much at stake in knowing about the case study theory and method; after all, much of practice knowledge is produced and disseminated through the case, and limited to the case (Charlton and Walston 1998 ; Florek and Dellavalle 2016 ; Nissen and Wynn 2014a , b ). And much of daily practice and struggles circulate around difficult cases, anomalous and quotidian; and much of professional accountability is reconciled through the successful execution or completion of cases. Supervision, consultation, and professional identity development are rooted in the day-to-day direction and redirection of complex cases. Indeed, one could make the argument that professional identity development and career success is rooted in the detailed understanding, execution, and communication about particular cases. And while health insurance companies grotesquely reduce and average cases , they ultimately approve and adjudicate individual cases. Much of the history of social work is marked by the significance of the case: the caseworker, the case record, the case example, the case manager, case management (Floersch 2000 ). And the outcomes and metrics (especially during this era of neoliberal managerialism) are ultimately rooted in the particulars of a case, their success or failure, often not based on measures of physical, emotional or social wellbeing, but on pecuniary logics, financial mandates and imperatives, and distorting algorithms (Kitchin 2014a , b ; Mittelstadt et al. 2016 ; Tufekci 2015 ). In the practice of medicine and mental health it is through the case that we consider the ethics and limits of evidence-based practice (Gupta 2007 , 2014 ; Gwande 2014 ). Indeed, we never make normative evaluations of social worker action (praxis) based on the average of cases. Referral networks are developed and maintained through the case and professional associations are used for the purpose of presenting, discussing, and debating the case (ironically, even when it’s a Big Data case). Anomalous cases allow for particular ways of knowing and comparative cases are used to consider the actions of nations, organizations, and businesses (Siggelkow 2007 ). It is to the case record that jurors and judges turn. Bioethicists use the case to explore our deepest values and convictions about medical practice and decision-making. And historians of the welfare state turn to comparative case histories of nation states:
scholars….make use of comparative history to bring out the unique feature of each particular case…and to show how these unique features affect the working-out of putatively general social processes. Above all, contrasts are drawn between and among individual cases (Skocpol and Sommers 1980 , p. 178).
Second, we believe that the era of big data (Kitchin 2014a , b ; Kitchin and Lauriault 2015 ; O’Neil 2016 ), and the gold standard for evidence-based practice, the randomized control trial, or RCT, (Cartwright 2007 , 2011 ; Ioannidis et al. 2001 ; Sampson 2010 ), and positivism in the human sciences have reached points of crisis (Steinmetz 2005 ; Longhofer and Floersch 2012 , 2014 ). While we do not have the space here to offer a full account of how and why we believe positivism is in crisis, we do believe it is important to offer a brief statement of the key questions: (1) in the human sciences, systems are continuously open and changing and thus beyond our capacity to predict, unless we artificially close systems using experimental designs or limit research to pre-specified numbers of variables; (2) positivism, by reducing the ought to the is, elides the fundamental role of values in the determination of the questions to be ask, the methods to be used, the theories deployed, and the different modes of knowledge representation; and (3) because explanation is reduced to prediction, causality is simplified and reduced.
Third, it is through the case study that we can best understand the things that matter most to people (Flyvbjerg 2001 ; Longhofer and Floersch 2012 , 2014 ). We believe that it is through the case that we can be truly engaged with those we serve, that is, engaged scholarship (Longhofer and Floersch 2012 , 2014 ; Van de Ven 2007 ). It is in the particularities of the case that value propositions and normative claims can be made transparent and considered; indeed, the case study may be crucial to our ongoing dialogue with our communities of interest, individual and collective. And it is through the case that our clients and communities come to know researchers’ motivations and intentions, values, and proposed actions. It is through the case study that we’re most likely to escape what Pierre Bourdieu ( 1990 , 2000 ) called the scholastic fallacy : the many ways that our methods and means of knowledge production obscure the things that matter most to people (Floersch and Longhofer 2016 ).
Fourth, when historians (Tice 1998 ) and sociologists (Maroglin 1997 ) turn social work practice into objects of study, using and reading only the case record, (see Floersch 2000 ) much is left out: the oral, the context-dependent interactions, the hidden record, the kinesthetic, the moment-to-moment dynamics, the gradual formation and dissolution of the working alliances, the quick moves to correct action along with all of the situated knowledge that governs the movement from novice to expert practitioners (Benner 1982 , 2004 ; Dreyfus and Dreyfus 2005 ). The failure to consider the singularity of the oral—the dialogues never recorded between social workers and clients, social workers and social workers—-has led to fundamental misrecognition of social work practices; in short, there will always be overdetermined and situated dynamics in the practitioner-client experience and those dynamics will not only escape our efforts at manualization but will also limit researcher efforts to capture those complexities (Floersch 2002 ) using experience-distant methodologies.
Finally, it is with the richness of case material that we reach wide audiences and the world finds our work compelling and important (Longhofer and Floersch 2014 ). People read cases, with interest. Compelling cases reach national and international audiences. It is with the case that writers have engaged students and the general public about our most compelling social problems and individual struggles: Anthropologists on Mars , Oliver Sacks; When the Breath Becomes Air , Paul Kalanathi; and, The Spirit Catches You and You Fall Down , Anne Fadiman. In these works of particularity and singularity, readers find little bits and pieces of the familiar, sometimes entirely familiar lives, events, places.
Readers will find two omissions from this collection. We have not included essays from a significant literature on the ethics of writing cases (Alfonso 2002 ; Antommaria 2004 ; Aron 2000 , 2016 ; Blechner 2012 ; Carlson 2010 ; Fisher 2013 ; Kantrowitz 2004 ; Shaw 2013 ; Sieck 2012 ; Sperry and Pies 2010 ; Winship 2007 ; Willemsen et al. 2017 ). We made this decision because we believe this requires a more in depth treatment in a separate volume. We are aware that writing about lives, individual and collective, is and should be driven, like all research, by value claims, normative understandings, and a concern for privacy (Longhofer and Floersch 2014 ). Moreover, because there is no value-free science (nor should there be), there is no value-free writing of cases. And while we understand that writing cases with a sensitivity to privacy and confidentiality is central to effective intervention and treatment, at the same time, in a forthcoming collection of essays, we will explore what happens to privacy and confidentiality in our culture’s shift from print to screen. And we will ask contributors to reflect on the “the end of privacy”, and how with the end of privacy we must ask new questions about the writing of cases. Having said this, however, we believe that the ethics of case study writing becomes almost meaningless in comparison to the problems that come with the invasions of privacy enabled by our machine culture and Big Data. There is no doubt that the social, cultural, and technological transformation brought about by machine learning poses much greater risk to individual privacy and democracy than the risk posed by the writing of case studies. And there is no doubt that social work practice (and research) is being transformed by big data. And for these reasons case study methods should be used to explore what this will ultimately mean for social work’s ways of knowing (epistemology) and doing (practice), as well as its negotiations of value and ethics. Second we have omitted a discussion of case study evaluation. In his contribution to this special issue Daniel Fishman suggests how comparative analysis might be used to evaluate case studies and Cartwright and Hardie elaborate on a reflexive practice used to recursively evaluate intervention. We believe that Lee et al. (2010) have provided us with useful strategies for case study evaluations.
Thus, in this special issue we have asked the contributors to make a case for the case study. In education, Gary Thomas explores the importance of ethnographic case studies in understanding the relationships among schools, teachers, and students. Lance Dodes and Josh Dodes use the case study to articulate a psychoanalytic approach to addiction. In policy and generalist practice, Nancy Cartwright and Jeremy Hardie elaborate a model for a case-by-case approach to prediction and the swampy ground prediction serves up to practitioners. Christian Salas and Oliver Turnbull persuasively write about the role of the case study in neuro-psychoanalysis and illustrate it with a case vignette. In political science, Sanford Schram argues for a bottom up and ethnographic approach to studying policy implementation by describing a case of a home ownership program in Philadelphia. Eric Hartman queers the case study by articulating its role in deconstructing normative explanations of sexuality. And finally, in applied psychology, Daniel Fishman describes a comprehensive applied psychology perspective on the paradigmatic case study. Each contributor brings a unique perspective to the use of the case study in their field, yet they share practical and philosophical assumptions.
And there is more: two commentaries. We invited Miriam Jaffe, a Rutgers DSW Writing faculty, to share her first-person experience in teaching case study writing. Facing the blank page can present many difficulties and often comes with inhibitions. And the lack of writing experience keeps many from handwriting and typing. However, it need not be. Writing experts like Miriam have de-mystified the writing process and in her article you will find concrete and helpful advice for how to overcome the myth that only expert writers can narrate practice experience. There is much more to be said about writing pedagogy, especially in our time, when most writing is done on the screen, not for print; and Miriam is not addressing those questions here. And we are well aware that many in the psychoanalytic community have given significant thought to writing (for print) about cases and the pedagogy of writing (Bernstein 2008a , b ; Michels 2000 ; Naiburg 2015 ). Their approach to case writing pedagogy differs in significant ways from Jaffe’s. Hers is a phenomenological approach to teaching. She stays close to the writer’s experience, not to the filters of those experiences (psychoanalytic, behavioral, or cognitive).
Finally, we have included a commentary by Richard Miller on the move from print to screen and what this means for case study dissemination via the Internet. In our time, with the historic shift from writing for print to writing for screen our habits and expectations have fundamentally changed. We are now writing at the end of privacy: with the cyber-webbed world and the proliferation of hand-held devices comes instant publication and global distribution of anything. Image, sound, text is now on demand, instant and continuously distributed. Miller challenges us to examine the moral spaces of communicating, disseminating, and viewing—and the connections among them.
We hope you enjoy these articles as much as we have and we hope it inspires you to engage unfamiliar literature and think in new ways about the case study in social work.
We are grateful to Carol Tosone for accepting our proposal to develop a special issue on the case study. We have no conflicts of interest to report, no research subjects were involved, therefore no informed consent was necessary.
Aastrup, J., & Halldórsson, Á (2008). Epistemological role of case studies in logistics: A critical realist perspective. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 38 (10), 746–763.
Article Google Scholar
Abbott, A. (1992). What do cases do? Some notes on activity in sociological analysis. In C. C. Ragin, & H. S. Becker (Eds.), What is a case?: Exploring the foundations of social inquiry (pp. 53–82). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Google Scholar
Ahbel-Rappe, K. (2009). “After a long pause”: How to read Dora as history. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 57 (3), 595–629.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Alfonso, C. A. (2002). Frontline—writing psychoanalytic case reports: Safeguarding privacy while preserving integrity. Journal of the American Academy of Psychoanalysis and Dynamic Psychiatry, 30 (2), 165–172.
Altstein, R. (2016). Finding words: How the process and products of psychoanalytic writing can channel the therapeutic action of the very treatment it sets out to describe. Psychoanalytic Perspectives, 13 (1), 51–70.
Anderson, W. (2013). The case of the archive. Critical Inquiry, 39 (3), 532–547.
Antommaria, A. (2004). Do as I say, not as I do: Why bioethicists should seek informed consent for some case studies. Hastings Center Report, 34 (3), 28–34.
Archer, M. S. (2010). Routine, reflexivity, and realism. Sociological Theory , 28 (3), 272–303.
Aron, L. (2000). Ethical considerations in the writing of psychoanalytic case histories. Psychoanalytic Dialogues, 10 (2), 231–245.
Aron, L. (2016). Ethical considerations in psychoanalytic writing revisited. Psychoanalytic Perspectives, 13 (3), 267–290.
Barth, M., & Thomas, I. (2012). Synthesising case-study research: Ready for the next step? Environmental Education Research, 18 (6), 751–764.
Benner, P. (1982). From novice to expert. The American Journal of Nursing, 82 (3), 402–407.
PubMed Google Scholar
Benner, P. (2000a). The wisdom of our practice. The American Journal of Nursing, 100 (10), 99–105.
Benner, P. (2000b). The roles of embodiment, emotion and lifeworld for rationality and agency in nursing practice. Nursing Philosophy, 1 (1), 5–19.
Benner, P. (2004). Using the Dreyfus model of skill acquisition to describe and interpret skill acquisition and clinical judgment in nursing practice and education. Bulletin of Science, Technology & Society, 24 (3), 188–199.
Bennett, A., & Elman, C. (2006). Qualitative research: Recent developments in case study methods. Annual Review of Political Science, 9 , 455–476.
Bennett, A., & Elman, C. (2007). Case study methods in the international relations subfield. Comparative Political Studies, 40 (2), 170–195.
Bergene, A. (2007). Towards a critical realist comparative methodology. Journal of Critical Realism, 3 (1), 5–27.
Berlant, L. (2007). On the case. Critical Inquiry, 33 (4), 663–672.
Bernstein, S. B. (2008a). Writing about the psychoanalytic process. Psychoanalytic Inquiry, 28 (4), 433–449.
Bernstein, S. B. (2008b). Writing, rewriting, and working through. Psychoanalytic Inquiry, 28 (4), 450–464.
Blechner, M. (2012). Confidentiality: Against disguise, for consent. Psychotherapy, 49 (1), 16–18.
Bornstein, R. F. (2007). Nomothetic psychoanalysis. Psychoanalytic Psychology, 24 (4), 590–602.
Bourdieu, P. (1990). The scholastic point of view. Cultural Anthropology, 5 (4), 380–391.
Bourdieu, P. (2000). Pascalian meditations . Stanford: Stanford University Press.
Boyce, N. (2015). Dora in the 21st century. Lancet, 386 (9997), 948–949.
Brandell, J., & Varkas, T. (2010). Narrative case studies. In B. Thyer (Ed.), The handbook of social work research methods (Chap. 20, pp. 375–396). Los Angeles: SAGE
Bunch, W. H., & Dvonch, V. M. (2000). Moral decisions regarding innovation: The case method. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 378 , 44–49.
Burawoy, M. (1998). The extended case method. Sociological theory, 16 (1), 4–33.
Campbell, D. T. (1975). “Degrees of freedom” and the case study. Comparative Political Studies, 8 (2), 178–193.
Carlson, J. (2010). Commentary: Writing about clients—ethical and professional issues in clinical case reports. Counseling and Values, 54 (2), 154–157.
Cartwright, N. (2007). Are RCTs the gold standard? BioSocieties, 2 (1), 11–20.
Cartwright, N. (2011). A philosopher’s view of the long road from RCTs to effectiveness. Lancet, 377 (9775), 1400–1401.
Charlton, B. G., & Walston, F. (1998). Individual case studies in clinical research. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice, 4 (2), 147–155.
Colombo, D., & Michels, R. (2007). Can (should) case reports be written for research use? Psychoanalytic Inquiry, 27 (5), 640–649.
Damousi, J., Lang, B., & Sutton, K. (Eds.) (2015). Case studies and the dissemination of knowledge . London: Routledge Press.
Desmet, M., Meganck, R., Seybert, C., Willemsen, J., Geerardyn, F., Declercq, F., & Schindler, I. (2012). Psychoanalytic single cases published in ISI-ranked journals: The construction of an online archive. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 82 (2), 120–121.
Dobson, P. J. (2001). Longitudinal case research: A critical realist perspective. Systemic Practice and Action Research, 14 (3), 283–296.
Dreyfus, H. L. (2008). On the internet . London: Routledge Press.
Dreyfus, H. L., & Dreyfus, S. E. (2005). Peripheral vision expertise in real world contexts. Organization Studies, 26 (5), 779–792.
Easton, G. (2010). Critical realism in case study research. Industrial Marketing Management, 39 (1), 118–128.
Edelson, M. (1985). The hermeneutic turn and the single case study in psychoanalysis. Psychoanalysis & Contemporary Thought, 8 , 567–614.
Feagin, J. R., Orum, A. M., & Sjoberg, G. (Eds.) (1991). A case for the case study . Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
Ferguson, H. (2016). Researching social work practice close up: Using ethnographic and mobile methods to understand encounters between social workers, children and families. British Journal of Social Work, 46 (1), 153–168.
Fisher, M. A. (2013). The ethics of conditional confidentiality: A practice model for mental health professionals . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Fleischman, J. (2002). Phineas Gage: A gruesome but true story about brain science . New York: Houghton Mifflin.
Floersch, J. (2000). Reading the case record: The oral and written narratives of social workers. Social Service Review, 74 (2), 169–192.
Floersch, J. (2002). Meds, money, and manners: The case management of severe mental illness . Columbia: Columbia University Press.
Floersch, J., & Longhofer, J. (2016). Social work and the scholastic fallacy. Investigacao Em Trabalho Social, 3 , 71–91. https://www.isssp.pt/si/web_base.gera_pagina?p_pagina=21798 .
Florek, A. G., & Dellavalle, R. P. (2016). Case reports in medical education: A platform for training medical students, residents, and fellows in scientific writing and critical thinking. Journal of Medical Case Reports, 10 (1), 1.
Flyvbjerg, B. (2001). Making social science matter: Why social inquiry fails and how it can succeed again . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Flyvbjerg, B. (2006). Five misunderstandings about case-study research. Qualitative Inquiry, 12 (2), 219–245.
Flyvbjerg, B., Landman, T., & Schram, S. (Eds.). (2012). Real social science: Applied phronesis . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Forrester, J. (1996). If p, then what? Thinking in cases. History of the Human Sciences, 9 (3), 1–25.
Forrester, J. (2007). On Kuhn’s case: Psychoanalysis and the paradigm. Critical Inquiry, 33 (4), 782–819.
Foucault, M. (1994). The birth of the clinic: An archaeology of medical perception . London: Routledge Press.
Freeman, W. J. (2000). How brains make up their minds . New York: Columbia University Press.
Freud, S. (1905). Fragment of an analysis of a case of hysteria. Standard Edition , 7 , 7–122.
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia in a five-year-old boy. Standard Edition , 10 , 5–147.
Freud, S. (1909b). Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis. Standard Edition , 10 , 151–318.
Freud, S. (1911). Psycho-analytic notes on an autobiographical account of a case of paranoia (dementia paranoides). Standard Edition , 12 , 9–79.
Freud, S. (1918). From the history of an infantile neurosis. Standard Edition , 17 , 7–122.
George, A. L. & Bennett, A. (2004). Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Gerring, J. (2004). What is a case study and what is it good for? American Political Science Review, 98 (02), 341–354.
Gerring, J. (2007a). Case study research: Principles and practices . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Gerring, J. (2007b). Is there a (viable) crucial-case method? Comparative Political Studies, 40 (3), 231–253.
Gilgun, J. F. (1994). A case for case studies in social work research. Social Work, 39 , 371–380.
Gottdiener, W. H., & Suh, J. J. (2012). Expanding the single-case study: A proposed psychoanalytic research program. The Psychoanalytic Review, 99 (1), 81–102.
Gupta, M. (2007). Does evidence-based medicine apply to psychiatry? Theoretical Medicine and Bioethics, 28 (2), 103–120.
Gupta, M. (2014). Is evidence-based psychiatry ethical? Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Gwande, A. (2014). Being mortal: Medicine and what matters most in the end . New York: Metropolitan Books.
Haas, L. (2001). Phineas Gage and the science of brain localisation. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 71 (6), 761.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hacking, I. (1999). The social construction of what? Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Haggis, T. (2008). ‘Knowledge must be contextual’: Some possible implications of complexity and dynamic systems theories for educational research. Educational Philosophy and Theory, 40 (1), 158–176.
Hare-Mustin, R. T. (1983). An appraisal of the relationship between women and psychotherapy: 80 years after the case of Dora. American Psychologist, 38 (5), 593–601.
Held, B. S. (2009). The logic of case-study methodology. Pragmatic Case Studies in Psychotherapy, 5 (3), 90–100.
Hoffman, I. Z. (2009). Doublethinking our way to “scientific” legitimacy: The desiccation of human experience. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 57 (5), 1043–1069.
Hollan, D., & Throop, C. J. (2008). Whatever happened to empathy?: Introduction. Ethos, 36 (4), 385–401.
Hurwitz, B. (2011). Clinical cases and case reports: Boundaries and porosities. The Case and the Canon. Anomalies, Discontinuities, Metaphors Between Science and Literature , 45–57.
Ioannidis, J. P., Haidich, A. B., & Lau, J. (2001). Any casualties in the clash of randomized and observational evidence? British Medical Journal, 322 , 879–880.
Iosifides, T. (2012). Migration research between positivistic scientism and relativism: A critical realist way out. In C. Vargas-Silva (Ed.), Handbook of research methods in migration (pp. 26–49). Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing.
Kächele, H., Schachter, J., & Thomä, H. (2011). From psychoanalytic narrative to empirical single case research: Implications for psychoanalytic practice (vol. 30). New York: Taylor & Francis.
Kantrowitz, J. L. (2004). Writing about patients: I. Ways of protecting confidentiality and analysts’ conflicts over choice of method. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 52 (1), 69–99.
Ketokivi, M., & Choi, T. (2014). Renaissance of case research as a scientific method. Journal of Operations Management, 32 (5), 232–240.
Kitchin, R. (2014a). Big data, new epistemologies and paradigm shifts. Big Data & Society, 1 (1), 1–12.
Kitchin, R. (2014b). The data revolution: Big data, open data, data infrastructures and their consequences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Press.
Kitchin, R., & Lauriault, T. P. (2015). Small data in the era of big data. GeoJournal, 80 (4), 463–475.
Koenig, G. (2009). Realistic evaluation and case studies stretching the potential. Evaluation, 15 (1), 9–30.
Lahire, B. (2011). The plural actor . Cambridge: Polity.
Leong, S. M. (1985). Metatheory and metamethodology in marketing, a lakatosian reconstruction. Journal of Marketing, 49 (4), 23–40.
Levy, J. S. (2008). Case studies: Types, designs, and logics of inference. Conflict Management and Peace Science, 25 (1), 1–18.
Longhofer, J., & Floersch, J. (2012). The coming crisis in social work: Some thoughts on social work and science. Research on Social Work Practice, 22 (5), 499–519.
Longhofer, J., & Floersch, J. (2014). Values in a science of social work: Values-informed research and research-informed values. Research on Social Work Practice, 24 (5), 527–534.
Longhofer, J., Floersch, J., & Hoy, J. (2013). Qualitative methods for practice research. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Luyten, P., Corveleyn, J., & Blatt, S. J. (2006). Minding the gap between positivism and hermeneutics in psychoanalytic research. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 54 (2), 571–610.
Macmillan, M. (2000). Restoring phineas gage: A 150th retrospective. Journal of the History of the Neurosciences, 9 (1), 46–66.
Mahoney, J., Kimball, E., & Koivu, K. L. (2009). The logic of historical explanation in the social sciences. Comparative Political Studies, 42 (1), 114–146.
Marchal, B., Westhorp, G., Wong, G., Van Belle, S., Greenhalgh, T., Kegels, G., & Pawson, R. (2013). Realist RCTs of complex interventions: An oxymoron. Social Science & Medicine, 94 (12), 124–128.
Maroglin, L. (1997). Under the cover of kindness. The invention of social work . Charlottesville: University Press of Virginia.
McKeown, A. (2015). Critical realism and empirical bioethics: A methodological exposition. Health Care Analysis, 1–21. doi: 10.1007/s10728-015-0290-2 .
McLeod, J. (2010). Case study research in counseling and psychotherapy . Thousand Oaks, LA: Sage Publications.
McLeod, J. (2015). Reading case studies to inform therapeutic practice. In Psychotherapie forum (vol. 20, No. 1–2, pp. 3–9). Vienna: Springer.
McLeod, J., & Balamoutsou, S. (1996). Representing narrative process in therapy: Qualitative analysis of a single case. Counseling Psychology Quarterly, 9 (1), 61–76.
Mearsheimer, J. J., & Walt, S. M. (2013). Leaving theory behind: Why simplistic hypothesis testing is bad for international relations. European Journal of International Relations, 19 (3), 427–457.
Michels, R. (2000). The case history. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 48 (2), 355–375.
Miller, E. (2009). Writing about patients: What clinical and literary writers share. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 57 (5), 1097–1120.
Mingers, J. (2004). Realizing information systems: Critical realism as an underpinning philosophy for information systems. Information and Organization, 14 (2), 87–103.
Mishna, F. (2004). A qualitative study of bullying from multiple perspectives. Children & Schools, 26 (4), 234–247.
Mittelstadt, B. D., Allo, P., Taddeo, M., Wachter, S., & Floridi, L. (2016). The ethics of algorithms: Mapping the debate. Big Data & Society , 3(2), 2053951716679679
Morgan, M. S. (2012). Case studies: One observation or many? Justification or discovery? Philosophy of Science, 79 (5), 667–677.
Naiburg, S. (2015). Structure and spontaneity in clinical prose: A writer’s guide for psychoanalysts and psychotherapists . London: Routledge Press.
Nissen, T., & Wynn, R. (2014a). The clinical case report: A review of its merits and limitations. BMC Research Notes, 7 (1), 1–7.
Nissen, T., & Wynn, R. (2014b). The history of the case report: A selective review. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Open, 5 (4), 1–5. doi: 10.1177/2054270414523410 .
O’Neil, C. (2016). Weapons of math destruction: How big data increases inequality and threatens democracy . New York: Crown Publishing Group.
Payne, S., Field, D., Rolls, L., Hawker, S., & Kerr, C. (2007). Case study research methods in end-of-life care: Reflections on three studies. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 58 (3), 236–245.
Perry, C. (1998). Processes of a case study methodology for postgraduate research in marketing. European Journal of Marketing, 32 (9/10), 785–802.
Pinter, H. (1982). A kind of alaska: A premier . Retrieved from http://www.haroldpinter.org/plays/plays_alaska.shtml .
Probst, B. (2015). The eye regards itself: Benefits and challenges of reflexivity in qualitative social work research. Social Work Research Social Work Research , 39 (1), 37–48.
Romano, C. (2015). Freud and the Dora case: A promise betrayed . London: Karnac Books.
Ruddin, L. P. (2006). You can generalize stupid! Social scientists, Bent Flyvbjerg, and case study methodology. Qualitative Inquiry, 12 (4), 797–812.
Sacks, O. (1970). The man who mistook his wife for a hat . New York: Touchstone.
Sacks, O. (1995). An anthropologist on mars: Seven paradoxical tales . New York: Alfred A. Knopf.
Sacks, O. (2015). On the move: A life . New York: Alfred A. Knopf.
Safran, J. D. (2009). Clinical and empirical issues: Disagreements and agreements. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 57 (5), 1043–1069.
Sampson, R. J. (2010). Gold standard myths: Observations on the experimental turn in quantitative criminology. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 26 (4), 489–500.
Sayer, A. (2011). Why things matter to people: Social science, values and ethical life . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Shaw, E. (2013). Sacred cows and sleeping dogs: Confidentiality: Not as straightforward as we would have thought. Psychotherapy in Australia, 19 (4), 65–66.
Sieck, B. C. (2012). Obtaining clinical writing informed consent versus using client disguise and recommendations for practice. Psychotherapy, 49 (1), 3–11.
Siggelkow, N. (2007). Persuasion with case studies. Academy of Management Journal, 50 (1), 20–24.
Skocpol, T., & Sommers, M. (1980). The uses of comparative theory in macrosocial inquiry. Comparative Studies in Society and History, 22 (2), 174–197.
Smith, C. (2011). What is a person?: Rethinking humanity, social life, and the moral good from the personup . Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Sperry, L., & Pies, R. (2010). Writing about clients: Ethical considerations and options. Counseling and Values, 54 (2), 88–102.
Steinmetz, G. (2004). Odious comparisons: Incommensurability, the case study, and “small N’s” in sociology. Sociological Theory, 22 (3), 371–400.
Steinmetz, G. (2005). The politics of method in the human. In G. Steinmetz (Ed.), Sciences . Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
Sutherland, E. (2016). The case study in telecommunications policy research. Info, 18 (1), 16–30.
Taylor, C., & White, S. (2001). Knowledge, truth and reflexivity: The problem of judgement in social work. Journal of social work , 1 (1), 37–59.
Taylor, C., & White, S. (2006). Knowledge and reasoning in social work: Educating for humane judgement. British Journal of Social Work , 36 (6), 937–954.
Thacher, D. (2006). The Normative Case Study 1. American journal of sociology , 111 (6), 1631–1676.
Tice, K. W. (1998). Tales of wayward girls and immoral women: Case records and the professionalization of social work . Chicago: University of Illinois Press.
Tsang, E. W. (2014). Case studies and generalization in information systems research: A critical realist perspective. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 23 (2), 174–186.
Tsang, E. W. (2014). Generalizing from research findings: The merits of case studies. International Journal of Management Reviews, 16 (4), 369–383.
Tufekci, Z. (2015). Algorithmic harms beyond Facebook and Google: Emergent challenges of computational agency. Journal on Telecommunication, 13 , 203–218.
Van de Ven, A. H. (2007). Engaged scholarship: A guide for organizational and social research: A guide for organizational and social research . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Van Haselen, R. A. (2015). Towards improving the reporting quality of clinical case reports in complementary medicine: Assessing and illustrating the need for guideline development. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 23 (2), 141–148.
Welch, C., Piekkari, R., Plakoyiannaki, E., & Paavilainen-Mäntymäki, E. (2011). Theorising from case studies: Towards a pluralist future for international business research. Journal of International Business Studies, 42 (5), 740–762.
Wilgus, J., & Wilgus, B. (2009). Face to face with Phineas Gage. Journal of the History of the Neurosciences, 18 (3), 340–345.
Willemsen, J., Cornelis, S., Geerardyn, F. M., Desmet, M., Meganck, R., Inslegers, R., & Cauwe, J. M. (2015). Theoretical pluralism in psychoanalytic case studies. Frontiers in Psychology, 6 , 1466
Willemsen, J., Della Rosa, E., & Kegerreis, S. (2017). Clinical case studies in psychoanalytic and psychodynamic treatment. Frontiers in Psychology, 8 , 1–7. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00108 .
Winship, G. (2007). The ethics of reflective research in single case study inquiry. Perspectives in Psychiatric Care, 43 (4), 174–182.
Wolpert, L., & Fonagy, P. (2009). There is no place for the psychoanalytic case report in the British Journal of Psychiatry. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 195 , 483–487.
Woolcock, M. (2013). Using case studies to explore the external validity of ‘complex’ development interventions. Evaluation, 19 (3), 229–248.
Wynn, D. Jr., & Williams, C. K. (2012). Principles for conducting critical realist case study research in information systems. Mis Quarterly, 36 (3), 787–810.
Yang, D. D. (2006). Empirical social inquiry and models of causal inference. The New England Journal of Political Science, 2 (1), 51–88.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Rutgers School of Social Work, New Brunswick, USA
Jeffrey Longhofer & Jerry Floersch
DSW Program, Rutgers School of Social Work, New Brunswick, USA
Eric Hartmann
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jeffrey Longhofer .
About this article
Longhofer, J., Floersch, J. & Hartmann, E. A Case for the Case Study: How and Why They Matter. Clin Soc Work J 45 , 189–200 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10615-017-0631-8
Download citation
Published : 06 June 2017
Issue Date : September 2017
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10615-017-0631-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Case study research
- Critical realism
- Psychoanaltyic case study
- Social work clinical research
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

The case study analysis is a tried and true method of instruction and evaluation in many academic fields, including social sciences. Researchers frequently use parallel or similar case studies as real-life examples when they begin the questioning process for their research process. For students and scholars, case studies have the potential to impact social growth without employing other expensive, time-consuming methods.
Case-based reasoning allows the social researcher to learn and dissect cultures, moral values, and traditions without concrete intrusions. They can be used to dictate practice in general principle decision-making and following through on potential outcomes and results, or used to develop theory through abstract thought with the comparison of multiple events.
On the whole, case studies are used as instructional tools, methods of choosing a plan of treatment, or strategizing. In the social sciences, this is essential to make decisions or assumptions about a person, group, or society, without directly evaluating each individual.
Social Research and the Need for Different Methods
Social sciences are different from other fields of humanities because they are based predominantly on epistemic studies, or strategizing theories based on knowledge of a subset of people, beliefs, or attitudes. Case studies are used in social science research to illustrate what is known about a concept or a statement that is made or a postulated theory. They’re also used to make a claim of an outcome after exhaustive research has been made.
Using case studies in social research aids the researcher in determining hypotheses about situations that have or would possibly happen. Although there is no way to use scientific evidence, as there would be in a mathematical theorem or biological question, the case study itself, when used correctly, is an epistemic strategy that can stand up to scrutiny under staunch measures to demonstrate credibility and relevancy of the hypothesis and predicted outcome.
With no way of predicting potentially widespread results on a population without a problem already occurring, it is obvious that social research requires different methodological practices than other sciences employ
Challenges to Using Case Studies in Social Research
Without concrete formulas and evidence, case studies are bound to have some challenges when they are used. Knowing the obstacles that can move the research results from quantitative to qualitative or diminish their credibility can help the researcher overcome issues before releasing their findings.
Common challenges include:
● A focus on generalization, but an inability to generalize findings. As a theory, social sciences use case studies and other methods to predict the beliefs, behaviors, or attitudes of a generalized population.
This often leads to a need for further exploration of other areas in order to determine the causation or effects of the research’s outcome.
● Length of time to complete a study. Case studies consist of an action play of interviewing participants, gathering and analyzing data, readjusting focus groups, and repeating as necessary. Deadlines can be delineated but often require adjustments due to other people’s changing circumstances.
There is no way to put a scientific cap on measuring the time necessary to obtain information in a case study, and these tend to take extensive time for data collection and analysis.
● Difficulty obtaining permission status, since for research of people to be unbiased or skewed, anonymity is often preserved. This way, the participants aren’t concerned about backlash or problems should their honest answers be revealed.
Promises of non-disclosure are usually given, but case studies are detailed reviewings of a situation. It’s difficult to ensure the material is accurate without the permission of the participant, which can’t always be obtained in anonymous works and can be time-consuming to attempt.
Many challenges make using case studies a difficult practice, but the benefits outweigh these obstacles in social research.
Case Studies Have Advantages
As case studies have grown in the significance of use, they’ve overcome all but the diehard skeptic criticism. In the past, case studies were considered a method of last resort, only to be used if no other alternative existed.
But now, there is a better understanding and acceptance of the potential case studies offer as the opportunity to use knowledge to formulate hypotheses, establish determinations off of findings, and then turn those results into a generalization that can benefit society.
The use of case studies as a methodology in research allows the researcher to obtain a holistic review of a subject. An entire picture is given, rather than a small idea. With this larger understanding, the researcher can thoroughly build information on the subject with which to continue exploring smaller details in the midst of the situation.
With case studies, researchers have the opportunity to evaluate and understand a wide range of perspectives, reducing the potential for bias to exist. As long as a diverse study is performed with a wide pool of participants, no one single individual can determine the outcome.
The need for case studies in social sciences to postulate and prevent societal issues has gradually seen this practice become its own methodology.
Publish Your Findings With Impactio
Social scientists often find their work scrutinized on a deeper level than other experts. To ensure your work is as professional as possible, use Impactio when you publish.
Impactio is an all-in-one platform used by scholars around the world to compile their findings into one program. With Impactio , you can display your research efforts and achievements on a single platform. When you’re ready, turn the results into professional PDF documents or web pages and share them with your audience or the wide network of other experts in the Impactio community!
- Afghanistan
- Åland Islands
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bolivia (Plurinational State of)
- Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bouvet Island
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- Brunei Darussalam
- Burkina Faso
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Congo (Democratic Republic of the)
- Cook Islands
- Côte d'Ivoire
- Curacao !Curaçao
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands (Malvinas)
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- French Southern Territories
- Guinea-Bissau
- Heard Island and McDonald Islands
- Iran (Islamic Republic of)
- Isle of Man
- Korea (Democratic Peoples Republic of)
- Korea (Republic of)
- Lao People's Democratic Republic
- Liechtenstein
- Marshall Islands
- Micronesia (Federated States of)
- Moldova (Republic of)
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- North Macedonia
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Palestine, State of
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Puerto Rico
- Russian Federation
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Martin (French part)
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Sierra Leone
- Sint Maarten (Dutch part)
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- South Sudan
- Svalbard and Jan Mayen
- Switzerland
- Syrian Arab Republic
- Tanzania, United Republic of
- Timor-Leste
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
- United States of America
- United States Minor Outlying Islands
- Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of)
- Virgin Islands (British)
- Virgin Islands (U.S.)
- Wallis and Futuna
- Western Sahara
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
The purpose of a field report in the social sciences is to describe the deliberate observation of people, places, and/or events and to analyze what has been observed in order to identify and categorize common themes in relation to the research problem underpinning the study. The content represents the researcher's interpretation of meaning found in data that has been gathered during one or more observational events.
Flick, Uwe. The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Data Collection . London: SAGE Publications, 2018; Lofland, John, David Snow, Leon Anderson, and Lyn H. Lofland. Analyzing Social Settings: A Guide to Qualitative Observation and Analysis. Long Grove, IL: Waveland Press, 2022; Baker, Lynda. "Observation: A Complex Research Method." Library Trends 55 (Summer 2006): 171-189.; Kellehear, Allan. The Unobtrusive Researcher: A Guide to Methods . New York: Routledge, 2020.
How to Approach Writing a Field Report
How to Begin
Field reports are most often assigned in disciplines of the applied social sciences [e.g., social work, anthropology, gerontology, criminal justice, education, law, the health care services] where it is important to build a bridge of relevancy between the theoretical concepts learned in the classroom and the practice of actually doing the work you are being taught to do. Field reports are also common in certain science disciplines [e.g., geology] but these reports are organized differently and serve a different purpose than what is described below.
Professors will assign a field report with the intention of improving your understanding of key theoretical concepts by applying methods of careful and structured observation of, and reflection about, people, places, or phenomena existing in their natural settings. Field reports facilitate the development of data collection techniques and observation skills and they help you to understand how theory applies to real world situations. Field reports are also an opportunity to obtain evidence through methods of observing professional practice that contribute to or challenge existing theories.
We are all observers of people, their interactions, places, and events; however, your responsibility when writing a field report is to conduct research based on data generated by the act of designing a specific study, deliberate observation, synthesis of key findings, and interpretation of their meaning.
When writing a field report you need to:
- Systematically observe and accurately record the varying aspects of a situation . Always approach your field study with a detailed protocol about what you will observe, where you should conduct your observations, and the method by which you will collect and record your data.
- Continuously analyze your observations . Always look for the meaning underlying the actions you observe. Ask yourself: What's going on here? What does this observed activity mean? What else does this relate to? Note that this is an on-going process of reflection and analysis taking place for the duration of your field research.
- Keep the report’s aims in mind while you are observing . Recording what you observe should not be done randomly or haphazardly; you must be focused and pay attention to details. Enter the observation site [i.e., "field"] with a clear plan about what you are intending to observe and record in relation to the research problem while, at the same time, being prepared to adapt to changing circumstances as they may arise.
- Consciously observe, record, and analyze what you hear and see in the context of a theoretical framework . This is what separates data gatherings from reporting. The theoretical framework guiding your field research should determine what, when, and how you observe and act as the foundation from which you interpret your findings in relation to the underlying assumptions embedded in the theoretical framework .
Techniques to Record Your Observations Although there is no limit to the type of data gathering techniques you can use, these are the most frequently used methods:
Note Taking This is the most common and easiest method of recording your observations. Tips for taking notes include: organizing some shorthand symbols beforehand so that recording basic or repeated actions does not impede your ability to observe, using many small paragraphs, which reflect changes in activities, who is talking, etc., and, leaving space on the page so you can write down additional thoughts and ideas about what’s being observed, any theoretical insights, and notes to yourself that are set aside for further investigation. See drop-down tab for additional information about note-taking.
Photography With the advent of smart phones, an almost unlimited number of high quality photographs can be taken of the objects, events, and people observed during a field study. Photographs can help capture an important moment in time as well as document details about the space where your observation takes place. Taking a photograph can save you time in documenting the details of a space that would otherwise require extensive note taking. However, be aware that flash photography could undermine your ability to observe unobtrusively so assess the lighting in your observation space; if it's too dark, you may need to rely on taking notes. Also, you should reject the idea that photographs represent some sort of "window into the world" because this assumption creates the risk of over-interpreting what they show. As with any product of data gathering, you are the sole instrument of interpretation and meaning-making, not the object itself. Video and Audio Recordings Video or audio recording your observations has the positive effect of giving you an unfiltered record of the observation event. It also facilitates repeated analysis of your observations. This can be particularly helpful as you gather additional information or insights during your research. However, these techniques have the negative effect of increasing how intrusive you are as an observer and will often not be practical or even allowed under certain circumstances [e.g., interaction between a doctor and a patient] and in certain organizational settings [e.g., a courtroom]. Illustrations/Drawings This does not refer to an artistic endeavor but, rather, refers to the possible need, for example, to draw a map of the observation setting or illustrating objects in relation to people's behavior. This can also take the form of rough tables, charts, or graphs documenting the frequency and type of activities observed. These can be subsequently placed in a more readable format when you write your field report. To save time, draft a table [i.e., columns and rows] on a separate piece of paper before an observation if you know you will be entering data in that way.
NOTE: You may consider using a laptop or other electronic device to record your notes as you observe, but keep in mind the possibility that the clicking of keys while you type or noises from your device can be obtrusive, whereas writing your notes on paper is relatively quiet and unobtrusive. Always assess your presence in the setting where you're gathering the data so as to minimize your impact on the subject or phenomenon being studied.
ANOTHER NOTE: Techniques of deliberate observation and data gathering are not innate skills; they are skills that must be learned and practiced in order to achieve proficiency. Before your first observation, practice the technique you plan to use in a setting similar to your study site [e.g., take notes about how people choose to enter checkout lines at a grocery store if your research involves examining the choice patterns of unrelated people forced to queue in busy social settings]. When the act of data gathering counts, you'll be glad you practiced beforehand.
YET ANOTHER NOTE: An issue rarely discussed in the literature about conducting field research is whether you should move around the study site while observing or remaining situated in one place. Moving around can be intrusive, but it facilitates observing people's behavior from multiple vectors. However, if you remain in one place throughout the observation [or during each observation], you will eventually blend into the background and diminish the chance of unintentionally influencing people's behavior. If the site has a complex set of interactions or interdependent activities [e.g., a play ground], consider moving around; if the study site is relatively fixed [e.g., a classroom], then consider staying in one place while observing.
Examples of Things to Document While Observing
- Physical setting . The characteristics of an occupied space and the human use of the place where the observation(s) are being conducted.
- Objects and material culture . This refers to the presence, placement, and arrangement of objects that impact the behavior or actions of those being observed. If applicable, describe the cultural artifacts representing the beliefs [i.e., the values, ideas, attitudes, and assumptions] of the individuals you are observing [e.g., the choice of particular types of clothing in the observation of family gatherings during culturally specific holidays].
- Use of language . Don't just observe but listen to what is being said, how is it being said, and the tone of conversations among participants.
- Behavior cycles . This refers to documenting when and who performs what behavior or task and how often they occur. Record at which stage this behavior is occurring within the setting.
- The order in which events unfold . Note sequential patterns of behavior or the moment when actions or events take place and their significance. Also, be prepared to note moments that diverge from these sequential patterns of behavior or actions.
- Physical characteristics of subjects. If relevant, document personal characteristics of individuals being observed. Note that, unless this data can be verified in interviews or from documentary evidence, you should only focus on characteristics that can be clearly observed [e.g., clothing, physical appearance, body language].
- Expressive body movements . This would include things like body posture or facial expressions. Note that it may be relevant to also assess whether expressive body movements support or contradict the language used in conversation [e.g., detecting sarcasm].
Brief notes about all of these examples contextualize your observations; however, your observation notes will be guided primarily by your theoretical framework, keeping in mind that your observations will feed into and potentially modify or alter these frameworks.
Sampling Techniques
Sampling refers to the process used to select a portion of the population for study . Qualitative research, of which observation is one method of data gathering, is generally based on non-probability and purposive sampling rather than probability or random approaches characteristic of quantitatively-driven studies. Sampling in observational research is flexible and often continues until no new themes emerge from the data, a point referred to as data saturation.
All sampling decisions are made for the explicit purpose of obtaining the richest possible source of information to answer the research questions. Decisions about sampling assumes you know what you want to observe, what behaviors are important to record, and what research problem you are addressing before you begin the study. These questions determine what sampling technique you should use, so be sure you have adequately answered them before selecting a sampling method.
Ways to sample when conducting an observation include:
- Ad Libitum Sampling -- this approach is not that different from what people do at the zoo; they observe whatever seems interesting at the moment. There is no organized system of recording the observations; you just note whatever seems relevant at the time. The advantage of this method is that you are often able to observe relatively rare or unusual behaviors that might be missed by more deliberately designed sampling methods. This method is also useful for obtaining preliminary observations that can be used to develop your final field study. Problems using this method include the possibility of inherent bias toward conspicuous behaviors or individuals, thereby missing mundane or repeated patterns of behavior, and that you may miss brief interactions in social settings.
- Behavior Sampling -- this involves watching the entire group of subjects and recording each occurrence of a specific behavior of interest and with reference to which individuals were involved. The method is useful in recording rare behaviors missed by other sampling methods and is often used in conjunction with focal or scan methods [see below]. However, sampling can be biased towards particular conspicuous behaviors.
- Continuous Recording -- provides a faithful record of behavior including frequencies, durations, and latencies [the time that elapses between a stimulus and the response to it]. This is a very demanding method because you are trying to record everything within the setting and, thus, measuring reliability may be sacrificed. In addition, durations and latencies are only reliable if subjects remain present throughout the collection of data. However, this method facilitates analyzing sequences of behaviors and ensures obtaining a wealth of data about the observation site and the people within it. The use of audio or video recording is most useful with this type of sampling.
- Focal Sampling -- this involves observing one individual for a specified amount of time and recording all instances of that individual's behavior. Usually you have a set of predetermined categories or types of behaviors that you are interested in observing [e.g., when a teacher walks around the classroom] and you keep track of the duration of those behaviors. This approach doesn't tend to bias one behavior over another and provides significant detail about a individual's behavior. However, with this method, you likely have to conduct a lot of focal samples before you have a good idea about how group members interact. It can also be difficult within certain settings to keep one individual in sight for the entire period of the observation without being intrusive.
- Instantaneous Sampling -- this is where observation sessions are divided into short intervals divided by sample points. At each sample point the observer records if predetermined behaviors of interest are taking place. This method is not effective for recording discrete events of short duration and, frequently, observers will want to record novel behaviors that occur slightly before or after the point of sampling, creating a sampling error. Though not exact, this method does give you an idea of durations and is relatively easy to do. It is also good for recording behavior patterns occurring at a specific instant, such as, movement or body positions.
- One-Zero Sampling -- this is very similar to instantaneous sampling, only the observer records if the behaviors of interest have occurred at any time during an interval instead of at the instant of the sampling point. The method is useful for capturing data on behavior patterns that start and stop repeatedly and rapidly, but that last only for a brief period of time. The disadvantage of this approach is that you get a dimensionless score for an entire recording session, so you only get one one data point for each recording session.
- Scan Sampling -- this method involves taking a census of the entire observed group at predetermined time periods and recording what each individual is doing at that moment. This is useful for obtaining group behavioral data and allows for data that are evenly representative across individuals and periods of time. On the other hand, this method may be biased towards more conspicuous behaviors and you may miss a lot of what is going on between observations, especially rare or unusual behaviors. It is also difficult to record more than a few individuals in a group setting without missing what each individual is doing at each predetermined moment in time [e.g., children sitting at a table during lunch at school]. The use of audio or video recording is useful with this type of sampling.
Alderks, Peter. Data Collection. Psychology 330 Course Documents. Animal Behavior Lab. University of Washington; Emerson, Robert M. Contemporary Field Research: Perspectives and Formulations . 2nd ed. Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland Press, 2001; Emerson, Robert M. et al. “Participant Observation and Fieldnotes.” In Handbook of Ethnography . Paul Atkinson et al., eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2001), 352-368; Emerson, Robert M. et al. Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes . 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2011; Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Hazel, Spencer. "The Paradox from Within: Research Participants Doing-Being-Observed." Qualitative Research 16 (August 2016): 446-457; Pace, Tonio. Writing Field Reports. Scribd Online Library; Presser, Jon and Dona Schwartz. “Photographs within the Sociological Research Process.” In Image-based Research: A Sourcebook for Qualitative Researchers . Jon Prosser, editor (London: Falmer Press, 1998), pp. 115-130; Pyrczak, Fred and Randall R. Bruce. Writing Empirical Research Reports: A Basic Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences . 5th ed. Glendale, CA: Pyrczak Publishing, 2005; Report Writing. UniLearning. University of Wollongong, Australia; Wolfinger, Nicholas H. "On Writing Fieldnotes: Collection Strategies and Background Expectancies.” Qualitative Research 2 (April 2002): 85-95; Writing Reports. Anonymous. The Higher Education Academy.
Structure and Writing Style
How you choose to format your field report is determined by the research problem, the theoretical framework that is driving your analysis, the observations that you make, and/or specific guidelines established by your professor. Since field reports do not have a standard format, it is worthwhile to determine from your professor what the preferred structure and organization should be before you begin to write. Note that field reports should be written in the past tense. With this in mind, most field reports in the social sciences include the following elements:
I. Introduction The introduction should describe the research problem, the specific objectives of your research, and the important theories or concepts underpinning your field study. The introduction should describe the nature of the organization or setting where you are conducting the observation, what type of observations you have conducted, what your focus was, when you observed, and the methods you used for collecting the data. Collectively, this descriptive information should support reasons why you chose the observation site and the people or events within it. You should also include a review of pertinent literature related to the research problem, particularly if similar methods were used in prior studies. Conclude your introduction with a statement about how the rest of the paper is organized.
II. Description of Activities
Your readers only knowledge and understanding of what happened will come from the description section of your report because they were not witnesses to the situation, people, or events that you are writing about. Given this, it is crucial that you provide sufficient details to place the analysis that will follow into proper context; don't make the mistake of providing a description without context. The description section of a field report is similar to a well written piece of journalism. Therefore, a useful approach to systematically describing the varying aspects of an observed situation is to answer the "Five W’s of Investigative Reporting." As Dubbels notes [p. 19], these are:
- What -- describe what you observed. Note the temporal, physical, and social boundaries you imposed to limit the observations you made. What were your general impressions of the situation you were observing. For example, as a student teacher, what is your impression of the application of iPads as a learning device in a history class; as a cultural anthropologist, what is your impression of women's participation in a Native American religious ritual?
- Where -- provide background information about the setting of your observation and, if necessary, note important material objects that are present that help contextualize the observation [e.g., arrangement of computers in relation to student engagement with the teacher].
- When -- record factual data about the day and the beginning and ending time of each observation. Note that it may also be necessary to include background information or key events which impact upon the situation you were observing [e.g., observing the ability of teachers to re-engage students after coming back from an unannounced fire drill].
- Who -- note background and demographic information about the individuals being observed e.g., age, gender, ethnicity, and/or any other variables relevant to your study]. Record who is doing what and saying what, as well as, who is not doing or saying what. If relevant, be sure to record who was missing from the observation.
- Why -- why were you doing this? Describe the reasons for selecting particular situations to observe. Note why something happened. Also note why you may have included or excluded certain information.
III. Interpretation and Analysis
Always place the analysis and interpretations of your field observations within the larger context of the theoretical assumptions and issues you described in the introduction. Part of your responsibility in analyzing the data is to determine which observations are worthy of comment and interpretation, and which observations are more general in nature. It is your theoretical framework that allows you to make these decisions. You need to demonstrate to the reader that you are conducting the field work through the eyes of an informed viewer and from the perspective of a casual observer.
Here are some questions to ask yourself when analyzing your observations:
- What is the meaning of what you have observed?
- Why do you think what you observed happened? What evidence do you have for your reasoning?
- What events or behaviors were typical or widespread? If appropriate, what was unusual or out of the ordinary? How were they distributed among categories of people?
- Do you see any connections or patterns in what you observed?
- Why did the people you observed proceed with an action in the way that they did? What are the implications of this?
- Did the stated or implicit objectives of what you were observing match what was achieved?
- What were the relative merits of the behaviors you observed?
- What were the strengths and weaknesses of the observations you recorded?
- Do you see connections between what you observed and the findings of similar studies identified from your review of the literature?
- How do your observations fit into the larger context of professional practice? In what ways have your observations possibly changed or affirmed your perceptions of professional practice?
- Have you learned anything from what you observed?
NOTE: Only base your interpretations on what you have actually observed. Do not speculate or manipulate your observational data to fit into your study's theoretical framework.
IV. Conclusion and Recommendations
The conclusion should briefly recap of the entire study, reiterating the importance or significance of your observations. Avoid including any new information. You should also state any recommendations you may have based on the results of your study. Be sure to describe any unanticipated problems you encountered and note the limitations of your study. The conclusion should not be more than two or three paragraphs.
V. Appendix
This is where you would place information that is not essential to explaining your findings, but that supports your analysis [especially repetitive or lengthy information], that validates your conclusions, or that contextualizes a related point that helps the reader understand the overall report. Examples of information that could be included in an appendix are figures/tables/charts/graphs of results, statistics, pictures, maps, drawings, or, if applicable, transcripts of interviews. There is no limit to what can be included in the appendix or its format [e.g., a DVD recording of the observation site], provided that it is relevant to the study's purpose and reference is made to it in the report. If information is placed in more than one appendix ["appendices"], the order in which they are organized is dictated by the order they were first mentioned in the text of the report.
VI. References
List all sources that you consulted and obtained information from while writing your field report. Note that field reports generally do not include further readings or an extended bibliography. However, consult with your professor concerning what your list of sources should be included and be sure to write them in the preferred citation style of your discipline or is preferred by your professor [i.e., APA, Chicago, MLA, etc.].
Alderks, Peter. Data Collection. Psychology 330 Course Documents. Animal Behavior Lab. University of Washington; Dubbels, Brock R. Exploring the Cognitive, Social, Cultural, and Psychological Aspects of Gaming and Simulations . Hershey, PA: IGI Global, 2018; Emerson, Robert M. Contemporary Field Research: Perspectives and Formulations . 2nd ed. Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland Press, 2001; Emerson, Robert M. et al. “Participant Observation and Fieldnotes.” In Handbook of Ethnography . Paul Atkinson et al., eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2001), 352-368; Emerson, Robert M. et al. Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes . 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2011; Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Pace, Tonio. Writing Field Reports. Scribd Online Library; Pyrczak, Fred and Randall R. Bruce. Writing Empirical Research Reports: A Basic Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences . 5th ed. Glendale, CA: Pyrczak Publishing, 2005; Report Writing. UniLearning. University of Wollongong, Australia; Wolfinger, Nicholas H. "On Writing Fieldnotes: Collection Strategies and Background Expectancies.” Qualitative Research 2 (April 2002): 85-95; Writing Reports. Anonymous. The Higher Education Academy.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Study
- Next: About Informed Consent >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

Case Study Examples Social Work: Real-Life Insights

In the field of social work, case studies play a crucial role in educating and training future professionals. These real-life scenarios provide valuable insights into the varied issues that social workers confront and the strategies they employ to address them.
Table of Contents
In this article, we will explore case study examples in social work, focusing on how social workers assess and intervene in different situations. We will also discuss the importance of ethical considerations and the impact of intervention strategies on outcomes.
What is a Case Study?
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a particular individual, family, or community, aiming to understand the complexities of their situation and the challenges they face. It provides an opportunity for social workers to apply theories, skills, ethics, and supervision to real-life scenarios.
By examining case studies, social workers can learn from effective intervention strategies, ethical considerations, and the outcomes achieved.

Importance of Case Studies in Social Work Education
Case studies are an integral part of social work education programs, both at the undergraduate and master’s levels. They offer invaluable examples of real-life practice in diverse settings, including public child welfare.
These case studies provide detailed information that allows students to explore various aspects of social work practice, such as assessment, intervention, and collaboration with other professionals.

Assessing and Intervening in Child Welfare Cases
Child welfare presents a complex and challenging area for social workers. Case studies in this context shed light on the core competencies required to address the needs of children and families.
For example, one case study examines the experience of caring for a child with a mental health problem and the impact it has on the caregiver’s education.
The child welfare core competencies are based on underlying assumptions and skills that all social work graduates should possess. Through case studies, students can gain a deeper understanding of these competencies and how to apply them in practice.
They provide a bridge between theory and real-life situations, preparing students for the complex challenges they may face in their careers.

Real-Life Examples: Integrating Child Welfare Practice
The Real Cases Project is a comprehensive collection of case studies illustrating the integration of child welfare practice across the social work curriculum. This resource includes the full text of the case studies, teaching guides, and additional resources for social work educators and students.
It offers a unique opportunity to explore the application of social work theories, skills, ethics, and supervision in real-life scenarios.

Learning from Case Studies
By examining case study examples, social workers can gain valuable insights into various issues they may encounter in their practice. These examples offer an opportunity to learn about effective intervention strategies, ethical considerations, and the outcomes achieved.
They provide a platform for reflection, discussion, and continued professional development.

Recommended Product: Social Work Case Studies: Concentration Year
One highly recommended product for social work students and professionals is the book “Social Work Case Studies: Concentration Year.” This comprehensive resource includes a collection of case studies that cover a wide range of social work concentrations. It offers detailed analyses of complex scenarios, providing valuable learning opportunities and practical insights.
In conclusion, case study examples are a vital tool in social work education and practice. They allow social workers to gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of real-life situations, develop effective intervention strategies, and consider the ethical implications of their work.
By learning from these examples, social workers can enhance their skills and contribute to positive outcomes for individuals, families, and communities. For further exploration of case studies in social work, we highly recommend the book “Social Work Case Studies: Concentration Year” as a valuable resource.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you write a good case study for social work, what are the principles for writing social work case studies, how do you write a case study report in social work, can you provide an example of case work in social work, what is the relationship between social case work and group work, related posts.
Eiue Hotel Collection Bed Pillows – Super Soft Down Alternative Microfiber Filled – 2 Pack Queen Size, 20 X 30 Inches
Cute Garden Decor Metal Garden Sign Outdoor, 12″ X 8″, (263) – A Must-have For Gardening Enthusiasts!
Google L5 Salary Germany: Everything You Need To Know
Google Software Engineer Salary Germany Compared: Insights And Analysis
Google Software Engineer Salary Germany: What To Expect
Google Software Engineer Salary: The Ultimate Guide
Google Senior Software Engineer Salary: What You Need To Know
Amazon Senior Software Engineer Salary: What You Need To Know

Lora Turner
Lora Turner is an Experienced HR professional worked with the large organizations and holding 15 years of experience dealing with employee benefits. She holds expertise in simplifying the leave for the employee benefits. Contact us at: [email protected]
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


SOCIAL CASE STUDY REPORT SEPTEMBER 26, 2016 IDENTIFYING INFORMATION

Related Papers
International Journal of Social Science and Humanities Research
Argel B . Masanda
This study investigated the children"s experiences of the familial stresses as a gauge of looking into their family dynamics. Primary emphasis was focused on the children"s psychological functioning in the context of their experienced stresses in their family. Creative expressive approaches were utilized to facilitate data gathering from 3 abused children who were housed in a government facility. The 3 girls suffered physical and/or sexual abuse, neglect and/or abandonment or the combinations of those. Qualitative analyses (genogram and thematic analysis) were employed to make sense of the data. Results suggested that children"s experiences of societal stresses can be ranged from intrafamilial (from "within" the family) to extrafamilial (from "without" the family). In spite of being under too much stress, children were observed to be authentic "family mirrors": they can precisely measure and showcase the family"s dynamics including emotional patterns and overall functioning in an effortless and subconscious ways. This suggested that their experiences of stress seemed to be subliminal-they have a natural way of making sense of their experiences through their sheer ability to catch and understand the emotional contents of the messages they receive from the world, albeit uncritically. Hence, children"s behavior (or misbehavior) and ineffective ways of coping from their stressful experiences, tend to be a viable measure in appraising their family"s dynamics. Furthermore, it was likewise conclusive that marital relationship seemed to be a pivotal point in the maintenance of the family equilibrium.
The law of succession in Roman Egypt: Siblings and Non-siblings disputes over inheritance In: Proceedings of the 28th International Congress of Papyrology Barcelona 1-6 August 2016, Scripta Orientalia 3, Barcelona 2019, 475-483.
Marianna Thoma
Papyrus documents give evidence that in the multicultural society of Roman Egypt all children regardless their legal status inherited their father and after the SC Orfitianum of AD 178 children of Roman status could inherit their mothers. However, numerous petitions prove that various conflicts arose between family members especially about the division of parental property. For example, in P.Lond. II 177 (1st c. AD) the eldest sister of a family with her husband grabbed the paternal furniture and utensils, which also belonged to her brothers in terms of their father’s will. The conflicts between an heir and his guardian about the disposition of the inheritance are also common. In P.Oxy. XVII 2133 (4th c. AD) a daughter complains to the prefect, because her uncle-guardian deprived her of her share to the paternal inheritance in the form of dowry. While family conflicts about intestate succession and wills were a common phenomenon, the papyri give also evidence for violations of inherited property by non siblings. PSI X 1102 (3rd c. AD) preserves an important dispute about property rights between two children and three men who have stolen the property of the children’s father who died intestate. Furthermore, in P.Oxy.VII 1067 (3rd c. AD) Helen blaims her brother Petechon for neglecting the burial of their third brother and as a result a non-sibling woman inherited him. The purpose of the proposed paper is to discuss the various cases of conflicts over an inheritance between siblings and non-siblings. My interest will focus on the arguments and legal grounds used by the defendants in each case discussed with special attention paid to the differences between property claimed coming from intestate succession and testamentary disposition. By studying the various petitions to the judges, private letters or settlements and lawsuit proceedings I aim to investigate the legal and social ways in which people in Roman Egypt could protect their parental inheritance both from persons inside and outside the family.
Dominador N Marcaida Jr.
This is an updated copy of the profile for Barangay Marupit, Camaligan, Camarines Sur earlier published here at Academia.edu containing additional information and revisions that arose from later research by the author.
A socio-economic profile of Barangay Marupit, Camaligan, Camarines Sur, Philippines.
Princess Platero
Penn Thrasher
Rik Hoekstra
The cacicazgo, or indigenous lordship, was a pivotal institution in colonial Mexican Indian pueblos. Caciques, or Indian nobles, played a role, both in the largely indigenous world of the pueblo and in the regional economy that was dominated by Spaniards. This subject of this essay is the analysis of the evolution and daily operation and of a cacicazgo from the Indian settlement of Tepexí de la Seda near the city of Puebla de los Ángeles and the life of its caciques in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.In the sixteenth century the cacicazgo was in upheaval because of discord between the cacicazgos and their dependent Indians. A number of long-running accounts from the 1620s record in detail the daily operations of the cacicazgo of Doña Ana de Santa Bárbara of the Mendoza family, thus illustrating how caciques negotiated their positions and coped with their lives and the changes in it.
This is an updated copy of the profile for Barangay Sto. Tomas, Camaligan, Camarines Sur earlier published here at Academia.edu containing additional information and revisions that arose from later research by the author.
Irish Genealogist 13/4, 288-310
Paul MacCotter
Philippine Political Science Journal
Rizal Buendia
RELATED PAPERS
Delor Lauchang
Tessa Verhallen , Stef Slembrouck
Cid Pabalan
Historical Research
Richard Mortimer
Alexjander Santisteban
lanie laurio
Nottingham Medieval Studies
Katharine Keats-Rohan
erim kutsal
Columbia University Press
Charles Lindholm
Bryan Christian L.Alarcon
Legis Pangilinan
Abbas Bhuiya
Jayhze Dizon
European Review of History-revue Europeenne D Histoire
Simona Feci
Benedetta Borello , giulia Calvi , Amelia Almorza Hidalgo
Susan Baidawi
Neslie Agoto
Chizoro Okeke
Luca Biloni
Nobuhiko Fuwa
BEYOND BORDERS: Reflections on the Resistance & Resilience Among Immigrant Youth and Families
Daniela Domínguez
Junette Stronge
Abigeil Carlos
Journal of the Cork Historical and Archaeological Society
Sonja Tiernan
Rev. Antonio Manaytay
Bo Malmberg
Foundations
Rosie Bevan
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Writing a Case Study
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Reading Research Effectively
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Bibliography
The term case study refers to both a method of analysis and a specific research design for examining a problem, both of which are used in most circumstances to generalize across populations. This tab focuses on the latter--how to design and organize a research paper in the social sciences that analyzes a specific case.
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or among more than two subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in this writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a single case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- Does the case represent an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- Does the case provide important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- Does the case challenge and offer a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in practice. A case may offer you an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to the study a case in order to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- Does the case provide an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings in order to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- Does the case offer a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for exploratory research that points to a need for further examination of the research problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of Uganda. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a particular village can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community throughout rural regions of east Africa. The case could also point to the need for scholars to apply feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation.
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work. In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What was I studying? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why was this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the research problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would include summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to study the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in the context of explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular subject of analysis to study and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that frames your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; c) what were the consequences of the event.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experience he or she has had that provides an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of his/her experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using him or her as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, cultural, economic, political, etc.], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, why study Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research reveals Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks from overseas reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should be linked to the findings from the literature review. Be sure to cite any prior studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for investigating the research problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is more common to combine a description of the findings with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps to support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings It is important to remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations for the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and needs for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) restate the main argument supported by the findings from the analysis of your case; 2) clearly state the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in and your professor's preferences, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented applied to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were on social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood differently than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis.
Case Studies . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical (context-dependent) knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Reviewing Collected Essays
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2023 10:50 AM
- URL: https://libguides.pointloma.edu/ResearchPaper
- Content Writing Services
- Get in Touch
Why Are Case Studies Important? Top 4 Reasons
Updated April 2024: Has a boss or colleague ever asked you, “Why are case studies so important?” This is a question all SaaS marketers must be able to answer, especially when it comes time to create your marketing budget for the year.
SaaS case studies are still the #1 marketing tactic to increase sales
The importance of a case study can’t be underestimated. For the second year in a row, SaaS marketers ranked case studies the #1 most effective marketing tactic to increase sales —ahead of general website content, SEO, blog posts, social media and other marketing tactics.
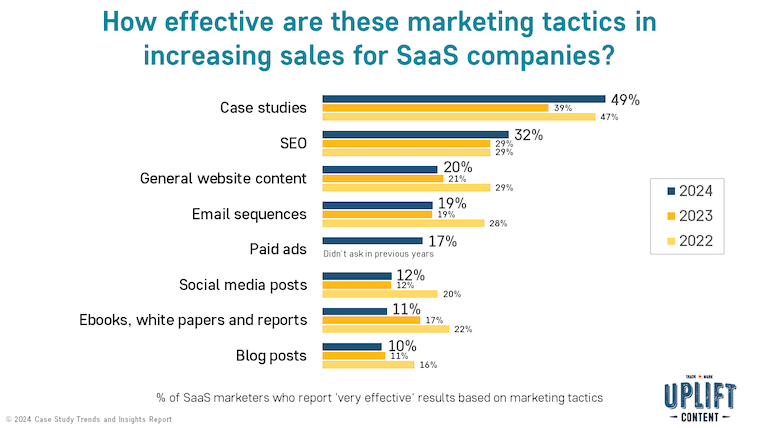
These metrics come from the 115 SaaS marketers we surveyed for our 2024 Customer Story Trends & Insights Report . (We’d encourage you to check out the report.)
Importance of a case study is undeniable
Why are case studies so important? What is the need and significance of a case study? Case studies are top-tier marketing tools for SaaS companies to showcase the value of their products to potential customers, helping to drive sales and revenue.
Customers are our best marketers. I love getting to know our customers through these stories, especially because documenting their successes helps advance their careers and gives more senior leaders the chance to celebrate their teams.

Why are case studies important in marketing?
Case studies are essentially a play-by-play of how your customer recognized that they had a challenge they needed to overcome, why they chose you, what products or services you provided, and how those products or services helped them solve their challenge.
And what makes case studies even more valuable? They’re a great investment because case studies can be repurposed so heavily —everything from PDFs and videos to infographics to social.
In this post, we’ll demonstrate the importance of a case study in business and discuss the top 4 advantages of using case studies in your marketing mix.
Need a hand with writing case studies? We are a SaaS content marketing agency that specializes in writing case studies for companies like ClickUp, WalkMe and LeanData. Check out our case study writing services .
What are 4 advantages of case studies?
1. case studies demonstrate your expertise in your niche.

As a SaaS marketer, your job is to know how to produce a business case study in a way that makes your product or service stand out among your competitors.
Creating case studies is an effective way to capture the attention of buyers in your industry because the content—including the products, services and use cases covered in the piece—will be highly relevant to your target audience and will therefore have a strong chance of resonating with them.
If you’re still wondering, “Why are case studies important?”, then put yourself in your buyer’s shoes. Say you’re evaluating several different customer relationship management (CRM) platforms. All three vendors have an eye-catching website with informative and clever product copy, but only one has a repository of case studies that illustrate how its clients have landed 50% more sales since they’ve implemented this particular CRM. Sounds like a winner to us (and it demonstrates case study importance)!
Case studies are important because our prospects want to see that we’ve helped customers who are in the same industry and have similar pain points. Reference calls are helpful, but it’s important to have stories that sales folks can share easily.

2. Case studies provide social proof in an original way

What is the importance of a case study? Well, nearly 90% of consumers read product reviews before they make a purchase, which means gathering and publishing social proof is a crucial activity for your SaaS company.
Changing consumer behavior is another reason why case studies are important. Case studies give your readers what they’re looking for, which is confirmation from other B2B buyers just like them that your products and services are the real deal.
Another advantage of case studies is that by nature, they’re original stories about individuals with specific challenges and goals. Knowing how to write a case study that goes beyond generic product reviews is critical.
When writing a case study, dig deep into everything from how your team helps customers implement your software to what your customer’s future use cases could include. This type of content gives your prospect thorough insight into what it’s like to use your products and work with your company.
Case studies offer social proof for how we provide value to our customers. Our sales team uses our case studies to build credibility and offer “proof points” for why (and how) Crossbeam can solve their problems.

3. Case studies help your SaaS company close sales

Let’s quickly recap the last 2 points:
1) Case studies capture your buyers’ attention with highly relevant content that positions your SaaS company as an expert in the products or services you deliver.
2) Case studies also build trust by sharing social proof in an interesting format that uses storytelling to weave a narrative. For those two reasons, case studies are fantastic content marketing tools to help you close sales.
In addition, especially if your offerings are complex, it’s essential to help potential customers understand how your software will meet their needs. Case studies give you an opportunity to explain— with real-world examples and visual aids —the more complicated aspects of your products and services.
Case studies are important because they provide real-life examples of positive customer outcomes and sentiment—a critical part of gaining buy-in from prospects during a sales cycle.

4. Strengthen customer relationships

If you’re hesitant to ask your customers to participate in case studies, you’re not alone. It’s normal to feel like you might be imposing on a customer by asking them to take time out of their busy schedule for an interview, but chances are they’d be happy to help you craft a case study to illustrate your mutual success working together.
When it comes to the question, “Why are case studies important?”, one of the best answers is that they can help you strengthen customer relationships by letting your customers know you believe they have a valuable story. This gesture of goodwill can increase customer retention, which can in turn grow your SaaS company’s revenue by as much as 95% .
Case studies are important because they give you the opportunity to celebrate an existing customer, which in and of itself is of immense value. Secondarily, for both customers and prospects alike, they always prefer to “see someone like them” rather than just hear you spew what-ifs at them.

Need a hand with your case studies ?
Now that you understand why case studies are so important, it’s time to take action—and we can help.
As a SaaS content marketing agency , we write case studies for high-growth B2B SaaS companies like ClickUp, WalkMe and Okta. Check out our case study writing service then get in touch.

As the founder of Uplift Content, Emily leads her team in creating done-for-you case studies, ebooks and blog posts for high-growth SaaS companies like ClickUp, Calendly and WalkMe. Connect with Emily on Linkedin
Sign up for the Content Huddle newsletter
Learn from Emily’s 17 years of aha moments, mistakes, observations, and insights—and find out how you can apply these lessons to your own marketing efforts.
You can unsubscribe any time. Visit our Terms of Use for information on our privacy practices.
Advertisement
Supported by
Columbia Bars Student Protester Who Said ‘Zionists Don’t Deserve to Live’
After video surfaced on social media, the student, Khymani James, said on Friday that his comments were wrong.
- Share full article

By Katherine Rosman
Katherine Rosman reported from the campus of Columbia University.
Columbia University announced on Friday that it had barred from its campus a leader in the pro-Palestinian student protest encampment who declared on video in January that “Zionists don’t deserve to live.”
Video of the incendiary comments resurfaced online Thursday evening, forcing the school to again confront an issue at the core of the conflict rippling across campuses nationwide: the tension between pro-Palestinian activism and antisemitism.
The student, Khymani James, made the comments during and after a disciplinary hearing with Columbia administrators that he recorded and then posted on Instagram.
The hearing, conducted by an administrator of the university’s Center for Student Success and Intervention , was focused on an earlier comment he shared on social media, in which he discussed fighting a Zionist. “I don’t fight to injure or for there to be a winner or a loser, I fight to kill,” he wrote.
A Columbia administrator asked, “Do you see why that is problematic in any way?”
Mr. James replied, “No.”
He also compared Zionists to white supremacists and Nazis. “These are all the same people,” he said. “The existence of them and the projects they have built, i.e. Israel, it’s all antithetical to peace. It’s all antithetical to peace. And so, yes, I feel very comfortable, very comfortable, calling for those people to die.”
And, Mr. James said, “Be grateful that I’m not just going out and murdering Zionists.”
In announcing their decision to bar Mr. James from campus, the university did not make clear if he had been suspended or permanently expelled.
Other protest groups condemned the comments and pointed out that one student’s statements do not reflect the tenor of the movement as a whole. But the remarks were widely shared on social media and go to the heart of a question that has animated criticism of the protests: How much of the movement in support of the Palestinian people in Gaza is tainted by antisemitism?
College administrators have pledged to Congress that they will take swift action against hateful attacks on Jewish students and antisemitic threats. “I promise you, from the messages I’m hearing from students, they are getting the message that violations of our policies will have consequences,” Columbia’s president, Nemat Shafik, told congressional leaders last week.
On Friday, a school spokesman said, “Calls of violence and statements targeted at individuals based on their religious, ethnic or national identity are unacceptable and violate university policy.”
Brian Cohen, the executive director of Columbia/Barnard Hillel, the center for Jewish campus life, described Mr. James’s statements as dangerous. “I think students who make comments like that don’t belong on campus,” he said.
Noa Fay, 23, a first-year student at the School of International and Public Affairs, said she was shocked by the “unabashedness” of the video. “It’s one of the more blatant examples of antisemitism and, just, rhetoric that is inconsistent with the values that we have at Columbia,” she said. “I was mostly very surprised to see that it was just so out in the open.”
Early Friday morning, Mr. James posted a statement on social media addressing his comments. “What I said was wrong,” he wrote. “Every member of our community deserves to feel safe without qualification.” He noted that he made these comments in January before he become involved with the protest movement and added that the leaders of the student protests did not condone the comments. “I agree with their assessment,” he wrote.
Mr. James did not respond to a request for comment, and student protesters declined to address the matter at a news conference on the Columbia campus Friday afternoon.
But in an interview earlier in the week, Mr. James drew a distinction between the ideas of anti-Zionism, which describes opposition to the Jewish state of Israel, and antisemitism. “There is a difference,” he said. “We’ve always had Jewish people as part of our community where they have expressed themselves, they feel safe, and they feel loved. And we want all people to feel safe in this encampment. We are a multiracial, multigenerational group of people.”
Sophie Ellman-Golan, the communications director of Jews for Racial & Economic Justice and a Barnard College graduate, said she found Mr. James’s comments awful and upsetting but she added that it was clear his views did not represent those of the other campus protesters.
Ms. Ellman-Golan said that in her 10 years as an organizer, there were always people who tried to inject hateful messages into public action, and that such messages tended to be amplified by those looking to smear entire movements.
“For people who want to believe that characterization, that our movements are inevitably and permanently hostile to us as Jews, this is catnip, right?” she said. “It’s irresistible.”
A spokeswoman for Jewish Voice for Peace, a pro-Palestinian advocacy group, said in a statement that the organization was glad Mr. James had realized he was wrong and had acknowledged that his words were harmful.
“We believe that all people have the capacity to transform — many of our own members once supported Israel’s violence against Palestinians,” the statement said, adding that “within the movement we are committed to holding one another accountable to respecting the dignity of all human beings.”
One student protester who is Jewish and who has spoken to Mr. James about the video said she believed he was committed to nonviolence and acceptance of all people. She said that he had reacted emotionally after being trolled online and that it was unfair that his decision to vent his frustration on social media was being used against him.
It remains unclear how many students are directing the Columbia protests, but Mr. James, 20, emerged as a public face of the demonstrations this week when he led a news conference to assert the demands the movement is making of the Columbia administration.
“This encampment — a peaceful, student-led demonstration — is part of the larger movement of Palestinian liberation,” Mr. James said at the conference.
In his biography on X, he calls himself an “anticapitalist” and “anti-imperialist.”
Mr. James was raised in Boston, and graduated from Boston Latin Academy, according to a 2021 interview with The Bay State Banner.
He told The Banner that at Columbia, he planned to study economics and political science. “The ultimate destination is Congress,” he said.
Eryn Davis , Stephanie Saul , Olivia Bensimon and Claire Fahy contributed reporting.
Katherine Rosman covers newsmakers, power players and individuals making an imprint on New York City. More about Katherine Rosman
Our Coverage of the U.S. Campus Protests
News and Analysis
Before counterprotesters violently attacked pro-Palestinian demonstrators, the University of California, Los Angeles, thought a tolerant approach to protests would work .
Police officers in riot gear arrested pro-Palestinian demonstrators at Fordham University’s Manhattan campus , the third university in New York City to face mass arrests.
President Biden, who has personally stayed relatively quiet during the protests, plans to speak out against antisemitism at a ceremony hosted by the U.S. Holocaust Memorial Museum.
Seeing Links to a Global Struggle: In many student protesters’ eyes, the war in Gaza is linked to other issues , such as policing, mistreatment of Indigenous people, racism and climate change.
Ending the Unrest: Across the nation, universities are looking for ways to quell the protests . Columbia has taken the spotlight after calling in the police twice , while Brown chose a different path .
A 63-Year-Old Career Activist: Videos show Lisa Fithian, whom the police called a “professional agitator,” working alongside protesters at Columbia who stormed Hamilton Hall.
A Makeshift Fortress: With wood pallets piled at the entrance, dozens of pro-Palestinian activists have been holed up in Portland State University’s library. Here’s a look inside .
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Reproductive rights in America
What's at stake as the supreme court hears idaho case about abortion in emergencies.

Selena Simmons-Duffin

The Supreme Court will hear another case about abortion rights on Wednesday. Protestors gathered outside the court last month when the case before the justices involved abortion pills. Tom Brenner for The Washington Post/Getty Images hide caption
The Supreme Court will hear another case about abortion rights on Wednesday. Protestors gathered outside the court last month when the case before the justices involved abortion pills.
In Idaho, when a pregnant patient has complications, abortion is only legal to prevent the woman's death. But a federal law known as EMTALA requires doctors to provide "stabilizing treatment" to patients in the emergency department.
The Biden administration sees that as a direct conflict, which is why the abortion issue is back – yet again – before the Supreme Court on Wednesday.
The case began just a few weeks after the justices overturned Roe v. Wade in 2022, when the federal Justice Department sued Idaho , arguing that the court should declare that "Idaho's law is invalid" when it comes to emergency abortions because the federal emergency care law preempts the state's abortion ban. So far, a district court agreed with the Biden administration, an appeals court panel agreed with Idaho, and the Supreme Court allowed the strict ban to take effect in January when it agreed to hear the case.

Supreme Court allows Idaho abortion ban to be enacted, first such ruling since Dobbs
The case, known as Moyle v. United States (Mike Moyle is the speaker of the Idaho House), has major implications on everything from what emergency care is available in states with abortion bans to how hospitals operate in Idaho. Here's a summary of what's at stake.
1. Idaho physicians warn patients are being harmed
Under Idaho's abortion law , the medical exception only applies when a doctor judges that "the abortion was necessary to prevent the death of the pregnant woman." (There is also an exception to the Idaho abortion ban in cases of rape or incest, only in the first trimester of the pregnancy, if the person files a police report.)
In a filing with the court , a group of 678 physicians in Idaho described cases in which women facing serious pregnancy complications were either sent home from the hospital or had to be transferred out of state for care. "It's been just a few months now that Idaho's law has been in effect – six patients with medical emergencies have already been transferred out of state for [pregnancy] termination," Dr. Jim Souza, chief physician executive of St. Luke's Health System in Idaho, told reporters on a press call last week.
Those delays and transfers can have consequences. For example, Dr. Emily Corrigan described a patient in court filings whose water broke too early, which put her at risk of infection. After two weeks of being dismissed while trying to get care, the patient went to Corrigan's hospital – by that time, she showed signs of infection and had lost so much blood she needed a transfusion. Corrigan added that without receiving an abortion, the patient could have needed a limb amputation or a hysterectomy – in other words, even if she didn't die, she could have faced life-long consequences to her health.
Attorneys for Idaho defend its abortion law, arguing that "every circumstance described by the administration's declarations involved life-threatening circumstances under which Idaho law would allow an abortion."
Ryan Bangert, senior attorney for the Christian legal powerhouse Alliance Defending Freedom, which is providing pro-bono assistance to the state of Idaho, says that "Idaho law does allow for physicians to make those difficult decisions when it's necessary to perform an abortion to save the life of the mother," without waiting for patients to become sicker and sicker.
Still, Dr. Sara Thomson, an OB-GYN in Boise, says difficult calls in the hospital are not hypothetical or even rare. "In my group, we're seeing this happen about every month or every other month where this state law complicates our care," she says. Four patients have sued the state in a separate case arguing that the narrow medical exception harmed them.
"As far as we know, we haven't had a woman die as a consequence of this law, but that is really on the top of our worry list of things that could happen because we know that if we watch as death is approaching and we don't intervene quickly enough, when we decide finally that we're going to intervene to save her life, it may be too late," she says.
2. Hospitals are closing units and struggling to recruit doctors
Labor and delivery departments are expensive for hospitals to operate. Idaho already had a shortage of providers, including OB-GYNS. Hospital administrators now say the Idaho abortion law has led to an exodus of maternal care providers from the state, which has a population of 2 million people.
Three rural hospitals in Idaho have closed their labor-and-delivery units since the abortion law took effect. "We are seeing the expansion of what's called obstetrical deserts here in Idaho," said Brian Whitlock, president and CEO of the Idaho Hospital Association.
Since Idaho's abortion law took effect, nearly one in four OB-GYNs have left the state or retired, according to a report from the Idaho Physician Well-Being Action Collaborative. The report finds the loss of doctors who specialize in high-risk pregnancies is even more extreme – five of nine full time maternal-fetal medicine specialists have left Idaho.
Administrators say they aren't able to recruit new providers to fill those positions. "Since [the abortion law's] enactment, St. Luke's has had markedly fewer applicants for open physician positions, particularly in obstetrics. And several out-of-state candidates have withdrawn their applications upon learning of the challenges of practicing in Idaho, citing [the law's] enactment and fear of criminal penalties," reads an amicus brief from St. Luke's health system in support of the federal government.
"Prior to the abortion decision, we already ranked 50th in number of physicians per capita – we were already a strained state," says Thomson, the doctor in Boise. She's experienced the loss of OB-GYN colleagues first hand. "I had a partner retire right as the laws were changing and her position has remained open – unfilled now for almost two years – so my own personal group has been short-staffed," she says.
ADF's Bangert says he's skeptical of the assertion that the abortion law is responsible for this exodus of doctors from Idaho. "I would be very surprised if Idaho's abortion law is the sole or singular cause of any physician shortage," he says. "I'm very suspicious of any claims of causality."
3. Justices could weigh in on fetal "personhood"
The state of Idaho's brief argues that EMTALA actually requires hospitals "to protect and care for an 'unborn child,'" an argument echoed in friend-of-the-court briefs from the U.S. Conference of Catholic Bishops and a group of states from Indiana to Wyoming that also have restrictive abortion laws. They argue that abortion can't be seen as a stabilizing treatment if one patient dies as a result.
Thomson is also Catholic, and she says the idea that, in an emergency, she is treating two patients – the fetus and the mother – doesn't account for clinical reality. "Of course, as obstetricians we have a passion for caring for both the mother and the baby, but there are clinical situations where the mom's health or life is in jeopardy, and no matter what we do, the baby is going to be lost," she says.
The Idaho abortion law uses the term "unborn child" as opposed to the words "embryo" or "fetus" – language that implies the fetus has the same rights as other people.

Shots - Health News
The science of ivf: what to know about alabama's 'extrauterine children' ruling.
Mary Ziegler , a legal historian at University of California - Davis, who is writing a book on fetal personhood, describes it as the "North Star" of the anti-abortion rights movement. She says this case will be the first time the Supreme Court justices will be considering a statute that uses that language.
"I think we may get clues about the future of bigger conflicts about fetal personhood," she explains, depending on how the justices respond to this idea. "Not just in the context of this statute or emergency medical scenarios, but in the context of the Constitution."
ADF has dismissed the idea that this case is an attempt to expand fetal rights. "This case is, at root, a question about whether or not the federal government can affect a hostile takeover of the practice of medicine in all 50 states by misinterpreting a long-standing federal statute to contain a hidden nationwide abortion mandate," Bangert says.
4. The election looms large
Ziegler suspects the justices will allow Idaho's abortion law to remain as is. "The Supreme Court has let Idaho's law go into effect, which suggests that the court is not convinced by the Biden administration's arguments, at least at this point," she notes.

Trump backed a federal abortion ban as president. Now, he says he wouldn't sign one
Whatever the decision, it will put abortion squarely back in the national spotlight a few months before the November election. "It's a reminder on the political side of things, that Biden and Trump don't really control the terms of the debate on this very important issue," Zielger observes. "They're going to be things put on everybody's radar by other actors, including the Supreme Court."
The justices will hear arguments in the case on Wednesday morning. A decision is expected by late June or early July.
Correction April 23, 2024
An earlier version of this story did not mention the rape and incest exception to Idaho's abortion ban. A person who reports rape or incest to police can end a pregnancy in Idaho in the first trimester.
- Abortion rights
- Supreme Court
Create an account
Create a free IEA account to download our reports or subcribe to a paid service.
Trends in electric cars
- Executive summary
Electric car sales
Electric car availability and affordability.
- Electric two- and three-wheelers
- Electric light commercial vehicles
- Electric truck and bus sales
- Electric heavy-duty vehicle model availability
- Charging for electric light-duty vehicles
- Charging for electric heavy-duty vehicles
- Battery supply and demand
- Battery prices
- Electric vehicle company strategy and market competition
- Electric vehicle and battery start-ups
- Vehicle outlook by mode
- Vehicle outlook by region
- The industry outlook
- Light-duty vehicle charging
- Heavy-duty vehicle charging
- Battery demand
- Electricity demand
- Oil displacement
- Well-to-wheel greenhouse gas emissions
- Lifecycle impacts of electric cars
Cite report
IEA (2024), Global EV Outlook 2024 , IEA, Paris https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2024, Licence: CC BY 4.0
Share this report
- Share on Twitter Twitter
- Share on Facebook Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn LinkedIn
- Share on Email Email
- Share on Print Print
Report options
Nearly one in five cars sold in 2023 was electric.
Electric car sales neared 14 million in 2023, 95% of which were in China, Europe and the United States
Almost 14 million new electric cars 1 were registered globally in 2023, bringing their total number on the roads to 40 million, closely tracking the sales forecast from the 2023 edition of the Global EV Outlook (GEVO-2023). Electric car sales in 2023 were 3.5 million higher than in 2022, a 35% year-on-year increase. This is more than six times higher than in 2018, just 5 years earlier. In 2023, there were over 250 000 new registrations per week, which is more than the annual total in 2013, ten years earlier. Electric cars accounted for around 18% of all cars sold in 2023, up from 14% in 2022 and only 2% 5 years earlier, in 2018. These trends indicate that growth remains robust as electric car markets mature. Battery electric cars accounted for 70% of the electric car stock in 2023.
Global electric car stock, 2013-2023
While sales of electric cars are increasing globally, they remain significantly concentrated in just a few major markets. In 2023, just under 60% of new electric car registrations were in the People’s Republic of China (hereafter ‘China’), just under 25% in Europe, 2 and 10% in the United States – corresponding to nearly 95% of global electric car sales combined. In these countries, electric cars account for a large share of local car markets: more than one in three new car registrations in China was electric in 2023, over one in five in Europe, and one in ten in the United States. However, sales remain limited elsewhere, even in countries with developed car markets such as Japan and India. As a result of sales concentration, the global electric car stock is also increasingly concentrated. Nevertheless, China, Europe and the United States also represent around two-thirds of total car sales and stocks, meaning that the EV transition in these markets has major repercussions in terms of global trends.
In China, the number of new electric car registrations reached 8.1 million in 2023, increasing by 35% relative to 2022. Increasing electric car sales were the main reason for growth in the overall car market, which contracted by 8% for conventional (internal combustion engine) cars but grew by 5% in total, indicating that electric car sales are continuing to perform as the market matures. The year 2023 was the first in which China’s New Energy Vehicle (NEV) 3 industry ran without support from national subsidies for EV purchases, which have facilitated expansion of the market for more than a decade. Tax exemption for EV purchases and non-financial support remain in place, after an extension , as the automotive industry is seen as one of the key drivers of economic growth. Some province-led support and investment also remains in place and plays an important role in China’s EV landscape. As the market matures, the industry is entering a phase marked by increased price competition and consolidation. In addition, China exported over 4 million cars in 2023, making it the largest auto exporter in the world, among which 1.2 million were EVs. This is markedly more than the previous year – car exports were almost 65% higher than in 2022, and electric car exports were 80% higher. The main export markets for these vehicles were Europe and countries in the Asia Pacific region, such as Thailand and Australia.
In the United States, new electric car registrations totalled 1.4 million in 2023, increasing by more than 40% compared to 2022. While relative annual growth in 2023 was slower than in the preceding two years, demand for electric cars and absolute growth remained strong. The revised qualifications for the Clean Vehicle Tax Credit, alongside electric car price cuts, meant that some popular EV models became eligible for credit in 2023. Sales of the Tesla Model Y, for example, increased 50% compared to 2022 after it became eligible for the full USD 7 500 tax credit. Overall, the new criteria established by the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) appear to have supported sales in 2023, despite earlier concerns that tighter domestic content requirements for EV and battery manufacturing could create immediate bottlenecks or delays, such as for the Ford F-150 Lightning . As of 2024, new guidance for the tax credits means the number of eligible models has fallen to less than 30 from about 45, 4 including several trim levels of the Tesla Model 3 becoming ineligible. However, in 2023 and 2024, leasing business models enable electric cars to qualify for the tax credits even if they do not fully meet the requirements, as leased cars can qualify for a less strict commercial vehicle tax credit and these tax credit savings can be passed to lease-holders. Such strategies have also contributed to sustained electric car roll-out.
In Europe, new electric car registrations reached nearly 3.2 million in 2023, increasing by almost 20% relative to 2022. In the European Union, sales amounted to 2.4 million, with similar growth rates. As in China, the high rates of electric car sales seen in Europe suggest that growth remains robust as markets mature, and several European countries reached important milestones in 2023. Germany, for example, became the third country after China and the United States to record half a million new battery electric car registrations in a single year, with 18% of car sales being battery electric (and another 6% plug-in hybrid).
However, the phase-out of several purchase subsidies in Germany slowed overall EV sales growth. At the start of 2023, PHEV subsidies were phased out, resulting in lower PHEV sales compared to 2022, and in December 2023, all EV subsidies ended after a ruling on the Climate and Transformation Fund. In Germany, the sales share for electric cars fell from 30% in 2022 to 25% in 2023. This had an impact on the overall electric car sales share in the region. In the rest of Europe, however, electric car sales and their sales share increased. Around 25% of all cars sold in France and the United Kingdom were electric, 30% in the Netherlands, and 60% in Sweden. In Norway, sales shares increased slightly despite the overall market contracting, and its sales share remains the highest in Europe, at almost 95%.
Electric car registrations and sales share in China, United States and Europe, 2018-2023
Sales in emerging markets are increasing, albeit from a low base, led by southeast asia and brazil.
Electric car sales continued to increase in emerging market and developing economies (EMDEs) outside China in 2023, but they remained low overall. In many cases, personal cars are not the most common means of passenger transport, especially compared with shared vans and minibuses, or two- and three-wheelers (2/3Ws), which are more prevalent and more often electrified, given their relative accessibility and affordability. The electrification of 2/3Ws and public or shared mobility will be key to achieve emissions reductions in such cases (see later sections in this report). While switching from internal combustion engine (ICE) to electric cars is important, the effect on overall emissions differs depending on the mode of transport that is displaced. Replacing 2/3Ws, public and shared mobility or more active forms of transport with personal cars may not be desirable in all cases.
In India, electric car registrations were up 70% year-on-year to 80 000, compared to a growth rate of under 10% for total car sales. Around 2% of all cars sold were electric. Purchase incentives under the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME II) scheme, supply-side incentives under the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, tax benefits and the Go Electric campaign have all contributed to fostering demand in recent years. A number of new models also became popular in 2023, such as Mahindra’s XUV400, MG’s Comet, Citroën’s e-C3, BYD’s Yuan Plus, and Hyundai’s Ioniq 5, driving up growth compared to 2022. However, if the forthcoming FAME III scheme includes a subsidy reduction, as has been speculated in line with lower subsidy levels in the 2024 budget, future growth could be affected. Local carmakers have thus far maintained a strong foothold in the market, supported by advantageous import tariffs , and account for 80% of electric car sales in cumulative terms since 2010, led by Tata (70%) and Mahindra (10%).
In Thailand, electric car registrations more than quadrupled year-on-year to nearly 90 000, reaching a notable 10% sales share – comparable to the share in the United States. This is all the more impressive given that overall car sales in the country decreased from 2022 to 2023. New subsidies, including for domestic battery manufacturing, and lower import and excise taxes, combined with the growing presence of Chinese carmakers , have contributed to rapidly increasing sales. Chinese companies account for over half the sales to date, and they could become even more prominent given that BYD plans to start operating EV production facilities in Thailand in 2024, with an annual production capacity of 150 000 vehicles for an investment of just under USD 500 million . Thailand aims to become a major EV manufacturing hub for domestic and export markets, and is aiming to attract USD 28 billion in foreign investment within 4 years, backed by specific incentives to foster investment.
In Viet Nam, after an exceptional 2022 for the overall car market, car sales contracted by 25% in 2023, but electric car sales still recorded unprecedented growth: from under 100 in 2021, to 7 000 in 2022, and over 30 000 in 2023, reaching a 15% sales share. Domestic front-runner VinFast, established in 2017, accounted for nearly all domestic sales. VinFast also started selling electric sports utility vehicles (SUVs) in North America in 2023, as well as developing manufacturing facilities in order to unlock domestic content-linked subsidies under the US IRA. VinFast is investing around USD 2 billion and targets an annual production of 150 000 vehicles in the United States by 2025. The company went public in 2023, far exceeding expectations with a debut market valuation of around USD 85 billion, well beyond General Motors (GM) (USD 46 billion), Ford (USD 48 billion) or BMW (USD 68 billion), before it settled back down around USD 20 billion by the end of the year. VinFast also looks to enter regional markets, such as India and the Philippines .
In Malaysia, electric car registrations more than tripled to 10 000, supported by tax breaks and import duty exemptions, as well as an acceleration in charging infrastructure roll-out. In 2023, Mercedes-Benz marketed the first domestically assembled EV, and both BYD and Tesla also entered the market.
In Latin America, electric car sales reached almost 90 000 in 2023, with markets in Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica and Mexico leading the region. In Brazil, electric car registrations nearly tripled year-on-year to more than 50 000, a market share of 3%. Growth in Brazil was underpinned by the entry of Chinese carmakers, such as BYD with its Song and Dolphin models, Great Wall with its H6, and Chery with its Tiggo 8, which immediately ranked among the best-selling models in 2023. Road transport electrification in Brazil could bring significant climate benefits given the largely low-emissions power mix, as well as reducing local air pollution. However, EV adoption has been slow thus far, given the national prioritisation of ethanol-based fuels since the late 1970s as a strategy to maintain energy security in the face of oil shocks. Today, biofuels are important alternative fuels available at competitive cost and aligned with the existing refuelling infrastructure. Brazil remains the world’s largest producer of sugar cane, and its agribusiness represents about one-fourth of GDP. At the end of 2023, Brazil launched the Green Mobility and Innovation Programme , which provides tax incentives for companies to develop and manufacture low-emissions road transport technology, aggregating to more than BRA 19 billion (Brazilian reals) (USD 3.8 billion) over the 2024-2028 period. Several major carmakers already in Brazil are developing hybrid ethanol-electric models as a result. China’s BYD and Great Wall are also planning to start domestic manufacturing, counting on local battery metal deposits, and plan to sell both fully electric and hybrid ethanol-electric models. BYD is investing over USD 600 million in its electric car plant in Brazil – its first outside Asia – for an annual capacity of 150 000 vehicles. BYD also partnered with Raízen to develop charging infrastructure in eight Brazilian cities starting in 2024. GM, on the other hand, plans to stop producing ICE (including ethanol) models and go fully electric, notably to produce for export markets. In 2024, Hyundai announced investments of USD 1.1 billion to 2032 to start local manufacturing of electric, hybrid and hydrogen cars.
In Mexico, electric car registrations were up 80% year-on-year to 15 000, a market share just above 1%. Given its proximity to the United States, Mexico’s automotive market is already well integrated with North American partners, and benefits from advantageous trade agreements, large existing manufacturing capacity, and eligibility for subsidies under the IRA. As a result, local EV supply chains are developing quickly, with expectations that this will spill over into domestic markets. Tesla, Ford, Stellantis, BMW, GM, Volkswagen (VW) and Audi have all either started manufacturing or announced plans to manufacture EVs in Mexico. Chinese carmakers such as BYD, Chery and SAIC are also considering expanding to Mexico. Elsewhere in the region, Colombia and Costa Rica are seeing increasing electric car sales, with around 6 000 and 5 000 in 2023, respectively, but sales remain limited in other Central and South American countries.
Throughout Africa, Eurasia and the Middle East, electric cars are still rare, accounting for less than 1% of total car sales. However, as Chinese carmakers look for opportunities abroad, new models – including those produced domestically – could boost EV sales. For example, in Uzbekistan , BYD set up a joint venture with UzAuto Motors in 2023 to produce 50 000 electric cars annually, and Chery International established a partnership with ADM Jizzakh. This partnership has already led to a steep increase in electric car sales in Uzbekistan, reaching around 10 000 in 2023. In the Middle East, Jordan boasts the highest electric car sales share, at more than 45%, supported by much lower import duties relative to ICE cars, followed by the United Arab Emirates, with 13%.
Strong electric car sales in the first quarter of 2024 surpass the annual total from just four years ago
Electric car sales remained strong in the first quarter of 2024, surpassing those of the same period in 2023 by around 25% to reach more than 3 million. This growth rate was similar to the increase observed for the same period in 2023 compared to 2022. The majority of the additional sales came from China, which sold about half a million more electric cars than over the same period in 2023. In relative terms, the most substantial growth was observed outside of the major EV markets, where sales increased by over 50%, suggesting that the transition to electromobility is picking up in an increasing number of countries worldwide.
Quarterly electric car sales by region, 2021-2024
From January to March of this year, nearly 1.9 million electric cars were sold in China, marking an almost 35% increase compared to sales in the first quarter of 2023. In March, NEV sales in China surpassed a share of 40% in overall car sales for the first time, according to retail sales reported by the China Passenger Car Association. As witnessed in 2023, sales of plug-in hybrid electric cars are growing faster than sales of pure battery electric cars. Plug-in hybrid electric car sales in the first quarter increased by around 75% year-on-year in China, compared to just 15% for battery electric car sales, though the former started from a lower base.
In Europe, the first quarter of 2024 saw year-on-year growth of over 5%, slightly above the growth in overall car sales and thereby stabilising the EV sales share at a similar level as last year. Electric car sales growth was particularly high in Belgium, where around 60 000 electric cars were sold, almost 35% more than the year before. However, Belgium represents less than 5% of total European car sales. In the major European markets – France, Germany, Italy and the United Kingdom (together representing about 60% of European car sales) – growth in electric car sales was lower. In France, overall EV sales in the first quarter grew by about 15%, with BEV sales growth being higher than for PHEVs. While this is less than half the rate as over the same period last year, total sales were nonetheless higher and led to a slight increase in the share of EVs in total car sales. The United Kingdom saw similar year-on-year growth (over 15%) in EV sales as France, about the same rate as over the same period last year. In Germany, where battery electric car subsidies ended in 2023, sales of electric cars fell by almost 5% in the first quarter of 2024, mainly as a result of a 20% year-on-year decrease in March. The share of EVs in total car sales was therefore slightly lower than last year. As in China, PHEV sales in both Germany and the United Kingdom were stronger than BEV sales. In Italy, sales of electric cars in the first three months of 2024 were more than 20% lower than over the same period in 2023, with the majority of the decrease taking place in the PHEV segment. However, this trend could be reversed based on the introduction of a new incentive scheme , and if Chinese automaker Chery succeeds in appealing to Italian consumers when it enters the market later this year.
In the United States, first-quarter sales reached around 350 000, almost 15% higher than over the same period the year before. As in other major markets, the sales growth of PHEVs was even higher, at 50%. While the BEV sales share in the United States appears to have fallen somewhat over the past few months, the sales share of PHEVs has grown.
In smaller EV markets, sales growth in the first months of 2024 was much higher, albeit from a low base. In January and February, electric car sales almost quadrupled in Brazil and increased more than sevenfold in Viet Nam. In India, sales increased more than 50% in the first quarter of 2024. These figures suggest that EVs are gaining momentum across diverse markets worldwide.
Since 2021, first-quarter electric car sales have typically accounted for 15-20% of the total global annual sales. Based on this observed trend, coupled with policy momentum and the seasonality that EV sales typically experience, we estimate that electric car sales could reach around 17 million in 2024. This indicates robust growth for a maturing market, with 2024 sales to surpass those of 2023 by more than 20% and EVs to reach a share in total car sales of more than one-fifth.
Electric car sales, 2012-2024
The majority of the additional 3 million electric car sales projected for 2024 relative to 2023 are from China. Despite the phase-out of NEV purchase subsidies last year, sales in China have remained robust, indicating that the market is maturing. With strong competition and relatively low-cost electric cars, sales are to grow by almost 25% in 2024 compared to last year, reaching around 10 million. If confirmed, this figure will come close to the total global electric car sales in 2022. As a result, electric car sales could represent around 45% of total car sales in China over 2024.
In 2024, electric car sales in the United States are projected to rise by 20% compared to the previous year, translating to almost half a million more sales, relative to 2023. Despite reporting of a rocky end to 2023 for electric cars in the United States, sales shares are projected to remain robust in 2024. Over the entire year, around one in nine cars sold are expected to be electric.
Based on recent trends, and considering that tightening CO 2 targets are due to come in only in 2025, the growth in electric car sales in Europe is expected to be the lowest of the three largest markets. Sales are projected to reach around 3.5 million units in 2024, reflecting modest growth of less than 10% compared to the previous year. In the context of a generally weak outlook for passenger car sales, electric cars would still represent about one in four cars sold in Europe.
Outside of the major EV markets, electric car sales are anticipated to reach the milestone of over 1 million units in 2024, marking a significant increase of over 40% compared to 2023. Recent trends showing the success of both homegrown and Chinese electric carmakers in Southeast Asia underscore that the region is set to make a strong contribution to the sales of emerging EV markets (see the section on Trends in the electric vehicle industry). Despite some uncertainty surrounding whether India’s forthcoming FAME III scheme will include subsidies for electric cars, we expect sales in India to remain robust, and to experience around 50% growth compared to 2023. Across all regions outside the three major EV markets, electric car sales are expected to represent around 5% of total car sales in 2024, which – considering the high growth rates seen in recent years – could indicate that a tipping point towards global mass adoption is getting closer.
There are of course downside risks to the 2024 outlook for electric car sales. Factors such as high interest rates and economic uncertainty could potentially reduce the growth of global electric car sales in 2024. Other challenges may come from the IRA restrictions on US electric car tax incentives, and the tightening of technical requirements for EVs to qualify for the purchase tax exemption in China. However, there are also upside potentials to consider. New markets may open up more rapidly than anticipated, as automakers expand their EV operations and new entrants compete for market share. This could lead to accelerated growth in electric car sales globally, surpassing the initial estimations.
More electric models are becoming available, but the trend is towards larger ones
The number of available electric car models nears 600, two-thirds of which are large vehicles and SUVs
In 2023, the number of available models for electric cars increased 15% year-on-year to nearly 590, as carmakers scaled up electrification plans, seeking to appeal to a growing consumer base. Meanwhile, the number of fully ICE models (i.e. excluding hybrids) declined for the fourth consecutive year, at an average of 2%. Based on recent original equipment manufacturer (OEM) announcements, the number of new electric car models could reach 1 000 by 2028. If all announced new electric models actually reach the market, and if the number of available ICE car models continues to decline by 2% annually, there could be as many electric as ICE car models before 2030.
As reported in GEVO-2023, the share of small and medium electric car models is decreasing among available electric models: in 2023, two-thirds of the battery-electric models on the market were SUVs, 5 pick-up trucks or large cars. Just 25% of battery electric car sales in the United States were for small and medium models, compared to 40% in Europe and 50% in China. Electric cars are following the same trend as conventional cars, and getting bigger on average. In 2023, SUVs, pick-up trucks and large models accounted for 65% of total ICE car sales worldwide, and more than 80% in the United States, 60% in China and 50% in Europe.
Several factors underpin the increase in the share of large models. Since the 2010s, conventional SUVs in the United States have benefited from less stringent tailpipe emissions rules than smaller models, creating an incentive for carmakers to market more vehicles in that segment. Similarly, in the European Union, CO 2 targets for passenger cars have included a compromise on weight, allowing CO 2 leeway for heavier vehicles in some cases. Larger vehicles also mean larger margins for carmakers. Given that incumbent carmakers are not yet making a profit on their EV offer in many cases, focusing on larger models enables them to increase their margins. Under the US IRA, electric SUVs can qualify for tax credits as long as they are priced under USD 80 000, whereas the limit stands at USD 55 000 for a sedan, creating an incentive to market SUVs if a greater margin can be gathered. On the demand side, there is now strong willingness to pay for SUVs or large models. Consumers are typically interested in longer-range and larger cars for their primary vehicles, even though small models are more suited to urban use. Higher marketing spend on SUVs compared to smaller models can also have an impact on consumer choices.
The progressive shift towards ICE SUVs has been dramatically limiting fuel savings. Over the 2010-2022 period, without the shift to SUVs, energy use per kilometre could have fallen at an average annual rate 30% higher than the actual rate. Switching to electric in the SUV and larger car segments can therefore achieve immediate and significant CO 2 emissions reductions, and electrification also brings considerable benefits in terms of reducing air pollution and non-tailpipe emissions, especially in urban settings. In 2023, if all ICE and HEV sales of SUVs had instead been BEV, around 770 Mt CO 2 could have been avoided globally over the cars’ lifetimes (see section 10 on lifecycle analysis). This is equivalent to the total road emissions of China in 2023.
Breakdown of battery electric car sales in selected countries and regions by segment, 2018-2023
Nevertheless, from a policy perspective, it is critical to mitigate the negative spillovers associated with an increase in larger electric cars in the fleet.
Larger electric car models have a significant impact on battery supply chains and critical mineral demand. In 2023, the sales-weighted average battery electric SUV in Europe had a battery almost twice as large as the one in the average small electric car, with a proportionate impact on critical mineral needs. Of course, the range of small cars is typically shorter than SUVs and large cars (see later section on ranges). However, when comparing electric SUVs and medium-sized electric cars, which in 2023 offered a similar range, the SUV battery was still 25% larger. This means that if all electric SUVs sold in 2023 had instead been medium-sized cars, around 60 GWh of battery equivalent could have been avoided globally, with limited impact on range. Accounting for the different chemistries used in China, Europe, and the United States, this would be equivalent to almost 6 000 tonnes of lithium, 30 000 tonnes of nickel, almost 7 000 tonnes of cobalt, and over 8 000 tonnes of manganese.
Larger batteries also require more power, or longer charging times. This can put pressure on electricity grids and charging infrastructure by increasing occupancy, which could create issues during peak utilisation, such as at highway charging points at high traffic times.
In addition, larger vehicles also require greater quantities of materials such as iron and steel, aluminium and plastics, with a higher environmental and carbon footprint for materials production, processing and assembly. Because they are heavier, larger models also have higher electricity consumption. The additional energy consumption resulting from the increased mass is mitigated by regenerative braking to some extent, but in 2022, the sales-weighted average electricity consumption of electric SUVs was 20% higher than that of other electric cars. 6
Major carmakers have announced launches of smaller and more affordable electric car models over the past few years. However, when all launch announcements are considered, far fewer smaller models are expected than SUVs, large models and pick-up trucks. Only 25% of the 400+ launches expected over the 2024-2028 period are small and medium models, which represents a smaller share of available models than in 2023. Even in China, where small and medium models have been popular, new launches are typically for larger cars.
Number of available car models in 2023 and expected new ones by powertrain, country or region and segment, 2024-2028
Several governments have responded by introducing policies to create incentives for smaller and lighter passenger cars. In Norway, for example, all cars are subject to a purchase tax based on weight, CO 2 and nitrogen oxides (NO x ) emissions, though electric cars were exempt from the weight-based tax prior to 2023. Any imported cars weighing more than 500 kg must also pay an entry fee for each additional kg. In France, a progressive weight-based tax applies to ICE and PHEV cars weighing above 1 600 kg, with a significant impact on price: weight tax for a Land Rover Defender 130 (2 550 kg) adds up to more than EUR 21 500, versus zero for a Renault Clio (1 100 kg). Battery electric cars have been exempted to date. In February 2024, a referendum held in Paris resulted in a tripling of city parking fees for visiting SUVs, applicable to ICE, hybrid and plug-in hybrid cars above 1 600 kg and battery electric ones above 2 000 kg, in an effort to limit the use of large and/or polluting vehicles. Other examples exist in Estonia, Finland, Switzerland and the Netherlands. A number of policy options may be used, such as caps and fleet averages for vehicle footprint, weight, and/or battery size; access to finance for smaller vehicles; and sustained support for public charging, enabling wider use of shorter-range cars.
Average range is increasing, but only moderately
Concerns about range compared to ICE vehicles, and about the availability of charging infrastructure for long-distance journeys, also contribute to increasing appetite for larger models with longer range.
With increasing battery size and improvements in battery technology and vehicle design, the sales-weighted average range of battery electric cars grew by nearly 75% between 2015 and 2023, although trends vary by segment. The average range of small cars in 2023 – around 150 km – is not much higher than it was in 2015, indicating that this range is already well suited for urban use (with the exception of taxis, which have much higher daily usage). Large, higher-end models already offered higher ranges than average in 2015, and their range has stagnated through 2023, averaging around 360-380 km. Meanwhile, significant improvements have been made for medium-sized cars and SUVs, the range of which now stands around 380 km, whereas it averaged around 150 km for medium cars and 270 km for SUVs in 2015. This is encouraging for consumers looking to purchase an electric car for longer journeys rather than urban use.
Since 2020, growth in the average range of vehicles has been slower than over the 2015-2020 period. This could result from a number of factors, including fluctuating battery prices, carmakers’ attempts to limit additional costs as competition intensifies, and technical constraints (e.g. energy density, battery size). It could also reflect that beyond a certain range at which most driving needs are met, consumers’ willingness to pay for a marginal increase in battery size and range is limited. Looking forward, however, the average range could start increasing again as novel battery technologies mature and prices fall.
More affordable electric cars are needed to reach a mass-market tipping point
An equitable and inclusive transition to electric mobility, both within countries and at the global level, hinges on the successful launch of affordable EVs (including but not limited to electric cars). In this section, we use historic sales and price data for electric and ICE models around the world to examine the total cost of owning an electric car, price trends over time, and the remaining electric premium, by country and vehicle size. 7 Specific models are used for illustration.
Total cost of ownership
Car purchase decisions typically involve consideration of retail price and available subsidies as well as lifetime operating costs, such as fuel costs, insurance, maintenance and depreciation, which together make up the total cost of ownership (TCO). Reaching TCO parity between electric and ICE cars creates important financial incentives to make the switch. This section examines the different components of the TCO, by region and car size.
In 2023, upfront retail prices for electric cars were generally higher than for their ICE equivalents, which increased their TCO in relative terms. On the upside, higher fuel efficiency and lower maintenance costs enable fuel cost savings for electric cars, lowering their TCO. This is especially true in periods when fuel prices are high, in places where electricity prices are not too closely correlated to fossil fuel prices. Depreciation is also a major factor in determining TCO: As a car ages, it loses value, and depreciation for electric cars tends to be faster than for ICE equivalents, further increasing their TCO. Accelerated depreciation could, however, prove beneficial for the development of second-hand markets.
However, the trend towards faster depreciation for electric vehicles might be reversed for multiple reasons. Firstly, consumers are gaining more confidence in electric battery lifetimes, thereby increasing the resale value of EVs. Secondly, strong demand and the positive brand image of some BEV models can mean they hold their value longer, as shown by Tesla models depreciating more slowly than the average petrol car in the United States. Finally, increasing fuel prices in some regions, the roll-out of low-emissions zones that restrict access for the most polluting vehicles, and taxes and parking fees specifically targeted at ICE vehicles could mean they experience faster depreciation rates than EVs in the future. In light of these two possible opposing depreciation trends, the same fixed annual depreciation rate for both BEVs and ICE vehicles has been applied in the following cost of ownership analysis.
Subsidies help lower the TCO of electric cars relative to ICE equivalents in multiple ways. A purchase subsidy lowers the original retail price, thereby lowering capital depreciation over time, and a lower retail price implies lower financing costs through cumulative interest. Subsidies can significantly reduce the number of years required to reach TCO parity between electric and ICE equivalents. As of 2022, we estimate that TCO parity could be reached in most cases in under 7 years in the three major EV markets, with significant variations across different car sizes. In comparison, for models purchased at 2018 prices, TCO parity was much harder to achieve.
In Germany, for example, we estimate that the sales-weighted average price of a medium-sized battery electric car in 2022 was 10-20% more expensive than its ICE equivalent, but 10-20% cheaper in cumulative costs of ownership after 5 years, thanks to fuel and maintenance costs savings. In the case of an electric SUV, we estimate that the average annual operating cost savings would amount to USD 1 800 when compared to the equivalent conventional SUV over a period of 10 years. In the United States, despite lower fuel prices with respect to electricity, the higher average annual mileage results in savings that are close to Germany at USD 1 600 per year. In China, lower annual distance driven reduces fuel cost savings potential, but the very low price of electricity enables savings of about USD 1 000 per year.
In EMDEs, some electric cars can also be cheaper than ICE equivalents over their lifetime. This is true in India , for example, although it depends on the financing instrument. Access to finance is typically much more challenging in EMDEs due to higher interest rates and the more limited availability of cheap capital. Passenger cars have also a significantly lower market penetration in the first place, and many car purchases are made in second-hand markets. Later sections of this report look at markets for used electric cars, as well as the TCO for electric and conventional 2/3Ws in EMDEs, where they are far more widespread than cars as a means of road transport.
Upfront retail price parity
Achieving price parity between electric and ICE cars will be an important tipping point. Even when the TCO for electric cars is advantageous, the upfront retail price plays a decisive role, and mass-market consumers are typically more sensitive to price premiums than wealthier buyers. This holds true not only in emerging and developing economies, which have comparatively high costs of capital and comparatively low household and business incomes, but also in advanced economies. In the United States, for example, surveys suggest affordability was the top concern for consumers considering EV adoption in 2023. Other estimates show that even among SUV and pick-up truck consumers, only 50% would be willing to purchase one above USD 50 000.
In this section, we examine historic price trends for electric and ICE cars over the 2018-2022 period, by country and car size, and for best-selling models in 2023.
Electric cars are generally getting cheaper as battery prices drop, competition intensifies, and carmakers achieve economies of scale. In most cases, however, they remain on average more expensive than ICE equivalents. In some cases, after adjusting for inflation, their price stagnated or even moderately increased between 2018 and 2022.
Larger batteries for longer ranges increase car prices, and so too do the additional options, equipment, digital technology and luxury features that are often marketed on top of the base model. A disproportionate focus on larger, premium models is pushing up the average price, which – added to the lack of available models in second-hand markets (see below) – limits potential to reach mass-market consumers. Importantly, geopolitical tension, trade and supply chain disruptions, increasing battery prices in 2022 relative to 2021, and rising inflation, have also significantly affected the potential for further cost declines.
Competition can also play an important role in bringing down electric car prices. Intensifying competition leads carmakers to cut prices to the minimum profit margin they can sustain, and – if needed – to do so more quickly than battery and production costs decline. For example, between mid-2022 and early-2024, Tesla cut the price of its Model Y from between USD 65 000 and USD 70 000 to between USD 45 000 and USD 55 000 in the United States. Battery prices for such a model dropped by only USD 3 000 over the same period in the United States, suggesting that a profit margin may still be made at a lower price. Similarly, in China, the price of the Base Model Y dropped from CNY 320 000 (Yuan renminbi) (USD 47 000) to CNY 250 000 (USD 38 000), while the corresponding battery price fell by only USD 1 000. Conversely, in cases where electric models remain niche or aimed at wealthier, less price-sensitive early adopters, their price may not fall as quickly as battery prices, if carmakers can sustain greater margins.
Price gap between the sales-weighted average price of conventional and electric cars in selected countries, before subsidy, by size, in 2018 and 2022
In China, where the sales share of electric cars has been high for several years, the sales-weighted average price of electric cars (before purchase subsidy) is already lower than that of ICE cars. This is true not only when looking at total sales, but also at the small cars segment, and is close for SUVs. After accounting for the EV exemption from the 10% vehicle purchase tax, electric SUVs were already on par with conventional ones in 2022, on average.
Electric car prices have dropped significantly since 2018. We estimate that around 55% of the electric cars sold in China in 2022 were cheaper than their average ICE equivalent, up from under 10% in 2018. Given the further price declines between 2022 and 2023, we estimate that this share increased to around 65% in 2023. These encouraging trends suggest that price parity between electric and ICE cars could also be reached in other countries in certain segments by 2030, if the sales share of electric cars continues to grow, and if supporting infrastructure – such as for charging – is sustained.
As reported in detail in GEVO-2023 , China remains a global exception in terms of available inexpensive electric models. Local carmakers already market nearly 50 small, affordable electric car models, many of which are priced under CNY 100 000 (USD 15 000). This is in the same range as best-selling small ICE cars in 2023, which cost from CNY 70 000 to CNY 100 000. In 2022, the best-selling electric car was SAIC’s small Wuling Hongguang Mini EV, which accounted for 10% of all BEV sales. It was priced around CNY 40 000, weighing under 700 kg for a 170-km range. In 2023, however, it was overtaken by Tesla models, among other larger models, as new consumers seek longer ranges and higher-end options and digital equipment.
United States
In the United States, the sales-weighted average price of electric cars decreased over the 2018-2022 period, primarily driven by a considerable drop in the price of Tesla cars, which account for a significant share of sales. The sales-weighted average retail price of electric SUVs fell slightly more quickly than the average SUV battery costs over the same period. The average price of small and medium models also decreased, albeit to a smaller extent.
Across all segments, electric models remained more expensive than conventional equivalents in 2022. However, the gap has since begun to close, as market size increases and competition leads carmakers to cut prices. For example, in 2023-2024, Tesla’s Model 3 could be found in the USD 39 000 to USD 42 000 range, which is comparable to the average price for new ICE cars, and a new Model Y priced under USD 50 000 was launched. Rivian is expecting to launch its R2 SUV in 2026 at USD 45 000, which is much less than previous vehicles. Average price parity between electric and conventional SUVs could be reached by 2030, but it may only be reached later for small and medium cars, given their lower availability and popularity.
Smaller, cheaper electric models have further to go to reach price parity in the United States. We estimate that in 2022, only about 5% of the electric cars sold in the United States were cheaper than their average ICE equivalent. In 2023, the cheapest electric cars were priced around USD 30 000 (e.g. Chevrolet Bolt, Nissan Leaf, Mini Cooper SE). To compare, best-selling small ICE options cost under USD 20 000 (e.g. Kia Rio, Mitsubishi Mirage), and many best-selling medium ICE options between USD 20 000 and USD 25 000 (e.g. Honda Civic, Toyota Corolla, Kia Forte, Hyundai Avante, Nissan Sentra).
Around 25 new all-electric car models are expected in 2024, but only 5 of them are expected below USD 50 000, and none under the USD 30 000 mark. Considering all the electric models expected to be available in 2024, about 75% are priced above USD 50 000, and fewer than 10 under USD 40 000, even after taking into account the USD 7 500 tax credit under the IRA for eligible cars as of February 2024. This means that despite the tax credit, few electric car models directly compete with small mass-market ICE models.
In December 2023, GM stopped production of its best-selling electric car, the Bolt, announcing it would introduce a new version in 2025. The Nissan Leaf (40 kWh) therefore remains the cheapest available electric car in 2024, at just under USD 30 000, but is not yet eligible for IRA tax credits. Ford announced in 2024 that it would move away from large and expensive electric cars as a way to convince more consumers to switch to electric, at the same time as increasing output of ICE models to help finance a transition to electric mobility. In 2024, Tesla announced it would start producing a next-generation, compact and affordable electric car in June 2025, but the company had already announced in 2020 that it would deliver a USD 25 000 model within 3 years. Some micro urban electric cars are already available between USD 5 000 and USD 20 000 (e.g. Arcimoto FUV, Nimbus One), but they are rare. In theory, such models could cover many use cases, since 80% of car journeys in the United States are under 10 miles .
Pricing trends differ across European countries, and typically vary by segment.
In Norway, after taking into account the EV sales tax exemption, electric cars are already cheaper than ICE equivalents across all segments. In 2022, we estimate that the electric premium stood around -15%, and even -30% for medium-sized cars. Five years earlier, in 2018, the overall electric premium was less advantageous, at around -5%. The progressive reintroduction of sales taxes on electric cars may change these estimates for 2023 onwards.
Germany’s electric premium ranks among the lowest in the European Union. Although the sales-weighted average electric premium increased slightly between 2018 and 2022, it stood at 15% in 2022. It is particularly low for medium-sized cars (10-15%) and SUVs (20%), but remains higher than 50% for small models. In the case of medium cars, the sales-weighted average electric premium was as low as EUR 5 000 in 2022. We estimate that in 2022, over 40% of the medium electric cars sold in Germany were cheaper than their average ICE equivalent. Looking at total sales, over 25% of the electric cars sold in 2022 were cheaper than their average ICE equivalent. In 2023, the cheapest models among the best-selling medium electric cars were priced between EUR 22 000 and EUR 35 000 (e.g. MG MG4, Dacia Spring, Renault Megane), far cheaper than the three front-runners priced above EUR 45 000 (VW ID.3, Cupra Born, and Tesla Model 3). To compare, best-selling ICE cars in the medium segment were also priced between EUR 30 000 and EUR 45 000 (e.g. VW Golf, VW Passat Santana, Skoda Octavia Laura, Audi A3, Audi A4). At the end of 2023, Germany phased out its subsidy for electric car purchases, but competition and falling model prices could compensate for this.
In France, the sales-weighted average electric premium stagnated between 2018 and 2022. The average price of ICE cars also increased over the same period, though more moderately than that of electric models. Despite a drop in the price of electric SUVs, which stood at a 30% premium over ICE equivalents in 2022, the former do not account for a high enough share of total electric car sales to drive down the overall average. The electric premium for small and medium cars remains around 40-50%.
These trends mirror those of some of the best-selling models. For example, when adjusting prices for inflation, the small Renault Zoe was sold at the same price on average in 2022-2023 as in 2018-2019, or EUR 30 000 (USD 32 000). It could be found for sale at as low as EUR 25 000 in 2015-2016. The earlier models, in 2015, had a battery size of around 20 kWh, which increased to around 40 kWh in 2018‑2019 and 50 kWh in newer models in 2022-2023. Yet European battery prices fell more quickly than the battery size increased over the same period, indicating that battery size alone does not explain car price dynamics.
In 2023, the cheapest electric cars in France were priced between EUR 22 000 and EUR 30 000 (e.g. Dacia Spring, Renault Twingo E-Tech, Smart EQ Fortwo), while best-selling small ICE models were available between EUR 10 000 and EUR 20 000 (e.g. Renault Clio, Peugeot 208, Citroën C3, Dacia Sandero, Opel Corsa, Skoda Fabia). Since mid-2024, subsidies of up to EUR 4 000 can be granted for electric cars priced under EUR 47 000, with an additional subsidy of up to EUR 3 000 for lower-income households.
In the United Kingdom, the sales-weighted average electric premium shrank between 2018 and 2022, thanks to a drop in prices for electric SUVs, as in the United States. Nonetheless, electric SUVs still stood at a 45% premium over ICE equivalents in 2022, which is similar to the premium for small models but far higher than for medium cars (20%).
In 2023, the cheapest electric cars in the United Kingdom were priced from GBP 27 000 to GBP 30 000 (USD 33 000 to 37 000) (e.g. MG MG4, Fiat 500, Nissan Leaf, Renault Zoe), with the exception of the Smart EQ Fortwo, priced at GBP 21 000. To compare, best-selling small ICE options could be found from GBP 10 000 to 17 000 (e.g. Peugeot 208, Fiat 500, Dacia Sandero) and medium options below GBP 25 000 (e.g. Ford Puma). Since July 2022, there has been no subsidy for the purchase of electric passenger cars.
Elsewhere in Europe, electric cars remain typically much more expensive than ICE equivalents. In Poland , for example, just a few electric car models could be found at prices competitive with ICE cars in 2023, under the PLN 150 000 (Polish zloty) (EUR 35 000) mark. Over 70% of electric car sales in 2023 were for SUVs, or large or more luxurious models, compared to less than 60% for ICE cars.
In 2023, there were several announcements by European OEMs for smaller models priced under EUR 25 000 in the near-term (e.g. Renault R5, Citroën e-C3, Fiat e-Panda, VW ID.2all). There is also some appetite for urban microcars (i.e. L6-L7 category), learning from the success of China’s Wuling. Miniature models bring important benefits if they displace conventional models, helping reduce battery and critical mineral demand. Their prices are often below USD 5 000 (e.g. Microlino, Fiat Topolino, Citroën Ami, Silence S04, Birò B2211).
In Europe and the United States, electric car prices are expected to come down as a result of falling battery prices, more efficient manufacturing, and competition. Independent analyses suggest that price parity between some electric and ICE car models in certain segments could be reached over the 2025-2028 period, for example for small electric cars in Europe in 2025 or soon after. However, many market variables could delay price parity, such as volatile commodity prices, supply chain bottlenecks, and the ability of carmakers to yield sufficient margins from cheaper electric models. The typical rule in which economies of scale bring down costs is being complicated by numerous other market forces. These include a dynamic regulatory context, geopolitical competition, domestic content incentives, and a continually evolving technology landscape, with competing battery chemistries that each have their own economies of scale and regional specificities.
Japan is a rare example of an advanced economy where small models – both for electric and ICE vehicles – appeal to a large consumer base, motivated by densely populated cities with limited parking space, and policy support. In 2023, about 60% of total ICE sales were for small models, and over half of total electric sales. Two electric cars from the smallest “Kei” category, the Nissan Sakura and Mitsubishi eK-X, accounted for nearly 50% of national electric car sales alone, and both are priced between JPY 2.3 million (Japanese yen) and JPY 3 million (USD 18 000 to USD 23 000). However, this is still more expensive than best-selling small ICE cars (e.g. Honda N Box, Daihatsu Hijet, Daihatsu Tanto, Suzuki Spacia, Daihatsu Move), priced between USD 13 000 and USD 18 000. In 2024, Nissan announced that it would aim to reach cost parity (of production, not retail price) between electric and ICE cars by 2030.
Emerging market and developing economies
In EMDEs, the absence of small and cheaper electric car models is a significant hindrance to wider market uptake. Many of the available car models are SUVs or large models, targeting consumers of high-end goods, and far too expensive for mass-market consumers, who often do not own a personal car in the first place (see later sections on second-hand car markets and 2/3Ws).
In India, while Tata’s small Tiago/Tigor models, which are priced between USD 10 000 and USD 15 000, accounted for about 20% of total electric car sales in 2023, the average best-selling small ICE car is priced around USD 7 000. Large models and SUVs accounted for over 65% of total electric car sales. While BYD announced in 2023 the goal of accounting for 40% of India’s EV market by 2030, all of its models available in India cost more than INR 3 million (Indian rupees) (USD 37 000), including the Seal, launched in 2024 for INR 4.1 million (USD 50 000).
Similarly, SUVs and large models accounted for the majority share of electric car sales in Thailand (60%), Indonesia (55%), Malaysia (over 85%) and Viet Nam (over 95%). In Indonesia, for example, Hyundai’s Ionic 5 was the most popular electric car in 2023, priced at around USD 50 000. Looking at launch announcements, most new models expected over the 2024-2028 period in EMDEs are SUVs or large models. However, more than 50 small and medium models could also be introduced, and the recent or forthcoming entry of Chinese carmakers suggests that cheaper models could hit the market in the coming years.
In 2022-2023, Chinese carmakers accounted for 40-75% of the electric car sales in Indonesia, Thailand and Brazil, with sales jumping as cheaper Chinese models were introduced. In Thailand, for example, Hozon launched its Neta V model in 2022 priced at THB 550 000 (Thai baht) (USD 15 600), which became a best-seller in 2023 given its relative affordability compared with the cheapest ICE equivalents at around USD 9 000. Similarly, in Indonesia, the market entry of Wuling’s Air EV in 2022-2023 was met with great success. In Colombia, the best-selling electric car in 2023 was the Chinese mini-car, Zhidou 2DS, which could be found at around USD 15 000, a competitive option relative to the country’s cheapest ICE car, the Kia Picanto, at USD 13 000.
Electric car sales in selected countries, by origin of carmaker, 2021-2023
Second-hand markets for electric cars are on the rise.
As electric vehicle markets mature, the second-hand market will become more important
In the same way as for other technology products, second-hand markets for used electric cars are now emerging as newer generations of vehicles progressively become available and earlier adopters switch or upgrade. Second-hand markets are critical to foster mass-market adoption, especially if new electric cars remain expensive, and used ones become cheaper. Just as for ICE vehicles – for which buying second-hand is often the primary method of acquiring a car in both emerging and advanced economies – a similar pattern will emerge with electric vehicles. It is estimated that eight out of ten EU citizens buy their car second-hand, and this share is even higher – around 90% – among low- and middle-income groups. Similarly, in the United States, about seven out of ten vehicles sold are second-hand, and only 17% of lower-income households buy a new car.
As major electric car markets reach maturity, more and more used electric cars are becoming available for resale. Our estimates suggest that in 2023, the market size for used electric cars amounted to nearly 800 000 in China , 400 000 in the United States and more than 450 000 for France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom combined. Second-hand sales have not been included in the numbers presented in the previous section of this report, which focused on sales of new electric cars, but they are already significant. On aggregate, global second-hand electric car sales were roughly equal to new electric car sales in the United States in 2023. In the United States, used electric car sales are set to increase by 40% in 2024 relative to 2023. Of course, these volumes are dwarfed by second-hand ICE markets: 30 million in the European countries listed above combined, nearly 20 million in China, and 36 million in the United States . However, these markets have had decades to mature, indicating greater longer-term potential for used electric car markets.
Used car markets already provide more affordable electric options in China, Europe and the United States
Second-hand car markets are increasingly becoming a source of more affordable electric cars that can compete with used ICE equivalents. In the United States, for example, more than half of second-hand electric cars are already priced below USD 30 000. Moreover, the average price is expected to quickly fall towards USD 25 000, the price at which used electric cars become eligible for the federal used car rebate of USD 4 000, making them directly competitive with best-selling new and used ICE options. The price of a second-hand Tesla in the United States dropped from over USD 50 000 in early 2023 to just above USD 33 000 in early 2024, making it competitive with a second-hand SUV and many new models as well (either electric or conventional). In Europe , second-hand battery electric cars can be found between EUR 15 000 and EUR 25 000 (USD 16 000‑27 000), and second-hand plug-in hybrids around EUR 30 000 (USD 32 000). Some European countries also offer subsidies for second-hand electric cars, such as the Netherlands (EUR 2 000), where the subsidy for new cars has been steadily declining since 2020, while that for used cars remains constant, and France (EUR 1 000). In China , used electric cars were priced around CNY 75 000 on average in 2023 (USD 11 000).
In recent years, the resale value 8 of electric cars has been increasing. In Europe, the resale value of battery electric cars sold after 12 months has steadily increased over the 2017-2022 period, surpassing that of all other powertrains and standing at more than 70% in mid-2022. The resale value of battery electric cars sold after 36 months stood below 40% in 2017, but has since been closing the gap with other powertrains, reaching around 55% in mid-2022. This is the result of many factors, including higher prices of new electric cars, improving technology allowing vehicles and batteries to retain greater value over time, and increasing demand for second-hand electric cars. Similar trends have been observed in China.
High or low resale values have important implications for the development of second-hand electric car markets and their contributions to the transition to road transport electrification. High resale values primarily benefit consumers of new cars (who retain more of the value of their initial purchase), and carmakers, because many consumers are attracted by the possibility of reselling their car after a few years, thereby fostering demand for newer models. High resale values also benefit leasing companies, which seek to minimise depreciation and resell after a few years.
Leasing companies have a significant impact on second-hand markets because they own large volumes of vehicles for a shorter period (under three years, compared to 3 to 5 years for a private household). Their impact on markets for new cars can also be considerable: leasing companies accounted for over 20% of new cars sold in Europe in 2022.
Overall, a resale value for electric cars on par with or higher than that of ICE equivalents contributes to supporting demand for new electric cars. In the near term, however, a combination of high prices for new electric cars and high resale values could hinder widespread adoption of used EVs among mass-market consumers seeking affordable cars. In such cases, policy support can help bridge the gap with second-hand ICE prices.
International trade for used electric cars to emerging markets is expected to increase
As the EV stock ages in advanced markets, it is likely that more and more used EVs will be traded internationally, assuming that global standards enable technology compatibility (e.g. for charging infrastructure). Imported used vehicles present an opportunity for consumers in EMDEs, who may not have access to new models because they are either too expensive or not marketed in their countries.
Data on used car trade flows are scattered and often contradictory, but the history of ICE cars can be a useful guide to what may happen for electric cars. Many EMDEs have been importing used ICE vehicles for decades. UNEP estimates that Africa imports 40% of all used vehicles exported worldwide, with African countries typically becoming the ultimate destination for used imports. Typical trade flows include Western European Union member states to Eastern European Union member states and to African countries that drive on the right-hand side; Japan to Asia and to African countries that drive on the left-hand side; and the United States to the Middle East and Central America.
Used electric car exports from large EV markets have been growing in recent years. For China, this can be explained by the recent roll-back of a policy forbidding exports of used vehicles of any kind. Since 2019 , as part of a pilot project, the government has granted 27 cities and provinces the right to export second-hand cars. In 2022, China exported almost 70 000 used vehicles, a significant increase on 2021, when fewer than 20 000 vehicles were exported. About 70% of these were NEVs, of which over 45% were exported to the Middle East. In 2023, the Ministry of Commerce released a draft policy on second-hand vehicle export that, once approved, will allow the export of second-hand vehicles from all regions of China. Used car exports from China are expected to increase significantly as a result.
In the European Union, the number of used electric cars traded internationally is also increasing . In both 2021 and 2022, the market size grew by 70% year-on-year, reaching almost 120 000 electric cars in 2022. More than half of all trade takes place between EU member states, followed by trade with neighbouring countries such as Norway, the United Kingdom and Türkiye (accounting for 20% combined). The remainder of used EVs are exported to countries such as Mexico, Tunisia and the United States. As of 2023, the largest exporters are Belgium, Germany, the Netherlands, and Spain.
Last year, just over 1% of all used cars leaving Japan were electric. However these exports are growing and increased by 30% in 2023 relative to 2022, reaching 20 000 cars. The major second-hand electric car markets for Japanese vehicles are traditionally Russia and New Zealand (over 60% combined). After Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022, second-hand trade of conventional cars from Japan to Russia jumped sharply following a halt in operations of local OEMs in Russia, but this trade was quickly restricted by the Japanese government, thereby bringing down the price of second-hand cars in Japan. New Zealand has very few local vehicle assembly or manufacturing facilities, and for this reason many cars entering New Zealand are used imports. In 2023, nearly 20% of all electric cars that entered New Zealand were used imports, compared to 50% for the overall car market.
In emerging economies, local policies play an important role in promoting or limiting trade flows for used cars. In the case of ICE vehicles, for example, some countries (e.g. Bolivia, Côte d’Ivoire, Peru) limit the maximum age of used car imports to prevent the dumping of highly polluting cars. Other countries (e.g. Brazil, Colombia, Egypt, India, South Africa) have banned used car imports entirely to protect their domestic manufacturing industries.
Just as for ICE vehicles, policy measures can either help or hinder the import of used electric cars, such as by setting emission standards for imported used cars. Importing countries will also need to simultaneously support roll-out of charging infrastructure to avoid problems with access like those reported in Sri Lanka after an incentive scheme significantly increased imports of used EVs in 2018.
The median age of vehicle imports tends to increase as the GDP per capita of a country decreases. In some African countries, the median age of imports is over 15 years. Beyond this timeframe, electric cars may require specific servicing to extend their lifetime. To support the availability of second-hand markets for electric cars, it will be important to develop strategies, technical capacity, and business models to swap very old batteries from used vehicles. Today, many countries that import ICE vehicles, including EMDEs, already have servicing capacity in place to extend the lifetimes of used ICE vehicles, but not used EVs. On the other hand, there are typically fewer parts in electric powertrains than in ICE ones, and these parts can even be more durable. Battery recycling capacity will also be needed, given that the importing country is likely to be where the imported EV eventually reaches end-of-life. Including end-of-life considerations in policy making today can help mitigate the risk of longer-term environmental harm that could result from the accumulation of obsolete EVs and associated waste in EMDEs.
Policy choices in more mature markets also have an impact on possible trade flows. For example, the current policy framework in the European Union for the circularity of EV batteries may prevent EVs and EV batteries from leaving the European Union, which brings energy security advantages but might limit reuse. In this regard, advanced economies and EMDEs should strengthen co-operation to facilitate second-hand trade while ensuring adequate end-of-life strategies. For example, there could be incentives or allowances associated with extended vehicle lifetimes via use in second-hand markets internationally before recycling, as long as recycling in the destination market is guaranteed, or the EV battery is returned at end of life.
Throughout this report, unless otherwise specified, “electric cars” refers to both battery electric and plug-in hybrid cars, and “electric vehicles” (EVs) refers to battery electric (BEV) and plug-in hybrid (PHEV) vehicles, excluding fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEV). Unless otherwise specified, EVs include all modes of road transport.
Throughout this report, unless otherwise specified, regional groupings refer to those described in the Annex.
In the Chinese context, the term New Energy Vehicles (NEVs) includes BEVs, PHEVs and FCEVs.
Based on model trim eligibility from the US government website as of 31 March 2024.
SUVs may be defined differently across regions, but broadly refer to vehicles that incorporate features commonly found in off-road vehicles (e.g. four-wheel drive, higher ground clearance, larger cargo area). In this report, small and large SUVs both count as SUVs. Crossovers are counted as SUVs if they feature an SUV body type; otherwise they are categorised as medium-sized vehicles.
Measured under the Worldwide Harmonised Light Vehicles Test Procedure using vehicle model sales data from IHS Markit.
Price data points collected from various data providers and ad-hoc sources cover 65-95% of both electric and ICE car sales globally. By “price”, we refer to the advertised price that the customer pays for the acquisition of the vehicle only, including legally required acquisition taxes (e.g. including Value-Added Tax and registration taxes but excluding consumer tax credits). Prices reflect not only the materials, components and manufacturing costs, but also the costs related to sales and marketing, administration, R&D and the profit margin. In the case of a small electric car in Europe, for example, these mark-up costs can account for around 40% of the final pre-tax price. They account for an even greater share of the final pre-tax price when consumers purchase additional options, or opt for larger models, for which margins can be higher. The price for the same model may differ across countries or regions (e.g. in 2023, a VW ID.3 could be purchased in China at half its price in Europe). Throughout the whole section, prices are adjusted for inflation and expressed in constant 2022 USD.
This metric of depreciation used in second-hand technology markets represents the value of the vehicle when being resold in relation to the value when originally purchased. A resale value of 70% means that a product purchased new will lose 30% of its original value, on average, and sell at such a discount relative to the original price.
Reference 1
Reference 2, reference 3, reference 4, reference 5, reference 6, reference 7, reference 8, subscription successful.
Thank you for subscribing. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the link at the bottom of any IEA newsletter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Research using a case study method must adhere to principles of intellectual honesty and academic integrity; a case analysis scenario can include misleading or false information. A case study paper must report research objectively and factually to ensure that any findings are understood to be logically correct and trustworthy.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
Case study research has an important role in many social sciences including sociology, anthropology, political science, education, organizational studies, psychology, and nursing. It should be noted that not all case study research is labeled as such. For example, ethnographic studies are typically not described as case studies.
The definitions of case study evolved over a period of time. Case study is defined as "a systematic inquiry into an event or a set of related events which aims to describe and explain the phenomenon of interest" (Bromley, 1990).Stoecker defined a case study as an "intensive research in which interpretations are given based on observable concrete interconnections between actual properties ...
Gilgun, J. F. (1994). A Case for Case Studies in Social Work Research. Social Work, 39, 4, 371-381. This article defines case study research, presents guidelines for evaluation of case studies, and shows the relevance of case studies to social work research. It also looks at issues such as evaluation and interpretations of case studies.
The main concern in evaluating a case study is to accurately assess its quality and ultimately to offer clients social work interventions informed by the best available evidence. To assess the quality of a case study, we propose criteria, including transferability/external validity, credibility/internal validity, confirmability/construct ...
The Case Study in Social Research proposes and develops an innovative, rigorous, and up to date methodological clarification of the case study approach in the social sciences to consistently and consciously apply it to different fields of social research. It aspires to provide the reader not with a set of prescriptive rules, but rather with a 'methodological awareness' of the complexity ...
The case study does not refer to a clinical case report or to a data collection method but rather to an evidence-based empiri- cal approach (Bergen & While, 2000; Yin, 1994).
In this special issue we have asked the contributors to make a case for the case study. The guest editors, Jeffrey Longhofer, Jerry Floersch and Eric Hartmann, intergrate ideas from across the disciplines to explore the complexties of case study methods and theory. In education, Gary Thomas explores the importance of ethnographic case studies in understanding the relationships among schools ...
Researchers often use case studies as part of their toolkit when approaching a research question. With qualitative and quantitative measures to choose from, many of which are expensive or time-consuming, case studies are thought to hold academic value, particularly in the field of social research. When used correctly, case studies can impact social growth significantly.
How to Begin. Field reports are most often assigned in disciplines of the applied social sciences [e.g., social work, anthropology, gerontology, criminal justice, education, law, the health care services] where it is important to build a bridge of relevancy between the theoretical concepts learned in the classroom and the practice of actually doing the work you are being taught to do.
The Importance of Case Studies in Public Health Education and Promotion. Health programs and practices are often conceived and delivered by community-based practitioners to address specific community health education and promotion needs ().Although, initially untested, such programs can provide important lessons for researchers and practitioners, alike.
This case work and case planning social work guide has been published to equip social workers to empower individuals and promote positive change through social casework. We will explore what is social case work, the models and theories of social case work, social work case studies, and real-life social work case examples, providing a ...
S.M. Holmes and Others. The Case Studies in Social Medicine demonstrate that when physicians use only biologic or individual behavioral interventions to treat diseases that stem from or are ...
in preparing social reports. That examination forms the basis of this overview report and case studies on each of the seven companies. The companies were chosen to represent dif-ferent industries, geographies and experience in reporting. The companies that participated in the project were: • Baxter International Inc. • Gap Inc. • Nestlé
Abstract. The paper is a social development case study report of a student who has been relying his education on scholarship. Unfortunately, challenges had been haunting him ever since he was ...
Case Study Research in the Social Sciences Petri Ylikoski and Julie Zahle1 Penultimate draft - published in 2019 in Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part A, 78:1-4. Abstract: In this paper, we offer an introduction to case study research in the social sciences. We begin with a discussion of the definition of case study research.
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a particular individual, family, or community, aiming to understand the complexities of their situation and the challenges they face. It provides an opportunity for social workers to apply theories, skills, ethics, and supervision to real-life scenarios. By examining case studies, social workers can learn ...
International Journal of Social Science and Humanities Research. Argel B . Masanda. This study investigated the children"s experiences of the familial stresses as a gauge of looking into their family dynamics. Primary emphasis was focused on the children"s psychological functioning in the context of their experienced stresses in their family.
Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. ... Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in ...
What is the importance of a case study? Well, nearly 90% of consumers read product reviews before they make a purchase, which means gathering and publishing social proof is a crucial activity for your SaaS company. Changing consumer behavior is another reason why case studies are important. Case studies give your readers what they're looking for, which is confirmation from other B2B buyers ...
Early Friday morning, Mr. James posted a statement on social media addressing his comments. "What I said was wrong," he wrote. "What I said was wrong," he wrote.
ABSTRACT. While extensive research exists on blogs, news-related blog translation has been relatively unexplored. This study delves into the realm of news-related blog translation through the case of What's on Weibo (hereafter WoW), an independent English-language news-related website that reports trending topics on Weibo. Given the unique nature of blog translation, the term bloglator is ...
The case, known as Moyle v.United States (Mike Moyle is the speaker of the Idaho House), has major implications on everything from what emergency care is available in states with abortion bans to ...
Electric car sales neared 14 million in 2023, 95% of which were in China, Europe and the United States. Almost 14 million new electric cars1 were registered globally in 2023, bringing their total number on the roads to 40 million, closely tracking the sales forecast from the 2023 edition of the Global EV Outlook (GEVO-2023). Electric car sales in 2023 were 3.5 million higher than in 2022, a 35 ...
There has been extensive commentary about historical First Nations' land management in Australia, including in tall, wet forests, and therefore their condition at the time of the British invasion in 1788. Popular texts have interpreted records kept by early British invaders to argue that extensive areas of tall, wet forest were kept open through frequent burning by the First Peoples. However ...