The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Find This link opens in a new window
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window

Get Organized
- Lit Review Prep Use this template to help you evaluate your sources, create article summaries for an annotated bibliography, and a synthesis matrix for your lit review outline.
Synthesize your Information
Synthesize: combine separate elements to form a whole.
Synthesis Matrix
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other.
After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables.
By arranging your sources by theme or variable, you can see how your sources relate to each other, and can start thinking about how you weave them together to create a narrative.
- Step-by-Step Approach
- Example Matrix from NSCU
- Matrix Template
- << Previous: Summarize
- Next: Integrate >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 10:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- 6. Synthesize
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
Synthesis Visualization
Synthesis matrix example.
- 7. Write a Literature Review
- Synthesis Worksheet
About Synthesis
Approaches to synthesis.
You can sort the literature in various ways, for example:

How to Begin?
Read your sources carefully and find the main idea(s) of each source
Look for similarities in your sources – which sources are talking about the same main ideas? (for example, sources that discuss the historical background on your topic)
Use the worksheet (above) or synthesis matrix (below) to get organized
This work can be messy. Don't worry if you have to go through a few iterations of the worksheet or matrix as you work on your lit review!
Four Examples of Student Writing
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D . For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.

Long description of "Four Examples of Student Writing" for web accessibility
- Download a copy of the "Four Examples of Student Writing" chart

Click on the example to view the pdf.

From Jennifer Lim
- << Previous: 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- Next: 7. Write a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: May 3, 2024 5:17 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
Literature Syntheis 101
How To Synthesise The Existing Research (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | August 2023
One of the most common mistakes that students make when writing a literature review is that they err on the side of describing the existing literature rather than providing a critical synthesis of it. In this post, we’ll unpack what exactly synthesis means and show you how to craft a strong literature synthesis using practical examples.
This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp . In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step. If it’s your first time writing a literature review, you definitely want to use this link to get 50% off the course (limited-time offer).
Overview: Literature Synthesis
- What exactly does “synthesis” mean?
- Aspect 1: Agreement
- Aspect 2: Disagreement
- Aspect 3: Key theories
- Aspect 4: Contexts
- Aspect 5: Methodologies
- Bringing it all together
What does “synthesis” actually mean?
As a starting point, let’s quickly define what exactly we mean when we use the term “synthesis” within the context of a literature review.
Simply put, literature synthesis means going beyond just describing what everyone has said and found. Instead, synthesis is about bringing together all the information from various sources to present a cohesive assessment of the current state of knowledge in relation to your study’s research aims and questions .
Put another way, a good synthesis tells the reader exactly where the current research is “at” in terms of the topic you’re interested in – specifically, what’s known , what’s not , and where there’s a need for more research .
So, how do you go about doing this?
Well, there’s no “one right way” when it comes to literature synthesis, but we’ve found that it’s particularly useful to ask yourself five key questions when you’re working on your literature review. Having done so, you can then address them more articulately within your actual write up. So, let’s take a look at each of these questions.

1. Points Of Agreement
The first question that you need to ask yourself is: “Overall, what things seem to be agreed upon by the vast majority of the literature?”
For example, if your research aim is to identify which factors contribute toward job satisfaction, you’ll need to identify which factors are broadly agreed upon and “settled” within the literature. Naturally, there may at times be some lone contrarian that has a radical viewpoint , but, provided that the vast majority of researchers are in agreement, you can put these random outliers to the side. That is, of course, unless your research aims to explore a contrarian viewpoint and there’s a clear justification for doing so.
Identifying what’s broadly agreed upon is an essential starting point for synthesising the literature, because you generally don’t want (or need) to reinvent the wheel or run down a road investigating something that is already well established . So, addressing this question first lays a foundation of “settled” knowledge.
Need a helping hand?
2. Points Of Disagreement
Related to the previous point, but on the other end of the spectrum, is the equally important question: “Where do the disagreements lie?” .
In other words, which things are not well agreed upon by current researchers? It’s important to clarify here that by disagreement, we don’t mean that researchers are (necessarily) fighting over it – just that there are relatively mixed findings within the empirical research , with no firm consensus amongst researchers.
This is a really important question to address as these “disagreements” will often set the stage for the research gap(s). In other words, they provide clues regarding potential opportunities for further research, which your study can then (hopefully) contribute toward filling. If you’re not familiar with the concept of a research gap, be sure to check out our explainer video covering exactly that .

3. Key Theories
The next question you need to ask yourself is: “Which key theories seem to be coming up repeatedly?” .
Within most research spaces, you’ll find that you keep running into a handful of key theories that are referred to over and over again. Apart from identifying these theories, you’ll also need to think about how they’re connected to each other. Specifically, you need to ask yourself:
- Are they all covering the same ground or do they have different focal points or underlying assumptions ?
- Do some of them feed into each other and if so, is there an opportunity to integrate them into a more cohesive theory?
- Do some of them pull in different directions ? If so, why might this be?
- Do all of the theories define the key concepts and variables in the same way, or is there some disconnect? If so, what’s the impact of this ?
Simply put, you’ll need to pay careful attention to the key theories in your research area, as they will need to feature within your theoretical framework , which will form a critical component within your final literature review. This will set the foundation for your entire study, so it’s essential that you be critical in this area of your literature synthesis.
If this sounds a bit fluffy, don’t worry. We deep dive into the theoretical framework (as well as the conceptual framework) and look at practical examples in Literature Review Bootcamp . If you’d like to learn more, take advantage of our limited-time offer to get 60% off the standard price.

4. Contexts
The next question that you need to address in your literature synthesis is an important one, and that is: “Which contexts have (and have not) been covered by the existing research?” .
For example, sticking with our earlier hypothetical topic (factors that impact job satisfaction), you may find that most of the research has focused on white-collar , management-level staff within a primarily Western context, but little has been done on blue-collar workers in an Eastern context. Given the significant socio-cultural differences between these two groups, this is an important observation, as it could present a contextual research gap .
In practical terms, this means that you’ll need to carefully assess the context of each piece of literature that you’re engaging with, especially the empirical research (i.e., studies that have collected and analysed real-world data). Ideally, you should keep notes regarding the context of each study in some sort of catalogue or sheet, so that you can easily make sense of this before you start the writing phase. If you’d like, our free literature catalogue worksheet is a great tool for this task.
5. Methodological Approaches
Last but certainly not least, you need to ask yourself the question: “What types of research methodologies have (and haven’t) been used?”
For example, you might find that most studies have approached the topic using qualitative methods such as interviews and thematic analysis. Alternatively, you might find that most studies have used quantitative methods such as online surveys and statistical analysis.
But why does this matter?
Well, it can run in one of two potential directions . If you find that the vast majority of studies use a specific methodological approach, this could provide you with a firm foundation on which to base your own study’s methodology . In other words, you can use the methodologies of similar studies to inform (and justify) your own study’s research design .
On the other hand, you might argue that the lack of diverse methodological approaches presents a research gap , and therefore your study could contribute toward filling that gap by taking a different approach. For example, taking a qualitative approach to a research area that is typically approached quantitatively. Of course, if you’re going to go against the methodological grain, you’ll need to provide a strong justification for why your proposed approach makes sense. Nevertheless, it is something worth at least considering.
Regardless of which route you opt for, you need to pay careful attention to the methodologies used in the relevant studies and provide at least some discussion about this in your write-up. Again, it’s useful to keep track of this on some sort of spreadsheet or catalogue as you digest each article, so consider grabbing a copy of our free literature catalogue if you don’t have anything in place.

Bringing It All Together
Alright, so we’ve looked at five important questions that you need to ask (and answer) to help you develop a strong synthesis within your literature review. To recap, these are:
- Which things are broadly agreed upon within the current research?
- Which things are the subject of disagreement (or at least, present mixed findings)?
- Which theories seem to be central to your research topic and how do they relate or compare to each other?
- Which contexts have (and haven’t) been covered?
- Which methodological approaches are most common?
Importantly, you’re not just asking yourself these questions for the sake of asking them – they’re not just a reflection exercise. You need to weave your answers to them into your actual literature review when you write it up. How exactly you do this will vary from project to project depending on the structure you opt for, but you’ll still need to address them within your literature review, whichever route you go.
The best approach is to spend some time actually writing out your answers to these questions, as opposed to just thinking about them in your head. Putting your thoughts onto paper really helps you flesh out your thinking . As you do this, don’t just write down the answers – instead, think about what they mean in terms of the research gap you’ll present , as well as the methodological approach you’ll take . Your literature synthesis needs to lay the groundwork for these two things, so it’s essential that you link all of it together in your mind, and of course, on paper.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

excellent , thank you
Thank you for this significant piece of information.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Literature Review Basics
- What is a Literature Review?
- Synthesizing Research
- Using Research & Synthesis Tables
- Additional Resources

Synthesis: What is it?
First, let's be perfectly clear about what synthesizing your research isn't :
- - It isn't just summarizing the material you read
- - It isn't generating a collection of annotations or comments (like an annotated bibliography)
- - It isn't compiling a report on every single thing ever written in relation to your topic
When you synthesize your research, your job is to help your reader understand the current state of the conversation on your topic, relative to your research question. That may include doing the following:
- - Selecting and using representative work on the topic
- - Identifying and discussing trends in published data or results
- - Identifying and explaining the impact of common features (study populations, interventions, etc.) that appear frequently in the literature
- - Explaining controversies, disputes, or central issues in the literature that are relevant to your research question
- - Identifying gaps in the literature, where more research is needed
- - Establishing the discussion to which your own research contributes and demonstrating the value of your contribution
Essentially, you're telling your reader where they are (and where you are) in the scholarly conversation about your project.
Synthesis: How do I do it?
Synthesis, step by step.
This is what you need to do before you write your review.
- Identify and clearly describe your research question (you may find the Formulating PICOT Questions table at the Additional Resources tab helpful).
- Collect sources relevant to your research question.
- Organize and describe the sources you've found -- your job is to identify what types of sources you've collected (reviews, clinical trials, etc.), identify their purpose (what are they measuring, testing, or trying to discover?), determine the level of evidence they represent (see the Levels of Evidence table at the Additional Resources tab ), and briefly explain their major findings . Use a Research Table to document this step.
- Study the information you've put in your Research Table and examine your collected sources, looking for similarities and differences . Pay particular attention to populations , methods (especially relative to levels of evidence), and findings .
- Analyze what you learn in (4) using a tool like a Synthesis Table. Your goal is to identify relevant themes, trends, gaps, and issues in the research. Your literature review will collect the results of this analysis and explain them in relation to your research question.
Analysis tips
- - Sometimes, what you don't find in the literature is as important as what you do find -- look for questions that the existing research hasn't answered yet.
- - If any of the sources you've collected refer to or respond to each other, keep an eye on how they're related -- it may provide a clue as to whether or not study results have been successfully replicated.
- - Sorting your collected sources by level of evidence can provide valuable insight into how a particular topic has been covered, and it may help you to identify gaps worth addressing in your own work.
- << Previous: What is a Literature Review?
- Next: Using Research & Synthesis Tables >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 12:06 PM
- URL: https://usi.libguides.com/literature-review-basics

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 7: Synthesizing Sources
Learning objectives.
At the conclusion of this chapter, you will be able to:
- synthesize key sources connecting them with the research question and topic area.
7.1 Overview of synthesizing
7.1.1 putting the pieces together.
Combining separate elements into a whole is the dictionary definition of synthesis. It is a way to make connections among and between numerous and varied source materials. A literature review is not an annotated bibliography, organized by title, author, or date of publication. Rather, it is grouped by topic to create a whole view of the literature relevant to your research question.

Your synthesis must demonstrate a critical analysis of the papers you collected as well as your ability to integrate the results of your analysis into your own literature review. Each paper collected should be critically evaluated and weighed for “adequacy, appropriateness, and thoroughness” ( Garrard, 2017 ) before inclusion in your own review. Papers that do not meet this criteria likely should not be included in your literature review.
Begin the synthesis process by creating a grid, table, or an outline where you will summarize, using common themes you have identified and the sources you have found. The summary grid or outline will help you compare and contrast the themes so you can see the relationships among them as well as areas where you may need to do more searching. Whichever method you choose, this type of organization will help you to both understand the information you find and structure the writing of your review. Remember, although “the means of summarizing can vary, the key at this point is to make sure you understand what you’ve found and how it relates to your topic and research question” ( Bennard et al., 2014 ).
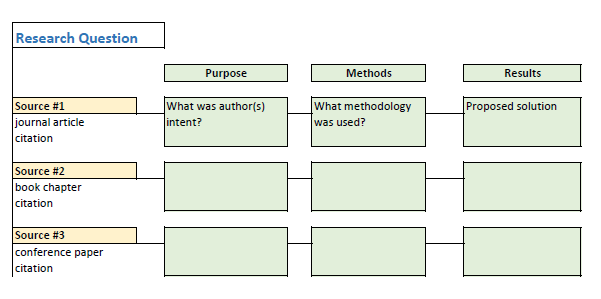
As you read through the material you gather, look for common themes as they may provide the structure for your literature review. And, remember, research is an iterative process: it is not unusual to go back and search information sources for more material.
At one extreme, if you are claiming, ‘There are no prior publications on this topic,’ it is more likely that you have not found them yet and may need to broaden your search. At another extreme, writing a complete literature review can be difficult with a well-trod topic. Do not cite it all; instead cite what is most relevant. If that still leaves too much to include, be sure to reference influential sources…as well as high-quality work that clearly connects to the points you make. ( Klingner, Scanlon, & Pressley, 2005 ).
7.2 Creating a summary table
Literature reviews can be organized sequentially or by topic, theme, method, results, theory, or argument. It’s important to develop categories that are meaningful and relevant to your research question. Take detailed notes on each article and use a consistent format for capturing all the information each article provides. These notes and the summary table can be done manually, using note cards. However, given the amount of information you will be recording, an electronic file created in a word processing or spreadsheet is more manageable. Examples of fields you may want to capture in your notes include:
- Authors’ names
- Article title
- Publication year
- Main purpose of the article
- Methodology or research design
- Participants
- Measurement
- Conclusions
Other fields that will be useful when you begin to synthesize the sum total of your research:
- Specific details of the article or research that are especially relevant to your study
- Key terms and definitions
- Strengths or weaknesses in research design
- Relationships to other studies
- Possible gaps in the research or literature (for example, many research articles conclude with the statement “more research is needed in this area”)
- Finally, note how closely each article relates to your topic. You may want to rank these as high, medium, or low relevance. For papers that you decide not to include, you may want to note your reasoning for exclusion, such as ‘small sample size’, ‘local case study,’ or ‘lacks evidence to support assertion.’
This short video demonstrates how a nursing researcher might create a summary table.
7.2.1 Creating a Summary Table

Summary tables can be organized by author or by theme, for example:
For a summary table template, see http://blogs.monm.edu/writingatmc/files/2013/04/Synthesis-Matrix-Template.pdf
7.3 Creating a summary outline
An alternate way to organize your articles for synthesis it to create an outline. After you have collected the articles you intend to use (and have put aside the ones you won’t be using), it’s time to identify the conclusions that can be drawn from the articles as a group.
Based on your review of the collected articles, group them by categories. You may wish to further organize them by topic and then chronologically or alphabetically by author. For each topic or subtopic you identified during your critical analysis of the paper, determine what those papers have in common. Likewise, determine which ones in the group differ. If there are contradictory findings, you may be able to identify methodological or theoretical differences that could account for the contradiction (for example, differences in population demographics). Determine what general conclusions you can report about the topic or subtopic as the entire group of studies relate to it. For example, you may have several studies that agree on outcome, such as ‘hands on learning is best for science in elementary school’ or that ‘continuing education is the best method for updating nursing certification.’ In that case, you may want to organize by methodology used in the studies rather than by outcome.
Organize your outline in a logical order and prepare to write the first draft of your literature review. That order might be from broad to more specific, or it may be sequential or chronological, going from foundational literature to more current. Remember, “an effective literature review need not denote the entire historical record, but rather establish the raison d’etre for the current study and in doing so cite that literature distinctly pertinent for theoretical, methodological, or empirical reasons.” ( Milardo, 2015, p. 22 ).
As you organize the summarized documents into a logical structure, you are also appraising and synthesizing complex information from multiple sources. Your literature review is the result of your research that synthesizes new and old information and creates new knowledge.
7.4 Additional resources:
Literature Reviews: Using a Matrix to Organize Research / Saint Mary’s University of Minnesota
Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources / Indiana University
Writing a Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix / Florida International University
Sample Literature Reviews Grid / Complied by Lindsay Roberts
Select three or four articles on a single topic of interest to you. Then enter them into an outline or table in the categories you feel are important to a research question. Try both the grid and the outline if you can to see which suits you better. The attached grid contains the fields suggested in the video .
Literature Review Table
Test yourself.
- Select two articles from your own summary table or outline and write a paragraph explaining how and why the sources relate to each other and your review of the literature.
- In your literature review, under what topic or subtopic will you place the paragraph you just wrote?
Image attribution
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students Copyright © by Linda Frederiksen is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Library Guides
Literature reviews: synthesis.
- Criticality
Synthesise Information
So, how can you create paragraphs within your literature review that demonstrates your knowledge of the scholarship that has been done in your field of study?
You will need to present a synthesis of the texts you read.
Doug Specht, Senior Lecturer at the Westminster School of Media and Communication, explains synthesis for us in the following video:
Synthesising Texts
What is synthesis?
Synthesis is an important element of academic writing, demonstrating comprehension, analysis, evaluation and original creation.
With synthesis you extract content from different sources to create an original text. While paraphrase and summary maintain the structure of the given source(s), with synthesis you create a new structure.
The sources will provide different perspectives and evidence on a topic. They will be put together when agreeing, contrasted when disagreeing. The sources must be referenced.
Perfect your synthesis by showing the flow of your reasoning, expressing critical evaluation of the sources and drawing conclusions.
When you synthesise think of "using strategic thinking to resolve a problem requiring the integration of diverse pieces of information around a structuring theme" (Mateos and Sole 2009, p448).
Synthesis is a complex activity, which requires a high degree of comprehension and active engagement with the subject. As you progress in higher education, so increase the expectations on your abilities to synthesise.
How to synthesise in a literature review:
Identify themes/issues you'd like to discuss in the literature review. Think of an outline.
Read the literature and identify these themes/issues.
Critically analyse the texts asking: how does the text I'm reading relate to the other texts I've read on the same topic? Is it in agreement? Does it differ in its perspective? Is it stronger or weaker? How does it differ (could be scope, methods, year of publication etc.). Draw your conclusions on the state of the literature on the topic.
Start writing your literature review, structuring it according to the outline you planned.
Put together sources stating the same point; contrast sources presenting counter-arguments or different points.
Present your critical analysis.
Always provide the references.
The best synthesis requires a "recursive process" whereby you read the source texts, identify relevant parts, take notes, produce drafts, re-read the source texts, revise your text, re-write... (Mateos and Sole, 2009).
What is good synthesis?
The quality of your synthesis can be assessed considering the following (Mateos and Sole, 2009, p439):
Integration and connection of the information from the source texts around a structuring theme.
Selection of ideas necessary for producing the synthesis.
Appropriateness of the interpretation.
Elaboration of the content.
Example of Synthesis
Original texts (fictitious):
Synthesis:
Animal experimentation is a subject of heated debate. Some argue that painful experiments should be banned. Indeed it has been demonstrated that such experiments make animals suffer physically and psychologically (Chowdhury 2012; Panatta and Hudson 2016). On the other hand, it has been argued that animal experimentation can save human lives and reduce harm on humans (Smith 2008). This argument is only valid for toxicological testing, not for tests that, for example, merely improve the efficacy of a cosmetic (Turner 2015). It can be suggested that animal experimentation should be regulated to only allow toxicological risk assessment, and the suffering to the animals should be minimised.
Bibliography
Mateos, M. and Sole, I. (2009). Synthesising Information from various texts: A Study of Procedures and Products at Different Educational Levels. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 24 (4), 435-451. Available from https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178760 [Accessed 29 June 2021].
- << Previous: Structure
- Next: Criticality >>
- Last Updated: Nov 18, 2023 10:56 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/literature-reviews
CONNECT WITH US
How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.
Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
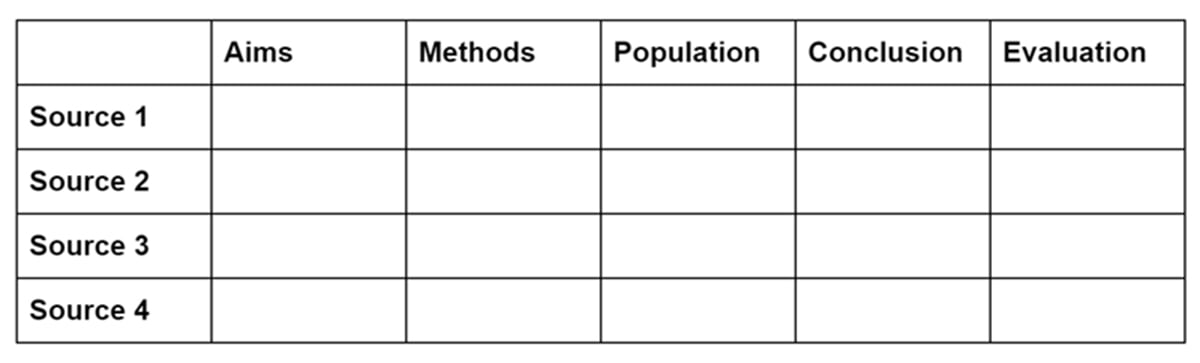
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
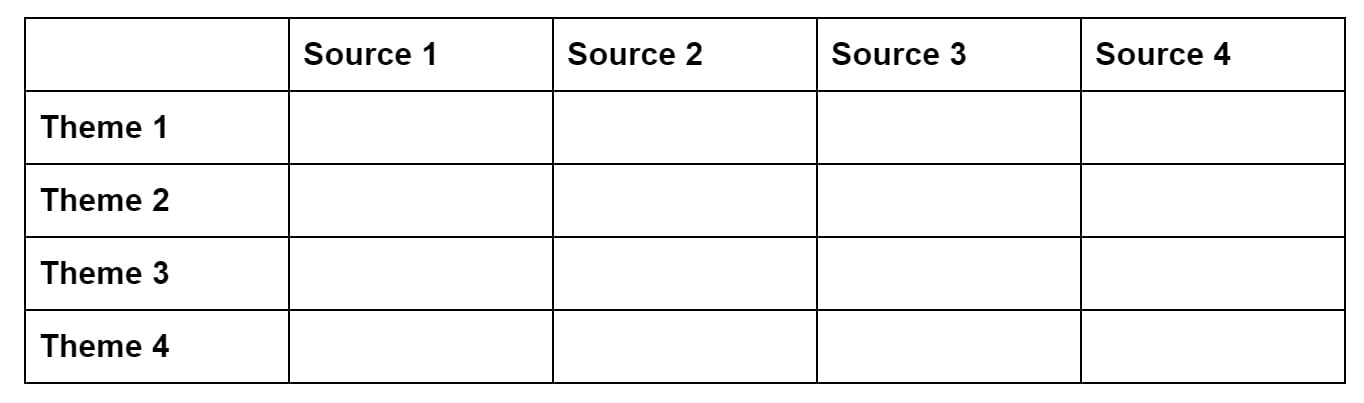
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
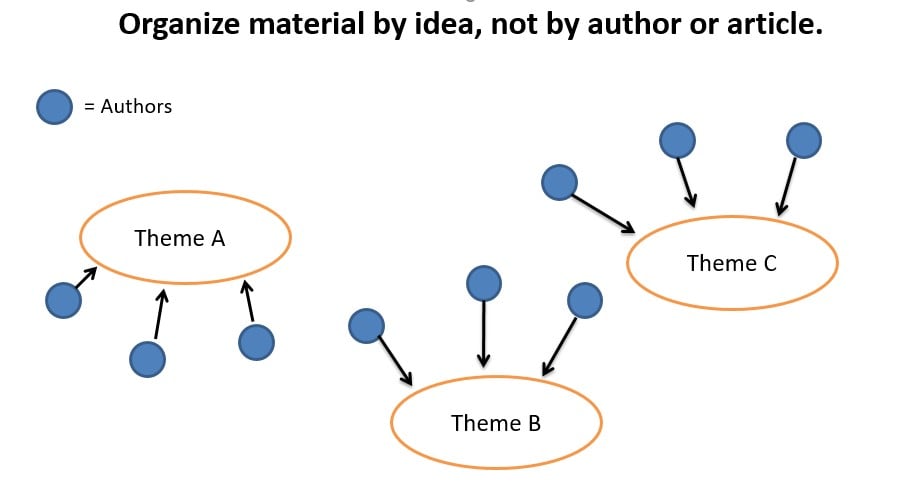
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay
Related Articles

Student Resources
How To Cite A YouTube Video In APA Style – With Examples

How to Write an Abstract APA Format

APA References Page Formatting and Example

APA Title Page (Cover Page) Format, Example, & Templates

How do I Cite a Source with Multiple Authors in APA Style?
How to Write a Psychology Essay

Writing a Literature Review: Organize, Synthesize, Evaluate
- Literature Review Process
- Literature Search
- Record your Search
- Organize, Synthesize, Evaluate
- Getting help
Table of Contents
On this page you will find:
Organizing Literature and Notes
How to scan an article.
- Reading for Comprehension
- Synthesis Matrix Information
Steps to take in organizing your literature and notes:
- Find common themes and organize the works into categories.
- Develop a subject level outline with studies you’ve found
- Expand or limit your search based on the information you found.
- How the works in each category relate to each other
- How the categories relate to each other and to your overall theme.
Available tools:
- Synthesis Matrix The "synthesis matrix" is an approach to organizing, monitoring, and documenting your search activities.
- Concept Mapping Concept Maps are graphic representations of topics, ideas, and their relationships. They allow users to group information in related modules so that the connections between and among the modules become more readily apparent than they might from an examination of a list. It can be done on paper or using specific software.
- Mind Mapping A mind map is a visual representation of hierarchical information that includes a central idea surrounded by connected branches of associated topics.
- NVIVO NVIVO is a qualitative data analysis software that can be applied for engineering literature review.
Synthesis Matrix
- Writing A Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix Writing Center, Florida International University
- The Matrix Method of Literature Reviews Article from Health Promotion Practice journal.
Sample synthesis matrix

Synthesis matrix video
Skim the article to get the “big picture” for relevancy to your topic. You don’t have to understand every single idea in a text the first time you read it.
- Where was the paper published?
- What kind of journal it is? Is the journal peer-reviewed?
- Can you tell what the paper is about?
- Where are they from?
- What are the sections of the article?
- Are these clearly defined?
- Can you figure out the purpose of the study, methodology, results and conclusion?
- Mentally review what you know about the topic
- Do you know enough to be able to understand the paper? If not, first read about the unfamiliar concepts
- What is the overall context?
- Is the problem clearly stated?
- What does the paper bring new?
- Did it miss any previous major studies?
- Identify all the author’s assumptions.
- Analyze the visuals for yourself and try to understand each of them. Make notes on what you understand. Write questions of what you do not understand. Make a guess about what materials/methods you expect to see. Do your own data interpretation and check them against the conclusions.
- Do you agree with the author’s opinion?
- As you read, write down terms, techniques, unfamiliar concepts and look them up
- Save retrieved sources to a reference manager
Read for Comprehension and Take Notes
Read for comprehension
- After first evaluation of sources, critically read the selected sources. Your goal is to determine how much of it to accept, determine its value, and decide whether you plan to include it in your literature review.
- Read the whole article, section by section but not necessarily in order and make sure you understand:
Introduction : What is known about the research and what is still unknown. Methods : What was measured? How was measured? Were the measurement appropriate? Did they offer sufficient evidence? Results : What is the main finding? Were there enough data presented? Were there problems not addressed? Discussions : Are these conclusions appropriate? Are there other factors that might have influenced? What does it need to be done to answer remaining questions?
- Find answers to your question from first step
- Formulate new questions and try to answer them
- Can you find any discrepancies? What would you have done differently?
- Re-read the whole article or just sections as many times you feel you need to
- When you believe that you have understood the article, write a summary in your own words (Make sure that there is nothing left that you cannot understand)
As you read, take (extensive) notes. Create your own system to take notes but be consistent. Remember that notes can be taken within the citation management tool.
What to write in your notes:
- identify key topic, methodology, key terms
- identify emphases, strengths, weaknesses, gaps (if any)
- determine relationships to other studies
- identify the relationship to your research topic
- new questions you have
- suggestions for new directions, new sources to read
- everything else that seems relevant
- << Previous: Record your Search
- Next: Writing >>
- Last Updated: Jan 5, 2024 9:17 AM
- URL: https://libguides.wpi.edu/c.php?g=1134107
How can we help?
- [email protected]
- Consultation
- 508-831-5410

Literature Review How To
- Things To Consider
- Synthesizing Sources
- Video Tutorials
- Books On Literature Reviews
What is Synthesis
What is Synthesis? Synthesis writing is a form of analysis related to comparison and contrast, classification and division. On a basic level, synthesis requires the writer to pull together two or more summaries, looking for themes in each text. In synthesis, you search for the links between various materials in order to make your point. Most advanced academic writing, including literature reviews, relies heavily on synthesis. (Temple University Writing Center)
How To Synthesize Sources in a Literature Review
Literature reviews synthesize large amounts of information and present it in a coherent, organized fashion. In a literature review you will be combining material from several texts to create a new text – your literature review.
You will use common points among the sources you have gathered to help you synthesize the material. This will help ensure that your literature review is organized by subtopic, not by source. This means various authors' names can appear and reappear throughout the literature review, and each paragraph will mention several different authors.
When you shift from writing summaries of the content of a source to synthesizing content from sources, there is a number things you must keep in mind:
- Look for specific connections and or links between your sources and how those relate to your thesis or question.
- When writing and organizing your literature review be aware that your readers need to understand how and why the information from the different sources overlap.
- Organize your literature review by the themes you find within your sources or themes you have identified.
- << Previous: Things To Consider
- Next: Video Tutorials >>
- Last Updated: Nov 30, 2018 4:51 PM
- URL: https://libguides.csun.edu/literature-review
Report ADA Problems with Library Services and Resources
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students.
Writing in the Health and Social Sciences: Literature Reviews and Synthesis Tools
- Journal Publishing
- Style and Writing Guides
- Readings about Writing
- Citing in APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Resources for Dissertation Authors
- Citation Management and Formatting Tools
- What are Literature Reviews?
- Conducting & Reporting Systematic Reviews
- Finding Systematic Reviews
- Tutorials & Tools for Literature Reviews
Systematic Literature Reviews: Steps & Resources
These steps for conducting a systematic literature review are listed below .
Also see subpages for more information about:
- The different types of literature reviews, including systematic reviews and other evidence synthesis methods
- Tools & Tutorials
Literature Review & Systematic Review Steps
- Develop a Focused Question
- Scope the Literature (Initial Search)
- Refine & Expand the Search
- Limit the Results
- Download Citations
- Abstract & Analyze
- Create Flow Diagram
- Synthesize & Report Results
1. Develop a Focused Question
Consider the PICO Format: Population/Problem, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome
Focus on defining the Population or Problem and Intervention (don't narrow by Comparison or Outcome just yet!)
"What are the effects of the Pilates method for patients with low back pain?"
Tools & Additional Resources:
- PICO Question Help
- Stillwell, Susan B., DNP, RN, CNE; Fineout-Overholt, Ellen, PhD, RN, FNAP, FAAN; Melnyk, Bernadette Mazurek, PhD, RN, CPNP/PMHNP, FNAP, FAAN; Williamson, Kathleen M., PhD, RN Evidence-Based Practice, Step by Step: Asking the Clinical Question, AJN The American Journal of Nursing : March 2010 - Volume 110 - Issue 3 - p 58-61 doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000368959.11129.79
2. Scope the Literature
A "scoping search" investigates the breadth and/or depth of the initial question or may identify a gap in the literature.
Eligible studies may be located by searching in:
- Background sources (books, point-of-care tools)
- Article databases
- Trial registries
- Grey literature
- Cited references
- Reference lists
When searching, if possible, translate terms to controlled vocabulary of the database. Use text word searching when necessary.
Use Boolean operators to connect search terms:
- Combine separate concepts with AND (resulting in a narrower search)
- Connecting synonyms with OR (resulting in an expanded search)
Search: pilates AND ("low back pain" OR backache )
Video Tutorials - Translating PICO Questions into Search Queries
- Translate Your PICO Into a Search in PubMed (YouTube, Carrie Price, 5:11)
- Translate Your PICO Into a Search in CINAHL (YouTube, Carrie Price, 4:56)
3. Refine & Expand Your Search
Expand your search strategy with synonymous search terms harvested from:
- database thesauri
- reference lists
- relevant studies
Example:
(pilates OR exercise movement techniques) AND ("low back pain" OR backache* OR sciatica OR lumbago OR spondylosis)
As you develop a final, reproducible strategy for each database, save your strategies in a:
- a personal database account (e.g., MyNCBI for PubMed)
- Log in with your NYU credentials
- Open and "Make a Copy" to create your own tracker for your literature search strategies
4. Limit Your Results
Use database filters to limit your results based on your defined inclusion/exclusion criteria. In addition to relying on the databases' categorical filters, you may also need to manually screen results.
- Limit to Article type, e.g.,: "randomized controlled trial" OR multicenter study
- Limit by publication years, age groups, language, etc.
NOTE: Many databases allow you to filter to "Full Text Only". This filter is not recommended . It excludes articles if their full text is not available in that particular database (CINAHL, PubMed, etc), but if the article is relevant, it is important that you are able to read its title and abstract, regardless of 'full text' status. The full text is likely to be accessible through another source (a different database, or Interlibrary Loan).
- Filters in PubMed
- CINAHL Advanced Searching Tutorial
5. Download Citations
Selected citations and/or entire sets of search results can be downloaded from the database into a citation management tool. If you are conducting a systematic review that will require reporting according to PRISMA standards, a citation manager can help you keep track of the number of articles that came from each database, as well as the number of duplicate records.
In Zotero, you can create a Collection for the combined results set, and sub-collections for the results from each database you search. You can then use Zotero's 'Duplicate Items" function to find and merge duplicate records.

- Citation Managers - General Guide
6. Abstract and Analyze
- Migrate citations to data collection/extraction tool
- Screen Title/Abstracts for inclusion/exclusion
- Screen and appraise full text for relevance, methods,
- Resolve disagreements by consensus
Covidence is a web-based tool that enables you to work with a team to screen titles/abstracts and full text for inclusion in your review, as well as extract data from the included studies.

- Covidence Support
- Critical Appraisal Tools
- Data Extraction Tools
7. Create Flow Diagram
The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagram is a visual representation of the flow of records through different phases of a systematic review. It depicts the number of records identified, included and excluded. It is best used in conjunction with the PRISMA checklist .

Example from: Stotz, S. A., McNealy, K., Begay, R. L., DeSanto, K., Manson, S. M., & Moore, K. R. (2021). Multi-level diabetes prevention and treatment interventions for Native people in the USA and Canada: A scoping review. Current Diabetes Reports, 2 (11), 46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-021-01414-3
- PRISMA Flow Diagram Generator (ShinyApp.io, Haddaway et al. )
- PRISMA Diagram Templates (Word and PDF)
- Make a copy of the file to fill out the template
- Image can be downloaded as PDF, PNG, JPG, or SVG
- Covidence generates a PRISMA diagram that is automatically updated as records move through the review phases
8. Synthesize & Report Results
There are a number of reporting guideline available to guide the synthesis and reporting of results in systematic literature reviews.
It is common to organize findings in a matrix, also known as a Table of Evidence (ToE).

- Reporting Guidelines for Systematic Reviews
- Download a sample template of a health sciences review matrix (GoogleSheets)
Steps modified from:
Cook, D. A., & West, C. P. (2012). Conducting systematic reviews in medical education: a stepwise approach. Medical Education , 46 (10), 943–952.
- << Previous: Citation Management and Formatting Tools
- Next: What are Literature Reviews? >>
- Last Updated: May 15, 2024 11:19 AM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/healthwriting
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design (2020)
Chapter: chapter 2 - literature review and synthesis.
Below is the uncorrected machine-read text of this chapter, intended to provide our own search engines and external engines with highly rich, chapter-representative searchable text of each book. Because it is UNCORRECTED material, please consider the following text as a useful but insufficient proxy for the authoritative book pages.
4 Literature Review and Synthesis Literature Review Purpose of Literature Review Performance-based seismic design (PBSD) for infrastructure in the United States is a developing field, with new research, design, and repair technologies; definitions; and method- ologies being advanced every year. A synthesis report, NCHRP Synthesis 440: Performance- Based Seismic Bridge Design (Marsh and Stringer 2013), was created to capture PBSD understanding up to that point. This synthesis report described the background, objec- tives, and research up until 2011 to 2012 and synthesized the information, including areas where knowledge gaps existed. The literature review in this research report focuses on new infor mation developed after the efforts of NCHRP Synthesis 440. The intention is that this research report will fuel the next challenge: developing a methodology to implement PBSD for bridge design. Literature Review Process Marsh and Stringer (2013) performed an in-depth bridge practice review by sending a questionnaire to all 50 states, with particular attention to regions with higher seismic hazards. The survey received responses from a majority of those agencies. This process was continued in the current project with a request for new information or research that the state depart- ment of transportation (DOT) offices have participated in or are aware of through other organizations. The research team reached out to the list of states and researchers in Table 1. An X within a box is placed in front of their names if they responded. The team also examined the websites of the state DOTs that participated to investigate whether something was studied locally, especially work being developed in California. The research team made an additional effort to perform a practice review of bridge designs, research, and other design industries, specifically in the building industry. The building industry has been developing PBSD for more than 20 years, and some of their developments are appli- cable to bridge design. These combined efforts have allowed the research team to assemble an overview of the state of PBSD engineering details and deployment since Marsh and Stringerâs (2013) report was published. NCHRP Synthesis 440 primarily dealt with the effects of strong ground motion shaking. Secondary effects such as tsunami/seiche, ground failure (surface rupture, liquefaction, or slope failure), fire, and flood were outside the scope of this study. Regardless, their impact on bridges may be substantial, and investigation into their effects is undoubtedly important. C H A P T E R 2
Literature Review and Synthesis 5 The following e-mail was sent to the owners and researchers. Dear (individual): We are assisting Modjeski & Masters with the development of proposed guidelines for Performance- Based Seismic Bridge Design, as part of NCHRP [Project] 12-106. Lee Marsh and our Team at BergerABAM are continuing our efforts from NCHRP Synthesis 440, which included a literature review up to December of 2011. From this timeframe forward, we are looking for published research, contractual language, or owner documents that deal with the following categories: 1. Seismic Hazards (seismic hazard levels, hazard curves, return periods, geo-mean vs. maximum direc- tion, probabilistic vs. deterministic ground motions, conditional mean spectrum, etc.) 2. Structure Response (engineering design parameters, materials and novel columns, isolation bearings, modeling techniques, etc.) 3. Damage Limit States (performance descriptions, displacement ductility, drift ratios, strain limits, rotation curvature, etc.) 4. Potential for Loss (damage descriptions, repairs, risk of collapse, economical loss, serviceability loss, etc.) 5. Performance Design Techniques (relating hazard to design to performance to risk, and how to assess [these] levels together) If you are aware of this type of resource, please provide a contact that we can work with to get this information or provide a published reference we can gather. Your assistance is appreciated. We want to minimize your time, and ask that you respond by Wednesday, 8 February 2017. Thank you again, Research Team Synthesis of PBSD (2012â2016) Objectives of NCHRP Synthesis 440 The synthesis gathered data from a number of different but related areas. Marsh and Stringer (2013), herein referred to as NCHRP Synthesis 440, set the basis for this effort. The research report outline follows what has been added to the NCHRP Synthesis 440 effort since 2012. The information gathered that supplements NCHRP Synthesis 440 includes, but is not limited to, the following topics. ⢠Public and engineering expectations of seismic design and the associated regulatory framework Participation State Alaska DOT Arkansas DOT California DOT (Caltrans) Illinois DOT Indiana DOT Missouri DOT Montana DOT Nevada DOT Oregon DOT South Carolina DOT Utah DOT Washington State DOT Table 1. List of state DOT offices and their participation.
6 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design ⢠Seismic hazard analysis ⢠Structural analysis and design ⢠Damage analysis ⢠Loss analysis ⢠Organization-specific criteria for bridges ⢠Project-specific criteria Where new or updated information is available for these areas, a summary is included. Marsh and Stringer (2013) also identified gaps in the knowledge base of PBSD, current as of 2012, that need to be closed. Knowledge gaps certainly exist in all facets of PBSD; however, key knowledge gaps that should be closed in order to implement PBSD are covered. ⢠Gaps related to seismic hazard prediction ⢠Gaps related to structural analysis ⢠Gaps related to damage prediction ⢠Gaps related to performance ⢠Gaps related to loss prediction ⢠Gaps related to regulatory oversight and training ⢠Gaps related to decision making These knowledge gaps have been filled in somewhat in this research report but, for the most part, these areas are still the key concepts that require additional development to further the development of a PBSD guide specification. Public and Engineering Expectations of Seismic Design and the Associated Regulatory Framework The public expectation of a structure, including a bridge, is that it will withstand an earthquake, but there is a limited understanding of what that actually means. Decision makers struggle to understand how a bridge meeting the current requirements of the AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design (2011), herein referred to as AASHTO guide specifications, will perform after either the expected (design) or a higher level earthquake. Decision makers understand the basis of life safety, wherein the expectation is that no one will perish from a structure collapsing, but often mistakenly believe that the structure will also be usable after the event. In higher level earthquakes, even in some lower level events, this is not true without repair, retrofit, or replacement. In the past decade, there has been an increased awareness by owners and decision makers as to the basis of seismic design. As a result, a need has developed for performance criteria so that economic and social impacts can be interwoven with seismic design into the decision processes (see Figure 1). Several states, including California, Oregon, and the State of Washington, are working toward resiliency plans, although these are developed under different titles or programs within the states. Resiliency has been defined in several ways: (1) amount of damage from an event measured in fatalities, structural replacement cost, and recovery time and (2) the time to resto- ration of lifelines, reoccupation of homes and structures, and, in the short term, resumption of normal living routines. The California DOT Caltrans has generated risk models and is in the process of developing a new seismic design specification to address PBSD in bridge design. The risk models and specifications are not published yet, but the use in PBSD is discussed in greater detail later in this chapter.
Literature Review and Synthesis 7 The State of Washington The State of Washingtonâs resiliency plan, outlined in Washington State Emergency Management CouncilâSeismic Safety Committee (2012), works to identify actions and policies before, during, and after an earthquake event that can leverage existing policies, plans, and initiatives to realize disaster resilience within a 50-year life cycle. The hazard level used for trans- portation planning is the 1000 year event. The goals for transportation systems vary depending on the type of service a route provides, as shown in following components of the plan. For major corridors such as Interstates 5, 90, and 405 and floating bridges SR 520, I-90, and Hood Canal, the target timeframe for response and recovery is between 1 to 3 days and 1 to 3 months, depending on location. The current anticipated timeframe based on current capacity and without modifications is between 3 months to 1 year and 1 to 3 years, depending on location. The actual response and recovery time will depend on a number of factors. For example: 1. The number of Washington State DOT personnel who are able to report to work may be limited by a variety of circumstances, including where personnel were at the time of the earthquake and whether they sustained injuries. 2. Bridges and roadways in earthquake-affected areas must be inspected. How long this takes will depend on the number and accessibility of the structures and the availability of qualified inspectors. 3. Some bridges and segments of road may be rendered unusable or only partially usable as a result of the earthquake or secondary effects. The response and recovery timeframe will depend on the number, the location, and the extent of the damage. 4. Certain earthquake scenarios could result in damage to the Ballard Locks and cause the water level in Lake Washington to drop below the level required to operate the floating bridges. 5. Depending on the scenario and local conditions, liquefaction and slope failure could damage both interstates and planned detours. During the first 3 days after the event, the Washington State Department of Transportation (Washington State DOT) will inspect bridges and begin repairs as needed. Washington State DOTâs first priority will be to open key routes for emergency response vehicles. Subsequent phases of recovery will include setting up detours where necessary and regulating the type and Figure 1. PBSD decision-making process (Guidelines Figure 2.0-1). References to guidelines figures and tables within parentheses indicate the proposed AASHTO guidelines.
8 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design volume of traffic, to give the public as much access as possible while damaged roads and bridges are repaired. For major and minor arterials, which encompass arterial roadways (including bridges) other than the interstates (so therefore includes state highways and many city and county roads), the target timeframe for response and recovery is between 0 to 24 hours and 3 months to 1 year, depending on location; the percentage of roadways that are open for use will increase over this period. Anticipated timeframe based on current capacity is between 1 week to 1 month and 1 to 3 years, depending on location; the percentage of roadways that are open for use will increase over this period. The goal of Washington State Emergency Management Councilâs resiliency plan is to establish a means to coordinate agencies, publicâprivate partnerships, and standards toward these resiliency goals. The plan outlines goals for recovery times for transportation systems in terms of hours, days, weeks, months, and years, with targets to achieve different levels of recovery (see Table 2) as follows. Similar recovery timeframe processes were established for service sectors (e.g., hospitals, law enforcement, and education); utilities; ferries, airports, ports, and navigable waterways; mass transit; and housing. The overall resiliency plan also discusses the degree to which the recovery of one component or sector would depend on the restoration of another. The key interdependencies that the participants identified include information and communication technologies, transportation, electricity, fuel, domestic water supplies, wastewater systems, finance and banking, and planning and community development. It appears that the implementation of the Washington State Emergency Management Councilâs initiative, originally assumed to take 2.5 to 3 years in 2012, has not seen significant development since then. However, the Stateâs initiative to develop a more resilient community has been extended down to the county level, with King Countyâs efforts referenced in Rahman et al. (2014) and, at the city level, with the City of Seattle referenced in CEMP (2015). This reflects the commitment needed not only by the legislature and the state departments but also by other agencies (e.g., county, city, or utilities) and the public to take an interest in, and provide funding for, the development of a resiliency plan. The recovery continuum is presented graphically in Figure 2. Developing this relationship with other agency plans is an iterative process that will take time, as shown in Figure 3. Identifying the critical sectors of the agency is necessary to develop a resiliency model and determine how to approach a disaster recovery framework. King County worked from Washington Stateâs initiative to develop Figure 4. The Oregon DOT Oregon DOT has developed a variation of the approach identified by the State of Wash- ington; further discussion is found later in this chapter. Other Resilience Documents The building industry has recently seen the development of two additional documents that address PBSD in terms of expectations and process. The REDi Rating System from REDi (2013) sets an example for incorporating resilience- based design into the PBSD process. This document outlines structural resilience objectives for organizational resilience, building resilience, loss assessment, and ambient resilience to evaluate and rate the decision making and design methodology using PBSD for a specific project.
Literature Review and Synthesis 9 The document is one of the only references that addresses a system to develop probabilistic methods to estimate downtime. The overall intent is to provide a roadmap to resilience. This roadmap is intended to allow owners to resume business operation and to provide livable conditions quickly after an earthquake. The Los Angeles Tall Buildings Structural Design Council (LATBSDC 2014) created an alter- native procedure specific to their location. Design specification criteria are identified and modi- fications are described as appropriate for the PBSD approach to tall buildings in this localized Minimal (A minimum level of service is restored, primarily for the use of emergency responders, repair crews, and vehicles transporting food and other critical supplies.) Functional (Although service is not yet restored to full capacity, it is sufficient to get the economy moving againâfor example, some truck/freight traffic can be accommodated. There may be fewer lanes in use, some weight restrictions, and lower speed limits.) Operational (Restoration is up to 80 to 90 percent of capacity: A full level of service has been restored and is sufficient to allow people to commute to school and to work.) Time needed for recovery to 80 to 90 percent operational given current conditions. Source: Washington State Emergency Management CouncilâSeismic Safety Committee (2012). Table 2. Washington Stateâs targets of recovery.
10 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design Source: Adapted from FHWA by CEMP (2015). Figure 2. Recovery continuum process. Source: CEMP (2015). Figure 3. Relationship of disaster recovery framework to other city plans. region. This procedure is a good example of how PBSD criteria and methodology need to be established locally, with a knowledge of risk, resources, and performance needs in order to set the criteria for true PBSD. Seismic Hazard Prediction As outlined in NCHRP Synthesis 440, the seismic hazard includes the regional tectonics and the local site characteristics from either a deterministic or probabilistic viewpoint. The deterministic form allows the assessment of shaking at a site as a function of the controlling earthquake that can occur on all the identified faults or sources. The probabilistic approach
Literature Review and Synthesis 11 defines an acceleration used in design that would be exceeded during a given window of time (e.g., a 7% chance of exceedance in 75 years). The following subsections provide a summary of procedures currently used within AASHTO, as well as new issues that should be eventually addressed in light of approaches used by the building industry. AASHTO Probabilistic Approach As summarized in the AASHTO guide specifications, the current approach used by AASHTO involves the use of a probabilistic hazard model with a nominal return period of 1000 years. Baker (2013) noted that the probabilistic seismic hazard analysis involves the following five steps: 1. Identify all earthquake sources capable of producing damaging ground motions. 2. Characterize the distribution of earthquake magnitudes (the rates at which earthquakes of various magnitudes are expected to occur). 3. Characterize the distribution of source-to-site distances associated with potential earthquakes. 4. Predict the resulting distribution of ground motion intensity as a function of earthquake magnitude, distance, and so forth. 5. Combine uncertainties in earthquake size, location, and ground motion intensity, using a calculation known as the total probability theorem. While implementation of the five steps in the probabilistic approach is beyond what most practicing bridge engineers can easily perform, AASHTO, working through the U.S. Geological Survey, developed a website hazard tool that allows implementation of the probabilistic proce- dure based on the latitude and longitude of a bridge site. The product of the website includes peak ground acceleration (PGA), spectral acceleration at 0.2 s (Ss), and spectral acceleration at 1 s (S1). These values are for a reference-site condition comprising soft rock/stiff soil, having a time-averaged shear wave velocity (Vs) over the upper 100 feet of soil profile equal to 2500 feet per second (fps). The Geological Survey website can also correct for local site conditions following procedures in the AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design. One of the limitations of the current U.S. Geological Survey hazard website is that it is based on a seismic hazard model developed in 2002. The Geological Survey updated its seismic model in 2008 and then in 2014; however, these updates are currently not implemented within the AASHTO hazard model on the Geological Surveyâs website. Oregon and the State of Washington have updated the seismic hazard map used by the Oregon DOT and the Washington State Source: Rahman et al. (2014). Figure 4. Resilient King County critical sectors and corresponding subsectors.
12 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design DOT to include the 2014 U.S. Geological Survey hazard model; however, most state DOTs are still using the out-of-date hazard model. Use of the outdated hazard model introduces some inconsistencies in ground motion prediction, relative to the current Geological Survey hazard website tool at some locations. Discussions are ongoing between NCHRP and the U.S. Geological Survey to update the 2002 website tool. Another issue associated with the current AASHTO probabilistic method is that it is based on the geomean of the ground motion. In other words, the ground motion prediction equations in the hazard model are based on the geomean of recorded earthquake motions. These motions are not necessarily the largest motion. The building industry recognized that the maximum direction could result in larger ground motions and introduced maximum direction corrections. These corrections increase spectral acceleration by a factor of 1.1 and S1 by a factor of 1.3. The relevance of this correction to bridges is discussed in the next subsection of this review. The building industry also introduced a risk-of-collapse correction to the hazard model results. This correction is made to Ss and S1. The size of the correction varies from approximately 0.8 to 1.2 within the continental United States. It theoretically adjusts the hazard curves to provide a 1% risk of collapse in 50 years. The risk-of-collapse corrections were developed by the U.S. Geological Survey for a range of building structures located throughout the United States. Although no similar corrections have been developed for bridges, the rationale for the adjust- ment needs to be further evaluated to determine if the rationale should be applied to bridge structures. As a final point within this discussion of probabilistic methods within the AASHTO guide specifications, there are several other areas of seismic response that need to be considered. These include near-fault and basin effects on ground motions, as well as a long-period transition factor. The near-fault and basin adjustments correct the Ss and S1 spectral accelerations for locations near active faults and at the edge of basins, respectively. These adjustments typically increase spectral accelerations at longer periods (> 1 s) by 10% to 20%, depending on specifics of the site. The long-period transition identifies the point at which response spectral ordinates are no longer proportional to the 1/T decay with increasing period. These near-fault, basin, and long-period adjustments have been quantified within the building industry guidance documents but remain, for the most part, undefined within the AASHTO guide specifications. As bridge discussions and research move closer to true probabilistic format for PBSD, these issues need to be addressed as part of a future implementation process. Correction for Maximum Direction of Motion Over the last decade, a debate has been under way within the building industry regarding the appropriate definition of design response spectra (Stewart et al. 2011). The essence of the argument relates to the representation of bidirectional motion via response spectra. In both the AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications (2014), as well as the AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design (SGS), response spectra are established by defining spectral ordinates at two or three different periods from design maps developed by the U.S. Geological Survey for a return period of 1000 years. The resulting spectra are then adjusted for local site conditions, resulting in the final design spectra. In establishing the design maps for parameters such as Ss and S1, the U.S. Geological Survey has traditionally relied upon probabilistic seismic hazard analysis, which utilizes ground motion prediction equations (GMPEs) defined by the geometric mean of the two principal directions of recorded motion. In 2006, Boore introduced a new rotation independent geometric mean definition termed GMRotI50 (Boore et al. 2006). Then, in 2010, Boore developed a new defini- tion that does not rely upon the geometric mean termed RotD50 spectra, which can be generi- cally expressed as RotDNN spectra, where NN represents the percentile of response (i.e., 50 is
Literature Review and Synthesis 13 consistent with the median, 0 is the minimum, and 100 is the maximum). The NGAâWest2 project GMPEs utilized RotD50 spectra for the ground motion models; however, the 2009 National Earthquake Hazards Reduction Program (NEHRP) provisions adopted a factor to modify the median response, RotD50, to the maximum possible response, RotD100 as the spectra for the design maps (Stewart et al. 2011). Introducing RotD100 resulted in a 10% to 30% increase in spectral ordinates results relative to the geometric mean, which has traditionally been used as a basis of seismic design. In order to appreciate the impact of these choices, a brief discussion of RotDNN spectra is warranted. As described in Boore (2010), for a given recording station, the two orthogonal- component time series are combined into a single time series corresponding to different rotation angles, as shown in Equation 1: aROT(t ; θ) = a1(t)cos(θ) + a2(t)sin(θ) (1) where a1(t ) and a2(t ) are the orthogonal horizontal component acceleration time series and θ is the rotation angle. For example, consider the two orthogonal horizontal component time series, H1 and H2, shown in Figure 5. The single time series corresponding to the rotation angle θ is created by combining the Direction 1 and Direction 2 time series. Then, the response spectrum for that single time series can be obtained, as shown in the figure. The process is repeated for a range of azimuths from 0° to one rotation-angle increment less than 180°. If the rotation-angle increment is θ, then there will be 180/θ single time series, as well as 180/θ corresponding response spectra. For example, if θ = 30°, then there will be six single time series (the original two, as well as four generated time series), as well as six response spectra, as shown in Figure 6. Once the response spectra for all rotation angles are obtained, then the nth percentile of the spectral amplitude over all rotation angles for each period is computed (e.g., RotD50 is the median value and RotD100 is the largest value for all rotation angles). For example, at a given period of 1 s, the response spectra values for all rotation angles are sorted, and the RotD100 value would be the largest value from all rotation angles while RotD50 would be the median. This is repeated for all periods, with potentially different rotation angles, producing the largest Source: Palma (2019). Figure 5. Combination of time series to generate rotation dependent spectra.
14 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design response at any given period (period-dependent rotation angle.) Figure 7 shows an example of the two orthogonal horizontal components, as well as the RotD50 and RotD100 spectra for the as-recorded ground motion from the 2011 Christchurch, New Zealand, earthquake at Kaiapoi North School station. As can be seen in the sample spectra (see Figure 7), the RotD100 spectrum represents a sub- stantial increase in demand when compared with the RotD50 spectrum. The main question facing the bridge community from this point onward is the appropriate selection of response spectra definition. This question can only be answered by developing sample designs to both the RotD50 and RotD100 spectra, which would then be evaluated via no-linear time history analysis. Such a study will require multiple bridge configurations and multiple ground motions. As an example of the potential impact, Figure 8 shows the results of a single-degree-of- freedom bridge column designed according to both RotD50 and RotD100 spectra, along with the resulting nonlinear time history analysis. The column was designed using direct displacement- based design to achieve a target displacement of 45 cm. It is clear from the results in Figure 8d that the nonlinear response of the column designed to the RotD100 spectrum matches the target Source: Palma (2019). Figure 6. Example of time series rotations with an angle increment (p) of 30ç. Source: Palma (2019). Figure 7. Sample spectra for a recorded ground motion pair.
Literature Review and Synthesis 15 reasonably well, while designing to the RotD50 spectrum results in displacements that are much greater than expected. This is, of course, only one result of an axisymmetric system. In the future (and outside the scope of this project), a systematic study could be conducted for both single degree of freedom and multiple degrees of freedom systems. The literature on this topic can be divided into two categories: (1) response spectra definitions and (2) impact on seismic response. The majority of the literature addresses the former. For example, Boore et al. (2006) and Boore (2010) introduced orientation-independent measures of seismic intensity from two horizontal ground motions. Boore et al. (2006) proposed two measures of the geometric mean of the seismic intensity, which are independent of the in-situ orientations of the sensors. One measure uses period-dependent rotation angles to quantify the spectral intensity, denoted GMRotDnn. The other measure is the GMRotInn, where I stands for period-independent. The ground motion prediction equations of Abrahamson and Silva (1997), Figure 8. Single bridge column designed according to both RotD50 and RotD100 spectra (Tabas EQ = Tabas earthquake and displ. = displacement).
16 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design Boore et al. (1997), Campbell and Bozorgnia (2003), and Sadigh et al. (1997) have been updated using GMRotI50 as the dependent variable. Since more users within the building industry expressed the desire to use the maximum spec- tral response over all the rotation angles without geometric means, Boore (2010) introduced the measures of ground-shaking intensity irrespective of the sensor orientation. The measures are RotDnn and RotInn, whose computation is similar to GMRotDnn and GMRotInn without computing the geometric means. With regard to impact on seismic response, the opinion paper by Stewart et al. (2011) and the work by Mackie et al. (2011) on the impact of incidence angle on bridge response are relevant. Specifically, Stewart et al. (2011) noted the importance of computational analysis of structures (which had not been done as of 2011) in proposing appropriate spectra definitions. Other Methodologies for Addressing Seismic Ground Motion Hazards There are several other reports that address the question of the methodology that may be utilized in developing the seismic hazard. These recent studies endeavored to create a method- ology that is easier for engineers, as users, to understand how to tie the seismic hazard to the performance expectation. The variability of these approaches also demonstrates the broad range of options and therefore a limited understanding by practitioners in the bridge design industry. Following are some examples that apply to PBSD. Wang et al. (2016) performed a probabilistic seismic risk analysis (SRA) based on a single ground motion parameter (GMP). For structures whose responses can be better predicted using multiple GMPs, a vector-valued SRA (VSRA) gives accurate estimates of risk. A simplified approach to VSRA, which can substantially improve computational efficiency without losing accuracy, and a new seismic hazard de-aggregation procedure are proposed. This approach and the new seismic hazard de-aggregation procedure would allow an engineer to determine a set of controlling earthquakes in terms of magnitude, sourceâsite distance, and occurrence rate for the site of interest. Wang et al. presented two numerical examples to validate the effectiveness and accuracy of the simplified approach. Factors affecting the approximations in the simplified approach were discussed. Kwong and Chopra (2015) investigated the issue of selecting and scaling ground motions as input excitations for response history analyses of buildings in performance-based earthquake engineering. Many ground motion selection and modification procedures have been developed to select ground motions for a variety of objectives. This report focuses on the selection and scaling of single, horizontal components of ground motion for estimating seismic demand hazard curves of multistory frames at a given site. Worden et al. (2012) used a database of approximately 200,000 modified Mercalli intensity (MMI) observations of California earthquakes collected from U.S. Geological Survey reports, along with a comparable number of peak ground motion amplitudes from California seismic networks, to develop probabilistic relationships between MMI and peak ground velocity (PGV), PGA, and 0.3-s, 1-s, and 3-s 5% damped pseudo-spectral acceleration. After associating each ground motion observation with an MMI computed from all the seismic responses within 2 kilometers of the observation, a joint probability distribution between MMI and ground motion was derived. A reversible relationship was then derived between MMI and each ground motion parameter by using a total least squares regression to fit a bilinear function to the median of the stacked probability distributions. Among the relationships, the fit-to-peak ground velocity has the smallest errors, although linear combinations of PGA and PGV give nominally better results. The magnitude and distance terms also reduce the overall residuals and are justifiable on an information theoretical basis.
Literature Review and Synthesis 17 Another approach to developing the appropriate seismic hazard comes out of Europe. Delavaud et al. (2012) presented a strategy to build a logic tree for ground motion prediction in European countries. Ground motion prediction equations and weights have been determined so that the logic tree captures epistemic uncertainty in ground motion prediction for six different tectonic regions in Europe. This includes selecting candidate GMPEs and simultaneously running them through a panel of six experts to generate independent logic trees and rank the GMPEs on available test data. The collaboration of this information is used to set a weight to the GMPEs and create a consensus logic tree. This output then is run through a sensitivity analysis of the proposed weights on the seismic hazard before setting a final logic tree for the GMPEs. Tehrani and Mitchell (2014) used updated seismic hazard maps for Montreal, Canada to develop a uniform hazard spectra for Site Class C and a seismic hazard curve to analyze bridges in the localized area. Kramer and Greenfield (2016) evaluated three case studies following the 2011 Tohoku earthquake to better understand and design for liquefaction. Existing case history databases are incomplete with respect to many conditions for which geotechnical engineers are often required to evaluate liquefaction potential. These include liquefaction at depth, liquefaction of relatively dense soils, and liquefaction of gravelly soils. Kramer and Greenfieldâs investigation of the three case histories will add to the sparse existing data for those conditions, and their interpretations will aid in the validation and development of predictive procedures for liquefaction potential evaluation. Structural Analysis and Design Predicting the structural response to the earthquake ground motions is critical for the PBSD process. NCHRP Synthesis 440 outlined several analysis methods that can be used to accomplish this task. The multimodal linear dynamic procedures are outlined in AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications (AASHTO 2014) and AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design (AASHTO 2011), although the Guide Specifications also include the parameters for performing a model pushover analysis in addition to prescriptive detail practices to ensure energy-dissipating systems behave as intended and other elements are capacity-protected. Other methods of analysis may be better suited for PBSD, but the initial PBSD approach will likely follow the procedures of the AASHTO guide specifications, with multi-level hazards and performance expectations. Limited research and code development have been accomplished since NCHRP Synthesis 440, but one new analysis method, outlined in Babazadeh et al. (2015), includes a three-dimensional finite element model simulation that is used to efficiently predict intermediate damage limit states in a consistent manner, with the experimental observations extracted from the actual tested columns. Other recent articles of structural analysis identified areas of improvement in the current design methodology that may be beneficial to PBSD. Huff and Pezeshk (2016) compared the substitute structure method methodology for isolated bearings with the displacement-based design methodology for ordinary bridges and showed that these two methodologies vary in estimating inelastic displacements. Huff (2016a) identified issues that are generally simplified or ignored in current practice of predicting inelastic behavior of bridges during earthquakes, both on the capacity (in the section of the element type and geometric nonlinearities) and demand (issues related to viscous dampening levels) sides of the process. The current SGS methodology for nonlinear static procedures were compared in Hajihashemi et al. (2017) with recent methodologies for multimodal pushover procedures that take into account all significant modes of the structure and with modified equivalent linearization procedures developed for
18 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design FEMA-440 (FEMA 2005). All of these analysis articles identify areas of current discussion on how to improve the analytical procedures proposed in the SGS. NCHRP Synthesis 440 focused primarily on new analysis methods, but a recent increased focus, in both academia and industry, has to do with new materials and systems and their impacts on PBSD. The evolution of enhanced seismic performance has been wrapped into several research topics, such as accelerated bridge construction (ABC), novel columns, and PBSD. The following are several aspects, though not all-encompassing, which have been improved upon in the last 6 years or so. Improving Structural Analysis Through Better Material Data The analysis and performance of a bridge are controlled with material property parameters incorporated into the seismic analysis models, specifically for the push-over analysis method. AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design (AASHTO 2011) specifies the strain limits to use for ASTM A706 (Grade 60) and ASTM A615 Grade 60 reinforcement. These strain limits come from Caltrans study of 1,100 mill certificates for ASTM A706 Grade 60 in the mid-1990s for projects in Caltrans bridge construction. The results were reported as elongationânot strainâat peak stress, so select bar pull tests were performed to correlate elongation to strain at peak stress. This was assumed to be a conservative approach, though it has recently been validated with a new ASTM A706 Grade 80 study at North Carolina State University by Overby et al. (2015a), which showed Caltrans numbers, by comparison, for Grade 60 are reasonable and conservative. Overby et al. (2015b) developed stress strain parameters for ASTM A706 Grade 80 reinforcing steel. Approximately 800 tests were conducted on bars ranging from #4 to #18 from multiple heats from three producing mills. Statistical results were presented for elastic modulus, yield strain and stress, strain-hardening strain, strain at maximum stress, and ultimate stress. Research is currently under way at North Carolina State University that aims to identify strain limit states, plastic hinge lengths, and equivalent viscous damping models for bridge columns constructed from A706 Grade 80 reinforcing steel. Work is also under way at the University of California, San Diego, on applications of Grade 80 rebar for capacity-protected members such as bridge cap beams. Design Using New Materials and Systems Structural analysis and design are fundamentally about structural response to the earthquake ground motion and the analysis methods used to develop this relationship. The complexity of the analysis depends on the geometry of the structure and elements and the extent of inelastic behavior. This is coupled with the damage, or performance criteria but has been broken out for the purposes of this report and NCHRP Synthesis 440. Next generation bridge columns, often referred to as novel columns, are improving as a tool for engineers to control both the structural analysis, as the make-up of the material changes the inelastic behavior, and the element performance of bridges in higher seismic hazards. The energy-dissipating benefits of low damage materialsâsuch as ultrahigh-performance concrete (UHPC), engineered cementi- tious composites (ECC), and shape memory alloy, fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) wraps and tubes, elastomeric bearings, and post-tensioned strands or barsâcan be utilized by engineers to improve seismic performance and life-cycle costs after a significant seismic event. Recent (Saiidi et al. 2017) studies tested various combinations of these materials to determine if there are columns that can be built with these materials that are equivalent to, or better than, conventional reinforced concrete columns (in terms of cost, complexity, and construction duration) but that improve seismic performance, provide greater ductility, reduce damage, and accommodate a quicker recovery time and reduce loss in both the bridge and the economic environment.
Literature Review and Synthesis 19 Accelerated bridge construction is also a fast-developing field in bridge engineering, with draft guide specifications for design and construction currently being developed for adop- tion by AASHTO for AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications (AASHTO 2014). ABC has economic impacts that go beyond seismic engineering, but research is focusing on details and connections for accelerated construction in higher seismic regions, moving two research paths forward at the same time. Tazarv and Saiidi (2014) incorporated ABC research with novel column research to evaluate combined novel column materials that can be constructed quickly. The research focused on the performance of materials and how to incorporate them into practice. Key mechanical properties of reinforcing SMA were defined as follows: ⢠Observed yield strength (fyo) is the stress at the initiation of nonlinearity on the first cycle of loading to the upper plateau. ⢠Austenite modulus (k1) is the average slope between 15% to 70% of fyo. ⢠Post yield stiffness (k2) is the average slope of curve between 2.5% and 3.5% of strain on the upper plateau of the first cycle of loading to 6% strain. ⢠Austenite yield strength (fy) is the stress at the intersection of line passing through origin with slope of k1 and line passing through stress at 3% strain with slope of k2. ⢠Lower plateau inflection strength (fi) is the stress at the inflection point of lower plateau during unloading from the first cycle to 6% strain. ⢠Lower plateau stress factor, β = 1 â (fi/fy). ⢠Residual strain (eres) is the tensile strain after one cycle to 6% and unloading to 1 ksi (7 MPa). ⢠Recoverable super-elastic strain (er) is maximum strain with at least 90% strain recovery capacity. Using the ASTM standard for tensile testing, er ⤠6%. ⢠Martensite modulus (k3) is the slope of the curve between 8% to 9% strain, subsequent to one cycle of loading to 6% strain, unloading to 1 ksi (7 MPa) and reloading to the ultimate stress. ⢠Secondary post-yield stiffness ratio, α = k3/k1. ⢠Ultimate strain (eu) is strain at failure. A graphical representation is shown in Figure 9, and minimum and expected mechanical properties are listed in Table 3. Other researchers, such as at the University of Washington, are currently testing grouted bars using conventional grouts and finding that these development lengths can be reduced greatly. However, it is the force transfer of the grouted duct to the reinforcing outside the duct that may Figure 9. NiTi SE SMA nonlinear model.
20 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design require additional length to adequately develop the energy-dissipating or capacity-protecting system that was intended by the designer for performance of the bridge in a high seismic event. Tazarv and Saiidi (2014) identified other material properties such as UHPC and ECC, shown in Tables 4 and 5, respectively. Tazarv and Saiidi (2014) also addressed grouted splice sleeve couplers, self-consolidating concrete (SCC), and other connection types that could be used in ABC and novel column configurations, testing these materials in the laboratory to see if various combinations produced a logical system to be carried forward in research, design, and implementation. Trono et al. (2015) studied a rocking post-tensioned hybrid fiber-reinforced concrete (HyFRC) bridge column that was designed to limit damage and residual drifts and that was tested dynamically under earthquake excitation. The column utilized post-tensioned strands, HyFRC, and a combination of unbonded and headed longitudinal reinforcement. There have been two projects related to the field of novel columns and ABC through the National Cooperative Highway Research Program. One project was NCHRP Project 12-101, which resulted in NCHRP Report 864, 2 volumes (Saiidi et al. 2017), and the other project was NCHRP Project 12-105, which resulted in NCHRP Research Report 935 (Saiidi et al. 2020). NCHRP Project 12-101 identified three novel column systemsâspecifically, SMA and ECC, ECC and FRP, and hybrid rocking column using post-tensioned strands and fiber-reinforced Parameter Tensile Compressive,ExpectedbExpectedbMinimuma Table 3. Minimum expected reinforcing NiTi SE SMA mechanical properties. Properties Range Poissonâs Ratio 0.2 Creep Coefficient* 0.2 to 0.8 Total Shrinkage** *Depends on curing conditions and age of loading. up to 900x10-6 Equation Compressive Strength (f'UHPC) f'UHPC 20 to 30 ksi, (140 to 200 MPa) Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (5.5 to 8.5)x10 -6/°F, (10 to 15)x10-6/°C Specific Creep* (0.04 to 0.3)x10 -6/psi, (6 to 45)x10-6/MPa A time-dependent equation for UHPC strength is available. Tensile Cracking Strength (ft,UHPC) ft,UHPC = 6.7 (psi) f'UHPCEUHPC = 49000 (psi) 0.9 to 1.5 ksi, (6 to 10 MPa) Modulus of Elasticity (EUHPC) 6000 to 10000 ksi, (40 to 70 GPa) **Combination of drying shrinkage and autogenous shrinkage and depends on curing method. Table 4. UHPC mechanical properties.
Literature Review and Synthesis 21 polymer confinementâand compared them to a conventional reinforced column. The research and properties of the material are provided; incorporating laboratory tests and calibration, design examples are created to help engineers understand how to use these advanced materials in a linear elastic seismic demand model and to determine performance using a pushover analysis. It is worth noting that ductility requirements do not accurately capture the perfor- mance capabilities of these novel columns, and drift ratio limits are being used instead, similar to the building industry. NCHRP Project 12-101 also provided evaluation criteria that can be evaluated and incorporated by AASHTO into a guide specification or into AASHTO Guide Specifications for LRFD Seismic Bridge Design (AASHTO 2011) directly. NCHRP Project 12-105 synthesized research, design codes, specifications, and contract language throughout all 50 states and combined the knowledge base and lessons learned for ABC into proposed guide specifications for both design and construction. This work focused on connections, and most of that information is related to seismic performance of ABC elements and systems. Earthquake resisting elements (ERE) and earthquake resisting systems (ERS) are specifically identified, defined, and prescribed for performance in AASHTO guide specifica- tions (AASHTO 2011) but only implicitly applied in AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications (AASHTO 2014). Since NCHRP Project 12-105 is applicable to both of these design resources, ERE and ERS are discussed in terms of how to apply performance to the force-based seismic design practice of AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications (AASHTO 2014). The proposed guide specification language also identifies when performance of materials have to be incor- porated into the design, say in higher seismic hazards, and when it is acceptable to apply ABC connections and detailing practices with prescriptive design methodologies. As the industryâs understanding of performance increases, the engineering industry is accepting the benefits that come from a more user-defined engineering practice that is implemented by identifying material properties; evaluating hazards and soil and structural responses; and verifying performance through strain limits, damage limits states, moment curvature, displacements, and ductility. These tools and advancements in ABC and novel column designs, including other material property performance and analytical methodologies, are allowing PBSD to advance in other areas, such as hazard prediction, loss prediction, and the owner decision-making process. Feng et al. (2014a) studied the application of fiber-based analysis to predict the nonlinear response of reinforced concrete bridge columns. Specifically considered were predictions of overall force-deformation hysteretic response and strain gradients in plastic hinge regions. The authors also discussed the relative merits of force-based and displacement-based fiber elements and proposed a technique for prediction of nonlinear strain distribution based on the modified compression field theory. Fulmer et al. (2013) developed a new steel bridge system that is based upon ABC techniques that employ an external socket to connect a circular steel pier to a cap beam through the use of grout and shear studs. The resulting system develops a plastic hinge in the pipe away from the column-to-cap interface. An advantage of the design is ease of construction, as no field welding Properties Range Flexural Strength 1.5 to 4.5 ksi (10 to 30 MPa) Modulus of Elasticity 2600 to 5000 ksi (18 to 34 GPa) Ultimate Tensile Strain 1 to 8% Ultimate Tensile Strength 0.6 to 1.7 ksi (4 to 12 MPa) First Crack Strength 0.4 to 1.0 ksi (3 to 7 MPa) Compressive Strength 3 to 14 ksi (20 to 95 MPa) Table 5. ECC mechanical properties.
22 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design is required: the two assemblies are placed together and the annular space between the column and cap filled with grout. Figure 10 shows the details of this connection, and Figure 11 shows a test of the system. Another system being investigated is isolation bearings or dampening devices. Xie and Zhiang (2016) investigated the effectiveness and optimal design of protective devices for the seismic protection of highway bridges. Fragility functions are first derived by probabilistic seismic demand analysis, repair cost ratios are then derived using a performance-based methodol- ogy, and the associated component failure probability. Subsequently, the researchers tried to identify the optimal design parameters of protective devices for six design cases with various combinations of isolation bearings and fluid dampers and discussed the outcomes. Damage mitigation through isolation and energy dissipation devices is continually improving based on research, development, and implementation in the field. Recent events within the State of Washington, Alaska, and other state agencies have shown that the benefits of these tools can be compromised if the intended performance cannot be sustained for the 75-year design life of the structure. Mackie and Stojadinovic (2015) outlined performance criteria for fabrica- tion and construction that need to be administered properly, and engineers should consider the effects of moisture, salts, or other corrosive environmental conditions that can affect the performance of the isolation or energy-dissipating system. Another constraint with these systems can be the proprietary nature that occurs as a specific isolation or energy-dissipating system is utilized to develop a specific performance expectation that can only be accomplished with the prescribed system. This proprietary nature of these systems can create issues for certain funding sources that require equal bidding opportunities and the project expense that can accompany a proprietary system. To address this type of design constraint, Illinois DOT has been developing an earthquake-resisting system (ERS) to leverage the displacement capacity available at typical bearings in order to provide seismic protection to substructures of typical bridges. LaFave et al. (2013a) identified the effects and design parameters, Source: Fulmer et al. (2013). 5" 4 at 5" O.C. A A A-A Connection Details 45° UT 100% 3 8" 12 Studs Spaced Around Cross Section 30°Typ. 15° Offset Studs Inside Pipe from Cap Beam CL HSS16x0.500 Pipe 24x0.500 2'-0"2 14 " 4 at 5" O.C. 212"-34 "à Shear Studs 1'-11" Pipe Stud Detail Grout Provided By and Placed by NCSU Figure 10. Grouted shear stud bridge system.
Literature Review and Synthesis 23 such as fuse capacity, shear response, and sliding response, which can be used to account for more standard bearing configurations in seismic analysis, especially lower seismic hazard regions. A variation on the use of bearings in order to improve seismic performance of a pier wall configuration was outlined in Bignell et al. (2006). Historically, pinned, rocking, and sliding bearings have been used with interior pier walls and steel girder superstructures. These bearing configurations were compared with replacement elastomeric bearing configurations and details for structural analysis techniques, damage limit states, and structural fragility, and performance through probability distributions were utilized as a PBSD process for determining solutions to seismic isolation and enhanced seismic performance. The foundation conditions, pier wall effects, bearing type, and even embankment effects to structural performance were included in this evaluation. Another approach to enhanced performance is modifications to foundation elements or increased understanding and modeling of soilâstructure interaction, specifically where lateral spread or liquefaction design conditions make conventional bridge design and elements imprac- tical. One example of this is the seismic design and performance of bridges constructed with rocking foundations, as evaluated in Antonellis and Panagiotou (2013). This type of rocking goes beyond the loss of contact area currently allowed in the guide specifications. The applica- tion of columns supported on rocking foundations accommodates large deformations, while there is far less damage, and can re-center after large earthquakes. Another approach is to tie a tolerable displacement of an individual deep foundation element to a movement that would cause adverse performance, excessive maintenance issues, or functionality problems with the bridge structure. Roberts et al. (2011) established a performance-based soilâstructureâinteraction design approach for drilled shafts. Chiou and Tsai (2014) evaluated displacement ductility of an in-ground hinging of a fixed head pile. Assessment formulas were developed for the displacement ductility capacity of a fixed-head pile in cohesion-less soils. The parameters in the formulas included the sectional over-strength ratio and curvature ductility capacity, as well as a modification factor for consider- ing soil nonlinearity. The modification factor is a function of the displacement ratio of the pileâs ultimate displacement to the effective soil yield displacement, which is constructed through a number of numerical pushover analyses. Source: Fulmer et al. (2013). Figure 11. Photograph of completed system before seismic testing showing hinge locations.
24 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design Damage Analysis As stated in NCHRP Synthesis 440, it is a fundamental need for the PBSD methodology to determine the type of damage and the likelihood that such damage will occur in the particular components of the structural system. This determination is of vital importance, as the damage sustained by a structure (and its nonstructural components) is directly relatable to the use or loss of a system after an earthquake. Therefore, there is a need to be able to reliably link structural and nonstructural response (internal forces, deformations, accelerations, and displacements) to damage. This is the realm of damage analyses, where damage is defined as discrete observable damage states (e.g., yield, spalling, longitudinal bar buckling, and bar fracture). Although the primary focus of the discussions is on structural components, similar considerations must be made for nonstructural components as well. NCHRP Synthesis 440 outlined an initial discussion on types of structural damage observed during historic earthquakes and laboratory experiments, prefaced the methods that have been developed to predict damage, identified structural details and concepts that could be used to reduce damage even in strong ground shaking, and reviewed post-event inspection tools. The new materials discussed in previous sections also apply to this discussion but are not repeated herein. Accurate damage prediction relies upon accurate definitions of performance limit states at the material level (i.e., strain limits) and the corresponding relationship between strain and displacement. Examples of recent research follow. Research by Feng et al. (2014b, 2014c) used finite element analysis validated by experimental test results to develop a model for predicting the tension strain corresponding to bar buckling. The model considers the impact of loading history on the boundary conditions of longitudinal bar restraint provided by the transverse steel. Goodnight et al. (2016a) identified strain limits to initiate bar buckling based on experimental results from 30 column tests (Equation 2). Following additional bidirectional tests on 12 columns, Equation 2 was revised to Equation 3. In addition, strain limit state equations were proposed for the compression strain in concrete to cause spiral yielding (Goodnight et al. 2017a). Goodnight et al. (2016b) also developed a new plastic hinge length model based on the data collected during those tests, which accounts for the actual curvature distribution in RC bridge columns. The revised model separates the strain penetration component from the flexural component while also recognizing that the hinge length for compression is smaller than that for tension. Brown et al. (2015) developed strain limit state (Equation 4) (tube wall local buckling) and equivalent viscous damping equations for reinforced concrete filled steel tubes (RCFSTs). The recommendations of the authors were based upon reversed cyclic tests of 12 RCFSTs of variable D/t (diameter to thickness) ratios. 0.03 700 0.1 (2)bucklingbar f E P f A s s yhe s ce g ε = + Ï â â² 0.032 790 0.14 (3)bucklingbar f E P f A s s yhe s ce g ε = + Ï â â² 0.021 9100 (4)tension buckling D t yε = â ⥠ε
Literature Review and Synthesis 25 where rs = reinforcement ratio, fyhe = expected yield strength of the steel tube (ksi), Es = elastic modulus of steel (ksi), P = axial load (kip), f â²ce = expected concrete strength (ksi), Ag = gross area of concrete (in.2), D = diameter of tube (in.), t = thickness of tube (in.), and ey = yield strain for steel (in./in.). Loss Analysis The PBSD combines the seismic hazard, structural, and damage analysis into a performance matrix that can be estimated into a loss metric. There are many loss metrics that can be used by, and that are important to, stakeholders and decision makers (discussed in detail in NCHRP Synthesis 440), but all these metrics can be boiled down to three main categories: deaths, dollars, and downtime. Bertero (2014) discussed earthquake lessons, in terms of loss, to be considered in both design and construction of buildings. At the beginning of 2010, two large earthquakes struck the Americas. The January 12, 2010, Haiti earthquake with a magnitude 7.0 produced about 300,000 deaths (second by the number of fatalities in world history after the 1556 Shaanxi, China earthquake). A month later, the February 27, 2010, Maule Chilean earthquake with a magnitude 8.8 (an energy release 500 times bigger than that from the Haiti earthquake) produced 500 deaths, most due to the resulting tsunami. However, the Chilean earthquake caused more than $30 billion of direct damage, left dozens of hospitals and thousands of schools nonoperational, and caused a general blackout for several hours, as well as the loss of service of essential communications facilities, crucial to take control of the chaotic after-earthquake situ- ation. Bertero (2014) compared the severity of both earthquakes and comments on their effects to life and the economy of the affected countries, as well as the features of the seismic codes or the absence of codes. An example of risk analysis with PBSD is utilized in Bensi et al. (2011), with the development of a Bayesian network (BN) methodology for performing infrastructure seismic risk assessment and providing decision support with an emphasis on immediate post-earthquake applications. A BN is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of random variables and their probabilistic dependencies. The proposed methodology consists of four major components: (1) a seismic demand model of ground motion intensity as a spatially distributed random field, accounting for multiple sources and including finite fault rupture and directivity effects; (2) a model for seismic performance of point-site and distributed components; (3) models of system performance as a function of component states; and (4) models of post-earthquake decision making for inspection and operation or shutdown of components. The use of the term Bayesian to describe this approach comes from the well-known Bayes rule, attributed to the 18th-century mathematician and philosopher Thomas Bayes: A B AB B B A B A( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) ( )= =Pr Pr Pr Pr Pr Pr (5) Pr(AB) is the probability of joint occurrence of Events A and B; Pr(A) is the marginal probability of Event A; Pr(A|B) is the conditional probability of Event A, given that Event B
26 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design has occurred; and Pr(B) is the marginal probability of Event B. The quantity Pr(B | A) is known as the likelihood of the observed Event B. Note that the probability of Event A appears on both sides of Equation 5. The Bayes rule describes how the probability of Event A changes given information gained about the occurrence of Event B. For discrete nodes, a conditional probability table is attached to each node that provides the conditional probability mass function (PMF) of the random variable represented by the node, given each of the mutually exclusive combinations of the states of its parents. For nodes without parents (e.g., X1 and X2 in Figure 12), known as root nodes, a marginal probability table is assigned. The joint PMF of all random variables X in the BN is constructed as the product of the conditional PMFs: (6) 1 p x p x Pa xi ii nâ( ) ( )( )= = Bensi et al. (2011) goes on to introduce BN models further and discusses how to incorporate BN-based seismic demand models into bridge design. The BN methodology is applied to modeling of random fields, construction of an approximate transformation matrix, and numer- ical investigation of approximation methods, including a discussion on the effect of correlation approximations on system reliability. Modeling component performance with BNs to capture seismic fragility of point-site components and distributed components, as well as modeling system performance of BNs with both qualitative and conventional methods, is explained. This reference goes on to identify efficient minimal link set (MLS), minimal cut set (MCS) formulations, optimal ordering of efficient MLS and MCS formulations, and heuristic augmen- tation that can be utilized with the BN methodology. Bensi et al. (2011) continues the PBSD process by addressing the owner decision-making process (see more discussion later in the report) and how to incorporate this model into that process. Two example problems are provided utilizing this methodology, including a California high-speed rail system that incorporates the bridge modeling into the example. Similarly, in Tehrani and Mitchell (2014), the seismic performance of 15 continuous four- span bridges with different arrangements of column heights and diameters was studied using incremental dynamic analysis (IDA). These bridges were designed using the Canadian Highway Bridge Design Code provisions (CSA 2006). The IDA procedure has been adopted by some guidelines to determine the seismic performance, collapse capacity, and fragility of buildings. Similar concepts can be used for the seismic assessment of bridges. Fragility curves can be devel- oped using the IDA results to predict the conditional probability that a certain damage state is exceeded at a given intensity measure value. Assuming that the IDA data are lognormally distributed, it is possible to develop the fragility curves at collapse (or any other damage state) by computing only the median collapse capacity and the logarithmic standard deviation of the IDA results for any given damage state. The fragility curves can then be analytically computed using Equation 7 as follows: ln ln (7)50% TOT P failure S x x S a a C( )( ) ( )= = Φ â β     where function F = cumulative normal distribution function, SCa 50% = median capacity determined from the IDA, and βTOT = total uncertainty caused by record-to-record variability, design requirements, test data, and structural modeling. Figure 12. A simple BN.
Literature Review and Synthesis 27 The seismic risk associated with exceeding different damage states in the columns, includ- ing yielding, cover spalling, bar buckling, and structural collapse (i.e., dynamic instability) was predicted. Some simplified equations were derived for Montreal, Quebec, Canada, to estimate the mean annual probability of exceeding different damage states in the columns using the IDA results. Repair and retrofit procedures are linked to loss predictions, as outlined in the FHWAâs retro- fitting manual (Buckle et al. 2006). Several chapters/articles address analysis, methodologies, effects, analytical tools, and costs for retrofit and repairs to mitigate damage or return a structure to a serviceable condition. Zimmerman et al. (2013) is one example, in which numerical techniques and seismic retrofit solutions for shear-critical reinforced concrete columns was investigated, utilizing test data of a reinforced concrete column with widely spaced transverse reinforcement. The study focused on the analysis method of nonlinear trusses and the retrofit option known as supplemental gravity columns, which is an example of how loss prediction and the analysis process are linked and should be iterated through PBSD. Organization-Specific Criteria for Bridges and Project-Specific Criteria NCHRP Synthesis 440 has two sections of criteria: organization-specific criteria for bridges and project-specific criteria. New information for both of these sections since NCHRP Synthesis 440 published is combined. The California DOT (Caltrans) Caltrans is currently updating their Seismic Design Criteria (SDC) to specify requirements to meet the performance goals for newly designed Ordinary Standard and Recovery Standard con- crete bridges. Nonstandard bridges require Project-Specific Seismic Design Criteria, in addition to the SDC, to address their nonstandard features. For both standard and nonstandard bridges, Caltrans is also categorizing their inventory in terms of Ordinary Bridges, Recovery Bridges, and Important Bridges. Some states have had issues with terms like Important or Essential, as a bridge is considered important to those that utilize each bridge. Caltrans is using these terms to correlate with loss analysis of an ownerâs infrastructure and the time to reopen the bridge to support lifeline and recovery corridors. The bridge performance is also evaluated using a dual-seismic hazard; for Caltrans SDC they are listed as a Safety Evaluation Earthquake (SEE) for Ordinary Bridges. Both SEE and Functional Evaluation Earthquake (FEE) for Recovery Bridges are summarized in Table 6. Caltrans SDC revisions will also provide updates to the design parameters in Chapter 3 of the SDC and updates to both the analysis methods and displacement ductility demand values in Chapter 4 of the SDC. The adjustments to the displacement ductility demand values are revised to limit the bridge displacements beyond the initial yielding point of the ERE, specifically if a recovery standard bridge is being designed. The revisions to their SDC is an example of how PBSD is being gradually introduced as a better method of dealing with the hazards, soilâstructure interaction, analysis tools, methodologies, material properties, damage states, performance, and loss. Similar revisions are being made to Seismic Design Specifications of Highway Bridges, as detailed in Japan Road Association (JRA) revisions in 2012. A synopsis of the revisions is provided in Kuwabara et al. (2013). The JRA specifications apply to Japanese road bridges and consist of five parts: Part I, Common; Part II, Steel Bridges; Part III, Concrete Bridges; Part IV, Substruc- tures; and Part V, Seismic Design. The revisions are based on improvements in terms of safety,
28 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design serviceability, and durability of bridges. Based on those lessons, design earthquake ground motions corresponding to the subduction-type earthquake were revised, and the requirements for easy and secure maintenance (inspection and repair works) for the bridges were clearly specified. JRA has clarified their performance of ERE conventionally reinforced columns for a dual-level (SPL 2 and SPL 3) seismic performance evaluation, as summarized in Table 7. The JRA 2012 revisions also address connection failures between reinforced concrete steel piles and the pile-supported spread footing to improve structural detailing and performance at the head of the piles. This is similar to research performed by the University of Washington, see Stephens et al. (2015) and Stephens et al. (2016) for both Caltrans and Washington State DOT, respectively, to evaluate capacity protecting this region and even considering the development of plastic hinges at these locations for combined hazard events or large lateral spreading and liquefaction occurrences. Caltrans also funded a study by Saini and Saiidi (2014) to address probabilistic seismic design of bridge columns using a probabilistic damage control approach and reliability analysis. Source: Caltrans. BRIDGE CATEGORY SEISMIC HAZARD EVALUATION LEVEL POST EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE STATE EXPECTED POST EARTHQUAKE SERVICE LEVEL Table 6. Caltrans draft proposed seismic design bridge performance criteria. SPL2 SPL3 Note: SPL1: Fully operational is required. Limit state of bridge is serviceability limit state. Negligible structural damage and nonstructural damage are allowed. Table 7. Seismic performance of bridge and limit states of conventionally reinforced concrete bridge column.
Literature Review and Synthesis 29 The probabilistic damage control approach uses the extent of lateral displacement nonlinearity defined by Damage Index (DI) to measure the performance of bridge columns. DI is a measure of damage from the lower measure of zero damage to the ultimate measure of a collapse mecha- nism for an element that has been subjected to base excitations. The performance objective was defined based on predefined apparent Damage States (DS), and the DS were correlated to DIs based on a previous study at the University of Nevada, Reno (Figure 13) (Vosooghi and Saiidi 2010). A statistical analysis of the demand damage index (DIL) was performed to develop fragility curves (load model) and to determine the reliability index for each DS. The results of the reliability analyses were analyzed, and a direct probabilistic damage control approach was developed to calibrate design DI to obtain a desired reliability index against failure. The calculated reliability indices and fragility curves showed that the proposed method could be effectively used in seismic design of new bridges, as well as in seismic assessment of existing bridges. The DS and DI are summarized with performance levels defined by Caltrans in Table 8, which shows the correlation between DS and DI. Figure 14 shows a fragility curve using lognormal distribution. Figure 15 shows both the fragility curves (upper two graphs) and reliability indices (lower two graphs) for four column bents (FCBs), with 4-foot diameter columns that are 30 feet in length in Site D for both the 1000 year and 2500 year seismic events. Note: O-ST = ordinary standard bridge, O-NST = ordinary nonstandard bridge, Rec. = recovery bridge, Imp. = important bridge, and NA = not applicable. Damage State (DS) Service to Public Service to Emergency Emergency Repair Design Damage Index (DI) Earthquake Levels (Years) Table 8. Design performance levels. DI P (D I { D S) Figure 13. Correlation between DS and DI.
30 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design Figure 14. Fragility curve. 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% 0.00 0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 P (D I L ) DIL 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 R el ia bi lit y In de x | D S DS3 DS4 DS5 DS6 Damage State (DS) 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 R el ia bi lit y In de x | D S DS3 DS4 DS5 DS6 Damage State (DS) (a) (b) (d)(c) 0.00 0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 DIL 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% P (D I L ) Figure 15. Fragility curves and reliability indices for FCBs with 4-foot columns in Site D. The Oregon DOT The Oregon DOT is developing a global plan for addressing resiliency in order to improve recovery for the next Cascadia Earthquake and Tsunami, using PBSD in terms of applying applicable hazards, identifying critical services, developing a comprehensive assessment of structures and systems, and updating public policies. The resilience goals are similar to those discussed at the beginning of this chapter, with the following statement: Oregon citizens will not only be protected from life-threatening physical harm, but because of risk reduction measures and pre-disaster planning, communities will recover more quickly and with less continuing vulnerability following a Cascadia subduction zone earthquake and tsunami.
Literature Review and Synthesis 31 Research has shown that the next great (magnitude 9.0) Cascadia subduction zone earth- quake is pending, as shown in Figure 16. This comparison of historical subduction zone earthquakes in northern California, Oregon, and Washington covers 10000 years of seismic history. The evidence of a pending event has made decision makers and the public take notice and put forth resources to develop strategies revolving around PBSD. Oregonâs performance-based features are modified from NCHRP Synthesis 440 to account for a third hazard condition: Cascadia Subduction Zone Earthquake (CSZE) in Oregon DOTâs Bridge Design and Drafting ManualâSection 1, Design (Oregon DOT 2016a; see also Oregon DOT 2016b). Design of new bridges on and west of US 97 references two levels of perfor- mance criteria: life safety and operational. Design of new bridges east of US 97 requires life safety criteria only. Seismic design criteria for life safety and operational criteria are described as follows. ⢠âLife Safetyâ Criteria: Design all bridges for a 1,000-year return period earthquake (7 percent prob- ability of exceedance in 75 years) to meet the âLife Safetyâ criteria using the 2014 USGS Hazard Maps. The probabilistic hazard maps for an average return period of 1,000 years and 500 years are available at ODOT Bridge Section website, but not available on USGS website. To satisfy the âLife Safetyâ criteria, use Response Modification Factors from LRFD Table 3.10.7.1-1 using an importance category of âother.â ⢠âOperationalâ Criteria: Design all bridges on and west of US 97 to remain âOperationalâ after a full rupture of Cascadia Subduction Zone Earthquake (CSZE). The full-rupture CSZE hazard maps are available at the ODOT Bridge Section website. To satisfy the âOperationalâ criteria, use Response Modification Factors from LRFD Table 3.10.7.1-1 using an importance category of âessential.â When requested in writing by a local agency, the âOperationalâ criteria for local bridges may be waived. The CSZE is a deterministic event, and a deterministic design response spectrum must be generated. To allow for consistency and efficiency in design for the CSZE, an application for generating the design response spectra has been developed by Portland State University (Nako et al. 2009). AASHTO guide specifications values for Table 3.4.2.3-1 are modified into two tables for (1) values of Site Factor, Fpga, at zero-period on the acceleration spectrum and (2) values of Site Factor, Fa, for short-period range of acceleration spectrum. Table 3.4.2.3-2 is replaced with values of Site Factor, Fv, for long-period range of acceleration spectrum. For seismic retrofit projects, the lower level ground motion is modified to be the CSZE with full rupture, as seen in Table 9. Performance levels, including performance level zero (PL0), are specified based on bridge importance and the anticipated service life (ASL) category required. Source: OSSPAC (2013). Figure 16. Cascadia earthquake timeline.
32 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design The South Carolina DOT South Carolina Department of Transportation (South Carolina DOT) has updated its geo- technical design manual (South Carolina DOT 2019). Chapters 12, 13, and 14 for geo technical seismic analysis, hazard, and design, respectively, have been updated to current practices and research, including incorporation of PBSD hazard prediction. South Carolina DOT is also updating their site coefficients to be more appropriate for South Carolinaâs geologic and seismic conditions; see Andrus et al. (2014). Note that with the revisions, South Carolina DOT issued a design memorandum in November 2015 that revised the substructure unit quantitative damage criteria (maximum ductility demand) table (Table 7.1 of the SCDOT Seismic Design Specifications for Highway Bridges). See Table 10. The Utah DOT The Utah DOT and Brigham Young University (see Franke et al. 2014a, 2014b, 2015a, 2015b, 2015c, 2016) are researching the ability for engineers to apply the benefits of the full performance- based probabilistic earthquake analysis without requiring specialized software, training, or education. There is an emphasis on differences between deterministic and performance-based procedures for assessing liquefaction hazards and how the output can vary significantly with these two methodologies, especially in areas of low seismicity. Guidance is provided regarding when to use each of the two methodologies and how to bind the analysis effort. Additionally, a simplified performance-based procedure for assessment of liquefaction triggering using liquefaction loading maps was developed with this research. The components of this tool, as well as step-by-step procedures for the liquefaction initiation and lateral spread displacement models, are provided. The tool incorporates the simplified performance-based procedures determined with this research. National Highway Institute Marsh et al. (2014) referenced a manual for the National Highway Instituteâs training course for engineers to understand displacement-based LRFD seismic analysis and design of bridges, which is offered through state agencies and open to industry engineers and geotechnical engi- neers. This course helps designers understand the principles behind both force-based AASHTO (AASHTO 2014) and displacement-based AASHTO (AASHTO 2011) methodologies, including a deeper understanding of what performance means in a seismic event. Other similar courses are also being offered to industry and are improving the understanding of practicing engineers. Federal Emergency Management Agency The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) has developed a series of design guidelines for seismic performance assessment of buildings and three of the five documents EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTION BRIDGE IMPORTANCE and SERVICE LIFE CATEGORY Table 9. Modifications to minimum performance levels for retrofitted bridges.
Literature Review and Synthesis 33 are referenced in FEMA (2012a, 2012b, 2012c). A step-by-step methodology and explanation of implementation are provided for an intensity-based assessment and for a time-based assess- ment. The process of identifying and developing appropriate fragility curves is demonstrated. A software program called Performance Assessment Calculation Tool has also been developed with a user manual that is included in the FEMA documents to help engineers apply PBSD to the building industry. Japan Road Association The Japan Road Association (JRA) Design Specifications have been revised based on the performance-based design code concept in response to the international harmonization of design codes and the flexible employment of new structures and new construction methods. Figure 17 shows the code structure for seismic design using the JRA Design Specifications. The performance matrix is based on a two-level ground motion (Earthquakes 1 and 2), with the first one based on an interpolate-type earthquake and magnitude of around 8, and the second one with a magnitude of around 7 with a short distance to the structure. Kuwabara et al. (2013) outlined the incremental revisions from the JRA Design Specif i- cations between 2002 and 2012. These revisions include, but are not limited to, the ductility design method of reinforced concrete bridges, plastic hinge length equation, evaluation of hollow columns, and the introduction of high-strength steel reinforcement. Following the 2016 earthquake in Kumamoto, Japan, a new version of the JRA Design Specifications is in the works. Note: Analysis for FEE is not required for OC III bridges. Source: South Carolina DOT (2015). Design Earthquake Operational Classification (OC)Bridge Systems Table 10. South Carolina DOT substructure unit quantitative damage criteria (maximum ductility demand ld).
34 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design Identification of Knowledge Gaps The resources to develop guide specifications for PBSD are improving with examples such as the upcoming Seismic Design Criteria, Version 2 from Caltrans, which will address aspects of PBSD and the building industryâs efforts to develop practices in PBSD and tools for engineers and owners to collaborate on solutions based on performance criteria and expectations. There is still a perception that the bridge industry could better predict likely performance in large, damaging earthquakes than is being done at the present, and there are still gaps in that knowledge base that need to be closed. Most of the knowledge gaps listed in Marsh and Stringer (2013) are still applicable today; see Table 11. The technology readiness levels represent what has been developed and used; what research is done, ongoing, and being discussed; and what only exists in concept. Knowledge gaps certainly exist in all facets of PBSD; however, other key knowledge gaps beyond those listed in NCHRP Synthesis 440 (Marsh and Stringer 2013) that should be closed in order to improve the implementation of PBSD are covered. Objectives of Codes Mandated Specifications Overall Goals Functional Requirements (Basic Requirements) Performance Requirement Level Verification Methods and Acceptable Solutions Can be Modified or May be Selected with Necessary Verifications Importance, Loads, Design Ground Motion, Limit States Principles of Performance Verification Verifications of Seismic Performances (Static and Dynamic Verifications) Evaluation of Limit States of Members (RC and Steel Columns, Bearings, Foundations and Superstructure) Unseating Prevention Systems Principles of Seismic Design Figure 17. Code structure for seismic design using JRA design specifications. TRL Description 0-25 25-50 50-75 75-100 1 PBSD concept exists 2 Seismic hazard deployable 3 Structural analysis deployable 4 Damage analysis deployable 5 Loss analysis deployable 6 Owners willing and skilled in PBSD 7 Design guidelines 8 Demonstration projects 9 Proven effectiveness in earthquake Technology Readiness Level (TRL) % of Development Complete Table 11. Technology readiness levels for PBSD.
Literature Review and Synthesis 35 Gaps related to structural analysis can include minimum and expected properties for reinforcing greater than Grade 80, stainless steel, and other materials that can improve serviceability and in some conditions performance. Oregon DOT has been using stainless steel in their bridges located along the coastline and other highly corrosive environments to extend the service life of the bridge; however, many of these locations are also prone to large CSZE and the use of these materials in earthquake resisting elements is still being developed. In the State of Washingtonâs resiliency plan, outlined in Washington State Emergency Management CouncilâSeismic Safety Committee (2012), what is missing is a link between damage levels and return to service. This is a knowledge gap given what we know structurally and what this report is suggesting as a desired goal for post-earthquake recovery. Gaps related to decision makers can include bridge collapse. It is not intended that the PBSD guide specifications will address tsunami events, but the JRA specifications do address tsunami as well as landslide effects. Figures 18 and 19 are examples of these other types of failure systems and show the collapse of bridges caused by effects other than ground motion (Kuwabara et al. 2013). The decision to combine these types of effects with a seismic hazard, even combining liquefaction, down drag, and lateral spreading effects, needs additional clarification and is currently left up to the owner to assess implications of probability, safety, and cost ramifications. Liang and Lee (2013) summarized that in order to update the extreme event design limit states in the AASHTO 2014, combinations of all nonextreme and extreme loads need to be formulated on the same probability-based platform. Accounting for more than one-time variable load creates a complex situation, in which all of the possible load combinations, even many that are not needed for the purpose of bridge design, have to be determined. A formulation of a criterion to determine if a specific term is necessary to be included or rejected is described, and a comparison of the value of a given failure probability to the total pre-set permissible design failure probability can be chosen as this criterion. Figure 18. Collapse of bridge due to landslide. (Note: Reprinted courtesy of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, U.S. Department of Commerce. Not copyrightable in the United States). Source: Kuwabara et al. (2013).
36 Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design While the seismic hazard definition was once thought to be relatively well understood, there is a growing knowledge gap related to the effect of rotation angle on intensity of ground motions and how the use of a geometric mean of the motions, or other methods of including the effect of rotation angle (RotDxx), should be incorporated into seismic design. This issue is not specific to PBSD; like all seismic design methods, PBSD is reliant on a full understanding of the hazard definition for proper implementation. The knowledge gaps identified in NCHRP Synthesis 440 are still applicable. Many of these knowledge gaps will become evident to both engineers and decision makers as the PBSD guidelines are developed. Overall, the baseline information to develop PBSD guide specifica- tions are in place. Industryâs end goal of understanding the relationship between risk-based decision making and design decisions and methodologies to meet performance goals is going to be an iterative process. Figure 19. Collapse of bridge due to tsunami. (Note: Reprinted courtesy of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, U.S. Department of Commerce. Not copyrightable in the United States). Source: Kuwabara et al. (2013).
Performance-based seismic design (PBSD) for infrastructure in the United States is a developing field, with new research, design, and repair technologies; definitions; and methodologies being advanced every year.
The TRB National Cooperative Highway Research Program's NCHRP Research Report 949: Proposed AASHTO Guidelines for Performance-Based Seismic Bridge Design presents a methodology to analyze and determine the seismic capacity requirements of bridge elements expressed in terms of service and damage levels of bridges under a seismic hazard. The methodology is presented as proposed AASHTO guidelines for performance-based seismic bridge design with ground motion maps and detailed design examples illustrating the application of the proposed guidelines and maps.
Supplemental materials to the report include an Appendix A - SDOF Column Investigation Sample Calculations and Results and Appendix B - Hazard Comparison.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND STUDIES

Related Papers
Ana Liza Sigue
Motoky Hayakawa
Rene E Ofreneo
... Rene E. Ofreneo University of the Philippines School of Labor and Industrial Relations ... Erickson, Christopher L.; Kuruvilla, Sarosh ; Ofreneo, Rene E.; and Ortiz, Maria Asuncion , &quot;Recent Developments in Employment Relations in the Philippines&quot; (2001). ...
Lucita Lazo
This book begins by looking at the status of women in Filipino society and their place in the general socio-economic situation. It continues with sections on education and training in the Philippines and work and training. The next section reviews the constraints to women’s participation in training. In the summary the author gives a general overview of the situation of women and opportunities for work and training in the Philippines and offers some practical suggestions for the enhancement of women’s training and development.
EducationInvestor Global
Tony Mitchener
Rosalyn Eder
In this article, I examine the role of CHED and the Technical Panels (TPs) in the “production” of the globally competitive Filipina/o worker. For this paper, I draw on relevant literature on the topic and take nurse education, which is rooted in the colonial system established during the US-American occupation, as an example of how CHED and the TPs could be more linked to labor migration. I use the colonial difference - a space that offers critical insights and interpretation - to illustrate how coloniality remains hidden under the cloak of modernity. Link to the article: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00131946.2016.1214913
Asia Pacific Journal of Management and Sustainable Development ISSN 2782-8557(Print)
Ryan O Tayco , Pio Supat
This study aims to determine the employability of the Negros Oriental State University graduates from 2016 to 2020. Employability is measured using different dimensions-from the graduates' side including the perspectives of the employers. A total of 1, 056 NORSU graduates and 68 employers locally and abroad answered the questionnaire through online and offline survey methods. Basic statistics were used and simple linear regression was also used to estimate the relationship between manifestations of respondents in NORSU VMGOs and the job performance as perceived by the employers. Most of the respondents in the study are presently employed and work locally. Many of them stay and accept the job because of the salaries and benefits they received, a career challenge, and related to the course they have taken in college. The study shows that the curriculum used and competencies learned by the NORSU graduates are relevant to their job. Competencies such as communication skills, human relations skills, critical thinking skills, and problem-solving skills are found to be useful by the respondents. It is found that the manifestation of the respondents is very high and homogenous. The same can be said with job performance as perceived by employers in terms of attitudes and values, skills and competencies, and knowledge. Furthermore, job performance and the manifestation of NORSU VMGOs have a significant relationship. That is, those respondents who have higher job performance in terms of attitude and values, skills and competencies, and knowledge have higher manifestations of NORSU VMGOs.
Annals of Tropical Research
Pedro Armenia
Ezekiel Succor
RELATED PAPERS
Conceptos básicos y estrategias para el desarrollo y optimización de bioprocesos
César Reyes Reyes
Lisans Bitirme Tezi
Tuğba Demir
Simon Mimouni
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease
Samadhi Moreno Campuzano
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
Cold Regions Science and Technology
Don Spencer
Pollarise GROUPS
Resources and Conservation
Rodrigo Jordan
Inorganica Chimica Acta
S. Stavchansky
Journal of Cell Science
Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis
Yogita A Deshmukh
Josefina Vivar
IJIRMPS - International Journal of Innovative Research in Engineering & Multidisciplinary Physical Sciences
Pravin Mali
Michael LaMontagne
Somendra Pant
Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine
Linn Goldberg
Revista de Educación Matemática
Hernan Vazquez , Juan Pablo Jorge
Revista Internacional de …
Jesus Arias Escobar
Jurnal Ilmu Komunikasi
Denik Witarti
Journal of Network and Computer Applications
Ahmed LOUNIS
Mechanisms of Development
Jacek Kubiak
susana sneiderman
John Dunphy
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other. After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables. By arranging your sources by theme or ...
Synthesis Matrix Example; 7. Write a Literature Review; Need Help? Synthesize. ... In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D. For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.
This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp. In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step. If it's your first time writing a literature review, you definitely want to use this link to get 50% off the course (limited-time offer).
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question. It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation, or research paper, in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
The synthesis matrix is a chart that allows a researcher to sort and categorize the different arguments presented on an issue. Across the top of the chart are the spaces to record sources, and along the side of the chart are the spaces to record the main points of argument on the topic at hand. As you examine your first source, you will work ...
Analyze what you learn in (4) using a tool like a Synthesis Table. Your goal is to identify relevant themes, trends, gaps, and issues in the research. Your literature review will collect the results of this analysis and explain them in relation to your research question. Analysis tips
A literature review is not an annotated bibliography, organized by title, author, or date of publication. Rather, it is grouped by topic to create a whole view of the literature relevant to your research question. Figure 7.1. Your synthesis must demonstrate a critical analysis of the papers you collected as well as your ability to integrate the ...
Create your own literature review synthesis matrix using the Word or Excel files available in the Activity box. Organize and synthesize literature related to your topic using your synthesis matrix; Synthesize and Apply. When writing a literature review, your objective is to provide an overview of the current state of knowledge about your topic. ...
Synthesis is an important element of academic writing, demonstrating comprehension, analysis, evaluation and original creation. With synthesis you extract content from different sources to create an original text. While paraphrase and summary maintain the structure of the given source (s), with synthesis you create a new structure.
On This Page: Step 1 Organize your sources. Step 2 Outline your structure. Step 3 Write paragraphs with topic sentences. Step 4 Revise, edit and proofread. When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and ...
Steps to take in organizing your literature and notes: Find common themes and organize the works into categories. Develop a subject level outline with studies you've found. Expand or limit your search based on the information you found. Write brief paragraphs outlining your categories: How the works in each category relate to each other.
Synthesis writing is a form of analysis related to comparison and contrast, classification and division. On a basic level, synthesis requires the writer to pull together two or more summaries, looking for themes in each text. ... In a literature review you will be combining material from several texts to create a new text - your literature ...
Conducting a review of related literature (RRL) is a crucial step in the process of writing an MBA dissertation. To perform a thorough RRL, start by identifying key themes and concepts relevant to your dissertation topic. Utilize academic databases and journals to search for scholarly articles, books, and other sources that provide insights ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
There are a number of reporting guideline available to guide the synthesis and reporting of results in systematic literature reviews. Example: It is common to organize findings in a matrix, also known as a Table of Evidence (ToE). Tools & Additional Resources: Reporting Guidelines for Systematic Reviews
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say ...
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE. January 2019; Authors: ... It is an analysis and synthesis of the source materials, written in a specific style which flows. ... The sample compromised 40 ...
Literature Review and Synthesis 35 Gaps related to structural analysis can include minimum and expected properties for reinforcing greater than Grade 80, stainless steel, and other materials that can improve serviceability and in some conditions performance.
The synthesis resul ts in the. identification of five m ajor stages fo r conducting literature reviews for publication, i.e. (1) Define the protocol, (2) Search the literature, (3) Select the ...
10. Chapter 2 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE. Introduction Presented in chapter 2 is a synthesis of research that supports the evaluation of the attendance policy and attendance program of Newport News Public Schools. Included in the chapter is a historical overview of attendance, the importance of attendance, overview of Newport News Public ...
study. Chapter 2 is divided into 4 parts, namely : (1) E-. Learning, (2) Conventional classroom learning, (3) English. Achievement; and (4) Synthesis. The first topic, E-Learning, is a discussion ...
A Critical Paper: The Miseducation of the Filipinos. Ezekiel Succor. Download Free PDF. View PDF. CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND STUDIES This chapter presents the related literature and studies after the thorough and in-depth search done by the researchers.