
- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 13

Results of the implementation of a double-check protocol with point-of-care ultrasound for acute heart failure in the emergency department
To determine the effectiveness of a double-check protocol using Point-of-Care Ultrasound in the management of patients diagnosed with Acute Heart Failure in an Emergency Department.
- View Full Text
Impaired cerebral autoregulation detected in early prevasospasm period is associated with unfavorable outcome after spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage: an observational prospective pilot study
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) patients with cerebral autoregulation (CA) impairment at an early post-SAH period are at high risk of unfavorable outcomes due to delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI) or other complica...
Utility of the Venous Excess Ultrasound (VEXUS) score to track dynamic change in volume status in patients undergoing fluid removal during haemodialysis – the ACUVEX study
The use of ultrasound assessment, including the Venous Excess Ultrasound (VEXUS) score, is increasingly being utilised as part of fluid status assessment in clinical practice. We aime...
Roberto Copetti, MD (1954–2024)
Canadian internal medicine ultrasound (cimus) consensus statement: recommendations for mandatory ultrasound competencies for ultrasound-guided thoracentesis, paracentesis, and central venous catheterization.
To develop a Canadian Internal Medicine Ultrasound (CIMUS) consensus statement on recommended mandatory point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) competencies for ultrasound-guided thoracentesis, paracentesis, and cent...
Lung ultrasound score predicts outcomes in patients with acute respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 treated with non-invasive respiratory support: a prospective cohort study
Lung ultrasound has demonstrated its usefulness in several respiratory diseases management. One derived score, the Lung Ultrasound (LUS) score, is considered a good outcome predictor in patients with Acute Res...
Integrating a self-directed ultrasound curriculum for the internal medicine clerkship
Incorporating ultrasound into the clinical curriculum of undergraduate medical education has been limited by a need for faculty support. Without integration into the clinical learning environment, ultrasound s...
Point-of-care ultrasound to inform antiviral treatment initiation in chronic hepatitis B virus infection in low-resource settings – the PUSH protocol
Chronic Hepatitis B (CHB) is prevalent worldwide and most related deaths occur in low-resource settings. Antiviral treatment of CHB is indicated in those with significant liver disease and markers of viral rep...
Right ventricular free wall longitudinal strain during weaning from mechanical ventilation using high-flow or conventional oxygen treatment: a pilot study
Medico-legal risks of point-of-care ultrasound: a closed-case analysis of canadian medical protective association medico-legal cases.
Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) has become a core diagnostic tool for many physicians due to its portability, excellent safety profile, and diagnostic utility. Despite its growing use, the potential risks of ...
Test characteristics of point-of-care ultrasonography in patients with acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury is a common disorder that is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Point-of-care ultrasonography (PoCUS) is an imaging modality performed at the bedside and is used to assess...
Ultrasound contrast agent assisted ultrasonography guidance percutaneous nephrostomy for non-hydronephrotic kidney
Given the limited success rate and considerable challenges associated with conventional ultrasonography (US) guidance for percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN) in non-hydronephrotic kidneys, this study proposed a sol...
The usefulness of point-of-care ultrasound in dehydrated patients in a pediatric emergency department
Dehydration is among the most common causes of Pediatric Emergency Department admission; however, no clinical signs, symptoms, or biomarkers have demonstrated sufficient sensitivity, specificity, or reliabilit...
Evaluation of point-of-care ultrasound training among healthcare providers: a pilot study
The use of Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) has become prevalent across a variety of clinical settings. Many healthcare professionals have started getting hands-on training. To evaluate the effectiveness of su...
Thoracic ultrasound use in hospitalized and ambulatory adult patients: a quantitative picture
Thoracic ultrasound (TUS) has been established as a powerful diagnostic and monitoring tool in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). However, studies outside the critical care setting are scarce. The aim of this stud...
Can absence of cardiac activity on point-of-care echocardiography predict death in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest? A systematic review and meta-analysis
The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to evaluate the accuracy of the absence of cardiac motion on point-of-care echocardiography (PCE) in predicting termination of resuscitation (TOR), s...
Point-of-Care Ultrasound training in undergraduate education in the European Union: current situation and perspectives
Given the widespread use of Point-of-Care UltraSound (PoCUS) in clinical practice, with ultrasound machines becoming more portable and affordable, recommendations and position statements from ultrasound societ...
Assessment of quadriceps muscle mass by ultrasound in the postoperative period of cardiac surgery
Patients undergoing cardiac surgery are exposed to many factors that activate catabolic and inflammatory pathways, which affect skeletal muscle and are, therefore, related to unfavorable hospital outcomes. Giv...
Lung ultrasound and supine chest X-ray use in modern adult intensive care: mapping 30 years of advancement (1993–2023)
In critically ill patients with acute respiratory failure, thoracic images are essential for evaluating the nature, extent and progression of the disease, and for clinical management decisions. For this purpos...
Comparing contamination rates of sterile-covered and uncovered transducers for ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous lines
Physicians frequently use point-of-care ultrasound for intravenous access and bloodwork in the ED. Recently, AIUM and ACEP released recommendations on ultrasound-guided peripheral intravenous lines (USPIVs), b...
Change in economy of ultrasound probe motion among general medicine trainees
To observe change in economy of 9 ultrasound probe movement metrics among internal medicine trainees during a 5-day training course in cardiac point of care ultrasound (POCUS).
The role of point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) imaging in clinical outcomes during cardiac arrest: a systematic review
Cardiac arrest in hospital and out-of-hospital settings is associated with high mortality rates. Therefore, a bedside test that can predict resuscitation outcomes of cardiac arrest patients is of great value. ...
Advancement in pleura effusion diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of point-of-care ultrasound versus radiographic thoracic imaging
Pleural effusion is a fluid buildup in the pleural space that mostly result from congestive heart failure, bacterial pneumonia, malignancy, and pulmonary embolism. The diagnosis of this condition can be challe...
Correction: Utility of ultrasound in managing acute medical conditions in space: a scoping review
The original article was published in The Ultrasound Journal 2023 15 :47
Replacement of fluoroscopy by ultrasonography in the evaluation of hemidiaphragm function, an exploratory prospective study
Dysfunction of the diaphragm may ultimately lead to respiratory insufficiency and compromise patient outcome. Evaluation of diaphragm function is cumbersome. Fluoroscopy has been the gold standard to measure d...
Utility of ultrasound in managing acute medical conditions in space: a scoping review
In long-distance spaceflight, the challenges of communication delays and the impracticality of rapid evacuation necessitate the management of medical emergencies by onboard physicians. Consequently, these phys...
The Correction to this article has been published in The Ultrasound Journal 2024 16 :2
Additional predictive value of optic nerve sheath diameter for neurological prognosis after cardiac arrest: a prospective cohort study
The goal is to estimate the additional value of ultrasonographic optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) measurement on days 1–3, on top of electroencephalography (EEG), pupillary light reflexes (PLR), and somatose...
Optic nerve sheath diameter measurement for the paediatric patient with an acute deterioration in consciousness
Ocular Point of Care Ultrasound (PoCUS) is emerging as a valuable utility within emergency medicine. Optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) has been demonstrated to correlate closely with intracranial pressure (IC...
Correction: Feasibility of using a handheld ultrasound device to detect and characterize shunt and deep vein thrombosis in patients with COVID-19: an observational study
The original article was published in The Ultrasound Journal 2020 12 :49
Correction: A survey demonstrating that the procedural experience of residents in internal medicine, critical care and emergency medicine is poor: training in ultrasound is required to rectify this
The original article was published in The Ultrasound Journal 2021 13 :20
Internal jugular access using pocket ultrasound in a simulated model: comparison between biplane and monoplane visualization techniques
Ultrasound is the current standard for central venous access due to its advantages in efficiency and safety. In-plane and out-of-plane visualization techniques are commonly used, but there is no clear evidence...
Abscess pulsatility: a sonographic sign of osteomyelitis
Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment of acute osteomyelitis may improve prognosis and prevent further complications. Sonography is useful in the evaluation of osteomyelitis. It can demonstrate early signs ...
The diagnostic accuracy of lung ultrasound to determine PiCCO-derived extravascular lung water in invasively ventilated patients with COVID-19 ARDS
Lung ultrasound (LUS) can detect pulmonary edema and it is under consideration to be added to updated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) criteria. However, it remains uncertain whether different LUS sc...
Development of a novel observed structured clinical exam to assess clinical ultrasound proficiency in undergraduate medical education
A pilot study was performed to develop and test an observed structured clinical exam (OSCE) for clinical ultrasound in second-year medical students. The goal was to assess a longitudinal clinical ultrasound cu...
Echocardiographic parameters in COVID-19 patients and their association with ICU mortality: a prospective multicenter observational study
Echocardiography has become an integral part of the management of critically ill patients. It helps to diagnose and treat various conditions. COVID-19 patients can develop cardiac dysfunction. We planned to st...
The correlation between epicardial fat thickness and longitudinal left atrial reservoir strain in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and controls
Diabetes mellitus (DM) has been documented among the strongest risk factors for developing heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). The earliest imaging changes in patients with DM are the left ...
The association of attentional foci and image interpretation accuracy in novices interpreting lung ultrasound images: an eye-tracking study
It is unclear, where learners focus their attention when interpreting point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) images. This study seeks to determine the relationship between attentional foci metrics with lung ultrasou...
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)-guided transvenous pacing (TVP) in emergency department
Placement of a temporary pacemaker is a vital skill in the emergency setting in patients that present with life-threatening bradycardia. Transvenous pacing is the definitive method of stabilizing the arrhythmi...
Feasibility of chest ultrasound up to 42 m underwater
After recent advancements, ultrasound has extended its applications from bedside clinical practice to wilderness medicine. Performing ultrasound scans in extreme environments can allow direct visualization of ...
Evaluation of commercially available point-of-care ultrasound for automated optic nerve sheath measurement
Measurement of the optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) via ultrasonography has been proposed as a non-invasive metric of intracranial pressure that may be employed during in-field patient triage. However, first...
Simultaneous venous–arterial Doppler during preload augmentation: illustrating the Doppler Starling curve
Providing intravenous (IV) fluids to a patient with signs or symptoms of hypoperfusion is common. However, evaluating the IV fluid ‘dose–response’ curve of the heart is elusive. Two patients were studied in th...
Learning curves for point-of-care ultrasound image acquisition for novice learners in a longitudinal curriculum
A learning curve is graphical representation of the relationship between effort, such as repetitive practice or time spent, and the resultant learning based on specific outcomes. Group learning curves provide ...
Point-of-Care-ultrasound in undergraduate medical education: a scoping review of assessment methods
Point-of-Care-Ultrasound (POCUS) curricula have rapidly expanded in undergraduate medical education (UME). However, the assessments used in UME remain variable without national standards. This scoping review c...
Doppler flow morphology characteristics of epiaortic arteries in aortic valve pathologies: a retrospective study on a cohort of patients with ischemic stroke
Neurovascular ultrasound (nvUS) of the epiaortic arteries is an integral part of the etiologic workup in patients with ischemic stroke. Aortic valve disease shares similar vascular risk profiles and therefore ...
Real-time Remote Expert-guided Echocardiography by Medical Students
Echocardiography is a highly specialised examination performed by experienced healthcare professionals. These experienced healthcare professionals may not be available to patients during all hours in rural hea...

Ultrasound findings in Kaposi sarcoma patients: overlapping sonographic features with disseminated tuberculosis
Focused Assessment with Sonography for HIV-associated TB (FASH) is a diagnostic tool for extra-pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) in symptomatic patients with advanced HIV. As Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) is also prevalent ...
Ultrasound detected increase in optic disk height to identify elevated intracranial pressure: a systematic review
Elevated intracranial pressure (eICP) is a serious medical emergency that requires prompt identification and monitoring. The current gold standards of eICP detection require patient transportation, radiation, ...
Determinants of point-of-care ultrasound lung sliding amplitude in mechanically ventilated patients
Although lung sliding seen by point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is known to be affected to varying degrees by different physiologic and pathologic processes, it is typically only reported qualitatively in the c...
Femoral vein pulsatility: a simple tool for venous congestion assessment
Femoral vein Doppler (FVD) is simpler than the VExUS score which is a multimodal scoring system based on combination of IVC diameter, hepatic venous Doppler, portal vein pulsatility and renal vein Doppler, may...
Airway ultrasound to detect subglottic secretion above endotracheal tube cuff
Subglottic secretion had been proven as one of the causes of microaspiration and increased risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). The role of ultrasound to detect subglottic secretion has not yet been ...
- Editorial Board
- Sign up for article alerts and news from this journal
- Follow us on Twitter
- Follow us on Facebook
- ISSN: 2524-8987 (electronic)

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
106 Ultrasound Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Ultrasound technology has revolutionized the field of medicine, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize internal structures and organs without invasive procedures. As a result, ultrasound has become an essential tool for diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions. If you are a student studying ultrasound technology or a healthcare professional looking to expand your knowledge, here are 106 ultrasound essay topic ideas and examples to help you explore this fascinating field further.
- The history and development of ultrasound technology
- The physics behind ultrasound imaging
- The role of ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology
- Ultrasound-guided procedures in interventional radiology
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing musculoskeletal injuries
- Ultrasound imaging of the heart (echocardiography)
- The benefits and limitations of 3D/4D ultrasound imaging
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for liver imaging
- Ultrasound elastography for assessing tissue stiffness
- The role of ultrasound in diagnosing breast cancer
- Ultrasound imaging in emergency medicine
- Point-of-care ultrasound in critical care settings
- The use of ultrasound in vascular imaging
- Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks for pain management
- The future of ultrasound technology in healthcare
- Ultrasound imaging of the thyroid gland
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing gallbladder disease
- Ultrasound-guided biopsy procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the kidneys
- The role of ultrasound in diagnosing appendicitis
- Ultrasound imaging of the pancreas
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing gastrointestinal disorders
- Ultrasound-guided injections for joint pain
- Ultrasound imaging of the urinary tract
- The benefits of portable ultrasound technology
- Ultrasound imaging of the prostate gland
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing testicular conditions
- Ultrasound-guided drainage procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the spleen
- The role of ultrasound in diagnosing hernias
- Ultrasound-guided nerve ablation for pain management
- Ultrasound imaging of the placenta
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing fetal anomalies
- Ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the adrenal glands
- The benefits of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for liver imaging
- Ultrasound-guided joint injections for arthritis
- Ultrasound imaging of the parathyroid glands
- The role of ultrasound in diagnosing lymph node abnormalities
- Ultrasound-guided breast biopsy procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the thymus gland
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing mediastinal masses
- Ultrasound-guided pleural procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the pericardium
- The benefits of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for vascular imaging
- Ultrasound-guided nerve blocks for chronic pain management
- Ultrasound imaging of the carotid arteries
- The role of ultrasound in diagnosing peripheral vascular disease
- Ultrasound-guided varicose vein procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the aorta
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing deep vein thrombosis
- Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy for spider veins
- Ultrasound imaging of the liver and biliary system
- The benefits of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for renal imaging
- Ultrasound-guided renal biopsy procedures
- The role of ultrasound in diagnosing adrenal tumors
- Ultrasound-guided adrenal vein sampling procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the pancreas and spleen
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing pancreatic cancer
- Ultrasound-guided pancreatic biopsy procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the gallbladder and biliary system
- The benefits of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for pancreatic imaging
- Ultrasound-guided percutaneous cholecystostomy procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the gastrointestinal tract
- The role of ultrasound in diagnosing inflammatory bowel disease
- Ultrasound-guided intestinal biopsy procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the kidneys and urinary tract
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing kidney stones
- Ultrasound-guided percutaneous nephrolithotomy procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the female reproductive system
- The benefits of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for gynecologic imaging
- Ultrasound-guided ovarian cyst aspiration procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the male reproductive system
- The role of ultrasound in diagnosing testicular cancer
- Ultrasound-guided testicular biopsy procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the musculoskeletal system
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing sports injuries
- Ultrasound-guided joint aspiration procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the nervous system
- The benefits of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for neuroimaging
- Ultrasound-guided nerve conduction studies
- Ultrasound imaging of the head and neck
- The role of ultrasound in diagnosing thyroid nodules
- Ultrasound-guided thyroid fine-needle aspiration biopsy procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the chest and lungs
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing pleural effusions
- Ultrasound-guided thoracentesis procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the heart and blood vessels
- The benefits of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for cardiac imaging
- Ultrasound-guided cardiac catheterization procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the liver and spleen
- The role of ultrasound in diagnosing liver cirrhosis
- Ultrasound-guided liver biopsy procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the pancreas and biliary system
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing pancreatic pseudocysts
- Ultrasound-guided percutaneous drainage procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys
- The benefits of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for urologic and gastrointestinal imaging
- Ultrasound-guided percutaneous nephrostomy procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the female reproductive system and bladder
- The role of ultrasound in diagnosing pelvic organ prolapse
- Ultrasound-guided bladder sling procedures
- Ultrasound imaging of the male reproductive system and prostate
- The use of ultrasound in diagnosing benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy procedures
These essay topic ideas and examples cover a wide range of ultrasound applications and specialties, providing you with ample opportunities to explore and research this exciting field further. Whether you are a student or a healthcare professional, delving into these topics can deepen your understanding of ultrasound technology and its role in modern medicine.
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
Open Access is an initiative that aims to make scientific research freely available to all. To date our community has made over 100 million downloads. It’s based on principles of collaboration, unobstructed discovery, and, most importantly, scientific progression. As PhD students, we found it difficult to access the research we needed, so we decided to create a new Open Access publisher that levels the playing field for scientists across the world. How? By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers.
We are a community of more than 103,000 authors and editors from 3,291 institutions spanning 160 countries, including Nobel Prize winners and some of the world’s most-cited researchers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too.
Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective
Want to get in touch? Contact our London head office or media team here
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing.
Home > Books > Medical Imaging
Ultrasound Imaging - Current Topics

Book metrics overview
3,903 Chapter Downloads
Impact of this book and its chapters
Total Chapter Downloads on intechopen.com
Total Chapter Citations
Academic Editor
Gregory University , Nigeria
Published 11 May 2022
Doi 10.5772/intechopen.95178
ISBN 978-1-78985-186-1
Print ISBN 978-1-78984-877-9
eBook (PDF) ISBN 978-1-78985-331-5
Copyright year 2022
Number of pages 154
Ultrasound Imaging - Current Topics presents complex and current topics in ultrasound imaging in a simplified format. It is easy to read and exemplifies the range of experiences of each contributing author. Chapters address such topics as anatomy and dimensional variations, pediatric gastrointestinal emergencies, musculoskeletal and nerve imaging as well as molecular sonography. The book is...
Ultrasound Imaging - Current Topics presents complex and current topics in ultrasound imaging in a simplified format. It is easy to read and exemplifies the range of experiences of each contributing author. Chapters address such topics as anatomy and dimensional variations, pediatric gastrointestinal emergencies, musculoskeletal and nerve imaging as well as molecular sonography. The book is a useful resource for researchers, students, clinicians, and sonographers looking for additional information on ultrasound imaging beyond the basics.
By submitting the form you agree to IntechOpen using your personal information in order to fulfil your library recommendation. In line with our privacy policy we won’t share your details with any third parties and will discard any personal information provided immediately after the recommended institution details are received. For further information on how we protect and process your personal information, please refer to our privacy policy .
Cite this book
There are two ways to cite this book:
Edited Volume and chapters are indexed in
Table of contents.
By Solomon Demissie, Mulatie Atalay and Yonas Derso
By Ercan Ayaz
By Haithem Zaafouri, Meryam Mesbahi, Nizar Khedhiri, Wassim Riahi, Mouna Cherif, Dhafer Haddad and Anis Ben Maamer
By Felix Okechukwu Erondu
By Stefan Cristian Dinescu, Razvan Adrian Ionescu, Horatiu Valeriu Popoviciu, Claudiu Avram and Florentin Ananu Vreju
By María Eugenia Aponte-Rueda and María Isabel de Abreu
By Jong Hwa Lee, Jae Uk Lee and Seung Wan Yoo
By J.M. López Álvarez, O. Pérez Quevedo, S. Alonso-Graña López-Manteola, J. Naya Esteban, J.F. Loro Ferrer and D.L. Lorenzo Villegas
By Arthur Fleischer and Sai Chennupati
IMPACT OF THIS BOOK AND ITS CHAPTERS
3,903 Total Chapter Downloads
1 Crossref Citations
2 Dimensions Citations
Order a print copy of this book
Available on

Delivered by
£119 (ex. VAT)*
Hardcover | Printed Full Colour
FREE SHIPPING WORLDWIDE
* Residents of European Union countries need to add a Book Value-Added Tax Rate based on their country of residence. Institutions and companies, registered as VAT taxable entities in their own EU member state, will not pay VAT by providing IntechOpen with their VAT registration number. This is made possible by the EU reverse charge method.
As an IntechOpen contributor, you can buy this book for an Exclusive Author price with discounts from 30% to 50% on retail price.
Log in to your Author Panel to purchase a book at the discounted price.
For any assistance during ordering process, contact us at [email protected]
Related books
Medical imaging.
Edited by Felix Okechukwu Erondu
Medical Imaging in Clinical Practice
Medical and biological image analysis.
Edited by Robert Koprowski
Edited by Yongxia Zhou
Ultrasound Elastography
Edited by Monica Lupsor Platon
New Advances in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Edited by Denis Larrivee
Frontiers in Neuroimaging
Edited by Xianli Lv
Optical Coherence Tomography
Edited by Giuseppe Lo Giudice
Updates in Endoscopy
Edited by Somchai Amornyotin
Elastography
Edited by Dana Stoian
Call for authors
Submit your work to intechopen.

Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Ultrasonography articles from across Nature Portfolio
Ultrasonography is an imaging technique that uses the reflections of high-frequency sound waves to create an image of a structure located within the body.
Adapting vision–language AI models to cardiology tasks
Vision–language models can be trained to read cardiac ultrasound images with implications for improving clinical workflows, but additional development and validation will be required before such models can replace humans.
- Rima Arnaout
Related Subjects
- Echocardiography
Latest Research and Reviews
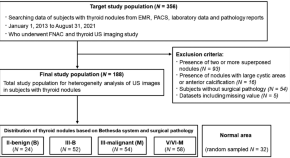
Differential diagnosis of thyroid nodules using heterogeneity quantification software on ultrasound images: correlation with the Bethesda system and surgical pathology
- Young Jae Ryu
- Jin Woong Kim
- Tae-Hoon Kim
Deep learning prediction of renal anomalies for prenatal ultrasound diagnosis
- Olivier X. Miguel
- Emily Kaczmarek
- Mark C. Walker
Comparing three cardiothoracic ratio measurement techniques and creating multivariable scoring system to predict Bart’s hydrops fetalis at 17–22 weeks’ gestation
- Sanitra Anuwutnavin
- Patsawee Rangseechamrat
- Sommai Viboonchard
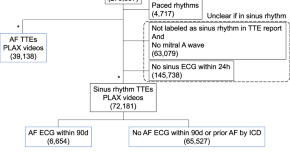
Deep learning evaluation of echocardiograms to identify occult atrial fibrillation
- Nathan R. Stein
- David Ouyang
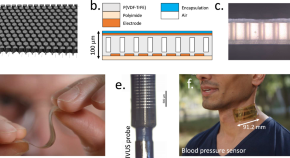
Flexible large-area ultrasound arrays for medical applications made using embossed polymer structures
Current ultrasound transducers are bulky and rigid. Here, the authors describe a new way to realize large-area and mechanically flexible ultrasound arrays on polymer foils suited for wearable ultrasound applications
- Paul L. M. J. van Neer
- Laurens C. J. M. Peters
- Gerwin H. Gelinck
Fatty liver classification via risk controlled neural networks trained on grouped ultrasound image data
- Tso-Jung Yen
- Chih-Ting Yang
- Hsin-Chou Yang
News and Comment
Factors identified that predict resolution of subclinical synovitis.
New findings provide insight into the natural history of subclinical synovitis, a reported predictor of the development of rheumatoid arthritis, and identify various factors associated with its reversal.
- Jessica McHugh
AI outperforms sonographers at diagnosing cardiac function on echocardiography
An artificial intelligence-guided workflow for initial evaluation of left ventricular ejection fraction in echocardiography is non-inferior to initial assessment by a sonographer, according to findings from a blinded, randomized, non-inferiority clinical trial.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
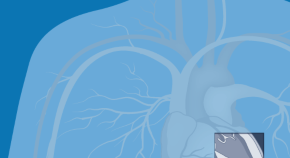
A wearable ultrasonic device to image cardiac function
Researchers have engineered a wearable device that adheres to the skin and uses ultrasound imaging and a deep learning model to produce a dynamic, real-time assessment of cardiac function.
- Gregory B. Lim
Secukinumab reduces synovitis in PsA
- Sarah Onuora
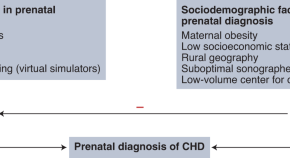
Deep learning for detecting congenital heart disease in the fetus
New advances in machine learning could facilitate and reduce disparities in the prenatal diagnosis of congenital health disease, the most common and lethal birth defect.
- Shaine A. Morris
- Keila N. Lopez
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Ultrasound News
Top headlines, latest headlines.
- Biomedical Imaging Technology
- Focused Ultrasound Can Relieve Pain
- Ultrasound and Oxygen Saturation in Blood
- Ultrasound Imaging: Ultrafast Tech
- Soundwaves Harden 3D-Printed Treatments in Body
- Network of Robots to Monitor Pipes Acoustically
- 2 Droplets Levitated and Mixed
- New Laser Setup Probes Metamaterials
- Medical Imaging Fails Dark Skin: Researchers ...
- Ultrasound May Rid Groundwater of Toxic ...
Earlier Headlines
Thursday, august 31, 2023.
- Researchers Develop Ultra-Sensitive Photoacoustic Microscopy for Wide Biomedical Application Potential
Friday, July 28, 2023
- A Wearable Ultrasound Scanner Could Detect Breast Cancer Earlier
Wednesday, July 26, 2023
- A Quick Look Inside a Human Being
Tuesday, June 27, 2023
- Researchers Use Ultrasound to Control Orientation of Small Particles
Thursday, June 22, 2023
- When Soft Spheres Make Porous Media Stiffer
Thursday, June 15, 2023
- A 'spy' In the Belly
Wednesday, June 7, 2023
- Sponge Makes Robotic Device a Soft Touch
Monday, May 22, 2023
- A Giant Leap Forward in Wireless Ultrasound Monitoring for Subjects in Motion
Tuesday, May 2, 2023
- Wearable Ultrasound Patch Provide Non-Invasive Deep Tissue Monitoring
Tuesday, April 4, 2023
- Detecting, Predicting, and Preventing Aortic Ruptures With Computational Modeling
Friday, March 10, 2023
- New Ultrasound Method Could Lead to Easier Disease Diagnosis
Wednesday, March 1, 2023
- The Future of Touch
Tuesday, February 28, 2023
- Ultrasound Device May Offer New Treatment Option for Hypertension
Friday, February 24, 2023
- Faster and Sharper Whole-Body Imaging of Small Animals With Deep Learning
Thursday, February 23, 2023
- Making Engineered Cells Dance to Ultrasound
Wednesday, February 22, 2023
- Study Offers Details on Using Electric Fields to Tune Thermal Properties of Ferroelectric Materials
Monday, February 13, 2023
- Creating 3D Objects With Sound
Tuesday, January 31, 2023
- Focused Ultrasound Technique Leads to Release of Neurodegenerative Disorders Biomarkers
Wednesday, January 25, 2023
- Wearable Sensor Uses Ultrasound to Provide Cardiac Imaging on the Go
Friday, January 13, 2023
- A Precision Arm for Miniature Robots
Tuesday, January 3, 2023
- Tracking Radiation Treatment in Real Time Promises Safer, More Effective Cancer Therapy
- Team Writes Letters With Ultrasonic Beam, Develops Deep Learning Based Real-Time Ultrasonic Hologram Generation Technology
Thursday, December 1, 2022
- An Exotic Interplay of Electrons
Wednesday, September 21, 2022
- The Super-Fast MRI Scan That Could Revolutionize Heart Failure Diagnosis
Friday, August 12, 2022
- Using Sound and Bubbles to Make Bandages Stickier and Longer Lasting
Tuesday, August 9, 2022
- Ultrasound Could Save Racehorses from Bucked Shins
Thursday, July 28, 2022
- Engineers Develop Stickers That Can See Inside the Body
Thursday, July 21, 2022
- Flexible Method for Shaping Laser Beams Extends Depth-of-Focus for OCT Imaging
Wednesday, June 15, 2022
- High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) Can Control Prostate Cancer With Fewer Side Effects
- Moth Wing-Inspired Sound Absorbing Wallpaper in Sight After Breakthrough
Tuesday, May 31, 2022
- Direct Sound Printing Is a Potential Game-Changer in 3D Printing
Monday, May 30, 2022
- Ultrasound-Guided Microbubbles Boost Immunotherapy Efficacy
Thursday, May 5, 2022
- How MRI Could Revolutionize Heart Failure Diagnosis
Wednesday, April 27, 2022
- 3D Bimodal Photoacoustic Ultrasound Imaging to Diagnose Peripheral Vascular Diseases
Monday, April 18, 2022
- Tumors Partially Destroyed With Sound Don't Come Back
Tuesday, April 12, 2022
- Ultrasound Gave Us Our First Baby Pictures Can It Also Help the Blind See?
Monday, April 4, 2022
- Dual-Mode Endoscope Offers Unprecedented Insights Into Uterine Health
Wednesday, March 23, 2022
- Concert Hall Acoustics for Non-Invasive Ultrasound Brain Treatments
Tuesday, March 22, 2022
- Quantum Dots Shine Bright to Help Scientists See Inflammatory Cells in Fat
Friday, March 11, 2022
- Acoustic Propulsion of Nanomachines Depends on Their Orientation
Monday, February 28, 2022
- Ultrasound Scan Can Diagnose Prostate Cancer
Friday, February 25, 2022
- Ultrasounds for Endangered Abalone Mollusks
Thursday, February 24, 2022
- Transparent Ultrasound Chip Improves Cell Stimulation and Imaging
Tuesday, February 22, 2022
- Low-Cost, 3D Printed Device May Broaden Focused Ultrasound Use
Tuesday, February 15, 2022
- Speed of Sound Used to Measure Elasticity of Materials
Tuesday, January 25, 2022
- Ultrasound Technique Predicts Hip Dysplasia in Infants
Wednesday, January 5, 2022
- The First Topological Acoustic Transistor
Friday, December 17, 2021
- New Research Sheds Light on How Ultrasound Could Be Used to Treat Psychiatric Disorders
Wednesday, December 8, 2021
- CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Boosts Effectiveness of Ultrasound Cancer Therapy
Wednesday, November 10, 2021
- A Personalized Exosuit for Real-World Walking
Monday, November 1, 2021
- Noninvasive Imaging Strategy Detects Dangerous Blood Clots in the Body
Friday, September 10, 2021
- Acoustic Illusions
Tuesday, August 24, 2021
- Researchers Developing New Cancer Treatments With High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound
Tuesday, August 17, 2021
- Prediction Models May Reduce False-Positives in MRI Breast Cancer Screening
Tuesday, August 3, 2021
- Does Visual Feedback of Our Tongues Help in Speech Motor Learning?
Tuesday, July 27, 2021
- Researchers Demonstrate Technique for Recycling Nanowires in Electronics
Thursday, July 22, 2021
- Soft Skin Patch Could Provide Early Warning for Strokes, Heart Attacks
Monday, July 12, 2021
- Magnetic Field from MRI Affects Focused-Ultrasound-Mediated Blood-Brain Barrier
Monday, June 21, 2021
- A Tiny Device Incorporates a Compound Made from Starch and Baking Soda to Harvest Energy from Movement

Friday, May 28, 2021
- New Tool Activates Deep Brain Neurons by Combining Ultrasound, Genetics
Monday, May 24, 2021
- Silicon Chips Combine Light and Ultrasound for Better Signal Processing
Tuesday, May 11, 2021
- Tiny, Wireless, Injectable Chips Use Ultrasound to Monitor Body Processes
Wednesday, May 5, 2021
- Release of Drugs from a Supramolecular Cage
- LATEST NEWS
- Top Science
- Top Physical/Tech
- Top Environment
- Top Society/Education
- Health & Medicine
- Mind & Brain
- Living Well
- Space & Time
- Matter & Energy
- Business & Industry
- Automotive and Transportation
- Consumer Electronics
- Energy and Resources
- Engineering and Construction
- Telecommunications
- Textiles and Clothing
- Biochemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Thermodynamics
- Electricity
- Energy Technology
- Alternative Fuels
- Energy Policy
- Fossil Fuels
- Nuclear Energy
- Solar Energy
- Wind Energy
- Engineering
- 3-D Printing
- Civil Engineering
- Construction
- Electronics
- Forensic Research
- Materials Science
- Medical Technology
- Microarrays
- Nanotechnology
- Robotics Research
- Spintronics
- Sports Science
- Transportation Science
- Virtual Environment
- Weapons Technology
- Wearable Technology
- Albert Einstein
- Nature of Water
- Quantum Computing
- Quantum Physics
- Computers & Math
- Plants & Animals
- Earth & Climate
- Fossils & Ruins
- Science & Society
- Education & Learning
Strange & Offbeat
- Simulations Support Dark Matter Theory
- 3D Printed Programmable Living Materials
- Emergence of Animals: Magnetic Field Collapse
- Ice Shelves Crack from Weight of Meltwater Lakes
- Countries' Plans to Remove CO2 Not Enough
- Toward Robots With Human-Level Touch Sensitivity
- 'Doubling' in Origin of Cancer Cells
- New Catalyst for Using Captured Carbon
- Random Robots Are More Reliable
- Significant Discovery in Teleportation Research
Trending Topics
59 Ultrasound Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best ultrasound topic ideas & essay examples, ✅ good essay topics on ultrasound, 📑 interesting topics to write about ultrasound.
- Use of Ultrasound-Guidance for Arterial Puncture All the anthropometric and demographic variables were recorded, as well as the main diagnosis of admission, comorbidities, the placement of the central venous catheter, and the course of the procedure.
- MRI and Ultrasound for Determining Abnormalities in Preterm Infants Neonatal cranial ultrasound is used in detecting brain injury in preterm infants and can be used repetitively without harming the infant. We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts 808 writers online Learn More
- Benefits of 3D Ultrasound to Pregnant Mothers This is coherent to the 3D planar imaging are improved technology previously applied in the 2D ultrasound technology. As an extrapolation from 3D technology, 3D ultrasound is applied as a medical diagnostic technique that utilizes […]
- The Biological Effects of Ultrasound The paper also evaluates the physical mechanisms for the biological effects of ultrasound and the effects of ultrasound on living tissues in vivo and vitriol.
- The Recent Advances in Real Time Imaging in Ultrasound In point of fact, Medical imaging provides the most perfect task of diagnostic to Ultrasound, whereas, the main usage of therapeutic Ultrasound is to treat the numerous types of diseases and disorders in human beings.
- Comparison of MRI and Ultrasound for Determining Abnormalities in Preterm Infants Medical Imaging helps in detecting and diagnosing diseases at its earliest and treatable stage and helps in determining most appropriate and effective care for the patient.”Medical imaging provides a picture of the inside of the […]
- Ultrasound Techniques Applied to Body Fat Measurement in Male and Female The main objective of this paper is to evaluate the accuracy of body fat by using portable ultra sound device which results are reliable and authentic. The ultra sound technique is widely used to measure […]
- Benefits of 3D/4D Ultrasound in Prenatal Care The information that is obtained from this exam assists the health care providers in counseling parents on the development of the fetus especially in the nature of anomalies, prognosis, and the postnatal consideration of the […]
- Biologic Effects of Ultrasound in Healthcare Setting The instrument performing the emission of the sound waves and the recording of their bouncing back is referred to as the transducer and the medical practitioner generally gently presses the transducer against the skin of […]
- Ultrasound Scanning: Diagnosing Health Conditions The calculation is based on the time taken by the wave to return by measuring the distance, mass, nature, and stability of the object hit.
- Mammography vs. Ultrasound for Breast Tissue Analysis Mammography screening is one of the most recognized options for analyzing breast tissue in adult women. In contrast, the accuracy of this procedure allows it to be an alternative for women who cannot undergo mammography […]
- Ultrasound Physics and Instrumentation The camera is often not in harmony with the perception of the depth of a human vision. The level of such an acoustic signal distortion within a tissue is dependent on the emitted pulse’s amplitude […]
- Low-Back Pain and Ultrasound Therapy In the meantime, their opponents highlight that the beneficial aspects of the treatment course outweigh the risks related to the use of ultrasound equipment.
- Ultrasound in Treatment and Side-Effect Reduction Within the framework of the research project conducted by Ebadi et al, the research problem consisted in the fact that the effects of continuous ultrasound were underresearched.
- Ultrasound in Achilles Tendinitis Diagnosis In this research, the case study approach is applicable due to the fact that various patients suffering from tendon Achilles problem will be used as a basis for gauging the effectiveness of the method of […]
- Ultrasound Technology in Podiatry Surgery First, it is important to briefly outline the peculiarities of the RCT to understand the researchers’ point. They will be able to use the technology in numerous settings.
- Abdominal Ultrasound and Diagnoses The examiner explains to the patient how the procedure will be performed and how much time is necessary to finish the examination.
- Ultrasound and Color Doppler-Guided Surgery The purpose of the study is to examine the opinions of the trainees attending a training course concerning the use of technology.
- Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in Focal Liver Lesions In addition, inaccessibility to the eighth of the liver is a major setback in detecting lesions in the segment. With the advent of Doppler ultrasound, more insight in the diagnosis of liver lesions has been […]
- Ultrasound in Chemistry: Sonochemistry
- Intravascular Ultrasound: Current Role and Future Perspectives
- The Difference Between an Echocardiogram and an Ultrasound of the Heart
- Cooperative Control With Ultrasound Guidance for Radiation Therapy
- Optically Generated Ultrasound: A New Paradigm for Intracoronary Imaging
- Nondestructive Testing: Principle of Flaw Detection With Ultrasound
- Closed-Loop Transcranial Ultrasound Stimulation for Real-Time Non-invasive Neuromodulation
- Consumer Application of Ultrasound: A Television Remote
- Roles of Low-Intensity Ultrasound in Differentiating Cell Death
- High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Development: Destroying the Target Tissue
- Using Ultrasound to Enhance the Mechanical and Physical Properties of Metals
- The Security Implications of the Machine-Learning Supply Chain: Professionalism in the Ultrasound Department
- Ultrasound Neuromodulation: Mechanisms and the Potential of Multimodal Stimulation for Neuronal Function Assessment
- How Ultrasound Can Produce Sonoluminescence
- Preparation for an Ultrasound of a Gallbladder and a Pelvic
- Endorectal and Endoanal Ultrasound Technique
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: Is It Painful, Purpose, and Results
- Endoscopic Ultrasound in Diagnosing Cancer: One of the Most Common Imaging Procedures
- Ultrasound Skin Imaging in Dermatology, Aesthetic Medicine, and Cosmetology
- Ultrasound Physical Medical Treatment in Healing Following an Acute Injury or a Chronic Condition
- How Do Ultrasound Scans Work
- Americas Ultrasound Systems Market: From USD 7.9 Billion to USD 10.23 Billion
- How Ultrasound Imaging Helps Us Understand Speech and Accent Variation
- Cerebral Ultrasound Time-Harmonic Elastography: Softening of the Human Brain Due to Dehydration
- Wireless Communication in “Audio Beacons” Using Ultrasound
- Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
- Thyroid Ultrasound: Purpose, Procedure, Benefits
- Blood Pressure Modulation With Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound
- Accuracy of Ultrasounds in Diagnosing Birth Defects
- Functional Ultrasound During Awake Brain Surgery
- Live Animal Ultrasound Explained by Dr. Allen Williams
- Ultrasound Waves in Acoustic Microscopy
- Chemical and Physical Effects of Ultrasound: Sonoluminescence and Materials
- Focused Ultrasound for Noninvasive, Focal Pharmacologic Neurointervention
- Lung Ultrasound Findings in COVID-19 Pneumonia
- High-Power Ultrasound in Dry Corn Milling Plants
- History of Ultrasound of Physics and the Properties of the Transducer
- Relationship Between Ultrasound Viewing and Proceeding to Abortion
- Transrectal Ultrasound of the Prostate With a Biopsy
- Iron-Based Catalysts Used in Water Treatment Assisted by Ultrasound
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, January 24). 59 Ultrasound Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/ultrasound-essay-topics/
"59 Ultrasound Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 24 Jan. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/ultrasound-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2023) '59 Ultrasound Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 24 January.
IvyPanda . 2023. "59 Ultrasound Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." January 24, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/ultrasound-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "59 Ultrasound Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." January 24, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/ultrasound-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "59 Ultrasound Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." January 24, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/ultrasound-essay-topics/.
- X-Ray Questions
- Health Promotion Research Topics
- Gynecology Research Ideas
- Osteoarthritis Ideas
- Pneumonia Questions
- Cardiomyopathy Titles
- Heart Disease Titles
- Epigenetics Essay Titles
- Hypertension Topics
- Biomedicine Essay Topics
- Deontology Questions
- Breast Cancer Ideas
- Health Insurance Research Topics
- Evidence-Based Practice Titles
- Healthcare Questions
Head Start Your Radiology Residency [Online] ↗️
- Radiology Thesis – More than 400 Research Topics (2022)!
Please login to bookmark

Introduction
A thesis or dissertation, as some people would like to call it, is an integral part of the Radiology curriculum, be it MD, DNB, or DMRD. We have tried to aggregate radiology thesis topics from various sources for reference.
Not everyone is interested in research, and writing a Radiology thesis can be daunting. But there is no escape from preparing, so it is better that you accept this bitter truth and start working on it instead of cribbing about it (like other things in life. #PhilosophyGyan!)
Start working on your thesis as early as possible and finish your thesis well before your exams, so you do not have that stress at the back of your mind. Also, your thesis may need multiple revisions, so be prepared and allocate time accordingly.
Tips for Choosing Radiology Thesis and Research Topics
Keep it simple silly (kiss).
Retrospective > Prospective
Retrospective studies are better than prospective ones, as you already have the data you need when choosing to do a retrospective study. Prospective studies are better quality, but as a resident, you may not have time (, energy and enthusiasm) to complete these.
Choose a simple topic that answers a single/few questions
Original research is challenging, especially if you do not have prior experience. I would suggest you choose a topic that answers a single or few questions. Most topics that I have listed are along those lines. Alternatively, you can choose a broad topic such as “Role of MRI in evaluation of perianal fistulas.”
You can choose a novel topic if you are genuinely interested in research AND have a good mentor who will guide you. Once you have done that, make sure that you publish your study once you are done with it.
Get it done ASAP.
In most cases, it makes sense to stick to a thesis topic that will not take much time. That does not mean you should ignore your thesis and ‘Ctrl C + Ctrl V’ from a friend from another university. Thesis writing is your first step toward research methodology so do it as sincerely as possible. Do not procrastinate in preparing the thesis. As soon as you have been allotted a guide, start researching topics and writing a review of the literature.
At the same time, do not invest a lot of time in writing/collecting data for your thesis. You should not be busy finishing your thesis a few months before the exam. Some people could not appear for the exam because they could not submit their thesis in time. So DO NOT TAKE thesis lightly.
Do NOT Copy-Paste
Reiterating once again, do not simply choose someone else’s thesis topic. Find out what are kind of cases that your Hospital caters to. It is better to do a good thesis on a common topic than a crappy one on a rare one.
Books to help you write a Radiology Thesis
Event country/university has a different format for thesis; hence these book recommendations may not work for everyone.

- Amazon Kindle Edition
- Gupta, Piyush (Author)
- English (Publication Language)
- 206 Pages - 10/12/2020 (Publication Date) - Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. (Publisher)
In A Hurry? Download a PDF list of Radiology Research Topics!
Sign up below to get this PDF directly to your email address.
100% Privacy Guaranteed. Your information will not be shared. Unsubscribe anytime with a single click.
List of Radiology Research /Thesis / Dissertation Topics
- State of the art of MRI in the diagnosis of hepatic focal lesions
- Multimodality imaging evaluation of sacroiliitis in newly diagnosed patients of spondyloarthropathy
- Multidetector computed tomography in oesophageal varices
- Role of positron emission tomography with computed tomography in the diagnosis of cancer Thyroid
- Evaluation of focal breast lesions using ultrasound elastography
- Role of MRI diffusion tensor imaging in the assessment of traumatic spinal cord injuries
- Sonographic imaging in male infertility
- Comparison of color Doppler and digital subtraction angiography in occlusive arterial disease in patients with lower limb ischemia
- The role of CT urography in Haematuria
- Role of functional magnetic resonance imaging in making brain tumor surgery safer
- Prediction of pre-eclampsia and fetal growth restriction by uterine artery Doppler
- Role of grayscale and color Doppler ultrasonography in the evaluation of neonatal cholestasis
- Validity of MRI in the diagnosis of congenital anorectal anomalies
- Role of sonography in assessment of clubfoot
- Role of diffusion MRI in preoperative evaluation of brain neoplasms
- Imaging of upper airways for pre-anaesthetic evaluation purposes and for laryngeal afflictions.
- A study of multivessel (arterial and venous) Doppler velocimetry in intrauterine growth restriction
- Multiparametric 3tesla MRI of suspected prostatic malignancy.
- Role of Sonography in Characterization of Thyroid Nodules for differentiating benign from
- Role of advances magnetic resonance imaging sequences in multiple sclerosis
- Role of multidetector computed tomography in evaluation of jaw lesions
- Role of Ultrasound and MR Imaging in the Evaluation of Musculotendinous Pathologies of Shoulder Joint
- Role of perfusion computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral blood flow, blood volume and vascular permeability of cerebral neoplasms
- MRI flow quantification in the assessment of the commonest csf flow abnormalities
- Role of diffusion-weighted MRI in evaluation of prostate lesions and its histopathological correlation
- CT enterography in evaluation of small bowel disorders
- Comparison of perfusion magnetic resonance imaging (PMRI), magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) in and positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET/CT) in post radiotherapy treated gliomas to detect recurrence
- Role of multidetector computed tomography in evaluation of paediatric retroperitoneal masses
- Role of Multidetector computed tomography in neck lesions
- Estimation of standard liver volume in Indian population
- Role of MRI in evaluation of spinal trauma
- Role of modified sonohysterography in female factor infertility: a pilot study.
- The role of pet-CT in the evaluation of hepatic tumors
- Role of 3D magnetic resonance imaging tractography in assessment of white matter tracts compromise in supratentorial tumors
- Role of dual phase multidetector computed tomography in gallbladder lesions
- Role of multidetector computed tomography in assessing anatomical variants of nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses in patients of chronic rhinosinusitis.
- magnetic resonance spectroscopy in multiple sclerosis
- Evaluation of thyroid nodules by ultrasound elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) imaging
- Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Intractable Epilepsy
- Evaluation of suspected and known coronary artery disease by 128 slice multidetector CT.
- Role of regional diffusion tensor imaging in the evaluation of intracranial gliomas and its histopathological correlation
- Role of chest sonography in diagnosing pneumothorax
- Role of CT virtual cystoscopy in diagnosis of urinary bladder neoplasia
- Role of MRI in assessment of valvular heart diseases
- High resolution computed tomography of temporal bone in unsafe chronic suppurative otitis media
- Multidetector CT urography in the evaluation of hematuria
- Contrast-induced nephropathy in diagnostic imaging investigations with intravenous iodinated contrast media
- Comparison of dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced perfusion magnetic resonance imaging and single photon emission computed tomography in patients with little’s disease
- Role of Multidetector Computed Tomography in Bowel Lesions.
- Role of diagnostic imaging modalities in evaluation of post liver transplantation recipient complications.
- Role of multislice CT scan and barium swallow in the estimation of oesophageal tumour length
- Malignant Lesions-A Prospective Study.
- Value of ultrasonography in assessment of acute abdominal diseases in pediatric age group
- Role of three dimensional multidetector CT hysterosalpingography in female factor infertility
- Comparative evaluation of multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) virtual tracheo-bronchoscopy and fiberoptic tracheo-bronchoscopy in airway diseases
- Role of Multidetector CT in the evaluation of small bowel obstruction
- Sonographic evaluation in adhesive capsulitis of shoulder
- Utility of MR Urography Versus Conventional Techniques in Obstructive Uropathy
- MRI of the postoperative knee
- Role of 64 slice-multi detector computed tomography in diagnosis of bowel and mesenteric injury in blunt abdominal trauma.
- Sonoelastography and triphasic computed tomography in the evaluation of focal liver lesions
- Evaluation of Role of Transperineal Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Urinary Stress incontinence in Women
- Multidetector computed tomographic features of abdominal hernias
- Evaluation of lesions of major salivary glands using ultrasound elastography
- Transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in female urinary incontinence
- MDCT colonography and double-contrast barium enema in evaluation of colonic lesions
- Role of MRI in diagnosis and staging of urinary bladder carcinoma
- Spectrum of imaging findings in children with febrile neutropenia.
- Spectrum of radiographic appearances in children with chest tuberculosis.
- Role of computerized tomography in evaluation of mediastinal masses in pediatric
- Diagnosing renal artery stenosis: Comparison of multimodality imaging in diabetic patients
- Role of multidetector CT virtual hysteroscopy in the detection of the uterine & tubal causes of female infertility
- Role of multislice computed tomography in evaluation of crohn’s disease
- CT quantification of parenchymal and airway parameters on 64 slice MDCT in patients of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Comparative evaluation of MDCT and 3t MRI in radiographically detected jaw lesions.
- Evaluation of diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography, colour Doppler sonography and low dose computed tomography in acute appendicitis
- Ultrasonography , magnetic resonance cholangio-pancreatography (MRCP) in assessment of pediatric biliary lesions
- Multidetector computed tomography in hepatobiliary lesions.
- Evaluation of peripheral nerve lesions with high resolution ultrasonography and colour Doppler
- Multidetector computed tomography in pancreatic lesions
- Multidetector Computed Tomography in Paediatric abdominal masses.
- Evaluation of focal liver lesions by colour Doppler and MDCT perfusion imaging
- Sonographic evaluation of clubfoot correction during Ponseti treatment
- Role of multidetector CT in characterization of renal masses
- Study to assess the role of Doppler ultrasound in evaluation of arteriovenous (av) hemodialysis fistula and the complications of hemodialysis vasular access
- Comparative study of multiphasic contrast-enhanced CT and contrast-enhanced MRI in the evaluation of hepatic mass lesions
- Sonographic spectrum of rheumatoid arthritis
- Diagnosis & staging of liver fibrosis by ultrasound elastography in patients with chronic liver diseases
- Role of multidetector computed tomography in assessment of jaw lesions.
- Role of high-resolution ultrasonography in the differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid lesions
- Radiological evaluation of aortic aneurysms in patients selected for endovascular repair
- Role of conventional MRI, and diffusion tensor imaging tractography in evaluation of congenital brain malformations
- To evaluate the status of coronary arteries in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation using 256 multirow detector CT scan
- A comparative study of ultrasonography and CT – arthrography in diagnosis of chronic ligamentous and meniscal injuries of knee
- Multi detector computed tomography evaluation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and correlation with severity of disease
- Diffusion weighted and dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in chemoradiotherapeutic response evaluation in cervical cancer.
- High resolution sonography in the evaluation of non-traumatic painful wrist
- The role of trans-vaginal ultrasound versus magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis & evaluation of cancer cervix
- Role of multidetector row computed tomography in assessment of maxillofacial trauma
- Imaging of vascular complication after liver transplantation.
- Role of magnetic resonance perfusion weighted imaging & spectroscopy for grading of glioma by correlating perfusion parameter of the lesion with the final histopathological grade
- Magnetic resonance evaluation of abdominal tuberculosis.
- Diagnostic usefulness of low dose spiral HRCT in diffuse lung diseases
- Role of dynamic contrast enhanced and diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging in evaluation of endometrial lesions
- Contrast enhanced digital mammography anddigital breast tomosynthesis in early diagnosis of breast lesion
- Evaluation of Portal Hypertension with Colour Doppler flow imaging and magnetic resonance imaging
- Evaluation of musculoskeletal lesions by magnetic resonance imaging
- Role of diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in assessment of neoplastic and inflammatory brain lesions
- Radiological spectrum of chest diseases in HIV infected children High resolution ultrasonography in neck masses in children
- with surgical findings
- Sonographic evaluation of peripheral nerves in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Role of perfusion computed tomography in the evaluation of neck masses and correlation
- Role of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of knee joint lesions
- Role of ultrasonography in evaluation of various causes of pelvic pain in first trimester of pregnancy.
- Role of Magnetic Resonance Angiography in the Evaluation of Diseases of Aorta and its Branches
- MDCT fistulography in evaluation of fistula in Ano
- Role of multislice CT in diagnosis of small intestine tumors
- Role of high resolution CT in differentiation between benign and malignant pulmonary nodules in children
- A study of multidetector computed tomography urography in urinary tract abnormalities
- Role of high resolution sonography in assessment of ulnar nerve in patients with leprosy.
- Pre-operative radiological evaluation of locally aggressive and malignant musculoskeletal tumours by computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
- The role of ultrasound & MRI in acute pelvic inflammatory disease
- Ultrasonography compared to computed tomographic arthrography in the evaluation of shoulder pain
- Role of Multidetector Computed Tomography in patients with blunt abdominal trauma.
- The Role of Extended field-of-view Sonography and compound imaging in Evaluation of Breast Lesions
- Evaluation of focal pancreatic lesions by Multidetector CT and perfusion CT
- Evaluation of breast masses on sono-mammography and colour Doppler imaging
- Role of CT virtual laryngoscopy in evaluation of laryngeal masses
- Triple phase multi detector computed tomography in hepatic masses
- Role of transvaginal ultrasound in diagnosis and treatment of female infertility
- Role of ultrasound and color Doppler imaging in assessment of acute abdomen due to female genetal causes
- High resolution ultrasonography and color Doppler ultrasonography in scrotal lesion
- Evaluation of diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography with colour Doppler vs low dose computed tomography in salivary gland disease
- Role of multidetector CT in diagnosis of salivary gland lesions
- Comparison of diagnostic efficacy of ultrasonography and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in obstructive jaundice: A prospective study
- Evaluation of varicose veins-comparative assessment of low dose CT venogram with sonography: pilot study
- Role of mammotome in breast lesions
- The role of interventional imaging procedures in the treatment of selected gynecological disorders
- Role of transcranial ultrasound in diagnosis of neonatal brain insults
- Role of multidetector CT virtual laryngoscopy in evaluation of laryngeal mass lesions
- Evaluation of adnexal masses on sonomorphology and color Doppler imaginig
- Role of radiological imaging in diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma
- Comprehensive imaging of renal masses by magnetic resonance imaging
- The role of 3D & 4D ultrasonography in abnormalities of fetal abdomen
- Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and characterization of brain tumors in correlation with conventional MRI
- Role of diffusion weighted MRI imaging in evaluation of cancer prostate
- Role of multidetector CT in diagnosis of urinary bladder cancer
- Role of multidetector computed tomography in the evaluation of paediatric retroperitoneal masses.
- Comparative evaluation of gastric lesions by double contrast barium upper G.I. and multi detector computed tomography
- Evaluation of hepatic fibrosis in chronic liver disease using ultrasound elastography
- Role of MRI in assessment of hydrocephalus in pediatric patients
- The role of sonoelastography in characterization of breast lesions
- The influence of volumetric tumor doubling time on survival of patients with intracranial tumours
- Role of perfusion computed tomography in characterization of colonic lesions
- Role of proton MRI spectroscopy in the evaluation of temporal lobe epilepsy
- Role of Doppler ultrasound and multidetector CT angiography in evaluation of peripheral arterial diseases.
- Role of multidetector computed tomography in paranasal sinus pathologies
- Role of virtual endoscopy using MDCT in detection & evaluation of gastric pathologies
- High resolution 3 Tesla MRI in the evaluation of ankle and hindfoot pain.
- Transperineal ultrasonography in infants with anorectal malformation
- CT portography using MDCT versus color Doppler in detection of varices in cirrhotic patients
- Role of CT urography in the evaluation of a dilated ureter
- Characterization of pulmonary nodules by dynamic contrast-enhanced multidetector CT
- Comprehensive imaging of acute ischemic stroke on multidetector CT
- The role of fetal MRI in the diagnosis of intrauterine neurological congenital anomalies
- Role of Multidetector computed tomography in pediatric chest masses
- Multimodality imaging in the evaluation of palpable & non-palpable breast lesion.
- Sonographic Assessment Of Fetal Nasal Bone Length At 11-28 Gestational Weeks And Its Correlation With Fetal Outcome.
- Role Of Sonoelastography And Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography In Evaluation Of Lymph Node Metastasis In Head And Neck Cancers
- Role Of Renal Doppler And Shear Wave Elastography In Diabetic Nephropathy
- Evaluation Of Relationship Between Various Grades Of Fatty Liver And Shear Wave Elastography Values
- Evaluation and characterization of pelvic masses of gynecological origin by USG, color Doppler and MRI in females of reproductive age group
- Radiological evaluation of small bowel diseases using computed tomographic enterography
- Role of coronary CT angiography in patients of coronary artery disease
- Role of multimodality imaging in the evaluation of pediatric neck masses
- Role of CT in the evaluation of craniocerebral trauma
- Role of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the evaluation of spinal dysraphism
- Comparative evaluation of triple phase CT and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in patients with liver cirrhosis
- Evaluation of the relationship between carotid intima-media thickness and coronary artery disease in patients evaluated by coronary angiography for suspected CAD
- Assessment of hepatic fat content in fatty liver disease by unenhanced computed tomography
- Correlation of vertebral marrow fat on spectroscopy and diffusion-weighted MRI imaging with bone mineral density in postmenopausal women.
- Comparative evaluation of CT coronary angiography with conventional catheter coronary angiography
- Ultrasound evaluation of kidney length & descending colon diameter in normal and intrauterine growth-restricted fetuses
- A prospective study of hepatic vein waveform and splenoportal index in liver cirrhosis: correlation with child Pugh’s classification and presence of esophageal varices.
- CT angiography to evaluate coronary artery by-pass graft patency in symptomatic patient’s functional assessment of myocardium by cardiac MRI in patients with myocardial infarction
- MRI evaluation of HIV positive patients with central nervous system manifestations
- MDCT evaluation of mediastinal and hilar masses
- Evaluation of rotator cuff & labro-ligamentous complex lesions by MRI & MRI arthrography of shoulder joint
- Role of imaging in the evaluation of soft tissue vascular malformation
- Role of MRI and ultrasonography in the evaluation of multifidus muscle pathology in chronic low back pain patients
- Role of ultrasound elastography in the differential diagnosis of breast lesions
- Role of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in evaluating dilated common bile duct in patients with symptomatic gallstone disease.
- Comparative study of CT urography & hybrid CT urography in patients with haematuria.
- Role of MRI in the evaluation of anorectal malformations
- Comparison of ultrasound-Doppler and magnetic resonance imaging findings in rheumatoid arthritis of hand and wrist
- Role of Doppler sonography in the evaluation of renal artery stenosis in hypertensive patients undergoing coronary angiography for coronary artery disease.
- Comparison of radiography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in the detection of sacroiliitis in ankylosing spondylitis.
- Mr evaluation of painful hip
- Role of MRI imaging in pretherapeutic assessment of oral and oropharyngeal malignancy
- Evaluation of diffuse lung diseases by high resolution computed tomography of the chest
- Mr evaluation of brain parenchyma in patients with craniosynostosis.
- Diagnostic and prognostic value of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in dilated cardiomyopathy
- Role of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in the detection of early carcinoma prostate
- Role of magnetic resonance imaging in white matter diseases
- Role of sonoelastography in assessing the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced breast cancer.
- Role of ultrasonography in the evaluation of carotid and femoral intima-media thickness in predialysis patients with chronic kidney disease
- Role of H1 MRI spectroscopy in focal bone lesions of peripheral skeleton choline detection by MRI spectroscopy in breast cancer and its correlation with biomarkers and histological grade.
- Ultrasound and MRI evaluation of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer.
- Role of sonography and magnetic resonance imaging in evaluating chronic lateral epicondylitis.
- Comparative of sonography including Doppler and sonoelastography in cervical lymphadenopathy.
- Evaluation of Umbilical Coiling Index as Predictor of Pregnancy Outcome.
- Computerized Tomographic Evaluation of Azygoesophageal Recess in Adults.
- Lumbar Facet Arthropathy in Low Backache.
- “Urethral Injuries After Pelvic Trauma: Evaluation with Uretrography
- Role Of Ct In Diagnosis Of Inflammatory Renal Diseases
- Role Of Ct Virtual Laryngoscopy In Evaluation Of Laryngeal Masses
- “Ct Portography Using Mdct Versus Color Doppler In Detection Of Varices In
- Cirrhotic Patients”
- Role Of Multidetector Ct In Characterization Of Renal Masses
- Role Of Ct Virtual Cystoscopy In Diagnosis Of Urinary Bladder Neoplasia
- Role Of Multislice Ct In Diagnosis Of Small Intestine Tumors
- “Mri Flow Quantification In The Assessment Of The Commonest CSF Flow Abnormalities”
- “The Role Of Fetal Mri In Diagnosis Of Intrauterine Neurological CongenitalAnomalies”
- Role Of Transcranial Ultrasound In Diagnosis Of Neonatal Brain Insults
- “The Role Of Interventional Imaging Procedures In The Treatment Of Selected Gynecological Disorders”
- Role Of Radiological Imaging In Diagnosis Of Endometrial Carcinoma
- “Role Of High-Resolution Ct In Differentiation Between Benign And Malignant Pulmonary Nodules In Children”
- Role Of Ultrasonography In The Diagnosis Of Knee Joint Lesions
- “Role Of Diagnostic Imaging Modalities In Evaluation Of Post Liver Transplantation Recipient Complications”
- “Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Diagnosis And
- Characterization Of Brain Tumors In Correlation With Conventional Mri”
- The Role Of PET-CT In The Evaluation Of Hepatic Tumors
- “Role Of Computerized Tomography In Evaluation Of Mediastinal Masses In Pediatric patients”
- “Trans Vaginal Ultrasound And Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Female Urinary Incontinence”
- Role Of Multidetector Ct In Diagnosis Of Urinary Bladder Cancer
- “Role Of Transvaginal Ultrasound In Diagnosis And Treatment Of Female Infertility”
- Role Of Diffusion-Weighted Mri Imaging In Evaluation Of Cancer Prostate
- “Role Of Positron Emission Tomography With Computed Tomography In Diagnosis Of Cancer Thyroid”
- The Role Of CT Urography In Case Of Haematuria
- “Value Of Ultrasonography In Assessment Of Acute Abdominal Diseases In Pediatric Age Group”
- “Role Of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Making Brain Tumor Surgery Safer”
- The Role Of Sonoelastography In Characterization Of Breast Lesions
- “Ultrasonography, Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) In Assessment Of Pediatric Biliary Lesions”
- “Role Of Ultrasound And Color Doppler Imaging In Assessment Of Acute Abdomen Due To Female Genital Causes”
- “Role Of Multidetector Ct Virtual Laryngoscopy In Evaluation Of Laryngeal Mass Lesions”
- MRI Of The Postoperative Knee
- Role Of Mri In Assessment Of Valvular Heart Diseases
- The Role Of 3D & 4D Ultrasonography In Abnormalities Of Fetal Abdomen
- State Of The Art Of Mri In Diagnosis Of Hepatic Focal Lesions
- Role Of Multidetector Ct In Diagnosis Of Salivary Gland Lesions
- “Role Of Virtual Endoscopy Using Mdct In Detection & Evaluation Of Gastric Pathologies”
- The Role Of Ultrasound & Mri In Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- “Diagnosis & Staging Of Liver Fibrosis By Ultraso Und Elastography In
- Patients With Chronic Liver Diseases”
- Role Of Mri In Evaluation Of Spinal Trauma
- Validity Of Mri In Diagnosis Of Congenital Anorectal Anomalies
- Imaging Of Vascular Complication After Liver Transplantation
- “Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography And Digital Breast Tomosynthesis In Early Diagnosis Of Breast Lesion”
- Role Of Mammotome In Breast Lesions
- “Role Of MRI Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) In Assessment Of Traumatic Spinal Cord Injuries”
- “Prediction Of Pre-eclampsia And Fetal Growth Restriction By Uterine Artery Doppler”
- “Role Of Multidetector Row Computed Tomography In Assessment Of Maxillofacial Trauma”
- “Role Of Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Assessment Of Neoplastic And Inflammatory Brain Lesions”
- Role Of Diffusion Mri In Preoperative Evaluation Of Brain Neoplasms
- “Role Of Multidetector Ct Virtual Hysteroscopy In The Detection Of The
- Uterine & Tubal Causes Of Female Infertility”
- Role Of Advances Magnetic Resonance Imaging Sequences In Multiple Sclerosis Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy In Multiple Sclerosis
- “Role Of Conventional Mri, And Diffusion Tensor Imaging Tractography In Evaluation Of Congenital Brain Malformations”
- Role Of MRI In Evaluation Of Spinal Trauma
- Diagnostic Role Of Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging In Neck Masses
- “The Role Of Transvaginal Ultrasound Versus Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Diagnosis & Evaluation Of Cancer Cervix”
- “Role Of 3d Magnetic Resonance Imaging Tractography In Assessment Of White Matter Tracts Compromise In Supra Tentorial Tumors”
- Role Of Proton MR Spectroscopy In The Evaluation Of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
- Role Of Multislice Computed Tomography In Evaluation Of Crohn’s Disease
- Role Of MRI In Assessment Of Hydrocephalus In Pediatric Patients
- The Role Of MRI In Diagnosis And Staging Of Urinary Bladder Carcinoma
- USG and MRI correlation of congenital CNS anomalies
- HRCT in interstitial lung disease
- X-Ray, CT and MRI correlation of bone tumors
- “Study on the diagnostic and prognostic utility of X-Rays for cases of pulmonary tuberculosis under RNTCP”
- “Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the characterization of female adnexal pathology”
- “CT angiography of carotid atherosclerosis and NECT brain in cerebral ischemia, a correlative analysis”
- Role of CT scan in the evaluation of paranasal sinus pathology
- USG and MRI correlation on shoulder joint pathology
- “Radiological evaluation of a patient presenting with extrapulmonary tuberculosis”
- CT and MRI correlation in focal liver lesions”
- Comparison of MDCT virtual cystoscopy with conventional cystoscopy in bladder tumors”
- “Bleeding vessels in life-threatening hemoptysis: Comparison of 64 detector row CT angiography with conventional angiography prior to endovascular management”
- “Role of transarterial chemoembolization in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma”
- “Comparison of color flow duplex study with digital subtraction angiography in the evaluation of peripheral vascular disease”
- “A Study to assess the efficacy of magnetization transfer ratio in differentiating tuberculoma from neurocysticercosis”
- “MR evaluation of uterine mass lesions in correlation with transabdominal, transvaginal ultrasound using HPE as a gold standard”
- “The Role of power Doppler imaging with trans rectal ultrasonogram guided prostate biopsy in the detection of prostate cancer”
- “Lower limb arteries assessed with doppler angiography – A prospective comparative study with multidetector CT angiography”
- “Comparison of sildenafil with papaverine in penile doppler by assessing hemodynamic changes”
- “Evaluation of efficacy of sonosalphingogram for assessing tubal patency in infertile patients with hysterosalpingogram as the gold standard”
- Role of CT enteroclysis in the evaluation of small bowel diseases
- “MRI colonography versus conventional colonoscopy in the detection of colonic polyposis”
- “Magnetic Resonance Imaging of anteroposterior diameter of the midbrain – differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy from Parkinson disease”
- “MRI Evaluation of anterior cruciate ligament tears with arthroscopic correlation”
- “The Clinicoradiological profile of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis with prognostic evaluation using MR sequences”
- “Role of MRI in the evaluation of pelvic floor integrity in stress incontinent patients” “Doppler ultrasound evaluation of hepatic venous waveform in portal hypertension before and after propranolol”
- “Role of transrectal sonography with colour doppler and MRI in evaluation of prostatic lesions with TRUS guided biopsy correlation”
- “Ultrasonographic evaluation of painful shoulders and correlation of rotator cuff pathologies and clinical examination”
- “Colour Doppler Evaluation of Common Adult Hepatic tumors More Than 2 Cm with HPE and CECT Correlation”
- “Clinical Relevance of MR Urethrography in Obliterative Posterior Urethral Stricture”
- “Prediction of Adverse Perinatal Outcome in Growth Restricted Fetuses with Antenatal Doppler Study”
- Radiological evaluation of spinal dysraphism using CT and MRI
- “Evaluation of temporal bone in cholesteatoma patients by high resolution computed tomography”
- “Radiological evaluation of primary brain tumours using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging”
- “Three dimensional colour doppler sonographic assessment of changes in volume and vascularity of fibroids – before and after uterine artery embolization”
- “In phase opposed phase imaging of bone marrow differentiating neoplastic lesions”
- “Role of dynamic MRI in replacing the isotope renogram in the functional evaluation of PUJ obstruction”
- Characterization of adrenal masses with contrast-enhanced CT – washout study
- A study on accuracy of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
- “Evaluation of median nerve in carpal tunnel syndrome by high-frequency ultrasound & color doppler in comparison with nerve conduction studies”
- “Correlation of Agatston score in patients with obstructive and nonobstructive coronary artery disease following STEMI”
- “Doppler ultrasound assessment of tumor vascularity in locally advanced breast cancer at diagnosis and following primary systemic chemotherapy.”
- “Validation of two-dimensional perineal ultrasound and dynamic magnetic resonance imaging in pelvic floor dysfunction.”
- “Role of MR urethrography compared to conventional urethrography in the surgical management of obliterative urethral stricture.”
Search Diagnostic Imaging Research Topics
You can also search research-related resources on our custom search engine .
Free Resources for Preparing Radiology Thesis
- Radiology thesis topics- Benha University – Free to download thesis
- Radiology thesis topics – Faculty of Medical Science Delhi
- Radiology thesis topics – IPGMER
- Fetal Radiology thesis Protocols
- Radiology thesis and dissertation topics
- Radiographics
Proofreading Your Thesis:
Make sure you use Grammarly to correct your spelling , grammar , and plagiarism for your thesis. Grammarly has affordable paid subscriptions, windows/macOS apps, and FREE browser extensions. It is an excellent tool to avoid inadvertent spelling mistakes in your research projects. It has an extensive built-in vocabulary, but you should make an account and add your own medical glossary to it.

Guidelines for Writing a Radiology Thesis:
These are general guidelines and not about radiology specifically. You can share these with colleagues from other departments as well. Special thanks to Dr. Sanjay Yadav sir for these. This section is best seen on a desktop. Here are a couple of handy presentations to start writing a thesis:
Read the general guidelines for writing a thesis (the page will take some time to load- more than 70 pages!
A format for thesis protocol with a sample patient information sheet, sample patient consent form, sample application letter for thesis, and sample certificate.
Resources and References:
- Guidelines for thesis writing.
- Format for thesis protocol
- Thesis protocol writing guidelines DNB
- Informed consent form for Research studies from AIIMS
- Radiology Informed consent forms in local Indian languages.
- Sample Informed Consent form for Research in Hindi
- Guide to write a thesis by Dr. P R Sharma
- Guidelines for thesis writing by Dr. Pulin Gupta.
- Preparing MD/DNB thesis by A Indrayan
- Another good thesis reference protocol
Hopefully, this post will make the tedious task of writing a Radiology thesis a little bit easier for you. Best of luck with writing your thesis and your residency too!
More guides for residents :
- Guide for the MD/DMRD/DNB radiology exam!
Guide for First-Year Radiology Residents
- FRCR Exam: THE Most Comprehensive Guide (2022)!
- Radiology Practical Exams Questions compilation for MD/DNB/DMRD !
- Radiology Exam Resources (Oral Recalls, Instruments, etc )!
- Tips and Tricks for DNB/MD Radiology Practical Exam
- FRCR 2B exam- Tips and Tricks !
- FRCR exam preparation – An alternative take!
- Why did I take up Radiology?
- Radiology Conferences – A comprehensive guide!
ECR (European Congress Of Radiology)
- European Diploma in Radiology (EDiR) – The Complete Guide!
- Radiology NEET PG guide – How to select THE best college for post-graduation in Radiology (includes personal insights)!
- Interventional Radiology – All Your Questions Answered!
- What It Means To Be A Radiologist: A Guide For Medical Students!
- Radiology Mentors for Medical Students (Post NEET-PG)
- MD vs DNB Radiology: Which Path is Right for Your Career?
- DNB Radiology OSCE – Tips and Tricks
More radiology resources here: Radiology resources This page will be updated regularly. Kindly leave your feedback in the comments or send us a message here . Also, you can comment below regarding your department’s thesis topics.
Note: All topics have been compiled from available online resources. If anyone has an issue with any radiology thesis topics displayed here, you can message us here , and we can delete them. These are only sample guidelines. Thesis guidelines differ from institution to institution.
Image source: Thesis complete! (2018). Flickr. Retrieved 12 August 2018, from https://www.flickr.com/photos/cowlet/354911838 by Victoria Catterson
About The Author
Dr. amar udare, md, related posts ↓.

7 thoughts on “Radiology Thesis – More than 400 Research Topics (2022)!”
Amazing & The most helpful site for Radiology residents…
Thank you for your kind comments 🙂
Dr. I saw your Tips is very amazing and referable. But Dr. Can you help me with the thesis of Evaluation of Diagnostic accuracy of X-ray radiograph in knee joint lesion.
Wow! These are excellent stuff. You are indeed a teacher. God bless
Glad you liked these!
happy to see this
Glad I could help :).
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Get Radiology Updates to Your Inbox!
This site is for use by medical professionals. To continue, you must accept our use of cookies and the site's Terms of Use. Learn more Accept!
Wish to be a BETTER Radiologist? Join 14000 Radiology Colleagues !
Enter your email address below to access HIGH YIELD radiology content, updates, and resources.
No spam, only VALUE! Unsubscribe anytime with a single click.
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
- National Institutes of Health

En Español | Site Map | Staff Directory | Contact Us
- Science Education
- Science Topics
What is medical ultrasound?
How does it work, what is ultrasound used for, are there risks, what are examples of nibib-funded projects using ultrasound.
Medical ultrasound falls into two distinct categories: diagnostic and therapeutic.
Diagnostic ultrasound can be further sub-divided into anatomical and functional ultrasound. Anatomical ultrasound produces images of internal organs or other structures. Functional ultrasound combines information such as the movement and velocity of tissue or blood, softness or hardness of tissue, and other physical characteristics, with anatomical images to create “information maps.” These maps help doctors visualize changes/differences in function within a structure or organ.
Therapeutic ultrasound also uses sound waves above the range of human hearing but does not produce images. Its purpose is to interact with tissues in the body such that they are either modified or destroyed. Among the modifications possible are: moving or pushing tissue, heating tissue, dissolving blood clots, or delivering drugs to specific locations in the body. These destructive, or ablative, functions are made possible by use of very high-intensity beams that can destroy diseased or abnormal tissues such as tumors. The advantage of using ultrasound therapies is that, in most cases, they are non-invasive. No incisions or cuts need to be made to the skin, leaving no wounds or scars.
Ultrasound waves are produced by a transducer, which can both emit ultrasound waves, as well as detect the ultrasound echoes reflected back. In most cases, the active elements in ultrasound transducers are made of special ceramic crystal materials called piezoelectrics. These materials are able to produce sound waves when an electric field is applied to them, but can also work in reverse, producing an electric field when a sound wave hits them. When used in an ultrasound scanner, the transducer sends out a beam of sound waves into the body. The sound waves are reflected back to the transducer by boundaries between tissues in the path of the beam (e.g. the boundary between fluid and soft tissue or tissue and bone). When these echoes hit the transducer, they generate electrical signals that are sent to the ultrasound scanner. Using the speed of sound and the time of each echo’s return, the scanner calculates the distance from the transducer to the tissue boundary. These distances are then used to generate two-dimensional images of tissues and organs.
During an ultrasound exam, the technician will apply a gel to the skin. This keeps air pockets from forming between the transducer and the skin, which can block ultrasound waves from passing into the body.
Click here to watch a short video about how ultrasound works.
Diagnostic ultrasound. Diagnostic ultrasound is able to non-invasively image internal organs within the body. However, it is not good for imaging bones or any tissues that contain air, like the lungs. Under some conditions, ultrasound can image bones (such as in a fetus or in small babies) or the lungs and lining around the lungs, when they are filled or partially filled with fluid. One of the most common uses of ultrasound is during pregnancy, to monitor the growth and development of the fetus, but there are many other uses, including imaging the heart, blood vessels, eyes, thyroid, brain, breast, abdominal organs, skin, and muscles. Ultrasound images are displayed in either 2D, 3D, or 4D (which is 3D in motion).
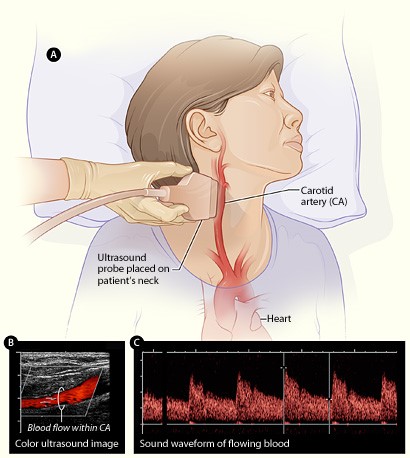
Functional ultrasound. Functional ultrasound applications include Doppler and color Doppler ultrasound for measuring and visualizing blood flow in vessels within the body or in the heart. It can also measure the speed of the blood flow and direction of movement. This is done using color-coded maps called color Doppler imaging. Doppler ultrasound is commonly used to determine whether plaque build-up inside the carotid arteries is blocking blood flow to the brain.
Another functional form of ultrasound is elastography, a method for measuring and displaying the relative stiffness of tissues, which can be used to differentiate tumors from healthy tissue. This information can be displayed as either color-coded maps of the relative stiffness; black-and white maps that display high-contrast images of tumors compared with anatomical images; or color-coded maps that are overlayed on the anatomical image. Elastography can be used to test for liver fibrosis, a condition in which excessive scar tissue builds up in the liver due to inflammation.
Ultrasound is also an important method for imaging interventions in the body. For example, ultrasound-guided needle biopsy helps physicians see the position of a needle while it is being guided to a selected target, such as a mass or a tumor in the breast. Also, ultrasound is used for real-time imaging of the location of the tip of a catheter as it is inserted in a blood vessel and guided along the length of the vessel. It can also be used for minimally invasive surgery to guide the surgeon with real-time images of the inside of the body.
Therapeutic or interventional ultrasound. Therapeutic ultrasound produces high levels of acoustic output that can be focused on specific targets for the purpose of heating, ablating, or breaking up tissue. One type of therapeutic ultrasound uses high-intensity beams of sound that are highly targeted, and is called High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU). HIFU is being investigated as a method for modifying or destroying diseased or abnormal tissues inside the body (e.g. tumors) without having to open or tear the skin or cause damage to the surrounding tissue. Either ultrasound or MRI is used to identify and target the tissue to be treated, guide and control the treatment in real time, and confirm the effectiveness of the treatment. HIFU is currently FDA approved for the treatment of uterine fibroids, to alleviate pain from bone metastases, and most recently for the ablation of prostate tissue. HIFU is also being investigated as a way to close wounds and stop bleeding, to break up clots in blood vessels, and to temporarily open the blood brain barrier so that medications can pass through.
Diagnostic ultrasound is generally regarded as safe and does not produce ionizing radiation like that produced by x-rays. Still, ultrasound is capable of producing some biological effects in the body under specific settings and conditions. For this reason, the FDA requires that diagnostic ultrasound devices operate within acceptable limits. The FDA, as well as many professional societies, discourage the casual use of ultrasound (e.g. for keepsake videos) and recommend that it be used only when there is a true medical need.
The following are examples of current research projects funded by NIBIB that are developing new applications of ultrasound that are already in use or that will be in use in the future:
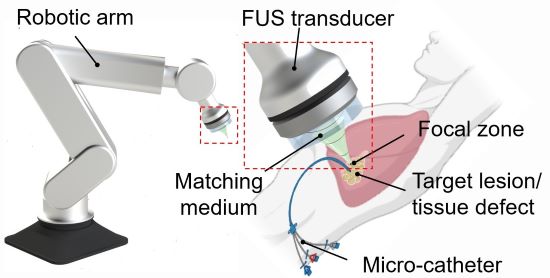
3D printing through the skin : Researchers at Duke University have developed a method to 3D print biocompatible structures through thick, multi-layered tissues. The approach entails using focused ultrasound to solidify a special ink that has been injected into the body to repair bone or repair soft tissues, for example. Initial experiments in animal tissue suggest the method could turn highly invasive surgical procedures into safer, less invasive ones. (Image on left courtesy of Junjie Yao (Duke University) and Yu Shrike Zhang (Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital)).
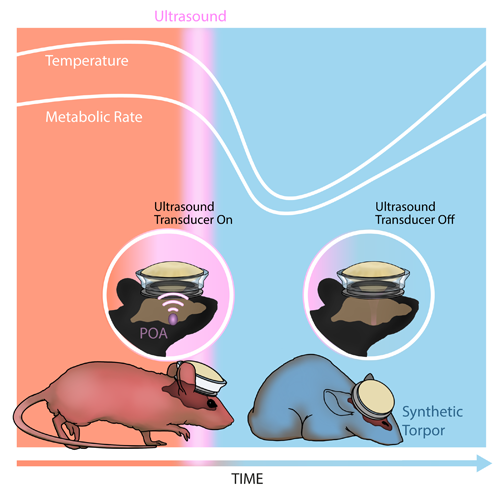
Inducing a hibernation-like state : Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis used ultrasound waves directed into the brain to lower the body temperature and metabolic rates of mice, inducing a hibernation-like state, called torpor. The researchers replicated some of these results in rats, which, like humans, don’t naturally enter torpor. Inducing torpor could help minimize damage from stroke or heart attack and buy precious time for patients in critical care. (Image on right courtesy of Yang et al./Washington University in St. Louis).
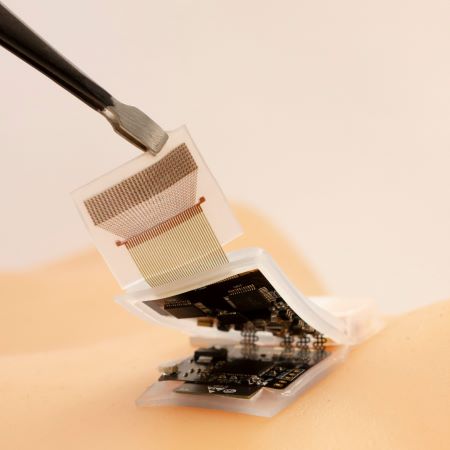
High-quality imaging at home : Brigham and Women’s Hospital researchers compared ultrasound scans acquired by experts with those taken by inexperienced volunteers, finding little difference in the image quality of the two groups. The unconventional approach of having patients take ultrasound images of themselves at home and share them with healthcare professionals could allow for remote monitoring and reduce the need for hospitalization. (Image on right courtesy of Duggan et al./Brigham and Women's Hospital).
Reviewed December 2023
Explore More
Heath Topics
- Breast Cancer
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Digestive Diseases
- Heart Disease
- Musculoskeletal Disease
- Reproductive Health
- Women's Health
Research Topics
- Optical Imaging
- Ultrasound (US) diagnostic
- Ultrasound (US) therapy
PROGRAM AREAS
- Ultrasound: Diagnostic and Interventional
Inside NIBIB
- Director's Corner
- Funding Policies
- NIBIB Fact Sheets
- Press Releases
- Frontiers in Rehabilitation Sciences
- Rehabilitation for Musculoskeletal Conditions
- Research Topics
Advances in Musculoskeletal Ultrasound
Total Downloads
Total Views and Downloads
About this Research Topic
Musculoskeletal ultrasound is becoming an important and effective tool for the diagnosis of various soft tissue and joint disorders. It is accurate, safe, affordable, efficient, and dynamic. Musculoskeletal ultrasound is also a useful tool for guided therapy. The advances of musculoskeletal imaging in recent ...
Keywords : Ultrasound, Musculoskeletal, Rehabilitation, Diagnosis, Intervention
Important Note : All contributions to this Research Topic must be within the scope of the section and journal to which they are submitted, as defined in their mission statements. Frontiers reserves the right to guide an out-of-scope manuscript to a more suitable section or journal at any stage of peer review.
Topic Editors
Topic coordinators, recent articles, submission deadlines.
Submission closed.
Participating Journals
Total views.
- Demographics
No records found
total views article views downloads topic views
Top countries
Top referring sites, about frontiers research topics.
With their unique mixes of varied contributions from Original Research to Review Articles, Research Topics unify the most influential researchers, the latest key findings and historical advances in a hot research area! Find out more on how to host your own Frontiers Research Topic or contribute to one as an author.
Department of Circulation and Medical Imaging
- Master's programmes in English
- For exchange students
- PhD opportunities
- All programmes of study
- Language requirements
- Application process
- Academic calendar
- NTNU research
- Research excellence
- Strategic research areas
- Innovation resources
- Student in Trondheim
- Student in Gjøvik
- Student in Ålesund
- For researchers
- Life and housing
- Faculties and departments
- International researcher support
Språkvelger
Master thesis and projects - ultrasound technology - studies - department of circulation and medical imaging.
- Master thesis and projects
- Specialisation courses
Master's thesis and projects
Master's thesis and projects.
The Department of circulation and medical imaging offers projects and master's thesis topics for technology students of most of the different technical study programmes at NTNU. There is a seperate page for the supplementary specialisation courses .
List of topics
Topics for thesis and projects are given below. Most of the topics can be adjusted to the students qualifications and wishes.
Don't hesitate to take contact with the corresponding supervisor - we're looking forward to a discussion with you!
Asset Publisher
Blood flow imaging projects, estimation of true flow velocity using ultrasound, fusion of multi-modal cardiac data, pocket size ultrasound technology, pulse-echo based method for estimation of speed of sound, ultrasonic imaging through solids, surf imaging topics, ultrasound mediated drug delivery, real-time monitoring of left ventricular function under interventional procedures, fighting cancer with cw shear-wave elastography, adaptive clutter filtering for coronary heart disease, patient adaptive imaging in echocardiography, how to write ....
- a good abstract
- a good introduction
person-portlet
Lasse løvstakken professor.
- Open access
- Published: 26 April 2024
Why are medical students so motivated to learn ultrasound skills? A qualitative study
- Anina Pless 1 na1 ,
- Roman Hari 1 na1 &
- Michael Harris 1 , 2
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 458 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
212 Accesses
Metrics details
The introduction of ultrasound (US) courses into medical undergraduate courses is usually met with a particularly high level of student motivation. The reasons for this are unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the factors that contribute to undergraduate medical students’ motivation to learn US skills. Understanding what motivates students to learn US will inform the efforts of faculty to foster students’ motivation to learn.
We carried out in-depth semi-structured one-to-one interviews with medical students participating in an optional US course at two Swiss universities. The interview guide consisted of 10 main questions. The content was informed by experts in the field of medical education and US, as well as by a literature review of motivation theories for learning, in particular by self-determination theory (SDT). SDT was used to guide the development of the interview guide and to reflect on the resulting themes in the discussion section. The interview guide was piloted with two medical students. The interviews lasted an average of 45 min and were audio recorded and transcribed. Thematic analysis was used to analyse the data.
Fourteen undergraduate medical students in their preclinical (year 3) and clinical studies (years 4 and 5) elaborated on a wide range of reasons for their high motivation to learn US. They were motivated for US training because of the positive nimbus of the US modality, emphasising the advantages of visualisation. Students acknowledged the potential professional benefits of learning US and described it as a fun, exciting group activity.
Conclusions
The four themes we found in our analysis can all be related to the three universal needs described in SDT. The strong focus on the visual aspect and the positive nimbus of the modality goes beyond that and reflects the visuo-centric Zeitgeist, which claims the superiority of visual information over other data. Educators should be aware that motivation to learn is affected by the Zeitgeist and ensuing preconceptions, such as the perception of the positive nimbus surrounding a topic. Other key elements that can be implemented to motivate students are just-in-time feedback, enabling group experiences and creating awareness of the clinical relevance of learning content.
Peer Review reports
The introduction of mandatory ultrasound (US) courses at our University was greeted with a standing ovation. This is not the usual reaction to the implementation of new courses and is worth exploring. We hope to understand factors that contribute to students’ motivation for learning to foster such factors when teaching.
High levels of motivation correlate with better grades throughout medical studies [ 1 , 2 ]. Kusurkar et al. examined “the effect of quality of motivation on performance” and found that motivation stemming from personal interest positively affects academic performance [ 3 ]. There is a positive correlation between motivation from personal interest and the intention to continue ones studies [ 1 ]. Motivation seems also to be correlated with learners’ well-being [ 4 ].
Several theories try to explain why students are motivated to learn. According to Self-determination theory (SDT), developed by Deci and Ryan, motivation varies not only in quantity but also in quality [ 5 ]. A central idea of the theory is that there is a distinction between autonomous motivation and controlled motivation. Autonomous motivation can be defined as engaging in an activity because one finds it interesting: doing something of one’s own free will. Controlled motivation is the norm, especially after early childhood, when social demands and roles require individuals to take responsibility for non-intrinsically interesting tasks. Students’ motivation to learn ultrasound, as perceived in our experience and as described in the literature, would mainly be classified as “autonomous” motivation in SDT, as they are engaging in an activity that they find interesting [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Three universal psychological needs add to the autonomous motivation: autonomy (being free to choose whatever one considers useful to do), competence (the desire to master a task and to feel effective) and relatedness (the feeling of wanting to connect with others and have a sense of belonging) [ 8 , 9 ]. Figure 1 depicts states of motivated behaviour and its relation to autonomy, competence and relatedness. At one end of the continuum is amotivation, the state of lacking an intention to act. When amotivated, people either do not act at all or they act without purpose. Amotivation results from not appreciating an activity, not feeling competent to do it, or not expecting it to achieve a desired outcome. Intrinsic motivation is placed at the other end of the continuum, emphasising that it is the essential form of self-determined activity, based solely on an internal desire to act. Extrinsically motivated behaviours cover the states between amotivation and intrinsic motivation, varying in the extent to which their regulation is autonomous [ 7 ].
The Self-Determination Continuum, adapted from Ryan and Deci, 2000, Cook and Artino, 2016 and ten Cate et al., 2011
Our observation of students’ reception of the implementation of US teaching is in line with recent evidence [ 10 ]. Evaluations of US training programmes report positive feedback from over 95% of students, approval rates rarely seen in other fields of medical education [ 11 , 12 ]. In a USA study, 97% of students agreed that it was important for them to learn basic US skills during medical school [ 13 ]. A German questionnaire study of medical students found a similar number (98.2%) reporting a high or very high interest in curricular US in medical education, with the large majority (94.4%) of respondents agreeing or strongly agreeing that US education should be a mandatory part of their curriculum [ 14 ]. In another study, a large majority of teachers (97%) felt that the students were interested in the course [ 15 ]. Another development that underlines the attractiveness of US education for students is the introduction of extracurricular, student-led peer-tutoring initiatives [ 16 ].
The scarce evidence on why students are motivated to learn US skills, suggests that they believe that US education helps them to be prepared for clinical practice before and after graduation [ 14 , 17 ]. They also describe educational benefits beyond the mastering of US skills, for example learning physical examination skills or improving their understanding of anatomy and physiology [ 11 , 13 , 14 , 18 ]. In a recent study, Wang et al. explored why pre-clinical medical students wanted to learn US by applying Existence, Relatedness and Growth Theory, a model with three categories often used for analysing employee work performance. Students gave reasons related to all three categories, foremost existence needs (e.g. future work requirement) and growth needs (e.g. improving diagnostic skills), with relatedness needs being mentioned less often [ 19 ]. Given SDT’s three basic psychological needs of autonomy, competence and relatedness, the spectrum of reasons is likely to be broader than this.
The aim of this study was to investigate the factors that contribute to undergraduate medical students’ motivation to learn US skills, using SDT as a conceptual framework.
Study design
This was a qualitative study following a constructivist paradigm. We used semi-structured one-to-one interviews to allow the exploration of sensitive topics and motivators. We used thematic analysis to analyse the data [ 20 , 21 ]. We adhered to the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research Checklist (COREQ) in the reporting of this study (for full COREQ checklist see supplementary Appendix 1) [ 22 ].
Study setting and participants
We interviewed 14 medical students from two different Swiss medical schools (University of Bern, University of Zurich) between 2019 and 2022. Both Universities had developed identical, optional medical student courses in abdominal US education that used volunteer peer-tutors. The blended learning programme was available to all Swiss medical students. The ultrasound course curriculum for the students consisted of five modules, with five hours of e-learning and 16 hours of peer-led tutoring. After completing a summative practical assessment, participants could obtain an internationally recognised course certificate in abdominal ultrasound [ 23 ]. Approximately 20% of medical students participated in these courses.
Recruitment and sampling method
We used purposive sampling. We contacted all the students that were enrolled in a voluntary, extracurricular US course ( n = 95). Potential participants were invited by an email forwarded to them by the course organisers and were also approached directly at US courses. While we had aimed to stratify participants with regards to gender, University site and age, recruitment was difficult during the COVID-19 pandemic, so we interviewed all the students willing to participate. All the students who agreed to take part had already participated in at least two tutored sessions and gave written, informed consent. After initial contact had been made, none of the participants declined to take part in the study or dropped out of it.
Ethical considerations
The study was submitted to the regional ethics committee which stated that the study does not fall under the Swiss Human Research Act (BASEC-Nr. Req-2018-00059).
All participants gave written informed consent. To ensure participant anonymity, each participant was identified only by a code after interview transcription.
Development of the interview guide
The semi-structured interview guide was informed by a literature review of motivation theories for learning, in particular by SDT, and discussions with faculty who are involved in US education, including medical educators, clinicians and US experts. Based on this information the research team discussed how to phrase questions that would be broad enough to encompass a variety of factors which can contribute to motivation according to SDT [ 7 , 9 ]. The interview guide consisted of 10 main questions which focussed on participants’ reasons to learn US and the perceived benefits (see Appendix 2). Each main question had probes to get more in-depth information. The interview guide was piloted with two students, and changes were made where necessary.
Data collection
All 14 interviews were carried out by the lead researcher AP, who had no prior relationship with the participants and was not affiliated with the US course. The interviewees were told that AP had an interest in their views of learning US skills. The risk of respondent bias, in this case the tendency to give socially desirable answers, was minimised by careful question design. The interviewer was not much older than the participants, preventing a feeling of hierarchy. Only the interviewee and AP were present during the interviews, which lasted an average of 45 min and were audio-recorded. Short field notes were made after each interview, commenting on the mood of the interview and reflecting the interviewer’s role and potential influence. The interviews were conducted at a location of the participants’ choice, most often at a public venue or at the University. Interviews were conducted in Swiss German and transcribed verbatim using High German diction. The transcriptions were done by AP as well as BB and KL, two medical students, all of whom are native Swiss German speakers. We wrote and used a transcription manual to ensure that transcripts were consistent. No repeat interviews were carried out and interview transcripts were not returned to the participants. Analysis was conducted using the High German transcripts.
Data analysis
AP, a medical doctor as well as a medical educator, did the primary analysis. She and MH, an experienced medical doctor, medical educator and qualitative researcher, independently coded three of the transcripts and compared their results to look for inconsistencies. Throughout the process, data was read and reread, using constant comparison with earlier data. Themes which derived from the data were labelled using a process of open coding to identify and later categorise phenomena in the data [ 24 ]. The interviews and analysis of the data were carried out in iterative cycles, going back and forth between the data gathering and analysis, allowing for new insights to inform changes to the interview guide [ 20 , 25 ]. Both coders regularly revised and refined the codes. No software was used.
After 14 interviews, the question of data saturation was discussed among the research team (AP, MH, RH, BB). As no new themes were arising, it was agreed that data saturation had been achieved [ 26 ].
The research team reviewed the findings individually then met to discuss the thematic structure. Each member of the team first presented their initial thoughts as to the themes. The team identified and continuously reviewed the themes until there was consensus [ 21 ]. For the sake of clarity and focus, the analysis focused on ultrasound-related factors and excluded themes related to course design in general.
We sent an overview of the key themes to four of the participants and asked for their comments. No changes needed to be made as a result of this.
14 students participated in the interviews. Table 1 shows participants’ characteristics.
We identified four US-specific themes that contribute to high levels of motivation to learn US skills. Table 2 shows the themes and subthemes.
The themes and subthemes are described in more detail below, with quotations identified by participant number.
Perception of professional benefits
All participants expressed that learning US would be an advantage professionally. This could be during their studies, or as practicing physicians. Learning US as early as possible was seen as adding to this benefit.
Benefits as a medical student
Some participants wanted to understand US images shown in lectures: Now, if we now have an US image in a lecture, I think “yes, ok, I can follow now”. (Participant(P)6)
For most participants, revising and deepening their knowledge of anatomy, as well as applying that knowledge to the patient’s body, were key benefits and motivators. Many participants felt learning US improved their spatial thinking: US gives you a different feeling of the relationships between the organs in the body. And uh, somehow you really know where the kidneys are or where the liver is. (P9)
One participant appreciated that US also put into perspective what was clinically relevant for their future career: And it was always reassuring for me that “yes, what is really relevant, I know” and if I no longer have the twenty-seventh branch of this artery in my head (…) so I was able to put in perspective the anatomical knowledge. For my future medical career. (P9)
Benefits as a physician
All participants stated that having US skills could be relevant to their future as physicians. They thought it was important to understand the indications and be able to interpret US images. Many participants were certain US would be part of their clinical life. One participant stated: Yes, it is also an examination method that is actually used in many disciplines. That means that sooner or later I will be asked to perform it on a patient. (P2) Several participants felt that they needed to be well prepared for their transition from student to resident: And that that’s my goal more or less, things that you can already acquire now, that I have them ready at hand. That at least that will work. (P2) There was also the notion that having US skills would help (…) avoid and reduce unnecessary imaging procedures and refer less patients to specialists. (P6)
The “exciting experience” component
For many participants, the motivation was connected to the feeling of experiencing something inherently fun and exciting: So, yes, it’s also a fascinating, so it’s still a “wow”. A “wow moment”. (laughs) (P3). Participants were intrinsically fascinated with the topic of US and the aspect of visualisation added to this: What I really find interesting is that my fascination still doesn’t let up (…) well, I just found it fascinating to somehow see my own organs for once (laughs). (P9)
The social aspects of learning US
Interpersonal factors played an important role, to learn and interact in small groups with other participants was described as similar to engaging in a new hobby, as well as a way of escaping everyday student life: Um, and what did I always enjoy the most? I think it was simply the interaction with the others. It’s just something that we don’t have much of in our studies. (P9)
While most participants said that the social aspect did not influence the decision to apply for the course, it was important for their positive perception of, and continuing engagement in, the course. They noted that the course gave them the opportunity to meet new people or do something with friends.
A practical skill
Many participants enjoyed doing something practical, as opposed to simply learning theory: Yes, and that’s actually kind of cool. Yeah, not exactly like a surgeon, but still a little bit hands-on. Yes. (P3)
They found learning US also enabled them to put their learning into a clinical perspective, giving them an insight into what they were working towards. One participant described how their US skills helped her become an active member of a clinical team during the practical year: I was allowed to scan a child because I said I had done this course. And afterwards I felt like one of them, not just like a trainee standing at the back, but that I had been fully interactive. (P12)
Learning US as a challenge
Participants found learning US to be a positive challenge: If you just get it or, also with the kidney, if you get it and then you recognize everything, that’s a pleasure. (P11)
Most participants performing US was not a natural gift but something they had to learn, requiring practice, diligence, and effort: Sure, there’s a mega process behind it until it’s intuitive, and it’s not the case with me at all yet, but I can imagine that, that it’s, um, doable with practice. Like the driving test, maybe. (P13)
The positive nimbus of US
Many participants said that they believed US to be an up-and-coming modality in medicine, with many advantages. We summarise these recurrent themes under the concept of the “positive nimbus” of US, referring to its positive image in public and medical discourse.
US as a modern tool
Many participants stated that US was the diagnostic tool of the future, which would become part of every physician’s basic equipment. This was often something that they had heard from others (peers, lecturers, physicians): (…) there was a doctor who said it was super important that you can do it and I should definitely take every opportunity. (P5)
Participants had a positive impression of US as a tool, ascribing many favourable attributes to it, principally that it was fast and easy. The participants found US to be versatile in terms of when and where it could be used (which body part, but also which geographical location), and for which indications to use it. They commented that they were fascinated by the breadth of what can be done with US: Yes, what I find interesting about US is that it can really be used in many different areas. (P7)
Advantages for patients
US as a tool was also described as having advantages for patients because it did not entail radiation, was non-invasive, and not painful. Another benefit for patients was that they could watch the examination “live”: You can show an image directly and that you can say to the patient “there it is and that’s how it is now. It’s good the way it is.” (P7) .
The power of visualisation
One key theme was the appeal of visualising things with US, and this contributed to the positive nimbus of US. For some participants, visualising organs was helpful because it matched their learning style: Well, personally, I’m just very much a visual person. (P8)
Most participants found it impressive to see inside the body and thereby gather a lot of information. It gave them a sense of security and the feeling that US was more objective and precise than other forms of examination: So yes, it seems to me that US is a bit more objective. (P5)
With the help of US, participants were easily able to confirm or exclude pathologies, which they found fascinating. Being able to capture an image was thought to be helpful too: some participants stated that it allowed them to show the image to others if they had any uncertainties, and to check that they had done it correctly: Something that you can see can perhaps be better discussed with other people afterwards. (P8)
Principal findings
In this qualitative interview study, medical students gave a range of reasons for their high motivation to learn US: the positive image surrounding the modality in general, with an emphasis on the advantages of visualisation; they perceived potential professional benefits; and they described it as a fun, exciting activity and a way to interact positively with other learners.
Interpretation of the results
The four themes we identified can be related to the three universal needs of autonomy, competence and relatedness described in SDT.
Mastering US skills contributed to a feeling of competence and autonomy. At the same time, feeling competent in performing US supported students in preparing for their transition from student to resident, giving them confidence in clinical situations and in interactions with patients, thus providing a professional advantage.
Learning US was described as an exciting and fun group activity. This perception aligns with the need for relatedness as described in SDT. The feeling that US was a practical alternation to their theoretical student life and a positive challenge map across to the need for competence.
The idea of learning to use a “modern”, technical tool, gave a feeling of autonomy and competence. Additionally, the fact that US is a mobile device compared to other imaging modalities was seen to offer a high degree of autonomy when deciding when and where to use it.
The visual aspect of US allows for just-in-time feedback and the immediate feeling of success when getting the right image, thus meeting the need for competence.
Whereas all four themes can be linked to the universal needs of SDT, the visual aspect of US and the positive nimbus surrounding US are more related to the “Zeitgeist”. In our study, participants’ comments suggested that they associated US with positive attributes and thought it would become increasingly important in the future. The sense that being able to visualise something was superior to other ways of examining– another subtheme we found– was central to this notion.
Comparison with existing literature
Other studies confirm that students believe learning US is an advantage in their medical studies [ 11 , 13 , 14 ]. A cross-sectional survey of graduates confirms that early US training yields physicians who are better prepared to integrate it into clinical practice [ 27 ]. While the transition from medical school to residency differs depending on the national context, it has been described as stressful and challenging in studies from different countries [ 28 , 29 ]. Early exposure to clinical environments in undergraduate years may help reduce the stress of this transition [ 29 ]. Integrating theoretical knowledge into practice in medical education has been an important issue in medical education for over a decade and remains so today. US teaching in undergraduate studies can aid professional identity formation [ 30 ]. Our results correspond with Wang et al.’s findings, that students are motivated to learn ultrasound because they believe it to be a necessity and/or advantage in their future work or current studies and because they want to learn out of interest. Wang et al. point out that relatedness played less of a role for students’ motivation, while in our study relatedness played an important role in the theme of “fun and exciting activity”. One possible explanation for this discrepancy could be that a distinction between motivation to initiate behaviour (e.g. sign up for a course) and to maintain motivation (e.g. stay motivated during the course) is seldom made. Participants in Wang et al’s study were questioned on motivation to initiate US learning, while in our study, participants had already begun or finished the US course and relatedness contributed to continuing motivation during the course but was seldom discussed as a reason for initial interest [ 19 ].
Our participants felt that visualisation enhanced the objectivity and reliability of an examination, providing a feeling of security, corresponding with Feilchenfeld et al.’s statement that “US’s visual evidence is viewed as truth, more accurate (truthful) than clinical information provided via other senses” [ 31 ]. This “Zeitgeist”, the “visuo-centric discourse” which claims the superiority of visual information over other data, may be common among medical students: a paper on body pedagogics states that “oculocentrism” (a perception of superiority of vision over other senses) is typical in Western society, especially in the medical profession [ 32 ]. The current discourse in our (medical) society that seeing is superior to, and more legitimate than, perceiving with other senses and is thus also beneficial for patient care seems to add to the “positive nimbus” of US and has an effect on students’ high motivation to learn the skill [ 26 , 28 ].
This is the first qualitative study designed to study medical students’ motivation for US education. The design of the interview guide and the interpretation of the results were guided by a consistent theoretical framework (SDT). We interviewed participants from two different medical schools. We piloted the interview guides carefully, achieved data saturation and member-checked the findings.
Limitations
Our participants were from a population taking part in a course with no curricular accreditation, making it likely that they had a high degree of motivation. The participants were students who volunteered to take part in the study, resulting in a risk of self-selection bias. We assumed that the students participating in a voluntary course and voluntarily taking part in the study would be especially highly motivated. Because our aim was to explore high levels of motivation for ultrasound, we hypothesise that the sample was in line with our research question. The factors motivating these students may not apply to other students, for example students with low motivation to learn ultrasound. Including a more varied sample might have given us other insights. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, we could not stratify participants as intended, as US courses were put on hold for some time. Many students were busy with volunteer work at health facilities and may have been less willing to meet face-to-face. However, there was an equal number of participants from both Universities, and the gender distribution approximately reflects the gender distribution in Swiss medical studies. Also, the participants came from a homogenous group, which makes it more likely that the sample was adequate [ 33 ].
Implications for research and practice
Understanding the mechanisms of motivation in medical education helps to create a supportive learning environment and to nurture autonomous motivation. While some of our findings were specific to the modality of US, some can also be applied to other teaching areas:
Visualisation aids learning, providing immediate feedback, a sense of competence and of autonomy, adding to the motivation. For areas where visualisation is not an option, educators should consider using alternative ways to give immediate feedback, when planning educational programmes. This could mean verbally providing immediate and constructive feedback, or using a portfolio to visually track learners’ progress.
Participants found learning US fun and exciting. Not all areas of learning allow for the hands-on experience of US education, but reflecting on where practical aspects can be integrated into teaching and how to challenge students optimally– making tasks not too easy nor too difficult– could enhance students’ motivation. One example is the “gameification” of learning content, which may add to the fun factor. Educators should enable group experiences and interaction when possible. This could be supported by encouraging students to actively participate in group work, giving a structure to educational units, while also providing enough room to learn in a self-directed way as a group. Facilitators to this can be a setting of mutual trust and open dialogue, and adjusting the learning environment, for example by considering seating arrangements.
Students are motivated to learn things that will benefit them professionally, making awareness of the clinical relevance of learning content essential. Explicitly addressing concerns about transitioning from medical school to residency and providing information on how a specific skill will help for this transition could increase students’ motivation to learn. Pointing out the relevance of the subject to medical practice could help less enthusiastic students see the importance of it and result in a more autonomous– rather than controlled– choice to learn something [ 34 ].
Educators should be aware that learning happens in the context and discourse of society, and that this can affect both educators’ and learners’ perspectives and motivation. While educators cannot influence the discourse directly, it is important to understand its existence, to modify barriers and facilitate motivation. The mechanisms of such discourses and their possible impact on students’ views require more research.
Future quantitative studies could explore to which extent a more general medical student population relates to the identified themes in order to validate them. Including students with low motivation for ultrasound or students with high motivation in other areas as participants and comparing and contrasting these results with those of this study could also provide a more comprehensive view of motivational factors and be an interesting area for further research. Factors which initially sparked participants’ interest and motivation to sign up for the course may be different to those which maintained and increased their motivation during the course. Longitudinal studies would enable a deeper understanding of such nuances and other changes in motivation over time.
We found four themes that have not yet been described in the literature: US was perceived as helpful in contextualising and exemplifying other learning content and supporting the transition into professional identity and, ultimately, clinical practice; the group setting with just-in-time feedback provides a fun and positive learning experience; participants reported being motivated to learn US because it was the tool of the future, and being able to visualise something trumped other forms of examination, reflecting the visuo-centric Zeitgeist. Knowledge and understanding of these themes may be relevant to other areas of medical education.
Data availability
The datasets used and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
participant
Sobral DT. What kind of motivation drives medical students’ learning quests? Medical Education [Internet]. 2004 [cited 2019 Apr 16];38(9):950–7. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2004.01913.x .
Moulaert V, Verwijnen MGM, Rikers R, Scherpbier AJJA. The effects of deliberate practice in undergraduate medical education. Med Educ [Internet]. 2004 Oct [cited 2020 May 27];38(10):1044–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2004.01954.x .
Kusurkar RA, Ten Cate TJ, Vos CMP, Westers P, Croiset G. How motivation affects academic performance: a structural equation modelling analysis. Advances in Health Sciences Education [Internet]. 2013 Mar [cited 2020 May 4];18(1):57–69. http://link.springer.com/ https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-012-9354-3 .
Babenko O, Daniels L, Ross S, White J, Oswald A. Medical student well-being and lifelong learning: A motivational perspective. Educ Health [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 Jul 11];32(1):25. https://journals.lww.com/ https://doi.org/10.4103/efh.EfH_237_17 .
Ryan RM, Deci EL. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivations: Classic Definitions and New Directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology [Internet]. 2000 Jan [cited 2019 Jul 4];25(1):54–67. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0361476X99910202 .
Kusurkar RA. Autonomous motivation in medical education. Medical Teacher [Internet]. 2019 Sep 2 [cited 2023 Jul 11];41(9):1083–4. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/0142159X.2018.1545087 .
Ryan RM, Deci EL. Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being. American Psychologist. 2000;11.
Cook DA, Artino AR. Motivation to learn: an overview of contemporary theories. Medical Education [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2019 Apr 10];50(10):997–1014. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/medu.13074 .
ten Cate OTJ, Kusurkar RA, Williams GC. How self-determination theory can assist our understanding of the teaching and learning processes in medical education. AMEE Guide No. 59. Medical Teacher [Internet]. 2011 Dec [cited 2020 Sep 5];33(12):961–73. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/ https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2011.595435 .
Birrane J, Misran H, Creaney M, Shorten G, Nix CM. A Scoping Review of Ultrasound Teaching in Undergraduate Medical Education. MedSciEduc [Internet]. 2018 Mar [cited 2019 Jul 3];28(1):45–56. http://link.springer.com/ https://doi.org/10.1007/s40670-017-0491-4 .
Hammoudi N, Arangalage D, Boubrit L, Renaud MC, Isnard R, Collet JP et al. Ultrasound-based teaching of cardiac anatomy and physiology to undergraduate medical students. Archives of Cardiovascular Diseases [Internet]. 2013 Oct [cited 2020 May 5];106(10):487–91. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1875213613001976 .
Limchareon S, Asawaworarit N, Klinwichit W, Dinchuthai P. Development of the ultrasonography learning model for undergraduate medical students: A case study of the Faculty of Medicine, Burapha University. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association [Internet]. 2016 Aug [cited 2020 May 5];79(8):445–9. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1726490116300077 .
Rempell JS, Saldana F, DiSalvo D, Kumar N, Stone MB, Chan W et al. Pilot Point-of-Care Ultrasound Curriculum at Harvard Medical School: Early Experience. West J Emerg Med [Internet]. 2016 Nov [cited 2019 Jul 3];17(6):734–40. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5102600/ .
Recker F, Barth G, Lo H, Haverkamp N, Nürnberg D, Kravchenko D et al. Students’ Perspectives on Curricular Ultrasound Education at German Medical Schools. Front Med [Internet]. 2021 Nov 25 [cited 2024 Mar 5];8:758255. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/ https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.758255/full .
Dietrich CF, Hoffmann B, Abramowicz J, Badea R, Braden B, Cantisani V et al. Medical Student Ultrasound Education: A WFUMB Position Paper, Part I. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology [Internet]. 2019 Feb [cited 2023 Jul 11];45(2):271–81. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0301562918304174 .
Jahns J, Recker F, Thiessen V, Rüenauver K, Bailer B. Sono4Students– sonographische Lehre nach dem Peer-teaching Prinzip. Ultraschall in der Medizin - European Journal of Ultrasound [Internet]. 2014 Sep 24 [cited 2020 May 5];35(S 01). http://www.thieme-connect.de/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-0034-1389403 .
Hoppmann RA, Rao VV, Bell F, Poston MB, Howe DB, Riffle S et al. The evolution of an integrated ultrasound curriculum (iUSC) for medical students: 9-year experience. Crit Ultrasound J [Internet]. 2015 Dec [cited 2020 Aug 26];7(1):18. https://theultrasoundjournal.springeropen.com/articles/ https://doi.org/10.1186/s13089-015-0035-3 .
Kefala-Karli P, Sassis L, Sassi M, Zervides C. Introduction of ultrasound-based living anatomy into the medical curriculum: a survey on medical students’ perceptions. Ultrasound J [Internet]. 2021 Dec [cited 2023 Jul 11];13(1):47. https://theultrasoundjournal.springeropen.com/articles/ https://doi.org/10.1186/s13089-021-00247-1 .
Wang TC, Chen WT, Kang YN, Lin CW, Cheng CY, Suk FM et al. Why do pre-clinical medical students learn ultrasound? Exploring learning motivation through ERG theory. BMC Med Educ [Internet]. 2021 Dec [cited 2024 Mar 5];21(1):438. https://bmcmededuc.biomedcentral.com/articles/ https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02869-4 .
Ng SL, Baker L, Cristancho S, Kennedy TJ, Lingard L. Qualitative Research in Medical Education: Methodologies and Methods. In: Swanwick T, Forrest K, O’Brien BC, editors. Understanding Medical Education [Internet]. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2018 [cited 2020 May 5]. pp. 427–41. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119373780.ch29 .
Castleberry A, Nolen A. Thematic analysis of qualitative research data: Is it as easy as it sounds? Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning [Internet]. 2018 Jun [cited 2020 May 5];10(6):807–15. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1877129717300606 .
Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care [Internet]. 2007 Sep 16 [cited 2024 Apr 7];19(6):349–57. https://academic.oup.com/intqhc/article-lookup/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1093/intqhc/mzm042 .
Räschle N, Hari R. «Blended Learning»-Basiskurs Sonografie: Im Peer-Tutoring zu einem SGUM-akkreditierten Ultraschall-Kurs. Praxis [Internet]. 2018 Nov [cited 2024 Mar 13];107(23):1255–9. https://econtent.hogrefe.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1024/1661-8157/a003116 .
Charmaz K. Constructing grounded theory. 2nd edition. London; Thousand Oaks, Calif: Sage; 2014. 388 p. (Introducing qualitative methods).
Cristancho S, Goldszmidt M, Lingard L, Watling C. Qualitative research essentials for medical education. Singapore Medical Journal [Internet]. 2018 Dec [cited 2020 May 5];59(12):622–7. http://www.smj.org.sg/article/qualitative-research-essentials-medical-education .
Morse JM. The Significance of Saturation. Qualitative Health Research [Internet]. 1995 May [cited 2020 May 5];5(2):147–9. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/104973239500500201 .
Prats MI, Royall NA, Panchal AR, Way DP, Bahner DP. Outcomes of an Advanced Ultrasound Elective: Preparing Medical Students for Residency and Practice. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine [Internet]. 2016 May [cited 2023 Jul 11];35(5):975–82. https://doi.org/10.7863/ultra.15.06060 .
Chang LY, Eliasz KL, Cacciatore DT, Winkel AF. The Transition From Medical Student to Resident: A Qualitative Study of New Residents’ Perspectives. Academic Medicine [Internet]. 2020 Sep [cited 2020 Sep 7];95(9):1421–7. https://journals.lww.com/ https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0000000000003474 .
Brennan N, Corrigan O, Allard J, Archer J, Barnes R, Bleakley A et al. The transition from medical student to junior doctor: today’s experiences of Tomorrow’s Doctors. Medical Education [Internet]. 2010 May [cited 2020 Sep 8];44(5):449–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.2009.03604.x .
Darici D, Missler M, Schober A, Masthoff M, Schnittler H, Schmitz M. Fun slipping into the doctor’s role—The relationship between sonoanatomy teaching and professional identity formation before and during the Covid-19 pandemic. Anatomical Sciences Ed [Internet]. 2022 May [cited 2023 Jul 11];15(3):447–63. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.2178 .
Feilchenfeld Z, Kuper A, Whitehead C. Stethoscope of the 21st century: dominant discourses of ultrasound in medical education. Medical Education [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2019 Jul 3];52(12):1271–87. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.13714 .
Kelly M, Ellaway R, Scherpbier A, King N, Dornan T. Body pedagogics: embodied learning for the health professions. Med Educ [Internet]. 2019 Oct [cited 2020 Aug 11];53(10):967–77. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/ https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.13916 .
Guest G, Bunce A, Johnson L. How Many Interviews Are Enough? An Experiment with Data Saturation and Variability. Field Methods [Internet]. 2006 Feb [cited 2020 Sep 5];18(1):59–82. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/ https://doi.org/10.1177/1525822X05279903 .
Kusurkar RA, Croiset G, Ten Cate OTJ. Twelve tips to stimulate intrinsic motivation in students through autonomy-supportive classroom teaching derived from Self-Determination Theory. Medical Teacher [Internet]. 2011 Dec [cited 2024 Mar 4];33(12):978–82. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/ https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2011.599896 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Benjamin Bulling for his literature review of motivation theories and for the transcription of interviews. We thank Katharina Lüscher for the interview transcription.
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Anina Pless, Roman Hari contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Institute of Primary Health Care (BIHAM), University of Bern, Mittelstrasse 43, 3012, Bern, Switzerland
Anina Pless, Roman Hari & Michael Harris
College of Medicine & Health, University of Exeter Medical School, Exeter, UK
Michael Harris
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
AP and RH contributed to the conception of the work. AP, RH and MH contributed to the design of the work. AP did the acquisition and primary analysis. AP, MH and RH interpreted the data. AP wrote the main manuscript and MH and RH substantively revised it. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Anina Pless .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was submitted to the regional ethics committee (Kantonale Ehtikkommission für die Forschung, Gesundheits- und Fürsorgedirektion des Kantons Bern). A waiver was issued, stating that the study does not fall under the Swiss Human Research Act (BASEC-Nr. Req-2018-00059).
Consent for publication
Additional information, publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Pless, A., Hari, R. & Harris, M. Why are medical students so motivated to learn ultrasound skills? A qualitative study. BMC Med Educ 24 , 458 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05420-3
Download citation
Received : 08 February 2024
Accepted : 12 April 2024
Published : 26 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05420-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Medical education
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
In Reversal, Expert Panel Recommends Breast Cancer Screening at 40
Some researchers said the advice did not go far enough. The panel also declined to recommend extra scans for women with dense breast tissue.

By Roni Caryn Rabin
Citing rising breast cancer rates in young women, an expert panel on Tuesday recommended starting regular mammography screening at age 40, reversing longstanding and controversial guidance that most women wait until 50.
The panel, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, finalized a draft recommendation made public last year . The group issues influential advice on preventive health, and its recommendations usually are widely adopted in the United States.
In 2009, the task force raised the age for starting routine mammograms to 50 from 40, sparking wide controversy. At the time, researchers were concerned that earlier screening would do more harm than good, leading to unnecessary treatment in younger women, including alarming findings that lead to anxiety-producing procedures that are invasive but ultimately unnecessary.
But now breast cancer rates among women in their 40s are on the rise, increasing by 2 percent a year between 2015 and 2019, said Dr. John Wong, vice chair of the task force. The panel continues to recommend screening every two years for women at average risk of breast cancer, though many patients and providers prefer annual screening.
“There is clear evidence that starting screening every other year at age 40 provides sufficient benefit that we should recommend it for all women in this country to help them live longer and have a better quality of life,” said Dr. Wong, a primary care clinician at Tufts Medical Center who is the director of comparative effectiveness research for the Tufts Clinical Translational Science Institute.
The recommendations have come under harsh criticism from some women’s health advocates, including Representative Rosa DeLauro, Democrat of Connecticut, and Representative Debbie Wasserman Schultz, Democrat of Florida, who say the advice does not go far enough.
In a letter to the task force in June , they said that the guidance continued to “fall short of the science, create coverage gaps, generate uncertainty for women and their providers, and exacerbate health disparities.”
Weighing in again on a hotly debated topic, the task force also said there was not enough evidence to endorse extra scans, such as ultrasounds or magnetic resonance imaging, for women with dense breast tissue.
That means that insurers do not have to provide full coverage of additional screening for these women, whose cancers can be missed by mammograms alone and who are at higher risk for breast cancer to begin with. About half of all women aged 40 and older fall into this category.
In recent years, more mammography providers have been required by law to inform women when they have dense breast tissue and to tell them that mammography may be an insufficient screening tool for them.
Beginning in September, all mammography centers in the United States will be required to give patients that information.
Doctors often prescribe additional or “supplementary” scans for these patients. But these patients frequently find they have to pay all or some of the charges themselves, even when the additional tests are performed as part of preventive care, which under law should be offered without cost.
Medicare, the government health plan for older Americans, does not cover the additional scans. In the private insurance market, coverage is scattershot, depending on state laws, the type of plan and the plan’s design, among other factors.
The task force sets the standards for what preventive care services must be covered by law by health insurers at no cost to patients.
The panel’s decision not to endorse the extra scans has significant implications for patients, said Robert Traynham, a spokesman for AHIP, the association that represents health insurance companies.
“What that means for coverage is that there is no mandate to cover these specific screenings for women with dense breasts at zero-dollar cost-sharing,” he said.
While some employers may choose to have their health insurance plans do so, it is not required by law, Mr. Traynham said.
Kathleen Costello, a retiree in Southern California who was diagnosed with breast cancer in 2017 when she was 59, said she was convinced that mammograms missed her cancer for many years.
She underwent screening annually, and every year she received a letter saying that she was cancer-free. The letters also told her that she had dense breast tissue and that additional screening was available but not covered by insurance.
Six months after an all-clear mammogram in 2016, she told her doctor that her right breast felt stiff. The doctor ordered a mammogram and an ultrasound.
“In 30 seconds, the ultrasound found the cancer,” Ms. Costello said in an interview, adding that she knew because “the technician blanched and left the room.”
The mass was four centimeters in size, Ms. Costello added: “It’s hard for me to accept that it grew in six months from undetectable to four centimeters.”
But Dr. Wong, of the task force, said there was no scientific evidence to prove that supplemental imaging, by either M.R.I. or ultrasound, reduces breast cancer progression and extends life for women with dense breast tissue.
There is ample evidence, on the other hand, that supplemental screenings may lead to frequent false-positive findings and to biopsies, contributing to stress and unnecessary invasive procedures.
“It’s tragic,” Dr. Wong said. “We are as frustrated as women are. They deserve to know whether supplemental screenings would be helpful.”
But medical organizations like the American College of Radiology endorse supplemental screening for women with dense breast tissue. There is research showing that ultrasound in conjunction with mammography does detect additional cancers in patients with dense tissue, said Dr. Stamatia Destounis, chair of the college’s breast imaging commission.
For women with dense breasts who are at average risk of breast cancer, recent research indicates that M.R.I. is the best supplemental scan, Dr. Destounis said, “with far better cancer detection and more favorable positive predictive values.”
The college also recommends annual screening for women at average cancer risk, rather than screening every two years as recommended by the panel. The radiologists group is pressing for a recommendation that all women should be assessed for breast cancer risk before age 25, so that women at high risk can start screening even before they turn 40.
Growing evidence shows that Black, Jewish and other minority women develop breast cancer and die from it before age 50 more frequently than do other women, Dr. Destounis noted.
Trans men who have not had mastectomies must continue to be screened for breast cancer, she added, and trans women, whose hormone use puts them at greater risk for breast cancer than the average man, should discuss screening with their doctor.
While the panel’s advice to start screening at age 40 is “an improvement,” Dr. Destounis said, the final recommendations “do not go far enough to save women’s lives.”
Roni Caryn Rabin is a Times health reporter focused on maternal and child health, racial and economic disparities in health care, and the influence of money on medicine. More about Roni Caryn Rabin
The Fight Against Breast Cancer
Citing rising breast cancer rates in young women, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommended starting regular mammography screening at age 40 , reversing longstanding guidance that most women wait until 50.
Clinics around the United States are starting to offer patients a new service: having their mammograms read not just by a radiologist, but also by an A.I. model .
Risk calculators can offer a more personalized picture of an individual patient’s breast cancer risk. But experts warn that the results need to be interpreted with the help of a doctor.
We asked doctors to weigh in on the new mammograms guidelines and how younger women can understand and mitigate their breast cancer risk .
Scientists have long known that dense breast tissue is linked to an increased risk of breast cancer. A recent study adds a new twist .
share this!
May 3, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
Economies take off with new airports: Research shows positive impacts of airport investments
by Singapore University of Technology and Design
Be it for work or vacation, chances are that many will have passed through an airport. In the largest cities, the airport presents to travelers the first glimpse of a new land and a reflection of the surrounding city. Beyond first impressions, airports stand as an important economic hub for local policymakers, with a continuous flow of goods and passengers fueling the urban economy.
However, current literature on the economic impact of airport investment is primarily based on developed cities localized to North America and Europe. In these cases, airport capacity development is focused on upgrading existing infrastructure. For emerging cities in less developed countries, especially for those intending to build their first airport, the economic benefits are not as clear-cut.
Recognizing the importance of a more generalizable analysis, Assistant Professor Jin Murakami of the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) collaborated with researchers in Japan to close this gap.
In their paper " Does new airport investment promote urban economic development?: Global evidence from nighttime light data ," Asst Prof Murakami highlights that developing new airport infrastructure often requires billions in capital investment , with evidence and information on long-term returns playing a key role in decision-making. The research is published in the journal Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice .
To conduct the study, the team first required access to city-scale statistical data across the global regions, including emerging economies in Asia and the Middle East. Previous studies on large cities used the gross domestic product (GDP) and employment rates as key indicators for economic growth. In smaller cities, however, these statistics are poor and inconsistent, and in some cases, altogether unavailable.
Inspired by other empirical studies on emerging economies, the team used nighttime light intensity (NTL) as a proxy for the degree of economic development. Urban researchers have noted that urbanization, employment, industrial production, and energy consumption activities can be tied to light emissions at night.
With modern satellite observation technologies, nighttime images over a wide span of geographical locations and time periods have become readily available. Asst Prof Murakami and his team were able to examine cities with and without new airport construction across the world at finer spatial resolution and more regular time intervals.
Modeling the relationship between airport development and economic growth proved to be a difficult task. "The two-way causal relationships between transport infrastructure investment and urban economic growth have long been debatable. It is also likely that rapid urban economic growth calls for new airport construction projects," explains Asst Prof Murakami.
To distill the "net" economic impact of new airport construction, a difference-in-differences (DID) method was applied that compares the changes in NTL over the years between similar cities that differ only by local airport construction. The team scoured more than 13,000 cities worldwide to identify suitable control groups for comparison, systematically matching each case study .
The team found that less-developed cities without airports would benefit the most from constructing their first airport. The increased accessibility to the global aviation network brings about broader economic benefits and opportunities to such communities.
The researchers suggest that new airports go beyond expanding capacity to meet air transport demand—they promote inclusive growth and connectivity to people living in remote locations.
The holistic analysis of recent airport construction projects provides new generalizable global evidence that can help small towns and cities to make pivotal decision where regional accessibility is a concern.
With their findings, Asst Prof Murakami hopes to encourage global investors, policymakers, and financial institutions to reassess the bankability or economic feasibility of airport development projects in emerging economies based on current environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing criteria.
"This study stresses the importance of incorporating the wider economic benefits to be attained in relatively small and/or geographically remote cities, towns, and communities in airport capital investment evaluation practices for regional network connectivity and inclusive economic growth , particularly in Asia and the Middle East," emphasizes Asst Prof Murakami.
Provided by Singapore University of Technology and Design
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Nanotech opens door to future of insulin medication
9 hours ago
How evolving landscapes impacted First Peoples' early migration patterns into Australia
13 hours ago

Saturday Citations: Parrots on the internet; a map of human wakefulness; the most useless rare-earth element
When injecting pure spin into chiral materials, direction matters
18 hours ago
New quantum sensing scheme could lead to enhanced high-precision nanoscopic techniques

Boeing's Starliner finally ready for first crewed mission

Hungry, hungry white dwarfs: Solving the puzzle of stellar metal pollution
How E. coli get the power to cause urinary tract infections

Male or female? Scientists discover the genetic mechanism that determines sex development in butterflies

New study is first to use statistical physics to corroborate 1940s social balance theory
Relevant physicsforums posts, cover songs versus the original track, which ones are better.
2 hours ago
What are your favorite Disco "Classics"?
4 hours ago
Interesting anecdotes in the history of physics?
May 1, 2024
Why Is Two-Tone Ska Rock Popular on Retro Radio?
Apr 29, 2024
Biographies, history, personal accounts
Apr 28, 2024
History of Railroad Safety - Spotlight on current derailments
More from Art, Music, History, and Linguistics
Related Stories

China touts engineering feats of new international airport
Mar 1, 2019

Websites of several German airports not reachable
Feb 16, 2023

Global airport capacity crisis amid passenger boom: IATA
Jun 4, 2018

IATA chief warns about rising cost of airport expansion
Feb 5, 2018

Highway links benefit businesses, unless they are based outside cities
May 17, 2022

Scientists quantify dramatic uneven urbanization of large cities throughout the world in recent decades
Oct 26, 2020
Recommended for you

Ridesourcing platforms thrive on socio-economic inequality, say researchers
Apr 26, 2024

Which countries are more at risk in the global supply chain?
Apr 19, 2024

Study finds world economy already committed to income reduction of 19% due to climate change
Apr 17, 2024

Building footprints could help identify neighborhood sociodemographic traits
Apr 10, 2024

Can the bias in algorithms help us see our own?
Apr 9, 2024

Public transit agencies may need to adapt to the rise of remote work, says new study
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
HPI-MIT design research collaboration creates powerful teams
Press contact :.

Previous image Next image
The recent ransomware attack on ChangeHealthcare, which severed the network connecting health care providers, pharmacies, and hospitals with health insurance companies, demonstrates just how disruptive supply chain attacks can be. In this case, it hindered the ability of those providing medical services to submit insurance claims and receive payments. This sort of attack and other forms of data theft are becoming increasingly common and often target large, multinational corporations through the small and mid-sized vendors in their corporate supply chains, enabling breaks in these enormous systems of interwoven companies. Cybersecurity researchers at MIT and the Hasso Plattner Institute (HPI) in Potsdam, Germany, are focused on the different organizational security cultures that exist within large corporations and their vendors because it’s that difference that creates vulnerabilities, often due to the lack of emphasis on cybersecurity by the senior leadership in these small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Keri Pearlson, executive director of Cybersecurity at MIT Sloan (CAMS); Jillian Kwong, a research scientist at CAMS; and Christian Doerr, a professor of cybersecurity and enterprise security at HPI, are co-principal investigators (PIs) on the research project, “Culture and the Supply Chain: Transmitting Shared Values, Attitudes and Beliefs across Cybersecurity Supply Chains.”
Their project was selected in the 2023 inaugural round of grants from the HPI-MIT Designing for Sustainability program , a multiyear partnership funded by HPI and administered by the MIT Morningside Academy for Design (MAD). The program awards about 10 grants annually of up to $200,000 each to multidisciplinary teams with divergent backgrounds in computer science, artificial intelligence, machine learning, engineering, design, architecture, the natural sciences, humanities, and business and management. The 2024 Call for Applications is open through June 3. Designing for Sustainability grants support scientific research that promotes the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) on topics involving sustainable design, innovation, and digital technologies, with teams made up of PIs from both institutions. The PIs on these projects, who have common interests but different strengths, create more powerful teams by working together.
Transmitting shared values, attitudes, and beliefs to improve cybersecurity across supply chains
The MIT and HPI cybersecurity researchers say that most ransomware attacks aren’t reported. Smaller companies hit with ransomware attacks just shut down, because they can’t afford the payment to retrieve their data. This makes it difficult to know just how many attacks and data breaches occur. “As more data and processes move online and into the cloud, it becomes even more important to focus on securing supply chains,” Kwong says. “Investing in cybersecurity allows information to be exchanged freely while keeping data safe. Without it, any progress towards sustainability is stalled.”
One of the first large data breaches in the United States to be widely publicized provides a clear example of how an SME cybersecurity can leave a multinational corporation vulnerable to attack. In 2013, hackers entered the Target Corporation’s own network by obtaining the credentials of a small vendor in its supply chain: a Pennsylvania HVAC company. Through that breach, thieves were able to install malware that stole the financial and personal information of 110 million Target customers, which they sold to card shops on the black market.
To prevent such attacks, SME vendors in a large corporation’s supply chain are required to agree to follow certain security measures, but the SMEs usually don’t have the expertise or training to make good on these cybersecurity promises, leaving their own systems, and therefore any connected to them, vulnerable to attack.
“Right now, organizations are connected economically, but not aligned in terms of organizational culture, values, beliefs, and practices around cybersecurity,” explains Kwong. “Basically, the big companies are realizing the smaller ones are not able to implement all the cybersecurity requirements. We have seen some larger companies address this by reducing requirements or making the process shorter. However, this doesn’t mean companies are more secure; it just lowers the bar for the smaller suppliers to clear it.”
Pearlson emphasizes the importance of board members and senior management taking responsibility for cybersecurity in order to change the culture at SMEs, rather than pushing that down to a single department, IT office, or in some cases, one IT employee.
The research team is using case studies based on interviews, field studies, focus groups, and direct observation of people in their natural work environments to learn how companies engage with vendors, and the specific ways cybersecurity is implemented, or not, in everyday operations. The goal is to create a shared culture around cybersecurity that can be adopted correctly by all vendors in a supply chain.
This approach is in line with the goals of the Charter of Trust Initiative, a partnership of large, multinational corporations formed to establish a better means of implementing cybersecurity in the supply chain network. The HPI-MIT team worked with companies from the Charter of Trust and others last year to understand the impacts of cybersecurity regulation on SME participation in supply chains and develop a conceptual framework to implement changes for stabilizing supply chains.
Cybersecurity is a prerequisite needed to achieve any of the United Nations’ SDGs, explains Kwong. Without secure supply chains, access to key resources and institutions can be abruptly cut off. This could include food, clean water and sanitation, renewable energy, financial systems, health care, education, and resilient infrastructure. Securing supply chains helps enable progress on all SDGs, and the HPI-MIT project specifically supports SMEs, which are a pillar of the U.S. and European economies.
Personalizing product designs while minimizing material waste
In a vastly different Designing for Sustainability joint research project that employs AI with engineering, “Personalizing Product Designs While Minimizing Material Waste” will use AI design software to lay out multiple parts of a pattern on a sheet of plywood, acrylic, or other material, so that they can be laser cut to create new products in real time without wasting material.
Stefanie Mueller, the TIBCO Career Development Associate Professor in the MIT Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and a member of the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, and Patrick Baudisch, a professor of computer science and chair of the Human Computer Interaction Lab at HPI, are co-PIs on the project. The two have worked together for years; Baudisch was Mueller’s PhD research advisor at HPI.
Baudisch’s lab developed an online design teaching system called Kyub that lets students design 3D objects in pieces that are laser cut from sheets of wood and assembled to become chairs, speaker boxes, radio-controlled aircraft, or even functional musical instruments. For instance, each leg of a chair would consist of four identical vertical pieces attached at the edges to create a hollow-centered column, four of which will provide stability to the chair, even though the material is very lightweight.
“By designing and constructing such furniture, students learn not only design, but also structural engineering,” Baudisch says. “Similarly, by designing and constructing musical instruments, they learn about structural engineering, as well as resonance, types of musical tuning, etc.”
Mueller was at HPI when Baudisch developed the Kyub software, allowing her to observe “how they were developing and making all the design decisions,” she says. “They built a really neat piece for people to quickly design these types of 3D objects.” However, using Kyub for material-efficient design is not fast; in order to fabricate a model, the software has to break the 3D models down into 2D parts and lay these out on sheets of material. This takes time, and makes it difficult to see the impact of design decisions on material use in real-time.
Mueller’s lab at MIT developed software based on a layout algorithm that uses AI to lay out pieces on sheets of material in real time. This allows AI to explore multiple potential layouts while the user is still editing, and thus provide ongoing feedback. “As the user develops their design, Fabricaide decides good placements of parts onto the user's available materials, provides warnings if the user does not have enough material for a design, and makes suggestions for how the user can resolve insufficient material cases,” according to the project website.
The joint MIT-HPI project integrates Mueller’s AI software with Baudisch’s Kyub software and adds machine learning to train the AI to offer better design suggestions that save material while adhering to the user’s design intent.
“The project is all about minimizing the waste on these materials sheets,” Mueller says. She already envisions the next step in this AI design process: determining how to integrate the laws of physics into the AI’s knowledge base to ensure the structural integrity and stability of objects it designs.
AI-powered startup design for the Anthropocene: Providing guidance for novel enterprises
Through her work with the teams of MITdesignX and its international programs, Svafa Grönfeldt, faculty director of MITdesignX and professor of the practice in MIT MAD, has helped scores of people in startup companies use the tools and methods of design to ensure that the solution a startup proposes actually fits the problem it seeks to solve. This is often called the problem-solution fit.
Grönfeldt and MIT postdoc Norhan Bayomi are now extending this work to incorporate AI into the process, in collaboration with MIT Professor John Fernández and graduate student Tyler Kim. The HPI team includes Professor Gerard de Melo; HPI School of Entrepreneurship Director Frank Pawlitschek; and doctoral student Michael Mansfeld.
“The startup ecosystem is characterized by uncertainty and volatility compounded by growing uncertainties in climate and planetary systems,” Grönfeldt says. “Therefore, there is an urgent need for a robust model that can objectively predict startup success and guide design for the Anthropocene.”
While startup-success forecasting is gaining popularity, it currently focuses on aiding venture capitalists in selecting companies to fund, rather than guiding the startups in the design of their products, services and business plans.
“The coupling of climate and environmental priorities with startup agendas requires deeper analytics for effective enterprise design,” Grönfeldt says. The project aims to explore whether AI-augmented decision-support systems can enhance startup-success forecasting.
“We're trying to develop a machine learning approach that will give a forecasting of probability of success based on a number of parameters, including the type of business model proposed, how the team came together, the team members’ backgrounds and skill sets, the market and industry sector they're working in and the problem-solution fit,” says Bayomi, who works with Fernández in the MIT Environmental Solutions Initiative. The two are co-founders of the startup Lamarr.AI, which employs robotics and AI to help reduce the carbon dioxide impact of the built environment.
The team is studying “how company founders make decisions across four key areas, starting from the opportunity recognition, how they are selecting the team members, how they are selecting the business model, identifying the most automatic strategy, all the way through the product market fit to gain an understanding of the key governing parameters in each of these areas,” explains Bayomi.
The team is “also developing a large language model that will guide the selection of the business model by using large datasets from different companies in Germany and the U.S. We train the model based on the specific industry sector, such as a technology solution or a data solution, to find what would be the most suitable business model that would increase the success probability of a company,” she says.
The project falls under several of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals, including economic growth, innovation and infrastructure, sustainable cities and communities, and climate action.
Furthering the goals of the HPI-MIT Joint Research Program
These three diverse projects all advance the mission of the HPI-MIT collaboration. MIT MAD aims to use design to transform learning, catalyze innovation, and empower society by inspiring people from all disciplines to interweave design into problem-solving. HPI uses digital engineering concentrated on the development and research of user-oriented innovations for all areas of life.
Interdisciplinary teams with members from both institutions are encouraged to develop and submit proposals for ambitious, sustainable projects that use design strategically to generate measurable, impactful solutions to the world’s problems.
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Cybersecurity at MIT Sloan
- MIT Morningside Academy for Design
- Hasso Plattner Institute
Related Topics
- Manufacturing
- Collaboration
- Supply chains
- Cybersecurity
- Business and management
- Artificial intelligence
- Climate change
- Cleaner industry
- Renewable energy
- Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs)
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship (I&E)
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL)
- Environmental Solutions Initiative
- MIT Sloan School of Management
- School of Architecture and Planning
Related Articles

A new way to integrate data with physical objects

New research collaboration aims to tackle global societal challenges through design

MIT Morningside Academy for Design created as a new hub for cross-disciplinary education, research, and innovation
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

Creating bespoke programming languages for efficient visual AI systems
Read full story →

MIT conductive concrete consortium cements five-year research agreement with Japanese industry

One of MIT’s best-kept secrets lives in the Institute’s basement

Exploring frontiers of mechanical engineering

President Mokgweetsi Masisi of Botswana visits the Legatum Center at MIT

Weaving memory into textiles
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
More than 80% of Americans believe elected officials don’t care what people like them think
Americans are more likely than people in many other countries to believe that most elected officials don’t care what people like them think. More than eight-in-ten U.S. adults said this in a spring 2023 Pew Research Center survey , compared with a median of 74% of adults across the 24 countries surveyed.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to further explore Americans’ discontent with elected officials, following a Center report finding widespread discontent with the country’s political system .
This analysis is based on recent Center surveys as well as data from the U.S. Census Bureau and Duke University. Links to these data sources are available in the text. The links to the Center surveys include information about the field dates, sample sizes and other methodological details.
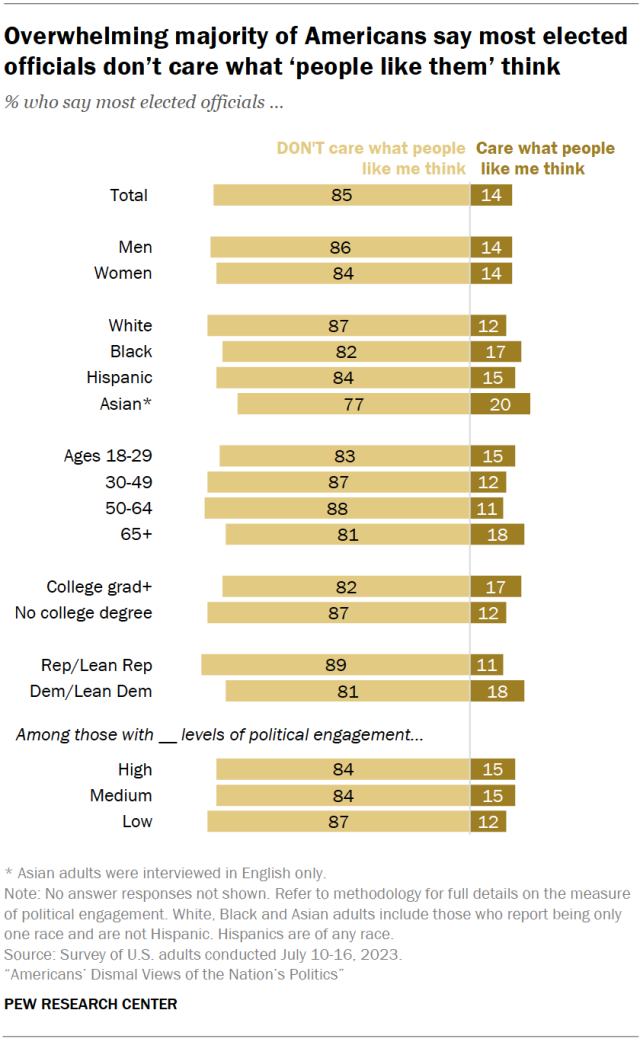
The U.S. public doubled down on this view in a separate Center survey conducted in July 2023 , when 85% said most elected officials don’t care what people like them think. In the early 2000s, by comparison, a much smaller majority of Americans felt this way .
There are only modest demographic and political differences in these views among Americans today.
Why do Americans feel this way?
We also asked a broader series of questions about the U.S. political system in Center surveys conducted in June and July 2023. Overall, Americans broadly distrust the system and question whose interests it’s serving.
For example, only 4% of Americans think the political system is working extremely or very well today, and an equally tiny share have a lot of confidence in its future. Americans have long felt “frustrated” toward the federal government, and just 16% trust the government to do the right thing most or just about all of the time.
In part, these feelings are related to Americans’ perceptions of elected officials and their reasons for serving. Seven-in-ten Americans say ordinary people have too little influence over the decisions members of Congress make. And majorities say that large employers in their districts, lobbyists and special interest groups, and wealthy donors have too much influence.
When it comes to what Americans think motivates today’s elected officials , 63% say that most or all of them ran for office because they wanted to make a lot of money; by comparison, only 15% say most or all wanted to serve the public. And a large majority of Americans (85%) say that the cost of political campaigns can make it hard for good people to run for office.
Who becomes state legislators?
Elected officials have a different demographic profile than the U.S. public as a whole. For example, women have long been underrepresented in Congress, according to Center research.
At the state level, Duke University researchers recently gathered demographic data for lawmakers serving in 2023 and 2024. That data shows that several groups are currently underrepresented in state politics relative to their shares of the U.S. population . Those groups include women and Americans without bachelor’s degrees, as well as Hispanic and Asian Americans.
However, Americans who belong to these groups are not necessarily the most likely to say that elected officials don’t care what people like them think. For example, women are as likely as men to say this.
And in the July 2023 Center survey , most Americans said it’s not too or not at all important to them that the political candidates they support are from the same racial and ethnic background or are the same gender as them. By far, what’s most important to them is that candidates share their political views.
- Election System & Voting Process
- State & Local Government
- Trust in Government
Jenn Hatfield is a writer/editor at Pew Research Center .
From Businesses and Banks to Colleges and Churches: Americans’ Views of U.S. Institutions
7 facts about americans’ views of money in politics, americans’ dismal views of the nation’s politics, public trust in government: 1958-2023, favorable views of supreme court fall to historic low, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Correction: Feasibility of using a handheld ultrasound device to detect and characterize shunt and deep vein thrombosis in patients with COVID-19: an observational study. Rajkumar Rajendram, Arif Hussain, Naveed Mahmood and Mubashar Kharal. The Ultrasound Journal 2023 15 :44. Correction Published on: 23 November 2023.
These essay topic ideas and examples cover a wide range of ultrasound applications and specialties, providing you with ample opportunities to explore and research this exciting field further. Whether you are a student or a healthcare professional, delving into these topics can deepen your understanding of ultrasound technology and its role in ...
Ultrasound articles from across Nature Portfolio. Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses the differential reflectance of acoustic waves at ultrasonic frequencies to detect ...
Medical ultrasound represented by ultrasound imaging is generally believed to be well-known area in research, because ultrasound imaging systems has been widely distributed and actively used in the world since the 1960s. ... Hence, this special issue is designed to bring in various ultrasound-related topics in medicine. We also tried to invite ...
The ongoing rapid expansion of point-of-care ultrasound ... This timely paper 10 aims to improve CCE research data reporting, such that clinical providers may more easily use data to support their clinical decision making when caring for critically ill patients. A critical appraisal of the existing literature from 2000-2017 was conducted, and ...
Ultrasound Imaging - Current Topics presents complex and current topics in ultrasound imaging in a simplified format. It is easy to read and exemplifies the range of experiences of each contributing author. ... Open Access is an initiative that aims to make scientific research freely available to all. To date our community has made over 100 ...
A wearable ultrasonic device to image cardiac function. Researchers have engineered a wearable device that adheres to the skin and uses ultrasound imaging and a deep learning model to produce a ...
Jan. 31, 2023 — New research found that using focused-ultrasound-mediated liquid biopsy in a mouse model released more tau proteins and another biomarker into the blood than without the ...
The Journal of the British Medical Ultrasound Society, Ultrasound is dedicated solely to publishing ultrasound-related topics for users of this rapidly evolving specialty. It provides a forum for presentation of relevant scientific and technical advances in both diagnostic and therapeutic applications of ultrasound. ... Sage Research Methods ...
The purpose of this editorial update is to provide readers with some recent information and to share my views on the journal and its future directions. During the last 4 years, Ultrasonography has published a total of 160 peer-reviewed articles. In 2017, the Ultrasonography home page had over 85,000 hits per month, with over 2,300 downloads of ...
Ultrasound Quarterly provides coverage of the newest, most sophisticated ultrasound techniques as well as in-depth analysis of important developments in this dynamic field. The journal publishes reviews of a wide variety of topics including trans-vaginal ultrasonography, detection of fetal anomalies, color Doppler flow imaging, pediatric ultrasonography, and breast sonography.
After years of research, an NIH-funded team has developed a wearable cardiac ultrasound imager that can non-invasively capture real-time images of the human heart. The prototype patch, which is about the size of a postage stamp, can be worn during exercise, providing valuable cardiac information when the heart is under stress.
Relationship Between Ultrasound Viewing and Proceeding to Abortion. Transrectal Ultrasound of the Prostate With a Biopsy. Iron-Based Catalysts Used in Water Treatment Assisted by Ultrasound. 88 Tourism Management Essay Topic Ideas & Examples 64 Virtual Team Essay Topic Ideas & Examples.
A thesis or dissertation, as some people would like to call it, is an integral part of the Radiology curriculum, be it MD, DNB, or DMRD. We have tried to aggregate radiology thesis topics from various sources for reference. Not everyone is interested in research, and writing a Radiology thesis can be daunting.
Keywords: medical ultrasound imaging, therapeutic ultrasound, non-destructive evaluation, nonlinear ultrasonics, physics of ultrasound, underwater ultrasound, ultrasonic transducers . Important Note: All contributions to this Research Topic must be within the scope of the section and journal to which they are submitted, as defined in their mission statements.
Transparent ultrasound chip improves cell stimulation and imaging. Ultrasound scans, best known for monitoring pregnancies or imaging organs, can also be used to stimulate cells and direct cell function. A team of Penn State researchers has developed an easier, more effective way to harness the technology for biomedical applications.
One of the most common uses of ultrasound is during pregnancy, to monitor the growth and development of the fetus, but there are many other uses, including imaging the heart, blood vessels, eyes, thyroid, brain, breast, abdominal organs, skin, and muscles. Ultrasound images are displayed in either 2D, 3D, or 4D (which is 3D in motion).
About this Research Topic. Submission closed. Musculoskeletal ultrasound is becoming an important and effective tool for the diagnosis of various soft tissue and joint disorders. It is accurate, safe, affordable, efficient, and dynamic. Musculoskeletal ultrasound is also a useful tool for guided therapy. The advances of musculoskeletal imaging ...
Topic Description: This article presents how the use of a framework approach for establishing areas of advanced practice can support individuals and departments with safely and successfully developing new roles in ultrasound. The authors illustrate this via the example of a gastrointestinal ultrasound role, developed in an NHS department ...
List of topics. Topics for thesis and projects are given below. Most of the topics can be adjusted to the students qualifications and wishes. Don't hesitate to take contact with the corresponding supervisor - we're looking forward to a discussion with you!
The goals of research in ultrasound usage in space environments are: (1) Determine accuracy of ultrasound in novel clinical conditions. (2) Determine optimal training methodologies, (3) Determine microgravity associated changes and (4) Develop intuitive ultrasound catalog to enhance autonomous medical care.
The introduction of ultrasound (US) courses into medical undergraduate courses is usually met with a particularly high level of student motivation. The reasons for this are unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the factors that contribute to undergraduate medical students' motivation to learn US skills. Understanding what motivates students to learn US will inform the efforts of ...
There is research showing that ultrasound in conjunction with mammography does detect additional cancers in patients with dense tissue, said Dr. Stamatia Destounis, chair of the college's breast ...
Expanding research opportunities. From the beginning, the MICRO program was designed as a fully remote, rigorous education and mentoring program targeted toward students from underserved backgrounds interested in pursuing graduate school in materials science or related fields. ... Their presentations covered a wide range of topics, including ...
The Cardiovascular Ultrasound Systems market in the U.S. is estimated at US$423.3 Million in the year 2023. China, the world's second largest economy, is forecast to reach a projected market size ...
Global evidence from nighttime light data, Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.tra.2023.103948 Provided by Singapore University of Technology and Design
Research initiatives under the HPI-MIT Designing for Sustainability program span cybersecurity in supply chains, AI-driven material efficiency, and AI-powered startup success forecasting. Interdisciplinary teams from MIT and the Hasso Plattner Institute tackle pressing sustainability challenges and drive impactful solutions forward.
Jenn Hatfield. Americans are more likely than people in many other countries to believe that most elected officials don't care what people like them think. More than eight-in-ten U.S. adults said this in a spring 2023 Pew Research Center survey, compared with a median of 74% of adults across the 24 countries surveyed.