

What Is the Watson Glaser Test?
Who uses the watson glaser test and why, why is it so important to be a critical thinker, what is the watson glaser red model, how to pass a watson glaser test in 2024, how to prepare for a watson glaser critical appraisal in 2024, frequently asked questions, the watson glaser critical thinking appraisal.
Updated May 8, 2024

Modern employers have changed the way that they recruit new candidates. They are no longer looking for people who have the technical skills on paper that match the job description.
Instead, they are looking for candidates who can demonstrably prove that they have a wider range of transferrable skills.
One of those key skills is the ability to think critically .
Firms (particularly those in sectors such as law, finance, HR and marketing ) need to know that their employees can look beyond the surface of the information presented to them.
They want confidence that their staff members can understand, analyze and evaluate situations or work-related tasks. There is more on the importance of critical thinking later in this article.
This is where the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking test comes into play.
The Watson Glaser critical thinking test is a unique assessment that provides a detailed analysis of a participant’s ability to think critically.
The test lasts 30 minutes and applicants can expect to be tested on around 40 questions in five distinct areas :
Assumptions
Interpretation.
The questions are multiple-choice and may be phrased as true/false statements in a bid to see how well the participant has understood and interpreted the information provided.
Employers around the world use it during recruitment campaigns to help hiring managers effectively filter their prospective candidates .
The Watson Glaser test has been used for more than 85 years; employers trust the insights that the test can provide.
In today’s competitive jobs market where every candidate has brought the best of themselves, it can be increasingly difficult for employers to decide between applicants. On paper, two candidates may appear identical, with a similar level of education, work experience, and even interests and skills.
But that does not necessarily mean both or either of them is right for the job.
There is much information available on creating an effective cover letter and resume, not to mention advice on making a good impression during an interview.
As a result, employers are increasingly turning to psychometric testing to look beyond the information that they have.
They want to find the right fit: someone who has the skills that they need now and in the future. And with recruitment costs rising each year, making the wrong hiring decision can be catastrophic.
This is where the Watson Glaser test can help.
It can provide hiring managers with the additional support and guidance they need to help them make an informed decision.
The Watson Glaser test is popular among firms working in professional services (such as law, banking and insurance) . It is used for recruitment for junior and senior positions and some of the world’s most recognized establishments are known for their use of the test.
The Bank of England, Deloitte, Hiscox, Linklaters and Hogan Lovells are just a few employers who enhance their recruitment processes through Watson Glaser testing.
Critical thinking is all about logic and rational thought. Finding out someone’s critical thinking skill level is about knowing whether they can assess whether they are being told the truth and how they can use inferences and assumptions to aid their decision-making.
If you are working in a high-pressure environment, having an instinctive ability to look beyond the information provided to the underlying patterns of cause-and-effect can be crucial to do your job well.
Although it is often thought of concerning law firms and finance teams, it is easy to see how critical thinking skills could be applied to a wide range of professions.
For example, HR professionals dealing with internal disputes may need to think critically. Or social workers and other health professionals may need to use critical thinking to assess whether someone is vulnerable and in need of help and support when that person does not or cannot say openly.
Practice Watson Glaser Test with TestHQ
Critical thinking is about questioning what you already know . It is about understanding how to find the facts and the truth about a situation or argument without being influenced by other people’s opinions .
It is also about looking at the bigger picture and seeing how decisions made now may have short-term benefits but long-term consequences.
For those working in senior managerial roles, this ability to think objectively can make a big difference to business success.
As part of the critical thinking assessment, the Watson Glaser Test focuses on the acronym, 'RED':
- R ecognize assumptions
- E valuate arguments
- D raw conclusions
Put simply, the RED model ensures you can understand how to move beyond subconscious bias in your thinking. It ensures that you can identify the truth and understand the differences between fact and opinion.
To recognize assumptions , you must understand yourself and others: what your thought patterns and past experiences have led you to conclude about the world.
Evaluating arguments requires you to genuinely consider the merits of all options in a situation, and not just choose the one you feel that you ‘ought’ to.
Finally, to draw an accurate and beneficial conclusion you must trust your decision-making and understanding of the situation.
Watson Glaser Practice Test Questions & Answers
As mentioned earlier, the Watson Glaser Test assesses five core elements. Here, they will be examined in more depth:
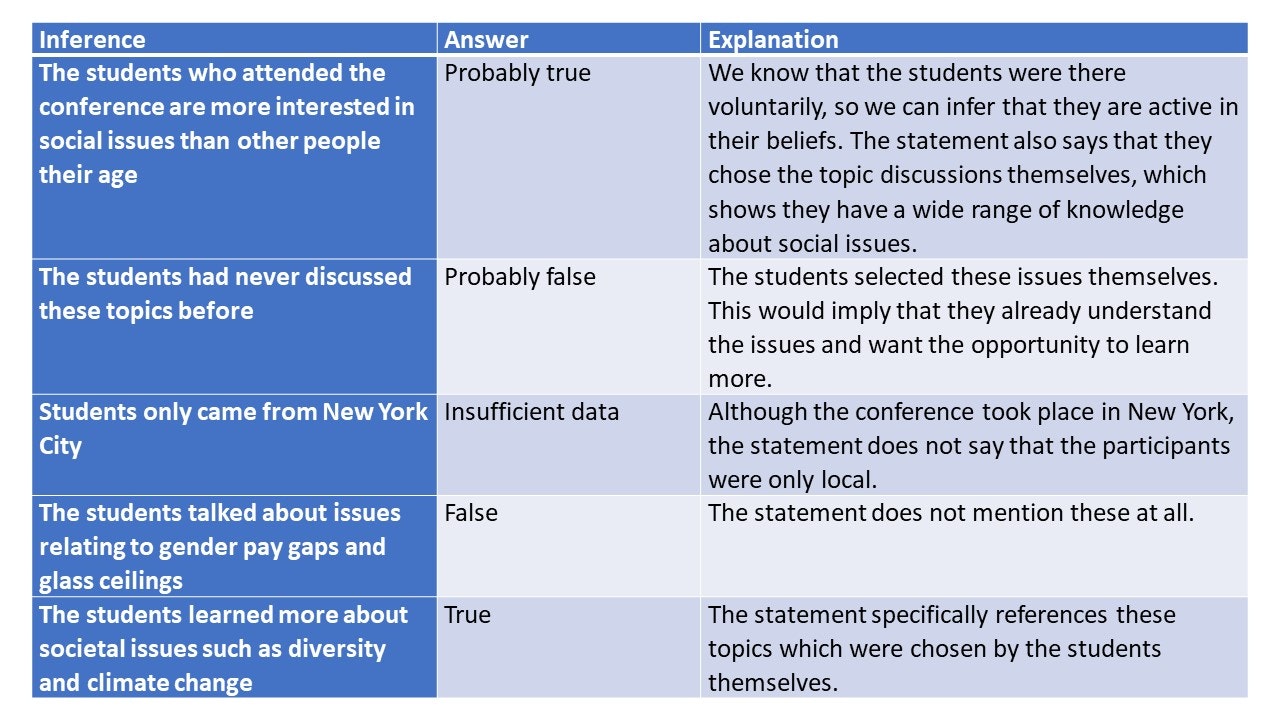
This part of the test is about your ability to draw conclusions based on facts . These facts may be directly provided or may be assumptions that you have previously made.
Within the assessment, you can expect to be provided with a selection of text. Along with the text will be a statement.
You may need to decide whether that statement is true, probably true, insufficient data (neither true nor false), probably false or false.
The test looks to see if your answer was based on a conclusion that could be inferred from the text provided or if it is based on an assumption you previously made.
Watson Glaser Practice Test
Example Statement:
500 students recently attended a voluntary conference in New York. During the conference, two of the main topics discussed were issues relating to diversity and climate change. This is because these are the two issues that the students selected that are important to them.
Many people make decisions based on assumptions. But you need to be able to identify when assumptions are being made.
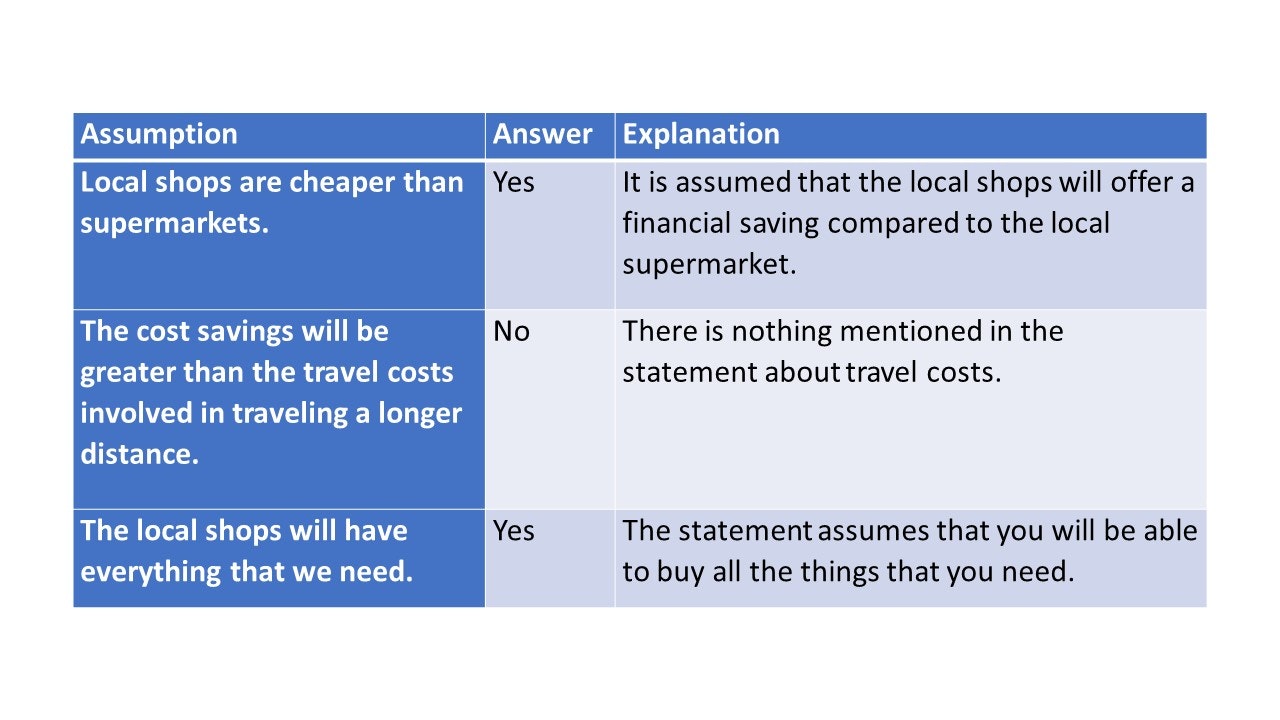
Within the Watson Glaser test , you will be provided with a written statement as well as an assumption.
You will be asked to declare whether that assumption was made in the text provided or not .
This is an important part of the test; it allows employers to understand if you have any expectations about whether things are true or not . For roles in law or finance, this is a vital skill.
We need to save money, so we’ll visit the local shops in the nearest town rather than the local supermarket
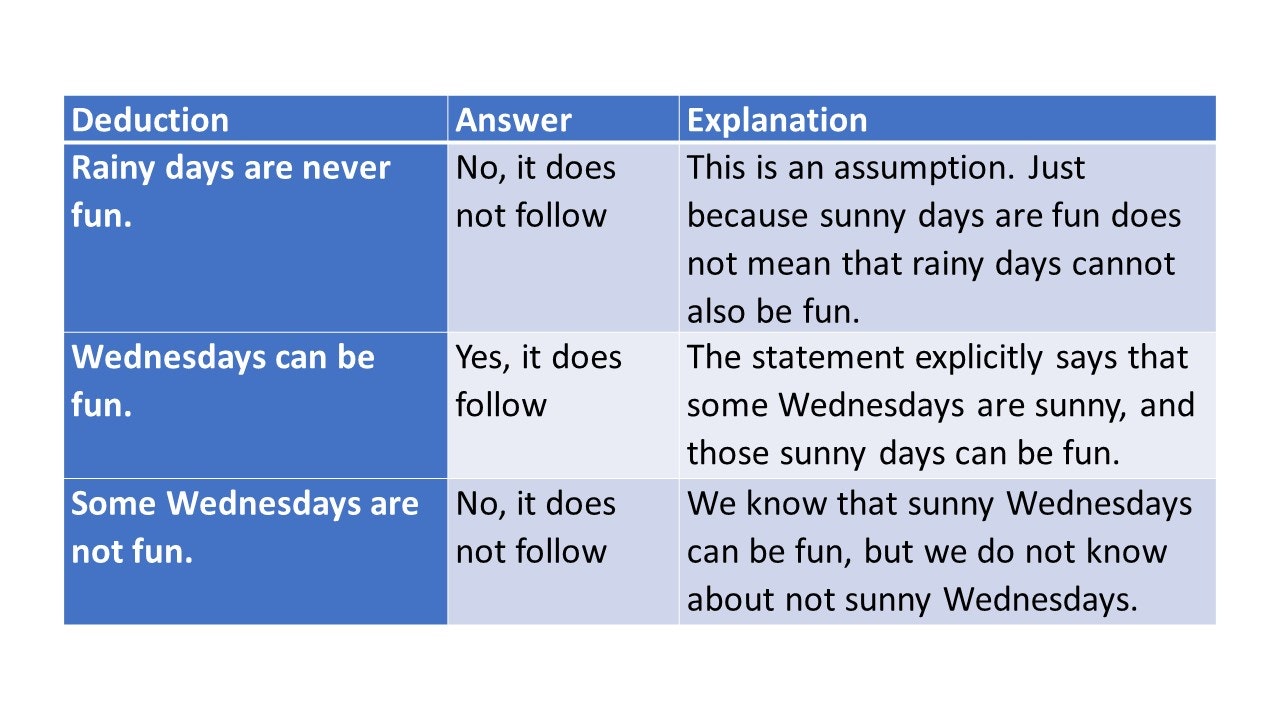
As a core part of critical thinking, 'deduction' is the ability to use logic and reasoning to come to an informed decision .
You will be presented with several facts, along with a variety of conclusions. You will be tasked with confirming whether those conclusions can be made from the information provided in that statement.
The answers are commonly in a ‘Yes, it follows/No, it does not follow’ form.
It is sometimes sunny on Wednesdays. All sunny days are fun. Therefore…
If you need to prepare for a number of different employment tests and want to outsmart the competition, choose a Premium Membership from TestHQ . You will get access to three PrepPacks of your choice, from a database that covers all the major test providers and employers and tailored profession packs.
Get a Premium Package Now
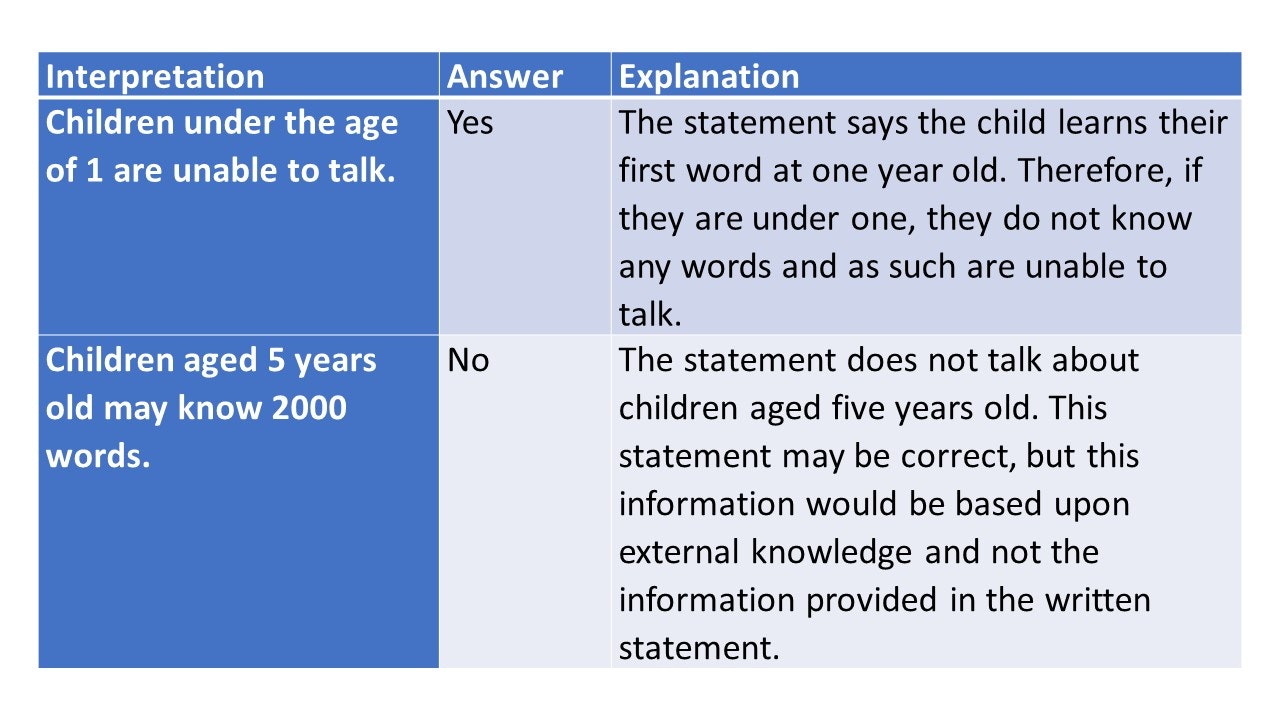
Critical thinking is also about interpreting the information correctly. It is about using the information provided to come to a valuable, informed decision .
Like the deduction questions, you will be provided with a written statement, which you must assume to be true.
You will also be provided with a suggested interpretation of that written statement. You must decide if that interpretation is correct based on the information provided, using a yes/no format.
A study of toddlers shows that their speech can change significantly between the ages of 10 months and three years old. At 1 year old, a child may learn their first word whereas at three years old they may know 200 words
Evaluation of Arguments
This final part requires you to identify whether an argument is strong or weak . You will be presented with a written statement and several arguments that can be used for or against it. You need to identify which is the strongest argument and which is the weakest based on the information provided.
Should all 18-year-olds go to college to study for a degree after they have graduated from high school?
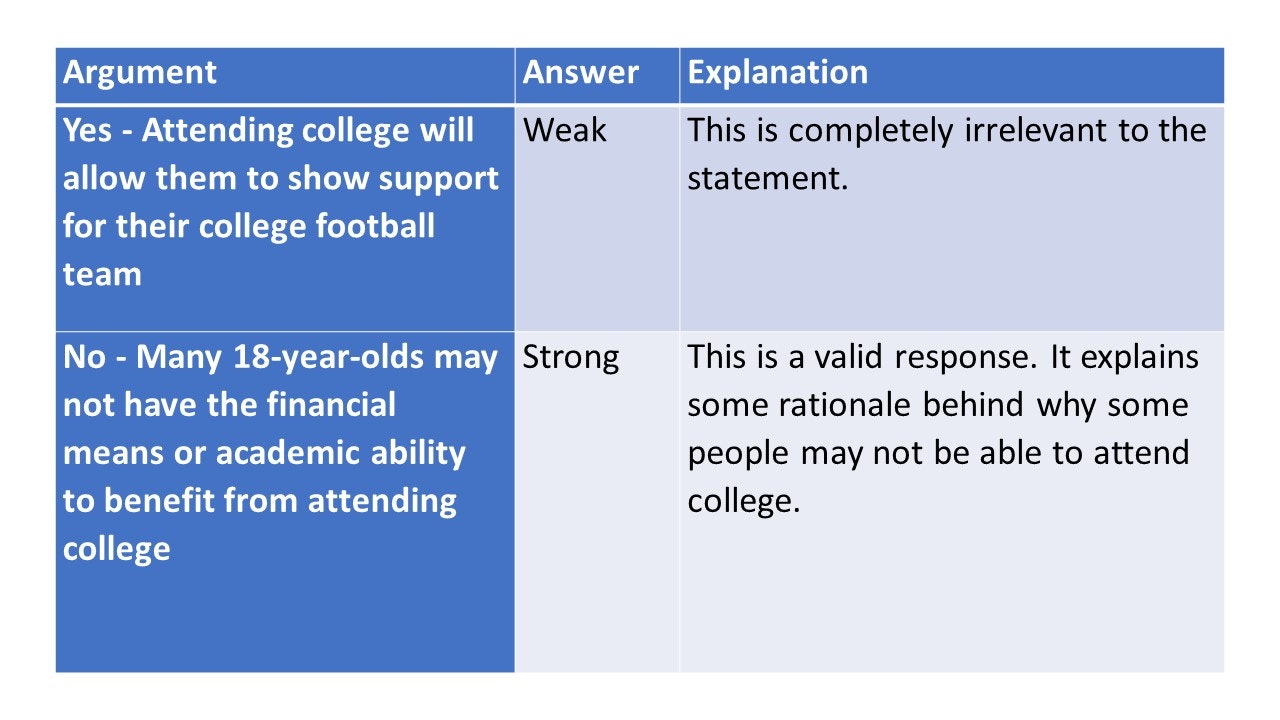
There are no confirmed pass/fail scores for Watson Glaser tests; different sectors have different interpretations of what is a good score .
Law firms, for example, will require a pass mark of at least 75-80% because the ability to think critically is an essential aspect of working as a lawyer.
As a comparative test, you need to consider what the comparative ‘norm’ is for your chosen profession. Your score will be compared to other candidates taking the test and you need to score better than them.
It is important to try and score as highly as you possibly can. Your Watson Glaser test score can set you apart from other candidates; you need to impress the recruiters as much as possible.
Your best chance of achieving a high score is to practice as much as possible in advance.
Everyone will have their own preferred study methods, and what works for one person may not necessarily work for another.
However, there are some basic techniques everyone can use, which will enhance your study preparation ahead of the test:
Step 1 . Pay Attention to Online Practice Tests
There are numerous free online training aids available; these can be beneficial as a starting point to your preparation.
However, it should be noted that they are often not as detailed as the actual exam questions.
When researching for online test questions, make sure that any questions are specific to the Watson Glaser Test , not just critical thinking.
General critical thinking questions can help you improve your skills but will not familiarize you with this test. Therefore, make sure you practice any questions which follow the ‘rules’ and structure of a Watson Glaser Test .
Step 2 . Paid-for Preparation Packs Can Be Effective
If you are looking for something that mimics the complexity of a Watson Glaser test , you may wish to look at investing in a preparation pack.
There are plenty of options available from sites such as TestHQ . These are often far more comprehensive than free practice tests.
They may also include specific drills (which take you through each of the five stages of the test) as well as study guides, practice tests and suggestions of how to improve your score.
Psychologically, if you have purchased a preparation pack, you may be more inclined to increase your pre-test practice/study when compared to using free tools, due to having invested money.
Step 3 . Apply Critical Thinking to All Aspects of Your Daily Routine
The best way to improve your critical thinking score is to practice it every day.
It is not just about using your skills to pass an exam question; it is about being able to think critically in everyday scenarios. Therefore, when you are reading the news or online articles, try to think whether you are being given facts or you are making deductions and assumptions from the information provided.
The more you practice your critical thinking in these scenarios, the more it will become second nature to you.
You could revert to the RED model: recognize the assumptions being made, by you and the author; evaluate the arguments and decide which, if any, are strong; and draw conclusions from the information provided and perhaps see if they differ from conclusions drawn using your external knowledge.
Prepare for Watson Glaser Test with TestHQ
Nine Top Tips for Ensuring Success in Your Watson Glaser Test
If you are getting ready to participate in a Watson Glaser test, you must be clear about what you are being asked to do.
Here are a few tips that can help you to improve your Watson Glaser test score.
1. Practice, Practice, Practice
Critical thinking is a skill that should become second nature to you. You should practice as much as possible, not just so that you can pass the test, but also to feel confident in using your skills in reality.
2. The Best Success Is Based on the Long-Term Study
To succeed in your Watson Glaser test , you need to spend time preparing. Those who begin studying in the weeks and months beforehand will be far more successful than those who leave their study to the last minute.
3. Acquaint Yourself With the Test Format
The Watson Glaser test has a different type of question to other critical thinking tests. Make sure that you are aware of what to expect from the test questions. The last thing you want is to be surprised on test day.
4. Read the Instructions Carefully
This is one of the simplest but most effective tips. Your critical thinking skills start with understanding what you are being asked to do. Take your time over the question. Although you may only have 30 minutes to complete the test, it is still important that you do not rush through and submit the wrong answers. You do not get a higher score if you finish early, so use your time wisely.
5. Only Use the Information Provided in the Question
Remember, the purpose of the test is to see if you can come to a decision based on the provided written statement. This means that you must ignore anything that you think you already know and focus only on the information given in the question.
6. Widen Your Non-Fictional Reading
Reading a variety of journals, newspapers and reports, and watching examples of debates and arguments will help you to improve your skills. You will start to understand how the same basic facts can be presented in different ways and cause people to draw different conclusions. From there, you can start to enhance your critical thinking skills to go beyond the perspective provided in any given situation.
7. Be Self-Aware
We all have our own biases and prejudices whether we know them or not. It is important to think about how your own opinions and life experiences may impact how you perceive and understand situations. For example, someone who has grown up with a lot of money may have a different interpretation of what it is like to “go without”, compared to someone who has grown up in extreme poverty. It is important to have this self-awareness as it is important for understanding other people; this is useful if you are working in sectors such as law.
8. Read the Explanations During Your Preparation
To make the most of practice tests, make sure you read the analysis explaining the answers, regardless of if you got the question right or wrong. This is the crux of your study; it will explain the reasoning why a certain answer is correct, and this will help you understand how to choose the correct answers.
9. Practice Your Timings
You know that you will have five sections to complete in the test. You also know that you have 30 minutes to complete the test. Therefore, make sure that your timings are in sync within your practice, so you can work your way through the test in its entirety. Time yourself on how long each section takes you and put in extra work on your slowest.
What score do you need to pass the Watson Glaser test?
There is no standard benchmark score to pass the Watson Glaser test . Each business sector has its own perception of what constitutes a good score and every employer will set its own requirements.
It is wise to aim for a Watson Glaser test score of at least 75%. To score 75% or higher, you will need to correctly answer at least 30 of the 40 questions.
The employing organization will use your test results to compare your performance with other candidates within the selection pool. The higher you score in the Watson Glaser test , the better your chances of being hired.
Can you fail a Watson Glaser test?
It is not possible to fail a Watson Glaser test . However, your score may not be high enough to meet the benchmark set by the employing organization.
By aiming for a score of at least 75%, you stand a good chance of progressing to the next stage of the recruitment process.
Are Watson Glaser tests hard?
Many candidates find the Watson Glaser test hard. The test is designed to assess five different aspects of logical reasoning skills. Candidates must work under pressure, which adds another dimension of difficulty.
By practicing your critical thinking skills, you can improve your chances of achieving a high score on the Watson Glaser test .
How do I prepare for Watson Glaser?
To prepare for Watson Glaser , you will need to practice your critical thinking abilities. This can be achieved through a range of activities; for example, reading a variety of newspapers, journals and other literature.
Try applying the RED model to your reading – recognize the assumptions being made (both by you and the writer), evaluate the arguments and decide which of these (if any) are strong.
You should also practice drawing conclusions from the information available to you.
Online Watson Glaser practice assessments are a useful way to prepare for Watson Glaser. These practice tests will give you an idea of what to expect on the day, although the questions are not usually as detailed as those in the actual test.
You might also consider using a paid-for Watson Glaser preparation pack, such as the one available from TestHQ . Preparation packs provide a comprehensive test guide, including practice tests and recommendations on how to improve your test score.
How long does the Watson Glaser test take?
Candidates are allowed 30 minutes to complete the Watson Glaser test . The multiple-choice test questions are grouped into five distinct areas - assumptions, deduction, evaluation, inference and interpretation.
Which firms use the Watson Glaser test?
Companies all over the world use the Watson Glaser test as part of their recruitment campaigns.
It is a popular choice for professional service firms, including banking, law, and insurance. Firms using the Watson Glaser test include the Bank of England, Hiscox, Deloitte and Clifford Chance.
How many times can you take the Watson Glaser test?
Most employers will only allow you to take the Watson Glaser test once per application. However, you may take the Watson Glaser test more than once throughout your career.
What is the next step after passing the Watson Glaser test?
The next step after passing the Watson Glaser test will vary between employers. Some firms will ask you to attend a face-to-face interview after passing the Watson Glaser test, others will ask you to attend an assessment center. Speak to the hiring manager to find out the process for the firm you are applying for.
Start preparing in advance for the Watson Glaser test
The Watson Glaser test differs from other critical thinking tests. It has its own rules and formations, and the exam is incredibly competitive. If you are asked to participate in a Watson Glaser test it is because your prospective employer is looking for the ‘best of the best’. Your aim is not to simply pass the test; it is to achieve a higher score than anyone else taking that test .
Therefore, taking the time to prepare for the Watson Glaser test is vital for your chances of success. You need to be confident that you know what you are being asked to do, and that you can use your critical thinking skills to make informed decisions.
Your study is about more than helping you to pass a test; it is about providing you with the skills and capability to think critically about information in the ‘real world’ .
You might also be interested in these other Psychometric Success articles:

Or explore the Aptitude Tests / Test Types sections.
Watson-Glaser Assessments: Guidelines & Practice Examples
Originally designed by Goodwin Watson and Edward Glaser, The Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (Form AM) was a measurement of “how well you are able to reason analytically and logically.” After their extensive use during World War One, experts increasingly used the tests as a tool to rank and filter individuals in contexts including (but not limited to) education and employment. In this article, we’ll be providing you with an overview of The Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal, its test format, and question examples for your practice.
Table of Contents
What is a Watson Glaser test?
The Watson Glaser Assessment (Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal) is designed by Pearson Talentlens – a part of the famous Pearson education publishing house. The assessment is a quick, consistent, and accurate measurement of the test-takers ability to analyze, reason, interpret and draw logical conclusions from written information .
This critical thinking test has five scales which are the elementary units of critical thinking and reasoning . These five units serve as parameters to measure all areas of critical thinking ability.
The test is administered to appraising adults (16 years and above) with questions of varying difficulty and format.
Watson Glaser Test format
The Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal is a timed test. It can be administered both online and offline, depending on the company you are applying to.
- For the online version (W-G III), the test is suitable for the unproctored screening of job applicants . Questions are selected randomly from a larger pool of questions called “item bank”. This helps minimize the possibility of cheating due to the fact that there are no applicants having the same set of questions.
- For the offline version (W-G II Forms D and E), applicants have to take the test under supervised conditions .
Upon finishing, applicants receive a percentile score with norm groups either provided by Pearson Talentlens or designed by the company.
Popular test formats are as follows:
- 40 questions – 30 minutes
- 80 questions – 60 minutes
The question distribution in a 40-question Watson Glaser test includes the following:
- Inference – 5 questions
- Recognition of assumptions – 12 questions
- Deduction – 5 questions
- Interpretation – 6 questions
- Evaluation – 12 questions
Watson Glaser test: 5 question types & examples
Five types of questions appearing in the test are
Infer questions
- Recognize Assumption questions
Deduce questions
Interpret questions.
- Evaluate Argument questions
/case_thumb/1672123157635_2022_watson_glaser_test.png)
You will find five choices of answers for each inference in the question: True, Probably True, Insufficient Data, Probably False, and False. Your job is to determine which choice best fits the hypothesis.

- True : If you think the inference is definitely TRUE; that it properly follows beyond a reasonable doubt from the statement of facts given.
- Probably True : If, in the light of the facts given, you think the inference is Probably True; that it is more likely to be true than false.
- Insufficient Data : If you decide that there are Insufficient Data; that you cannot tell from the facts given whether the inference is likely to be true or false; if the facts provide no basis for judging one way or another.
- Probably False : If, in the light of the facts given, you think the inference is Probably False; that it is more likely to be true than false.
- False : If you think the inference is definitely False; that it is wrong, either because it misinterprets the facts given, or because it contradicts the facts or necessary inferences from those facts.
Unlike popular aptitude tests where you use solely given information, this test allows the use of specific commonly accepted knowledge or information that practically every person has.

Source: Pearson Talentlens
During the past month, managers scheduled for international assignments voluntarily attended our company’s cross-cultural business training workshop. All of the managers reported that the quality of the training was high and focused on valuable work skills that could be immediately applied.
The majority of training was devoted to rules and regulations for doing business in this country.
A. True B. Probably True C. Insufficient Data D. Probably False E. False
Answer : Probably False
Explanation : Probably False because the training focused on cross-cultural business. It cannot be considered definitely false because the specific course content is not provided.
Practice Example:
Chamonix is one of the oldest ski resorts in France. Last year, the Chamonix-Mont-Blanc Valley authorities introduced a climate and energy action plan, the first in the French Alps. The plan commits to reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the area by 22 percent. Among the proposed measures is a ban on the most polluting lorries using the nearby Mont Blanc tunnel. Climate change will have a major impact on the valley’s main economic activities: less snow on low-altitude ski slopes and the risk of increased pressure on high-altitude ski slopes have been recorded in recent studies. Natural habitats, river patterns, forests, and agriculture might be radically transformed, increasing the likelihood of hazards such as avalanches, floods, and landslides.
Although air quality is a great concern for those living at the foot of Mont Blanc, noise pollution is arguably the most noticeable at a local level.
A. True B. ProbablyTrue C. Insufficient Data D. Probably False E. False
Answer : Insufficient Data
Explanation : The passage does not mention noise pollution, as well as its existence at local level.
Recognize assumption questions

In this question, you are presented with a statement and two choices “ Assumption made ” or “ Assumption not made “. Your job is to determine whether the statement is an assumption taken for granted (Assumption made) or an assumption not necessarily taken for granted (Assumption not made).

We need to save time in getting there so we’d better go by plane.
There is a plane service available to us for at least part of the distance to the destination.
A. Assumption made B. Assumption not made
Answer : Assumption made
Explanation :
This is assumed in the statement because, in order to save time by plane, it must be possible to go by plane.
While owning a pet can be expensive and is occasionally an inconvenience, it’s a good thing to do if you want to improve your chances of living a satisfying life.
Pet owners will always lead more satisfying lives than those who don’t own pets.
Answer : Assumption not made
From the given premises, we can only see that: if you want a satisfying life, it is a good thing to have a pet. However, having a pet does not definitely lead to a satisfying life. There is no indication to compare the satisfaction between having a pet or not having a pet as a way to live a satisfying life.

In this type of question, each item contains several statements (premises) followed by several suggested conclusions. For the purposes of the test, you must consider the given statements as true without exception. The question presents you with two options
- Conclusion follows : If you think the conclusion necessarily follows from the statements given;
- Conclusion does not follow : If you think it is not a necessary conclusion from the statements given.
Since the test requires you to regard given statements as completely true, you have to try not to let your common sense and existing knowledge interfere. You have to stick to only the given statements (premises) and make judgments as to whether it necessarily follows from the statement or not.
One thing to note is the use of the word “Some” in this type of question. It means an indefinite part or quantity of a class of things. It can be either a portion or perhaps all of the class.

Sample:
Some Sundays are rainy. All rainy days are boring. Therefore …
Some Sundays are boring.
A. Conclusion follows B. Conclusion does not follow
Answer : Conclusion follows
The conclusion necessarily follows from the statements because, according to them, rainy Sundays must be boring.
Damage to roads in the area has made them unsuitable for loads over one ton. These loads are being transported to the capital by air, but as air resources are limited they are restricted to carrying food and medical supplies. Roads cannot be repaired until medical emergencies are dealt with. Therefore, …
Food can be taken to the capital by road.
Answer : Conclusion does not follow
Roads can not be used to transport food in loads over one ton. Food loads over one ton are being transported by air. We are not sure whether food in loads under one ton are delivered by road or anything else.

An interpret question provides you with a short paragraph followed by several suggested conclusions. You must assume that everything in the short paragraph is true, for the purpose of the test. To answer the question, you have to judge whether or not each of the suggested conclusions logically follows beyond a reasonable doubt from the information presented in the paragraph.
You have two answer choices:
- Conclusion follows : If you think the conclusions follow beyond a reasonable doubt (although they may not follow absolutely and necessarily);
- Conclusion does not follow : If you think the conclusions doesn’t follow beyond a reasonable doubt from the facts given in the short paragraph.
As a rule of thumb, you should judge each conclusion independently from your common sense or outside knowledge.

Source: Watson Glaser
A study of vocabulary growth in children from ages eight months to six years old shows that the size of spoken vocabulary increases from zero words at age eight months to 2562 words at age six years.
Vocabulary is slowest during the period when children are learning to walk.
Answer : Conclusion does not follow.
The conclusion does not follow because there is no information given that relates the growth of vocabulary to walking.
An accounting computer program, MagicNumber, is Wisdom Software’s biggest-selling product, with its development involving 20% of programmers and 30% of marketing staff. DesignAid, a graphic design program, is the latest offering from the company. It is definitely expected to sell more copies than MagicNumber and will have fewer programmers working on its design, but more marketing staff.
DesignAid will bring in greater profits for the company than MagicNumber.
The paragraph only mentioned that DesignAid is expected to sell more than MagicNumber. This does not necessarily mean that DesignAid uiwll bring greater profit than MagicNumber.
Evaluate argument questions

The question involves distinguishing between strong and weak arguments, as far as the question at issue is concerned. In each question, there is a series of arguments that you must regard as true. Your job is to determine whether or not each of these arguments is a strong or a weak one.
- Argument strong : If you think the argument is strong;
- Argument weak: If you think the argument is weak.
For an objective evaluation of the argument, you must judge each argument independently on its own merit, without the influence of your personal perception.
One thing to note is the use of the word Should. By using Should at the beginning of each question, it means “Would the proposed action promote the general welfare of the people in your country?”

Should young adults in this country go to university?
No; a large percentage of young adults do not have enough ability or interest to derive any benefit from university training.
A. Argument strong B. Argument weak
Answer : Argument strong.
If this is true, as the directions require us to assume, it is a weighty argument against all young adults going to university.
Practice Example 5:
Is it worthwhile for a business to invest in training employees?
Yes, research shows the amount of money spent on training is positively related to profitability.
A. Argument Strong B. Argument Weak
Answer : Argument Strong
The explanation show that business can increase their profit by invest more money on training. This is a direct back up evidence for the claim.
Which companies use Watson Glaser tests?
Watson Glaser Tests are popular in the pre-employment process across sectors such as medical, marketing, education, legal, and professional services. The test can be used for different job levels like Graduates, Execs and Managerial, Supervisors, and Professionals., depending on the company hiring request.
There are a great number of UK companies using it for their pre-employment screening process. The names include the following
- Simmons & Simmons
- Hill Dickinson
- Bank of England
- Burges Salmon
- Ince & Co
- Government Legal Service
- Irwin Mitchell
- Clifford Chance
- Hogan Lovells
Prepare for aptitude tests with MConsultingPrep
Explore MConsultingPrep’s Aptitude Test – a strategic & comprehensive practicing platform with
- A question bank of +1000 aptitude questions (Numerical, Verbal & Logical)
- A comprehensive explanation of every question
- Evaluation and recording tools for performance reviews
You’ll be practicing more strategically with our test packages, to gain more confidence for every test question you might experience in your future aptitude tests.
Our massive question bank consists of a significant number of question variations from many test publishers and companies, across different companies & businesses.
With questions organized by type, you can leverage your preparation by
- Focusing on practicing questions in specific types
- Improving your performance in questions that you struggle with
With evaluation tools coming in handy, you have better insights into your overall performance, what you excel at, and what you need improvements on.
Scoring in the McKinsey PSG/Digital Assessment
The scoring mechanism in the McKinsey Digital Assessment
Related product
/filters:quality(75)//case_thumb/public/1699589977462_aptitude_tests_package_4_x.png)
Aptitude Test Package
Simulating most common test publishers, this package provides you with 1400+ numerical, verbal and logical reasoning questions. Ace the aptitude test with our practical study guides tailored to each question type.
Let’s dive deep into aptitude tests: definition, different types, and free practice materials for this world-famous assessment tool!
Aptitude tests are usually compulsory in the application process. So how much time should you spend on learning to get a high score?
While the majority of aptitude tests contain multiple-choice questions, some test providers provide gamified assessments. Dive in the details now!
Get 25% off all test packages.
Get 25% off all test packages!
Click below to get 25% off all test packages.

Watson Glaser Tests
- https://www.talentlens.co.uk/product/watson-glaser/
- 228 questions
Watson Glaser tests are a form of psychometric assessment that fall under the category of critical thinking tests. They are designed to determine how well an individual can process information from a logical perspective, and then evaluate, analyse and make sound judgements. As such, they are commonly used in the recruitment process for professions that rely on these skills.
What is a Watson Glaser test?
Watson Glaser test is a comprehensive psychometric assessment that falls under the category of critical thinking tests. It is designed to determine how well an individual can process information from a logical perspective, and then evaluate, analyze and make sound judgments. Watson Glaser test is commonly used in the recruitment process for professions that rely on these skills.
Watson Glaser tests have been around since 1925 when they were first developed by American psychologists Goodwin Watson and Edwin Glaser. Subject to many revisions and improvements over the years, they are now produced by test publisher TalentLens and are considered one of the most trusted methods of evaluating critical reasoning.
Critical thinking is a complex skill that requires the ability to interpret information, differentiate fact from fallacy, draw evidence-based conclusions and identify sound arguments, all while remaining objective.
Like many critical thinking tests , the Watson Glaser test measures these skills through verbal information: that is, statements or passages of text from which an individual is required to make deductions and inferences, pinpoint assumptions needed to validate a proposition, and weigh up the strength of an argument.
These are inherent skills, more prominent in some than others. The Watson Glaser test, therefore, requires no prior knowledge. Success relies on existing knowledge being put to one side, the sole focus being the evidence laid out in each question.
You may be asked to sit a Watson Glaser test by the potential employer if applying for a graduate, professional or managerial level position in a sector where critical thinking is a prerequisite. Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal is most commonly used in the legal sector, but also the selection process of organizations like the Bank of England.
The test may be used for screening purposes in the initial stages of the hiring process, or at a later date as part of an assessment day .
What is the format of a Watson Glaser test?
The Watson Glaser test is a timed, multiple-choice assessment, the most recent version of which consists of 40 critical reasoning questions with a 30-minute time constraint.
Questions are split across five areas of logical reasoning ability:
Drawing inferences
To draw inferences is essential to make an educated guess based on the evidence in front of you, without being swayed by any pre-existing knowledge or subconscious bias.
You’ll be presented with a short paragraph, followed by a set of inferred statements. Potential employees need to critically analyse the information in the given paragraph to determine if these statements are true, probably true, false, probably false, or if there is insufficient proof to determine either way.
Recognising assumptions
Assumptions relating to what we understand to be true without needing solid proof. They are the underlying facts that give an argument its validity.
In this section of the test, you’ll be presented with a statement and a set of assumptions. If the statement relies on the assumption being true, you would mark it as ‘assumption made’.
If the assumption is irrelevant to the statement or bears no weight on its validity, you would mark it as ‘assumption not made.
Deductive reasoning is the act of arriving at a fact-based conclusion through a logical thought process. A deduction differs from an assumption in that it is what we take away from an argument, as opposed to the facts on which an argument needs to stand.
Based solely on the evidence presented in a statement or short paragraph, you’ll need to determine if a list of conclusions does or does not logically follow the information in front of you.
Interpreting
The interpretation section of the Watson Glaser test is similar to the deduction section, in that you’ll be asked to determine whether a given conclusion can logically be drawn from an argument.
However, with these questions, you’ll need to be able to identify significant pieces of information and decide if a logical interpretation can be applied in support of the conclusion in question.
Evaluating arguments
This last section looks at your ability to separate a weak argument from a strong one. It is designed to test your impartial evaluation of arguments, not your personal opinion.
A question will be posted, followed by a set of arguments on either side of the debate. You’ll need to decide if an argument is relevant and challenging, and therefore strong, or vague and unrealistic, and therefore weak.
What skills does it look to measure?
The five sections combined to give an overall picture of your performance in key areas, and measure your ability to:
Define a problem
Select key points of information to formulate a solution
Understand when an assumption has been made, and when it has not
Hypothesise, or select an applicable hypothesis based on limited evidence
Draw fact-based conclusions
Determine the probability of an inference
What is a passing score on the Watson Glaser tests?
The results of your Watson Glaser test will be assessed against a norm group: individuals of a comparative educational background or professional standing – within a relevant field – that have previously sat the exam.
It is therefore difficult to state an exact pass score on the test since it depends entirely on the performance of your peers. Ideally, you’d look to reach 75% and above to give yourself a competitive edge.
Which professions use Watson Glaser tests, and why?
Watson Glaser tests are used to assess suitability for several occupations including those in the medical profession, marketing, and education. Those critical reasoning tests are most common in law firms and professional services sectors.
Many positions in law, banking, and finance, for example, require that an individual make informed decisions that can be justified, are rooted in fact, and are free from bias. Since critical thinking is an essential skill here, employers use Watson Glaser tests to determine how well-suited a candidate is for these professions.
How to prepare for a Watson Glaser test
Practice is the first port of call when preparing for your Watson Glaser test. Although critical thinking is an inherent skill, it can be nurtured and improved upon.
Watson Glaser tests are built around a model known as RED . Try to keep this in mind as you approach both practice tests and daily tasks.
The components associated with the RED model are:
Recognising assumptions . Instead of simply taking things at face value, such as the news or a part of a conversation with a friend or co-worker, ask yourself if what you’re hearing can be classified as true, and what the facts are that back it up. Are they evidential, or based on assumptions?
Evaluating arguments . We’re all guilty of seeking out information that confirms our perspective. Instead, actively look for opinions that contradict your own and assess them from an objective point of view. The better you become at seeing both sides of a story, the more prepared you’ll be to critically evaluate arguments in your Watson Glaser test.
Drawing conclusions . Try to get used to drawing fact-based conclusions, rather than those based on emotional reactions or subconscious bias. These conclusions may not align with your perspective, but a Watson Glaser test requires that you conclude impartially – and as with most things in life, practice makes perfect here.
Prepare yourself for leading employers

Tips for Watson Glaser tests
Study the practice questions.
In the official test, you’ll have the opportunity to complete practice questions. These are there for a reason, so use them wisely. Each section of the test differs slightly in its approach, and the more comfortable you are with what is being asked of you, the more clearly you’ll be able to approach the problem.
Leave instinct and intuition at the door
To succeed on a Watson Glaser test, you need to go against human nature and ignore everything you think you know. Each question will contain all the relevant information you need. Whether you believe it to be true, agree with it, or not, is irrelevant. For the sake of the test, evaluate only the information given. Any outside knowledge should temporarily be forgotten.
Examine each question carefully
The key to strategic critical thinking is to fully understand what is being presented. You cannot draw a valid conclusion, or understand what assumptions support an argument, if you do not fully comprehend what is put forward. You may feel the need to rush under the time pressure, but attention to detail is vital.
Look for keywords and phrases
The statement, proposition or paragraph of text at the start of each question will inevitably include keywords or phrases that relate directly to the assumptions, inferences or conclusions given. These are your clues. Identify them, and you’ll find it much easier to analyse each scenario objectively.
Split your time evenly
Remember, you have a set amount of time to work through all five sections of the test. Split this evenly across the board before you start, and keep track of how much time you spend on each question. It may seem counterintuitive to add to the pressure, but in setting yourself a time frame, you eliminate the risk of dedicated excessive attention to any one part of the test.
For further advice, check out our full set of tips for Watson Glaser tests .
Practice Aptitude Tests is not associated with Watson Glaser. We provide preparation services for Watson Glaser psychometric tests. Our tests are not designed to be identical to any style, employer or industry. Visit https://www.talentlens.co.uk/product/watson-glaser/ to find out more.
Sample Watson Glaser Tests question Test your knowledge!
What can be inferred from the following statement? 'Despite increased competition, sales figures for Company Y have improved.'
- Increased competition has had a direct negative effect on sales figures.
- Company Y has possibly employed successful strategies to overcome competitive challenges.
- The overall market has been declining.
- Company Y's products are unaffected by competition.
Which of the following conclusions can logically be drawn from the information given? Despite its small size, Company X is the market leader in its segment.
- Company X's market segment prefers quality over size.
- Company X has a larger market share in its segment than its bigger competitors.
- The size of a company is not related to its market leadership.
- Company X is the smallest company in its market segment.
After reading the passage, what is the author's main argument?
- Traditional education systems are adequate to meet current workforce needs.
- Workplaces need to ensure their employees are consistently learning to keep up with technological changes.
- Technological innovation has little impact on the skills required by the workforce.
- Education systems are evolving faster than workplaces can keep up.
Which assumption is implicit in the following statement? 'We expect our customer base to double when we expand our services internationally.'
- International markets are eager for the company's services.
- The company has conducted ample market research on international markets.
- The company's services are currently not available internationally.
- Customers are dissatisfied with the current services.
Evaluate the strength of the given argument: 'Since implementing the new safety protocol, our factory has seen a 30% reduction in workplace injuries.'
- The new safety protocol is ineffective and should be reviewed.
- The 30% reduction in workplace injuries can be solely attributed to the new safety protocol.
- The factory should promote the person responsible for the new safety protocol.
- The new safety protocol may have contributed to the reduction in workplace injuries.
Start your success journey
Access one of our Watson Glaser tests for FREE.
The tests were well suited to the job that I’ve applied for. They are easy to do and loads of them.
Sophie used Practice Aptitude Tests to help pass her aptitude tests for Deloitte.

Hire better talent
At Neuroworx we help companies build perfect teams

Watson Glaser Tests Tips
1 understand the test structure.
Before you dive into practicing for the Watson Glaser tests, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with their structure. These tests aim to assess critical thinking skills across a range of areas, which TalentLens categorizes as ‘select’, ‘develop’, and ‘engage’. By understanding the types of questions and sections you will encounter, you can tailor your test preparation strategy effectively.
2 Focus on Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is at the heart of Watson Glaser tests. It’s not just about what you know but how you apply your knowledge to analyze, evaluate, and make decisions. Spend time honing your reasoning skills—practice breaking down complex information into manageable parts and consider arguments from multiple perspectives.
3 Manage Your Time Wisely
Like many aptitude tests, the Watson Glaser tests require you to balance accuracy with speed. Practice managing your time efficiently so you can give each question the attention it deserves while ensuring you complete the test within the allotted time frame. Use timers in your practice sessions at Practice Aptitude Tests to simulate real test conditions.
4 Sharpen Your Reading Skills
Reading comprehension is essential for Watson Glaser tests, as you’ll need to interpret written material quickly and accurately. Practice reading dense and challenging texts to improve your absorption and analysis capabilities. The key here is to not only understand the passages but also to critically evaluate them.
5 Stay Calm and Confident
Test anxiety can affect your performance. Remember to stay calm, take deep breaths, and approach each question with confidence. Regular practice at Practice Aptitude Tests will help build your familiarity with the question types and format, which in turn will boost your test-taking confidence.
Prepare for your Watson Glaser Test
Immediate access. Cancel anytime.
- 30 Numerical reasoning tests
- 30 Verbal reasoning tests
- 30 Diagrammatic reasoning tests
- 30 Situational judgement tests
- 34 Publisher packages e.g. Watson Glaser
- 252 Employer packages e.g. HSBC
- 29 Extra packages e.g Mechanical
- Dashboard performance tracking
- Full solutions and explanations
- Tips, tricks, guides and resources
- Access to free tests
- Basic performance tracking
- Solutions & explanations
- Tips and resources
Watson Glaser Tests FAQs
How does watson glaser define critical thinking.
According to the methodology behind Watson Glaser tests, critical thinking is the ability to observe a scenario and consider it from various perspectives, whilst identifying what is fact, what is assumed and what is mere opinion. In doing so, you should be able to draw logical conclusions and use these for informed decision making.
How can I improve my critical thinking skills?
Critical thinking is a part of our daily lives; we’re just not always aware that we’re doing it. To improve your skills, tune in to the world around you, ask questions, read actively and look for evidence in every statement or argument you come across. Take practice tests regularly to assess your progress.
Is the Watson Glaser test hard?
Watson Glaser tests are considered among the most challenging of all critical thinking assessments, since they test five separate aspects of logical reasoning ability . Time constraints also add to the pressure. That said, they are typically no harder than the careers for which they test your suitability, and with dedicated practice, you can hone your skills and make critical thinking second nature.
Where can I practice Watson Glaser tests?
There are multiple online resources available to help you prepare for your Watson Glaser test, including our own free practice tests . We recommended you work through these questions to familiarise yourself with the format and improve your critical thinking skills.
Reviews of our Watson Glaser tests
What our customers say about our Watson Glaser tests
Jozef Bailey
United Kingdom
April 05, 2022
Doesn't cover all aspects of Watson-Glaser tests but useful
The WGCTA uses more categories to assess critical thinking, but this was useful for the inference section.
April 01, 2022
Just practicing for an interview
Good information and liked that it had a countdown clock, to give you that real feel in the test situation.
Jerico Kadhir
March 31, 2022
Aptitude test
It was OK, I didn't understand personally whether or not the "cannot say" option was acceptable or not in a lot of the questions, as it may have been a trick option.
Salvarina Viknesuari
March 15, 2022
I like the test because the platform is simple and engaging while the test itself is different than most of the Watson Glaser tests I've taken.
Alexis Sheridan
March 02, 2022
Some of the ratios were harder than I thought!
I like how clear the design and layout is - makes things very easy (even if the content itself is not!)
Cyril Lekgetho
February 17, 2022
Mental arithmetic
I enjoyed the fact that there were multiple questions pertaining to one passage of information, rather than multiple passages. However I would've appreciated a more varied question type.
Madupoju Manish
February 16, 2022
Analytics are the best questions
I like the test because of its time schedule. The way the questions are prepared makes it easy to crack the original test.
Chelsea Franklin
February 02, 2022
Interesting
I haven't done something like this for ages. Very good for the brain - although I certainly experienced some fog whilst doing it.
January 04, 2022
Population/exchange rates were the hardest
Great test as it felt a bit time pressured. Very different types of questions in terms of difficulty.
faezeh tavakoli
January 02, 2022
More attention to detail + be more time conscious
It was asking about daily stuff we all deal with, but as an assessment it's scrutinising how we approach these problems.
By using our website you agree with our Cookie Policy.

What Is Critical Thinking?
Why is critical thinking important to potential employers, how to prepare for a watson glaser test in 2024, tips to pass the watson glaser test, frequently asked questions, watson-glaser critical thinking test (2024 guide).
Updated May 8, 2024

All products and services featured are independently selected by WikiJob. When you register or purchase through links on this page, we may earn a commission.
The Watson Glaser critical thinking test , initially developed by Goodwin Watson and Edward Glaser and now published by Talentlens/Pearson, is designed to assess an individual’s ability to digest and understand situations and information.
It is a psychometric test often used by organisations where the ability to critically consider arguments or propositions is particularly important, such as law firms .
Most people complete the Watson Glaser test within 50 minutes (approximately 10 minutes per sub-test). Tests administrators normally allow candidates one hour to complete the test.
The Watson-Glaser test has been co-normed on a sample of over 1,500 respondents representative of graduate-level candidates. You will be judged against this respondent group when you sit the test.
You can practise realistic Watson Glaser Tests here .
Get Our Watson Glaser Practice Test with TestHQ
Critical thinking is the ability to logically and rationally consider information.
Rather than accepting arguments and conclusions presented, a person with strong critical thinking will question and seek to understand the evidence provided.
They will look for logical connections between ideas , consider alternative interpretations of information and evaluate the strength of arguments presented.
Everyone inherently experiences some degree of subconscious bias in their thinking. Critical thinking skills can help an individual overcome these and separate out facts from opinions.
The Watson Glaser critical thinking appraisal is based around the RED model of critical thinking:
Recognise assumptions . This is all about comprehension. Actually understanding what is being stated and considering whether the information presented is true, and whether any evidence has been provided to back it up. Correctly identifying when assumptions have been made is an essential part of this, and being able to critically consider the validity of these assumptions – ideally from a number of different perspectives – can help identify missing information or logical inconsistencies.
Evaluate arguments . This skill is about the systematic analysis of the evidence and arguments provided. Being able to remain objective, while logically working through arguments and information. Critical evaluation of arguments requires an individual to suspend their judgement, which can be challenging when an argument has an emotional impact. It is all too easy to unconsciously seek information which confirms a preferred perspective, rather than critically analyse all of the information.
Draw conclusions . This is the ability to pull together a range of information and arrive at a logical conclusion based on the evidence. An individual with strong critical thinking skills will be able to adjust their conclusion should further evidence emerge which leads to a different conclusion.
Critical reasoning tests are a common feature of the job application process in many different industries.
Critical thinking is important to employers because individuals who engage in quality thinking make better decisions. They arrive at conclusions which are impartial, well informed and objective.
Furthermore, such people are able to make decisions with limited supervision, enabling them to independently make judgements: in a world where time can be money, waiting for someone else to validate decisions can be costly and result in missed opportunities.
Practice Watson Glaser Test with TestHQ
What Is Involved in the Watson Glaser Test?
The Watson Glaser test evaluates a candidate’s critical thinking ability in five separate areas:
- Recognition of Assumptions
- Interpretations
- Evaluation of arguments
Each of these skills is tested separately and there are therefore five different types of questions in the Watson Glaser test. We will explore each of these below.
1. Inferences
An inference is a conclusion based on evidence and reasoning . It enables conclusions to be drawn that are not explicitly stated. For example, if we see someone driving a Ferrari we may conclude that they are wealthy.
However, there are a number of alternative explanations: they may have rented or borrowed the car, or they may have acquired huge debt as a result of buying the car.
The problem with inferences is that people often reach a conclusion based on insufficient data, and the conclusion may not, therefore, be correct.
An inference question typically involves a statement (which you are to assume is true) and a number of inferences based on that statement. Your job is to evaluate whether the inference is correct. You can do this using both the information contained within the passage and information which is commonly accepted knowledge or information that practically every person has.
You will be given five potential responses and you have to select which you feel is most accurate. These options are:
- Definitely True – from the facts given there is no reasonable possibility of it being incorrect.
- Probably True – in light of the facts given, it is more likely to be true than false.
- Insufficient Data – in light of the facts given it is impossible to say whether it is true or not.
- Probably False – in lights of the facts given, it is more likely to be false than true.
- Definitely False – from the facts given, there is no reasonable possibility of it being true.
Example Question
If you need to prepare for a number of different employment tests and want to outsmart the competition, choose a Premium Membership from TestHQ . You will get access to three PrepPacks of your choice, from a database that covers all the major test providers and employers and tailored profession packs.
Get a Premium Package Now
2. Recognition of Assumptions
An assumption is something we take for granted. An example might be: “When I retire I will receive a final salary pension”. This assumes that you will get to retire, that you will be alive at retirement age, that your pension fund performs well, and that your pension arrangements will not change.
People make many assumptions which may not necessarily be correct; being able to identify these is a key aspect of critical thinking.
An assumption question typically involves a statement and a number of assumptions. Your job is to identify whether an assumption has been made or not, and you will have a choice of two answers: yes or no.

3. Deductions
A deduction is the drawing of a conclusion in a particular instance, by referring to a general law or premise. However, there may be occasions when such deduction is incorrect.
For example, in the statement: "Satsumas, oranges and clementines are all citrus fruits. They are all orange; therefore all citrus fruits are orange." Clearly this is incorrect.
The deduction section will include a statement (which you must assume is true), followed by a number of potential conclusions.
Your job is to identify whether the conclusion logically follows from the given statement and you will have two options: yes or no.
4. Interpretation
An interpretation is an evaluation of whether a conclusion can logically follow from the information or evidence provided. This requires an individual to understand the precise meaning or significance of a piece of information and applying this information appropriately.
For example, if you are told in a study that the wavelength of light visible to the human eye range from 380–750 nm, you can conclude that no humans can see light at 30 nm.
5. Evaluation of Arguments
This set of questions examines your ability to evaluate the strength of an argument.
You might be faced with strong arguments or weak arguments, and to be strong an argument must be important and directly related to the question.
In these questions, you will be presented by a statement followed by a number of arguments (which you should assume are true) and you must then decide whether each argument is strong or weak.
Take a Free Practice Watson Glaser Test If you would like to practise a simulation Watson Glaser test, please try the one below, which was created by TestHQ in association with psychometric experts, and is closely modelled on real tests. The test consists of 10 questions to be answered in 10 minutes approx (although there is no timer on the test itself). Our test is slightly harder than the real thing, in order to make it sufficiently challenging practice. You need to get 70% correct to pass the test. Don't forget to first check out the test techniques section further down this page beforehand. You can take the test as many times as you like. Click the 'Take test' link below to get started.
Watson Glaser Test By Our Partner TestHQ
A Watson Glaser test is designed to assess your ability to digest and understand situations and information; it is frequently used by law firms. Try these 15 questions as an introduction.
Get Our Watson Glaser Practice with Free Tests
Step 1 . Practice Critical Thinking
Critical thinking ability can be significantly improved by practice . It is a skill that can be learned, although it does come more easily to some people than others.
Look for opportunities to think critically about information every day. Once you start practising, you’ll find useful material everywhere: blog posts, newspapers, and journal articles are great places to look.
It can be useful to organise your thinking and practice around the RED model mentioned earlier in the article:
Recognise assumptions . Practise identifying the assumption made in the material. What can be objectively proven and what is inferred? Where might there be gaps in your logic? What information is important and relevant, and what isn’t? What is missing? Is there any information that needs to be included which isn’t?
Evaluate arguments . Practice carefully analysing the arguments presented. What is your perspective on the evidence? Could someone else have a different perspective? Consider the impacts of the arguments from a range of different viewpoints (it can be useful to use a model like PESTLE – political, economic, socio-demographic, technological, legal and environmental – to organise your thoughts). How would someone argue against your position? What merits are there to their arguments?
Draw conclusions . After you have considered all of the facts, what is the best possible conclusion? Could there be any other conclusions? What new information might change your conclusion? Does this conclusion seem sensible based on your common sense and experience? What are the implications of this conclusion?
Step 2 . Develop Self-Awareness
It is also useful to develop your self-awareness. Understanding your biases and thinking patterns can help you identify where your thinking might be limited.
In most of these critical thinking questions, you will need to analyse the text given to you without including any prior knowledge you have.
Step 3 . Take Practice Tests
Finally, take some practice questions .
It can be really helpful to work through some examples with explanations as you will really start to understand how they work and how to think through the questions and arrive at the correct answer.
Here are a few tips to help you prepare for and pass the Watson Glaser test:
Familiarize Yourself with the Test: Gain an understanding of the test format, question types and time constraints. Obtain practice materials, such as sample questions or practice tests, to become familiar with the style of questions and improve your performance.
Develop Critical Thinking Skills: Enhance your critical thinking abilities by practicing logical reasoning, analyzing complex information, evaluating arguments and drawing sound conclusions. Read articles, engage in debates and solve puzzles to sharpen your critical thinking skills.
Time Management: The Watson Glaser test is typically timed, so practice working under time constraints. Learn to allocate your time efficiently across the different sections and questions.
Read Instructions Carefully: Pay close attention to the instructions provided for each question. Understand what is being asked, and ensure you are addressing the specific requirements of the question.
Practice with Realistic Scenarios: The Watson Glaser test often presents scenarios that simulate real-life situations. Practice analyzing and evaluating arguments and making informed judgments based on the information provided.
Review Logical Fallacies: Familiarize yourself with common logical fallacies, such as false assumptions, weak correlations, and flawed arguments. Being aware of these fallacies can help you identify weaknesses in the arguments presented.
Remember that preparation is key to performing well on the Watson Glaser test.
By practicing, honing your critical thinking skills, and familiarizing yourself with the test format, you can increase your chances of success.
What is a good score on the Watson Glaser test?
There is no set pass or fail mark for the Watson Glaser test.
Each employer will have a different benchmark but it is sensible to aim for a score of at least 75%. To achieve this, you will need to correctly answer at least 30 of the 40 test questions.
The recruiting organization will use Watson Glaser test results to compare candidates within the selection pool. The higher your Watson Glaser test score, the better your employment prospects.
How is Watson Glaser scored?
Watson Glaser tests comprise 40 multiple-choice questions. Many questions have just two possible answers.
A test-takers score is used to work out their relative position within a norm group. Candidates with the highest relative Watson Glaser test score will progress to the next stage of the hiring process.
Watson Glaser test results are split into a development report and a profile report. Both reports are passed directly to the recruiting organization.
- The development report highlights strengths and areas for development.
- The profile report provides a percentile score, including the raw number of correct answers.
The Watson Glaser score system accounts for the difficulty level of each question, meaning candidates can earn more points for correctly answering a difficult question. The percentile score also considers the education level, occupation and position of the candidate’s norm group.
Is the Watson Glaser test free?
Watson Glaser test candidates are not required to pay a fee to take the test. The recruiting organization will need to pay a fee to use the Watson Glaser test within the hiring process.
Which firms require the Watson Glaser test?
Watson Glaser tests are a popular recruitment tool for law firms in particular, including Allen & Overy, Clifford Chance, Dentons and Linklaters.
What is a good score on the Watson Glaser Test?
The Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal is typically scored on a scale from 0 to 100, with a higher score indicating a better performance.
However, what constitutes a 'good' score can vary depending on the context and the specific requirements of the employer or organization using the test.
Generally, a score above 70 is considered a strong performance, demonstrating strong critical thinking skills and the ability to analyze and evaluate complex information effectively.
What employers use the Watson Glaser?
The Watson Glaser test is widely used by employers across various industries to assess critical thinking skills and decision-making abilities of job candidates.
It is commonly utilized in the fields of law, finance, consulting, business, and other roles that require strong analytical and problem-solving capabilities.
Many law firms, financial institutions, consulting firms and large corporations incorporate the Watson Glaser test into their selection processes.
Versions and forms of the Watson Glaser Test
The Watson Glaser test has different versions and forms available, depending on the specific needs of employers.
These variations may include different question formats, content areas, or levels of difficulty. Some commonly used versions include the Watson Glaser Form A, Form B and Form S.
The different forms may contain different question types, such as arguments, deductions, interpretations and evaluations, but they generally assess similar critical thinking skills.
You might also be interested in these other Wikijob articles:

Or explore the Aptitude Tests / Test Types sections.

How to Prepare and Pass the Watson-Glaser Test

In the following article, we will explore one of the most challenging pre-employment tests in the UK and worldwide – the Watson Glaser test – which is most commonly used for recruitment in the legal sector.
Included are an overview of the test, its main challenges, and how to overcome them with effective practice methods. The article also features two brief introductory videos:
Video #1 – Structure, content, and practice tips
Video #2 – Step-by-step solutions to five Watson Glaser sample questions, to exemplify the rules and requirements of the test.
What Is the Watson Glaser Test?
The Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (WGCTA) is a pre-employment test used primarily in the law industry. Some of the major employers using the test are Linklaters, Clifford Chance, Hogan Lovells, and the Government Legal Service. The test assesses your critical thinking – namely, your ability to analyse and interpret verbal information, draw conclusions, evaluate arguments, etc.
The test contains 40 questions divided into 5 sections, each one assessing a different aspect of critical thinking:
- Recognition of Assumptions
- Interpretation
- Evaluation of Arguments
Visit the Complete Watson Glaser Test Guide for a full overview of the test sections and content, including sample questions and a free sample test.
The Watson Glaser Test Guide
Check out the following 3.5-minutes video for a complete overview of the Watson Glaser test:
What Are the Main Challenges of the Watson Glaser Test and How to Overcome Them?
The Watson Glaser test is indeed considered a difficult test, designed with very specific rules, and often requiring counterintuitive solving methods. And yet, with a good understanding of the three main challenges of the test and the ways to overcome them, you CAN improve your score and get the offers you want. Let’s see how:
Challenge #1 – A Single Trait Measured
The Watson Glaser test is aimed at assessing one thing only – your critical thinking. It does so in five different ways and being successful on all of them is the best guarantee to passing the test.
Overcoming Challenge #1 – Prepare for Test Sections as They Are
You have a test, so prepare for the test.
Learn how the Watson Glaser test questions look like, and practise that.
Once you have a grasp of the test, you can certainly construct your own practice plan using open sources. However, structured preparation plans such as JobTestPrep’s Watson Glaser Preparation Pack make it much easier, with practice material replicating the actual test’s rules and formatting.
Challenge #2 – A Unique Set of Rules
The Watson Glaser has its own set of rules, unparalleled by any other critical thinking test. For example:
- Generalisation equals existence
- “Probably True” and “Probably False” answer choices.
This makes the Watson Glaser test a unique, tailored testing experience, which requires a tailored preparation plan.
Overcoming Challenge #2 – Learn to Let Go
A major part of your preparation will be to uproot all your misconceptions about how to solve critical thinking questions and to learn how to ignore any irrelevant information. This may be the hardest part of you preparation. You will learn to go against what you believe to be true, just to get the question right. To beat your competitors, you must think like the test does and not like you do.
Want to see the test rules in action? Watch the following video , where we explain the logic behind five sample Watson Glaser questions, one of each category.
Challenge #3 – Intuition and Knowledge Will Fail You
The Watson Glaser test uses a collection of tactics to constantly elude, distract, and mislead you with near-correct answers. To avoid these pitfalls, you must understand the exact rules of the test and disregard anything else.
Up for the challenge? Try a 7-minutes free Watson Glaser sample test
Overcoming Challenge #3 – Develop Thinking Algorithms
One of the best ways to make sure you set your own beliefs and opinions aside is developing thinking algorithms – a methodical series of simple Q&As that lead you to the correct answer. For instance:
- Evaluation of Arguments– ITDN table
- Recognition of Assumptions – The Negative Test
- Inference – Common Inference vs. Common Knowledge
With some focused practice, thinking algorithms will replace your intuition and personal knowledge as your main critical thinking tool.
This article was written by Shlomik Silbiger, JobTestPrep’s expert on the Watson Glaser test. If you have any questions, contact [email protected]
Free access to JobTestPrep for Oxford University students
As an Oxford University student, you can get free access to JobTestPrep via the Careers Service to practise for a wide variety of online recruitment tests, including Watson Glaser CTA, e-tray exercises and assessment centres as well as numerical-, verbal- and spatial-reasoning tests. Find out how you can gain access >>
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
A Short Guide to Building Your Team’s Critical Thinking Skills
- Matt Plummer

Critical thinking isn’t an innate skill. It can be learned.
Most employers lack an effective way to objectively assess critical thinking skills and most managers don’t know how to provide specific instruction to team members in need of becoming better thinkers. Instead, most managers employ a sink-or-swim approach, ultimately creating work-arounds to keep those who can’t figure out how to “swim” from making important decisions. But it doesn’t have to be this way. To demystify what critical thinking is and how it is developed, the author’s team turned to three research-backed models: The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment, Pearson’s RED Critical Thinking Model, and Bloom’s Taxonomy. Using these models, they developed the Critical Thinking Roadmap, a framework that breaks critical thinking down into four measurable phases: the ability to execute, synthesize, recommend, and generate.
With critical thinking ranking among the most in-demand skills for job candidates , you would think that educational institutions would prepare candidates well to be exceptional thinkers, and employers would be adept at developing such skills in existing employees. Unfortunately, both are largely untrue.
- Matt Plummer (@mtplummer) is the founder of Zarvana, which offers online programs and coaching services to help working professionals become more productive by developing time-saving habits. Before starting Zarvana, Matt spent six years at Bain & Company spin-out, The Bridgespan Group, a strategy and management consulting firm for nonprofits, foundations, and philanthropists.
Partner Center
- Numerical Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning
- Inductive Reasoning
- Diagrammatic Reasoning
- Logical Reasoning
- Mechanical Reasoning
- Situational Judgement
- Deductive reasoning
- Critical thinking
- Spatial reasoning
- Error checking
- Verbal comprehension
- Reading comprehension
- Psychometric tests
- Personality test
- In-Tray exercise
- E-Tray exercise
- Group exercise
- Roleplay exercise
- Presentation exercise
- Analysis exercise
- Case study exercise
- Game based assessments
- Competency based assessment
- Strengths based assessment
- Strengths based interview
- Video interview
- Saville Assessment
- Talent Q / Korn Ferry
- Watson Glaser
- Test Partnership
- Clevry (Criterion)
- Criteria Corp
- Aon / Cut-e
- Sova Assessment
- For Practice
- For Business
Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Tests
Complex and challenging critical thinking tests, including the Watson-Glaser, are used mostly by law firms.
Page contents:
About critical thinking tests and how they work, free practice critical thinking tests, the watson glaser critical thinking appraisal, what is measured by a watson glaser critical thinking test, what should i know before taking a watson glaser critical thinking test, major publishers' critical thinking tests, advice for all critical thinking tests, assessmentday's practice tests can help you to prepare for a critical thinking test, one final point, other test publishers.
Updated: 08 September 2022
Critical thinking tests, or critical reasoning tests, are psychometric tests used in recruitment at all levels, graduate, professional and managerial, but predominantly in the legal sector. However, it is not uncommon to find companies in other sectors using critical thinking tests as part of their selection process. This is an intense test, focusing primarily on your analytical, or critical thinking, skills. Some tests are still conducted by paper and pen, but, just like other psychometric tests, critical thinking tests are mostly administered online at home or on a computer at a testing center.
The questions are multiple choice, and these choices and the style of questions are explained in more detail further down the page. The tests will often follow these two common timings:
- 30 questions with a 40 minute time limit
- 80 questions with a 60 minute time limit
Critical Thinking can be defined in many ways and an exact description is disputed, however, most agree on a broad definition of critical thinking, that 'critical thinking involves rational, purposeful, and goal-directed thinking...by using certain cognitive skills and strategies.' An absence or lack of critical thinking skills at times may lead us to believe things which aren't true, because we haven't sufficiently analysed and criticized the information we've received or used this to formulate and independently test our own theories, arguments and ideas. These are all examples of critical thinking skills put into practice. Glaser (An Experiment in the Development of Critical Thinking, 1941) stated that to think critically involved three key parts:
- An attitude of being disposed to consider in a thoughtful way the problems and subjects that come within the range of one's experiences
- Knowledge of the methods of logical inquiry and reasoning
- Some skill in applying those methods
Note: AssessmentDay and its products are not affiliated with Pearson or TalentLens. Our practice tests are for candidates to prepare for the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal; we do not sell tests for employers to select candidates.
Free Critical Thinking Test
Here, we have a full critical thinking test for you to practice for free. You can dive straight in and practice the full test (in blue at the bottom), or tackle each individual section one at a time.
All answers and explanations are included at the end of the test, or alternatively you can download the Solutions PDF. Each test has been given a generous time limit.
Critical Thinking Test 1
- 40 questions
Critical Thinking Test 2
Critical thinking test 3, critical thinking test 4.
TalentLens' Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (WGCTA) is the most common critical thinking test. You can visit their official site here: Watson Glaser . Most other critical thinking tests are based on the Watson Glaser format. More than 90 years' of experience have led to many modifications and improvements in the test.
The Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal is widely regarded as a good predictor of work productivity and at identifying candidates with a good potential to become managers and occupy other positions as a senior member of staff. The latest edition of the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Test has improved its validity, appealed more to businesses by focusing on business-relevant topics, switched to the Item Response Theory (IRT) for its scoring, updated norm groups, and integrated anti-cheat measures by having an online retest, which can be used to validate results.
Developed by Goodwin Watson and Edward Glaser, the Watson Glaser test is favored by law firms , keen to measure people's abilities to reason, reach conclusions and know when leaps in logic have been made. Skills which are required in the legal sector. The questions in each of the 5 sections aims to evaluate the candidate's ability to:
- 1. Arrive at correct inferences
- 2. Identify when an assumption has been made
- 3. Use deductive reasoning
- 4. Reach logical conclusions
- 5. Evaluate the effectiveness of arguments
Did You Know
The most recent revision of the W-GCTA was published in 2011 with notable improvements being better face validity and business-relevant items, scoring based on Item Response Theory (IRT), updated norm groups, and an online retest which can be used to validate a paper and pencil test result.
A Critical thinking tests assesses your ability in 5 key areas mentioned above; assumptions, arguments, deductions, inferences and interpreting information. Often in this order. A short paragraph of text a few sentences long or a single sentence is used as a starting point. This passage will contain information which you will base your answer to the question on. Another sentence is then presented to you and you will be asked to judge something about this sentence based on the information in the short paragraph. The five sections are explained in more detail here:
- Assumptions - You are being asked to state whether the information in the second set of text you are presented is an assumption made in the first paragraph. Quite a tricky concept to get your head around at first. In a nutshell, when people speak or make arguments, there are underlying assumptions in those arguments. Here you are presented with some assumptions and are asked to judge if that is being made in the original statement. For example in the statement "only people earning a high salary can afford a fast car," what's being assumed is that fast cars are expensive because only people who are earning a lot of money can buy one, however, what's not being assumed is that people without high salaries aren't legally allowed to buy a fast car. You are asked to choose whether an assumption has been made or has not been made.
- Arguments - You are presented with an argument, such as "Should college fees be abolished?" Regardless of your own opinions and thoughts on the argument, you are then presented with statements related to this original argument. You are asked to say whether the responses to the original argument of "Should college fees be abolished?" make for strong or weak arguments. Arguments are considered strong if they are related to the topic such as, "Yes, many people who would benefit from a college education do not because they cannot afford it. This hurts the country's economic growth." The argument presented is sound, related to the original question. Compare this with a weak argument, "No, I do not trust people who read a lot of books." It is clear that the second argument bears very little relation to the subject of the abolition of college tuition fees. This is not to say that an argument against the original argument will always be a weak one, or that an argument in favor will always be a strong one. For example, "Yes, I like people that read books," is in favor of the abolition as indicated by "yes," but that person's like or dislike of others that read books isn't related, or hasn't been explained how it's related to removing the fees. Carefully considering what is being said, remove it from your own personal opinions and political views to objectively analyse what someone else has put forward.
- Deductions - A few sentences of information are presented to you. Another separate short statement will also be shown to you, which is supposed to represent a conclusion that someone has reached. You will have to determine whether this conclusion logically follows from the information given to you. Can the statement be deduced from the information available>? If so, and without a doubt, then the conclusion follows, if not, then the conclusion does not follow. Your decision must be based on the information given and not from your own knowledge.
- Inferences - A short scenario is described to you, followed by possible inferences. The inferences are short statements. Imagine that these are what people have said is inferred from the scenario. Use your judgement and the short scenario to assess whether what's being said has actually been inferred from the passage and the likelihood of this inference. You are asked to rank each inference as either 'true,' 'false,' 'possibly true,' 'possibly false.' For some proposed inferences there isn't enough information to say either 'true' or 'false' so a fifth option is included; 'more information required.' You can only select one option from the five.
- Interpreting Information - Following a similar format to the previous four sections, a short passage of information and then a series of statements are shown to you. You are asked to judge whether the information in the passage can be interpreted as the statements suggest. The answer options are straightforward here; you either select 'conclusion follows,' or 'conclusion does not follow,' depending on whether or not you believe that the statement can be logically reached from the information given. Again, for this section and all others, you are to base your choice of answer on what you're given, not on any specialized knowledge you might have.
If a watson glaser critical thinking test is used in the early stages of the application process it's likely to be used as a screening tool. This puts some pressure on candidates to meet a minimum pass mark, which will allow them to be selected to go on to the next stage of the selection process. If it's used at a later stage in the process, the results from this will be combined with performance in other assessments, tests, exercises and interviews. All the information you need to answer the questions will be in the test. Below the details of a few companies' critical thinking tests are pointed out.
Here is a list of critical reasoning tests on the market at present, which candidates may be likely to encounter for recruitment, selection or development.
- W-GCTA - The Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal as it is formally called is the most ubiquitous critical thinking test out there. This is the one that you are most likely to encounter.
- GMAT - The general management aptitude test, used by business schools and colleges test students' critical thinking ability. The critical thinking questions are written in a business or finance context.
- SHL - SHL have produced the Critical Reasoning Test Battery composed of 60 critical reasoning questions with a strict time limit of 30 minutes.
- Cornell - Cornell have developed a critical thinking test to be used in educational environments. The two levels, X and Z, are aimed at children and adults, respectively.
- Area-specific - There are tests which focus on either numerical critical reasoning skills and verbal critical reasoning skills. These tests will ask only numerical or only verbal questions to assess your skills in a specific area.
Here is some general advice to help you perform to the best of your ability for your critical reasoning test.
- No prior knowledge - The key point here is that critical reasoning tests are measuring your ability to think, or the method that you use to reach a conclusion. You should therefore not rely on prior knowledge to answer the question. Questions will be written so that you do not need to know any specialist knowledge to answer the question. For example, you will not be expected to know mathematical formulas or laws of nature and to answer questions with that information. If you are given the formula and its description in the questions, you are expected to use that information to reach the answer.
- Carefully read the instructions - There are 5 sections to most critical thinking tests and each will assess a slightly different skill. Make sure you have read the instructions and understand what it is you are expected to do to answer the questions for this section. There is quite a difference between the Assumptions section and the Deductions section for example. Applying the rules of one to the other would lead to just guessing the answers and making many mistakes.
- Keep your eye on the timer - These tests are complex. You might find yourself fixated on answering one question and taking up a lot of the time you are allowed. Checking how much time you have every so often can help you to more evenly distribute your time between the questions. This is done to avoid spending too much time on one question when that time would be better spent answering more or checking your answers. This time management applies to all tests, but is particularly important with Critical Thinking tests, as many people believe they have such a large amount of time, but underestimate the number of questions they have to answer.
- Logical fallacies - Identifying logical fallacies is key to many parts of this test, and researching the difference between sound and fallacious logic will prove helpful in a critical reasoning test. A fallacy is an error in reasoning due to a misconception or a presumption, and an argument which employs a formal fallacy, logical fallacy or a deductive fallacy in its reasoning becomes an invalid argument. Researching the different types of fallacy (i.e. red herring argument, straw man argument, confusing correlation and causation etc.) can help you spot these in the test and correctly answer the question.
The practice tests that we have cover all of the sections of the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking test and these overlap with many of the variations in Critical Thinking tests produced by major publishers. practice helps to increase your confidence, gives you a chance to learn from your mistakes in a risk-free environment, and can reduce stress before an exam.
The best place to get advice on taking a critical thinking tests is the test publisher's website, for example this one for the Watson Glaser .
If you have already successfully passed a few initial stages of the application process, it's unlikely that companies will focus solely on your results in the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking test when deciding whether or not to hire you. This type of selection by results on one test is more likely if it is part of the early stages of the process. However, towards the later stages the company will look at your results across interviews, group exercises, other aptitude tests and your résumé and will collate all of this information before reaching a decision. If you have been invited to undertake a critical reasoning test then the organisation clearly has an interest in hiring you, let that fact inspire confidence and perform to the best of your ability on your test, good luck!
You may also be interested in these popular tests sections.
- Practice Tests
- Predictive Index
- Firefighter
- Hogan Assessments
- Leadership Assessment
- GardaWorld Pre Board
- Criticall Dispatcher
- Ramsay Technician Course
- Watson-Glaser
- Cubiks Course
- NEO Personality Inventory
- Texas Success Initiative
- TSA Prep Booster™ Course
- TSA Practice Test
- TSA Written Skills Assessment
- TSA CBT X-Ray Object Recognition Test
- SHL Assessment Prep Course
- Practice Test & Answers
- SHL Practice Tests
- SHL Test Answers
- SHL Inductive Reasoning Test
- SHL Numerical Reasoning Test
- SHL Verbal Reasoning Test
- SHL Verify G+ Test
- SHL Mechanical Comprehension Test
- SHL Situational Judgment Test
- SHL OPQ Personality Test
- Predictive Index Test Behavioral & Cognitive Assessment Course
- Predictive Index Cognitive Assessment Course
- Predictive Index Behavioral Assessment Course
- Predictive Index Practice Test
- Predictive Index Results
- Caliper Course
- Caliper Test Prep With Real Practice Test
- USPS Postal Exam
- Postal Exam 474
- Postal Exam 475
- Postal Exam 476
- Postal Exam 477
- USPS Postal Exam Prep
- Pass the 2024 Postal Exam With Practice Tests
- Virtual Entry Assessment (VEA)
- General Police Prep Course
- Police Situational Judgement Test
- Police Psychological Exam Course
- Massachusetts State Police Exam
- Pennsylvania Police Exam
- Philadelphia Police Exam
- Nassau County Police Exam Course
- Suffolk County Police Exam
- Correctional Officer Exam
- MTA Police Exam
- New York State Police Exam Prep Course
- School Safety Agent Course
- Police Officer NYPD Exam
- Police Fitness Prep Course
- Exam Formats
- EB Jacobs Law Enforcement Aptitude Battery
- CJBAT Study Guide
- DELPOE Police Exam
- Texas LEVEL Test With Expert Guides
- PELLETB Course
- FBI Test Phase 1 (Special Agent Exam): Guide with Practice Test [2024]
- Police Test Preparation Suite
- Pass a Polygraph Test (Lie Detector): Expert Tips & Questions – 2024
- Firefighter Aptitude and Character Test
- Firefighter Psych Test
- FCTC Firefighter Prep Course
- NFSI Firefighter Prep Course
- FireTeam Prep Course
- FDNY Firefighter Prep Course
- Firefighter Test
- Master Course
- Hogan Assessments Master Course
- Personality Courses
- Hogan Personality Inventory (HPI)
- Hogan Development Survey (HDS)
- Hogan Motives, Values & Preferences Inventory (MVPI)
- Busines Reasoning Course
- Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory (HBRI)
- Leadership Assessment Test
- GardaWorld Pre Board Primer
- Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test II (BMCT-II) Success Prep Course
- Beat the 2024 BMCT With Industry Expert Guides & Realistic Practice Tests
- 911 Dispatcher Course
- Criticall Dispatcher Course
- Criticall Dispatcher Test
- CCAT Course
- Beat the 2024 Criteria Cognitive Aptitude Test & Guide & Free CCAT Practice Test
- Criteria Pre-employment Testing: Personality, Aptitude & Skill Tests
- CRITERIA COGNITIVE APTITUDE TEST
- Korn Ferry Course
- Ace the 2024 Korn Ferry Assessment With Practice Test & Expert Guides
- Ramsay Electrical Course
- Ramsay Maintenance Course
- Ramsay Mechanical Course
- Ramsay Multicraft Course
- Ramsay Electrical Practice Test
- Ramsay Maintenance Practice Test
- Ramsay Mechanical Practice Test
- Ramsay Multicraft Practice Test
- Ramsay Test Prep
- SIFT Practice Test & Study Guide
- Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Course
Beat the Watson Glaser and Upgrade Your Career
- Take on the Watson Glaser and Secure your Future Career
- Cubiks Test: Guide on all Test Types and Free Cubiks Practice Test
- Cubiks PAPI Test: Focus Areas and Test Format (2024)
- Cubiks Assessment Test to Start Working at KPMG
- Texas Success Initiative Course
- TSI Practice Test 2024: Math, Reading & Writing
- TSI Reading Practice Test: 15 Q&A with Explanations
- Pass our Free TSI Math Practice Test (2024 Update)
- Take our Free TSI Writing Practice Test (2024)
- How it Works
Prepare for the Watson Glaser with industry expert-made guides and realistic practice test, and show prospective employers that you’re the right choice.
The Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (WGCTA) is the first step you will need to take when applying for many high-profile job positions. This is especially common with legal professional and managerial jobs. High performance on the Watson Glaser critical thinking test demonstrates to prospective employers that you’re the best fit for the job, both in skill set & competence.
The Watson-Glaser aptitude test is believed to be one of the most difficult and demanding tests on the psychometric test market, and proper prep is essential if you wish to stand a chance against other applicants who are vying for the same job. Prepterminal’s Watson Glaser Prep Course has been designed by industry experts to prepare you for this difficult exam so you can take on the real thing with confidence. Click on Get Started to begin your prep immediately or read on for further information.
What Is the Watson Glaser Test?
Created by Goodwin Watson and Edward Glaser, The Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal Test (WGCTA) evaluates and interprets the critical thinking skills of the test-taker.
Critical thinking assessments are psychometric tests used for recruitment at various levels including, professional, managerial, and graduate and are used in many sectors. However, they are most commonly seen in the legal field.
Employers use this test to measure the abilities of a candidate and to see how they understand arguments, identify assumptions, and form conclusions founded on those assumptions.
The Watson Glaser Test mainly assesses a candidate’s ability to think critically and analytically. For many applicants, this will cover topics they haven’t had to deal with in many years – preparation with Prepterminal’s Watson Glaser Prep Course provides an excellent summary of each topic covered with realistic practice questions and expert guides.
The Structure of the Watson Glaser Test
The Watson Glaser test consists of 40 questions. There is a timed version and an untimed version. Those taking the timed version have 30 minutes to finish the 40 questions.
The test is made up of 5 sections:
- Identification of assumptions
- Interpretation of information
- Assessment of arguments
All questions on the test have multiple-choice answers (five choices are given in the inference section and two choices are given in all the rest of the questions).
There are currently two available versions of the test:
- Watson-Glaser II forms D & E (computerized or pen & paper)
- Watson-Glaser III (only computerized).
The central difference between the two versions is that the Watson Glaser III uses an item bank of questions and doesn’t require a test officer.
The test can be taken offline or online, and keep in mind that no marks are taken off for choosing an incorrect answer.
Start preparing today by taking PrepTerminal’s Free Watson Glaser Practice Test.
Free arguments practice test questions, free inferences practice test questions, free recognizing assumptions practice test, free deduction practice test, free interpretation practice test, what’s included, quick online prep pack.
Get an immediate access to our advanced and adaptive learning software and get fully prepared to beat the Watson-Glaser within a few hours.
Top Quality Watson Glaser Materials
Prepare within a few hours, with the most up-to-date, accurate & effective Watson-Glaser prep materials.
Watson-Glaser Practice Tests
3 timed, full-length Watson Glaser-style practice tests with 10 module quizzes.
Watson-Glaser Expert Lessons
Quickly learn the best tactics for all 5 types of Watson-Glaser questions with fluff-free guides and practice on any device, 100% online.
Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Course Modules
- 1 Introduction Buy this Course: Get full access to all lessons, practice tests and guides.
- Evaluating Arguments - Written Guide
- Arguments Questions
- Arguments Questions 2
- Evaluating Assumptions - Written Guide
- Assumptions Questions
- Assumptions Questions 2
- Evaluating Deductions - Written Guide
- Deduction Questions Part 1
- Deduction Questions Part 2
- Evaluating Inferences - Written Guide
- Inferences Questions
- Inferences Questions 2
- Interpreting Information - Written Guide
- Interpreting Information Questions
- Interpreting Information Questions 2
- Watson Glaser Full Practice Test 1
- Watson Glaser Full Practice Test 2
- Watson Glaser Full Practice Test 3
- 8 BONUS Interview Prep Video Guide Buy this Course: Get full access to all lessons, practice tests and guides.
What does the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Test Measure?
The Watson Glaser test measures your abilities in 5 key areas: assumptions, arguments, deductions, inferences, and interpreting information. Let’s take a look at each of these question types individually.
You will be presented with a short scenario and then will be given possible inferences. The inferences are concise statements. You will need to assess whether these concise statements have been inferred from the passage.
You will also have to decide the likelihood of the inference. You will be asked to say if the inference is ‘true,’ ‘false,’ possibly true,’ ‘possibly false’ or ‘more information is required.’ You can only select one answer.
Identification of Assumptions
When people have discussions or present arguments, there are underlying assumptions in their arguments. In the test, you will be given an initial statement. You will also be presented with various assumptions. You will be asked to decide if the assumption is evident in the initial statement.
For example, in the statement “only people earning a high salary can buy a big house”, what is being assumed is that big houses are costly because only individuals who earn a high salary can purchase one. However, what’s not being assumed is that people who are not high earners aren’t legally permitted to buy a big house.
In these question types, it is your job to choose whether an assumption has or has not been made. You will need to answer: yes or no.
You will be given a few sentences of information. Another different short statement will also be presented to you, which is meant to be a conclusion that an individual has made. You will need to decide if the conclusion is logical, based on the information presented to you.
If yes, then the conclusion follows on from the information available. If no, then the conclusion does not follow on from the information given. You need to base your decision on the information given and not on your previous experience or knowledge.
Interpreting information
You will be presented with a passage of information and then will be shown various statements. You will be asked to decide whether the ‘conclusion follows,’ or ‘conclusion does not follow’. You choose one of these answers depending on whether or not you think that the statement can be logically arrived at from the information provided.
Here like before you need to base your answer solely on the information given to you in the question.
You will be given an argument, such as “Should school uniforms be compulsory?” You will then be given statements that relate to this argument. You are asked to state whether the statements or responses to the argument “Should school uniform be compulsory?” create a strong or weak argument.
Arguments are deemed strong if they directly relate to the topic. For example, “Yes, many people would benefit from wearing school uniforms because school kids will be less likely to form opinions about each other based on their choice of fashion. This makes for a less judgmental school environment.” The argument given is reasonable and relates to the question.
A weak argument could be something like “No, I don’t trust people who wear baggy clothes”. This second argument has little to do with the topic of making school uniforms compulsory. When you are presented with these questions you need to think objectively about the argument being made and put aside your personal judgments and opinions.
How is the Watson Glaser Test Scored?
A candidate’s score on the Watson Glaser test is given in comparison to a norm group.
A potential employer will compare and contrast the profile of all potential applicants. Applicants with the highest relative scores will pass the Watson Glaser test and likely move on to the next stage of the hiring process.
Doing well on the Watson Glaser test may not be enough, as candidates will have to do better than their competitors if they want to stand out.
A good score on the Watson Glaser test is dependent on the company a candidate is applying to. Ultimately, an applicant should aim to score 80% or more, to be considered a likely candidate for the job.
Practice is thus essential. Prepterminal’s Watson Glaser Test prep course provides Watson Glaser practice test questions and more.
Which Companies Use the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Test?
The top five companies that use the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal as part of their hiring process:
- Clifford Chance – Ranked among the top 10 multinational law firms, in the world, Clifford Chance is a key member of the “Magic Circle”.
- Linklater – Linklaters is a “Magic Circle” member and is one of the top three law firms in England.
- Dentons – This is a relatively young law firm. However, it has grown to be the 5th largest law firm – based on revenue.
- Hogan Lovells – This American-British law firm is the 11th largest international law firm.
- GLS – The British Government Legal Services hires lawyers who represent the government in court and give legal advice to the government.
- Clifford Chance – Ranked among the top 10 multinational law firms, Clifford Chance is a key member of the “Magic Circle”.
- Dentons – This is a relatively young law firm. However, it has grown to be the 5th largest law firm based on revenua.
How To Prepare For Watson Glaser Test: Top Tips
Answer solely based on the information provided.
Answer each question using only the facts and conditions given in the question itself. Do not use your own knowledge of the subject matter, even if you are well-versed in a particular area.
Read each question slowly and carefully
Some of the questions featured on the Watson Glaser Practice Test may be long, and you may want to skim through them. Refrain from doing so. If you quickly scan a question, you may skip over valuable information. Read each question thoroughly before choosing an answer.
Manage your time effectively
The Watson Glaser test features both long and short questions, so it may be hard to ascertain in advance how much time you need for each question. Nevertheless, the more you practice the more familiar you will become with the question types and the better you will be at pacing yourself.
Practice, practice, practice
To do well on this test you will need to practice. Take as many practice tests as you can so you can learn to anticipate the type and structure of the questions. This way you can approach the test with confidence.
How Difficult is the Watson Glaser Test?
As you have seen the Watson Glaser test is very tricky. It is especially hard for individuals who are not familiar with the question types.
Enrolling in Prepterminal’s preparatory Watson Glaser Test course with Watson Glaser Practice Test questions will help you become familiar with the structure and nature of the questions featured in this notoriously difficult test.
We will help you understand the specific nuanced rules of the Watson Glaser test and how to accept the statements presented to you in the test and more.
6 Benefits of Prepterminal’s Watson-Glaser Test Prep Course
- Learn how to think like the creators of the test require you to think.
- Understand how to base your judgments exclusively on the information given to you in the test.
- Understand the specific rules of the test.
- Learn how to accept statements presented to you in the test at face value.
- Practice using carefully crafted course material that covers the specific subject matter of the Watson Glaser test.
- Learn how to make decisions without being influenced by your past experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It’s 100% online and you get immediate access sent to your email as soon as you sign up. No books, No DVDs, No PDFs. You can study and practice on your computer or your phone. It works on any device with an internet connection!
Don’t worry – send an email to Matt, our Watson-Glaser expert, at [email protected] and he’ll be back to help you ASAP!
You’ll only be charged once for your course license. There are no recurring payments, and no hidden fees.

Created by: Matthew Appleyard
Psychometric tutor, prepterminal test expert, 6876 students, 4.8 , 1396 reviews.
I’m Matt, Prepterminal’s Watson-Glaser Test Prep Expert. Any questions about the course? Let me know at [email protected]
- Aptitude Tests Preparation
- Critical Thinking Tests
Critical Thinking Test Practice ▷ Free Critical Reasoning Samples & Tips 2024
Start Preparing for Your Critical Thinking Test. This page features a brief introduction, followed by question examples with detailed explanations, and a free test sample.
Table of Contents :
✻ What is a Critical Thinking Test ?
✻ Sample Questions
Related links
✻ Free Critical Thinking Practice Test
✻ Watson Glaser Practice Test
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking, also known as critical reasoning, is the ability to assess a situation and consider/understand various perspectives, all while acknowledging, extracting and deciphering facts, opinions and assumptions. Critical thinking tests are a sub-type of aptitude exams or psychometric tests used in pre-employment assessment for jobs reacquiring advanced analytical and learning skills.
The Skills You Will Be Tested On
Critical thinking tests can have 5 major sections or sub-tests that assess and measure a variety of aspects.
1) Inference
In this section, you are asked to draw conclusions from observed or supposed facts. You are presented with a short text containing a set of facts you should consider as true.
Below the text is a statement that could be inferred from the text. You need to make a judgement on whether this statement is valid or not, based on what you have read.
Furthermore, you are asked to evaluate whether the statement is true, probably true, there is insufficient data to determine, probably false, or false.
For example: if a baby is crying and it is his feeding time, you may infer that the baby is hungry. However, the baby may be crying for other reasons—perhaps it is hot.
2) Recognising Assumptions
In this section, you are asked to recognise whether an assumption is justifiable or not.
Here you are given a statement followed by an assumption on that statement. You need to establish whether this assumption can be supported by the statement or not.
You are being tested on your ability to avoid taking things for granted that are not necessarily true. For example, you may say, "I’ll have the same job in three months," but you would be taking for granted the fact that your workplace won't make you redundant, or that you won’t decide to quit and explore various other possibilities.
You are asked to choose between the options of assumption made and assumption not made.
3) Deduction
This section tests your ability to weigh information and decide whether given conclusions are warranted.
You are presented with a statement of facts followed by a conclusion on what you have read. For example, you may be told, "Nobody in authority can avoid making uncomfortable decisions."
You must then decide whether a statement such as "All people must make uncomfortable decisions" is warranted from the first statement.
You need to assess whether the conclusion follows or the conclusion does not follow what is contained in the statement. You can read more about our deductive logical thinking test resources here.
4) Interpretation
This section measures your ability to understand the weighing of different arguments on a particular question or issue.
You are given a short paragraph to read, which you are expected to take as true. This paragraph is followed by a suggested conclusion, for which you must decide if it follows beyond a reasonable doubt.
You have the choice of conclusion follows and conclusion does not follow.
5) Evaluation of Arguments
In this section you are asked to evaluate the strength of an argument.
You are given a question followed by an argument. The argument is considered to be true, but you must decide whether it is a strong or weak argument, i.e. whether it is both important and directly related to the question.
Create Your Own Assessment Prep Kit!
Job-seeking can be a long and frustrating process that can take several months. As part of this journey, you'll have to take a number of pre-employment tests or video interviews.
We've designed our Premium Membership to guide you through the entire journey:
Mix & match 3 PrepPacks of your choice at a 50% discount for 1 month / 3 months / 6 months.
Critical Thinking Question Examples
As there are various forms of critical thinking and critical reasoning, we've provided a number of critical thinking sample questions.
You can take our full Critical Thinking Sample Test to see more questions.

Example 1: Argument Analysis
Read the following:
In a recent study, anthropologists surveyed 250 adults who own pets and 250 adults who do not own pets on their interpersonal capacities. The questions asked of both those who own pets and those who do not own pets included tests for 'computational requirements', that is, tuning in to all the little signals necessary to operate as a couple. While members of each group displayed outstanding interpersonal capacities, in general, the adults who own pets were much more empathetic than those who do not own pets. This indicates that people who are especially empathetic are more likely to adopt a pet in spite of the personal sacrifice and the occasional inconvenience than people who are less empathetic.
Which of the following is true?
- Most of the people surveyed, whether they own pets or do not own pets, displayed outstanding interpersonal capacities.
- The adoption of a pet involves personal sacrifice and occasional inconvenience.
- People with high degrees of empathy are more likely to adopt pets than people with low degrees of empathy.
- Interpersonal capacities entail tuning in to all the little signals necessary to operate as a couple.
- A person's degree of empathy is highly correlated with his or her capacity for personal sacrifice.
The correct answer is C
Answer explanation: In a question of this type, the rule is very simple: the main conclusion of an argument is found either in the first or the last sentence. If, however, the main conclusion appears in the middle of an argument, it will begin with a signal word such as thus, therefore, or so. Regardless of where the main conclusion appears, the rest of the passage will give the reasons why the conclusion is true or should be adopted. The main conclusion in this passage is the last sentence, signaled by the words, 'This indicates that people who are especially empathetic are more likely to adopt a pet than people who are less empathetic'.
Example 2: Argument Practice
A: No. Differential bonuses have been found to create a hostile working environment, which leads to a decrease in the quality and quantity of products .
This argument is:
The correct answer is A (Strong)
Schema of the statement: Differential cash bonuses (productivity↑) → workplace↑
Explanation: This argument targets both the action and the consequences of the action on the object of the statement. It states that the action (implementing differential cash bonuses) has a negative effect on the workplace (a decrease in the quality and quantity of products). Therefore, it is an important argument, one that is relevant for the workplace. Note that this argument does not specifically target differential cash bonuses. Still, they are considered a sub-group of the subject of the argument (differential bonuses).
Example 3 – Interpretations
Proposed assumption: Vicki and Bill encountered a personal battle because they couldn’t come to terms with their disease.
A. Conclusion follows
B. Conclusion does not follow
The correct answer is B (Conclusion does not follow)
It is plausible that the reason people who suffer from sleep apnoea encounter a personal battle is because of an inability to come to terms with this disease. However, since the passage does not provide an actual reason, you cannot reach this conclusion without reasonable doubt.
The most common type of Critical Thinking Assessment is the Watson Glaser .
Difficult and time-pressured, the Watsong Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (WGCTA) takes a unique testing approach that breaks away from more traditional assessments. To see examples, check out our free Watson Glaser practice test .
Our expertly curated practice programme for the Watson Glaser will provide you with:
- A full-length diagnostic simulation
- Focused practice tests for the different test sections: inferences, assumptions, deductive reasoning, interpretations, and arguments.
- 3 additional full-length simulations
- Interactive tutorials
Or learn more about the Watson Glaser Test
Critical Thinking Tests FAQs

What critical reasoning test am I most likely to take?
Very Likely the Watson-Glaser test
Another popular critical thinking assessment, Watson-Glaser is a well-established psychometric test produced by Pearson Assessments.
The Watson-Glaser test is used for two main purposes: job selection/talent management and academic evaluations. The Watson-Glaser test can be administered online or in-person.
For Watson Glaser practice questions, click here !
What skills do critical reasoning test measure?
Critical Thinking can refer to various skills:
- Defining the problem
- Selecting the relevant information to solve the problem
- Recognising assumptions that are both written and implied in the text
- Creating hypotheses and selecting the most relevant and credible solutions
- Reaching valid conclusions and judging the validity of inferences
Pearson TalentLens condenses critical thinking into three major areas:
- R ecognise assumptions – the ability to notice and question assumptions, recognise information gaps or unfounded logic. Basically not taking anything for granted.
- E valuate arguments – the ability to analyse information objectively without letting your emotions affect your opinion.
- D raw conclusions – the ability to reach focused conclusions and inferences by considering diverse information, avoiding generalisations and disregarding information that is not available.
These are abilities that employers highly value in their employees, because they come into play in many stages of problem-solving and decision-making processes in the workplace, especially in business, management and law.
Why are critical thinking tests important to employers?
Critical thinking, or critical reasoning, is important to employers because they want to see that when dealing with an issue, you are able to make logical decisions without involving emotions.
Being able to look past emotions will help you to be open-minded, confident, and decisive—making your decisions more logical and sound.
What professions use critical thinking tests?
Below are some professions that use critical thinking tests and assessments during the hiring process as well as some positions that demand critical thinking and reasoning skills:
Preparation Packs for Critical Thinking & Critical Reasoning AssessmentsThe Critical Thinking PrepPack™ provides you with the largest assembly of practice tests, study guides and tutorials.Our tests come complete with straightforward expert explanations and predictive score reports to let you know your skill level as well as your advancement.By using our materials you can significantly increase your potential within a few days and secure yourself better chances to get the job.
Don't Leave the Preparation to Your Competition
Continue Your Practice Now

Money-Back Guarantee
Are you about to apply for a role in the finance industry?
Several major banking and consulting employers evaluate their applicants using critical thinking tests, among others. Visit your potential employer's page to understand better the tests you are about to face, and start preparing today!
HSBC | UBS | Bain & Co | Macquarie | Morgan Stanley | Barclays | EIB | Deloitte | Deutsche Bank | KPMG | PWC | Lazard | EY | Nomura | BCG | BNP Paribas | Jefferies | Moelis & Co
- Free Watson Glaser Test & Prep Guide
- Clifford-Chance Watson Glaser
- Dentons Watson Glaser Test
- Linklaters Watson Glaser Test
- Hogan-Lovells Watson Glaser
- Watson Glaser + RANA - Practice Bundle
- Watson Glaser Tailored PrepPack™
- AON Hewitt G.A.T.E.
- PI Cognitive Assessment (PLI Test)
- Korn Ferry Leadership Assessment
- Berke Assessment
- Ergometrics
- Thomas International
- Predictive Index (PI)
- NEO Personality Inventory
- Leadership Assessment
- Gallup’s CliftonStrengths
- Sales Personality Tests
- Personality Management Tests
- Saville Wave
- McQuaig Word Survey
- Bell Personality Test
- Myers Briggs Personality Test
- DISC Personality Test
- Management SJT
- Supervisory SJT
- Administrative SJT
- Call Center SJT
- Customer Service SJT
- Firefighter SJT
- Numerical Reasoning Tests
- Verbal Reasoning Tests
- Logical Reasoning Tests
- Cognitive Ability Tests
- Technical Aptitude Tests
- Spatial Reasoning Tests
- Abstract Reasoning Test
- Deductive Reasoning Tests
- Inductive Reasoning Tests
- Mechanical Reasoning Tests
- Diagrammatic Reasoning Tests
- Fault Finding Aptitude Tests
- Mathematical Reasoning Tests
- Critical Thinking Tests
- Analytical Reasoning Tests
- Raven’s Progressive Matrices Test
- Criteria’s CCAT
- Matrigma Test
- Air Traffic Controller Test
- Administrative Assistant Exam
- Clerical Ability Exam
- School Secretary Tests
- State Trooper Exam
- Probation Officer Exam
- FBI Entrance Exam
- Office Assistant Exam
- Clerk Typist Test
- Police Records Clerk Exam
- Canada’s Public Service Exams
- Firefighter Exams
- Police Exams
- Army Aptitude Tests
- USPS Postal Exams
- Hiring Process by Professions
Select Page
Critical Thinking Test: Online Preparation & Free Practice Questions – 2024

- Information
- Free Example Questions
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is a form of decision making and reasoning using data and observations. Someone who is a strong critical thinker can find quality solutions efficiently and can evaluate issues objectively.
What Is a Critical Thinking Test?
Critical thinking tests provide companies valuable insight into the leadership, reasoning, and overall capabilities of candidates. Because strong critical thinking skills are highly sought after, the critical thinking test can be applicable to any field and discipline across multiple levels of expertise from recent graduate to executive. However, it is commonly administered to those applying for criminal justice and business-related occupations.
Job seekers with upcoming critical thinking tests will be evaluated on more than their ability to rationalize, critical thinking tests also measure the following subsets:
- Organizing & Planning
- Strategizing
- Decision Making
- Problem Solving
The format of the critical thinking uses hypothetical scenarios to assess candidates. The scenarios are typically relevant to the field you are interested in to assess your knowledge of the role. There will also be general questions concerning more basic issues or problems that commonly occur in a workplace environment.
The critical thinking test is multiple-choice with thirty minutes to complete the assessment. Candidates will receive a notification stating whether or not they passed within a week of completion.
How Is the Critical Thinking Test Scored?
The critical reasoning test is scored based on your raw score and your percentile in comparison with your norm group. It’s important to note that these will not be the same number.
A norm group is a collection of scores from individuals in your field at your level of experience. The percentile score is used to alert employers if you exceed, meet or miss the benchmark for the average expectations of candidates. You will be rated on a scale of one to one hundred with fifty consisting of the mean and median scores.
A raw score is simply the number of correct answers. The critical thinking test comprises your raw score based on the performance in the following areas:
- Recognizing Assumptions The candidate must be able to understand when a statement is made with no supporting evidence and how this can affect a decision. Further, candidates are asked to identify these discrepancies, whether they are stated explicitly or implicitly, and assess its relevance to the given scenario.
- Evaluating Arguments Candidates must evaluate arguments without considering inferences or being subjective. Beyond that, candidates must assess the supporting evidence, the structure of the argument and the degree of its influence. It is very important to dismiss emotions for this portion of the critical thinking test.
- Drawing Conclusions Drawing conclusions puts a large emphasis on reasoning. In this section, it’s important to assess all of the available evidence and data to form a plausible conclusion that accurately applies to all the given information. Employers also want to see candidates that will consider all possible solutions rather than making the evidence fit a desired narrative.
Employers will receive all of this information in a performance report construed by the assessment company. Employers will also be given insight into your overall potential, job knowledge, creativity and job performance per the report.
Where Will I Take a Critical Thinking Test?
Critical thinking tests are non-proctored online assessments that are typically sent via email after an initial screening. For some occupations, the company may ask that the candidate take the critical thinking test again on-site either before their final interview or during an assessment day. The most common test candidates are asked to take is the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (WGCTA) created by the popular assessment company, Pearson . This assessment company is on their third edition with new scoring and subsets described above. The WGCTA gained popularity because of its ability to assess a candidate’s potential alongside their aptitude. Another established assessment is the SHL Critical Reasoning Battery that contains sixty questions with a thirty-minute time limit. Both of the aforementioned critical thinking tests are multiple choice.
How to Prepare for the Critical Thinking Test?
The critical thinking test is difficult to study for because the test is designed to assess your bare knowledge and raw skills. In order to prepare successfully, it is important to focus on the areas of the test that you can equip yourself for. One aspect of the test that demands preparation is the time limit. Many candidates’ scores are negatively impacted because they skip or guess too many of the questions in an attempt to beat the clock. If you want to optimize your chances of achieving a good score, use online practice tests to acquaint yourself with the time constraint and the general theme of the questions. By utilizing the online practice tests, you can find the pace that works best for you. Another helpful way to prepare is running through sample questions. This way, you can warm-up your brain and gain an understanding of the expectations that both the test and the company have of you.
Free Sample Questions to Practice
- Look over her past quizzes to see what she missed.
- Set aside more time during the week to review the material for the quiz.
- Get to class on early Wednesday and briefly look over the chapters.
- Get a good night’s sleep.
- Parents should find an alternative way to get their kids to school next week.
- The premiums must be over-priced.
- Collective bargaining is no longer a feasible solution.
- Their employers are being unreasonable.
- People in Hawaii dislike living on an island.
- Colder climates induce more happiness than warmer climates.
- The high scores on the Alaska survey were produced by people who enjoy snow.
- People in Hawaii should move to Alaska.
- Jenny’s credit card was declined at the mall.
- Jenny’s bank keeps charging her $30 overdraft fees.
- Jenny’s check bounced when she attempted to purchase a new TV.
- Jenny spends more money than she makes.
- Lori has thirty cans of soda in a refrigerator in her garage and another fourteen sitting on the counter. Lori does not have anymore cans of soda. Therefore, Lori has 44 cans of soda.
- The accounting department loves math. My friend works in the accounting department. My friend loves math.
- Everyone southbound on the freeway yesterday was late to work. Jackie was southbound on the freeway. Jackie was late to work.
- Adrian lives in either Springfield, California, or Springfield, Illinois. If he lives in Illinois, then he is an American.
Aptitude Tests
- Aptitude Tests Guide
- Numerical Reasoning Test
- Verbal Reasoning Test
- Cognitive Ability Test
- Critical Thinking Test
- Logical Reasoning Test
- Spatial Reasoning Test
- Technical Aptitude Test
- Inductive Reasoning Test
- Analytical Reasoning Test
- Deductive Reasoning Test
- Mechanical Reasoning Test
- Non-Verbal Reasoning Tests
- Diagrammatic Reasoning Test
- Concentration Assessment Test
- Finance Reasoning Aptitude Test
- Fault Finding (Fault Diagnosis) Test
- Senior Management Aptitude Tests
- Error Checking Tests
- In-Basket Exercise
Unfortunately, your browser does not meet our new security requirements. Before March 17, 2018, upgrade your browser to the newest version to avoid any interruption in accessing PearsonVUE.com.
This website is scheduled to undergo routine maintenance on Saturday, 11 May 8:00 p.m. CDT - Sunday, 12 May 1:00 a.m. CDT. During this time, you may not be able to schedule, reschedule or cancel test appointments. We apologize for this inconvenience and thank you for your patience.
This website is scheduled to undergo routine maintenance on Saturday, 20 January 5:00 p.m. CST - Sunday, 21 January 2:00 a.m. CST. During this time, you may not be able to schedule, reschedule or cancel test appointments. We apologize for this inconvenience and thank you for your patience.
To schedule, reschedule or cancel an exam:
- Create account
- Forgot my username
- Forgot my password
- COVID-19 FAQs
- Find a test center
- Need help? Contact customer service
Related links
- What to expect in a Pearson VUE test center
Uniformed Division Entrance Exam (UDEE)

The Uniformed Division Entrance Exam (UDEE) is an important step in the Secret Service Uniformed Division Officer hiring process. The UDEE is a competency-based assessment designed to evaluate an applicant’s knowledge, skills, and abilities necessary to be successful upon entry into the Uniformed Division Officer job. The UDEE is made up of six timed sections: (1) Critical Thinking Test, (2) Situational Judgment Test, (3) Memory Skills Test, (4) Figural Reasoning Test, (5) Officer Writing Test, and (6) Work Style Inventory.
Section 1: Critical Thinking Test - This section contains passages which describe a series of facts. The applicants must analyze these facts and answer questions about them. Section 1 contains 23 questions. Applicants will have 30 minutes to complete this section.
Section 2: Situational Judgment Test - This section contains animated videos that depict various hypothetical situations an officer may encounter on the job. Applicants will watch a situation and rate the effectiveness of responses to the situation. Section 2 contains 82 questions. Applicants will have 34 minutes to complete this section.
Section 3: Memory Skills Test - In this section, applicants will answer questions concerning the details of the situations presented in Section 2: Situational Judgment. Applicants will be asked to recall various aspects of the situations. Section 3 contains 12 questions. Applicants will have 8 minutes to complete this section.
Section 4: Figural Reasoning Test - This section presents a set of figures which follow a specific pattern. The patterns may be based on the figure’s shape, size, shading, location, orientation, number of objects, or a combination of these factors. Applicants are tasked with selecting the correct figure from a list of options which will continue the pattern. Section 4 contains 14 questions. Applicants will have 32 minutes to complete this section.
Section 5: Officer Writing Test - The questions in this test measure applicants’ understanding of the standard English writing skills required as a Uniformed Division Officer. Applicants are asked to correct passages and statements that contain errors in grammar, spelling, punctuation, syntax, and word usage. Section 5 contains 3 item types and a total of 30 questions. Applicants will have 35 minutes to complete this section.
Section 6: Work Style Inventory - This section contains statements regarding the applicants’ beliefs, values, and attitudes in the workplace or workplace-like settings. Applicants will indicate the extent to which they agree or disagree with the statements based on their individual experiences. Section 6 contains 139 questions. Applicants will have 25 minutes to complete this section.
What to Expect at a Pearson VUE Testing Center
Admission policy.
Please arrive at the test center 30 minutes before your scheduled testing appointment. This will allow you enough time to complete the check-in procedures before beginning your exam. If you arrive more than 15 minutes late for your scheduled testing appointment, you will be refused admission, denoted as a no-show , and removed from consideration in the hiring process. As a no-show, you will have to wait 6 months from the date you were refused admission to be able to attempt to take the UDEE again. You will also have to reapply to the position and submit a new application packet when there is an open vacancy announcement posted.
Please be prepared to show one current and valid form of personal identification (ID) that includes both your photo and signature. Acceptable forms of IDs are Driver’s License, Travel Passport book/Card, and National/State/Local ID.
You will not be allowed to take any personal items with you into the testing room. This includes all bags, backpacks, purses, books, newspapers, notes, cellular phones, tablets, watches and wallets. Lockers are available to secure your personal belongings. All devices must be turned off before placing them in the lockers. Pearson Professional Centers are not responsible if your personal belongings are lost, stolen, or misplaced. Food and drinks are not allowed in the testing room.
If you need to request a reasonable accommodation for taking the UDEE, please send an e-mail to [email protected] with your request and supporting documents prior to scheduling your test appointment. Requests for reasonable accommodations for taking the UDEE are reviewed on a case-by-case basis. Accommodation requests must be submitted and approved in advance of scheduling.
Reschedule Policy
If you wish to reschedule your exam, you must contact Pearson VUE at least 48 hours prior to your scheduled testing appointment. Rescheduling less than 48 hours prior to your testing appointment will result in removal from consideration in the hiring process. Please note that rescheduling alternatives are limited to the testing time frame or testing window in which you have been provided. Rescheduling outside of this testing window is not permitted.
If you reschedule your testing appointment with less than the required 48-hour notice, you will be considered a no-show and removed from consideration in the hiring process. You will have to wait 6 months from your most recent missed scheduled testing appointment date to be able to attempt to take the UDEE again. Note that you will have to reapply to the position and submit a new application packet when there is an open vacancy announcement posted.
Cancellation Policy
If you wish to cancel your exam, you must contact Pearson VUE at least 48 hours prior to your scheduled testing appointment. Cancelling an exam less than 48 hours prior to your testing appointment or missing your exam will result in removal from consideration in the hiring process.
If you cancel your scheduled testing appointment with less than the required 48-hour notice, you will be considered a no-show and removed from consideration in the hiring process. You will have to wait 6 months from the most recent missed scheduled testing appointment date to be able to attempt to take the UDEE again. Note that you will have to reapply to the position and submit a new application packet when there is an open vacancy announcement posted.
Withdrawal Policy
If you are scheduled to take the UDEE but are no longer interested in the Uniformed Division Officer position, you must first cancel your scheduled exam at least 48 hours prior to your scheduled testing appointment . Next, you must notify the Secret Service Talent & Employee Acquisition Management Division, Uniformed Division Support Branch of your intent to withdraw by email at [email protected]. You will be removed from further consideration and may reapply during the next available open vacancy announcement period.
If you are scheduled to take the UDEE and wish to withdraw but fail to cancel your scheduled exam at least 48 hours prior to your scheduled testing appointment, you will be considered a no-show and removed from consideration in the hiring process. As a no-show , you will have to wait 6 months from the most recent missed scheduled testing appointment date to be able to attempt to take the UDEE again. Note that you will have to reapply to the position and submit a new application packet when there is an open vacancy announcement posted.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It should take approximately 3 ½ hours to complete the UDEE.
You may reschedule your appointment at a test center within 48 hours of your scheduled testing appointment. If you need to cancel your appointment, you must do so no less than 48 hours prior to your scheduled testing appointment. You may reschedule or cancel online or by calling a Pearson VUE Call Center. Use the following links:
Reschedule or cancel online » Locate a Pearson VUE Call Center phone number »
You will receive your results immediately upon completion of the UDEE at the test center. If you receive a passing score, you will continue in the hiring process and will be notified by the Secret Service Talent & Employee Acquisition Management Division, Uniformed Division Support Branch of the next phase of the process via email. However, if you do not pass, you will receive no further consideration and will be discontinued from the hiring process.
If you receive a failing score on the UDEE, you will be eligible to retake the test after a period of 6 months from your most recent fail date. In order to be retested, you must reapply for the position and submit a new application packet when there is an open vacancy announcement posted.
If you receive a passing score on the UDEE, your score will be valid indefinitely unless the exam has been compromised or there are significant changes to the exam. However, if you receive a failing score, you will be eligible to retake the test after a period of 6 months from your most recent fail date. Note: In order to be retested, you must reapply to the position and submit a new application packet when there is an open vacancy announcement posted.
If you are unable to test during your assigned testing window, you must contact the Secret Service Talent & Employee Acquisition Management Division, Uniformed Division Support Branch within the designated testing window. You will be removed from further consideration and may reapply during the next available open vacancy announcement period. Exceptions to this policy are only made for extreme emergency situations, and are reviewed and approved by the Secret Service on a case by case basis.
Your interest in pursuing career opportunities with the United States Secret Service is important. Due to the large volume of inquiries you are encouraged to search www.secretservice.gov/join and the frequently asked questions section there.
If additional assistance is needed, please contact the Career Connector and Applicant Assistance Hotline at 202-406-5458.
An online study guide is available at www.secretservice.gov/join .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For nearly a century, the Watson-Glaser™ Critical Thinking Appraisal has been helping companies make data-driven decisions on staffing and development, and is now the leading critical thinking test available. Can your employees, managers and future leaders examine a situation and clearly understand it from multiple perspectives, while ...
ISBN: 978 0 749107 66 6. DIRECTIONS. Turn this booklet over and carefully tear off the back cover. Place it next to this booklet so that the words Practice Test Record Formare facing up. Don't look at the reverse of the Record Form as that's where the answers are. Read the instructions below and then do the practice test.
The Watson Glaser critical thinking test is a unique assessment that provides a detailed analysis of a participant's ability to think critically. The test lasts 30 minutes and applicants can expect to be tested on around 40 questions in five distinct areas: Inference. Assumptions. Deduction.
The Watson Glaser Assessment (Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal) is designed by Pearson Talentlens - a part of the famous Pearson education publishing house. The assessment is a quick, consistent, and accurate measurement of the test-takers ability to analyze, reason, interpret and draw logical conclusions from written information.
The Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal is a timed online test. Applicants are allowed a maximum of 30 minutes to complete the test. Along with test instructions and untimed practice questions, the total time to administer may be up to 40 minutes. The critical thinking test comprises of 40 items (questions) that include a new bank of ...
Take a Free Critical Thinking Test. This is not a live test, but is intended for you to get a better understanding of how the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking test works, what the questions in each of the different subtests are like, and the skills needed to answer them. As the questions contained in this test haven't been extensively trialled ...
228 questions. Watson Glaser tests are a form of psychometric assessment that fall under the category of critical thinking tests. They are designed to determine how well an individual can process information from a logical perspective, and then evaluate, analyse and make sound judgements. As such, they are commonly used in the recruitment ...
Researching Watson-Glaser. We assembled evidence from a range of sources to support the validity, reliability, and fairness of the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal in assessing critical thinking ability. The above finding about the test's ability to predict likely course success is based on one study with a group of business school ...
The Watson Glaser critical thinking test, initially developed by Goodwin Watson and Edward Glaser and now published by Talentlens/Pearson, is designed to assess an individual's ability to digest and understand situations and information.. It is a psychometric test often used by organisations where the ability to critically consider arguments or propositions is particularly important, such as ...
Challenge #2 - A Unique Set of Rules. The Watson Glaser has its own set of rules, unparalleled by any other critical thinking test. For example: Generalisation equals existence. "Probably True" and "Probably False" answer choices. This makes the Watson Glaser test a unique, tailored testing experience, which requires a tailored ...
The Watson-Glaser assessment presents test-takers with a series of passages or scenarios, each accompanied by a number ... critical thinking as a requirement in job postings in the United States more than doubled between 2009 and 2014. For many, the purpose of earning a post-secondary degree is ... Pearson is committed to reporting on the ...
Available via our test platform it is a verbal ability test designed to measure critical thinking ability to: Analyse, interpret and draw logical conclusions from written information. Recognise assumptions from facts. Evaluate the strength of arguments. Draw correct inferences. The test is now mandatory for anyone wishing to study to become a ...
To demystify what critical thinking is and how it is developed, the author's team turned to three research-backed models: The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment, Pearson's RED Critical ...
Critical thinking tests, or critical reasoning tests, are psychometric tests used in recruitment at all levels, graduate, professional and managerial, but predominantly in the legal sector. ... Note: AssessmentDay and its products are not affiliated with Pearson or TalentLens. Our practice tests are for candidates to prepare for the Watson ...
Created by Goodwin Watson and Edward Glaser, The Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal Test (WGCTA) evaluates and interprets the critical thinking skills of the test-taker. Critical thinking assessments are psychometric tests used for recruitment at various levels including, professional, managerial, and graduate and are used in many sectors.
Critical thinking tests are a sub-type of aptitude exams or psychometric tests used in pre-employment assessment for jobs reacquiring advanced analytical and learning skills. ... Another popular critical thinking assessment, Watson-Glaser is a well-established psychometric test produced by Pearson Assessments.
The most common test candidates are asked to take is the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (WGCTA) created by the popular assessment company, Pearson. This assessment company is on their third edition with new scoring and subsets described above.
the test are timed, though the recommended time limit is intentionally generous. There is also an optional follow-up interview component, which administrators can use to gain more insight into the raw test scores. Pearson also offers professional development support for the 1 critical thinking
in critical thinking skills. The third edition of the Watson-Glaser™ III (W-G III) is an online, item-banked assessment. Each administration of the test includes 40 items that are randomly selected from a large pool of scenarios and questions. This is a much more secure way of administering tests online in an unsupervised
Everyone inherently experiences some degree of subconscious bias in their thinking. Critical thinking skills can help an individual overcome these and separate out facts from opinions. The Watson Glaser critical thinking test is based around the RED model of critical thinking: • Recognize assumptions. This is all about comprehension. Actually ...
Thinking Critically About Critical Thinking. Psychology 1. The Science of Psychology Thinking Critically About Critical Thinking.
The UDEE is made up of six timed sections: (1) Critical Thinking Test, (2) Situational Judgment Test, (3) Memory Skills Test, (4) Figural Reasoning Test, (5) Officer Writing Test, and (6) Work Style Inventory. ... If you wish to cancel your exam, you must contact Pearson VUE at least 48 hours prior to your scheduled testing appointment ...
The RED model for developing critical thinking skills is a process recommended by Pearson and TalentLens to help two things: Improve the standard of critical thinking within your business. Naturally, this will result in improved critical thinking test scores and pass marks, but it also helps grow your businesses thinking capabilities. The RED ...