- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources

How to Write the Rationale of the Study in Research (Examples)
What is the Rationale of the Study?
The rationale of the study is the justification for taking on a given study. It explains the reason the study was conducted or should be conducted. This means the study rationale should explain to the reader or examiner why the study is/was necessary. It is also sometimes called the “purpose” or “justification” of a study. While this is not difficult to grasp in itself, you might wonder how the rationale of the study is different from your research question or from the statement of the problem of your study, and how it fits into the rest of your thesis or research paper.
The rationale of the study links the background of the study to your specific research question and justifies the need for the latter on the basis of the former. In brief, you first provide and discuss existing data on the topic, and then you tell the reader, based on the background evidence you just presented, where you identified gaps or issues and why you think it is important to address those. The problem statement, lastly, is the formulation of the specific research question you choose to investigate, following logically from your rationale, and the approach you are planning to use to do that.
Table of Contents:
How to write a rationale for a research paper , how do you justify the need for a research study.
- Study Rationale Example: Where Does It Go In Your Paper?
The basis for writing a research rationale is preliminary data or a clear description of an observation. If you are doing basic/theoretical research, then a literature review will help you identify gaps in current knowledge. In applied/practical research, you base your rationale on an existing issue with a certain process (e.g., vaccine proof registration) or practice (e.g., patient treatment) that is well documented and needs to be addressed. By presenting the reader with earlier evidence or observations, you can (and have to) convince them that you are not just repeating what other people have already done or said and that your ideas are not coming out of thin air.
Once you have explained where you are coming from, you should justify the need for doing additional research–this is essentially the rationale of your study. Finally, when you have convinced the reader of the purpose of your work, you can end your introduction section with the statement of the problem of your research that contains clear aims and objectives and also briefly describes (and justifies) your methodological approach.
When is the Rationale for Research Written?
The author can present the study rationale both before and after the research is conducted.
- Before conducting research : The study rationale is a central component of the research proposal . It represents the plan of your work, constructed before the study is actually executed.
- Once research has been conducted : After the study is completed, the rationale is presented in a research article or PhD dissertation to explain why you focused on this specific research question. When writing the study rationale for this purpose, the author should link the rationale of the research to the aims and outcomes of the study.
What to Include in the Study Rationale
Although every study rationale is different and discusses different specific elements of a study’s method or approach, there are some elements that should be included to write a good rationale. Make sure to touch on the following:
- A summary of conclusions from your review of the relevant literature
- What is currently unknown (gaps in knowledge)
- Inconclusive or contested results from previous studies on the same or similar topic
- The necessity to improve or build on previous research, such as to improve methodology or utilize newer techniques and/or technologies
There are different types of limitations that you can use to justify the need for your study. In applied/practical research, the justification for investigating something is always that an existing process/practice has a problem or is not satisfactory. Let’s say, for example, that people in a certain country/city/community commonly complain about hospital care on weekends (not enough staff, not enough attention, no decisions being made), but you looked into it and realized that nobody ever investigated whether these perceived problems are actually based on objective shortages/non-availabilities of care or whether the lower numbers of patients who are treated during weekends are commensurate with the provided services.
In this case, “lack of data” is your justification for digging deeper into the problem. Or, if it is obvious that there is a shortage of staff and provided services on weekends, you could decide to investigate which of the usual procedures are skipped during weekends as a result and what the negative consequences are.
In basic/theoretical research, lack of knowledge is of course a common and accepted justification for additional research—but make sure that it is not your only motivation. “Nobody has ever done this” is only a convincing reason for a study if you explain to the reader why you think we should know more about this specific phenomenon. If there is earlier research but you think it has limitations, then those can usually be classified into “methodological”, “contextual”, and “conceptual” limitations. To identify such limitations, you can ask specific questions and let those questions guide you when you explain to the reader why your study was necessary:
Methodological limitations
- Did earlier studies try but failed to measure/identify a specific phenomenon?
- Was earlier research based on incorrect conceptualizations of variables?
- Were earlier studies based on questionable operationalizations of key concepts?
- Did earlier studies use questionable or inappropriate research designs?
Contextual limitations
- Have recent changes in the studied problem made previous studies irrelevant?
- Are you studying a new/particular context that previous findings do not apply to?
Conceptual limitations
- Do previous findings only make sense within a specific framework or ideology?
Study Rationale Examples
Let’s look at an example from one of our earlier articles on the statement of the problem to clarify how your rationale fits into your introduction section. This is a very short introduction for a practical research study on the challenges of online learning. Your introduction might be much longer (especially the context/background section), and this example does not contain any sources (which you will have to provide for all claims you make and all earlier studies you cite)—but please pay attention to how the background presentation , rationale, and problem statement blend into each other in a logical way so that the reader can follow and has no reason to question your motivation or the foundation of your research.
Background presentation
Since the beginning of the Covid pandemic, most educational institutions around the world have transitioned to a fully online study model, at least during peak times of infections and social distancing measures. This transition has not been easy and even two years into the pandemic, problems with online teaching and studying persist (reference needed) .
While the increasing gap between those with access to technology and equipment and those without access has been determined to be one of the main challenges (reference needed) , others claim that online learning offers more opportunities for many students by breaking down barriers of location and distance (reference needed) .
Rationale of the study
Since teachers and students cannot wait for circumstances to go back to normal, the measures that schools and universities have implemented during the last two years, their advantages and disadvantages, and the impact of those measures on students’ progress, satisfaction, and well-being need to be understood so that improvements can be made and demographics that have been left behind can receive the support they need as soon as possible.
Statement of the problem
To identify what changes in the learning environment were considered the most challenging and how those changes relate to a variety of student outcome measures, we conducted surveys and interviews among teachers and students at ten institutions of higher education in four different major cities, two in the US (New York and Chicago), one in South Korea (Seoul), and one in the UK (London). Responses were analyzed with a focus on different student demographics and how they might have been affected differently by the current situation.
How long is a study rationale?
In a research article bound for journal publication, your rationale should not be longer than a few sentences (no longer than one brief paragraph). A dissertation or thesis usually allows for a longer description; depending on the length and nature of your document, this could be up to a couple of paragraphs in length. A completely novel or unconventional approach might warrant a longer and more detailed justification than an approach that slightly deviates from well-established methods and approaches.
Consider Using Professional Academic Editing Services
Now that you know how to write the rationale of the study for a research proposal or paper, you should make use of our free AI grammar checker , Wordvice AI, or receive professional academic proofreading services from Wordvice, including research paper editing services and manuscript editing services to polish your submitted research documents.
You can also find many more articles, for example on writing the other parts of your research paper , on choosing a title , or on making sure you understand and adhere to the author instructions before you submit to a journal, on the Wordvice academic resources pages.

Community Blog
Keep up-to-date on postgraduate related issues with our quick reads written by students, postdocs, professors and industry leaders.
How do you Write the Rationale for Research?
- By DiscoverPhDs
- October 21, 2020

What is the Rationale of Research?
The term rationale of research means the reason for performing the research study in question. In writing your rational you should able to convey why there was a need for your study to be carried out. It’s an important part of your research paper that should explain how your research was novel and explain why it was significant; this helps the reader understand why your research question needed to be addressed in your research paper, term paper or other research report.
The rationale for research is also sometimes referred to as the justification for the study. When writing your rational, first begin by introducing and explaining what other researchers have published on within your research field.
Having explained the work of previous literature and prior research, include discussion about where the gaps in knowledge are in your field. Use these to define potential research questions that need answering and explain the importance of addressing these unanswered questions.
The rationale conveys to the reader of your publication exactly why your research topic was needed and why it was significant . Having defined your research rationale, you would then go on to define your hypothesis and your research objectives.
Final Comments
Defining the rationale research, is a key part of the research process and academic writing in any research project. You use this in your research paper to firstly explain the research problem within your dissertation topic. This gives you the research justification you need to define your research question and what the expected outcomes may be.

Stay up to date with current information being provided by the UK Government and Universities about the impact of the global pandemic on PhD research studies.

A concept paper is a short document written by a researcher before starting their research project, explaining what the study is about, why it is needed and the methods that will be used.

The term monotonic relationship is a statistical definition that is used to describe the link between two variables.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Browse PhDs Now

Statistical treatment of data is essential for all researchers, regardless of whether you’re a biologist, computer scientist or psychologist, but what exactly is it?

This post explains the difference between the journal paper status of In Review and Under Review.

Rose is a final year PhD student at the University of St Andrews. Her research is focussed on modelling stars similar to the sun in its youth and understanding better the magnetic fields of these stars.

Dr Dillon gained her PhD in Molecular Cancer Studies at the University of Manchester in 2015. She now works at a biotech company called HairClone, optimising treatments for androgenic alopecia.
Join Thousands of Students
How to Write the Rationale for a Research Paper
- Research Process
- Peer Review
A research rationale answers the big SO WHAT? that every adviser, peer reviewer, and editor has in mind when they critique your work. A compelling research rationale increases the chances of your paper being published or your grant proposal being funded. In this article, we look at the purpose of a research rationale, its components and key characteristics, and how to create an effective research rationale.
Updated on September 19, 2022

The rationale for your research is the reason why you decided to conduct the study in the first place. The motivation for asking the question. The knowledge gap. This is often the most significant part of your publication. It justifies the study's purpose, novelty, and significance for science or society. It's a critical part of standard research articles as well as funding proposals.
Essentially, the research rationale answers the big SO WHAT? that every (good) adviser, peer reviewer, and editor has in mind when they critique your work.
A compelling research rationale increases the chances of your paper being published or your grant proposal being funded. In this article, we look at:
- the purpose of a research rationale
- its components and key characteristics
- how to create an effective research rationale
What is a research rationale?
Think of a research rationale as a set of reasons that explain why a study is necessary and important based on its background. It's also known as the justification of the study, rationale, or thesis statement.
Essentially, you want to convince your reader that you're not reciting what other people have already said and that your opinion hasn't appeared out of thin air. You've done the background reading and identified a knowledge gap that this rationale now explains.
A research rationale is usually written toward the end of the introduction. You'll see this section clearly in high-impact-factor international journals like Nature and Science. At the end of the introduction there's always a phrase that begins with something like, "here we show..." or "in this paper we show..." This text is part of a logical sequence of information, typically (but not necessarily) provided in this order:

Here's an example from a study by Cataldo et al. (2021) on the impact of social media on teenagers' lives.

Note how the research background, gap, rationale, and objectives logically blend into each other.
The authors chose to put the research aims before the rationale. This is not a problem though. They still achieve a logical sequence. This helps the reader follow their thinking and convinces them about their research's foundation.
Elements of a research rationale
We saw that the research rationale follows logically from the research background and literature review/observation and leads into your study's aims and objectives.
This might sound somewhat abstract. A helpful way to formulate a research rationale is to answer the question, “Why is this study necessary and important?”
Generally, that something has never been done before should not be your only motivation. Use it only If you can give the reader valid evidence why we should learn more about this specific phenomenon.
A well-written introduction covers three key elements:
- What's the background to the research?
- What has been done before (information relevant to this particular study, but NOT a literature review)?
- Research rationale
Now, let's see how you might answer the question.
1. This study complements scientific knowledge and understanding
Discuss the shortcomings of previous studies and explain how'll correct them. Your short review can identify:
- Methodological limitations . The methodology (research design, research approach or sampling) employed in previous works is somewhat flawed.
Example : Here , the authors claim that previous studies have failed to explore the role of apathy “as a predictor of functional decline in healthy older adults” (Burhan et al., 2021). At the same time, we know a lot about other age-related neuropsychiatric disorders, like depression.
Their study is necessary, then, “to increase our understanding of the cognitive, clinical, and neural correlates of apathy and deconstruct its underlying mechanisms.” (Burhan et al., 2021).
- Contextual limitations . External factors have changed and this has minimized or removed the relevance of previous research.
Example : You want to do an empirical study to evaluate the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the number of tourists visiting Sicily. Previous studies might have measured tourism determinants in Sicily, but they preceded COVID-19.
- Conceptual limitations . Previous studies are too bound to a specific ideology or a theoretical framework.
Example : The work of English novelist E. M. Forster has been extensively researched for its social, political, and aesthetic dimensions. After the 1990s, younger scholars wanted to read his novels as an example of gay fiction. They justified the need to do so based on previous studies' reliance on homophobic ideology.
This kind of rationale is most common in basic/theoretical research.
2. This study can help solve a specific problem
Here, you base your rationale on a process that has a problem or is not satisfactory.
For example, patients complain about low-quality hospital care on weekends (staff shortages, inadequate attention, etc.). No one has looked into this (there is a lack of data). So, you explore if the reported problems are true and what can be done to address them. This is a knowledge gap.
Or you set out to explore a specific practice. You might want to study the pros and cons of several entry strategies into the Japanese food market.
It's vital to explain the problem in detail and stress the practical benefits of its solution. In the first example, the practical implications are recommendations to improve healthcare provision.
In the second example, the impact of your research is to inform the decision-making of businesses wanting to enter the Japanese food market.
This kind of rationale is more common in applied/practical research.
3. You're the best person to conduct this study
It's a bonus if you can show that you're uniquely positioned to deliver this study, especially if you're writing a funding proposal .
For an anthropologist wanting to explore gender norms in Ethiopia, this could be that they speak Amharic (Ethiopia's official language) and have already lived in the country for a few years (ethnographic experience).
Or if you want to conduct an interdisciplinary research project, consider partnering up with collaborators whose expertise complements your own. Scientists from different fields might bring different skills and a fresh perspective or have access to the latest tech and equipment. Teaming up with reputable collaborators justifies the need for a study by increasing its credibility and likely impact.
When is the research rationale written?
You can write your research rationale before, or after, conducting the study.
In the first case, when you might have a new research idea, and you're applying for funding to implement it.
Or you're preparing a call for papers for a journal special issue or a conference. Here , for instance, the authors seek to collect studies on the impact of apathy on age-related neuropsychiatric disorders.
In the second case, you have completed the study and are writing a research paper for publication. Looking back, you explain why you did the study in question and how it worked out.
Although the research rationale is part of the introduction, it's best to write it at the end. Stand back from your study and look at it in the big picture. At this point, it's easier to convince your reader why your study was both necessary and important.
How long should a research rationale be?
The length of the research rationale is not fixed. Ideally, this will be determined by the guidelines (of your journal, sponsor etc.).
The prestigious journal Nature , for instance, calls for articles to be no more than 6 or 8 pages, depending on the content. The introduction should be around 200 words, and, as mentioned, two to three sentences serve as a brief account of the background and rationale of the study, and come at the end of the introduction.
If you're not provided guidelines, consider these factors:
- Research document : In a thesis or book-length study, the research rationale will be longer than in a journal article. For example, the background and rationale of this book exploring the collective memory of World War I cover more than ten pages.
- Research question : Research into a new sub-field may call for a longer or more detailed justification than a study that plugs a gap in literature.
Which verb tenses to use in the research rationale?
It's best to use the present tense. Though in a research proposal, the research rationale is likely written in the future tense, as you're describing the intended or expected outcomes of the research project (the gaps it will fill, the problems it will solve).
Example of a research rationale
Research question : What are the teachers' perceptions of how a sense of European identity is developed and what underlies such perceptions?

Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3(2), 77-101.
Burhan, A.M., Yang, J., & Inagawa, T. (2021). Impact of apathy on aging and age-related neuropsychiatric disorders. Research Topic. Frontiers in Psychiatry
Cataldo, I., Lepri, B., Neoh, M. J. Y., & Esposito, G. (2021). Social media usage and development of psychiatric disorders in childhood and adolescence: A review. Frontiers in Psychiatry , 11.
CiCe Jean Monnet Network (2017). Guidelines for citizenship education in school: Identities and European citizenship children's identity and citizenship in Europe.
Cohen, l, Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2018). Research methods in education . Eighth edition. London: Routledge.
de Prat, R. C. (2013). Euroscepticism, Europhobia and Eurocriticism: The radical parties of the right and left “vis-à-vis” the European Union P.I.E-Peter Lang S.A., Éditions Scientifiques Internationales.
European Commission. (2017). Eurydice Brief: Citizenship education at school in Europe.
Polyakova, A., & Fligstein, N. (2016). Is European integration causing Europe to become more nationalist? Evidence from the 2007–9 financial crisis. Journal of European Public Policy , 23(1), 60-83.
Winter, J. (2014). Sites of Memory, Sites of Mourning: The Great War in European Cultural History . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
Ensure your structure and ideas are consistent and clearly communicated
Pair your Premium Editing with our add-on service Presubmission Review for an overall assessment of your manuscript.

Setting Rationale in Research: Cracking the code for excelling at research
Knowledge and curiosity lays the foundation of scientific progress. The quest for knowledge has always been a timeless endeavor. Scholars seek reasons to explain the phenomena they observe, paving way for development of research. Every investigation should offer clarity and a well-defined rationale in research is a cornerstone upon which the entire study can be built.
Research rationale is the heartbeat of every academic pursuit as it guides the researchers to unlock the untouched areas of their field. Additionally, it illuminates the gaps in the existing knowledge, and identifies the potential contributions that the study aims to make.
Table of Contents
What Is Research Rationale and When Is It Written
Research rationale is the “why” behind every academic research. It not only frames the study but also outlines its objectives , questions, and expected outcomes. Additionally, it helps to identify the potential limitations of the study . It serves as a lighthouse for researchers that guides through data collection and analysis, ensuring their efforts remain focused and purposeful. Typically, a rationale is written at the beginning of the research proposal or research paper . It is an essential component of the introduction section and provides the foundation for the entire study. Furthermore, it provides a clear understanding of the purpose and significance of the research to the readers before delving into the specific details of the study. In some cases, the rationale is written before the methodology, data analysis, and other sections. Also, it serves as the justification for the research, and how it contributes to the field. Defining a research rationale can help a researcher in following ways:
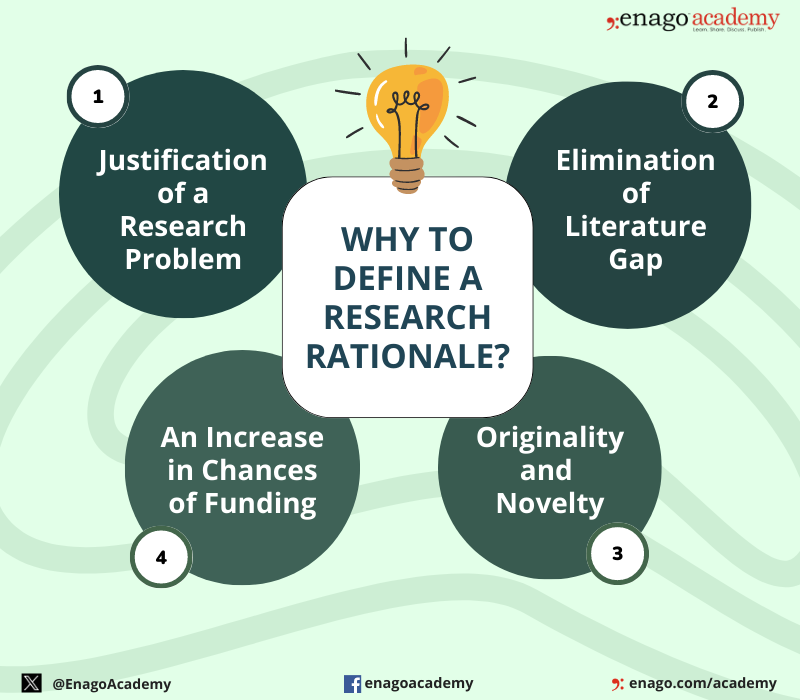
1. Justification of a Research Problem
- Research rationale helps to understand the essence of a research problem.
- It designs the right approach to solve a problem. This aspect is particularly important for applied research, where the outcomes can have real-world relevance and impact.
- Also, it explains why the study is worth conducting and why resources should be allocated to pursue it.
- Additionally, it guides a researcher to highlight the benefits and implications of a strategy.
2. Elimination of Literature Gap
- Research rationale helps to ideate new topics which are less addressed.
- Additionally, it offers fresh perspectives on existing research and discusses the shortcomings in previous studies.
- It shows that your study aims to contribute to filling these gaps and advancing the field’s understanding.
3. Originality and Novelty
- The rationale highlights the unique aspects of your research and how it differs from previous studies.
- Furthermore, it explains why your research adds something new to the field and how it expands upon existing knowledge.
- It highlights how your findings might contribute to a better understanding of a particular issue or problem and potentially lead to positive changes.
- Besides these benefits, it provides a personal motivation to the researchers. In some cases, researchers might have personal experiences or interests that drive their desire to investigate a particular topic.
4. An Increase in Chances of Funding
- It is essential to convince funding agencies , supervisors, or reviewers, that a research is worth pursuing.
- Therefore, a good rationale can get your research approved for funding and increases your chances of getting published in journals; as it addresses the potential knowledge gap in existing research.
Overall, research rationale is essential for providing a clear and convincing argument for the value and importance of your research study, setting the stage for the rest of the research proposal or manuscript. Furthermore, it helps establish the context for your work and enables others to understand the purpose and potential impact of your research.
5 Key Elements of a Research Rationale
Research rationale must include certain components which make it more impactful. Here are the key elements of a research rationale:

By incorporating these elements, you provide a strong and convincing case for the legitimacy of your research, which is essential for gaining support and approval from academic institutions, funding agencies, or other stakeholders.
How to Write a Rationale in Research
Writing a rationale requires careful consideration of the reasons for conducting the study. It is usually written in the present tense.
Here are some steps to guide you through the process of writing a research rationale:
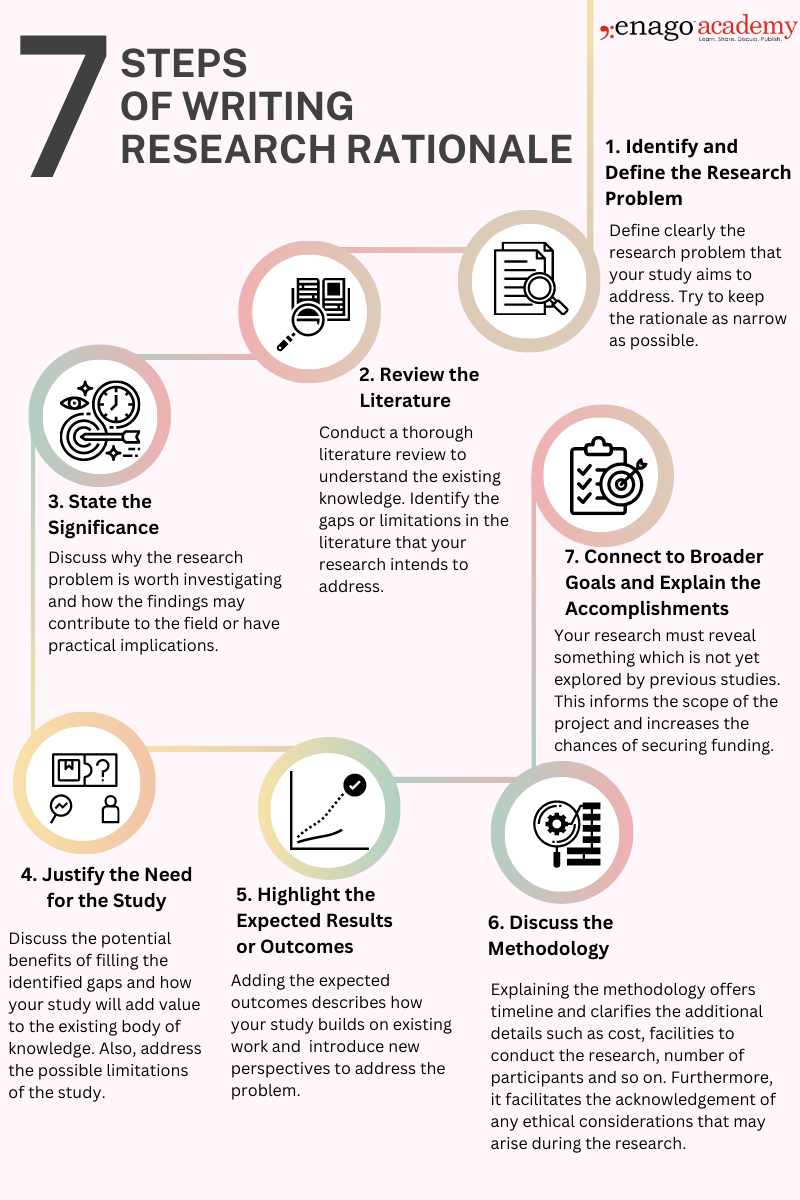
After writing the initial draft, it is essential to review and revise the research rationale to ensure that it effectively communicates the purpose of your research. The research rationale should be persuasive and compelling, convincing readers that your study is worthwhile and deserves their attention.
How Long Should a Research Rationale be?
Although there is no pre-defined length for a rationale in research, its length may vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project. It also depends on the academic institution or organization, and the guidelines set by the research advisor or funding agency. In general, a research rationale is usually a concise and focused document.
Typically, it ranges from a few paragraphs to a few pages, but it is usually recommended to keep it as crisp as possible while ensuring all the essential elements are adequately covered. The length of a research rationale can be roughly as follows:
1. For Research Proposal:
A. Around 1 to 3 pages
B. Ensure clear and comprehensive explanation of the research question, its significance, literature review , and methodological approach.
2. Thesis or Dissertation:
A. Around 3 to 5 pages
B. Ensure an extensive coverage of the literature review, theoretical framework, and research objectives to provide a robust justification for the study.
3. Journal Article:
A. Usually concise. Ranges from few paragraphs to one page
B. The research rationale is typically included as part of the introduction section
However, remember that the quality and content of the research rationale are more important than its length. The reasons for conducting the research should be well-structured, clear, and persuasive when presented. Always adhere to the specific institution or publication guidelines.
Example of a Research Rationale

In conclusion, the research rationale serves as the cornerstone of a well-designed and successful research project. It ensures that research efforts are focused, meaningful, and ethically sound. Additionally, it provides a comprehensive and logical justification for embarking on a specific investigation. Therefore, by identifying research gaps, defining clear objectives, emphasizing significance, explaining the chosen methodology, addressing ethical considerations, and recognizing potential limitations, researchers can lay the groundwork for impactful and valuable contributions to the scientific community.
So, are you ready to delve deeper into the world of research and hone your academic writing skills? Explore Enago Academy ‘s comprehensive resources and courses to elevate your research and make a lasting impact in your field. Also, share your thoughts and experiences in the form of an article or a thought piece on Enago Academy’s Open Platform .
Join us on a journey of scholarly excellence today!
Frequently Asked Questions
A rationale of the study can be written by including the following points: 1. Background of the Research/ Study 2. Identifying the Knowledge Gap 3. An Overview of the Goals and Objectives of the Study 4. Methodology and its Significance 5. Relevance of the Research
Start writing a research rationale by defining the research problem and discussing the literature gap associated with it.
A research rationale can be ended by discussing the expected results and summarizing the need of the study.
A rationale for thesis can be made by covering the following points: 1. Extensive coverage of the existing literature 2. Explaining the knowledge gap 3. Provide the framework and objectives of the study 4. Provide a robust justification for the study/ research 5. Highlight the potential of the research and the expected outcomes
A rationale for dissertation can be made by covering the following points: 1. Highlight the existing reference 2. Bridge the gap and establish the context of your research 3. Describe the problem and the objectives 4. Give an overview of the methodology
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![write rationale research What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…
Mitigating Survivorship Bias in Scholarly Research: 10 tips to enhance data integrity
The Power of Proofreading: Taking your academic work to the next level
Facing Difficulty Writing an Academic Essay? — Here is your one-stop solution!

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
- Academic Skills
- Reading, writing and referencing
- Writing effectively
Writing a rationale
How to write a rationale.
What is a rationale?
A rationale is when you are asked to give the reasoning or justification for an action or a choice you make.
There is a focus on the ‘ why ’ in a rationale: why you chose to do something, study or focus on something. It is a set of statements of purpose and significance and often addresses a gap or a need.
A rationale in Australian academic writing is rarely a whole task by itself. It is often a part of a bigger task. For example, a part of a lesson plan might be to provide a rationale for why you chose to teach particular content or use a certain resource or activity, or you may be asked to provide a rationale as to why you chose a particular theory to apply or a concept to support.
You may be called upon to provide a rationale:
prior to an action or decision; why you plan to do something and how, or
- after you have acted or decided something; reflecting, looking back, why you did something and how it worked or not.
You can use language to signal you are clearly providing a rationale in your writing. You can link your rationale to learning outcomes or aims for a lesson, activity or assessment task.
A model: problem-solution-rationale
A rationale can be provided by offering longer essay-based support for why it is important to do something in a certain way – in that sense, a whole paper can be a rationale.
However, a more specific or focused way of thinking about a rationale is how we can overtly show we are justifying our choices with the language we use.
One way of doing this is to consider the problem or issue requiring attention, the solution and then the rationale or justification for the solution (the ‘why’). This sets the rationale (the reason) within a context.
A diagnostic assessment determined that the students required more attention to addition and subtraction of mixed fractions. This activity intends to address this problem by having the children engage with the task with blocks before it is done with figures. The reason I chose to do this is because students have higher comprehension levels when presented with visual or tangible representations of abstract problems (Benson, 2016). I also did this as I wanted to allow the children to ‘play’ with maths, to see that it can be a fun activity and in doing so, to breakdown some of the ‘anti-mathematics prejudices’ that Gaines (2017, p. 4) talks about.
The important thing here is the language used to signal the rationale , in this case:
The reason I chose to do this is because … and I also did this as …
Another problem / solution / rationale example:
Scaffolding is the support provided by the teacher or a significant other, such as a classmate, which helps students in learning (Gibbons, 2015). Some students were having difficulty with the language at entry while others, particularly those who had completed the pre-tasks, had few problems. Therefore, in order to address this disparity in level and understanding, mixed-ability pairs were created where the more competent student helped the other. On reflection, this was an effective way to run the activity for two reasons : it allowed peer-to-peer teaching which solidified both students’ understanding; and it scaffolded the support in a way that allowed me to roam the room lending advice to pairs as needed.
The language used to signal our rationale in this example:
in order to and for two reasons …
Language to signal rationale
in order to
the reason this was done/chosen …
for the following reason(s) …
for two/three reasons …
Language for further justification - showing importance
This was important / significant because …
This meant that I could…
This enabled me to …
… which enabled / allowed me to…
… which pointed to / highlighted that / showed me that …
The key thing to remember about rationale writing is to stand back from the writing, look at it in a big picture sense and ask yourself, ‘ Have I explained why? ’ If that is clearly articulated, you have provided a rationale.

Looking for one-on-one advice?
Get tailored advice from an Academic Skills Adviser by booking an Individual appointment, or get quick feedback from one of our Academic Writing Mentors via email through our Writing advice service.
Go to Student appointments

How to Write a Rationale: A Guide for Research and Beyond
Ever found yourself scratching your head, wondering how to justify your choice of a research topic or project? You’re not alone! Writing a rationale, which essentially means explaining the ‘why’ behind your decisions, is crucial to any research process. It’s like the secret sauce that adds flavour to your research recipe. So, the only thing you need to know is how to write a rationale.

What is a Rationale?
A rationale in research is essentially the foundation of your study. It serves as the justification for undertaking a particular research project. At its core, the rationale explains why the research was conducted or needs to be conducted, thus addressing a specific knowledge gap or research question.
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements involved in crafting a rationale:
Linking Background to Research Question:
The rationale should connect the background of the study to your specific research question. It involves presenting and discussing existing data on your topic, identifying gaps or issues in the current understanding, and explaining why addressing them is important.
Objectives and Significance:
Your rationale should clearly outline your research objectives – what you hope to discover or achieve through the study. It should also emphasize the subject’s significance in your field and explain why more or better research is needed.
Methodological Approach:
The rationale should briefly describe your proposed research method , whether qualitative (descriptive) or quantitative (experimental), and justify this choice.
Justifying the Need for Research:
The rationale isn’t just about what you’re doing and why it’s necessary. It can involve highlighting methodological, contextual, or conceptual limitations in previous studies and explaining how your research aims to overcome these limitations. Essentially, you’re making a case for why your research fills a crucial gap in existing knowledge.
Presenting Before and After Research:
Interestingly, the rationale can be presented before and after the research. Before the research, it forms a central part of the research proposal, setting out the plan for the work. After the research, it’s presented in a research article or dissertation to explain the focus on a specific research question and link it to the study’s aims and outcomes.
Elements to Include:
A good rationale should include a summary of conclusions from your literature review, identify what is currently unknown, discuss inconclusive or contested results from previous studies, and emphasize the necessity to improve or build on previous research.
Creating a rationale is a vital part of the research process, as it not only sets the stage for your study but also convinces readers of the value and necessity of your work.

How to Write a Rationale:
Writing a rationale for your research is crucial in conducting and presenting your study. It involves explaining why your research is necessary and important. Here’s a guide to help you craft a compelling rationale:
Identify the Problem or Knowledge Gap:
Begin by clearly stating the issue or gap in knowledge that your research aims to address. Explain why this problem is important and merits investigation. It is the foundation of your rationale and sets the stage for the need for your research.
Review the Literature:
Conduct a thorough review of existing literature on your topic. It helps you understand what research has already been done and what gaps or open questions exist. Your rationale should build on this background by highlighting these gaps and emphasizing the importance of addressing them.
Define Your Research Questions/Hypotheses:
Based on your understanding of the problem and literature review, clearly state the research questions or hypotheses that your study aims to explore. These should logically stem from the identified gaps or issues.
Explain Your Research Approach:
Describe the methods you will use for your research, including data collection and analysis techniques. Justify why these methods are appropriate for addressing your research questions or hypotheses.
Discuss the Potential Impact of Your Research: Explain the significance of your study. Consider both theoretical contributions and practical implications. For instance, how does your research advance existing knowledge? Does it have real-world applications? Is it relevant to a specific field or community?
Consider Ethical Considerations:
If your research involves human or animal subjects, discuss the ethical aspects and how you plan to conduct your study responsibly.
Contextualise Your Study:
Justify the relevance of your research by explaining how it fits into the broader context. Connect your study to current trends, societal needs, or academic discussions.
Support with Evidence:
Provide evidence or examples that underscore the need for your research. It could include citing relevant studies, statistics, or scenarios that illustrate the problem or gap your research addresses.
Methodological, Contextual, and Conceptual Limitations:
Address any limitations of previous research and how your study aims to overcome them. It can include methodological flaws in previous studies, changes in external factors that make past research less relevant, or the need to study a phenomenon within a new conceptual framework.
Placement in Your Paper:
Typically, the rationale is written toward the end of the introduction section of your paper, providing a logical lead-in to your research questions and methodology.
By following these steps and considering your audience’s perspective, you can write a strong and compelling rationale that clearly communicates the significance and necessity of your research project.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What makes a good research rationale.
A good rationale clearly identifies a gap in existing knowledge, builds on previous research, and outlines why your study is necessary and significant.
How detailed should my literature review be in the rationale?
Your literature review should be comprehensive enough to highlight the gaps your research aims to fill, but it should not overshadow the rationale itself.
Conclusion:
A well-crafted rationale is your ticket to making your research stand out. It’s about bridging gaps, challenging norms, and paving the way for new discoveries. So go ahead, make your rationale the cornerstone of your research narrative!
Award-Winning Results
Team of 11+ experts, 10,000+ page #1 rankings on google, dedicated to smbs, $175,000,000 in reported client revenue.
Up until working with Casey, we had only had poor to mediocre experiences outsourcing work to agencies. Casey & the team at CJ&CO are the exception to the rule.
Communication was beyond great, his understanding of our vision was phenomenal, and instead of needing babysitting like the other agencies we worked with, he was not only completely dependable but also gave us sound suggestions on how to get better results, at the risk of us not needing him for the initial job we requested (absolute gem).
This has truly been the first time we worked with someone outside of our business that quickly grasped our vision, and that I could completely forget about and would still deliver above expectations.
I honestly can't wait to work in many more projects together!
Related Articles
View All Post

Conversion Rate Optimization , Copywriting , Customer Experience
How to Tap Into What Your Customers Love & Hate
Casey Jones

Advertising , Copywriting
What does a Copywriter do at an Ad Agency: Things You Should Know if You’re a Copywriter

Copywriting
How to Write a Marketing Script: Take Your Marketing to the Next Level in 2023
*The information this blog provides is for general informational purposes only and is not intended as financial or professional advice. The information may not reflect current developments and may be changed or updated without notice. Any opinions expressed on this blog are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect the views of the author’s employer or any other organization. You should not act or rely on any information contained in this blog without first seeking the advice of a professional. No representation or warranty, express or implied, is made as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained in this blog. The author and affiliated parties assume no liability for any errors or omissions.

- Researching
How to write a research rationale

When you are doing a research assessment piece in History, you’ll often be asked to write a rationale. This is particularly true for the source investigation assessment piece.
What is a ‘rationale’?
A rationale is a written explanation about your research task that helps your teacher understand the decisions you made before beginning your source research .
A research rationale is a statement that explains the reasons behind conducting a particular research study.
It outlines the background, context, and significance of the research and why it is important to answer the main inquiry question.
A rationale seeks to answer three questions:
- Why have you chosen this particular topic to research?
- What questions do you specifically want answered as a result of your research?
- How do you plan on finding the best sources during your research?
How to write a rationale
Based upon the three questions mentioned above, your rationale should have three distinct sections that answer each one.
Please note that you can answer all three in a single paragraph, but the examples below will show them as three separate paragraphs.
Part 1: Explain your topic choice
You should explain as clearly as possible why this particular subject interested you.
Don’t just say “it is interesting”: give specific reasons why.
The more precise you are, the better your mark will be.
Useful sentence starters for explaining topic choice:
- I was curious to discover…
- I wanted to know…
- I was confused by…
- I always wanted to know…
- I have always been fascinated by…
- I am particularly interested in…
- I was surprised to learn that … and I wanted to know more
Example explanation of topic choice:
Imperial Japan’s decision to surrender at the end of World War II seemed like a historical anomaly based upon what we learned in class about the Japanese ideologies behind bushido and the samurai. I wanted to know to what degree the atomic bombs had an influence upon the ultimate decision to surrender. I specifically want to know what the Japanese primary sources said at the time of the events to see their perspective. In particular, want to know if Emperor Hirohito left any documents that explained his decisions.
Part 2: Explain your research questions
You need to explain the steps that helped you to create your Key Inquiry Question and Sub-Questions .
Remember that these questions should constantly be refined to include specific historical terms and information that you found during your background research .
Explain to your teacher why you have included specific information in your research questions.
Useful sentence starters for explaining research questions:
- The three specific aspects that I wanted to focus upon are…
- I knew that I had to develop my understanding of…
- My background research focused upon…
Example explanation of research questions:
Since I wanted to focus my research on the Japanese primary sources, my Key Inquiry Question is primarily about the role that the atomic bombs had upon the emperor’s decision to surrender at the end of World War II. I guess that there may not be a lot of primary sources written by the emperor himself, so I have formed three separate questions to look at his decisions from different angles. My first question focuses on what Japanese primary sources said at the time, including the emperor. My second question looks at how contemporary Japanese historians interpret this event. Finally, my third question seeks to understand how western historians understand Hirohito’s motivations.
Part 3: Explain how you will find your sources
You need to explain what strategies you have to help you find great sources to answer your research questions.
In this section, you want to specifically name the databases, museums or other research resources you know you will utilise to find the best sources on your topic.
It may also be useful to specifically name important historians or primary sources that you know in advance that you’ll need to read closely to help answer your questions.
Useful sentence starters for explaining source research:
- I have chosen to use…
- One of the best sources I found was…
- The most important sources I have use are…
- To ensure I had a range of perspectives I…
- It was important to include as one of my sources…
Example explanation of source research:
I knew that finding Japanese primary sources was going to be hard, as I fear that many of them have not been translated into English. As a result, I am going to start my research by looking at what western historians say by gathering some academic articles from the JSTOR database. I hope that these historians will reference some translated Japanese primary sources and that will lead me to some great resources. After that, I know that the Tokyo Museum website has some primary source documents that may be of use to me, so look through their resources. Finally, during my background research, I stumbled across the prominent Japanese historian, Suzuki, who focuses a lot on this period, so I want to find out what his opinion is of these events. I believe that these resources should give me ample information to help answer my research questions.
Word limit advice
Answering all of these sections in a limited word count can be a challenge.
Therefore, don’t waste space on things that don’t matter, such as simply describing a historical event or person, or talking about simplistic decision-making choices (such as “I just really like wars”).
The rationale’s purpose is to explain your decision-making process. Therefore, if what you’re saying is not relevant, don’t waste space talking about it.
Example rationale
After learning about Ned Kelly in class, I was fascinated to discover that historians disagree about his motivations. What I wanted to learn about is the role that racist attitudes towards the Irish in colonial Australia had upon his life. I don’t know much about the social division between the English and Irish in Australian history, so I want to see how people who lived during these events described Ned Kelly, in order to see if racism was an important factor.
As a result, I have written my Key Inquiry Question to focus on the representation of Ned Kelly in the popular media. To help answer this, I have written my sub-questions to focus on different media types: my first question asks about how the newspapers reported on Kelly; my second is about how he is mentioned in religious sermons of the day; and my third question focuses on his representation in public posters, such as the ‘wanted’ signs for his arrest.
Since my questions are focused heavily on the primary sources, I know that I will have to start my source research on the Trove newspaper database website. This will allow me to quickly find newspaper reports about the main events in Kelly’s life. Secondly, I know that I will have trouble finding church sermons and public posters, so I will have to look for museum websites that may have these resources already, such as the Museum of Victoria and the State Library of New South Wales. I know that they often have educational resources for teachers that include primary sources. Finally, I know from my background research that Manning Clark has done a lot of research on Kelly’s life, so I hope he will mention important primary sources that can help me out, including the Jerilderie Letter.
Watch a video explanation on the History Skills YouTube channel:
Watch on YouTube
Need a digital Source Investigation template?

What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email

Rationale for the Study
It is important for you to be able to explain the importance of the research you are conducting by providing valid arguments. Rationale for the study, also referred to as justification for the study, is reason why you have conducted your study in the first place. This part in your paper needs to explain uniqueness and importance of your research. Rationale for the study needs to be specific and ideally, it should relate to the following points:
1. The research needs to contribute to the elimination of a gap in the literature. Elimination of gap in the present literature is one of the compulsory requirements for your study. In other words, you don’t need to ‘re-invent the wheel’ and your research aims and objectives need to focus on new topics. For example, you can choose to conduct an empirical study to assess the implications of COVID-19 pandemic on the numbers of tourists visitors in your city. This might be previously undressed topic, taking into account that COVID-19 pandemic is a relatively recent phenomenon.
Alternatively, if you cannot find a new topic to research, you can attempt to offer fresh perspectives on existing management, business or economic issues. For example, while thousands of studies have been previously conducted to study various aspects of leadership, this topic as far from being exhausted as a research area. Specifically, new studies can be conducted in the area of leadership to analyze the impacts of new communication mediums such as TikTok, and other social networking sites on leadership practices.
You can also discuss the shortcomings of previous works devoted to your research area. Shortcomings in previous studies can be divided into three groups:
a) Methodological limitations . Methodology employed in previous study may be flawed in terms of research design, research approach or sampling.
b) Contextual limitations . Relevance of previous works may be non-existent for the present because external factors have changed.
c) Conceptual limitations . Previous studies may be unjustifiably bound up to a particular model or an ideology.
While discussing the shortcomings of previous studies you should explain how you are going to correct them. This principle is true to almost all areas in business studies i.e. gaps or shortcomings in the literature can be found in relation to almost all areas of business and economics.
2. The research can be conducted to solve a specific problem. It helps if you can explain why you are the right person and in the right position to solve the problem. You have to explain the essence of the problem in a detailed manner and highlight practical benefits associated with the solution of the problem. Suppose, your dissertation topic is “a study into advantages and disadvantages of various entry strategies into Chinese market”. In this case, you can say that practical implications of your research relates to assisting businesses aiming to enter Chinese market to do more informed decision making.
Alternatively, if your research is devoted to the analysis of impacts of CSR programs and initiatives on brand image, practical contributions of your study would relate to contributing to the level of effectiveness of CSR programs of businesses.
Additional examples of studies that can assist to address specific practical problems may include the following:
- A study into the reasons of high employee turnover at Hanson Brick
- A critical analysis of employee motivation problems at Esporta, Finchley Road, London
- A research into effective succession planning at Microsoft
- A study into major differences between private and public primary education in the USA and implications of these differences on the quality of education
However, it is important to note that it is not an obligatory for a dissertation to be associated with the solution of a specific problem. Dissertations can be purely theory-based as well. Examples of such studies include the following:
- Born or bred: revising The Great Man theory of leadership in the 21 st century
- A critical analysis of the relevance of McClelland’s Achievement theory to the US information technology industry
- Neoliberalism as a major reason behind the emergence of the global financial and economic crisis of 2007-2009
- Analysis of Lewin’s Model of Change and its relevance to pharmaceutical sector of France
3. Your study has to contribute to the level of professional development of the researcher . That is you. You have to explain in a detailed manner in what ways your research contributes to the achievement of your long-term career aspirations.
For example, you have selected a research topic of “ A critical analysis of the relevance of McClelland’s Achievement theory in the US information technology industry ”. You may state that you associate your career aspirations with becoming an IT executive in the US, and accordingly, in-depth knowledge of employee motivation in this industry is going to contribute your chances of success in your chosen career path.
Therefore, you are in a better position if you have already identified your career objectives, so that during the research process you can get detailed knowledge about various aspects of your chosen industry.

My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline.
John Dudovskiy
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Study Rationale
Last Updated: May 19, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 56,425 times.
A study rationale explains the reason for a study and the importance of its findings for a particular field. Commonly, you'll need to write a study rationale as part of a university course of study, although you may also need to write one as a professional researcher to apply for funding or other support. As a student, your study rationale also justifies how it fulfills the requirements for your degree program or course of study. Do research before you write your study rationale so that you can discuss the previous work your study builds on and explain its significance to your field. Thorough research is also important in the professional context because your rationale will likely become part of the contract if funding or support is approved. [1] X Research source
Describing What You Hope to Accomplish

- For example, suppose you want to study how working the night shift affects the academic performance of college students who are taking classes during the day. A narrow question would measure a specific impact based on a specific amount of hours worked.

- Justify the methodology you're using. If there's another methodology that might accomplish the same result, describe it and explain why your methodology is superior — perhaps because it's more efficient, takes less time, or uses fewer resources. For example, you might get more information out of personal interviews, but creating an online questionnaire is more cost-effective.
- Particularly if you're seeking funding or support, this section of your rationale will also include details about the cost of your study and the facilities or resources you'll need. [3] X Research source
Tip: A methodology that is more complex, difficult, or expensive requires more justification than one that is straightforward and simple.

- For example, if you're studying the effect of working the night shift on academic performance, you might hypothesize that working 4 or more nights a week lowers students' grade point averages by more than 1 point.

- Use action words, such as "quantify" or "establish," when writing your goals. For example, you might write that one goal of your study is to "quantify the degree to which working at night inhibits the academic performance of college students."
- If you are a professional researcher, your objectives may need to be more specific and concrete. The organization you submit your rationale to will have details about the requirements to apply for funding and other support. [5] X Research source
Explaining Your Study's Significance

- Going into extensive detail usually isn't necessary. Instead, highlight the findings of the most significant work in the field that addressed a similar question.
- Provide references so that your readers can examine the previous studies for themselves and compare them to your proposed study.

- Methodological limitations: Previous studies failed to measure the variables appropriately or used a research design that had problems or biases
- Contextual limitations: Previous studies aren't relevant because circumstances have changed regarding the variables measured
- Conceptual limitations: Previous studies are too tied up in a specific ideology or framework

- For example, if a previous study had been conducted to support a university's policy that full-time students were not permitted to work, you might argue that it was too tied up in that specific ideology and that this biased the results. You could then point out that your study is not intended to advance any particular policy.
Tip: If you have to defend or present your rationale to an advisor or team, try to anticipate the questions they might ask you and include the answers to as many of those questions as possible.
Including Academic Proposal Information

- As a student, you might emphasize your major and specific classes you've taken that give you particular knowledge about the subject of your study. If you've served as a research assistant on a study with a similar methodology or covering a similar research question, you might mention that as well.
- If you're a professional researcher, focus on the experience you have in a particular field as well as the studies you've done in the past. If you have done studies with a similar methodology that were important in your field, you might mention those as well.
Tip: If you don't have any particular credentials or experience that are relevant to your study, tell the readers of your rationale what drew you to this particular topic and how you became interested in it.

- For example, if you are planning to conduct the study as fulfillment of the research requirement for your degree program, you might discuss any specific guidelines for that research requirement and list how your study meets those criteria.

- In most programs, there will be specific wording for you to include in your rationale if you're submitting it for a certain number of credits. Your instructor or advisor can help make sure you've worded this appropriately.
Study Rationale Outline and Example

Expert Q&A
- This article presents an overview of how to write a study rationale. Check with your instructor or advisor for any specific requirements that apply to your particular project. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://research.com/research/how-to-write-research-methodology
- ↑ https://ris.leeds.ac.uk/applying-for-funding/developing-your-proposal/resources-and-tips/key-questions-for-researchers/
- ↑ https://www.cwauthors.com/article/how-to-write-the-rationale-for-your-research
- ↑ http://www.writingcentre.uct.ac.za/sites/default/files/image_tool/images/167/Rationale.pdf
- ↑ https://www.niaid.nih.gov/grants-contracts/write-research-plan
- ↑ https://www.esc.edu/degree-planning-academic-review/degree-program/student-degree-planning-guide/rationale-essay-writing/writing-tips/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors

Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How To Make Rationale in Research: A Thorough Overview
Struggling to make the right rationale for your research? Learn how to make rationale in research to create the perfect plan for success.
Any academic or scientific discipline relies heavily on research. However, in order to do research properly, it is necessary to comprehend the rationale behind it. A research rationale is a succinct explanation of why a certain research project is required, describing the justifications for the study as well as the advantages it is expected to provide.
Writing a persuasive rationale is critical for obtaining approval for your research project and communicating the importance of your research. However, developing a convincing one can be difficult, especially for people new to research or unfamiliar with academic expectations.
After reading this thorough overview on “how to make rationale in research”, you will be better equipped to justify your research and communicate its significance to your academic community. Whether you are a student or a seasoned researcher, this article will provide valuable insights and strategies for creating a powerful research rationale.
What is a Rationale in Research?
A research rationale provides an organized strategy for the whole research and acts as the cornerstone of the research project. It contributes to the research’s rationale by stating why the study is significant, what its aims are, and what the expected findings are. In essence, it is a compelling argument for why the study should be carried out.
A well-written research rationale should be concise, precise, and persuasive. It should clarify the problem or issue that the study attempts to solve, the knowledge or understanding gap that the study seeks to fill, and the possible advantages that it may provide. Furthermore, the reasoning should demonstrate that the research is possible, ethical, and pertinent to the subject of study.
A research project that lacks a strong rationale may lack direction and may fail to address the stated problem or issue. It can also make obtaining financing or permission from institutional review boards (IRBs) or other governing bodies difficult. As a result, devoting effort to developing a compelling research rationale is critical to the success of any research.
Why is a Research Rationale Important?
For many reasons, a research rationale is crucial. For starters, it helps to explain the necessity for the research project by demonstrating why the study is required and what gaps in knowledge or understanding it attempts to fill.
Second, it includes a clear and succinct problem statement that outlines the precise research questions or objectives that the study intends to answer.
Finally, it aids in demonstrating the research’s potential influence by demonstrating how it may lead to the creation of new knowledge, practices, or policies.
To achieve this, you should focus on communicating the potential benefits of your project, while also acknowledging its limitations. This requires a thorough understanding of the research problem and a critical evaluation of the proposed methods and approaches.
It is also important to include sufficient detail about the methods you plan to use, any ethical considerations to consider, and how you will evaluate your results. This helps to demonstrate that you have a well-developed and thoughtful research plan, which is essential for securing funding or gaining approval from academic institutions.
Consider an example of a research project to demonstrate this. Assume you want to investigate the effectiveness of a new teaching style in enhancing student learning results. A compelling rationale for this study might include:
- Demonstrating the need for the study: You may explain that there is a rising concern in the educational environment about low student performance and that standard teaching approaches may not be helpful for all students.
- Providing a clear problem statement: For example, you might say that the study will look into whether the new teaching approach is effective at enhancing student learning outcomes and what factors may impact its effectiveness.
- Highlighting the research’s potential impact: You might argue that if the study shows that if the new teaching approach is effective, it will be adopted in other schools, increasing student learning results.
The research rationale in this example gives a clear and compelling explanation for the necessity to perform the study, emphasizing its relevance, problem statement, and possible impact.
A Model: Problem-Solution-Rationale
The Problem-Solution-Rationale model is a helpful framework for developing a strong research rationale, it can assist you in organizing your rationale and ensuring that it clearly conveys all information required for an effective research rationale. This model consists of three major components: identifying the problem, proposing a solution, and explaining the rationale for why the proposed solution is necessary.
Identifying the Problem
The first stage in this model is to identify the problem that the study will attempt to solve. This could entail assessing existing research on the topic, finding gaps in knowledge or understanding, or emphasizing new difficulties or issues that have occurred. A clear problem statement serves as the research’s foundation, outlining the specific research questions or objectives that the study seeks to address.
Proposing a Solution
The model’s second stage is to suggest a solution to the identified problem. This might include creating a new theoretical framework, putting a new hypothesis to the test, or suggesting a new intervention or practice. The proposed solution should be based on a thorough review of the literature and a clear understanding of the research problem.
Providing a Rationale
The model’s final stage is to present a rationale for why the suggested solution is required. This might include emphasizing the possible advantages of the suggested solution, explaining how it builds on past research, or demonstrating how it fills a knowledge or understanding gap.
Language to Signal Rationale
Effective communication is crucial when it comes to justifying the significance of your research. One of the ways you can achieve this is by using specific language that signals the rationale to your intended audience. By doing so, you can clearly convey the reasons for your study and its potential benefits to your audience. Here are a couple of such examples:
- “The goal of this research is to fill a knowledge gap on…”
- “We selected this methodology because it allows us to address the research question more effectively.”
- “Our approach is informed by the need to address the practical challenges of…”
- “This research is significant because it contributes to our understanding of…”
Using statements like these can assist to convey the rationale to your audience and stress the significance of your research.
Language for Further Justification – Showing Importance
Once you’ve indicated the rationale for your research, it’s critical to give further justification that emphasizes the relevance of your study. Here are some sentences that might be used to emphasize the significance of your research:
- “By addressing this gap in knowledge, we can gain a better understanding of…”
- “This study is significant because it contributes to the development of…”
- “The implications of this research are far-reaching, and it can inform…”
- “By examining this issue, we can shed light on the broader implications of…”
How to Make Rationale In Research
Writing a compelling rationale for a research proposal is critical to obtaining funds and support for the research you are conducting. In this section, you will learn how to make rationale in research by implementing the four crucial aspects of a rationale: background on all previous research on the issue, the study’s open questions, identification of gaps in the literature, and the importance of filling these gaps.
Background on All Previous Research:
You must clarify the existing level of knowledge of the topic to offer a clear grasp of your research proposal. This entails analyzing all past research on the subject and determining what has been done previously. It is critical to present a thorough summary of existing research, including major results, hypotheses, and methodology. This can assist in demonstrating that you have a deep awareness of the field’s present state of knowledge and how your planned study might contribute to it.
The Study’s Open Questions
The next stage is to identify the study’s open questions. This entails investigating areas where existing knowledge falls short and comprehension gaps exist. You may highlight the need for more research and explain how your research will address these gaps by identifying unanswered questions.
Literature Gaps
Once you’ve discovered the open questions, describe how your research will solve them. This requires recognizing gaps in the current literature and describing how your research will address these gaps. Make it a point to explain how the proposed research differs from prior studies and how it will add to existing knowledge in the subject.
The Importance of Filling These Gaps:
Finally, it is critical to demonstrate the importance of filling these gaps in the current literature. This includes showing the possible advantages of the research and outlining how it will help the field if it can result in new ideas or new approaches, or the impact it will have on real society implications.
Unleash the Power of Infographics with Mind the Graph
Whether you’re a seasoned scientist or just starting out in your research career, Mind the Graph is a valuable, user-friendly, and intuitive tool that can help to elevate the impact of your research by making it more engaging, accessible, and understandable to a wider audience.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Unlock Your Creativity
Create infographics, presentations and other scientifically-accurate designs without hassle — absolutely free for 7 days!
About Jessica Abbadia
Jessica Abbadia is a lawyer that has been working in Digital Marketing since 2020, improving organic performance for apps and websites in various regions through ASO and SEO. Currently developing scientific and intellectual knowledge for the community's benefit. Jessica is an animal rights activist who enjoys reading and drinking strong coffee.
Content tags

How to write the rationale for research?

How to evaluate bias in meta-analysis within meta-epidemiological studies?

How to handle discrepancies while you collect data for systemic review
The research’s rationale describes why the study was undertaken (in a thesis or article) or why the study should be accompanied (in a proposal). This implies that the research justification should explain why the study is/was necessary to the reader or examiner. It is sometimes known as a study’s “purpose” or “justification.” While this is not difficult to understand in and of itself, you may be questioning how the study’s reasoning differs from your research question or the explanation of the problem of your study and how it turns into the remainder of your thesis or research paper.
Introduction
The rationale of your research is the objective of the study. The reason should explain why the research was started in the first place. It’s an essential part of your work since it demonstrates the significance and uniqueness of your research. As a result, it’s often referred to as the study’s reason. Your analysis would be arranged in an ideal world: observation, justification, hypothesis, objectives, methodology, findings, and conclusions. To begin writing your rationale, offer background information on all the research on your study topic. Then consider, “What is missing?” or “What are the research’s unanswered questions?” Identify the gaps in the literature and explain why they must be filled. Finally, it resolves to serve as the foundation for your investigation.
A study’s reason might be provided before and after the investigation.
- Before : The reason is essential to your research proposal since it represents the work plan you developed before carrying out your investigation.
- After : When the investigation is over, the justification is given in a literature research paper or thesis to explain why you choose to focus on the specific subject. In this case, you would connect your research project’s logic to the study’s goals and outcomes.

The rationale for the study
Consider a research rationale, a set of arguments explaining why a study is required and significant in light of its context. It is also the study’s reason, rationale, or thesis statement. Essentially, you want to persuade your reader that you are not repeating what others have already stated and that your perspective did not emerge from thin air. You’ve researched and found a knowledge gap that this justification now fills.
Basic elements of the research rationale
Typically, a clinical research justification is provided near the conclusion of the introduction. This area is prominent in high-impact-factor international publications such as Nature and Science. There is usually a line after the introduction that begins with “here we show” or “in this paper, we demonstrate.” This paragraph is part of a logical sequence of information, which is often (but not always) presented in the following order:
- Research background : What brings you here? Present (and cite) previous research and data on the subject.
- A gap in the literature : Which gaps haven’t been addressed based on the background evidence presented? Or, what is the problem that needs to be solved/process that needs to be improved?
- Research rationale : Why is it critical to fill these gaps or to solve/improve this problem/process?
- Research objectives and methodology : What will you investigate (your research question/goal)? How are you going to approach it (methods)?

Hope to accomplish
Describe the issue that your research will address: The problem your study will address, also known as your research subject, informs the reader about the scope of your investigation. Your research topic should be as detailed as possible, especially in a professional environment. In addition, specific research topics are more likely to lead to financing opportunities for your project.
Discourse the methodology for your study: Explain to your audience how you intend to conduct your clinical research and offer a broad timeline for each stage. Include details about how you plan to contact research participants if your study spans several months or years.
Predict the results of your study: A hypothesis isn’t always necessary, but it might assist in supporting your case. If you can make a more than speculative forecast, include it in your rationale. To represent your research topic, make your hypothesis as detailed as possible.
Clarify what you hope your study will accomplish: Your clinical research should uncover something fresh that has not before been explored in your sector. Finding something that no one else has discovered isn’t enough. You must also explain that your findings will significantly advance your field or that they will clear up a past misunderstanding.
In a journal-accepted research manuscript, your justification should be no more than a few words long (no longer than one brief paragraph). A longer description is generally allowed in a manuscript or thesis; depending on the length and type of your material, this might be up to several paragraphs lengthy. A wholly new or unique technique may require a more prolonged and extensive justification than one that deviates somewhat from well-established procedures and approaches.
It is critical to discuss the reason for your study to understand the relevance and uniqueness of your research effort. You will have persuaded readers of the significance of your work once you have adequately expressed the reason(s) for your study. Defining the justification research is a critical component of the research process and academic writing in any reasoning research endeavour . This is what you use in your research paper for the first time to explain the research problem inside your dissertation subject. This will give you the research reason you require to define your research topic and potential outcomes.
About Pubrica
Pubrica’s research team generates scientific and medical research articles that practitioners and authors may use as a resource. Pubrica medical writers help you create and modify the introduction by advising the reader of any defects or holes in the chosen research subject. Our experts are familiar with the structure that begins with a broad topic and then continues to a problem and background before going on to a targeted issue to provide the hypothesis.
- Huggett, Kathryn N., and William B. Jeffries. “Overview of active learning research and rationale for active learning.” How-to Guide for Active Learning . Springer, Cham, 2021. 1-7.
- Bandrowski, Anita, et al. “Sparc data structure: Rationale and design of a fair standard for biomedical research data.” bioRxiv (2021).
- Andriotis, Konstantinos. “RATIONALE FOR LAUNCHING A NEW JOURNAL.” Journal of Qualitative Research 1.1 (2020): 1-6.
- Russell, David R. “Retreading, Non-ing, and a TPC Rationale for Sub-disciplining in Writing Studies.” College English 82.5 (2020): 472-483.
pubrica-academy
Related posts.
Causes of Prolonged Use of Masks during Covid- 19 Pandemic

How to Structure your research article

How Evidence-based practice (EBP) can be translated as health communication or patient education materials
Comments are closed.
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
How to Write the Rationale for a Research Proposal
Table of Contents
Writing a research proposal can be intimidating, especially when you are expected to explain the rationale behind your project. This article will help you learn how to write the rationale for a research proposal to provide justification for why it should be pursued. A good rationale should give readers an understanding of why your project is worth undertaking and how it will contribute to existing knowledge. It should outline any practical implications that could come from your work. By thoroughly preparing this section of your proposal , you will increase the chances of having your research approved.
What Is a Rationale in Research?
A research rationale provides a detailed explanation of why a study is necessary and should be carried out. It convinces the reader or examiner of the importance of the research by outlining its relevance, significance, and potential contribution to existing knowledge. Additionally, it helps transition from the research problem to the methods used in the study, connecting both elements into one comprehensive argument. The research rationale justifies why the researcher chose to conduct this particular study over any other possible alternative studies.
Why Is a Research Rationale Important?
A well-written rationale can help demonstrate your commitment to the project. It can convince reviewers that you have put thought into developing a high-quality research plan. When composing this section, focus on the scientific merit of your proposed study by providing clear and concise reasons for conducting the research. Your goal is to communicate the potential benefits of your project and show that you understand its limitations. Include sufficient detail about the methods you plan to use, any ethical considerations to consider, and how you will evaluate your results. Explaining why your research is important and necessary is essential for getting approval from funding bodies or academic institutions. Your rationale should provide a convincing argument for why the project needs to be conducted. The rationale must make it clear that there are potential benefits that justify its costs. Consider the broader impact of your work and describe how it could contribute to furthering knowledge in the field.

The rationale for research is also known as the justification of the study. Make a mention of the following points while writing the rationale for a research proposal:
Background on All Previous Research on the Subject of Your Study
It is important to include background information on what research has already been done on the study topic. This will help to build a foundation for understanding the current knowledge, open questions, and gaps.
The Open Questions of the Study
Highlighting the open questions related to the study topic helps to identify potential areas for further exploration. It gives readers an understanding of where new research could be helpful. It is essential to state these questions to have clear objectives and goals for the research proposal.
Identify the Gaps in Literature
Identifying literature gaps helps highlight areas that have not yet been studied. This provides the opportunity to add new information and understanding to the field. By including these points in the rationale, the writer can showcase how his work will contribute to existing research.
Highlight the Significance of Addressing These Gaps
Emphasizing why it is important to address those gaps is vital in any research proposal. It allows readers to understand why this particular project needs to be undertaken. By clearly outlining why addressing these gaps is crucial, the writer can successfully argue why his proposed project should be given consideration.
A rationale for a research proposal can help convince the reader of the importance and relevance of your study. This article explains the importance of a rationale and discusses the key elements to learn how to write the rationale for a research proposal . Following these tips will let you create a powerful research rationale that will help convince others of the value of your project.

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Proposal Generator Articles
Creative terms and conditions agreement in business proposal.
In business, proposals are essential for securing contracts and agreements with clients. However, a proposal is only complete with terms…
- Proposal Generator
Free guide to a statement of proposal sample
A statement of proposal is a document that outlines a proposed project or initiative in detail. It is typically used…
Free Proposal Letter for Training and Development for a Head Start
Training and development are essential to improve employees’ skills, knowledge, and productivity. A well-crafted training proposal can help an organization…
Detailed Guide to Free HR Consulting Proposal
HR consulting is an essential service for businesses of all sizes. HR consultants provide expert guidance to organizations on various…
Key Guide to Better Remote Work Proposal
The rise of remote work has been a significant trend in the business world over the last few years. With…
Guide to Free E-Commerce Proposal Template
E-commerce has become one of the most popular ways of doing business recently. With the increasing number of people using…

Masks work, our comprehensive review has found
Professor of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford
Professor of Global Biosecurity, NHMRC L3 Research Fellow, Head, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney
Professor in the Division of Epidemiology, University of Toronto
Disclosure statement
In relation to the research reported here, there was no direct funding. Trish Greenhalgh has received funding for related work from Wellcome Trust and National Institute for Health and Care Research. She is a member of Independent SAGE (unpaid role to engage directly with the public on COVID-19 related science).
C Raina MacIntyre receives funding from NHMRC (L3 Investigator grant and Centre for Research Excellence) and MRFF (Aerosol transmission of SARS-CoV-2 experimentally and in an intensive care setting) currently. She currently receives funding from Sanofi for research on influenza and pertussis. She is the director of EPIWATCH®️, which is a UNSW, Kirby Institute initiative.
David Fisman receives funding from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research. Over the past 5 years he has served on paid advisory boards for companies that manufacture vaccines against respiratory pathogens, including SARS-CoV-2, influenza and Streptococcus pneumoniae, including Sequirus, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Merck and Sanofi-Pasteur. During the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic he served as a paid legal expert for the Ontario Nurses Association and the Elementary Teachers Federation of Ontario on issues related to workplace safety in the face of an airborne virus like SARS-CoV-2.
University of Toronto provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation CA.
University of Oxford provides funding as a member of The Conversation UK.
UNSW Sydney provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
University of Toronto provides funding as a member of The Conversation CA-FR.
View all partners
When a Texan farm worker caught bird flu from cattle recently, social media was abuzz with rumours. While bird flu is not a human pandemic, scientists and policymakers the world over are keen to prepare as best they can for when such a pandemic emerges – a tricky task, given that science is messy, policy must be pragmatic and people’s values don’t always align.
It’s time for masks to enter the chat. At the beginning of a pandemic caused by a novel or newly mutated virus, there may be no vaccine, no firm knowledge about how bad things will get and no specific treatment. Slowing transmission until more is known will be critical.
Getting most people to wear a mask could nip the outbreak in the bud, preventing a pandemic or lessening its impact. Wearing a mask is inconvenient, but not as inconvenient as lockdowns.
But do masks work? A review of masks and respirators, that looked only at clinical trials, concluded that there was not enough evidence to assess whether mask wearing reduces the risk of spreading or contracting respiratory diseases. However, we disagree with that.
The review, by the not-for-profit Cochrane Collaboration, failed to influence recent guidance issued by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in response to the troubling news of bird flu transmission to humans. The CDC recommended well-fitting respirators – along with overalls and safety goggles – for anyone working with potentially infected cattle until the bird flu threat subsides.
Is this latest guidance based on sound evidence? According to our new review of the evidence , yes. Like the Cochrane team, we pooled data from randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and analysed the combined data – a so-called meta-analysis.
Unlike them, we also examined non-RCT evidence, including dozens of laboratory studies which showed that respiratory infections, including the common cold, COVID, flu, measles and TB, spread mainly through the air .
Laboratory evidence showed that different mask materials are better or worse at filtering tiny particles, and more or less breathable – especially when damp. This explains why a cloth or paper mask that’s become soggy from the moisture in exhaled air gets harder to breathe through and may be less protective.
Whereas medical masks are typically tied loosely around the face (hence air can bypass the filter), respirators fit snugly and if worn at work must be fit-tested to make sure that all air inhaled or exhaled passes through a high-grade filter.
All this non-RCT evidence is crucially important for the design of RCTs. Because respiratory viruses float in the air, to be optimally effective a mask must be made of high-filtration material and must be fit closely. It should not be removed while indoors or the person will immediately be exposed to infectious particles in the air.
It follows that we should not expect RCTs of badly designed masks, masks that don’t fit or masks that are worn only some of the time, to show an effect. Neither should we expect mere advice to wear masks to have any effect unless it is followed.

Finally, when comparing respirators with masks in places where there is a high risk of infection, such as a hospital, the respirator needs to be worn continuously until the person leaves the building , not just popped on occasionally when doing so-called “aerosol-generating procedures” – such as intubating a patient.
If we take these crucial details of RCT design into account, rather than just comparing any masks-on, masks-off experiments, we find that masks are effective, and respirators even more effective, in reducing the spread of respiratory disease. We can also explain why some previous reviews appeared to show that this wasn’t the case.
Most RCTs of mask-wearing by the public were actually trials of advice to wear masks. In both RCTs and observational studies (such as real-world experiments), there was a dose-response effect: the more people wore their masks, the more effective the masks turned out to be. And when there’s a looming pandemic, people do tend to wear their masks.
The bottom line
When we looked at RCTs, we found that masks do protect in the community, and N95 respirators (masks made using higher-grade filtration material and designed to fit closely around the face to protect against airborne contaminants) are superior to masks in healthcare workers, especially when respirators were worn continuously at work. Non-RCT evidence also shows that masks work and respirators work better.
Let’s hope we’re not heading for another pandemic. But as we contemplate that possibility, the bottom line from our recent review is masks work. Along with improving indoor air quality and avoiding crowded, underventilated places, they provide the best way to avoid catching a respiratory infection . And our findings support previous advice to not just wear any mask but wear the best mask available .
- Public health
- Coronavirus
- Airborne virus

Research Fellow

Senior Research Fellow - Women's Health Services

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Why writing by hand beats typing for thinking and learning
Jonathan Lambert

If you're like many digitally savvy Americans, it has likely been a while since you've spent much time writing by hand.
The laborious process of tracing out our thoughts, letter by letter, on the page is becoming a relic of the past in our screen-dominated world, where text messages and thumb-typed grocery lists have replaced handwritten letters and sticky notes. Electronic keyboards offer obvious efficiency benefits that have undoubtedly boosted our productivity — imagine having to write all your emails longhand.
To keep up, many schools are introducing computers as early as preschool, meaning some kids may learn the basics of typing before writing by hand.
But giving up this slower, more tactile way of expressing ourselves may come at a significant cost, according to a growing body of research that's uncovering the surprising cognitive benefits of taking pen to paper, or even stylus to iPad — for both children and adults.
Is this some kind of joke? A school facing shortages starts teaching standup comedy
In kids, studies show that tracing out ABCs, as opposed to typing them, leads to better and longer-lasting recognition and understanding of letters. Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning. In adults, taking notes by hand during a lecture, instead of typing, can lead to better conceptual understanding of material.
"There's actually some very important things going on during the embodied experience of writing by hand," says Ramesh Balasubramaniam , a neuroscientist at the University of California, Merced. "It has important cognitive benefits."
While those benefits have long been recognized by some (for instance, many authors, including Jennifer Egan and Neil Gaiman , draft their stories by hand to stoke creativity), scientists have only recently started investigating why writing by hand has these effects.
A slew of recent brain imaging research suggests handwriting's power stems from the relative complexity of the process and how it forces different brain systems to work together to reproduce the shapes of letters in our heads onto the page.
Your brain on handwriting
Both handwriting and typing involve moving our hands and fingers to create words on a page. But handwriting, it turns out, requires a lot more fine-tuned coordination between the motor and visual systems. This seems to more deeply engage the brain in ways that support learning.

Shots - Health News
Feeling artsy here's how making art helps your brain.
"Handwriting is probably among the most complex motor skills that the brain is capable of," says Marieke Longcamp , a cognitive neuroscientist at Aix-Marseille Université.
Gripping a pen nimbly enough to write is a complicated task, as it requires your brain to continuously monitor the pressure that each finger exerts on the pen. Then, your motor system has to delicately modify that pressure to re-create each letter of the words in your head on the page.
"Your fingers have to each do something different to produce a recognizable letter," says Sophia Vinci-Booher , an educational neuroscientist at Vanderbilt University. Adding to the complexity, your visual system must continuously process that letter as it's formed. With each stroke, your brain compares the unfolding script with mental models of the letters and words, making adjustments to fingers in real time to create the letters' shapes, says Vinci-Booher.
That's not true for typing.
To type "tap" your fingers don't have to trace out the form of the letters — they just make three relatively simple and uniform movements. In comparison, it takes a lot more brainpower, as well as cross-talk between brain areas, to write than type.
Recent brain imaging studies bolster this idea. A study published in January found that when students write by hand, brain areas involved in motor and visual information processing " sync up " with areas crucial to memory formation, firing at frequencies associated with learning.
"We don't see that [synchronized activity] in typewriting at all," says Audrey van der Meer , a psychologist and study co-author at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. She suggests that writing by hand is a neurobiologically richer process and that this richness may confer some cognitive benefits.
Other experts agree. "There seems to be something fundamental about engaging your body to produce these shapes," says Robert Wiley , a cognitive psychologist at the University of North Carolina, Greensboro. "It lets you make associations between your body and what you're seeing and hearing," he says, which might give the mind more footholds for accessing a given concept or idea.
Those extra footholds are especially important for learning in kids, but they may give adults a leg up too. Wiley and others worry that ditching handwriting for typing could have serious consequences for how we all learn and think.
What might be lost as handwriting wanes
The clearest consequence of screens and keyboards replacing pen and paper might be on kids' ability to learn the building blocks of literacy — letters.
"Letter recognition in early childhood is actually one of the best predictors of later reading and math attainment," says Vinci-Booher. Her work suggests the process of learning to write letters by hand is crucial for learning to read them.
"When kids write letters, they're just messy," she says. As kids practice writing "A," each iteration is different, and that variability helps solidify their conceptual understanding of the letter.
Research suggests kids learn to recognize letters better when seeing variable handwritten examples, compared with uniform typed examples.
This helps develop areas of the brain used during reading in older children and adults, Vinci-Booher found.
"This could be one of the ways that early experiences actually translate to long-term life outcomes," she says. "These visually demanding, fine motor actions bake in neural communication patterns that are really important for learning later on."
Ditching handwriting instruction could mean that those skills don't get developed as well, which could impair kids' ability to learn down the road.
"If young children are not receiving any handwriting training, which is very good brain stimulation, then their brains simply won't reach their full potential," says van der Meer. "It's scary to think of the potential consequences."
Many states are trying to avoid these risks by mandating cursive instruction. This year, California started requiring elementary school students to learn cursive , and similar bills are moving through state legislatures in several states, including Indiana, Kentucky, South Carolina and Wisconsin. (So far, evidence suggests that it's the writing by hand that matters, not whether it's print or cursive.)
Slowing down and processing information
For adults, one of the main benefits of writing by hand is that it simply forces us to slow down.
During a meeting or lecture, it's possible to type what you're hearing verbatim. But often, "you're not actually processing that information — you're just typing in the blind," says van der Meer. "If you take notes by hand, you can't write everything down," she says.
The relative slowness of the medium forces you to process the information, writing key words or phrases and using drawing or arrows to work through ideas, she says. "You make the information your own," she says, which helps it stick in the brain.
Such connections and integration are still possible when typing, but they need to be made more intentionally. And sometimes, efficiency wins out. "When you're writing a long essay, it's obviously much more practical to use a keyboard," says van der Meer.
Still, given our long history of using our hands to mark meaning in the world, some scientists worry about the more diffuse consequences of offloading our thinking to computers.
"We're foisting a lot of our knowledge, extending our cognition, to other devices, so it's only natural that we've started using these other agents to do our writing for us," says Balasubramaniam.
It's possible that this might free up our minds to do other kinds of hard thinking, he says. Or we might be sacrificing a fundamental process that's crucial for the kinds of immersive cognitive experiences that enable us to learn and think at our full potential.
Balasubramaniam stresses, however, that we don't have to ditch digital tools to harness the power of handwriting. So far, research suggests that scribbling with a stylus on a screen activates the same brain pathways as etching ink on paper. It's the movement that counts, he says, not its final form.
Jonathan Lambert is a Washington, D.C.-based freelance journalist who covers science, health and policy.
- handwriting
A systematic literature review of empirical research on ChatGPT in education
- Open access
- Published: 26 May 2024
- Volume 3 , article number 60 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Yazid Albadarin ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0005-8068-8902 1 ,
- Mohammed Saqr 1 ,
- Nicolas Pope 1 &
- Markku Tukiainen 1
Over the last four decades, studies have investigated the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into education. A recent prominent AI-powered technology that has impacted the education sector is ChatGPT. This article provides a systematic review of 14 empirical studies incorporating ChatGPT into various educational settings, published in 2022 and before the 10th of April 2023—the date of conducting the search process. It carefully followed the essential steps outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) guidelines, as well as Okoli’s (Okoli in Commun Assoc Inf Syst, 2015) steps for conducting a rigorous and transparent systematic review. In this review, we aimed to explore how students and teachers have utilized ChatGPT in various educational settings, as well as the primary findings of those studies. By employing Creswell’s (Creswell in Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research [Ebook], Pearson Education, London, 2015) coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation, we sought to gain insight into their initial attempts at ChatGPT incorporation into education. This approach also enabled us to extract insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. The results of this review show that learners have utilized ChatGPT as a virtual intelligent assistant, where it offered instant feedback, on-demand answers, and explanations of complex topics. Additionally, learners have used it to enhance their writing and language skills by generating ideas, composing essays, summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar. Moreover, learners turned to it as an aiding tool to facilitate their directed and personalized learning by assisting in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks. However, the results of specific studies (n = 3, 21.4%) show that overuse of ChatGPT may negatively impact innovative capacities and collaborative learning competencies among learners. Educators, on the other hand, have utilized ChatGPT to create lesson plans, generate quizzes, and provide additional resources, which helped them enhance their productivity and efficiency and promote different teaching methodologies. Despite these benefits, the majority of the reviewed studies recommend the importance of conducting structured training, support, and clear guidelines for both learners and educators to mitigate the drawbacks. This includes developing critical evaluation skills to assess the accuracy and relevance of information provided by ChatGPT, as well as strategies for integrating human interaction and collaboration into learning activities that involve AI tools. Furthermore, they also recommend ongoing research and proactive dialogue with policymakers, stakeholders, and educational practitioners to refine and enhance the use of AI in learning environments. This review could serve as an insightful resource for practitioners who seek to integrate ChatGPT into education and stimulate further research in the field.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Educational technology, a rapidly evolving field, plays a crucial role in reshaping the landscape of teaching and learning [ 82 ]. One of the most transformative technological innovations of our era that has influenced the field of education is Artificial Intelligence (AI) [ 50 ]. Over the last four decades, AI in education (AIEd) has gained remarkable attention for its potential to make significant advancements in learning, instructional methods, and administrative tasks within educational settings [ 11 ]. In particular, a large language model (LLM), a type of AI algorithm that applies artificial neural networks (ANNs) and uses massively large data sets to understand, summarize, generate, and predict new content that is almost difficult to differentiate from human creations [ 79 ], has opened up novel possibilities for enhancing various aspects of education, from content creation to personalized instruction [ 35 ]. Chatbots that leverage the capabilities of LLMs to understand and generate human-like responses have also presented the capacity to enhance student learning and educational outcomes by engaging students, offering timely support, and fostering interactive learning experiences [ 46 ].
The ongoing and remarkable technological advancements in chatbots have made their use more convenient, increasingly natural and effortless, and have expanded their potential for deployment across various domains [ 70 ]. One prominent example of chatbot applications is the Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer, known as ChatGPT, which was introduced by OpenAI, a leading AI research lab, on November 30th, 2022. ChatGPT employs a variety of deep learning techniques to generate human-like text, with a particular focus on recurrent neural networks (RNNs). Long short-term memory (LSTM) allows it to grasp the context of the text being processed and retain information from previous inputs. Also, the transformer architecture, a neural network architecture based on the self-attention mechanism, allows it to analyze specific parts of the input, thereby enabling it to produce more natural-sounding and coherent output. Additionally, the unsupervised generative pre-training and the fine-tuning methods allow ChatGPT to generate more relevant and accurate text for specific tasks [ 31 , 62 ]. Furthermore, reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), a machine learning approach that combines reinforcement learning techniques with human-provided feedback, has helped improve ChatGPT’s model by accelerating the learning process and making it significantly more efficient.
This cutting-edge natural language processing (NLP) tool is widely recognized as one of today's most advanced LLMs-based chatbots [ 70 ], allowing users to ask questions and receive detailed, coherent, systematic, personalized, convincing, and informative human-like responses [ 55 ], even within complex and ambiguous contexts [ 63 , 77 ]. ChatGPT is considered the fastest-growing technology in history: in just three months following its public launch, it amassed an estimated 120 million monthly active users [ 16 ] with an estimated 13 million daily queries [ 49 ], surpassing all other applications [ 64 ]. This remarkable growth can be attributed to the unique features and user-friendly interface that ChatGPT offers. Its intuitive design allows users to interact seamlessly with the technology, making it accessible to a diverse range of individuals, regardless of their technical expertise [ 78 ]. Additionally, its exceptional performance results from a combination of advanced algorithms, continuous enhancements, and extensive training on a diverse dataset that includes various text sources such as books, articles, websites, and online forums [ 63 ], have contributed to a more engaging and satisfying user experience [ 62 ]. These factors collectively explain its remarkable global growth and set it apart from predecessors like Bard, Bing Chat, ERNIE, and others.
In this context, several studies have explored the technological advancements of chatbots. One noteworthy recent research effort, conducted by Schöbel et al. [ 70 ], stands out for its comprehensive analysis of more than 5,000 studies on communication agents. This study offered a comprehensive overview of the historical progression and future prospects of communication agents, including ChatGPT. Moreover, other studies have focused on making comparisons, particularly between ChatGPT and alternative chatbots like Bard, Bing Chat, ERNIE, LaMDA, BlenderBot, and various others. For example, O’Leary [ 53 ] compared two chatbots, LaMDA and BlenderBot, with ChatGPT and revealed that ChatGPT outperformed both. This superiority arises from ChatGPT’s capacity to handle a wider range of questions and generate slightly varied perspectives within specific contexts. Similarly, ChatGPT exhibited an impressive ability to formulate interpretable responses that were easily understood when compared with Google's feature snippet [ 34 ]. Additionally, ChatGPT was compared to other LLMs-based chatbots, including Bard and BERT, as well as ERNIE. The findings indicated that ChatGPT exhibited strong performance in the given tasks, often outperforming the other models [ 59 ].
Furthermore, in the education context, a comprehensive study systematically compared a range of the most promising chatbots, including Bard, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, and Ernie across a multidisciplinary test that required higher-order thinking. The study revealed that ChatGPT achieved the highest score, surpassing Bing Chat and Bard [ 64 ]. Similarly, a comparative analysis was conducted to compare ChatGPT with Bard in answering a set of 30 mathematical questions and logic problems, grouped into two question sets. Set (A) is unavailable online, while Set (B) is available online. The results revealed ChatGPT's superiority in Set (A) over Bard. Nevertheless, Bard's advantage emerged in Set (B) due to its capacity to access the internet directly and retrieve answers, a capability that ChatGPT does not possess [ 57 ]. However, through these varied assessments, ChatGPT consistently highlights its exceptional prowess compared to various alternatives in the ever-evolving chatbot technology.
The widespread adoption of chatbots, especially ChatGPT, by millions of students and educators, has sparked extensive discussions regarding its incorporation into the education sector [ 64 ]. Accordingly, many scholars have contributed to the discourse, expressing both optimism and pessimism regarding the incorporation of ChatGPT into education. For example, ChatGPT has been highlighted for its capabilities in enriching the learning and teaching experience through its ability to support different learning approaches, including adaptive learning, personalized learning, and self-directed learning [ 58 , 60 , 91 ]), deliver summative and formative feedback to students and provide real-time responses to questions, increase the accessibility of information [ 22 , 40 , 43 ], foster students’ performance, engagement and motivation [ 14 , 44 , 58 ], and enhance teaching practices [ 17 , 18 , 64 , 74 ].
On the other hand, concerns have been also raised regarding its potential negative effects on learning and teaching. These include the dissemination of false information and references [ 12 , 23 , 61 , 85 ], biased reinforcement [ 47 , 50 ], compromised academic integrity [ 18 , 40 , 66 , 74 ], and the potential decline in students' skills [ 43 , 61 , 64 , 74 ]. As a result, ChatGPT has been banned in multiple countries, including Russia, China, Venezuela, Belarus, and Iran, as well as in various educational institutions in India, Italy, Western Australia, France, and the United States [ 52 , 90 ].
Clearly, the advent of chatbots, especially ChatGPT, has provoked significant controversy due to their potential impact on learning and teaching. This indicates the necessity for further exploration to gain a deeper understanding of this technology and carefully evaluate its potential benefits, limitations, challenges, and threats to education [ 79 ]. Therefore, conducting a systematic literature review will provide valuable insights into the potential prospects and obstacles linked to its incorporation into education. This systematic literature review will primarily focus on ChatGPT, driven by the aforementioned key factors outlined above.
However, the existing literature lacks a systematic literature review of empirical studies. Thus, this systematic literature review aims to address this gap by synthesizing the existing empirical studies conducted on chatbots, particularly ChatGPT, in the field of education, highlighting how ChatGPT has been utilized in educational settings, and identifying any existing gaps. This review may be particularly useful for researchers in the field and educators who are contemplating the integration of ChatGPT or any chatbot into education. The following research questions will guide this study:
What are students' and teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in education?
What are the main findings derived from empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into learning and teaching?
2 Methodology
To conduct this study, the authors followed the essential steps of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) and Okoli’s [ 54 ] steps for conducting a systematic review. These included identifying the study’s purpose, drafting a protocol, applying a practical screening process, searching the literature, extracting relevant data, evaluating the quality of the included studies, synthesizing the studies, and ultimately writing the review. The subsequent section provides an extensive explanation of how these steps were carried out in this study.
2.1 Identify the purpose
Given the widespread adoption of ChatGPT by students and teachers for various educational purposes, often without a thorough understanding of responsible and effective use or a clear recognition of its potential impact on learning and teaching, the authors recognized the need for further exploration of ChatGPT's impact on education in this early stage. Therefore, they have chosen to conduct a systematic literature review of existing empirical studies that incorporate ChatGPT into educational settings. Despite the limited number of empirical studies due to the novelty of the topic, their goal is to gain a deeper understanding of this technology and proactively evaluate its potential benefits, limitations, challenges, and threats to education. This effort could help to understand initial reactions and attempts at incorporating ChatGPT into education and bring out insights and considerations that can inform the future development of education.
2.2 Draft the protocol
The next step is formulating the protocol. This protocol serves to outline the study process in a rigorous and transparent manner, mitigating researcher bias in study selection and data extraction [ 88 ]. The protocol will include the following steps: generating the research question, predefining a literature search strategy, identifying search locations, establishing selection criteria, assessing the studies, developing a data extraction strategy, and creating a timeline.
2.3 Apply practical screen
The screening step aims to accurately filter the articles resulting from the searching step and select the empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into educational contexts, which will guide us in answering the research questions and achieving the objectives of this study. To ensure the rigorous execution of this step, our inclusion and exclusion criteria were determined based on the authors' experience and informed by previous successful systematic reviews [ 21 ]. Table 1 summarizes the inclusion and exclusion criteria for study selection.
2.4 Literature search
We conducted a thorough literature search to identify articles that explored, examined, and addressed the use of ChatGPT in Educational contexts. We utilized two research databases: Dimensions.ai, which provides access to a large number of research publications, and lens.org, which offers access to over 300 million articles, patents, and other research outputs from diverse sources. Additionally, we included three databases, Scopus, Web of Knowledge, and ERIC, which contain relevant research on the topic that addresses our research questions. To browse and identify relevant articles, we used the following search formula: ("ChatGPT" AND "Education"), which included the Boolean operator "AND" to get more specific results. The subject area in the Scopus and ERIC databases were narrowed to "ChatGPT" and "Education" keywords, and in the WoS database was limited to the "Education" category. The search was conducted between the 3rd and 10th of April 2023, which resulted in 276 articles from all selected databases (111 articles from Dimensions.ai, 65 from Scopus, 28 from Web of Science, 14 from ERIC, and 58 from Lens.org). These articles were imported into the Rayyan web-based system for analysis. The duplicates were identified automatically by the system. Subsequently, the first author manually reviewed the duplicated articles ensured that they had the same content, and then removed them, leaving us with 135 unique articles. Afterward, the titles, abstracts, and keywords of the first 40 manuscripts were scanned and reviewed by the first author and were discussed with the second and third authors to resolve any disagreements. Subsequently, the first author proceeded with the filtering process for all articles and carefully applied the inclusion and exclusion criteria as presented in Table 1 . Articles that met any one of the exclusion criteria were eliminated, resulting in 26 articles. Afterward, the authors met to carefully scan and discuss them. The authors agreed to eliminate any empirical studies solely focused on checking ChatGPT capabilities, as these studies do not guide us in addressing the research questions and achieving the study's objectives. This resulted in 14 articles eligible for analysis.
2.5 Quality appraisal
The examination and evaluation of the quality of the extracted articles is a vital step [ 9 ]. Therefore, the extracted articles were carefully evaluated for quality using Fink’s [ 24 ] standards, which emphasize the necessity for detailed descriptions of methodology, results, conclusions, strengths, and limitations. The process began with a thorough assessment of each study's design, data collection, and analysis methods to ensure their appropriateness and comprehensive execution. The clarity, consistency, and logical progression from data to results and conclusions were also critically examined. Potential biases and recognized limitations within the studies were also scrutinized. Ultimately, two articles were excluded for failing to meet Fink’s criteria, particularly in providing sufficient detail on methodology, results, conclusions, strengths, or limitations. The review process is illustrated in Fig. 1 .
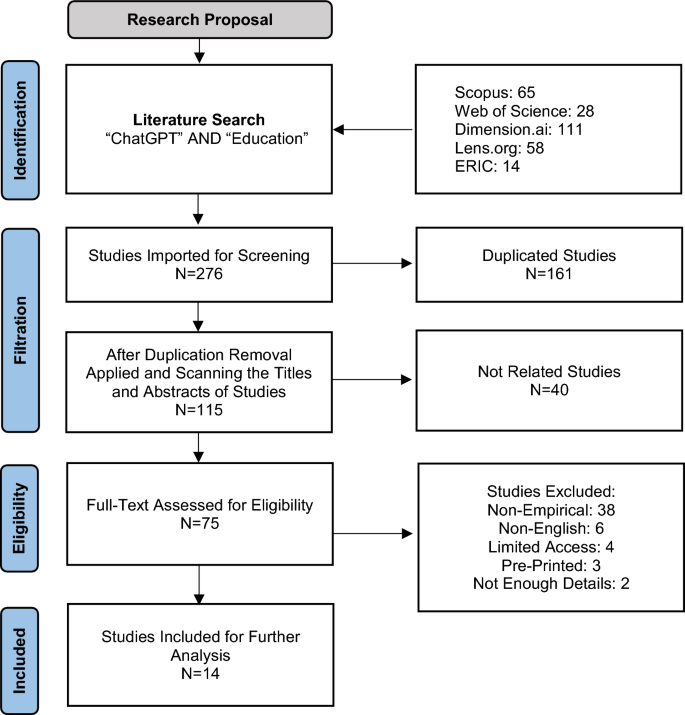
The study selection process
2.6 Data extraction
The next step is data extraction, the process of capturing the key information and categories from the included studies. To improve efficiency, reduce variation among authors, and minimize errors in data analysis, the coding categories were constructed using Creswell's [ 15 ] coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation. The coding process involves three sequential steps. The initial stage encompasses open coding , where the researcher examines the data, generates codes to describe and categorize it, and gains a deeper understanding without preconceived ideas. Following open coding is axial coding , where the interrelationships between codes from open coding are analyzed to establish more comprehensive categories or themes. The process concludes with selective coding , refining and integrating categories or themes to identify core concepts emerging from the data. The first coder performed the coding process, then engaged in discussions with the second and third authors to finalize the coding categories for the first five articles. The first coder then proceeded to code all studies and engaged again in discussions with the other authors to ensure the finalization of the coding process. After a comprehensive analysis and capturing of the key information from the included studies, the data extraction and interpretation process yielded several themes. These themes have been categorized and are presented in Table 2 . It is important to note that open coding results were removed from Table 2 for aesthetic reasons, as it included many generic aspects, such as words, short phrases, or sentences mentioned in the studies.
2.7 Synthesize studies
In this stage, we will gather, discuss, and analyze the key findings that emerged from the selected studies. The synthesis stage is considered a transition from an author-centric to a concept-centric focus, enabling us to map all the provided information to achieve the most effective evaluation of the data [ 87 ]. Initially, the authors extracted data that included general information about the selected studies, including the author(s)' names, study titles, years of publication, educational levels, research methodologies, sample sizes, participants, main aims or objectives, raw data sources, and analysis methods. Following that, all key information and significant results from the selected studies were compiled using Creswell’s [ 15 ] coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation to identify core concepts and themes emerging from the data, focusing on those that directly contributed to our research questions and objectives, such as the initial utilization of ChatGPT in learning and teaching, learners' and educators' familiarity with ChatGPT, and the main findings of each study. Finally, the data related to each selected study were extracted into an Excel spreadsheet for data processing. The Excel spreadsheet was reviewed by the authors, including a series of discussions to ensure the finalization of this process and prepare it for further analysis. Afterward, the final result being analyzed and presented in various types of charts and graphs. Table 4 presents the extracted data from the selected studies, with each study labeled with a capital 'S' followed by a number.
This section consists of two main parts. The first part provides a descriptive analysis of the data compiled from the reviewed studies. The second part presents the answers to the research questions and the main findings of these studies.
3.1 Part 1: descriptive analysis
This section will provide a descriptive analysis of the reviewed studies, including educational levels and fields, participants distribution, country contribution, research methodologies, study sample size, study population, publication year, list of journals, familiarity with ChatGPT, source of data, and the main aims and objectives of the studies. Table 4 presents a comprehensive overview of the extracted data from the selected studies.
3.1.1 The number of the reviewed studies and publication years
The total number of the reviewed studies was 14. All studies were empirical studies and published in different journals focusing on Education and Technology. One study was published in 2022 [S1], while the remaining were published in 2023 [S2]-[S14]. Table 3 illustrates the year of publication, the names of the journals, and the number of reviewed studies published in each journal for the studies reviewed.
3.1.2 Educational levels and fields
The majority of the reviewed studies, 11 studies, were conducted in higher education institutions [S1]-[S10] and [S13]. Two studies did not specify the educational level of the population [S12] and [S14], while one study focused on elementary education [S11]. However, the reviewed studies covered various fields of education. Three studies focused on Arts and Humanities Education [S8], [S11], and [S14], specifically English Education. Two studies focused on Engineering Education, with one in Computer Engineering [S2] and the other in Construction Education [S3]. Two studies focused on Mathematics Education [S5] and [S12]. One study focused on Social Science Education [S13]. One study focused on Early Education [S4]. One study focused on Journalism Education [S9]. Finally, three studies did not specify the field of education [S1], [S6], and [S7]. Figure 2 represents the educational levels in the reviewed studies, while Fig. 3 represents the context of the reviewed studies.

Educational levels in the reviewed studies
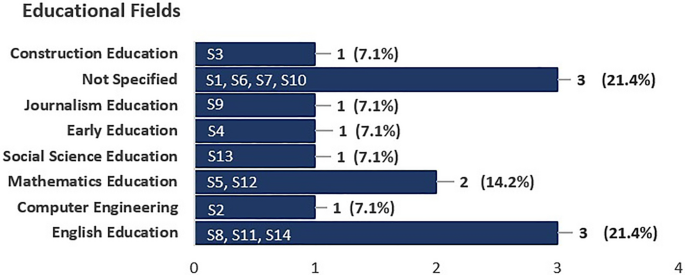
Context of the reviewed studies
3.1.3 Participants distribution and countries contribution
The reviewed studies have been conducted across different geographic regions, providing a diverse representation of the studies. The majority of the studies, 10 in total, [S1]-[S3], [S5]-[S9], [S11], and [S14], primarily focused on participants from single countries such as Pakistan, the United Arab Emirates, China, Indonesia, Poland, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, Spain, Tajikistan, and the United States. In contrast, four studies, [S4], [S10], [S12], and [S13], involved participants from multiple countries, including China and the United States [S4], China, the United Kingdom, and the United States [S10], the United Arab Emirates, Oman, Saudi Arabia, and Jordan [S12], Turkey, Sweden, Canada, and Australia [ 13 ]. Figures 4 and 5 illustrate the distribution of participants, whether from single or multiple countries, and the contribution of each country in the reviewed studies, respectively.
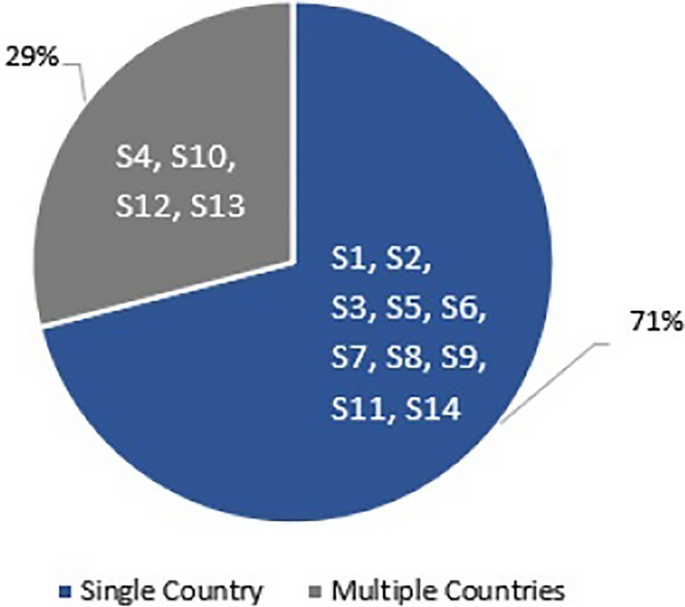
The reviewed studies conducted in single or multiple countries
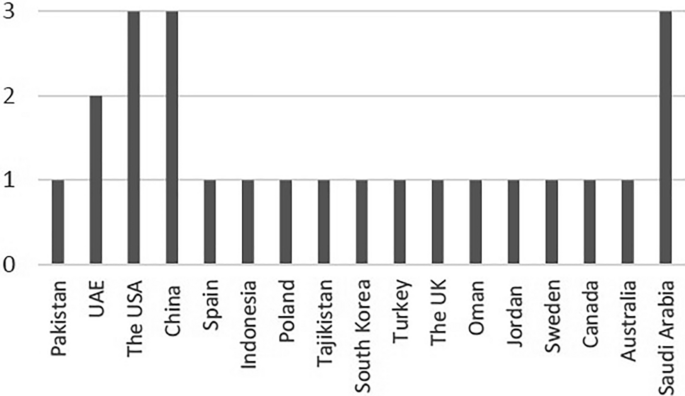
The Contribution of each country in the studies
3.1.4 Study population and sample size
Four study populations were included: university students, university teachers, university teachers and students, and elementary school teachers. Six studies involved university students [S2], [S3], [S5] and [S6]-[S8]. Three studies focused on university teachers [S1], [S4], and [S6], while one study specifically targeted elementary school teachers [S11]. Additionally, four studies included both university teachers and students [S10] and [ 12 , 13 , 14 ], and among them, study [S13] specifically included postgraduate students. In terms of the sample size of the reviewed studies, nine studies included a small sample size of less than 50 participants [S1], [S3], [S6], [S8], and [S10]-[S13]. Three studies had 50–100 participants [S2], [S9], and [S14]. Only one study had more than 100 participants [S7]. It is worth mentioning that study [S4] adopted a mixed methods approach, including 10 participants for qualitative analysis and 110 participants for quantitative analysis.
3.1.5 Participants’ familiarity with using ChatGPT
The reviewed studies recruited a diverse range of participants with varying levels of familiarity with ChatGPT. Five studies [S2], [S4], [S6], [S8], and [S12] involved participants already familiar with ChatGPT, while eight studies [S1], [S3], [S5], [S7], [S9], [S10], [S13] and [S14] included individuals with differing levels of familiarity. Notably, one study [S11] had participants who were entirely unfamiliar with ChatGPT. It is important to note that four studies [S3], [S5], [S9], and [S11] provided training or guidance to their participants before conducting their studies, while ten studies [S1], [S2], [S4], [S6]-[S8], [S10], and [S12]-[S14] did not provide training due to the participants' existing familiarity with ChatGPT.
3.1.6 Research methodology approaches and source(S) of data
The reviewed studies adopted various research methodology approaches. Seven studies adopted qualitative research methodology [S1], [S4], [S6], [S8], [S10], [S11], and [S12], while three studies adopted quantitative research methodology [S3], [S7], and [S14], and four studies employed mixed-methods, which involved a combination of both the strengths of qualitative and quantitative methods [S2], [S5], [S9], and [S13].
In terms of the source(s) of data, the reviewed studies obtained their data from various sources, such as interviews, questionnaires, and pre-and post-tests. Six studies relied on interviews as their primary source of data collection [S1], [S4], [S6], [S10], [S11], and [S12], four studies relied on questionnaires [S2], [S7], [S13], and [S14], two studies combined the use of pre-and post-tests and questionnaires for data collection [S3] and [S9], while two studies combined the use of questionnaires and interviews to obtain the data [S5] and [S8]. It is important to note that six of the reviewed studies were quasi-experimental [S3], [S5], [S8], [S9], [S12], and [S14], while the remaining ones were experimental studies [S1], [S2], [S4], [S6], [S7], [S10], [S11], and [S13]. Figures 6 and 7 illustrate the research methodologies and the source (s) of data used in the reviewed studies, respectively.
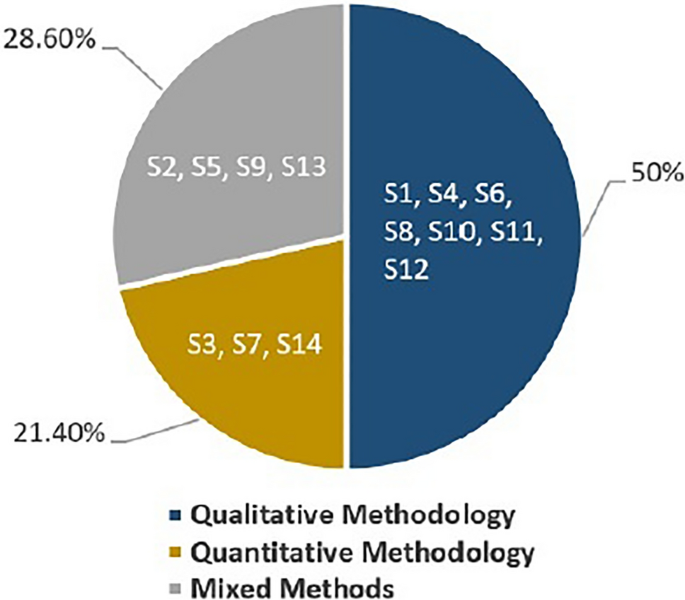
Research methodologies in the reviewed studies
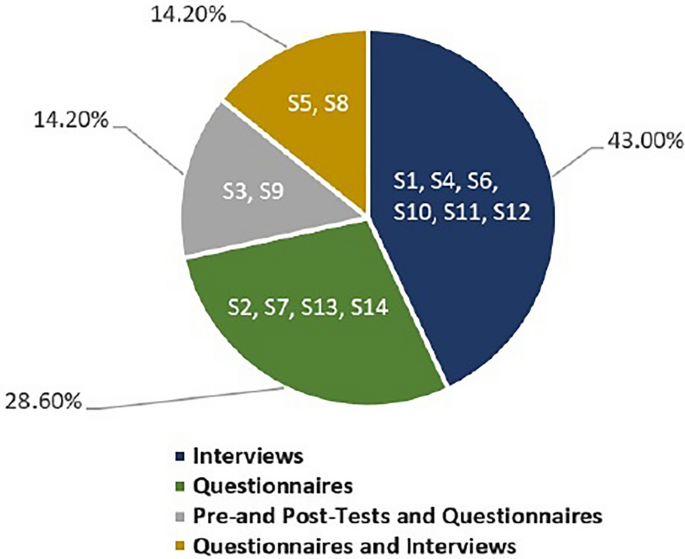
Source of data in the reviewed studies
3.1.7 The aim and objectives of the studies
The reviewed studies encompassed a diverse set of aims, with several of them incorporating multiple primary objectives. Six studies [S3], [S6], [S7], [S8], [S11], and [S12] examined the integration of ChatGPT in educational contexts, and four studies [S4], [S5], [S13], and [S14] investigated the various implications of its use in education, while three studies [S2], [S9], and [S10] aimed to explore both its integration and implications in education. Additionally, seven studies explicitly explored attitudes and perceptions of students [S2] and [S3], educators [S1] and [S6], or both [S10], [S12], and [S13] regarding the utilization of ChatGPT in educational settings.
3.2 Part 2: research questions and main findings of the reviewed studies
This part will present the answers to the research questions and the main findings of the reviewed studies, classified into two main categories (learning and teaching) according to AI Education classification by [ 36 ]. Figure 8 summarizes the main findings of the reviewed studies in a visually informative diagram. Table 4 provides a detailed list of the key information extracted from the selected studies that led to generating these themes.
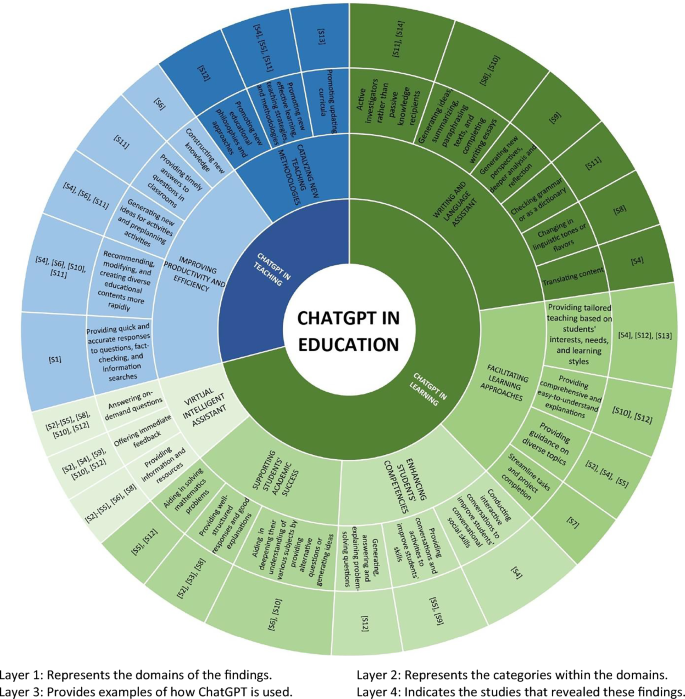
The main findings in the reviewed studies
4 Students' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in learning and main findings from students' perspective
4.1 virtual intelligent assistant.
Nine studies demonstrated that ChatGPT has been utilized by students as an intelligent assistant to enhance and support their learning. Students employed it for various purposes, such as answering on-demand questions [S2]-[S5], [S8], [S10], and [S12], providing valuable information and learning resources [S2]-[S5], [S6], and [S8], as well as receiving immediate feedback [S2], [S4], [S9], [S10], and [S12]. In this regard, students generally were confident in the accuracy of ChatGPT's responses, considering them relevant, reliable, and detailed [S3], [S4], [S5], and [S8]. However, some students indicated the need for improvement, as they found that answers are not always accurate [S2], and that misleading information may have been provided or that it may not always align with their expectations [S6] and [S10]. It was also observed by the students that the accuracy of ChatGPT is dependent on several factors, including the quality and specificity of the user's input, the complexity of the question or topic, and the scope and relevance of its training data [S12]. Many students felt that ChatGPT's answers were not always accurate and most of them believed that it requires good background knowledge to work with.
4.2 Writing and language proficiency assistant
Six of the reviewed studies highlighted that ChatGPT has been utilized by students as a valuable assistant tool to improve their academic writing skills and language proficiency. Among these studies, three mainly focused on English education, demonstrating that students showed sufficient mastery in using ChatGPT for generating ideas, summarizing, paraphrasing texts, and completing writing essays [S8], [S11], and [S14]. Furthermore, ChatGPT helped them in writing by making students active investigators rather than passive knowledge recipients and facilitated the development of their writing skills [S11] and [S14]. Similarly, ChatGPT allowed students to generate unique ideas and perspectives, leading to deeper analysis and reflection on their journalism writing [S9]. In terms of language proficiency, ChatGPT allowed participants to translate content into their home languages, making it more accessible and relevant to their context [S4]. It also enabled them to request changes in linguistic tones or flavors [S8]. Moreover, participants used it to check grammar or as a dictionary [S11].
4.3 Valuable resource for learning approaches
Five studies demonstrated that students used ChatGPT as a valuable complementary resource for self-directed learning. It provided learning resources and guidance on diverse educational topics and created a supportive home learning environment [S2] and [S4]. Moreover, it offered step-by-step guidance to grasp concepts at their own pace and enhance their understanding [S5], streamlined task and project completion carried out independently [S7], provided comprehensive and easy-to-understand explanations on various subjects [S10], and assisted in studying geometry operations, thereby empowering them to explore geometry operations at their own pace [S12]. Three studies showed that students used ChatGPT as a valuable learning resource for personalized learning. It delivered age-appropriate conversations and tailored teaching based on a child's interests [S4], acted as a personalized learning assistant, adapted to their needs and pace, which assisted them in understanding mathematical concepts [S12], and enabled personalized learning experiences in social sciences by adapting to students' needs and learning styles [S13]. On the other hand, it is important to note that, according to one study [S5], students suggested that using ChatGPT may negatively affect collaborative learning competencies between students.
4.4 Enhancing students' competencies
Six of the reviewed studies have shown that ChatGPT is a valuable tool for improving a wide range of skills among students. Two studies have provided evidence that ChatGPT led to improvements in students' critical thinking, reasoning skills, and hazard recognition competencies through engaging them in interactive conversations or activities and providing responses related to their disciplines in journalism [S5] and construction education [S9]. Furthermore, two studies focused on mathematical education have shown the positive impact of ChatGPT on students' problem-solving abilities in unraveling problem-solving questions [S12] and enhancing the students' understanding of the problem-solving process [S5]. Lastly, one study indicated that ChatGPT effectively contributed to the enhancement of conversational social skills [S4].
4.5 Supporting students' academic success
Seven of the reviewed studies highlighted that students found ChatGPT to be beneficial for learning as it enhanced learning efficiency and improved the learning experience. It has been observed to improve students' efficiency in computer engineering studies by providing well-structured responses and good explanations [S2]. Additionally, students found it extremely useful for hazard reporting [S3], and it also enhanced their efficiency in solving mathematics problems and capabilities [S5] and [S12]. Furthermore, by finding information, generating ideas, translating texts, and providing alternative questions, ChatGPT aided students in deepening their understanding of various subjects [S6]. It contributed to an increase in students' overall productivity [S7] and improved efficiency in composing written tasks [S8]. Regarding learning experiences, ChatGPT was instrumental in assisting students in identifying hazards that they might have otherwise overlooked [S3]. It also improved students' learning experiences in solving mathematics problems and developing abilities [S5] and [S12]. Moreover, it increased students' successful completion of important tasks in their studies [S7], particularly those involving average difficulty writing tasks [S8]. Additionally, ChatGPT increased the chances of educational success by providing students with baseline knowledge on various topics [S10].
5 Teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in teaching and main findings from teachers' perspective
5.1 valuable resource for teaching.
The reviewed studies showed that teachers have employed ChatGPT to recommend, modify, and generate diverse, creative, organized, and engaging educational contents, teaching materials, and testing resources more rapidly [S4], [S6], [S10] and [S11]. Additionally, teachers experienced increased productivity as ChatGPT facilitated quick and accurate responses to questions, fact-checking, and information searches [S1]. It also proved valuable in constructing new knowledge [S6] and providing timely answers to students' questions in classrooms [S11]. Moreover, ChatGPT enhanced teachers' efficiency by generating new ideas for activities and preplanning activities for their students [S4] and [S6], including interactive language game partners [S11].
5.2 Improving productivity and efficiency
The reviewed studies showed that participants' productivity and work efficiency have been significantly enhanced by using ChatGPT as it enabled them to allocate more time to other tasks and reduce their overall workloads [S6], [S10], [S11], [S13], and [S14]. However, three studies [S1], [S4], and [S11], indicated a negative perception and attitude among teachers toward using ChatGPT. This negativity stemmed from a lack of necessary skills to use it effectively [S1], a limited familiarity with it [S4], and occasional inaccuracies in the content provided by it [S10].
5.3 Catalyzing new teaching methodologies
Five of the reviewed studies highlighted that educators found the necessity of redefining their teaching profession with the assistance of ChatGPT [S11], developing new effective learning strategies [S4], and adapting teaching strategies and methodologies to ensure the development of essential skills for future engineers [S5]. They also emphasized the importance of adopting new educational philosophies and approaches that can evolve with the introduction of ChatGPT into the classroom [S12]. Furthermore, updating curricula to focus on improving human-specific features, such as emotional intelligence, creativity, and philosophical perspectives [S13], was found to be essential.
5.4 Effective utilization of CHATGPT in teaching
According to the reviewed studies, effective utilization of ChatGPT in education requires providing teachers with well-structured training, support, and adequate background on how to use ChatGPT responsibly [S1], [S3], [S11], and [S12]. Establishing clear rules and regulations regarding its usage is essential to ensure it positively impacts the teaching and learning processes, including students' skills [S1], [S4], [S5], [S8], [S9], and [S11]-[S14]. Moreover, conducting further research and engaging in discussions with policymakers and stakeholders is indeed crucial for the successful integration of ChatGPT in education and to maximize the benefits for both educators and students [S1], [S6]-[S10], and [S12]-[S14].
6 Discussion
The purpose of this review is to conduct a systematic review of empirical studies that have explored the utilization of ChatGPT, one of today’s most advanced LLM-based chatbots, in education. The findings of the reviewed studies showed several ways of ChatGPT utilization in different learning and teaching practices as well as it provided insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. The results of the reviewed studies came from diverse fields of education, which helped us avoid a biased review that is limited to a specific field. Similarly, the reviewed studies have been conducted across different geographic regions. This kind of variety in geographic representation enriched the findings of this review.
In response to RQ1 , "What are students' and teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in education?", the findings from this review provide comprehensive insights. Chatbots, including ChatGPT, play a crucial role in supporting student learning, enhancing their learning experiences, and facilitating diverse learning approaches [ 42 , 43 ]. This review found that this tool, ChatGPT, has been instrumental in enhancing students' learning experiences by serving as a virtual intelligent assistant, providing immediate feedback, on-demand answers, and engaging in educational conversations. Additionally, students have benefited from ChatGPT’s ability to generate ideas, compose essays, and perform tasks like summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar, thereby enhancing their writing and language competencies. Furthermore, students have turned to ChatGPT for assistance in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks, which fosters a supportive home learning environment, allowing them to take responsibility for their own learning and cultivate the skills and approaches essential for supportive home learning environment [ 26 , 27 , 28 ]. This finding aligns with the study of Saqr et al. [ 68 , 69 ] who highlighted that, when students actively engage in their own learning process, it yields additional advantages, such as heightened motivation, enhanced achievement, and the cultivation of enthusiasm, turning them into advocates for their own learning.
Moreover, students have utilized ChatGPT for tailored teaching and step-by-step guidance on diverse educational topics, streamlining task and project completion, and generating and recommending educational content. This personalization enhances the learning environment, leading to increased academic success. This finding aligns with other recent studies [ 26 , 27 , 28 , 60 , 66 ] which revealed that ChatGPT has the potential to offer personalized learning experiences and support an effective learning process by providing students with customized feedback and explanations tailored to their needs and abilities. Ultimately, fostering students' performance, engagement, and motivation, leading to increase students' academic success [ 14 , 44 , 58 ]. This ultimate outcome is in line with the findings of Saqr et al. [ 68 , 69 ], which emphasized that learning strategies are important catalysts of students' learning, as students who utilize effective learning strategies are more likely to have better academic achievement.
Teachers, too, have capitalized on ChatGPT's capabilities to enhance productivity and efficiency, using it for creating lesson plans, generating quizzes, providing additional resources, generating and preplanning new ideas for activities, and aiding in answering students’ questions. This adoption of technology introduces new opportunities to support teaching and learning practices, enhancing teacher productivity. This finding aligns with those of Day [ 17 ], De Castro [ 18 ], and Su and Yang [ 74 ] as well as with those of Valtonen et al. [ 82 ], who revealed that emerging technological advancements have opened up novel opportunities and means to support teaching and learning practices, and enhance teachers’ productivity.
In response to RQ2 , "What are the main findings derived from empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into learning and teaching?", the findings from this review provide profound insights and raise significant concerns. Starting with the insights, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have demonstrated the potential to reshape and revolutionize education, creating new, novel opportunities for enhancing the learning process and outcomes [ 83 ], facilitating different learning approaches, and offering a range of pedagogical benefits [ 19 , 43 , 72 ]. In this context, this review found that ChatGPT could open avenues for educators to adopt or develop new effective learning and teaching strategies that can evolve with the introduction of ChatGPT into the classroom. Nonetheless, there is an evident lack of research understanding regarding the potential impact of generative machine learning models within diverse educational settings [ 83 ]. This necessitates teachers to attain a high level of proficiency in incorporating chatbots, such as ChatGPT, into their classrooms to create inventive, well-structured, and captivating learning strategies. In the same vein, the review also found that teachers without the requisite skills to utilize ChatGPT realized that it did not contribute positively to their work and could potentially have adverse effects [ 37 ]. This concern could lead to inequity of access to the benefits of chatbots, including ChatGPT, as individuals who lack the necessary expertise may not be able to harness their full potential, resulting in disparities in educational outcomes and opportunities. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. A potential solution is offering training, support, and competency development for teachers to ensure that all of them can leverage chatbots, including ChatGPT, effectively and equitably in their educational practices [ 5 , 28 , 80 ], which could enhance accessibility and inclusivity, and potentially result in innovative outcomes [ 82 , 83 ].
Additionally, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have the potential to significantly impact students' thinking abilities, including retention, reasoning, analysis skills [ 19 , 45 ], and foster innovation and creativity capabilities [ 83 ]. This review found that ChatGPT could contribute to improving a wide range of skills among students. However, it found that frequent use of ChatGPT may result in a decrease in innovative capacities, collaborative skills and cognitive capacities, and students' motivation to attend classes, as well as could lead to reduced higher-order thinking skills among students [ 22 , 29 ]. Therefore, immediate action is needed to carefully examine the long-term impact of chatbots such as ChatGPT, on learning outcomes as well as to explore its incorporation into educational settings as a supportive tool without compromising students' cognitive development and critical thinking abilities. In the same vein, the review also found that it is challenging to draw a consistent conclusion regarding the potential of ChatGPT to aid self-directed learning approach. This finding aligns with the recent study of Baskara [ 8 ]. Therefore, further research is needed to explore the potential of ChatGPT for self-directed learning. One potential solution involves utilizing learning analytics as a novel approach to examine various aspects of students' learning and support them in their individual endeavors [ 32 ]. This approach can bridge this gap by facilitating an in-depth analysis of how learners engage with ChatGPT, identifying trends in self-directed learning behavior, and assessing its influence on their outcomes.
Turning to the significant concerns, on the other hand, a fundamental challenge with LLM-based chatbots, including ChatGPT, is the accuracy and quality of the provided information and responses, as they provide false information as truth—a phenomenon often referred to as "hallucination" [ 3 , 49 ]. In this context, this review found that the provided information was not entirely satisfactory. Consequently, the utilization of chatbots presents potential concerns, such as generating and providing inaccurate or misleading information, especially for students who utilize it to support their learning. This finding aligns with other findings [ 6 , 30 , 35 , 40 ] which revealed that incorporating chatbots such as ChatGPT, into education presents challenges related to its accuracy and reliability due to its training on a large corpus of data, which may contain inaccuracies and the way users formulate or ask ChatGPT. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. One possible solution is to equip students with the necessary skills and competencies, which include a background understanding of how to use it effectively and the ability to assess and evaluate the information it generates, as the accuracy and the quality of the provided information depend on the input, its complexity, the topic, and the relevance of its training data [ 28 , 49 , 86 ]. However, it's also essential to examine how learners can be educated about how these models operate, the data used in their training, and how to recognize their limitations, challenges, and issues [ 79 ].
Furthermore, chatbots present a substantial challenge concerning maintaining academic integrity [ 20 , 56 ] and copyright violations [ 83 ], which are significant concerns in education. The review found that the potential misuse of ChatGPT might foster cheating, facilitate plagiarism, and threaten academic integrity. This issue is also affirmed by the research conducted by Basic et al. [ 7 ], who presented evidence that students who utilized ChatGPT in their writing assignments had more plagiarism cases than those who did not. These findings align with the conclusions drawn by Cotton et al. [ 13 ], Hisan and Amri [ 33 ] and Sullivan et al. [ 75 ], who revealed that the integration of chatbots such as ChatGPT into education poses a significant challenge to the preservation of academic integrity. Moreover, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have increased the difficulty in identifying plagiarism [ 47 , 67 , 76 ]. The findings from previous studies [ 1 , 84 ] indicate that AI-generated text often went undetected by plagiarism software, such as Turnitin. However, Turnitin and other similar plagiarism detection tools, such as ZeroGPT, GPTZero, and Copyleaks, have since evolved, incorporating enhanced techniques to detect AI-generated text, despite the possibility of false positives, as noted in different studies that have found these tools still not yet fully ready to accurately and reliably identify AI-generated text [ 10 , 51 ], and new novel detection methods may need to be created and implemented for AI-generated text detection [ 4 ]. This potential issue could lead to another concern, which is the difficulty of accurately evaluating student performance when they utilize chatbots such as ChatGPT assistance in their assignments. Consequently, the most LLM-driven chatbots present a substantial challenge to traditional assessments [ 64 ]. The findings from previous studies indicate the importance of rethinking, improving, and redesigning innovative assessment methods in the era of chatbots [ 14 , 20 , 64 , 75 ]. These methods should prioritize the process of evaluating students' ability to apply knowledge to complex cases and demonstrate comprehension, rather than solely focusing on the final product for assessment. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. One possible solution would be the development of clear guidelines, regulatory policies, and pedagogical guidance. These measures would help regulate the proper and ethical utilization of chatbots, such as ChatGPT, and must be established before their introduction to students [ 35 , 38 , 39 , 41 , 89 ].
In summary, our review has delved into the utilization of ChatGPT, a prominent example of chatbots, in education, addressing the question of how ChatGPT has been utilized in education. However, there remain significant gaps, which necessitate further research to shed light on this area.
7 Conclusions
This systematic review has shed light on the varied initial attempts at incorporating ChatGPT into education by both learners and educators, while also offering insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. From the analysis of 14 selected studies, the review revealed the dual-edged impact of ChatGPT in educational settings. On the positive side, ChatGPT significantly aided the learning process in various ways. Learners have used it as a virtual intelligent assistant, benefiting from its ability to provide immediate feedback, on-demand answers, and easy access to educational resources. Additionally, it was clear that learners have used it to enhance their writing and language skills, engaging in practices such as generating ideas, composing essays, and performing tasks like summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar. Importantly, other learners have utilized it in supporting and facilitating their directed and personalized learning on a broad range of educational topics, assisting in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks. Educators, on the other hand, found ChatGPT beneficial for enhancing productivity and efficiency. They used it for creating lesson plans, generating quizzes, providing additional resources, and answers learners' questions, which saved time and allowed for more dynamic and engaging teaching strategies and methodologies.
However, the review also pointed out negative impacts. The results revealed that overuse of ChatGPT could decrease innovative capacities and collaborative learning among learners. Specifically, relying too much on ChatGPT for quick answers can inhibit learners' critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Learners might not engage deeply with the material or consider multiple solutions to a problem. This tendency was particularly evident in group projects, where learners preferred consulting ChatGPT individually for solutions over brainstorming and collaborating with peers, which negatively affected their teamwork abilities. On a broader level, integrating ChatGPT into education has also raised several concerns, including the potential for providing inaccurate or misleading information, issues of inequity in access, challenges related to academic integrity, and the possibility of misusing the technology.
Accordingly, this review emphasizes the urgency of developing clear rules, policies, and regulations to ensure ChatGPT's effective and responsible use in educational settings, alongside other chatbots, by both learners and educators. This requires providing well-structured training to educate them on responsible usage and understanding its limitations, along with offering sufficient background information. Moreover, it highlights the importance of rethinking, improving, and redesigning innovative teaching and assessment methods in the era of ChatGPT. Furthermore, conducting further research and engaging in discussions with policymakers and stakeholders are essential steps to maximize the benefits for both educators and learners and ensure academic integrity.
It is important to acknowledge that this review has certain limitations. Firstly, the limited inclusion of reviewed studies can be attributed to several reasons, including the novelty of the technology, as new technologies often face initial skepticism and cautious adoption; the lack of clear guidelines or best practices for leveraging this technology for educational purposes; and institutional or governmental policies affecting the utilization of this technology in educational contexts. These factors, in turn, have affected the number of studies available for review. Secondly, the utilization of the original version of ChatGPT, based on GPT-3 or GPT-3.5, implies that new studies utilizing the updated version, GPT-4 may lead to different findings. Therefore, conducting follow-up systematic reviews is essential once more empirical studies on ChatGPT are published. Additionally, long-term studies are necessary to thoroughly examine and assess the impact of ChatGPT on various educational practices.
Despite these limitations, this systematic review has highlighted the transformative potential of ChatGPT in education, revealing its diverse utilization by learners and educators alike and summarized the benefits of incorporating it into education, as well as the forefront critical concerns and challenges that must be addressed to facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. This review could serve as an insightful resource for practitioners who seek to integrate ChatGPT into education and stimulate further research in the field.
Data availability
The data supporting our findings are available upon request.
Abbreviations
- Artificial intelligence
AI in education
Large language model
Artificial neural networks
Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer
Recurrent neural networks
Long short-term memory
Reinforcement learning from human feedback
Natural language processing
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
AlAfnan MA, Dishari S, Jovic M, Lomidze K. ChatGPT as an educational tool: opportunities, challenges, and recommendations for communication, business writing, and composition courses. J Artif Intell Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37965/jait.2023.0184 .
Article Google Scholar
Ali JKM, Shamsan MAA, Hezam TA, Mohammed AAQ. Impact of ChatGPT on learning motivation. J Engl Stud Arabia Felix. 2023;2(1):41–9. https://doi.org/10.56540/jesaf.v2i1.51 .
Alkaissi H, McFarlane SI. Artificial hallucinations in ChatGPT: implications in scientific writing. Cureus. 2023. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.35179 .
Anderson N, Belavý DL, Perle SM, Hendricks S, Hespanhol L, Verhagen E, Memon AR. AI did not write this manuscript, or did it? Can we trick the AI text detector into generated texts? The potential future of ChatGPT and AI in sports & exercise medicine manuscript generation. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2023;9(1): e001568. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjsem-2023-001568 .
Ausat AMA, Massang B, Efendi M, Nofirman N, Riady Y. Can chat GPT replace the role of the teacher in the classroom: a fundamental analysis. J Educ. 2023;5(4):16100–6.
Google Scholar
Baidoo-Anu D, Ansah L. Education in the Era of generative artificial intelligence (AI): understanding the potential benefits of ChatGPT in promoting teaching and learning. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4337484 .
Basic Z, Banovac A, Kruzic I, Jerkovic I. Better by you, better than me, chatgpt3 as writing assistance in students essays. 2023. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.04536 .
Baskara FR. The promises and pitfalls of using chat GPT for self-determined learning in higher education: an argumentative review. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Ilmu Keguruan IAIM Sinjai. 2023;2:95–101. https://doi.org/10.47435/sentikjar.v2i0.1825 .
Behera RK, Bala PK, Dhir A. The emerging role of cognitive computing in healthcare: a systematic literature review. Int J Med Inform. 2019;129:154–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.04.024 .
Chaka C. Detecting AI content in responses generated by ChatGPT, YouChat, and Chatsonic: the case of five AI content detection tools. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.2.12 .
Chiu TKF, Xia Q, Zhou X, Chai CS, Cheng M. Systematic literature review on opportunities, challenges, and future research recommendations of artificial intelligence in education. Comput Educ Artif Intell. 2023;4:100118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2022.100118 .
Choi EPH, Lee JJ, Ho M, Kwok JYY, Lok KYW. Chatting or cheating? The impacts of ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence language models on nurse education. Nurse Educ Today. 2023;125:105796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2023.105796 .
Cotton D, Cotton PA, Shipway JR. Chatting and cheating: ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. Innov Educ Teach Int. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2190148 .
Crawford J, Cowling M, Allen K. Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: Character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI). J Univ Teach Learn Pract. 2023. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.3.02 .
Creswell JW. Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research [Ebook]. 4th ed. London: Pearson Education; 2015.
Curry D. ChatGPT Revenue and Usage Statistics (2023)—Business of Apps. 2023. https://www.businessofapps.com/data/chatgpt-statistics/
Day T. A preliminary investigation of fake peer-reviewed citations and references generated by ChatGPT. Prof Geogr. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/00330124.2023.2190373 .
De Castro CA. A Discussion about the Impact of ChatGPT in education: benefits and concerns. J Bus Theor Pract. 2023;11(2):p28. https://doi.org/10.22158/jbtp.v11n2p28 .
Deng X, Yu Z. A meta-analysis and systematic review of the effect of Chatbot technology use in sustainable education. Sustainability. 2023;15(4):2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042940 .
Eke DO. ChatGPT and the rise of generative AI: threat to academic integrity? J Responsib Technol. 2023;13:100060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrt.2023.100060 .
Elmoazen R, Saqr M, Tedre M, Hirsto L. A systematic literature review of empirical research on epistemic network analysis in education. IEEE Access. 2022;10:17330–48. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3149812 .
Farrokhnia M, Banihashem SK, Noroozi O, Wals AEJ. A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: implications for educational practice and research. Innov Educ Teach Int. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2195846 .
Fergus S, Botha M, Ostovar M. Evaluating academic answers generated using ChatGPT. J Chem Educ. 2023;100(4):1672–5. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00087 .
Fink A. Conducting research literature reviews: from the Internet to Paper. Incorporated: SAGE Publications; 2010.
Firaina R, Sulisworo D. Exploring the usage of ChatGPT in higher education: frequency and impact on productivity. Buletin Edukasi Indonesia (BEI). 2023;2(01):39–46. https://doi.org/10.56741/bei.v2i01.310 .
Firat, M. (2023). How chat GPT can transform autodidactic experiences and open education. Department of Distance Education, Open Education Faculty, Anadolu Unive . https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8707-5918
Firat M. What ChatGPT means for universities: perceptions of scholars and students. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.22 .
Fuchs K. Exploring the opportunities and challenges of NLP models in higher education: is Chat GPT a blessing or a curse? Front Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2023.1166682 .
García-Peñalvo FJ. La percepción de la inteligencia artificial en contextos educativos tras el lanzamiento de ChatGPT: disrupción o pánico. Educ Knowl Soc. 2023;24: e31279. https://doi.org/10.14201/eks.31279 .
Gilson A, Safranek CW, Huang T, Socrates V, Chi L, Taylor A, Chartash D. How does ChatGPT perform on the United States medical Licensing examination? The implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9: e45312. https://doi.org/10.2196/45312 .
Hashana AJ, Brundha P, Ayoobkhan MUA, Fazila S. Deep Learning in ChatGPT—A Survey. In 2023 7th international conference on trends in electronics and informatics (ICOEI) . 2023. (pp. 1001–1005). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/icoei56765.2023.10125852
Hirsto L, Saqr M, López-Pernas S, Valtonen T. (2022). A systematic narrative review of learning analytics research in K-12 and schools. Proceedings . https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3383/FLAIEC22_paper_9536.pdf
Hisan UK, Amri MM. ChatGPT and medical education: a double-edged sword. J Pedag Educ Sci. 2023;2(01):71–89. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.31280.23043/1 .
Hopkins AM, Logan JM, Kichenadasse G, Sorich MJ. Artificial intelligence chatbots will revolutionize how cancer patients access information: ChatGPT represents a paradigm-shift. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1093/jncics/pkad010 .
Househ M, AlSaad R, Alhuwail D, Ahmed A, Healy MG, Latifi S, Sheikh J. Large Language models in medical education: opportunities, challenges, and future directions. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9: e48291. https://doi.org/10.2196/48291 .
Ilkka T. The impact of artificial intelligence on learning, teaching, and education. Minist de Educ. 2018. https://doi.org/10.2760/12297 .
Iqbal N, Ahmed H, Azhar KA. Exploring teachers’ attitudes towards using CHATGPT. Globa J Manag Adm Sci. 2022;3(4):97–111. https://doi.org/10.46568/gjmas.v3i4.163 .
Irfan M, Murray L, Ali S. Integration of Artificial intelligence in academia: a case study of critical teaching and learning in Higher education. Globa Soc Sci Rev. 2023;8(1):352–64. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2023(viii-i).32 .
Jeon JH, Lee S. Large language models in education: a focus on the complementary relationship between human teachers and ChatGPT. Educ Inf Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11834-1 .
Khan RA, Jawaid M, Khan AR, Sajjad M. ChatGPT—Reshaping medical education and clinical management. Pak J Med Sci. 2023. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.39.2.7653 .
King MR. A conversation on artificial intelligence, Chatbots, and plagiarism in higher education. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2023;16(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-022-00754-8 .
Kooli C. Chatbots in education and research: a critical examination of ethical implications and solutions. Sustainability. 2023;15(7):5614. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075614 .
Kuhail MA, Alturki N, Alramlawi S, Alhejori K. Interacting with educational chatbots: a systematic review. Educ Inf Technol. 2022;28(1):973–1018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11177-3 .
Lee H. The rise of ChatGPT: exploring its potential in medical education. Anat Sci Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.2270 .
Li L, Subbareddy R, Raghavendra CG. AI intelligence Chatbot to improve students learning in the higher education platform. J Interconnect Netw. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219265921430325 .
Limna P. A Review of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education during the Digital Era. 2022. https://ssrn.com/abstract=4160798
Lo CK. What is the impact of ChatGPT on education? A rapid review of the literature. Educ Sci. 2023;13(4):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13040410 .
Luo W, He H, Liu J, Berson IR, Berson MJ, Zhou Y, Li H. Aladdin’s genie or pandora’s box For early childhood education? Experts chat on the roles, challenges, and developments of ChatGPT. Early Educ Dev. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409289.2023.2214181 .
Meyer JG, Urbanowicz RJ, Martin P, O’Connor K, Li R, Peng P, Moore JH. ChatGPT and large language models in academia: opportunities and challenges. Biodata Min. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13040-023-00339-9 .
Mhlanga D. Open AI in education, the responsible and ethical use of ChatGPT towards lifelong learning. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4354422 .
Neumann, M., Rauschenberger, M., & Schön, E. M. (2023). “We Need To Talk About ChatGPT”: The Future of AI and Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1109/seeng59157.2023.00010
Nolan B. Here are the schools and colleges that have banned the use of ChatGPT over plagiarism and misinformation fears. Business Insider . 2023. https://www.businessinsider.com
O’Leary DE. An analysis of three chatbots: BlenderBot, ChatGPT and LaMDA. Int J Intell Syst Account, Financ Manag. 2023;30(1):41–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/isaf.1531 .
Okoli C. A guide to conducting a standalone systematic literature review. Commun Assoc Inf Syst. 2015. https://doi.org/10.17705/1cais.03743 .
OpenAI. (2023). https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt
Perkins M. Academic integrity considerations of AI large language models in the post-pandemic era: ChatGPT and beyond. J Univ Teach Learn Pract. 2023. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.02.07 .
Plevris V, Papazafeiropoulos G, Rios AJ. Chatbots put to the test in math and logic problems: A preliminary comparison and assessment of ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4, and Google Bard. arXiv (Cornell University) . 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2305.18618
Rahman MM, Watanobe Y (2023) ChatGPT for education and research: opportunities, threats, and strategies. Appl Sci 13(9):5783. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095783
Ram B, Verma P. Artificial intelligence AI-based Chatbot study of ChatGPT, google AI bard and baidu AI. World J Adv Eng Technol Sci. 2023;8(1):258–61. https://doi.org/10.30574/wjaets.2023.8.1.0045 .
Rasul T, Nair S, Kalendra D, Robin M, de Oliveira Santini F, Ladeira WJ, Heathcote L. The role of ChatGPT in higher education: benefits, challenges, and future research directions. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.29 .
Ratnam M, Sharm B, Tomer A. ChatGPT: educational artificial intelligence. Int J Adv Trends Comput Sci Eng. 2023;12(2):84–91. https://doi.org/10.30534/ijatcse/2023/091222023 .
Ray PP. ChatGPT: a comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet Things Cyber-Phys Syst. 2023;3:121–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.04.003 .
Roumeliotis KI, Tselikas ND. ChatGPT and Open-AI models: a preliminary review. Future Internet. 2023;15(6):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15060192 .
Rudolph J, Tan S, Tan S. War of the chatbots: Bard, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, Ernie and beyond. The new AI gold rush and its impact on higher education. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.23 .
Ruiz LMS, Moll-López S, Nuñez-Pérez A, Moraño J, Vega-Fleitas E. ChatGPT challenges blended learning methodologies in engineering education: a case study in mathematics. Appl Sci. 2023;13(10):6039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106039 .
Sallam M, Salim NA, Barakat M, Al-Tammemi AB. ChatGPT applications in medical, dental, pharmacy, and public health education: a descriptive study highlighting the advantages and limitations. Narra J. 2023;3(1): e103. https://doi.org/10.52225/narra.v3i1.103 .
Salvagno M, Taccone FS, Gerli AG. Can artificial intelligence help for scientific writing? Crit Care. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-023-04380-2 .
Saqr M, López-Pernas S, Helske S, Hrastinski S. The longitudinal association between engagement and achievement varies by time, students’ profiles, and achievement state: a full program study. Comput Educ. 2023;199:104787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2023.104787 .
Saqr M, Matcha W, Uzir N, Jovanović J, Gašević D, López-Pernas S. Transferring effective learning strategies across learning contexts matters: a study in problem-based learning. Australas J Educ Technol. 2023;39(3):9.
Schöbel S, Schmitt A, Benner D, Saqr M, Janson A, Leimeister JM. Charting the evolution and future of conversational agents: a research agenda along five waves and new frontiers. Inf Syst Front. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-023-10375-9 .
Shoufan A. Exploring students’ perceptions of CHATGPT: thematic analysis and follow-up survey. IEEE Access. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3268224 .
Sonderegger S, Seufert S. Chatbot-mediated learning: conceptual framework for the design of Chatbot use cases in education. Gallen: Institute for Educational Management and Technologies, University of St; 2022. https://doi.org/10.5220/0010999200003182 .
Book Google Scholar
Strzelecki A. To use or not to use ChatGPT in higher education? A study of students’ acceptance and use of technology. Interact Learn Environ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2209881 .
Su J, Yang W. Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: a framework for applying generative AI in education. ECNU Rev Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/20965311231168423 .
Sullivan M, Kelly A, McLaughlan P. ChatGPT in higher education: Considerations for academic integrity and student learning. J ApplLearn Teach. 2023;6(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.17 .
Szabo A. ChatGPT is a breakthrough in science and education but fails a test in sports and exercise psychology. Balt J Sport Health Sci. 2023;1(128):25–40. https://doi.org/10.33607/bjshs.v127i4.1233 .
Taecharungroj V. “What can ChatGPT do?” analyzing early reactions to the innovative AI chatbot on Twitter. Big Data Cognit Comput. 2023;7(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7010035 .
Tam S, Said RB. User preferences for ChatGPT-powered conversational interfaces versus traditional methods. Biomed Eng Soc. 2023. https://doi.org/10.58496/mjcsc/2023/004 .
Tedre M, Kahila J, Vartiainen H. (2023). Exploration on how co-designing with AI facilitates critical evaluation of ethics of AI in craft education. In: Langran E, Christensen P, Sanson J (Eds). Proceedings of Society for Information Technology and Teacher Education International Conference . 2023. pp. 2289–2296.
Tlili A, Shehata B, Adarkwah MA, Bozkurt A, Hickey DT, Huang R, Agyemang B. What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learn Environ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-023-00237-x .
Uddin SMJ, Albert A, Ovid A, Alsharef A. Leveraging CHATGPT to aid construction hazard recognition and support safety education and training. Sustainability. 2023;15(9):7121. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097121 .
Valtonen T, López-Pernas S, Saqr M, Vartiainen H, Sointu E, Tedre M. The nature and building blocks of educational technology research. Comput Hum Behav. 2022;128:107123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2021.107123 .
Vartiainen H, Tedre M. Using artificial intelligence in craft education: crafting with text-to-image generative models. Digit Creat. 2023;34(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/14626268.2023.2174557 .
Ventayen RJM. OpenAI ChatGPT generated results: similarity index of artificial intelligence-based contents. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4332664 .
Wagner MW, Ertl-Wagner BB. Accuracy of information and references using ChatGPT-3 for retrieval of clinical radiological information. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/08465371231171125 .
Wardat Y, Tashtoush MA, AlAli R, Jarrah AM. ChatGPT: a revolutionary tool for teaching and learning mathematics. Eurasia J Math, Sci Technol Educ. 2023;19(7):em2286. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/13272 .
Webster J, Watson RT. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: writing a literature review. Manag Inf Syst Quart. 2002;26(2):3.
Xiao Y, Watson ME. Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J Plan Educ Res. 2017;39(1):93–112. https://doi.org/10.1177/0739456x17723971 .
Yan D. Impact of ChatGPT on learners in a L2 writing practicum: an exploratory investigation. Educ Inf Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11742-4 .
Yu H. Reflection on whether Chat GPT should be banned by academia from the perspective of education and teaching. Front Psychol. 2023;14:1181712. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1181712 .
Zhu C, Sun M, Luo J, Li T, Wang M. How to harness the potential of ChatGPT in education? Knowl Manag ELearn. 2023;15(2):133–52. https://doi.org/10.34105/j.kmel.2023.15.008 .
Download references
The paper is co-funded by the Academy of Finland (Suomen Akatemia) Research Council for Natural Sciences and Engineering for the project Towards precision education: Idiographic learning analytics (TOPEILA), Decision Number 350560.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Computing, University of Eastern Finland, 80100, Joensuu, Finland
Yazid Albadarin, Mohammed Saqr, Nicolas Pope & Markku Tukiainen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
YA contributed to the literature search, data analysis, discussion, and conclusion. Additionally, YA contributed to the manuscript’s writing, editing, and finalization. MS contributed to the study’s design, conceptualization, acquisition of funding, project administration, allocation of resources, supervision, validation, literature search, and analysis of results. Furthermore, MS contributed to the manuscript's writing, revising, and approving it in its finalized state. NP contributed to the results, and discussions, and provided supervision. NP also contributed to the writing process, revisions, and the final approval of the manuscript in its finalized state. MT contributed to the study's conceptualization, resource management, supervision, writing, revising the manuscript, and approving it.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yazid Albadarin .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
See Table 4
The process of synthesizing the data presented in Table 4 involved identifying the relevant studies through a search process of databases (ERIC, Scopus, Web of Knowledge, Dimensions.ai, and lens.org) using specific keywords "ChatGPT" and "education". Following this, inclusion/exclusion criteria were applied, and data extraction was performed using Creswell's [ 15 ] coding techniques to capture key information and identify common themes across the included studies.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Albadarin, Y., Saqr, M., Pope, N. et al. A systematic literature review of empirical research on ChatGPT in education. Discov Educ 3 , 60 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44217-024-00138-2
Download citation
Received : 22 October 2023
Accepted : 10 May 2024
Published : 26 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s44217-024-00138-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Large language models
- Educational technology
- Systematic review
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
Amy Ettinger (Image credit: Dan White)
Amy Jordana Ettinger, a Bay Area author and Stanford Continuing Studies writing instructor, died March 20 at her home in Santa Cruz. She was 49.
Ettinger began teaching in the Stanford Continuing Studies creative writing program in 2019 and continued teaching after she was diagnosed with leiomyosarcoma, a rare and incurable form of cancer. During her time at Stanford, she taught 14 non-fiction writing classes, including courses like CNF 75: Creative Nonfiction Book: From Idea to Proposal and CNF 76: Pitch and Publish Your Nonfiction Stories .
“Amy graciously and generously shared her love of writing with students who gravitated to her for her energy, enthusiasm, and unflagging support,” said Malena Watrous, the creative writing coordinator at Stanford Continuing Studies. “She wanted them to know that being a published writer was within the realm of possibility for anyone who was willing to pursue a story and put in the work of getting it on paper and revising it until it shone.”
Ettinger taught two courses in the program until she began hospice care.
She wrote about her experiences with a terminal illness in two pieces for the Washington Post – her final story published in print the day before she died – in which she reflected on some of the meaningful moments during her final months. One of the highlights she shared was teaching at Stanford to the very end of her life.
“Amy had a generous spirit. She never did anything in half measures, whether she was writing a personal essay for the Washington Post or teaching her writing classes at Stanford,” said Ettinger’s husband, Dan White. “She cared very much about her students, and she was so proud of the work they did.”
Helping students find their own sweet spot
Ettinger was an accomplished writer herself.
She began her career writing for the Monterey Bay Herald before becoming a freelance journalist. Her pieces appeared in national outlets including the New York Times , the Washington Post , New York Magazine , Salon , CNN , and Newsweek . In 2017, Ettinger published her own nonfiction book, Sweet Spot: An Ice Cream Binge Across America (Penguin Random House).
“Amy loved to connect to large audiences with her writing, but teaching added a whole new dimension to her career,” said White. “She loved the idea of helping students demystify the process of getting published and writing proposals, or removing some of the fear factor and help them consider the perspective of the editors and publishers who would be looking at their work.”
Ettinger encouraged her Stanford Continuing Studies students to find their own sweet spot.
Ettinger’s classes filled with both new and returning students, including Alyssa Lauren Stone who took two courses with Ettinger in 2022. Within months of working with Ettinger, Stone published her own work in well-known news outlets. She credits her early success to working with Ettinger, particularly her advice on pitching compelling ideas to editors.
“Amy had a real knack for knowing what stories editors like,” Stone said. “Amy was a generous teacher who did not hold back from sharing her tools for success.”
Ettinger was also a mentor to another instructor in the Stanford Continuing Studies creative writing program, Gregg Wrenn.
“Amy was an extraordinary creative nonfiction instructor who gave me the emotional support and editorial expertise I needed to finish my memoir,” said Wren. “Her work touched hundreds of students just like me who will miss her deeply.”
Ettinger is survived by her husband Dan and their daughter, Julianna.
Research puts dollar figure on climate savings from electric school buses
A substantial portion of the half-million school buses in the United States are “highly polluting old diesel vehicles,” the researchers write.
Switching to electric school buses could yield significant health and climate benefits, researchers suggest in a new analysis that seeks to quantify those gains in dollar terms.
Published in the journal PNAS, the study estimated the per-mile benefits of replacing diesel buses with electric ones in 3,108 U.S. counties. Researchers combined data about average diesel bus pollution with statistical estimates of the cost of maintenance and repair, the environmental impact of diesel emissions, and the dollar value of new childhood asthma cases and deaths that could be attributed to such pollution.
A substantial portion of the half-million school buses in the United States are “highly polluting old diesel vehicles,” the researchers write. Though emissions have fallen over time thanks to increased regulation, they add, older, more polluting diesel models are still common. As of June 2023, they write, just 2,277 electric school buses had been ordered or delivered, or were operating nationwide.
Replacing the average diesel bus would generate a benefit of $84,200 per bus, split nearly evenly between health and climate effects. Such a replacement would cut 181 metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions per bus and reduce childhood deaths and asthma cases from diesel emissions, the researchers conclude.
The benefits would vary depending on the location, with buses generating as much as $247,600 in benefits in dense metropolitan areas. Impacts would be smaller in rural areas because diesel emissions affect smaller populations there.
The benefits would come at a cost, the researchers acknowledge; they estimate an unsubsidized electric school bus costs an average of $156,000 more than a new diesel school bus over the vehicle’s lifetime. But in large metropolitan areas, they write, “replacing a relatively small number of miles driven by [diesel buses] could lead to substantial public health benefits.”
“In a dense urban setting where old diesel buses still comprise most school bus fleets, the savings incurred from electrifying these buses outweigh the costs of replacement,” Kari Nadeau, a professor of climate and population studies and environmental health at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and the study’s senior author, said in a news release . “Not to mention how the tangible benefits of electric school buses can improve lives — especially for racial minorities and those living in low-income communities who are disproportionately impacted by the everyday health risks of air pollution.”
Black, Hispanic and low-income Americans would probably experience the greatest health benefits of large metropolitan areas electrifying their school bus fleet, the researchers write. They call for more research on the exposure of the children riding the buses to particulate pollution, because data on in-cabin pollution generated by newer buses is still unclear.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to Write a Rationale for a Research Paper . The basis for writing a research rationale is preliminary data or a clear description of an observation. If you are doing basic/theoretical research, then a literature review will help you identify gaps in current knowledge. In applied/practical research, you base your rationale on an existing ...
The rationale for research is also sometimes referred to as the justification for the study. When writing your rational, first begin by introducing and explaining what other researchers have published on within your research field. Having explained the work of previous literature and prior research, include discussion about where the gaps in ...
The rationale for your research is the reason why you decided to conduct the study in the first place. The motivation for asking the question. The knowledge gap. This is often the most significant part of your publication. It justifies the study's purpose, novelty, and significance for science or society.
Research rationale helps to ideate new topics which are less addressed. Additionally, it offers fresh perspectives on existing research and discusses the shortcomings in previous studies. It shows that your study aims to contribute to filling these gaps and advancing the field's understanding. 3. Originality and Novelty.
To write your rationale, you should first write a background on what all research has been done on your study topic. Follow this with 'what is missing' or 'what are the open questions of the study'. Identify the gaps in the literature and emphasize why it is important to address those gaps. This will form the rationale of your study.
A rationale in Australian academic writing is rarely a whole task by itself. It is often a part of a bigger task. For example, a part of a lesson plan might be to provide a rationale for why you chose to teach particular content or use a certain resource or activity, or you may be asked to provide a rationale as to why you chose a particular ...
A good rationale should include a summary of conclusions from your literature review, identify what is currently unknown, discuss inconclusive or contested results from previous studies, and emphasize the necessity to improve or build on previous research . Creating a rationale is a vital part of the research process, as it not only sets the ...
Charlesworth Author Services; 19 November, 2021; How to write the Rationale for your research. The rationale for one's research is the justification for undertaking a given study. It states the reason(s) why a researcher chooses to focus on the topic in question, including what the significance is and what gaps the research intends to fill.In short, it is an explanation that rationalises the ...
Answer: The rationale for research basically outlines why you wanted to conduct research on the topic of your choice. The rationale is the justification of the study, and specifies the need to conduct research on the topic. In science, in fact, it is easier to come up with a rationale for research. You should first do a thorough literature ...
1 Answer to this question. Answer: The Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines "rationale" as "an explanation of controlling principles" or "the underlying reason for something." Thus, the rationale for your study should explain your reason for conducting the study. We have discussed this topic at some length in some of our existing posts.
Part 1: Explain your topic choice. You should explain as clearly as possible why this particular subject interested you. Don't just say "it is interesting": give specific reasons why. The more precise you are, the better your mark will be. Useful sentence starters for explaining topic choice: I was curious to discover….
Rationale for the study, also referred to as justification for the study, is reason why you have conducted your study in the first place. This part in your paper needs to explain uniqueness and importance of your research. Rationale for the study needs to be specific and ideally, it should relate to the following points: 1. The research needs ...
3. Identify the ways your study will correct those shortcomings. Carefully explain the ways in which your study will answer the research question in a way that the previous studies failed to do so. Be persuasive to convince your readers that your study will contribute something both useful and necessary to the field.
A research rationale provides an organized strategy for the whole research and acts as the cornerstone of the research project. It contributes to the research's rationale by stating why the study is significant, what its aims are, and what the expected findings are. In essence, it is a compelling argument for why the study should be carried out.
convincing rationale for a research study' Coaching: An International Journal of Theory, Research. and Practice 5.1 1-7. Abstract. Explaining the purpos e of a research study and providing a ...
In brief. The research's rationale describes why the study was undertaken (in a thesis or article) or why the study should be accompanied (in a proposal). This implies that the research justification should explain why the study is/was necessary to the reader or examiner. It is sometimes known as a study's "purpose" or "justification.".
Writing a research proposal can be intimidating, especially when you are expected to explain the rationale behind your project. This article will help you learn how to write the rationale for a research proposal to provide justification for why it should be pursued. A good rationale should give readers an understanding of why your project is worth undertaking and how it will contribute to ...
One of the most frequent criticisms of manuscripts is the lack of contributions to theory and/or practice. Often, these papers neglect a critical component of the paper: rationale. The rationale is necessary to justify the need for the research and the approach taken. We argue that contributions flow naturally if the rationale for the study is ...
Research rationale helps to ideate new topics which are less addressed. Additionally, it offers fresh perspectives on existing research and discusses the shortcomings in previous studies. It shows that your study aims to contribute to filling these gaps and advancing the field's understanding. 3. Originality and Novelty.
If you search Google Scholar for the phrase "as an AI language model", you'll find plenty of AI research literature and also some rather suspicious results. For example, one paper on ...
Binge drinking is a growing public health crisis − a neurobiologist explains how research on alcohol use disorder has shifted ... Write an article and join a growing community of more than ...
In relation to the research reported here, there was no direct funding. ... Write an article and join a growing community of more than 184,200 academics and researchers from 4,969 institutions ...
As schools reconsider cursive, research homes in on handwriting's brain benefits : ... Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning.
1 Answer to this question. The term used to imply why the study was needed in the first place is "rationale for research" or "rationale of a study." It is also sometimes referred to as the justification of the study. I have edited your question to reflect this. The rationale of a study is a very important part of the manuscript.
Over the last four decades, studies have investigated the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into education. A recent prominent AI-powered technology that has impacted the education sector is ChatGPT. This article provides a systematic review of 14 empirical studies incorporating ChatGPT into various educational settings, published in 2022 and before the 10th of April 2023—the ...
Jan 06, 2023. The rationale of your research is an important part of your publication. In your rationale, you state the need and reason to conduct your research. The rationale of your research brings forth the significance and novelty of your research. In this infographic, we have listed how you may write the rationale of your research:
She began her career writing for the Monterey Bay Herald before becoming a freelance journalist. Her pieces appeared in national outlets including the New York Times , the Washington Post , New ...
Published in the journal PNAS, the study estimated the per-mile benefits of replacing diesel buses with electric ones in 3,108 U.S. counties. Researchers combined data about average diesel bus ...
Thus, the rationale of your research should begin by identifying the gap in research that your study will address. Explain the gap in the literature and emphasize why it is important to address this gap. This will form the rationale of your study. The rationale should be followed by a hypothesis and objectives. Related reading:
The research team based its conclusions on data from satellites that send radar waves to penetrate the Earth's surface and detect hidden features. It also relied on sediment cores and maps from ...