

Dissertation Preparation
- Creating a Research Plan
- Collecting Data
- Writing a Dissertation
- Function of Structures
- Detailed Structures
Developing an Argument
- Finding Dissertations
- Additional Sources
- Citation Management
An important aspect running through your dissertation will be your argument for:
- why this specific topic is worth researching;
- why this is a good way to research it;
- why this method of analysis is appropriate; and
- why your interpretations and conclusions are reasonable.
You will refer to the work of others as you make your argument. This may involve critiquing the work of established leaders in the field. While it is important to be respectful in the way that you discuss others’ ideas and research, you are expected to engage directly, and even openly disagree with existing writing.
In Taylor’s (1989) book on writing in the arts and social sciences, he suggests that the following different approaches offer a range of academically legitimate ways to engage with published work.
- Agree with, accede to, defend, or confirm a particular point of view.
- Propose a new point of view.
- Concede that an existing point of view has certain merits but that it needs to be qualified in certain important respects.
- Reformulate an existing point of view or statement of it, such that the new version makes a better explanation.
- Dismiss a point of view or another person’s work on account of its inadequacy, irrelevance, incoherence, or by recourse to other appropriate criteria.
- Reject, rebut or refute another’s argument on various reasoned grounds.
- Reconcile two positions that may seem at variance by appealing to some ‘higher’ or ‘deeper’ principal.
- Develop an existing point of view, perhaps by utilizing it on larger or more complex datasets, or applying a theory to a new context
(Adapted from Taylor 1989:67)
It is important that you are assertive about what you are arguing, but it is unlikely that, in a dissertation project, you will be able to be definitive in closing an established academic debate. You should be open about where the gaps are in your research, and cautious about overstating what you have found. Aim to be modest but realistic in relating your own research to the broader context.
Improving Structure and Content
Once you have the dissertation in draft form it becomes easier to see where you can improve it. To make it easier to read you can use clear signposting at the beginning of chapters, and write links between sections to show how they relate to each other. Another technique to improve academic writing style is to ensure that each individual paragraph justifies its inclusion. More ideas will be presented in the Study Guide The art of editing.
You may choose to review your draft from the standpoint of a dissertation examiner, which might involve preparing a list of questions that you want to see answered, then reading through your dissertation scribbling comments, suggestions, criticisms, and ideas in the margin. If you have a marking guide then apply it to your dissertation and see if there are aspects that you can improve.
While you do this, be aware of whether you need to increase the number of words, or decrease it to reach your target. As you read you can then cross through material that appears unnecessary, and mark points that could be expanded. This will then form the basis for your next, improved, draft.
When to Stop
Just as it can be difficult to begin writing, it can also be difficult to know when to stop. You may begin to feel that your dissertation will never be good enough and that you need to revise it again and again. It may be helpful to divert your attention for a while to the finishing off activities you need to attend to:
- writing the abstract and the introduction;
- checking the reference list;
- finalizing the appendices; and
- checking your contents page.
Coming back afresh to look critically at the main text may then enable you to complete it to your satisfaction. Remember the dissertation needs to demonstrate your ability to undertake and report research rather than to answer every question on a topic.
It is important to allow yourself enough time for the final checking and proofreading of the finished document.
- Devote time to planning the structure of the dissertation.
- Plan a structure that will enable you to present your argument effectively.
- Fill in the detail, concentrating on getting everything recorded rather than sticking to the word limit at this stage.
- Regard writing as part of the research process, not an after-thought.
- Expect to edit and re-edit your material several times as it moves towards its final form.
- Leave time to check and proofread thoroughly.
Barrass R. (1979) Scientists must write. A guide to better writing for scientists, engineers and students. London:Chapman and Hall.
Taylor G. (1989) The Student’s Writing Guide for the Arts and Social Sciences. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- << Previous: Detailed Structures
- Next: Finding Dissertations >>
Article Categories
Book categories, collections.
- Academics & The Arts Articles
- Language & Language Arts Articles
- Writing Articles
How to Present Dissertation Arguments
Writing a dissertation for dummies.

Sign up for the Dummies Beta Program to try Dummies' newest way to learn.
Many different ways exist to argue in a dissertation and what you choose to do depends on your research question, your field, and the available literature, amongst other things. However, some elements are to be expected in all fields regardless of the research question or the literature, and these include logic, coherence, careful use of evidence and clarity.
In a non-empirical dissertation you use desk research and argument to answer your research question. You can approach this task in a variety of ways, for example:
Reject someone's idea using reason and logic
Corroborate a particular viewpoint providing new or additional evidence
Compare two contradictory views and decide which is the most compelling
Re-evaluate an existing idea, improving it somehow
Present a new way of understanding something
Dissertation argument: Deductive vs. inductive reasoning
One issue to take into account concerns different types of reasoning. Commonly, you may find guides and support for dissertation writing that discuss deductive and inductive reasoning and so it’s worth getting to grips with what these words mean.
Deductive arguments tend to verify theories and hypotheses. They’re more associated with quantitative research and a kind of positivist framework. Often, but not always, deductive thinking moves from the general to the particular, and results in clear statements. A good deductive argument is described as ‘valid’.
Deductive arguments can play out in numerous ways and some of those most useful for undergraduate dissertations involve syllogism, which is a form of logic. Here’s an example of an argument that is trying to show a cause-effect relationship:
Start with a main idea, or premiss, for your work, in this case improved funding for your work. This leads to a connected idea – more facilities can be provided for young people. The effect of better facilities is that less young people hang around the street in the evenings, getting into trouble. With these premisses and through examining the cause and effect, the next logical move is to the conclusion that increased funding will result in less trouble caused by young people.
Inductive reasoning usually (not always) involves deriving theory from specific examples and because of this, results in statements that are more or less likely to be true, rather than a fixed absolute response. A good inductive argument is strong or ‘cogent’. As with deductive reasoning, different ways of arguing are possible. Here are examples of the ones most likely to be used by undergraduates:
Deriving evidence from an expert: In this case you need to be completely certain that the source of your evidence is authoritative, accurate and valid. ‘Professor Brown construes that children in care are less likely than children in families to achieve a university place in the UK. This conclusion is based on several major longitudinal research projects . . .’. (Here’s where you cite dates and other details and really get down to the nitty gritty.)
Using relevant examples: Rather than the single key source noted in the previous example, this form of inductive reasoning relies on building a conclusion from a selection of relevant, valid examples from reliable literature. ‘Various studies have clearly demonstrated that university places are more commonly won by students whose parents have degrees.’ (Green and Black, 2003; Lilac, 1999; Gray, 2000).
Cause and effect: You need to be very careful with cause and effect and be absolutely sure how the connections are made. Has x caused y or has y caused x? Are the connections any more than coincidence?
Dissertation argument: Face your protagonists head on
There’s no point pretending that no disagreements exist. It won’t be a strong case if you assert that you agree with someone but provide no evidence that you’ve thought through potential criticisms and discovered ways they can be rebuffed. The most convincing arguments take into account all aspects of an issue and concede points when necessary.
Each argument should get the same treatment – interrogate the premiss, evidence and problems of all the arguments, as this allows the strongest arguments to emerge.
Some arguments will be more central than others, but all need to be treated reasonably. By this, don't over-criticise the arguments that you dislike and give an easy ride to those you feel you'd like to support. You need to dispense even-handed analysis, but don't shy away from pointing out fallacies.
Criticise, don’t denigrate, otherwise you'll weaken your own argument. Garner support genuinely, don’t twist people’s words to suit your purposes.
Dissertation argument: Follow threads of logic
In building a strong argument, there’s no one single absolute correct structure. Whichever route you choose, you must ensure logical links through your argument. Following are some alternative structures for building argument in non-empirical dissertations. These structures include all aspects of the thesis (such as literature review, methodologies and conclusion).
Visit the virtues of alternative arguments
Present the context of your argument; discuss the academic literature; discuss any relevant professional literature; explain the underpinning assumptions of the main argument; corroborate with relevant academic and professional evidence; present alternative arguments, highlight their deficits and fallacies with reference to relevant academic and professional evidence; show how the conclusion is inevitable as the main thesis has superior supporting evidence.
Evaluate an existing study
Present context; give rationale for why the study is being evaluated, including the impact of this study on policy and/or practice; present an overview of the literature; explain the evaluative methods to be used, taking into account issues such as validity, reliability, quality of evidence; evaluate the study providing support for any criticisms of the study's research design, conclusions and implications
Next make an overall judgement on the quality of the study including implications and recommendations for improving policy and practice; conclude by summarising the key themes (without repeating everything).
Critique a particular theory
Contextualise this theory within the current field; provide a rationale for evaluating the theory; explain (briefly) any methodologies you may utilise; show the importance of the theory through a review of the literature; describe the origins, nature and impact of the theory; critique the theory by referencing evidence, examining its validity, consistency and suppositions.
Next compare the inferences made from the theory with those you can now make having identified fallacies in the theory; suggest improvements; and conclude by summarising the key themes (without repeating everything).
About This Article
This article is from the book:.
- Writing a Dissertation For Dummies ,
About the book author:
Dr Carrie Winstanley is a Principal Lecturer in Education at Roehampton University, London, where she works with both undergraduate and postgraduate students. Carrie was recently named one of the Top 50 university teachers in the UK by the Higher Education Academy, for which she was awarded a national teaching fellowship.
This article can be found in the category:
- Essential Networking when Writing a Dissertation
- Obeying the Dissertation Rules and Regulations<b> </b>
- Optimising Your Dissertation Writing
- Organising Your Working Methods while Writing a Dissertation
- Settling on Your Dissertation Research Question
- View All Articles From Book
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
Other frequently assigned papers, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Writing Arguments
Steps to Writing an Argument
Develop your argument.
When you develop your argument, you are confirming your own position, and building your case for the readers. Use empirical evidence—facts and statistics—to support your claims. Appeal to your audience’s rational and logical thinking. Argue your case from the authority of your evidence and research.
Your list of strengths and weaknesses can help you develop your argument. Here is how to do that:
First, prioritize the strengths and weaknesses of each position and then decide on the top three to five strengths and weaknesses.
Then, using a technique for developing content ideas, begin to expand your understanding of each item on your list (see the section in chapter 2 titled “ Techniques to Get Started ”).
Evaluate each one in terms of how you can support it—by reasoning, providing details, adding an example, or offering evidence.
Again, prioritize your list of strengths and weaknesses, this time noting the supporting comments that need more work, call for more evidence, or may be irrelevant to your argument. At this stage, it is better to overlook nothing and keep extensive notes for later reference.
As you develop your ideas, remember that you are presenting them in a fair-minded and rational way, counting on your readers’ intelligence, experience, and insight to evaluate your argument and see your point of view.
Techniques for Appealing to Your Readers
The success of your argument depends on your skill in convincing your readers—through sound reasoning, persuasion, and evidence—of the strength of your point of view. But how can you do that in the most effective way? There are three fundamental types of appeal in presenting an argument: reason, ethics, and emotion. As a writer, use all three of these techniques in your writing.
But let’s learn more about these types of appeal:
Clear thinking requires that you state your claim and support it with concrete, specific facts. This approach appeals to our common sense and rational thinking.
Formal reasoning involves following certain established logical methods to arrive at certain pieces of information or conclusions. Generally, these logical methods are known as inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning.
What is inductive reasoning? Inductive thinking is when our logical thinking states specific facts (called premises) and then draws a conclusion, or generalization. Inductive reasoning lets us examine the specific details, considering how well they add up to the generalization. When we think inductively, we are asking whether the evidence clearly supports the conclusions.
Example of Inductive Reasoning
Premise: Swans nest near this pond every summer.
Hypothesis: This summer, swans will probably nest near this pond.
What is deductive reasoning? In deductive reasoning, you take two premises to create a conclusion based on reasoning and evidence. When we think logically, we start with the generalization. As we apply our generalization to a specific situation, we examine the individual premises that make that generalization reasonable or unreasonable. When our logical thinking starts with the generalization, or conclusion, we may then apply the generalization to a particular situation to see if that generalization follows from the premises. Our deductive thinking can be expressed as a syllogism or an enthymeme —a shortened form of the syllogism.
Syllogisms can be written like this:
All A are B.
All C are A.
Therefore, all C are B.
Example of Deductive Reasoning Using a Syllogism:
Major premise: All birds have feathers.
Minor premise: A parrot is a bird.
Conclusion: A parrot has feathers.
Enthymemes can be written like this:
If A=B and B=C, then A=C.
But with enthymemes, B=C is implied.
Example of Deductive Reasoning Using an Enthymeme:
Conclusion: A parrot is a bird.
(We assume that a parrot has feathers)
Think of ethics as the force of a speaker’s character as it is represented in writing. If you misrepresent the evidence of one of your sources, your readers will question your ethics.
In any situation in which you must rely on your readers’ goodwill and common sense, you will lose their open-minded stance toward your argument if you support it by using unethical methods. This can happen intentionally, by misrepresenting evidence and experts and by seeking to hurt individuals or groups. It can also happen unintentionally—you may undermine your argument by inadvertently misunderstanding the evidence and the implications of your position. This can occur if you don’t research the evidence responsibly, preferring instead to express your own and others’ unfounded opinions.
Using emotions as a support for argument can be tricky. Attempts to play on your readers’ emotions can seem manipulative and are often mistrusted. To use emotional appeal successfully, you must apply discretion and restraint. Choose examples that represent and illustrate your ideas fairly, and then present your arguments as objectively as possible. The writer must carefully draw the connections between the ideas and illustrations, choosing diction in such a way that readers don’t question motives as manipulative. Strong evidence accumulated by careful research often addresses this potential problem well.
Example of an Appeal to Emotion
Rather than continuing these tax-and-spend policies, we plan to return your hard-earned tax money to you.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .

Organizing an Argument
As with other aspects of writing an argument, your organizational strategy will vary according to the requirements of its disciplinary context, your knowledge and level of expertise within the field, and your previous experience preparing arguments.
There are probably as many ways to draft an argument as there are arguments; however, there are a few tried and true methods-from adversarial to mediation based, and deductive to inductive reasoning-which work well in the academic world. None of them are carved in stone, however. Here we'll explore a number of useful methods to guide you in drafting your own argument.
Rogerian Method
Most of the time we think of arguments as adversarial, taking place between people who fundamentally disagree. One will be right and the other wrong; one wins and the other loses. This works in legal systems as well as in the context of many other situations. But often-especially in academic arguing-no single position regarding a controversy is completely right.
When you're working on an issue or problem about which more than one viewpoint may be valid, you may want to try drafting an argument that is oriented more toward mediation. Unlike adversarial arguments, which typically begin with a firm claim, an argument that mediates will postpone stating a position until much later in the presentation, often the middle or the end.
There are a number of ways to do this; one of the best being based on the work of psychologist Carl Rogers. A Rogerian argument presumes that if author and audience find common ground regarding an issue or problem, they will be more likely to find, or agree upon, a common solution. It succeeds only when the author understands the audience. He or she must present the audience's perspective clearly, accurately, and fairly before asking them to consider an alternative position or solution.
This method downplays emotional appeals in favor of the rational and is particularly useful in dealing with emotionally charged, highly divisive issues and allows for people of good will on different sides of an issue to find, or agree upon, solutions together.
Parts of a Rogerian Argument
The introduction typically points out how both the author and the audience are similarly affected. Rather than presenting a thesis demanding agreement, which is often seen as an attack on whomever holds an opposing view; this presentation emphasizes unity, putting the audience first.
The audience perspective comes next. Described as clearly and accurately as possible-typically in neutral language-the author acknowledges their point of view and the circumstances and contexts in which their perspective or position is valid. Done well, the author builds good will and credibility with the audience, a crucial step leading toward potential compromise. Honest, heartfelt sincerity is the key here: if the audience perceives an attempt at manipulation, the Rogerian argument strategy generally backfires.
The author's perspective comes in the next chunk of the argument. For the audience to give it a listen it must be presented in as fair-minded a way as was theirs, in language as equally neutral and clear. To be convincing, besides describing the circumstances or contexts in which the position is valid, it must contain the evidence that supports the claim.
The closing of a Rogerian argument doesn't ask the audience to give up their position, but shows how they would benefit from moving closer toward that of the author's. In other words, it ends by laying out the ways a compromise or alternative solution benefits both audience and author under a wider variety of circumstances than either can account for alone.
Deductive Method
The traditional academic argument is deductive, placing the author's position in the introduction and devoting the rest of the argument to presenting the evidence. Unless you are in a field where inductive reasoning is the norm, you can hardly go wrong with this method.
In some cases, all the evidence may be directed at proving the main point; in others, each piece may lead to a sub-point that needs proving before a convincing argument for the main point can be made. Depending on how directly each piece of evidence relates to the position, a deductive argument can be organized in a variety of ways.
When All Evidence Relates...
When all evidence relates directly to your main point, or thesis, and each piece of evidence is equally relevant, a typical arrangement simply introduces the position and presents each piece. Transitions connect each to the thesis.
Depending on their strengths and weaknesses, the order in which each piece of evidence is presented, as well as the rebuttals of opposing arguments, can differ greatly.
More often than not, even when all evidence is directly relevant, some pieces may be more convincing-less open to question or interpretation-than others. In these cases, arguments are typically arranged as follows:
- Introduction establishing the context of the argument as well as the author's position.
- Body of Evidence presented, depending on the audience analysis, from most to least, or least to most convincing.
- Conclusion summarizing the argument, presenting a call to action, or suggesting further research.
When Seemingly Unrelated Sub-Points...
When seemingly unrelated sub-points need to be made and proven in order to prove the main point, the author must show how the particular premises of each, along with its supporting evidence, connect, collectively and logically, to support the main position.
An argument supporting a ban on logging in rain forests might first need to establish and provide evidence regarding five other environmental premises, each supporting the author's position, regarding the effects of logging. For instance:
- It causes soil erosion
- It affects global warming
- It destroys native species
- It alters water routes and levels
- It destroys indigenous lifestyles
Each premise is a debatable issue in and of itself. Therefore, some measure of the supportive evidence behind each-at least enough to connect them as reasonably evidentiary links-must be given before they can be used to collectively support the author's main position. In these cases, arguments are typically arranged as follows:
- Brief Preview outlining each premise, or reason, to be used as evidence supporting the claim.
- Body of Evidence presented, depending on audience analysis, in an order which will make the most sense to the audience.
- Conclusion summarizing the argument and demonstrating how each premise leads logically to the author's position, presents a call to action, or suggests further research.
Note: This arrangement is ideal for content sub-headings where each heading describes the premise/reason to be discussed.
When Opposing Arguments...
When opposing arguments or points of view must be addressed there are a variety of ways to argue against or refute them. They can be place almost anywhere in the text, however, the strength and power of the opposing arguments and how familiar your audience is with them should be your main considerations. Here are a couple of options:
When opposing arguments are less persuasive or, at best, equal to, rebuttals are best saved till last where the opposing argument will appear less credible in light of your own:
Introduction Your argument and evidence Rebuttal of opposition claims Conclusion
When opposing arguments are particularly strong and readily accepted, discrediting them point-by-point may be the best strategy for convincing an audience to consider alternative points or support a different position.
Introduction Rebut first opposing argument followed by first counter-argument Rebut next opposing arguments, followed by further counter-arguments as you go along Conclusion
Inductive Method
Inductive arguments are more difficult for an audience to follow, thus they are less commonly found in the academic world than deductive arguments. Typically they begin with the author introducing an issue without proposing a solution or stating a position. Instead, various takes and opposing positions are introduced and argued, for and against, all of which then leads up to the author stating his or her position.
The goal of an inductive strategy is to present all the evidence and information in a manner such that, when the author's position is finally stated, the audience has been moved, or persuaded to agree that it is the one and only logical conclusion.
Inductive arguments can be organized in a variety of ways depending either on your assessment of what position the audience already holds or, on whether you are arguing a position from original research. It may be completely inductive, saving your position for the end, or partially inductive, introducing your position somewhere in the middle of the argument.
When an Audience Completely Disagrees...
When an audience completely disagrees with your position convincing them that their reasons for disagreeing are faulty before presenting your own position may be the best strategy.
Introduction: States the issue to be addressed and why it is important.
Body of Argument: Examines positions already proposed and refutes each one, showing why they are inadequate. Typically organized like this.
Position 1 Your refutation of position 1 Position 2 Your refutation of position 2
Alternatively, all positions might be examined first and then refuted second.
Position 1 Position 2 Your refutation of position 1 Your refutation of position 2
Conclusion/Position Statement: Once all other positions are shown to be inadequate, conclude with your position as the only logical choice.
When an Audience Partially Disagrees...
When an audience partially disagrees with your position, the best strategy still looks a great deal like when they completely disagree: convincing them that their reasoning is faulty before presenting your own position.
Position Statement: Introduced as the only logical choice after the positions your audience finds most persuasive are shown to be inadequate.
Presentation of Evidence: Supports your position as not only reasonable, but the best one available as well.
When an Audience is Completely Unfamiliar...
When an audience is completely unfamiliar with the issue, presenting evidence and leading to a logical conclusion may be the best choice because you are informing the audience while simultaneously proving the position.
Body of Argument: Presents the different work done on the issue and the conclusions reached.
Logical Connections: Looks at how conclusions reached in the research fit together leading to a particular answer to the problem or position on the issue. An alternative arrangement would include connections between each conclusion presented and proven.
Conclusion/Position Statement: ends the argument with your position as the only logical choice.
When Original Research Forms the Basis...
When original research forms the basis for an argument, particularly in the sciences, the study itself and the results must be discussed before a conclusion or interpretation of the data can be discussed. It must be made obvious to the audience that your position emerges from the research rather than being one you are ensuring the research will support. A deductive arrangement, starting with the conclusion or position, implies that the research may be biased.
Research questions: Describes study and the issue, problem or question it was designed specifically to answer.
Methods: Describes in detail the methods employed in the study.
Results: Summarizes and provides a detailed presentation of findings.
Conclusion/Position Statement: Argues for a particular interpretation of the results which leads to a conclusion addressing or answering the original issue, problem or question investigated.
Tying it All Together
American methods of academic argument are best depicted as a straight line. No matter what-be it evidence, sub-points, refutations of other positions, or personal anecdotes-everything used must lead clearly back to the position being argued. Although the relevance of each is always clear to the author, their connections are not always so obvious to the audience. Therefore, it is up to the author to carefully explain them.
Toulmin Method
One of the best ways to demonstrate why a given piece of evidence supports the thesis, claim or position of an argument is to explain the reasoning process by which they are logically connected. In the Toulmin method, these explanations are referred to as warrants.
First, for each claim that is debatable, or open to question, a reason is offered that supports the claim's validity. A warrant-consisting of a sentence or two-then follows, explaining the reason. Finally, evidence is supplied that supports connecting the reason to a given point or the overall claim of the paper.
Example of the Toulmin Method
Thesis, Claim or Position
Grading should be optional in non-major courses.
Reason/Point #1
Non-major courses are designed to help students become intelligent, well-rounded citizens. If the goal of such courses is the exploration and acquisition of knowledge, grades only get in the way.
Rather than learning for the sake of becoming a better person, grades encourage performance for the sake of a better GPA. The focus grading puts on performance undercuts learning opportunities when students choose courses according to what might be easiest rather than what they'd like to know more about. [Introduces why proof is relevant to point]
For example, students polled at CSU in a College of Liberal Arts study cite the following reasons for choosing non-major courses:
- Easy grading (80%)
- Low quantity of work (60%)
- What was available (40%)
- Personality of teacher (30%)
- Something they were interested in knowing more about (10%)
Similarly, in an interview I conducted with graduating seniors, only two of the 20 people I spoke with found their non-major courses valuable. The other 18 reported that non-major courses were a waste of time for a variety of reasons:
- I'm never going to do anything with them.
- I just took whatever wouldn't distract me from my major so I didn't work very hard in them, just studying enough to get an A on the test.
- Non-major courses are a joke. Everyone I know took the simplest, stupidest, 100-level courses needed to fulfill the requirements. I can't even remember the ones I took now.
Although not everyone in the interviews or the CLA poll cited grades explicitly as the reason for choosing easy, irrelevant, non-major courses, we can read such reasoning into many of the less explicit references as well. Clearly, students are not choosing courses based on what they can learn from them. Yet they are fairly consistent in their choices: 100-level courses with little work. Although laziness might be seen as the cause of such choices, it is just as likely that choosing according to the amount of work, selecting simple courses, or only studying for the exam are a result of the GPA system. Higher work loads and more complex topics obviously could mean receiving a lower grade; thus, they should be avoided. [Demonstrates how proof leads to point as necessary conclusion.]
Using Subheadings and Transitions
Chunking text into sections according to where a new point is being made, a new reason in support of your thesis is offered, or a new opposing argument is being addressed helps establish coherence among the various parts of your argument. Using sub-headings to label these different sections will help the audience follow your argument.
In addition, transitions explaining why one section helps support the point made in the previous one or how the next point follows logically from the first helps the reader see more clearly how these points ultimately relate to the claim, or position being argued.
Using Subheadings and Transitions: An Example
Thesis/Claim: Greenlife's proposal to ban all logging in rain forests should be supported.
Reason #1: It would help prevent global warming. [This sentence then gets developed, followed by a transition leading to Reason #2.]
Transition between #1 and #2: Although global warming may be the most persuasive reason to stop logging in rainforests due to the effect it has on the entire planet's population, the effect on local culture, affecting a much smaller number of people, is just as important. Losing native habitats destroys ways of life which can never be replaced, displacing people and devastating cultures that can never be restored. [ Logic: both are equally important reasons to stop logging.]
Reason #2: Logging destroys indigenous lifestyles. [This gets developed, followed by a transition leading to Reason #3.]
Transition between #2 and #3: Not only is the effect on indigenous cultures and global climate impossible to reverse but logging also has a lasting effect on the local environment that could have equally disastrous consequences. The erosion caused by logging results in a change in the ecosystem, particularly the loss of rich, fertile soil essential to both plant and animal life. [ Logic: human effects of global warming and loss of indigenous cultures are not the only considerations: effects on ecosystems are also consequences of logging.]
Reason #3: Logging produces erosion in the local environment. [This gets developed, followed by a transition leading to Opposing Position #1.]
Transition between reason 3 and opposition #1: Of course, many have argued that the loss of plant life and soil should be considered necessary damages if they work in favor of increasing the quality of human life. [ Logic: Introduces opposing argument #1 and leads to its refutation.]
Opposition #1: The argument that human life is more important than plant life, however, simply does not hold up when considering that the devastation of an ecosystem also affects human life. These effects, as I've already shown, can be measured not only in terms of climate change and the loss of indigenous cultures, but also in terms of losses to farming and other local economic systems. [ Logic: Demonstrates that opposition to point 3 is not viable because of points 1, 2, and 3.]
Using Topic Sentences or Explanatory Paragraphs
Another good way to help an audience follow the logic of your argument is to use of topic sentences literally telling them how each point relates to the claim, clearly connecting them so that there isn't any question how or why they relate. In longer arguments, entire paragraphs can serve this purpose by explaining the connections between extended summaries of evidence or the logical arguments of sub-points to the main claim.
Paragraph Example
Claim/Thesis of Paper: Writing teachers fail to deal with multicultural issues to the detriment of their students.
Section One: An analysis of the weaknesses of current curricular approaches to writing
Transitional Paragraph tying analysis to thesis and next section: As the analysis above shows, none of the available curricular models address multiculturalism except in the most cursory manner. Worse, their very superficiality does more damage than good. By introducing the topic of writing for multiple communities, the pedagogies make an attempt to bring diversity into the classroom; yet their focus remains on teaching academic writing with standard usage and grammar. Although they admit that such teaching is only for this context, putting such emphasis on standard forms introduces the issue: which forms of writing have more power in society, something none of the pedagogies address. By putting forth the academic model as the one which must be taught and learned in schools, they implicitly devalue other forms. The failure to foreground these power issues, then, leads students of difference to conclude that although their language and forms of writing might be acceptable in certain places, they are not welcome in the places which count in society. The effect of such an implicit message can be devastating to maintaining cultural values and difference.
Section Two: Discussion of research on multicultural student reactions' to writing classes.
Topic Sentence Example
Main Claim or Thesis of Paper: Professor X is a good teacher and should retain her job at CSU.
Introduction: Agues that determining whether Professor X is a good teacher involves evaluating her performance against criteria for good teachers.
Body of Argument: Works through several criteria to judge Professor X's teaching quality.
Topic Sentence Example: The first and probably most important criteria for judging the quality of a teacher is student opinion and, by any measure of student opinion-course evaluations, interviews, and class enrollment-Professor X is clearly one of the best teachers at CSU. [Paper goes on to offer summaries of all three forms of proof listed and then moves onto the second criteria with a topic sentence that ties back to the overall judgment of Prof. X as a good teacher.]
Example of When Methods are Combined
Claim of Paper: Decreasing the average work week to 32 hours would help support family values.
From Body of Paper: Although most of us know that working too much affects family time and thus family structure, we usually assume that this is the case only for people who work 40+ hours a week. Studies of how work-related stress influences family time, however, suggest that too much work, even within what is considered "normal," has detrimental effects on family time. [Topic sentence connects evidence (studies) to the point that 40 hour work weeks have negative affects on families.] For example, in Smith's 1987 study of 15 average, middle-class families, he describes the undue pressure a 9-5 schedule puts on families. In particular, he notes that this time schedule translates to at least three forms of unnecessary family stress: (1) "rushed" mornings where parents desperately try sticking to a rigid time schedule that gets the children off to school and themselves to work between the hours of 7 and 9; (2) financial pressure of paying babysitters or day care facilities during school holidays and the 2 or 3 hours after school while parents are still at work; (3) overly frantic weekends where, since many businesses close at 5:00, all errands must be done before then. [Note how the author highlights only the parts of the study that influence family pressures.] The stresses Smith documents are not in families where parents work 60-70 hours a week. The parents working 40 hours a week are secretaries, mechanics, bank employees, etc. The effects on them, he notes, clearly translate to less time spent with family members because of work demands as well as increased pressure when the family is together. [Warrant explaining why proof shows the problem is the 40-hour work week discussed in the initial point made]
Such pressures can't help but influence the quality of time the family spends together, influencing its ability to stay together or to have the type of time most conducive to instilling family values. [Topic sentences which ties point 1 to overall claim of paper] In fact, as psychological studies show, the type of time spent together has a great influence on family cohesiveness. [Transition connecting point 1--effect of 40 hour week on families--to point 2: the influence of time pressures on keeping family together]
Next Paragraph: Summaries of psychological studies to support the new claim of effect on cohesiveness.
Reviewing and Revising Your Connections
After drafting an argument you'll want take a step back and check the logic of its organization. You want to make sure that everything is connected and that every connection will make sense to an audience.
Analyze by Outlining
Chunk your argument into numbered sections: read through the text and place a number in the margin every time you change focus, even slightly. These changes may or may not come at regular intervals: one section might take three paragraphs while another takes only one. When you are finished, ask the following questions:
- Do similar points come up in different sections? If so, put them together.
- Are any sections only a few sentences long? Are they relevant? If so, expand them; if not, cut them out.
- Can you define the relationship each section has to the position being argued? How is each one relevant? Look at your revised argument and create a list of reasons that connect each section to the position being argued. Those that don't should be cut. Save this list, the reasons you have identified will make excellent transitions between argument sections.
- Can you explain why section #2 follows section #1 and so on? If not consider how sections might be moved around so that you have a clear reason for why each one follows another. Make another list, including these reasons. Consider using them as transitions between argument sections as well.
Get Some Peer-Review
Have a friend or several friends read through your argument. Ask them to mark where they get lost or are not sure of your point or where you are going next. These are places where rearrangement or clearer transitions are probably necessary. Also, try reading the argument aloud, to yourself and your friends. Frequently, when you hear an argument out loud, you can pinpoint where its logic doesn't add up. Changes can then be made.
Cut and Paste
Cut and paste. Play around with your organizational structure. Literally cut your paper into paragraphs and then make piles out of those which have things in common. If only part of a paragraph does, then cut some more. Save the leftovers in a separate pile. What do the pieces in each pile have in common? Construct a title for each pile based on the reason: Finally, ask yourself: what is the relationship between each pile: How are they related? Don't be afraid to shuffle them around and look at them in different positions. This will help you order the sections of your argument when pasting it back together. Look at your pile of left over pieces to see if they belong. If they do, consider expanding them so their relevance is made clear. If not, leave them out. Remember, throwing stuff out is not a sign of failure; it's an integral part of rewriting.
LeCourt, Donna, Kate Kiefer, & Peter Connor. (1996). Organizing an Argument. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=56

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Student blogs and videos
- Why Cambridge
- Qualifications directory
- How to apply
- Fees and funding
- Frequently asked questions
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Visiting the University
- Term dates and calendars
- Video and audio
- Find an expert
- Publications
- International Cambridge
- Public engagement
- Giving to Cambridge
- For current students
- For business
- Colleges & departments
- Libraries & facilities
- Museums & collections
- Email & phone search
Planning your dissertation: Constructing an argument
- Faculty of Modern and Medieval Languages and Linguistics
- About overview
- Governance of the Faculty overview
- Governance at MML
- Faculty Board overview
- Board Overview
- Membership and Contacts
- Student Engagement
- Staff-Student Liaison Committee overview
- Committee Overview
- News & Events
- Academic Visitors
- Public Engagement
- IT Services
- The University Library
- Language Centre
- Research Facilities
- MMLL privacy policy
- Health and Safety at MMLL
- Subjects overview
- Modern Greek
- Spanish and Portuguese
- Slavonic Studies overview
- Slavonic Studies virtual event for Years 11 & 12
- Theoretical and Applied Linguistics
- Undergraduates overview
- The Courses: Key Facts overview
- Course costs
- The courses we offer
- The MML Course overview
- MML: The First Year
- MML: The Second Year
- MML: The Year Abroad
- MML: The Fourth Year
- The Linguistics Course
- The History and Modern Languages Course overview
- Course structure overview
- How We Teach
- How You Learn
- Resources for teachers and supporters
- Alumni testimonials overview
- Matthew Thompson
- Rosie Sargeant
- Mark Austin
- Esther Wilkinson
- Katherine Powlesland
- Gillian McFarland
- Katya Andrusz
- Frequently asked questions overview
- Choosing your course
- Applications
- Resources and reading lists for prospective students
- Did you know...?
- Student Perspectives overview
- Alfie Vaughan
- Romany Whittall
- Postgraduates
- Careers and Employment
- Offer Holders overview
- French overview
- Summer Preparation
- German overview
- Beginners Course overview
- Post A-Level Course overview
- Italian and Greek overview
- Portuguese overview
- Spanish overview
- History & Modern Languages Tripos
- From Our Students
- Current undergraduates overview
- Year Abroad overview
- Current Students
- Thinking about your Year Abroad overview
- Studying overview
- Finance overview
- Turing Scheme
- Safety and Insurance
- Year Abroad FAQs
- Year Abroad Project FAQs
- Modern and Medieval Languages Tripos overview
- MML Part IA List of Papers
- Part I Oral Examination A and B
- MML Part IB List of Papers
- MML IB Assessment by Long Essay
- The Year Abroad Project
- MML Part II List of Papers overview
- MML Part II List of Borrowed Papers
- CS5: The Body
- CS6: European Film
- Oral C Examination
- MML Part II Optional Dissertation
- MML with Classics
- Linguistics within the Modern and Medieval Languages Tripos
- Linguistics Tripos overview
- Linguistics Tripos - List of Papers
- Transferable Skills
- History and Modern Languages Tripos
- Marking Criteria
- Supervision Guidelines
- Teaching Provision
- Examinations Data Retention Policy (PDF)
- Learning Resources
- Additional Course Costs
- Faculty guidance on plagiarism
- Translation Toolkit overview
- 1. Translation as a Process
- 2. Translation as a Product
- 3. Equivalence and Translation Loss
- Email etiquette at MMLL
- Overall Degree Classification
- Current postgraduates
- Research in MMLL overview
- Research by Section overview
- Italian overview
- CIRN Home overview
- CIRN Events overview
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2015
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2016
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2017
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2018
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2019
- CIRN Annual Lecture 2019-20
- CIRN Annual Symposium 2015
- CIRN Annual Symposium 2016
- CIRN Annual Symposium 2017
- CIRN Annual Symposium 2018
- CIRN Annual Symposium 2019
- CIRN News and Events archive
- Slavonic Studies
- Research by Language overview
- Research by Period overview
- Medieval and Pre-Modern
- Early Modern
- Eighteenth Century
- Nineteenth Century
- 1900 - 1945
- 1945 - present
- Research by Thematic Field overview
- Literature, Visual Culture and the Arts overview
- Colonial, Postcolonial and Decolonial Studies
- Contemporary Culture and Society
- Drama, Music and Performance
- Environmental Criticism and Posthumanism
- Film and Visual Culture
- Gender, Feminism and Queer Studies
- Intellectual and Cultural History
- Literary Theory, Philosophy and Political Thought
- Material Culture and History of the Book
- Poetry, Rhetoric and Poetics
- Language and Linguistics overview
- Comparative Syntax
- Computational Linguistics
- Dialectology
- Experimental Phonetics and Phonology
- Historical Linguistics
- Language Acquisition
- Language Change
- Language Contact
- Multilingualism
- Psycholinguistics
- Semantics, Pragmatics and Philosophy
- Translation Theory and Practice
- Funded Projects
- Apply for Research Funding overview
- Research Strategy Committee
- Leverhulme Early Career Fellowships
- British Academy Postdoctoral Fellowships
- Management of Ongoing Grants
- Funding Opportunities
- MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships
- Centres overview
- Cambridge Film and Screen
- Cambridge Italian Research Network (CIRN)
- Centre of Latin American Studies (CLAS)
- Cambridge Language Sciences
- Cambridge Endangered Languages and Cultures Group (CELC) overview
- Seminar Series
- Past conferences
- Cambridge Centre for Greek Studies
- Centre for the Study of Global Human Movement
- Equality and Diversity overview
- EDI Committee
- Accessibility Statement
- Accessible Materials
- Recording Lectures
- Athena SWAN
- Mentoring and Career Development
- Parents and Carers
- EDI Related Links
- Harassment and Discrimination
- Outreach overview
- Resources overview
- Open Day Resources for Prospective Students
- CCARL A-level Resources overview
- Why Not Languages? resources overview
- Student Q&A
- Events for Students overview
- Events for Teachers overview
- Diversity in French and Francophone Studies: A CPD workshop series for teachers of French
- Diversity in German Studies - CPD Workshop series aimed at secondary teachers of German
- Workshop for Spanish Teachers
- Workshop for Teachers of German: Diversity in German Culture
- Access and Widening Participation
- Prospective Students
- Equality and Diversity
Identifying an argument
Ultimately, you are aiming to produce a series of propositions in relation to your material: usually a main proposition (thesis or argument) with some sub-propositions.
Asking yourself the following questions may help you think critically about your material and identify some potential arguments:
- How can I bring together the various different ideas that interest me about my topic?
- What difficulties am I experiencing in organising my material, comparing texts or coming to conclusions about them? Are these difficulties significant, i.e. do they tell me something interesting about the nature of the material I am dealing with?
- Did my reading and research throw up anything unexpected?
- What are the polemical aspects of this topic? How can I bring out those contradictions, account for them or investigate them further?
- How do my interpretations converge or diverge from analysis that has already been published on the topic?
- Does my analysis support one or more viewpoints in an existing critical or theoretical debate in the wider field?
Writing summary statements
You need to reach the stage at which you can reduce your argument(s) down to one or more full sentences. Imagine explaining the central idea of your dissertation to a supervisor or fellow student. Try to express your main argument in a couple of summary sentences, and then expand these into four or five sentences, giving greater detail or including sub-points. It is best to have a draft of your summary sentences ready before you start writing, as this will dictate how you should organize your material. But it is entirely normal (and very healthy!) for your ideas to change as you start writing. If that happens, simply go back to your summary and your plan and make sure they reflect your current thinking. It is also very common (and again, a good sign) for your argument to change or develop quite radically after you have composed your first draft. Think of it as a continual, circular process: of refining your summary argument(s), which leads to changes in your written draft, which lead to further refinements of your argument(s), which lead to more alterations to the draft, etc.
Search form
Related links.
- Student Support
- Wellbeing at Cambridge
- Year Abroad FAQ
- Polyglossia Magazine
- The Cambridge Language Collective
- Information for current undergraduates
- Visiting and Erasmus Students
- Dissertation Toolkit home
- 1. Approaching the dissertation
- 2. Initial ideas and finding a supervisor
- 3. Getting the most from your supervisor
- 4. Avoiding common pitfalls
- 5. Choosing and defining a topic
- 6. Producing a work schedule
- 7. Reading for your dissertation
- 8. Planning your dissertation
- 9. Writing a first draft
- 10. Reworking and editing your dissertation
- 11. Inserting quotations
- 12. Referencing other works
- 13. Presenting your bibliography
- 14. Plagiarism
- 15. Using images in your dissertation
- 16. Preparing your dissertation for printing and binding
Keep in touch

- University of Cambridge Privacy Policy
- Student complaints and Examination Reviews
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- University A-Z
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Terms and conditions
- Undergraduate
- Spotlight on...
- About research at Cambridge
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples, & Template
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program.
Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you’ve ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating to know where to begin.
Your department likely has guidelines related to how your dissertation should be structured. When in doubt, consult with your supervisor.
You can also download our full dissertation template in the format of your choice below. The template includes a ready-made table of contents with notes on what to include in each chapter, easily adaptable to your department’s requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
- In the US, a dissertation generally refers to the collection of research you conducted to obtain a PhD.
- In other countries (such as the UK), a dissertation often refers to the research you conduct to obtain your bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
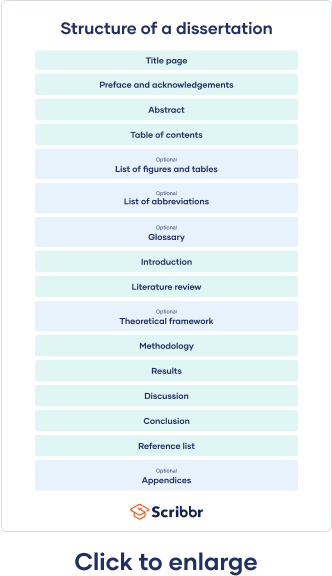
Dissertation committee and prospectus process, how to write and structure a dissertation, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your dissertation, free checklist and lecture slides.
When you’ve finished your coursework, as well as any comprehensive exams or other requirements, you advance to “ABD” (All But Dissertation) status. This means you’ve completed everything except your dissertation.
Prior to starting to write, you must form your committee and write your prospectus or proposal . Your committee comprises your adviser and a few other faculty members. They can be from your own department, or, if your work is more interdisciplinary, from other departments. Your committee will guide you through the dissertation process, and ultimately decide whether you pass your dissertation defense and receive your PhD.
Your prospectus is a formal document presented to your committee, usually orally in a defense, outlining your research aims and objectives and showing why your topic is relevant . After passing your prospectus defense, you’re ready to start your research and writing.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The structure of your dissertation depends on a variety of factors, such as your discipline, topic, and approach. Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an overall argument to support a central thesis , with chapters organized around different themes or case studies.
However, hard science and social science dissertations typically include a review of existing works, a methodology section, an analysis of your original research, and a presentation of your results , presented in different chapters.
Dissertation examples
We’ve compiled a list of dissertation examples to help you get started.
- Example dissertation #1: Heat, Wildfire and Energy Demand: An Examination of Residential Buildings and Community Equity (a dissertation by C. A. Antonopoulos about the impact of extreme heat and wildfire on residential buildings and occupant exposure risks).
- Example dissertation #2: Exploring Income Volatility and Financial Health Among Middle-Income Households (a dissertation by M. Addo about income volatility and declining economic security among middle-income households).
- Example dissertation #3: The Use of Mindfulness Meditation to Increase the Efficacy of Mirror Visual Feedback for Reducing Phantom Limb Pain in Amputees (a dissertation by N. S. Mills about the effect of mindfulness-based interventions on the relationship between mirror visual feedback and the pain level in amputees with phantom limb pain).
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. In some cases, your acknowledgements are part of a preface.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150 to 300 words long. Though this may seem very short, it’s one of the most important parts of your dissertation, because it introduces your work to your audience.
Your abstract should:
- State your main topic and the aims of your research
- Describe your methods
- Summarize your main results
- State your conclusions
Read more about abstracts
The table of contents lists all of your chapters, along with corresponding subheadings and page numbers. This gives your reader an overview of your structure and helps them easily navigate your document.
Remember to include all main parts of your dissertation in your table of contents, even the appendices. It’s easy to generate a table automatically in Word if you used heading styles. Generally speaking, you only include level 2 and level 3 headings, not every subheading you included in your finished work.
Read more about tables of contents
While not usually mandatory, it’s nice to include a list of figures and tables to help guide your reader if you have used a lot of these in your dissertation. It’s easy to generate one of these in Word using the Insert Caption feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
Similarly, if you have used a lot of abbreviations (especially industry-specific ones) in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
In addition to the list of abbreviations, if you find yourself using a lot of highly specialized terms that you worry will not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary. Here, alphabetize the terms and include a brief description or definition.
Read more about glossaries
The introduction serves to set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance. It tells the reader what to expect in the rest of your dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving the background information needed to contextualize your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of your research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your research questions and objectives
- Outline the flow of the rest of your work
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant. By the end, the reader should understand the what, why, and how of your research.
Read more about introductions
A formative part of your research is your literature review . This helps you gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic.
Literature reviews encompass:
- Finding relevant sources (e.g., books and journal articles)
- Assessing the credibility of your sources
- Critically analyzing and evaluating each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g., themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps) to strengthen your overall point
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing sources. Your literature review should have a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear justification for your own research. It may aim to:
- Address a gap in the literature or build on existing knowledge
- Take a new theoretical or methodological approach to your topic
- Propose a solution to an unresolved problem or advance one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework. Here, you define and analyze the key theories, concepts, and models that frame your research.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to critically assess its credibility. Your methodology section should accurately report what you did, as well as convince your reader that this was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- The overall research approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative ) and research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment )
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Any tools and materials you used (e.g., computer programs, lab equipment)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses , or themes, but avoid including any subjective or speculative interpretation here.
Your results section should:
- Concisely state each relevant result together with relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Briefly state how the result relates to the question or whether the hypothesis was supported
- Report all results that are relevant to your research questions , including any that did not meet your expectations.
Additional data (including raw numbers, full questionnaires, or interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix. You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results. Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is your opportunity to explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research question. Here, interpret your results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. Refer back to relevant source material to show how your results fit within existing research in your field.
Some guiding questions include:
- What do your results mean?
- Why do your results matter?
- What limitations do the results have?
If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your dissertation’s conclusion should concisely answer your main research question, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your central argument and emphasizing what your research has contributed to the field.
In some disciplines, the conclusion is just a short section preceding the discussion section, but in other contexts, it is the final chapter of your work. Here, you wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you found, with recommendations for future research and concluding remarks.
It’s important to leave the reader with a clear impression of why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known? Why is your research necessary for the future of your field?
Read more about conclusions
It is crucial to include a reference list or list of works cited with the full details of all the sources that you used, in order to avoid plagiarism. Be sure to choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your dissertation. Each style has strict and specific formatting requirements.
Common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA , but which style you use is often set by your department or your field.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
Your dissertation should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents such as interview transcripts or survey questions can be added as appendices, rather than adding them to the main body.
Read more about appendices
Making sure that all of your sections are in the right place is only the first step to a well-written dissertation. Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing and proofreading, as grammar mistakes and sloppy spelling errors can really negatively impact your work.
Dissertations can take up to five years to write, so you will definitely want to make sure that everything is perfect before submitting. You may want to consider using a professional dissertation editing service , AI proofreader or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect prior to submitting.
After your written dissertation is approved, your committee will schedule a defense. Similarly to defending your prospectus, dissertation defenses are oral presentations of your work. You’ll present your dissertation, and your committee will ask you questions. Many departments allow family members, friends, and other people who are interested to join as well.
After your defense, your committee will meet, and then inform you whether you have passed. Keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality; most committees will have resolved any serious issues with your work with you far prior to your defense, giving you ample time to fix any problems.
As you write your dissertation, you can use this simple checklist to make sure you’ve included all the essentials.
Checklist: Dissertation
My title page includes all information required by my university.
I have included acknowledgements thanking those who helped me.
My abstract provides a concise summary of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of my key results or arguments.
I have created a table of contents to help the reader navigate my dissertation. It includes all chapter titles, but excludes the title page, acknowledgements, and abstract.
My introduction leads into my topic in an engaging way and shows the relevance of my research.
My introduction clearly defines the focus of my research, stating my research questions and research objectives .
My introduction includes an overview of the dissertation’s structure (reading guide).
I have conducted a literature review in which I (1) critically engage with sources, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, (2) discuss patterns, themes, and debates in the literature, and (3) address a gap or show how my research contributes to existing research.
I have clearly outlined the theoretical framework of my research, explaining the theories and models that support my approach.
I have thoroughly described my methodology , explaining how I collected data and analyzed data.
I have concisely and objectively reported all relevant results .
I have (1) evaluated and interpreted the meaning of the results and (2) acknowledged any important limitations of the results in my discussion .
I have clearly stated the answer to my main research question in the conclusion .
I have clearly explained the implications of my conclusion, emphasizing what new insight my research has contributed.
I have provided relevant recommendations for further research or practice.
If relevant, I have included appendices with supplemental information.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
I have listed every source in a reference list at the end of my dissertation.
I have consistently followed the rules of my chosen citation style .
I have followed all formatting guidelines provided by my university.
Congratulations!
The end is in sight—your dissertation is nearly ready to submit! Make sure it's perfectly polished with the help of a Scribbr editor.
If you’re an educator, feel free to download and adapt these slides to teach your students about structuring a dissertation.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation Binding and Printing | Options, Tips, & Comparison
- Example of a dissertation abstract
- Figure and Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Purpose and structure of an advisory report
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Shorten your abstract or summary
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What is your plagiarism score?
- 301 Academic Skills Centre
- Study skills online
Developing an academic argument
Information on how to structure an academic argument, from establishing your claim to concluding.
The importance of academic arguments
Arguments and ideas lie at the heart of most academic writing. Academic essays usually follow an established organisational structure that helps the writer to express their ideas in a clear way and the reader to follow the thread of their argument.
Essay structure is guided by its content and argument, so every essay will pose unique structural challenges, but the skill of getting a clear and articulate argument across is an important part of the writing process.
301 Recommends:
Our Developing and Academic Argument workshop will outline how to develop a coherent argument from making an initial claim through to presenting a convincing conclusion. It will address the ways in which academic arguments are expressed to reflect the strength and reliability of data and evidence and it will look at the ways in which the structural features of a piece of writing can be used to convince your reader.
The structure of an argument
At the heart of all arguments is a claim – the main premise that you are interested in proving.
Establishing your claim is one of the most important parts of any piece of academic work; an essay, a presentation, a dissertation, research paper or thesis.
A good claim should be bold, exciting and, most importantly, worth arguing over. A version of your claim will probably be included somewhere in your introduction.
To convince your reader of your claim, you will need to provide some proof . Your proof will be in the form of evidence, data, sources and examples, all of which will need to be fully referenced in the appropriate style .
However, it is important to recognise that relevant evidence does not automatically prove a claim. There is usually some work to be done to convince your reader that there is a connection – ie how and why this evidence informs your thinking.
This part of the argument is sometimes called a warrant .
It's also important to consider and actively seek out alternative points of view and potential objections .
There is sometimes a tendency to be drawn to ideas that explicitly or implicitly support our own ways of thinking – the echo chamber – which can result in narrow or flawed arguments.
By engaging deliberately with objections and building them into our own thinking, we can develop more nuanced and rounded arguments.
Your conclusion will draw on this process of research and thinking to present a balanced summary of the argument, using cautious language as appropriate to the strength of your findings.
You may be able to use this as an opportunity to make some predictions or recommendations, suggest some practical applications or identify openings for further research.
Be bold and make sure that your argument is something worth arguing over.
Watch out for logical fallacies. Just because you have some evidence, it doesn't automatically prove your argument. You need to explain how and why your evidence is sufficient, valid and reliable
Engage with opposing viewpoints to ensure that you have considered all possible counter-arguments
Don't be afraid to go beyond the source material to draw your own informed conclusions
English Language Teaching Centre (ELTC) academic literacy resources – Building an argument .
Download this template to map out your argument (PDF, 437KB) and use this list of logical fallacies to watch out for (PDF, 419KB) to avoid developing a flawed argument.
Watch this short Study skills hacks video for some ideas on how to develop your academic argument.
Purdue University – What is the Toulmin method?
Related information
Essay structure and planning
Proofreading

The Summer Skills Spark: 5 weeks to ignite your research skills
Are you working on a dissertation or research project this summer?
The Summer Skills Spark offers workshops to support you through every step of the process. You'll have opportunities to plan your projects, develop your research skills, explore dissemination techniques, and consider a future career in research.
Collaboration between 301 Academic Skills Centre, the University Library, Digital Learning, and the Careers and Employability Service.
Sheffield is a research university with a global reputation for excellence. We're a member of the Russell Group: one of the 24 leading UK universities for research and teaching.

Russian (dolls) to the rescue – how to structure an argument in your PhD
Feb 10, 2019

At the core of the PhD are arguments. Lots of them. Some more important and some very specific.
If you understand how to structure an argument , your thesis reads clearly and logically. If you don’t, the reader ends up confused and your thesis suffers.
In this post, we discuss how to structure the arguments in your PhD, what the different types of arguments are, how they relate and how to nest them.
Keep things simple
If you remember one thing from this post it is this: keep things simple, present one argument at a time and make sure that all arguments are logically coherent.
Why? The simpler and more logical the text, the easier it is for the reader to follow and understand.
This doesn’t mean that you should have simple ideas and a simple thesis. No.The PhD requires complex ideas. The trick is to do present your complex ideas in a simple way.
There are different types of argument
The most effective way to present your complex ideas is to understand how they differ.
There are different types of arguments. You need to recognise what they are and then nest them within one another. Think of Russian Dolls . The broad arguments first, then the more specific, then the most specific.

Some arguments run through the whole thesis. These are the overarching arguments. They are the bullet points of what the thesis is trying to argue and form the frame from which everything else hangs. In our PhD Writing Template , they are the ‘Aims & Objectives’ in the top left.
Next, you have chapter arguments. This is the argument that runs through each chapter.
Then, you have standalone arguments . These are the ‘mini’ arguments that are used to justify your chapter argument and, ultimately, your thesis argument.
Let’s look at my own PhD thesis to illustrate these:
- The overarching argument running through my entire PhD was that we haven’t paid enough attention to the role that local governments play in dealing with climate change and that they play a bigger role than we give them credit for. This was the framework around which the whole study was based.
- Then, each chapter had its own argument. For example, my empirical chapter argued that one of my case studies was acting as a pioneer of a particular type of sustainability policy.
- Then, within each chapter there were many standalone arguments. For example, in the literature review, I wrote about how particular authors argued particular things.
That’s the Russian doll at work. You can see the broad, overarching study and then how each of the more specific arguments nests within it.
Each type of argument slots into the one above it. Your standalone arguments are there to reinforce your chapter arguments. Your chapter arguments are there to reinforce your thesis argument.
What this means though is that you have to present them in the right order.
Get to the point
Present your argument clearly. Do so as early as possible. Follow this format:
- The opening lines of the thesis should summarise the thesis argument.
- The opening line of the chapter should summarise the chapter argument.
- The opening line of each paragraph or sub-section should summarise the standalone argument presented in that paragraph or sub-section.
Let’s look at my own PhD thesis for examples.
The overarching argument is laid out right on page one of the thesis.

Now let’s look at a chapter argument. Don’t worry about the technical language, just notice that the argument (underlined) is presented right away:

Now let us look at a sub-section for an example of a standalone argument. Again, you can see the argument is clearly presented early on:

How should I word things?
Sometimes it may be as simple as saying ‘In this chapter I will argue’.
However, watch out when you’re discussing the standalone arguments; starting each paragraph with ’this paragraph will argue…’ will soon get boring. Instead, just get to the point. Present the main idea you want to convey in that paragraph in the first sentence.
Working in this way leaves your reader in no doubt about what it is you are trying to say. Remember, you are writing the thesis primarily for your examiners. Their job is to judge how well you have justified the arguments you are trying to make. The clearer those arguments are, the easier their job will be. Nest your arguments and make them flow.
Your examiners will thank you for it.
Hello, Doctor…
Sounds good, doesn’t it? Be able to call yourself Doctor sooner with our five-star rated How to Write A PhD email-course. Learn everything your supervisor should have taught you about planning and completing a PhD.
Now half price. Join hundreds of other students and become a better thesis writer, or your money back.
Share this:
This is quite informative. Thank you
You’re welcome. I’m glad you found it useful.
Great. I’m glad you think so.
I love this. Keep up the good work.
I just found your site and I feel it’s what I was looking for. This idea about arguments (and their hierarchy) was explained in two different books I read this week, but it was only when I visualise them as ‘Russian dolls’ that everything made sense. Thanks for that.
I’m so glad! Thanks!
really useful -thanks. Can you please extend this and talk about how we should write i.e some of the features of thesis /PhD writing too?
Hey – we’ve got hundreds of guides on thesis structure/writing on the rest of The PhD Knowledge Base. Click here for more.
Found this really useful, thanks

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Your PhD and Covid
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice

Writing The Methodology Chapter
5 Time-Saving Tips & Tools
By: David Phair (PhD) and Amy Murdock (PhD) | July 2022
The methodology chapter is a crucial part of your dissertation or thesis – it’s where you provide context and justification for your study’s design. This in turn demonstrates your understanding of research theory, which is what earns you marks .
Over the years, we’ve helped thousands of students navigate this tricky section of the research process. In this post, we’ll share 5 time-saving tips to help you effectively write up your research methodology chapter .
Overview: Writing The Methodology Chapter
- Develop a (rough) outline before you start writing
- Draw inspiration from similar studies in your topic area
- Justify every research design choice that you make
- Err on the side of too much detail , rather than too little
- Back up every design choice by referencing literature

1. Develop an outline before you start writing
The first thing to keep in mind when writing your methodology chapter (and the rest of your dissertation) is that it’s always a good idea to sketch out a rough outline of what you are going to write about before you start writing . This will ensure that you stay focused and have a clear structural logic – thereby making the writing process simpler and faster.
An easy method of finding a structure for this chapter is to use frameworks that already exist, such as Saunder’s “ research onion ” as an example. Alternatively, there are many free methodology chapter templates for you to use as a starting point, so don’t feel like you have to create a new one from scratch.
Next, you’ll want to consider what your research approach is , and how you can break it down from a top-down angle, i.e., from the philosophical down to the concrete/tactical level. For example, you’ll need to articulate the following:
- Are you using a positivist , interpretivist , or pragmatist approach ?
- Are you using inductive or deductive reasoning?
- Are you using a qualitative , quantitative, or mixed methods study?
Keep these questions front of mind to ensure that you have a clear, well-aligned line of argument that will maintain your chapter’s internal and external consistency.
Remember, it’s okay if you feel overwhelmed when you first start the methodology chapter. Nobody is born with an innate knowledge of how to do this, so be prepared for the learning curve associated with new research projects. It’s no small task to write up a dissertation or thesis, so be kind to yourself!

2. Take inspiration from other studies
Generally, there are plenty of existing journal articles that will share similar methodological approaches to your study. With any luck, there will also be existing dissertations and theses that adopt a similar methodological approach and topic. So, consider taking inspiration from these studies to help curate the contents of your methodology chapter.
Students often find it difficult to choose what content to include in the methodology chapter and what to leave for the appendix. By reviewing other studies with similar approaches, you will get a clearer sense of your discipline’s norms and characteristics . This will help you, especially in terms of deciding on the structure and depth of discussion.
While you can draw inspiration from other studies, remember that it’s vital to pay close attention to your university’s specific guidelines, so you can anticipate departmental expectations of this section’s layout and content (and make it easier to work with your supervisor). Doing this is also a great way to figure out how in-depth your discussion should be. For example, word-count guidelines can help you decide whether to include or omit certain information.
Need a helping hand?
3. Justify every design choice you make
The golden rule of the methodology chapter is that you need to justify each and every design choice that you make, no matter how small or inconsequential it may seem. We often see that students merely state what they did instead of why they did what they did – and this costs them marks.
Keep in mind that you need to illustrate the strength of your study’s methodological foundation. By discussing the “what”, “why” and “how” of your choices, you demonstrate your understanding of research design and simultaneously justify the relevancy and efficacy of your methodology – both of which will earn you marks.
It’s never an easy task to conduct research. So, it’s seldom the case that you’ll be able to use the very best possible methodology for your research (e.g. due to time or budgetary constraints ). That’s okay – but make sure that you explain and justify your use of an alternate methodology to help justify your approach.
Ultimately, if you don’t justify and explain the logic behind each of your choices, your marker will have to assume that you simply didn’t know any better . So, make sure that you justify every choice, especially when it is a subpar choice (due to a practical constraint, for example). You can see an example of how this is done here.

4. Err on the side of too much detail
We often see a tendency in students to mistakenly give more of an overview of their methodology instead of a step-by-step breakdown . Since the methodology chapter needs to be detailed enough for another researcher to replicate your study, your chapter should be particularly granular in terms of detail.
Whether you’re doing a qualitative or quantitative study, it’s crucial to convey rigor in your research. You can do this by being especially detailed when you discuss your data, so be absolutely clear about your:
- Sampling strategy
- Data collection method(s)
- Data preparation
- Analysis technique(s)
As you will likely face an extensive period of editing at your supervisor/reviewer’s direction, you’ll make it much easier for yourself if you have more information than you’d need. Some supervisors expect extensive detail around a certain aspect of your dissertation (like your research philosophy), while others may not expect it at all.
Remember, it’s quicker and easier to remove/ trim down information than it is to add information after the fact, so take the time to show your supervisor that you know what you’re talking about (methodologically) and you’re doing your best to be rigorous in your research.

5. Provide citations to support each design choice
Related to the issue of poor justification (tip #3), it’s important include high-quality academic citations to support the justification of your design choices. In other words, it’s not enough to simply explain why you chose a specific approach – you need to support each justification with reference to academic material.
Simply put, you should avoid thinking of your methodology chapter as a citation-less section in your dissertation. As with your literature review, your methods section must include citations for every decision you make, since you are building on prior research. You must show that you are making decisions based on methods that are proven to be effective, and not just because you “feel” that they are effective.
When considering the source of your citations, you should stick to peer-reviewed academic papers and journals and avoid using websites or blog posts (like us, hehe). Doing this will demonstrate that you are familiar with the literature and that you are factoring in what credible academics have to say about your methodology.
As a final tip, it’s always a good idea to cite as you go . If you leave this for the end, then you’ll end up spending a lot of precious time retracing your steps to find your citations and risk losing track of them entirely. So, be proactive and drop in those citations as you write up . You’ll thank yourself later!
Let’s Recap…
In this post, we covered 5 time-saving tips for writing up the methodology chapter:
- Look at similar studies in your topic area
- Justify every design choice that you make
- Back up every design choice by referencing methodology literature
If you’ve got any questions relating to the methodology chapter, feel free to drop a comment below. Alternatively, if you’re interested in getting 1-on-1 help with your thesis or dissertation, be sure to check out our private coaching service .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
What data analysis method can work best for my study. I am using a mixed method in the study. I am developing a framework to address the challenges faced by the taxi operators as entrepreneurs. I will need to analyse both using qualitative and quantitative.
How to find standard deviation for non numerical data
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Justify Your Methods in a Thesis or Dissertation

4-minute read
- 1st May 2023
Writing a thesis or dissertation is hard work. You’ve devoted countless hours to your research, and you want your results to be taken seriously. But how does your professor or evaluating committee know that they can trust your results? You convince them by justifying your research methods.
What Does Justifying Your Methods Mean?
In simple terms, your methods are the tools you use to obtain your data, and the justification (which is also called the methodology ) is the analysis of those tools. In your justification, your goal is to demonstrate that your research is both rigorously conducted and replicable so your audience recognizes that your results are legitimate.
The formatting and structure of your justification will depend on your field of study and your institution’s requirements, but below, we’ve provided questions to ask yourself as you outline your justification.
Why Did You Choose Your Method of Gathering Data?
Does your study rely on quantitative data, qualitative data, or both? Certain types of data work better for certain studies. How did you choose to gather that data? Evaluate your approach to collecting data in light of your research question. Did you consider any alternative approaches? If so, why did you decide not to use them? Highlight the pros and cons of various possible methods if necessary. Research results aren’t valid unless the data are valid, so you have to convince your reader that they are.
How Did You Evaluate Your Data?
Collecting your data was only the first part of your study. Once you had them, how did you use them? Do your results involve cross-referencing? If so, how was this accomplished? Which statistical analyses did you run, and why did you choose them? Are they common in your field? How did you make sure your data were statistically significant ? Is your effect size small, medium, or large? Numbers don’t always lend themselves to an obvious outcome. Here, you want to provide a clear link between the Methods and Results sections of your paper.
Did You Use Any Unconventional Approaches in Your Study?
Most fields have standard approaches to the research they use, but these approaches don’t work for every project. Did you use methods that other fields normally use, or did you need to come up with a different way of obtaining your data? Your reader will look at unconventional approaches with a more critical eye. Acknowledge the limitations of your method, but explain why the strengths of the method outweigh those limitations.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
What Relevant Sources Can You Cite?
You can strengthen your justification by referencing existing research in your field. Citing these references can demonstrate that you’ve followed established practices for your type of research. Or you can discuss how you decided on your approach by evaluating other studies. Highlight the use of established techniques, tools, and measurements in your study. If you used an unconventional approach, justify it by providing evidence of a gap in the existing literature.
Two Final Tips:
● When you’re writing your justification, write for your audience. Your purpose here is to provide more than a technical list of details and procedures. This section should focus more on the why and less on the how .
● Consider your methodology as you’re conducting your research. Take thorough notes as you work to make sure you capture all the necessary details correctly. Eliminating any possible confusion or ambiguity will go a long way toward helping your justification.
In Conclusion:
Your goal in writing your justification is to explain not only the decisions you made but also the reasoning behind those decisions. It should be overwhelmingly clear to your audience that your study used the best possible methods to answer your research question. Properly justifying your methods will let your audience know that your research was effective and its results are valid.
Want more writing tips? Check out Proofed’s Writing Tips and Academic Writing Tips blogs. And once you’ve written your thesis or dissertation, consider sending it to us. Our editors will be happy to check your grammar, spelling, and punctuation to make sure your document is the best it can be. Check out our services for free .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Writing Worksheets and Other Writing Resources
- Thesis, Analysis, & Structure
Suggestions for Developing Argumentative Essays
About the slc.
- Our Mission and Core Values

1. Select an arguable topic, preferably one which interests, puzzles, or appeals to you.
Make sure your topic is neither too broad--something which warrants a dissertation--nor too limited. Decide what your goals are for the paper. What is your purpose? What opinion, view, or idea do you want to prove? Try to articulate your purpose clearly before you begin writing. If you cannot state your purpose clearly, try to freewrite about your topic.
2. Take a position on your topic, and form a thesis statement.
Your thesis must be arguable; it must assert or deny something about your topic. To be arguable, a thesis must have some probability of being true. It should not, however, be generally accepted as true; it must be a statement with which people may disagree. Keep in mind that a thesis contains both an observation and an opinion:
|
|
A good way to test the strength of your thesis is to see if it yields a strong antithesis.
Common thesis pitfalls:
- A thesis expressed as a fragment.
- A thesis which is too broad.
- A thesis worded as a question. (Usually the answer to the question yields the thesis)
- A thesis which includes extraneous information.
- A thesis which begins with I think or in my opinion.
- A thesis which deals with a stale or trite issue.
- A thesis which contains words which lead to faulty generalizations (all, none, always, only, everyone, etc.)
Thesis writing tips:
- A thesis evolves as you work with your topic. Brainstorm, research, talk, and think about your topic before settling on a thesis. If you are having trouble formulating a thesis, begin freewriting about your topic. Your freewrite may suggest a workable thesis.
- During the writing process, consider your thesis a working thesis and be willing to modify and re-focus it as you draft and revise your paper.
- Copy your working thesis on an index card and keep it in front of you as you research and write. Having your thesis in plain view may help focus your writing.
3. Consider your audience.
Plan your paper with a specific audience in mind. Who are your readers? Are they a definable group--disinterested observers, opponents of your point of view, etc.? Perhaps you are writing to your classmates. Ask your professor or GSI who you should consider your target audience. If you are not certain of your audience, direct your argument to a general audience.
4. Present clear and convincing evidence.
Strong essays consist of reasons supported by evidence . Reasons can be thought of as the main points supporting your claim or thesis. Often they are the answers to the question, "Why do you make that claim?" An easy way to think of reasons is to see them as "because phrases." In order to validate your reasons and make your argument successful, support your reasons with ample evidence.
The St. Martin's Guide to Writing (Axelrod & Cooper, 2nd ed., New York: St. Martin's Press, 1988) lists the following forms of evidence:
- authorities
- textual evidence
For most college papers, you will include evidence you have gathered from various sources and texts. Make sure you document your evidence properly. When using evidence, make sure you (1) introduce it properly, and (2) explain its significance. Do not assume that your evidence will speak for itself--that your readers will glean from your evidence that which you want them to glean. Explain the importance of each piece of evidence-- how it elucidates or supports your point, why it is significant. Build evidence into your text, and use it strategically to prove your points.
In addition to using evidence, thoughtful writers anticipate their readers' counterarguments Counterarguments include objections, alternatives, challenges, or questions to your argument. Imagine readers responding to your argument as it unfolds. How might they react? A savvy writer will anticipate and address counterarguments. A writer can address counterarguments by acknowledging , accommodating , and/or refuting them.
5. Draft your essay.
As is the case with any piece of writing, you should take your argumentative essay through multiple drafts. When writing and revising your drafts, make sure you:
- provide ample evidence , presented logically and fairly
- deal with the opposing point of view
- pay particular attention to the organization of your essay. Make sure its structure suits your topic and audience
- address and correct any fallacies of logic
- include proper transitions to allow your reader to follow your argument
6. Edit your draft.
After you have written a developed draft, take off your writer's hat and put on your reader's hat. Evaluate your essay carefully and critically. Exchange a draft of your essay with classmates to get their feedback. Carefully revise your draft based on your assessment of it and suggestions from your peers. For self-assessment and peer response to your draft, you may want to use a peer editing sheet. A peer editing sheet will guide you and your peers by asking specific questions about your text (i.e., What is the thesis of this essay? Is it arguable? Does the writer include ample evidence? Is the structure suitable for the topic and the audience?).
You may also want to avail yourself of the Writing Drop-In Tutoring or By-Appointment Tutoring at the Student Learning Center .
Luisa Giulianetti Student Learning Center, University of California, Berkeley ©1996 UC Regents
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
3 Strong Argumentative Essay Examples, Analyzed
General Education

Need to defend your opinion on an issue? Argumentative essays are one of the most popular types of essays you’ll write in school. They combine persuasive arguments with fact-based research, and, when done well, can be powerful tools for making someone agree with your point of view. If you’re struggling to write an argumentative essay or just want to learn more about them, seeing examples can be a big help.
After giving an overview of this type of essay, we provide three argumentative essay examples. After each essay, we explain in-depth how the essay was structured, what worked, and where the essay could be improved. We end with tips for making your own argumentative essay as strong as possible.
What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is an essay that uses evidence and facts to support the claim it’s making. Its purpose is to persuade the reader to agree with the argument being made.
A good argumentative essay will use facts and evidence to support the argument, rather than just the author’s thoughts and opinions. For example, say you wanted to write an argumentative essay stating that Charleston, SC is a great destination for families. You couldn’t just say that it’s a great place because you took your family there and enjoyed it. For it to be an argumentative essay, you need to have facts and data to support your argument, such as the number of child-friendly attractions in Charleston, special deals you can get with kids, and surveys of people who visited Charleston as a family and enjoyed it. The first argument is based entirely on feelings, whereas the second is based on evidence that can be proven.
The standard five paragraph format is common, but not required, for argumentative essays. These essays typically follow one of two formats: the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model.
- The Toulmin model is the most common. It begins with an introduction, follows with a thesis/claim, and gives data and evidence to support that claim. This style of essay also includes rebuttals of counterarguments.
- The Rogerian model analyzes two sides of an argument and reaches a conclusion after weighing the strengths and weaknesses of each.
3 Good Argumentative Essay Examples + Analysis
Below are three examples of argumentative essays, written by yours truly in my school days, as well as analysis of what each did well and where it could be improved.
Argumentative Essay Example 1
Proponents of this idea state that it will save local cities and towns money because libraries are expensive to maintain. They also believe it will encourage more people to read because they won’t have to travel to a library to get a book; they can simply click on what they want to read and read it from wherever they are. They could also access more materials because libraries won’t have to buy physical copies of books; they can simply rent out as many digital copies as they need.
However, it would be a serious mistake to replace libraries with tablets. First, digital books and resources are associated with less learning and more problems than print resources. A study done on tablet vs book reading found that people read 20-30% slower on tablets, retain 20% less information, and understand 10% less of what they read compared to people who read the same information in print. Additionally, staring too long at a screen has been shown to cause numerous health problems, including blurred vision, dizziness, dry eyes, headaches, and eye strain, at much higher instances than reading print does. People who use tablets and mobile devices excessively also have a higher incidence of more serious health issues such as fibromyalgia, shoulder and back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and muscle strain. I know that whenever I read from my e-reader for too long, my eyes begin to feel tired and my neck hurts. We should not add to these problems by giving people, especially young people, more reasons to look at screens.
Second, it is incredibly narrow-minded to assume that the only service libraries offer is book lending. Libraries have a multitude of benefits, and many are only available if the library has a physical location. Some of these benefits include acting as a quiet study space, giving people a way to converse with their neighbors, holding classes on a variety of topics, providing jobs, answering patron questions, and keeping the community connected. One neighborhood found that, after a local library instituted community events such as play times for toddlers and parents, job fairs for teenagers, and meeting spaces for senior citizens, over a third of residents reported feeling more connected to their community. Similarly, a Pew survey conducted in 2015 found that nearly two-thirds of American adults feel that closing their local library would have a major impact on their community. People see libraries as a way to connect with others and get their questions answered, benefits tablets can’t offer nearly as well or as easily.
While replacing libraries with tablets may seem like a simple solution, it would encourage people to spend even more time looking at digital screens, despite the myriad issues surrounding them. It would also end access to many of the benefits of libraries that people have come to rely on. In many areas, libraries are such an important part of the community network that they could never be replaced by a simple object.
The author begins by giving an overview of the counter-argument, then the thesis appears as the first sentence in the third paragraph. The essay then spends the rest of the paper dismantling the counter argument and showing why readers should believe the other side.
What this essay does well:
- Although it’s a bit unusual to have the thesis appear fairly far into the essay, it works because, once the thesis is stated, the rest of the essay focuses on supporting it since the counter-argument has already been discussed earlier in the paper.
- This essay includes numerous facts and cites studies to support its case. By having specific data to rely on, the author’s argument is stronger and readers will be more inclined to agree with it.
- For every argument the other side makes, the author makes sure to refute it and follow up with why her opinion is the stronger one. In order to make a strong argument, it’s important to dismantle the other side, which this essay does this by making the author's view appear stronger.
- This is a shorter paper, and if it needed to be expanded to meet length requirements, it could include more examples and go more into depth with them, such as by explaining specific cases where people benefited from local libraries.
- Additionally, while the paper uses lots of data, the author also mentions their own experience with using tablets. This should be removed since argumentative essays focus on facts and data to support an argument, not the author’s own opinion or experiences. Replacing that with more data on health issues associated with screen time would strengthen the essay.
- Some of the points made aren't completely accurate , particularly the one about digital books being cheaper. It actually often costs a library more money to rent out numerous digital copies of a book compared to buying a single physical copy. Make sure in your own essay you thoroughly research each of the points and rebuttals you make, otherwise you'll look like you don't know the issue that well.

Argumentative Essay Example 2
There are multiple drugs available to treat malaria, and many of them work well and save lives, but malaria eradication programs that focus too much on them and not enough on prevention haven’t seen long-term success in Sub-Saharan Africa. A major program to combat malaria was WHO’s Global Malaria Eradication Programme. Started in 1955, it had a goal of eliminating malaria in Africa within the next ten years. Based upon previously successful programs in Brazil and the United States, the program focused mainly on vector control. This included widely distributing chloroquine and spraying large amounts of DDT. More than one billion dollars was spent trying to abolish malaria. However, the program suffered from many problems and in 1969, WHO was forced to admit that the program had not succeeded in eradicating malaria. The number of people in Sub-Saharan Africa who contracted malaria as well as the number of malaria deaths had actually increased over 10% during the time the program was active.
One of the major reasons for the failure of the project was that it set uniform strategies and policies. By failing to consider variations between governments, geography, and infrastructure, the program was not nearly as successful as it could have been. Sub-Saharan Africa has neither the money nor the infrastructure to support such an elaborate program, and it couldn’t be run the way it was meant to. Most African countries don't have the resources to send all their people to doctors and get shots, nor can they afford to clear wetlands or other malaria prone areas. The continent’s spending per person for eradicating malaria was just a quarter of what Brazil spent. Sub-Saharan Africa simply can’t rely on a plan that requires more money, infrastructure, and expertise than they have to spare.
Additionally, the widespread use of chloroquine has created drug resistant parasites which are now plaguing Sub-Saharan Africa. Because chloroquine was used widely but inconsistently, mosquitoes developed resistance, and chloroquine is now nearly completely ineffective in Sub-Saharan Africa, with over 95% of mosquitoes resistant to it. As a result, newer, more expensive drugs need to be used to prevent and treat malaria, which further drives up the cost of malaria treatment for a region that can ill afford it.
Instead of developing plans to treat malaria after the infection has incurred, programs should focus on preventing infection from occurring in the first place. Not only is this plan cheaper and more effective, reducing the number of people who contract malaria also reduces loss of work/school days which can further bring down the productivity of the region.
One of the cheapest and most effective ways of preventing malaria is to implement insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs). These nets provide a protective barrier around the person or people using them. While untreated bed nets are still helpful, those treated with insecticides are much more useful because they stop mosquitoes from biting people through the nets, and they help reduce mosquito populations in a community, thus helping people who don’t even own bed nets. Bed nets are also very effective because most mosquito bites occur while the person is sleeping, so bed nets would be able to drastically reduce the number of transmissions during the night. In fact, transmission of malaria can be reduced by as much as 90% in areas where the use of ITNs is widespread. Because money is so scarce in Sub-Saharan Africa, the low cost is a great benefit and a major reason why the program is so successful. Bed nets cost roughly 2 USD to make, last several years, and can protect two adults. Studies have shown that, for every 100-1000 more nets are being used, one less child dies of malaria. With an estimated 300 million people in Africa not being protected by mosquito nets, there’s the potential to save three million lives by spending just a few dollars per person.
Reducing the number of people who contract malaria would also reduce poverty levels in Africa significantly, thus improving other aspects of society like education levels and the economy. Vector control is more effective than treatment strategies because it means fewer people are getting sick. When fewer people get sick, the working population is stronger as a whole because people are not put out of work from malaria, nor are they caring for sick relatives. Malaria-afflicted families can typically only harvest 40% of the crops that healthy families can harvest. Additionally, a family with members who have malaria spends roughly a quarter of its income treatment, not including the loss of work they also must deal with due to the illness. It’s estimated that malaria costs Africa 12 billion USD in lost income every year. A strong working population creates a stronger economy, which Sub-Saharan Africa is in desperate need of.
This essay begins with an introduction, which ends with the thesis (that malaria eradication plans in Sub-Saharan Africa should focus on prevention rather than treatment). The first part of the essay lays out why the counter argument (treatment rather than prevention) is not as effective, and the second part of the essay focuses on why prevention of malaria is the better path to take.
- The thesis appears early, is stated clearly, and is supported throughout the rest of the essay. This makes the argument clear for readers to understand and follow throughout the essay.
- There’s lots of solid research in this essay, including specific programs that were conducted and how successful they were, as well as specific data mentioned throughout. This evidence helps strengthen the author’s argument.
- The author makes a case for using expanding bed net use over waiting until malaria occurs and beginning treatment, but not much of a plan is given for how the bed nets would be distributed or how to ensure they’re being used properly. By going more into detail of what she believes should be done, the author would be making a stronger argument.
- The introduction of the essay does a good job of laying out the seriousness of the problem, but the conclusion is short and abrupt. Expanding it into its own paragraph would give the author a final way to convince readers of her side of the argument.

Argumentative Essay Example 3
There are many ways payments could work. They could be in the form of a free-market approach, where athletes are able to earn whatever the market is willing to pay them, it could be a set amount of money per athlete, or student athletes could earn income from endorsements, autographs, and control of their likeness, similar to the way top Olympians earn money.
Proponents of the idea believe that, because college athletes are the ones who are training, participating in games, and bringing in audiences, they should receive some sort of compensation for their work. If there were no college athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t exist, college coaches wouldn’t receive there (sometimes very high) salaries, and brands like Nike couldn’t profit from college sports. In fact, the NCAA brings in roughly $1 billion in revenue a year, but college athletes don’t receive any of that money in the form of a paycheck. Additionally, people who believe college athletes should be paid state that paying college athletes will actually encourage them to remain in college longer and not turn pro as quickly, either by giving them a way to begin earning money in college or requiring them to sign a contract stating they’ll stay at the university for a certain number of years while making an agreed-upon salary.
Supporters of this idea point to Zion Williamson, the Duke basketball superstar, who, during his freshman year, sustained a serious knee injury. Many argued that, even if he enjoyed playing for Duke, it wasn’t worth risking another injury and ending his professional career before it even began for a program that wasn’t paying him. Williamson seems to have agreed with them and declared his eligibility for the NCAA draft later that year. If he was being paid, he may have stayed at Duke longer. In fact, roughly a third of student athletes surveyed stated that receiving a salary while in college would make them “strongly consider” remaining collegiate athletes longer before turning pro.
Paying athletes could also stop the recruitment scandals that have plagued the NCAA. In 2018, the NCAA stripped the University of Louisville's men's basketball team of its 2013 national championship title because it was discovered coaches were using sex workers to entice recruits to join the team. There have been dozens of other recruitment scandals where college athletes and recruits have been bribed with anything from having their grades changed, to getting free cars, to being straight out bribed. By paying college athletes and putting their salaries out in the open, the NCAA could end the illegal and underhanded ways some schools and coaches try to entice athletes to join.
People who argue against the idea of paying college athletes believe the practice could be disastrous for college sports. By paying athletes, they argue, they’d turn college sports into a bidding war, where only the richest schools could afford top athletes, and the majority of schools would be shut out from developing a talented team (though some argue this already happens because the best players often go to the most established college sports programs, who typically pay their coaches millions of dollars per year). It could also ruin the tight camaraderie of many college teams if players become jealous that certain teammates are making more money than they are.
They also argue that paying college athletes actually means only a small fraction would make significant money. Out of the 350 Division I athletic departments, fewer than a dozen earn any money. Nearly all the money the NCAA makes comes from men’s football and basketball, so paying college athletes would make a small group of men--who likely will be signed to pro teams and begin making millions immediately out of college--rich at the expense of other players.
Those against paying college athletes also believe that the athletes are receiving enough benefits already. The top athletes already receive scholarships that are worth tens of thousands per year, they receive free food/housing/textbooks, have access to top medical care if they are injured, receive top coaching, get travel perks and free gear, and can use their time in college as a way to capture the attention of professional recruiters. No other college students receive anywhere near as much from their schools.
People on this side also point out that, while the NCAA brings in a massive amount of money each year, it is still a non-profit organization. How? Because over 95% of those profits are redistributed to its members’ institutions in the form of scholarships, grants, conferences, support for Division II and Division III teams, and educational programs. Taking away a significant part of that revenue would hurt smaller programs that rely on that money to keep running.
While both sides have good points, it’s clear that the negatives of paying college athletes far outweigh the positives. College athletes spend a significant amount of time and energy playing for their school, but they are compensated for it by the scholarships and perks they receive. Adding a salary to that would result in a college athletic system where only a small handful of athletes (those likely to become millionaires in the professional leagues) are paid by a handful of schools who enter bidding wars to recruit them, while the majority of student athletics and college athletic programs suffer or even shut down for lack of money. Continuing to offer the current level of benefits to student athletes makes it possible for as many people to benefit from and enjoy college sports as possible.
This argumentative essay follows the Rogerian model. It discusses each side, first laying out multiple reasons people believe student athletes should be paid, then discussing reasons why the athletes shouldn’t be paid. It ends by stating that college athletes shouldn’t be paid by arguing that paying them would destroy college athletics programs and cause them to have many of the issues professional sports leagues have.
- Both sides of the argument are well developed, with multiple reasons why people agree with each side. It allows readers to get a full view of the argument and its nuances.
- Certain statements on both sides are directly rebuffed in order to show where the strengths and weaknesses of each side lie and give a more complete and sophisticated look at the argument.
- Using the Rogerian model can be tricky because oftentimes you don’t explicitly state your argument until the end of the paper. Here, the thesis doesn’t appear until the first sentence of the final paragraph. That doesn’t give readers a lot of time to be convinced that your argument is the right one, compared to a paper where the thesis is stated in the beginning and then supported throughout the paper. This paper could be strengthened if the final paragraph was expanded to more fully explain why the author supports the view, or if the paper had made it clearer that paying athletes was the weaker argument throughout.

3 Tips for Writing a Good Argumentative Essay
Now that you’ve seen examples of what good argumentative essay samples look like, follow these three tips when crafting your own essay.
#1: Make Your Thesis Crystal Clear
The thesis is the key to your argumentative essay; if it isn’t clear or readers can’t find it easily, your entire essay will be weak as a result. Always make sure that your thesis statement is easy to find. The typical spot for it is the final sentence of the introduction paragraph, but if it doesn’t fit in that spot for your essay, try to at least put it as the first or last sentence of a different paragraph so it stands out more.
Also make sure that your thesis makes clear what side of the argument you’re on. After you’ve written it, it’s a great idea to show your thesis to a couple different people--classmates are great for this. Just by reading your thesis they should be able to understand what point you’ll be trying to make with the rest of your essay.
#2: Show Why the Other Side Is Weak
When writing your essay, you may be tempted to ignore the other side of the argument and just focus on your side, but don’t do this. The best argumentative essays really tear apart the other side to show why readers shouldn’t believe it. Before you begin writing your essay, research what the other side believes, and what their strongest points are. Then, in your essay, be sure to mention each of these and use evidence to explain why they’re incorrect/weak arguments. That’ll make your essay much more effective than if you only focused on your side of the argument.
#3: Use Evidence to Support Your Side
Remember, an essay can’t be an argumentative essay if it doesn’t support its argument with evidence. For every point you make, make sure you have facts to back it up. Some examples are previous studies done on the topic, surveys of large groups of people, data points, etc. There should be lots of numbers in your argumentative essay that support your side of the argument. This will make your essay much stronger compared to only relying on your own opinions to support your argument.
Summary: Argumentative Essay Sample
Argumentative essays are persuasive essays that use facts and evidence to support their side of the argument. Most argumentative essays follow either the Toulmin model or the Rogerian model. By reading good argumentative essay examples, you can learn how to develop your essay and provide enough support to make readers agree with your opinion. When writing your essay, remember to always make your thesis clear, show where the other side is weak, and back up your opinion with data and evidence.
What's Next?
Do you need to write an argumentative essay as well? Check out our guide on the best argumentative essay topics for ideas!
You'll probably also need to write research papers for school. We've got you covered with 113 potential topics for research papers.
Your college admissions essay may end up being one of the most important essays you write. Follow our step-by-step guide on writing a personal statement to have an essay that'll impress colleges.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Classical Argument

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A (Very) Brief History of Rhetoric
The study of rhetoric has existed for thousands of years, predating even Socrates, Plato and the other ancient Greek philosophers that we often credit as the founders of Western philosophy. Although ancient rhetoric is most commonly associated with the ancient Greeks and Romans, early examples of rhetoric date all the way back to ancient Akkadian writings in Mesopotamia.
In ancient Greece and Rome, rhetoric was most often considered to be the art of persuasion and was primarily described as a spoken skill. In these societies, discourse occurred almost exclusively in the public sphere, so learning the art of effective, convincing speaking was essential for public orators, legal experts, politicians, philosophers, generals, and educators. To prepare for the speeches they would need to make in these roles, students engaged in written exercises called progymnasmata . Today, rhetorical scholars still use strategies from the classical era to conceptualize argument. However, whereas oral discourse was the main focus of the classical rhetoricians, modern scholars also study the peculiarities of written argument.
Aristotle provides a crucial point of reference for ancient and modern scholars alike. Over 2000 years ago, Aristotle literally wrote the book on rhetoric. His text Rhētorikḗ ( On Rhetoric ) explores the techniques and purposes of persuasion in ancient Greece, laying the foundation for the study and implementation of rhetoric in future generations. Though the ways we communicate and conceptualize rhetoric have changed, many of the principles in this book are still used today. And this is for good reason: Aristotle’s strategies can provide a great guide for organizing your thoughts as well as writing effective arguments, essays, and speeches.
Below, you will find a brief guide to some of the most fundamental concepts in classical rhetoric, most of which originate in On Rhetoric.
The Rhetorical Appeals
To understand how argument works in On Rhetoric , you must first understand the major appeals associated with rhetoric. Aristotle identifies four major rhetorical appeals: ethos (credibility), logos (logic), pathos (emotion), and Kairos(time).
- Ethos – persuasion through the author's character or credibility. This is the way a speaker (or writer) presents herself to the audience. You can build credibility by citing professional sources, using content-specific language, and by showing evidence of your ethical, knowledgeable background.
- Logos – persuasion through logic. This is the way a speaker appeals to the audience through practicality and hard evidence. You can develop logos by presenting data, statistics, or facts by crafting a clear claim with a logically-sequenced argument. ( See enthymeme and syllogism )
- Pathos – persuasion through emotion or disposition . This is the way a speaker appeals to the audience through emotion, pity, passions, or dispositions. The idea is usually to evoke and strengthen feelings already present within the audience. This can be achieved through story-telling, vivid imagery, and an impassioned voice. Academic arguments in particular benefit from understanding pathos as appealing to an audience's academic disposition on a given topic, subject, or argument.
- Kairos – an appeal made through the adept use of time. This is the way a speaker appeals to the audience through notions of time. It is also considered to be the appropriate or opportune time for a speaker to insert herself into a conversation or discourse, using the three appeals listed above. A Kairotic appeal can be made through calls to immediate action, presenting an opportunity as temporary, and by describing a specific moment as propitious or ideal.
*Note: When using these terms in a Rhetorical Analysis, make sure your syntax is correct. One does not appeal to ethos, logos, or pathos directly. Rather, one appeals to an audience's emotion/disposition, reason/logic, or sense of the author's character/credibility within the text. Ethos, pathos, and logos are themselves the appeals an author uses to persuade an audience.
An easy way to conceptualize the rhetorical appeals is through advertisements, particularly infomercials or commercials. We are constantly being exposed to the types of rhetoric above, whether it be while watching television or movies, browsing the internet, or watching videos on YouTube.
Imagine a commercial for a new car. The commercial opens with images of a family driving a brand-new car through rugged, forested terrain, over large rocks, past waterfalls, and finally to a serene camping spot near a tranquil lake surrounded by giant redwood trees. The scene cuts to shots of the interior of the car, showing off its technological capacities and its impressive spaciousness. A voiceover announces that not only has this car won numerous awards over its competitors but that it is also priced considerably lower than comparable models, while getting better gas mileage. “But don’t wait,” the voiceover says excitedly, “current lessees pay 0% APR financing for 12 months.”
In just a few moments, this commercial has shown masterful use of all four appeals. The commercial utilizes pathos by appealing to our romantic notions of family, escape, and the great outdoors. The commercial develops ethos by listing its awards, and it appeals to our logical tendencies by pointing out we will save money immediately because the car is priced lower than its competitors, as well as in the long run because of its higher MPG rate. Finally, the commercial provides an opportune and propitious moment for its targeted audience to purchase a car immediately.
Depending on the nature of the text, argument, or conversation, one appeal will likely become most dominant, but rhetoric is generally most effective when the speaker or writer draws on multiple appeals to work in conjunction with one another. To learn more about Aristotle's rhetorical appeals, click here.
Components and Structure
The classical argument is made up of five components, which are most commonly composed in the following order:
- Exordium – The introduction, opening, or hook.
- Narratio – The context or background of the topic.
- Proposito and Partitio – The claim/stance and the argument.
- Confirmatio and/or Refutatio – positive proofs and negative proofs of support.
- Peroratio – The conclusion and call to action.
Think of the exordium as your introduction or “hook.” In your exordium, you have an opportunity to gain the interest of your reader, but you also have the responsibility of situating the argument and setting the tone of your writing. That is, you should find a way to appeal to the audience’s interest while also introducing the topic and its importance in a professional and considerate manner. Something to include in this section is the significance of discussing the topic in this given moment (Kairos). This provides the issue a sense of urgency that can validate your argument.
This is also a good opportunity to consider who your intended audience is and to address their concerns within the context of the argument. For example, if you were writing an argument on the importance of technology in the English classroom and your intended audience was the board of a local high school, you might consider the following:
- New learning possibilities for students (General Audience Concerns)
- The necessity of modern technology in finding new, up-to-date information (Hook/Kairos)
- Detailed narrative of how technology in one school vastly improved student literacy (Hook/Pathos)
- Statistics showing a link between exposure to technology and rising trends in literacy (Hook/Logos)
- Quotes from education and technology professors expressing an urgency for technology in English classrooms (Hook/Ethos)
Of course, you probably should not include all of these types of appeals in the opening section of your argument—if you do, you may end up with a boring, overlong introduction that doesn’t function well as a hook. Instead, consider using some of these points as evidence later on. Ask yourself: What will be most important to my audience? What information will most likely result in the action I want to bring about? Think about which appeal will work best to gain the attention of your intended audience and start there.
The narratio provides relevant foundational information and describes the social context in which your topic exists. This might include information on the historical background, including recent changes or updates to the topic, social perception, important events, and other academic research. This helps to establish the rhetorical situation for the argument: that is, the situation the argument is currently in, as impacted by events, people, opinion, and urgency of some kind. For your argument on technology in the English classroom, you might include:
- Advances in education-related technology over the centuries
- Recent trends in education technology
- A description of the importance of digital literacy
- Statistics documenting the lack of home technology for many students
- A selection of expert opinions on the usefulness of technology in all classrooms
Providing this type of information creates the setting for your argument. In other words, it provides the place and purpose for the argument to take place. By situating your argument within in a viable context, you create an opportunity to assert yourself into the discussion, as well as to give your reader a genuine understanding of your topic’s importance.
Propositio and Partitio
These two concepts function together to help set up your argument. You can think of them functioning together to form a single thesis. The propositio informs your audience of your stance, and the partitio lays out your argument. In other words, the propositio tells your audience what you think about a topic, and the partitio briefly explains why you think that way and how you will prove your point.
Because this section helps to set up the rest of your argument, you should place it near the beginning of your paper. Keep in mind, however, that you should not give away all of your information or evidence in your partitio. This section should be fairly short: perhaps 3-4 sentences at most for most academic essays. You can think of this section of your argument like the trailer for a new film: it should be concise, should entice the audience, and should give them a good example of what they are going to experience, but it shouldn’t include every detail. Just as a filmgoer must see an entire film to gain an understanding of its significance or quality, so too must your audience read the rest of your argument to truly understand its depth and scope.
In the case of your argument on implementing technology in the English classroom, it’s important to think not only of your own motivations for pursuing this technology in the classroom, but also of what will motivate or persuade your respective audience(s). Some writing contexts call for an audience of one. Some require consideration of multiple audiences, in which case you must find ways to craft an argument which appeals to each member of your audience. For example, if your audience included a school board as well as parents andteachers, your propositio might look something like this:
“The introduction of newer digital technology in the English classroom would be beneficial for all parties involved. Students are already engaged in all kinds of technological spaces, and it is important to implement teaching practices that invest students’ interests and prior knowledge. Not only would the marriage of English studies and technology extend pedagogical opportunities, it would also create an ease of instruction for teachers, engage students in creative learning environments, and familiarize students with the creation and sharing technologies that they will be expected to use at their future colleges and careers. Plus, recent studies suggest a correlation between exposure to technology and higher literacy rates, a trend many education professionals say isn’t going to change.”
Note how the above paragraph considers the concerns and motivations of all three audience members, takes a stance, and provides support for the stance in a way that allows for the rest of the argument to grow from its ideas. Keep in mind that whatever you promise in your propositio and partitio (in this case the new teaching practices, literacy statistics, and professional opinion) must appear in the body of your argument. Don’t make any claims here that you cannot prove later in your argument.
Confirmatio and Refutatio
These two represent different types of proofs that you will need to consider when crafting your argument. The confirmatio and refutatio work in opposite ways, but are both very effective in strengthening your claims. Luckily, both words are cognates—words that sound/look in similar in multiple languages—and are therefore are easy to keep straight. Confirmatio is a way to confirm your claims and is considered a positive proof; refutatio is a way to acknowledge and refute a counterclaim and is considered a negative proof.
The confirmatio is your argument’s support: the evidence that helps to support your claims. For your argument on technology in the English classroom, you might include the following:
- Students grades drastically increase when technology is inserted into academics
- Teachers widely agree that students are more engaged in classroom activities that involve technology
- Students who accepted to elite colleges generally possess strong technological skills
The refutatio provides negative proofs. This is an opportunity for you to acknowledge that other opinions exist and have merit, while also showing why those claims do not warrant rejecting your argument.
If you feel strange including information that seems to undermine or weaken your own claims, ask yourself this: have you ever been in a debate with someone who entirely disregarded every point you tried to make without considering the credibility of what you said? Did this make their argument less convincing? That’s what your paper can look like if you don’t acknowledge that other opinions indeed exist and warrant attention.
After acknowledging an opposing viewpoint, you have two options. You can either concede the point (that is, admit that the point is valid and you can find no fault with their reasoning), or you can refute their claim by pointing out the flaws in your opponent’s argument. For example, if your opponent were to argue that technology is likely to distract students more than help them (an argument you’d be sure to include in your argument so as not to seem ignorant of opposing views) you’d have two options:
- Concession: You might concede this point by saying “Despite all of the potential for positive learning provided by technology, proponents of more traditional classroom materials point out the distractive possibilities that such technology would introduce into the classroom. They argue that distractions such as computer games, social media, and music-streaming services would only get in the way of learning.”
In your concession of the argument, you acknowledge the merit of the opposing argument, but you should still try to flip the evidence in a positive way. Note how before conceding we include “despite all of the potential for positive learning.” This reminds your reader that, although you are conceding a single point, there are still many reasons to side with you.
- Refutation: To refute this same point you might say something like, “While proponents of more traditional English classrooms express concerns about student distraction, it’s important to realize that in modern times, students are already distracted by the technology they carry around in their pockets. By redirecting student attention to the technology administered by the school, this distraction is shifted to class content. Plus, with website and app blocking resources available to schools, it is simple for an institution to simply decide which websites and apps to ban and block, thereby ensuring students are on task.”
Note how we acknowledged the opposing argument, but immediately pointed out its flaws using straightforward logic and a counterexample. In so doing, we effectively strengthen our argument and move forward with our proposal.
Your peroratio is your conclusion. This is your final opportunity to make an impact in your essay and leave an impression on your audience. In this section, you are expected to summarize and re-evaluate everything you have proven throughout your argument. However, there are multiple ways of doing this. Depending on the topic of your essay, you might employ one or more of the following in your closing:
- Call to action (encourage your audience to do something that will change the situation or topic you have been discussing).
- Discuss the implications for the future. What might happen if things continue the way they are going? Is this good or bad? Try to be impactful without being overly dramatic.
- Discuss other related topics that warrant further research and discussion.
- Make a historical parallel regarding a similar issue that can help to strengthen your argument.
- Urge a continued conversation of the topic for the future.
Remember that your peroratio is the last impression your audience will have of your argument. Be sure to consider carefully which rhetorical appeals to employ to gain a desirable effect. Make sure also to summarize your findings, including the most effective and emphatic pieces of evidence from your argument, reassert your major claim, and end on a compelling, memorable note. Good luck and happy arguing!

- Advanced Search
Scribble-based complementary graph reasoning network for weakly supervised salient object detection
New citation alert added.
This alert has been successfully added and will be sent to:
You will be notified whenever a record that you have chosen has been cited.
To manage your alert preferences, click on the button below.
New Citation Alert!
Please log in to your account
Information & Contributors
Bibliometrics & citations, view options, recommendations, complementary characteristics fusion network for weakly supervised salient object detection.
Salient object detection (SOD) is a challenging and fundamental research in computer vision and image processing. Since the cost of pixel-level annotations is high, scribble annotations are usually used as weak supervisions. However, ...
- We propose an edge fusion module using the local and high-level semantic information.
Weakly-supervised Salient Object Detection with Label Decoupling Siamese Network
Weakly-supervised salient object detection (SOD) does not require a lot of manually annotated pixel-level labels. To further improve the detection accuracy of weakly-supervised SOD, we introduce a label decoupling siamese network (LDSN), which ...
Local saliency consistency‐based label inference for weakly supervised salient object detection using scribble annotations
Recently, weak supervision has received growing attention in the field of salient object detection due to the convenience of labelling. However, there is a large performance gap between weakly supervised and fully supervised salient object ...
Information
Published in.
Elsevier Science Inc.
United States
Publication History
Author tags.
- Salient object detection
- Weakly supervision
- Graph learning
- Cross fusion
- Research-article
Contributors
Other metrics, bibliometrics, article metrics.
- 0 Total Citations
- 0 Total Downloads
- Downloads (Last 12 months) 0
- Downloads (Last 6 weeks) 0
View options
Login options.
Check if you have access through your login credentials or your institution to get full access on this article.
Full Access
Share this publication link.
Copying failed.
Share on social media
Affiliations, export citations.
- Please download or close your previous search result export first before starting a new bulk export. Preview is not available. By clicking download, a status dialog will open to start the export process. The process may take a few minutes but once it finishes a file will be downloadable from your browser. You may continue to browse the DL while the export process is in progress. Download
- Download citation
- Copy citation
We are preparing your search results for download ...
We will inform you here when the file is ready.
Your file of search results citations is now ready.
Your search export query has expired. Please try again.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The basic format for the Toulmin Method is as follows: Claim: In this section, you explain your overall thesis on the subject. In other words, you make your main argument. Data (Grounds): You should use evidence to support the claim. In other words, provide the reader with facts that prove your argument is strong.
Sound logic. Ensuring that your arguments are underpinned by firm logic is… logical. You want to convince your audience, so you need to make sense when building and stating your argument. When making your argument, select your line of reasoning: deductive or inductive.
• Overview of methodology: This section out-lines the methodological type or approach, the research setting, the sample, instrumen-tation (if relevant), and methods of data collection and analysis used. • Rationale and significance: Rationale is the justification for the study presented as a logical argument. Significance addresses the
An important aspect running through your dissertation will be your argument for: why this specific topic is worth researching; why this is a good way to research it; why this method of analysis is appropriate; and; why your interpretations and conclusions are reasonable. You will refer to the work of others as you make your argument.
Dissertation argument: Deductive vs. inductive reasoning. ... explain the evaluative methods to be used, taking into account issues such as validity, reliability, quality of evidence; evaluate the study providing support for any criticisms of the study's research design, conclusions and implications ...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
When you develop your argument, you are confirming your own position, and building your case for the readers. Use empirical evidence—facts and statistics—to support your claims. Appeal to your audience's rational and logical thinking. Argue your case from the authority of your evidence and research. Your list of strengths and weaknesses ...
Regardless of the amount or type of research involved, argumentative essays must establish a clear thesis and follow sound reasoning. The structure of the argumentative essay is held together by the following. A clear, concise, and defined thesis statement that occurs in the first paragraph of the essay. ... A common method for writing an ...
American methods of academic argument are best depicted as a straight line. No matter what-be it evidence, sub-points, refutations of other positions, or personal anecdotes-everything used must lead clearly back to the position being argued. ... Example of the Toulmin Method. Thesis, Claim or Position. Grading should be optional in non-major ...
Identifying an argument. Ultimately, you are aiming to produce a series of propositions in relation to your material: usually a main proposition (thesis or argument) with some sub-propositions. Asking yourself the following questions may help you think critically about your material and identify some potential arguments:
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
The structure of an argument Claim. At the heart of all arguments is a claim - the main premise that you are interested in proving. Establishing your claim is one of the most important parts of any piece of academic work; an essay, a presentation, a dissertation, research paper or thesis.
Writing an Argument Thesis in a Scholarly Context. Big Picture Scholars advance knowledge by making arguments about sources, issues, and topics. ... Leidner notes that carefully chosen methods allowed managers to extract the names of uncooperative crew people from their fellow workers (Leidner 80). Cooperation between workers was encouraged ...
When you're writing a persuasive essay, you need more than just an opinion to make your voice heard. Even the strongest stance won't be compelling if it's not structured properly and reinforced with solid reasoning and evidence. Learn what elements every argumentative essay should include and how to structure it depending on your audience ...
Check my paper. Using paper checkers responsibly. You may also use the following Purdue OWL resources to help you with your argument paper: Creating a Thesis Statement. Organizing Your Argument. Organizing Your Argument Slide Presentation. Logic in Argumentative Writing. Paragraphs and Paragraphing. Transitions and Transitional Devices.
In our PhD Writing Template, they are the 'Aims & Objectives' in the top left. Next, you have chapter arguments. This is the argument that runs through each chapter. Then, you have standalone arguments. These are the 'mini' arguments that are used to justify your chapter argument and, ultimately, your thesis argument.
The methodology chapter is a crucial part of your dissertation or thesis - it's where you provide context and justification for your study's design. This in turn demonstrates your understanding of research theory, which is what earns you marks.. Over the years, we've helped thousands of students navigate this tricky section of the research process.
Two Final Tips: When you're writing your justification, write for your audience. Your purpose here is to provide more than a technical list of details and procedures. This section should focus more on the why and less on the how. Consider your methodology as you're conducting your research.
some thesis or argument, often a thesis or argument that has been presented by another philosopher (a thesis is argument, you may be asked to do one or more of the following: explain it, offer an argument in support of it, offer an objection to it, defend against an objection to it, evaluate the arguments for and against it, discuss
Common thesis pitfalls: A thesis expressed as a fragment. A thesis which is too broad. A thesis worded as a question. (Usually the answer to the question yields the thesis) A thesis which includes extraneous information. A thesis which begins with I think or in my opinion. A thesis which deals with a stale or trite issue.
Here, the thesis doesn't appear until the first sentence of the final paragraph. That doesn't give readers a lot of time to be convinced that your argument is the right one, compared to a paper where the thesis is stated in the beginning and then supported throughout the paper. This paper could be strengthened if the final paragraph was ...
The classical argument is made up of five components, which are most commonly composed in the following order: Exordium - The introduction, opening, or hook. Narratio - The context or background of the topic. Proposito and Partitio - The claim/stance and the argument. Confirmatio and/or Refutatio - positive proofs and negative proofs of ...
Methods of Argumentation Argumentation, which can be abstractly defi ned as the interaction of different arguments for and against some conclusion, is an important skill to learn for everyday life, law, science, politics and business. The best way to learn it is to try it out on real instances of arguments found in everyday conversational exchanges
AbstractCurrent salient object detection (SOD) methods rely heavily on accurate pixel-level annotations. To reduce the annotation workload, some scribble-based methods have emerged. ... Highlights •A novel complementary graph reasoning network (CGRNet) and cross graph interaction structure (GCU) is proposed, which can capture long-distance ...