ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Role of social media marketing activities in influencing customer intentions: a perspective of a new emerging era.

- 1 School of Economics and Management, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China
- 2 Department of Management Sciences and Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 3 Faisalabad Business School, National Textile University, Faisalabad, Pakistan
The aim of this study is to explore social media marketing activities (SMMAs) and their impact on consumer intentions (continuance, participate, and purchase). This study also analyzes the mediating roles of social identification and satisfaction. The participants in this study were experienced users of two social media platforms Facebook and Instagram in Pakistan. A self-administered questionnaire was used to collect data from respondents. We used an online community to invite Facebook and Instagram users to complete the questionnaire in the designated online questionnaire system. Data were collected from 353 respondents, and structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to analyze the data. Results show that SMMAs have a significant impact on the intentions of users. Furthermore, social identification mediates the relationship between social media activities and satisfaction, and satisfaction mediates the relationship between social media activities and the intentions of users. This will help marketers how to attract customers to develop their intentions. This is the first novel study that used SMMAs to address the user intentions with the role of social identification and satisfaction in the context of Pakistan.

Introduction
There has been tremendous growth in the use of social media platforms such as WhatsApp, Instagram, and Facebook over the past decade ( Chen and Qasim, 2021 ). People are using these platforms to communicate with one another, and popular brands use them to market their products. Social activities have been brought from the real world to the virtual world courtesy of social networking sites. Messages are sent in real time which now enable people to interact and share information. As a result, companies consider social media platforms as vital tools for succeeding in the online marketplace ( Ebrahim, 2020 ). The use of social media to commercially promote processes or events to attract potential consumers online is referred to as social media marketing (SMM). With the immense rise in community websites, a lot of organizations have started to find the best ways to utilize these sites in creating strong relationships and communications with users to enable friendly and close relationships to create online brand communities ( Ibrahim and Aljarah, 2018 ).
Social media marketing efficiently fosters communications between customers and marketers, besides enabling activities that enhance brand awareness ( Hafez, 2021 ). For that reason, SMM remains to be considered as a new marketing strategy, but how it impacts intentions is limited. But, to date, a lot of research on SMM is focused on consumer’s behavior, creative strategies, content analysis and the benefits of user-generated content, and their relevance to creating virtual brand communities ( Ibrahim, 2021 ).
New channels of communication have been created, and there have been tremendous changes in how people interact because of the internet developing various applications and tools over time ( Tarsakoo and Charoensukmongkol, 2020 ). Companies now appreciate that sharing brand information and consumer’s experience is a new avenue for brand marketing due to the widespread use of smartphones and the internet, with most people now relying on social media brands. Therefore, developing online communities has become very efficient. Social groups create a sense of continuity for their members without meeting physically ( Yadav and Rahman, 2017 ). A community that acquires products from a certain brand is referred to as a virtual brand community. Customers are not just interested in buying goods and services but also in creating worthwhile experiences and strong relationships with other customers and professionals. So, when customers are part of online communities, there is a cohesion that grows among the customers, which impacts the market. Therefore, it is up to the companies to identify methods or factors that will encourage customers to take part in these communities ( Ismail et al., 2018 ).
The online community’s nature is like that of actual communities when it comes to creating shared experiences, enabling social support, and attending to the members’ need to identify themselves, regardless of the similarities and variances existing between real-world communities and online communities ( Seo and Park, 2018 ). Regarding manifestations and technology, online communities are distinct from real-life communities since the former primarily use computers to facilitate their operation. A certain brand product or service is used to set up a brand community. Brand communities refer to certain communities founded based on interactions that are not limited by geographical restrictions between brand consumers ( Chen and Lin, 2019 ). Since consumers’ social relationships create brand communities, these communities have customs, traditions, rituals, and community awareness. The group members learn from each other and share knowledge about a product, hence appreciating each other’s actions and ideas. So, once a consumer joins a particular brand community, automatically, the brand becomes a conduit and common language linking the community members together because of sharing brand experiences ( Arora and Sanni, 2019 ).
Based on the perspective of brand owners, most research has focused on how social communities can benefit brands. However, there are also some discussions regarding the benefits that come from brand community members according to the members themselves to analyze how social community impacts its members ( Shareef et al., 2019 ). Consumer’s behavior is influenced by value so, when a consumer is constantly receiving value, it leads to consumer’s loyalty toward that brand. According to Alalwan et al. (2017) , a valuable service provider will create loyalty to a company and enhance brand awareness. Consumer value is essentially used in evaluating social networking sites. With better and easier options to create websites coming around, most consumers are attracted to a social community to know about a company and its goods. Furthermore, operators can learn consumer’s behavior through maintaining social interactions with customers. However, the social community should have great value. It should be beneficial to the potential customers by providing them with information relevant to the brand in question. Furthermore, customers should be able to interact with one another, thus creating a sense of belonging. From that, it is evident that a brand social community’s satisfaction affects community retention and selection.
Literature Review
Social media marketing activities.
Most businesses use online marketing strategies such as blogger endorsements, advertising on social media sites, and managing content generated by users to build brand awareness among consumers ( Wang and Kim, 2017 ). Social media is made up of internet-associated applications anchored on technological and ideological Web 2.0 principles, which enables the production and sharing of the content generated by users. Due to its interactive characteristics that enable knowledge sharing, collaborative, and participatory activities available to a larger community than in media formats such as radio, TV, and print, social media is considered the most vital communication channel for spreading brand information. Social media comprises blogs, internet forums, consumer’s review sites, social networking websites (Twitter, Blogger, LinkedIn, and Facebook), and Wikis ( Arrigo, 2018 ).
Social media facilitates content sharing, collaborations, and interactions. These social media platforms and applications exist in various forms such as social bookmarking, rating, video, pictures, podcasts, wikis, microblogging, social blogs, and weblogs. Social networkers, governmental organizations, and business firms are using social media to communicate, with its use increasing tremendously ( Cheung et al., 2021 ). Governmental organizations and business firms use social media for marketing and advertising. Integrated marketing activities can be performed with less cost and effort due to the seamless interactions and communication among consumer partners, events, media, digital services, and retailers via social media ( Tafesse and Wien, 2018 ).
According to Liu et al. (2021) , marketing campaigns for luxury brands consist of main factors such as customization, reputation, trendiness, interaction, and entertainment which significantly impact customers’ purchase intentions and brand equity. Activities that involve community marketing accrue from interactions between events and the mental states of individuals, whereas products are external factors for users ( Parsons and Lepkowska-White, 2018 ). But even though regardless of people experience similar service activities, there is a likelihood of having different ideas and feelings about an event; hence, outcomes for users and consumers are distinct. In future marketing, competition will focus more on brand marketing activities; hence, the marketing activities ought to offer sensory stimulation and themes that give customers a great experience. Now brands must provide quality features but also focus on enabling an impressive customer’s experience ( Beig and Khan, 2018 ).
Social Identification
A lot of studies about brand communities involve social identification, appreciating the fact that a member of a grand community is part and parcel of that community. Social identity demystifies how a person enhances self-affirmation and self-esteem using comparison, identity, and categorization ( Chen and Lin, 2019 ). There is no clear definition of the brand community or the brand owner, strengthening interactions between the community and its members or creating a rapport between the brand and community members. As a result, members of a community are separated into groups based on their educational attainment, occupation, and living environment. Members of social networks categorize each other into various groups or similar groups according to their classification in social networks ( Salem and Salem, 2021 ).
Brand identification and identification of brand communities emanate from a similar process. Users can interact freely, hence creating similar ideologies about the community, alongside strengthening bonds among members, hence enabling them to identify with that community. The brand community identity can also be considered as a convergence of values between the principles of the social community and the values of the users ( Wibowo et al., 2021 ).
According to Lee et al. (2021) , members of a brand social community share their ideas by taking part in community activities to help create solutions. When customers join a brand community, they happily take part in activities or discussions and are ready to help each other. So, it is evident that social community participation is impacting community identity positively. Community involvement entails a person sharing professional understanding or knowledge with other members to enhance personal growth and create a sense of belonging ( Gupta and Syed, 2021 ). According to Haobin Ye et al. (2021) , it is high time community identity be incorporated in virtual communities since it is a crucial factor that affects the operations of virtual communities. Also, community identity assists in facilitating positive interactions among members of the community, encouraging them to actively take part in community activities ( Assimakopoulos et al., 2017 ). This literature review suggests that social communities need members to work together. Individuals who can identify organizational visions and goals become dedicated to that virtual company.
Satisfaction
Customer’s satisfaction involves comparing expected and after-service satisfaction with the standards emanating from accumulated previous experiences. According to implementation confirmation theory, satisfaction is a consumer’s expected satisfaction with how the services have lived up to those expectations. Customers usually determine the level of satisfaction by comparing the satisfaction previously experienced and the current one ( Pang, 2021 ).
According to recent studies, community satisfaction impacts consumer’s loyalty and community participation. A study community’s level of satisfaction is determined by how its members rate it ( Jarman et al., 2021 ). Based on previous interactions, the community may be evaluated. When the members are satisfied with their communities, it is manifested through joyful emotions, which affect the behavior of community members. In short, satisfaction creates active participation and community loyalty ( Shujaat et al., 2021 ).
Types of Intentions
A lot of studies about information and marketing systems have used continuance intention in measuring if a customer continues to use a certain product or service. The willingness of customers to continue using a good or service determines if service providers will be successful or not. According to Zollo et al. (2020) , an efficient information marketing system should persuade users to use it, besides retaining previous users to guarantee continued use.
Operators of social networks must identify the reason propelling continued use of social network sites, alongside attracting more users. Nevertheless, previous studies on information systems in the last two decades have mainly concentrated on behavior–cognition approaches, for instance, the technology acceptance model (TAM), theory of planned behavior (TPB), and theory of reasoned action (TRA) with their variants ( Tarsakoo and Charoensukmongkol, 2020 ; Jamil et al., 2021b ). According to Ismail et al. (2018) , perceived use and satisfaction positively impact a user’s continuance intention. The continued community members’ participation has two intentions. Continuance intention is the first one. It defines the community member’s intent to keep on using the community ( Beig and Khan, 2018 ; Dunnan et al., 2020 ). Then, recommendation intention, also known as mouth marketing, describes every informal communication that takes place among community members regarding the virtual brand community. Previous studies about members of a virtual community mostly entailed the continuous utilization of information systems ( Seo and Park, 2018 ; Sarfraz et al., 2021 ). Unlike previous studies, this study focuses on factors that support the continued participation of community members. So, besides determining how usage purpose affects continuance intention, the study also investigated the factors that influence users’ willingness to take part in community activities ( Gul et al., 2021 ).
Nevertheless, it is hard to determine and monitor whether a certain action occurred (recommendation or purchase) during empirical investigations. Consumers will seek relevant information associated with their external environment and experiences when purchasing goods ( Shareef et al., 2019 ). Once they have collected significant information, they will evaluate it, and draw comparisons from which customer’s behavior is determined. Since purchase intention refers to a customer’s affinity toward a particular product, it is a metric of a customer’s behavioral intention. According to Liu et al. (2021) , the probability of a customer buying a particular product is known as an intention to buy. So, when the probability is high, it simply means that the willingness to purchase is high. Past studies consider purchase intention as a factor that can predict consumer’s behavior alongside the subjective possibility of consumer’s purchases. According to Chen and Qasim (2021) , from a marketing viewpoint, if a company wants to retain its community besides achieving community targets while establishing successful marketing via the community, at least three objectives are needed. They include membership continuance intention, which entails members living up to their promises in the community and also the willingness to belong to the community ( Yadav and Rahman, 2018 ; Naseem et al., 2020 ). On the other side, community recommendation intention entails the willingness of members to recommend or refer community members to other people who are not members ( Jamil et al., 2021a ; Mohsin et al., 2021 ). The next consideration is the community participation intention of a member, which involves their willingness to participate in the activities of the brand community. Unlike past literature about using information systems, this study demystified how SMMAs influence purchase intention and participation intention ( Alalwan et al., 2017 ).
Development of Hypotheses
People with similar interests can get a virtual platform to discuss and share ideas courtesy of social media. Sustained communication of social media allows users to create a community. Long-lasting sharing of growth and information fosters the development of strong social relationships. The information posted on social media platforms by an individual positively correlates with the followers the user has. Regarding the discussion above, we proposed the following hypothesis:
H1: Social media marketing activities (SMMAs) have a significant impact on social identification.
The study of Farivar and Richardson (2021) on users’ continuance intention confirmed that it is influenced by satisfaction after service. Social media studies are also of the thought that satisfaction significantly affects continuance intention. So, a consumer will measure the satisfaction of service after using it. Mahendra (2021) claims that satisfaction influences repurchase behavior. Repurchase intention emanates from a customer’s satisfaction with a good or service. People who have similar interests may interact and cooperate in a virtual world via social media platforms. A community on social media may be formed by regularly connecting with people and exchanging information with them. Members benefit from long-term information and growth exchanges that enable them to create strong social relationships. A lot of studies have pointed out that repurchase intention and customer’s satisfaction are positively and highly related. Besides, marketing studies noted that satisfactory experience after using a product would impact the intention of future repurchase. Hence, we proposed the following hypothesis:
H2: SMMAs have a significant impact on satisfaction.
The study by Suman et al. (2021) on American consumer’s behavior suggested that members taking part in community activities (meetups, discussion, and browsing) influence their brand-associated behavior. According to Di Minin et al. (2021) , the brand identity of a consumer has a positive impact on satisfaction. Consumers capitalize on online communities to share their experiences and thoughts about a grand regularly and easily ( Sirola et al., 2021 ). These experiences make up the customer to brand experiences and establish a sense of belonging, trust, and group identity. In a nutshell, this study suggests that identity will enable members to recognize their community, hence confirming that members have similar experiences and feelings with a particular brand and feel united in the group ( Shujaat et al., 2021 ). Strong group identity means that members are integrated closely into the brand communities and highly regard the community. Hence, we proposed the following hypothesis:
H3: Social identification has a significant impact on satisfaction.
Brand communities are beneficial in the sense that they enable sharing of marketing information, managing a community, and exploring demands ( Dutot, 2020 ). These activities are likely to enhance consumer’s rights and increase customer’s satisfaction ( Sahibzada et al., 2020 ). A customer who makes an online transaction will be highly satisfied with a website that provides a great experience ( Koçak et al., 2021 ). Enhancing customer’s satisfaction, encouraging customer intentions, creating community loyalty, and fostering communication and interactions between community users are crucial to lasting community platform management ( Pang, 2021 ). Hence, we proposed the following hypotheses:
H4: Satisfaction has a significant impact on continuance intention.
H5: Satisfaction has a significant impact on participate intention.
H6: Satisfaction has a significant impact on purchase intention.
Thaler (1985) proposed transaction utility theory, in which consumers’ willingness to spend money is influenced by their perceptions of value. Researchers such as Dodds (1991) claimed that buyers only become ready to purchase after they have established a sense of value for a product. According to Petrick et al. (2001) , a product’s quality is dependent on the customer’s satisfaction. Several studies have shown that enjoyment, perceived value, and behavioral intention are all linked together. Hence, we proposed the following hypothesis:
H7: Social identification mediates the relationship between SMMA and satisfaction.
When it comes to information systems, Bhattacherjee et al. (2008) discovered that people’s continual intention is derived from their satisfaction with the system after they have used it. Studies on employee’s satisfaction in the workplace have shown that it has a substantial influence on CI. The amount of satisfaction that users have with the system that they have previously used is the most important factor in determining their CI, according to research on information system utilization intention.
In other words, the customer’s contentment with the product leads to the establishment of a desire to buy the thing again, as mentioned by Assimakopoulos et al. (2017) . Numerous studies show a strong link between customer’s satisfaction and their propensity to return for another transaction. According to a lot of marketing studies, customers who have a pleasant experience with a product are more likely to repurchase it. Hence, we proposed the following hypotheses:
H8: Satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and continuance intention.
H9: Satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and participate intention.
H10: Satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and purchase intention.
Figure 1 shows the research framework of this study.
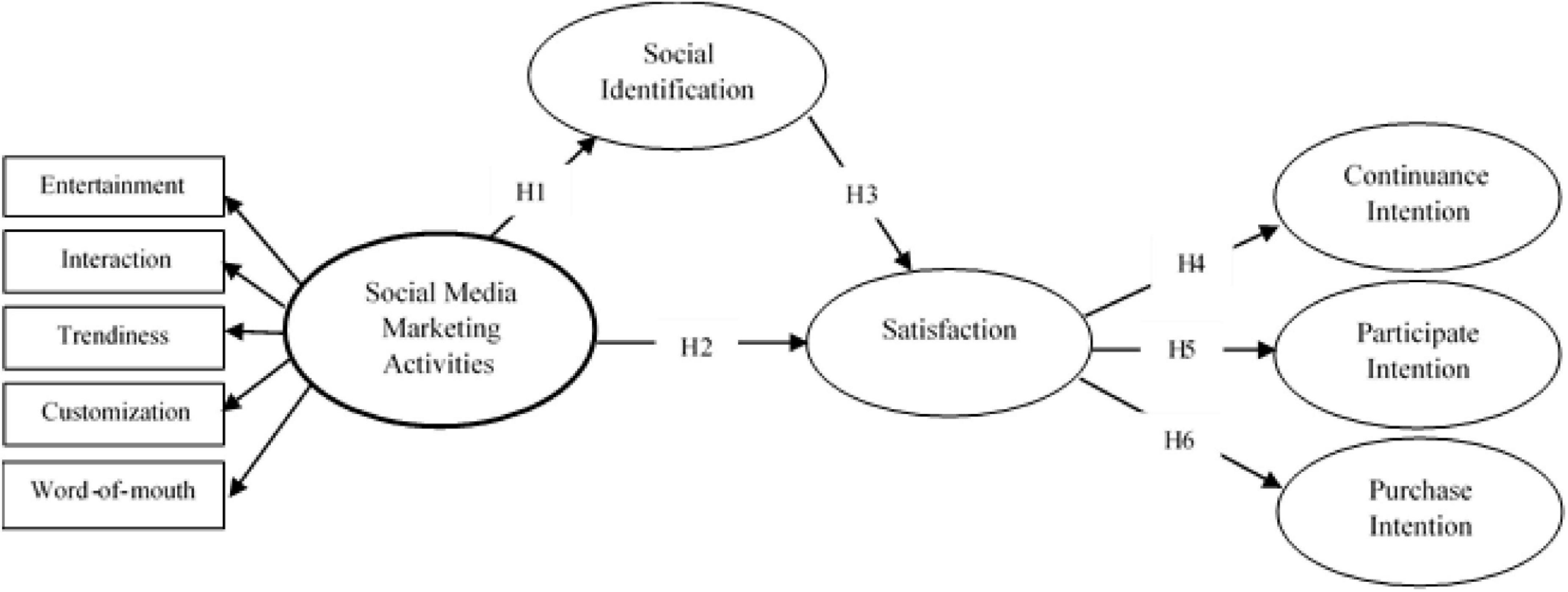
Figure 1. Conceptual framework.
Conceptual Framework
Research methodology.
This study designed a questionnaire according to the hypotheses stated above. The participants in this study were experienced users of two social media platforms Facebook and Instagram in Pakistan. A self-administered questionnaire was used to collect data from respondents. A pilot study with 40 participants was carried out. Since providing recommendations, revisions were made to the final questionnaire to make it more understandable for the study’s respondents. To ensure the content validity of the measures, three academic experts of marketing analyzed and make improvements in the items of constructs. The experts searched for spelling errors and grammatical errors and ensured that the items were correct. The experts have proposed minor text revisions to social identification and satisfaction items and advised that the original number of items is to be maintained. This study used an online community to invite Facebook and Instagram users to complete the questionnaire in the designated online questionnaire system. Online questionnaires have the following advantages ( Tan and Teo, 2000 ): (1) sampling is not restricted to a single geological location, (2) lower cost, and (3) faster questionnaire responses. A total of 353 questionnaires were returned from respondents. There were 353 appropriate replies considered for the final analysis.
The study used items established from prior research to confirm the reliability and validity of the measures. All items are evaluated through 5-point Likert-type scales where “1” (strongly disagree), “3” (neutral), and “5” (strongly agree).
Dependent Variable
To get a response about three dimensions of intention (continuance, participate, and purchase), we used eight items adopted from prior studies;
1. Continuance intention is measured by three items from the study of Bhattacherjee et al. (2008) , and the sample item is, “I intend to continue buying social media rather than discontinue its use.”
2. Participate intention is evaluated by three items from the work of Debatin et al. (2009) , and the sample item is, “my intentions are to continue participating in the social media activities.”
3. Purchase intention was determined by two items adapted from the work of Pavlou et al. (2007) , and the sample item is, “I intend to buy using social media in the near future.”
Independent Variable
To analyze the five dimensions of SMMAs, we used eleven items adopted from a prior study of Kim and Ko (2012) .
1. Entertainment is determined by two items and the sample item is, “using social media for shopping is fun.”
2. Interaction is evaluated by three items, and the sample item is, “conversation or opinion exchange with others is possible through brand pages on social media.”
3. Trendiness is measured by two items, and the sample item is, “contents shown in social media is the newest information.”
4. Customization is measured by two items, and the sample item is, “brand’s pages on social media offers customized information search.”
5. Word of mouth is measured by two items, and the sample item is, “I would like to pass along information on the brand, product, or services from social media to my friends.”
Mediating Variables
We used two mediating variables in this study,
1. Social identification was measured with five items adopted from the prior study of Bhattacharya and Sen (2003) , and the sample item is, “I see myself as a part of the social media community.”
2. Satisfaction was evaluated with six items adopted from the study of Chen et al. (2015) , and the sample item is, “overall, I am happy to purchase my desired product from social media.”
This research employs a partial least square (PLS) modeling technique, instead of other covariance-based approaches such as LISREL and AMOS. The reason behind why we pick PLS-SEM is that it is most suitable for confirmatory and also exploratory research ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). Structural equation modeling (SEM) has two approaches, namely covariance-based and PLS-SEM ( Hair et al., 2014 ). PLS is primarily used to validate hypotheses, whereas SEM is most advantageous in hypothesis expansion ( Podsakoff et al., 2012 ). A PLS-SEM-based methodology would be done in two phases, first weighing and then measurement ( Sarstedt et al., 2014 ). PLS-SEM is ideal for a multiple-order, multivariable model. To do small data analysis is equally useful in PLS-SEM ( Hair et al., 2014 ). PLS-SEM allows it easy to calculate all parameter calculations ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). The present analysis was conducted using SmartPLS 3.9.
Model Measurement
Table 1 shows this study model based on 31 items of the seven variables. The reliability of this study model is measured with Cronbach’s alpha ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). As shown in Table 1 , all items’ reliability is robust, Cronbach’s alpha (α) is greater than 0.7. Moreover, composite reliability (CR) fluctuates from.80 to.854, which surpassed the prescribed limit of 0.70, affirming that all loadings used for this research have shown up to satisfactory indicator reliability. Ultimately, all item’s loadings are over the 0.6 cutoff, which meets the threshold ( Henseler et al., 2015 ).
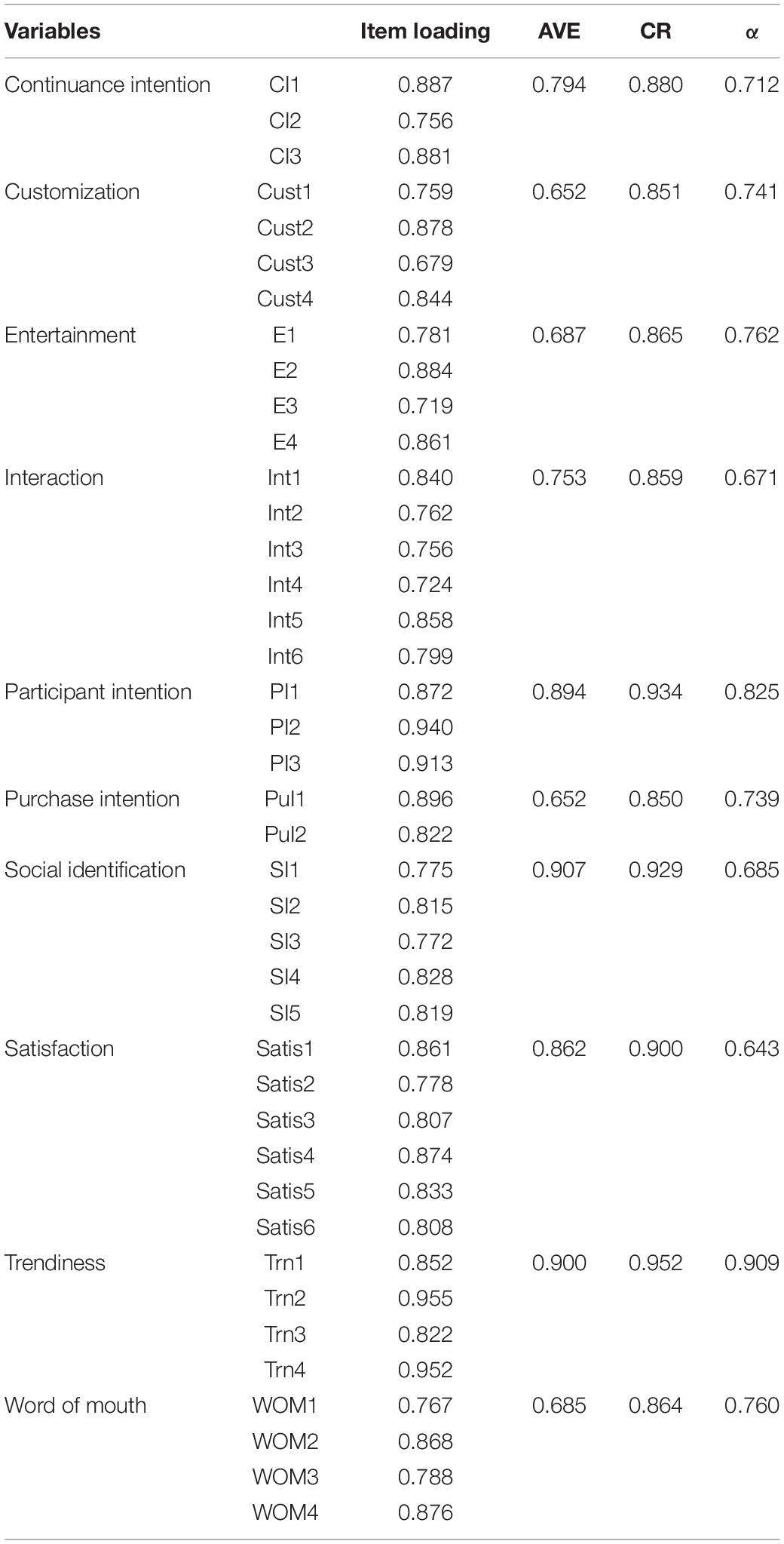
Table 1. Inner model evaluation.
The Cronbach’s alpha value for all constructs must be greater than 0.70 is acceptable ( Hair et al., 2014 ). All the values of α are greater than 0.7 as shown in Table 1 and Figure 2 .
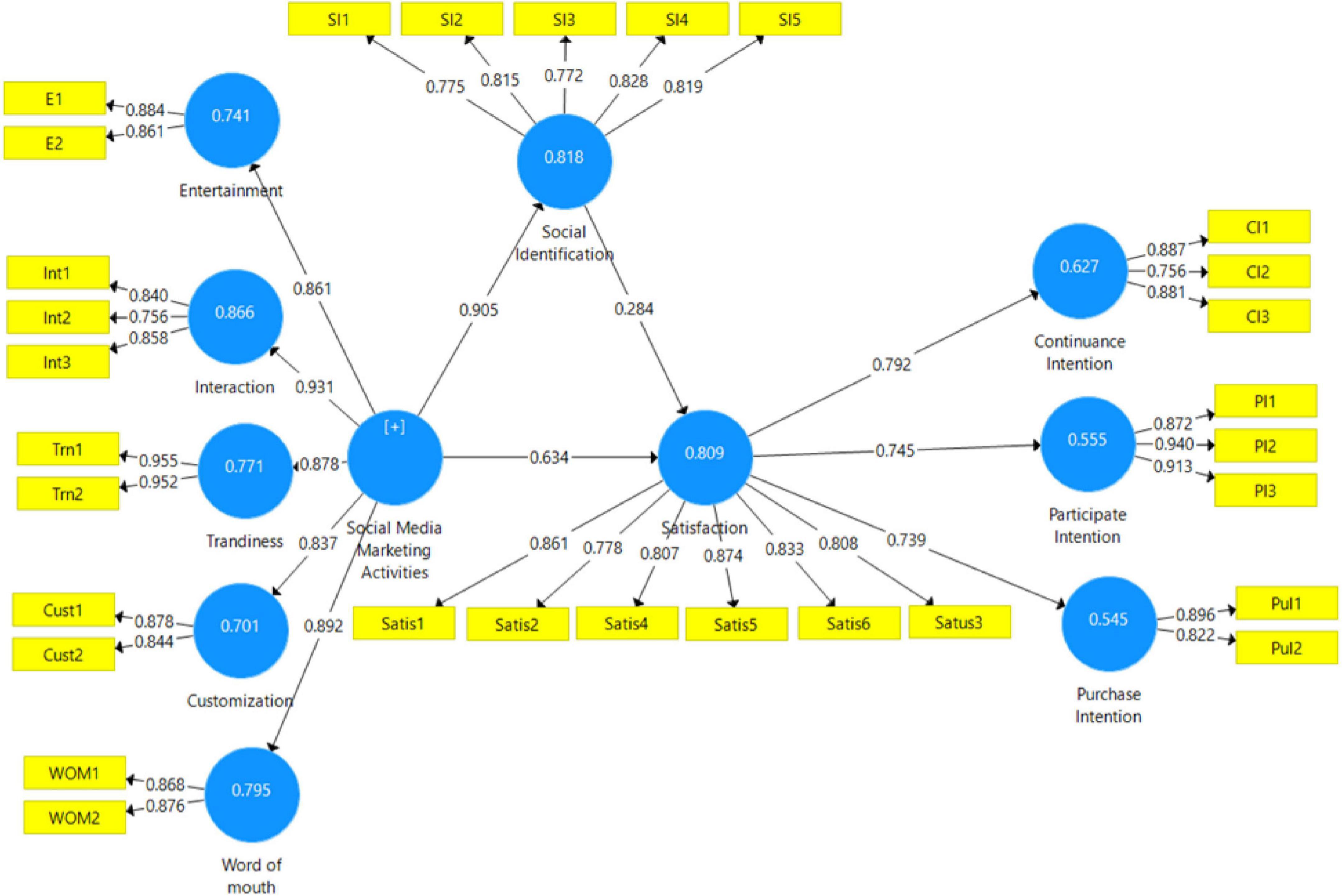
Figure 2. Measurement model.
Convergent validity is measured by CR and AVE, and scale reliability for each item ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). The scholar says that CR and AVE should be greater than 0.7 and 0.5, respectively. By utilizing CR and average variance extracted scores, convergent validity was estimated ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981 ). As elaborated in Table 3 , the average variance extracted scores of all the indicators are greater than 0.50 and CR is higher than.70 which is elaborating an acceptable threshold of convergent validity and internal consistency. It is stated that a value of CR, that is, not less than 0.70, is acceptable and evaluated as a good indicator of internal consistency ( Sarstedt et al., 2014 ). Moreover, average variance extracted scores of more than 0.50 demonstrate an acceptable convergent validity, as this implies that a specific construct with greater than 50% variations is clarified by the required indicators.
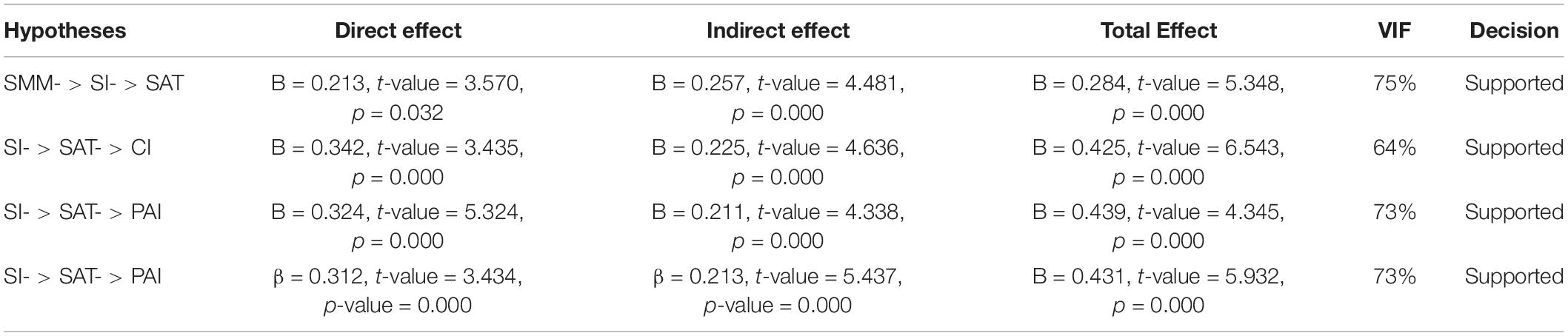
Table 2. A mediation analysis.
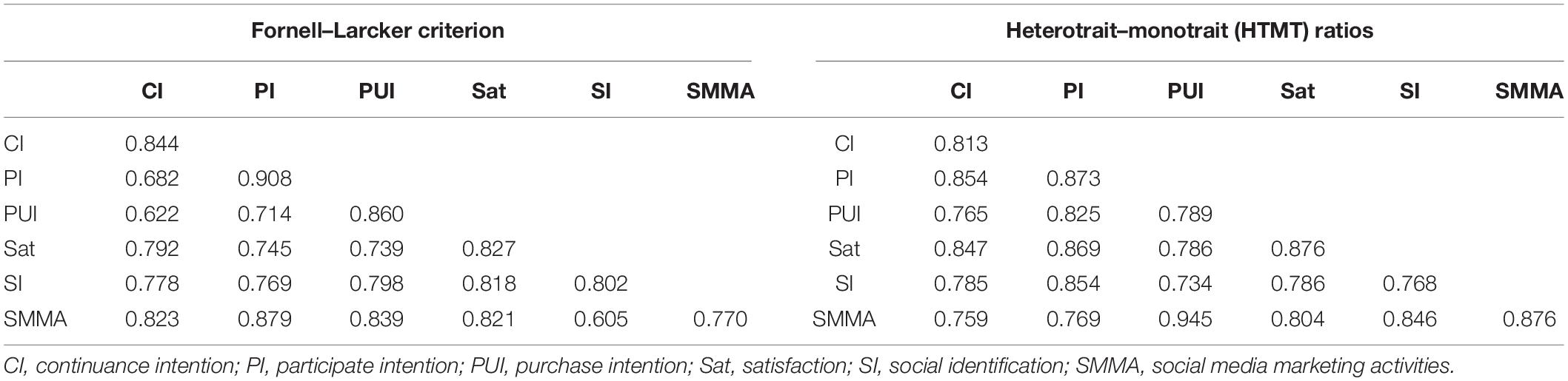
Table 3. Discriminant validity.
This study determines the discriminant validity through two techniques named Fornell–Larcker criterion and heterotrait–monotrait (HTMT) ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). In line with Fornell and Larcker (1981) , the upper right-side diagonal values should be greater than the correlation with other variables, which is the square root of AVE, which indicates the discriminant validity of the model. Table 3 states that discriminant validity was developed top value of variable correlation with itself is highest. The HTMT ratios must be less than 0.85, although values in the range of 0.90 to 0.95 are appropriate ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). Table 3 displays that all HTMT ratios are less than 0.90, which reinforces the statement that discriminant validity was supported in this study’s classification.
To determine the problem of multicollinearity in the model, VIF was calculated for this purpose. The experts said that if the value of VIF is greater than 5, there is no collinearity issue in findings ( Hair et al., 2014 ). The results indicate that the inner value of VIF for all indicators must fall in the range of 1.421 to 1.893. Furthermore, these study findings show no issue of collinearity with data, and the study has stable results.
To evaluate “the explanatory power of the model,” the R 2 value was analyzed for every predicted variable. It shows the degree to which independent variables illustrate the dependent variables. R 2 value in “between 0 and 1 with higher values shows a higher level of predictive accuracy. Subsequent values of R 2 describe 0.25 for weak, 0.50 for moderate, and 0.75 for” substantial. An appropriate model is indicated by R 2 greater than 0.5 in primary results. In Figure 2 , the value of R 2 greater than 0.5 on all exogenous constructs, which also means that the model has strong predictive accuracy ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ).
Table 4 displays the percentage of variance clarified for every variable: 62.7% of continuous intention, 55.5% of participate intention, 54.5% for purchase intention, 80.9% for satisfaction, and 81.8% for social identification. In general, results demonstrate that values of R 2 of endogenous variables are greater than 80%, which is the sign of a substantial “parsimonious model” ( Sarstedt et al., 2014 ). Most importantly, the outputs give a significant validation of the model. Q 2 values of all four 5 latent variables suggest that the model is extremely predictive ( Hair et al., 2014 ).
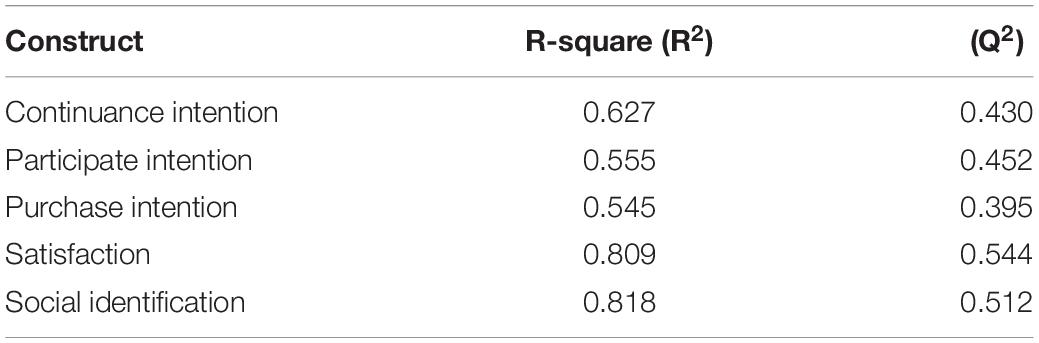
Table 4. Predictive accuracy and relevance of the model.
Hypothesis Testing
This study evaluates the significance of relationships using bootstrapping at 5,000 with a replacement sample ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ; Awan et al., 2021 ). The findings show that SMMAs have significant relationship with social identification (β = 0.905, t -value = 36.570, p = 0.000) which accept the H1. The findings show that SMM significantly influences the satisfaction (β = 0.634, t -value = 8.477, p = 0.000). Social identification has significant positive relationship with satisfaction as shown in Table 5 (β = 0.284, t -value = 4.348, p = 0.000) which accept the H3. The results show that satisfaction has significant relationship with continuous intention (β = 0.792, t -value = 15.513, p = 0.000) which support the H4. The findings show that satisfaction has strong positive relationship with participant intention (β = 0.745, t -value = 12.041, p = 0.000), which support the H5. The findings show that satisfaction has strong positive relationship with purchase intention (β = 0.739, t -value = 12.397, p = 0.000) which support the H6. The findings of the current investigation support H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, and H6. The results show that H4, H1a, H1b, H3a, H3b, H2a, and H2b are accepted (refer to Table 5 and Figure 3 ).
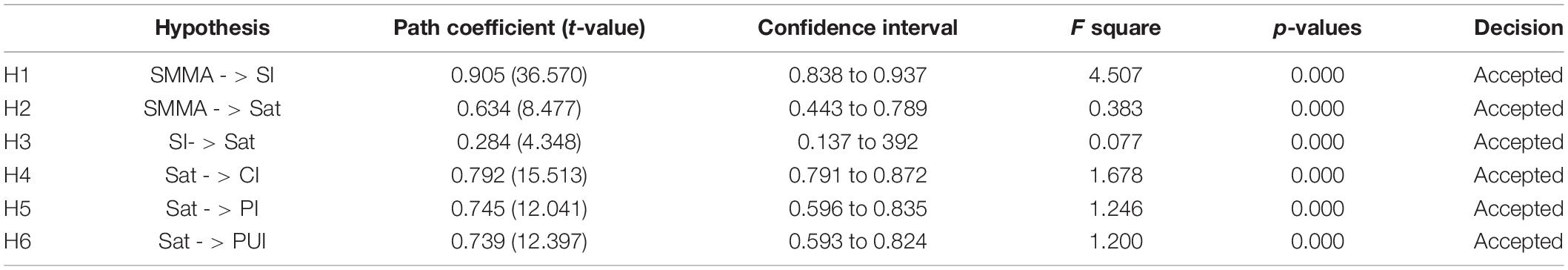
Table 5. Hypothesis testing.
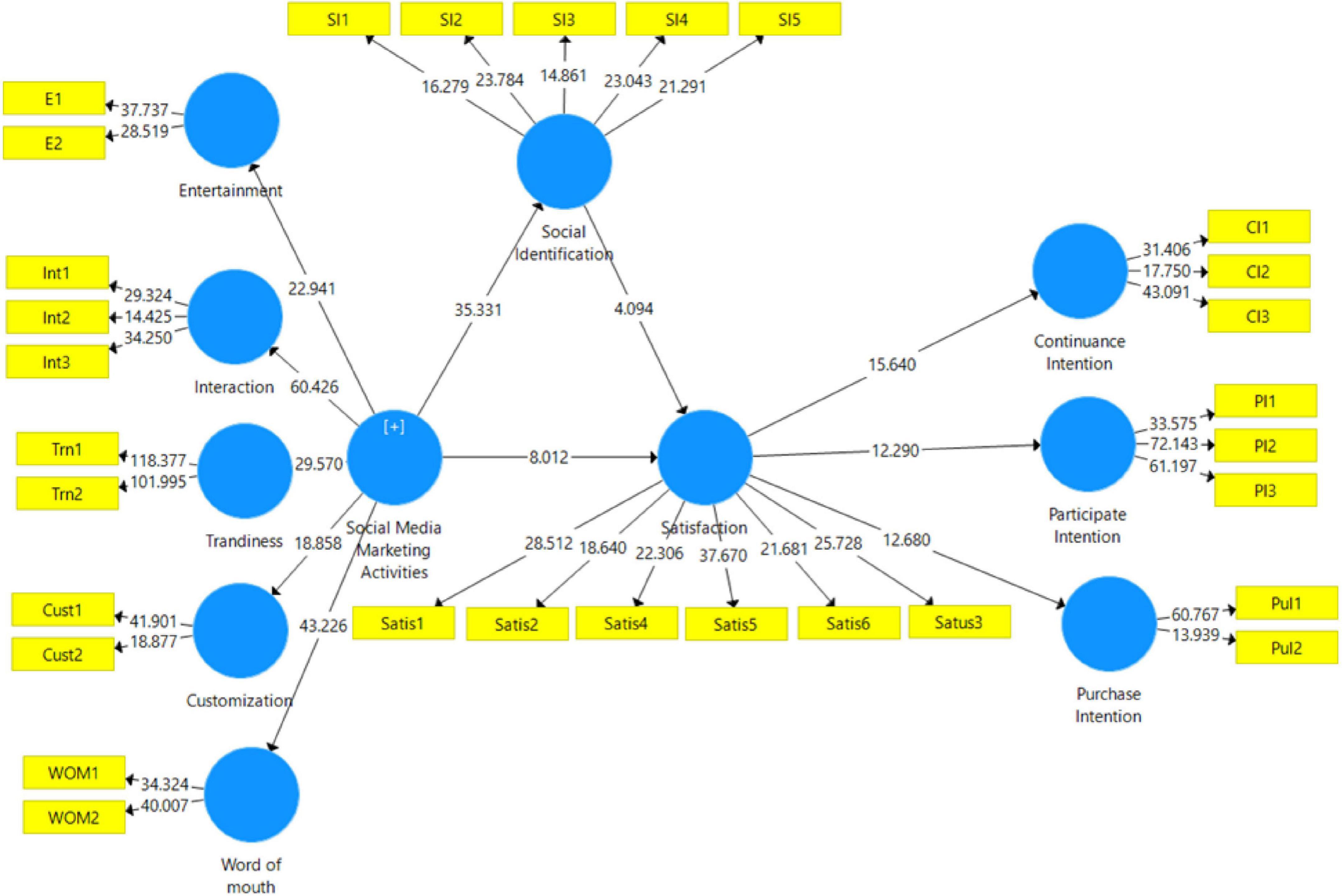
Figure 3. Structural model.
Preacher and Hayes (2008) argue that if the VIF value is greater than 80%, then it shows full mediation, and value of VIF equal to 20 to 80% which indicate the partial mediation and if VIF falls below 20%, then there is no mediation. The findings show that social identification mediates the relationship between SMM and satisfaction (β = 0.213, t -value = 3.570, p -value = 0.000) and indirect effect (β = 0.257, t -value = 4.481, p -value = 0.000) with variance accounted for (VAF) 75% which show partial mediation. In this, the VAF describes the size of the indirect effect in relation to the total effect ( Hayes and Preacher, 2010 ). The findings show that satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and continuous intention (β = 0.342, t -value = 3.435, p -value = 0.000) and indirect effect (β = 0.225, t -value = 4.636, p -value = 0.000) with VAF 64% which show partial mediation. In this, the VAF describes the size of the indirect effect in relation to the total effect ( Hayes, 2009 ). The findings show that satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and participant intention (β = 0.324, t -value = 5.325, p -value = 0.000) and indirect effect (β = 0.211, t -value = 4.338, p -value = 0.000) with VAF 73% which show partial mediation. The findings show that satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and purchase intention (β = 0.312, t -value = 3.434, p -value = 0.000) and indirect effect (β = 0.3.213, t -value = 5.437, p -value = 0.000) with VAF 78% which show partial mediation (refer to Table 2 ).
Discussion and Conclusion
The study was about SMMAs as proposed by Kim and Ko (2012) , and it investigated which factors influence social media usage. The findings of the study include the following:
Most studies about social websites have not exhausted the impact of SMMAs. According to this study, SMMAs significantly affect social identification, which ultimately influences purchase decisions, participation decisions, continuance intention, and satisfaction. The study demystified social media usage intention. The findings were that SMMAs could sustain corporate brands. According to Beig and Khan (2018) , unlike blog marketing and keyword advertising that were associated with content, SMM gets to the targeted audiences to enhance the impact of the information being shared by creating strong relationships in the online community. Therefore, service providers of social media must put into consideration means of increasing the impact of SMMAs. To boost SMMAs, operators should increase activity on the forum. The members of a community can be allowed to explain the guiding factors behind choosing a particular brand over that of competitors for other members to know the competing brands. From the discussions and sharing of knowledge, members get an opportunity to understand why they like a particular brand, thus enhancing brand loyalty and community cohesion ( Yadav and Rahman, 2017 ).
The study also confirmed that most administrators are concerned with the influence of brand community management in creating business advantage. According to Tarsakoo and Charoensukmongkol (2020) , marketing strategies and tools have undergone tremendous changes since the inception of social media. Consumers no longer must rely on traditional media to acquire information about a product before making their purchase since social media can effectively and easily avail such information. For that reason, social media service providers must come up with effective measures of controlling publication timing, frequency, and content to achieve the set marketing targets. According to this study, if a company can successfully assist users to easily identify with a particular brand community, strong relationships will be fostered between the consumers and the brand, hence creating customer’s loyalty ( Ebrahim, 2020 ). Besides, users may stop using competitors’ products. So, companies need to appreciate that proper management of online strategies and brand community in creating community identity enhances brand’s competitiveness and inspires members of the brand community to shun using goods and services from competitors.
Limitations and Recommendations
Regardless of the efforts geared toward enabling in-depth data collection, research methodology, and research structure, there were still various limitations that ought to be dealt with in studies to be conducted in the future. For instance, using online questionnaires in data collection, some members might have been very willing to fill them because of their community identity, hence enabling self-selection bias that may impact the validity and authenticity of the outcomes. Besides, a cross-sectional sample was used in the study; hence, results from the analysis can only demystify individual usage patterns on well-known social media. Nevertheless, the different social media platforms provide different services; hence, long-term usage needs long-term observation. The outcomes of growth model analysis with the experimental values and browsing experiences of users at the various phases in longitudinal studies to be conducted in the future may be increasingly conclusive on casual relationships with variables. The third limitation of the study is that different countries or areas have different preferences regarding social media. Future studies should unravel the reasons behind individuals from various cultural backgrounds or countries using different social media platforms and what might be the demands and motivations behind their preferences. Besides, new social networking sites such as Facebook and Twitter have unique characteristics which are different from traditional sites. Future studies should also focus on this shift. For this study, the emphasis was on SMMAs’ influence on user’s behavior and usage demands.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
This study was partly supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (no. 19ZDA081).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The reviewer ZA declared a shared affiliation with one of the authors, SG, to the handling editor at time of review.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Alalwan, A. A., Rana, N. P., Dwivedi, Y. K., and Algharabat, R. (2017). Social media in marketing: A review and analysis of the existing literature. Telem. Inform. 34, 1177–1190. doi: 10.1016/j.tele.2017.05.008
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Arora, A. S., and Sanni, S. A. (2019). Ten years of ‘social media marketing’research in the Journal of Promotion Management: Research synthesis, emerging themes, and new directions. J. Promot. Manag. 25, 476–499. doi: 10.1080/10496491.2018.1448322
Arrigo, E. (2018). Social media marketing in luxury brands. Manag. Res. Rev. 41, 657–679. doi: 10.1108/MRR-04-2017-0134
Assimakopoulos, C., Antoniadis, I., Kayas, O. G., and Dvizac, D. (2017). Effective social media marketing strategy: Facebook as an opportunity for universities. International J. Retail Distribut. Manag. 45, 532–549. doi: 10.1108/IJRDM-11-2016-0211
Awan, F. H., Dunnan, L., Jamil, K., Gul, R. F., Guangyu, Q., and Idrees, M. (2021). Impact of Role Conflict on Intention to leave Job with the moderating role of Job Embeddedness in Banking sector employees. Front. Psychol. 12:719449. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.719449
Beig, F. A., and Khan, M. F. (2018). Impact of social media marketing on brand experience: A study of select apparel brands on Facebook. Vision 22, 264–275. doi: 10.1177/0972262918785962
Bhattacharya, C. B., and Sen, S. (2003). Consumer–company identification: A framework for understanding consumers’ relationships with companies. J. Marke. 67, 76–88. doi: 10.1509/jmkg.67.2.76.18609
Bhattacherjee, A., Perols, J., and Sanford, C. (2008). Information technology continuance: A theoretic extension and empirical test. J. Comput. Inform. Systems 49, 17–26.
Google Scholar
Chen, S. C., and Lin, C. P. (2019). Understanding the effect of social media marketing activities: The mediation of social identification, perceived value, and satisfaction. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 140, 22–32. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2018.11.025
Chen, X., and Qasim, H. (2021). Does E-Brand experience matter in the consumer market? Explaining the impact of social media marketing activities on consumer-based brand equity and love. J. Consumer Behav. 20, 1065–1077. doi: 10.1002/cb.1915
Chen, Y.-S., Lin, C.-Y., and Weng, C.-S. (2015). The influence of environmental friendliness on green trust: The mediation effects of green satisfaction and green perceived quality. Sustainability 7, 10135–10152.
Cheung, M. L., Pires, G. D., Rosenberger, P. J. III, Leung, W. K. S., and Ting, H. (2021). Investigating the role of social media marketing on value co-creation and engagement: An empirical study in China and Hong Kong. Austral. Marke. J. 29, 118–131. doi: 10.1016/j.ausmj.2020.03.006
Debatin, B., Lovejoy, J. P., Horn, A.-K., and Hughes, B. N. (2009). Facebook and online privacy: Attitudes, behaviors, and unintended consequences. J. Comput. Med. Commun. 15, 83–108.
Di Minin, E., Fink, C., Hausmann, A., Kremer, J., and Kulkarni, R. (2021). How to address data privacy concerns when using social media data in conservation science. Conservat. Biol. 35, 437–446. doi: 10.1111/cobi.13708
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Dodds, W. B. (1991). In search of value: how price and store name information influence buyers’ product perceptions. J. Consumer Marke. 8, 15–24. doi: 10.1108/07363769110034974
Dunnan, L., Jamil, K., Abrar, U., Arain, B., Guangyu, Q., and Awan, F. H. (2020). “Analyzing the green technology market focus on environmental performance in Pakistan,” in 2020 3rd International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (ICoMET) (Sukkur: IEEE), 1–5. doi: 10.1016/s1351-4180(08)70002-3
Dutot, V. (2020). A social identity perspective of social media’s impact on satisfaction with life. Psychol. Marke. 37, 759–772. doi: 10.1111/j.1547-5069.2011.01394.x
Ebrahim, R. S. (2020). The role of trust in understanding the impact of social media marketing on brand equity and brand loyalty. J. Relat. Marke. 19, 287–308. doi: 10.1080/15332667.2019.1705742
Farivar, F., and Richardson, J. (2021). Workplace digitalisation and work-nonwork satisfaction: the role of spillover social media. Behav. Inform. Technol. 40, 747–758. doi: 10.1080/0144929x.2020.1723702
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Marke. Res. 18, 39–50. doi: 10.2307/3151312
Gul, R. F., Liu, D., Jamil, K., Baig, S. A., Awan, F. H., and Liu, M. (2021). Linkages between market orientation and brand performance with positioning strategies of significant fashion apparels in Pakistan. Fashion Textiles 8, 1–19.
Gupta, M., and Syed, A. A. (2021). Impact of online social media activities on marketing of green products. International J. Organizat. Anal. [Epub online ahead of print]. doi: 10.1108/IJOA-02-2020-2037
Hafez, M. (2021). The impact of social media marketing activities on brand equity in the banking sector in Bangladesh: the mediating role of brand love and brand trust. International J. Bank Marke. 39, 1353–1376. doi: 10.1108/IJBM-02-2021-0067
Hair, J. F. Jr., Sarstedt, M., Hopkins, L., and Kuppelwieser, V. G. (2014). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Eur. Bus. Rev. 26, 106–121. doi: 10.1108/EBR-10-2013-0128
Hair Joe, J., Sarstedt, M., Matthews, L. M., and Ringle, C. M. (2016). Identifying and treating unobserved heterogeneity with FIMIX-PLS: part I – method. Eur. Bus. Rev. 28, 63–76. doi: 10.1108/EBR-09-2015-0094
Haobin Ye, B., Fong, L. H. N., and Luo, J. M. (2021). Parasocial interaction on tourism companies’ social media sites: antecedents and consequences. Curr. Issues Tourism 24, 1093–1108. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2020.1764915
Hayes, A. F. (2009). Beyond Baron and Kenny: Statistical mediation analysis in the new millennium. Commun. Monogr. 76, 408–420. doi: 10.1080/03637750903310360
Hayes, A. F., and Preacher, K. J. (2010). Quantifying and testing indirect effects in simple mediation models when the constituent paths are nonlinear. Multiv. Behav. Res. 45, 627–660. doi: 10.1080/00273171.2010.498290
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., and Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Marke. Sci. 43, 115–135. doi: 10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
Ibrahim, B. (2021). Social Media Marketing Activities and Brand Loyalty: A Meta-Analysis Examination. J. Promot. Manag. 28, 60–90.
Ibrahim, B., and Aljarah, A. (2018). Dataset of relationships among social media marketing activities, brand loyalty, revisit intention Evidence from the hospitality industry in Northern Cyprus. Data Brief 21, 1823–1828. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.11.024
Ismail, A. R., Nguyen, B., and Melewar, T. C. (2018). Impact of perceived social media marketing activities on brand and value consciousness: roles of usage, materialism and conspicuous consumption. International J. Internet Marke. Adv. 12, 233–254. doi: 10.1504/ijima.2018.10013343
Jamil, K., Liu, D., Gul, R. F., Hussain, Z., Mohsin, M., Qin, G., et al. (2021b). Do remittance and renewable energy affect CO2 emissions? An empirical evidence from selected G-20 countries. Energy Environ. [preprint]. doi: 10.1177/0958305X211029636
Jamil, K., Hussain, Z., Gul, R. F., Shahzad, M. A., and Zubair, A. (2021a). The effect of consumer self-confidence on information search and share intention. Inform. Discov. Deliv. [Epub online ahead of print]. doi: 10.1108/IDD-12-2020-0155
Jarman, H. K., Marques, M. D., McLean, S. A., Slater, A., and Paxton, S. J. (2021). Social media, body satisfaction and well-being among adolescents: A mediation model of appearance-ideal internalization and comparison. Body Image 36, 139–148. doi: 10.1016/j.bodyim.2020.11.005
Kim, A. J., and Ko, E. (2012). Do social media marketing activities enhance customer equity? An empirical study of luxury fashion brand. J. Bus. Res. 65, 1480–1486. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2011.10.014
Koçak, O., İlme, E., and Younis, M. Z. (2021). Mediating Role of Satisfaction with Life in the Effect of Self-Esteem and Education on Social Media Addiction in Turkey. Sustainability 13:9097. doi: 10.3390/su13169097
Lee, H.-W., Kim, S., and Liew, J. (2021). Spectator sports as context for examining observers’ agreeableness, social identification, and empathy in a high-stakes conflict situation. Psychol. Rep. 124, 1788–1806. doi: 10.1177/0033294120948228
Liu, X., Shin, H., and Burns, A. C. (2021). Examining the impact of luxury brand’s social media marketing on customer engagement: Using big data analytics and natural language processing. J. Bus. Res. 125, 815–826. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.04.042
Mahendra, P. T. (2021). Improve Customer Satisfaction through Product Innovation in Social Media. Hum. Soc. Sci. 4, 3719–3729. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14885-4
Mohsin, M., Zhu, Q., Naseem, S., Sarfraz, M., and Ivascu, L. (2021). Mining Industry Impact on Environmental Sustainability, Economic Growth, Social Interaction, and Public Health: An Application of Semi-Quantitative Mathematical Approach. Processes 9:972. doi: 10.3390/pr9060972
Naseem, S., Fu, G. L., Mohsin, M., Aunjam, M. S., Rafiq, M. Z., Jamil, K., et al. (2020). Development of an inexpensive functional textile product by applying accounting cost benefit analysis. Industria Textila 71, 17–22. doi: 10.35530/it.071.01.1692
Pang, H. (2021). Identifying associations between mobile social media users’ perceived values, attitude, satisfaction, and eWOM engagement: The moderating role of affective factors. Telematics Inform. 59:101561. doi: 10.1016/j.tele.2020.101561
Parsons, A. L., and Lepkowska-White, E. (2018). Social media marketing management: A conceptual framework. J. Internet Commerce 17, 81–95. doi: 10.1080/15332861.2018.1433910
Pavlou, P. A., Liang, H., and Xue, Y. (2007). Understanding and mitigating uncertainty in online exchange relationships: A principal-agent perspective. MIS Quarterly 31, 105–136. doi: 10.2307/25148783
Petrick, J. F., Backman, S. J., Bixler, R., and Norman, W. C. (2001). Analysis of golfer motivations and constraints by experience use history. J. Leisure Res. 33, 56–70. doi: 10.1080/00222216.2001.11949930
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., and Podsakoff, N. P. (2012). Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 63, 539–569. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100452
Preacher, K. J., and Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav. Res. Methods 40, 879–891. doi: 10.3758/brm.40.3.879
Sahibzada, U. F., Cai, J., Latif, K. F., and Sahibzada, H. F. (2020). Knowledge management processes, knowledge worker satisfaction, and organizational performance. Aslib J. Inform. Manag. 72, 112–129. doi: 10.1108/AJIM-10-2019-0276
Salem, S. F., and Salem, S. O. (2021). Effects of social media marketing and selected marketing constructs on stages of brand loyalty. Global Bus. Rev. 22, 650–673. doi: 10.1177/0972150919830863
Sarfraz, M., Mohsin, M., Naseem, S., and Kumar, A. (2021). Modeling the relationship between carbon emissions and environmental sustainability during COVID-19: A new evidence from asymmetric ARDL cointegration approach. Environ. Devel. Sustain. 23, 16208–16226. doi: 10.1007/s10668-021-01324-0
Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., Henseler, J., and Hair, J. F. (2014). On the emancipation of PLS-SEM: A commentary on Rigdon (2012). Long Range Plan. 47, 154–160. doi: 10.1016/j.lrp.2014.02.007
Seo, E.-J., and Park, J.-W. (2018). A study on the effects of social media marketing activities on brand equity and customer response in the airline industry. J. Air Transp. Manag. 66, 36–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jairtraman.2017.09.014
Shareef, M. A., Mukerji, B., Dwivedi, Y. K., Rana, N. P., and Islam, R. (2019). Social media marketing: Comparative effect of advertisement sources. J. Retail. Consum. Ser. 46, 58–69. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2017.11.001
Shujaat, A., Rashid, A., and Muzaffar, A. (2021). Exploring the Effects of Social Media Use on Employee Performance: Role of Commitment and Satisfaction. Pennsylvania: IGI Global, 1788–1809.
Sirola, A., Kaakinen, M., Savolainen, I., Paek, H.-J., Zych, I., and Oksanen, A. (2021). Online identities and social influence in social media gambling exposure: A four-country study on young people. Telematics Inform. 60:101582. doi: 10.1016/j.tele.2021.101582
Suman, C., Chaudhary, R. S., Saha, S., and Bhattacharyya, P. (2021). An attention based multi-modal gender identification system for social media users. Mult. Tools Appl. 1183, 1–23. doi: 10.1109/access.2021.3136552
Tafesse, W., and Wien, A. (2018). Implementing social media marketing strategically: an empirical assessment. J. Marke. Manag. 34, 732–749. doi: 10.1080/0267257x.2018.1482365
Tan, M., and Teo, T. S. H. (2000). Factors influencing the adoption of Internet banking. J. Assoc. Inform. Syst. 1:5.
Tarsakoo, P., and Charoensukmongkol, P. (2020). Dimensions of social media marketing capabilities and their contribution to business performance of firms in Thailand. J. Asia Bus. Stud. 14, 441–461. doi: 10.1108/JABS-07-2018-0204
Thaler, R. (1985). Mental accounting and consumer choice. Marke. Sci. 4, 199–214. doi: 10.1287/mksc.4.3.199
Wang, Z., and Kim, H. G. (2017). Can social media marketing improve customer relationship capabilities and firm performance? Dynamic capability perspective. J. Interact. Marke. 39, 15–26. doi: 10.1016/j.intmar.2017.02.004
Wibowo, A., Chen, S.-C., Wiangin, U., Ma, Y., and Ruangkanjanases, A. (2021). Customer behavior as an outcome of social media marketing: The role of social media marketing activity and customer experience. Sustainability 13:189. doi: 10.3390/su13010189
Yadav, M., and Rahman, Z. (2017). Measuring consumer perception of social media marketing activities in e-commerce industry: Scale development & validation. Telematics Inform. 34, 1294–1307. doi: 10.1016/j.tele.2017.06.001
Yadav, M., and Rahman, Z. (2018). The influence of social media marketing activities on customer loyalty. Benchmarking 25, 3882–3905. doi: 10.1108/BIJ-05-2017-0092
Zollo, L., Filieri, R., Rialti, R., and Yoon, S. (2020). Unpacking the relationship between social media marketing and brand equity: The mediating role of consumers’ benefits and experience. J. Bus. Res. 117, 256–267. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.05.001
Keywords : social media marketing activities, social identification, satisfaction, continuance intention, participate intention, purchase intention
Citation: Jamil K, Dunnan L, Gul RF, Shehzad MU, Gillani SHM and Awan FH (2022) Role of Social Media Marketing Activities in Influencing Customer Intentions: A Perspective of a New Emerging Era. Front. Psychol. 12:808525. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.808525
Received: 03 November 2021; Accepted: 20 December 2021; Published: 17 January 2022.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2022 Jamil, Dunnan, Gul, Shehzad, Gillani and Awan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Syed Hussain Mustafa Gillani, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
Role of Social Media Marketing Activities in Influencing Customer Intentions: A Perspective of a New Emerging Era
Khalid jamil.
1 School of Economics and Management, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China
Rana Faizan Gul
Muhammad usman shehzad.
2 Department of Management Sciences and Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Syed Hussain Mustafa Gillani
3 Faisalabad Business School, National Textile University, Faisalabad, Pakistan
Fazal Hussain Awan
Associated data.
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The aim of this study is to explore social media marketing activities (SMMAs) and their impact on consumer intentions (continuance, participate, and purchase). This study also analyzes the mediating roles of social identification and satisfaction. The participants in this study were experienced users of two social media platforms Facebook and Instagram in Pakistan. A self-administered questionnaire was used to collect data from respondents. We used an online community to invite Facebook and Instagram users to complete the questionnaire in the designated online questionnaire system. Data were collected from 353 respondents, and structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to analyze the data. Results show that SMMAs have a significant impact on the intentions of users. Furthermore, social identification mediates the relationship between social media activities and satisfaction, and satisfaction mediates the relationship between social media activities and the intentions of users. This will help marketers how to attract customers to develop their intentions. This is the first novel study that used SMMAs to address the user intentions with the role of social identification and satisfaction in the context of Pakistan.
Introduction
There has been tremendous growth in the use of social media platforms such as WhatsApp, Instagram, and Facebook over the past decade ( Chen and Qasim, 2021 ). People are using these platforms to communicate with one another, and popular brands use them to market their products. Social activities have been brought from the real world to the virtual world courtesy of social networking sites. Messages are sent in real time which now enable people to interact and share information. As a result, companies consider social media platforms as vital tools for succeeding in the online marketplace ( Ebrahim, 2020 ). The use of social media to commercially promote processes or events to attract potential consumers online is referred to as social media marketing (SMM). With the immense rise in community websites, a lot of organizations have started to find the best ways to utilize these sites in creating strong relationships and communications with users to enable friendly and close relationships to create online brand communities ( Ibrahim and Aljarah, 2018 ).
Social media marketing efficiently fosters communications between customers and marketers, besides enabling activities that enhance brand awareness ( Hafez, 2021 ). For that reason, SMM remains to be considered as a new marketing strategy, but how it impacts intentions is limited. But, to date, a lot of research on SMM is focused on consumer’s behavior, creative strategies, content analysis and the benefits of user-generated content, and their relevance to creating virtual brand communities ( Ibrahim, 2021 ).
New channels of communication have been created, and there have been tremendous changes in how people interact because of the internet developing various applications and tools over time ( Tarsakoo and Charoensukmongkol, 2020 ). Companies now appreciate that sharing brand information and consumer’s experience is a new avenue for brand marketing due to the widespread use of smartphones and the internet, with most people now relying on social media brands. Therefore, developing online communities has become very efficient. Social groups create a sense of continuity for their members without meeting physically ( Yadav and Rahman, 2017 ). A community that acquires products from a certain brand is referred to as a virtual brand community. Customers are not just interested in buying goods and services but also in creating worthwhile experiences and strong relationships with other customers and professionals. So, when customers are part of online communities, there is a cohesion that grows among the customers, which impacts the market. Therefore, it is up to the companies to identify methods or factors that will encourage customers to take part in these communities ( Ismail et al., 2018 ).
The online community’s nature is like that of actual communities when it comes to creating shared experiences, enabling social support, and attending to the members’ need to identify themselves, regardless of the similarities and variances existing between real-world communities and online communities ( Seo and Park, 2018 ). Regarding manifestations and technology, online communities are distinct from real-life communities since the former primarily use computers to facilitate their operation. A certain brand product or service is used to set up a brand community. Brand communities refer to certain communities founded based on interactions that are not limited by geographical restrictions between brand consumers ( Chen and Lin, 2019 ). Since consumers’ social relationships create brand communities, these communities have customs, traditions, rituals, and community awareness. The group members learn from each other and share knowledge about a product, hence appreciating each other’s actions and ideas. So, once a consumer joins a particular brand community, automatically, the brand becomes a conduit and common language linking the community members together because of sharing brand experiences ( Arora and Sanni, 2019 ).
Based on the perspective of brand owners, most research has focused on how social communities can benefit brands. However, there are also some discussions regarding the benefits that come from brand community members according to the members themselves to analyze how social community impacts its members ( Shareef et al., 2019 ). Consumer’s behavior is influenced by value so, when a consumer is constantly receiving value, it leads to consumer’s loyalty toward that brand. According to Alalwan et al. (2017) , a valuable service provider will create loyalty to a company and enhance brand awareness. Consumer value is essentially used in evaluating social networking sites. With better and easier options to create websites coming around, most consumers are attracted to a social community to know about a company and its goods. Furthermore, operators can learn consumer’s behavior through maintaining social interactions with customers. However, the social community should have great value. It should be beneficial to the potential customers by providing them with information relevant to the brand in question. Furthermore, customers should be able to interact with one another, thus creating a sense of belonging. From that, it is evident that a brand social community’s satisfaction affects community retention and selection.
Literature Review
Social media marketing activities.
Most businesses use online marketing strategies such as blogger endorsements, advertising on social media sites, and managing content generated by users to build brand awareness among consumers ( Wang and Kim, 2017 ). Social media is made up of internet-associated applications anchored on technological and ideological Web 2.0 principles, which enables the production and sharing of the content generated by users. Due to its interactive characteristics that enable knowledge sharing, collaborative, and participatory activities available to a larger community than in media formats such as radio, TV, and print, social media is considered the most vital communication channel for spreading brand information. Social media comprises blogs, internet forums, consumer’s review sites, social networking websites (Twitter, Blogger, LinkedIn, and Facebook), and Wikis ( Arrigo, 2018 ).
Social media facilitates content sharing, collaborations, and interactions. These social media platforms and applications exist in various forms such as social bookmarking, rating, video, pictures, podcasts, wikis, microblogging, social blogs, and weblogs. Social networkers, governmental organizations, and business firms are using social media to communicate, with its use increasing tremendously ( Cheung et al., 2021 ). Governmental organizations and business firms use social media for marketing and advertising. Integrated marketing activities can be performed with less cost and effort due to the seamless interactions and communication among consumer partners, events, media, digital services, and retailers via social media ( Tafesse and Wien, 2018 ).
According to Liu et al. (2021) , marketing campaigns for luxury brands consist of main factors such as customization, reputation, trendiness, interaction, and entertainment which significantly impact customers’ purchase intentions and brand equity. Activities that involve community marketing accrue from interactions between events and the mental states of individuals, whereas products are external factors for users ( Parsons and Lepkowska-White, 2018 ). But even though regardless of people experience similar service activities, there is a likelihood of having different ideas and feelings about an event; hence, outcomes for users and consumers are distinct. In future marketing, competition will focus more on brand marketing activities; hence, the marketing activities ought to offer sensory stimulation and themes that give customers a great experience. Now brands must provide quality features but also focus on enabling an impressive customer’s experience ( Beig and Khan, 2018 ).
Social Identification
A lot of studies about brand communities involve social identification, appreciating the fact that a member of a grand community is part and parcel of that community. Social identity demystifies how a person enhances self-affirmation and self-esteem using comparison, identity, and categorization ( Chen and Lin, 2019 ). There is no clear definition of the brand community or the brand owner, strengthening interactions between the community and its members or creating a rapport between the brand and community members. As a result, members of a community are separated into groups based on their educational attainment, occupation, and living environment. Members of social networks categorize each other into various groups or similar groups according to their classification in social networks ( Salem and Salem, 2021 ).
Brand identification and identification of brand communities emanate from a similar process. Users can interact freely, hence creating similar ideologies about the community, alongside strengthening bonds among members, hence enabling them to identify with that community. The brand community identity can also be considered as a convergence of values between the principles of the social community and the values of the users ( Wibowo et al., 2021 ).
According to Lee et al. (2021) , members of a brand social community share their ideas by taking part in community activities to help create solutions. When customers join a brand community, they happily take part in activities or discussions and are ready to help each other. So, it is evident that social community participation is impacting community identity positively. Community involvement entails a person sharing professional understanding or knowledge with other members to enhance personal growth and create a sense of belonging ( Gupta and Syed, 2021 ). According to Haobin Ye et al. (2021) , it is high time community identity be incorporated in virtual communities since it is a crucial factor that affects the operations of virtual communities. Also, community identity assists in facilitating positive interactions among members of the community, encouraging them to actively take part in community activities ( Assimakopoulos et al., 2017 ). This literature review suggests that social communities need members to work together. Individuals who can identify organizational visions and goals become dedicated to that virtual company.
Satisfaction
Customer’s satisfaction involves comparing expected and after-service satisfaction with the standards emanating from accumulated previous experiences. According to implementation confirmation theory, satisfaction is a consumer’s expected satisfaction with how the services have lived up to those expectations. Customers usually determine the level of satisfaction by comparing the satisfaction previously experienced and the current one ( Pang, 2021 ).
According to recent studies, community satisfaction impacts consumer’s loyalty and community participation. A study community’s level of satisfaction is determined by how its members rate it ( Jarman et al., 2021 ). Based on previous interactions, the community may be evaluated. When the members are satisfied with their communities, it is manifested through joyful emotions, which affect the behavior of community members. In short, satisfaction creates active participation and community loyalty ( Shujaat et al., 2021 ).
Types of Intentions
A lot of studies about information and marketing systems have used continuance intention in measuring if a customer continues to use a certain product or service. The willingness of customers to continue using a good or service determines if service providers will be successful or not. According to Zollo et al. (2020) , an efficient information marketing system should persuade users to use it, besides retaining previous users to guarantee continued use.
Operators of social networks must identify the reason propelling continued use of social network sites, alongside attracting more users. Nevertheless, previous studies on information systems in the last two decades have mainly concentrated on behavior–cognition approaches, for instance, the technology acceptance model (TAM), theory of planned behavior (TPB), and theory of reasoned action (TRA) with their variants ( Tarsakoo and Charoensukmongkol, 2020 ; Jamil et al., 2021b ). According to Ismail et al. (2018) , perceived use and satisfaction positively impact a user’s continuance intention. The continued community members’ participation has two intentions. Continuance intention is the first one. It defines the community member’s intent to keep on using the community ( Beig and Khan, 2018 ; Dunnan et al., 2020 ). Then, recommendation intention, also known as mouth marketing, describes every informal communication that takes place among community members regarding the virtual brand community. Previous studies about members of a virtual community mostly entailed the continuous utilization of information systems ( Seo and Park, 2018 ; Sarfraz et al., 2021 ). Unlike previous studies, this study focuses on factors that support the continued participation of community members. So, besides determining how usage purpose affects continuance intention, the study also investigated the factors that influence users’ willingness to take part in community activities ( Gul et al., 2021 ).
Nevertheless, it is hard to determine and monitor whether a certain action occurred (recommendation or purchase) during empirical investigations. Consumers will seek relevant information associated with their external environment and experiences when purchasing goods ( Shareef et al., 2019 ). Once they have collected significant information, they will evaluate it, and draw comparisons from which customer’s behavior is determined. Since purchase intention refers to a customer’s affinity toward a particular product, it is a metric of a customer’s behavioral intention. According to Liu et al. (2021) , the probability of a customer buying a particular product is known as an intention to buy. So, when the probability is high, it simply means that the willingness to purchase is high. Past studies consider purchase intention as a factor that can predict consumer’s behavior alongside the subjective possibility of consumer’s purchases. According to Chen and Qasim (2021) , from a marketing viewpoint, if a company wants to retain its community besides achieving community targets while establishing successful marketing via the community, at least three objectives are needed. They include membership continuance intention, which entails members living up to their promises in the community and also the willingness to belong to the community ( Yadav and Rahman, 2018 ; Naseem et al., 2020 ). On the other side, community recommendation intention entails the willingness of members to recommend or refer community members to other people who are not members ( Jamil et al., 2021a ; Mohsin et al., 2021 ). The next consideration is the community participation intention of a member, which involves their willingness to participate in the activities of the brand community. Unlike past literature about using information systems, this study demystified how SMMAs influence purchase intention and participation intention ( Alalwan et al., 2017 ).
Development of Hypotheses
People with similar interests can get a virtual platform to discuss and share ideas courtesy of social media. Sustained communication of social media allows users to create a community. Long-lasting sharing of growth and information fosters the development of strong social relationships. The information posted on social media platforms by an individual positively correlates with the followers the user has. Regarding the discussion above, we proposed the following hypothesis:
- H1: Social media marketing activities (SMMAs) have a significant impact on social identification.
The study of Farivar and Richardson (2021) on users’ continuance intention confirmed that it is influenced by satisfaction after service. Social media studies are also of the thought that satisfaction significantly affects continuance intention. So, a consumer will measure the satisfaction of service after using it. Mahendra (2021) claims that satisfaction influences repurchase behavior. Repurchase intention emanates from a customer’s satisfaction with a good or service. People who have similar interests may interact and cooperate in a virtual world via social media platforms. A community on social media may be formed by regularly connecting with people and exchanging information with them. Members benefit from long-term information and growth exchanges that enable them to create strong social relationships. A lot of studies have pointed out that repurchase intention and customer’s satisfaction are positively and highly related. Besides, marketing studies noted that satisfactory experience after using a product would impact the intention of future repurchase. Hence, we proposed the following hypothesis:
- H2: SMMAs have a significant impact on satisfaction.
The study by Suman et al. (2021) on American consumer’s behavior suggested that members taking part in community activities (meetups, discussion, and browsing) influence their brand-associated behavior. According to Di Minin et al. (2021) , the brand identity of a consumer has a positive impact on satisfaction. Consumers capitalize on online communities to share their experiences and thoughts about a grand regularly and easily ( Sirola et al., 2021 ). These experiences make up the customer to brand experiences and establish a sense of belonging, trust, and group identity. In a nutshell, this study suggests that identity will enable members to recognize their community, hence confirming that members have similar experiences and feelings with a particular brand and feel united in the group ( Shujaat et al., 2021 ). Strong group identity means that members are integrated closely into the brand communities and highly regard the community. Hence, we proposed the following hypothesis:
- H3: Social identification has a significant impact on satisfaction.
Brand communities are beneficial in the sense that they enable sharing of marketing information, managing a community, and exploring demands ( Dutot, 2020 ). These activities are likely to enhance consumer’s rights and increase customer’s satisfaction ( Sahibzada et al., 2020 ). A customer who makes an online transaction will be highly satisfied with a website that provides a great experience ( Koçak et al., 2021 ). Enhancing customer’s satisfaction, encouraging customer intentions, creating community loyalty, and fostering communication and interactions between community users are crucial to lasting community platform management ( Pang, 2021 ). Hence, we proposed the following hypotheses:
- H4: Satisfaction has a significant impact on continuance intention.
- H5: Satisfaction has a significant impact on participate intention.
- H6: Satisfaction has a significant impact on purchase intention.
Thaler (1985) proposed transaction utility theory, in which consumers’ willingness to spend money is influenced by their perceptions of value. Researchers such as Dodds (1991) claimed that buyers only become ready to purchase after they have established a sense of value for a product. According to Petrick et al. (2001) , a product’s quality is dependent on the customer’s satisfaction. Several studies have shown that enjoyment, perceived value, and behavioral intention are all linked together. Hence, we proposed the following hypothesis:
- H7: Social identification mediates the relationship between SMMA and satisfaction.
When it comes to information systems, Bhattacherjee et al. (2008) discovered that people’s continual intention is derived from their satisfaction with the system after they have used it. Studies on employee’s satisfaction in the workplace have shown that it has a substantial influence on CI. The amount of satisfaction that users have with the system that they have previously used is the most important factor in determining their CI, according to research on information system utilization intention.
In other words, the customer’s contentment with the product leads to the establishment of a desire to buy the thing again, as mentioned by Assimakopoulos et al. (2017) . Numerous studies show a strong link between customer’s satisfaction and their propensity to return for another transaction. According to a lot of marketing studies, customers who have a pleasant experience with a product are more likely to repurchase it. Hence, we proposed the following hypotheses:
- H8: Satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and continuance intention.
- H9: Satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and participate intention.
- H10: Satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and purchase intention.
Figure 1 shows the research framework of this study.

Conceptual framework.
Conceptual Framework
Research methodology.
This study designed a questionnaire according to the hypotheses stated above. The participants in this study were experienced users of two social media platforms Facebook and Instagram in Pakistan. A self-administered questionnaire was used to collect data from respondents. A pilot study with 40 participants was carried out. Since providing recommendations, revisions were made to the final questionnaire to make it more understandable for the study’s respondents. To ensure the content validity of the measures, three academic experts of marketing analyzed and make improvements in the items of constructs. The experts searched for spelling errors and grammatical errors and ensured that the items were correct. The experts have proposed minor text revisions to social identification and satisfaction items and advised that the original number of items is to be maintained. This study used an online community to invite Facebook and Instagram users to complete the questionnaire in the designated online questionnaire system. Online questionnaires have the following advantages ( Tan and Teo, 2000 ): (1) sampling is not restricted to a single geological location, (2) lower cost, and (3) faster questionnaire responses. A total of 353 questionnaires were returned from respondents. There were 353 appropriate replies considered for the final analysis.
The study used items established from prior research to confirm the reliability and validity of the measures. All items are evaluated through 5-point Likert-type scales where “1” (strongly disagree), “3” (neutral), and “5” (strongly agree).
Dependent Variable
To get a response about three dimensions of intention (continuance, participate, and purchase), we used eight items adopted from prior studies;
- 1. Continuance intention is measured by three items from the study of Bhattacherjee et al. (2008) , and the sample item is, “I intend to continue buying social media rather than discontinue its use.”
- 2. Participate intention is evaluated by three items from the work of Debatin et al. (2009) , and the sample item is, “my intentions are to continue participating in the social media activities.”
- 3. Purchase intention was determined by two items adapted from the work of Pavlou et al. (2007) , and the sample item is, “I intend to buy using social media in the near future.”
Independent Variable
To analyze the five dimensions of SMMAs, we used eleven items adopted from a prior study of Kim and Ko (2012) .
- 1. Entertainment is determined by two items and the sample item is, “using social media for shopping is fun.”
- 2. Interaction is evaluated by three items, and the sample item is, “conversation or opinion exchange with others is possible through brand pages on social media.”
- 3. Trendiness is measured by two items, and the sample item is, “contents shown in social media is the newest information.”
- 4. Customization is measured by two items, and the sample item is, “brand’s pages on social media offers customized information search.”
- 5. Word of mouth is measured by two items, and the sample item is, “I would like to pass along information on the brand, product, or services from social media to my friends.”
Mediating Variables
We used two mediating variables in this study,
- 1. Social identification was measured with five items adopted from the prior study of Bhattacharya and Sen (2003) , and the sample item is, “I see myself as a part of the social media community.”
- 2. Satisfaction was evaluated with six items adopted from the study of Chen et al. (2015) , and the sample item is, “overall, I am happy to purchase my desired product from social media.”
This research employs a partial least square (PLS) modeling technique, instead of other covariance-based approaches such as LISREL and AMOS. The reason behind why we pick PLS-SEM is that it is most suitable for confirmatory and also exploratory research ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). Structural equation modeling (SEM) has two approaches, namely covariance-based and PLS-SEM ( Hair et al., 2014 ). PLS is primarily used to validate hypotheses, whereas SEM is most advantageous in hypothesis expansion ( Podsakoff et al., 2012 ). A PLS-SEM-based methodology would be done in two phases, first weighing and then measurement ( Sarstedt et al., 2014 ). PLS-SEM is ideal for a multiple-order, multivariable model. To do small data analysis is equally useful in PLS-SEM ( Hair et al., 2014 ). PLS-SEM allows it easy to calculate all parameter calculations ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). The present analysis was conducted using SmartPLS 3.9.
Model Measurement
Table 1 shows this study model based on 31 items of the seven variables. The reliability of this study model is measured with Cronbach’s alpha ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). As shown in Table 1 , all items’ reliability is robust, Cronbach’s alpha (α) is greater than 0.7. Moreover, composite reliability (CR) fluctuates from.80 to.854, which surpassed the prescribed limit of 0.70, affirming that all loadings used for this research have shown up to satisfactory indicator reliability. Ultimately, all item’s loadings are over the 0.6 cutoff, which meets the threshold ( Henseler et al., 2015 ).
Inner model evaluation.
The Cronbach’s alpha value for all constructs must be greater than 0.70 is acceptable ( Hair et al., 2014 ). All the values of α are greater than 0.7 as shown in Table 1 and Figure 2 .

Measurement model.
Convergent validity is measured by CR and AVE, and scale reliability for each item ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). The scholar says that CR and AVE should be greater than 0.7 and 0.5, respectively. By utilizing CR and average variance extracted scores, convergent validity was estimated ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981 ). As elaborated in Table 3 , the average variance extracted scores of all the indicators are greater than 0.50 and CR is higher than.70 which is elaborating an acceptable threshold of convergent validity and internal consistency. It is stated that a value of CR, that is, not less than 0.70, is acceptable and evaluated as a good indicator of internal consistency ( Sarstedt et al., 2014 ). Moreover, average variance extracted scores of more than 0.50 demonstrate an acceptable convergent validity, as this implies that a specific construct with greater than 50% variations is clarified by the required indicators.
Discriminant validity.
CI, continuance intention; PI, participate intention; PUI, purchase intention; Sat, satisfaction; SI, social identification; SMMA, social media marketing activities.
This study determines the discriminant validity through two techniques named Fornell–Larcker criterion and heterotrait–monotrait (HTMT) ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). In line with Fornell and Larcker (1981) , the upper right-side diagonal values should be greater than the correlation with other variables, which is the square root of AVE, which indicates the discriminant validity of the model. Table 3 states that discriminant validity was developed top value of variable correlation with itself is highest. The HTMT ratios must be less than 0.85, although values in the range of 0.90 to 0.95 are appropriate ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ). Table 3 displays that all HTMT ratios are less than 0.90, which reinforces the statement that discriminant validity was supported in this study’s classification.
To determine the problem of multicollinearity in the model, VIF was calculated for this purpose. The experts said that if the value of VIF is greater than 5, there is no collinearity issue in findings ( Hair et al., 2014 ). The results indicate that the inner value of VIF for all indicators must fall in the range of 1.421 to 1.893. Furthermore, these study findings show no issue of collinearity with data, and the study has stable results.
To evaluate “the explanatory power of the model,” the R 2 value was analyzed for every predicted variable. It shows the degree to which independent variables illustrate the dependent variables. R 2 value in “between 0 and 1 with higher values shows a higher level of predictive accuracy. Subsequent values of R 2 describe 0.25 for weak, 0.50 for moderate, and 0.75 for” substantial. An appropriate model is indicated by R 2 greater than 0.5 in primary results. In Figure 2 , the value of R 2 greater than 0.5 on all exogenous constructs, which also means that the model has strong predictive accuracy ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ).
Table 4 displays the percentage of variance clarified for every variable: 62.7% of continuous intention, 55.5% of participate intention, 54.5% for purchase intention, 80.9% for satisfaction, and 81.8% for social identification. In general, results demonstrate that values of R 2 of endogenous variables are greater than 80%, which is the sign of a substantial “parsimonious model” ( Sarstedt et al., 2014 ). Most importantly, the outputs give a significant validation of the model. Q 2 values of all four 5 latent variables suggest that the model is extremely predictive ( Hair et al., 2014 ).
Predictive accuracy and relevance of the model.
Hypothesis Testing
This study evaluates the significance of relationships using bootstrapping at 5,000 with a replacement sample ( Hair Joe et al., 2016 ; Awan et al., 2021 ). The findings show that SMMAs have significant relationship with social identification (β = 0.905, t -value = 36.570, p = 0.000) which accept the H1. The findings show that SMM significantly influences the satisfaction (β = 0.634, t -value = 8.477, p = 0.000). Social identification has significant positive relationship with satisfaction as shown in Table 5 (β = 0.284, t -value = 4.348, p = 0.000) which accept the H3. The results show that satisfaction has significant relationship with continuous intention (β = 0.792, t -value = 15.513, p = 0.000) which support the H4. The findings show that satisfaction has strong positive relationship with participant intention (β = 0.745, t -value = 12.041, p = 0.000), which support the H5. The findings show that satisfaction has strong positive relationship with purchase intention (β = 0.739, t -value = 12.397, p = 0.000) which support the H6. The findings of the current investigation support H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, and H6. The results show that H4, H1a, H1b, H3a, H3b, H2a, and H2b are accepted (refer to Table 5 and Figure 3 ).
Hypothesis testing.

Structural model.
Preacher and Hayes (2008) argue that if the VIF value is greater than 80%, then it shows full mediation, and value of VIF equal to 20 to 80% which indicate the partial mediation and if VIF falls below 20%, then there is no mediation. The findings show that social identification mediates the relationship between SMM and satisfaction (β = 0.213, t -value = 3.570, p -value = 0.000) and indirect effect (β = 0.257, t -value = 4.481, p -value = 0.000) with variance accounted for (VAF) 75% which show partial mediation. In this, the VAF describes the size of the indirect effect in relation to the total effect ( Hayes and Preacher, 2010 ). The findings show that satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and continuous intention (β = 0.342, t -value = 3.435, p -value = 0.000) and indirect effect (β = 0.225, t -value = 4.636, p -value = 0.000) with VAF 64% which show partial mediation. In this, the VAF describes the size of the indirect effect in relation to the total effect ( Hayes, 2009 ). The findings show that satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and participant intention (β = 0.324, t -value = 5.325, p -value = 0.000) and indirect effect (β = 0.211, t -value = 4.338, p -value = 0.000) with VAF 73% which show partial mediation. The findings show that satisfaction mediates the relationship between social identification and purchase intention (β = 0.312, t -value = 3.434, p -value = 0.000) and indirect effect (β = 0.3.213, t -value = 5.437, p -value = 0.000) with VAF 78% which show partial mediation (refer to Table 2 ).
A mediation analysis.
Discussion and Conclusion
The study was about SMMAs as proposed by Kim and Ko (2012) , and it investigated which factors influence social media usage. The findings of the study include the following:
Most studies about social websites have not exhausted the impact of SMMAs. According to this study, SMMAs significantly affect social identification, which ultimately influences purchase decisions, participation decisions, continuance intention, and satisfaction. The study demystified social media usage intention. The findings were that SMMAs could sustain corporate brands. According to Beig and Khan (2018) , unlike blog marketing and keyword advertising that were associated with content, SMM gets to the targeted audiences to enhance the impact of the information being shared by creating strong relationships in the online community. Therefore, service providers of social media must put into consideration means of increasing the impact of SMMAs. To boost SMMAs, operators should increase activity on the forum. The members of a community can be allowed to explain the guiding factors behind choosing a particular brand over that of competitors for other members to know the competing brands. From the discussions and sharing of knowledge, members get an opportunity to understand why they like a particular brand, thus enhancing brand loyalty and community cohesion ( Yadav and Rahman, 2017 ).
The study also confirmed that most administrators are concerned with the influence of brand community management in creating business advantage. According to Tarsakoo and Charoensukmongkol (2020) , marketing strategies and tools have undergone tremendous changes since the inception of social media. Consumers no longer must rely on traditional media to acquire information about a product before making their purchase since social media can effectively and easily avail such information. For that reason, social media service providers must come up with effective measures of controlling publication timing, frequency, and content to achieve the set marketing targets. According to this study, if a company can successfully assist users to easily identify with a particular brand community, strong relationships will be fostered between the consumers and the brand, hence creating customer’s loyalty ( Ebrahim, 2020 ). Besides, users may stop using competitors’ products. So, companies need to appreciate that proper management of online strategies and brand community in creating community identity enhances brand’s competitiveness and inspires members of the brand community to shun using goods and services from competitors.
Limitations and Recommendations
Regardless of the efforts geared toward enabling in-depth data collection, research methodology, and research structure, there were still various limitations that ought to be dealt with in studies to be conducted in the future. For instance, using online questionnaires in data collection, some members might have been very willing to fill them because of their community identity, hence enabling self-selection bias that may impact the validity and authenticity of the outcomes. Besides, a cross-sectional sample was used in the study; hence, results from the analysis can only demystify individual usage patterns on well-known social media. Nevertheless, the different social media platforms provide different services; hence, long-term usage needs long-term observation. The outcomes of growth model analysis with the experimental values and browsing experiences of users at the various phases in longitudinal studies to be conducted in the future may be increasingly conclusive on casual relationships with variables. The third limitation of the study is that different countries or areas have different preferences regarding social media. Future studies should unravel the reasons behind individuals from various cultural backgrounds or countries using different social media platforms and what might be the demands and motivations behind their preferences. Besides, new social networking sites such as Facebook and Twitter have unique characteristics which are different from traditional sites. Future studies should also focus on this shift. For this study, the emphasis was on SMMAs’ influence on user’s behavior and usage demands.
Data Availability Statement
Author contributions.
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer ZA declared a shared affiliation with one of the authors, SG, to the handling editor at time of review.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
This study was partly supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (no. 19ZDA081).
- Alalwan A. A., Rana N. P., Dwivedi Y. K., Algharabat R. (2017). Social media in marketing: A review and analysis of the existing literature. Telem. Inform. 34 1177–1190. 10.1016/j.tele.2017.05.008 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Arora A. S., Sanni S. A. (2019). Ten years of ‘social media marketing’research in the Journal of Promotion Management: Research synthesis, emerging themes, and new directions. J. Promot. Manag. 25 476–499. 10.1080/10496491.2018.1448322 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Arrigo E. (2018). Social media marketing in luxury brands. Manag. Res. Rev. 41 657–679. 10.1108/MRR-04-2017-0134 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Assimakopoulos C., Antoniadis I., Kayas O. G., Dvizac D. (2017). Effective social media marketing strategy: Facebook as an opportunity for universities. International J. Retail Distribut. Manag. 45 532–549. 10.1108/IJRDM-11-2016-0211 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Awan F. H., Dunnan L., Jamil K., Gul R. F., Guangyu Q., Idrees M. (2021). Impact of Role Conflict on Intention to leave Job with the moderating role of Job Embeddedness in Banking sector employees. Front. Psychol. 12 :719449. 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.719449 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beig F. A., Khan M. F. (2018). Impact of social media marketing on brand experience: A study of select apparel brands on Facebook. Vision 22 264–275. 10.1177/0972262918785962 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bhattacharya C. B., Sen S. (2003). Consumer–company identification: A framework for understanding consumers’ relationships with companies. J. Marke. 67 76–88. 10.1509/jmkg.67.2.76.18609 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bhattacherjee A., Perols J., Sanford C. (2008). Information technology continuance: A theoretic extension and empirical test. J. Comput. Inform. Systems 49 17–26. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen S. C., Lin C. P. (2019). Understanding the effect of social media marketing activities: The mediation of social identification, perceived value, and satisfaction. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 140 22–32. 10.1016/j.techfore.2018.11.025 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen X., Qasim H. (2021). Does E-Brand experience matter in the consumer market? Explaining the impact of social media marketing activities on consumer-based brand equity and love. J. Consumer Behav. 20 1065–1077. 10.1002/cb.1915 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen Y.-S., Lin C.-Y., Weng C.-S. (2015). The influence of environmental friendliness on green trust: The mediation effects of green satisfaction and green perceived quality. Sustainability 7 10135–10152. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheung M. L., Pires G. D., Rosenberger P. J., III, Leung W. K. S., Ting H. (2021). Investigating the role of social media marketing on value co-creation and engagement: An empirical study in China and Hong Kong. Austral. Marke. J. 29 118–131. 10.1016/j.ausmj.2020.03.006 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Debatin B., Lovejoy J. P., Horn A.-K., Hughes B. N. (2009). Facebook and online privacy: Attitudes, behaviors, and unintended consequences. J. Comput. Med. Commun. 15 83–108. [ Google Scholar ]
- Di Minin E., Fink C., Hausmann A., Kremer J., Kulkarni R. (2021). How to address data privacy concerns when using social media data in conservation science. Conservat. Biol. 35 437–446. 10.1111/cobi.13708 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dodds W. B. (1991). In search of value: how price and store name information influence buyers’ product perceptions. J. Consumer Marke. 8 15–24. 10.1108/07363769110034974 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dunnan L., Jamil K., Abrar U., Arain B., Guangyu Q., Awan F. H. (2020). “ Analyzing the green technology market focus on environmental performance in Pakistan ,” in 2020 3rd International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (ICoMET) (Sukkur: IEEE; ), 1–5. 10.1016/s1351-4180(08)70002-3 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dutot V. (2020). A social identity perspective of social media’s impact on satisfaction with life. Psychol. Marke. 37 759–772. 10.1111/j.1547-5069.2011.01394.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ebrahim R. S. (2020). The role of trust in understanding the impact of social media marketing on brand equity and brand loyalty. J. Relat. Marke. 19 287–308. 10.1080/15332667.2019.1705742 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Farivar F., Richardson J. (2021). Workplace digitalisation and work-nonwork satisfaction: the role of spillover social media. Behav. Inform. Technol. 40 747–758. 10.1080/0144929x.2020.1723702 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fornell C., Larcker D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Marke. Res. 18 39–50. 10.2307/3151312 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gul R. F., Liu D., Jamil K., Baig S. A., Awan F. H., Liu M. (2021). Linkages between market orientation and brand performance with positioning strategies of significant fashion apparels in Pakistan. Fashion Textiles 8 1–19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gupta M., Syed A. A. (2021). Impact of online social media activities on marketing of green products. International J. Organizat. Anal. [Epub online ahead of print]. 10.1108/IJOA-02-2020-2037 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hafez M. (2021). The impact of social media marketing activities on brand equity in the banking sector in Bangladesh: the mediating role of brand love and brand trust. International J. Bank Marke. 39 1353–1376. 10.1108/IJBM-02-2021-0067 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hair J. F., Jr., Sarstedt M., Hopkins L., Kuppelwieser V. G. (2014). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Eur. Bus. Rev. 26 106–121. 10.1108/EBR-10-2013-0128 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hair Joe J., Sarstedt M., Matthews L. M., Ringle C. M. (2016). Identifying and treating unobserved heterogeneity with FIMIX-PLS: part I – method. Eur. Bus. Rev. 28 63–76. 10.1108/EBR-09-2015-0094 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Haobin Ye B., Fong L. H. N., Luo J. M. (2021). Parasocial interaction on tourism companies’ social media sites: antecedents and consequences. Curr. Issues Tourism 24 1093–1108. 10.1080/13683500.2020.1764915 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hayes A. F. (2009). Beyond Baron and Kenny: Statistical mediation analysis in the new millennium. Commun. Monogr. 76 408–420. 10.1080/03637750903310360 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hayes A. F., Preacher K. J. (2010). Quantifying and testing indirect effects in simple mediation models when the constituent paths are nonlinear. Multiv. Behav. Res. 45 627–660. 10.1080/00273171.2010.498290 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Henseler J., Ringle C. M., Sarstedt M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Marke. Sci. 43 115–135. 10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ibrahim B. (2021). Social Media Marketing Activities and Brand Loyalty: A Meta-Analysis Examination. J. Promot. Manag. 28 60–90. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ibrahim B., Aljarah A. (2018). Dataset of relationships among social media marketing activities, brand loyalty, revisit intention Evidence from the hospitality industry in Northern Cyprus. Data Brief 21 1823–1828. 10.1016/j.dib.2018.11.024 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ismail A. R., Nguyen B., Melewar T. C. (2018). Impact of perceived social media marketing activities on brand and value consciousness: roles of usage, materialism and conspicuous consumption. International J. Internet Marke. Adv. 12 233–254. 10.1504/ijima.2018.10013343 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jamil K., Liu D., Gul R. F., Hussain Z., Mohsin M., Qin G., et al. (2021b). Do remittance and renewable energy affect CO2 emissions? An empirical evidence from selected G-20 countries. Energy Environ. [preprint]. 10.1177/0958305X211029636 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jamil K., Hussain Z., Gul R. F., Shahzad M. A., Zubair A. (2021a). The effect of consumer self-confidence on information search and share intention. Inform. Discov. Deliv. [Epub online ahead of print]. 10.1108/IDD-12-2020-0155 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jarman H. K., Marques M. D., McLean S. A., Slater A., Paxton S. J. (2021). Social media, body satisfaction and well-being among adolescents: A mediation model of appearance-ideal internalization and comparison. Body Image 36 139–148. 10.1016/j.bodyim.2020.11.005 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim A. J., Ko E. (2012). Do social media marketing activities enhance customer equity? An empirical study of luxury fashion brand. J. Bus. Res. 65 1480–1486. 10.1016/j.jbusres.2011.10.014 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Koçak O., İlme E., Younis M. Z. (2021). Mediating Role of Satisfaction with Life in the Effect of Self-Esteem and Education on Social Media Addiction in Turkey. Sustainability 13 :9097. 10.3390/su13169097 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee H.-W., Kim S., Liew J. (2021). Spectator sports as context for examining observers’ agreeableness, social identification, and empathy in a high-stakes conflict situation. Psychol. Rep. 124 1788–1806. 10.1177/0033294120948228 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu X., Shin H., Burns A. C. (2021). Examining the impact of luxury brand’s social media marketing on customer engagement: Using big data analytics and natural language processing. J. Bus. Res. 125 815–826. 10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.04.042 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mahendra P. T. (2021). Improve Customer Satisfaction through Product Innovation in Social Media. Hum. Soc. Sci. 4 3719–3729. 10.1007/s11356-021-14885-4 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mohsin M., Zhu Q., Naseem S., Sarfraz M., Ivascu L. (2021). Mining Industry Impact on Environmental Sustainability, Economic Growth, Social Interaction, and Public Health: An Application of Semi-Quantitative Mathematical Approach. Processes 9 :972. 10.3390/pr9060972 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naseem S., Fu G. L., Mohsin M., Aunjam M. S., Rafiq M. Z., Jamil K., et al. (2020). Development of an inexpensive functional textile product by applying accounting cost benefit analysis. Industria Textila 71 17–22. 10.35530/it.071.01.1692 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pang H. (2021). Identifying associations between mobile social media users’ perceived values, attitude, satisfaction, and eWOM engagement: The moderating role of affective factors. Telematics Inform. 59 :101561. 10.1016/j.tele.2020.101561 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Parsons A. L., Lepkowska-White E. (2018). Social media marketing management: A conceptual framework. J. Internet Commerce 17 81–95. 10.1080/15332861.2018.1433910 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pavlou P. A., Liang H., Xue Y. (2007). Understanding and mitigating uncertainty in online exchange relationships: A principal-agent perspective. MIS Quarterly 31 105–136. 10.2307/25148783 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Petrick J. F., Backman S. J., Bixler R., Norman W. C. (2001). Analysis of golfer motivations and constraints by experience use history. J. Leisure Res. 33 56–70. 10.1080/00222216.2001.11949930 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Podsakoff P. M., MacKenzie S. B., Podsakoff N. P. (2012). Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 63 539–569. 10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100452 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Preacher K. J., Hayes A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav. Res. Methods 40 879–891. 10.3758/brm.40.3.879 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sahibzada U. F., Cai J., Latif K. F., Sahibzada H. F. (2020). Knowledge management processes, knowledge worker satisfaction, and organizational performance. Aslib J. Inform. Manag. 72 112–129. 10.1108/AJIM-10-2019-0276 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salem S. F., Salem S. O. (2021). Effects of social media marketing and selected marketing constructs on stages of brand loyalty. Global Bus. Rev. 22 650–673. 10.1177/0972150919830863 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sarfraz M., Mohsin M., Naseem S., Kumar A. (2021). Modeling the relationship between carbon emissions and environmental sustainability during COVID-19: A new evidence from asymmetric ARDL cointegration approach. Environ. Devel. Sustain. 23 16208–16226. 10.1007/s10668-021-01324-0 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sarstedt M., Ringle C. M., Henseler J., Hair J. F. (2014). On the emancipation of PLS-SEM: A commentary on Rigdon (2012). Long Range Plan. 47 154–160. 10.1016/j.lrp.2014.02.007 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seo E.-J., Park J.-W. (2018). A study on the effects of social media marketing activities on brand equity and customer response in the airline industry. J. Air Transp. Manag. 66 36–41. 10.1016/j.jairtraman.2017.09.014 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shareef M. A., Mukerji B., Dwivedi Y. K., Rana N. P., Islam R. (2019). Social media marketing: Comparative effect of advertisement sources. J. Retail. Consum. Ser. 46 58–69. 10.1016/j.jretconser.2017.11.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shujaat A., Rashid A., Muzaffar A. (2021). Exploring the Effects of Social Media Use on Employee Performance: Role of Commitment and Satisfaction. Pennsylvania: IGI Global, 1788–1809. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sirola A., Kaakinen M., Savolainen I., Paek H.-J., Zych I., Oksanen A. (2021). Online identities and social influence in social media gambling exposure: A four-country study on young people. Telematics Inform. 60 :101582. 10.1016/j.tele.2021.101582 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suman C., Chaudhary R. S., Saha S., Bhattacharyya P. (2021). An attention based multi-modal gender identification system for social media users. Mult. Tools Appl. 1183 1–23. 10.1109/access.2021.3136552 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tafesse W., Wien A. (2018). Implementing social media marketing strategically: an empirical assessment. J. Marke. Manag. 34 732–749. 10.1080/0267257x.2018.1482365 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tan M., Teo T. S. H. (2000). Factors influencing the adoption of Internet banking. J. Assoc. Inform. Syst. 1 :5. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tarsakoo P., Charoensukmongkol P. (2020). Dimensions of social media marketing capabilities and their contribution to business performance of firms in Thailand. J. Asia Bus. Stud. 14 441–461. 10.1108/JABS-07-2018-0204 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thaler R. (1985). Mental accounting and consumer choice. Marke. Sci. 4 199–214. 10.1287/mksc.4.3.199 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang Z., Kim H. G. (2017). Can social media marketing improve customer relationship capabilities and firm performance? Dynamic capability perspective. J. Interact. Marke. 39 15–26. 10.1016/j.intmar.2017.02.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wibowo A., Chen S.-C., Wiangin U., Ma Y., Ruangkanjanases A. (2021). Customer behavior as an outcome of social media marketing: The role of social media marketing activity and customer experience. Sustainability 13 :189. 10.3390/su13010189 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yadav M., Rahman Z. (2017). Measuring consumer perception of social media marketing activities in e-commerce industry: Scale development & validation. Telematics Inform. 34 1294–1307. 10.1016/j.tele.2017.06.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yadav M., Rahman Z. (2018). The influence of social media marketing activities on customer loyalty. Benchmarking 25 3882–3905. 10.1108/BIJ-05-2017-0092 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zollo L., Filieri R., Rialti R., Yoon S. (2020). Unpacking the relationship between social media marketing and brand equity: The mediating role of consumers’ benefits and experience. J. Bus. Res. 117 256–267. 10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.05.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Social Media Adoption, Usage And Impact In Business-To-Business (B2B) Context: A State-Of-The-Art Literature Review
- Open access
- Published: 02 February 2021
- Volume 25 , pages 971–993, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Yogesh K. Dwivedi 1 ,
- Elvira Ismagilova 2 ,
- Nripendra P. Rana 2 &
- Ramakrishnan Raman 3
100k Accesses
68 Citations
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Social media plays an important part in the digital transformation of businesses. This research provides a comprehensive analysis of the use of social media by business-to-business (B2B) companies. The current study focuses on the number of aspects of social media such as the effect of social media, social media tools, social media use, adoption of social media use and its barriers, social media strategies, and measuring the effectiveness of use of social media. This research provides a valuable synthesis of the relevant literature on social media in B2B context by analysing, performing weight analysis and discussing the key findings from existing research on social media. The findings of this study can be used as an informative framework on social media for both, academic and practitioners.
Similar content being viewed by others


The future of social media in marketing
Social media marketing strategy: definition, conceptualization, taxonomy, validation, and future agenda
Social media influencer marketing: foundations, trends, and ways forward
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The Internet has changed social communications and social behaviour, which lead to the development of new forms of communication channels and platforms (Ismagilova et al. 2017 ). Social media plays an important part in the digital transformation of businesses (Kunsman 2018 ). Digital transformation refers to the globally accelerated process of technical adaptation by companies and communities as a result of digitalisation (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ; Westerman et al. 2014 ). Web is developed from a tool used to provide passive information into the collaborative web, which allows and encourages active user engagement and contribution. If before social networks were used to provide the information about a company or brand, nowadays businesses use social media in their marketing aims and strategies to improve consumers’ involvement, relationship with customers and get useful consumers’ insights (Alalwan et al. 2017 ). Business-to-consumer (B2C) companies widely use social media as part of their digital transformation and enjoy its benefits such as an increase in sales, brand awareness, and customer engagement to name a few (Barreda et al. 2015 ; Chatterjee and Kar 2020 ; Harrigan et al. 2020 ; Kamboj et al. 2018 ; Kapoor et al. 2018 ).
From a marketing and sales research perspective, social media is defined as “the technological component of the communication, transaction and relationship building functions of a business which leverages the network of customers and prospects to promote value co-creation” (Andzulis et al. 2012 p.308). Industrial buyers use social media for their purchase as they compare products, research the market and build relationships with salesperson (Itani et al. 2017 ). Social media changed the way how buyers and sellers interact (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ) by enabling open and broad communications and cooperation between them (Rossmann and Stei 2015 ). Social media is an important facilitator of relationships between a company and customers (Agnihotri et al. 2012 ; Tedeschi 2006 ). Customers are more connected to companies, which make them more knowledgable about product selection and more powerful in buyer-seller relationships (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ). Social media also helps companies to increase business exposure, traffic and providing marketplace insight (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Stelzner 2011 ). As a result, the use of social media supports business decision processes and helps to improve companies’ performance (Rossmann and Stei 2015 ).
Due to digitalisation customers are becoming more informed and rely less on traditional selling initiatives (Ancillai et al. 2019 ). Buyers are relying more on digital resources and their buying process more often involves the use of social media. For example, in the research B2B buyer survey, 82% of buyers stated that social media content has a significant impact on the purchase decision (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Minsky and Quesenberry 2016 ). As a result, these changes in consumer behaviour place high pressure on B2B salespeople and traditional sales companies (Ancillai et al. 2019 ). By using evidence from major B2B companies and consultancy report some studies claim that social media can be applied in sales to establish effective dialogues with buyers (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Kovac 2016 ; McKinsey and Company 2015 ).
Now, business-to-business (B2B) companies started using social media as part of their digital transformation. 83% of B2B companies use social media, which makes it the most common marketing tactic (Pulizzi and Handley 2017 ; Sobal 2017 ). More than 70% of B2B companies use at least one of the “big 4” social media sites such as LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook and YouTube. Additionally, 50% of the companies stated that social media has improved their marketing optimization and customer experience, while 25% stated that their revenue went up (Gregorio 2017 ; Sobal 2017 ). Even though B2B companies are benefitting from social media used by marketers, it is argued that research on that area is still in the embryonic stage and future research is needed (Salo 2017 ; Siamagka et al. 2015 ; Juntunen et al. 2020 ; Iannacci et al. 2020 ). There is a limited understanding of how B2B companies need to change to embrace recent technological innovations and how it can lead to business and societal transformation (Chen et al. 2012 ; Loebbecke and Picot 2015 ; Pappas et al. 2018 ).
The topic of social media in the context of B2B companies has started attracting attention from both academics and practitioners. This is evidenced by the growing number of research output within academic journals and conference proceedings. Some studies provided a comprehensive literature review on social media use by B2B companies (Pascucci et al. 2018 ; Salo 2017 ), but focused only on adoption of social media by B2B or social media influence, without providing the whole picture of the use of social media by B2B companies. Thus, this study aims to close this gap in the literature by conducting a comprehensive analysis of the use of social media by B2B companies and discuss its role in the digital transformation of B2B companies. The findings of this study can provide an informative framework for research on social media in the context of B2B companies for academics and practitioners.
The remaining sections of the study are organised as follows. Section 2 offers a brief overview of the methods used to identify relevant studies to be included in this review. Section 3 synthesises the studies identified in the previous section and provides a detailed overview. Section 4 presents weight analysis and its findings. Next section discusses the key aspects of the research, highlights any limitations within existing studies and explores the potential directions for future research. Finally, the paper is concluded in Section 6 .
2 Literature Search Method
The approach utilised in this study aligns with the recommendations in Webster and Watson ( 2002 ). This study used a keyword search-based approach for identifying relevant articles (Dwivedi et al. 2019b ; Ismagilova et al. 2020a ; Ismagilova et al. 2019 ; Jeyaraj and Dwivedi 2020 ; Williams et al. 2015 ). Keywords such as “Advertising” OR “Marketing” OR “Sales” AND TITLE (“Social Media” OR “Web 2.0” OR “Facebook” OR “LinkedIn” OR “Instagram” OR “Twitter” OR “Snapchat” OR “Pinterest” OR “WhatsApp” OR “Social Networking Sites”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (“B2B” OR “B to B” OR “Business to Business” OR “Business 2 Business”) were searched via the Scopus database. Scopus database was chosen to ensure the inclusion of only high quality studies. Use of online databases for conducting a systematic literature review became an emerging culture used by a number of information systems research studies (Dwivedi et al. 2019a ; Gupta et al. 2019 ; Ismagilova et al. 2020b ; Muhammad et al. 2018 ; Rana et al. 2019 ). The search resulted in 80 articles. All studies were processed by the authors in order to ensure relevance and that the research offered a contribution to the social media in the context B2B discussion. The search and review resulted in 70 articles and conference papers that formed the literature review for this study. The selected studies appeared in 33 separate journals and conference proceedings, including journals such as Industrial Marketing Management, Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing and Journal of Business Research.
3 Literature Synthesis
The studies on social media research in the context of B2B companies were divided into the following themes: effect of social media, adoption of social media, social media strategies, social media use, measuring the effectiveness of use of social media, and social media tools (see Table 1 ). The following subsections provide an overview of each theme.
3.1 Effect of Social Media
Some studies focus on the effect of social media for B2B companies, which include customer satisfaction, value creation, intention to buy and sales, building relationships with customers, brand awareness, knowledge creation, perceived corporate credibility, acquiring of new customers, salesperson performance, employee brand engagement, and sustainability (Table 2 ).
3.1.1 Customer Satisfaction
Some studies investigated how the use of social media affected customer satisfaction (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Rossmann and Stei 2015 ). For example, Agnihotri et al. ( 2016 ) investigated how the implementation of social media by B2B salesperson affects consumer satisfaction. Salesperson’s social media use is defined as a “salesperson’s utilization and integration of social media technology to perform his or her job” (Agnihotri et al. 2016 , p.2). The study used data from 111 sales professionals involved in B2B industrial selling to test the proposed hypotheses. It was found that a salesperson’s use of social media will have a positive effect on information communication, which will, in turn, lead to improved customer satisfaction with the salesperson. Also, it was investigated that information communication will be positively related to responsiveness, which impacts customer satisfaction.
Another study by Rossmann and Stei ( 2015 ) looked at the antecedents of social media use, social media use by B2B companies and their effect on customers. By using data from 362 chief information officers of B2B companies the study found the following. Social media usage of sales representative has a positive impact on customer satisfaction. Age has a negative effect on content generation. It seems that older salespeople use social media in passive ways or interacting with the customer rather than creating their own content. It was found that the quality of corporate social media strategy has a positive impact on social media usage in terms of the consumption of information, content generation, and active interaction with customers. Also, the expertise of a salesperson in the area of social media has a positive impact on social media usage.
3.1.2 Value Creation
Research in B2B found that social media can create value for customers and salesperson (Agnihotri et al. 2012 ; Agnihotri et al. 2017 ). Agnihotri et al. ( 2012 ) proposed a theoretical framework to explain the mechanisms through which salespeople’s use of social media operates to create value and propose a strategic approach to social media use to achieve competitive goals. The study draws on the existing literature on relationship marketing, task–technology fit theory, and sales service behavior to sketch a social media strategy for business-to-business sales organizations with relational selling objectives. The proposed framework describes how social media tools can help salespeople perform service behaviors (information sharing, customer service, and trust-building) leading to value creation.
Some researchers investigated the role of the salesperson in the value creation process after closing the sale. By employing salesperson-customer data within a business-to-business context, Agnihotri et al. ( 2017 ) analysed the direct effects of sales-based CRM technology on the post-sale service behaviors: diligence, information communication, inducements, empathy, and sportsmanship. Additionally, the study examines the interactive effects of sales-based CRM technology and social media on these behaviors. The results indicate that sales-based CRM technology has a positive influence on salesperson service behaviors and that salespeople using CRM technology in conjunction with social media are more likely to exhibit higher levels of SSBs than their counterparts with low social media technology use. Data were collected from 162 salespeople from India. SmartPLS was used to analyse the data.
3.1.3 Intention to Buy and Sales
Another group of studies investigated the effect of social media on the level of sales and consumer purchase intention (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Salo 2017 ; Hsiao et al. 2020 ; Mahrous 2013 ). For example, Itani et al. ( 2017 ) used the theory of reasoned actions to develop a model that tests the factors affecting the use of social media by salesperson and its impact. By collecting data from 120 salespersons from different industries and using SmartPLS to analyse the data, it was found that attitude towards social media usefulness did not affect the use of social media. It was found that social media use positively affects competitive intelligence collection, adaptive selling behaviour, which in turn influenced sales performance. Another study by Ancillai et al. ( 2019 ) used in-depth interviews with social selling professionals. The findings suggest that the use of social media improves not only the level of sales but also affects relationship and customer performance (trust, customer satisfaction, customer referrals); and organisational performance (organisational selling performance and brand performance).
It was investigated that social media has a positive effect on the intention to purchase (Hsiao et al. 2020 ; Mahrous 2013 ). For instance, Mahrous ( 2013 ) by reviewing the literature on B2B and B2C companies concluded that social media has a significant influence on consumer buying behaviour.
3.1.4 Customer Relationships
Another group of studies focused on the effect of social media on customer relationships (Bhattacharjya and Ellison 2015 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gruner and Power 2018 ; Hollebeek 2019 ; Iankova et al. 2018 ; Jussila et al. 2011 ; Kho 2008 ; Niedermeier et al. 2016 ; Ogilvie et al. 2018 ). For example, Bhattacharjya and Ellison ( 2015 ) investigated the way companies build relationships with customers by using responsive customer relationship management. The study analysed customer relationship management activities from Twitter account of a Canadian company Shopify (B2B service provider). The company uses Twitter to engage with small business customers, develops and consumers. Jussila et al. ( 2011 ), by reviewing the literature, found that social media leads to increased customer focus and understanding, increased level of customer service and decreased time-to-market.
Gáti et al. ( 2018 ) focused their research efforts on social media use in customer relationship performance, particularly in customer relations. The study investigated the adoption and impact of social media by salespeople of B2B companies. By using data of 112 salespeople from several industries the study found that the intensity of technology use positively affects attitude towards social media, which positively affects social media use. Intensive technology use in turn positively affects customer relationship performance (customer retention). PLS-SEM was applied for analysis.
Another study by Gruner and Power ( 2018 ) investigated the effectiveness of the use of multiple social media platforms in communications with customers. By using data from 208 large Australian organisations, the paper explores how companies’ investment in one form of social media impacts activity on another form of social media. A regression analysis was performed to analyse the data. It was found that widespread activities on LinkedIn, Twitter and YouTube have a negative effect on a company’s marketing activity on Facebook. Thus, having it is more effective for the company to focus on a specific social media platform in forming successful inter-organisational relationships with customers.
Hollebeek ( 2019 ) proposed an integrative S-D logic/resource-based view (RBV) model of customer engagement. The proposed model considers business customer actors and resources in driving business customer resource integration, business customer resource integration effectiveness and business customer resource integration efficiency, which are antecedents of business customer engagement. Business customer engagement, in turn, results in business customer co-creation and relationship productivity.
Niedermeier et al. ( 2016 ) investigated the use of social media among salespeople in the pharmaceutical industry in China. Also, the study investigated the impact of social media on building culturally specific Guanxi relationships-it involves the exchange of factors to build trust and connection for business purpose. By using in-depth interviews with 3 sales managers and a survey of 42 pharmaceutical sales representatives that study found that WeChat is the most common social media platform used by businesses. Also, it was found to be an important tool in building Guanxi. Future studies should focus on other industries and other types of cultural features in doing business.
Ogilvie et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the effect of social media technologies on customer relationship performance and objective sales performance by using two empirical studies conducted in the United States. The first study used 375 salespeople from 1200 B2B companies. The second study used 181 respondents from the energy solution company. It was found that social media significantly affects salesperson product information communication, diligence, product knowledge and adaptability, which in turn affect customer relationship performance. It was also found that the use of social media technologies without training on technology will not lead to good results. Thus, the results propose that companies should allocate the resources required for the proper implementation of social media strategies. Future research should examine how the personality traits of a salesperson can moderate the implementation of social media technologies.
While most of the studies focused on a single country, Iankova et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the perceived effectiveness of social media by different types of businesses in two countries. By using 449 respondents from the US and the UK businesses, it was found that social media is potentially less important, at the present time, for managing ongoing relationships in B2B organizations than for B2C, Mixed or B2B2C organizations. All types of businesses ascribe similar importance to social media for acquisition-related activities. Also it was found that B2B organizations see social media as a less effective communication channel, and to have less potential as a channel for the business.
3.1.5 Brand Awareness
Some researchers argued that social media can influence brand awareness (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Hsiao et al. 2020 ). For instance, Hsiao et al. ( 2020 ) investigated the effect of social media in the fashion industry. By collecting 1395 posts from lookbook.nu and employing regression analysis it was found that the inclusion of national brand and private fashion brands in the post increased the level of popularity which leads to purchasing interest and brand awareness.
3.1.6 Knowledge Creation
Multiple types of collaborative web tools can help and significantly increase the collaboration and the use of the distributed knowledge inside and outside of the company (McAfee 2006 ). Kärkkäinen et al. ( 2011 ) by analysing previous literature on social media proposed that social media use has a positive effect on sharing and creation of customer information and knowledge in the case of B2B companies.
3.1.7 Corporate Credibility
Another study by Kho ( 2008 ) states the advantages of using social media by B2B companies, which include faster and more personalised communications between customer and vendor, which can improve corporate credibility and strengthen the relationships. Thanks to social media companies can provide more detailed information about their products and services. Kho ( 2008 ) also mentions that customer forums and blog comments in the B2B environment should be carefully monitored in order to make sure that inappropriate discussions are taken offline and negative eWOM communications should be addressed in a timely manner.
3.1.8 Acquiring New Customers
Meire et al. ( 2017 ) investigated the impact of social media on acquiring B2B customers. By using commercially purchased prospecting data, website data and Facebook data from beverage companies the study conducted an experiment and found that social media us an effective tool in acquiring B2B customers. Future work might assess the added value of social media pages for profitability prediction instead of prospect conversion. When a longer timeframe becomes available (e.g., after one year), the profitability of the converted prospects can be assessed.
3.1.9 Salesperson Performance
Moncrief et al. ( 2015 ) investigated the impact of social media technologies on the role of salesperson position. It was found that social media affects sales management functions (supervision, selection, training, compensation, and deployment) and salesperson performance (role, skill, and motivation). Another study by Rodriguez et al. ( 2012 ) examines the effect of social media on B2B sales performance by using social capital theory and collecting data from 1699 B2B salespeople from over 25 different industries. By employing SEM AMOS, the study found that social media usage has a positive significant relationship with selling companies’ ability to create opportunities and manage relationships. The study also found that social media usage has a positive and significant relationship with sales performance (based on relational measurers of sales that focus on behaviours that strengthen the relationship between buyers and sellers), but not with outcome-based sales performance (reflected by quota achievement, growth in average billing size, and overall revenue gain).
3.1.10 Employee Brand Management
The study by Pitt et al. ( 2018 ) focuses on employee engagement with B2B companies on social media. By using results from Glassdoor (2315 five-star and 1983 one-star reviews for the highest-ranked firms, and 1013 five star and 1025 one-star reviews for lowest ranked firms) on employee brand engagement on social media, two key drivers of employee brand engagement by using the content analysis tool DICTION were identified-optimism and commonality. Individuals working in top-ranked companies expressed a higher level of optimism and commonality in comparison with individuals working in low-ranked companies. As a result, a 2 × 2 matrix was constructed which can help managers to choose strategies in order to increase and improve employee brand engagement. Another study by Pitt et al. ( 2017 ) focused on employee engagement of B2B companies on social media. By using a conceptual framework based on a theory of word choice and verbal tone and 6300 reviews collected from Glassdoor and analysed using DICTION. The study found that employees of highly ranked B2B companies are more positive about their employer brand and talk more optimistically about these brands. For low ranked B2B companies it was found that employees express a greater level of activity, certainty, and realism. Also, it was found that they used more aggressive language.
3.1.11 Sustainability
Sustainability refers to the strategy that helps a business “to meet its current requirements without compromising its ability to meet future needs” (World Commission Report on Environment and Development 1987 , p 41). Two studies out of 70 focused on the role of social media for B2B sustainability (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ; Kasper et al. 2015 ). For example, Sivarajah et al. ( 2019 ) argued that big data and social media within a participatory web environment to enable B2B organisations to become profitable and remain sustainable through strategic operations and marketing related business activities.
Another study by Kasper et al. ( 2015 ) proposed the Social Media Matrix which helps companies to decide which social media activities to execute based on their corporate and communication goals. The matrix includes three parts. The first part is focusing on social media goals and task areas, which were identified and matched. The second part consists of five types of social media activities (content, interaction/dialog, listening and analysing, application and networking). The third part provides a structure to assess the suitability of each activity type on each social media platform for each goal. The matrix was successfully tested by assessing the German B2B sector by using expert interviews with practitioners.
Based on the reviewed studies, it can be seen that if used appropriately social media have positive effect on B2B companies before and after sales, such as customer satisfaction, value creation, intention to buy and sales, customer relationships, brand awareness, knowledge creation, corporate credibility, acquiring new customers, salesperson performance, employee brand management, and sustainability. However, limited research is done on the negative effect of social media on b2b companies.
3.2 Adoption of Social Media
Some scholars investigated factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies (Buratti et al. 2018 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gazal et al. 2016 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Kumar and Möller 2018 ; Lacka and Chong 2016 ). For instance, Lacka and Chong ( 2016 ) investigated factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies from different industries in China. The study collected the data from 181 respondents and used the technology acceptance model with Nielsen’s model of attributes of system acceptability as a theoretical framework. By using SEM AMOS for analysis the study found that perceived usability, perceived usefulness, and perceived utility positively affect adoption and use of social media by B2B marketing professionals. The usefulness is subject to the assessment of whether social media sites are suitable means through which marketing activities can be conducted. The ability to use social media sites for B2B marketing purposes, in turn, is due to those sites learnability and memorability attributes.
Another study by Müller et al. ( 2018 ) investigated factors affecting the usage of social media. By using survey data from 100 Polish and 39 German sensor suppliers, it was found that buying frequency, the function of a buyer, the industry sector and the country does not affect the usage of social media in the context of sensor technology from Poland and Germany. The study used correlation analysis and ANOVA.
Lashgari et al. ( 2018 ) studied the adoption and use of social media by using face-to-face interviews with key managers of four multinational corporations and observations from companies’ websites and social media platforms. It was found that that the elements essential in forming the B2B firm’s social media adoption strategies are content (depth and diversity), corresponding social media platform, the structure of social media channels, the role of moderators, information accessibility approaches (public vs. gated-content), and online communities. These elements are customized to the goals and target group the firm sets to pursue. Similarly, integration of social media into other promotional channels can fall under an ad-hoc or continuous approach depending on the scope and the breadth of the communication plan, derived from the goal.
Similar to Lashgari et al. ( 2018 ), Shaltoni ( 2017 ) used data from managers. The study applied technology organisational environmental framework and diffusion of innovations to investigate factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies. By using data from marketing managers or business owners of 480 SMEs, the study found that perceived relative advance, perceive compatibility, organizational innovativeness, competitor pressure, and customer pressure influence the adoption of social media by B2B companies. The findings also suggest that many decision-makers in B2B companies think that Internet marketing is not beneficial, as it is not compatible with the nature of B2B markets.
Buratti et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the adoption of social media by tanker shipping companies and ocean carriers. By using data from 60 companies the following was found. LinkedIn is the most used tool, with a 93.3% adoption rate. Firm size emerges as a predictor of Twitter’s adoption: big companies unveil a higher attitude to use it. Finally, the country of origin is not a strong influential factor in the adoption rate. Nonetheless, Asian firms clearly show a lower attitude to join SM tools such as Facebook (70%) and LinkedIn (86.7%), probably also due to governmental web restrictions imposed in China. External dimensions such as the core business, the firm size, the geographic area of origin, etc., seem to affect network wideness. Firm size, also, discriminates the capacity of firms to build relational networks. Bigger firms create networks larger than small firms do. Looking at geographical dimensions, Asian firms confirm to be far less active on SM respect to European and North American firms. Finally, the study analyzed the format of the contents disclosed by sample firms, observing quite limited use of photos and videos: in the sample industries, informational contents seem more appropriate for activating a dialogue with stakeholders and communication still appears formulated in a very traditional manner. Preliminary findings suggest that companies operating in conservative B2B services pursue different strategic approaches toward SMM and develop ad hoc communication tactics. Nonetheless, to be successful in managing SM tools, a high degree of commitment and a clear vision concerning the role of SM within communication and marketing strategy is necessary.
Gazal et al. ( 2016 ) investigated the adoption and measuring of the effectiveness of social media in the context of the US forest industry by using organisational-level adoption framework and TAM. By using data from 166 companies and performing regression analysis, the following results were received. Years in business, new sales revenue, product type, amount of available information on a company website, perceived importance of e-commerce and perceived ease of use of social media significantly affected social media use. Also, it was found that companies’ strategies and internal resources and capabilities and influence a company’s decision to adopt social media. Also, it was found that 94 of respondents do not measure the ROI from social media use. The reason is that the use of social media in marketing is relatively new and companies do not possess the knowledge of measuring ROI from the use of social media. Companies mostly use quantitative metrics (number of site visits, number of social network friends, number of comments and profile views) and qualitative metrics (growth of relationships with the key audience, audience participation, moving from monologue to dialogue with consumers. Facebook was found to be the most effective social media platform reported by the US forest industry.
The study by Kumar and Möller ( 2018 ) investigated the role of social media for B2B companies in their recruitment practices. By using data from international B2B company with headquarter in Helsinki, Finland comprised of 139 respondents it was found that brand familiarity encourages them to adopt social media platforms for a job search; however, the effect of the persuasiveness of recruitment messages on users’ adoption of social media platforms for their job search behavior is negative. The study used correlation analysis and descriptive analysis to analyse the data.
Nunan et al. ( 2018 ) identified areas for future research such as patterns of social media adoption, the role of social media platforms within the sales process, B2B consumer engagement and social media, modeling the ROI of social media, and the risks of social media within B2B sales relationships.
The study by Pascucci et al. ( 2018 ) conducted a systematic literature review on antecedents affecting the adoption and use of social media by B2B companies. By reviewing 29 studies published in academic journal and conferences from 2001 to 2017, the study identified external (pressure from customers, competitors, availability of external information about social media) and internal factors (personal characteristics -managers age, individual commitment, perceptions of social media-perceived ease of use, perceived usefulness, perceived utility), which can affect adoption of social media.
The study by Siamagka et al. ( 2015 ) aims to investigate factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B organisations. The conceptual model was based on the technology acceptance model and the resource-based theory. AMOS software and Structural equation modelling were employed to test the proposed hypotheses. By using a sample of 105 UK companies, the study found that perceived usefulness of social media is influenced by image, perceived ease of use and perceived barriers. Also, it was found that social media adoption is significantly determined by organisational innovativeness and perceived usefulness. Additionally, the study tested the moderating role of organisational innovativeness and found that it does not affect the adoption of social media by B2B organisations. The study also identified that perceived barriers to SNS (uncertainty about how to use SNS to achieve objectives, employee’s lack of knowledge about SNS, high cost of investment needed to adopt the technology) have a negative impact on perceived usefulness of social media by B2B organisations. The study also used nine in-depth interviews with B2B senior managers and social media specialists about adoption of social media by B2B. It was found that perceived pressure from stakeholders influences B2B organisations’ adoption intention of social media. Future research should test it by using quantitative methods.
While most of the studies focused on the antecedents of social media adoption by B2B companies, Michaelidou et al. ( 2011 ) investigated the usage, perceived barriers and measuring the effectiveness of social media. By using data from 92 SMEs the study found that over a quarter of B2B SMEs in the UK are currently using SNS to achieve brand objectives, the most popular of which is to attract new customers. The barriers that prevent SMEs from using social media to support their brands were lack of staff familiarity and technical skills. Innovativeness of a company determined the adoption of social media. It was found that most of the companies do not evaluate the effectiveness of their SNS in supporting their brand. The most popular measures were the number of users joining the groups/discussion and the number of comments made. The findings showed that the size of the company does not influence the usage of social media for small and medium-sized companies. Future research should investigate the usage of social media in large companies and determine if the size can have and influence on the use. The benefits of using social media include increasing awareness and communicating the brand online. B2B companies can employ social media to create customer value in the form of interacting with customers, as well as building and fostering customer relationships. Future research should investigate the reasons why most of the users do not assess the effectiveness of their SNS. Future research should also investigate how the attitude towards technology can influence the adoption of social media.
Based on the reviewed studies it can be seen that the main factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies are perceived usability, technical skills of employees, pressure from stakeholders, perceived usefulness and innovativeness.
3.3 Social Media Strategies
Another group of studies investigated types of strategies B2B companies apply (Cawsey and Rowley 2016 ; Huotari et al. 2015 ; Kasper et al. 2015 ; McShane et al. 2019 ; Mudambi et al. 2019 ; Swani et al. 2013 ; Swani et al. 2014 ; Swani et al. 2017 ; Watt 2010 ). For example, Cawsey and Rowley ( 2016 ) focused on the social media strategies of B2B companies. By conducting semi-structured interviews with marketing professionals from France, Ireland, the UK and the USA it was found that enhancing brand image, extending brand awareness and facilitating customer engagement were considered the most common social media objective. The study proposed the B2B social media strategy framework, which includes six components of a social media strategy: 1) monitoring and listening 2) empowering and engaging employees 3) creating compelling content 4) stimulating eWOM 5) evaluating and selecting channels 6) enhancing brand presence through integrating social media.
Chirumalla et al. ( 2018 ) focused on the social media engagement strategies of manufacturing companies. By using semi-structured interviews (36), observations (4), focus group meetings (6), and documentation, the study developed the process of social media adoption through a three-phase engagement strategy which includes coordination, cooperation, and co-production.
McShane et al. ( 2019 ) proposed social media strategies to influence online users’ engagement with B2B companies. Taking into consideration fluency lens the study analysed Twitter feeds of top 50 social B2B brands to examine the influence of hashtags, text difficulty embedded media and message timing on user engagement, which was evaluated in terms of likes and retweets. It was found that hashtags and text difficulty are connected to lower levels of engagement while embedded media such as images and videos improve the level of engagement.
Swani et al. ( 2014 ) investigate the use of Twitter by B2B and B2C companies and predict factors that influence message strategies. The study conducted a longitudinal content analysis by collecting 7000 tweets from Fortune 500 companies. It was found that B2B and B2C companies used different message appeals, cues, links and hashtags. B2B companies tend to use more emotional than functional appeals. It was found that B2B and B2C companies do not use hard-sell message strategies.
Another study by Swani et al. ( 2013 ) aimed to investigate message strategies that can help in promoting eWOM activity for B2B companies. By applying content analysis and hierarchical linear modeling the study analysed 1143 wall post messages from 193 fortune 500 Facebook accounts. The study found that B2B account posts will be more effective if they include corporate brand names and avoid hard sell or explicitly commercial statement. Also, companies should use emotional sentiment in Facebook posts.
Huotari et al. ( 2015 ) aimed to investigate how B2B marketers can influence content creation in social media. By conducting four face-to-face interviews with B2B marketers, it was found that a B2B company can influence content creation in social media directly by adding new content, participating in a discussion and removing content through corporate user accounts and controlling employees social media behaviour. Also, it can influence it indirectly by training employees to create desired content and perfuming marketing activities that influence other users to create content that is favorable for the company.
Most of the studies investigated the strategies and content of social media communications of B2B companies. However, the limited number of studies investigated the importance of CEO engagement on social media in the company’s strategies. Mudambi et al. ( 2019 ) emphasise the importance of the CEO of B2B companies to be present and active on social media. The study discusses the advantages of social media presence for the CEO and how it will benefit the company. For example, one of the benefits for the CEO can be perceived as being more trustworthy and effective than non-social CEOs, which will benefit the company in increased customer trust. Mudambi et al. ( 2019 ) also discussed the platforms the CEO should use and posting frequencies depending on the content of the post.
From the above review of the studies, it can be seen that B2B companies social media strategies include enhancing brand image, extending brand awareness and facilitating customer engagement. Companies use various message strategies, such as using emotional appeal, use of brand names, and use of hashtags. Majority of the companies avoid hard sell or explicitly commercial statement.
3.4 Social Media Use
Studies investigated the way how companies used social media and factors affecting the use of social media by B2B (Andersson et al. 2013 ; Bernard 2016 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ; Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü 2018 ; Dyck 2010 ; Guesalaga 2016 ; Habibi et al. 2015 ). For example, Vasudevan and Kumar ( 2018 ) investigated how B2B companies use social media by analysing 325 brand posts of Canon India, Epson India, and HP India on Linkedin, Facebook, and Twitter. By employing content analysis the study found that most of the posts had a combination of text and message. More than 50% of the posts were about product or brand-centric. The study argued that likes proved to be an unreliable measure of engagement, while shares were considered a more reliable metric. The reason was that likes had high spikes when brand posts were boosted during promotional activities.
Andersson and Wikström ( 2017 ) used case studies of three B2B companies to investigate reasons for using social media. It was found that companies use social media to enhance customer relationships, support sales and build their brands. Also, social media is used as a recruiting tool, a seeking tool, and a product information and service tool.
Bell and Shirzad ( 2013 ) aimed to conduct social media use analysis in the context of pharmaceutical companies. The study analysed 54,365 tweets from the top five pharmaceutical companies. The study analysed the popular time slots, the average number of positive and negative tweets and its content by using Nvivo9.
Bernard ( 2016 ) aims to examine how chief marketing officers use social media. By using case studies from IBM experience with social media it was found that B2B CMO’s are not ready to make use of social media. It was proposed that social media can be used for after-sales service, getting sales leads, engaging with key influencers, building the company’s reputation and enhancing the industry status of key individuals. B2B firms need to exploit the capabilities of processing massive amounts of data to get the most from social media.
Bolat et al. ( 2016 ) explore how companies apply mobile social media. By employing a grounded theory approach to analyse interviews from 26 B2B company representatives from UK advertising and marketing sector companies. It was found that companies use social media for branding, sensing market, managing relationships, and developing content.
Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü ( 2018 ) investigated how social media usage influence stakeholder engagement focusing on the corporate Facebook page of 30 3PLs companies. In total 1532 Facebook posts were analysed. It was found that the number of followers, post sharing frequency, negatively affect stakeholder engagement. It was found that content including photos facilitates more stakeholder engagement (likes, comment, share) in comparison with other forms. Vivid posts and special day celebration posts strengthen relationships with stakeholders.
Dyck ( 2010 ) discussed the advantages of using social media for the device industry. Social media can be used for product innovation and development, to build a team and collaborate globally. Also, there is an opportunity to connect with all of the stakeholders needed in order to deliver the device to the market. Additionally, it provides to receive feedback from customers (doctors, hospitals) in real-time.
The study by Guesalaga ( 2016 ) draws on interactional psychology theory to propose and test a model of usage of social media in sales, analysing individual, organizational, and customer-related factors. It was found that organizational competence and commitment to social media are key determinants of social media usage in sales, as well as individual commitment. Customer engagement with social media also predicts social media usage in sales, both directly and (mostly) through the individual and organizational factors analysed, especially organizational competence and commitment. Finally, the study found evidence of synergistic effects between individual competence and commitment, which is not found at the organizational level. The data obtained by surveying 220 sales executives in the United States were analysed using regression analysis.
Habibi et al. ( 2015 ) proposed a conceptual model for the implementation of social media by B2B companies. Based on existing B2B marketing, social media and organisational orientational literature the study proposed that four components of electronic market orientation (philosophical, initiation, implementation and adoption) address different implementation issues faced in implementing social media.
Katona and Sarvary ( 2014 ) presented a case of using social media by Maersk-the largest container shipping company in the world. The case provided details on the program launch and the integration strategy which focused on integrating the largest independent social media operation into the company’s broader marketing efforts.
Moore et al. ( 2013 ) provided insights into the understanding of the use of social media by salespersons. 395 salespeople in B2B and B2C markets, utilization of relationship-oriented social media applications are presented and examined. Overall, findings show that B2B practitioners tend to use media targeted at professionals whereas their B2C counterparts tend to utilize more sites targeted to the general public for engaging in one-on-one dialogue with their customers. Moreover, B2B professionals tend to use relationship-oriented social media technologies more than B2C professionals for the purpose of prospecting, handling objections, and after-sale follow-up.
Moore et al. ( 2015 ) investigated the use of social media between B2B and B2C salespeople. By using survey data from 395 sales professionals from different industries they found that B2B sales managers use social selling tools significantly more frequently than B2C managers and B2C sales representatives while conducting sales presentations. Also, it was found that B2B managers used social selling tools significantly more frequently than all sales representatives while closing sales.
Müller et al. ( 2013 ) investigated social media use in the German automotive market. By using online analysis of 10 most popular car manufacturers online social networks and surveys of six manufacturers, 42 car dealers, 199 buyers the study found that social media communication relations are widely established between manufacturers and (prospective) buyers and only partially established between car dealers and prospective buyers. In contrast to that, on the B2B side, social media communication is rarely used. Social Online Networks (SONs) are the most popular social media channels employed by businesses. Manufacturers and car dealers focus their social media engagement, especially on Facebook. From the perspective of prospective buyers, however, forums are the most important source of information.
Sułkowski and Kaczorowska-Spychalska ( 2016 ) investigated the adoption of social media by companies in the Polish textile-clothing industry. By interviewing seven companies representatives of small and medium-sized enterprises the study found that companies started implementing social media activities in their marketing activities.
Vukanovic ( 2013 ) by reviewing previous literature on social media outlined advantages of using social media for B2B companies, which include: increase customer loyalty and trust, building and improving corporate reputation, facilitating open communications, improvement in customer engagement to name a few.
Keinänen and Kuivalainen ( 2015 ) investigated factors affecting the use of social media by B2B customers by conducting an online survey among 82 key customer accounts of an information technology service company. Partial least squares path modelling was used to analysed the proposed hypotheses. It was found that social media private use, colleague support for using SM, age, job position affected the use of social media by B2B customers. The study also found that corporate culture, gender, easiness to use, and perception of usability did not affect the use of social media by B2B customers.
By using interviews and survey social media research found that mostly B2B companies use social media to enhance customer relationships, support sales, build their brands, sense market, manage relationships, and develop content. Additionally, some companies use it social media as a recruitment tool. The main difference between B2B and B2C was that B2B sales managers use social selling tools significantly more frequently than B2C managers.
3.5 Measuring the Effectiveness of Social Media
It is important for a business to be able to measure the effectiveness of social media by calculating return on investment (ROI). ROI is the relationship between profit and the investment that generate that profit. Some studies focused on the ways B2B companies can measure ROI and the challenges they face (Gazal et al. 2016 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ; Vasudevan and Kumar 2018 ). For example, Gazal et al. ( 2016 ) investigated the adoption and measuring of the effectiveness of social media in the context of the US forest industry by using organisational-level adoption framework and TAM. By using data from 166 companies it was found that 94% of respondents do not measure the ROI from social media use. The reason is that the use of social media in marketing is relatively new and companies do not possess the knowledge of measuring ROI from the use of social media. Companies mostly use quantitative metrics (number of site visits, number of social network friends, number of comments and profile views) and qualitative metrics (growth of relationships with the key audience, audience participation, moving from monologue to dialogue with consumers).
Another study by Michaelidou et al. ( 2011 ) found that most of the companies do not evaluate the effectiveness of their SNS in supporting their brand. The most popular measures were the number of users joining the groups/discussion and the number of comments made.
Vasudevan and Kumar ( 2018 ) investigated how B2B companies use social media and measure ROI from social media by analysing 325 brand posts of Canon India, Epson India, and HP India on Linkedin, Facebook, and Twitter. By employing content analysis the study found that most of the post has a combination of text and message. More than 50% of the posts were about product or brand-centric. The study argued that likes proved to be an unreliable measure of engagement, while shares were considered a more reliable metric. The reason was that likes had high spikes when brand posts were boosted during promotional activities. Future research should conduct longitudinal studies.
By reviewing the above studies, it can be concluded that companies still struggle to find ways of measuring ROI and applying correct metrics. By gaining knowledge in how to measure ROI from social media activities, B2B companies will be able to produce valuable insights leading to better marketing strategies (Lal et al. 2020 ).
3.6 Social Media Tools
Some studies proposed tools that could be employed by companies to advance their use of social media. For example, Mehmet and Clarke ( 2016 ) proposed a social semiotic multimodal (SSMM) framework that improved the analysis of social media communications. This framework employs multimodal extensions to systemic functional linguistics enabling it to be applying to analysing non-language as well as language constituents of social media messages. Furthermore, the framework also utilises expansion theory to identify, categorise and analyse various marketing communication resources associated with marketing messages and also to reveal how conversations are chained together to form extended online marketing conversations. This semantic approach is exemplified using a Fairtrade Australia B2B case study demonstrating how marketing conversations can be mapped and analysed. The framework emphasises the importance of acknowledging the impact of all stakeholders, particularly messages that may distract or confuse the original purpose of the conversation.
Yang et al. ( 2012 ) proposed the temporal analysis technique to identify user relationships on social media platforms. The experiment was conducted by using data from Digg.com . The results showed that the proposed techniques achieved substantially higher recall but not very good at precision. This technique will help companies to identify their future consumers based on their user relationships.
Based on the literature review, it can be seen that B2B companies can benefit by using the discussed tools. However, it is important to consider that employee should have some technical skills and knowledge to use these tools successfully. As a result, companies will need to invest some resources in staff training.
4 Weight Analysis
Weight analysis enables scrutiny of the predictive power of independent variables in studied relationships and the degree of effectiveness of the relationships (Jeyaraj et al. 2006 ; Rana et al. 2015 ; Ismagilova et al. 2020a ). The results of weight analysis are depicted in Table 3 providing information about an independent variable, dependent variable, number of significant relationships, number of non-significant relationships, the total number of relationships and weight. To perform weight analysis, the number of significant relationships was divided by the total number of analysed relationships between the independent variable and the dependent variable (Jeyaraj et al. 2006 ; Rana et al. 2015 ). For example, the weight for the relationship between attitude towards social media and social media is calculated by dividing ‘1’ (the number of significant relationships) by ‘2’ (the total number of relationships) which equals 0.5.
A predictor is defined as well-utilised if it was examined five or more times, otherwise, it is defined as experimental. It can be seen from Table 3 that all relationships were examined less than five times. Thus all studied predictors are experimental. The predictor is defined as promising when it has been examined less than five times by existing studies but has a weight equal to ‘1’ (Jeyaraj et al. 2006 ). From the predictors affecting the adoption of social media, it can be seen that two are promising, technical skills of employees and pressure from stakeholders. Social media usage is a promising predictor for acquiring new customers, sales, stakeholder engagement and customer satisfaction. Perceived ease of use and age of salesperson are promising predictors of social media usage. Even though this relationship was found to be significant every time it was examined, it is suggested that this variable, which can also be referred to as experimental, will need to be further tested in order to qualify as the best predictor. Another predictor, average rating of product/service, was examined less than five times with a weight equal to 0.75, thus it is considered as an experimental predictor.
Figure 1 shows the diagrammatic representation of the factors affecting different relationships in B2B social media with their corresponding weights, based on the results of weight analysis. The findings suggest that promising predictors should be included in further empirical studies to determine their overall performance.
Diagrammatic representation of results of weight analysis. Note: experimental predictors
It can be seen from Fig. 1 that social media usage is affected by internal (e.g. attitude towards social media, technical skills of employees) and external factors (e.g. pressure from stakeholders) of the company. Also, the figure depicts the effect of social media on the business (e.g. sales) and society (e.g. customer satisfaction).
5 Discussion
In reviewing the publications gathered for this paper, the following themes were identified. Some studies investigated the effect of social media use by B2B companies. By using mostly survey to collect the data from salespeople and managers, the studies found that social media has a positive effect on number of outcomes important for the business such as customer satisfaction, value creation, intention to buy and sales, customer relationships, brand awareness, knowledge creation, corporate credibility, acquiring new customers, salespersons performance, employee brand management, and sustainability. Most of the outcomes are similar to the research on social media in the context of B2C companies. However, some of the outcomes are unique for B2B context (e.g. employee brand management, company credibility). Just recently, studies started investigating the impact of the use of social media on sustainability.
Another group of studies looked at the adoption of social media by B2B companies (Buratti et al. 2018 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gazal et al. 2016 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Kumar and Möller 2018 ). The studies investigated it mostly from the perspectives of salespersons and identify some of the key factors which affect the adoption, such as innovativeness, technical skills of employees, pressure from stakeholders, perceived usefulness, and perceived usability. As these factors are derived mostly from surveys conducted with salespersons findings can be different for other individuals working in the organisation. This it is important to conduct studies that will examine factors affecting the adoption of social media across the entire organisation, in different departments. Using social media as part of the digital transformation is much bigger than sales and marketing, it encompasses the entire company. Additionally, most of the studies were cross-sectional, which limits the understanding of the adoption of social media by B2B over time depending on the outcomes and environment (e.g. competitors using social media).
Some studies looked at social media strategies of B2B companies (Cawsey and Rowley 2016 ; Huotari et al. 2015 ; Kasper et al. 2015 ; McShane et al. 2019 ; Mudambi et al. 2019 ). By employing interviews with companies’ managers and analysing its social media platforms (e.g. Twitter) it was found that most of the companies follow the following strategies: 1) monitoring and listening 2) empowering and engaging employees 3) creating compelling content 4) stimulating eWOM 5) evaluating and selecting channels 6) enhancing brand presence through integrating social media (Cawsey and Rowley 2016 ). Some studies investigated the difference between social media strategies of B2B and B2C companies. For example, a study by Swani et al. ( 2017 ) focused on effective social media strategies. By applying psychological motivation theory the study examined the key differences in B2B and B2C social media message strategies in terms of branding, message appeals, selling, and information search. The study used Facebook posts on brand pages of 280 Fortune companies. In total, 1467 posts were analysed. By using Bayesian models, the results showed that the inclusion of corporate brand names, functional and emotional appeals and information search cues increases the popularity of B2B messages in comparison with B2C messages. Also, it was found that readers of B2B content show a higher message liking rate and lower message commenting rate in comparison with readers of B2C messages.
The next group of studies looked at social media use by B2B companies (Andersson et al. 2013 ; Bernard 2016 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ; Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü 2018 ; Dyck 2010 ; Guesalaga 2016 ; Habibi et al. 2015 ). B2B companies use social media for enhancing and managing customer relationships (Andersson and Wikström 2017 ; Bolat et al. ( 2016 ); branding (Andersson and Wikström 2017 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ), sensing market (Bolat et al. 2016 ) and co-production (Chirumalla et al. 2018 ). Additionally, it was mentioned that some of the B2B companies use social media as a recruiting tool, and tool which helps to collaborate globally (Andersson and Wikström 2017 ; Dyck 2010 ).
It is important for companies to not only use social media to achieve positive business outcomes but also it is important to measure their achievements. As a result, some of the studies focused on the measuring effectiveness of social media (Gazal et al. 2016 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ; Vasudevan and Kumar 2018 ). Surprisingly, it was found that not so many companies measure ROI from social media (Gazal et al. 2016 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ). The ones who do it mostly use quantitative metrics (number of site visits, number of social network friends, number of comments and profile views) and qualitative metrics (growth of relationships with key audience, audience participation, moving from monologue to dialogue with consumers) (Gazal et al. 2016 ). Some future studies should investigate how ROI influences the strategy of B2B companies over period of time.
The last group of studies focused on social media tools used by B2B companies (Keinänen and Kuivalainen 2015 ; Mehmet and Clarke 2016 ; Yang et al. 2012 ). By using number of social media tools (Social Semiotic Multimodal) companies are able to improve their analysis of social media communications and identify their future consumers based on their user relationships. Studies investigating barriers and factors adoption of various social media tools by B2B companies are needed.
After reviewing studies on b2B social media, weight analysis was performed. Based on the results of weight analysis the conceptual model for future studies was proposed (Fig. 2 ). It is important to note that a limited number of studies focused and empirically tested factors affecting the adoption, use, and effect of social media. As a result, identified factors were considered as experimental (examined less than five times). It is too early to label these experimental predictors as worst or best, thus their further investigation is encouraged.
Social media impact on digital transformation and sustainable societies
Additionally, our review of the literature on B2B social media identified dominant research methods used by scholars. Qualitative and quantitative techniques were used by most of these studies. Closer analysis of 70 publications reviewed in this study revealed the multiple techniques applied for gathering data. Quantitative methods used in the studies mostly used surveys (see Table 4 ).
The data was mostly gathered from salespersons, managers and data from social media platforms (e.g. Twitter, Facebook). Just a limited number of studies employed consumer reported data (see Table 5 ).
On the other hand, publications using qualitative methods mainly used interviews and web scraping for the collection of the required data. To analyse the data studies used a variety of techniques including SEM, regression analysis and content analysis being one of the most used (see Table 6 ).
5.1 Digital Transformation and Sustainability Model
Based on the conducted literature review and adapting the model by Pappas et al. ( 2018 ) Fig. 2 presents the digital transformation and sustainability model in the context of B2B companies, which conceptualise the social media ecosystems, and the factors that need to collaborate to enable the use of social media towards the achievement of digital transformation and the creation of sustainable societies. The model comprises of social media stakeholders, the use of social media by B2B companies, and effect of social media on business and society.
5.1.1 Social Media Stakeholders
Building on the discussion and model provided by Pappas et al. ( 2018 ), this paper posits that the social media ecosystem comprises of the data stakeholders (company, society), who engage on social media (posting, reading, using information from social media). The use of social media by different stakeholders will lead to different effects affecting companies, customers and society. This is an iterative process based on which the stakeholders use their experience to constantly improve and evolve their use of social media, which has impacts on both, business and society. The successful implementation of this process is key to digital transformation and the creation of sustainable societies. Most of the current studies (Andersson et al. 2013 ; Bernard 2016 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ; Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü 2018 ; Dyck 2010 ; Guesalaga 2016 ) focus mostly on the company as a stakeholder. However, more research is needed on other types of stakeholders (e.g. society).
5.1.2 Use of Social Media by B2B Companies
Social media affects not only ways how companies connect with their clients, but it is also changing their business models, the way how the value is delivered and profit is made. To successfully implement and use social media, B2B companies need to consider various social media tools, antecedents/barriers of its adoption, identify suitable social media strategies which are in line with the company’s overall strategy, and measure effectiveness of the use of social media. There are various factors that affect the use of social media by B2B companies. The study found that social media usage is influenced by perceived ease of use, adoption of social media, attitude towards social media and age of salesperson.
The majority of the studies focus on the management of the marketing department. However, digital transformation is much bigger than just marketing as it encompasses the entire organisation. As a result, future studies should look like the entire organisation and investigate barriers and factors affecting the use of social media.
It is crucial for companies to design content which will be noticed on social media by their potential, actual and former customers. Social media content should be interesting and offer some beneficial information, rather than just focus on services the company provides. Companies could use fresh views on relevant industry news, provide information how they are contributing to society and environment, include humour in their posts, share information about the team, make it more personal. It is also useful to use images, infographics, and video content.
It is also important for companies to measure digital marketing actions. More studies are needed on how to isolate the impact of specific media marketing actions to demonstrate their impact on the desired business outcomes (Salo 2017 ). Thus, future studies can consider how particular social media channels (e.g. Facebook, LinkedIn) in a campaign of a new product/ service influence brand awareness and sales level. Also, a limited number of studies discussed the way B2B companies can measure ROI. Future research should investigate how companies can measure intangible ROI, such as eWOM, brand awareness, and customer engagement (Kumar and Mirchandani 2012 ). Also, future research should investigate the reasons why most of the users do not assess the effectiveness of their SNS. Furthermore, most of the studies focused on likes, shares, and comments to evaluate social media engagement. Future research should focus on other types of measures. More research needs considering the impact of legislation on the use of social media by companies. Recent B2B studies did not consider recent legislation (General Data Protection Regulation 2018 ) in the context B2B (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ).
5.1.3 Effect of Social Media on Business and Society
Social media plays an important part in the company’s decision-making process. Social media can bring positive changes into company, which will result in improving customer satisfaction, value creation, increase in sales, building relationships with customers, knowledge creation, improve the perception of corporate credibility, acquisition of new customers, and improve employment brand engagement. Using information collected from social media can help companies to have a set of reliable attributes that comprise social, economic and environmental aspects in their decision-making process (Tseng 2017 ). Additionally, by using social media B2B companies can provide information to other stakeholders on their sustainability activities. By using data from social media companies will be able to provide products and services which are demanded by society. It will improve the quality of life and result in less waste. Additionally, social media can be considered as a tool that helps managers to integrate business practices with sustainability (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ). As a result, social media use by B2B companies can lead to business and societal changes.
A limited number of studies investigated the effect of social media on word of mouth communications in the B2B context. Future research should investigate the differences and similarities between B2C and B2B eWOM communications. Also, studies should investigate how these types of communications can be improved and ways to deal with negative eWOM. It is important for companies to respond to comments on social media. Additionally, future research should investigate its perceived helpfulness by customers.
Majority of studies (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Rossmann and Stei 2015 ; Agnihotri et al. 2012 ; Agnihotri et al. 2017 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Salo 2017 ; Bhattacharjya and Ellison 2015 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gruner and Power 2018 ; Hollebeek 2019 ) investigated positive effect of social media such consumer satisfaction, consumer engagement, and brand awareness. However, it will be interesting to consider the dark side of social media use such as an excessive number of requests on social media to salespeople (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ), which can result in the reduction of the responsiveness; spread of misinformation which can damage the reputation of the company.
Studies were performed in China (Lacka and Chong 2016 ; Niedermeier et al. 2016 ), the USA (Guesalaga 2016 ; Iankova et al. 2018 ; Ogilvie et al. 2018 ), India (Agnihotri et al. 2017 ; Vasudevan and Kumar 2018 ), the UK (Bolat et al. 2016 ; Iankova et al. 2018 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ). It is strongly advised that future studies conduct research in other countries as findings can be different due to the culture and social media adoption rates. Future studies should pay particular attention to other emerging markets (such as Russia, Brazil, and South Africa) as they suffer from the slow adoption rate of social media marketing. Some companies in these countries still rely more on traditional media for advertising of their products and services, as they are more trusted in comparison with social media channels (Olotewo 2016 ). The majority of studies investigate the effect of social media in B2B or B2C context. Future studies should pay attention to other contexts (e.g. B2B2B, B2B2C). Another limitation of the current research on B2B companies is that most of the studies on social media in the context of B2B focus on the effect of social media use only on business outcomes. It is important for future research to focus on societal outcomes.
Lastly, most of the studies on social media in the context of B2B companies use a cross-sectional approach to collect the data. Future research can use the longitudinal approach in order to advance understanding of social media use and its impact over time.
5.2 Research Propositions
Based on the social media research in the context of B2B companies and the discussion above the following is proposed, which could serve as a foundation for future empirical work.
Social media is a powerful tool to deliver information to customers. However, social media can be used to get consumer and market insights (Kazienko et al. 2013 ). A number of studies highlighted how information obtained from a number of social media platforms could be used for various marketing purposes, such as understanding the needs and preferences of consumers, marketing potential for new products/services, and current market trends (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Constantinides et al. 2008 ). It is advised that future research employs a longitudinal approach to study the impact of social media use on understanding customers. Therefore, the following proposition can be formulated:
Proposition 1
Social media usage of B2B companies has a positive influence on understanding its customers.
By using social media companies can examiner valuable information on competitors. It can help to understand competitors’ habits and strategies, which can lead to the competitive advantage and help strategic planning (Dey et al. 2011 ; Eid et al. 2019 ; Teo and Choo 2001 ). It is advised that future research employs a longitudinal approach to study the impact of social media use on understanding its competitors. As a result, using social media to understand customers and competitors can create business value (Mikalef et al. 2020a ) for key stakeholders and lead to positive changes in the business and societies. The above discussion leads to the following proposition:
Proposition 2
Social media usage of B2B companies has a positive influence on understanding its competitors.
Proposition 3
Culture influences the adoption and use of social media by B2B companies.
Usage of social media can result in some positive marketing outcomes such as building new customer relationships, increasing brand awareness, and level of sales to name a few (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Dwivedi et al. 2020 ; Rossmann and Stei 2015 ). However, when social media is not used appropriately it can lead to negative consequences. If a company does not have enough resources to implement social media tools the burden usually comes on a salesperson. A high number of customer inquiries, the pressure to engage with customers on social media, and monitor communications happening on various social media platforms can result in the increased workload of a salesperson putting extra pressure (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ). As a result, a salesperson might not have enough time to engage with all the customers online promptly or engage in reactive and proactive web care. As a result, customer satisfaction can be affected as well as company reputation. To investigate the negative impact of social media research could apply novel methods for data collection and analysis such as fsQCA (Pappas et al. 2020 ), or implying eye-tracking (Mikalef et al. 2020b ). This leads to the following proposition:
Proposition 4
Inappropriate use of social media by B2B companies has a negative effect on a) customer satisfaction and b) company reputation.
According to Technology-Organisation-Environment (TOE) framework environmental context significantly affects a company’s use of innovations (Abed 2020 ; Oliveira and Martins 2011 ). Environment refers to the factors which affect companies from outside, including competitors and customers. Adopting innovation can help companies to change the rules of the competition and reach a competitive advantage (Porter and Millar 1985 ). In a competitive environment, companies have a tendency to adopt an innovation. AlSharji et al. ( 2018 ) argued that the adoption of innovation can be extended to social media use by companies. A study by AlSharji et al. ( 2018 ) by using data from 1700 SMEs operating in the United Arab Emirates found that competitive pressure significantly affects the use of social media by SMEs. It can be explained by the fact that companies could feel pressure when other companies in the industry start adopting a particular technology and as a result adopt it to remain competitive (Kuan and Chau 2001 ). Based on the above discussion, the following proposition can be formulated:
Proposition 5
Competitive pressure positively affects the adoption of social media by B2B companies.
Companies might feel that they are forced to adopt and use IT innovations because their customers would expect them to do so. Meeting customers’ expectations could result in adoption of new technologies by B2B companies. Some research studies investigated the impact of customer pressure on companies (AlSharji et al. 2018 ; Maduku et al. 2016 ). For example, a study by Maduku et al. ( 2016 ) found that customer pressure has a positive effect on SMEs adoption of mobile marketing in the context of South Africa. Future research could implement longitudinal approach to investigate how environment affects adoption of social media by B2B companies. This leads to the formulation of the following proposition:
Proposition 6
Customer pressure positively affects the adoption of social media by B2B companies.
6 Conclusion
The aim of this research was to provide a comprehensive systematic review of the literature on social media in the context of B2B companies and propose the framework outlining the role of social media in the digital transformation of B2B companies. It was found that B2B companies use social media, but not all companies consider it as part of their marketing strategies. The studies on social media in the B2B context focused on the effect of social media, antecedents, and barriers of adoption of social media, social media strategies, social media use, and measuring the effectiveness of social media. Academics and practitioners can employ the current study as an informative framework for research on the use of social media by B2B companies. The summary of the key observations provided from this literature review is the following: [i] Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn are the most famous social media platforms used by B2B companies, [ii] Social media has a positive effect on customer satisfaction, acquisition of new customers, sales, stakeholder engagement, and customer relationships, [iii] In systematically reviewing 70 publications on social media in the context of B2B companies it was observed that most of the studies use online surveys and online content analysis, [iv] Companies still look for ways to evaluate the effectiveness of social media, [v] Innovativeness, pressure from stakeholders, perceived usefulness, and perceived usability have a significant positive effect on companies’ adoption to use social media, [vi] Lack of staff familiarity and technical skills are the main barriers that affect the adoption of social media by B2B, [vii] Social media has an impact not only on business but also on society, [viii] There is a dark side of social media: fake online reviews, an excessive number of requests on social media to salespeople, distribution of misinformation, negative eWOM, [ix] Use of social media by companies has a positive effect on sustainability, and [x] For successful digital transformation social media should change not only the way how companies integrate it into their marketing strategies but the way how companies deliver values to their customers and conduct their business. This research has a number of limitations. First, only publications from the Scopus database were included in literature analysis and synthesis. Second, this research did not use meta-analysis. To provide a broader picture of the research on social media in the B2B context and reconcile conflicting findings of the existing studies future research should conduct a meta-analysis (Ismagilova et al. 2020c ). It will advance knowledge of the social media domain.
Abed, S. S. (2020). Social commerce adoption using TOE framework: An empirical investigation of Saudi Arabian SMEs. International Journal of Information Management, 53 , 102118.
Article Google Scholar
Agnihotri, R., Kothandaraman, P., Kashyap, R., & Singh, R. (2012). Bringing “social” into sales: The impact of salespeople’s social media use on service behaviors and value creation. Journal of Personal Selling and Sales Management, 32 (3), 333–348. https://doi.org/10.2753/PSS0885-3134320304 .
Agnihotri, R., Dingus, R., Hu, M. Y., & Krush, M. T. (2016). Social media: Influencing customer satisfaction in B2B sales. Industrial Marketing Management, 53 , 172–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.09.003 .
Agnihotri, R., Trainor, K. J., Itani, O. S., & Rodriguez, M. (2017). Examining the role of sales-based CRM technology and social media use on post-sale service behaviors in India. Journal of Business Research, 81 , 144–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.08.021 .
Alalwan, A. A., Rana, N. P., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Algharabat, R. (2017). Social media in marketing: A review and analysis of the existing literature. Telematics and Informatics, 34 (7), 1177–1190.
AlSharji, A., Ahmad, S. Z., & Bakar, A. R. A. (2018). Understanding social media adoption in SMEs. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, 10 (2), 302–328.
Ancillai, C., Terho, H., Cardinali, S., & Pascucci, F. (2019). Advancing social media driven sales research: Establishing conceptual foundations for B-to-B social selling. Industrial Marketing Management, 82 , 293–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2019.01.002 .
Andersson, S., & Wikström, N. (2017). Why and how are social media used in a B2B context, and which stakeholders are involved? Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 32 (8), 1098–1108. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-07-2016-0148 .
Andersson, S., Evers, N., & Griot, C. (2013). Local and international networks in small firm internationalization: Cases from the Rhône-Alpes medical technology regional cluster. Entrepreneurship & Regional Development, 25 (9–10), 867–888.
Andzulis, J. M., Panagopoulos, N. G., & Rapp, A. (2012). A review of social media and implications for the sales process. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 32 (3), 305–316.
Barreda, A. A., Bilgihan, A., Nusair, K., & Okumus, F. (2015). Generating brand awareness in online social networks. Computers in Human Behavior, 50 , 600–609.
Bell, D., & Shirzad, S, R. (2013). Social media domain analysis (SoMeDoA): A pharmaceutical study. 9th international conference on web information systems and technologies, 561–570. https://doi.org/10.5220/0004499105610570 .
Bernard, M. (2016). The impact of social media on the B2B CMO. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 31 (8), 955–960. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-268 .
Bhattacharjya, J., & Ellison, A, B. (2015). Building business resilience with social media in B2B environments: The emergence of responsive customer relationship management processes on twitter. Working Conference on Virtual Enterprises doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24141-8_15 .
Bolat, E., Kooli, K., & Wright, L. T. (2016). Businesses and mobile social media capability. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 31 (8), 971–981. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-270 .
Buratti, N., Parola, F., & Satta, G. (2018). Insights on the adoption of social media marketing in B2B services. TQM Journal, 30 (5), 490–529. https://doi.org/10.1108/TQM-11-2017-0136 .
Cawsey, T., & Rowley, J. (2016). Social media brand building strategies in B2B companies. Marketing Intelligence and Planning, 34 (6), 754–776. https://doi.org/10.1108/MIP-04-2015-0079 .
Chatterjee, S., & Kar, A. K. (2020). Why do small and medium enterprises use social media marketing and what is the impact: Empirical insights from India. International Journal of Information Management, 53 , 102103.
Chen, H., Chiang, R. H., & Storey, V. C. (2012). Business intelligence and analytics: From big data to big impact. MIS Quarterly, 36 , 1165–1188.
Chirumalla, K., Oghazi, P., & Parida, V. (2018). Social media engagement strategy: Investigation of marketing and R&D interfaces in manufacturing industry. Industrial Marketing Management, 74 , 138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.10.001 .
Constantinides, E., Romero, C. L., & Boria, M. A. G. (2008). Social media: A new frontier for retailers?. In European retail research (pp. 1–28) . Wiesbaden: Gabler Verlag.
Google Scholar
Denktaş-Şakar, G., & Sürücü, E. (2018). Stakeholder engagement via social media: An analysis of third-party logistics companies. Service Industries Journal, 40 , 866–889. https://doi.org/10.1080/02642069.2018.1561874 .
Dey, L., Haque, S, M., Khurdiya, A., & Shroff, G. (2011). Acquiring competitive intelligence from social media. In proceedings of the 2011 joint workshop on multilingual OCR and analytics for noisy unstructured text data (pp. 1-9) . https://doi.org/10.1145/2034617.2034621 .
Dwivedi, Y. K., Rana, N. P., Jeyaraj, A., Clement, M., & Williams, M. D. (2019a). Re-examining the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT): Towards a revised theoretical model. Information Systems Frontiers, 21 (3), 719–734.
Dwivedi, Y, K., Hughes, L., Ismagilova, E., Aarts, G., Coombs, C., Crick, T., ... & Galanos, V. (2019b). Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. International Journal of Information Management , 101994, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.08.002 .
Dwivedi, Y, K., Ismagilova, E., Hughes, D. L., Carlson, J., Filieri, R., Jacobson, J., ... & Kumar, V. (2020). Setting the future of digital and social media marketing research: Perspectives and research propositions. International Journal of Information Management , 102168, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102168 .
Dyck, P. V. (2010). As social media evolves, the device industry must also. Medical Device and Diagnostic Industry, 32 (8).
Eid, R., Abdelmoety, Z., & Agag, G. (2019). Antecedents and consequences of social media marketing use: An empirical study of the UK exporting B2B SMEs. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing., 35 , 284–305.
Gáti, M., Mitev, A., & Bauer, A. (2018). Investigating the impact of salespersons’ use of technology and social media on their customer relationship performance in B2B settings. Trziste, 30 (2), 165–176. https://doi.org/10.22598/mt/2018.30.2.165 .
Gazal, K., Montague, I., Poudel, R., & Wiedenbeck, J. (2016). Forest products industry in a digital age: Factors affecting social media adoption. Forest Products Journal, 66 (5-6), 343–353. https://doi.org/10.13073/FPJ-D-15-00007 .
General Data Protection Regulation (2018). Guide to the General Data Protection Regulation. Available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/guide-to-the-general-data-protection-regulation . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Gregorio, J. (2017). 10 reasons to diversify your digital marketing efforts. Digital marketing Philippines. Available at https://digitalmarketingphilippines.com/10-reasons-to-diversify-your-digital-marketing-efforts// Accessed on April , 27 , 2019.
Gruner, R. L., & Power, D. (2018). To integrate or not to integrate? Understanding B2B social media communications. Online Information Review, 42 (1), 73–92. https://doi.org/10.1108/OIR-04-2016-0116 .
Guesalaga, R. (2016). The use of social media in sales: Individual and organizational antecedents, and the role of customer engagement in social media. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.12.002 .
Gupta, P., Chauhan, S., & Jaiswal, M. P. (2019). Classification of smart city research-a descriptive literature review and future research agenda. Information Systems Frontiers, 21 (3), 661–685.
Habibi, F., Hamilton, C. A., Valos, M. J., & Callaghan, M. (2015). E-marketing orientation and social media implementation in B2B marketing. European Business Review, 27 (6), 638–655. https://doi.org/10.1108/EBR-03-2015-0026 .
Harrigan, P., Miles, M. P., Fang, Y., & Roy, S. K. (2020). The role of social media in the engagement and information processes of social CRM. International Journal of Information Management, 54 , 102151.
Hollebeek, L. D. (2019). Developing business customer engagement through social media engagement-platforms: An integrative SD logic/RBV-informed model. Industrial Marketing Management, 81 , 89–98.
Hsiao, S. H., Wang, Y. Y., Wang, T., & Kao, T. W. (2020). How social media shapes the fashion industry: The spillover effects between private labels and national brands. Industrial Marketing Management, 86 , 40–51.
Huotari, L., Ulkuniemi, P., Saraniemi, S., & Mäläskä, M. (2015). Analysis of content creation in social media by B2B companies. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 30 (6), 761–770. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-05-2013-0118 .
Iankova, S., Davies, I., Archer-Brown, C., Marder, B., & Yau, A. (2018). A comparison of social media marketing between B2B, B2C and mixed business models. Industrial Marketing Management, 81 , 169–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.01.001 .
Iannacci, F., Fearon, C., & Pole, K. (2020). From acceptance to adaptive acceptance of social media policy change: A set-theoretic analysis of b2b SMEs. Information Systems Frontiers , 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-020-09988-1 .
Ismagilova, E., Dwivedi, Y. K., Slade, E., & Williams, M. D. (2017). Electronic word of mouth (eWOM) in the marketing context: A state of the art analysis and future directions . Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52459-7 .
Ismagilova, E., Hughes, L., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Raman, K. R. (2019). Smart cities: Advances in research—An information systems perspective. International Journal of Information Management, 47 , 88–100.
Ismagilova, E., Slade, E. L., Rana, N. P., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2020a). The effect of electronic word of mouth communications on intention to buy: A meta-analysis. Information Systems Frontiers, 22 , 1203–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-019-09924-y .
Ismagilova, E., Slade, E., Rana, N. P., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2020b). The effect of characteristics of source credibility on consumer behaviour: A meta-analysis. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 53 , 101736.
Ismagilova, E., Rana, N, P., Slade, E., & Dwivedi, Y, K. (2020c). A meta-analysis of the factors affecting eWOM providing behaviour. European Journal of Marketing. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/EJM-07-2018-0472 , ahead-of-print.
Itani, O. S., Agnihotri, R., & Dingus, R. (2017). Social media use in B2b sales and its impact on competitive intelligence collection and adaptive selling: Examining the role of learning orientation as an enabler. Industrial Marketing Management, 66 , 64–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.06.012 .
Jeyaraj, A., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2020). Meta-analysis in information systems research: Review and recommendations. International Journal of Information Management, 55 , 102226.
Jeyaraj, A., Rottman, J. W., & Lacity, M. C. (2006). A review of the predictors, linkages, and biases in IT innovation adoption research. Journal of Information Technology, 21 (1), 1–23.
Juntunen, M., Ismagilova, E., & Oikarinen, E. L. (2020). B2B brands on twitter: Engaging users with a varying combination of social media content objectives, strategies, and tactics. Industrial Marketing Management, 89 , 630–641.
Jussila, J. J., Kärkkäinen, H., & Leino, M. (2011). Benefits of social media in business-to-business customer interface in innovation. 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments . MindTrek, 2011 , 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1145/2181037.2181065 .
Kamboj, S., Sarmah, B., Gupta, S., & Dwivedi, Y. (2018). Examining branding co-creation in brand communities on social media: Applying the paradigm of stimulus-organism-response. International Journal of Information Management, 39 , 169–185.
Kapoor, K. K., Tamilmani, K., Rana, N. P., Patil, P., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Nerur, S. (2018). Advances in social media research: Past, present and future. Information Systems Frontiers, 20 (3), 531–558.
Kärkkäinen, H., Jussila, J., & Janhonen, J. (2011). Managing customer information and knowledge with social media in business-to-business companies. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/2024288.2024309 .
Kasper, H., Koleva, I., & Kett, H. (2015). Social media matrix matching corporate goals with external social media activities doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46641-4_17 .
Katona, Z., & Sarvary, M. (2014). Maersk line: B2B social media-“it’s communication, not marketing. California Management Review , 56(3), 142–156. doi: https://doi.org/10.1525/cmr.2014.56.3.142 .
Kazienko, P., Szozda, N., Filipowski, T., & Blysz, W. (2013). New business client acquisition using social networking sites. Electronic Markets, 23 (2), 93–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12525-013-0123-9 .
Keinänen, H., & Kuivalainen, O. (2015). Antecedents of social media B2B use in industrial marketing context: Customers’ view. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 30 (6), 711–722. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-04-2013-0095 .
Kho, N. D. (2008). B2B gets social media. EContent, 31 (3), 26–30.
Kovac, M. (2016). Social media works for B2B sales, too. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2016/01/social-media-worksfor-b2b-sales-too . Accessed on April , 27 , 2020 .
Kuan, K. K., & Chau, P. Y. (2001). A perception-based model for EDI adoption in small businesses using a technology–organization–environment framework. Information & Management, 38 (8), 507–521.
Kumar, V., & Mirchandani, R. (2012). Increasing the ROI of social media marketing. MIT Sloan Management Review, 54 (1), 55–61.
Kumar, A., & Möller, K. (2018). Extending the boundaries of corporate branding: An exploratory study of the influence of brand familiarity in recruitment practices through social media by B2B firms. Corporate Reputation Review, 21 (3), 101–114. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41299-018-0046-7 .
Kunsman, T. (2018). Internal marketing: Why your company should prioritize it. https://everyonesocial.com/blog/internal-marketing/ . Accessed on September, 25, 2019.
Lacka, E., & Chong, A. (2016). Usability perspective on social media sites' adoption in the B2B context. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.01.001 .
Lal, B., Ismagilova, E., Dwivedi, Y.,. K., & Kwayu, S. (2020). Return on Investment in Social Media Marketing: Literature review and suggestions for future research. In Digital and Social Media Marketing (pp. 3–17) . Cham: Springer.
Lashgari, M., Sutton-Brady, C., Solberg Søilen, K., & Ulfvengren, P. (2018). Adoption strategies of social media in B2B firms: A multiple case study approach. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 33 (5), 730–743. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-0242 .
Loebbecke, C., & Picot, A. (2015). Reflections on societal and business model transformation arising from digitization and big data analytics: A research agenda. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24 (3), 149–157.
Maduku, D. K., Mpinganjira, M., & Duh, H. (2016). Understanding mobile marketing adoption intention by south African SMEs: A multi-perspective framework. International Journal of Information Management, 36 (5), 711–723.
Mahrous, A, A. (2013). Social media marketing: Prospects for marketing theory and practice on the social web. E-marketing in developed and developing countries: Emerging practices (pp. 56-68) doi: https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-4666-3954-6.ch004 Retrieved from www.scopus.com .
McAfee, A. P. (2006). Enterprise 2.0: The dawn of emergent collaboration. Enterprise, 2 , 15–26.
McKinsey & Company (2015). Transforming the business through social tools. McKinsey.com , ( http://www.mckinsey.com/industries/high-tech/our-insights/transformingthe-business-through-social-tools ).
McShane, L., Pancer, E., & Poole, M. (2019). The influence of B to B social media message features on brand engagement: A fluency perspective. Journal of Business-to-Business Marketing, 26 (1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/1051712X.2019.1565132 .
Mehmet, M. I., & Clarke, R. J. (2016). B2B social media semantics: Analysing multimodal online meanings in marketing conversations. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 92–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.12.006 .
Meire, M., Ballings, M., & Van den Poel, D. (2017). The added value of social media data in B2B customer acquisition systems: A real-life experiment. Decision Support Systems, 104 , 26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2017.09.010 .
Michaelidou, N., Siamagka, N. T., & Christodoulides, G. (2011). Usage, barriers and measurement of social media marketing: An exploratory investigation of small and medium B2B brands. Industrial Marketing Management, 40 (7), 1153–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2011.09.009 .
Mikalef, P., Pappas, I. O., Krogstie, J., & Pavlou, P. A. (2020a). Big data and business analytics: A research agenda for realizing business value. Information & Management, 57 (1), 103237.
Mikalef, P., Sharma, K., Pappas, I, O., & Giannakos, M. (2020b). Seeking information on social commerce: An examination of the impact of user-and marketer-generated content through an eye-tracking study. Information Systems Frontiers , 1-14, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-020-10034-3 .
Minsky, L., & Quesenberry, K, A. (2016). How B2B sales can benefit from social selling . Harvard Business Review. Available at https://hbr.org/2016/11/84-of-b2b-sales-start-with-a-referral-not-a-salesperson . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Moncrief, W. C., Marshall, G. W., & Rudd, J. M. (2015). Social media and related technology: Drivers of change in managing the contemporary sales force. Business Horizons, 58 (1), 45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2014.09.009 .
Moore, J. N., Hopkins, C. D., & Raymond, M. A. (2013). Utilization of relationship-oriented social media in the selling process: A comparison of consumer (B2C) and industrial (B2B) salespeople. Journal of Internet Commerce, 12 (1), 48–75. https://doi.org/10.1080/15332861.2013.763694 .
Moore, J. N., Raymond, M. A., & Hopkins, C. D. (2015). Social selling: A comparison of social media usage across process stage, markets, and sales job functions. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 23 (1), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/10696679.2015.980163 .
Mudambi, S. M., Sinha, J. I., & Taylor, D. S. (2019). Why B-to-B CEOs should be more social on social media. Journal of Business-to-Business Marketing, 26 (1), 103–105. https://doi.org/10.1080/1051712X.2019.1565144 .
Muhammad, S. S., Dey, B. L., & Weerakkody, V. (2018). Analysis of factors that influence customers’ willingness to leave big data digital footprints on social media: A systematic review of literature. Information Systems Frontiers, 20 (3), 559–576.
Müller, L., Griesbaum, J., & Mandl, T. (2013). Social media relations in the german automotive market. Paper presented at the proceedings of the IADIS international conference ICT, society and human beings 2013, Proceedings of the IADIS International Conference e-Commerce 2013, 19–26.
Müller, J. M., Pommeranz, B., Weisser, J., & Voigt, K. I. (2018). Digital, social media, and Mobile marketing in industrial buying: Still in need of customer segmentation? Empirical evidence from Poland and Germany. Industrial Marketing Management, 73 , 70–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.01.033 .
Niedermeier, K. E., Wang, E., & Zhang, X. (2016). The use of social media among business-to-business sales professionals in China: How social media helps create and solidify guanxi relationships between sales professionals and customers. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 10 (1), 33–49. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIM-08-2015-0054 .
Nunan, D., Sibai, O., Schivinski, B., & Christodoulides, G. (2018). Reflections on “social media: Influencing customer satisfaction in B2B sales” and a research agenda. Industrial Marketing Management, 75 , 31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.03.009 .
Ogilvie, J., Agnihotri, R., Rapp, A., & Trainor, K. (2018). Social media technology use and salesperson performance: A two study examination of the role of salesperson behaviors, characteristics, and training. Industrial Marketing Management, 75 , 55–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.03.007 .
Oliveira, T., & Martins, M. F. (2011). Literature review of information technology adoption models at firm level. Electronic Journal of Information Systems Evaluation, 14 (1), 110.
Olotewo, J. (2016). Social media marketing in emerging markets. International Journal of Online Marketing Research, 2 (2), 10–18.
Pappas, I. O., Mikalef, P., Giannakos, M. N., Krogstie, J., & Lekakos, G. (2018). Big data and business analytics ecosystems: Paving the way towards digital transformation and sustainable societies. Information Systems and e-Business Management, 16 , 479–491.
Pappas, I. O., Papavlasopoulou, S., Mikalef, P., & Giannakos, M. N. (2020). Identifying the combinations of motivations and emotions for creating satisfied users in SNSs: An fsQCA approach. International Journal of Information Management, 53 , 102128.
Pascucci, F., Ancillai, C., & Cardinali, S. (2018). Exploring antecedents of social media usage in B2B: A systematic review. Management Research Review, 41 (6), 629–656. https://doi.org/10.1108/MRR-07-2017-0212 .
Pitt, C. S., Plangger, K. A., Botha, E., Kietzmann, J., & Pitt, L. (2017). How employees engage with B2B brands on social media: Word choice and verbal tone. Industrial Marketing Management, 81 , 130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.09.012 .
Pitt, C. S., Botha, E., Ferreira, J. J., & Kietzmann, J. (2018). Employee brand engagement on social media: Managing optimism and commonality. Business Horizons, 61 (4), 635–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2018.04.001 .
Porter, M. E., & Millar, V. E. (1985). How information gives you competitive advantage. Harvard Business Review, 63 (4), 149–160.
Pulizzi, J., & Handley, A. (2017). B2C content marketing-2018 benchmarks, budgets, and trends—North America. Available at https://contentmarketinginstitute.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/2017_B2B_Research_FINAL.pdf Accessed on April , 27 , 2020.
Rana, N. P., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Williams, M. D. (2015). A meta-analysis of existing research on citizen adoption of e-government. Information Systems Frontiers, 17 (3), 547–563.
Rana, N. P., Luthra, S., Mangla, S. K., Islam, R., Roderick, S., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2019). Barriers to the development of smart cities in Indian context. Information Systems Frontiers, 21 (3), 503–525.
Rodriguez, M., Peterson, R. M., & Krishnan, V. (2012). Social media's influence on business-to-business sales performance. Journal of Personal Selling and Sales Management, 32 (3), 365–378. https://doi.org/10.2753/PSS0885-3134320306 .
Rossmann, A., & Stei, G. (2015). Sales 2.0 in business-to-business (B2B) networks: Conceptualization and impact of social media in B2B sales relationships . Paper presented at the Lecture Notes in Informatics (LNI), Proceedings - Series of the Gesellschaft Fur Informatik (GI), 244 67–78. Available at https://subs.emis.de/LNI/Proceedings/Proceedings244/67.pdf . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Salo, J. (2017). Social media research in the industrial marketing field: Review of literature and future research directions. Industrial Marketing Management, 66 , 115–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.07.013 .
Shaltoni, A. M. (2017). From websites to social media: Exploring the adoption of internet marketing in emerging industrial markets. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 32 (7), 1009–1019. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-06-2016-0122 .
Siamagka, N. T., Christodoulides, G., Michaelidou, N., & Valvi, A. (2015). Determinants of social media adoption by B2B organizations. Industrial Marketing Management, 51 , 89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.05.005 .
Sivarajah, U., Irani, Z., Gupta, S., & Mahroof, K. (2019). Role of big data and social media analytics for business to business sustainability: A participatory web context. Industrial Marketing Management . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2019.04.005 .
Sobal, A. (2017). 30 statistics about B2B social media usage. Available at https://www.weidert.com/blog/statistics-about-b2b-social-media-usage Accessed on April , 27 , 2020.
Stelzner, M. (2011). 2012 social media marketing industry report. Social media examiner . Available at https://www.socialmediaexaminer.com/socialmedia-marketing-industry-report-2012/ . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Sułkowski, Ł., & Kaczorowska-Spychalska, D. (2016). Social media in the process of marketing evolution in polish textile-clothing industry. Fibres and Textiles in Eastern Europe, 24 (5), 15–20. https://doi.org/10.5604/12303666.1215521 .
Swani, K., Milne, G., & Brown, B. P. (2013). Spreading the word through likes on facebook: Evaluating the message strategy effectiveness of fortune 500 companies. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 7 (4), 269–294. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIM-05-2013-0026 .
Swani, K., Brown, B. P., & Milne, G. R. (2014). Should tweets differ for B2B and B2C? An analysis of fortune 500 companies' twitter communications. Industrial Marketing Management, 43 (5), 873–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2014.04.012 .
Swani, K., Milne, G. R., Brown, B. P., Assaf, A. G., & Donthu, N. (2017). What messages to post? Evaluating the popularity of social media communications in business versus consumer markets. Industrial Marketing Management, 62 , 77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.07.006 .
Tedeschi, B. (2006). Like shopping? Social networking? Try social shopping. New York Times, 11 , 09.
Teo, T. S., & Choo, W. Y. (2001). Assessing the impact of using the internet for competitive intelligence. Information & Management, 39 (1), 67–83.
Tseng, M. L. (2017). Using social media and qualitative and quantitative information scales to benchmark corporate sustainability. Journal of Cleaner Production, 142 , 727–738.
Vasudevan, S., & Kumar, F. J. P. (2018). Social media and B2B brands: An Indian perspective. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology, 9 (9), 767–775.
Vukanovic, Z. (2013). Managing social media value networks: From publisher (broadcast) to user-centric (broadband-narrowcast) business models. Handbook of social media management: Value chain and business models in changing media markets (pp. 269-288) doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28897-5_16 .
Wang, Y., Rod, M., Ji, S., & Deng, Q. (2017). Social media capability in B2B marketing: Toward a definition and a research model. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 32 (8), 1125–1135. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-0250 .
Watt, I. (2010). Changing visions of parliamentary libraries: From the enlightenment to Facebook. IFLA Journal, 36 (1), 47–60. https://doi.org/10.1177/0340035209359574 .
Webster, J., & Watson, R.,. T. (2002). Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. MIS quarterly, 26 (2), xiii–xxiii.
Westerman, G., Bonnet, D., & McAfee, A. (2014). Leading digital: Turning technology into business transformation . Boston, MA: Harvard Business Press.
Williams, M. D., Rana, N. P., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2015). The unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT): A literature review. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 28 (3), 443–488.
World Commission Report on Environment and Development. (1987). Our Common Future . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Yang, C. C., Yang, H., Tang, X., & Jiang, L. (2012). Identifying implicit relationships between social media users to support social commerce. In ACM international conference proceeding series (pp. 41–47). https://doi.org/10.1145/2346536.2346544 .
Chapter Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Emerging Markets Research Centre (EMaRC), School of Management, Swansea University, Bay Campus, Swansea, UK
Yogesh K. Dwivedi
School of Management, University of Bradford, Bradford, UK
Elvira Ismagilova & Nripendra P. Rana
Symbiosis Institute of Business Management, Pune & Symbiosis International, Deemed University, Pune, India
Ramakrishnan Raman
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yogesh K. Dwivedi .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Dwivedi, Y.K., Ismagilova, E., Rana, N.P. et al. Social Media Adoption, Usage And Impact In Business-To-Business (B2B) Context: A State-Of-The-Art Literature Review. Inf Syst Front 25 , 971–993 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-021-10106-y
Download citation
Accepted : 07 January 2021
Published : 02 February 2021
Issue Date : June 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-021-10106-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Business-to-business
- Digital transformation
- Information systems
- Literature review
- Social media
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table 1 presents the top articles on social media influencer marketing. The most cited article is De Veirman et al.'s [] (464 citations), which focused on social media influencer marketing using Instagram and revealed the impact of the number of followers and product divergence on brand attitudes among the followers of social media influencers.The burgeoning interest on Instagram as seen ...
Vidan and Das (2021) revealed that social media gave birth to influencer marketing, which is 11 times more effective than traditional advertising due to the increased number of internet users.
This strategy-value perspective of social media can help us categorize the extant literature on social media marketing into five research streams, namely: (a) social media as a promotion and selling outlet; (b) social media as a communication and branding channel; (c) social media as a monitoring and intelligence source; (d) social media as a ...
In response, this paper is the first to consolidate the present state of research on IM within social media settings. More specifically, a systematic review of relevant studies published in peer-reviewed academic journals across diverse fields was conducted in order to identify key themes and dominant concepts.
Distribution of Papers across Journals and Years. All identified articles were published between 2008 and 2018. Figure 1 shows that research on social media started to flourish in the top advertising and marketing journals in 2011, with 18 articles published that year. The highest number of articles was published in 2017 (25), followed by 2014 (23).
Broad search terms, such as 'social media marketing' and 'social media strategy', were deemed suitable. Since we observed trends suggesting that early SMM research largely considers adoption-related issues, we decided to include additional keywords, such as 'social media adoption' and 'social media use'.
Businesses invest considerable sums in influencer marketing efforts as social media influencers (SMIs) continue to gain popularity. To understand how marketers might utilize influencer marketing as a strategy in the digital era, researchers are still examining the effectiveness and impact of using SMIs.
short video platform to enhance the promotion of the region's history and culture. 5. Conclusion. Brand marketing via social media has become an unavoidable and prevalent trend in today's world ...
Although social media use is gaining increasing importance as a component of firms' portfolio of strategies, scant research has systematically consolidated and extended knowledge on social media marketing strategies (SMMSs). To fill this research gap, we first define SMMS, using social media and marketing strategy dimensions. This is followed by a conceptualization of the developmental ...
Given the global scenario that most brands operate in, research could focus on cross-country effects of owned social media to determine whether country-of-origin effects play a role, by comparing domestic versus foreign brands. Furthermore, social media research in less digitally and economically advanced countries would enrich current ...
The first major finding concerns the relationship between the type of post (sponsored or nonsponsored) and social media engagement. This finding adds to the literature on influencer marketing as an advertising strategy on social media (Lou and Yuan Citation 2019). Our results show that users engage more with sponsored posts than with NSPs.
The objective of the examination as mentioned was to better understand the new marketing strategy, i.e., influencer marketing. ... Social media marketing efforts of luxury brands: Influence on brand equity and consumer behavior. Journal of Business Research, 69(12), ...
Most businesses use online marketing strategies such as blogger endorsements, advertising on social media sites, and managing content generated by users to build brand awareness among consumers (Wang and Kim, 2017). Social media is made up of internet-associated applications anchored on technological and ideological Web 2.0 principles, which ...
The Monitoring Capabilities of Social Media Marketing (MC-SMM) are defined as "the ability of a brand to monitor future decisions by tracking and reporting users' activity on brand social media platforms." Marketing professionals should regularly evaluate the effectiveness of their social media marketing (SMM) by analysing various metrics ...
This section synthesizes the existing literature focusing on digital and social media marketing and discusses each theme listed in Table 1 from a review of the extant literature. Studies included in this section were identified using the Scopus database by using the following combination of keywords "Social media", "digital marketing" and "social media marketing".
Georgios T simonis Sergios Dimitriadis , (2014),"Brand strategies in social media", Marketing Intelligence & Planning, Vol. 32 Iss 3 pp. 328 - 344 Permanent link to this document:
Social media allows people to freely interact with others and offers multiple ways for marketers to reach and engage with consumers. Considering the numerous ways social media affects individuals and businesses alike, in this article, the authors focus on where they believe the future of social media lies when considering marketing-related topics and issues. Drawing on academic research ...
The pervasive impact of social media marketing on consumer behavior within the retail industry serves as the focal point of this comprehensive review. This paper aims to dissect the intricate relationship between social media marketing initiatives and their effects on consumer purchasing patterns, brand loyalty, and engagement. By collating and examining a broad spectrum of literature ...
Social Media Marketing Activities. Most businesses use online marketing strategies such as blogger endorsements, advertising on social media sites, and managing content generated by users to build brand awareness among consumers (Wang and Kim, 2017).Social media is made up of internet-associated applications anchored on technological and ideological Web 2.0 principles, which enables the ...
6. Conclusion. The aim of this study was to determine the features of social media advertisements that influence consumer perception and their effect on purchase intention. Data was obtained with the help of a questionnaire and analyzed using exploratory factor analysis and structural equation modeling methods.
This paper explores the concept and scope of social media marketing, as well as its benefits and challenges for businesses. It also discusses the strategies and tools that can be used to implement ...
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, the emergence of internet celebrities, known as "Wanghong" in China, has revolutionized social media, technology, and commerce. This research delves into uncharted territory by examining the profound impact of the Chinese Internet celebrity economy on consumer behavior. While previous studies have explored the role of online celebrities in brand ...
purchase (Teixeira, 2014). Companies develop clear strategies on social media marketing to create brand awareness by producing contents that consumers share with their friends to help their brands stay top in minds of current consumers and to attract new customers (Kottler, 2016). Social media presence is one way small business can increase global
1. Introduction. Consumers and marketers have gradually embraced the activities of online based-brand communities (OBBC's) especially using social media as a communication tool (Algesheimer, Dholakia, & Herrmann, Citation 2005; Hutter, Hautz, Dennhardt, & Füller, Citation 2013).In view of this, the marketing of diversified consumer goods has taken a new direction with producers and sellers ...
The role of social media in marketing and e-commerce has grown exponentially as the Internet has had a transformative influence on consumer behavior. And, the trend of online shopping is gradually becoming the dominant way of consumption and surpassing the traditional sales model, particularly in the context of the significant impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. The article highlights key ...
Social media plays an important part in the digital transformation of businesses. This research provides a comprehensive analysis of the use of social media by business-to-business (B2B) companies. The current study focuses on the number of aspects of social media such as the effect of social media, social media tools, social media use, adoption of social media use and its barriers, social ...
The current research established hypotheses from Katz (1959) based on the "UGT" and TRB. In the present study, too, the theory has helped explain the role of social media marketing strategies and tendency to online interaction as motivators for user engagement on social media with brand-related content.