myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- Class 11 Mathematics Case...

Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you’re seeking a comprehensive and dependable study resource with Class 11 mathematics case study questions for CBSE, myCBSEguide is the place to be. It has a wide range of study notes, case study questions, previous year question papers, and practice questions to help you ace your examinations. Furthermore, it is routinely updated to bring you up to speed with the newest CBSE syllabus. So, why delay? Begin your path to success with myCBSEguide now!
The rationale behind teaching Mathematics
The general rationale to teach Mathematics at the senior secondary level is to assist students:
- In knowledge acquisition and cognitive understanding of basic ideas, words, principles, symbols, and mastery of underlying processes and abilities, notably through motivation and visualization.
- To experience the flow of arguments while demonstrating a point or addressing an issue.
- To use the information and skills gained to address issues using several methods wherever possible.
- To cultivate a good mentality in order to think, evaluate, and explain coherently.
- To spark interest in the subject by taking part in relevant tournaments.
- To familiarise pupils with many areas of mathematics utilized in daily life.
- To pique students’ interest in studying mathematics as a discipline.
Case studies in Class 11 Mathematics
A case study in mathematics is a comprehensive examination of a specific mathematical topic or scenario. Case studies are frequently used to investigate the link between theory and practise, as well as the connections between different fields of mathematics. A case study will frequently focus on a specific topic or circumstance and will investigate it using a range of methodologies. These approaches may incorporate algebraic, geometric, and/or statistical analysis.
Sample Class 11 Mathematics case study questions
When it comes to preparing for Class 11 Mathematics, one of the best things Class 11 Mathematics students can do is to look at some Class 11 Mathematics sample case study questions. Class 11 Mathematics sample case study questions will give you a good idea of the types of Class 11 Mathematics sample case study questions that will be asked in the exam and help you to prepare more effectively.
Looking at sample questions is also a good way to identify any areas of weakness in your knowledge. If you find that you struggle with a particular topic, you can then focus your revision on that area.
myCBSEguide offers ample Class 11 Mathematics case study questions, so there is no excuse. With a little bit of preparation, Class 11 Mathematics students can boost their chances of getting the grade they deserve.
Some samples of Class 11 Mathematics case study questions are as follows:
Class 11 Mathematics case study question 1
- 9 km and 13 km
- 9.8 km and 13.8 km
- 9.5 km and 13.5 km
- 10 km and 14 km
- x ≤ −1913
- x < −1613
- −1613 < x < −1913
- There are no solution.
- y ≤ 12 x+2
- y > 12 x+2
- y ≥ 12 x+2
- y < 12 x+2
Answer Key:
- (b) 9.8 km and 13.8 km
- (a) −1913 ≤ x
- (b) y > 12 x+2
- (d) (-5, 5)
Class 11 Mathematics case study question 2
- 2 C 1 × 13 C 10
- 2 C 1 × 10 C 13
- 1 C 2 × 13 C 10
- 2 C 10 × 13 C 10
- 6 C 2 × 3 C 4 × 11 C 5
- 6 C 2 × 3 C 4 × 11 C 5
- 6 C 2 × 3 C 5 × 11 C 4
- 6 C 2 × 3 C 1 × 11 C 5
- (b) (13) 4 ways
- (c) 2860 ways.
Class 11 Mathematics case study question 3
Read the Case study given below and attempt any 4 sub parts: Father of Ashok is a builder, He planned a 12 story building in Gurgaon sector 5. For this, he bought a plot of 500 square yards at the rate of Rs 1000 /yard². The builder planned ground floor of 5 m height, first floor of 4.75 m and so on each floor is 0.25 m less than its previous floor.
Class 11 Mathematics case study question 4
Read the Case study given below and attempt any 4 sub parts: villages of Shanu and Arun’s are 50km apart and are situated on Delhi Agra highway as shown in the following picture. Another highway YY’ crosses Agra Delhi highway at O(0,0). A small local road PQ crosses both the highways at pints A and B such that OA=10 km and OB =12 km. Also, the villages of Barun and Jeetu are on the smaller high way YY’. Barun’s village B is 12km from O and that of Jeetu is 15 km from O.
Now answer the following questions:
- 5x + 6y = 60
- 6x + 5y = 60
- (a) (10, 0)
- (b) 6x + 5y = 60
- (b) 60/√ 61 km
- (d) 2√61 km
A peek at the Class 11 Mathematics curriculum
The Mathematics Syllabus has evolved over time in response to the subject’s expansion and developing societal requirements. The Senior Secondary stage serves as a springboard for students to pursue higher academic education in Mathematics or professional subjects such as Engineering, Physical and Biological Science, Commerce, or Computer Applications. The current updated curriculum has been prepared in compliance with the National Curriculum Framework 2005 and the instructions provided by the Focus Group on Teaching Mathematics 2005 in order to satisfy the rising demands of all student groups. Greater focus has been placed on the application of various principles by motivating the themes from real-life events and other subject areas.
Class 11 Mathematics (Code No. 041)
| I. | Sets and Functions | 60 | 23 |
| II. | Algebra | 50 | 25 |
| III. | Coordinate Geometry | 50 | 12 |
| IV. | Calculus | 40 | 08 |
| V. | Statistics and Probability | 40 | 12 |
| Internal Assessment |
Design of Class 11 Mathematics exam paper
CBSE Class 11 mathematics question paper is designed to assess students’ understanding of the subject’s essential concepts. Class 11 mathematics question paper will assess their problem-solving and analytical abilities. Before beginning their test preparations, students in Class 11 maths should properly review the question paper format. This will assist Class 11 mathematics students in better understanding the paper and achieving optimum scores. Refer to the Class 11 Mathematics question paper design provided.
Class 11 Mathematics Question Paper Design
| 1. | Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. | 44 | 55 |
| Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas | |||
| 2 | Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. | 20 | 25 |
| 3 | Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations | 16 | 20 |
| Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria. | |||
- No chapter-wise weightage. Care to be taken to cover all the chapters.
- Suitable internal variations may be made for generating various templates keeping the overall weightage to different forms of questions and typology of questions the same.
Choice(s): There will be no overall choice in the question paper. However, 33% of internal choices will be given in all the sections.
| Periodic Tests (Best 2 out of 3 tests conducted) | 10 Marks |
| Mathematics Activities | 10 Marks |
Prescribed Books:
- Mathematics Textbook for Class XI, NCERT Publications
- Mathematics Exemplar Problem for Class XI, Published by NCERT
- Mathematics Lab Manual class XI, published by NCERT
myCBSEguide guarantees LHS=RHS
With myCBSEguide it will always be LHS=RHS, Hence Proved!
myCBSEguide is a prominent streaming resource for students studying for CBSE examinations. The site offers extensive study material, practice papers, case study questions, online examinations, and other resources at the push of a click. myCBSEguide also has a mobile app for learning on the move. There’s no excuse not to try myCBSEguide with so much convenience and simplicity of access! Hence Proved!
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Computer Science Case Study Questions
1 thought on “Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions”
teri meri meri teri prem kahani hai muskil dolabjo main sayana hop jaye ek ladka aur ek ladki ki prem kahani hai muskil
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths Sets Free PDF

Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Sets in order to fully complete your preparation . They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Case Study Based Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams!
I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams. To download the latest CBSE Case Study Questions , just click ‘ Download PDF ’.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths Sets PDF
Checkout our case study questions for other chapters.
- Chapter 2 Relations and Functions Case Study Questions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Case Study Questions
- Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction Case Study Questions
- Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Case Study Questions
How should I study for my upcoming exams?
First, learn to sit for at least 2 hours at a stretch
Solve every question of NCERT by hand, without looking at the solution.
Solve NCERT Exemplar (if available)
Sit through chapter wise FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS
Practice MCQ Questions (Very Important)
Practice Assertion Reason & Case Study Based Questions
Sit through FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS involving MCQs. Assertion reason & Case Study Based Questions
After Completing everything mentioned above, Sit for atleast 6 full syllabus TESTS.
Contact Form
Privacy Policy
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 3 Class 11 Trigonometric Functions
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
NCERT Solutions of Chapter 3 Class 11 Trigonometry is available free at teachoo. You can check the detailed explanation of all questions of exercises, examples and miscellaneous by clicking on the Exercise link below.
We had learned Basics of Trigonometry in Class 10. In this chapter, we will learn
- What is a positive or a negative angle
- Measuring angles in Degree , Minutes and Seconds
- Radian measure of an angle
- Converting Degree to Radians , and vice-versa
- Sign of sin, cos, tan in all 4 quadrants
- Finding values of trigonometric functions when one value is given (Example: Finding value of sin, cot, cosec, tan, sec, when cos x = -3/5 is given)
- Finding Value of trigonometric functions, given angle
- Solving questions by formula like (x + y) formula, 2x 3x formula, Cos x + cos y formula , 2 sin x sin y formula
- Finding principal and general solutions of a trigonometric equation
- Sin and Cosine Formula with supplementary Questions
Important questions are marked, and Formula sheet is also provided. Click on an exercise or topic to begin.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
CBSE Class 11 Maths – Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions- Study Materials
NCERT Solutions Class 11 All Subjects Sample Papers Past Years Papers
Sets : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
- Concepts of Trigonometric Functions
- Trigonometric Functions Master File
- Trigonometric Functions Revision Notes
- R D Sharma Solution of Trigonometric Functions
- NCERT Solution Trigonometric Functions
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Trigonometric Functions
- Trigonometric Functions : Solved Example 1
CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
Angle Angle is a measure of rotation of a given ray about its initial point. The original ray is called the initial side and the final position of ray after rotation is called terminal side of the angle. The point of rotation is called vertex. If the direction of rotation is anti-clockwise, the angle is said to be positive and if the direction of rotation is clockwise, then the angle is negative.
Measuring Angles There are two systems of measuring angles Sexagesimal system (degree measure): If a rotation from the initial side to terminal side is ( 1 360 ) t h of a revolution, the angle is said to have a measure of one degree, written as 1°. One sixtieth of a degree is called a minute, written as 1′ and one-sixtieth of a minute is called a second, written as 1″ Thus, 1° = 60′ and 1′ = 60″
Circular system (radian measure): A radian is an angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc, whose length is equal to the radius of the circle. We denote 1 radian by 1°.
Relation Between Radian and Degree We know that a complete circle subtends at its centre an angle whose measure is 2π radians as well as 360°. 2π radian = 360°. Hence, π radian = 180° or 1 radian = 57° 16′ 21″ (approx) 1 degree = 0.01746 radian
Six Fundamental Trigonometric Identities
- sinx = 1 c o s e c x
- cos x = 1 s e c x
- tan x = 1 c o t x
- sin 2 x + cos 2 x = 1
- 1 + tan 2 x = sec 2 x
- 1 + cot 2 x = cosec 2 x
Trigonometric Functions – Class 11 Maths Notes
Trigonometric ratios are defined for acute angles as the ratio of the sides of a right angled triangle. The extension of trigonometric ratios to any angle in terms of radian measure (real number) are called trigonometric function. The signs of trigonometric function in different quadrants have been given in following table.
| Sin x | + | + | – | – |
| Cos x | + | – | – | + |
| Tan x | + | – | + | – |
| Cosec x | + | + | – | – |
| Sec x | + | – | – | + |
| Cot x | + | – | + | – |
Domain and Range of Trigonometric Functions
| Sine | R | [-1, 1] |
| Cos | R | [-1, 1] |
| Tan | R – {(2n + 1) π2 : n ∈ Z | R |
| Cot | R – {nπ: n ∈ Z} | R |
| Sec | R – {(2n + 1) π2 : n ∈ Z | R – (-1, 1) |
| Cosec | R – {nπ: n ∈ Z} | R – (-1, 1) |
Sine, Cosine, and Tangent of Some Angles Less Than 90°
Allied or Related Angles The angles n π 2 ± θ are called allied or related angle and θ ± n × (2π) are called coterminal angles. For general reduction, we have following rules, the value of trigonometric function for ( n π 2 ± θ ) is numerically equal to
- the value of the same function, if n is an even integer with the algebraic sign of the function as per the quadrant in which angle lies.
- the corresponding co-function of θ, if n is an odd integer with the algebraic sign of the function for the quadrant in which it lies, here sine and cosine, tan and cot, sec and cosec are cofunctions of each other.
Functions of Negative Angles
For any acute angle of θ. We have,
- sin(-θ) = – sinθ
- cos (-θ) = cosθ
- tan (-θ) = – tanθ
- cot (-θ) = – cotθ
- sec (-θ) = secθ
- cosec (-θ) = – cosecθ
Some Formulae Regarding Compound Angles
An angle made up of the sum or difference of two or more angles is called compound angles. The basic results in direction are called trigonometric identities as given below: (i) sin (x + y) = sin x cos y + cos x sin y (ii) sin (x – y) = sin x cos y – cos x sin y (iii) cos (x + y) = cos x cos y – sin x sin y (iv) cos (x – y) = cos x cos y + sin x sin y
(ix) sin(x + y) sin (x – y) = sin 2 x – sin 2 y = cos 2 y – cos 2 x (x) cos (x + y) cos (x – y) = cos 2 x – sin 2 y = cos 2 y – sin 2 x
Transformation Formulae
- 2 sin x cos y = sin (x + y) + sin (x – y)
- 2 cos x sin y = sin (x + y) – sin (x – y)
- 2 cos x cos y = cos (x + y) + cos (x – y)
- 2 sin x sin y = cos (x – y) – cos (x + y)
- sin x + sin y = 2 sin( x + y 2 ) cos( x − y 2 )
- sin x – sin y = 2 cos( x + y 2 ) sin( x − y 2 )
- cos x + cos y = 2 cos( x + y 2 ) cos( x − y 2 )
- cos x – cos y = -2 sin( x + y 2 ) sin( x − y 2 )
Trigonometric Ratios of Multiple Angles
Product of Trigonometric Ratios
- sin x sin (60° – x) sin (60° + x) = 1 4 sin 3x
- cos x cos (60° – x) cos (60° + x) = 1 4 cos 3x
- tan x tan (60° – x) tan (60° + x) = tan 3x
- cos 36° cos 72° = 1 4
- cos x . cos 2x . cos 2 2 x . cos 2 3 x … cos 2 n-1 = s i n 2 n x 2 n s i n x
Sum of Trigonometric Ratio, if Angles are in A.P.
Trigonometric Equations Equation which involves trigonometric functions of unknown angles is known as the trigonometric equation.
Solution of a Trigonometric Equation A solution of a trigonometric equation is the value of the unknown angle that satisfies the equation. A trigonometric equation may have an infinite number of solutions.
Principal Solution The solutions of a trigonometric equation for which 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π are called principal solutions.
General Solutions A solution of a trigonometric equation, involving ‘n’ which gives all solution of a trigonometric equation is called the general solutions.
General Solutions of Trigonometric Equation
- sin x = 0 ⇔ x = nπ, n ∈ Z
- cos x = 0 ⇔ x = (2n + 1) π 2 , n ∈ Z
- tan x = 0 ⇔ x = nπ, n ∈ Z
- sin x = sin y ⇔ x = nπ + (-1) n y, n ∈ Z
- cos x = cos y ⇔ x = 2nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- tan x = tan y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- sin 2 x = sin 2 y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- cos 2 x = cos 2 y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- tan 2 x = tan 2 y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
Basic Rules of Triangle
In a triangle ABC, the angles are denoted by capital letters A, B and C and the lengths of sides of opposite to these angles are denoted by small letters a, b and c, respectively. Sine Rule s i n A a = s i n B b = s i n C c
Cosine Rule a 2 = b 2 + c 2 – 2bc cos A b 2 = c 2 + a 2 – 2ac cos B c 2 = a 2 + b 2 – 2ab cos C
Projection Rule a = b cos C + c cos B b = c cos A + a cos C c = a cos B + b cos A
Trigonometric Functions Class 11 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1. The value of cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × cos (x + y) is (a) sin (x + y) (b) sin² (x + y) (c) sin³ (x + y) (d) sin 4 (x + y)
Answer: (b) sin² (x + y) Hint: cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × cos(x + y) {since cos(x + y) = cos x × cos y – sin x × sin y } = cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × (cos x × cos y – sin x × sin y) = cos² x + cos² y – 2cos² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = cos² x + cos² y – cos² x × cos² y – cos² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = (cos² x – cos² x × cos² y) + (cos² y – cos² x × cos² y) + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = cos² x(1- cos² y) + cos² y(1 – cos² x) + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = sin² y × cos² x + sin² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y (since sin² x + cos² x = 1 ) = sin² x × cos² y + sin² y × cos² x + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = (sin x × cos y)² + (sin y × cos x)² + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = (sin x × cos y + sin y × cos x)² = {sin (x + y)}² = sin² (x + y)
Question 2. If a×cos x + b × cos x = c, then the value of (a × sin x – b²cos x)² is (a) a² + b² + c² (b) a² – b² – c² (c) a² – b² + c² (d) a² + b² – c²
Answer: (d) a² + b² – c² Hint: We have (a×cos x + b × sin x)² + (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b² ⇒ c² + (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b² ⇒ (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b² – c²
Question 3. If cos a + 2cos b + cos c = 2 then a, b, c are in (a) 2b = a + c (b) b² = a × c (c) a = b = c (d) None of these
Answer: (a) 2b = a + c Hint: Given, cos A + 2 cos B + cos C = 2 ⇒ cos A + cos C = 2(1 – cos B) ⇒ 2 cos((A + C)/2) × cos((A-C)/2 = 4 sin²(B/2) ⇒ 2 sin(B/2)cos((A-C)/2) = 4sin² (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2sin (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) – cos((A+C)/2) = cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ 2sin(A/2)sin(C/2) = sin(B/2) ⇒ 2{√(s-b)(s-c)√bc} × {√(s-a)(s-b)√ab} = √(s-a)(s-c)√ac ⇒ 2(s – b) = b ⇒ a + b + c – 2b = b ⇒ a + c – b = b ⇒ a + c = 2b
Question 4. The value of cos 5π is (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) -1 (d) None of these
Answer: (c) -1 Hint: Given, cos 5π = cos (π + 4π) = cos π = -1
Question 5. In a triangle ABC, cosec A (sin B cos C + cos B sin C) equals (a) none of these (b) c/a (c) 1 (d) a/c
Answer: (c) 1 Hint: Given cosec A (sin B cos C + cos B sin C) = cosec A × sin(B+C) = cosec A × sin(180 – A) = cosec A × sin A = cosec A × 1/cosec A = 1
Question 6. If the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5, then the ratio of the greatest side to the smallest side is (a) 4 : (√5 – 1) (b) 5 : 4 (c) (√5 – 1) : 4 (d) none of these
Answer: (a) 4 : (√5 – 1) Hint: Given, the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5 ⇒ x + 4x + 5x = 180 ⇒ 10x = 180 ⇒ x = 180/10 ⇒ x = 18 So, the angle are: 18, 72, 90 Since a : b : c = sin A : sin B : sin C ⇒ a : b : c = sin 18 : sin 72 : sin 90 ⇒ a : b : c = (√5 – 1)/4 : {√(10 + 2√5)}/4 : 1 ⇒ a : b : c = (√5 – 1) : {√(10 + 2√5)} : 4 Now, c /a = 4/(√5 – 1) ⇒ c : a = 4 : (√5 – 1)
Question 7. The value of cos 180° is (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) -1 (d) infinite
Answer: (c) -1 Hint: 180 is a standard degree generally we all know their values but if we want to go theoretically then cos(90 + x) = – sin(x) So, cos 180 = cos(90 + 90) = -sin 90 = -1 {sin 90 = 1} So, cos 180 = -1
Question 8. The perimeter of a triangle ABC is 6 times the arithmetic mean of the sines of its angles. If the side b is 2, then the angle B is (a) 30° (b) 90° (c) 60° (d) 120°
Answer: (b) 90° Hint: Let the lengths of the sides if ∆ABC be a, b and c Perimeter of the triangle = 2s = a + b + c = 6(sinA + sinB + sinC)/3 ⇒ (sinA + sinB + sinC) = ( a + b + c)/2 ⇒ (sinA + sinB + sinC)/( a + b + c) = 1/2 From sin formula,Using sinA/a = sinB/b = sinC/c = (sinA + sinB + sinC)/(a + b + c) = 1/2 Now, sinB/b = 1/2 Given b = 2 So, sinB/2 = 1/2 ⇒ sinB = 1 ⇒ B = π/2
Question 9: If 3 × tan(x – 15) = tan(x + 15), then the value of x is (a) 30 (b) 45 (c) 60 (d) 90
Answer: (b) 45 Hint: Given, 3×tan(x – 15) = tan(x + 15) ⇒ tan(x + 15)/tan(x – 15) = 3/1 ⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = (3 + 1)/(3 – 1) ⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = 4/2 ⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = 2 ⇒ sin(x + 15 + x – 15)/sin(x + 15 – x + 15) = 2 ⇒ sin 2x/sin 30 = 2 ⇒ sin 2x/(1/2) = 2 ⇒ 2 × sin 2x = 2 ⇒ sin 2x = 1 ⇒ sin 2x = sin 90 ⇒ 2x = 90 ⇒ x = 45
Question 10. If the sides of a triangle are 13, 7, 8 the greatest angle of the triangle is (a) π/3 (b) π/2 (c) 2π/3 (d) 3π/2
Answer: (c) 2π/3 Hint: Given, the sides of a triangle are 13, 7, 8 Since greatest side has greatest angle, Now Cos A = (b² + c² – a²)/2bc ⇒ Cos A = (7² + 8² – 13²)/(2×7×8) ⇒ Cos A = (49 + 64 – 169)/(2×7×8) ⇒ Cos A = (113 – 169)/(2×7×8) ⇒ Cos A = -56/(2×56) ⇒ Cos A = -1/2 ⇒ Cos A = Cos 2π/3 ⇒ A = 2π/3 So, the greatest angle is = 2π/3
Question 11. The value of tan 20 × tan 40 × tan 80 is (a) tan 30 (b) tan 60 (c) 2 tan 30 (d) 2 tan 60
Answer: (b) tan 60 Hint: Given, tan 20 × tan 40 × tan 80 = tan 40 × tan 80 × tan 20 = [{sin 40 × sin 80}/{cos 40 × cos 80}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{2 * sin 40 × sin 80}/{2 × cos 40 × cos 80}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{cos 40 – cos 120}/{cos 120 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{cos 40 – cos (90 + 30)}/{cos (90 + 30) + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{cos 40 + sin30}/{-sin30 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{(2 × cos 40 + 1)/2}/{(-1 + cos 40)/2}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{2 × cos 40 + 1}/{-1 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{2 × cos 40 × sin 20 + sin 20}/{-cos 20 + cos 40 × cos 20}] = (sin 60 – sin 20 + sin 20)/(-cos 20 + cos 60 + cos 20) = sin 60/cos 60 = tan 60 So, tan 20 × tan 40 × tan 80 = tan 60
Question 12. If the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5, then the ratio of the greatest side to the smallest side is (a) 4 : (√5 – 1) (b) 5 : 4 (c) (√5 – 1) : 4 (d) none of these
Question 13. The general solution of √3 cos x – sin x = 1 is (a) x = n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) (b) x = π/3 – n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) (c) x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) (d) x = π/3 – n × π + (π/6)
Answer: (c) x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) Hint: √3 cos x-sin x=1 ⇒ (√3/2)cos x – (1/2)sin x = 1/2 ⇒ sin 60 × cos x – cos 60 × sin x = 1/2 ⇒ sin (x – 60) = 1/2 ⇒ sin (x – π/3) = sin 30 ⇒ sin (x – π/3) = sinπ/6 ⇒ x – π/3 = n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) {where n ∈ Z} ⇒ x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6)
Question 14. If tan² θ = 1 – e², then the value of sec θ + tan³ θ × cosec θ is (a) 2 – e² (b) (2 – e²) 1/2 (c) (2 – e²)² (d) (2 – e²) 3/2
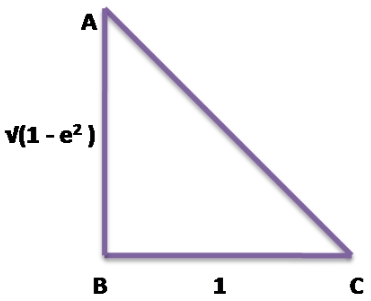
Question 15. The value of cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65 is (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) -1 (d) None of these
Answer: (b) 1 Hint: Given, cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65 = cos 20 + 1 – cos 110 – √2 sin65 {since cos 2x = 1 – 2sin² x} = 1 + cos 20 – cos 110 – √2 sin65 = 1 – 2 × sin {(20 + 110)/2 × sin{(20 – 110)/2} – √2 sin65 {Apply cos C – cos D formula} = 1 – 2 × sin 65 × sin (-45) – √2 sin65 = 1 + 2 × sin 65 × sin 45 – √2 sin65 = 1 + (2 × sin 65)/√2 – √2 sin65 = 1 + √2 ( sin 65 – √2 sin 65 = 1 So, cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65 = 1
Question 16. If the radius of the circumcircle of an isosceles triangle PQR is equal to PQ ( = PR), then the angle P is (a) 2π/3 (b) π/3 (c) π/2 (d) π/6
Answer: (a) 2π/3 Hint: Let S be the center of the circumcircle of triangle PQR. So, SP = SQ = SR = PQ = PR, where SP, SQ & SR are radii. Thus SPQ & SPR are equilateral triangles. ⇒ ∠QSP = 60°; Similarly ∠RQP = 60° ⇒ Angle at the center QSP = 120° So, SRPQ is a rhombus, since all the four sides are equal. Hence, its opposite angles are equal; so ∠P = ∠QSP = 120°
Question 17. If cos a + 2cos b + cos c = 2 then a, b, c are in (a) 2b = a + c (b) b² = a × c (c) a = b = c (d) None of these
Answer: (a) 2b = a + c Hint: Given, cos A + 2 cos B + cos C = 2 ⇒ cos A + cos C = 2(1 – cos B) ⇒ 2 cos((A + C)/2) × cos((A-C)/2 = 4 sin² (B/2) ⇒ 2 sin(B/2)cos((A-C)/2) = 4sin² (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2sin (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) – cos((A+C)/2) = cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ 2sin(A/2)sin(C/2) = sin(B/2) ⇒ 2{√(s-b)(s-c)√bc} × {√(s-a)(s-b)√ab} = √(s-a)(s-c)√ac ⇒ 2(s – b) = b ⇒ a + b + c – 2b = b ⇒ a + c – b = b ⇒ a + c = 2b
Question 18. The value of 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) is (a) sin x (b) sin 2x (c) sin 3x (d) sin 4x
Answer: (c) sin 3x Hint: Given, 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) = 4 × sin x × {sin x × cos π/3 + cos x × sin π/3} × {sin x × cos 2π/3 + cos x × sin 2π/3} = 4 × sin x × {(sin x)/2 + (√3 × cos x)/2} × {-(sin x)/2 + (√3 × cos x)/2} = 4 × sin x × {-(sin 2x)/4 + (3 × cos 2x)/4} = sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 × cos 2x} = sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 × (1 – sin 2x)} = sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 – 3 × sin 2x} = sin x × {3 – 4 × sin 2x} = 3 × sin x – 4 sin 3x = sin 3x So, 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) = sin 3x
Question 19. If tan A – tan B = x and cot B – cot A = y, then the value of cot (A – B) is (a) x + y (b) 1/x + y (c) x + 1/y (d) 1/x + 1/y
Answer: (d) 1/x + 1/y Hint: Given, tan A – tan B = x ……………. 1 and cot B – cot A = y ……………. 2 From equation, 1/cot A – 1/cot B = x ⇒ (cot B – cot A)/(cot A × cot B) = x ⇒ y/(cot A × cot B) = x {from equation 2} ⇒ y = x × (cot A × cot B) ⇒ cot A × cot B = y/x Now, cot (A – B) = (cot A × cot B + 1)/(cot B – cot A) ⇒ cot (A – B) = (y/x + 1)/y ⇒ cot (A – B) = (y/x) × (1/y) + 1/y ⇒ cot (A – B) = 1/x + 1/y
Question 20. The value of (sin 7x + sin 5x) /(cos 7x + cos 5x) + (sin 9x + sin 3x) / (cos 9x + cos 3x) is (a) tan 6x (b) 2 tan 6x (c) 3 tan 6x (d) 4 tan 6x
Answer: (b) 2 tan 6x Hint: Given, (sin 7x + sin 5x) /(cos 7x + cos 5x) + (sin 9x + sin 3x) / (cos 9x + cos 3x) ⇒ [{2 × sin(7x+5x)/2 × cos(7x-5x)/2}/{2 × cos(7x+5x)/2 × cos(7x-5x)/2}] + [{2 × sin(9x+3x)/2 × cos(9x-3x)/2}/{2 × cos(9x+3x)/2 × cos(9x-3x)/2}] ⇒ [{2 × sin 6x × cosx}/{2 × cos 6x × cosx}] + [{2 × sin 6x × cosx}/{2 × cos 6x × cosx}] ⇒ (sin 6x/cos 6x) + (sin 6x/cos 6x) ⇒ tan 6x + tan 6x ⇒ 2 tan 6x
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions are available at BYJU’S, which are prepared by our expert teachers. All these solutions are written as per the latest update on the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24 and its guidelines. BYJU’S provides step-by-step solutions by considering the different understanding levels of students and the marking scheme. Chapter 3, Trigonometric Functions, comes under NCERT Class 11 Maths and is an important chapter for students. Though the chapter has numerous mathematical terms and formulae, BYJU’S has made NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths easy for the students to understand and remember with the usage of tricks.
Trigonometry has been developed to solve geometric problems involving triangles. Students cannot skip Trigonometric chapters since this is used in many areas, such as finding the heights of tides in the ocean, designing electronic circuits, etc. In the earlier classes, students have already studied trigonometric identities and applications of trigonometric ratios. In Class 11 , trigonometric ratios are generalised to trigonometric function and their properties. However, the NCERT Solutions of BYJU’S help the students to attain more knowledge and score full marks in this chapter of the examination.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
In this section, a few important terms are defined, such as principal solution and general solution of trigonometric functions, which are explained using examples too. Exercise 3.1 Solutions 7 Questions Exercise 3.2 Solutions 10 Questions Exercise 3.3 Solutions 25 Questions Exercise 3.4 Solutions 9 Questions Miscellaneous Exercise On Chapter 3 Solutions 10 Questions
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3
Exercise 3.1 page: 54
1. Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures:
(i) 25° (ii) – 47° 30′ (iii) 240° (iv) 520°

2. Find the degree measures corresponding to the following radian measures (Use π = 22/7)
Here π radian = 180°

3. A wheel makes 360 revolutions in one minute. Through how many radians does it turn in one second?
It is given that
No. of revolutions made by the wheel in
1 minute = 360
1 second = 360/60 = 6
We know that
The wheel turns an angle of 2π radian in one complete revolution.
In 6 complete revolutions, it will turn an angle of 6 × 2π radian = 12 π radian
Therefore, in one second, the wheel turns an angle of 12π radian.
4. Find the degree measure of the angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius 100 cm by an arc of length 22 cm (Use π = 22/7).

5. In a circle of diameter 40 cm, the length of a chord is 20 cm. Find the length of minor arc of the chord.
The dimensions of the circle are
Diameter = 40 cm
Radius = 40/2 = 20 cm
Consider AB be as the chord of the circle i.e. length = 20 cm

Radius of circle = OA = OB = 20 cm
Similarly AB = 20 cm
Hence, ΔOAB is an equilateral triangle.
θ = 60° = π/3 radian
In a circle of radius r unit, if an arc of length l unit subtends an angle θ radian at the centre
We get θ = 1/r
Therefore, the length of the minor arc of the chord is 20π/3 cm.
6. If in two circles, arcs of the same length subtend angles 60° and 75° at the centre, find the ratio of their radii.

7. Find the angle in radian though which a pendulum swings if its length is 75 cm and the tip describes an arc of length
(i) 10 cm (ii) 15 cm (iii) 21 cm
In a circle of radius r unit, if an arc of length l unit subtends an angle θ radian at the centre, then θ = 1/r
We know that r = 75 cm
(i) l = 10 cm
θ = 10/75 radian
By further simplification
θ = 2/15 radian
(ii) l = 15 cm
θ = 15/75 radian
θ = 1/5 radian
(iii) l = 21 cm
θ = 21/75 radian
θ = 7/25 radian
Exercise 3.2 page: 63
Find the values of other five trigonometric functions in Exercises 1 to 5.
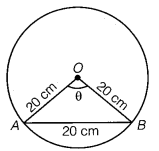
1. cos x = -1/2, x lies in third quadrant.

2. sin x = 3/5, x lies in second quadrant.
sin x = 3/5
We can write it as

sin 2 x + cos 2 x = 1
cos 2 x = 1 – sin 2 x

3. cot x = 3/4, x lies in third quadrant.
cot x = 3/4

1 + tan 2 x = sec 2 x
1 + (4/3) 2 = sec 2 x
Substituting the values
1 + 16/9 = sec 2 x
cos 2 x = 25/9
sec x = ± 5/3
Here x lies in the third quadrant so the value of sec x will be negative
sec x = – 5/3

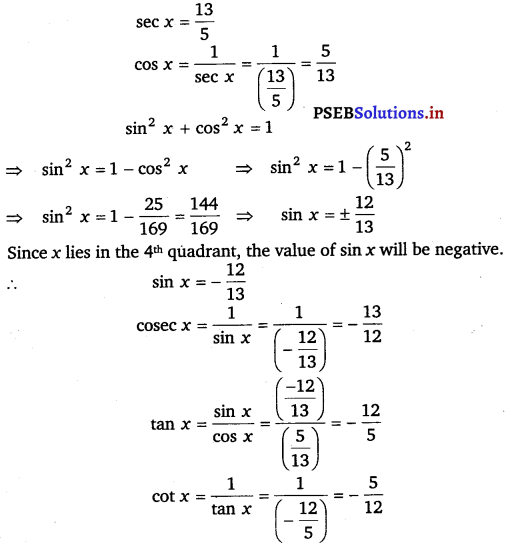
4. sec x = 13/5, x lies in fourth quadrant.
sec x = 13/5

sin 2 x = 1 – cos 2 x
sin 2 x = 1 – (5/13) 2
sin 2 x = 1 – 25/169 = 144/169
sin 2 x = ± 12/13
Here x lies in the fourth quadrant so the value of sin x will be negative
sin x = – 12/13

5. tan x = -5/12, x lies in second quadrant.
tan x = – 5/12

1 + (-5/12) 2 = sec 2 x
1 + 25/144 = sec 2 x
sec 2 x = 169/144
sec x = ± 13/12
Here x lies in the second quadrant so the value of sec x will be negative
sec x = – 13/12

Find the values of the trigonometric functions in Exercises 6 to 10.
6. sin 765°
We know that values of sin x repeat after an interval of 2π or 360°

By further calculation
7. cosec (–1410°)
We know that values of cosec x repeat after an interval of 2π or 360°

= cosec 30 o = 2

We know that values of tan x repeat after an interval of π or 180°

Exercise 3.3 page: 73
Prove that:

= 1/2 + 4/4

5. Find the value of:
(i) sin 75 o
(ii) tan 15 o

(ii) tan 15°
It can be written as
= tan (45° – 30°)
Using formula

Prove the following:

= sin x cos x (tan x + cot x)

10. sin ( n + 1) x sin ( n + 2) x + cos ( n + 1) x cos ( n + 2) x = cos x
LHS = sin ( n + 1) x sin ( n + 2) x + cos ( n + 1) x cos ( n + 2) x

Using the formula

12. sin 2 6 x – sin 2 4 x = sin 2 x sin 10 x

13. cos 2 2 x – cos 2 6 x = sin 4 x sin 8 x

= (2 sin 4 x cos 4 x ) (2 sin 2 x cos 2 x )
= sin 8x sin 4x
14. sin 2x + 2sin 4x + sin 6x = 4cos 2 x sin 4x

= 2 sin 4x cos (– 2x) + 2 sin 4x
= 2 sin 4x cos 2x + 2 sin 4x
Taking common terms
= 2 sin 4x (cos 2x + 1)
= 2 sin 4x (2 cos 2 x – 1 + 1)
= 2 sin 4x (2 cos 2 x)
= 4cos 2 x sin 4x
15. cot 4 x (sin 5 x + sin 3 x ) = cot x (sin 5 x – sin 3 x )
LHS = cot 4x (sin 5x + sin 3x)

= 2 cos 4x cos x
Hence, LHS = RHS.

22. cot x cot 2 x – cot 2 x cot 3 x – cot 3 x cot x = 1

LHS = tan 4x = tan 2(2x)
By using the formula

24. cos 4 x = 1 – 8sin 2 x cos 2 x
LHS = cos 4x
= cos 2(2 x )
Using the formula cos 2 A = 1 – 2 sin 2 A
= 1 – 2 sin 2 2 x
Again by using the formula sin2 A = 2sin A cos A
= 1 – 2(2 sin x cos x ) 2
= 1 – 8 sin 2 x cos 2 x
25. cos 6 x = 32 cos 6 x – 48 cos 4 x + 18 cos 2 x – 1
L.H.S. = cos 6 x
= cos 3(2 x )
Using the formula cos 3 A = 4 cos 3 A – 3 cos A
= 4 cos 3 2 x – 3 cos 2 x
Again by using formula cos 2 x = 2 cos 2 x – 1
= 4 [(2 cos 2 x – 1) 3 – 3 (2 cos 2 x – 1)
= 4 [(2 cos 2 x ) 3 – (1) 3 – 3 (2 cos 2 x ) 2 + 3 (2 cos 2 x )] – 6cos 2 x + 3
= 4 [8cos 6 x – 1 – 12 cos 4 x + 6 cos 2 x ] – 6 cos 2 x + 3
By multiplication
= 32 cos 6 x – 4 – 48 cos 4 x + 24 cos 2 x – 6 cos 2 x + 3
On further calculation
= 32 cos 6 x – 48 cos 4 x + 18 cos 2 x – 1
Exercise 3.4 PAGE: 78
Find the principal and general solutions of the following equations:
1. tan x = √3

2. sec x = 2

3. cot x = – √3

4. cosec x = – 2

Find the general solution for each of the following equations:
5. cos 4x = cos 2x

6. cos 3x + cos x – cos 2x = 0

7. sin 2x + cos x = 0
sin 2x + cos x = 0
2 sin x cos x + cos x = 0
cos x (2 sin x + 1) = 0
cos x = 0 or 2 sin x + 1 = 0
Let cos x = 0

8. sec 2 2x = 1 – tan 2x
sec 2 2x = 1 – tan 2x
1 + tan 2 2x = 1 – tan 2x
tan 2 2x + tan 2x = 0
tan 2x (tan 2x + 1) = 0
tan 2x = 0 or tan 2x + 1 = 0
If tan 2x = 0
tan 2x = tan 0
2x = nπ + 0, where n ∈ Z
x = nπ/2, where n ∈ Z
tan 2x + 1 = 0
tan 2x = – 1

2x = nπ + 3π/4, where n ∈ Z
x = nπ/2 + 3π/8, where n ∈ Z
Hence, the general solution is nπ/2 or nπ/2 + 3π/8, n ∈ Z.
9. sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0
sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0
(sin x + sin 5x) + sin 3x = 0

2 sin 3x cos (-2x) + sin 3x = 0
2 sin 3x cos 2x + sin 3x = 0
By taking out the common terms
sin 3x (2 cos 2x + 1) = 0
sin 3x = 0 or 2 cos 2x + 1 = 0
If sin 3x = 0
3x = nπ, where n ∈ Z
x = nπ/3, where n ∈ Z
If 2 cos 2x + 1 = 0
cos 2x = – 1/2
= – cos π/3
= cos (π – π/3)
cos 2x = cos 2π/3

Miscellaneous Exercise page: 81

2. (sin 3 x + sin x ) sin x + (cos 3 x – cos x ) cos x = 0
LHS = (sin 3x + sin x) sin x + (cos 3x – cos x) cos x
= sin 3x sin x + sin 2 x + cos 3x cos x – cos 2 x
Taking out the common terms
= cos 3x cos x + sin 3x sin x – (cos 2 x – sin 2 x)
cos (A – B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
= cos (3x – x) – cos 2x
= cos 2x – cos 2x

LHS = (cos x + cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2
By expanding using formula we get
= cos 2 x + cos 2 y + 2 cos x cos y + sin 2 x + sin 2 y – 2 sin x sin y
Grouping the terms
= (cos 2 x + sin 2 x) + (cos 2 y + sin 2 y) + 2 (cos x cos y – sin x sin y)
Using the formula cos (A + B) = (cos A cos B – sin A sin B)
= 1 + 1 + 2 cos (x + y)
= 2 + 2 cos (x + y)
Taking 2 as common
From the formula cos 2A = 2 cos 2 A – 1

LHS = (cos x – cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2
By expanding using formula
= cos 2 x + cos 2 y – 2 cos x cos y + sin 2 x + sin 2 y – 2 sin x sin y
= (cos 2 x + sin 2 x) + (cos 2 y + sin 2 y) – 2 (cos x cos y + sin x sin y)
Using the formula cos (A – B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
From formula cos 2A = 1 – 2 sin 2 A

5. sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x + sin 7x = 4 cos x cos 2x sin 4x

8. Find sin x/2, cos x/2 and tan x/2 in each of the following:

cos x = -3/5
From the formula

9. cos x = -1/3, x in quadrant III

10. sin x = 1/4, x in quadrant II

This chapter has 6 exercises and a miscellaneous exercise to help students understand the concepts related to Trigonometric Functions clearly. BYJU’S provides all the concepts and solutions for Chapter 3 of Class 11 Maths with clear explanations and formulas. The PDF of Maths NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chapter 3 includes the topics and sub-topics listed below. 3.1 Introduction The basic trigonometric ratios and identities are given here, along with the applications of trigonometric ratios in solving the word problems related to heights and distances. 3.2 Angles 3.2.1 Degree measure 3.2.2 Radian measure 3.2.3 Relation between radian and real numbers 3.2.4 Relation between degree and radian In this section, different terms related to trigonometry are discussed, such as terminal side, initial sides, measuring an angle in degrees and radian, etc. 3.3 Trigonometric Functions 3.3.1 Sign of trigonometric functions 3.3.2 Domain and range of trigonometric functions After studying this section, students are able to understand the generalised trigonometric functions with signs. Also, they can gain knowledge on domain and range of trigonometric functions with examples. 3.4 Trigonometric Functions of Sum and Difference of Two Angles This section contains formulas related to the sum and difference of two angles in trigonometric functions.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
Studying the Trigonometric Functions of Class 11 enables the students to understand the following:
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
- Positive and negative angles
- Measuring angles in radians and in degrees and conversion of one into other
- Definition of trigonometric functions with the help of unit circle
- Truth of the sin 2x + cos 2x = 1, for all x
- Signs of trigonometric functions
- Domain and range of trigonometric functions
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
- Expressing sin (x±y) and cos (x±y) in terms of sin x, sin y, cos x & cosy and their simple application, identities related to sin 2x, cos 2x, tan 2x, sin 3x, cos 3x and tan 3x
- The general solution of trigonometric equations of the type sin y = sin a, cos y = cos a and tan y = tan a
Disclaimer –
Dropped Topics –
3.5 Trigonometric Equations (up to Exercise 3.4) Last five points in the Summary 3.6 Proofs and Simple Applications of Sine and Cosine Formulae
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3
What are the topics discussed in chapter 3 of ncert solutions for class 11 maths, as per the latest update of the cbse syllabus, how many exercises are there in chapter 3 of ncert solutions for class 11 maths, what will i learn in chapter 3 trigonometric functions of ncert solutions for class 11 maths, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Thank you very much. It is a boon for all students who refer to it, please.
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Syllabus for the Session 2023-24
CBSE Syllabus
Case Study Questions
Case Study on Sets CS-2 CS-3 CS-4 CS-5
Case Study on Relations & Functions CS-2 CS-3
Case Study on Trigonometric Functions
Case Study on Complex Numbers
Case Study on Linear Inequalities
Case Study on Permutations and Combinations
Case Study on Sequences & Series
Case Study on Straight Lines
Case Study on Conic Sections
Case Study on Statistics
Case Study on Probability
Pdf of Case Studies
MCQs for Practice
Chapter 1 - Sets
Chapter 2 - Relations & Functions
Chapter 3 - Trigonometric Functions
Chapter 4 - Complex Numbers & Quadratic Equations
Chapter 5 - Linear Inequalities
Chapter 6 - Permutations & Combinations
Chapter 7 - Binomial Theorem
Chapter 8 - Sequences & Series
Chapter 9 - Straight Line
Chapter 1 0 - Conic Sections
Chapter 1 1 - Introduction to Three-dimensional Geometry
Chapter 12 - Limits & D erivatives
Chapter 13 - Statistics
Chapter 14 - Probability
Answers of MCQs
Assertion & Reasoning Questions
Relations & Functions
Trigonometric Functions
Complex Numbers
Linear Inequalities
Permutations & Combinations
Binomial Theorem
Sequences & Series
Straight Lines
Conic Sections
Introduction to Three-Dimensional Geometry
Limits & derivatives
Probability
Topic Wise Assignments of Previous Year Questions
Relations and Functions
Straight Line
Limits & Derivatives
Question Papers - DoE, Delhi
Session 2015-2016
SA2(QP) SA2(MS) COMP(QP) COMP(MS)
Session 201 6 -20 17
SA1(QP) SA2(QP) SA2(MS) COMP(QP) COMP(MS)
Session 201 7 -201 8
SA2(QP) SA2(MS) COMP(QP) COMP(MS)
Session 201 8 -201 9
SA2(QP) SA2(MS) COMP(QP) COMP(MS)
Session 201 9 -20 20
SA2(QP) SA2(MS)
Session 2020-21
Video Explanation: Part A Part B Section III Part B Section IV Part B Section V
Session 2021-22
Question Paper
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C
Session 2022-23
Sample Question Paper for Mid-Term Exam
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C Section D Section E
Mid-Term Exam: Question Paper
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C Section D Section E
Practice Paper for Final Exam
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C Section D Section E
Final Exam: Question Paper Marking Scheme
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C Section D Section E
Support Material Issued by DoE, Delhi
Session 202 3 -24
Mid-Term Exam: Question Paper
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C Section D Section E
Practice Paper 1 for Final Exam: Question Paper
Practice Paper 2 for Final Exam: Question Paper
Short Capsules (Notes to Revise Concepts)
Chapter 1 - Sets
Chapter 4 - Mathematical Induction
Chapter 5 - Complex Numbers & Quadratic Equations
Chapter 6 - Linear Inequalities
Chapter 7 - Permutations & Combinations
Chapter 8 - Binomial Theorem
Chapter 9 - Sequences & Series
Chapter 10 - Straight Line
Chapter 11 - Conic Sections
Chapter 12 - Introduction to Three-dimensional Geometry
Chapter 13 - Limits & derivatives
Chapter 14 - Mathematical Reasoning
Chapter 15 - Statistics
Chapter 16 - Probability
Some Basic Concepts to Revise:
Number System
Mensuration Results
Quadratic Equations
Solution of Polynomial Inequality - Wavy Curve Method
Probability__Revision of the Topics studied in Earlier Classes
Result Sheets
Trigonometric Identities
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
September 22, 2019 by phani
Get Free NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3.1, Ex 3.2, Ex 3.3, Ex 3.4, and Miscellaneous Exercise PDF in Hindi and English Medium. Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions are extremely helpful while doing your homework. Trigonometric Functions All Exercises Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions were prepared by Experienced LearnCBSE.in Teachers.
Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions NCERT Solutions in English Medium and Hindi Medium
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.1
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.2
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.3
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.4
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Miscellaneous Exercise
त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.1 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.2 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.3 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.4 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन विविध प्रश्नावली का हल हिंदी में
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Functions Class 11 Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Trig Cheat Sheet
- JEE Main Trigonometry Previous Year Questions
Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3.1, Ex 3.2, Ex 3.3, Ex 3.4, and Miscellaneous Exercise PDF in Hindi Medium as well as in English Medium for CBSE, Uttarakhand, Bihar, MP Board, Gujarat Board, BIE, Intermediate and UP Board students, who are using NCERT Books based on updated CBSE Syllabus for the session 2019-20.
| 3.1 | Introduction |
| 3.2 | Angles |
| 3.3 | Trigonometric Functions |
| 3.4 | Trigonometric Functions of Sum and Difference of Two Angles |
| 3.5 | Trigonometric Equations |
| 3.6 | Summary |
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 1: Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures: (i) 25° (ii) – 47° 30′ (iii) 240° (iv) 520° Ans:
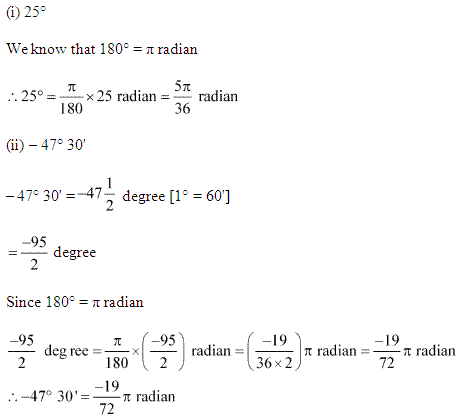
(i) \(\frac{11}{16}\) We know that: π radian = 180° ∴ \(\frac{11}{16}\) radain = \(\frac{180}{\pi} \times \frac{11}{16}\) × degree
= \(\frac{45 \times 11}{\pi \times 4}\) degree
= \(\frac{45 \times 11 \times 7}{22 \times 4}\) degree
= \(\frac{315}{8}\) degree
= 39 \(\frac{3}{8}\) degree
= 39° + \(\frac{3 \times 60}{8}\) minutes [1° = 60′]
= 39° + 22′ + \(\frac{1}{2}\) minutes
= 39°22’30” [1′ = 60°].

More Resources for CBSE Class 11
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Business Studies
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Psychology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Entrepreneurship
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Indian Economic Development
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Computer Science
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 3: A wheel makes 360 revolutions in one minute. Through how many radians does it turn in one second? Ans: Number of revolutions made by the wheel in 1 minute = 360 ∴ Number of revolutions made by the wheel in 1 second = \(\frac{360}{6}\) = 6 In one complete revolution, the wheel turns an angle of 2π radian. Hence, in 6 complete revolutions, it will turn an angle of 6 × 2π radian, i.e., 12π radian Thus, in one second, the wheel turns an angle of 12π radian. Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 4: Find the degree measure of the angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius 100 cm y an arc of length 22 cm (Use π = \(\frac{22}{7}\)). Ans:
We know that in a circle of radius r unit, if an arc of length l unit subtends an angle θ radian at the centre, then θ = \(\frac{l}{r}\) Therefore, for r = 100 cm, l = 22 cm, we have
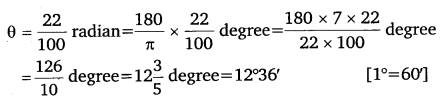
Thus, the required angle is 12°36′.
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 5: In a circle of diameter 40 cm, the length of a chord is 20 cm. Find the length of minor arc of the chord. Ans:
Given, diameter = 40 cm ∴ radius (r) = \(\frac{40}{2}\) = 20 cm and length of chord, AB = 20 cm Thus, ∆OAB is an equilateral triangle. We know that, θ = \(\frac{\text { Arc } A B}{\text { radius }}\) ⇒ Arc AB = θ × r = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) × 20 . = \(\frac{20}{3}\) π cm.
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 6: If in two circles, arcs of the same length subtend angles 60° and 75° at the centre, find the ratio of their radii. Ans:
Let the radii of the two circles be r 1 and r 2 . Let an arc of length l subtend an angle of 60° at the centre of the circle of radius r 1 , while let an arc of length l subtend an angle of 75° at the centre of the circle of radius r 2 . Now, 6o° = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) radian and 75° = \(\frac{5 \pi}{12}\) radian We know that in a circle of radius r unit, if an arc of length l unit subtends an angle θ radian at the centre, then θ = \(\frac{l}{r}\) or l = rθ ∴ l = \(\frac{r_{1} \pi}{3}\) and
l = \(\frac{r_{2} 5 \pi}{12}\)
⇒ \(\frac{r_{1} \pi}{3}=\frac{r_{2} 5 \pi}{12}\)
⇒ r = \(\frac{r_{2} 5}{4}\)
\(\frac{r_{1}}{r_{2}}=\frac{5}{4}\) Thus, the ratio of the radii is 5 : 4.
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 7: Find the angle in radian through which a pendulum swings if its length is 75 cm and the tip describes an arc of length (i) 10 cm (ii) 15 cm (iii) 21 cm. Ans:
We know that in a circle of radius r unit, if an arc of length l unit subtends an angle θ radian at the centre, then θ = \(\frac{l}{r}\). It is given that r = 75 cm
(i) Here, l = 10 cm θ = \(\frac{10}{75}\) radian = \(\frac{2}{15}\) radian
(ii) Here, l = 15 cm θ = \(\frac{15}{75}\) radian θ = \(\frac{1}{5}\) radian
(iii) Here, l = 21 cm θ = \(\frac{21}{75}\) radian = \(\frac{7}{75}\) radian.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.2
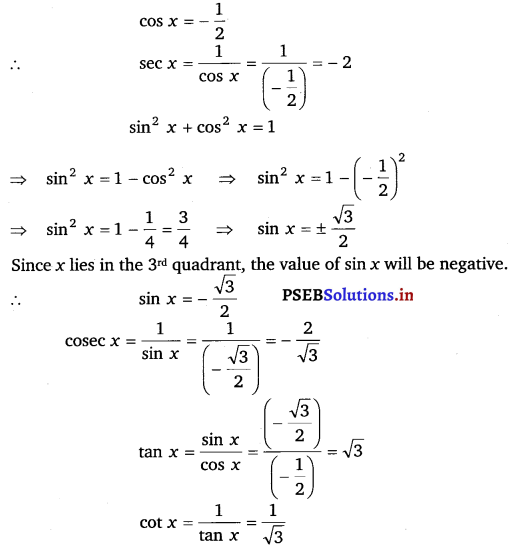
sin x = \(\frac{3}{5}\)
cosec x = \(\frac{1}{\sin x}=\frac{1}{\left(\frac{3}{5}\right)}=\frac{5}{3}\) sin 2 x + cos 2 x = 1 ⇒ cos 2 x = 1 – sin 2 x ⇒ cos 2 x = 1 – (\(\frac{3}{5}\)) 2
⇒ cos 2 x = 1 – \(\frac{9}{25}\)
⇒ cos 2 x = \(\frac{16}{25}\)
⇒ cos x = ± \(\frac{4}{5}\) Since x lies in the 2nd quadrant, the value of cos x will be negative
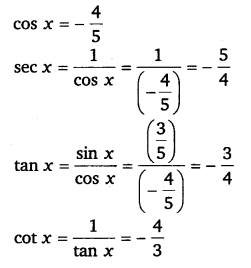
⇒ \(\frac{4}{3}=\frac{\sin x}{\frac{-3}{5}}\) ⇒ sin x = \(\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \times\left(\frac{-3}{5}\right)=-\frac{4}{5}\) ⇒ cosec x = \(\frac{1}{\sin x}=-\frac{5}{4}\).
tan x = – \(\frac{5}{12}\)
cot x = \(\frac{1}{\tan x}=\frac{1}{\left(-\frac{5}{12}\right)}=-\frac{12}{5}\)
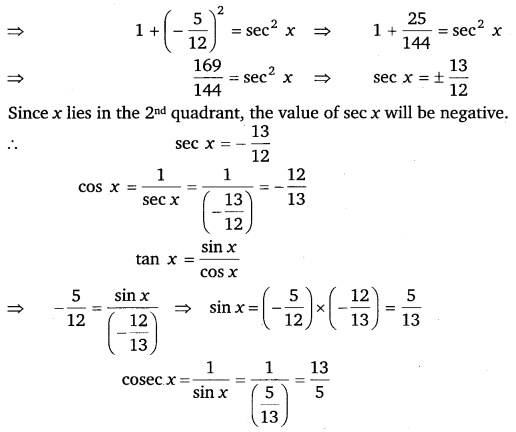
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 6: Find the value of the trigonometric function sin 765°. Ans: It is known that the values of sin x repeat after an interval of 2π or 360°. ∴ sin 765° = sin (2 × 360° + 45°) = sin 45° = 1 Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 7: Find the value of the trigonometric function cosec (- 1410°) Ans: It is known that the values of cosec x repeat after an interval of 2π or 360°. ∴ cosec (- 1410°) = cosec (- 1410° + 4 x 360°) = cosec (- 1410° + 1440°) = cosec 30° = 2. Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 8: Find the value of the trigonometric function tan \(\frac{19 \pi}{3}\). Ans:
It is known that the values of tan x repeat after an interval of π or 180°. ∴ \(\tan \frac{19 \pi}{3}=\tan 6 \frac{1}{3} \pi\)
= \(\tan \left(6 \pi+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=\tan \frac{\pi}{3}\)
= tan 60° = √3.
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 9: Find the value of the trigonometric function sin \(\left(-\frac{11 \pi}{3}\right)\). Ans:
It is known that the values of cot x repeat after an interval of π or 180°.
∴ \(\sin \left(\frac{11 \pi}{3}\right)=\sin \left(-\frac{11 \pi}{3}+2 \times 2 \pi\right)\)
= \(\sin \left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=\sin 60^{\circ}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 10: Find the value of the trigonometric function cot \(\left(-\frac{15 \pi}{4}\right)\). Ans:
It is known that the values of cot x repeat after an interval of ir or 1800. ∴ \(\cot \left(-\frac{15 \pi}{4}\right)=\cot \left(-\frac{15 \pi}{4}+4 \pi\right)=\cot \frac{\pi}{4}\) = 1.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.3
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 1:
Prove that: sin 2 \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) + cos 2 \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) – tan 2 \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) = – \(\frac{1}{2}\) Ans:
L.H.S.= sin 2 \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) + cos 2 \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) – tan 2 \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
= \(\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}+\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}\) – (1) 2
= \(\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{4}-1=-\frac{1}{2}\)
= R.H.S. Hence proved.
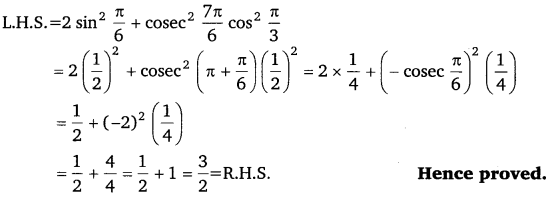
L.H.S = \(2 \sin ^{2} \frac{3 \pi}{4}+2 \cos ^{2} \frac{\pi}{4}+2 \sec ^{2} \frac{\pi}{3}\)
= \(2\left\{\sin \left(\pi-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\right\}^{2}+2\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)^{2}+2(2)^{2}\)
= \(2\left\{\sin \frac{\pi}{4}\right\}^{2}+2 \times \frac{1}{2}+8\)
= 2 \(\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)^{2}\) + 1 + 8
= 1 + 1 + 8 = 10 = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 5: Find the value of: (i) sin 75°, (ii) tan 15° Ans:
(i) sin 75° sin (45° + 30°) = sin 45° cos 30° + cos 45° sin 30° [∵ sin (x + y) = sin x cos y + cos x sin y] = \(\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\left(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)+\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)\)
= \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2 \sqrt{2}}+\frac{1}{2 \sqrt{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2 \sqrt{2}}\)
(ii) tan 15° = tan (45° – 30°)
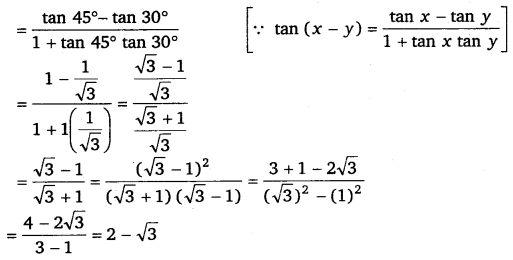
L.H.S = \(\frac{\cos (\pi+x) \cos (-x)}{\sin (\pi-x) \cos \left(\frac{\pi}{2}+x\right)}\)
= \(\frac{[-\cos x][\cos x]}{(\sin x)(-\sin x)}=\frac{-\cos ^{2} x}{-\sin ^{2} x}\)
= R.H.S Hence proved.
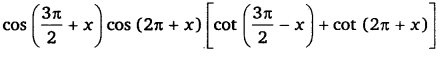
It is known that cos A – cos B = \(-2 \sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cdot \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
∴ L.H.S.= \(=\cos \left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}+x\right)-\cos \left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}-x\right)\)
= \(– 2 \sin \left\{\frac{\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}+x\right)+\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}-x\right)}{2}\right\} \cdot \sin \left\{\frac{\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}+x\right)-\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}-x\right)}{2}\right\}\)
= – 2 sin (\(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\)) sin x
= – 2 sin (- \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)) sin x
= – √2 sin x = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 12: Prove that: sin 2 6x – sin 2 4x = sin 2x sin 10 x Ans:
It is known that sin A + sin B = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
sin A – sin B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\) L.H.S.= sin 2 6x – sin 2 4x = (sin 6x + sin 4x) (sin 6x – sin 4x) = (2 sin 5x cos x) (2 cos 5x sin x) = (2 sin 5x cos 5x) (2 sin x cos x) = sin 10x sin 2x = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 13: Prove that: cos 2 2x cos 2 6x = sin 4x sin 8x Ans:
It is known that cos A + cos B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
cos A – cos = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
∴ L.H.S = cos 2 2x – cos 2 6x = (cos 2x + cos 6x) (cos 2x – 6x) = \(\left[2 \cos \left(\frac{2 x+6 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{2 x-6 x}{2}\right)\right]\left[-2 \sin \left(\frac{2 x+6 x}{2}\right) \sin \frac{(2 x-6 x)}{2}\right]\) ∴ L.H.S.= cos 2 2x – cos 2 6x = (cos 2x + cos 6x) (cos 2x – 6x) = [2 cos 4x cos (-2x)] [- 2 sin 4x sin (- 2x)] = [2 cos 4x cos 2x] [- 2 sin 4x (- sin 2x)] = (2 sin 4x cos 4x) (2 sin 2x cos 2x) = sin 8x sin 4x = R.H.S. Hence proved.
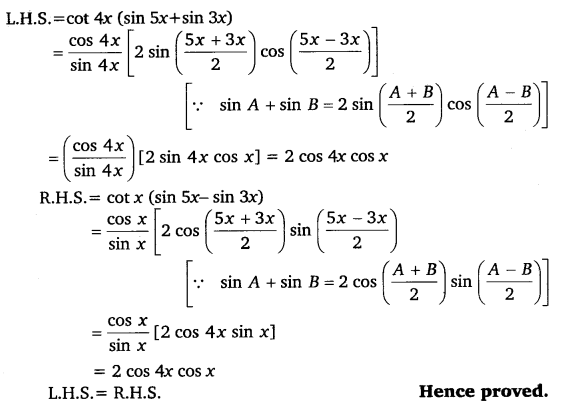
It is known that sin A + sin = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
cos A + cos = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
∴ L.H.S = \(\frac{\sin 5 x+\sin 3 x}{\cos 5 x+\cos 3 x}\)
= \(\frac{2 \sin \left(\frac{5 x+3 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{5 x-3 x}{2}\right)}{2 \cos \left(\frac{5 x+3 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{5 x-3 x}{2}\right)}\)
= \(\frac{2 \sin 4 x \cos x}{2 \cos 4 x \cos x}=\frac{\sin 4 x}{\cos 4 x}\)
= tan 4x = R.H.S. Hence proved.
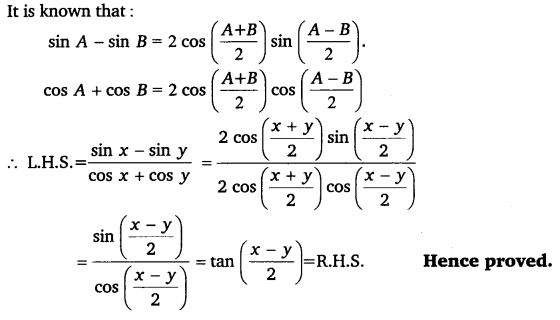
It is known that sin A – sin B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
cos 2 A – sin 2 A = cos 2A
∴ L.H.S. = \(=\frac{\sin x-\sin 3 x}{\sin ^{2} x-\cos ^{2} x}\)
= \(\frac{2 \cos \left(\frac{x+3 x}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{x-3 x}{2}\right)}{-\cos 2 x}\)
= \(\frac{2 \cos 2 x \sin (-x)}{-\cos 2 x}\)
= – 2 × (- sin x) = 2 sin x
Hence proved.
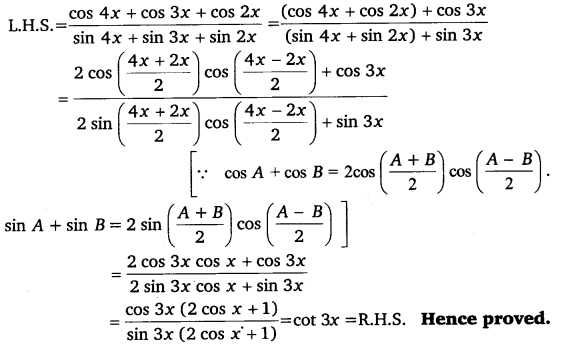
Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 3 Exercise 3.4
cos 4x = cos 2x cos 4x – cos 2x = 0 – 2 sin \(\left(\frac{4 x+2 x}{2}\right)\) sin \(\left(\frac{4 x-2 x}{2}\right)\) = 0
[∵ cos A – cos B = 2 \sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\(\)]
sin 3x sin x = 0 sin 3x = 0or sin x = 0 3x = nπ or x = nπ, where n ∈ Z x = \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) or x = nπ, where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 6: Find the general solution of the equation cos 3x + cosx – cos 2x = 0 Ans:
cos 3x + cos x – cos 2x = 0 2 cos \(\left(\frac{3 x+x}{2}\right)\) cos \(\left(\frac{3 x-x}{2}\right)\) – cos 2x = 0
[∵ cos A + cos B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)]
2 cos 2x cos x – cos 2x = 0 cos 2x (2 cos x – 1) = 0 cos 2x = 0 or 2 cos x – 1 = 0 cos 2x = 0 or cos x = \(\frac{1{2}\) ∴ 2x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) or cos x = cos \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) or x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 7: Find the general solution of the equation sin 2x + cos x = 0 Ans:
sin 2x + cos x = 0 ⇒ 2sin x cos x + cos x = 0 ⇒ cos x (2 sin x + 1) = 0 ⇒ cos x = 0 or 2 sin x + 1 = 0 Now, cos x = 0 ⇒ x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) , where n ∈ Z. or 2 sin x + 1 = 0 ⇒ sin x = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= – sin \(\frac{\pi}{6}\)
= sin (π + \(\frac{\pi}{6}\))
= sin \(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\)
x = nπ + (- 1) n \(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\) where n ∈ Z Therefore, the general solution is (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) or nπ + (- 1) n \(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\) where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 8: Find the general solution of the equation sec 2 2x = 1 – tan 2x. Ans:
sec 2 2x = 1 – tan 2x 1 + tan 2 2x = 1 – tan 2x tan 2 x + tan 2x = 0 => tan 2x (tan 2x + 1) = 0 => tan 2x = 0 or tan 2x + 1 = 0 Now, tan 2x = 0 => tan 2x = tan 0 2x = nπ + 0, where n ∈ Z x = \(\frac{n \pi}{2}\), where n ∈ Z or tan 2x + 1 = 0 = tan 2x = – 1 = – tan \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
= tan (π – \(\frac{\pi}{4}\))
= tan \(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\)
2x = nπ + \(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\) where n ∈ Z
x = \(\frac{n \pi}{2}+\frac{3 \pi}{8}\), where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is \(\frac{n \pi}{2}\) or \(\frac{n \pi}{2}+\frac{3 \pi}{8}\) where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 9: Find the general solution of the equation sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0 Ans:
sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0 ⇒ (sin x + sin 5x) + sin 3x = 0
\(\left[2 \sin \left(\frac{x+5 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{x-5 x}{2}\right)\right]\) + sin 3x = 0
[∵ sin A + sin B = 2 sin \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)]
2 sin 3x cos (2x) + sin 3x = 0 2 sin 3x cos 2x + sin 3x = 0 sin 3x (2 cos 2x +1) = 0 sin 3x = 0 or 2 cos 2x + 1 = 0 Now sin 3x = 0 ⇒ 3x = nπ, where n ∈ Z i.e., x = \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) where n ∈ Z or 2 cos 2x + 1 = 0 cos 2x = \(-\frac{1}{2}\)
= – cos \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
= cos (π – \(\frac{\pi}{3}\))
cos 2x = cos \(\frac{2 \pi}{3}\)
⇒ 2x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{2\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
⇒ x = nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) or nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Miscellaneous Exercise
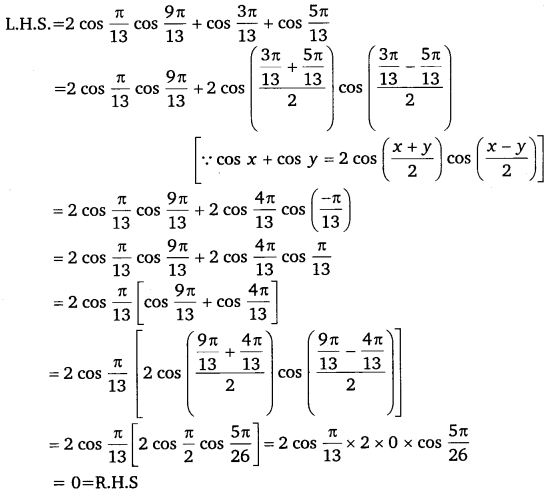
L.H.S. = (sin 3x + sin x) sin x + (cos 3x – cos x) cos x = sin 3x sin x + sin 2 x + cos 3x cos x – cos 2 x = cos 3x cos x + sin 3x sin x – (cos 2 x – sin 2 x) = cos (3x – x) – cos 2x [∵ cos(A – B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B] = cos 2x – cos 2x = 0 =R.H.S. Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 3:
Prove that: (cos x + cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2 = 4 cos 2 \(\left(\frac{x+y}{2}\right)\)
L.H.S.= (cos x + cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2 = cos 2 x + cos 2 y + 2 cos x cos y + sin 2 x + sin 2 y – 2 sin x sin y = (cos 2 x + sin 2 x) + (cos 2 y + sin 2 y) + 2 (cos x cos y – sin x sin y) = 1 + 1 + 2 cos (x + y) [∵ cos (A + B) = (cos A cos B – sin A sin B)] = 2 + 2 cos (x + y) = 2 [1 + cos (x + y)] = 2[1 + \(2 \cos ^{2}\left(\frac{x+y}{2}\right)\) – 1] [∵ cos 2A = 2 cos 2 A – 1] = 4 c0s 2 \(\left(\frac{x+y}{2}\right)\) = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 4: Prove that: (cos x – cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2 = 4 sin 2 \(\frac{x-y}{2}\) Ans:
L.H.S.= (cos x – cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2 = cos 2 x + cos 2 y – 2 cos x cos y + sin 2 x + sin 2 y – 2 sin x sin y = (cos 2 x + sin 2 x) + (cos 2 y + sin 2 y) – 2 [cos x cos y + sin x sin y] = 1 + 1 – 2 [cos (x – y)] = 2 [1 – {1 – 2 sin 2 \(\left(\frac{x-y}{2}\right)\)}] [∵ cos 2A = 1 – 2 sin 2 A] = 4 sin 2 \(\left(\frac{x-y}{2}\right)\) = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 5: Prove that: sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x + sin 7x = 4 cos x cos 2x sin 4x Ans:
It is known that sin A + sin B = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cdot \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\) ∴ L.H.S. = (sin x + sin 3x) + (sin 5x + sin 7x) = (sin x + sin 5x) + (sin 3x + sin 7x) = \(2 \sin \left(\frac{x+5 x}{2}\right)\) . \(\cos \left(\frac{x-5 x}{2}\right)+2 \sin \left(\frac{3 x+7 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{3 x-7 x}{2}\right)\) = 2 sin 3x cos (- 2x) + 2 sin 5x cos (- 2x) = 2 sin 3x cos 2x + 2 sin 5x cos 2x = 2 cos 2x [sin 3x + sin 5x] = 2 cos 2x [latex]2 \sin \left(\frac{3 x+5 x}{2}\right) \cdot \cos \left(\frac{3 x-5 x}{2}\right)[/latex] = 2 cos 2x [2 sin 4x . cos (- x)] = 4 cos 2x sin 4x cos x = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 6: Prove that: \(\frac{(\sin 7 x+\sin 5 x)+(\sin 9 x+\sin 3 x)}{(\cos 7 x+\cos 5 x)+(\cos 9 x+\cos 3 x)}\) = tan 6x Ans: It is known that
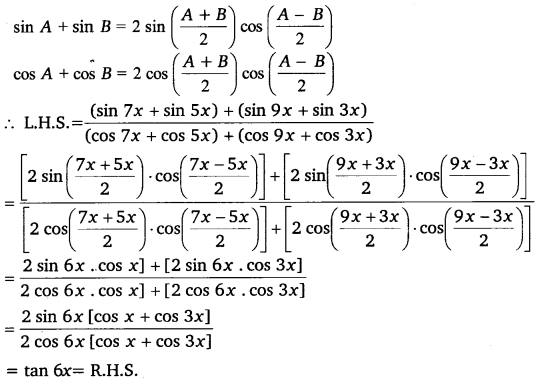
प्रश्न 3. एक-पहिया एक मिनट में 360° परिक्रमण करता है तो एक सेकंड में कितने रेडियन माप का कोण बनाएगा? हल: परिक्रमण में पहिया द्वारा बना कोण = 27 रेडियन 360 परिक्रमण में पहिया द्वारा बना कोण = 360 x 2π रेडियन 1 मिनट अर्थात् 60 सेकण्ड में 360 x 2π रेडियन का कोण बनता है। 1 सेकण्ट में चहिया द्वारा बना कोण = \(\frac { 360\times 2\pi }{ 60 }\) = 12π रेडियन।

Exercise 3.1
Q.1: Calculate the radian measurement of the given degree measurement:
(ii). 240 ∘
(iii). − 47 ∘ 30 ‘
(iv). 520 ∘
Q.2: Calculate the degree measurement of the given degree measurement: [Use π = \(\\ \frac { 22 }{ 7 } \)]
(i) \(\\ \frac { 11 }{ 16 } \)
(iii) \(\frac { 5\pi }{ 3 } \)
(iv) \(\frac { 7\pi }{ 6 } \)
Q.3: In a minute, wheel makes 360 revolutions. Through how many radians does it turn in 1 second?
Q.4: Calculate the degree measurement of the angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius 100 m by an arc of length 22 m.
Q.5: In a circle of diameter 40 m, the length of the chord 20 m. Find the length of minor arc of chord.
Q.6: In two circles, arcs which has same length subtended at an angle of 60 ∘ and 75 ∘ at the center. Calculate the ratio of their radii.
Q.7: Calculate the angle in radian through which a pendulum swings if the length is 75 cm and the tip describes an arc of length
(iii) 21 cm
Exercise 3.2
Q.1: Calculate the values of five trigonometric func. if cos y = \(– \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) and y lies in 3 rd quadrant.
(iii) cosec y
Q.2: Calculate the other five trigonometric function if we are given the values for sin y = \(\\ \frac { 3 }{ 5 } \), where y lies in second quadrant.
Q.3: Find the values of other five trigonometric functions if c o t y =\(\\ \frac { 3 }{ 4 } \) , where y lies in the third quadrant.
Q.4: Find the values of other five trigonometric if s e c y =\(\\ \frac { 13 }{ 5 } \) , where y lies in the fourth quadrant.
Q.5: Find the values of other five trigonometric function if tan y = \(– \frac { 5 }{ 12 } \) and y lies in second quadrant.
Q.6: Calculate the value of trigonometric function sin 765°.
Q.7: Calculate the value of trigonometric function cosec [-1410°]
Q.8: Calculate the value of the trigonometric function tan \(\frac { 19\pi }{ 3 } \) .
Q.9: Calculate the value of the trigonometric function sin \(-\frac { 11\pi }{ 3 } \) .
Q.10: Calculate the value of the trigonometric function cot \(-\frac { 15\pi }{ 4 } \)
Exercise 3.3
Q.1: Prove:
sin²\(\frac { \pi }{ 6 } \) + cos² \(\frac { \pi }{ 3 } \) – tan² \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) = \(– \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
Q.2: Prove:
2 sin² \(\frac { \pi }{ 6 } \) + c o s e c ² \(\frac { 7\pi }{ 6 } \) 6 cos ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 3 } \) =\(\\ \frac { 3 }{ 2 } \)
Q.3: Prove:
cot ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 6 } \) + c o s e c \(\frac { 5\pi }{ 6 } \) + 3 tan ² latex s=2]\frac { \pi }{ 6 } [/latex] = 6
Q.4: Prove:
2 sin ² \(\frac { 3\pi }{ 4 } \) + 2 cos ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) + 2 sec ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 3 } \) = 10
Q.5: Calculate the value of:
(i). sin 75 ∘
(ii). tan 15 ∘
cos ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – x ) cos ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – y ) – sin ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – x ) sin ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – y ) = sin ( x + y )
Q.7: Prove:
\(\frac { tan(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } +x) }{ tan(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } -x) } ={ \left( \frac { 1+tanx }{ 1-tanx } \right) }^{ 2 }\)
Q.8: Prove:
\(\frac { cos(\pi +x)cos(-x) }{ sin(\pi -x)cos\left( \frac { \pi }{ 2 } +x \right) } ={ cot }^{ 2 }x\)
Q.9: Prove:
\(cos(\frac { 3\pi }{ 2 } +x)cos(2\pi +x)[cot(\frac { 3\pi }{ 2 } -x)+cot(2\pi +x)]=1\)
Q.10: Prove:
sin ( n + 1 ) x sin ( n + 2 ) x + cos ( n + 1 ) x cos ( n + 2 ) x = cos x
Q.11 Prove:
\(cos(\frac { 3\pi }{ 4 } +x)-cos(\frac { 3\pi }{ 4 } -x)\)= − √2 sin x
Q.12: Prove:
sin² 6 x – sin ² 4 x = sin2 x sin 10 x
Q.13: Prove:
cos ² 2 x – cos ² 6 x = sin 4 x sin 8 x
Q.14:Prove:
sin 2 x + 2 sin 4 x + sin 6 x = 4 cos ² x sin 4 x
Q.15: Prove:
cot 4 x ( sin 5 x + sin 3 x ) = cot x ( sin 5 x – sin 3 x )
Q.16: Prove:
\(\frac { cos9x-cos5x }{ sin17x-sin3x } =-\frac { sin2x }{ cos10x } \)
Q.17: Prove:
\(\frac { sin5x+sin3x }{ cos5x+cos3x } =tan4x\)
Q.18: Prove:
\(\frac { sinx-siny }{ cosx+cosy } =tan\frac { x-y }{ 2 } \)
Q.19: Prove:
\(\frac { sinx+sin3x }{ cosx+cos3x } =tan2x\)
Q.20: Prove:
\(\frac { sinx-sin3x }{ { sin }^{ 2 }x-{ cos }^{ 2 }x } =2sinx\)
Q.21: Prove:
\(\frac { cos4x+cos3x+cos2x }{ sin4x+sin3x+sin2x } =cot3x\)
Q.22: Prove:
cot x cot 2 x – cot 2 x cot 3 x – cot 3 x cot x = 1
Q.23: Prove:
\(tan4x=\frac { 4tanx(1-{ tan }^{ 2 }x) }{ 1-6{ tan }^{ 2 }x+{ tan }^{ 4 }x } \)
Q.24: Prove:
cos 4 x = 1 – 8 sin² x cos² x
Q.25: Prove:
cos 6 x = 32 cos 6 x – 48 cos 4 x + 18 cos 2 x − 1
Exercise 3.4
Q.1: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: tan x = √3
Q.2: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: sec x = 2
Q.3: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: cot = − √3
Q.4: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: cosec x = -2
Q.5: Find the general solution of the given equation: cos 4x = cos 2x
Q.6: Find the general solution of the given equation: cos 3x + cos x – cos 2x = 0
Q.7: Find the general solution of the given equation: sin 2x + cos x = 0
Q.8: Find the general solution of the given equation: sec² 2 x = 1 – tan 2 x
Q.9: Find the general solution of the given equation: sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0
Miscellaneous Exercise
Q.1: Prove that:
\(2cos\frac { \pi }{ 13 } cos\frac { 9\pi }{ 13 } +cos\frac { 3\pi }{ 13 } +cos\frac { 5\pi }{ 13 } =0\)
Q.2: Prove that:
( sin 3 x + sin x ) sin x + ( cos 3 x – cos x ) cos x = 0
Q-3: Prove that:
( cos x + cos y )² + ( sin x – sin y ) ² = 4 cos ²\(\\ \frac { x+y }{ 2 } \)
Q-4: Prove that:
( cos x – cos y ) ² + ( sin x – sin y ) ² = 4 sin ² \(\\ \frac { x-y }{ 2 } \)
Q-5: Prove that:
sin x + sin 3 x + sin 5 x + sin 7 x = 4 cos x cos 2 x cos 4 x
Q-6: Prove that:
\(\frac { (sin7x+sin5x)+(sin9x+sin3x) }{ (cos7x+cos5x)+(cos9x+cos3x) } =tan6x\)
Q-7: Show that: sin 3 y + sin 2 y – sin y = 4 sin y cos\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) cos\(\\ \frac { 3y }{ 2 } \)
Q-8: The value of tan y =\(– \frac { 4 }{ 2 } \) where y in in 2 nd quadrant then find out the values of sin\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) , cos\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) a n d tan\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) .
Q-9: The value of cos y = \(– \frac { 1 }{ 3 } \) where y in in 3 rd quadrant then find out the values of sin \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) , cos \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) a n d tan \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) .
Q-10: The value of sin y = \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 4 } \) where y in in 2 nd quadrant then find out the values of sin \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) , cos \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) a n d tan \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) .
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths All Chapters
- Chapter 1 Sets
- Chapter 2 Relations and Functions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction
- Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities
- Chapter 7 Permutation and Combinations
- Chapter 8 Binomial Theorem
- Chapter 9 Sequences and Series
- Chapter 10 Straight Lines
- Chapter 11 Conic Sections
- Chapter 12 Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry
- Chapter 13 Limits and Derivatives
- Chapter 14 Mathematical Reasoning
- Chapter 15 Statistics
- Chapter 16 Probability
Free Resources
Quick Resources

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF Download
NCERT Solutions are essential for all students who want to score well in their exams. Our subject matter experts have developed these solutions to help the students score good marks in their examinations. These solutions are well-explained and include each and every topic. Another essential benefit of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions is that it is created as per the latest pattern of CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education). These solutions also ensure that a student gets a clear understanding of each and every concept.
In the Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Solutions, each and every type of question is included. From easy to hard, the students will get an idea of all the types of questions which can appear in the exam. Also, apart from this, the students will also get to know about the most common questions which have a high chance of appearing in the exam.
It can be assumed that a student will score good marks in their exams if they will study the Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF NCERT Solution on a regular basis. Our subject matter experts at Selfstudys have invested a good amount of time in creating them so that the students do not find any difficulty studying from these solutions. As the experts have been in the education line for quite some time, they are aware of the learning potential of every student, which is why they have created these solutions in a simple way so that no student faces any difficulty studying from them. Students can also use these solutions at the time of revision.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions can be easily downloaded from the website of Selfstudys i.e. Selfstudys.com.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF
The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF can be easily downloaded from the website of Selfstudys. As they are in PDF format, it becomes easier for the students to access them. They are also mobile-friendly.
How to Download the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions?
Downloading the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions is if you know the right steps. The steps to download them are as follows:
- Visit the official website of Selfstudys i.e. Selfstudys.com.
- Once the website is completely loaded, you need to click on the three lines which you will find on the upper left side. Following that, you have to click on the ‘NCERT Books and Solutions’ column.
- After clicking on the option of ‘NCERT Books and Solutions’, a new list will open where you need to select the option of ‘NCERT Solutions’.
- Following that, you will be redirected to a page where you need to select the class and the subject for which you want to download the NCERT Solutions.
- In this case, you need to select class 10 and the subject Maths to download the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions.
What are the Features of the Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF NCERT Solution?
There are many features of the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions which can be very beneficial for all the students. The most important features include:
- Well-Elaborated: The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions is well-elaborated to make it easier for the students to understand all the concepts with in-depth knowledge.
- Includes every topic: Every important topic is covered in the Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Solutions which increases the confidence of the students as they feel that they know every topic and will eventually score good marks in their exams.
- 24*7 Online Availability: One more feature of the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions is that it is available 24*7. This is very beneficial for all the students as they can access these notes anytime either day or night.
- Simple Language Used: The language which is used in the Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Solutions is very easy. As we have mentioned earlier that our subject matter experts are aware of the learning power of all the students, so they have intentionally used the easiest language in these solutions so that no student faces any difficulty in learning them.
- Well-organized Format: One thing which makes our Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF NCERT Solution different from other solutions is that they are developed in a well-structured format. These solutions are organized systematically, following the order of the chapters and topics in the textbooks.
- Accuracy and reliability: Our subject matter experts have invested a good amount of time in developing these NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. They are accurate and reliable for the preparation of exams. These notes can also be helpful for the students who do self-study.
What are the Benefits of the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions has several benefits to offer to the students. Some of the most important of them are
- Clear Understanding of the Topic: The Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Solutions provides in-depth knowledge of each and every topic which is present in the syllabus. Each chapter is explained in detail in a step-by-step process. To make learning easier and more interesting for all the students, diagrams and examples are also given.
- Authentic Solutions: The Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF NCERT Solution are completely authentic and can be trusted 100%. The highly qualified subject matter experts at Selfstudys have created these solutions in an authentic way which makes it simple for all the students to learn all the concepts.
- Improved Problem-Solving Skills: By regularly practicing the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions, students can improve their problem-solving skills. They get the idea of the techniques and methods which are used to solve various types of maths problems.
- Conceptual Clarity: The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions focuses on building a strong foundation for all the students. Students can get a deep understanding of the fundamental principles of maths formulas, which serve as a basis for further mathematical topics.
- Boosts Confidence: If a student regularly goes through the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions, there is no doubt that the students will gain confidence in their maths power. This confidence can motivate them to explore more difficult topics and make a strong base for all of them.
What are the tips to study from the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions?
There are various tips that can help the students to study effectively from the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions:
- Go through the chapter thoroughly: It is very important for all the students to first go through the chapter as it will help them to understand the basics. If their basics will get strong, they will automatically be able to grasp the other concepts in a better way.
- Practice Problem solving step-by-step: It is advisable for all the students to solve the problems step-by-step which are present in the Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Solutions without looking at the answers. This will allow them to develop problem-solving skills and test their understanding of the concepts.
- Create a study schedule: It is important for students to create a study schedule and follow it consistently to stay focused. Devote at least 45 minutes to grasp the concepts thoroughly. Give enough time to each topic covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions and review them daily. Sticking to the schedule is recommended to ensure timely completion of all the topics.
- Do not get distracted: All the students should stay focused to concentrate better and should not get distracted. They should stay away from their mobile phones and other electronic gadgets, for example, TV, etc. to avoid all the distractions while studying Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF NCERT Solution.
- Practice Time Management: While doing exam preparation from the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions, it is advisable for all the students to practice time management by setting a time duration for solving problems. This will help you develop efficiency and improve your speed in solving problems accurately.
How to Master the Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF NCERT Solution ?
There are various ways to master NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. Some of the most important of them are:
- Study the NCERT Solutions: The students can start by studying the Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Solutions. It is advisable for them to read the solutions carefully and understand them stepwise manner used to solve each problem. They should use them regularly as it will help them to understand the concepts in a clear manner.
- Do regular practice of these solutions: It is advisable for all the students to regularly practice these NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions as it helps the students to do effective preparation for their exams. The conceptual knowledge of the students is also boosted by regularly practicing these solutions.
- Do group discussions with your peers: It is advisable for all the students to do group discussions with their peers as discussing the concepts, problem-solving techniques, and solutions with others can help you understand them in a better way. Teaching and explaining concepts to others can deepen your understanding of all the concepts.
- Revise regularly: Regularly revise the concepts and solutions from NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. Review your notes, summaries, and solved problems. Revisit the solutions and attempt to solve them again without referring to the provided solutions. This revision will help reinforce your understanding and improve retention.
- Take note of your mistakes and work on them: It is advisable for all the students to take note of their mistakes while solving the Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF NCERT Solution and work on them. Find your weaknesses and identify the specific concepts or steps that caused confusion. This will help you improve your problem-solving skills.
How to Maximise Your Learning Potential While Solving the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions?
To maximize your learning potential while solving the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions, here are the tips which can help you:
- Do a thorough reading of the chapter: All the students should read Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF NCERT Solution thoroughly to maximize their learning potential as it will help them to understand the basic concepts which will make it easier for them to grasp all the concepts.
- Practice regularly: One of the most important tips which every student should follow in order to maximize their learning potential is to practice these NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions regularly. It includes practicing the questions regularly in the Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Solutions. This will help them in understanding the concepts with a deep understanding which can help them to score high marks in their exams.
- Revise the concepts on a regular basis: It is very important for all the students to Revise all the concepts from the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions as it helps to recall all the information which they have studied during the preparation for the exam. You can also use different methods to revise the concepts on a regular basis, for example, making flashcards, notes, etc.
What Are the Methods To Study From NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions?
Studying for the exam requires focus and concentration. Below we will discuss various methods of how students can study for an Exam with the help of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions:
- Making a strong grip of basics: It is very important for all students to create a strong base for basics and learn them for NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions as it helps a student to get a clear understanding of the concepts. This makes it easier for the students to learn them fast.
- Study the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions on a regular basis: It is advisable for all the students to study Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Solutions on a regular basis as it will help them to do effective preparation for their exams and also increases the chances of the students to score good marks in their exams.
- Always read the summary of your textbook: It is advisable for all students to always read the summary which is included in the Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions PDF NCERT Solution. The students should read them on a regular basis as it will help them to get a thorough knowledge of all the topics and will also help them to prepare well for the exams. This will increase their chances of scoring good marks in the exams.
- Identify your strong and weak areas: It is very important for all the students to identify their strong and weak areas as it will help them to understand where they need to put more effort in order to do well in their exams.
- Do timely revision: All the students should do timely revision from the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions if they want to do extremely well in their exams as it will ensure that you have created a strong base of all the topics in their minds.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 3: Trigonometric functions
Degrees and radians.
- Intro to radians (Opens a modal)
- Radians & degrees (Opens a modal)
- Degrees to radians (Opens a modal)
- Radians to degrees (Opens a modal)
- Radian angles & quadrants (Opens a modal)
- Radians & degrees Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Unit circle
- Unit circle (Opens a modal)
- The trig functions & right triangle trig ratios (Opens a modal)
- Trig values of π/4 (Opens a modal)
- Trig unit circle review (Opens a modal)
- Plotting angles on unit circle Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Sign of trigonometric functions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Trig values of special angles Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Trigonometric functions
- Graph of y=sin(x) (Opens a modal)
- Graph of y=tan(x) (Opens a modal)
- Intersection points of y=sin(x) and y=cos(x) (Opens a modal)
- Find value of other trigonometric functions from given trigonometric function Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Trigonometric identities: Symmetry
- Sine & cosine identities: symmetry (Opens a modal)
- Tangent identities: symmetry (Opens a modal)
- Sine & cosine identities: periodicity (Opens a modal)
- Tangent identities: periodicity (Opens a modal)
Trigonometric identities: Sum and difference
- Trig angle addition identities (Opens a modal)
- Using the cosine angle addition identity (Opens a modal)
- Using the cosine double-angle identity (Opens a modal)
- Proof of the sine angle addition identity (Opens a modal)
- Proof of the cosine angle addition identity (Opens a modal)
- Trig challenge problem: cosine of angle-sum (Opens a modal)
- Trigonometric functions of sum and difference of angles Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Sum and difference of trigonometric functions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Evaluate trigonometric expressions (intermediate) Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Trigonometric equations
- Proof of the Pythagorean trig identity (Opens a modal)
- Using the Pythagorean trig identity (Opens a modal)
- Solving sinusoidal equations of the form sin(x)=d (Opens a modal)
- Solving cos(θ)=1 and cos(θ)=-1 (Opens a modal)
- Use the Pythagorean identity Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Principal solutions of trigonometric equation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- General solution of trigonometric equation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Solutions to select NCERT problems
- Select problems from exercise 3.3 (Opens a modal)
- Select problems from miscellaneous exercise (Opens a modal)

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Last modified on: 1 year ago
- Reading Time: 12 Minutes
[PDF] Download Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
Here we are providing assertion reason questions for class 11 maths. In this article, we are covering Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Assertion Reason Questions. Detailed Solutions are also provided at the end of questions so that students can check their answers after completing all the questions.
Related Posts
What is assertion reason questions.
Assertion Reason Questions are a type of question that can be asked in Class 11 Maths exams. These questions usually consist of two parts:
- Assertion: A statement that presents a claim or proposition that needs to be verified or evaluated.
- Reason: A statement that provides a logical explanation or justification for the assertion.
The student is required to evaluate both the assertion and the reason and determine whether they are true or false. Here are some examples of Assertion Reason Questions in Class 11 Maths:
Example 1: Assertion: The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. Reason: The angles of a triangle are in a ratio of 1:2:3.
Solution: The assertion is true as it is a well-known fact in geometry that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. However, the reason is false as the angles of a triangle are not necessarily in the ratio of 1:2:3. Therefore, the correct option is (a) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
Example 2: Assertion: The equation x^2 + 1 = 0 has no real solutions. Reason: The square of any real number is always non-negative.
Solution: The assertion is true as x 2 + 1 = 0 has no real solutions. The reason is also true as the square of any real number is always non-negative. Therefore, the correct option is (c) Assertion is true, and the reason is also true, and the reason is a correct explanation for the assertion.
Importance of Practicing Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths
Practicing Assertion Reason Questions in Class 11 Maths has several benefits:
- Develops critical thinking skills: Assertion Reason Questions require students to analyze and evaluate statements logically. By practicing such questions, students can develop their critical thinking skills and learn to reason effectively.
- Improves problem-solving ability: Assertion Reason Questions often involve complex concepts and require students to apply their knowledge to solve problems. Practicing such questions can help students improve their problem-solving ability and build a strong foundation in Maths.
- Helps in exam preparation: Assertion Reason Questions are frequently asked in Class 11 Maths exams. By practicing such questions regularly, students can get familiar with the exam pattern and improve their chances of scoring well in the exam.
- Enhances conceptual understanding: Assertion Reason Questions involve analyzing the relationship between concepts, which can help students understand the underlying principles better. By practicing such questions, students can improve their conceptual understanding of Maths.
- Builds confidence: Regular practice of Assertion Reason Questions can help students build confidence in their ability to solve complex problems and reason effectively. This can help them perform better in exams and in their future academic and professional pursuits.
Why CBSE Students Fear Assertion Reason Questions?
CBSE students may fear assertion-reasoning questions because they require a deeper level of understanding and analytical skills compared to regular multiple-choice questions. Assertion-reasoning questions consist of two statements: an assertion and a reason. The student must determine if both statements are true and if the reason explains the assertion.
These questions require the student to not only know the facts but also understand the relationships between them. Students may fear these types of questions if they are not confident in their ability to analyze and evaluate the information provided. Additionally, these questions often carry a good weightage, which can add to the pressure of performing well on the exam.
However, with practice and a solid understanding of the concepts, students can overcome their fear of assertion-reasoning questions and perform well on their exams. It is important for students to read the questions carefully, understand the meaning of each statement, and analyze the relationship between the two statements before selecting their answer.
What are the best ways to prepare for assertion reason questions?
Preparing for assertion-reasoning questions can be challenging, but with the right approach and strategies, you can improve your skills and perform well on exams. Here are some ways to prepare for assertion-reasoning questions:
- Understand the concepts: To answer assertion-reasoning questions correctly, you need to have a clear understanding of the concepts involved. Make sure you study the topic thoroughly and have a strong grasp of the fundamental principles.
- Practice regularly: Practice is key to improving your skills. Look for sample assertion-reasoning questions in textbooks or online resources and practice answering them. Try to identify the relationship between the two statements and determine if both are true and if the reason explains the assertion.
- Develop analytical skills: Assertion-reasoning questions require you to analyze and evaluate the information provided. Develop your analytical skills by reading and analyzing different types of texts, such as news articles or scientific research papers.
- Take notes: Taking notes while studying can help you remember important information and make connections between different concepts. Write down key points, definitions, and examples to refer to later.
- Seek help: If you are struggling with assertion-reasoning questions, don’t hesitate to seek help from your teacher or a tutor. They can provide you with additional resources and guidance on how to approach these types of questions.
By following these strategies and putting in the effort to practice, you can improve your skills and perform well on assertion-reasoning questions.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

case study questions class 11 maths trigonometry

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Last modified on: 10 months ago
- Reading Time: 8 Minutes

Table of Contents
[PDF] Download Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
Here we are providing case study questions for class 11 maths. In this article, we are sharing Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. All case study questions of class 11 maths are solved so that students can check their solutions after attempting questions.
What is meant by Case Study Question?
In the context of CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education), a case study question is a type of question that requires students to analyze a given scenario or situation and apply their knowledge and skills to solve a problem or answer a question related to the case study.
Case study questions typically involve a real-world situation that requires students to identify the problem or issue, analyze the relevant information, and apply their understanding of the relevant concepts to propose a solution or answer a question. These questions may involve multiple steps and require students to think critically, apply their problem-solving skills, and communicate their reasoning effectively.
Importance of Solving Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths
Case study questions are an important aspect of mathematics education at the Class 11 level. These questions require students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world scenarios, helping them develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills. Here are some reasons why case study questions are important in Class 11 maths education:
- Real-world application: Case study questions allow students to see how the concepts they are learning in mathematics can be applied in real-life situations. This helps students understand the relevance and importance of mathematics in their daily lives.
- Higher-order thinking: Case study questions require students to think critically, analyze data, and make connections between different concepts. This helps develop higher-order thinking skills, which are essential for success in both academics and real-life situations.
- Collaborative learning: Case study questions often require students to work in groups, which promotes collaborative learning and helps students develop communication and teamwork skills.
- Problem-solving skills: Case study questions require students to apply their knowledge and skills to solve complex problems. This helps develop problem-solving skills, which are essential in many careers and in everyday life.
- Exam preparation: Case study questions are included in exams and tests, so practicing them can help students prepare for these assessments.
Overall, case study questions are an important component of Class 11 mathematics education, as they help students develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills, which are essential for success in both academics and real-life situations.
Feature of Case Study Questions on This Website
Here are some features of a Class 11 Maths Case Study Questions Booklet:
Many Case Study Questions: This website contains many case study questions, each with a unique scenario and problem statement.
Different types of problems: The booklet includes different types of problems, such as optimization problems, application problems, and interpretation problems, to test students’ understanding of various mathematical concepts and their ability to apply them to real-world situations.
Multiple-choice questions: Questions contains multiple-choice questions to assess students’ knowledge, understanding, and critical thinking skills.
Focus on problem-solving skills: The questions are designed to test students’ problem-solving skills, requiring them to identify the problem, select appropriate mathematical tools, and analyze and interpret the results.
Emphasis on practical applications: The case studies in the booklet focus on practical applications of mathematical concepts, allowing students to develop an understanding of how mathematics is used in real-life situations.
Comprehensive answer key: The booklet includes a comprehensive answer key that provides detailed explanations and step-by-step solutions for all the questions, helping students to understand the concepts and methods used to solve each problem.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- Class 11 Mathematics Case...
Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
Mycbseguide app.
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you’re seeking a comprehensive and dependable study resource with Class 11 mathematics case study questions for CBSE, myCBSEguide is the place to be. It has a wide range of study notes, case study questions, previous year question papers, and practice questions to help you ace your examinations. Furthermore, it is routinely updated to bring you up to speed with the newest CBSE syllabus. So, why delay? Begin your path to success with myCBSEguide now!
The rationale behind teaching Mathematics
The general rationale to teach Mathematics at the senior secondary level is to assist students:
- In knowledge acquisition and cognitive understanding of basic ideas, words, principles, symbols, and mastery of underlying processes and abilities, notably through motivation and visualization.
- To experience the flow of arguments while demonstrating a point or addressing an issue.
- To use the information and skills gained to address issues using several methods wherever possible.
- To cultivate a good mentality in order to think, evaluate, and explain coherently.
- To spark interest in the subject by taking part in relevant tournaments.
- To familiarise pupils with many areas of mathematics utilized in daily life.
- To pique students’ interest in studying mathematics as a discipline.
Case studies in Class 11 Mathematics
A case study in mathematics is a comprehensive examination of a specific mathematical topic or scenario. Case studies are frequently used to investigate the link between theory and practise, as well as the connections between different fields of mathematics. A case study will frequently focus on a specific topic or circumstance and will investigate it using a range of methodologies. These approaches may incorporate algebraic, geometric, and/or statistical analysis.
Sample Class 11 Mathematics case study questions
When it comes to preparing for Class 11 Mathematics, one of the best things Class 11 Mathematics students can do is to look at some Class 11 Mathematics sample case study questions. Class 11 Mathematics sample case study questions will give you a good idea of the types of Class 11 Mathematics sample case study questions that will be asked in the exam and help you to prepare more effectively.
Looking at sample questions is also a good way to identify any areas of weakness in your knowledge. If you find that you struggle with a particular topic, you can then focus your revision on that area.
myCBSEguide offers ample Class 11 Mathematics case study questions, so there is no excuse. With a little bit of preparation, Class 11 Mathematics students can boost their chances of getting the grade they deserve.
Some samples of Class 11 Mathematics case study questions are as follows:
Class 11 Mathematics case study question 1
- 9 km and 13 km
- 9.8 km and 13.8 km
- 9.5 km and 13.5 km
- 10 km and 14 km
- x ≤ −1913
- x < −1613
- −1613 < x < −1913
- There are no solution.
- y ≤ 12 x+2
- y > 12 x+2
- y ≥ 12 x+2
- y < 12 x+2
Answer Key:
- (b) 9.8 km and 13.8 km
- (a) −1913 ≤ x
- (b) y > 12 x+2
- (d) (-5, 5)
Class 11 Mathematics case study question 2
- 2 C 1 × 13 C 10
- 2 C 1 × 10 C 13
- 1 C 2 × 13 C 10
- 2 C 10 × 13 C 10
- 6 C 2 × 3 C 4 × 11 C 5
- 6 C 2 × 3 C 4 × 11 C 5
- 6 C 2 × 3 C 5 × 11 C 4
- 6 C 2 × 3 C 1 × 11 C 5
- (b) (13) 4 ways
- (c) 2860 ways.
Class 11 Mathematics case study question 3
Read the Case study given below and attempt any 4 sub parts: Father of Ashok is a builder, He planned a 12 story building in Gurgaon sector 5. For this, he bought a plot of 500 square yards at the rate of Rs 1000 /yard². The builder planned ground floor of 5 m height, first floor of 4.75 m and so on each floor is 0.25 m less than its previous floor.
Class 11 Mathematics case study question 4
Read the Case study given below and attempt any 4 sub parts: villages of Shanu and Arun’s are 50km apart and are situated on Delhi Agra highway as shown in the following picture. Another highway YY’ crosses Agra Delhi highway at O(0,0). A small local road PQ crosses both the highways at pints A and B such that OA=10 km and OB =12 km. Also, the villages of Barun and Jeetu are on the smaller high way YY’. Barun’s village B is 12km from O and that of Jeetu is 15 km from O.
Now answer the following questions:
- 5x + 6y = 60
- 6x + 5y = 60
- (a) (10, 0)
- (b) 6x + 5y = 60
- (b) 60/√ 61 km
- (d) 2√61 km
A peek at the Class 11 Mathematics curriculum
The Mathematics Syllabus has evolved over time in response to the subject’s expansion and developing societal requirements. The Senior Secondary stage serves as a springboard for students to pursue higher academic education in Mathematics or professional subjects such as Engineering, Physical and Biological Science, Commerce, or Computer Applications. The current updated curriculum has been prepared in compliance with the National Curriculum Framework 2005 and the instructions provided by the Focus Group on Teaching Mathematics 2005 in order to satisfy the rising demands of all student groups. Greater focus has been placed on the application of various principles by motivating the themes from real-life events and other subject areas.
Class 11 Mathematics (Code No. 041)
| I. | Sets and Functions | 60 | 23 |
| II. | Algebra | 50 | 25 |
| III. | Coordinate Geometry | 50 | 12 |
| IV. | Calculus | 40 | 08 |
| V. | Statistics and Probability | 40 | 12 |
| Internal Assessment |
Design of Class 11 Mathematics exam paper
CBSE Class 11 mathematics question paper is designed to assess students’ understanding of the subject’s essential concepts. Class 11 mathematics question paper will assess their problem-solving and analytical abilities. Before beginning their test preparations, students in Class 11 maths should properly review the question paper format. This will assist Class 11 mathematics students in better understanding the paper and achieving optimum scores. Refer to the Class 11 Mathematics question paper design provided.
Class 11 Mathematics Question Paper Design
| 1. | Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. | 44 | 55 |
| Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas | |||
| 2 | Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. | 20 | 25 |
| 3 | Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations | 16 | 20 |
| Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria. | |||
- No chapter-wise weightage. Care to be taken to cover all the chapters.
- Suitable internal variations may be made for generating various templates keeping the overall weightage to different forms of questions and typology of questions the same.
Choice(s): There will be no overall choice in the question paper. However, 33% of internal choices will be given in all the sections.
| Periodic Tests (Best 2 out of 3 tests conducted) | 10 Marks |
| Mathematics Activities | 10 Marks |
Prescribed Books:
- Mathematics Textbook for Class XI, NCERT Publications
- Mathematics Exemplar Problem for Class XI, Published by NCERT
- Mathematics Lab Manual class XI, published by NCERT
myCBSEguide guarantees LHS=RHS
With myCBSEguide it will always be LHS=RHS, Hence Proved!
myCBSEguide is a prominent streaming resource for students studying for CBSE examinations. The site offers extensive study material, practice papers, case study questions, online examinations, and other resources at the push of a click. myCBSEguide also has a mobile app for learning on the move. There’s no excuse not to try myCBSEguide with so much convenience and simplicity of access! Hence Proved!
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Computer Science Case Study Questions
1 thought on “Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions”
teri meri meri teri prem kahani hai muskil dolabjo main sayana hop jaye ek ladka aur ek ladki ki prem kahani hai muskil
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 3 Class 11 Trigonometric Functions
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
NCERT Solutions of Chapter 3 Class 11 Trigonometry is available free at teachoo. You can check the detailed explanation of all questions of exercises, examples and miscellaneous by clicking on the Exercise link below.
We had learned Basics of Trigonometry in Class 10. In this chapter, we will learn
- What is a positive or a negative angle
- Measuring angles in Degree , Minutes and Seconds
- Radian measure of an angle
- Converting Degree to Radians , and vice-versa
- Sign of sin, cos, tan in all 4 quadrants
- Finding values of trigonometric functions when one value is given (Example: Finding value of sin, cot, cosec, tan, sec, when cos x = -3/5 is given)
- Finding Value of trigonometric functions, given angle
- Solving questions by formula like (x + y) formula, 2x 3x formula, Cos x + cos y formula , 2 sin x sin y formula
- Finding principal and general solutions of a trigonometric equation
- Sin and Cosine Formula with supplementary Questions
Important questions are marked, and Formula sheet is also provided. Click on an exercise or topic to begin.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.

Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 – Trigonometric Functions
Important questions for cbse class 11 maths chapter 3 - trigonometric functions, cbse class 11 maths chapter-3 important questions - free pdf download.
Free PDF download of Important Questions with solutions for CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 - Trigonometric Functions prepared by expert Maths teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books. CoolGyan.Org to score more marks in your Examination.
1 Marks Questions
1. Find the radian measure corresponding to 5° 37" 30""

Ans. 39°22"30""
3. Find the length of an arc of a circle of radius 5 cm subtending a central angle measuring 15°

5. Find the value of sin(–1125°)

6. Find the value of tan 15°

9. Express sin 12 θ + sin 4 θ as the product of sines and cosines.
Ans. 2 sin8θ cos4θ
10. Express 2 cos4x sin2x as an algebraic sum of sines or cosines.
Ans. sin 6x – sin2x
11. Write the range of cos θ
Ans. [–1,1]
12. What is domain of sec θ ?

13.Find the principal solutions of cotx = 3

14. Write the general solution of cos θ = 0

17.Convert into radian measures. – 47 0 30ʹ

18.Evaluate tan 75 0 .
Ans. tan 75 = tan (45 + 30)

Ans. L. H. S = Sin (40 + θ). Cos (10 + θ) – Cos (40 + θ). Sin (10 +θ)

22.Convert into radian measures. -37 0 30’

Ans. L.H.S = Cos (n+1) x Cos (n+2) x + Sin (n+1) x Sin (n+2) x

Ans. L. H. S = tan 36 0

32.Prove Cos 4x = 1 – 8 Sin 2 x. Cos 2 x
Ans. L. H. S = Cos 4x

Ans. L. H. S = tan 56 0
= tan (45 0 + 11 0 )

35.Prove that Cos 105 0 + Cos 15 0 = Sin 75 0 – Sin 15 0
Ans. L. H. S = Cos 105 0 + Cos 15 0

36.Find the value of Cos (- 1710 0 ).
Ans. Cos (-1710 0 ) = Cos (1800-90)[Cos (-θ) = Cos θ

37.A wheel makes 360 revolutions in 1 minute. Through how many radians does it turn in 1 second.
Ans. N. of revolutions made in 60 sec. = 360

38.Prove Sin 2 6x – Sin 2 4x = Sin2 x. Sin 10 x.
Ans. L. H. S = Sin 2 6x – Sin 2 4x
= Sin (6x + 4x). Sin (6x – 4x)
= Sin 10x . Sin 2x

Ans. L. H. S = tan (69 + 66)
= tan (135)
= tan (90 + 45)

4 Marks Questions
Prove the following Identities
1.The minute hand of a watch is 1.5 cm long. How far does it tip move in 40 minute?
Ans. r = 1.5 cm
Angle made in 60 mint = 360 0

2. Show that tan 3x. tan 2x. tan x = tan 3x – tan 2x – tan x
Ans. Let 3x = 2x + x
tan 3x = tan (2x + x)

5.If in two circles, arcs of the same length subtend angles 60 0 and 75 0 at the centre find the ratio of their radii.

6.Prove that Cos 6x= 32 Cos 6 x – 48 Cos 4 x + 18 Cos 2 x-1
Ans. L.H.S. = Cos 6x

7.Solve Sin2x-Sin4x+Sin6x=o

8.In a circle of diameter 40cm, the length of a chord is 20cm. Find the length of minor are of the chord.

Ans. L. H. S = tan 4x

Ans. L. H. S = (Cos x + Cos y) 2 + (Sin x – Sin y) 2

13.Prove that Sin x + Sin 3x + Sin 5x + Sin 7x = 4 Cos x. Cos 2x. Sin 4x
Ans. L. H. S. = Sin x + Sin 3x + Sin 5x + Sin 7x
= Sin x + Sin 7x + Sin 3x + Sin 5x

14.Find the angle between the minute hand and hour hand of a clock when the time is 7. 20.

Angle made by hour hand in 1 hr = 30 0

Angle made = 90 + 10 = 100 0

16.Prove that Cot 4x (Sin 5x + Sin 3x) = Cot x (Sin 5x – Sin 3x)
Ans. L. H. S = Cot 4x (Sin 5x + Sin 3x)

R. H. S = Cot x (Sin 5x – Sin 3x)

6 Marks Questions
1. Find the general solution of sin2x + sin4x + sin6x = 0

4. Prove that Cos α + Cos β + Cos γ + Cos ( α + β + γ )

Ans. L. H. S.

Ans. L.H.S.

7. Find the value of tan ( α + β ) Given that

Ans. L. H. S=

Ans. L. H. S = Cos 20 0 . Cos 40 0 . Cos 60 0 . Cos 80 0 .
= Cos 60. Cos 20 0 . Cos 40 0 . Cos 80.

Cos x is – tive

NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions are formulated to explain the fundamental application of trigonometric formulas and the graphs of their functions. Trigonometry is an important part of Class 11 maths that involves studying various relations between sides and angles of triangles . Trigonometric Functions are applied to define these relations and have numerous applications in various other fields, including science and engineering. They are often used for basic geometric calculations and to explain numeric solutions. The knowledge of Trigonometric Functions is vital for subjects like astronomy and geography. NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 will offer the right foundational skills in students to study trigonometric relations and functions along with their practical applications.
Chapter 3 of Class 11 Maths will enable students to generalize the concept of trigonometric ratios to trigonometric functions. Learning about the properties of Trigonometric Functions and operations based on them is crucial for math studies. With the regular practice of Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 3, students will quickly master the solutions to equations using Trigonometric Functions. The wide range of problems and examples provided in these solutions are beneficial in promoting an in-depth understanding of concepts. To learn and practice with NCERT Solutions Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions, download the exercises provided in the links below.
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Ex 3.1
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Ex 3.2
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Ex 3.3
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Ex 3.4
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Miscellaneous Ex
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 PDF
Trigonometry sees the use of many formulas, theorems, and steps to solve the sums hence, ensuring that kids allot an ample amount of time for practice is very important. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 are proficiently modeled to support higher-level math learning. The comprehensive format of these solutions is highly reliable to enhance problem-solving skills in engaging ways. To learn and practice trigonometric functions with these solutions, click on the links of the pdf file given below.
☛ Download Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
NCERT Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Download PDF
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
NCERT solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions are extremely beneficial in developing mathematical reasoning in students. With the help of these well-structured resources, students will gain a simplistic approach for efficient exam preparation. The carefully placed illustrations, questions, and examples present in these solutions are sufficient to enhance the fundamental math knowledge to excel in exams. Kids can easily plan their curriculum and revision format with the help of these solutions. To practice the exercise-wise NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions, try the links given below.
- Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Ex 3.1 - 7 Questions
- Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Ex 3.2 - 10 Questions
- Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Ex 3.3 - 25 Questions
- Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Ex 3.4 - 9 Questions
- Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Miscellaneous Ex - 10 Questions
☛ Download Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 NCERT Book
Topics Covered: NCERT solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions cover some important topics, including an introduction to trigonometric ratios and identities, the measure of angles, signs, domain and range of trigonometric functions . The other important topic included in these solutions is the trigonometric solutions of the sum and difference of two angles using formulas .
Total Questions: Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions has 51 questions in 4 exercises plus 10 questions in one miscellaneous exercise. These are primarily based on the representation of trigonometric functions, their applications, and formulas.
List of Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3
Memorizing important formulas and concepts is necessary to understand the terms and operations related to trigonometric functions clearly. NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 will provide detailed knowledge of all these along with their applications through interesting illustrations. Each concept in these solutions is well-explained with suitable examples and sample problems to promote an in-depth understanding of this topic. Formulas form an integral part of this lesson hence, creating a formulas sheet can be useful for students when they need to practice this topic. Some of the important terms, formulas, and concepts related to Trigonometric Functions explained in these solutions are listed below:
- Trigonometric Functions: Trigonometric Functions are real functions that relate the angle of a r ight-angled triangle to the ratio of the length of its sides. Sin, Cos, and Tan are the three primary functions.
- Trigonometric Equations: Trigonometric equations are equations that involve the use of trigonometric functions. These trigonometric equations are also known as trigonometric identities when the values of unknown angles for which the functions are defined are satisfied.
- Trigonometric Identities: A trigonometric equation that involves the sum and difference of angles represent a trigonometric identity. For example, sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ = 1
- Sum and Difference Identities: The sum and difference identities include the following formulas.
- sin(x+y) = sin(x)cos(y) + cos(x)sin(y)
- cos(x+y) = cos(x)cos(y) – sin(x)sin(y)
- tan(x+y) = (tan x + tan y)/ (1−tan x • tan y)
- sin(x–y) = sin(x)cos(y) – cos(x)sin(y)
- cos(x–y) = cos(x)cos(y) + sin(x)sin(y)
- tan(x−y) = (tan x–tan y)/ (1+tan x • tan y)
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3
What is the importance of ncert solutions for class 11 maths chapter 3 trigonometric functions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions are designed by well-qualified teachers and math experts to promote proficient math learning. Each exercise of these solutions is formulated as per the CBSE guidelines to support in-depth learning of Trigonometric Functions and their relations. These competently structured solutions are suitable to enhance math proficiency in students. Regular practice of these solutions will boost students’ confidence in scoring well.
What are the Important Topics Covered in NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3?
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 briefly introduces trigonometric ratios and identities along with some core concepts previously studied in grade 10. The important topics covered in these solutions are angle measures, trigonometric functions, their signs, domain, and range. The sum and difference of two angles using trigonometric functions are also included in this chapter.
Do I Need to Practice all Questions Provided in Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions Trigonometric Functions?
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions are designed in an effective way to facilitate the in-depth learning of concepts. Every question included in these solutions is aimed to improve the conceptual clarity for students to master them easily. The fundamental knowledge of Trigonometric Functions and their use will allow students to apply their knowledge in practical situations. These solutions also form the basis for studying advanced math topics, including calculus. Thus, all sums must be practiced with laser focus.
How Many Questions are there in Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions?
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions has 61 questions in 5 exercises. These problems are sufficient to provide a deep-seated understanding of the entire topic of trigonometric functions, including important formulas, identities, ratios, and operations related to Trigonometric Functions. The jargon-free and lucid math vocabulary used in these solutions are quite proficient in easily imparting a clear step-by-step understanding of each topic as well as subtopics.
What are the Important Formulas in Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 3?
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 explains the formulas related to the sum and difference of two angles in trigonometric functions. Some of the important concepts related to this topic are based on deriving expressions for trigonometric identities of the sum and difference of angles. These vital concepts are described comprehensively with the help of interesting examples for students to grasp them better. Additionally, kids need to also revise the formulas they have encountered in previous classes as those are also necessary to attempt class 11 trigonometry problems.
Why Should I Practice NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions?
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions is a reliable source of learning that gives full guidance for excellent exam preparation. With the help of these solutions, students can cover the whole syllabus of CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 3. The format of these solutions is quite intuitive to promote simple and easy learning. Thus, to get the best results kids need to practice these solutions.
CBSE Class 11 Maths – Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions- Study Materials
NCERT Solutions Class 11 All Subjects Sample Papers Past Years Papers
Sets : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
- Concepts of Trigonometric Functions
- Trigonometric Functions Master File
- Trigonometric Functions Revision Notes
- R D Sharma Solution of Trigonometric Functions
- NCERT Solution Trigonometric Functions
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Trigonometric Functions
- Trigonometric Functions : Solved Example 1
CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
Angle Angle is a measure of rotation of a given ray about its initial point. The original ray is called the initial side and the final position of ray after rotation is called terminal side of the angle. The point of rotation is called vertex. If the direction of rotation is anti-clockwise, the angle is said to be positive and if the direction of rotation is clockwise, then the angle is negative.
Measuring Angles There are two systems of measuring angles Sexagesimal system (degree measure): If a rotation from the initial side to terminal side is ( 1 360 ) t h of a revolution, the angle is said to have a measure of one degree, written as 1°. One sixtieth of a degree is called a minute, written as 1′ and one-sixtieth of a minute is called a second, written as 1″ Thus, 1° = 60′ and 1′ = 60″
Circular system (radian measure): A radian is an angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc, whose length is equal to the radius of the circle. We denote 1 radian by 1°.
Relation Between Radian and Degree We know that a complete circle subtends at its centre an angle whose measure is 2π radians as well as 360°. 2π radian = 360°. Hence, π radian = 180° or 1 radian = 57° 16′ 21″ (approx) 1 degree = 0.01746 radian
Six Fundamental Trigonometric Identities
- sinx = 1 c o s e c x
- cos x = 1 s e c x
- tan x = 1 c o t x
- sin 2 x + cos 2 x = 1
- 1 + tan 2 x = sec 2 x
- 1 + cot 2 x = cosec 2 x
Trigonometric Functions – Class 11 Maths Notes
Trigonometric ratios are defined for acute angles as the ratio of the sides of a right angled triangle. The extension of trigonometric ratios to any angle in terms of radian measure (real number) are called trigonometric function. The signs of trigonometric function in different quadrants have been given in following table.
| Sin x | + | + | – | – |
| Cos x | + | – | – | + |
| Tan x | + | – | + | – |
| Cosec x | + | + | – | – |
| Sec x | + | – | – | + |
| Cot x | + | – | + | – |
Domain and Range of Trigonometric Functions
| Sine | R | [-1, 1] |
| Cos | R | [-1, 1] |
| Tan | R – {(2n + 1) π2 : n ∈ Z | R |
| Cot | R – {nπ: n ∈ Z} | R |
| Sec | R – {(2n + 1) π2 : n ∈ Z | R – (-1, 1) |
| Cosec | R – {nπ: n ∈ Z} | R – (-1, 1) |
Sine, Cosine, and Tangent of Some Angles Less Than 90°
Allied or Related Angles The angles n π 2 ± θ are called allied or related angle and θ ± n × (2π) are called coterminal angles. For general reduction, we have following rules, the value of trigonometric function for ( n π 2 ± θ ) is numerically equal to
- the value of the same function, if n is an even integer with the algebraic sign of the function as per the quadrant in which angle lies.
- the corresponding co-function of θ, if n is an odd integer with the algebraic sign of the function for the quadrant in which it lies, here sine and cosine, tan and cot, sec and cosec are cofunctions of each other.
Functions of Negative Angles
For any acute angle of θ. We have,
- sin(-θ) = – sinθ
- cos (-θ) = cosθ
- tan (-θ) = – tanθ
- cot (-θ) = – cotθ
- sec (-θ) = secθ
- cosec (-θ) = – cosecθ
Some Formulae Regarding Compound Angles
An angle made up of the sum or difference of two or more angles is called compound angles. The basic results in direction are called trigonometric identities as given below: (i) sin (x + y) = sin x cos y + cos x sin y (ii) sin (x – y) = sin x cos y – cos x sin y (iii) cos (x + y) = cos x cos y – sin x sin y (iv) cos (x – y) = cos x cos y + sin x sin y
(ix) sin(x + y) sin (x – y) = sin 2 x – sin 2 y = cos 2 y – cos 2 x (x) cos (x + y) cos (x – y) = cos 2 x – sin 2 y = cos 2 y – sin 2 x
Transformation Formulae
- 2 sin x cos y = sin (x + y) + sin (x – y)
- 2 cos x sin y = sin (x + y) – sin (x – y)
- 2 cos x cos y = cos (x + y) + cos (x – y)
- 2 sin x sin y = cos (x – y) – cos (x + y)
- sin x + sin y = 2 sin( x + y 2 ) cos( x − y 2 )
- sin x – sin y = 2 cos( x + y 2 ) sin( x − y 2 )
- cos x + cos y = 2 cos( x + y 2 ) cos( x − y 2 )
- cos x – cos y = -2 sin( x + y 2 ) sin( x − y 2 )
Trigonometric Ratios of Multiple Angles
Product of Trigonometric Ratios
- sin x sin (60° – x) sin (60° + x) = 1 4 sin 3x
- cos x cos (60° – x) cos (60° + x) = 1 4 cos 3x
- tan x tan (60° – x) tan (60° + x) = tan 3x
- cos 36° cos 72° = 1 4
- cos x . cos 2x . cos 2 2 x . cos 2 3 x … cos 2 n-1 = s i n 2 n x 2 n s i n x
Sum of Trigonometric Ratio, if Angles are in A.P.
Trigonometric Equations Equation which involves trigonometric functions of unknown angles is known as the trigonometric equation.
Solution of a Trigonometric Equation A solution of a trigonometric equation is the value of the unknown angle that satisfies the equation. A trigonometric equation may have an infinite number of solutions.
Principal Solution The solutions of a trigonometric equation for which 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π are called principal solutions.
General Solutions A solution of a trigonometric equation, involving ‘n’ which gives all solution of a trigonometric equation is called the general solutions.
General Solutions of Trigonometric Equation
- sin x = 0 ⇔ x = nπ, n ∈ Z
- cos x = 0 ⇔ x = (2n + 1) π 2 , n ∈ Z
- tan x = 0 ⇔ x = nπ, n ∈ Z
- sin x = sin y ⇔ x = nπ + (-1) n y, n ∈ Z
- cos x = cos y ⇔ x = 2nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- tan x = tan y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- sin 2 x = sin 2 y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- cos 2 x = cos 2 y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- tan 2 x = tan 2 y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
Basic Rules of Triangle
In a triangle ABC, the angles are denoted by capital letters A, B and C and the lengths of sides of opposite to these angles are denoted by small letters a, b and c, respectively. Sine Rule s i n A a = s i n B b = s i n C c
Cosine Rule a 2 = b 2 + c 2 – 2bc cos A b 2 = c 2 + a 2 – 2ac cos B c 2 = a 2 + b 2 – 2ab cos C
Projection Rule a = b cos C + c cos B b = c cos A + a cos C c = a cos B + b cos A
Trigonometric Functions Class 11 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1. The value of cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × cos (x + y) is (a) sin (x + y) (b) sin² (x + y) (c) sin³ (x + y) (d) sin 4 (x + y)
Answer: (b) sin² (x + y) Hint: cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × cos(x + y) {since cos(x + y) = cos x × cos y – sin x × sin y } = cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × (cos x × cos y – sin x × sin y) = cos² x + cos² y – 2cos² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = cos² x + cos² y – cos² x × cos² y – cos² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = (cos² x – cos² x × cos² y) + (cos² y – cos² x × cos² y) + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = cos² x(1- cos² y) + cos² y(1 – cos² x) + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = sin² y × cos² x + sin² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y (since sin² x + cos² x = 1 ) = sin² x × cos² y + sin² y × cos² x + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = (sin x × cos y)² + (sin y × cos x)² + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = (sin x × cos y + sin y × cos x)² = {sin (x + y)}² = sin² (x + y)
Question 2. If a×cos x + b × cos x = c, then the value of (a × sin x – b²cos x)² is (a) a² + b² + c² (b) a² – b² – c² (c) a² – b² + c² (d) a² + b² – c²
Answer: (d) a² + b² – c² Hint: We have (a×cos x + b × sin x)² + (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b² ⇒ c² + (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b² ⇒ (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b² – c²
Question 3. If cos a + 2cos b + cos c = 2 then a, b, c are in (a) 2b = a + c (b) b² = a × c (c) a = b = c (d) None of these
Answer: (a) 2b = a + c Hint: Given, cos A + 2 cos B + cos C = 2 ⇒ cos A + cos C = 2(1 – cos B) ⇒ 2 cos((A + C)/2) × cos((A-C)/2 = 4 sin²(B/2) ⇒ 2 sin(B/2)cos((A-C)/2) = 4sin² (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2sin (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) – cos((A+C)/2) = cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ 2sin(A/2)sin(C/2) = sin(B/2) ⇒ 2{√(s-b)(s-c)√bc} × {√(s-a)(s-b)√ab} = √(s-a)(s-c)√ac ⇒ 2(s – b) = b ⇒ a + b + c – 2b = b ⇒ a + c – b = b ⇒ a + c = 2b
Question 4. The value of cos 5π is (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) -1 (d) None of these
Answer: (c) -1 Hint: Given, cos 5π = cos (π + 4π) = cos π = -1
Question 5. In a triangle ABC, cosec A (sin B cos C + cos B sin C) equals (a) none of these (b) c/a (c) 1 (d) a/c
Answer: (c) 1 Hint: Given cosec A (sin B cos C + cos B sin C) = cosec A × sin(B+C) = cosec A × sin(180 – A) = cosec A × sin A = cosec A × 1/cosec A = 1
Question 6. If the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5, then the ratio of the greatest side to the smallest side is (a) 4 : (√5 – 1) (b) 5 : 4 (c) (√5 – 1) : 4 (d) none of these
Answer: (a) 4 : (√5 – 1) Hint: Given, the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5 ⇒ x + 4x + 5x = 180 ⇒ 10x = 180 ⇒ x = 180/10 ⇒ x = 18 So, the angle are: 18, 72, 90 Since a : b : c = sin A : sin B : sin C ⇒ a : b : c = sin 18 : sin 72 : sin 90 ⇒ a : b : c = (√5 – 1)/4 : {√(10 + 2√5)}/4 : 1 ⇒ a : b : c = (√5 – 1) : {√(10 + 2√5)} : 4 Now, c /a = 4/(√5 – 1) ⇒ c : a = 4 : (√5 – 1)
Question 7. The value of cos 180° is (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) -1 (d) infinite
Answer: (c) -1 Hint: 180 is a standard degree generally we all know their values but if we want to go theoretically then cos(90 + x) = – sin(x) So, cos 180 = cos(90 + 90) = -sin 90 = -1 {sin 90 = 1} So, cos 180 = -1
Question 8. The perimeter of a triangle ABC is 6 times the arithmetic mean of the sines of its angles. If the side b is 2, then the angle B is (a) 30° (b) 90° (c) 60° (d) 120°
Answer: (b) 90° Hint: Let the lengths of the sides if ∆ABC be a, b and c Perimeter of the triangle = 2s = a + b + c = 6(sinA + sinB + sinC)/3 ⇒ (sinA + sinB + sinC) = ( a + b + c)/2 ⇒ (sinA + sinB + sinC)/( a + b + c) = 1/2 From sin formula,Using sinA/a = sinB/b = sinC/c = (sinA + sinB + sinC)/(a + b + c) = 1/2 Now, sinB/b = 1/2 Given b = 2 So, sinB/2 = 1/2 ⇒ sinB = 1 ⇒ B = π/2
Question 9: If 3 × tan(x – 15) = tan(x + 15), then the value of x is (a) 30 (b) 45 (c) 60 (d) 90
Answer: (b) 45 Hint: Given, 3×tan(x – 15) = tan(x + 15) ⇒ tan(x + 15)/tan(x – 15) = 3/1 ⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = (3 + 1)/(3 – 1) ⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = 4/2 ⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = 2 ⇒ sin(x + 15 + x – 15)/sin(x + 15 – x + 15) = 2 ⇒ sin 2x/sin 30 = 2 ⇒ sin 2x/(1/2) = 2 ⇒ 2 × sin 2x = 2 ⇒ sin 2x = 1 ⇒ sin 2x = sin 90 ⇒ 2x = 90 ⇒ x = 45
Question 10. If the sides of a triangle are 13, 7, 8 the greatest angle of the triangle is (a) π/3 (b) π/2 (c) 2π/3 (d) 3π/2
Answer: (c) 2π/3 Hint: Given, the sides of a triangle are 13, 7, 8 Since greatest side has greatest angle, Now Cos A = (b² + c² – a²)/2bc ⇒ Cos A = (7² + 8² – 13²)/(2×7×8) ⇒ Cos A = (49 + 64 – 169)/(2×7×8) ⇒ Cos A = (113 – 169)/(2×7×8) ⇒ Cos A = -56/(2×56) ⇒ Cos A = -1/2 ⇒ Cos A = Cos 2π/3 ⇒ A = 2π/3 So, the greatest angle is = 2π/3
Question 11. The value of tan 20 × tan 40 × tan 80 is (a) tan 30 (b) tan 60 (c) 2 tan 30 (d) 2 tan 60
Answer: (b) tan 60 Hint: Given, tan 20 × tan 40 × tan 80 = tan 40 × tan 80 × tan 20 = [{sin 40 × sin 80}/{cos 40 × cos 80}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{2 * sin 40 × sin 80}/{2 × cos 40 × cos 80}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{cos 40 – cos 120}/{cos 120 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{cos 40 – cos (90 + 30)}/{cos (90 + 30) + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{cos 40 + sin30}/{-sin30 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{(2 × cos 40 + 1)/2}/{(-1 + cos 40)/2}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{2 × cos 40 + 1}/{-1 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{2 × cos 40 × sin 20 + sin 20}/{-cos 20 + cos 40 × cos 20}] = (sin 60 – sin 20 + sin 20)/(-cos 20 + cos 60 + cos 20) = sin 60/cos 60 = tan 60 So, tan 20 × tan 40 × tan 80 = tan 60
Question 12. If the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5, then the ratio of the greatest side to the smallest side is (a) 4 : (√5 – 1) (b) 5 : 4 (c) (√5 – 1) : 4 (d) none of these
Question 13. The general solution of √3 cos x – sin x = 1 is (a) x = n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) (b) x = π/3 – n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) (c) x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) (d) x = π/3 – n × π + (π/6)
Answer: (c) x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) Hint: √3 cos x-sin x=1 ⇒ (√3/2)cos x – (1/2)sin x = 1/2 ⇒ sin 60 × cos x – cos 60 × sin x = 1/2 ⇒ sin (x – 60) = 1/2 ⇒ sin (x – π/3) = sin 30 ⇒ sin (x – π/3) = sinπ/6 ⇒ x – π/3 = n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) {where n ∈ Z} ⇒ x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6)
Question 14. If tan² θ = 1 – e², then the value of sec θ + tan³ θ × cosec θ is (a) 2 – e² (b) (2 – e²) 1/2 (c) (2 – e²)² (d) (2 – e²) 3/2

Question 15. The value of cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65 is (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) -1 (d) None of these
Answer: (b) 1 Hint: Given, cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65 = cos 20 + 1 – cos 110 – √2 sin65 {since cos 2x = 1 – 2sin² x} = 1 + cos 20 – cos 110 – √2 sin65 = 1 – 2 × sin {(20 + 110)/2 × sin{(20 – 110)/2} – √2 sin65 {Apply cos C – cos D formula} = 1 – 2 × sin 65 × sin (-45) – √2 sin65 = 1 + 2 × sin 65 × sin 45 – √2 sin65 = 1 + (2 × sin 65)/√2 – √2 sin65 = 1 + √2 ( sin 65 – √2 sin 65 = 1 So, cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65 = 1
Question 16. If the radius of the circumcircle of an isosceles triangle PQR is equal to PQ ( = PR), then the angle P is (a) 2π/3 (b) π/3 (c) π/2 (d) π/6
Answer: (a) 2π/3 Hint: Let S be the center of the circumcircle of triangle PQR. So, SP = SQ = SR = PQ = PR, where SP, SQ & SR are radii. Thus SPQ & SPR are equilateral triangles. ⇒ ∠QSP = 60°; Similarly ∠RQP = 60° ⇒ Angle at the center QSP = 120° So, SRPQ is a rhombus, since all the four sides are equal. Hence, its opposite angles are equal; so ∠P = ∠QSP = 120°
Question 17. If cos a + 2cos b + cos c = 2 then a, b, c are in (a) 2b = a + c (b) b² = a × c (c) a = b = c (d) None of these
Answer: (a) 2b = a + c Hint: Given, cos A + 2 cos B + cos C = 2 ⇒ cos A + cos C = 2(1 – cos B) ⇒ 2 cos((A + C)/2) × cos((A-C)/2 = 4 sin² (B/2) ⇒ 2 sin(B/2)cos((A-C)/2) = 4sin² (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2sin (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) – cos((A+C)/2) = cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ 2sin(A/2)sin(C/2) = sin(B/2) ⇒ 2{√(s-b)(s-c)√bc} × {√(s-a)(s-b)√ab} = √(s-a)(s-c)√ac ⇒ 2(s – b) = b ⇒ a + b + c – 2b = b ⇒ a + c – b = b ⇒ a + c = 2b
Question 18. The value of 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) is (a) sin x (b) sin 2x (c) sin 3x (d) sin 4x
Answer: (c) sin 3x Hint: Given, 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) = 4 × sin x × {sin x × cos π/3 + cos x × sin π/3} × {sin x × cos 2π/3 + cos x × sin 2π/3} = 4 × sin x × {(sin x)/2 + (√3 × cos x)/2} × {-(sin x)/2 + (√3 × cos x)/2} = 4 × sin x × {-(sin 2x)/4 + (3 × cos 2x)/4} = sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 × cos 2x} = sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 × (1 – sin 2x)} = sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 – 3 × sin 2x} = sin x × {3 – 4 × sin 2x} = 3 × sin x – 4 sin 3x = sin 3x So, 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) = sin 3x
Question 19. If tan A – tan B = x and cot B – cot A = y, then the value of cot (A – B) is (a) x + y (b) 1/x + y (c) x + 1/y (d) 1/x + 1/y
Answer: (d) 1/x + 1/y Hint: Given, tan A – tan B = x ……………. 1 and cot B – cot A = y ……………. 2 From equation, 1/cot A – 1/cot B = x ⇒ (cot B – cot A)/(cot A × cot B) = x ⇒ y/(cot A × cot B) = x {from equation 2} ⇒ y = x × (cot A × cot B) ⇒ cot A × cot B = y/x Now, cot (A – B) = (cot A × cot B + 1)/(cot B – cot A) ⇒ cot (A – B) = (y/x + 1)/y ⇒ cot (A – B) = (y/x) × (1/y) + 1/y ⇒ cot (A – B) = 1/x + 1/y
Question 20. The value of (sin 7x + sin 5x) /(cos 7x + cos 5x) + (sin 9x + sin 3x) / (cos 9x + cos 3x) is (a) tan 6x (b) 2 tan 6x (c) 3 tan 6x (d) 4 tan 6x
Answer: (b) 2 tan 6x Hint: Given, (sin 7x + sin 5x) /(cos 7x + cos 5x) + (sin 9x + sin 3x) / (cos 9x + cos 3x) ⇒ [{2 × sin(7x+5x)/2 × cos(7x-5x)/2}/{2 × cos(7x+5x)/2 × cos(7x-5x)/2}] + [{2 × sin(9x+3x)/2 × cos(9x-3x)/2}/{2 × cos(9x+3x)/2 × cos(9x-3x)/2}] ⇒ [{2 × sin 6x × cosx}/{2 × cos 6x × cosx}] + [{2 × sin 6x × cosx}/{2 × cos 6x × cosx}] ⇒ (sin 6x/cos 6x) + (sin 6x/cos 6x) ⇒ tan 6x + tan 6x ⇒ 2 tan 6x
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
September 22, 2019 by phani
Get Free NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3.1, Ex 3.2, Ex 3.3, Ex 3.4, and Miscellaneous Exercise PDF in Hindi and English Medium. Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions are extremely helpful while doing your homework. Trigonometric Functions All Exercises Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions were prepared by Experienced LearnCBSE.in Teachers.
Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions NCERT Solutions in English Medium and Hindi Medium
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.1
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.2
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.3
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.4
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Miscellaneous Exercise
त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.1 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.2 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.3 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.4 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन विविध प्रश्नावली का हल हिंदी में
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Functions Class 11 Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Trig Cheat Sheet
- JEE Main Trigonometry Previous Year Questions
Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3.1, Ex 3.2, Ex 3.3, Ex 3.4, and Miscellaneous Exercise PDF in Hindi Medium as well as in English Medium for CBSE, Uttarakhand, Bihar, MP Board, Gujarat Board, BIE, Intermediate and UP Board students, who are using NCERT Books based on updated CBSE Syllabus for the session 2019-20.

| 3.1 | Introduction |
| 3.2 | Angles |
| 3.3 | Trigonometric Functions |
| 3.4 | Trigonometric Functions of Sum and Difference of Two Angles |
| 3.5 | Trigonometric Equations |
| 3.6 | Summary |
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 1: Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures: (i) 25° (ii) – 47° 30′ (iii) 240° (iv) 520° Ans:
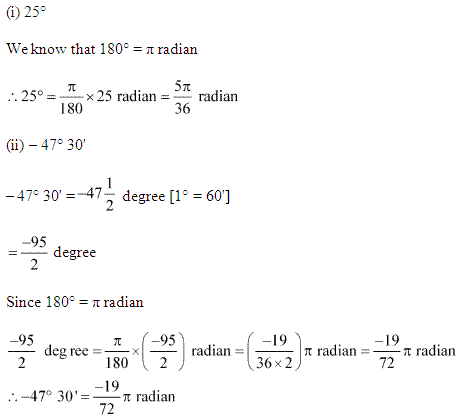
(i) \(\frac{11}{16}\) We know that: π radian = 180° ∴ \(\frac{11}{16}\) radain = \(\frac{180}{\pi} \times \frac{11}{16}\) × degree
= \(\frac{45 \times 11}{\pi \times 4}\) degree
= \(\frac{45 \times 11 \times 7}{22 \times 4}\) degree
= \(\frac{315}{8}\) degree
= 39 \(\frac{3}{8}\) degree
= 39° + \(\frac{3 \times 60}{8}\) minutes [1° = 60′]
= 39° + 22′ + \(\frac{1}{2}\) minutes
= 39°22’30” [1′ = 60°].

More Resources for CBSE Class 11
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Business Studies
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Psychology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Entrepreneurship
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Indian Economic Development
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Computer Science
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 3: A wheel makes 360 revolutions in one minute. Through how many radians does it turn in one second? Ans: Number of revolutions made by the wheel in 1 minute = 360 ∴ Number of revolutions made by the wheel in 1 second = \(\frac{360}{6}\) = 6 In one complete revolution, the wheel turns an angle of 2π radian. Hence, in 6 complete revolutions, it will turn an angle of 6 × 2π radian, i.e., 12π radian Thus, in one second, the wheel turns an angle of 12π radian. Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 4: Find the degree measure of the angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius 100 cm y an arc of length 22 cm (Use π = \(\frac{22}{7}\)). Ans:
We know that in a circle of radius r unit, if an arc of length l unit subtends an angle θ radian at the centre, then θ = \(\frac{l}{r}\) Therefore, for r = 100 cm, l = 22 cm, we have
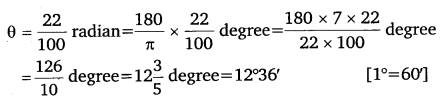
Thus, the required angle is 12°36′.
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 5: In a circle of diameter 40 cm, the length of a chord is 20 cm. Find the length of minor arc of the chord. Ans:

Given, diameter = 40 cm ∴ radius (r) = \(\frac{40}{2}\) = 20 cm and length of chord, AB = 20 cm Thus, ∆OAB is an equilateral triangle. We know that, θ = \(\frac{\text { Arc } A B}{\text { radius }}\) ⇒ Arc AB = θ × r = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) × 20 . = \(\frac{20}{3}\) π cm.
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 6: If in two circles, arcs of the same length subtend angles 60° and 75° at the centre, find the ratio of their radii. Ans:
Let the radii of the two circles be r 1 and r 2 . Let an arc of length l subtend an angle of 60° at the centre of the circle of radius r 1 , while let an arc of length l subtend an angle of 75° at the centre of the circle of radius r 2 . Now, 6o° = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) radian and 75° = \(\frac{5 \pi}{12}\) radian We know that in a circle of radius r unit, if an arc of length l unit subtends an angle θ radian at the centre, then θ = \(\frac{l}{r}\) or l = rθ ∴ l = \(\frac{r_{1} \pi}{3}\) and
l = \(\frac{r_{2} 5 \pi}{12}\)
⇒ \(\frac{r_{1} \pi}{3}=\frac{r_{2} 5 \pi}{12}\)
⇒ r = \(\frac{r_{2} 5}{4}\)
\(\frac{r_{1}}{r_{2}}=\frac{5}{4}\) Thus, the ratio of the radii is 5 : 4.
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 7: Find the angle in radian through which a pendulum swings if its length is 75 cm and the tip describes an arc of length (i) 10 cm (ii) 15 cm (iii) 21 cm. Ans:
We know that in a circle of radius r unit, if an arc of length l unit subtends an angle θ radian at the centre, then θ = \(\frac{l}{r}\). It is given that r = 75 cm
(i) Here, l = 10 cm θ = \(\frac{10}{75}\) radian = \(\frac{2}{15}\) radian
(ii) Here, l = 15 cm θ = \(\frac{15}{75}\) radian θ = \(\frac{1}{5}\) radian
(iii) Here, l = 21 cm θ = \(\frac{21}{75}\) radian = \(\frac{7}{75}\) radian.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.2
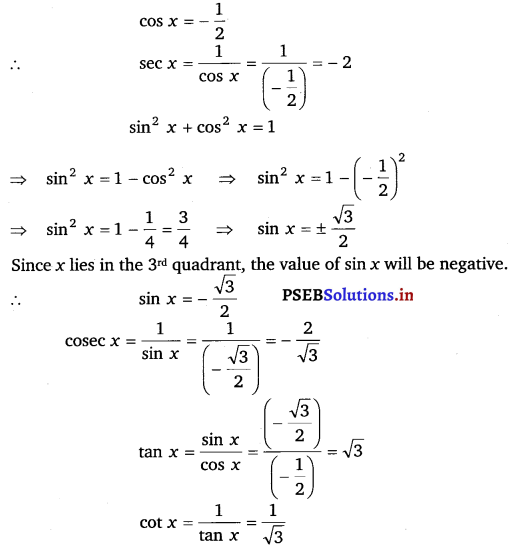
sin x = \(\frac{3}{5}\)
cosec x = \(\frac{1}{\sin x}=\frac{1}{\left(\frac{3}{5}\right)}=\frac{5}{3}\) sin 2 x + cos 2 x = 1 ⇒ cos 2 x = 1 – sin 2 x ⇒ cos 2 x = 1 – (\(\frac{3}{5}\)) 2
⇒ cos 2 x = 1 – \(\frac{9}{25}\)
⇒ cos 2 x = \(\frac{16}{25}\)
⇒ cos x = ± \(\frac{4}{5}\) Since x lies in the 2nd quadrant, the value of cos x will be negative
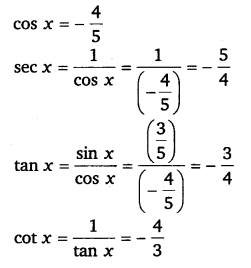
⇒ \(\frac{4}{3}=\frac{\sin x}{\frac{-3}{5}}\) ⇒ sin x = \(\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \times\left(\frac{-3}{5}\right)=-\frac{4}{5}\) ⇒ cosec x = \(\frac{1}{\sin x}=-\frac{5}{4}\).

tan x = – \(\frac{5}{12}\)
cot x = \(\frac{1}{\tan x}=\frac{1}{\left(-\frac{5}{12}\right)}=-\frac{12}{5}\)
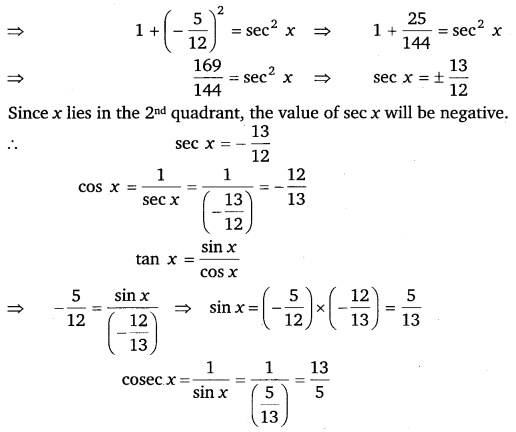
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 6: Find the value of the trigonometric function sin 765°. Ans: It is known that the values of sin x repeat after an interval of 2π or 360°. ∴ sin 765° = sin (2 × 360° + 45°) = sin 45° = 1 Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 7: Find the value of the trigonometric function cosec (- 1410°) Ans: It is known that the values of cosec x repeat after an interval of 2π or 360°. ∴ cosec (- 1410°) = cosec (- 1410° + 4 x 360°) = cosec (- 1410° + 1440°) = cosec 30° = 2. Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 8: Find the value of the trigonometric function tan \(\frac{19 \pi}{3}\). Ans:
It is known that the values of tan x repeat after an interval of π or 180°. ∴ \(\tan \frac{19 \pi}{3}=\tan 6 \frac{1}{3} \pi\)
= \(\tan \left(6 \pi+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=\tan \frac{\pi}{3}\)
= tan 60° = √3.
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 9: Find the value of the trigonometric function sin \(\left(-\frac{11 \pi}{3}\right)\). Ans:
It is known that the values of cot x repeat after an interval of π or 180°.
∴ \(\sin \left(\frac{11 \pi}{3}\right)=\sin \left(-\frac{11 \pi}{3}+2 \times 2 \pi\right)\)
= \(\sin \left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=\sin 60^{\circ}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 10: Find the value of the trigonometric function cot \(\left(-\frac{15 \pi}{4}\right)\). Ans:
It is known that the values of cot x repeat after an interval of ir or 1800. ∴ \(\cot \left(-\frac{15 \pi}{4}\right)=\cot \left(-\frac{15 \pi}{4}+4 \pi\right)=\cot \frac{\pi}{4}\) = 1.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.3
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 1:
Prove that: sin 2 \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) + cos 2 \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) – tan 2 \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) = – \(\frac{1}{2}\) Ans:
L.H.S.= sin 2 \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) + cos 2 \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) – tan 2 \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
= \(\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}+\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}\) – (1) 2
= \(\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{4}-1=-\frac{1}{2}\)
= R.H.S. Hence proved.
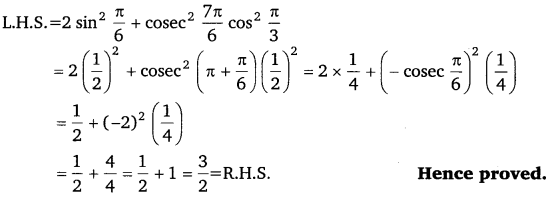
L.H.S = \(2 \sin ^{2} \frac{3 \pi}{4}+2 \cos ^{2} \frac{\pi}{4}+2 \sec ^{2} \frac{\pi}{3}\)
= \(2\left\{\sin \left(\pi-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\right\}^{2}+2\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)^{2}+2(2)^{2}\)
= \(2\left\{\sin \frac{\pi}{4}\right\}^{2}+2 \times \frac{1}{2}+8\)
= 2 \(\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)^{2}\) + 1 + 8
= 1 + 1 + 8 = 10 = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 5: Find the value of: (i) sin 75°, (ii) tan 15° Ans:
(i) sin 75° sin (45° + 30°) = sin 45° cos 30° + cos 45° sin 30° [∵ sin (x + y) = sin x cos y + cos x sin y] = \(\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\left(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)+\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)\)
= \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2 \sqrt{2}}+\frac{1}{2 \sqrt{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2 \sqrt{2}}\)
(ii) tan 15° = tan (45° – 30°)
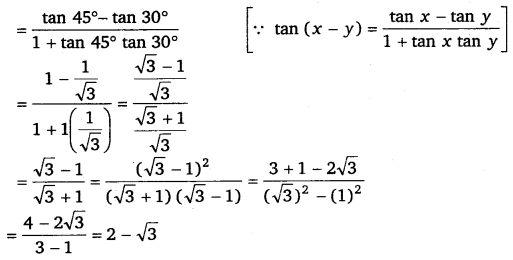
L.H.S = \(\frac{\cos (\pi+x) \cos (-x)}{\sin (\pi-x) \cos \left(\frac{\pi}{2}+x\right)}\)
= \(\frac{[-\cos x][\cos x]}{(\sin x)(-\sin x)}=\frac{-\cos ^{2} x}{-\sin ^{2} x}\)
= R.H.S Hence proved.
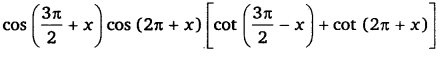
It is known that cos A – cos B = \(-2 \sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cdot \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
∴ L.H.S.= \(=\cos \left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}+x\right)-\cos \left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}-x\right)\)
= \(– 2 \sin \left\{\frac{\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}+x\right)+\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}-x\right)}{2}\right\} \cdot \sin \left\{\frac{\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}+x\right)-\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}-x\right)}{2}\right\}\)
= – 2 sin (\(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\)) sin x
= – 2 sin (- \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)) sin x
= – √2 sin x = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 12: Prove that: sin 2 6x – sin 2 4x = sin 2x sin 10 x Ans:
It is known that sin A + sin B = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
sin A – sin B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\) L.H.S.= sin 2 6x – sin 2 4x = (sin 6x + sin 4x) (sin 6x – sin 4x) = (2 sin 5x cos x) (2 cos 5x sin x) = (2 sin 5x cos 5x) (2 sin x cos x) = sin 10x sin 2x = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 13: Prove that: cos 2 2x cos 2 6x = sin 4x sin 8x Ans:
It is known that cos A + cos B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
cos A – cos = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
∴ L.H.S = cos 2 2x – cos 2 6x = (cos 2x + cos 6x) (cos 2x – 6x) = \(\left[2 \cos \left(\frac{2 x+6 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{2 x-6 x}{2}\right)\right]\left[-2 \sin \left(\frac{2 x+6 x}{2}\right) \sin \frac{(2 x-6 x)}{2}\right]\) ∴ L.H.S.= cos 2 2x – cos 2 6x = (cos 2x + cos 6x) (cos 2x – 6x) = [2 cos 4x cos (-2x)] [- 2 sin 4x sin (- 2x)] = [2 cos 4x cos 2x] [- 2 sin 4x (- sin 2x)] = (2 sin 4x cos 4x) (2 sin 2x cos 2x) = sin 8x sin 4x = R.H.S. Hence proved.

It is known that sin A + sin = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
cos A + cos = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
∴ L.H.S = \(\frac{\sin 5 x+\sin 3 x}{\cos 5 x+\cos 3 x}\)
= \(\frac{2 \sin \left(\frac{5 x+3 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{5 x-3 x}{2}\right)}{2 \cos \left(\frac{5 x+3 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{5 x-3 x}{2}\right)}\)
= \(\frac{2 \sin 4 x \cos x}{2 \cos 4 x \cos x}=\frac{\sin 4 x}{\cos 4 x}\)
= tan 4x = R.H.S. Hence proved.
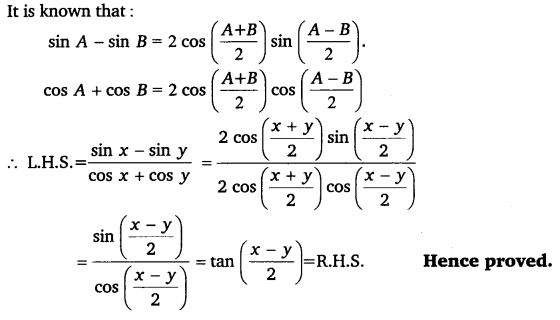
It is known that sin A – sin B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
cos 2 A – sin 2 A = cos 2A
∴ L.H.S. = \(=\frac{\sin x-\sin 3 x}{\sin ^{2} x-\cos ^{2} x}\)
= \(\frac{2 \cos \left(\frac{x+3 x}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{x-3 x}{2}\right)}{-\cos 2 x}\)
= \(\frac{2 \cos 2 x \sin (-x)}{-\cos 2 x}\)
= – 2 × (- sin x) = 2 sin x
Hence proved.
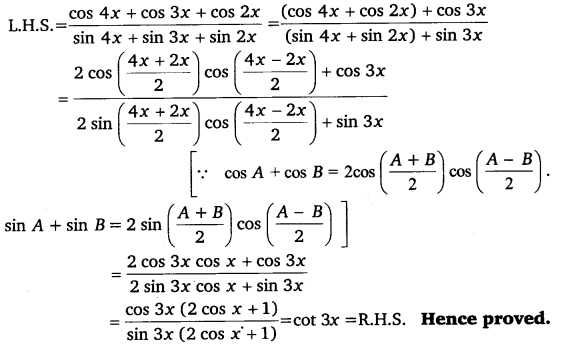
Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 3 Exercise 3.4

cos 4x = cos 2x cos 4x – cos 2x = 0 – 2 sin \(\left(\frac{4 x+2 x}{2}\right)\) sin \(\left(\frac{4 x-2 x}{2}\right)\) = 0
[∵ cos A – cos B = 2 \sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\(\)]
sin 3x sin x = 0 sin 3x = 0or sin x = 0 3x = nπ or x = nπ, where n ∈ Z x = \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) or x = nπ, where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 6: Find the general solution of the equation cos 3x + cosx – cos 2x = 0 Ans:
cos 3x + cos x – cos 2x = 0 2 cos \(\left(\frac{3 x+x}{2}\right)\) cos \(\left(\frac{3 x-x}{2}\right)\) – cos 2x = 0
[∵ cos A + cos B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)]
2 cos 2x cos x – cos 2x = 0 cos 2x (2 cos x – 1) = 0 cos 2x = 0 or 2 cos x – 1 = 0 cos 2x = 0 or cos x = \(\frac{1{2}\) ∴ 2x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) or cos x = cos \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) or x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 7: Find the general solution of the equation sin 2x + cos x = 0 Ans:
sin 2x + cos x = 0 ⇒ 2sin x cos x + cos x = 0 ⇒ cos x (2 sin x + 1) = 0 ⇒ cos x = 0 or 2 sin x + 1 = 0 Now, cos x = 0 ⇒ x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) , where n ∈ Z. or 2 sin x + 1 = 0 ⇒ sin x = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= – sin \(\frac{\pi}{6}\)
= sin (π + \(\frac{\pi}{6}\))
= sin \(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\)
x = nπ + (- 1) n \(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\) where n ∈ Z Therefore, the general solution is (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) or nπ + (- 1) n \(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\) where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 8: Find the general solution of the equation sec 2 2x = 1 – tan 2x. Ans:
sec 2 2x = 1 – tan 2x 1 + tan 2 2x = 1 – tan 2x tan 2 x + tan 2x = 0 => tan 2x (tan 2x + 1) = 0 => tan 2x = 0 or tan 2x + 1 = 0 Now, tan 2x = 0 => tan 2x = tan 0 2x = nπ + 0, where n ∈ Z x = \(\frac{n \pi}{2}\), where n ∈ Z or tan 2x + 1 = 0 = tan 2x = – 1 = – tan \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
= tan (π – \(\frac{\pi}{4}\))
= tan \(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\)
2x = nπ + \(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\) where n ∈ Z
x = \(\frac{n \pi}{2}+\frac{3 \pi}{8}\), where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is \(\frac{n \pi}{2}\) or \(\frac{n \pi}{2}+\frac{3 \pi}{8}\) where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 9: Find the general solution of the equation sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0 Ans:
sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0 ⇒ (sin x + sin 5x) + sin 3x = 0
\(\left[2 \sin \left(\frac{x+5 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{x-5 x}{2}\right)\right]\) + sin 3x = 0
[∵ sin A + sin B = 2 sin \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)]
2 sin 3x cos (2x) + sin 3x = 0 2 sin 3x cos 2x + sin 3x = 0 sin 3x (2 cos 2x +1) = 0 sin 3x = 0 or 2 cos 2x + 1 = 0 Now sin 3x = 0 ⇒ 3x = nπ, where n ∈ Z i.e., x = \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) where n ∈ Z or 2 cos 2x + 1 = 0 cos 2x = \(-\frac{1}{2}\)
= – cos \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
= cos (π – \(\frac{\pi}{3}\))
cos 2x = cos \(\frac{2 \pi}{3}\)
⇒ 2x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{2\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
⇒ x = nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) or nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Miscellaneous Exercise
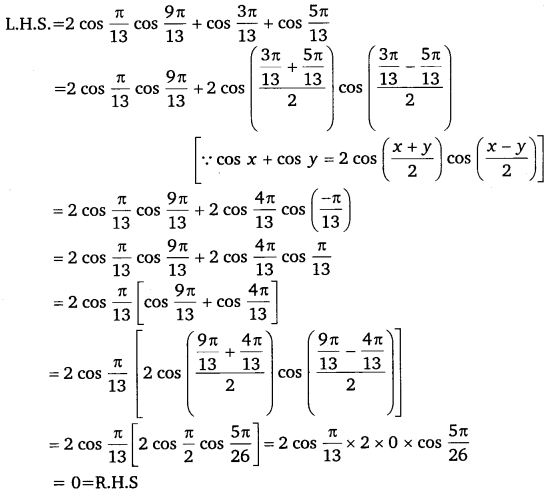
L.H.S. = (sin 3x + sin x) sin x + (cos 3x – cos x) cos x = sin 3x sin x + sin 2 x + cos 3x cos x – cos 2 x = cos 3x cos x + sin 3x sin x – (cos 2 x – sin 2 x) = cos (3x – x) – cos 2x [∵ cos(A – B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B] = cos 2x – cos 2x = 0 =R.H.S. Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 3:
Prove that: (cos x + cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2 = 4 cos 2 \(\left(\frac{x+y}{2}\right)\)
L.H.S.= (cos x + cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2 = cos 2 x + cos 2 y + 2 cos x cos y + sin 2 x + sin 2 y – 2 sin x sin y = (cos 2 x + sin 2 x) + (cos 2 y + sin 2 y) + 2 (cos x cos y – sin x sin y) = 1 + 1 + 2 cos (x + y) [∵ cos (A + B) = (cos A cos B – sin A sin B)] = 2 + 2 cos (x + y) = 2 [1 + cos (x + y)] = 2[1 + \(2 \cos ^{2}\left(\frac{x+y}{2}\right)\) – 1] [∵ cos 2A = 2 cos 2 A – 1] = 4 c0s 2 \(\left(\frac{x+y}{2}\right)\) = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 4: Prove that: (cos x – cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2 = 4 sin 2 \(\frac{x-y}{2}\) Ans:
L.H.S.= (cos x – cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2 = cos 2 x + cos 2 y – 2 cos x cos y + sin 2 x + sin 2 y – 2 sin x sin y = (cos 2 x + sin 2 x) + (cos 2 y + sin 2 y) – 2 [cos x cos y + sin x sin y] = 1 + 1 – 2 [cos (x – y)] = 2 [1 – {1 – 2 sin 2 \(\left(\frac{x-y}{2}\right)\)}] [∵ cos 2A = 1 – 2 sin 2 A] = 4 sin 2 \(\left(\frac{x-y}{2}\right)\) = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 5: Prove that: sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x + sin 7x = 4 cos x cos 2x sin 4x Ans:
It is known that sin A + sin B = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cdot \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\) ∴ L.H.S. = (sin x + sin 3x) + (sin 5x + sin 7x) = (sin x + sin 5x) + (sin 3x + sin 7x) = \(2 \sin \left(\frac{x+5 x}{2}\right)\) . \(\cos \left(\frac{x-5 x}{2}\right)+2 \sin \left(\frac{3 x+7 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{3 x-7 x}{2}\right)\) = 2 sin 3x cos (- 2x) + 2 sin 5x cos (- 2x) = 2 sin 3x cos 2x + 2 sin 5x cos 2x = 2 cos 2x [sin 3x + sin 5x] = 2 cos 2x [latex]2 \sin \left(\frac{3 x+5 x}{2}\right) \cdot \cos \left(\frac{3 x-5 x}{2}\right)[/latex] = 2 cos 2x [2 sin 4x . cos (- x)] = 4 cos 2x sin 4x cos x = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 6: Prove that: \(\frac{(\sin 7 x+\sin 5 x)+(\sin 9 x+\sin 3 x)}{(\cos 7 x+\cos 5 x)+(\cos 9 x+\cos 3 x)}\) = tan 6x Ans: It is known that
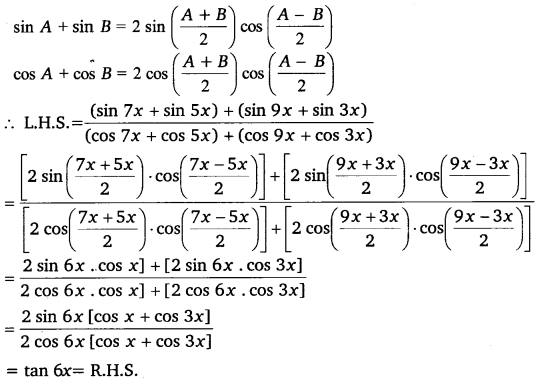
प्रश्न 3. एक-पहिया एक मिनट में 360° परिक्रमण करता है तो एक सेकंड में कितने रेडियन माप का कोण बनाएगा? हल: परिक्रमण में पहिया द्वारा बना कोण = 27 रेडियन 360 परिक्रमण में पहिया द्वारा बना कोण = 360 x 2π रेडियन 1 मिनट अर्थात् 60 सेकण्ड में 360 x 2π रेडियन का कोण बनता है। 1 सेकण्ट में चहिया द्वारा बना कोण = \(\frac { 360\times 2\pi }{ 60 }\) = 12π रेडियन।

Exercise 3.1
Q.1: Calculate the radian measurement of the given degree measurement:
(ii). 240 ∘
(iii). − 47 ∘ 30 ‘
(iv). 520 ∘
Q.2: Calculate the degree measurement of the given degree measurement: [Use π = \(\\ \frac { 22 }{ 7 } \)]
(i) \(\\ \frac { 11 }{ 16 } \)
(iii) \(\frac { 5\pi }{ 3 } \)
(iv) \(\frac { 7\pi }{ 6 } \)
Q.3: In a minute, wheel makes 360 revolutions. Through how many radians does it turn in 1 second?
Q.4: Calculate the degree measurement of the angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius 100 m by an arc of length 22 m.
Q.5: In a circle of diameter 40 m, the length of the chord 20 m. Find the length of minor arc of chord.
Q.6: In two circles, arcs which has same length subtended at an angle of 60 ∘ and 75 ∘ at the center. Calculate the ratio of their radii.
Q.7: Calculate the angle in radian through which a pendulum swings if the length is 75 cm and the tip describes an arc of length
(iii) 21 cm
Exercise 3.2
Q.1: Calculate the values of five trigonometric func. if cos y = \(– \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) and y lies in 3 rd quadrant.
(iii) cosec y
Q.2: Calculate the other five trigonometric function if we are given the values for sin y = \(\\ \frac { 3 }{ 5 } \), where y lies in second quadrant.
Q.3: Find the values of other five trigonometric functions if c o t y =\(\\ \frac { 3 }{ 4 } \) , where y lies in the third quadrant.
Q.4: Find the values of other five trigonometric if s e c y =\(\\ \frac { 13 }{ 5 } \) , where y lies in the fourth quadrant.
Q.5: Find the values of other five trigonometric function if tan y = \(– \frac { 5 }{ 12 } \) and y lies in second quadrant.
Q.6: Calculate the value of trigonometric function sin 765°.
Q.7: Calculate the value of trigonometric function cosec [-1410°]
Q.8: Calculate the value of the trigonometric function tan \(\frac { 19\pi }{ 3 } \) .
Q.9: Calculate the value of the trigonometric function sin \(-\frac { 11\pi }{ 3 } \) .
Q.10: Calculate the value of the trigonometric function cot \(-\frac { 15\pi }{ 4 } \)
Exercise 3.3
Q.1: Prove:
sin²\(\frac { \pi }{ 6 } \) + cos² \(\frac { \pi }{ 3 } \) – tan² \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) = \(– \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
Q.2: Prove:
2 sin² \(\frac { \pi }{ 6 } \) + c o s e c ² \(\frac { 7\pi }{ 6 } \) 6 cos ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 3 } \) =\(\\ \frac { 3 }{ 2 } \)
Q.3: Prove:
cot ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 6 } \) + c o s e c \(\frac { 5\pi }{ 6 } \) + 3 tan ² latex s=2]\frac { \pi }{ 6 } [/latex] = 6
Q.4: Prove:
2 sin ² \(\frac { 3\pi }{ 4 } \) + 2 cos ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) + 2 sec ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 3 } \) = 10
Q.5: Calculate the value of:
(i). sin 75 ∘
(ii). tan 15 ∘
cos ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – x ) cos ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – y ) – sin ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – x ) sin ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – y ) = sin ( x + y )
Q.7: Prove:
\(\frac { tan(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } +x) }{ tan(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } -x) } ={ \left( \frac { 1+tanx }{ 1-tanx } \right) }^{ 2 }\)
Q.8: Prove:
\(\frac { cos(\pi +x)cos(-x) }{ sin(\pi -x)cos\left( \frac { \pi }{ 2 } +x \right) } ={ cot }^{ 2 }x\)
Q.9: Prove:
\(cos(\frac { 3\pi }{ 2 } +x)cos(2\pi +x)[cot(\frac { 3\pi }{ 2 } -x)+cot(2\pi +x)]=1\)
Q.10: Prove:
sin ( n + 1 ) x sin ( n + 2 ) x + cos ( n + 1 ) x cos ( n + 2 ) x = cos x
Q.11 Prove:
\(cos(\frac { 3\pi }{ 4 } +x)-cos(\frac { 3\pi }{ 4 } -x)\)= − √2 sin x
Q.12: Prove:
sin² 6 x – sin ² 4 x = sin2 x sin 10 x
Q.13: Prove:
cos ² 2 x – cos ² 6 x = sin 4 x sin 8 x
Q.14:Prove:
sin 2 x + 2 sin 4 x + sin 6 x = 4 cos ² x sin 4 x
Q.15: Prove:
cot 4 x ( sin 5 x + sin 3 x ) = cot x ( sin 5 x – sin 3 x )
Q.16: Prove:
\(\frac { cos9x-cos5x }{ sin17x-sin3x } =-\frac { sin2x }{ cos10x } \)
Q.17: Prove:
\(\frac { sin5x+sin3x }{ cos5x+cos3x } =tan4x\)
Q.18: Prove:
\(\frac { sinx-siny }{ cosx+cosy } =tan\frac { x-y }{ 2 } \)
Q.19: Prove:
\(\frac { sinx+sin3x }{ cosx+cos3x } =tan2x\)
Q.20: Prove:
\(\frac { sinx-sin3x }{ { sin }^{ 2 }x-{ cos }^{ 2 }x } =2sinx\)
Q.21: Prove:
\(\frac { cos4x+cos3x+cos2x }{ sin4x+sin3x+sin2x } =cot3x\)
Q.22: Prove:
cot x cot 2 x – cot 2 x cot 3 x – cot 3 x cot x = 1
Q.23: Prove:
\(tan4x=\frac { 4tanx(1-{ tan }^{ 2 }x) }{ 1-6{ tan }^{ 2 }x+{ tan }^{ 4 }x } \)
Q.24: Prove:
cos 4 x = 1 – 8 sin² x cos² x
Q.25: Prove:
cos 6 x = 32 cos 6 x – 48 cos 4 x + 18 cos 2 x − 1
Exercise 3.4
Q.1: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: tan x = √3
Q.2: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: sec x = 2
Q.3: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: cot = − √3
Q.4: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: cosec x = -2
Q.5: Find the general solution of the given equation: cos 4x = cos 2x
Q.6: Find the general solution of the given equation: cos 3x + cos x – cos 2x = 0
Q.7: Find the general solution of the given equation: sin 2x + cos x = 0
Q.8: Find the general solution of the given equation: sec² 2 x = 1 – tan 2 x
Q.9: Find the general solution of the given equation: sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0
Miscellaneous Exercise
Q.1: Prove that:
\(2cos\frac { \pi }{ 13 } cos\frac { 9\pi }{ 13 } +cos\frac { 3\pi }{ 13 } +cos\frac { 5\pi }{ 13 } =0\)
Q.2: Prove that:
( sin 3 x + sin x ) sin x + ( cos 3 x – cos x ) cos x = 0
Q-3: Prove that:
( cos x + cos y )² + ( sin x – sin y ) ² = 4 cos ²\(\\ \frac { x+y }{ 2 } \)
Q-4: Prove that:
( cos x – cos y ) ² + ( sin x – sin y ) ² = 4 sin ² \(\\ \frac { x-y }{ 2 } \)
Q-5: Prove that:
sin x + sin 3 x + sin 5 x + sin 7 x = 4 cos x cos 2 x cos 4 x
Q-6: Prove that:
\(\frac { (sin7x+sin5x)+(sin9x+sin3x) }{ (cos7x+cos5x)+(cos9x+cos3x) } =tan6x\)
Q-7: Show that: sin 3 y + sin 2 y – sin y = 4 sin y cos\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) cos\(\\ \frac { 3y }{ 2 } \)
Q-8: The value of tan y =\(– \frac { 4 }{ 2 } \) where y in in 2 nd quadrant then find out the values of sin\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) , cos\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) a n d tan\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) .
Q-9: The value of cos y = \(– \frac { 1 }{ 3 } \) where y in in 3 rd quadrant then find out the values of sin \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) , cos \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) a n d tan \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) .
Q-10: The value of sin y = \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 4 } \) where y in in 2 nd quadrant then find out the values of sin \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) , cos \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) a n d tan \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) .
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths All Chapters
- Chapter 1 Sets
- Chapter 2 Relations and Functions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction
- Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities
- Chapter 7 Permutation and Combinations
- Chapter 8 Binomial Theorem
- Chapter 9 Sequences and Series
- Chapter 10 Straight Lines
- Chapter 11 Conic Sections
- Chapter 12 Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry
- Chapter 13 Limits and Derivatives
- Chapter 14 Mathematical Reasoning
- Chapter 15 Statistics
- Chapter 16 Probability
Free Resources
Quick Resources
Important Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions - PDF Download
| Video Lectures | Live Sessions |
| Study Material | Tests |
| Previous Year Paper | Revision |

CBSE class 11 maths chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions important questions are prepared for the students who are preparing for class 11 maths exams. Trigonometric functions class 11th maths important questions have been developed by subject experts of eSaral for enhancing the problem-solving ability to score good marks in exams. You can go through the trigonometry questions for class 11 which are based on the updated syllabus of CBSE. These important questions are solved in a step by step method which helps you to understand the concepts easily.
Class 11 maths chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions is one of the easiest chapters which includes questions based on different formulas. To solve trigonometric questions for class 11, you have to learn and remember all the essential formulas of trigonometric functions. Each and every concept of trigonometric functions has been covered in important questions of class 11 mathematics chapter 3 curated by eSaral that will help you to achieve great marks in final exams.
Students can refer to trigonometry questions with answers pdf provided by experts of mathematics. In class 11th trigonometry important questions, all the concepts are explained in precise language. This will give you a quick understanding of all the concepts and formulas while solving these important questions. Our expert teachers of mathematics at eSaral have also provided important questions of trigonometry class 11 in free PDF format which you can download from the official website of eSaral and practice these questions even before the main exam.
Important Topics & Sub-topics of Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Maths
Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions deals with the relation between angles and sides of triangles. This chapter is essential and a scoring one for the students of class 11. Thus, it is vital for students to have a thorough understanding of all the significant topics and sub-topics of trigonometric functions. In class 11 maths chapter 3, you will delve into the difficulties of trigonometric functions and concepts based on them. Our subject experts of eSaral have combined all the topics and sub-topics of trigonometric functions in the tabulated structure mentioned below.
|
|
|
| Introduction | |
| Angles | |
| Trigonometric Functions | |
| Trigonometric Functions of Sum and Difference of Two Angles |
Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Weightage
CBSE class 11 maths chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions forms solid foundations for advance level concepts of mathematical studies. In chapter 3, understanding the weightage of significant topics helps you to prioritize your preparations in an effective way. This chapter carries the highest marks in unit one. Thus, students should be thorough with the concepts of trigonometric functions chapter 3 class 11 maths to score desired marks in examination.
The weightage and marks distribution can vary from one education board to another one so students are advised to check the official website of CBSE to get the correct information regarding weightage of chapter 3. Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions has topics angles, domain and range of trigonometric functions, and trigonometric functions of sum and difference of two angles which you must be well-versed to solve questions effectively and easily in exam. In order to score full marks in trigonometric functions, practice important questions of trigonometry class 11 maths provided on eSaral. You can also solve examples and questions mentioned in exercises of chapter 3 to grasp the knowledge of essential topics of trigonometric functions.
Tips to Solve Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
Class 11 maths chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions is an easy chapter where you can score full marks by deeply analyzing and comprehending the main concepts of trigonometry. By solving 11th class trigonometry important questions, you will get to know some tips and tricks that help you to solve the questions quickly. Check out some useful tips provided below by eSaral’s subject experts of mathematics.
Firstly, Students should never miss the formulas of trigonometric functions as these formulas are crucial to solve the questions correctly.
To understand the concepts of trigonometry deeply, you should use the resources like trigonometry important questions for class 11 available on eSaral.
Trigonometric formulas are an essential part of chapter 3. Thus, forming a formula chart can be a helpful tool for students whenever they need to practice trigonometry based questions.
There are some significant topics such as domain and range of trigonometric functions, relation between degree and radian, degree measure of angles etc. which students need to understand to solve questions without any error.
Benefits of Solving Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Important Questions with Answers
Downloading and practicing important questions class 11 maths chapter 3 will give you an in-depth understanding of trigonometric functions. Students must solve trigonometry problems for class 11 by eSaral for better preparation of exams. Here, our subject experts of mathematics have provided numerous benefits of solving class 11 maths chapter 3 important questions which can be checked below.
Conceptual Understanding - By practicing class 11 maths important questions solidify the fundamental concepts of trigonometric functions. All the important questions of trigonometric functions class 11th have deeply included each question which describes the core principles of trigonometry. This process helps you to revise the concepts which you have studied in theoretical knowledge acquired in the classroom.
Preparing for Examination - Class 11 maths chapter 3 important questions not only help you to reinforce the theoretical knowledge of trigonometric functions but also familiarize you with question format and type of questions asked in board exams.
Boost Confidence - Solving class 11 maths chapter 3 important questions help students to recall all the vital concepts of trigonometry. You also get to learn the easy methods of solving trigonometric functions that boost your self-confidence.
Improve Time Management - By frequently practicing important questions of trigonometry class 11 maths chapter 3, You will be able to solve questions within the time allotted for question paper in the main exam. This will help you to improve your time management skills.
Frequently Asked Questions
Answer 1. To solve trigonometry based questions, students must memorize all the formulas of trigonometric functions which help you to solve any question asked in examinations related to trigonometric functions. You should also practice questions of exercises mentioned in chapter 3. This provides deep comprehension of concepts of trigonometric functions.
Answer 2. There are a total of 3 exercises as well as one miscellaneous exercise which must be solved to score good marks in the final exam.
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
Download Now
eSaral Gurukul
- JEE Coaching in Kota
- NEET Coaching in Kota
- NEET Question Paper
- NEET 2024 Question Paper
- NEET 2024 Exam Date
- JEE Main 2025
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main 2024 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2023 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2022 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
JEE Advanced
- JEE Advanced Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2023 Question Paper
Our Telegram Channel
- eSaral NEET
- eSaral Class 9-10
All Study Material
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Learn Insta
RD Sharma Solutions , RS Aggarwal Solutions and NCERT Solutions
MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions with Answers
November 16, 2020 by Prasanna
Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Maths MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Question 1. The value of cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × cos (x + y) is (a) sin (x + y) (b) sin² (x + y) (c) sin³ (x + y) (d) sin 4 (x + y)
Answer: (b) sin² (x + y) Hint: cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × cos(x + y) {since cos(x + y) = cos x × cos y – sin x × sin y } = cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × (cos x × cos y – sin x × sin y) = cos² x + cos² y – 2cos² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = cos² x + cos² y – cos² x × cos² y – cos² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = (cos² x – cos² x × cos² y) + (cos² y – cos² x × cos² y) + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = cos² x(1- cos² y) + cos² y(1 – cos² x) + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = sin² y × cos² x + sin² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y (since sin² x + cos² x = 1 ) = sin² x × cos² y + sin² y × cos² x + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = (sin x × cos y)² + (sin y × cos x)² + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y = (sin x × cos y + sin y × cos x)² = {sin (x + y)}² = sin² (x + y)
Question 2. If a×cos x + b × cos x = c, then the value of (a × sin x – b²cos x)² is (a) a² + b² + c² (b) a² – b² – c² (c) a² – b² + c² (d) a² + b² – c²
Answer: (d) a² + b² – c² Hint: We have (a×cos x + b × sin x)² + (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b² ⇒ c² + (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b² ⇒ (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b² – c²
Answer: (a) 2b = a + c Hint: Given, cos A + 2 cos B + cos C = 2 ⇒ cos A + cos C = 2(1 – cos B) ⇒ 2 cos((A + C)/2) × cos((A-C)/2 = 4 sin²(B/2) ⇒ 2 sin(B/2)cos((A-C)/2) = 4sin² (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2sin (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) – cos((A+C)/2) = cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ 2sin(A/2)sin(C/2) = sin(B/2) ⇒ 2{√(s-b)(s-c)√bc} × {√(s-a)(s-b)√ab} = √(s-a)(s-c)√ac ⇒ 2(s – b) = b ⇒ a + b + c – 2b = b ⇒ a + c – b = b ⇒ a + c = 2b
Answer: (c) 1 Hint: Given cosec A (sin B cos C + cos B sin C) = cosec A × sin(B+C) = cosec A × sin(180 – A) = cosec A × sin A = cosec A × 1/cosec A = 1
Question 6. If the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5, then the ratio of the greatest side to the smallest side is (a) 4 : (√5 – 1) (b) 5 : 4 (c) (√5 – 1) : 4 (d) none of these
Answer: (a) 4 : (√5 – 1) Hint: Given, the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5 ⇒ x + 4x + 5x = 180 ⇒ 10x = 180 ⇒ x = 180/10 ⇒ x = 18 So, the angle are: 18, 72, 90 Since a : b : c = sin A : sin B : sin C ⇒ a : b : c = sin 18 : sin 72 : sin 90 ⇒ a : b : c = (√5 – 1)/4 : {√(10 + 2√5)}/4 : 1 ⇒ a : b : c = (√5 – 1) : {√(10 + 2√5)} : 4 Now, c /a = 4/(√5 – 1) ⇒ c : a = 4 : (√5 – 1)
Answer: (c) -1 Hint: 180 is a standard degree generally we all know their values but if we want to go theoretically then cos(90 + x) = – sin(x) So, cos 180 = cos(90 + 90) = -sin 90 = -1 {sin 90 = 1} So, cos 180 = -1
Question 9: If 3 × tan(x – 15) = tan(x + 15), then the value of x is (a) 30 (b) 45 (c) 60 (d) 90
Answer: (b) 45 Hint: Given, 3×tan(x – 15) = tan(x + 15) ⇒ tan(x + 15)/tan(x – 15) = 3/1 ⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = (3 + 1)/(3 – 1) ⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = 4/2 ⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = 2 ⇒ sin(x + 15 + x – 15)/sin(x + 15 – x + 15) = 2 ⇒ sin 2x/sin 30 = 2 ⇒ sin 2x/(1/2) = 2 ⇒ 2 × sin 2x = 2 ⇒ sin 2x = 1 ⇒ sin 2x = sin 90 ⇒ 2x = 90 ⇒ x = 45
Answer: (c) 2π/3 Hint: Given, the sides of a triangle are 13, 7, 8 Since greatest side has greatest angle, Now Cos A = (b² + c² – a²)/2bc ⇒ Cos A = (7² + 8² – 13²)/(2×7×8) ⇒ Cos A = (49 + 64 – 169)/(2×7×8) ⇒ Cos A = (113 – 169)/(2×7×8) ⇒ Cos A = -56/(2×56) ⇒ Cos A = -1/2 ⇒ Cos A = Cos 2π/3 ⇒ A = 2π/3 So, the greatest angle is = 2π/3
Answer: (b) tan 60 Hint: Given, tan 20 × tan 40 × tan 80 = tan 40 × tan 80 × tan 20 = [{sin 40 × sin 80}/{cos 40 × cos 80}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{2 * sin 40 × sin 80}/{2 × cos 40 × cos 80}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{cos 40 – cos 120}/{cos 120 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{cos 40 – cos (90 + 30)}/{cos (90 + 30) + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{cos 40 + sin30}/{-sin30 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{(2 × cos 40 + 1)/2}/{(-1 + cos 40)/2}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{2 × cos 40 + 1}/{-1 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20) = [{2 × cos 40 × sin 20 + sin 20}/{-cos 20 + cos 40 × cos 20}] = (sin 60 – sin 20 + sin 20)/(-cos 20 + cos 60 + cos 20) = sin 60/cos 60 = tan 60 So, tan 20 × tan 40 × tan 80 = tan 60
Question 12. If the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5, then the ratio of the greatest side to the smallest side is (a) 4 : (√5 – 1) (b) 5 : 4 (c) (√5 – 1) : 4 (d) none of these
Question 13. The general solution of √3 cos x – sin x = 1 is (a) x = n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) (b) x = π/3 – n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) (c) x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) (d) x = π/3 – n × π + (π/6)
Answer: (c) x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) Hint: √3 cos x-sin x=1 ⇒ (√3/2)cos x – (1/2)sin x = 1/2 ⇒ sin 60 × cos x – cos 60 × sin x = 1/2 ⇒ sin (x – 60) = 1/2 ⇒ sin (x – π/3) = sin 30 ⇒ sin (x – π/3) = sinπ/6 ⇒ x – π/3 = n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) {where n ∈ Z} ⇒ x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6)
Question 14. If tan² θ = 1 – e², then the value of sec θ + tan³ θ × cosec θ is (a) 2 – e² (b) (2 – e²) 1/2 (c) (2 – e²)² (d) (2 – e²) 3/2
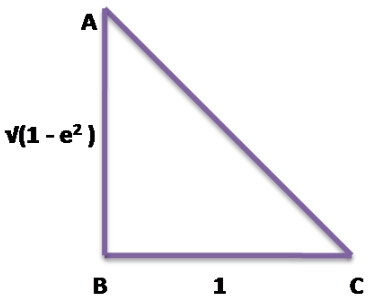
Question 15. The value of cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65 is (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) -1 (d) None of these
Answer: (b) 1 Hint: Given, cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65 = cos 20 + 1 – cos 110 – √2 sin65 {since cos 2x = 1 – 2sin² x} = 1 + cos 20 – cos 110 – √2 sin65 = 1 – 2 × sin {(20 + 110)/2 × sin{(20 – 110)/2} – √2 sin65 {Apply cos C – cos D formula} = 1 – 2 × sin 65 × sin (-45) – √2 sin65 = 1 + 2 × sin 65 × sin 45 – √2 sin65 = 1 + (2 × sin 65)/√2 – √2 sin65 = 1 + √2 ( sin 65 – √2 sin 65 = 1 So, cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65 = 1
Answer: (a) 2b = a + c Hint: Given, cos A + 2 cos B + cos C = 2 ⇒ cos A + cos C = 2(1 – cos B) ⇒ 2 cos((A + C)/2) × cos((A-C)/2 = 4 sin² (B/2) ⇒ 2 sin(B/2)cos((A-C)/2) = 4sin² (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2sin (B/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ cos((A-C)/2) – cos((A+C)/2) = cos((A+C)/2) ⇒ 2sin(A/2)sin(C/2) = sin(B/2) ⇒ 2{√(s-b)(s-c)√bc} × {√(s-a)(s-b)√ab} = √(s-a)(s-c)√ac ⇒ 2(s – b) = b ⇒ a + b + c – 2b = b ⇒ a + c – b = b ⇒ a + c = 2b
Answer: (c) sin 3x Hint: Given, 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) = 4 × sin x × {sin x × cos π/3 + cos x × sin π/3} × {sin x × cos 2π/3 + cos x × sin 2π/3} = 4 × sin x × {(sin x)/2 + (√3 × cos x)/2} × {-(sin x)/2 + (√3 × cos x)/2} = 4 × sin x × {-(sin 2x)/4 + (3 × cos 2x)/4} = sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 × cos 2x} = sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 × (1 – sin 2x)} = sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 – 3 × sin 2x} = sin x × {3 – 4 × sin 2x} = 3 × sin x – 4 sin 3x = sin 3x So, 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) = sin 3x
Question 19. If tan A – tan B = x and cot B – cot A = y, then the value of cot (A – B) is (a) x + y (b) 1/x + y (c) x + 1/y (d) 1/x + 1/y
Answer: (d) 1/x + 1/y Hint: Given, tan A – tan B = x ……………. 1 and cot B – cot A = y ……………. 2 From equation, 1/cot A – 1/cot B = x ⇒ (cot B – cot A)/(cot A × cot B) = x ⇒ y/(cot A × cot B) = x {from equation 2} ⇒ y = x × (cot A × cot B) ⇒ cot A × cot B = y/x Now, cot (A – B) = (cot A × cot B + 1)/(cot B – cot A) ⇒ cot (A – B) = (y/x + 1)/y ⇒ cot (A – B) = (y/x) × (1/y) + 1/y ⇒ cot (A – B) = 1/x + 1/y
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding CBSE Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Syllabus for the Session 2023-24
CBSE Syllabus
Case Study Questions
Case Study on Sets CS-2 CS-3 CS-4 CS-5
Case Study on Relations & Functions CS-2 CS-3
Case Study on Trigonometric Functions
Case Study on Complex Numbers
Case Study on Linear Inequalities
Case Study on Permutations and Combinations
Case Study on Sequences & Series
Case Study on Straight Lines
Case Study on Conic Sections
Case Study on Statistics
Case Study on Probability
Pdf of Case Studies
MCQs for Practice
Chapter 1 - Sets
Chapter 2 - Relations & Functions
Chapter 3 - Trigonometric Functions
Chapter 4 - Complex Numbers & Quadratic Equations
Chapter 5 - Linear Inequalities
Chapter 6 - Permutations & Combinations
Chapter 7 - Binomial Theorem
Chapter 8 - Sequences & Series
Chapter 9 - Straight Line
Chapter 1 0 - Conic Sections
Chapter 1 1 - Introduction to Three-dimensional Geometry
Chapter 12 - Limits & D erivatives
Chapter 13 - Statistics
Chapter 14 - Probability
Answers of MCQs
Assertion & Reasoning Questions
Relations & Functions
- Trigonometric Functions
Complex Numbers
Linear Inequalities
Permutations & Combinations
Binomial Theorem
Sequences & Series
Straight Lines
Conic Sections
Introduction to Three-Dimensional Geometry
Limits & derivatives
Probability
Topic Wise Assignments of Previous Year Questions
Relations and Functions
Straight Line
Limits & Derivatives
Question Papers - DoE, Delhi
Session 2015-2016
SA2(QP) SA2(MS) COMP(QP) COMP(MS)
Session 201 6 -20 17
SA1(QP) SA2(QP) SA2(MS) COMP(QP) COMP(MS)
Session 201 7 -201 8
SA2(QP) SA2(MS) COMP(QP) COMP(MS)
Session 201 8 -201 9
SA2(QP) SA2(MS) COMP(QP) COMP(MS)
Session 201 9 -20 20
SA2(QP) SA2(MS)
Session 2020-21
Video Explanation: Part A Part B Section III Part B Section IV Part B Section V
Session 2021-22
Question Paper
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C
Session 2022-23
Sample Question Paper for Mid-Term Exam
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C Section D Section E
Mid-Term Exam: Question Paper
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C Section D Section E
Practice Paper for Final Exam
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C Section D Section E
Final Exam: Question Paper Marking Scheme
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C Section D Section E
Support Material Issued by DoE, Delhi
Session 202 3 -24
Mid-Term Exam: Question Paper
Video Explanation: Section A Section B Section C Section D Section E
Practice Paper 1 for Final Exam: Question Paper
Practice Paper 2 for Final Exam: Question Paper
Short Capsules (Notes to Revise Concepts)
Chapter 1 - Sets
Chapter 4 - Mathematical Induction
Chapter 5 - Complex Numbers & Quadratic Equations
Chapter 6 - Linear Inequalities
Chapter 7 - Permutations & Combinations
Chapter 8 - Binomial Theorem
Chapter 9 - Sequences & Series
Chapter 10 - Straight Line
Chapter 11 - Conic Sections
Chapter 12 - Introduction to Three-dimensional Geometry
Chapter 13 - Limits & derivatives
Chapter 14 - Mathematical Reasoning
Chapter 15 - Statistics
Chapter 16 - Probability
Some Basic Concepts to Revise:
Number System
Mensuration Results
Quadratic Equations
Solution of Polynomial Inequality - Wavy Curve Method
Probability__Revision of the Topics studied in Earlier Classes
Result Sheets
Trigonometric Identities
- NCERT Class 11
- NCERT 11 Maths
- Chapter 3: Trigonometric Functions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Ex
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 - Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Exercise
Chapter 3, Trigonometric Functions of Class 11 Maths, is categorised under the CBSE Syllabus for 2023-24. The miscellaneous exercise contains questions covering the entire topics present in the chapter. The last exercise of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 – Trigonometric Functions is based on the following topics:
- Trigonometric Functions of Sum and Difference of Two Angles
- Trigonometric Equations
The solutions provided here are based on the latest guidelines of the syllabus prescribed by the CBSE. The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 can help the students in preparing well for the board examination.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 – Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Exercise
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access other exercise solutions of Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 – Trigonometric Functions
The NCERT Class 11 Maths Solutions for Chapter 3 can be referred to in PDF format by checking the links below.
Exercise 3.1 Solutions 7 Questions
Exercise 3.2 Solutions 10 Questions
Exercise 3.3 Solutions 25 Questions
Exercise 3.4 Solutions 9 Questions
Access Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Miscellaneous Exercise
Prove that:

2. (sin 3 x + sin x ) sin x + (cos 3 x – cos x ) cos x = 0
LHS = (sin 3x + sin x) sin x + (cos 3x – cos x) cos x
By further calculation,
= sin 3x sin x + sin 2 x + cos 3x cos x – cos 2 x
Taking out the common terms,
= cos 3x cos x + sin 3x sin x – (cos 2 x – sin 2 x)
Using the formula
cos (A – B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
= cos (3x – x) – cos 2x
= cos 2x – cos 2x

LHS = (cos x + cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2
By expanding using the formula, we get
= cos 2 x + cos 2 y + 2 cos x cos y + sin 2 x + sin 2 y – 2 sin x sin y
Grouping the terms,
= (cos 2 x + sin 2 x) + (cos 2 y + sin 2 y) + 2 (cos x cos y – sin x sin y)
Using the formula cos (A + B) = (cos A cos B – sin A sin B)
= 1 + 1 + 2 cos (x + y)
= 2 + 2 cos (x + y)
Taking 2 as common
From the formula cos 2A = 2 cos 2 A – 1

LHS = (cos x – cos y) 2 + (sin x – sin y) 2
By expanding using the formula,
= cos 2 x + cos 2 y – 2 cos x cos y + sin 2 x + sin 2 y – 2 sin x sin y
= (cos 2 x + sin 2 x) + (cos 2 y + sin 2 y) – 2 (cos x cos y + sin x sin y)
Using the formula cos (A – B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
From formula cos 2A = 1 – 2 sin 2 A

5. sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x + sin 7x = 4 cos x cos 2x sin 4x

8. Find sin x/2, cos x/2 and tan x/2 in each of the following.

cos x = -3/5
From the formula,

9. cos x = -1/3, x in quadrant III

10. sin x = 1/4, x in quadrant II

Class 11 Maths NCERT supplementary or miscellaneous exercise solutions PDFs are provided here.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
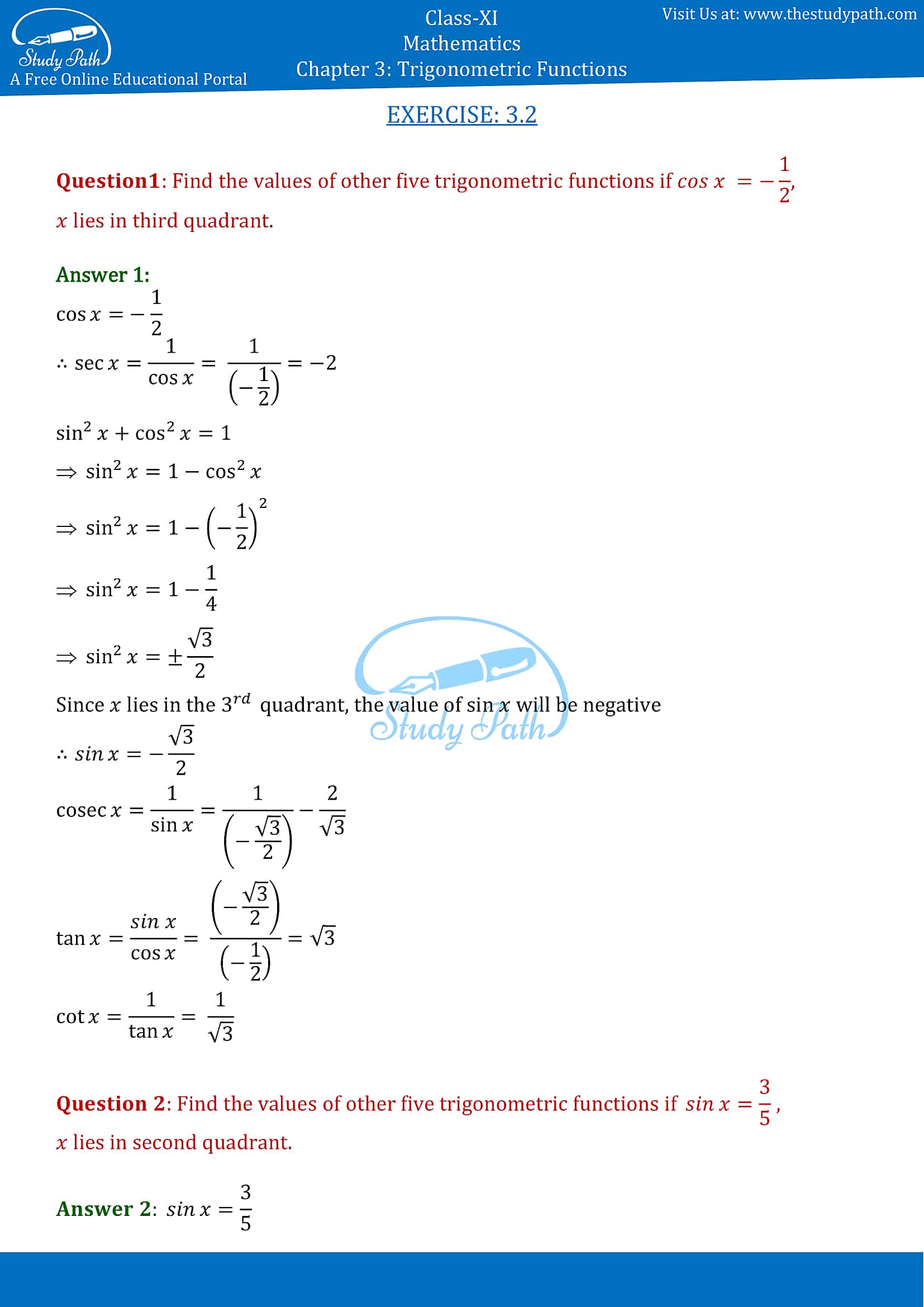
Importance of Solving Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths. Case study questions are an important aspect of mathematics education at the Class 11 level. These questions require students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world scenarios, helping them develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills.
Practice Questions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. Find the value of the below expression. Hint: Simplify the expression to. Find the general solution of the equation 5cos 2 θ + 7sin 2 θ - 6 = 0. If θ lies in the first quadrant and cos θ = 8/17, then find the value of cos (30° + θ) + cos (45° - θ) + cos (120 ...
Case Studies on the Topic Trigonometric Functions - Class 11 MathematicsThis video lecture discusses 2 case study questions on the topic of Trigonometric Fun...
Class 11 Mathematics case study question 2. A state cricket authority has to choose a team of 11 members, to do it so the authority asks 2 coaches of a government academy to select the team members that have experience as well as the best performers in last 15 matches. They can make up a team of 11 cricketers amongst 15 possible candidates.
CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter-3 Important Questions - Free PDF Download. Trigonometric functions class 11 important questions have been prepared for students of class 11 to help them score better marks in the examination. The complete topic of trigonometric functions is designed by the subject experts following the latest guidelines of CBSE.
NCERT Solutions of Chapter 3 Class 11 Trigonometry is available free at teachoo. You can check the detailed explanation of all questions of exercises, examples and miscellaneous by clicking on the Exercise link below. We had learned Basics of Trigonometry in Class 10. In this chapter, we will learn. What is a positive or a negative angle.
4 Marks Questions. Prove the following Identities. 1.The minute hand of a watch is 1.5 cm long. How far does it tip move in 40 minute? Ans. r = 1.5 cm Angle made in 60 mint = 360 0. Angle made in 1 min = = 60 0 Angle made in 40 mint = 6 40 = 240 0. Θ =
Exercises under NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. Exercise 3.1: In this exercise, students are introduced to trigonometric ratios of acute angles and their applications in solving problems related to heights and distances.
Students can view the set of important questions given below. Q1. Prove that sin5x−2sin3x+sinx / cos5x−cosx =tanx. A1. Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric difference identities for the sine function, we obtain. L.H.S.=sin5x+sinx−2sin3x / cos5x−cosx. =2sin3x.cos2x−2sin3x / −2sin3x.sin2x.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 PDF. Trigonometry sees the use of many formulas, theorems, and steps to solve the sums hence, ensuring that kids allot an ample amount of time for practice is very important. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 are proficiently modeled to support higher-level math learning.
Chapter 3, Trigonometric Functions, comes under NCERT Class 11 Maths and is an important chapter for students. Though the chapter has numerous mathematical terms and formulae, BYJU'S has made NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths easy for the students to understand and remember with the usage of tricks.
CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. Angle. Angle is a measure of rotation of a given ray about its initial point. The original ray is called the initial side and the final position of ray after rotation is called terminal side of the angle. The point of rotation is called vertex.
Class XI Maths www.vedantu.com 4 10. Express 2cos4xsin2x as an algebraic sum of sines or cosine. Ans: x x x 11. Write the range of sT Ans: The cosine function is a periodic function with a domain of and a range of > 1@. 12. What is domain of cT Ans: The secant function is the reciprocal of the cosine function, it has a domain of (2n 1) ;n 2 ½S
Important Questions For Class 11 Maths ... word which means 'Three', 'Gon' means 'length', and 'metry' means 'measurement'. So basically, trigonometry is a study of triangles, which has angles and lengths on its side. Trigonometry basics consist of sine, cosine and tangent functions. Trigonometry for class 11 contains ...
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. ... Long Answer Type Questions. Q20. If sin(θ + α) = a and sin(θ + β) = b , then prove that cos2(α - β) - 4abcos(α - β) = 1-2a 2-2b 2. Sol ...
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 1: Find the values of other five trigonometric functions if cos x = - 1 2 x lies in third quadrant. Ans: Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 2: Find the values of other five trigonometric functions if sin x = 35, x lies in second quadrant. Ans: sin x = 3 5. cosec x = 1 sin x = 1(3 5) = 5 3.
Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions deals with the relation between angles and sides of triangles. This chapter is essential and a scoring one for the students of class 11. Thus, it is vital for students to have a thorough understanding of all the significant topics and sub-topics of trigonometric functions. In class 11 maths chapter 3, you will ...
CLASSS 11 MATHS - CASE STUDY QUESTIONS - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
We have provided Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Maths MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well. Trigonometric Functions Class 11 MCQs Questions with Answers. Question 1. The value of cos² x + cos² y - 2cos x × cos y × cos (x + y) is (a) sin (x + y) (b) sin² (x + y)
Class 11. Syllabus for the Session 2023-24. CBSE Syllabus. Case Study Questions. Case Study on Sets CS-2 CS-3 CS-4 CS-5. Case Study on Relations & Functions CS-2 CS-3. Case Study on Trigonometric Functions. Case Study on Complex Numbers. Case Study on Linear Inequalities.
MCQs for Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Class 11 with Answers. 1. If sin θ and cos θ are the roots of ax2 - bx + c = 0, then the relation between a, b and c will be. 2. If tan A = 1/2 and tan B = 1/3, then the value of A + B is. 3. The value of cos 1° cos 2° cos 3° … cos 179° is. 4.
Nov 10, 2021 • 59m • 91 views. Use Code VMSIR to Unlock this Class . In this Class , Vishal Mahajan discuss the Case Study Based Questions .This Session will be beneficial Of Class 11 & all aspirants preparing for Competitive Exams.This session will be Conducted in English & Hindi and notes will be provided in English
Solution: 10. sin x = 1/4, x in quadrant II. Solution: Class 11 Maths NCERT supplementary or miscellaneous exercise solutions PDFs are provided here. NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Exercise can be accessed here. Students can also download these NCERT Solutions as a PDF for free.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case study questions are an important aspect of mathematics education at the Class 11 level. These questions require students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world scenarios, helping them develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills. Here are some reasons why case study questions are important in Class 11 maths ...
Class 11 Mathematics case study question 2. A state cricket authority has to choose a team of 11 members, to do it so the authority asks 2 coaches of a government academy to select the team members that have experience as well as the best performers in last 15 matches. They can make up a team of 11 cricketers amongst 15 possible candidates.
Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Sets in order to fully complete your preparation.They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Case Study Based Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams!. I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams.
Case Studies on the Topic Trigonometric Functions - Class 11 MathematicsThis video lecture discusses 2 case study questions on the topic of Trigonometric Fun...
Case study Based Question from chapter "Trigonometric functions"Next in playlist:https://youtu.be/vuFLIpZGmtk
Practice Questions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. Find the value of the below expression. Hint: Simplify the expression to. Find the general solution of the equation 5cos 2 θ + 7sin 2 θ - 6 = 0. If θ lies in the first quadrant and cos θ = 8/17, then find the value of cos (30° + θ) + cos (45° - θ) + cos (120 ...
Class 11 math (India) 15 units · 180 skills. Unit 1. Sets. Unit 2. Relations and functions. Unit 3. Trigonometric functions. Unit 4. Complex numbers. Unit 5. Linear inequalities. ... Find value of other trigonometric functions from given trigonometric function Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Trigonometric identities: Symmetry. Learn. Sine ...
NCERT Solutions of Chapter 3 Class 11 Trigonometry is available free at teachoo. You can check the detailed explanation of all questions of exercises, examples and miscellaneous by clicking on the Exercise link below. We had learned Basics of Trigonometry in Class 10. In this chapter, we will learn. What is a positive or a negative angle.
Trigonometric functions class 11 important questions have been prepared for students of class 11 to help them score better marks in the examination. The complete topic of trigonometric functions is designed by the subject experts following the latest guidelines of CBSE.The class 11th maths trigonometric functions important questions feature the step by step solutions for easy to difficult ...
CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. Angle is a measure of rotation of a given ray about its initial point. The original ray is called the initial side and the final position of ray after rotation is called terminal side of the angle. The point of rotation is called vertex.
Exercises under NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. Exercise 3.1: In this exercise, students are introduced to trigonometric ratios of acute angles and their applications in solving problems related to heights and distances.
Class 11 Maths Chapters. Chapter 1 Sets. Chapter 2 Relations and Functions. Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction. Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations. Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities. Chapter 7 Permutation and Combinations. Chapter 8 Binomial Theorem.
Trigonometry for class 11 with basic formulas as well as important functions of sum and product of angles. Solve trigonometric functions related questions here. ... word which means 'Three', 'Gon' means 'length', and 'metry' means 'measurement'. So basically, trigonometry is a study of triangles, which has angles and lengths ...
Case study based question from the chapter "Trigonometric Functions"Next in playlist:https://youtu.be/2s9EEGQPk8M
Class XI Maths www.vedantu.com 13 x 22 x sin10xsin2x. 39. Prove that 6 1 6 Ans: Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric difference identity for the tangent function, we obtain 6.S. 6 ) 5 5 1. 40. Prove that x tan 2 Ans: Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identities
The PDF of Maths NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chapter 3 includes the topics and sub-topics listed below. 3.1 Introduction. The basic trigonometric ratios and identities are given here, along with the applications of trigonometric ratios in solving the word problems related to heights and distances. 3.2 Angles.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Q4. If cos (α + ) =4/5 and sin (α- )=5/13 , where α lie between […]
Class 11. Syllabus for the Session 2023-24. CBSE Syllabus. Case Study Questions. Case Study on Sets CS-2 CS-3 CS-4 CS-5. Case Study on Relations & Functions CS-2 CS-3. Case Study on Trigonometric Functions. Case Study on Complex Numbers. Case Study on Linear Inequalities. Case Study on Permutations and Combinations.
Get Free NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3.1, Ex 3.2, Ex 3.3, Ex 3.4, and Miscellaneous Exercise PDF in Hindi and English Medium. Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions are extremely helpful while doing your homework. Trigonometric Functions All Exercises Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions were prepared by Experienced LearnCBSE.in Teachers.
In this case, you need to select class 10 and the subject Maths to download the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. ... It is advisable for all the students to study Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Miscellaneous Solutions on a regular basis as it will help them to do effective preparation for ...
Class 11. 14 units · 180 skills. Unit 1. Sets. Unit 2. Relations and functions. Unit 3. Trigonometric functions. Unit 4. Complex numbers and quadratic equations. Unit 5. ... Find value of other trigonometric functions from given trigonometric function Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Trigonometric identities: Symmetry. Learn. Sine & cosine ...
In this article, we are covering Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Assertion Reason Questions. Detailed Solutions are also provided at the end of questions so that students can check their answers after completing all the questions. ... Environment and Natural Resources Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 12 Political Science ...
Gurukul of Excellence. Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians. Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download. Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter