Assignment 1
Learning Aim A
5/A.P1 Explain the importance of promoting equality and diversity for individuals with different needs.
5/A.M1 Analyse the impact of preventing discrimination for individuals with different needs.
5/A.P2 Explain the skills and personal attributes necessary for professionals who care for individuals with different needs.
5/A.M2 Assess different methods professionals might use when building relationships and establishing trust with individuals with needs .
5/A.D1 Evaluate the success of promoting anti-discriminatory practice for specific individuals with different needs.
Learning Aim B
5/B.P3 Explain how to incorporate ethical principles into the provision of support for individuals with different needs
5/B.M3 Analyse how an ethical approach to providing support would benefit specific individuals with different needs.
Learning Aim C
5/C.P4 Explain the strategies and communication techniques used with individuals different needs to overcome different challenges.
5/C.M4 Assess the strategies and communication techniques used to overcome different challenges faced by individuals with different care and support needs.
5/C.P5 Explain the benefits of promoting personalisation when overcoming challenges faced by individuals with different needs.
5/BC.D2 Justify the strategies and techniques used to overcome ethical issues and challenges experienced by individuals with different needs when planning and providing care.
Assignment 2
Learning Aim D
5/D.P6 Explain why meeting the needs of the individuals requires the involvement of different agencies.
5/D.P7 Explain the roles and responsibilities of different members of the multidisciplinary team in meeting the needs of specific individuals
5/D.M5 Assess the benefits of multi-disciplinary and multi-agency working for specific individuals with care and support needs
5/D.D4 Evaluate how multiagency and multidisciplinary working can meet the care and support needs of specific individuals
5/D.P8 Explain the arrangements for managing information between professionals.
5/D.M6 Analyse the impact of legislation and codes of practice relating to information management on multidisciplinary working.
5/D.D3 Justify how organisations and professionals work together to meet individual needs while managing information and maintaining confidentiality.


Healthcare Project Management: Essential Guide & Best Practices
Table of contents.
Are you ready to revolutionize healthcare project management ? Dive into our comprehensive guide tailored to simplify the complexities of overseeing healthcare projects. From optimizing workflows to enhancing team collaboration, we’ve got you covered with practical strategies and expert insights. Discover how to navigate budget constraints, streamline communication, and ensure timely project delivery in the dynamic healthcare landscape. Stay ahead of the curve by mastering essential project management skills specific to the healthcare industry.
Understanding Project Management
Effective healthcare project management is crucial for ensuring the successful delivery of healthcare services. It plays a vital role in enhancing patient care , streamlining processes , and achieving organizational goals . Project management directly impacts patient outcomes by ensuring that projects are completed on time, within budget, and meet quality standards.
The significance of project management in healthcare lies in its ability to improve healthcare delivery by optimizing resource allocation , enhancing communication among stakeholders, and promoting collaboration across different departments. A well-managed project can lead to better patient experiences, increased efficiency in service delivery, and ultimately contribute to improved health outcomes for individuals and communities.
Healthcare organizations rely on effective project management practices to navigate the complex landscape of the healthcare industry. Managing healthcare projects involves dealing with unique challenges such as strict regulatory requirements , rapidly evolving technologies, and the need to balance clinical excellence with operational efficiency . The success of healthcare projects hinges on the ability to address these complexities while maintaining a focus on delivering high-quality patient care.
Managing healthcare projects presents a myriad of challenges that require a delicate balance between meeting patient needs and achieving project objectives. Healthcare project managers must navigate through intricate processes while adhering to regulations, managing risks, and ensuring stakeholder engagement . The complexity of healthcare project management stems from the dynamic nature of the healthcare environment and the diverse range of stakeholders involved.
Balancing quality patient care with project requirements is one of the primary challenges faced in healthcare project management. Project managers must prioritize patient safety and well-being while also meeting project deadlines and budget constraints. This delicate balance requires careful planning , effective communication , and continuous monitoring to ensure that both clinical outcomes and project goals are achieved successfully.
The regulatory demands imposed on healthcare organizations further add to the complexity of managing healthcare projects. Compliance with various regulations and standards is essential to ensure that projects meet legal requirements and industry best practices. Healthcare project managers must navigate through these regulatory frameworks while maintaining a focus on delivering high-quality care to patients.
Stages Overview
In healthcare project management, several key stages are essential for ensuring project success . These stages typically include initiation , planning, execution , monitoring & control , and closure . Each stage plays a critical role in guiding the project from conception to completion by providing a structured framework for managing resources, timelines, risks, and stakeholder expectations.
Initiation marks the beginning of a healthcare project where objectives are defined, stakeholders are identified, and initial planning activities take place. Planning involves developing a comprehensive roadmap that outlines project scope, deliverables, timelines, budgets, and resource requirements. Execution focuses on implementing the plan while monitoring & control involve tracking progress against milestones, managing risks, and making necessary adjustments to ensure project success.
A systematic approach is crucial throughout all stages of healthcare project management to maintain alignment with organizational goals and ensure efficient resource utilization. By following a structured methodology from initiation to closure, healthcare organizations can enhance transparency, accountability, and overall project performance.
Methodologies
Various project management methodologies are utilized in healthcare settings to effectively manage projects based on specific requirements. Agile methodology emphasizes iterative development cycles that allow for flexibility in responding to changing priorities or stakeholder needs. Lean methodology focuses on eliminating waste and improving efficiency by streamlining processes and reducing unnecessary steps.
Waterfall methodology follows a sequential approach where each phase of the project is completed before moving onto the next stage. While Agile is suitable for projects requiring adaptability and frequent feedback loops, Waterfall is ideal for projects with well-defined requirements and limited changes expected during implementation.
Selecting the right methodology is crucial in determining the success of healthcare projects as it influences how tasks are organized, resources allocated, risks managed, and progress monitored. By choosing an appropriate methodology tailored to specific project needs, healthcare organizations can enhance collaboration among team members, improve decision-making processes, and increase overall project efficiency.
High Stakes in Healthcare
Patient well-being.
Healthcare project management is crucial for ensuring optimal patient well-being and care delivery efficiency. The precise coordination of tasks directly influences patient outcomes and satisfaction levels. Error-free project execution is imperative in healthcare settings to prevent any adverse impact on patients’ health. Patient-centric project management approaches prioritize the needs and safety of individuals receiving medical care.
Cost Concerns
Managing costs effectively throughout a healthcare project is essential to ensure financial sustainability and affordability of services. Budgeting plays a critical role in controlling expenses and allocating resources efficiently. Strategies such as cost tracking and resource optimization help in maintaining financial stability during the project lifecycle.
Regulation Impact
Regulations play a significant role in shaping healthcare project management practices, requiring strict adherence to compliance standards. Challenges related to regulatory requirements necessitate thorough planning and monitoring to mitigate risks effectively. Staying updated with industry regulations is vital to avoid penalties and legal implications that could jeopardize project success.
Industry Changes
The dynamic nature of the healthcare industry constantly introduces new trends, technologies, and methodologies that impact project management practices. Adapting to these changes is crucial for ensuring the successful implementation of healthcare projects. Flexibility and innovation are key components in managing projects amidst evolving industry landscapes.
Project Management Stages
The initiation phase in healthcare project management is crucial as it sets the foundation for the entire project. Defining project scope and objectives accurately ensures alignment with stakeholders’ expectations. Thorough planning during initiation helps in identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies.
Key steps in the initiation phase include conducting a feasibility study to assess project viability, defining clear objectives, and establishing a project team. Engaging key stakeholders from the beginning ensures their input is considered in shaping project goals. The initiation phase lays the groundwork for successful project outcomes.
Planning plays a critical role in ensuring the success of healthcare projects by setting a roadmap for execution. Creating detailed project plans and timelines helps in organizing tasks effectively and allocating resources efficiently. Involving stakeholders during the planning phase ensures their buy-in and commitment to project goals.
Effective planning involves identifying project deliverables, defining roles and responsibilities, and establishing communication channels. Developing contingency plans for potential risks enhances project resilience. Stakeholder involvement fosters collaboration and ensures that diverse perspectives are considered in decision-making processes.
The execution phase involves implementing the project plan while monitoring progress closely to ensure milestones are met timely. Monitoring progress allows project managers to identify deviations from the plan and take corrective actions promptly. Addressing issues proactively minimizes disruptions and keeps the project on track.
Effective communication is essential during the execution phase to keep all team members informed about progress, changes, and challenges. Regular meetings, status updates, and feedback sessions facilitate smooth coordination among team members. Transparent communication builds trust and fosters a collaborative working environment.
Proper project closure is vital in healthcare to ensure that outcomes meet quality standards and stakeholder expectations. Wrapping up a healthcare project successfully involves completing all deliverables, obtaining approvals, and transitioning any remaining tasks or responsibilities. Documenting outcomes and lessons learned provides valuable insights for future projects.
Steps involved in closure include conducting a final project review , obtaining feedback from stakeholders, and celebrating achievements. Archiving project documentation ensures that information is accessible for future reference or audits. Reflecting on successes and challenges encountered during the project offers opportunities for continuous improvement.
Methodologies Tailored for Healthcare
Agile approach.
Agile project management in healthcare involves iterative development and constant collaboration among team members. This approach allows for flexibility and quick adaptation to changing project requirements. Healthcare organizations benefit from Agile’s ability to deliver value-driven results efficiently. For example , implementing electronic health records (EHR) using Agile has shown significant improvements in patient data accessibility .
Lean Methodology
Lean methodology focuses on reducing waste and improving efficiency in healthcare project management. By applying Lean principles, healthcare projects can streamline processes, enhance quality, and optimize resource utilization. In real-world scenarios , hospitals have successfully used Lean techniques to minimize patient wait times and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Waterfall Model
The Waterfall model follows a sequential approach where each phase must be completed before moving on to the next. In healthcare projects , this model is suitable for well-defined, stable requirements without much expected change. One advantage of the Waterfall model is its clear structure, ensuring each stage is thoroughly completed before progressing. However, limitations arise when changes are needed mid-project, making it challenging to backtrack without affecting timelines.
Unique Challenges Faced
Rising costs.
Healthcare projects often grapple with escalating costs , posing a significant challenge to project managers. The increasing expenses can impact the overall budget and timeline of the project. To address this issue, effective cost management strategies are crucial. Project managers must closely monitor expenses, identify cost-saving opportunities, and prioritize resource allocation efficiently. Cost control measures such as budget tracking, financial forecasting, and vendor negotiations play a vital role in managing rising costs in healthcare projects.
Heavy Regulation
The heavy regulation surrounding healthcare projects adds another layer of complexity to project management. Compliance with stringent healthcare regulations is imperative but can be daunting for project teams. Navigating through regulatory requirements demands meticulous planning and adherence to legal frameworks. Establishing robust regulatory frameworks within project management processes is essential to ensure compliance and mitigate risks associated with non-compliance.
Litigation Risks
Healthcare projects are susceptible to litigation risks , which can arise from various sources such as medical malpractice, contractual disputes, or regulatory violations. Project managers need to proactively identify potential legal pitfalls and implement strategies to mitigate these risks effectively. By integrating risk management practices into project planning and execution, teams can safeguard against legal challenges and ensure smooth project delivery in healthcare settings.
Diverse Stakeholders
Managing diverse stakeholders in healthcare projects presents a unique set of challenges for project managers. Stakeholders may include healthcare providers, patients, regulatory bodies, insurers, and community members, each with distinct interests and priorities. Effective stakeholder engagement is critical for project success, requiring clear communication channels, active involvement, and tailored approaches to meet stakeholder needs. Building strong relationships with stakeholders fosters collaboration, enhances project outcomes, and promotes stakeholder satisfaction throughout the project lifecycle.
Best Practices for Success
Effective communication.
Effective communication is vital in healthcare project management to ensure all team members are aligned. Clear and concise communication strategies help in avoiding misunderstandings and delays in project timelines. It is crucial to establish a communication plan outlining the frequency and mode of communication.
- Implement regular meetings to provide updates and address any concerns promptly.
- Utilize various communication channels such as emails, project management tools , and face-to-face discussions.
- Encourage an open-door policy for team members to raise issues or seek clarification.
Integrating project management software facilitates seamless communication among team members by centralizing project information. Gantt charts assist in visualizing project timelines, while collaboration platforms enable real-time collaboration on tasks and documents. Leveraging technology enhances efficiency and transparency in project communication.
Budgeting Techniques
In healthcare project management, utilizing various budgeting techniques is essential for financial sustainability. Accurate budget estimation at the onset of a project helps in allocating resources effectively. Continuous monitoring of expenses against the budget ensures that the project stays within financial constraints.
Importance of Budgeting
- Proper budgeting allows for resource allocation based on priority areas.
- Monitoring expenses helps in identifying cost overruns early for timely corrective actions.
- Budgeting plays a crucial role in ensuring the overall financial health of the project.
Stakeholder Relations
Maintaining positive stakeholder relations is key to the success and sustainability of healthcare projects. Engaging stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle fosters trust and support from key decision-makers. Effective communication strategies with stakeholders help in managing expectations and addressing concerns proactively.
Strategies for Engagement
- Regularly update stakeholders on project progress and milestones achieved.
- Seek feedback from stakeholders to incorporate their input into decision-making processes.
- Address stakeholder concerns promptly to maintain their confidence in the project.
Skills for Project Managers
Essential skills.
Project managers in healthcare need a diverse set of project management skills to succeed. Leadership is crucial for guiding teams towards common goals and fostering collaboration. Effective communication ensures clear instructions, updates, and feedback among team members. Problem-solving skills are essential for addressing issues promptly and keeping projects on track. emotional intelligence plays a vital role in understanding team dynamics and managing conflicts within diverse project teams.
Adaptation Strategies
Adapting to changes is key in healthcare project management. Being flexible allows project managers to adjust plans swiftly in response to evolving circumstances. Agility enables them to navigate unexpected challenges with ease, ensuring project continuity and success. For instance, when faced with budget constraints, a successful adaptation strategy could involve reallocating resources or renegotiating contracts to meet project goals.
Risk Management Solutions
Effective risk management is critical in mitigating project risks in healthcare settings. Proactive approaches involve identifying potential risks early on, assessing their impact, and developing mitigation strategies. Integrating risk management into every phase of the project lifecycle enhances preparedness and minimizes disruptions. For example, conducting regular risk assessments and implementing contingency plans can help project managers anticipate and address potential obstacles before they escalate.
Career in Healthcare Project Management
Becoming a manager.
Transitioning from a project team member to a project manager in healthcare involves taking on leadership roles and overseeing projects. As a manager, individuals are responsible for planning, executing, and monitoring healthcare projects. Effective project managers in healthcare need strong communication, organizational, and problem-solving skills .
To excel as a project manager in healthcare, professionals must possess the ability to lead teams , manage budgets , and ensure project timelines are met . The transition from team member to manager offers career growth opportunities such as advancement into senior management roles . However, it also comes with challenges like handling complex projects and balancing various stakeholders’ needs.
Salary Outlook
Healthcare project managers enjoy a favorable salary outlook due to the industry’s demand for skilled professionals. Factors influencing project manager salaries in healthcare include experience level , educational background , and the size of the organization. With the potential for career advancement, project managers can expect competitive compensation packages that reflect their expertise and contributions.
The salary outlook for healthcare project managers is promising, with ample opportunities for growth and development within the field. Competitive compensation packages are offered to attract top talent in healthcare project management. This reflects the industry’s recognition of the critical role that project managers play in ensuring successful project outcomes.
The job growth prospects for healthcare project managers are robust, driven by the increasing demand for skilled professionals who can oversee complex projects within the healthcare sector. As healthcare organizations continue to prioritize efficiency and quality improvement initiatives, there is a growing need for experienced project managers to lead these efforts.
In the dynamic healthcare industry, project managers have access to diverse career opportunities and job stability due to the sector’s continual growth and evolution. The demand for skilled project managers is expected to rise steadily, offering professionals in this field long-term career prospects and stability.
Benefits of Effective Management
Improved outcomes.
Effective management enhances healthcare outcomes by ensuring streamlined processes and optimal resource allocation . It improves patient care through efficient project execution. Successful projects like the implementation of electronic health records have significantly improved patient care quality.
Cost Reductions
Strategies for achieving cost reductions in healthcare projects include efficient budgeting, resource management, and process optimization. Implementing cost-effective solutions leads to significant savings without compromising the quality of care provided. Efficient project management ensures resources are utilized effectively, reducing unnecessary expenses.
Enhanced Stakeholder Relations
Enhancing stakeholder relations is crucial in healthcare projects to ensure successful outcomes. Positive relationships with patients, staff, and external partners foster collaboration and trust. Strong stakeholder relations positively impact project success rates and enhance the organization’s reputation.
Final Remarks
In the dynamic realm of healthcare project management, understanding the intricacies and nuances is paramount. High stakes demand meticulous planning and execution at every stage. Tailored methodologies, coupled with best practices and honed skills, pave the way for success amidst unique challenges. A career in healthcare project management offers a fulfilling path, with benefits extending beyond professional growth.
Embrace the opportunities to excel in this field. Equip yourself with the right tools, knowledge, and mindset to navigate the complexities of healthcare project management. Your journey towards impactful project delivery starts now.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key stages of healthcare project management.
Healthcare project management typically involves stages such as initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closing. Each stage is crucial for ensuring successful project completion within the healthcare industry.
What methodologies are commonly used in healthcare project management?
Popular methodologies tailored for healthcare projects include Lean, Six Sigma, Agile, and Waterfall. These approaches help streamline processes, improve efficiency, and ensure quality outcomes in healthcare project management.
What unique challenges do healthcare project managers face?
Healthcare project managers often encounter challenges like regulatory compliance, stakeholder communication, budget constraints, technology integration, and risk management due to the complex nature of the industry. Overcoming these hurdles requires specialized skills and strategic planning .

Why are effective management practices important in healthcare projects?
Effective management practices in healthcare projects lead to improved patient outcomes , cost savings , streamlined operations, enhanced team collaboration, and overall project success. By implementing best practices and strategies, healthcare organizations can achieve their project goals efficiently.
What skills are essential for a career in healthcare project management?
Critical skills for a successful career in healthcare project management include leadership abilities, communication skills, problem-solving expertise, adaptability to change, organization skills, risk management proficiency, and knowledge of healthcare regulations. Developing these skills is vital for managing complex projects effectively.
Ready to Take Your Projects to the Next Level?
We design, develop, and install custom Microsoft Project and Smartsheet solutions that help our clients maximize the value this tool offers.
We also provide project management consultants to supplement your PMO. The right talent at the right time.
Let’s connect
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
The MoSCoW method for prioritization: A guide for agile teams

In the messy world of technology, there is an immeasurable demand for the resources from product and development teams. This is where prioritization comes into play.

Prioritization is one of the core responsibilities of the product manager. With the proper prioritization framework and/or criteria, the product manager can save their team resources while moving closer to the business goals.
In this article, we will dive deep into one of the most widely used prioritization techniques, the MoSCoW method.
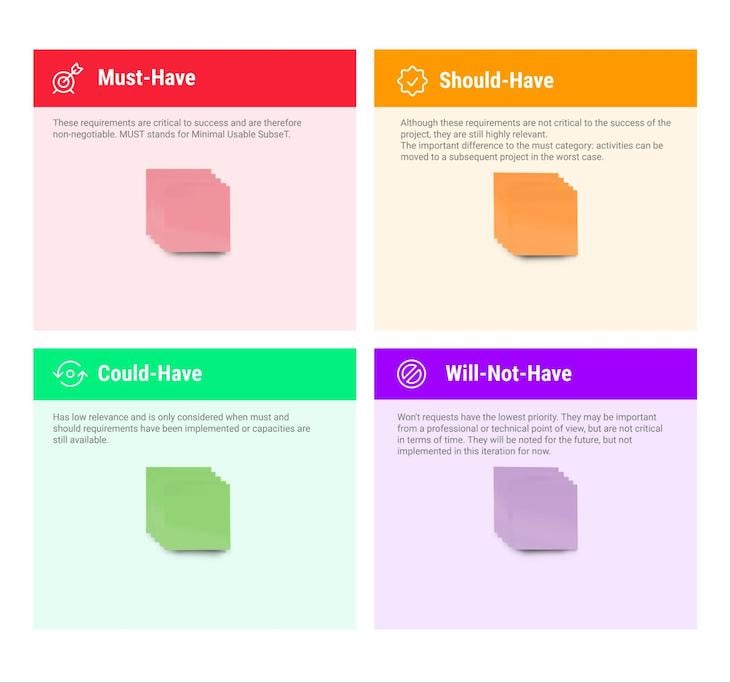
What is the MoSCoW method?
The MoSCoW method (also known as MoSCoW analysis) is one of many qualitative prioritization techniques used to prioritize features, user stories, and requirements.
The MoSCoW method groups the features into four groups:
- Should-have
- Could-have (or nice-to-have)
1. Must-have
Features or stories are critical for the product’s success. These features represent the non-negotiables which, if not implemented successfully, might put the product at risk of failing.
For example, let’s say you are the PM of a university’s e-learning system. A must-have feature might be the assignment submission feature because it serves a primary and essential need for both ideal customer profiles.
2. Should-have
This classification represents the features that are important, but not as crucial as the must-haves. These features, if not implemented, can cause a severe risk to the product’s success, but their risk is lower than the must-haves.
Typically, product teams use this classification for minor bug fixes and/or performance improvement initiatives.
Returning to our example, a should-have feature for our e-learning system might be an integrated plagiarism tool for teachers to use. This can be a should-have because it would not stop the teachers from doing their work, but not implementing it might lead them to churn and move to other platforms that save them time.
3. Could-have (or nice-to-have)
This classification represents desirable features that are not important to the core function of the product. Not implementing this feature will not cause any risk or failure.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Could-have features might help your product or do nothing at all. Features that are tagged with the could-have classification end up deprioritized and treated as a sprint filler.
For our e-learning, one feature could be the ability for the teachers to message other students through the platform. This is nice-to-have because this problem is typically dealt with through email and other platforms.
4. Won’t-have
This classification represents features that are not aligned with the vision and the strategy of the product. These are the features requested by other departments or stakeholders, but are entirely irrelevant.
If we were to reflect this in our e-learning example, this might be a feature that enables teachers to develop a curriculum collaboratively on the platform. This feature is a won’t-have because it doesn’t align with the vision of the product because the product is intended to mainly serve the students.
MoSCoW prioritization template
The MoSCoW prioritization method can be used to prioritize both the product backlog and the sprint backlog . This tells engineers what they need to deliver first and gives them an idea of what task could potentially spill over into the next sprint.
Below is a simple template that can get you up and running with the MoSCoW prioritization technique:
History of the MoSCoW method
The MoSCoW method was introduced first in 1994 by Dai Clegg , a British business consultant and software engineer.
Clegg was working on a software project with the British government and was looking for a method to prioritize the system requirements based on their urgency and criticality. He came up with the MoSCoW method to rank and prioritize the features and ensure the right investments were put into the top features.
How to use the MoSCoW prioritization method (5 steps)
Using the MoSCoW in the real world is more than tagging features with four different tags. It requires additional steps to ensure the proper prioritization is put into place and that features align with your stakeholders.
To apply the MoSCoW prioritization method in product management, take the following steps:
1. Groom your features
It is always a best practice to start by listing your features in your product backlog. Add some details to them like the basic idea of the feature, some simple user flows, and wireframes, and meet with your engineers/technical navigators, or system analysts to check on the technical feasibility and the edge cases.
More great articles from LogRocket:
- How to implement issue management to improve your product
- 8 ways to reduce cycle time and build a better product
- What is a PERT chart and how to make one
- Discover how to use behavioral analytics to create a great product experience
- Explore six tried and true product management frameworks you should know
- Advisory boards aren’t just for executives. Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
2. Prioritize initially
After you have all of your features groomed, start prioritizing them. Classify them into must-have, should-have, could-have, and won’t-have. Prioritize based on the available resources and insights gathered from any user research and product analytics.
3. Align with your stakeholders
Present your initial priority to your stakeholders. Gather their input and try to persuade them of your priority based on the insights and the data you have.
Don’t leave the meeting without alignment on the priority of each feature. The outcome of the meeting should be a prioritized list agreed on by each and every stakeholder.
4. Adjust your roadmap and announce
After finalizing the backlog, make sure to give it a final review and announce it publicly using your internal roadmap and any communication channel that includes all the stakeholders.
5. Communicate continuously
We are in the agile era . That means we should embrace change and understand that changes happen all the time.
A feature that is a could-have in this quarter might be a must-have in the next one. So make sure to communicate changes in the business and feature priorities continuously with your stakeholders.
Ensure all the related documents, like the roadmap and the backlog , are updated accordingly and on a timely basis to avoid any miscommunication and to make sure that everyone is aligned on the timeline and the priorities.
Final thoughts
The MoSCoW method is one of the most powerful and widely used prioritization techniques worldwide. It helps classify features and initiatives into four groups.
For the MoSCoW method to be applied effectively and deliver the intended value, it should include a lot of stakeholder alignment and involvement. The product manager should dedicate more time to the must-have features to come up with a killer solution that helps solve the major problem for the users.
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #prioritization

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

A guide to asynchronous communication
Asynchronous communication is a style of communication where participants don’t need to be simultaneously present.

Leader Spotlight: Prioritization strategies in veterinary software, with Ian Evans
Ian Evans talks about building a SaaS org from the ground up and how prioritization is one of the hardest components to address.

An overview of feature parity
Feature parity occurs when the features between two versions of a product remain balanced so that the customer experience isn’t impacted.

Leader Spotlight: Solving for everyday moments, with Shira Gershoni
Shira Gershoni talks about how her team thinks about real-life moments or frustrations that impact the customer’s overall experience.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Health&Social Care(New Spec)-Meeting Individual Needs-Unit 5- (P8&M6)-Lesson & Activities
Subject: Personal, social and health education
Age range: 16+
Resource type: Other
Last updated
3 April 2020
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 81%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
Health&Social Care BTEC: Unit 5 Meeting Individual Needs-WHOLE UNIT BUNDLE
Level 3 BTEC Within this bundle you find resources for all the assessment criteria from P1-P8 along with the merit and distinction tasks. Each task contains a variety of worksheets and power point presentations including: help sheets/lessons/activities/case studies/information/missing words etc. All of these resources have been created to help students prepare their own independent coursework assessments. My own students have thoroughly enjoyed this unit of work as it has allowed them to share their own experiences as well as learn something new for their own studies in health and social care. Enjoy!
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
BTEC National Health and Social Care Student Book 1: For the 2016 specifications (BTEC Nationals Health and Social Care 2016) page: 284 There are times when confidentiality has to be broken in order to safeguard a service user or others, for example if the individual has disclosed serious abuse which could lead to them being harmed or killed ...
A short summary of confidentiality and how to build these into your coursework.this video covers part 2 of section D
The Health and Social Care Information Centre is another name for NHS Digital. The Health and Social Care Act of 2012 established NHS Digital, which is a harbor for health and treatment records which is a unique legal obligation. Data and reports on those who use health and care facilities are collected by them.
This is my coursework for unit 5 - meeting care and support needs for individuals. This is section C and D and therefore covers the learning aims C and D unit ... Unit 7P6 - Health and social care, Unit 7 P 6, pass task; Related Studylists ... touching another person can send messages, for example care and affection or power and control.
UNIT 5 2 Meeting Individual Care and Support Needs Getting to know your unit To be able to provide the care and support that meets the needs of an individual in a health and social care environment, it is important that you understand the principles and practicalities that are the foundation of all the care disciplines. This unit introduces you ...
BTEC Level 3 National Health and Social Care: Student Book 1 N. Moonie, C. Aldworth. BTEC Level 3 National Health and Social Care: Student Book 2 M. Billingham, H. Talman. BTEC National Level 3 Health and Social Care E. Rasheed, A. Hetherington. Human Anatomy & Physiology E.N. Marieb, K.N. Hoehn. Level 3 Health & Social Care Diploma C. Morris ...
Compassion in Practice is the national strategy for nurses, midwives and care staff. It was launched in December 2012, following nationwide concern about the standard of nursing care after the failings at the Mid Staffordshire Hospital and Winterbourne View, a hospital for people with learning disabilities and autism.
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place. Bundle. Btec Level 3 Health and social Unit 5 & Unit 11 Coursework. I have received a distinction for unit 5. My assignments are top quality. P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 P8 M1 M2 M3 M4 M5 M6 D1 D2 D3 D4 I have received a distinction ...
Health&Social Care(New Spec)-Meeting Individual Needs-Unit 5- (P8&M6)-Lesson & Activities Health&Social Care (New Spec)Unit 5- (P4&P5)Meeting Individual Needs-Lessons & Help Sheet ... Health & Social Care Unit 5 Meeting Individual Needs Lesson Power Point on P1 M1 D1. ... All of these resources have been created to help students prepare their ...
Unit 5. Assignment 1. Learning Aim A. 5/A.P1 Explain the importance of promoting equality and diversity for individuals with different needs. 5/A.M1 Analyse the impact of preventing discrimination for individuals with different needs. 5/A.P2 Explain the skills and personal attributes necessary for professionals who care for individuals with ...
Empathy- the ability to share and understand the emotions of others, such as sadness, anxiety or happiness. Patience- the capacity to accept or tolerate problems without becoming annoyed or anxious. Engendering trust- the ability to get people to trust you.
Carers are given all of the information about treatment and care plans, for example the manager of the sheltered housing project should be informed of how the community centre are working with Aisha. 6. Support of the carer, in this case the manager, must be available. ... task 3 unit 14 coursework health and social care; Level 3-HSC-Unit-1 ...
A short summary of multi agency & multidisciplinary teams and how to build these into your coursework.this video covers part 1 of section D
BTEC Level 3 Health and Social Care Unit 5 Meeting Individual Care and Support Needs Learning Aim D Investigate the roles of professionals and how they work together to provide the care and support necessary to meet individual needs. This 8-page (11 task) learning guide is perfect for home learning, classwork, and revision as it covers all Unit 5: Learning Aim D topics, creating a detailed and ...
This coursework covers P6 P7 M5 and D4 in full detail, referring to multi agency working, policies, legislations, frameworks and health promotion. It also explains the roles and responsibilities for staff members and the benefits and drawbacks of multi agency working.
In healthcare project management, several key stages are essential for ensuring project success. These stages typically include initiation, planning, execution, monitoring & control, and closure. Each stage plays a critical role in guiding the project from conception to completion by providing a structured framework for managing resources ...
Won't Have need to be agreed with the business. Some examples are described above. However, the Must Have definition is not negotiable. Any requirement defined as a Must Have will have a critical impact on the success of the project. The Project Manager or Business Analyst should challenge requirements if they are not obvious Must Haves; it is up
Coursework kate vickery unit p1 meeting individual care and support needs promoting equality and diversity for individuals with different needs is central to ... knowing right from wrong, principals and how we behave. Staf in a health and social care seing, for example a hospital, need to be empatheic to their service users in order to show ...
The MoSCoW method is one of the most powerful and widely used prioritization techniques worldwide. It helps classify features and initiatives into four groups. For the MoSCoW method to be applied effectively and deliver the intended value, it should include a lot of stakeholder alignment and involvement. The product manager should dedicate more ...
The resources are for Level 3 BTEC Health and Social Care students. The resources cover the material for P6/M5 which relates to "Multi-Agency Working". The lesson and booklet provides students with a framework which sets them up so that they can independently start their coursework assignment.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the onion-domed churches in moscow are most clearly examples of that city's cultural what?, what current religion does not require its followers to identify with only one religion?, what effect did europe have on african religion? and more.
The resources are aimed at level 3 BTEC Health and Social Care students. The presentation contains activities and information on how to complete the P8 & M6 assessment criteria which relates to managing and sharing data between professionals within a health and social care setting.