

The PhD student experience – What is it really like for PhDs?
Are you curious about what it’s really like to be a PhD student, navigating the world of academia and research?
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the lesser-known aspects of the PhD journey, from the profound impact of your supervisor to the competitive environment you’ll face.
Discover the truth about the importance of publishing papers and the realities of funding and job security in academia.
We’ll also give you a glimpse into the daily life of a PhD student, and explore the highs and lows of this challenging yet rewarding experience.
So, buckle up and join us as we uncover the secrets of the PhD student experience that no one else will tell you!
The little known-facts that you need to know about the PhD experience,
This is what no one else will tell you!
What does the daily life of a PhD student look like?
Embarking on a PhD journey can be a thrilling yet demanding experience, as a doctoral student is constantly immersed in:
- academic responsibilities,
- and professional development.
From the early morning, the life of a PhD student begins with checking emails, planning the day, and setting priorities.
A typical day usually involves conducting experiments or research in the laboratory, analyzing data, and reading scientific literature to stay up-to-date with their field.
PhD students often participate in regular meetings with their supervisors, who provide guidance and advice on their research projects.
These meetings are crucial for maintaining momentum and ensuring a productive working relationship.
A typical daily schedule for a PhD student might look like this:
7:00 AM – Wake up, morning routine, breakfast
7:45 AM – Check emails, plan the day, and set priorities
8:30 AM – Arrive at the laboratory, set up experiments or research tasks
9:30 AM – Attend a class or seminar (if applicable)
11:00 AM – Conduct experiments or research in the laboratory
12:30 PM – Lunch break, socialize with fellow graduate students
1:30 PM – Analyze data and read scientific literature relevant to the research project
3:00 PM – Meeting with supervisor to discuss research progress and receive guidance
4:30 PM – Continue working on experiments, data analysis, or literature review
6:00 PM – Dinner break
8:00 PM – Draft or edit thesis, work on conference presentations or publications
10:00 PM – Wind down and engage in a hobby or leisure activity for mental health and work-life balance
11:00 PM – Bedtime routine, sleep
In addition to their primary research, many PhD students assist and mentor undergraduate students, contributing to a diverse and dynamic academic community.
Balancing the demands of coursework, research projects, and administrative responsibilities can make for long working hours, which is why it’s important for doctoral students to maintain their mental health and work-life balance.
Attending conferences, participating in social events, and engaging in professional development opportunities are important aspects of the PhD experience.
Given the commitment and dedication required, full-time PhD students often rely on funded positions to support their education and living expenses.
Despite the inherent difficulties, the experience equips students with a range of new skills and expertise, setting them on a path to contribute significantly to academia and the world beyond.
How stressful is being a PhD student?
Being a PhD student can be quite stressful due to the unique challenges and demands of the program.
It varies from person to person and the supervisor will have a huge impact on how stressful a PhD will be for a student.
Here is a case study of the highs and lows of a PhD from a PhDs student’s perspective:
This PhD student experienced frustration with experiments not working or yielding results, leading to feelings of imposter syndrome and demotivation. A lack of progress was a significant source of stress during this time, as well as comparing oneself to peers who seemed to be achieving more success.
However, there were also numerous highlights throughout the PhD experience. Attending conferences and presenting research offered opportunities to gain feedback, collaborate with others, and even travel. Engaging in scientific discussions and exploring the significance of one’s work provided a sense of purpose and satisfaction.
Furthermore, working with cutting-edge equipment, such as advanced microscopes, allowed the student to appreciate the unique and privileged nature of their research.
The pressure to produce significant contributions to one’s field and the uncertainty of achieving results within a limited time frame can induce anxiety.
For instance, many students find themselves constantly juggling various responsibilities, such as conducting experiments, analysing data, attending meetings with their supervisor, and writing their thesis or papers.
Aside from academic pressure, managing work-life balance can be difficult as well. It’s not uncommon for PhD students to work long hours, often sacrificing personal time and relationships.
The lack of a structured schedule and the need for self-motivation can add to the stress and the competitive environment in academia and the constant pursuit of funding can further exacerbate stress levels.
PhD student workloads and holidays
The life of a PhD student is often characterized by heavy workloads and limited opportunities for holidays.
In a typical PhD program, students juggle numerous responsibilities, including research projects, coursework, and professional development activities, such as attending conferences and training.
This is particularly true for funded PhD students, who are expected to adhere to strict timelines set by their supervisors and the university’s academic calendar.
In the science field, the workload can be even more demanding due to the nature of research, which often involves conducting experiments that can take months or years to complete.
This commitment means that even during holidays, PhD students may feel the need to work in order to meet deadlines, leading to burnout and stress.
Later Stage PhD ( Doctorate Candidates )
When PhD students reach the later stages of their doctorate program, they become PhDs preparing to complete their research project and thesis.
This stage comes with an intense academic workload, with high demand for researcher-level skills and scientific knowledge.
A typical day for a PhD at this stage involves conducting research, analysing data, and editing their findings to complete their thesis.
In my experience it is WRITING, WRITING and more WRITING…with a touch of editing.
There are deadlines to meet, and students may face pressure, but the reward of completing a doctorate degree is worth it.
At this point, a PhD is expected to demonstrate their ability to conduct independent research and contribute to their field of study.
The latter stages of the doctorate program offer a rigorous and rewarding challenge for students who want to pursue a career in science, education, and research.
Wrapping up – PhD and Doctoral Student experience
The PhD student experience is a complex and multifaceted journey that offers a unique blend of challenges and triumphs.
As we have explored in this blog, the road to obtaining a PhD is filled with personal growth, professional development, and numerous hurdles to overcome.
But, for those who persevere, the rewards can be immense, leading to a sense of accomplishment, increased expertise, and the potential to make a significant impact in their chosen field.
In navigating this adventure, it is essential for PhD students to maintain a healthy work-life balance and develop strong support networks to help them manage stress and maintain motivation.
The journey may be demanding, but with the right mindset and guidance, the experience can be truly transformative.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


PhD Admission Guide
Gain admission to your dream school, guide to phd admission.
While some students swear off further education after undergrad, some love the thrill of intellectual discovery and research. For these students, graduate school is a natural choice. Graduate degrees are separated into “professional” and “academic” categories. Professional degrees are JDs and MDs, while academic degrees are PhDs (literally “Doctorates of Philosophy” regardless of what field you actually study).
Whether or not you need to pursue a PhD depends entirely on what career you wish to have. Some require higher education, while many others do not. In this guide we’ll go over how to apply to PhD programs, what they are looking for, and how the application process works. This guide is focused on the US and Canada; Europe has a system which is simultaneously similar and very different.
What PhD Programs Look For

PhD programs want to make sure you are prepared academically for the rigors of the program, and that you have a concrete research goal in mind. PhD programs culminate with each student answering a research question they devise, contributing new knowledge to the world in the process.
Thus these programs seek to evaluate your intellectual ability, research goals, previous research experience, and how you will contribute to their program. To determine this, they ask for the following:
Letters of Recommendation
We’ll go through each of these in turn, and explain what graduate programs are looking for from each.
Your GPA in undergrad is the single most important factor in PhD admissions. If your GPA is too low your application will be dismissed out of hand. While there are no hard limits, we suggest a minimum GPA of 3.5 for serious contention, especially at top schools. If your GPA is below 3.0 then you will likely not get admitted into any PhD programs.
The reason for this is that PhD programs are a lot of work. Being intelligent is necessary, but is far from sufficient alone. Everyone in PhD programs is intelligent, and everyone is also willing to do the work. Your GPA is seen as the primary indicator of your willingness and ability to do academic work to a high standard, and your preparation for the rigors of a PhD program.
Along with your overall GPA, schools request your major GPA. This is your GPA when calculated only using courses in your major. This is usually expected to be higher than your overall GPA. Your major GPA should be over 3.5.
While taking harder courses in undergrad is a great experience, they can also harm your overall GPA. Of course, the best approach is to take very hard classes and do well in them, but this is not always possible. We recommend taking a blend of courses, so you are never overloaded, and able to give each the attention it needs to do well.
Academic Preparation
Your GPA and transcript is also used to judge your academic preparation for the program. You should have a solid grounding in the field, and have taken advanced courses as well. Taking graduate level courses in undergrad can exemplify this.
Some PhD programs also require research languages. This is more common in the social sciences and humanities, but all students will benefit from knowing other languages well enough to do research in them. You should look up language requirements when researching programs to apply to.
The Graduate Record Examinations (GRE) is a standardized test meant for students who intend to apply to graduate programs. Both MA and PhD programs ask for GRE scores. Much like the SAT or ACT in college exams, the test is meant to be a standardized measure of academic preparation and logical skill.
The test consists of six sections. The first is writing, next are two on verbal reasoning, then two on quantitative reasoning, and finally a research or experimental section, meant to test new questions. The entire test is offered on the computer, with one minute breaks after each section, and a ten minute break after the third section. While there is also a paper-based test, almost all testing is now done on a computer. Due to the pandemic, both testing centers and at-home testing are offered. The GRE is a multi-stage test, and how well you do on earlier sections determines the difficulty of later sections and questions.
The verbal sections each consist of 20 questions, to be answered over 30 minutes. The whole is scored on a scale of 130-170. The quantitative section is scored the same, and consists of two 20 question sections, each of which should be completed in 35 minutes. The writing section is scored from 0-6. For this section, you write an essay on a given issue in 30 minutes, and offer a response critiquing a provided argument for 30 minutes.
Your total score from the GRE is given from 130-170. While the exact scores you need to enter graduate school vary, higher is better. In addition, some programs only care about your verbal score, while others only care about your quantitative score. How much weight each program puts on GRE scores varies greatly.
We recommend studying for the GRE for some time before testing. You can take the GRE up to five times per year, but must wait at least 21 days between testing dates. Only scores from the past 5 years will be released or considered by graduate programs.
Curriculum Vitae
This is akin to a resume, but is dissimilar enough that the two cannot be used interchangeably. The purpose of a CV is, like a resume, to detail what you have accomplished academically and in your career. It is far more focused on academics however, and is widely used for academic careers.
We recommend finding a template for a CV online, or asking your college’s advisors for help in creating one. If you already have a resume, then you will easily be able to convert it into a CV.
What admissions officers are looking for in your activities is primarily signs of research. This should be in whatever field you intend to pursue a PhD in. Publications are also incredibly valuable. All of academia runs on publication, and getting an early start helps your career at every step.
You should try to do research while still in undergrad. What this looks like depends entirely on what field you are pursuing. While the research does not have to exactly line up with what you wish to pursue, it should teach you skills which are cross applicable. Higher level academic research has its own set of methods and language which must be learned, and students who are already familiar with the forms and structures of research have a leg up in graduate school.
Publication is not required, but is nice to see. If you have completed a master’s degree, you should have some publication history; of your thesis if nothing else. Speak with your academic advisors about getting your work published.
Each graduate school you apply to will ask for an essay. You will be able to use the same basic form for each, but will need to edit it to be about the particular program you are applying to. Most schools only require a single essay, although some programs ask for a second on diversity.
The purpose of this essay is to explain your research interests, what you have studied, your intended area of specialization, and what your focus will be on. Every PhD student is asking and trying to answer a very specific research question. This question forms the basis of their dissertation, and will be the focus of your life for several years if you are accepted.
Thus the essay is the most important part of your application. Your grades and GRE are required to see if you are academically ready for graduate school, but the essay lets readers know if you are a match for their program, and serious about your research.
Your essay should begin by stating which program you are applying to, and why. Next, go through your previous academic experience in the field, both coursework and research. You don’t have to go through every class, but cover the ones most relevant to your desired research topic.
You should discuss any prior research you have done in the field. If you completed a thesis for your undergraduate degree or a master’s program, cover that here. If you have any publication credits, cover those as well. This should relate directly to the field you are trying to enter. If you wish to pursue lab work, discuss your previous experiences; if instead you are pursuing field work, talk about your experiences there.
Next you should talk about the research you specifically wish to pursue through a PhD. You don’t need to have an exact research question worked out, but it is helpful to have some idea; you should at least know the subfield you will be focusing on. The more specific you are, the better. Having some discussion of methodology can be nice, but is not always necessary.
If there are any ongoing research projects ongoing at the school you wish to work on, cover those next. You should discuss how these projects specifically relate to your own research interests. Finally, you should talk about which professors you wish to work with. Professors take on graduate students to advise, and you ideally want one with a specialization at least tangentially related to your field of interest. The more closely related the professor’s studies are to your own, the better.
You will be able to leave much of this essay the same for each school you apply to, changing only the name of the program, the research projects, and the professors you wish to work with.
This essay should be a page and a half to two pages long, single spaced. You should go into sufficient detail for those reading it to understand the research you want to pursue. These essays are reviewed by the faculty who run the department, and they make the admissions decisions for PhD programs. There are many more applicants than there are spaces, and admissions rates are low. The more specific and detailed you are in this essay, the better the faculty will understand your research aims, and the better your chances will be.
Diversity Statements
Not all programs ask for these, but you will likely be able to reuse the same essay for those that do. The purpose of the diversity statement is to see what unique points of view and experiences you will be able to contribute to the program. PhDs are about learning, and the more viewpoints and ideas within a program, the broader the experience will be.
If you are a member of an underrepresented group, an immigrant, come from an underprivileged background, or come from an area which is generally underrepresented, we suggest discussing that in this essay. You should not write an essay about your interactions with members of these groups, or a study abroad experience.
Above all, this essay should be authentic to you and your experience. The goal is to show how your background has shaped you as a person, and how it impacts your view of the world.
As with college applications, letters of recommendation are required for PhD admissions. These tell admissions committees who you are as a student and researcher, and give their opinion on how you will perform when doing graduate level work. Academic fields are small and often insular, and the professors writing your letters will often be known by those reading them, either by reputation or in person.
Programs ask for two to four letters. These should primarily come from professors who know you and your work well. If you had a thesis advisor, they should write one of your letters. If you’ve worked doing research for some time, then a mentor or lab director can also be a good source of a letter, even if they haven’t taught you in class. Letters should not come from non-academic sources, unless you have worked professionally in that field.
While you have the option to read the letters that are written for you, you should always waive that right. If you don’t trust your writers to craft good letters for you, then you shouldn’t be asking them for letters. Asking to see letters is considered a sign of lack of trust, and is gauche. Many professors will decline to write letters if you insist on seeing them.
You should ask for letters well in advance of when they are due; we recommend at least a month or two. If you are asking non-tenured faculty for a letter, more leeway is recommended, as they have more on their plate, and are often more stressed. You may need to send a reminder as deadlines approach. You should also share a copy of your essay with letter writers, so they know exactly what subfield you intend to pursue, and can discuss this in their letters.
Finally, you should be aware of politics when asking for letters. Some professors do not like each other at all. If you are seen as the protege of a professor who others detest, this can impact your admissions chances. Always discuss which schools and programs you are applying to with your letter writers. You should also discuss your choices of writers with an advisor (for example a thesis advisor) familiar with the field. Academic politics are incredibly petty, but if you plan to pursue a PhD you need to be aware of the game, and how it is played.

If your application passes the first review, you will be invited to do an interview. This will be with faculty in the program you are applying to. This is to further get to know you, and to understand your research objectives.
You should be able to clearly explain what you want to research, and how this program will help you do so. The people talking to you will all be familiar with the field, though not necessarily your specific subfield. They are looking for your ability to communicate and explain your view. Be prepared to answer some questions about the specifics of your goals, though it’s ok if you don’t know everything right now.
Interviews are generally in person, though due to the pandemic, virtual interviews have become more common. This is also your chance to ask any questions you have about the program you were unable to find answers to online. You can practice for this interview with an advisor or mentor; many schools have career centers which hold mock grad school interviews as well.
When and How to Apply to Grad School
There is no unified platform for PhD applications. Instead you must apply to each program individually, through the school’s website. This will mean filling out information multiple times, but they fortunately don’t ask for much. Once you have your documents in order, the rest is personal, demographic, and contact information.
You will need to pay to have your GRE scores sent to each school you apply to. Even though this is all electronic, they still charge dearly for it.
Applications are generally due in December or January, with interviews held over the next few months. Applications open in September or October. We recommend getting your applications in before the due date, though most programs don’t use rolling admissions. Each program sets their own deadlines, so you should track when each of your applications is due carefully to make sure nothing gets overlooked.
Paying for Grad School
PhD programs are for the most part fully funded. This means you will not be paying tuition, and will also get funding to live on. This funding is generally contingent on academic standing, and doing work TAing, teaching, or on ongoing research projects (or most commonly, all of the above). Many grad students also work full or part time to support themselves.
While you will not need to take on additional debt to pay for graduate school, you will not be well paid either. While the exact amount graduate students receive varies by school and program, it is generally in the range of $20-30,000 annually. This goes towards food, housing, and supplies.
While you are in a PhD program, you will not have to make payments on any government loans you took out to pay for undergrad, though they will continue to accrue interest. Making payments on them during grad school is difficult, but will greatly cut down on the amount you need to pay back later.
There are also outside scholarships available to help pay for graduate studies. While the amounts offered by these vary, most are small. They can help greatly with paying for the necessities however, and applying to them is usually worth the time investment.
Grad School Admission FAQ
Now we’ll answer some of the most common questions about applying to PhD programs.
Can older students apply?
Yes. Many professionals return to school for a PhD long out of undergrad. We suggest taking some courses at a local university in the field you plan on entering before you do this however. Academic research advances quickly, and this will familiarize you with the latest developments. Further, this will introduce you to professors who can provide you with letters of recommendation.
What are my odds of acceptance?
This depends on both your field and program. Generally, however, it is quite difficult to gain admissions to a PhD program, and admission rates hover around 10%. Only the best students get accepted, and this is even more the case at the top schools and programs.
When should I start thinking about applications?
When you choose your major, you should decide what level you want to reach within that field. Some majors lend themselves to PhDs if you want to work in that field, while others allow employment at various levels.
Where should I apply?
You should find programs with professors who are dedicated to your particular subfield. A prestigious institution which does not focus on your area is far less useful, regardless of how famous its name is. You are looking for someone who will be able to advise you, and help you perform worthwhile research. Further, professors are looking for students studying fields similar to their own when they admit graduate students.
How long are PhD programs?
Generally programs last 4-5 years, though this can vary based on field. The exact structure of the programs also varies a lot based on field and program.

Ivy Scholars is the leading educational consultant in Sugar Land, Texas, providing admissions coaching, test prep, and more to help students enroll at top tier schools.

Get In Touch
Call us now: (281) 215-5148
Houston: 4265 San Felipe St, Suite 1100, Houston, TX 77027
Get Started
Subscribe for updates, © all rights reserved.

- Online Degrees
- Tuition & Financial Aid
- Transferring Credit
- The Franklin Experience
Request Information
We're sorry.
There was an unexpected error with the form (your web browser was unable to retrieve some required data from our servers). This kind of error may occur if you have temporarily lost your internet connection. If you're able to verify that your internet connection is stable and the error persists, the Franklin University Help Desk is available to assist you at [email protected] , 614.947.6682 (local), or 1.866.435.7006 (toll free).
Just a moment while we process your submission.
Popular Posts

What is a Doctorate: Everything You Need to Know
Do you already have a master's degree and want to continue your education? Maybe you’re still trying to determine what that means and what your next options are?
The pinnacle of educational attainment is the doctoral degree. But what exactly is a doctoral degree, what can you get your doctorate in and what is involved in the process? Consider this your introduction to doctoral degrees.
What Is a Doctorate Degree?
The doctorate is the most advanced academic degree you can earn, symbolizing that you have mastered a specific academic discipline or field of profession. Doctorate degrees require a significant level of research and articulation. Those who earn the degree must have researched a subject or topic thoroughly, conducted new research and analysis, and provided a new interpretation or solution to the field. Completing a doctorate program qualifies you for top-tier consulting and education career considerations and positions you as a leader in your field, giving you the edge to stay relevant in today’s competitive labor market. In many cases, completing a doctorate means achieving a lifelong personal goal.
Demand for Doctoral Degrees
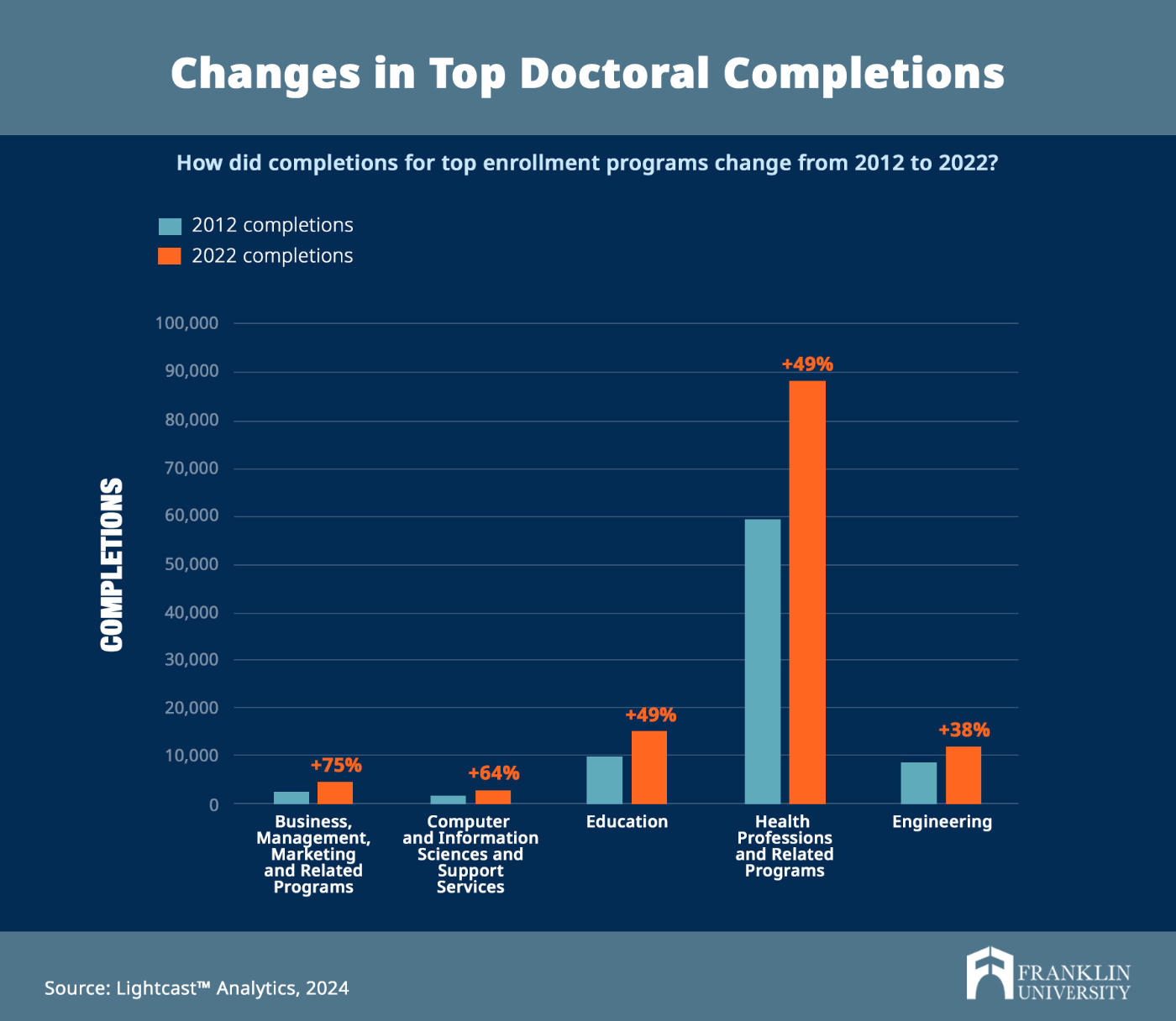
The demand for doctorate degrees depends on specific fields and positions, but trends in degree completions can help paint a picture of the state of doctoral-level education. According to Lightcast Analytics, from 2012 to 2022, the total number of doctoral degree completions grew by 20%, from 170,815 to 205,341. Doctoral categories that saw the greatest growth in demand over the 10-year period included Business , Management, Marketing and Related Programs (+75%), Computer and Information Sciences and Support Services (+64%), Education (+49%), Health Professions and Related Programs (+49%), and Engineering (+38%).
At a more granular level, doctoral programs that saw the greatest growth in demand included Occupational Therapy/Therapist (+1,134%), Nursing Practice (+614%), Organizational Leadership (+368%) and Social Work (+154%). Conversely, programs that saw the greatest decrease in demand included Divinity/Ministry (-42%), History (-26%), Law (-22%) and Psychology (-16%). These trends show that increasingly complex and growing industries tend to require employees with higher levels of expertise, resulting in more demand for doctoral degree holders, while stagnant industries that require less skills development tend to need fewer experts and, thus, fewer employees may feel the need to pursue doctorates.
Earning a doctorate is challenging and rewarding, but do you know what to really expect? Download this free guide for tips and insights to help you prepare for success.
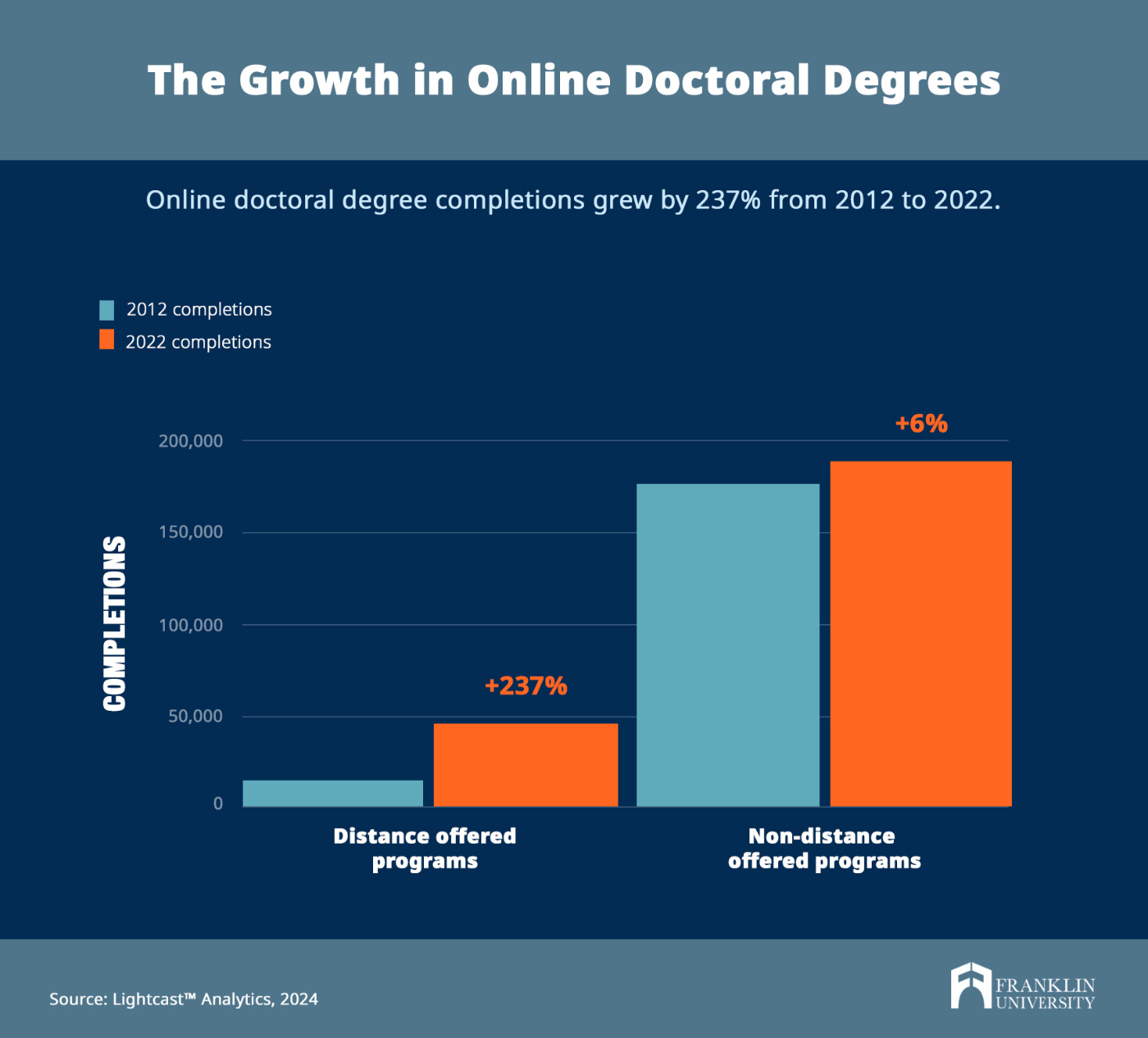
The rise of online doctorate degrees.
Traditionally, higher education institutions only offered doctorates in person, but lately, there has been a shift toward flexible online education. According to Lightcast Analytics, distance-offered doctoral degrees saw a 237% increase in graduates from 2012 to 2022, while non-distance offered programs only grew by 6%.
The increase in online doctoral degrees is evident in the fields examined earlier. Distance offered completions increased by 150% for Law, 986% for Nursing Practice, 427% for Educational Leadership and Administration (General), and 243% for Business Administration and Management (General).
So, what types of doctorates are available?
Two Types of Doctorate Degrees
There are two primary types of doctoral degrees : research-oriented degrees and professional application degrees (also called applied doctorates). The difference between the two types of programs may be murkier than you think. Here's a breakdown of the two common types of doctorate programs.
The Ph.D.: A Research-Oriented Doctorate
These research degrees are commonly referred to as Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.s). Some common research-oriented doctorates include the following:
- Doctor of Arts (D.A.)
- Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
- Doctor of Theology (Th.D.)
- Doctor of Public Health (DPH)
"Philosophy" refers to the concept of research and pursuit of knowledge, as opposed to the actual subject of philosophy. A core component of this type of degree is the dissertation process .
The Professional Doctorate: An Application-Oriented Program
A professional doctorate (also called an applied doctorate or terminal professional doctorate) is a degree that focuses on the application of a subject within real-world contexts or scenarios.
You'll likely want to pursue a professional doctorate if your goals include career advancement, meeting the requirements for specific high-level corporate jobs, establishing teaching credibility within the industry, or building a consulting business.
Some common professional doctorates include:
- Doctor of Business Administration (DBA)
- Doctor of Education (Ed.D.)
- Doctor of Healthcare Administration (DHA)
- Doctor of Professional Studies (DPS)
- Doctor of Finance (DPH)
- Doctor of Social Work (DSW)
- Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.)
- Juris Doctor (JD)
This type of doctorate program may or may not require a dissertation. Unlike the academia-focused research doctorate, the professional doctorate curriculum will encourage you to tackle real-world issues within your field, research, and present a solution.
How a Doctoral Degree Works
The path to a doctoral degree typically comprises four stages of coursework: a core set of research and prep classes, a set of major area emphasis courses, electives and dissertation courses.
The Research Core
In most doctoral programs, you begin the journey to your degree with a common core of classes. The research core establishes the foundational skills you will need to complete the level of work required for the degree. This core often includes advanced writing methods, research methodology and design, applied statistics, colloquium courses, and qualitative and quantitative research and analysis courses.
Major Focus Area
Once the research core is complete, you will typically take courses in your major emphasis of study.
For example,
- If you're earning a DBA ( Doctor of Business Administration ), you will likely take courses in organizational behavior, organizational systems, strategic thinking and decision making, ethics, and change management.
- If you're earning a DHA ( Doctor of Healthcare Administration ), you will likely take courses in healthcare policy and regulations, healthcare economics and finance, quality improvement and process improvement, and health information governance.
- If you're earning a Ph.D. in Human Services, you will likely take courses in advanced study in research methods for public service, social influences of behavior, ethics in decision making, and advanced communication for the human services leader.
In most doctoral programs, you must also take certain electives within your field. Taking electives helps provide a rounded worldview to apply your doctorate in real-world environments.
For example, if you're pursuing a Doctor of Education (Ed.D.), you can access focus areas like Higher Education Leadership , PK-12 Educational Leadership and Organizational Leadership .
Dissertation Requirements
Once you have completed your foundation work, major area of focus, and electives, you'll begin working on your dissertation. That can take different forms, determined by the Ph.D. or applied doctorate.
For Ph.D. students, the dissertation is typically a five-chapter dissertation, which is commonly broken into three phases. In phase 1, you'll submit a prospectus for approval from the dissertation committee. In phase 2, you'll finalize your dissertation's first chapters and begin collecting data. In phase 3, you'll complete the writing of your dissertation and orally defend it to the program leaders.
The dissertation may look different for applied doctorate students, as you will be required to create a solution to a real-world problem.
Investigate Dissertation Structures
Since your dissertation will be a crucial hurdle to defeat, you must know what you're getting yourself into from the beginning. Do some research on dissertation structures when you're looking at prospective schools to help narrow down your list. Ensuring the school will do everything to help you succeed with your dissertation can make all the difference when it comes down to crunch time.
Franklin University has intentionally designed a dissertation structure to help you complete your dissertation step-by-step, beginning with your enrollment in the program . The University also has built-in faculty mentoring, guidance and peer-to-peer support, so you're never left to "figure it out" alone.
For example, throughout your doctoral courses at Franklin, you'll develop essential research skills and the necessary writing prowess to publish a dissertation as a capstone project to your studies. Your dissertation will showcase your ability to identify a topic of interest within the workplace, develop a proposed solution to a problem, and test your hypotheses in the real world.
How Long Will It Take to Earn Your Doctoral Degree?
The answer depends on the path you choose. A doctoral degree program requires anywhere from 60 to 120 semester credit hours (or approximately 20-40 college classes). Most Ph.D.s require 120 hours, while most applied doctorates are closer to the lower end of that spectrum. For example, the DBA and DHA at Franklin require only 58 hours. On average, a Ph.D. may take up to eight years to complete . A doctorate degree typically takes four to six years to complete—however, this timing depends on the program design, the subject area you're studying, and the institution offering the program. Pro Tip: Some innovative institutions like Franklin University have streamlined their doctorate degree programs and offer creative transfer options . The program design, which includes an embedded dissertation and a community of support, also helps students earn their doctorate in as little as three years .
Who is a Good Fit For a Doctoral Program?
Other than holding a relevant master's degree or having professional experience, good doctoral students are organized, curious and have the time management skills to manage many tasks in their lives. Doctorate degrees can increase your current wage, open doors to roles in higher education or fulfill a lifelong desire.
Many doctoral candidates have full-time jobs and families and are active in their community; therefore, it is vital to have a strong motivation and resilience to pursue a doctorate. However, it is worthwhile because the impact of a doctorate on an individual's career and personal growth can be life-changing.
"I went from a successful 27-year career in the electric utility industry to higher education. This change has allowed me to positively affect literally thousands of lives over the past 18 years I have spent as a full-time educator," said Dr. Wendell Seaborne, the Dean of Doctoral Studies & Academic Research at Franklin University.
Franklin University provides applied doctorates with 8-week courses and recorded sessions for asynchronous learning designed for working professionals with personal commitments and a dream to make a change.

Why Choose to Earn a Doctorate Degree?
A doctoral program is a serious commitment with a serious return on investment for master's degree holders.
If you want to teach at a higher education institution, the degree is needed to get in the door. If you’d like to move into industry leadership, the degree can deliver substantial credibility. And, if you're eyeing that top-floor corner office, the degree can be a huge differentiator.
So, which one is right for you—research or applied? Check out these five truths about Applied Doctorates to learn more.

Related Articles

Franklin University 201 S Grant Ave. Columbus , OH 43215
Local: (614) 797-4700 Toll Free: (877) 341-6300 [email protected]
Copyright 2024 Franklin University
Your Guide to a Strong Ph.D. Application
Share this post.

Rarely is there discussion of how to prepare for doctoral programs in professional master’s programs. So when I came across a workshop on preparing Ph.D. applications by Assistant Dean for Graduate Student Development J. Alan Kendrick , I jumped right into it even though it was scheduled to be around midnight in my time zone. (Yes, graduate school remotely from Pakistan is tough and disorienting, but that is a topic for a different blog post.) Here was someone who, in addition earning a Ph.D. himself, has years of experience in selecting Ph.D. applicants, so there could not have been a better opportunity to get introduced to the process! In this piece I’ll touch upon some major points highlighted by Dr. Kendrick to explain what it means to aim for a Ph.D. program and build a solid Ph.D. application.
THe Master's Versus the Ph.D.
Starting off, it is crucial to know the difference between a master’s program and a Ph.D. program. Whereas a master’s degree will generally be more specific than an undergraduate degree and usually span one to three years, a Ph.D. program usually entails a more focused set of question(s) within a discipline and usually spans five or more years. In a Ph.D., the cost of attending is often covered through a combination of fellowships and stipends. Schools are more likely to look for applicants who secured funding from external sources, but this it is not always necessary. So, a good yardstick to measure your readiness and commitment for a Ph.D. program is your willingness and ability to work consistently for years on the academic inquiry you wish to pursue to push the frontiers of existing human knowledge. Scholars in STEM fields such as microbiology or solid-state physics usually spend most of their time in labs, so it is essential to get to know the work environment, culture, and expectations in your prospective labs.
A Strong Application
After getting clarity on what a Ph.D. program demands, let’s get into some major elements of a strong Ph.D. application. Broadly speaking, a Ph.D. application consists of previous academic grades, competitive examination scores, work experiences, letters of recommendation, and a personal statement. For a Ph.D. program, all previous academic grades are weighted and assessed including undergraduate transcripts, while standard examination scores (i.e., the GRE) are now becoming optional at many institutions. And while top-tier grades are a great foundation, they are not decisive as each application is looked at holistically with all its elements to give a better picture. Letters of recommendation from previous academic supervisors are weighted heavily along with your personal statement.
One thing Dr. Kendrick emphasized was to not just get recommendations as mere “character profiles” but rather what he called “ strong recommendations.” Before you ask for faculty recommendations, share your résumé with them, sit down with them over a Zoom call (at least during the pandemic) and share your aspirations and objectives, and then ask for strong recommendations. Additionally, you should waive your right to review recommendation letters in your applications as doing this will indicate that the referee has been candid in your assessment for the admissions committee.
Mastering the Personal Statement
Finally, I come to the part where the ball is really in your court: the personal statement! I say this because while other elements of your application—grades and transcripts, previous work experiences, etc. are no longer alterable—the personal essay is your space to unapologetically express your true self and how you have evolved to be the person you are today. You can explain how your intellectual life has brought you to your specific academic area and where you see yourself going forward. Your statement should make it clear why you are interested in the field, the institution and program you are applying for as well as your research and career goals. Your essay should be tailored to the institution and/or program. Red flag here: if you end up with an essay where you can just replace institution names, then you haven’t met your goal. Additionally, your statement should include details about your background that can help the faculty better understand your motivation for pursuing their program. This can be anything—people, events, challenges, and achievements that have aided your growth and add to your fitness for the program. Additionally, you should address any noticeable discrepancies or gaps in your profile or transcripts that are worth mentioning.
While the personal statement is crucial to your application and speaks on your behalf in a room full of faculty who are judging your application, it is important to understand that there is no standard format or template that you should follow. This space is supposed to be personal, and it is supposed to be yours. It is also equally important to understand that the faculty judging applications are humans like us and often have diverging opinions about different profiles. Also remember that funding and positions for Ph.D.s are often limited and hence a rejected profile does not necessarily make it an incompetent or ineligible one.
In a nutshell, for a strong Ph.D. application, you need academic questions that keep you up at night and the discipline to follow the guidelines Dr. Kendrick shared, so that you can demonstrate your willingness and ability to work under supervision to answer those academic questions. This session with Dr. Kendrick brought me much-needed clarity to tackle my Ph.D. applications, and I hope this post does the same for you!
Editors’ note: You can find additional resources on preparing a strong application on The Graduate School’s website.

Soman ul Haq
Master's candidate, Environmental Management, Nicholas School of the Environment
Soman is a Fulbright Scholar from Pakistan and a first year Master of Environmental Management candidate at the Nicholas School of the Environment concentrating in Energy and Environment. He is currently focused on energy access in developing countries, sustainable development, energy transition, and behavioral changes with energy transition and access. Prior to joining Duke, Soman worked with the German International Development Cooperation (GIZ) as a technical advisor for energy access in off-grid areas and energy transition in industrial sector in Pakistan. As a mechanical engineer, he has experience consulting commercial and industrial sectors in developing energy efficient practices to achieve their sustainability goals. He tweets at @somaanulhaq

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
How the PhD Program Works
Program Overview
Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending your doctoral dissertation.
Admission to candidacy.
You begin by taking courses required for your program of study. All programs requires a preliminary exam, which may be either oral or written.
Some programs may have further requirements, such as an additional exam or research paper. If you enter with a master’s degree or other transfer credit, you may satisfy the formal course requirements more quickly.
Beginning the Wharton PhD Curriculum How the first two years of the Wharton program helped students discover their interests, learn the tools of the profession, and fuel their passion for teaching.
The Doctoral Dissertation
Upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, you are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies.
Your doctoral dissertation should contain original research that meets standards for published scholarship in your field. You are expected to be an expert in the topic you choose to research.
You are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, but you can start thinking about and working on research of relevance at any time.
The dissertation process culminates with a “defense,” in which you defend the proposal orally before your dissertation committee.
While working on your dissertation, you interact extensively with Wharton faculty. Together with interested faculty, you create your own research community that includes your dissertation advisor and dissertation committee.
Policies and Procedures
Get more detailed explanation of course requirements, academic standards, the Teacher Development Program, time limits, and dissertation procedures and requirements.
Sample Program Sequence
Years 1 & 2.
Coursework Examination Research Papers Research Activities Field-Specific Requirements
Directed Reading & Research Admission to Candidacy Formulation of Research Topic
Years 4 & 5
Continued Research Oral Examination Dissertation
Hear From Our Doctoral Community
Wharton is the "perfect" place to do research, phd student creates a new pipeline for women in academia, the diverse skill set you need to become a professor.
- Our Culture
- Open and FAIR Data
- Research projects
- Publications
- Cellular Genomics
- Decoding Biodiversity
- Delivering Sustainable Wheat
- Earlham Biofoundry
- Transformative Genomics
- Scientific Groups Our groups work at the forefront of life science, technology development, and innovation.
- High-Performance Sequencing Dedicated and efficient high-throughput genomics led by experts in sequencing and bioinformatics.
- Single-cell and Spatial Analysis Platforms to support single- or multi-cell analysis, from cell isolation, to library preparation, sequencing and analysis.
- Earlham Biofoundry Providing expertise in synthetic biology approaches and access to laboratory automation
- Tools and resources Explore our software and datasets which enable the bioscience community to do better science.
- Cloud Computing Infrastructure for Data-intensive Bioscience
- Web Hosting for Sites, Tools and Web Services
- Earlham Enterprises Ltd
- Events Calendar Browse through our upcoming and past events.
- About our training High-quality, specialist training and development for the research community.
- Year in industry Supporting undergraduate students to develop skills and experience for future career development.
- Internships and opportunities Opportunities for the next generation of scientists to develop their skills and knowledge in the life sciences.
- Immersive visitors A bespoke, structured training programme, engaging with the faculty, expertise and facilities at the Earlham Institute.
- News Catch up on our latest news and browse the press archive.
- Articles Explore our science and impact around the world through engaging stories.
- Impact Stories Find out how we are contributing to the major challenges of our time.
- Impact Through Policy Advocacy Engaging across the political spectrum to exchange knowledge and inform public policy.
- Public engagement and outreach Communicating our research to inspire and engage learning.
- Communications at EI We work across digital, multimedia, creative design and public relations to communicate our research.
- Our Vision and Mission
- Inclusivity, diversity, equality and accessibility
- Scientific Advisory Board
- Our Management Team
- Operations Division
- Careers overview
- Postgraduate Studies
- Group leaders
- Fellowships
- Life at Earlham Institute
- Living in Norfolk

10 things you need to know before starting a PhD degree
So you want to do a PhD degree, huh? Here we've got everything you need to know about getting started.
So you want to do a PhD degree, huh? Are you sure about that? It’s not going to be an easy decision, so I’ve put together a list of 10 things you need to know before starting a PhD degree. Oh, and don’t panic!
I have recently graduated from the University of Manchester with a PhD in Plant Sciences after four difficult, but enjoyable, years. During those four years, I often felt slightly lost – and there was more than one occasion on which I didn’t even want to imagine writing up my thesis in fear of delving into fits of panic.
On reflection, I realise that – to quote a colleague – commencing my PhD was like “jumping in the deep end with your eyes closed.” If only I’d known to take a deep breath.
1. Are you sure you want to do a PhD degree?
Let’s be under no false impressions, completing a PhD isn’t easy. There will be times when you feel like Wile E Coyote chasing after the Roadrunner – a little bit out of your depth a lot of the time. It’s four years of your life, so make sure it is what you really want to do.
If you want to pursue a career in science, a PhD isn’t always necessary.
It is possible to make great inroads into industry without a doctoral degree. That said, a PhD can also be a very useful qualification with many transferable skills to add to your CV.
By the time you’ll have finished, you can include essentials such as time management, organisational skills, prioritising workloads, attention to detail, writing skills, presenting to an audience – and most importantly – resilience, to name but a few.
2. Choose your project, and supervisor, wisely.
This is very important.
Time after time, our experienced scientists at EI, including Erik Van-Den-Bergh (and I agree) say, “ make sure you’re extremely passionate about exactly that subject. ” When I saw the PhD opening that I eventually was offered, I remember being demonstrably ecstatic about the project before I’d even started it.
I was always interested in calcium signalling and organised a meeting with my potential supervisor immediately, which (to quote Billy Connolly) I leapt into in a mood of gay abandon.
Not only does this help you to keep engaged with your project even through the painstakingly slow times, it also greatly enhances your ability to sell yourself in an interview. If you can show passion and enthusiasm about the project and the science then you’ll be that one step ahead of other candidates – which is all the more important now that many studentships are competitive.
You have to be the best out of many, often exceptional candidates.
However, as important as it is to be passionate about your project, make sure that the person who will be supervising you is worthy.
Does your potential supervisor have a prolific track record of publishing work? What is the community of scientists like in the lab you may be working in? Are there experienced post-doctoral scientists working in the lab? Who will your advisor be? Is your supervisor an expert in the field you are interested in? Is the work you will be doing ground-breaking and novel, or is it quite niche?
There is nothing more frustrating – and I know many PhD degree students with this problem – than having a supervisor who is rarely there to talk to, shows little interest in your work, and cannot help when you are struggling in the third year of your project and some guidance would be much appreciated.
Personally, and I was very lucky to have this, I think it’s incredibly useful to have two supervisors. My PhD degree was split between the University of Manchester and the Marine Biological Association in Plymouth. Between my supervisors, I had two people with expertise in different fields, who could give me some fantastic advice from different perspectives. This also meant that I had two people to check through my thesis chapters and provide useful comments on my drafts.

Make sure you are passionate about your subject before taking it to PhD level. And by passionate I mean really passionate.
For a start, you will most likely have to write a literature review in your first three months, which if done well will form the main bulk of your thesis introduction and will save you a lot of stress and strain when it comes to writing up.
At the end of your first year, you will have to write a continuation report, which is your proof that you deserve to carry on to the end of your three or four years. This doesn’t leave much time for lab work, which means time management is incredibly important. If you think you’ll be able to swan in at 11 and leave at 3, think again.
Fundamentally, never, ever rest on your laurels! As tempting as it may be to slack-off slightly in the second year of your four year PhD, don’t.
4. Be organised.
This is a no-brainer but still, it’s worth a mention. Take an hour on a Monday morning to come up with a list of short-term and long-term goals. You’ll probably have to present your work at regular lab meetings, so it’s always worth knowing what has to be done (lest you look a pillock in front of the lab when there’s nothing to show for your last two weeks.)
It’s always good to have a timeline of what will be done when. If you have a PCR, maybe you can squeeze in another experiment, read a few papers, start writing the introduction to your thesis, or even start collecting the data you already have into figures.
The more good use you make of your time, the easier it’ll be to finish your PhD in the long run. Plus, it’s lovely to sit back and look at actual graphs, rather than worry about having enough to put into a paper. Once you’ve typed up your data, you’ll realise you’ve done far more than you had anticipated and the next step forward will be entirely more apparent.
5. Embrace change – don’t get bogged down in the details.
Felix Shaw – one of our bioinformatics researchers at EI – put it best when he said, “ it felt like I was running into brick walls all the way through [my PhD]… you’d run into a brick wall, surmount it, only to run straight into another. ”
You’ll find that, often, experiments don’t work. What might seem like a great idea could turn out to be as bad as choosing to bat first on a fresh wicket on the first day of the third Ashes test at Edgbaston. (Yeah, we don't know what that means either - Ed).
Resilience is key while completing your PhD. Be open to change and embrace the chance to experiment in different ways. You might even end up with a thesis chapter including all of your failures, which at the very least is something interesting to discuss during your viva voce .
6. Learn how to build, and use, your network.
As a PhD student, you are a complete novice in the world of science and most things in the lab will be – if not new to you – not exquisitely familiar. This matters not, if you take advantage of the people around you.
Firstly, there are lab technicians and research assistants, who have probably been using the technique you are learning for years and years. They are incredibly experienced at a number of techniques and are often very happy to help show you how things are done.
There are postdocs and other PhD students, too. Not only can they help you with day-to-day experiments, they can offer a unique perspective on how something is done and will probably have a handy back-catalogue of fancy new techniques to try.
There are also a bunch of PIs, not limited to your own, who are great to talk to. These people run labs of their own, have different ideas, and might even give you a job once you’ve completed your PhD.
Don’t limit yourself to the labs directly around you, however. There are a massive number of science conferences going on all around the world. Some of them, such as the Society of Biology Conference, take place every year at a similar time in different locations, attracting many of the leaders in their respective fields.
If you are terrified by the prospect of speaking at a full-blown science conference and having your work questioned by genuine skeptics, there are also many student-led conferences which will help you dangle your fresh toes in the murky waters of presenting your work.
One such conference, the Second Student Bioinformatics Symposium, which took place at Earlham Institute in October 2016, was a great place for candidates to share their projects with peers, who are often much more friendly than veteran researchers with 30 year careers to their name when it comes to the questions at the end of your talk.
Another great reason to attend conferences, of course, is the social-side too – make the most of this. You never know who you might meet and connect with over a few drinks once the talks are over and the party commences.
7. Keep your options open.
You should be aware that for every 200 PhD students, only 7 will get a permanent academic post , so it’s incredibly unlikely that you’ll become a Professor – and even if you make PI, it probably won’t be until your mid-forties.
You may also, despite having commenced along the academic path, decide that actually, working in a lab environment isn’t for you. Most PhD graduates, eventually, will not pursue an academic career, but move on to a wide range of other vocations.
It might be that Science Communication is more up your street. This was certainly the case for me – and I made sure that I took part in as many public engagement events as possible while completing my PhD. Most Universities have an active public engagement profile, while organisations such as STEM can provide you with ample opportunities to interact with schools and the general public.
You might also consider entrepreneurship as a route away from academia, which might still allow you to use your expert scientific knowledge. There are a variety of competitions and workshops available to those with a business mind, a strong example being Biotechnology YES.
I, for example, took part in the Thought for Food Challenge, through which I have been able to attend events around the world and meet a vast array of like-minded individuals. Many of the participants from the challenge have gone on to set up successful businesses and have even found jobs as a result of the competition.

8. Balance.
Remember that you still have a life outside of your PhD degree – and that this can be one of the greatest opportunities to make amazing friends from around the world.
A science institute is usually home to the brightest students from a variety of countries and can provide a chance to experience a delightful range of different people and cultures. Don’t just stick to the people in your lab, go to events for postgraduate students and meet people from all over campus.
There are usually academic happy hours happening on Fridays after work where you can buy cheap beer, or some lucky institutions even have their own bar. At Norwich Research Park, we not only have the Rec Centre, along with bar, swimming pool, calcetto, samba classes, archery, and a range of other activities, but there are also biweekly “Postdoc pub clubs” which are very fun to join on a Tuesday evening.
Maintain your hobbies and keep up with friends outside of your PhD and you’ll probably find it’s not that gruelling a process after all.
Plus, the people you meet and become friends with might be able to help you out – or at least be able to offer a sympathetic shoulder.

9. Practical advice.
If, after reading all of this, you’re still going to march forth and claim your doctorhood, then this section should be rather useful.
Firstly, make sure your data is backed up. It’s amazing how many people don’t do this and you’d be bonkers not to. Keep your work saved on a shared drive, so that if your computer decides to spontaneously combust upon pressing the return key, you won’t have lost all of your precious work – or have to go through every one of your lab books and type it all up again.
Secondly, don’t leave your bag in the pub with your half-written thesis in it. I did this, the bag was fine, I was in a state of terror for at least half an hour before the kind person at Weatherspoons located said bag.
Thirdly, read. Read broadly, read anything and everything that’s closely related to your project – or completely unrelated. It’s sometimes amazing where you might find a stroke of inspiration, a new technique you hadn’t thought of … or even in idea of where you might like to go next.
Finally, ask questions – all of the time. No matter how stupid it might sound in your head, everyone’s probably been asked it before, and if you don’t ask, you don’t get.
You’ll probably look far less stupid if you just ask the person standing next to you how the gradient PCR function works on your thermal cycler rather than standing there randomly prodding buttons and looking flustered, anyway.
10. Savour the positives.
At the end of all of this, it has to be said that doing a PhD is absolutely brilliant. There’s no other time in your life that you’ll be this free to pursue your very own project and work almost completely independently. By the time you come to the end of your PhD, you will be the leading expert in the world on something. A real expert! Until the next PhD student comes along …
Related reading.

A PhD, is it worth it? Just ask our students

The realities of doing a PhD

My advice for PhD students? See what bites

COVID and my PhD: to lockdown and back

How does a PhD work and how to find the right one

Building the confidence to take on a PhD
PhD life, 10 things we learned in our first six months

What’s the third year of a PhD like? Tips for navigating your PhD

PhD by experience
- Scientific Groups
- High-Performance Sequencing
- Single-cell and Spatial Analysis
- Tools and resources
- Events Calendar
- About our training
- Year in industry
- Internships and opportunities
- Immersive visitors
- Impact Stories
- Impact Through Policy Advocacy
- Public engagement and outreach
- Communications at EI
LET US HELP
Welcome to Capella
Select your program and we'll help guide you through important information as you prepare for the application process.
FIND YOUR PROGRAM
Connect with us
A team of dedicated enrollment counselors is standing by, ready to answer your questions and help you get started.

- Capella University Blog
- PhD/Doctorate
What are the steps in getting a PhD?
August 22, 2023
Reading Time: 2â3 minutes
The work required to complete a PhD varies across academic disciplines and universities, though earning a PhD typically requires the following elements :
- Completing coursework
- Completing one or more doctoral residency experiences
- Passing a comprehensive assessment or exam
- Developing and completing an independent research project
- Seeking approval of your completed dissertation manuscript
Hereâs a closer look at each step.
With this primary step in the PhD process, you will participate in courses related to your field of study. The goal here is to develop deep subject-matter expertise.
Youâll also become familiar with the key topics, theories, methodologies and concerns related to your discipline. The skills and foundational knowledge you gain in your coursework will serve as the basis for generating potential research topics, such as those you will use in your dissertation.
Often offered virtually, residencies provide structure, training and detailed feedback to guide you as you develop your research plan and gather essential elements for your dissertation. Residences give you a chance to focus on specific study and activities related to preparing your dissertation.
You will connect with faculty and peers during this rigorous academic experience. They can help you focus your research plan by giving feedback and discussing relevant topics.
Your residency is where you can make significant progress on your dissertation, including selecting an acceptable topic and developing a robust proposal for the project.
Learn more about doctoral virtual residency .
Capella offers both PhD and professional doctorate programs. Hereâs how theyâre different .
Comprehensive assessment
The comprehensive assessment is where you demonstrate what youâve learned and present your knowledge of the academic competencies required for your discipline. This examination may be oral, written or both.
Upon successfully completing this step in your doctoral journey, you should be prepared to begin work on your dissertation.
Learn more about the comprehensive exam .
Dissertation
A dissertation is a written compilation of your academic research and provides a detailed description of your project (typically a five-chapter document).
Most dissertations address a question or problem that has not been fully addressed within your field. Before you begin your independent research, other faculty experts representing your dissertation committee and the Institutional Review Board will assess the rigor and ethical underpinnings of your project.
Learn more about the dissertation .
Once the research and writing are complete, the dissertation must be approved by a faculty committee and the school dean.
There is a final defense involved in which you will answer questions about your research, analysis and conclusions.
In many fields, there are also specific professional standards expected of learners. For example, a PhD learner in a Counselor Education and Supervision program will be expected to meet the guidelines of the American Counseling Association.
Once all approvals have been received and youâve successfully defended, youâll publish your dissertation. Youâll have then completed all your program requirements and be conferred your PhD.
Capella University offers PhD and professional doctoral degree programs in a number of different fields:
- Health Sciences
- Information Technology
- Social Work
- Counseling & Therapy
Learn more about Capellaâs online doctoral programs
You may also like

Can I transfer credits into a doctoral program?
January 8, 2020

What are the steps in writing a dissertation?
December 11, 2019

The difference between a dissertation and doctoral capstone
November 25, 2019
Start learning today
Get started on your journey now by connecting with an enrollment counselor. See how Capella may be a good fit for you, and start the application process.
Please Exit Private Browsing Mode
Your internet browser is in private browsing mode. Please turn off private browsing mode if you wish to use this site.
Are you sure you want to cancel?

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
Wharton Stories
What to expect from a phd schedule.
Take a look at a current student’s schedule and get the insider perspective from doctoral students and coordinators on what to expect from a PhD schedule.
The life of a PhD candidate can be stressful as you adjust to a rigorous academic and research schedule. Penn and Wharton offer a variety of resources to help support you in the transition to PhD life.
Wharton’s sense of community offers a level of comfort when reaching out to faculty as well as fellow students to help solve problems. Doctoral students and coordinators give the insider view on what to expect from a PhD schedule.
Class and Research First
The first two years of a PhD program are mainly made up of classes and the beginning stages of research. Deborah Small , the doctoral coordinator for the Marketing program , said, “It starts with heavy duty coursework and a lot of specific requirements. At the end of your first year, there are qualifying exams on all the core marketing courses. Second year they still have a lot of coursework to do, but more of that is elective with a focus more on their interests. During those years they’re expected to get started on research.”
In addition to taking classes and getting started with research, the Marketing program requires students to write two papers. The first research paper is due at the end of the second year, the other is due at the end of the third year.
The Real Estate and Business Economics and Public Policy programs run like the Marketing program. Fernando Ferreira , coordinator for the programs, said, “During the first year they complete six core courses. In the second year, the focus shifts to field courses and to independent research. They have two professors advising them in that year.”
After completing the main courses, students shift to conducting independent research. For REAL and BEPP students this means writing three dissertation chapters during the third and fourth years.
Time for Conferences and Seminars
Because coursework is usually completed by the second half of the program, there’s time for students to attend lectures and seminars. Andrea Contigiani , a fifth year student in the Management program, said, “In my fourth year, I usually attended a seminar around lunchtime. Wharton has an incredible seminar series throughout the year, with a good seminar happening almost everyday. Occasionally, I attended other events, like MBA events or speaker series. I then go back to research for most of the afternoon.”
Prof. Small said, “Students are expected to actively participate in seminars and activities. They’re also encouraged to go to academic conferences and try to present their work at those conferences. It is similar to the expectations of being a faculty member, minus teaching.”
Classes take up the majority of the first two years of the programs. When the focus then switches to research, you’re expected to work independently. Sometimes that can be intimidating. You become your own boss, which is an adjustment from being told what to do and when to do it.
So how do you manage it? Get advice from students and coordinators.
Posted: August 4, 2017
- Work/Life Balance
Doctoral Programs
Matthew caulfield.
Hometown Ocean City, New Jersey
Concentration Management and Legal Studies & Business Ethics
Doctoral Stage Second Year
Typical Day at a Glance
8:30 am Wake up and get ready for the day
9:15 am Get to PhD Offices, respond to emails, check philosophy blogs and read news
10:30 am Journal article readings
11:30 am Meet with advisor
12:00 pm Attend departmental seminar speaker and lunch
1:30 pm Attend Wharton Social Impact Doctoral Community meeting
3:00 pm Attend business ethics seminar
5:00 pm Read for class
7:00 pm Meet with nonparametric statistics study group
8:00 pm Complete homework
12:00 am Go home
1:00 am Bedtime
What is your favorite part about Wharton?
First, the faculty are excellent. They are often leading experts in their fields, and they can offer advice that would be hard to find elsewhere.
Second, the other PhD students are just as passionate about research as you would hope. A huge part of my scholarly development has been due to the discussions I have had with other graduate students.
Third, the Wharton name can offer you serious advantages. In the course of research, I think industry practitioners as well as other academics have been more willing to talk or correspond with me because I am a graduate student at Wharton.
Related Content

Prof. Arthur van Benthem Talks About the Intersection of Corporate Strategy and Government Energy Policy

9 Ways for Students to Get Involved with Social Impact This Year

Welcome Back to Campus: 7 Social Impact Programs for Student Changemakers

Six Ways This Alum Used Wharton’s EMBA Program to Transition into a New Role in His Organization

Not All Business: How Passion Projects Help Wharton Undergrads Pursue Non-academic Interests

MBA, Philanthropist, and Former NFL Player Asks MBAs to Pledge ‘One for the World’

Sharing a Meal and Community at a One Wharton Week Dinner

The Future of AI: How Wharton Is Leading the Charge


Why These Wharton Faculty Love Teaching in San Francisco

Wharton’s First Prism Fellow Prepares to Join the MBA Community

An MBA Techie Shares 6 Strategies for Recruiting

Women of Wharton Events Provide Valuable Opportunities to Connect

How Wharton’s EMBA Program Helped this Alum Transition from Software Entrepreneur to Chief Strategy Officer

A Social Entrepreneur’s Inside Look at the Contraceptive Technology Conference

How the Wharton Network Helped This EMBA Alum Enact New Legislation to Decrease Drunk Driving
DiscoverDataScience.org
What Does a Ph.D. in Data Science Look Like? And Do I Need One?
Data science – a new frontier.
In the evolution of data science, most people will reference two major events that fundamentally contributed to the establishment of the discipline.
The first event was the release of the McKinsey Global Institute’s 2011 report on Big Data as the next frontier for innovation, competition and productivity – and the associated gap between the supply and the demand for deep analytical talent. At the time, the McKinsey report forecasted the “talent gap” – the number of positions requiring deep analytical talent above what the educational market was prepared to produce – as 140,000 to 190,000 positions. As it turns out, the talent gap is not only not closing, but it continues to widen. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), there are expected to be about 13,500 new data scientist job openings every year through 2031 — and some of them will require applicants with years of experience in a relatively new field.
The second event was Tom Davenport and D.J. Patil’s 2012 article referring to data science as the “sexiest job of the 21st century”. This article was every math and computer science geek’s high school revenge come true.
The Academy Responds
Academia, not typically known for its responsiveness to the needs of the market, actually did a pretty good job of developing programs in analytics and data science to address these issues.
In 2006, North Carolina State University developed one of the nation’s first masters level programs in analytics .
Today, there are over 200 masters level programs that are offered across the country. It is interesting to note that while most of these programs incorporate mathematics, statistics, programming and some kind of applied practicum, there is little consistency regarding where universities house their analytics and data science programs. Universities house these programs in colleges of business, science, engineering, mathematics and computing, resulting in slightly different strengths, weaknesses and specializations.
Can I Get a Ph.D. in Data Science? Do I Need To?
In 2015, Kennesaw State University developed the nation’s first Ph.D. program in Data Science .
Today, there are dozens of Ph.D. level data science programs offered by universities across the country with hundreds of students pursuing the advanced degree. Like the masters programs, most of the Ph.D. programs integrate advanced course work in mathematics, statistics and computer science. However, unlike masters programs, Ph.D. students must also engage in:
- Peer-review publication
- Produce a dissertation
Additional information about the specifics of Ph.D. data science programs can be found here .
Driving Demand Ph.D. Programs in Data Science
Most people who want to pursue a career in data science do not need a Ph.D. to be successful – although most do have a masters degree.
So, what is driving the demand for Ph.D. programs in data science?
The first is, of course, academia.
The talent gap identified by McKinsey and IBM exemplifies the need for not just deep analytical talent in the economy, but also for deep analytical talent in the classroom.
The “shadow” talent gap in universities is arguably a bigger issue – universities are challenged to produce the talent needed to close the gap without having the faculty talent to teach the material.
It is important to note that the 200+ masters programs offering programs in analytics and data science referenced above are currently doing so without people who have Ph.D.’s in data science. Most universities across the country have openings for faculty with Ph.D.’s in data science that they are struggling to fill.
With the “oldest” Ph.D. programs in the country (those started in 2015) just starting to graduate their data science Ph.D.’s, the “shadow” talent gap in academia will likely not close any time soon.
Opting for Work in the Private Sector
The reason the talent gap in academia is not closing is partially because, most people who complete a Ph.D. in data science will go to work in the private sector.
This is the first time in history that individuals earning Ph.D.’s are electing to NOT go into academia. While the statistics vary greatly, all indicate that over 50% of individuals who complete a Ph.D. in a STEM discipline will never teach.
This is true for at least two reasons.
- The first is simple economics – the demand for individuals with deep analytical skills continues to elevate salaries – with most organizations paying salaries substantively above what most universities can offer. According to the BLS’s May 2021 occupational survey, educational services offer data scientists a mean annual salary of $81,360 , a far cry from the $108,660 mean salary enjoyed by data scientists overall.
- The second reason is that heavily data-centric organizations place value on cutting edge research and innovation in data science , enabling individuals who want to engage in research and scholarship, an opportunity to work outside of a university. A recent study found that over 25% of all peer reviewed articles in “academic” journals related to data science, were actually authored by individuals with Ph.D.’s but no academic affiliation.
So, while individuals interested in pursuing a career as a data scientist can be successful with a masters degree, a Ph.D. may be worth considering – even if they have no intention of teaching.
Jennifer Lewis Priestley, Ph.D. is the Associate Dean of The Graduate College at Kennesaw State University. She is director of the Analytics and Data Science Institute and launched one of the first Ph.D. programs in Data Science in the country.
2021 US Bureau of Labor Statistics salary and employment figures for data scientists reflect national data, not school-specific information. Conditions in your area may vary. Data accessed January 2023.

- Related Programs
What It's Like to Do an MD-PhD Program
New section.
Two medical students answer questions about what it's like to do an MD-PhD program.

Elias (Eli) Wisdom
Undergraduate: Pacific University, Oregon Major: BS, Biology Medical school: Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) Anticipated Graduation Year: 2028 Bio: Eli Wisdom is an MD-PhD student at Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) studying the molecular mechanisms of Parkinson’s Disease. He grew up in the small rural town of La Grande, Oregon, where he gained a deep appreciation for community and service and a fascination with the natural world. At Pacific University, he completed his degree in Biology while also playing varsity baseball. After graduating, he was as an Associate in Neuroscience at Yale School of Medicine for two years before starting an MD-PhD program. Outside of school, he enjoys competing in triathlons, camping, and spending time with family.

Sreya Sanyal
Undergraduate: New Jersey Institute of Technology Major: Biology & History Double Major Medical school: Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School Anticipated Graduation Year: 2031 Bio: Sreya Sanyal is a MD-PhD student at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School and Princeton University. She is Bengali, and she aspires to become a laboratory principal investigator in the field of oncology. Outside of academia, she enjoys singing, cooking, going to museums, and lifting at the gym.
Why did you decide to pursue an MD-PhD program?
Eli: As an undergraduate student, I found my first biomedical research experience to be quite thrilling, and seriously considered pursuing a career in research. Medical school had surfaced as an opportunity, too, as I was deeply passionate about serving others and caring for the sick, but I felt that basic science research was the backbone of advancing clinical care. I first learned about combined MD-PhD programs during my senior year when I was taking part in a summer research program at another academic institute. I learned that in a dual-degree program, I could become rigorously trained as a research scientist and as a physician — and could do both in my future career. To learn more, I reached out to a few physician-scientists who shared how much they loved their careers. In the clinic, their patients and associated medical problems provided new ideas for exploration in the laboratory. And in the laboratory, the insights they gained could inform the way they treated their patients. Sreya: I’ve wanted to become an oncologist ever since I was 11 and my mother died from gastric cancer. When I shadowed hematologist oncologists in academic settings, I became more interested in their work in clinical trials and research. Entering college, I explored translational research through my undergraduate biomedical engineering lab experiences. As I met more people in the field of drug development and oncology, I realized that I wanted to be at the cutting edge of this work, but I still had the desire to see patients. Through a lot of soul searching and luck, I was able to embark on a career in medical research by pursuing an MD-PhD. Using my training as a physician-scientist, I plan to establish my own lab or work in other ways to improve translational research in the oncological space.
What kinds of career options does the MD-PhD program give you?
Eli: From my experience, rigorous training in medicine and scientific research prepares you best for a career in academic medicine. This often means working at a large teaching hospital, where you have an opportunity to conduct independent scientific research, care for patients, and teach students. While it can differ depending on the medical specialty or the individual, a typical physician-scientist may spend 80% of their time conducting research and 20% caring for patients. However, there are many other career paths available to MD-PhD graduates. Students may also pursue careers working for private research organizations, pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, or government agencies. Sreya: In my experience as an MD-PhD student interested in oncology, I have a wide array of career options to explore. As a clinician-scientist, I can lead research teams and conduct studies in cancer biology, treatment approaches, and translational medicine. In these roles, I can also mentor students interested in my field, allowing me to advance scientific knowledge while shaping the next generation of researchers. Alternatively, I could directly impact patients' lives by increasing my clinical time spent as an oncologist, developing personalized treatment plans, and contributing to clinical trials. The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries also present exciting opportunities for me where I would be able to work on drug development, clinical research, or medical affairs, playing an essential role in bringing innovative therapies to market. With my combined medical and research expertise, I am well-equipped to make a meaningful difference in oncology through various rewarding career paths.
What type of research experience did you have before entering the program?
Eli: I attended a liberal arts college where students engaged in scientific research through 2- to 4-month long classes, which were combined lecture and laboratory experiences. Building on excitement from these courses, I pursued a summer research internship at a large biomedical research institute the summer prior to my senior year. I loved this initial exposure to working in a high-powered scientific research center. From working in state-of-the-art reach laboratories, to solving scientific problems in creative ways, and watching physicians bounce between research and patient care — I was hooked. Sreya: Before starting my current program, I had two significant research experiences. First, I worked in a lab that focused on creating materials for drug delivery in the field of biomedical engineering. We used special gels to deliver important substances to specific parts of the body, which had significant effects on the surrounding tissues, such as promoting blood vessel growth and blocking certain enzymes. I spent about ten hours a week for three years in this lab and contributed to three published papers.
Secondly, I worked at a research institute where I studied mice that were genetically modified to show signs of anthrax toxin exposure. These modified toxins could be controlled to specifically target tumor cells in the body. I dedicated forty hours a week to this research, and as a result, we have two research papers in progress for publication
How did you prepare to apply to MD-PhD programs?
Eli: Since I had played varsity baseball throughout college (which was impactful training in its own right), I had limited time for research as an undergraduate. So, I decided to pursue an extended research position before applying to MD-PhD programs. After sending several emails to laboratories across the U.S. and applying to many formal postbacc research programs, I took a two-year job as a postgraduate researcher at an academic research institute. During my time working on a project in a laboratory, I also volunteered at the connected hospital. This allowed me to experience what it was like to conduct independent research during the first part of my day, then care for patients in the afternoon. This experience only confirmed my deeply held passions for both medicine and science, but also exposed me to the challenges that both careers entailed. I felt much more confident in my decision to pursue a dual-degree knowing these insights.
What is your favorite part about being an MD-PhD student?
Eli: Thus far, my favorite part of my training has been directly experiencing the intersection of clinical care and research. During the first two years of the MD-PhD, I was mainly focused on medical school courses and preparing for the first board exam. But now, as I am beginning my PhD, I am realizing how medical school has broadened my perspective. When I read research papers or craft a plan to tackle a hypothesis, I feel empowered with the knowledge I learned in my didactic medical school courses. For example, during one of my PhD research rotations, a scientist was having difficulty delivering a therapeutic to the brains of the mice they were studying. Immediately I recalled from my medical school courses how mannitol could be co-infused to transiently open the blood-brain barrier for drug delivery. It could easily be translated to this scenario. Similarly, my experiences with clinic patients have benefited from my MD-PhD training. Often, it can be as simple as the ability to explain to a patient or their family, the exact mechanism of a drug and the reason it could be effective for their ailment. Or, informing them about current basic science efforts in the field or current clinical trials they might be eligible for. As I advance further into my training, I am eager to see how clinical care and laboratory research can become even more intertwined. Sreya: I am very excited to learn new techniques and approaches to my field of interest. I am also glad that for MD-PhD students in my program, there is a huge emphasis on lifestyle and work/life balance. Many students in my program have become engaged, or married, and are starting families, while many medical students may feel pressure to push these milestones off. Being an MD-PhD student is a huge commitment, so I am especially grateful for all of the personal and professional support my program has to offer.
What do you wish you’d known before you started the program?
Eli: I wish I had known how important it would be to keep an open mind about the research topics that interested me most. I began the MD-PhD program with a rigid focus on a certain topic, thinking that it was the only topic that gave me real excitement. It was also the topic I was most versed in and comfortable in. But during my medical school courses, I was suddenly overwhelmed with several fascinating questions and problems that all seemed equally thrilling. It took a fair bit of mental wrestling with myself to broaden my own research interests and muster up the courage to explore a field I was fascinated with even if I didn’t have the most experience in it quite yet. Luckily, MD-PhD programs are usually quite supportive of students exploring new topics of interest and are eager to see you follow your motivations.
Sreya: One of the most important aspects to consider for MD-PhD students is the idea that this path is a marathon, not a sprint. There is a lot of temptation to overload on clubs, leadership, research, etc., to keep pace with MD colleagues, but in the long run, an MD-PhD is about the quality and depth of training. It’s important to build healthy habits, strong social relationships, and enjoy activities in a sustainable manner, since MD-PhD students have to do another graduate degree on top of medical training.
What advice would you give a student considering an MD-PhD program?
Eli: My advice is to accrue as many experiences as you can in medicine and research before applying. Through these, you can understand if pursuing both an MD and a PhD is the best fit for you, or, if you’d be completely satisfied pursuing a career with only training in one discipline. If you can, shadow physicians at both large academic hospitals and private practices. This can teach you if you’d enjoy treating patients daily and give you insight into how your experience will vary based on the setting. Seek out research experiences as early as possible. This may be difficult to procure, but having a longitudinal research experience that encompasses the successes and failures of science will inform you if this should be your future career. If you can, ask for opportunities to experience what it’s like to write a grant or an academic research article. These are not easy to write, yet they encompass a significant amount of time for professional physician-scientists, so, it is important to learn if you’d enjoy (or at least tolerate) the academic writing load. Lastly, don’t be intimidated by the amount time it takes to complete an MD-PhD. Yes, it is longer than most post-graduate training and takes up a significant portion of your early life. But it is a unique and worthy career path that is much needed in service to society. Sreya: My advice to anyone considering an MD-PhD would be to get both a variety and depth of research experiences. As a student, it’s very easy to continue down a path you already started, but you must try to explore before you commit to any one approach. MD-PhD programs appreciate students who know what they would like to research and the only way to discover this is to pursue broad research experiences. That said, once you find what drives and excites you, it’s important to stick with it and maintain good relationships with your PIs and mentors. It’s a small world among physician-scientists, so depth of work and networking will help you achieve and further your goals. Above all, remember that an MD-PhD is not necessary to do research as a physician. The goal of an MD-PhD is to provide the specific training needed to conduct research above and beyond what a physician alone can do. In this case, you must really be sure that research is fulfilling and allows you to achieve your career goals when applying to programs, as they will ask you about your aspirations.
- @AAMCpremed
Translating Pre-Medical Experiences into Clinical Skills
Michael Foster | May 3, 2023
Your time before medical school is golden. It is a unique time to explore where your passions lie (both within and beyond medicine) and lay a strong foundation of the inter- and intrapersonal skills needed for you to be the best physician you can be. The best advice is simple: challenge yourself, be honest, and have fun! […]
The AAMC offers trusted resources and services to help you navigate the journey from premed to residency and beyond.

- Doing a PhD in Biology
A PhD in Biological Sciences aims to train researchers on the evolution and sustainable use of biological diversity, as well as training for their future incorporation in universities, research institutions and management centres, both private and public administration.
A PhD in Biology usually focuses on the study of living things, their nature, origin, evolution and interactions with each other and their environment. It may also involve the study of plant and animal behaviour, structure, function and relationships to each other and the environment.
Browse available Biology PhD Projects
A next-generation genetic technology to identify biotechnologically-valuable enzymes and transporters, development of fluorescent organic molecules for application in super-resolution imaging techniques, ubiquitin-dependent signalling pathways in ageing, speciation in facultatively sexual species, energy dissipation in human soft tissue during impacts, what is it like to undertake a phd in biology.
As a Biological Sciences PhD student, your day to day activities will revolve around:
- Generating new scientific and technical knowledge in the Biological Sciences through original work. They will be able to handle and apply methodologies to solve research problems in the different areas of biological knowledge, with particular emphasis on the fields of biodiversity and molecular biology.
- Developing new technologies to solve problems, detect needs and opportunities inherent to their area of research. In particular, know and use contemporary statistical approaches.
- Formulating, managing and leading research projects, working in teams and interdisciplinary networks. As a result, they will be able to devise and implement working hypotheses, describe and interpret experimental results and critically analyse the findings presented in scientific publications.
- Managing new information and communication technologies that allow you to efficiently disseminate research and results in specialised journals, specialised circles and the social community to participate satisfactorily in higher and postgraduate education through the experience acquired in the academic activities of your doctorate.
- Advising undergraduate and postgraduate students on your research work.
Research Areas
One of the most significant factors in choosing a PhD project is what your supervisor is interested/expert in. Not every aspect of biology will suit every supervisor: however, there are many ways this can be decided. The largest factor in determining what area to research can be down to your supervisor’s previous interests and his/her research background.
You may also look at research areas based on job opportunities in the future or other practical applications for your findings, such as developing new drugs, vaccines, treatments etc. But these decisions will all depend on whether you are happy with the type of work that your supervisor wants you to do and, more important, whether it’s a research interest your passionate about.
As a biological sciences doctorate examines biological processes at interdisciplinary levels and encompasses various disciplines ranging from organisms to genes to evolution, there are many sub-disciplines that PhD research projects could centre around. Some of these include:
- Bioinformatics ,
- Cell biology,
- Evolutionary biology,
- Molecular biology,
- Molecular microbiology etc.
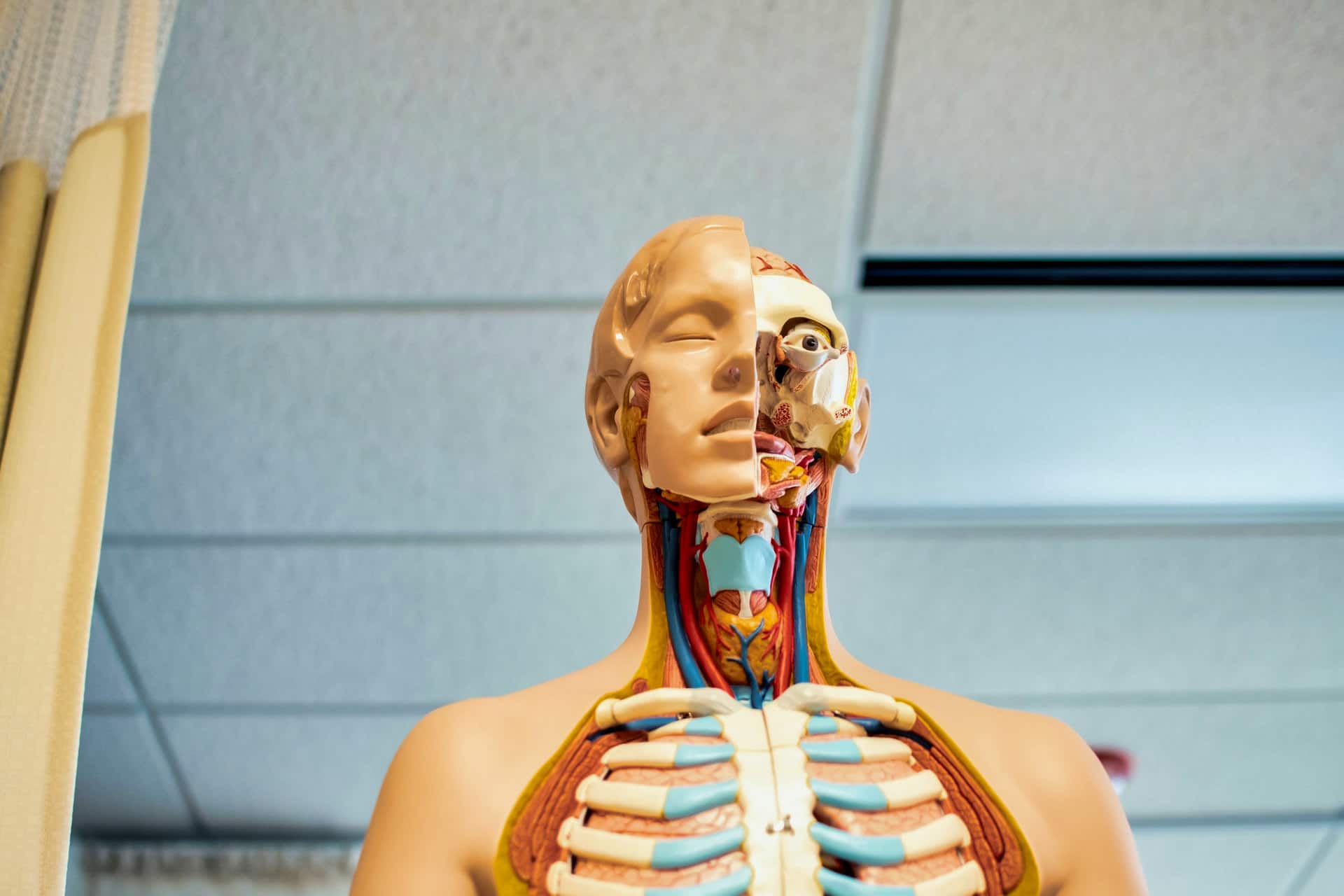

Entry Requirements and Application Process
A PhD in biology requires a good knowledge of mathematics, statistics and biology. Besides independent research, a PhD will entail advanced training in biology and developing skills in analytical thinking.
The typical entry requirements for a PhD in biology is a strong Masters degree (minimum of 2:1) in a relevant field of study. For example:
- BSc (Hons) in Biology, Genetics, Zoology, Biochemistry etc.
- BSc (Hons) in Environmental Science or Marine Biology.
- BVMS/BVM&S/BSc(Hons) Veterinary Science.
- LLB Law Degree with significant subject knowledge of biology.
If you are an international student, you may need to demonstrate your proficiency and knowledge in the English language. This is done through the English language requirements of an IELTS/TOEFL score or a recognised English proficiency test.
Typical Applicant Profile
To be admitted into a PhD programme, applicants will be expected to demonstrate:
- Ability for critical and reflective thinking that leads to the posing of problems and their resolution with impact in the area of health sciences.
- Ability to train human resources in the area of genomic medicine.
- Competence in research, teaching, extension and outreach activities.
- Attitude and aptitude to form multidisciplinary workgroups.
- Leadership for the consolidation of research lines.
- Management and handling of financial resources for research.
- The observance of professional ethical guidelines that contribute to sustainable development.
Average Length of Programme
The duration of a PhD can be up to five years, depending on which university you attend, the funding provided by the university (if any) and your own commitment to finishing it. The minimum time to undertake a PhD depends on the degree you are studying for, however, four years is usually the norm.
What Can You Do with A PhD in Biology?
A PhD in biology allows postgraduate research students to pursue a wide range of careers, primarily due to many transferable skills developed and the range of training received. Students can work in academia, which involves lecturing, laboratory research and academic publication. Lab research positions typically involve working in a team to study living organisms/bio-systems and applying this knowledge to answer specific questions.
Other career paths you could pursue are becoming a microbiologist, pharmacologist, biochemist, biotechnologist, biologist or medical research scientist.

Tuition Fees
On average, tuition fees for a PhD in a biological subject cost approximately £3,000 per year for UK students. International students will pay more in the range of £10,000 to £20,000 depending on their chosen university. Your tuition fees will vary depending on whether you are studying part-time or full-time and as to how much lab work is involved.
Funding Opportunities
The majority of PhD funding will come from the Department/University in the form of PhD studentships. However, depending on your research activity, some funding may also be available from other sources, such as:
- Postgraduate study programmes funded by charities and academic foundations.
- Applying for grants from various government organisations such as the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council ( BBSRC ), Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC). These are usually known as Doctoral Training Partnerships (DTPs).
- Applying for funding opportunities offered by large companies, pharmaceutical companies, research bodies and medical bodies.
If you are successful with securing funding, you could expect to receive around £17-19k per year for your project’s duration. This covers both your tuition fees and your living expenses, such as accommodation costs, utility bills etc. Deadlines for funding will depend on the specific opportunity; therefore, it is best to start your search as soon as possible to give yourself the best chance of succeeding.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Academic Degrees , Education Degree News
Considering a PhD in Education? Here’s What You Need to Know
Updated: February 13, 2024
Published: December 17, 2018

For anyone looking to pursue a career in education in academia or research, a Ph.D. in education is the degree to seek. A doctorate degree in education is a terminal degree in the field, which means it is the highest level degree you can get. So the natural next question is, “What can you do with a Ph.D. in education?
Here, we will share Ph.D. in education jobs, as well as answer all your big questions surrounding a doctorate degree in education.

What is a Ph.D. in education?
A doctor of philosophy (Ph.D.) in education is a graduate degree that is well-suited for anyone who wants to focus their career on academics or research. Just like a Ph.D. in education is a terminal degree, so is a Doctor of Education (EdD) degree.
Although it can be confusing when faced with two terminal degrees in the same field, it helps to clarify when we understand what each of their focus is. An EdD in education is more hands-on and practice-oriented, which means that it’s of use to those who want to work in education, for the government, or in a non-profit organization.
A Ph.D. in education is theoretically-focused and more study-based, in comparison. For this reason, it’s best for anyone looking to work in research or academia at the university level.
There are more differences between the two, including:
- A Ph.D. in education takes four years to complete, while an EdD takes two.
- A Ph.D. requires doing a dissertation, while an EdD doesn’t.
- A Ph.D. focuses on developing new research. EdD students, on the other hand, use existing research to guide decisions about issues within their area of study.
- A Ph.D. requires taking 90 credits, whereas an EdD requires 60.
Why Earn a Ph.D. in Education?
There are many reasons why a Ph.D. in education is valuable and worthy of your effort. Here’s why:
1. It’s one of the most highly respected credentials in education, and as mentioned, it is a terminal degree (which means its the highest level that you can achieve in this field).
2. You’ll use research-based methods to solve problems and identify gaps in your specialization of choice.
Plus, you will have the expertise and credentials to publish in professional journals and/or present your findings at conferences around the world.
3. You’ll be advancing in an area of education in which you’re passionate.
Are you fascinated by childhood development? Or do you have a passion for classroom management? If you have a desire to advance a particular field in education, a Ph.D. is an excellent way to do so.
4. You’ll earn respect in your field and gain personal satisfaction.
Since a Ph.D. in education requires doing a dissertation, that alone is not an easy feat! Accomplishing it will surely give you a rewarding feeling. Plus, being called Doctor isn’t so bad either. Just like any degree, a Ph.D. in education involves a certain skill set . Some learned along the way, and some you may have naturally. These are some skills involved in a Ph.D. in education:
Technical skills:
Analysis and problem-solving, project management and organization, research and information management, and written and oral communication are all important in such a research-based degree.
Soft skills:
Interpersonal and leadership skills, self-management and work habits, concentration, and patience are all important personal skills to have when you’re spending lots of time on one specific topic.
The Doctorate in Education Salaries You Can Expect
Did you know that in America, Ph.D. graduates will earn $1.3 million more than BA holders in their working lifetimes? There are all kinds of career options for Ph.D. education graduates.
Here are some examples of typical careers for Ph.D. in education holders, as well as their average salaries in the US:
- Clinical, Counseling and School Psychologists: $79,820
- Education Teachers, Postsecondary: $80,56 0
- Survey Researchers: $59,870
- Sociologists: $86,110
- Training and Development Specialists: $62,700
Many PhD in education graduates want to become professors. Here’s what the average annual salaries look like around the globe for professors in the top-paying countries (in their equivalent USD):
Denmark: $109,600
Switzerland: $185,000
UK: $110,000
US: $102,400
Finland: $95,000
Canada: $93,000
Germany:$92,000
France: $82,000
There are other career options as well, such as school administrator, superintendent, curriculum coordinator, and principal.

What are the Requirements?
Considering that a Ph.D. in education is the highest level you can achieve in education, it means that you will already have a bachelor’s under your belt, and in most cases, a master’s degree, as well. In other words, you probably like being a student. There are lots of years of studying that get dedicated to earning a Ph.D. If you plan on doing a doctorate in education, earning a master’s degree in education can be the right first step.
Another important thing to know is that almost all Ph.D. candidates have background experience in research. So if education is your field of interest, getting a Ph.D. will mean coming to the table with previous research experience from your undergraduate (and potentially graduate) degrees.
Every institution may differ on their prerequisites for enrolling in their Ph.D. in education program. Be sure to consult directly with your school of choice to find out what they are.
Where Can I Earn My Ph.D. in Education?
There are many schools that offer Ph.D. in education programs. Just like most subjects, there are going to be online /on-campus options as well as throughout the world. Some are even fully funded.
Online programs
University of the People has a Master’s in Education (M.Ed) degree. This could be a great choice for those of you who may be aiming for a Ph.D. in education but only have a BA. The next step is getting that MA. So, why not choose a tuition-free program ?
Liberty University, Walden University, University of Colorado, and the University of Nebraska are just a few popular universities that offer a Ph.D. in Education. Here’s a look at some of the most affordable online Ph.D. programs.
Studying in Europe
Studying in Europe can be both exciting and low-cost . Germany, Sweden, Norway, and Finland offer free doctorate tuition for university students, regardless of their nationality! France offers low-cost Ph.D. tuition fees. If you want to see some specific schools in these countries, look at this list.
Fully-funded Programs
Fully-funded sounds wonderful, and it is! But, it doesn’t mean there are no costs associated. Fully-funded actually means that your tuition is covered, but you’ll still have to cover costs for textbooks and supplies, living expenses, and other fees. no cost. That said, it’s still an awesome option. One condition: it has to be on campus. Why? Because you need to pay with your time — by teaching and performing research.
University of Michigan School of Education, Vanderbilt Peabody College, and Steinhardt School at NYU all offer tuition-free on-campus Ph.D. in education programs.
Online vs On-campus
You might be wondering what it’s like to get your Ph.D. online, as compared to on-campus institutions. Like all degrees, there are advantages and disadvantages to earning your degree entirely online. In regards to a Ph.D. in education, you will need to consider a few things.
Online Ph.D. programs are best suited to students who work better solo. They are also great for those who have worked in the field for some time and want to advance in their area of study. And, of course, it’s the best option for those who work and are raising families. On the other hand, you aren’t in the presence of peers and professors that can be a valuable resource in the research-driven program of a Ph.D.
Earning a Ph.D. on-campus has its pros and cons, too.. While they’re generally more expensive than online programs, on-campus Ph.D. programs allow you to communicate face-to-face with your professors, supervisors, and other students.
What You Can Expect to Study in a Ph.D. in Education
Completing a Ph.D. means doing your dissertation, or research thesis. Naturally, it is going to be based on the field of study that you are most interested in. You can specialize in a certain area. Some common specialization options for a Ph.D. in education are:
- Early Childhood Education
- Special Education
- Adult Education
- Teacher Leadership
- Curriculum and Pedagogy
- Educational Psychology
Aside from the research involved in planning and executing your thesis, you will also have professional development activities and coursework relevant to your area of study. They’re designed to help give you the skills needed to succeed in your research and your future career in education.
While the curriculum is going to vary according to your specialization, there are some general core courses that most PhDs in education involve. You will likely take the following: group psychology, leadership, learning models, ethics, education and globalization, and analytics courses as part of your curriculum.
Is a Ph.D. in Education for Me?
If you choose to study for a Ph.D. in education, chances are you’re passionate about teaching and learning, and everything in between. Even if you’re not looking to stand in front of a lecture hall and teach, you may wish to improve upon the field of education as a whole through research and other means. With a Ph.D. in Education, you open the door to that possibility and many more.
How you choose to earn your degree is up to you. Whether you conclude upon enrolling online or on-campus, prepare yourself for lots of reading, writing, researching, and communicating. Whatever you chose, we’re sure you’ll give it your best shot. Here’s to reaching the top in the field of education!
Related Articles
Real ID deadline is rapidly approaching, what to know about the new flight requirement

The really real deadline to make your state-issued identified card, or driver’s license Real ID compliant will be here before you know it.
And you won’t be fly domestically after 2025 without it. The government has been trying to make Real IDs a thing for a while, initially passing The Real ID act in 2005 in an attempt to set “minimum security standards” for state-issued identification documents.
The law was set to take effect in 2020 but was pushed back by the Department of Homeland Security over “backlogged transactions” at MVD offices nationwide as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to USA TODAY reporting .
The May 2025 extension was necessary, DHS says, as state driver’s licensing agencies worked to address the mountains of paperwork, which in turn impacted the MVD’s ability to make any real progress on the Real ID rollout.
“Following the enforcement deadline, federal agencies, including the Transportation Security Administration, will be prohibited from accepting driver’s licenses and identification cards that do not meet these federal standards,” DHS said in 2022.
Learn more: Best travel insurance
That means every every traveler, 18 or older, must have a compliant form of identification in order to travel.
Here’s what to know.
When does Real ID go into effect?
The Real ID “full enforcement date” is Wednesday, May 7, 2025, according to DHS.
When will a Real ID be required to fly?
You or your loved ones need to have a Real ID compliant document, driver’s license or identification card, by May 7, 2025.
If you have another form of identification that is TSA-approved, like an up to date passport or a permanent resident card then you probably don’t need a Real ID compliant document.
Here are a couple TSA-approved alternatives, if you’re on the fence about getting a Real ID.
- State issued enhanced driver’s license
- DHS trusted traveler cards (Global Entry, NEXUS, SENTRI, FAST)
- U.S. Department of Defense ID, including IDs issued to dependents
- Border crossing card
- An acceptable photo ID issued by a federally recognized Tribal Nation/Indian Tribe
- HSPD-12 PIV card
- Foreign government-issued passport
- Canadian provincial driver's license or Indian and Northern Affairs Canada card
- Transportation worker identification credential
- U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services Employment Authorization Card (I-766)
- U.S. Merchant Mariner Credential
- Veteran Health Identification Card (VHIC)
How long does it take to get a Real ID?
It will take about two weeks , or 15 business days to get your Real ID or Enhanced Driver’s License from your state's Motor Vehicle Department.
Enhanced driver’s licenses, which are only issued in a couple of states, including Washington, Michigan, Minnesota, New York and Vermont, are considered acceptable alternatives to REAL ID-compliant cards, DHS says.
How do I know if I have a Real ID?
All Real IDs will have a stamp on the right hand corner to show that the identification document meets federal standards set forth by The Real ID Act of 2005.
The symbol stamped on your Real ID card will vary, depending on which state you obtain your new identification card from.
What does a Real ID look like?
Your Real ID will have most, if not all of the information that’s included on your driver’s license.
The only difference is the seal included in the right-hand corner.
How to Get a Perfect Score on the LSAT
Here are some tips to help law school applicants who aim for a score of 180 on the Law School Admission Test.

Getty Images
Practice is not helpful unless it is methodical and purposeful. To practice the right way, you need to create a thoughtful study plan.
It's possible to walk into the LSAT with minimal practice and score a perfect 180. My college roommate managed this feat, and I cannot fathom how he did it. For those of us mortals who may need a little more help to hit such an elusive target, I'm happy to share some advice from my own experience as a longtime LSAT instructor who scored 179 after months of practice.
First, however, it is worth stepping back and asking: Why aim for 180?
What Does it Means to Score 180 on the LSAT?
The LSAT, formally known as the Law School Admission Test, is one of the most important factors in law school admissions. There is substantial evidence that those who score well on the test, like those who perform well academically in college, tend to get high grades in the first year of law school.
The LSAT is scored on a bell curve, ranging from 120 to 180. On recent tests, the hump of the curve has centered around 153. Percentiles vary slightly between tests, but generally around 25% of test-takers score 160 or higher, 5% score 170 or higher, and 1% score 175 or higher. Only one in 1,000 test-takers scores 180.
Remember: These scores are based on actual test-takers, not the population at large.
How Do Law Schools Look at a Score of 180?
The most prestigious law schools tend to have median LSAT scores in the 170s. Many candidates are admitted with lower scores, but they likely have high grades and other impressive qualifications .
There is no law school with a median LSAT score above 175. This is because the LSAT is only one of many factors in law school admissions, and it is also due to the shape of the bell curve.
Standardized tests like the LSAT are calibrated to evaluate the bulk of test-takers whose scores fall in the hump of the bell curve, rather than the outliers at extreme edges. The difference between a 177 and a 178 could be due to making the wrong choice between two similar answer choices on just one question. Since LSAT questions can be somewhat subjective, such differences are not statistically meaningful.
Thus, law schools know that 180 is not a magic number. To take your best shot at a top law school , aim for a score in the 170s, the mid-170s if possible.
A score of 180 will stand out, but it is not a golden ticket.
How Do You Practice to Achieve a Top LSAT Score?
Too many test-takers mistakenly believe that the key to scoring high on the LSAT is to take endless practice tests. After all, practice tests are hard, and those who work hardest do the best on the test, right?
This is not quite true. Practice is not helpful unless it is methodical and purposeful . To practice the right way, you need to create a thoughtful study plan .
First, you must learn the right techniques to tackle every question on the test, using the method that best fits your learning style. This may be self-study, a course or online application, or work with a tutor.
Once you have learned the basics, you can best improve your performance through a mix of timed and untimed practice tests and drilling the questions you find hardest.
Homing in on Your Weaknesses
To achieve a perfect score, you need to be a perfectionist. This means practicing questions at the toughest level of difficulty you can handle and carefully examining your results.
All the practice in the world won’t help you unless you are devoted to understanding the questions you get wrong .
If you are a champion martial artist and an opponent throws you to the ground, it is unhelpful to get upset or disappointed or fearful. Instead, you must get curious. How did this happen? How can I prevent it from happening again?
Likewise, what distinguishes top performers on the LSAT is how they respond to questions they get wrong. Instead of anger or apathy, they react to wrong answers with interest, gleaning the data they need to improve. Over time, this leads to breakthroughs in performance.
Mastering Your Mind
Test-takers who fall short of top scores often get so hyperfocused on the test that they exhaust themselves or become overly fixated on the clock.
Top performers understand that the mental side of the LSAT, like test anxiety and time management , are just as important to work on as other essential technical skills .
Instead of willing their brains to focus harder and work faster, they find ways to work with their mind to make the test manageable, sustainable and intrinsically rewarding.
Almost every client I work with who achieves a top score on the test hits a point where they find the LSAT surprisingly interesting. This make practice less of a chore, and it relieves the stress of the test and leads to new insights.
It is hard to get good at something if you hate it. I learned that as a kid, from years of fruitless piano lessons I grew to resent. My brother, who had the same teacher, was fascinated by piano practice and became a phenomenal pianist.
To score 180 on the LSAT, you must find a way to look forward to practice as much as my brother loved sitting down at the keyboard and treating every practice session as a chance to explore and to learn something new.
Tips to Boost a Law School Application

Tags: LSAT , law school , graduate schools , education , students
About Law Admissions Lowdown
Law Admissions Lowdown provides advice to prospective students about the law school application process, LSAT prep and potential career paths. Previously authored by contributors from Stratus Admissions Counseling, the blog is currently authored by Gabriel Kuris, founder of Top Law Coach , an admissions consultancy. Kuris is a graduate of Harvard Law School and has helped hundreds of applicants navigate the law school application process since 2003. Got a question? Email [email protected] .
Popular Stories
Best Colleges

Applying to Graduate School

Paying for College

Medical School Admissions Doctor

Applying to College

You May Also Like
Get accepted to multiple top b-schools.
Anayat Durrani May 16, 2024
Premeds and Emerging Medical Research
Zach Grimmett May 14, 2024
Premeds Take 5 Public Health Courses
Rachel Rizal May 7, 2024

Fortune 500 CEOs With a Law Degree
Cole Claybourn May 7, 2024

Why It's Hard to Get Into Med School
A.R. Cabral May 6, 2024

Pros, Cons of Unaccredited Law Schools
Gabriel Kuris May 6, 2024

An MBA and Management Consulting
Sammy Allen May 2, 2024

Med School Access for Minority Students
Cole Claybourn May 2, 2024

Different jobs with med degree
Jarek Rutz April 30, 2024

Completing Medical School in Five Years
Kate Rix April 30, 2024

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What Really Motivates You at Work?
- Carrie Ott-Holland

To get the recognition that matters most to you, start by identifying exactly what that looks like.
When we work hard, we generally expect our efforts to be recognized by our employer. And most employers will do just that — showering someone with praise at a company meeting, taking a team to a nice dinner, or quietly delivering a cash bonus. But sometimes an employer’s broader recognition strategy does not align with what its individual workers want and need. Some workers may be incentivized by more paid time off, while others may appreciate a gift card to a local shop. And some workers may be motivated by monetary rewards, while others hope to be assigned the role of team lead on the next high-stakes project. In this article, the author offers five practical techniques you can start using today to increase the likelihood of getting the rewards and recognition you value most.
Most of us want to feel rewarded and recognized for a job well done. And most employers want to incentivize their workers to perform well and stay engaged. While these two things should align, employers unfortunately don’t always get it right. A team dinner can be a fun culmination of a group project, or it can feel like a frustrating stand-in if you were hoping for a monetary reward. On the flip side, a cash bonus quietly appearing in your inbox may feel strange if you expected public recognition for a heroic work accomplishment. Yet some people would rather call in sick than stand in front of their colleagues to receive an award.
- Carrie Ott-Holland works as principal people analyst at Klaviyo. She has worked in people analytics and talent management in the tech industry for the past decade and is an organizational psychologist by training.
Partner Center
College of Nursing
Easing the pressure: supporting icu nurse decision making through digital innovation.

College of Nursing Assistant Professor Anna Krupp , PhD, MSHP, RN and Associate Professor Karen Dunn Lopez , PhD, MPH, RN, FAAN understand that intensive care unit (ICU) patients have a greater chance of developing functional decline, which may include new limitations in walking or a decreased ability to manage basic physical needs after hospital discharge. One common contributing factor for this is long periods of immobility, or remaining in bed, during ICU hospitalization.
With funding from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality , Krupp and Dunn Lopez are proposing to develop a decision support tool in the electronic health record. The goal is to make complex decisions about when it is safe to assist ICU patients out of bed more efficient for nurses. Currently, nurses look in multiple locations in the EHR for this information. The tool will summarize key patient information on one screen.
“ICU nurses make hundreds of decisions during a shift and the decision to assist a patient to sit on the edge of the bed or walk in the room requires that nurses know a lot about the patient and their stability over the previous shift,” said Clinical Assistant Professor and Co-Investigator Heather Dunn , PhD, ACNP-BC, ARNP. “Enhancing mobility in the ICU is crucial for positive patient outcomes. However, assessing readiness for activities like walking is challenging when data needs to be gathered from multiple sections of the medical record.”

The project will be conducted in two phases. First, they’ll develop the decision support tool with input from practicing ICU nurses. Next, the tool will be studied in two environments—a simulated EHR with nurses from across the nation and a real-world trial in the ICU.
Both Krupp and Dunn Lopez bring differing expertise. Dunn Lopez will use her knowledge with usability science and focus her time in a simulated setting identifying the ease, use, and effectiveness of the tool.
“One thing we know is that if something is not easy to use, it isn’t going to get used. But there are methods that can make sure that what you are developing is useful to the people who use it,” Dunn Lopez said.
Krupp will apply her ICU-based clinical expertise with her implementation science training to plan and study how decision support is used in everyday clinical practice.

“The best-designed tool does not guarantee routine use in complex healthcare settings. Implementation science identifies and addresses contextual factors to help promote its use,” said Krupp.
Krupp and Dunn Lopez suspect the results of the study will influence a “pragmatic way of accelerating the use of patient data with guideline recommendations at the point of care to support ICU clinicians in delivering evidence-based care, decreasing the duration of bed rest, and reducing hospital-acquired functional decline.”
Read more from our spring 2024 alumni newsletter .
Where to see northern lights Saturday night, what times they will be visible
A severe geomagnetic storm powered by five coronal ejections from the sun will result in a vivid aurora borealis. Here are some tips for seeing it this weekend.

This article has been updated to include a recap of Friday’s aurora activity and Saturday’s forecast.
One of the strongest geomagnetic storms in two decades hit Earth on Friday afternoon, with more activity continuing through the weekend.
Friday’s storm already brought beautiful northern lights displays as far south as Mexico. It also disrupted some power grids and radio and GPS communications, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Geomagnetic storms occur when the sun sends a punch of charged particles and parts of its magnetic field to Earth, often through eruptions from its surface called coronal mass ejections. This severe geomagnetic storm — rated a Level 5 out of 5 — resulted from numerous coronal mass ejections this week, some of which are catching up with one another as they hurtle through space.
Forecasters said the sun has launched additional coronal mass ejections , which could extend geomagnetic activity and displays of the northern lights through this weekend and into early next week.
Both Saturday and Sunday nights could offer more celestial viewing, though early Sunday morning and Sunday evening could be more promising, with displays as far south as Friday night if forecasts hold.
Here’s what you need to know about your chances to see the aurora and threats to satellite systems.
Where are the best places to see the northern lights this weekend?
The northern lights appeared unusually far south in the Northern Hemisphere on Friday night. People snapped photos in Italy, southern Switzerland and India. In North America, people reported sightings in Florida, Southern California and even Mexico.
In the Southern Hemisphere, aurora were photographed in Chile , Argentina and New Zealand , where they are known as aurora australis or the southern lights. Activity was exceptionally strong Friday night to Saturday morning Eastern time, hitting a Level of 5 out of 5.
Current NOAA models show geomagnetic storm activity will initially be less intense Saturday night. By the pre-dawn hours Sunday, however, storm activity may increase markedly, offering early risers a memorable display of the northern lights, especially after around 4 a.m. Eastern. The exact timing of the increase in storminess is very uncertain, though.
If the storm activity reaches a Level 4 or 5 early Sunday, which NOAA indicates is possible, the northern lights may become visible again in most of the United States.
A secondary peak in the current solar storms appears likely... pic.twitter.com/WMlbGKNfaB — NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center (@NWSSWPC) May 12, 2024
When the storm activity increases, the aurora will tend to be most vibrant in northern areas and will become more faint to the south — in some places only visible through cameras.
“Cellphones are much better than our eyes at capturing light,” Brent Gordon, chief of NOAA’s Space Weather Services Branch, said in a news conference Friday. “Just go out your back door and take a picture with a newer cellphone, and you’d be amazed at what you see in that picture versus what you see with your eyes.”
If severe to extreme geomagnetic storm activity (Levels 4 and 5) lasts into the evening Sunday, the northern lights may continue to be visible unusually far south for yet another night.
Will the aurora be blocked by clouds?
Even if geomagnetic activity is high, clouds can block out the light show. Unfortunately, considerable cloud cover will blanket the Northeast and south-central United States, although some gaps in the cloud canopy are probable. Clear skies are most likely over the Midwest, Southeast and Western United States.
If you are in a cloud-free area, make sure you find a dark sky location away from city lights.
What will the aurora look like near me?
Not all auroras look the same. Some are undulating bright green and purple curtains, and others are a diffuse red and orange glow. The colors and structure of the aurora appear differently depending on the latitude and altitude.
Auroras are created when solar particles and plasma temporarily disturb Earth’s magnetosphere. Some solar particles get trapped along Earth’s magnetic field lines into the upper atmosphere. Here, they excite nitrogen and oxygen molecules and release photons of light in different colors. Excited oxygen atoms shine red when they are more than 120 miles above the surface and glow green from 60 to 120 miles. Excited nitrogen atoms give off pink or purple hues below 120 miles.
Dancing green or purple auroras are typically seen at higher latitudes. Lower latitudes usually see more red auroras because red occurs at higher altitudes and can be seen further away from the poles. If you’re in the mid-latitudes (in Virginia or Arizona, for example), your aurora may appear more red than those in Canada or Finland.
Will this affect communications systems or the power grid?
A severe geomagnetic storm can cause issues with power systems, spacecraft operations, radio communications and even pipeline systems, if not appropriately prepared for.
“Our role is to alert the operators of these different systems so that they’re aware and can take actions to mitigate these kinds of impacts,” Rob Steenburgh, a space scientist at NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center, said at a news conference Friday.
Steenburgh and his colleagues work with grid operators across North America to ensure high-voltage transmission lines can withstand the incoming surge of energy from the sun. Over past decades, engineers have built systems that can protect power lines rapidly and keep them online during geomagnetic storms.
Geomagnetic storms can also affect satellite and radio communications, sometimes interfering with signals transmitted in our ionosphere. Anyone using high-frequency radio in the aurora viewing zone may experience some disruptions, said Shawn Dahl, service coordinator for the Space Weather Prediction Center. Under some circumstances, the influx of solar particles can cause low-Earth orbiting satellites to drag lower into the atmosphere.
For the most part, individuals should not be affected or take extra precautions beyond what they might for a typical severe weather storm. If a power outage does occur, people should make sure they have batteries, weather radio and a generator, if necessary.
“They don’t need to do anything out of the extraordinary, if they’ve already got these measures taken care of, because these events are very rare,” Dahl said.
Jason Samenow contributed to this report.

- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Supplements
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What External Hemorrhoids Look Like and How to Get Rid of Them
- Who Is At Risk?
- At-Home Treatment
- Other Treatment Options
- Seeking Medical Care
Hemorrhoids , also known as piles, are swollen or inflamed veins in your rectum or anus. They develop from increased pressure on the skin in and around the anal area. Hemorrhoids can be internal or external. External hemorrhoids can be the most painful. They form under the skin around your anus. They can cause anal itching and swelling when the skin around them is irritated.
Most external hemorrhoids resolve on their own, with or without treatment. Home treatments can often relieve symptoms. If blood clots form in external hemorrhoids, surgery may be needed to remove them.
This article describes the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of external hemorrhoids. It also explains treatments, when medical care is needed, and ways to prevent them.
Ijubaphoto / Getty Images
What Do External Hemorrhoids Look Like?
External hemorrhoids look like swollen, bluish-colored lumps near the opening of your anus. Unlike internal hemorrhoids which are invisible from the outside of your body, you can usually see or feel external hemorrhoids.
External hemorrhoids are flat and soft. They are covered with a layer of skin or mucus. External hemorrhoids can become uncomfortable as the overlying skin becomes irritated and deteriorates.
If a thrombosis (blood clot) forms in a hemorrhoid, it can appear blue, purple, black, gray, or dark brown, depending on your skin color.
What Are the Symptoms of External Hemorrhoids?
External hemorrhoids are usually not problematic. However, they can be very painful if a blood clot forms. Common symptoms of external hemorrhoids include:
- Painless, bright red blood from your rectum
- Anal itching
- Anal aching or pain, especially when sitting
- Pain during bowel movements
- One or more tender or hard lumps near your anus
Blood in the Stool
External hemorrhoids can sometimes bleed. The bleeding can result in bright red blood in your stool , on toilet tissue, or in the toilet bowl as the blood drips. This may occur after a bowel movement.
Blood Clots in the Hemorrhoid
An external hemorrhoid with a blood clot inside it is called a thrombosed hemorrhoid . The extra pressure of the blood clot on the surrounding tissue can cause constant and severe pain.
What Causes External Hemorrhoids?
While the exact causes of external hemorrhoids are unknown, these growths are linked with physical features and behaviors that weaken and produce too much pressure on the veins around your anus. This interferes with blood flow to and from the anal area, causing the blood to pool and enlarge the blood vessels there. Over time, the swollen and inflamed veins appear as external hemorrhoids.
Straining during a bowel movement is a common cause of extra pressure on the anal area that leads to external hemorrhoids. Physical changes, such as the extra pressure exerted on the veins around the anus during pregnancy, can also contribute to external hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids increase with age because the connective tissue that supports and holds them in place can weaken over time.
There is also evidence that some people may be predisposed to hemorrhoids. Research indicates that people with hemorrhoids are likely to have an anal canal that tends to be tighter than average, even without straining. The extra straining that occurs during a bowel movement increases the pressure in the anal canal.
Who Is at Risk of External Hemorrhoids?
While it is difficult to predict who will develop external hemorrhoids, certain habits and physical characteristics can exert extra pressure on your rectum and anus. This can cause swelling in the area and increase your potential for hemorrhoids.
The following risk factors can increase your chances of having external hemorrhoids:
- Straining during bowel movements
- Frequent lifting of heavy objects
- Low-fiber diet
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Genetics that predispose you to developing hemorrhoids
- Activities in which you stand or sit for long periods
- Pregnancy or childbirth
- Sitting on the toilet for long periods
- Abnormal bowel function due to laxative or enema overuse
How Are External Hemorrhoids Diagnosed?
External hemorrhoids are diagnosed by a healthcare provider based on your medical history and a physical examination. During a physical exam, your healthcare provider will check your anal area for signs of external hemorrhoids and the following problems that often accompany them:
- Lumps or swelling
- Prolapsed internal hemorrhoids (internal hemorrhoids that have fallen through the anal opening)
- Leakage of bowel movements or mucus
- Skin irritation
- Anal skin tags (extra skin that remains after a blood clot in an external hemorrhoid dissolves)
- Anal fissures (small anal tears that cause pain, itching, or bleeding)
Based on the results of your physical examination, your healthcare provider may perform one or more of the following diagnostic procedures to identify issues such as tumors , inflammation, and internal hemorrhoids:
- Digital rectal exam : With this exam, your healthcare provider uses a gloved, lubricated finger to perform a manual examination of your anal canal and rectum. The exam checks for muscle tone and signs of internal hemorrhoids, bleeding, lumps, or masses.
- Anoscopy : This examination involves the use of an anoscope (a hollow tube with a light at the end) to examine the lining of your lower rectum and anus.
- Sigmoidoscopy : This internal examination uses a sigmoidoscope (a tubelike instrument with a light and lens) to closely examine the lining of your anus, rectum, and lower colon.
- Colonoscopy : A colonoscopy involves the use of a colonoscope (a flexible tube with a camera on the end) to examine your anus and entire colon closely. It is performed while you are under sedation to rule out colon cancer .
How to Get Rid of External Hemorrhoids at Home
Most external hemorrhoids go away on their own after a few days. If not, you can relieve pain at home with simple conservative measures. These treatments typically relieve pain within one to two weeks.
The following strategies can treat hemorrhoids at home:
- Shorten bathroom trips : Limit toilet use to one to two minutes when possible to avoid straining.
- Consume more fiber and drink more water : Get 25–30 grams of fiber daily from fiber-rich foods (fresh fruits, leafy vegetables, and whole-grain breads) or fiber supplements to help stools pass easier and reduce the need for straining.
- Use a stool softener : Stool softeners increase the water your stool absorbs, making them easier to pass without straining.
- Use over-the-counter topical hemorrhoid treatments : Topical hemorrhoid creams containing a local anesthetic like lidocaine can temporarily soothe pain. Witch hazel wipes and creams that contain hydrocortisone can also soothe inflammation.
- Use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other over-the-counter pain relievers to relieve pain : Pain relievers that include Tylenol ( acetaminophen ) , and NSAIDs like Advil, Motrin ( ibuprofen ) , or Aleve ( naproxen ) can help relieve the throbbing pain of external hemorrhoids.
- Take a sitz bath : A sitz bath is a warm water bath for soaking the area between your genitals and anus (perineum). Soaking in this way can relieve irritation and spasms of the anal sphincter muscle . For best results, soak for about 20 minutes after each bowel movement plus two or three times daily. Add Epsom salts or baking soda to the water for better results.
- Apply ice packs : Apply ice to the irritated area for five to 10 minutes. Use a towel between your skin and the ice pack to prevent skin damage.
- Practice regular physical exercise : Moderate aerobic exercise , such as brisk walking 20 to 30 minutes daily, can stimulate bowel function and reduce constipation.
- Maintain proper hygiene in the perineal area : Fill a squirt bottle (peri bottle) with warm water and use it to cleanse the perineal area after urinating or a bowel movement. This cleanses the area gently and thoroughly.
Other External Hemorrhoids Treatment Options
Medical treatment for external hemorrhoids is limited to specific cases. Treating external hemorrhoids is reserved for cases in which the external hemorrhoids are very large, thrombosed (filled with blood clots), and/or causing intense pain.
Surgical Removal
When medical treatment is justified, external hemorrhoids are removed with a surgical procedure called a hemorrhoidectomy . This involves using a laser, scalpel, or electricity through a device to remove the affected area or the entire hemorrhoid, depending on the technique used.
The two approaches to hemorrhoidectomy are:
- An excisional hemorrhoidectomy is the conventional operative approach. It involves surgically removing the entire external hemorrhoids. This procedure is performed in an operating room, often under intravenous (IV) sedation , spinal block, or general anesthesia .
- An incisional hemorrhoidectomy involves making a cut over the skin of the external hemorrhoid and removing the clot and the overlying skin of the thrombosed hemorrhoid. This in-office procedure is performed after the injection of local anesthesia to numb the affected area.
Treatments During Pregnancy
Medical treatment for external hemorrhoids during pregnancy and in the immediate postpartum period is not routinely administered. Surgical removal of external hemorrhoids via hemorrhoidectomy during this time is reserved for cases that involve severe complications.
Ways to Prevent External Hemorrhoids
You can help prevent hemorrhoids by taking the following steps to ensure healthy bowel habits and avoid constipation:
- Maintain a high-fiber diet : Limit the amount of low-fiber and processed foods you consume.
- Avoid heavy lifting when possible : Straining when you lift heavy objects exerts extra pressure on your rectal ad anal veins.
- Limit the time you spend on the toilet : Don't delay going to the bathroom. Try to spend no more than 10 to 15 minutes on the toilet when having a bowel movement. Avoid straining or forcing if possible.
- Reduce distractions when sitting on the toilet : Avoid losing track of time by looking at your phone or reading on the toilet.
- Avoid laxatives, except bulk-forming laxatives with psyllium : Other types of laxatives can cause diarrhea, which can worsen hemorrhoids.
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
Contact a healthcare provider about your external hemorrhoids if you have the following symptoms:
- Rectal bleeding
- Worsening or new symptoms
- Symptoms that do not improve after one week of home treatments
- Weight or appetite loss or other changes that affect your entire body
The following symptoms indicate a possible medical emergency. Seek immediate medical care if you have any of the following symptoms with external hemorrhoids:
- Severe pain in your anal area
- Rectal bleeding that won't stop
- Severe abdominal pain
- Dizziness or fainting, especially during bleeding
External hemorrhoids occur as a result of extra pressure on the veins in your anal area. Straining with bowel movements or sitting for long periods on the toilet can increase your risk. These growths are more common with pregnancy, obesity, and aging.
Most external hemorrhoids resolve on their own even without treatment. Home treatments can help relieve symptoms of itching, swelling, and pain. Lifestyle changes like eating more fiber can reduce your risk and prevent them from recurring.
Contact your healthcare provider if you have external hemorrhoids that do not improve after a week of home treatments. Seek prompt medical treatment if you also have a lot of bleeding, intense pain, dizziness, and/or other signs of severe illness with external hemorrhoids.
Temple Health. Everything you need to know about hemorrhoids .
Harvard Health Publishing Harvard Medical School. Hemorrhoids and what to do about them .
American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS). Hemorrhoids: Expanded information .
Aurora Health Care. Hemorrhoid treatment .
Penn Medicine. Hemorrhoids .
Keck Medicine of USC. Is it hemorrhoids or colon cancer?
American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS). Hemorrhoids .
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Diagnosis of hemorrhoids .
New York-Presbyterian. Hemorrhoids .
American Academy of Family Physicians. Hemorrhoids .
Lohsiriwat V. Treatment of hemorrhoids: A coloproctologist’s view . World J Gastroenterol . 2015;21(31):9245-9252. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9245
Higuero T, Abramowitz L, Castinel A, et al. Guidelines for the treatment of hemorrhoids (short report) . Journal of Visceral Surgery . 2016;153(3):213-218. doi:10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2016.03.004
Johns Hopkins Medicine. Hemorrhoids .
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Symptoms & causes of hemorrhoids .
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Treatment of hemorrhoids .
MedlinePlus. Hemorrhoids .
By Anna Giorgi Giorgi is a freelance writer with more than 25 years of experience writing health and wellness-related content.
What are geomagnetic storms and why do they produce the aurora australis and borealis?
Flares and coronal ejections shooting off from the Sun's surface struck the Earth overnight, causing a severe geomagnetic storm .
It was the strongest such event in about 20 years, leading to stunning aurora australis light displays in skies across southern parts of Australia and the southern hemisphere.
People in the northern hemisphere also saw and photographed stunning images of pink, red, green and violet skies brought on by the aurora borealis early on Saturday morning.
The solar event is predicted to continue over the weekend, bringing more bright aurora light shows with it.
But what are geomagnetic storms exactly, and how do they produce auroras?
What is a geomagnetic storm?
Geomagnetic storms originate from a specific type of activity taking place on the Sun.
Large "clouds" containing billions of tonnes of plasma embedded within an ejected magnetic field erupt from the Sun's outer atmosphere, or corona.
These eruptions are known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
Unlike solar flares, which travel at the speed of light and reach Earth in about eight minutes, CMEs travel at a more sedate pace.
Officials put the current average at 800 kilometres per second.
These ejections sometimes travel towards Earth, where they can temporarily disturb the Earth's magnetosphere , resulting in geomagnetic storms.
The current storm was caused by an ejection that emanated from a massive sunspot cluster that is 17 times wider than Earth.
The Bureau of Meteorology's (BOM) Space Weather Forecasting Centre issued a geomagnetic storm warning on Friday.
It categorised the storm as level G4, which is severe.
The G-scale is a measure of global geomagnetic activity, which refers to fluctuations in Earth's magnetic field. The G scale ranges from G1 (minor) to G5 (extreme).
"G4 geomagnetic conditions are expected on 10 May 2024, reducing to G3 with a chance of G4 on May 11," the bureau said.
What is causing the auroras?
Andrew Cole from the University of Tasmania's physics department says the auroras seen across the Earth's skies Saturday morning are a direct result of the geomagnetic storm .
"About a day or two ago, the Sun had a large burst of magnetic activity and ejected a pretty big blob of material into space, and that happened to intersect with the Earth last night," Dr Cole said on Saturday.
"That disturbs the upper atmosphere and the Earth's magnetic field, which in turn causes charged particles to glow and produce the really beautiful southern and northern lights."
He said multiple ejections looked to have occurred, with the first effectively clearing the way for a second one to strike Earth "much more quickly and more powerfully than predicted ".
He said only strong geomagnetic storms produced light displays that were visible to the naked eye.
"[If] you get a really strong display, it can look like anything from a dim pinkish or greenish glow, which could just be on the southern horizon, to curtains of shimmering light or pillars extending up nearly vertically," he said.
"Typically the colours will be reddish or green, but in very, very strong auroras like this one, you can get violet as well.
"It's spectacular to see with the eye. It's actually kind of emotionally affecting — much more than a still photo because you can see things moving in real time.
"It's not a special effect. It's just nature doing its thing and on an enormous scale — the whole horizon lit up and changing from second to second, minute to minute."
How rare is this event?
Coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are happening all the time and, like other solar activities, they ramp up as the Sun approaches the peak of its 11-year cycle.
"The Sun goes through periods where it's quite active or it's very quiet, and we happen to be in an active phase at the moment," Dr Cole said.
While storms at level G1 can happen 1,700 times each cycle, G4 storms like the current one don't happen often.
Dr Cole said this geomagnetic storm, which was expected to continue into Monday, was "the strongest event of this kind to hit the Earth in about 20 years".
The last one of this strength occurred in October 2003 during a series of solar storms dubbed the "Halloween storms".
The last one before that took place in 1989, Dr Cole said.
"These events are rare enough that people remember the dates and keep them marked down for study," he said.
The most powerful geomagnetic storm in recorded history, known as the Carrington Event, occurred in September 1859.
It was named after Richard Carrington, the British astronomer who recorded a solar flare for the first time during the phenomenon.
Are geomagnetic storms dangerous?
Geomagnetic storms are not considered dangerous to human bodies.
However, they can cause power outages and impact satellite services , which can have devastating consequences.
The 2003 Halloween storms caused blackouts in Sweden and damaged power infrastructure in South Africa.
The BOM issued warnings that there could be similar disruptions here, and urged airlines and those in charge of the power grid to take precautionary steps.
The fluctuating magnetic fields associated with geomagnetic storms induce currents in long wires — including power lines — which can potentially lead to blackouts .
Excess currents on telegraph lines during the Carrington Event resulted in telegraph technicians receiving electrical shocks, and even caused some telegraph equipment to catch fire.
Long metal pipes can also become electrified , leading to engineering problems.
Spacecraft are also at risk from high doses of radiation , though the atmosphere prevents this radiation from reaching Earth.
Astronauts are also kept safe by a dedicated NASA team guiding those on the International Space Station to move to places within the outpost that are better shielded.
Animals such as pigeons that have internal biological compasses, however, can be affected.
Pigeon handlers have noted a reduction in birds coming home during geomagnetic storms, according to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Can I still see the southern lights?
Yes, there's a strong chance you can see the aurora australis again in eastern parts of Australia on Saturday night — but it may not be as bright as last night's display.
Geomagnetic events can last for days, but it's not known how long exactly this one will continue.
Dr Cole said people interested in seeing the display should go outside and check as soon as it got dark in the early evening because the Moon would set and provide "darker skies and better visibility".
But the most important thing, he said, was to find a spot that had clear skies and was away from city lights .
Early Saturday morning in Australia, the southern lights were a bit obscured by cloud and the sunrise, Dr Cole said, while people in Europe were able to see much stronger displays later in the day.
Brent Gordon, from America's National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, encouraged the public to try to photograph the night sky with their phone cameras even if they could not see the lights with their naked eyes.
"Just go out your back door and take a picture with the newer cell phones, and you'd be amazed at what you see in that picture versus what you see with your eyes," he said.
ABC with wires
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
Thick atmosphere discovered around super-earth in nearby solar system.
NASA sends software update 24 billion kilometres to restore communication with Voyager 1
James Webb Telescope captures iconic Horsehead Nebula in unprecedented detail
- Astronomy (Space)
- Planets and Asteroids
- Weather Phenomena

COMMENTS
PhD stands for Doctor of Philosophy. This is one of the highest level academic degrees that can be awarded. PhD is an abbreviation of the Latin term (Ph)ilosophiae (D)octor. Traditionally the term 'philosophy' does not refer to the subject but its original Greek meaning which roughly translates to 'lover of wisdom'.
These meetings are crucial for maintaining momentum and ensuring a productive working relationship. A typical daily schedule for a PhD student might look like this: 7:00 AM - Wake up, morning routine, breakfast. 7:45 AM - Check emails, plan the day, and set priorities. 8:30 AM - Arrive at the laboratory, set up experiments or research tasks.
This should be in whatever field you intend to pursue a PhD in. Publications are also incredibly valuable. All of academia runs on publication, and getting an early start helps your career at every step. You should try to do research while still in undergrad. What this looks like depends entirely on what field you are pursuing.
9. There are no real breaks. In a stereotypical "9-to-5" job, when the workday is over or the weekend arrives, you can generally forget about your work. And a vacation provides an even longer respite. But in a PhD program, your schedule becomes "whenever you find time to get your work done."
I condensed twenty, 20-min interviews into a 10-min video that explains what a PhD is really like to do! I asked about workloads, social life, best parts vs ...
The doctorate is the most advanced academic degree you can earn, symbolizing that you have mastered a specific academic discipline or field of profession. Doctorate degrees require a significant level of research and articulation. Those who earn the degree must have researched a subject or topic thoroughly, conducted new research and analysis ...
Learn more about whether earning a PhD could benefit your career. A Doctor of Philosophy, often known as a PhD, is a terminal degree —or the highest possible academic degree you can earn in a subject. While PhD programs (or doctorate programs) are often structured to take between four and five years, some graduate students may take longer as ...
Prepare for the Standardized Tests. Most PhD programs require students to take the Graduate Record Examinations (GRE). Having high test scores is a key part of an application as it tests skills learned over the course of many years in school. Quantitative skills are especially important when applying to doctoral programs in business areas.
Broadly speaking, a Ph.D. application consists of previous academic grades, competitive examination scores, work experiences, letters of recommendation, and a personal statement. For a Ph.D. program, all previous academic grades are weighted and assessed including undergraduate transcripts, while standard examination scores (i.e., the GRE) are ...
How the PhD Program Works. Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending ...
5. Embrace change - don't get bogged down in the details. Felix Shaw - one of our bioinformatics researchers at EI - put it best when he said, " it felt like I was running into brick walls all the way through [my PhD]… you'd run into a brick wall, surmount it, only to run straight into another. It's true.
The work required to complete a PhD varies across academic disciplines and universities, though earning a PhD typically requires the following elements: Completing coursework. Completing one or more doctoral residency experiences. Passing a comprehensive assessment or exam. Developing and completing an independent research project.
The first two years of a PhD program are mainly made up of classes and the beginning stages of research. Deborah Small, the doctoral coordinator for the Marketing program, said, "It starts with heavy duty coursework and a lot of specific requirements. At the end of your first year, there are qualifying exams on all the core marketing courses.
The reason the talent gap in academia is not closing is partially because, most people who complete a Ph.D. in data science will go to work in the private sector. This is the first time in history that individuals earning Ph.D.'s are electing to NOT go into academia. While the statistics vary greatly, all indicate that over 50% of individuals ...
There is a lot of temptation to overload on clubs, leadership, research, etc., to keep pace with MD colleagues, but in the long run, an MD-PhD is about the quality and depth of training. It's important to build healthy habits, strong social relationships, and enjoy activities in a sustainable manner, since MD-PhD students have to do another ...
A PhD in biology requires a good knowledge of mathematics, statistics and biology. Besides independent research, a PhD will entail advanced training in biology and developing skills in analytical thinking. The typical entry requirements for a PhD in biology is a strong Masters degree (minimum of 2:1) in a relevant field of study.
A Ph.D. in education takes four years to complete, while an EdD takes two. A Ph.D. requires doing a dissertation, while an EdD doesn't. A Ph.D. focuses on developing new research. EdD students, on the other hand, use existing research to guide decisions about issues within their area of study. A Ph.D. requires taking 90 credits, whereas an ...
7 stages of the PhD journey. A PhD has a few landmark milestones along the way. The three to four year you'll spend doing a PhD can be divided into these seven stages. Preparing a research proposal. Carrying out a literature review. Conducting research and collecting results. Completing the MPhil to PhD upgrade.
Similarly, a PhD student is expected to know a lot more theory/background knowledge in the field and research skills compared to an undergrad. PhD students are also expected to do research contributing to their dissertation, which means they must work with their advisor to keep focused on their topic and their scope.
Here are a couple TSA-approved alternatives, if you're on the fence about getting a Real ID. State issued enhanced driver's license DHS trusted traveler cards (Global Entry, NEXUS, SENTRI, FAST)
To score 180 on the LSAT, you must find a way to look forward to practice as much as my brother loved sitting down at the keyboard and treating every practice session as a chance to explore and to ...
It was useful to get a snappy answer without combing through reviews or articles. But the type of AI used by Google and ChatGPT essentially generates an average or typical response to your search.
To get the recognition that matters most to you, start by identifying exactly what that looks like. by . Carrie Ott-Holland; by . Carrie Ott-Holland; May 16, 2024 PM Images/Getty Images. Post.
The tool will summarize key patient information on one screen."ICU nurses make hundreds of decisions during a shift and the decision to assist a patient to sit on the edge of the bed or walk in the room requires that nurses know a lot about the patient and their stability over the previous shift," said Clinical Assistant Professor and Co ...
Not all auroras look the same. Some are undulating bright green and purple curtains, and others are a diffuse red and orange glow. The colors and structure of the aurora appear differently ...
Digital rectal exam: With this exam, your healthcare provider uses a gloved, lubricated finger to perform a manual examination of your anal canal and rectum.The exam checks for muscle tone and signs of internal hemorrhoids, bleeding, lumps, or masses. Anoscopy: This examination involves the use of an anoscope (a hollow tube with a light at the end) to examine the lining of your lower rectum ...
This interactive map complements the static control-of-terrain maps that ISW daily produces with high-fidelity.
He said only strong geomagnetic storms produced light displays that were visible to the naked eye. "[If] you get a really strong display, it can look like anything from a dim pinkish or greenish ...