How to Write a Thesis Summary
Your thesis summary is the distilled essence of your thesis: a tool to underline the strengths of your research and make yourself recognizable as a competent scholar.

The importance of writing a good thesis summary is often underestimated and it is not too difficult to understand why. Even in the cases where a student has seriously engaged in writing his thesis, the summary is usually the last thing that gets done. The typical scenario is therefore the following: the bulk of the work has finally been done, the deadline to submit the thesis is imminent. Time is running out and, consequently, when it comes to set the summary down, this is written in a very hasty way… I am pretty sure that you can relate to this situation and – trust me – you are not the only one. Yet, this is a pity! Your thesis summary deserves to be written with a certain care for several good reasons. An effective summary is the best way to impress your readers. It will be the first thing to be read and – as hard as it is to admit – the first impression is what really counts. You should therefore think of the summary as a distilled and concentrated essence of your thesis: a tool to underline the strengths of your research and make yourself recognizable as a competent scholar.
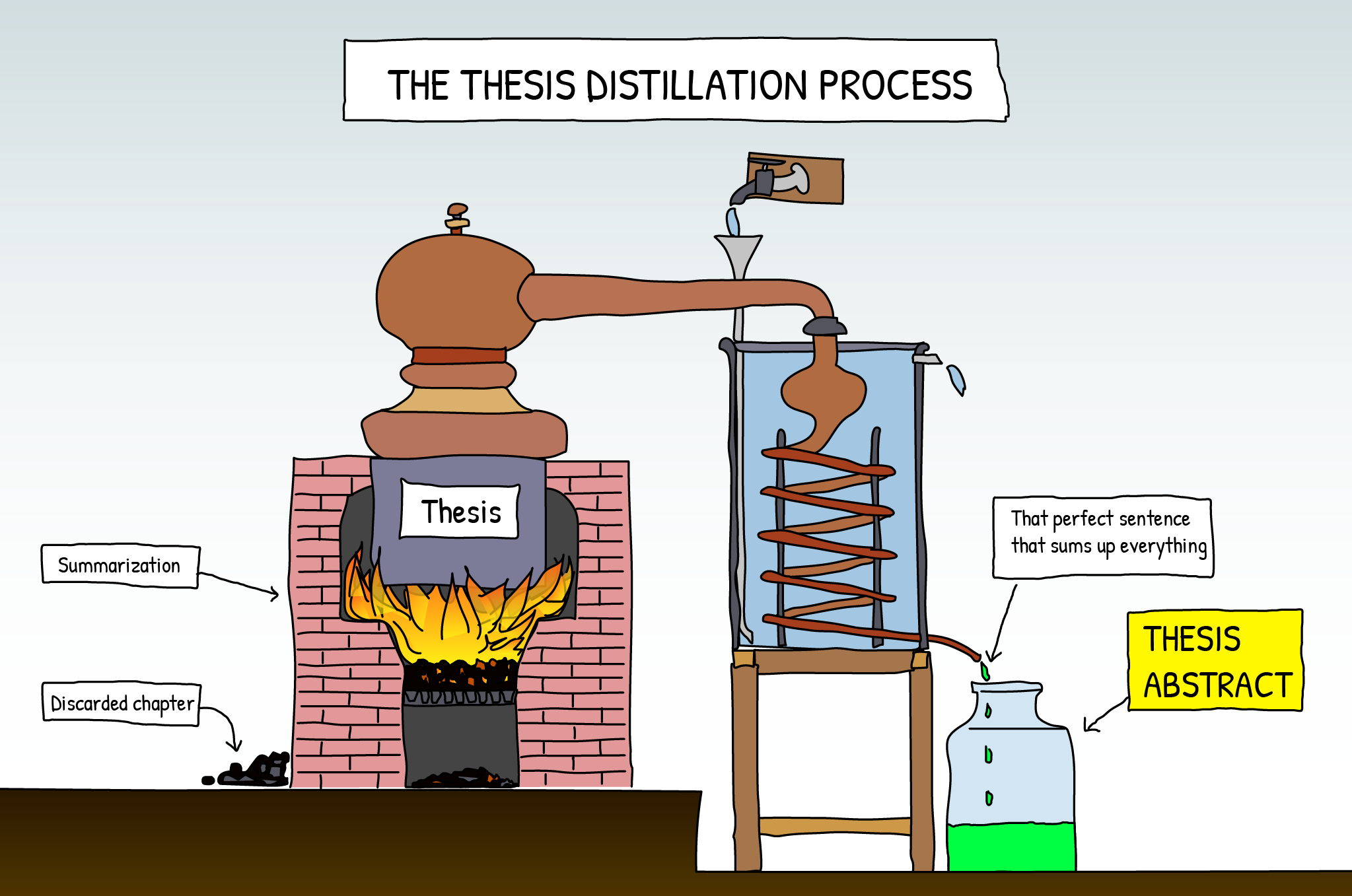
Especially if your thesis is written in another language, setting down an accurate, compelling summary in English can be the first step to internationally disseminate your work. In this regard, keep also in mind that an English summary of your thesis may be required for a job application or a PhD-position. Having said that, how to proceed? Here you are some useful steps to write an effective summary.

Elaborate a thesis statement
The thesis statement . is the most important part. This is a sentence usually placed at the beginning of the summary and it is aimed at clarifying the main research questions of your work. The thesis statement must be clear and concise. MA theses, but also PhD dissertations, usually concern very narrow topics. So, avoid being vague and explain the central idea of your research as specific as possible. Let’s do some practical examples. A sentence like:
“the aim of the present study is to show how English skills can be improved in several ways” is certainly too vague.
Instead, a statement like:
“the aim of the present research is to show how the use of Ludwig can improve English writing skills, by providing reliable texts to get inspiration”
defines a narrower field of research. In addition, as the last example demonstrates, a good thesis statement can be enforced with further arguments.
For example, one could state that:
taking inspiration from a database of 300 million English sentences can indeed help a student to perfect their phrasing, by seeing words in the context of real sentences. A mere automatic correction tool, instead, carries the risk of worsening the student performance, for example by favouring the memorization of wrong phrases and expressions.

Explain the structure of the thesis
Each thesis is usually divided into diverse chapters, such as an introduction, a section dedicated to explaining the terminology, a chapter for the methodology, the discussion of the data, the results of the research etc. A good summary must give a clear idea of how you have organized your research step by step. So be very clear and use sentences like “in the first chapter of my thesis I treated”, “while in the second…”, “the analysis of the data has shown that” etc. And, of course, do not hesitate to use Ludwig if you need examples to take inspiration from. Keep in mind, you may have made the discovery of the century… but if you are not able to explain how you achieved such a result, you will be considered a charlatan.
How to write a thesis summary: a practical example
In this regard, it is good practice to read a number of thesis summaries and to analyse how they are written. Nowadays all the most prestigious universities offer free access to their online repositories, where one can find great inspirational models. See, for example, this website by Cambridge University. Now, let's analyse the structure of one of them:
The Italian giallo film was a type of thriller that was produced in huge numbers between the early 1960s and the late 1980s. This thesis contributes to recent scholarly attempts to situate the giallo within its socio-cultural historical context but resists the critical tendency to read these films as passive and transparent reflections of social attitudes in post-war Italy. Rather, I attend concretely to the form of these films and, specifically, to their critically neglected sound designs . I argue that the giallo’s voice tracks were conditioned by the commercial imperatives of Italy’s post-war popular film industry and that these commercial imperatives were in turn shaped by wider social, economic and political phenomena. By theorising the voice as a mediator between the giallo text and its industrial and social contexts, I show that these films both registered and reified social change. Chapter 1 demonstrates that the anonymous narrator of Mario Bava’s The Girl Who Knew Too Much (1963) adopts a range of sonorous modes throughout the film. Each of these sonorous modes invokes a specific set of intertexts which are vital to tracing both the giallo’s cultural origins and the increasingly globalised socio- cultural landscape from which it emerged. This chapter then shows that Dario Argento’s The Bird with the Crystal Plumage (1970) uses the model of the cinematic voice-over to explore the subjective experience of urban space in post-war Italy. The film suggests that by 1970 the ability to vocally ‘narrate’ and thus control space had become a fundamental assumption of the modern, cosmopolitan subject. Chapter 2 analyses Lucio Fulci’s Don’t Torture a Duckling (1972) and Sergio Martino’s Torso (1973). Both films draw on longstanding Italian cultural stereotypes to pitch the silence of the rural against the vocality of the urban. The films use silence and the voice as ‘cartographic’ tools to delineate the profound socio-economic divisions between Italy’s rural South and its more urban North, but they also illustrate the giallo’s underlying affinities with its silent cinema ancestors and so challenge the assumed temporal borders between cinematic eras. Chapter 3 argues that Argento’s Tenebrae (1982) and Fulci’s The New York Ripper (1982) variously mimic the vocal aesthetics of television. These films lay bare both the increasing dominance of the Italian cultural landscape by imported commercial television in the 1980s and the neoliberal economic project that underpinned that trend. Ultimately, they question the stability of the nation itself, precisely because the voice — now fractured across a global mediascape — is unable to signal national specificity.
The sentences in bold highlight how the author carefully organized the structure of the text. He started with a well elaborate thesis statement. As you can see, the object of the research is well defined and narrow: the study focuses on Italian thrillers , produced during a specific historical period between the early 1960s and the late 1980s. Moreover, the investigation depeens a specific aspect: the use of sounds in this movie genre. Then, the scholar explains in detail how he organized his work step by step, by summarizing the content of each chapter.

Ultimately, we can say that to write a theis summary is a less daunting task than one might imagine at first sight!
Keep in mind why and for whom you are writing
There is a huge difference between writing a summary for the theses database of your university and to write a summary for a more ambitious purpose. As mentioned above, a summary of your thesis may be required for a job application or to get a PhD position. So, if you are facing this kind of situation, you must “use” your summary in a smart way. Are there any points of contact between your thesis and the position you hope to get? If yes which ones? Is it the topic? Or, perhaps, in order to undertake your research, you have used a tool/method/program that could be pertinent with this position? So, tailor your summary in order to highlight what you need to stand out from the crowd and… good luck!
Others from Academic English

MLA, APA, Chicago, IEEE - What’s the best citation style for your paper?

The Fall of the Five-Paragraph Essay

Should I publish it in English? About the role of English in the scientific community

How to write the perfect abstract: do not displease your reviewers and get published
Subscribe to new posts.
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
How to write a fantastic thesis introduction (+15 examples)

The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write a powerful thesis introduction.
Elements of a fantastic thesis introduction
An introductory chapter plays an integral part in every thesis. The first chapter has to include quite a lot of information to contextualise the research. At the same time, a good thesis introduction is not too long, but clear and to the point.
This list can feel quite overwhelming. However, with some easy tips and tricks, you can accomplish all these goals in your thesis introduction. (And if you struggle with finding the right wording, have a look at academic key phrases for introductions .)
Ways to capture the reader’s attention
Open with a (personal) story.
An established way to capture the reader’s attention in a thesis introduction is by starting with a story. Regardless of how abstract and ‘scientific’ the actual thesis content is, it can be useful to ease the reader into the topic with a short story.
| |
Start by providing data or statistics
So if your thesis topic lends itself to being kick-started with data or statistics, you are in for a quick and easy way to write a memorable thesis introduction.
| , 2022)! While awareness of marine pollution is increasing, there is a lack of concrete actions to tackle this environmental problem. In this thesis, I provide a comparative analysis of interventions to reduce marine pollution in five European countries. |
Begin with a problem
Emphasising the thesis’ relevance
A good thesis is a relevant thesis. No one wants to read about a concept that has already been explored hundreds of times, or that no one cares about.
Define a clear research gap
Every thesis needs a crystal-clear research gap. Spell it out instead of letting your reader figure out why your thesis is relevant.
| “ ” (Liu and Agur, 2022: 2)*. |
Describe the scientific relevance of the thesis
Scientific relevance comes in different forms. For instance, you can critically assess a prominent theory explaining a specific phenomenon. Maybe something is missing? Or you can develop a novel framework that combines different frameworks used by other scholars. Or you can draw attention to the context-specific nature of a phenomenon that is discussed in the international literature.
Describe the societal relevance of the thesis
Formulating a compelling argument.
Arguments are sets of reasons supporting an idea, which – in academia – often integrate theoretical and empirical insights. Think of an argument as an umbrella statement, or core claim. It should be no longer than one or two sentences.
Write down the thesis’ core claim in 1-2 sentences
Support your argument with sufficient evidence.
The core claim of your thesis should be accompanied by sufficient evidence. This does not mean that you have to write 10 pages about your results at this point.
Consider possible objections
Think about reasons or opposing positions that people can come up with to disagree with your claim. Then, try to address them head-on.
Providing a captivating preview of findings
Address the empirical research context.
If you did all your research in a lab, this section is obviously irrelevant. However, in that case you should explain the setup of your experiment, etcetera.
| . As a consequence, the marine and terrestrial ecosystems of the Islands are increasingly disrupted. |
Give a taste of the thesis’ empirical analysis
Hint at the practical implications of the research.
You already highlighted the practical relevance of your thesis in the introductory chapter. However, you should also provide a preview of some of the practical implications that you will develop in your thesis based on your findings.
| . . . |
Presenting a crystal clear thesis structure
Provide a reading guide.
The reading guide basically tells the reader what to expect in the chapters to come.
Briefly summarise all chapters to come
Design a figure illustrating the thesis structure.
Especially for longer theses, it tends to be a good idea to design a simple figure that illustrates the structure of your thesis. It helps the reader to better grasp the logic of your thesis.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox, the most useful academic social networking sites for phd students, 10 reasons not to do a master's degree, related articles, better thesis writing with the pomodoro® technique, phd thesis types: monograph and collection of articles, why you cannot write a phd thesis in 3-6 months, the top 10 thesis defense questions (+ how to prepare strong answers).
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Structure for a summary of a thesis/research paper
When asked for a 15-page summary of the thesis/research paper, should I write it by chapter (Introduction, Methodology, etc) ?
The only guideline given is to include introduction, research objectives, methodology, etc. But no specific format was given.
The summary was a requirement for a colloquium.
- academic-writing
- 4 Welcome to Writers. We have some people who know more about academic writing than I do, but I'll ask the obvious question: Does your school or department have any guidance on this, like a style sheet or a style guide you follow? – Goodbye Stack Exchange Commented Oct 19, 2015 at 15:51
- Probably more suited for: academia.stackexchange.com – Therac Commented Aug 17, 2018 at 16:41
3 Answers 3
It actually depends on the field you are working on, but here are a few general pointers.
If done right, your thesis probably looks like this:
Chapter 1. Introduction, in particular motivation, i.e. why you're working on that particular topic, What applications are there for your invention or your ideas, why is it relevant for society, for your institution, for your readership; what your expectations were when you started working on it, whether you achieved what you expected.
Chapter 2. Basics, i.e. an introduction to the main topic, in particular all the knowledge your readers require to even understand the rest of the thesis.
Chapters 3 – 10. Your actual dissertation. Probably these chapters are more or less independent from each other, so each chapter will replicate the general structure of the thesis within the chapter; i.e. the chapter starts explaining why the topic of the chapter is necessary, then you introduce the basic concepts, then you introduce and develop your contribution (i.e. discuss your novel ideas, or introduce your new invention, explain how you developed it, what methods you used, etc). Then you prove that your contribution is sound and why it is worth publishing it. Finally, you summarise what you have done in the chapter and maybe already explain why the next chapter is necessary.
Chapter 11. The final evaluation of all the new concepts and ideas (your contribution). Here's where you put everything into perspective and formally prove that your whole work is worth something.
Chapter 12. The big conclusion. First, you briefly summarise Chapter 1, then you briefly list the most important achievements and conclusions of Chapters 3 – 10; then, you summarise Chapter 11. Finally, you provide an outlook. What will future work look like, or what will the impact of your thesis be.
Now, if you have to summarise all this, this is what you do:
Chapter 1 . Keep most of it, if not all of it. The audience wants to understand why they should keep reading a 15-page summary or your whole thesis.
Chapter 2 . Skip completely, unless you fear that what's to come can't be understood without a few basics. In that case, include only the most necessary stuff.
Chapters 3 – 10. For each chapter, your summary should include the chapter's introduction and motivation, a brief summary of your contribution, but not the details that nobody is going to understand anyway. You have probably worked on this for years. It may all be crystal clear to you, but for people seeing it for the first time, it may be very complex. Keep it simple and concentrate more on the relevance of the results than on how exactly you achieved them.
Chapters 11 - 12. Include only the things that prove that your work has relevance and how it will impact the audience.
Final remark: In general, make summaries easy to read and understand. You might even consider using a bullet list instead of proper prosa.
- What would be the possible title of chapter 2? – Mohammad Commented Apr 24, 2018 at 17:32
Putting section-titles will help give your summary structure so you can focus on summarizing different aspects in different subjects. Just remember that a summary is supposed to be short and very broad, using only relevant information.
Think of your audience.
Your summary should serve as a brief introduction into and overview of your research. The purpose of that summary is to allow your audience to understand your research, discuss it with you, and give you helpful feedback.
Just condensing your dissertation may not help them with their task of helping you.
What I would do is create an interesting narrative. Look at some TED talks to give you an idea what that might entail. Generally, it begins with a very brief (one to a few sentences) summary of what you research, goes on to explain why you research this (i.e. why is this important and to whom), then you explain how you research it, but keep your explanations general and avoid jargon, to that an intelligent non-expert can understand it (imagine that you write for the New York Times), and finally you explain the problems that you currently face and ask your audience for ideas in how to solve them.
That is, on every level of your narrative you draw your audience in. First you make your research relevant to them. Then you explain it in a non-boring way, then you ask them to get thinking about how to do it better.
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by artificial intelligence tools are not allowed on Writing Stack Exchange. Learn more
Sign up or log in
Post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged academic-writing or ask your own question .
- Featured on Meta
- Site maintenance - Tuesday, July 23rd 2024, 8 PM - Midnight ET (12 AM - 4 AM...
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
Hot Network Questions
- How is Agile model more flexible than the Waterfall model?
- The run_duration column from the msdb.dbo.sysjobhistory returns negative values
- If a unitary operator is close to the identity, will it leave any state it acts on unchanged?
- How do you calculate the mass of diproton helium-2 nucleus?
- convn Template Function Implementation for Image in C++
- What is this interference?
- Does the "anti-dynasty" provision of the Philippines have parallels in other countries?
- Can epic magic escape the Demiplane of Dread?
- Why the will to power?
- How to Series Expand an Expression in Mathematica with Smaller Cross Terms Compared to Diagonal Terms?
- One hat's number is the sum of the other 2. How did A figure out his hat number?
- Predict trajectory of a bouncing ball
- Does Event Viewer have any sensitive information like password, or such info?
- How deep should I check references of a papers I am going to cite?
- Braille-based Base64
- Why do Bell states have all real coefficients?
- With SHA-1 broken, can the old Linux /dev/(u)random algorithm be trusted?
- How to calculate Gibbs free of a reaction?
- Why are the categories of category theory called "category"?
- Looking for title about time traveler finding empty cities and dying human civilization
- "One-time discount" fraud: is any crime committed?
- Complexity of finding graph automorphism group vs. canonization
- How to create a new layer that shows the number of intersecting vector layers at each point in QGIS
- Determining coordinates of point B and C given distance and coordinates from point A to point B and C in QGIS
- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Table of contents.

Definition:
Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student’s original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
History of Thesis
The concept of a thesis can be traced back to ancient Greece, where it was used as a way for students to demonstrate their knowledge of a particular subject. However, the modern form of the thesis as a scholarly document used to earn a degree is a relatively recent development.
The origin of the modern thesis can be traced back to medieval universities in Europe. During this time, students were required to present a “disputation” in which they would defend a particular thesis in front of their peers and faculty members. These disputations served as a way to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and were often the final requirement for earning a degree.
In the 17th century, the concept of the thesis was formalized further with the creation of the modern research university. Students were now required to complete a research project and present their findings in a written document, which would serve as the basis for their degree.
The modern thesis as we know it today has evolved over time, with different disciplines and institutions adopting their own standards and formats. However, the basic elements of a thesis – original research, a clear research question, a thorough review of the literature, and a well-argued conclusion – remain the same.
Structure of Thesis
The structure of a thesis may vary slightly depending on the specific requirements of the institution, department, or field of study, but generally, it follows a specific format.
Here’s a breakdown of the structure of a thesis:
This is the first page of the thesis that includes the title of the thesis, the name of the author, the name of the institution, the department, the date, and any other relevant information required by the institution.
This is a brief summary of the thesis that provides an overview of the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
This page provides a list of all the chapters and sections in the thesis and their page numbers.
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the research question, the context of the research, and the purpose of the study. The introduction should also outline the methodology and the scope of the research.
Literature Review
This chapter provides a critical analysis of the relevant literature on the research topic. It should demonstrate the gap in the existing knowledge and justify the need for the research.
Methodology
This chapter provides a detailed description of the research methods used to gather and analyze data. It should explain the research design, the sampling method, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures.
This chapter presents the findings of the research. It should include tables, graphs, and charts to illustrate the results.
This chapter interprets the results and relates them to the research question. It should explain the significance of the findings and their implications for the research topic.
This chapter summarizes the key findings and the main conclusions of the research. It should also provide recommendations for future research.
This section provides a list of all the sources cited in the thesis. The citation style may vary depending on the requirements of the institution or the field of study.
This section includes any additional material that supports the research, such as raw data, survey questionnaires, or other relevant documents.
How to write Thesis
Here are some steps to help you write a thesis:
- Choose a Topic: The first step in writing a thesis is to choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. You should also consider the scope of the topic and the availability of resources for research.
- Develop a Research Question: Once you have chosen a topic, you need to develop a research question that you will answer in your thesis. The research question should be specific, clear, and feasible.
- Conduct a Literature Review: Before you start your research, you need to conduct a literature review to identify the existing knowledge and gaps in the field. This will help you refine your research question and develop a research methodology.
- Develop a Research Methodology: Once you have refined your research question, you need to develop a research methodology that includes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis procedures.
- Collect and Analyze Data: After developing your research methodology, you need to collect and analyze data. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, experiments, or analyzing existing data.
- Write the Thesis: Once you have analyzed the data, you need to write the thesis. The thesis should follow a specific structure that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- Edit and Proofread: After completing the thesis, you need to edit and proofread it carefully. You should also have someone else review it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Submit the Thesis: Finally, you need to submit the thesis to your academic advisor or committee for review and evaluation.
Example of Thesis
Example of Thesis template for Students:
Title of Thesis
Table of Contents:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Literature Review
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
Chapter 4: Results
Chapter 5: Discussion
Chapter 6: Conclusion
References:
Appendices:
Note: That’s just a basic template, but it should give you an idea of the structure and content that a typical thesis might include. Be sure to consult with your department or supervisor for any specific formatting requirements they may have. Good luck with your thesis!
Application of Thesis
Thesis is an important academic document that serves several purposes. Here are some of the applications of thesis:
- Academic Requirement: A thesis is a requirement for many academic programs, especially at the graduate level. It is an essential component of the evaluation process and demonstrates the student’s ability to conduct original research and contribute to the knowledge in their field.
- Career Advancement: A thesis can also help in career advancement. Employers often value candidates who have completed a thesis as it demonstrates their research skills, critical thinking abilities, and their dedication to their field of study.
- Publication : A thesis can serve as a basis for future publications in academic journals, books, or conference proceedings. It provides the researcher with an opportunity to present their research to a wider audience and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.
- Personal Development: Writing a thesis is a challenging task that requires time, dedication, and perseverance. It provides the student with an opportunity to develop critical thinking, research, and writing skills that are essential for their personal and professional development.
- Impact on Society: The findings of a thesis can have an impact on society by addressing important issues, providing insights into complex problems, and contributing to the development of policies and practices.
Purpose of Thesis
The purpose of a thesis is to present original research findings in a clear and organized manner. It is a formal document that demonstrates a student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. The primary purposes of a thesis are:
- To Contribute to Knowledge: The main purpose of a thesis is to contribute to the knowledge in a particular field of study. By conducting original research and presenting their findings, the student adds new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- To Demonstrate Research Skills: A thesis is an opportunity for the student to demonstrate their research skills. This includes the ability to formulate a research question, design a research methodology, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- To Develop Critical Thinking: Writing a thesis requires critical thinking and analysis. The student must evaluate existing literature and identify gaps in the field, as well as develop and defend their own ideas.
- To Provide Evidence of Competence : A thesis provides evidence of the student’s competence in their field of study. It demonstrates their ability to apply theoretical concepts to real-world problems, and their ability to communicate their ideas effectively.
- To Facilitate Career Advancement : Completing a thesis can help the student advance their career by demonstrating their research skills and dedication to their field of study. It can also provide a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
When to Write Thesis
The timing for writing a thesis depends on the specific requirements of the academic program or institution. In most cases, the opportunity to write a thesis is typically offered at the graduate level, but there may be exceptions.
Generally, students should plan to write their thesis during the final year of their graduate program. This allows sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis. It is important to start planning the thesis early and to identify a research topic and research advisor as soon as possible.
In some cases, students may be able to write a thesis as part of an undergraduate program or as an independent research project outside of an academic program. In such cases, it is important to consult with faculty advisors or mentors to ensure that the research is appropriately designed and executed.
It is important to note that the process of writing a thesis can be time-consuming and requires a significant amount of effort and dedication. It is important to plan accordingly and to allocate sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis.
Characteristics of Thesis
The characteristics of a thesis vary depending on the specific academic program or institution. However, some general characteristics of a thesis include:
- Originality : A thesis should present original research findings or insights. It should demonstrate the student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study.
- Clarity : A thesis should be clear and concise. It should present the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions in a logical and organized manner. It should also be well-written, with proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Research-Based: A thesis should be based on rigorous research, which involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources. The research should be well-designed, with appropriate research methods and techniques.
- Evidence-Based : A thesis should be based on evidence, which means that all claims made in the thesis should be supported by data or literature. The evidence should be properly cited using appropriate citation styles.
- Critical Thinking: A thesis should demonstrate the student’s ability to critically analyze and evaluate information. It should present the student’s own ideas and arguments, and engage with existing literature in the field.
- Academic Style : A thesis should adhere to the conventions of academic writing. It should be well-structured, with clear headings and subheadings, and should use appropriate academic language.
Advantages of Thesis
There are several advantages to writing a thesis, including:
- Development of Research Skills: Writing a thesis requires extensive research and analytical skills. It helps to develop the student’s research skills, including the ability to formulate research questions, design and execute research methodologies, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Contribution to Knowledge: Writing a thesis provides an opportunity for the student to contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. By conducting original research, they can add new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- Preparation for Future Research: Completing a thesis prepares the student for future research projects. It provides them with the necessary skills to design and execute research methodologies, analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Career Advancement: Writing a thesis can help to advance the student’s career. It demonstrates their research skills and dedication to their field of study, and provides a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
- Personal Growth: Completing a thesis can be a challenging and rewarding experience. It requires dedication, hard work, and perseverance. It can help the student to develop self-confidence, independence, and a sense of accomplishment.
Limitations of Thesis
There are also some limitations to writing a thesis, including:
- Time and Resources: Writing a thesis requires a significant amount of time and resources. It can be a time-consuming and expensive process, as it may involve conducting original research, analyzing data, and producing a lengthy document.
- Narrow Focus: A thesis is typically focused on a specific research question or topic, which may limit the student’s exposure to other areas within their field of study.
- Limited Audience: A thesis is usually only read by a small number of people, such as the student’s thesis advisor and committee members. This limits the potential impact of the research findings.
- Lack of Real-World Application : Some thesis topics may be highly theoretical or academic in nature, which may limit their practical application in the real world.
- Pressure and Stress : Writing a thesis can be a stressful and pressure-filled experience, as it may involve meeting strict deadlines, conducting original research, and producing a high-quality document.
- Potential for Isolation: Writing a thesis can be a solitary experience, as the student may spend a significant amount of time working independently on their research and writing.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Informed Consent in Research – Types, Templates...

Research Topics – Ideas and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Research Methodology – Types, Examples and...

Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.
Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings . In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process . It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to your field.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
In the final product, you can also provide a chapter outline for your readers. This is a short paragraph at the end of your introduction to inform readers about the organizational structure of your thesis or dissertation. This chapter outline is also known as a reading guide or summary outline.
Table of contents
How to outline your thesis or dissertation, dissertation and thesis outline templates, chapter outline example, sample sentences for your chapter outline, sample verbs for variation in your chapter outline, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis and dissertation outlines.
While there are some inter-institutional differences, many outlines proceed in a fairly similar fashion.
- Working Title
- “Elevator pitch” of your work (often written last).
- Introduce your area of study, sharing details about your research question, problem statement , and hypotheses . Situate your research within an existing paradigm or conceptual or theoretical framework .
- Subdivide as you see fit into main topics and sub-topics.
- Describe your research methods (e.g., your scope , population , and data collection ).
- Present your research findings and share about your data analysis methods.
- Answer the research question in a concise way.
- Interpret your findings, discuss potential limitations of your own research and speculate about future implications or related opportunities.
For a more detailed overview of chapters and other elements, be sure to check out our article on the structure of a dissertation or download our template .
To help you get started, we’ve created a full thesis or dissertation template in Word or Google Docs format. It’s easy adapt it to your own requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template

It can be easy to fall into a pattern of overusing the same words or sentence constructions, which can make your work monotonous and repetitive for your readers. Consider utilizing some of the alternative constructions presented below.

Example 1: Passive construction
The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise.
Example 2: IS-AV construction
You can also present your information using the “IS-AV” (inanimate subject with an active verb ) construction.
A chapter is an inanimate object, so it is not capable of taking an action itself (e.g., presenting or discussing). However, the meaning of the sentence is still easily understandable, so the IS-AV construction can be a good way to add variety to your text.
Example 3: The “I” construction
Another option is to use the “I” construction, which is often recommended by style manuals (e.g., APA Style and Chicago style ). However, depending on your field of study, this construction is not always considered professional or academic. Ask your supervisor if you’re not sure.
Example 4: Mix-and-match
To truly make the most of these options, consider mixing and matching the passive voice , IS-AV construction , and “I” construction .This can help the flow of your argument and improve the readability of your text.
As you draft the chapter outline, you may also find yourself frequently repeating the same words, such as “discuss,” “present,” “prove,” or “show.” Consider branching out to add richness and nuance to your writing. Here are some examples of synonyms you can use.
| Address | Describe | Imply | Refute |
| Argue | Determine | Indicate | Report |
| Claim | Emphasize | Mention | Reveal |
| Clarify | Examine | Point out | Speculate |
| Compare | Explain | Posit | Summarize |
| Concern | Formulate | Present | Target |
| Counter | Focus on | Propose | Treat |
| Define | Give | Provide insight into | Underpin |
| Demonstrate | Highlight | Recommend | Use |
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
The title page of your thesis or dissertation goes first, before all other content or lists that you may choose to include.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved July 23, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/dissertation-thesis-outline/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation table of contents in word | instructions & examples, figure and table lists | word instructions, template & examples, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

How To Write Chapter 1 Of A PhD Thesis Proposal (A Practical Guide)

After submitting a concept paper and your supervisor gives you the go-ahead, then it is time to start writing the proposal for your PhD thesis or dissertation.
The format of a thesis proposal varies from one institution to another but generally has three main chapters: chapter 1 (introduction), chapter 2 (literature review), and chapter 3 (research methodology).
Related post: How To Choose a Research Topic For Your PhD Thesis (7 Key Factors to Consider)
While in some institutions PhD students may be required to write more chapters, these three chapters are the meat of any thesis proposal. This article focuses on how to write chapter 1 of a PhD thesis proposal.
Chapter 1 of a thesis proposal has about 10 sections discussed below:
Introduction to the chapter
Background to the study, statement of the problem, justification of the study, significance of the study, objectives of the study and/or research questions, scope of the study, limitations and delimitations of the study, definition of terms, chapter summary, final thoughts on how to write chapter 1 of a phd thesis proposal, related posts.
This is the first section of chapter 1 of a thesis proposal. It is normally short about a paragraph in length. Its purpose is to inform the readers what the chapter is all about.
This section is the longest in chapter 1 of a thesis proposal.
It provides the context within which the study will be undertaken.
It gives a historical explanation of the issue under investigation.
It is important to use existing data and statistics to show the magnitude of the issue. Grey literature (for instance, reports from the government, non-governmental organisations, local institutions and international organisations among others) play an important role when providing the background to the study.
The background is often given starting from a general perspective and narrows down to a specific perspective.
For example, if the proposal is on maternal health in South Africa, then the background of the study will discuss maternal health from the global perspective, then maternal health in Africa, and then it will narrow down to maternal health in South Africa. It will provide data and statistics provided by reports from the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and demographic and health surveys (DHS) of various countries and specifically South Africa, among other reports. Such information paints a clear picture of the problem under investigation and sets the stage for the discussion of the problem statement.
The background to the study should be clear and comprehensive enough such that your readers will be on the same page after reading the section, irrespective of their prior knowledge in your research topic.
While reviewing literature for this section, a good practice is to build mind maps that highlight the important concepts for the study topic and how those concepts relate to each other.
It is also referred to as problem statement or issue under investigation.
The statement of the problem is the elephant in the “chapter 1” room. It is what most students struggle with and the area that can make or break a proposal defense.
It is very common to hear supervisors or defense panelists make comments such as:
“I don’t see any problem here.”
“This problem is not a problem.”
“This problem does not warrant a PhD-level study.”
When writing the statement of the problem, start the section with the problem, as in… The problem (or issue) under investigation is ….
After stating the problem then follow it up with an explanation of why it is a problem.
For PhD students, the problem under investigation should be complex enough to warrant a doctoral-level study and at the same time it should add to the body of knowledge in your chosen field of study. The latter – addition to knowledge – is what distinguishes a PhD-level thesis from a Masters-level thesis.
While crafting the problem statement it is also important to remember that the problem will influence the research objectives and the research methodology as well. The student should therefore think through these aspects carefully.
The justification is used to address the need for conducting the study and addressing the problem. It therefore follows the problem statement.
It is also referred to as the rationale for the study and addresses the “why” of the study: Why does this problem warrant an investigation? What is the purpose for carrying out the study?
In the example of maternal health in South Africa, the rationale or justification for the study would be the high maternal mortality ratios in South Africa and their undesirable effects on children and family. Therefore the study would help bring to light the major causes of maternal mortality in the country and how they can best be mitigated.
Whereas the justification of the study addresses the need for the study, the significance of the study highlights the benefits that would accrue after the study is completed.
The significance can be looked at from two perspectives:
- Academic perspective
- Practical perspective
For the academic perspective , the significance entails how the study would contribute to the existing body of knowledge in the chosen topic. Will it add to the methodology? Theory? New data? Will it study a population or phenomenon that has been neglected?
For PhD students, the addition to the body of knowledge is key, and should always be at the back of the student’s mind.
For the practical perspective , the significance of the study would be the impact and benefits that different stakeholders would derive from the findings of the study.
Depending on the study, the stakeholders may include: the Government, policymakers, different ministries and their agencies, different institutions, individuals, a community etc. This will vary from one study to another.
The significance of the study is best presented from a general to specific manner, like an inverted pyramid.
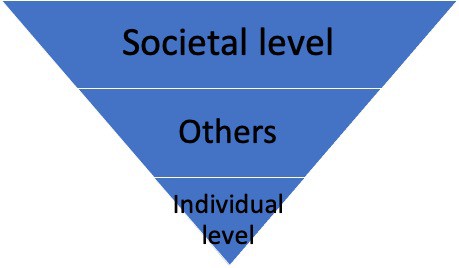
Each beneficiary is discussed separately.
Research questions are the question form of the research objectives. Depending on your institution and/or department where you are doing your PhD you may have both objectives and research questions or either.
There are two types of objectives: the general objective and the specific objectives. The general objective is a reflection of the study topic while the specific objectives are a breakdown of the general objective.
Coming up with good research objectives is an important step of any PhD thesis proposal. This is because the research objectives will determine whether the research problem will be adequately addressed and at the same time it will influence the research methodology that the study will adopt.
Research objectives should therefore emanate from the research problem.
While crafting the objectives, think about all those things that you would like to accomplish for your study and if by doing them they will address the research problem in totality.
Once you’ve noted all those activities that you would like to undertake, group the like ones together so as to narrow them down to 4 or 5 strong objectives.
The number of research objectives that PhD students should come up with will be determined by the requirements of their institution. However, the objectives should be adequate enough such that a single paper can be produced from each objective. This is important in ensuring that the PhD student publishes as many papers as is required by their institution.
Objectives are usually stated using action verbs. For instance: to examine, to analyse, to understand, to review, to investigate… etc.
It is important to understand the meaning of the action verbs used in the research objectives because different action verbs imply different methodology approaches. For instance: to analyse implies a quantitative approach, whereas to explore implies a qualitative approach.
Therefore, if a study will use purely quantitative research methodology, then the action verbs for the research objectives should strictly reflect that. Same case applies to qualitative studies. Studies that use a mixed-methods approach can have a mix of the action verbs.
Have a variety of the action verbs in your research objectives. Don’t just use the same action verb throughout.
Useful tip: To have a good idea of the action verbs that scholars use, create an Excel file with three columns: 1) action verb, 2) example of research objective, and 3) research methodology used. Then every time you read a journal paper, note down the objectives stated in that paper and fill in the three columns respectively. Besides journal papers, past PhD theses and dissertations are a good source of how research objectives are stated.
Another important point to remember is that the research objectives will form the basis of the discussion chapter. Each research objective will be discussed separately and will form its own sub-chapter under the discussion chapter. This is why the complexity of the research objectives is important especially for PhD students.
The scope of the study simply means the boundaries or the space within which the study will be undertaken.
Most studies have the potential of covering a wider scope than stated but because of time and budget constraints the scope gets narrowed down.
When defining the scope for a PhD study, it should not be too narrow or too wide but rather it should be adequate enough to meet the requirements of the program.
The scope chosen by the student should always be justified.
Limitations refer to factors that may affect a study which are not under the control of the student.
Delimitations on the other hand are factors that may affect the study for which the student has control.
Limitations are therefore caused by circumstances while delimitations are a matter of choice of the student.
It is therefore important for the student to justify their delimitations and mitigate their study’s limitations.
Examples of study limitations:
– political unrest in a region of interest: this can be mitigated by choosing another region for the study.
– covid-19 restrictions may limit physical collection of data: this can be mitigated by collecting data via telephone interviews or emailing questionnaires to the respondents.
Examples of study delimitations:
– choice of a particular community as the unit of the study: in this case the student should justify why that particular community was chosen over others.
– use of quantitative research methodology only: in this case the student should justify why they chose the research methodology over mixed-methods research.
The definition of key terms used in the study is important because it helps the readers understand the main concepts of the study. Not all readers have the background information or knowledge about the focus of the study.
However, the definitions used should be the denotative definitions, rather than the connotative (dictionary) definitions. Therefore the context within which the terms have been used should be provided.
This is the last section of the introduction chapter and it basically informs the reader what the chapter covered.
Like the introduction to the chapter, the chapter summary should be short: about one paragraph in length.
Chapter 1 of a PhD thesis proposal is an important chapter because it lays the foundation for the rest of the proposal and the thesis itself. Its role is to inspire and motivate the readers to read on. The most challenging task with chapter 1 is learning how to state the problem in a manner that is clear and to the point. For PhD students, the research problem should be complex enough to warrant a doctoral-level study.
Whereas the format of the chapter may vary from one institution to another, the sections presented in this article provide a guide to most of what is required for the chapter to be complete. Learning how to write chapter 1 of a PhD thesis proposal requires constant writing practice as well as reading of many past PhD theses and dissertations.
How To Write Chapter 2 Of A PhD Thesis Proposal (A Beginner’s Guide)
How To Write Chapter 3 Of A PhD Thesis Proposal (A Detailed Guide)
Grace Njeri-Otieno
Grace Njeri-Otieno is a Kenyan, a wife, a mom, and currently a PhD student, among many other balls she juggles. She holds a Bachelors' and Masters' degrees in Economics and has more than 7 years' experience with an INGO. She was inspired to start this site so as to share the lessons learned throughout her PhD journey with other PhD students. Her vision for this site is "to become a go-to resource center for PhD students in all their spheres of learning."
Recent Content
SPSS Tutorial #12: Partial Correlation Analysis in SPSS
Partial correlation is almost similar to Pearson product-moment correlation only that it accounts for the influence of another variable, which is thought to be correlated with the two variables of...
SPSS Tutorial #11: Correlation Analysis in SPSS
In this post, I discuss what correlation is, the two most common types of correlation statistics used (Pearson and Spearman), and how to conduct correlation analysis in SPSS. What is correlation...
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
How to write dissertation chapter 1, published by steve tippins on july 19, 2022 july 19, 2022.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 04:48 am
Congratulations, you’ve made it to the dissertation stage! You should be incredibly happy. However, beginning to write chapter one might be a little daunting. We’re going to cover a broad overview on chapter one here in this article so that you know the territory before you set out.
Purpose of Chapter One
The purpose of chapter one is to introduce the reader to what’s coming. Chapter one usually runs around 15 pages, and it gives the reader the highlights of what’s coming. Typically, you start with an introduction.
#1. Introduction
The introduction includes a few citations and says, “Hey, we’re going to talk about ___.” Fill in the blank with your topic (educational policy, or management handling of turnover, etc.). Also, don’t say “hey” like we did (that wouldn’t be very good academic writing).

#2. Background of the Problem
The next section is the background of the problem. I like to think of this as a very short literature review , showing the reader that there’s a foundation of scholarly research about this topic.
#3. Theoretical/Conceptual Framework
Follow that up by the theoretical or conceptual framework . Think of this as the seminal research upon which your study is based. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, for example, is an incredibly popular conceptual framework. Erickson’s theories are popular in education, and systems theory is being used in many disciplines now.
#4. Problem Statement
Next comes what many consider to be the guts or the foundation of the dissertation: your problem statement . Your problem statement is typically one line. Now it might be surrounded by a paragraph or two, but the actual problem statement is one sentence. It should begin, “The problem to be studied is…” and finish with something that directly aligns with your purpose and research questions. For example, “…we don’t know the impact of extra after school education on student grades in math,” or “…we are not aware of the perceptions of employees regarding management, changing retirement plans.”
Over 50% of doctoral candidates don’t finish their dissertations.
#5. Purpose Statement
Next comes your purpose statement . The purpose is directly related to the problem. If the problem is that the impact of management decisions on employee turnover is unknown, then our purpose would be to determine the impact of management decisions on employee turnover.
#6. Research Questions

Follow this by the research questions. Your research questions should be highly aligned with your problem and your purpose. For example, your research question could be: “what is the relationship between management decisions and employee turnover?” Or for another topic, “what are the perceptions of parents regarding teacher pay raises?”
Quick aside: You’re going to say things over and over and over again in your dissertation. Say them the exact same way. You get in trouble when you try to get interesting and use different terms, because doing so actually introduces new meanings. Be okay with sounding boring.
#7. Methodology
Next is a brief Methodology section. Am I going to use a quantitative approach? Am I going to use a qualitative approach? What sources am I going to use? Is this going to be secondary data? Am I going to interview parents? Quickly tell the reader that you’re going to have a whole chapter (chapter three) to really go further on this.
#8. Definition of Key Terms
Many chapter ones include a definition of key terms. If I’m talking about phenomenology, I’d better tell the reader what phenomenology is. If I’m talking about special ed teachers, I’m going to say what a special ed teacher is.
#9. Validity
You also may have a section in chapter one on validity. This is going to be somewhere in your dissertation, and it’s going to assure the reader that you’re following all the ethical steps and that results can be transferable.
#10. Conclusion and Segway to Chapter Two
Finally, you’re going to have a conclusion wrapping everything up, summarizing for the reader what they heard, and a segue into chapter two.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
Dissertation memes.
Sometimes you can’t dissertate anymore and you just need to meme. Don’t worry, I’ve got you. Here are some of my favorite dissertation memes that I’ve seen lately. My Favorite Dissertation Memes For when you Read more…

Surviving Post Dissertation Stress Disorder
The process of earning a doctorate can be long and stressful – and for some people, it can even be traumatic. This may be hard for those who haven’t been through a doctoral program to Read more…

PhD by Publication
PhD by publication, also known as “PhD by portfolio” or “PhD by published works,” is a relatively new route to completing your dissertation requirements for your doctoral degree. In the traditional dissertation route, you have Read more…
Writing the Research Paper
A Companion Website
Chapter Summaries
Click on a chapter title to be redirected to a summary of that chapter
Chapter 01: Introduction
Chapter 1 introduces the purpose of the book. A brief introduction to the characteristics of a research paper is also provided, along with an explanation of the differences between a research paper and an essay. The chapter also discusses the importance of recognizing other peoples’ perspectives, applying critical thinking, and recognizing the audience of papers. The chapter also includes a guide to the format of the chapters, the companion website, and key terminology.
Chapter 02: Critical Thinking
Chapter 2 examines critical thinking , explaining its meaning, and its relevance in our lives and our writing. The chapter shows how and why ‘critical thinking’ is the act of asking difficult questions and answering those questions with uncomfortable honesty. The chapter explains that the on-going process of critical thinking is important throughout the writing process. Because of its importance, this chapter emphasizes the fact that critical thinking will be a feature of every chapter of the book.
Chapter 03: The Research Paper
Chapter 3 looks at the research paper . It explains what the purpose of the research paper is, and shows how a research paper is a development in the reader’s perspective, a development in the field in general, and a development in the writer’s own knowledge and skills. The chapter explains the importance of the primary audience for a research paper, the quality of an argument, and the evidence that generate and supports the position of the paper. The chapter shows how the method through which we create a research paper requires us to engage in the practices of critical thinking , source evaluation , organization , and presentation . It also shows how and why it is a natural process for a research paper to evolve over time.
Chapter 04: Themes and Topics
Chapter 4 addresses themes and topics and the differences between them. The chapter goes on to show how assessing the viability of a topic requires writers to consider issues of interest, source availability, and flexibility. It further explains the preliminary research stage of project investigation and how that research allows writers to distinguish what they already know from what they need to know. The chapter also shows the importance of argumentative papers and their ultimate reliance on the collection of quality evidence.
Chapter 05: The Thesis
Chapter 5 addresses the thesis , with particular focus of the structure of the short thesis . The chapter also discusses the relationship between the thesis, the research question, and the counter thesis. It explains their differences and similarities through a variety of examples. The chapter also emphasizes the importance of having a clear idea of a thesis, a research question, and a counter-thesis so that they can act as a guide for students as they embark on focused research.
Chapter 06: Focused Research
Chapter 6 addresses the issue of focused research . It discusses both in-text and full text citations. The chapter also presents quantitative and qualitative sources, showing how each can include useful data to support arguments. The chapter goes on to present students with important information on ranking sources, searching databases, and how this stage of the research process requires a considerable amount of time and careful planning.
Chapter 07: Paraphrasing, Summarizing, Quoting, and Plagiarizing
Chapter 07 looks at the three critical skills of paraphrasing, summarizing, and quoting. It explains the differences between these three skills and discusses the skills that students need when incorporating paraphrasing, summarizing, and quoting into their research papers. The chapter integrates the discussion of these skills with examples of plagiarism, emphasizing the often nuanced and troublesome difference between these factors.
Chapter 08: Arguments and Evidence
Chapter 8 discusses arguments and evidence , showing how an argumentative research paper is composed of layers of arguments and evidence. It further breaks down arguments and evidence into ‘supporting-arguments,’ ‘supporting-evidence,’ ‘counter-arguments,’ and ‘counter-evidence.’ The chapter also shows how the long thesis (or ‘thesis statement’) can be formed from a combination of the short thesis, counter-argument, and a summary of the supporting-arguments.
Chapter 09: Plans and Proposals
Chapter 9 looks at plans and proposals . It explains how the planning stage is a critical part of the writing process, and how a plan must be flexible. The chapter shows how planning allows students to identify what they understand and guides them to what the need to do. It looks at the nine elements of plans and proposals: Theme/Topic, Introduction, Research Method, Annotated Bibliography, Scheduling, Concerns, Outline, Writing Style, and the Reference Section. As this chapter explains, planning allows instructors to provide students with the vital feedback that they will use for their forthcoming draft.
Chapter 10: The Drafting Process
Chapter 10 presents the drafting process . It shows how the drafting process includes any and all drafts of the paper up and until the final submission of the final document. The chapter looks at the three major sections of a research paper: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. It also shows how any draft will need to follow the five key ingredients: The structure of the presentation, the coherence of the writing, the content of the paper, the tone of the paper, and the persuasiveness of the argument. The chapter further includes a discussion of peer-reviewing, explaining its usefulness and necessity.
Chapter 11: The Writer’s Introduction
Chapter 11 looks at the Writer’s Introduction . It explains how the Writer’s Introduction includes all the information needed to move forward with the paper. The chapter introduces the differences between Writer’s Introduction and the Reader’s Introduction, and the purposes of each at engaging the audience with the topic and the issues. The chapter also explains why and how frozen expressions and In-text citations should be included in an introduction.
Chapter 12: The Body
Chapter 12 looks at the body of the paper. It explains the importance of considering the audience, and how this consideration determines the order of presentation for the arguments and evidence that comprise the body section. The chapter presents several common patterns that can be considered for organizing a paper. It also offers a guide to formatting for headers and sections.
Chapter 13: The Paragraph
Chapter 13 looks at the function of paragraphs and useful ways of thinking about what paragraphs are and how they can be presented. The chapter shows how many paragraphs can often be formed by beginning with a topic opener, developing with supporting sentences, and ending with a topic closer. The chapter also shows how critical thinking is needed to assess how a paragraph’s structure best serves the purpose of the paper.
Chapter 14: Cohesion
Chapter 14 addresses cohesion . It explains how cohesion issues often stem from the “curse of knowledge”: meaning that the writer has wrongly assumed that the reader already has critical information. The chapter explains how writing cohesively requires students to generate questions after each sentence, and then answer those questions in the subsequent sentence. The chapter also shows the need for explicit bridges that guide readers from one sentence to the next. It further shows how recycling key terms, employing transitionals, or using this + noun constructions often helps to close cohesion gaps.
Chapter 15: The Conclusion
Chapter 15 looks at the conclusion section of the research paper. It explains how the conclusion serves the purpose of providing the audience with the take-home message of a paper. The chapter goes on to discuss what conclusion sections typically should and should not include. This chapter shows how organizing conclusion components depend on honest answers to critical thinking questions and how the selection of a sign-off strategy will depend on the writer’s critical evaluation as to which strategy will best serves the purpose of the paper.
Chapter 16: The Reader’s Introduction
Chapter 16 looks at the Reader’s Introduction . It explains how the Reader’s Introduction needs to contain all the elements of the Writer’s Introduction but that it may also include a hook and a background section. The chapter presents different types of hook, and shows how the writer needs to identify the approach that best serves the purpose of the paper. The chapter explains how a background section can be a useful addition to the introduction; however, it also cautions that its content, focus, and length depend on the writer’s evaluation of the contribution it makes to the persuasiveness of the paper.
Share this:

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

Thesis Summary
Ai generator.
Considering that you have finished writing your thesis, it is high time that you started working on your thesis summary or abstract as the last and final part of your research paper before submitting it to your instructor. Writing an abstract is actually the simplest way for your audience, the teachers and the panel of publishers (if you wish for it to be published) to know what your research paper is about without going through the bulk of your paper.
What is an Abstract?
According to an article found in the Simon Fraser University database, the abstract is deemed a critical part of your thesis and it is presented at the beginning of the thesis, as it is a summary of the whole thesis. The thesis summary is a substantive description of your work read by an external examiner by presenting all the major elements of your work in a highly condensed form.
Size and Structure
Normally, a thesis summary would only contain 120 or less (for undergraduate theses), 150 words (for Masters theses) and 350 words (for a doctoral dissertation).
- For doctoral dissertations, it is best to limit it to only 280 words with a format of one double-spaced page, to preserve visual coherence.
- The structure of the abstract should mirror the structure of the whole thesis, and should represent all its major elements.
- For instance, if your thesis has five chapters (rationale, literature review, methodology, results, conclusion), limit each chapter to only a sentence or two for each chapter in order to maximize some parts that need more substantial backing.
Clearly Specify Your Research Questions
- Research questions are important in making sure that the abstract is coherent and logically structured as they form the backbone to which other elements adhere; they should be presented near the beginning of the abstract.
- Depending on the length of your research paper, there is only room for one to three questions. If there are more than three major research questions in your thesis, try to rearrange them by reducing some to subsidiary status.
Don’t Forget the Results
- One of the most common mistakes in writing abstracts is the failure to indicate the results.
- The primary function of your thesis (and by extension your abstract) is not to tell readers what you did, it is to tell them what you discovered. Other information, such as the account of your research methods, is needed mainly to back the claims you make about your results.
- The final part of your thesis should be about summarizing your results as well as interpreting them.
- Although it is sometimes not necessary, you can choose to add keywords below your abstract as the most important terms that can be found in the thesis.
Listed below are some thesis summary examples:
This study aimed to analyze and identify the most frequent news category and rhetoric of the three local English dailies as well as assess whether they align to the readers’ news preference. These factors served as the sources of the data gathered by the researchers: ninety tertiary students, each local publication’s respective editorial board, and banner stories. Findings indicated that even though the editors would usually select their stories based on impact, the banner story content however focused more on news like crime and politics which are mostly conflict-based issues, instead of human interest stories that readers prefer the most. In conclusion, the respective editorial boards of each publication are not presenting the readers with their main interests in the banner story. Keywords: banner stories, news values, news categories, gatekeeping/gatekeepers, and readers’ preference
An example of a summary format The aim or goal or purpose of this graduation thesis (title) is to … (analyse, characterize, compare, examine, illustrate, present, survey, design, reconstruct) … The graduation thesis is composed of five chapters, each of them dealing with different aspect of … Chapter 1 is introductory and (defines, describes, reviews, deals with) … The chapter is subdivided into two parts. Part 1 describes … and explains … . Part 2 deals with … Chapter 2 examines … . The chapter consists of three parts. Part 1 focuses on … . Part 2 investigates … . Part 3 addresses the issue of … . Chapter 3 is subdivided into two parts and provides an outline of relevant … Part 1 illustrates … . Part 2 looks at … . Chapter 4 concentrates on problems resulting from … Part 1 describes …. Part 2 recommends changes to be made in legislation … Conclusions are drawn in Chapter 5. The main aim of the graduation thesis has been reached. The author suggests that …………………… should be changed/introduced/applied.
The aim of this graduation thesis entitled Development of Yamakawa Technologies to Ascertain the Existence of Cheese on the Moon is to test the use of Yamakawa technologies in ascertaining the existence of cheese on the moon. Yamakawa technologies have been successfully used to test the existence of water in Wakanda, but to date no further applications are known. For this reason the author decided to test further applications, with the aim of describing the technology’s suitability for further development. This thesis first examines the testing procedures for the water in Wakanda experiment, and presents the results. In a second stage several adaptations to Yamakawa for the testing of the existence of cheese on the moon are undertaken. Finally the technology is applied to the question of cheese on the moon, within a six-week testing phase. At the end of each week the testing apparatus is fine tuned, and experiment results are charted every twenty-four hours. The results of the experiment show that Yamakawa technologies are well suited to ascertaining the presence of water in Wakanda, but were unable to be sufficiently modified for the purpose of ascertaining the existence of cheese on the moon. The author recommends further modification to the technology before any other uses are considered.
After writing the said abstract in your research paper, then congratulations! You are now ready to move to the next step of your thesis journey, defending it. Just remember this, always know your thesis by heart. Believe me, if you do, you will not have a hard time and eventually, you will learn to enjoy it too. Good luck!
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Dissertation Chapter 1 – What Should Be Included
- July 20, 2020
- Essay Guides and Topics
Here's What We'll Cover
Chapter 1 of the dissertation plays a fundamental role in helping readers acknowledge your area of study in a lengthy manner. Therefore, you must always follow the right outline and format . You will agree with me that dissertation chapter one plays an integral role in providing an excellent dissertation paper.
However, many students get the whole dissertation wrong due to availing a wrongly written chapter one. All hope isn’t lost as you can buy your term paper online to reduce the stress and the hustle of writing one.

Even so, you still need to understand how chapter one of your dissertation should be. This article provides you with insightful information on what a dissertation chapter 1 includes.
Introduction To The Dissertation Chapter 1
The introduction segment helps introduce the subject at hand to the readers.
In order to do this,
You need to use the funnel approach to start with a broadened perspective while narrowing your study to your dissertation topic. Using the funnel approach helps mark your research territories.
Therefore, your introduction must provide a few quotes from other researchers.
As a researcher, you need to do your study and understand the research gaps available for your study area.
Through availing quotations from other researchers, you will showcase the possible research gap and the need to fill that gap.
Background Of The Problem
The problem has been prevailing for years, and you need to showcase this.
Therefore, consider showing the history, geographical setting, and the extent of the problem.
Through the background information you avail, your readers will understand the practicality of the problem and how it has affected life and existence.
Background of the problem helps prepare your readers to understand the relevance of the paper.
Statement Of The problem
Once you introduce your dissertation, you need to have a statement of the problem.
Every essay must have a problem to be addressed.
Therefore, writing an ideal statement of the problem helps you avail of a powerfully crafted dissertation chapter 1.
There are five different parts of the statement of the problem and they include;
- Showcase the research gap
Deficiencies
- Significance of the study
- Purpose of the study
- Research questions
- Research hypothesis
- Definition of terms
- Assumptions, limitations, and delimitations
The topic helps you identify and state the problem that your research focuses on or addresses.
You need to state the problem from both the practical and theoretical perspectives.
Showcase The Research Gap
Other researchers must have investigated the problem in the past years but haven’t availed a remarkable solution yet.
Therefore, ensure that you showcase the gap available by showing how previous researchers have failed to avail of a proven solution.
The gap in your SOP is different from the one in your introduction. Your introduction’s research gap is broad, but this one must have clarity.
Your readers need irrefutable proof that the problem exists.
Therefore, consider writing a maximum of two paragraphs showcasing what other researchers and papers have written proving the problem’s existence.
You need to demonstrate how your investigation filled the available gap hence solving the problem.
Your statement of the problem must never provide a specific solution to the problem but should guide readers towards a great solution.
Who is your targeted audience? You need to identify who your investigation and research eyes focus on and areas where it would be useful.
Your statement of the problem should have at least five paragraphs, with each paragraph focusing on a specific area.
You cannot provide irrefutable resources when writing your SOP section unless it’s the evidence part.
Significance Of The Study
Detailing is necessary for this section. Therefore, ensure that you show the significance of your investigation and research to other researchers and people concerned with your specific area of study.
Therefore, ensure that you answer the questions “why and how the study is important?”
Consider showing the research gap available but uniquely from how you presented the gap in your SOP and introduction sections.
The main idea is showcasing the significance of your research in chapter 1 of the dissertation.
Purpose Of The Study
What will your investigation unveil? Your readers need to acknowledge what you are looking for in your studies and what you purpose on revealing.
Research Questions
Your research must have answers to specific questions. Therefore, understand those questions that you will be answering throughout the study or investigation.
Your research questions should be the same as your purpose, but they are supposed to be in question form.
The section should have jotted down questions that your research shall answer. It would be best if you considered precision and concision when developing these questions.
Research Hypothesis
This section gives you a platform to answer the questions in the previous sections.
It would help if you settled for the null hypotheses while answering the questions. Your answers must be detailed but concise.
Definition Of Terms
Your chapter 1 should have keywords and terms not commonly used, but they are variables to your dissertation.
Therefore, ensure that you note the keywords and have them defined from a theoretical and operational perspective.
To define a keyword theoretically, you will have to go through other related research and understand their definition for the particular keywords.
Once you have scanned the papers and identified their keyword definitions, consider quoting these definitions.
Once you have theoretically defined the keywords, ensure to have another paragraph availing an empirical definition.
Empirical definitions help state how your research defines the keywords.
Assumptions, limitations, And Delimitations
During your investigation process for chapter 1 of your dissertation, you are prone to have some assumptions and experience some limitations.
You also need to understand the difference between limitation and delimitation.
While a limitation is out of your control as a researcher, delimitation is chosen by you in your research.
For instance, it is your choice to have teenagers answer your questionnaires and not adults. Therefore, you have delimited yourself to having teenagers answer your questions.
Dissertation chapter 1 must have a conclusion. The conclusion helps remind the reader of the purpose of the research and the statement of the problem.
Without the problem, your thesis becomes null and void. Therefore, ensure that you remain precise and relevant in your conclusion .

How thorough you are with your chapter 1 determines how relevant and remarkable your dissertation will be.
Therefore, you should ensure that you understand the outline and what each section brings to the table.

Share This Infographic With Your Audience
What should be in Chapter 1 of a dissertation?
In chapter one you make a compelling case regarding the problem under research.
What is Chapter 1 of a dissertation?
Identify the need for the study and why it is of concern to the researcher. The purpose of the Study section of Chapter 1 provides a reflection of the problem statement and identifies how the study will be accomplished. It explains how the proposed study will contribute to the field.
What are the 5 chapters of a dissertation?
They include; introduction, literature review, methodology, findings, conclusion, discussion, and future consideration.
Let Us Help You Get Better Grades
Achieve academic success with Bright Writers
Unlocking A+ Essays
Insider Tips Your Professor Won't Share
Don't leave before you grab this deal!!
Get 20% OFF your first order. Professional essays at $10 a page
Do you need better
Let us handle your essays today

COMMENTS
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION. 1. The purpose of this qualitative grounded theory study was to identify what motivates. women to stay in or return to science, technology, engineering, and math professions. (STEM), leading to a motivation model. As illustrated in the literature review, research has. abbreviations. introduce introduce you can use Once ...
Basically, a summary of any chapter would just highlight the main points that have been discussed in that chapter. It should be a highly condensed version of whatever you have covered in that chapter. If you wish to know about the "Thesis Summary," I would suggest you first go through the guidelines provided by your univeristy/institution.
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
Elaborate a thesis statement. The thesis statement. is the most important part. This is a sentence usually placed at the beginning of the summary and it is aimed at clarifying the main research questions of your work. The thesis statement must be clear and concise. MA theses, but also PhD dissertations, usually concern very narrow topics.
1. Understand the elements and objectives of chapter 1 In a dissertation or thesis, the introduction always appears as chapter 1 right after the table of contents. To write an effective chapter 1, you first need to grasp the key elements that build up the introductory chapter and the main purposes of an introduction. Writing this chapter entails painting a clear picture to your readers of what ...
The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write
First, you briefly summarise Chapter 1, then you briefly list the most important achievements and conclusions of Chapters 3 - 10; then, you summarise Chapter 11. Finally, you provide an outlook. What will future work look like, or what will the impact of your thesis be. Now, if you have to summarise all this, this is what you do: Chapter 1 ...
Chapter Summary in Thesis. ... Chapter Summary: Chapter 1: Introduction . This chapter provides an overview of the research problem, which is the impact of social media on mental health. It presents the purpose of the study, the research questions, and the methodology used to conduct the research.
This is a brief summary of the thesis that provides an overview of the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions. Table of Contents. ... Chapter 1: Introduction [The introduction sets the stage for your thesis, providing background information on the topic, explaining the research problem or question, and outlining the scope and ...
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
Time to recap…. And there you have it - the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows: Title page. Acknowledgments page. Abstract (or executive summary) Table of contents, list of figures and tables.
This is a short paragraph at the end of your introduction to inform readers about the organizational structure of your thesis or dissertation. This chapter outline is also known as a reading guide or summary outline. ... IS-AV construction Chapter 1 presents an introduction to the problem and Chapter 2 discusses the relevant literature.
Chapter summary; Final thoughts on how to write chapter 1 of a PhD thesis proposal; Related posts; Introduction to the chapter . This is the first section of chapter 1 of a thesis proposal. It is normally short about a paragraph in length. Its purpose is to inform the readers what the chapter is all about. Background to the study. This section ...
This section introduces Chapter 5 as a comprehensive summary of the study. framework including a recap of the essential 10 strategic points of Chapters 1-3. It. reminds the reader of the importance of the topic and briefly explains how the study. intended to contribute to the body of knowledge on the topic.
Dissertation OverviewThe traditional dissertation is organized into 5 chapters and includes the following elements and pages:Title page (aka cover page) Signature ...
Chapter one usually runs around 15 pages, and it gives the reader the highlights of what's coming. Typically, you start with an introduction. #1. Introduction. The introduction includes a few citations and says, "Hey, we're going to talk about ___.". Fill in the blank with your topic (educational policy, or management handling of ...
1.1. Introduction. e research study that was conductedwith Black professi. al women in dual career m. riage, autonomy and satisfaction intheir marriages and th. study is explained and an. verviewof the thesis is provided. The Chapter starts. ff by presenting the context withinwhich this study was conducted as we.
It shows that on the pre-test majority of the. respondents had a low range score in Endurance Dimension of AQ® (49 or. 27.07%) and the rest got a below average score (61 or 33.70%), 47 or 25.97%. got an average score, 19 or 10.48% got an above average score and 5 or 2.76%. got a high score.
Generally, the summary is about 200-350 words long, but you should verify this with your supervisor. Also, it generally follows an introduction-body-conclusion structure. Related reading: The basics of converting your PhD thesis into journal articles. Answered by Editage Insights on 13 Sep, 2017.
1.0 Summary. The first chapter of this thesis opens with the background of the study and further. ip and the internationalization ofsmall and med. um enterprises (SMEs) in Malaysi. . This is followed by the researchobjectives, research quest. ons and significance. f the study. The chapter concludesw.
Chapter 3 looks at the research paper. It explains what the purpose of the research paper is, and shows how a research paper is a development in the reader's perspective, a development in the field in general, and a development in the writer's own knowledge and skills. The chapter explains the importance of the primary audience for a ...
An example of a summary format. The aim or goal or purpose of this graduation thesis (title) is to … (analyse, characterize, compare, examine, illustrate, present, survey, design, reconstruct) …. The graduation thesis is composed of five chapters, each of them dealing with different aspect of …. Chapter 1 is introductory and (defines ...
They include; introduction, literature review, methodology, findings, conclusion, discussion, and future consideration. When writing a dissertation, it is good to introduce what you are going to focus on in chapter one. Here is what a dissertation chapter 1 should include.